- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000

Non-Performing Assets (NPA): How serious is India’s bad loan problem?
Last updated on October 10, 2023 by ClearIAS Team

In the best interest of our readers, we have come up with a comprehensive post on NPAs, in which analyze the entire issue in detail.
We will also list out the steps taken by the Government and RBI to counter the situation.
Also read: Infrastructure and Economic Development
Table of Contents
What is a Non-Performing Asset (NPA)?
- You may note that for a bank, the loans given by the bank is considered as its assets. So if the principle or the interest or both the components of a loan is not being serviced to the lender (bank), then it would be considered as a Non-Performing Asset (NPA).
- Any asset which stops giving returns to its investors for a specified period of time is known as Non-Performing Asset (NPA).
- Generally, that specified period of time is 90 days in most of the countries and across the various lending institutions. However, it is not a thumb rule and it may vary with the terms and conditions agreed upon by the financial institution and the borrower.
An example of NPA:
Suppose the State Bank of India (SBI) gives a loan of Rs. 10 crores to a company (Eg: Kingfisher Airlines). Consider that they agreed upon for an interest rate of say 10% per annum. Now suppose that initially everything was good and the market forces were working in support to the airline industry, therefore, Kingfisher was able to service the interest amount. Later, due to administrative, technical or corporate reasons suppose the company is not able to pay the interest rates for 90 days. In that case, a loan given to the Kingfisher Airlines is a good case for the consideration as NPA.
Also read: Loan Loss Provisions
NPAs definition by Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- An asset, including a leased asset, becomes nonperforming when it ceases to generate income for the bank.
Technical definition by RBI on NPA on different cases
NPA is a loan or an advance where…
- Interest and/ or instalment of principal remain overdue for a period of more than 90 day s in respect of a term loan.
- The account remains ‘ out of orde r’ in respect of an Overdraft/Cash Credit (OD/CC).
- The bill remains overdue for a period of more than 90 days in the case of bills purchased and discounted.
- The instalment of principal or interest thereon remains overdue for two crop seasons for short duration crops.
- The instalment of principal or interest thereon remains overdue for one crop season for long duration crops .
- The amount of liquidity facility remains outstanding for more than 90 days , in respect of a securitisation transaction undertaken in terms of guidelines on securitisation dated February 1, 2006.
- In respect of derivative transactions, the overdue receivables representing positive mark-to-market value of a derivative contract, if these remain unpaid for a period of 90 days from the specified due date for payment.
Categories of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs)
Based upon the period to which a loan has remained as NPA, it is classified into 3 types:
How serious is India’s NPA issue?
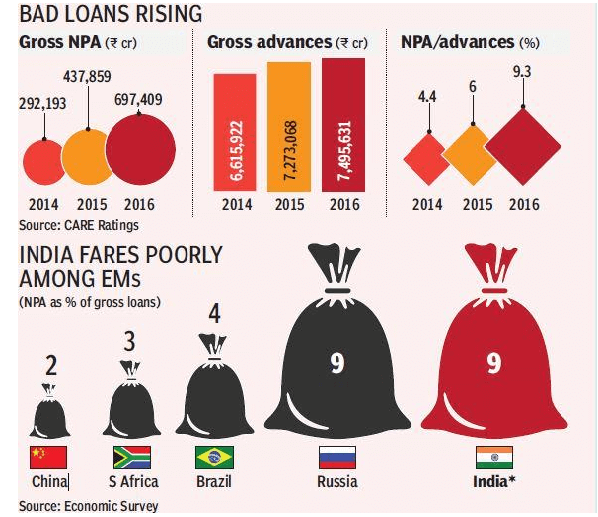
- More than Rs. 7 lakh crore worth loans are classified as Non-Performing Loans in India. This is a huge amount.
- The figure roughly translates to near 10% of all loans given.
- This means that about 10% of loans are never paid back, resulting in substantial loss of money to the banks.
- When restructured and unrecognised assets are added the total stress would be 15-20% of total loans.
- NPA crisis in India is set to worsen.
- Restructuring norms are being misused.
- This bad performance is not a good sign and can result in crashing of banks as happened in the sub-prime crisis of 2008 in the United States of America.
- Also, the NPA problem in India is worst when comparing other emerging economies in BRICS.
What can be the possible reasons for NPAs?
- Diversification of funds to unrelated business/fraud.
- Lapses due to diligence.
- Busines losses due to changes in business/regulatory environment.
- Lack of morale, particularly after government schemes which had written off loans.
- Global, regional or national financial crisis which results in erosion of margins and profits of companies, therefore, stressing their balance sheet which finally results into non-servicing of interest and loan payments. (For example, the 2008 global financial crisis).
- The general slowdown of entire economy for example after 2011 there was a slowdown in the Indian economy which resulted in the faster growth of NPAs.
- The slowdown in a specific industrial segment , therefore, companies in that area bear the heat and some may become NPAs.
- Unplanned expansion of corporate houses during the boom period and loan taken at low rates later being serviced at high rates, therefore, resulting in NPAs.
- Due to mal-administration by the corporates, for example, willful defaulters.
- Due to misgovernance and policy paralysis which hampers the timeline and speed of projects, therefore, loans become NPAs. For example the Infrastructure Sector.
- Severe competition in any particular market segment. For example the Telecom sector in India.
- Delay in land acquisition due to social, political, cultural and environmental reasons.
- A bad lending practice which is a non-transparent way of giving loans.
- Due to natural reasons such as floods, droughts, disease outbreak, earthquakes, tsunami etc.
- Cheap import due to dumping leads to business loss of domestic companies. For example the Steel sector in India.
What is the impact of NPAs?
- Lenders suffer a lowering of profit margins.
- Stress in banking sector causes less money available to fund other projects, therefore, negative impact on the larger national economy.
- Higher interest rates by the banks to maintain the profit margin.
- Redirecting funds from the good projects to the bad ones.
- As investments got stuck, it may result in it may result in unemployment.
- In the case of public sector banks, the bad health of banks means a bad return for a shareholder which means that the government of India gets less money as a dividend. Therefore it may impact easy deployment of money for social and infrastructure development and results in social and political cost .
- Investors do not get rightful returns.
- Balance sheet syndrome of Indian characteristics that is both the banks and the corporate sector have stressed balance sheet and causes halting of the investment-led development process.
- NPAs related cases add more pressure to already pending cases with the judiciary .
What are the various steps taken to tackle NPAs?
NPAs story is not new in India and there have been several steps taken by the GOI on legal, financial, policy level reforms. In the year 1991, Narsimham committee recommended many reforms to tackle NPAs. Some of them were implemented.
The Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRTs) – 1993
To decrease the time required for settling cases. They are governed by the provisions of the Recovery of Debt Due to Banks and Financial Institutions Act, 1993. However, their number is not sufficient therefore they also suffer from time lag and cases are pending for more than 2-3 years in many areas.
Credit Information Bureau – 2000
A good information system is required to prevent loan falling into bad hands and therefore prevention of NPAs. It helps banks by maintaining and sharing data of individual defaulters and willful defaulters.
Lok Adalats – 2001
They are helpful in tackling and recovery of small loans however they are limited up to 5 lakh rupees loans only by the RBI guidelines issued in 2001. They are positive in the sense that they avoid more cases into the legal system.
Compromise Settlement – 2001
It provides a simple mechanism for recovery of NPA for the advances below Rs. 10 Crores. It covers lawsuits with courts and DRTs (Debt Recovery Tribunals) however willful default and fraud cases are excluded.
SARFAESI Act – 2002
The Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002 – The Act permits Banks / Financial Institutions to recover their NPAs without the involvement of the Court, through acquiring and disposing of the secured assets in NPA accounts with an outstanding amount of Rs. 1 lakh and above. The banks have to first issue a notice. Then, on the borrower’s failure to repay, they can:
- Take ownership of security and/or
- Control over the management of the borrowing concern.
- Appoint a person to manage the concern.
Further, this act has been amended last year to make its enforcement faster.
ARC (Asset Reconstruction Companies)
The RBI gave license to 14 new ARCs recently after the amendment of the SARFAESI Act of 2002. These companies are created to unlock value from stressed loans. Before this law came, lenders could enforce their security interests only through courts, which was a time-consuming process.
Corporate Debt Restructuring – 2005
It is for reducing the burden of the debts on the company by decreasing the rates paid and increasing the time the company has to pay the obligation back.
5:25 rule – 2014
Also known as , Flexible Structuring of Long Term Project Loans to Infrastructure and Core Industries . It was proposed to maintain the cash flow of such companies since the project timeline is long and they do not get the money back into their books for a long time, therefore, the requirement of loans at every 5-7 years and thus refinancing for long term projects.
Joint Lenders Forum – 2014
It was created by the inclusion of all PSBs whose loans have become stressed. It is present so as to avoid loan to the same individual or company from different banks. It is formulated to prevent the instances where one person takes a loan from one bank to give a loan of the other bank.
Mission Indradhanush – 2015
The Indradhanush framework for transforming the PSBs represents the most comprehensive reform effort undertaken since banking nationalization in the year 1970 to revamp the Public Sector Banks (PSBs) and improve their overall performance by ABCDEFG.
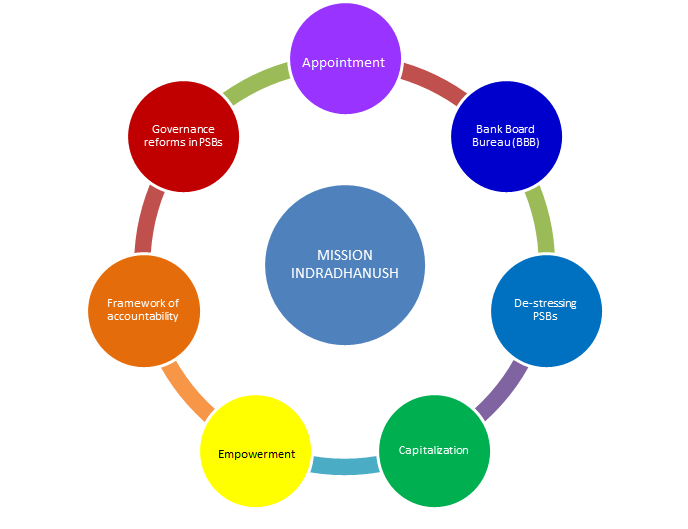
B-Bank Board Bureau : The BBB will be a body of eminent professionals and officials, which will replace the Appointments Board for the appointment of Whole-time Directors as well as non-Executive Chairman of PSBs
C-Capitalization: As per finance ministry, the capital requirement of extra capital for the next four years up to FY 2019 is likely to be about Rs.1,80,000 crore out of which 70000 crores will be provided by the GOI and the rest PSBs will have to raise from the market.
D-DEstressing: PSBs and strengthening risk control measures and NPAs disclosure.
E-Employment: GOI has said there will be no interference from Government and Banks are encouraged to take independent decisions keeping in mind the commercial the organizational interests.
F-Framework of Accountability: New KPI(key performance indicators) which would be linked with performance and also the consideration of ESOPs for top management PSBs.
G-Governance Reforms : For Example, Gyan Sangam, a conclave of PSBs and financial institutions. Bank board Bureau for transparent and meritorious appointments in PSBs.
Strategic debt restructuring (SDR) – 2015
Under this scheme banks who have given loans to a corporate borrower gets the right to convert the complete or part of their loans into equity shares in the loan taken company. Its basic purpose is to ensure that more stake of promoters in reviving stressed accounts and providing banks with enhanced capabilities for initiating a change of ownership in appropriate cases.
Asset Quality Review – 2015
Classify stressed assets and provisioning for them so as the secure the future of the banks and further early identification of the assets and prevent them from becoming stressed by appropriate action.
Sustainable structuring of stressed assets (S4A) – 2016
It has been formulated as an optional framework for the resolution of largely stressed accounts . It involves the determination of sustainable debt level for a stressed borrower and bifurcation of the outstanding debt into sustainable debt and equity/quasi-equity instruments which are expected to provide upside to the lenders when the borrower turns around.
Insolvency and Bankruptcy code Act-2016
It has been formulated to tackle the Chakravyuaha Challenge ( Economic Survey ) of the exit problem in India. The aim of this law is to promote entrepreneurship, availability of credit, and balance the interests of all stakeholders by consolidating and amending the laws relating to reorganization and insolvency resolution of corporate persons, partnership firms and individuals in a time-bound manner and for maximization of value of assets of such persons and matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
Pubic ARC vs. Private ARC – 2017
This debate is recently in the news which is about the idea of a Public Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARC) fully funded and administered by the government as mooted by this year’s Economic Survey Vs. the private ARC as advocated by the deputy governor of RBI Mr. Viral Acharya. Economic survey calls it as PARA (Public Asset Rehabilitation Agency) and the recommendation is based on a similar agency being used during the East Asian crisis of 1997 which was a success.
Bad Banks – 2017
Economic survey 16-17 , also talks about the formation of a bad bank which will take all the stressed loans and it will tackle it according to flexible rules and mechanism. It will ease the balance sheet of PSBs giving them the space to fund new projects and continue the funding of development projects.
The need of the hour to tackle NPAs is some urgent remedial measures. This should include:
- Technology and data analytics to identify the early warning signals.
- Mechanism to identify the hidden NPAs.
- Development of internal skills for credit assessment.
- Forensic audits to understand the intent of the borrower.
Article by: Nishant Raj. The author is an IIT Kharagpur Alumnus.

Top 10 Best-Selling ClearIAS Courses
Upsc prelims cum mains (pcm) gs course: unbeatable batch 2025 (online), rs.75000 rs.29000, upsc prelims test series (pts) 2025 (online), rs.9999 rs.4999, upsc mains test series (mts) (online), rs.19999 rs.9999, csat course 2025 (online), current affairs course 2025: important news & analysis (online), ncert foundation course (online), essay writing course for upsc cse (online), ethics course for upsc cse (online), fight back: repeaters program with daily tests (online or offline), rs.55000 rs.25000.

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
June 11, 2017 at 5:13 am
Very Deeply Elaborated with Details
January 30, 2018 at 8:24 pm
This is “THE BASE” of Current economy, for technical background people.
June 29, 2018 at 1:13 am
In mission indradhnush It’s E for Empowerment not employment… Correct me if I am wrong
November 30, 2018 at 6:09 pm
January 2, 2019 at 11:08 am
Please seen that pic frnd it has represented the correct form..
February 27, 2020 at 10:25 am
Strict action should be taken against froud companies and hereafter loan amount should be deducted automatically from company account.Company and related person should not be allowed to open an account in other bank.Cash tranziction should be not be allowed.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
ClearIAS Programs: Admissions Open
Thank You 🙌
UPSC Prelims 2024: Revised Answer Key!
Download Self-Study Plan

Analyse Your Performance and Track Your Progress
Download Study Plan
IAS/IPS/IFS Online Coaching: Target CSE 2025

Cover the entire syllabus of UPSC CSE Prelims and Mains systematically.

- TRP for UPSC Personality Test
- Interview Mentorship Programme – 2023
- Daily News & Analysis
- Daily Current Affairs Quiz
- Baba’s Explainer
- Dedicated TLP Portal
- 60 Day – Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – 2024
- English Magazines
- Hindi Magazines
- Yojana & Kurukshetra Gist
- PT20 – Prelims Test Series
- Gurukul Foundation
- Gurukul Advanced – Launching Soon
- Prelims Exclusive Programme (PEP)
- Prelims Test Series (AIPTS)
- Integrated Learning Program (ILP) – 2025
- Connect to Conquer(C2C) 2024
- TLP Plus – 2024
- Public Administration FC – 2024
- Anthropology Foundation Course
- Anthropology Optional Test Series
- Sociology Foundation Course – 2024
- Sociology Test Series – 2023
- Geography Optional Foundation Course
- Geography Optional Test Series – Coming Soon!
- PSIR Foundation Course
- PSIR Test Series – Coming Soon
- ‘Mission ಸಂಕಲ್ಪ’ – KPSC Foundation Course
- ‘Mission ಸಂಕಲ್ಪ’ – KPSC Prelims Crash Course
- CTI (COMMERCIAL TAX INSPECTOR) Test Series & Video Classes
- Monthly Magazine
- January 19, 2021
UPSC Articles

ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment. GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Context: With commercial banks set to witness a spike in NPAs, or bad loans , in the wake of the contraction in the economy as a result of the Covid-19 pandemic, Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Governor Shaktikanta Das recently agreed to look at the proposal for the creation of a bad bank.
What’s a bad bank and how does it work?
- Idea of Bad Bank: Technically, a bad bank is an asset reconstruction company (ARC) or an asset management company that takes over the bad loans of commercial banks, manages them and finally recovers the money over a period of time.
- Utility of Bad Bank: The bad bank is not involved in lending and taking deposits, but helps commercial banks clean up their balance sheets and resolve bad loans in
- Working of Bad Bank: The takeover of bad loans is normally below the book value of the loan (provides certain margin to ARC). The bad bank subsequently tries to recover as much as possible using its expertise in stressed asset resolution.
- Support of Government: The bad bank concept is in some ways similar to an ARC but is funded by the government initially, with banks and other investors co-investing in due course. The presence of the government is seen as a means to speed up the clean-up process.
- US-based Mellon Bank created the first bad bank in 1988.
Merits of Having Bad Bank –
- Banks’ Burden is Reduced : The burden of recovering those loans is reduced for other banks.
- Specialisation leads to faster recovery: Speed of recovery will be better as Bad Bank’s main work is recovery and they are specialised in that.
- Positive Impact on Financial Sector: Bad Bank will help improve the banking sector’s health and fasten the recovery aspects of ailing by putting back frozen assets back into economic circulation.
- Increased Profitability of Banks : Bad Bank increases profitability of other banks as they can focus more on lending, acquiring more customers and upgrading technology without spending too much time on recovery or resolution of bad loans
- Feasibility : Bad banks can make profits as they usually keep high margin before acquiring the bad loans. The concept of Bad Bank has been implemented in other countries including Sweden, Finland, France and Germany.
Demerits of Bad Bank-
- Shifting of Problem : Former RBI Governor Raghuram Rajan had opposed the idea of setting up a bad bank in which banks hold a majority stake. He was of the opinion that bad bank idea as merely shifting loans from one government pocket (the public sector banks) to another (the bad bank).
- Reckless Lending : Other banks may not concentrate on the quality of loans as they always an option of shifting bad loans to ARC/ Bad Bank. This leads to doling out loans without proper diligence leading to reckless lending
- Efficacy Debate : Bad banks may not acquire critical loans which are difficult to recover and only concentrate on easily recoverable loans. As a result, troubled Commercial banks continue to face the issue of bad loans. There is also the fear that it end up as another case of throwing good money after bad.
- Profitability of Banks: High margin of Bad banks may curtail the profits of other banks which can in turn impact their lending capabilities.
- Moral Issues : Due to pressure bad banks may employ some unethical ways to recover loans. Another issue is that other banks may not show the actual position of loan accounts by doing window dressing.
What has been the stand of the RBI with regard to resolving stressed loans?
- Viral Acharya, when he was the RBI Deputy Governor, had said it would be better to limit the objective of these asset management companies to the orderly resolution of stressed assets, followed by a graceful exit.
- The first is a private asset management company (PAMC), which is said to be suitable for stressed sectors where the assets are likely to have an economic value in the short run, with moderate levels of debt forgiveness.
- The second model is the National Asset Management Company (NAMC), which would be necessary for sectors where the problem is not just one of excess capacity but possibly also of economically unviable assets in the short to medium terms.
- While the RBI did not show much enthusiasm about a bad bank all these years, there are signs that it can look at the idea now. Recently, Governor Das indicated that the RBI can consider the idea of a bad bank.
Do we need a Bad Bank now?
- The idea gained currency during Raghuram Rajan’s tenure as RBI Governor.
- The RBI had then initiated an asset quality review (AQR) of banks and found that several banks had suppressed or hidden bad loans to show a healthy balance sheet.
- However, the idea remained on paper amid lack of consensus on the efficacy of such an institution.
- Now, with the pandemic hitting the banking sector , the RBI fears a spike in bad loans in the wake of a six-month moratorium it has announced to tackle the economic slowdown.
How serious is the NPA issue in the wake of the pandemic?
- The RBI noted in its recent Financial Stability Report that the gross NPAs of the banking sector are expected to shoot up to 14.8% of advances by September 2021, from 7.5% in September 2020
- Among bank groups, the NPA ratio of PSU banks, which was 9.7% in September 2020, may increase to 16.2% by September 2021 under the baseline scenario.
- The K V Kamath Committee, which helped the RBI with designing a one-time restructuring scheme, also noted that corporate sector debt worth Rs 15.52 lakh crore has come under stress after Covid-19 hit India, while another Rs 22.20 lakh crore was already under stress before the pandemic.
- This effectively means Rs 37.72 crore (72% of the banking sector debt to industry) remains under stress. This is almost 37% of the total non-food bank credit.
- The panel led by Kamath, a veteran banker, has said companies in sectors such as retail trade, wholesale trade, roads and textiles are facing stress. Sectors that have been under stress pre-Covid include NBFCs, power, steel, real estate and construction. Setting up a bad bank is seen as crucial against this backdrop
Why is it crucial to tackle toxic loans?
- Banks and other financial institutions are the key drivers of economic growth, as they are the formal channels of credit.
- As things stand, lenders, particularly the state-owned ones, are saddled with massive bad loans.
- Growing NPAs has made Banks risk-averse and eroded their capacity to lend to help spur economic recovery from the shock of the covid-19 pandemic that has roiled the world.
- Banks will find it tough and exorbitantly expensive to raise capital from the market if the asset-quality trajectory remains uncertain, delaying and even jeopardizing, economic growth.
Has the banking system made any proposal with regard to Bad Bank?
- The banking sector, led by the Indian Banks’ Association , had submitted a proposal in May 2020 for setting up a bad bank to resolve the NPA problem, proposing equity contribution from the government and banks.
- The proposal was also discussed at the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) meeting, but it did not find favour with the government which preferred a market-led resolution process.
- The banking industry’s proposal was based on an idea proposed by a panel on faster resolution of stressed assets in public sector banks headed by former Punjab National Bank Chairman Sunil Mehta.
- Sunil Mehta panel had proposed a company, Sashakt India Asset Management, for resolving large bad loans two years ago.
- The idea of a bad bank was discussed in 2018 too, but it never took shape.
- During the pandemic, banks and India Inc were also pitching for one-time restructuring of loans and NPA reclassification norms from 90 days to 180 days as relief measures to tackle the impact of the lockdown and the slowdown in the economy.
- Currently, loans in which the borrower fails to pay principal and/or interest charges within 90 days are classified as NPAs and provisioning is made accordingly.
Will a bad bank solve the problem of NPAs?
- Complements Previous Measures: Despite a series of measures by the RBI for better recognition and provisioning against NPAs, as well as massive doses of capitalisation of public sector banks by the government, the problem of NPAs continues in the banking sector, especially among the weaker banks. Having a Bad Bank will complement other measures taken by RBI & government to clean up banking sector.
- Helps solve economic aftershocks of Pandemic : As the Covid-related stress pans out in the coming months, proponents of the concept feel that a professionally-run bad bank, funded by the private lenders and supported the government, can be an effective mechanism to deal with NPAs.
- Experience from Other Countries: Many other countries had set up institutional mechanisms such as the Troubled Asset Relief Programme (TARP) in the US to deal with a problem of stress in the financial system in the wake of 2008 financial crisis.
Banks and other financial institutions are the key drivers of economic growth. However, many borrowers may find it difficult to service their loans, requiring lenders to set aside capital to cover those losses. A bad bank can free them up to start lending. However, adequate measures need to be put in place so as to overcome the pitfalls of bad bank
For a dedicated peer group, Motivation & Quick updates, Join our official telegram channel – https://t.me/IASbabaOfficialAccount
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel HERE to watch Explainer Videos, Strategy Sessions, Toppers Talks & many more…

Related Posts :
New anubhava mantapa, synopsis [19th january,2021] day 8: iasbaba’s tlp (phase 1): upsc mains answer writing (general studies).

- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam –20th June 2024
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 20th June 2024
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam –19th June 2024
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 19th June 2024
- [Admissions Open] TLP PLUS (+) Mains Test Series cum Mentorship Based Programme (OFFLINE and ONLINE) For UPSC 2024
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam –18th June 2024
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 18th June 2024
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 17th June 2024
- GENERAL STUDIES (CSAT) PAPER- 2 | GS2 Paper 2024 Question Paper – UPSC IAS (Preliminary) Examination, 2024
- GENERAL STUDIES PAPER- 1 | GS1 Paper 2024 Question Paper – UPSC IAS (Preliminary) Examination, 2024
Don’t lose out on any important Post and Update. Learn everyday with Experts!!
Email Address
Search now.....
Sign up to receive regular updates.
Sign Up Now !
The ABCD of Bad Banks
Context: Budget 2021-22 recommended for setting up an Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) Ltd and an Asset Management Company (AMC) for dealing with stressed debt, signals a green light for ‘Bad Bank’
Arguments favouring setting up of ‘Bad Banks’
- It benefits Commercial banks: by transferring their bad loans to bad banks and thereby reducing loan book risks and provisioning losses and allows them to refocus on their core business.
- Bad banks are bad, for good: It purchases distressed loans and sell the assets at a profit and thereby returns the money with capital gains to its shareholders.
Arguments against setting up of ‘Bad Banks’ in India
- Bad banks have never worked where industrial, corporate- and conglomerate-level bad loans predominate. E.g. failure of bad loan resolutions in Mexico, Brazil, Argentina.
- No clarity about protection to bank’s management for providing such discounts: especially in the case of Public Sector Banks (PSBs) where gross non-performing assets (NPAs) of 15%.
- PSBs constitute ‘the State’ under Article 12 of the constitution of India, and hence its actions will be scrutinised by the Parliament, the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) etc.
- Bad banks are just recapitalisation schemes: thus, it cannot clean up the structure of commercial banks as previous recapitalisations of PSBs since 1992-93 failed to do so.
- Ownership issues: Government cannot own bad bank as they will be major sellers of bad debt. Hence equity holders of an entity that buys such debt should be any other party .
Conclusion: Many reforms are needed in law, legal procedures and in freeing PSBs from debilitating State oversight and investigations before the financial system can resolve distressed loans through bad banks.
Answer our survey to get FREE CONTENT

Feel free to get in touch! We will get back to you shortly
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Ethics Enrichment Program
- Intensive News Analysis (INA)
- Topper's UPSC PYQ Answer
- Essay Enrichment Program
- PSIR Optional
- NEEV GS + CSAT Foundation
- News-CRUX-10
- Daily Headlines
- Geo. Optional Monthly Editorials
- Past Papers
- © Copyright 2024 - theIAShub
Talk To Our Counsellor
- NCERT Study Material
- Current Affairs
Comprehensive content tailored For Success
Bad Bank- UPSC Current Affairs
Jun 13, 2022
Navigate Quickly

Recently, the Finance Minister announced that the National Asset Reconstruction Company (NARCL) along with the India Debt Resolution Company (IDRCL) will take over the first set of bad loans from banks.
The creation of a bad bank to tackle Non- Performing Assets (NPAs) is a step in the right direction if backed by long-due governance reforms in Public Sector Banks. Comment.
- The troubled asset relief program, also known as TARP , implemented by the U.S. Treasury in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, was modelled around the idea of a bad bank.
- Under the program, the U.S. Treasury bought troubled assets such as mortgage-backed securities from U.S. banks at the peak of the crisis and later resold it when market conditions improved.
- It is estimated that the Treasury through its operations earned a nominal profit of anything between $11 billion to $30 billion, although some contest these figures.
- In Budget 2021-22, the Government announced the setting up of a National Asset Reconstruction Company (a bad bank ) and India Debt Resolution Company Ltd (IDRCL) as part of the resolution of bad loans.
- NARCL proposes to acquire stressed assets of about Rs. 2 Lakh crore in phases within extant regulations of RBI.
- It intends to acquire these stressed assets through 15% Cash and 85% in Security Receipts (SRs).
- Existing Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) have been helpful in the resolution of stressed assets, especially for smaller value loans. Various available resolution mechanisms, including Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, have proved to be useful.
- However, considering the large stock of NPAs, additional options/alternatives are needed which led to the creation of the NARCL-IRDCL framework in Union-Budget 2021-22.
- A bad bank is a financial entity set up to buy non-performing assets (NPAs), or bad loans, from banks.
- Aim: To ease the burden on banks by taking bad loans off their balance sheets and getting them to lend again to customers without constraints.
- After the purchase of a bad loan from a bank, the bad bank may later try to restructure and sell the NPA to investors who might be interested in purchasing it.
- A bad bank makes a profit in its operations if it manages to sell the loan at a price higher than what it paid to acquire the loan from a commercial bank.
- Technically, a bad bank is an asset reconstruction company (ARC) or an asset management company that manages bad loans of commercial banks and finally recovers the money over a period of time.
- It is not involved in lending and taking deposits.
- One of the key ideas behind formation of bad banks is to de-stress the balance sheets of the banks.
- Once Non-Performing Assets are taken over by bad banks; Commercial banks will be in a position to lend more to consumers.
- In the past, the Government had to infuse fresh capital to prove the financial health of PSBs. The government infusing fresh capital in PSBs means less money for other schemes.
- A bad bank backed by the government will merely shift bad assets from the hands of public sector banks, which are owned by the government, to the hands of a bad bank, which is again owned by the government.
- Unlike a bad bank set up by the private sector, a bad bank backed by the government is likely to pay too much for stressed assets which is bad news for taxpayers who will once again have to foot the bill for bailing out troubled banks.
- After all, the safety net provided by a bad bank gives these banks more reason to lend recklessly and thus further exacerbates the bad loan crisis.
Also, watch a detailed video on Bad Banks & National Asset Reconstruction Company Limited by Vivek Singh Sir, our faculty for Economy, to understand the topic better and Upgrade your civils preparation :
- This becomes a more daunting task especially when governments are facing the issue of containing the fiscal deficit.
- Lack of Governance Reforms: In the wake of the absence of governance reforms in the public sector banks, setting up of Bad banks may serve as an ad-hoc mechanism to tackle NPAs , as these banks may go on doing business the way they have been doing in the past and may end up piling-up of bad debts again.
- The price at which bad assets are transferred from commercial banks to the bad bank will not be market-determined and price discovery will not happen.
- NARCL and IDRCL will have an exclusive arrangement that will be as per the scope defined in the ‘Debt Management Agreement’ to be executed between these two entities.
- This arrangement will be on a ‘Principal-Agent’ basis and final approvals and ownership for the resolution shall lie with NARCL.
- Further, the NARCL will purchase bad loans through a 15:85 structure, where it will pay 15 per cent of the sale consideration in cash and issue security receipts (SRs) for the remaining 85 per cent.
- The SRs will be guaranteed by the government which essentially aims to cover the gap between the face value of the security receipts and realised the value of the assets when eventually sold to the prospective buyers.
- A key reason behind the bad loan crisis in public sector banks, some critics point out, is the nature of their ownership.
- Unlike private banks, which are owned by individuals who have strong financial incentives to manage them well, public sector banks are managed by bureaucrats who may often not have the same commitment to ensuring these lenders’ profitability.
- To that extent, bailing out banks through a bad bank does not really address the root problem of the bad loan crisis.
| NARCL has been incorporated under the Companies Act and has applied to the Reserve Bank of India for a licence as an Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC). NARCL has been set up by banks to aggregate and consolidates stressed assets for their subsequent resolution.PSBs will maintain51% ownership in NARCL. IDRCL is a service company/operational entity which will manage the asset and engage market professionals and turnaround experts. Public Sector Banks (PSBs) and Public FIs will hold a maximum of 49% stake and the rest will be with private-sector lenders. A non performing asset (NPA) is a loan or advance for which the principal or interest payment remained overdue for a period of 90 days. |
News Source: The Hindu
Download the PrepLadder app to amplify your UPSC exam preparation and to experience a revolution in UPSC CSE education.
You can also join our Telegram channel for UPSC exam preparation to apprise yourself with the latest information about the exam.
Own Your Dream
Team PrepLadder

PrepLadder IAS
Get quick access to the latest happenings across the globe. Articles revolving around factual data that aims to boost your UPSC CSE preparation and make your dreams become a reality!
- +91-7558644556

Bad Banks: Indian Economy
- Last Updated : 28-Oct-2023
Introduction
Describe a bad bank:, need of bad bank, bad bank in india, significance, any suggestions or correction in this article - please click here ( [email protected] ), related posts:, recapitalization of banks - indian economy.
- 15/Jun/2024
Poverty Alleviation: Indian Economy
- 14/Jun/2024
Net Domestic Product at Market Prices (NDPMP)
- 13/Jun/2024
Difference Between Capital And Consumer Goods
- 10/Jun/2024
Dual Government In Bengal (176
- 107581 Views
Civil Disobedience Movement
- 79719 Views
- 79480 Views
Human Values And Ethics
- 67857 Views
Anti-Partition Campaign Under
Administration of the chera dy, hartog committee (1929): educa, the moral subjectivism: explai.

- भाषा : हिंदी
- Classroom Courses
- Our Selections
- Student Login
- About NEXT IAS
- Director’s Desk
- Advisory Panel
- Faculty Panel
- General Studies Courses
- Optional Courses
- Interview Guidance Program
- Postal Courses
- Test Series
- Current Affairs
- Student Portal

- Recently, the government has approved extending a guarantee of Rs 30,600 crore to the National Asset Reconstruction Company Ltd (NARCL) to help clear the banking sector’s stressed assets of around Rs 2 lakh crore in a time-bound manner .
- A total of Rs 90,000 crore of stressed assets, against which banks have made 100 percent provisions in their books of accounts, will be transferred to NARCL in the first phase.
- The India Debt Resolution Company Ltd has already been set up and will function as the asset management company.
- Ownerships: Public sector banks will have a 51% ownership in the NARCL, while their shareholding along with that of public sector financial institutions will be capped at 49% for the IDRC, with private lenders bringing in the rest of the equity capital.
- The GoI Guarantee of up to Rs 30,600 crore will back Security Receipts (SRs) issued by NARCL. The guarantee will be valid for 5 years.
- If the bad bank is unable to sell the bad loan, or has to sell it at a loss, then the government guarantee will be invoked.
- The guarantee shall cover the shortfall between the face value of the SR and the actual realisation.
- A 15% cash payment would be made to the banks based on some valuation and the rest (85%) will be given as security receipts.
- Resolution mechanisms of this nature which deal with a backlog of NPAs typically require a backstop from the Government.
- This imparts credibility and provides for contingency buffers.
- It will support the regulatory provisioning requirement of the RBI.
- In the last six fiscal years, banks had made recoveries of ?5.01-lakh crore with as much as ?3.1-lakh crore since March 2018. In 2018-19, banks recovered a record ?1.2-lakh crore.
Significance of Move
- Growth Capital: Most of the big-ticket NPAs (Non Performing Assets) will be transferred to NARCL, thereby cleaning up banks’ balance sheets and freeing up growth capital for them to support economic activity.
- Clean & Transparent: This will result in banks’ balance sheets and books being cleaner, transparent, they will now be able to stand on their own and do business.
- Positive step: The government guarantee for the proposed security receipts is a positive stepping stone for unlocking stressed assets’ value. A guarantee helps in improving the value of security receipts, their liquidity and tradability.
- Inbuilt Incentives: There is an inbuilt incentive structure within the overall framework that will drive both banks and NARCL to ensure resolution of the bad loans within a period of 5 years.
- Quicker Resolution: The recent moves include elements that have been missing in the functioning of the existing ARCs and hence, the large assets that have hitherto been left unaddressed will see resolution going ahead.
- Completing Cycle: Since 2015, resolution, recovery of NPAs, healthy capital infusion has been done alongside a series of reforms to resurrect the public sector banks. NARCL is completing the entire cycle of cleaning up India’s banking system that began with the recognition of the extent of bad loans in 2015.
| ownership in NARCL. as its shareholders. The authorised share capital of the company is Rs 100 crore divided into 10 crore shares of Rs 10 each. stake and the rest will be with private-sector lenders.
|
Issues with NPA
- Needs Provisioning: The bad loans lead to banks’ having to save a part of their operating revenue to account for bad loans. This is called Provisioning. The technical term used for provisioning is Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) or Capital to Risk (weighted) Assets Ratio (CRAR).
- Loss of Profit: The banks are required to provision for bad loans out of their operating income. The concerned bank becomes less profitable because it has to use some of its profits from other loans to make up for the loss on the bad loans.
- Becomes Risk-averse: The officials of such banks hesitate from extending loans to business ventures that may remotely appear risky for the fear of aggravating an already high level of non-performing assets (or NPAs).
- Affects Valuation: Any reduction in the perceived valuation of the banks might lead to loss of share value of the banks, leading to general downfall in the share markets. This could result in wiping out shareholders’ wealth from the financial markets.
- Rising Bad Loans: In spite of various efforts, a substantial amount of NPAs continue on balance sheets of banks primarily because the stock of bad loans as revealed by the Asset Quality Review is not only large but fragmented across various lenders.
(Image Courtesy: BS )
Various Steps Taken for NPA
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC);
- Strengthening of Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Securities Interest (SARFAESI Act) and Debt Recovery Tribunals;
- Setting up of dedicated Stressed Asset Management Verticals (SAMVs) in banks for large-value NPA accounts etc.
- Existing ARCs have been helpful in resolution of stressed assets especially for smaller value loans.
- However, considering the large stock of legacy NPAs, additional options/alternatives are needed and the NARCL-IRDCL structure announced in the Union Budget is this initiative.
- An Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) or Bad Bank is a specialized financial institution which buys stressed assets from banks and financial institutions.
- Asset reconstruction is the purchase of title or rights of the banks or financial institutions in loans, bonds, debentures, etc., for the sole purpose of its recovery or realization.
- Banks can sell their stressed or bad assets to the ARC at a mutually agreeable price, thereby helping banks to clean up their balance sheets and concentrate on delivering normal banking services.
- Thereafter, it is the responsibility of the ARC to recover the bad debts or associated securities in a market-led process.
Need for Bad Bank
- Enhanced Lending: A bad bank can take over the bad loans of the bank, thereby freeing up the bank from the provisioning requirements. This means since the banks are not required to provision for the bad loans, the same money can be utilised for lending purposes.
- Revival of Credit: The more money banks have, the more they can advance to the needy. This is useful for the revival of the credit cycle and boosting investments in the economy.
- More Recovery: A bad bank would be specialised in maximising the recovery out of a bad loan, as this would be its primary task.
- Impetus to Industry : A bad bank can provide an impetus to the industry by freeing up the books of banks.
- Decreases Recapitalisation Needs: Recapitalisation of banks is required to fulfill the capital adequacy ratio of the banks. With the formation of a bad bank, it is expected that this amount can be utilised elsewhere, including towards public welfare and infrastructure creation.
- Mitigating Slowdown: Reports have pointed to a potential increase in stressed assets due to economic slowdown in India. To resolve such a situation, it is necessary to work out a solution which can be optimised to reverse the effects of slowdown in the country.
Image Courtesy: ET
Concerns With the Bad Bank
- Incomplete Solution: A bad bank is expected to take over the debts of commercial banks under itself. Therefore, the bad bank can only be expected to aggregate, but not resolve the problem.
- Huge Expenditure: A huge amount is needed for setting up a bad bank. In the times of global recession as well as COVID-induced lockdown, this might prove to be tricky for the government as it is already pressed to provide for increased healthcare costs and is constrained by decreasing revenues.
- Banks Management: The haircuts taken by the banks would reflect on its profit and loss account and affect its profitability. This might raise questions on both the management of the bank as well as its decision making regarding both earlier and future haircuts.
- Rise in Unethical Practices: The employees might turn towards unethical practices to boost recovery out of a bad loan. This has been a continuing problem earlier as there have been reports of harassment of the banks’ clients, who were unable to pay their dues.
- The sovereign guarantee would allow the banks to free up the capital without the burden of additional provisioning, effectively allowing more participation from the banks to resolve their NPAs through the bad bank.
- However, the success of the bad bank will depend on the implementation and management of the transferred NPAs.
|
A sub-standard asset is one which is classified as an NPA for a period not exceeding twelve months. A doubtful asset is one which has remained as an NPA for a period exceeding twelve months. A loss asset is one where loss has already been identified by the bank or an external institution, but it is not yet completely written off, due to its recovery value, however little it may be.
Image Courtesy: It proposed the idea of setting up a Public Sector Asset Rehabilitation Agency to tackle the growing menace of NPAs, which had started affecting the economy of the country. : A committee was set up by the then Finance minister to study the suitability of transferring the NPAs to a bad bank or an ARC. The finance minister has announced the setting up of a bad bank to take over the bad loans of commercial banks in India. India formally set up a bad bank as part of the nation’s ongoing efforts to remove one of the world’s largest piles of soured debt from the balance sheet of financiers and accelerate lending.
|
Sources : IE + TH
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Daily current affairs 20-06-2024, daily current affairs 19-06-2024, daily current affairs 18-06-2024, headlines of the day 21-06-2024.

Next Generation Institute for UPSC Civil Services Examination Preparation.
- Video Gallery
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- UPSC CSE Posts
- Testimonials
NEXT IAS (Delhi)
Old rajinder nagar.
- 27-B, Pusa Road, Metro Pillar no.118, Near Karol Bagh Metro, New Delhi-110060
Mukherjee Nagar
- 1422, Main Mukherjee Nagar Road. Near Batra Cinema New Delhi-110009
NEXT IAS (Jaipur)
- NEXT IAS - Plot No - 6 & 7, 3rd Floor, Sree Gopal Nagar, Gopalpura Bypass, Above Zudio Showroom Jaipur (Rajasthan) - 302015

NEXT IAS (Prayagraj)
- 31/31, Sardar Patel Marg, Civil Lines, Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh - 211001
NEXT IAS (Bhopal)
- Plot No. 46 Zone - 2 M.P Nagar Bhopal - 462011
- 8827664612 ,
Answer Writing Practice
What is a ‘Bad Bank’? List out the objectives behind setting up ‘Bad Bank’?

IAS 2024 - Your dream can come true!
Download the ultimate guide to upsc cse preparation.

Bad Bank, Definition, Concept, Examples, Pros & Cons
A bad bank is a specialized financial institution set up to acquire, manage, and resolve non-performing loans or distressed assets from commercial banks. Read all about Bad Bank Concept for UPSC exam

Table of Contents
A bad bank is a financial institution that is specifically created to address the issue of non-performing assets (NPAs) or bad loans held by commercial banks. The primary goal of a bad bank is to relieve the burden on commercial banks by purchasing their bad loans and removing them from their balance sheets. By doing so, the bad bank aims to enable commercial banks to resume lending to customers without constraints.
When a bad bank purchases a bad loan from a commercial bank, it takes on the responsibility of managing that loan. The bad bank may attempt to restructure the loan in order to improve its value or sell it to investors who are interested in acquiring distressed assets.
While a bad bank can generate profits through the sale of these bad loans at a price higher than its acquisition cost, profit generation is not typically the main objective. The primary purpose of a bad bank is to alleviate the burden on commercial banks by allowing them to offload their stressed assets, which enables them to actively engage in lending again.
Read about: Non-Performing Assets
How does Bad Banks work?
A bad bank operates by segregating a bank’s assets into good assets and toxic assets, with the latter being classified as bad or non-performing loans. Good assets are those in which loans are being repaid as scheduled, while toxic assets refer to loans that have defaulted or are at risk of defaulting.
The bad bank is established with the primary objective of aiding in the recovery of these risky assets. It allows commercial banks to remove toxic assets from their books, thereby cleaning up and reducing their exposure to such assets. This process helps banks to improve their financial position and focus on their core lending activities.
Once the toxic assets are identified, they are transferred from the commercial banks to the bad bank. The bad bank assumes the responsibility of managing these assets, which may involve various strategies to recover their value. This could include restructuring the loans, renegotiating terms with borrowers, or selling the assets to interested investors.
When the bad bank acquires toxic assets, it typically does so at a price below its book value. This discount reflects the distressed nature of these assets and compensates the bad bank for the associated risks. The bad bank then aims to recover as much value as possible from these assets over time.
The recovery process may involve actively working with borrowers to rehabilitate their loans, seeking legal remedies for loan defaulters, or exploring opportunities to sell the assets to interested parties. The bad bank’s ultimate goal is to maximize the recovery of funds and, if possible, generate profits by selling the toxic assets at a price higher than the acquisition cost.
By transferring the toxic assets to the bad bank, commercial banks can focus on their core business of lending and financial intermediation, as they are no longer burdened by the management of distressed loans. The bad bank takes on the specialized task of dealing with these assets, facilitating the cleanup of the banking system and promoting the flow of credit in the economy.
Read about: India Post Payment Bank
Bad Bank in India
The Indian government has proposed the creation of a bad bank called the National Asset Reconstruction Company Limited (NARCL) or “Bad Bank” to tackle the issue of bad loans in the banking system. The proposed NARCL aims to acquire and manage stressed assets from public sector banks and facilitate their resolution. It is important to note that the establishment and implementation of the bad bank in India may have progressed since my knowledge cutoff date, so it is advisable to refer to the latest updates and developments in this regard.
Read about: Micro ATMs
Examples of Bad Bank
Here are a few examples of bad banks that have been established in various countries:
| NAMA (National Asset Management Agency) | Ireland’s bad bank created in 2009 to manage and sell off toxic assets from the country’s troubled banks. |
| FMS (Federal Ministry of Finance’s Financial Market Stabilization Agency) | Germany’s bad bank established in 2008 to absorb toxic assets from banks during the financial crisis. |
| RTC (Resolution Trust Corporation) | A U.S. government-owned asset management company created in the 1990s to address the savings and loan crisis. |
| AMCON (Asset Management Corporation of Nigeria) | Nigeria’s bad bank was established in 2010 to resolve non-performing loans in the banking sector. |
Read about: MCLR Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate
Pros of a Bad Bank
Consolidation.
A bad bank can consolidate all bad loans from various banks into a single entity, simplifying the management and resolution of these troubled assets.
International Precedence
The concept of a bad bank has been successfully implemented in countries like the United States, Germany, Japan, and others during financial crises. Learning from their experiences can provide valuable insights for establishing an effective bad bank.
Capital Liberation
By removing bad loans from the balance sheets of struggling banks, a bad bank can unlock significant amounts of capital that were previously tied up as provisions against these loans. This freed-up capital can be utilized by banks to extend new loans and stimulate lending activities.
Capital Buffer Enhancement
A well-designed bad bank can enhance the capital buffers of banks, not by simply shoring up reserves, but by freeing up capital. This can instil confidence in banks, encouraging them to actively engage in lending once again.
Read about: Reserve Bank of India
Cons of a Bad Bank
Government ownership shifting.
If a bad bank is government-backed, transferring bad assets from government-owned public sector banks to another government-owned entity may not effectively resolve the bad loan crisis. Merely shifting assets between different government pockets may not address the underlying issues and incentives that contribute to the problem.
Ownership Dynamics
Public sector banks, managed by bureaucrats, may lack the same financial incentives and commitment to profitability as private banks owned by individuals. A bad bank bailout does not directly address the root problems of inefficiencies and governance issues within public sector banks.
Moral Hazard Risk
Banks that are bailed out by a bad bank may have limited motivation to improve their lending practices. The safety net provided by a bad bank can potentially incentivize reckless lending behaviour, exacerbating the bad loan crisis in the long run.
Read about: National Payments Corporation of India
Bad Bank Concept Way forward
Moving forward, it is important to recognize that while a bad bank can be a valuable solution, addressing the root causes of the banking system’s structural problems is crucial. One of the key challenges lies in ensuring that the management of public sector banks is not influenced by politicians and bureaucrats, allowing for greater professionalism and adherence to prudential lending norms.
Therefore, alongside the establishment of a bad bank, it is imperative to implement comprehensive reforms aimed at addressing the underlying issues in the banking sector. These reforms should focus on enhancing corporate governance, promoting autonomy in decision-making, and reducing political interference in the functioning of banks.
Additionally, improving the professionalism of bank management through targeted training and recruitment processes can help foster a culture of sound risk management and responsible lending practices. This can be achieved by attracting skilled professionals who possess the necessary expertise and commitment to ensure the profitability and stability of banks.
Furthermore, regulatory reforms should be introduced to strengthen prudential norms, enhance risk assessment capabilities, and ensure effective oversight of the banking system. This will help prevent the recurrence of bad loans and promote a healthier lending environment.
Read about: Difference Between Organised and Unorganised Sector
Bad Bank Concept UPSC
The topic of bad banks is important for the UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) examination as it is relevant to several areas of the UPSC Syllabus , such as economics, banking, and governance. Understanding the concept of bad banks, their pros and cons, and their role in resolving the issue of bad loans in the banking sector is essential for candidates preparing for the UPSC examination. To excel in the examination, candidates can make use of UPSC Online Coaching and practice with UPSC Mock Test to strengthen their knowledge and analytical skills in this topic and its broader context.
Read about: Payment Banks
Sharing is caring!
Bad Bank FAQs
Who gave the concept of bad bank.
The concept of bad bank was initially proposed by Paul Keating, the former Prime Minister of Australia, in the early 1990s.
What is the objective of bad bank?
The objective of a bad bank is to help ease the burden on commercial banks by taking bad loans off their balance sheets and encouraging them to lend actively again.
What is a bad bank in Indian economy?
In the Indian economy, a bad bank refers to a specialized financial entity set up to purchase and manage non-performing assets (NPAs) or bad loans from commercial banks.
What is bad loan bank?
A bad loan bank is a financial institution established to acquire, restructure, and sell non-performing loans, with the aim of resolving the bad loan crisis and improving the overall health of the banking system.
I, Sakshi Gupta, am a content writer to empower students aiming for UPSC, PSC, and other competitive exams. My objective is to provide clear, concise, and informative content that caters to your exam preparation needs. I strive to make my content not only informative but also engaging, keeping you motivated throughout your journey!

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Exam 2024
- UPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Mains Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPSC Age Limit 2024
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Full Form

Recent Posts
- UPPSC Exam 2024
- UPPSC Calendar
- UPPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPPSC Application Form 2024
- UPPSC Eligibility Criteria 2024
- UPPSC Admit card 2024
- UPPSC Salary And Posts
- UPPSC Cut Off
- UPPSC Previous Year Paper
BPSC Exam 2024
- BPSC 70th Notification
- BPSC 69th Exam Analysis
- BPSC Admit Card
- BPSC Syllabus
- BPSC Exam Pattern
- BPSC Cut Off
- BPSC Question Papers
IB ACIO Exam
- IB ACIO Salary
- IB ACIO Syllabus
CSIR SO ASO Exam
- CSIR SO ASO Exam 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Result 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date
- CSIR SO ASO Question Paper
- CSIR SO ASO Answer key 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Syllabus 2024
Study Material Categories
- Daily The Hindu Analysis
- Daily Practice Quiz for Prelims
- Daily Answer Writing
- Daily Current Affairs
- Indian Polity
- Environment and Ecology
- Art and Culture
- General Knowledge
- Biographies
IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy

- Visit Our Blog about Russia to know more about Russian sights, history
- Check out our Russian cities and regions guides
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook to better understand Russia
- Info about getting Russian visa , the main airports , how to rent an apartment
- Our Expert answers your questions about Russia, some tips about sending flowers

Russian regions
- Altay republic
- Irkutsk oblast
- Kemerovo oblast
- Khakassia republic
- Krasnoyarsk krai
- Novosibirsk oblast
- Omsk oblast
- Tomsk oblast
- Tuva republic
- Map of Russia
- All cities and regions
- Blog about Russia
- News from Russia
- How to get a visa
- Flights to Russia
- Russian hotels
- Renting apartments
- Russian currency
- FIFA World Cup 2018
- Submit an article
- Flowers to Russia
- Ask our Expert
Irkutsk Oblast, Russia
The capital city of Irkutsk oblast: Irkutsk .
Irkutsk Oblast - Overview
Irkutsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia located in Eastern Siberia, in the south-eastern part of the Siberian Federal District. Irkutsk is the capital city of the region.
The population of Irkutsk Oblast is about 2,357,000 (2022), the area - 774,846 sq. km.
Irkutsk oblast flag
Irkutsk oblast coat of arms.

Irkutsk oblast map, Russia
Irkutsk oblast latest news and posts from our blog:.
19 April, 2023 / Steam Locomotive of the Circum-Baikal Railway .
8 June, 2021 / Irkutsk - the view from above .
4 April, 2019 / Cities of Russia at Night - the Views from Space .
16 November, 2017 / The Lost World of Tofalaria .
22 September, 2016 / The train ride along the shore of Lake Baikal .
More posts..
News, notes and thoughts:
5 October, 2013 / Typical news from Russia. In Irkutsk region, the bear made his way in one of the cottages located near Ust-Ilimsk. By night, the bear climbed onto the veranda through the window and ate the whole pot of borsch while owners were in the banya. Arrived on the scene the police shot into the air and the bear ran into the woods.
Irkutsk Oblast - Economy
Irkutsk Oblast is rich in such natural resources as oil, natural gas, gold, iron, coal. It is an important transport hub of Siberia - the Trans-Siberian Railway and the Baikal-Amur Railway pass through its territory. The main rivers are the Angara, Belaya, Iya, Kitoy, Irkut, Oka, Lena, Kirenga, and Nizhnaya Tunguska.
This region plays a significant role in the Russian industry. In the all-Russian production it makes about 6,5% of power production, 15% of timber export, 6% of coal mining, almost 20% of pulp production, over 10% of carton, about 9% of oil.
The following industries are the most developed: timber and wood-processing, pulp and paper, mining, fuel, non-ferrous metallurgy, power engineering, machine-building, chemical and oil, food and ferrous metallurgy. Hydro-power industry is also well developed (the main dams: Irkutsk Dam, Bratsk Dam, Ust-Ilimsk Dam). Industrial enterprises are mainly located in Irkutsk and several district centers.
The railway is the main means of transport. The main transport line is the Trans-Siberian Railway. The western part of the Baikal-Amur Railway stretches from the town of Taishet to the east through the territory of the region. The total length of railways is about 2,500 km.
There are two airports in the cities of Irkutsk and Bratsk, they are international airports and offer flights to China, Mongolia, Tajikistan, Thailand, Uzbekistan, South Korea.
Several large navigable rivers flow through the region - the Angara, Lena, Nizhnyaya Tunguska. The largest ports are located on the Lena - Kirensk and Osetrovo. They provide cargo transportation to the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) and the northern seaport of Tixi.
Nature of Irkutsk Oblast

Beautiful nature of the Irkutsk region
Author: Kovalev Maksim

River in Irkutsk Oblast
Author: Roman Romanov

Lake in Irkutsk Oblast
Author: V.Chokan
Irkutsk Oblast - Features
Irkutsk Oblast is a large subject of the Russian Federation that is almost equal to the territory of Turkey. It is the largest region of Russia that has no outlet to the sea. From north to south the region stretches for about 1,450 km, from west to east - for 1,318 km.
The distance from Irkutsk to Moscow by rail - 5,192 km, to Vladivostok - 4,106 km. Time difference between Irkutsk and Moscow - 5 hours. The largest cities and towns of Irkutsk Oblast are Irkutsk (617,200), Bratsk (222,500), Angarsk (220,000), Ust-Ilimsk (78,700), Usolie-Sibirskoye (73,800).
The climate in the Irkutsk region is sharply continental, with long cold winters and short hot and dry summers.
Irkutsk Oblast has a rich history: ancient sites, the Russians settling in eastern Siberia, Decembrists, the Soviet construction sites - there are historical monuments in almost every settlement. Over 60 museums are open in the region, they attract historians and tourists from Europe and Asia.
Attractions of Irkutsk Oblast
Baikal , the largest freshwater lake in the world, occupies a special place among the riches of Siberia. This lake is a wonderful natural monument known for its extremely clean, very clear water. Baikal is a unique sea-lake sung in legends and tales of antiquity, one the centers of Asian culture. It is a great place for eco-tourism.
The Circum-Baikal Railway , offering stunning views of the lake and its surroundings, is one of the most visited places of the region. It is an amazing piece of engineering, a historical monument of the 19th century. There are 38 tunnels with total length of 9,063 m, 15 stone galleries, 3 concrete galleries, 248 bridges and viaducts, 172 architectural monuments.
Olkhon , the largest on Lake Baikal, is also popular among tourists. In Buryat folk legends, Olkhon Island is a mysterious place; to this day it is known as the center of shamanism.
Khamar-Daban, Primorsky, North Baikal ridges, Sayan spurs, Olkhinskoye plateau are unique place not only for mountaineering but also for downhill skiing. Tourists are also attracted by mountain skiing in Baikalsk city.
About 60 km from Irkutsk there is an architectural and ethnographical museum “Taltsy”.
Irkutsk oblast of Russia photos
Pictures of irkutsk oblast.

Early autumn in the Irkutsk region
Author: Taranovsky

Sunset in Irkutsk Oblast
Author: Konstantin Vavilov

Church in Irkutsk Oblast

Orthodox church in the Irkutsk region
Author: Gennady Taraskov
- Currently 3.06/5
Rating: 3.1 /5 (170 votes cast)
Ilim Group Presents its New KLB Mill to Industry Players
Presentation of the largest kraftliner production site in Russia took place at the 27th International Exhibition of the Packaging Industry RosUpack

The presentation of the Big Ust-Ilimsk Project, involving the construction of Russia’s one-of-a-kind pulp and board (KLB) mill in the Irkutsk Oblast, was one of the key events at RosUpack 2023. When speaking at the plenary session on corrugated board packaging market development, Alexey Chenyaev, Ilim’s Senior Vice President, Sales, Supply Chain Management and Packaging, focused on the advanced manufacturing and environmental solutions implemented at the new KLB Mill and prospects for sales market expansion it will secure.
After KLB Mill ramp-up (600,000 tons of kraftliner per year), the total annual output of Ilim Group will amount to 4.3 million tons. The Company will be one of the world’s largest producers of unbleached packaging materials and will strengthen its leadership in the Chinese market of wood-free corrugated materials with a share of approximately 50 to 60%.
The Big Ust-Ilimsk project was met by exhibitors with great interest. This year the event was attended by more than 740 companies from 19 countries. Ilim’s booth with an area of 140 m2 was one of the largest one at the site and was operated by about 50 experts from Sales and Corrugated Box Business Management Departments. The booth was attended by over 60 key accounts and more than 120 representatives of various companies, including such major ones as Heinz, MARS and KDV-Group.
Reference information:
Ilim Group is the leader of the Russian pulp and paper industry and one of the industry leaders globally. Ilim Group has three pulp and paper mills in the Arkhangelsk (Koryazhma) and Irkutsk (Bratsk and Ust-Ilimsk) Oblasts, two modern corrugated box plants in the Leningrad and Moscow Oblasts (Kommunar and Dmitrov, respectively), and Sibgiprobum engineering and design institute (Irkutsk).
Share on social networks
Achievers Corner
- Topper's Interview
- About Civil Services
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus
- GS Prelims Strategy
- Prelims Analysis
- GS Paper-I (Year Wise)
- GS Paper-I (Subject Wise)
- CSAT Strategy
- Previous Years Papers
- Practice Quiz
- Weekly Revision MCQs
- 60 Steps To Prelims
- Prelims Refresher Programme 2020
Mains & Interview
- Mains GS Syllabus
- Mains GS Strategy
- Mains Answer Writing Practice
- Essay Strategy
- Fodder For Essay
- Model Essays
- Drishti Essay Competition
- Ethics Strategy
- Ethics Case Studies
- Ethics Discussion
- Ethics Previous Years Q&As
- Papers By Years
- Papers By Subject
- Be MAINS Ready
- Awake Mains Examination 2020
- Interview Strategy
- Interview Guidance Programme
Current Affairs
- Daily News & Editorial
- Daily CA MCQs
- Sansad TV Discussions
- Monthly CA Consolidation
- Monthly Editorial Consolidation
- Monthly MCQ Consolidation
Drishti Specials
- To The Point
- Important Institutions
- Learning Through Maps
- PRS Capsule
- Summary Of Reports
- Gist Of Economic Survey
Study Material
- NCERT Books
- NIOS Study Material
- IGNOU Study Material
- Yojana & Kurukshetra
- Chhatisgarh
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
Test Series
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Mains Test Series
- UPPCS Prelims Test Series
- UPPCS Mains Test Series
- BPSC Prelims Test Series
- RAS/RTS Prelims Test Series
- Daily Editorial Analysis
- YouTube PDF Downloads
- Strategy By Toppers
- Ethics - Definition & Concepts
- Mastering Mains Answer Writing
- Places in News
- UPSC Mock Interview
- PCS Mock Interview
- Interview Insights
- Prelims 2019
- Product Promos
- Daily Updates
Social Justice
Make Your Note
Pros & Cons of Bad Bank
- 24 Mar 2021
- GS Paper - 2
- Salient Features of Indian Society
- Role of Women
This article is based on “Bad bank, good move” which was published in The Indian Express on 23/03/2021. It talks about the pros and cons of a bad bank.
For a banking sector-dependent economy like India, the good health of the banks is very important to ensure accessible financial services and flow of credit to support the growing economy. However, for many years, Indian banks have been dealing with the NPA crisis that has created problems for them and the entire economy.
Further, the economic fallout due to the coronavirus crisis has increased the banking sector’s stress. Therefore, to restore banks’ health, the Budget 2021 has proposed one such measure i.e. the idea of setting up a National bad bank . However, the idea of a bad bank is itself much debatable.
What is a Bad Bank
- A bad bank is an entity that acts as an aggregator of bad loans or non-performing assets (NPA’s) and purchases them from across the banking sector at a discounted price and then works towards their recovery and resolution.
- These loans are classified as non-performing and are at the verge of or already in the state of default. These bad loans negatively impact a bank’s balance sheet.
- The bad bank is similar to an Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC), where they absorb these loans from the banks and then manage them to recover as much amount as possible.
Proposed Model for Bad Bank
The budget 2021 proposed an Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC)-Asset Management Company (AMC) structure, wherein the ARC will aggregate the debt, while the AMC will act as a resolution manager.
- The proposed structure envisages the setting up of a National Asset Reconstruction Company (NARC) to acquire stressed assets in an aggregated manner from lenders, which will be resolved by the National Asset Management Company (NAMC).
- A skilled and professional set-up dedicated to Stressed Asset Resolution will be ably supported by attracting institutional funding in stressed assets through strategic investors, AIFs, special situation funds, stressed asset funds, etc for participation in the resolution process.
- Further, transferring these stressed assets to bad banks will entail recovery of 15% in cash and 85% in sovereign guaranteed security receipts. This government guarantees but will carry a zero-risk weight, for a specified period of time.
- The net effect of this approach would be to build an open architecture and a vibrant market for stressed assets.
Arguments For Bad Banks
- Capital being freed up from less than fully provisioned bad assets.
- Capital freed up from security receipts because of a sovereign guarantee.
- Cash receipts that come back to the banks and can be leveraged for lending, also freeing up provisions from the balance sheet.
- The US implemented the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) after the 2008 financial crisis, which helped the US economy after the subprime crisis.
- It was modeled around the idea of a bad bank.
- Revival of Credit Flow Post-Covid: Some experts believe that a bad bank can help free capital of over ₹5 lakh crore that is locked in by banks as provisions against the bad loans.
Arguments Against a Bad Bank
- Without fundamental reforms to solve the NPA problem, the bad bank is likely to become a warehouse for bad loans without any recovery taking place.
- Tight Fiscal Position: Furthermore, an important concern is regarding mobilizing capital for the bad bank. In an economy hit by the pandemic, it is hard to find buyers for distressed assets and the Government is also in a tight fiscal position.
- No Clear Procedure: Also, there is no clear procedure to determine at what price and which loans should be transferred to the bad bank. This may create political challenges for the Government.
- Moral Hazard: Former Governor of the reserve bank, Raghuram Rajan believes that setting a bad bank may also create moral hazard problems among the banks that would enable them to continue with their reckless lending practices, further exacerbating the NPA problem.
So long as Public sector banks managements remain beholden to politicians and bureaucrats, their deficit in professionalism will remain and subsequently, prudential norms in lending will continue to suffer.
Therefore, a bad bank is a good idea, but the main challenge lies with tackling the underlying structural problems in the banking system and making reforms to improve the public sector banks.
|
Setting up a bad bank is the right step in tackling the NPA crisis, but it is not at all the panacea. Discuss. |

- International
- Today’s Paper
- T20 World Cup
- Express Shorts
- Mini Crossword
- Premium Stories
- Health & Wellness
‘Koi ummid hai nahi…’: Father’s angry message to son who gave UPSC exam goes viral
The viral post shows father's reaction to his son's confession about upsc marks..
The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) Civil Services Exam is considered one of the toughest examinations in India. Approximately 10 lakh candidates appear yearly in the UPSC exams, out of which only 180 candidates become IAS officers. A post showing an angry father bashing his son expected to score only 75 marks in his UPSC CSE Prelims 2024 got the Internet talking about toxic parenting.
The viral message begins with the father saying, “ Tumko hum pahle v bole the isme samay barbad nahi karo. Ab tum kahi ke nahi raha (I warned you not to waste your time on this. Now you are nowhere).”

“ Ghar akar bat karo. Satyam ka dekho 120 question sahi hai (Come home and talk to me. Satyam got 120 questions correct),” the angry father says comparing his son’s marks with some other student. However, UPSC CSE Prelims has only 100 questions.
“ Humko bap kuch nahi diya hum ijjat se Delhi jaisa shar me rahkar jo kiya wo tum dekha. Raha tumhara bat tum se na humko koi ummid hai, nahi humko koi ummid hai nahi humko kuch tum de payega (My father gave me nothing. I started a new life in a city like Delhi. As far as you are concerned, I don’t have any hope from you. I don’t think you can give me anything),” the message read.
“ Aaj v agar tum imandari se padhai kare to upsc kya kuch v nikal denge is bar ka question me v20 questions mujhe aata that aur tum 40 kiye ise se samjho ki tum kya karoge galimat hai ki tum sirf sahi bata diya. Tumhara padhai ka aukat ab sab Delhi se lekar ristedar tak samajh gaya (If I start preparing for UPSC now, I’ll crack it easily. I knew 20 questions already from this year’s question paper and you only did 40. One can only imagine what you have done. But at least you didn’t lie to me. Now everyone, including our relatives, knows your calibre),” the message ended.
Take a look at the post here:
This was a response of a dad when his Son told he is getting 75 in UPSC Prelims 2024 https://t.co/VPHDPlt1QO pic.twitter.com/0xJTUce3rj — Don Muji (Muji Ka Parivar) (@mujifren) June 17, 2024

With over 1.2 million views, the post prompted chatter around the UPSC exam, and toxic parenting. Many users were left perplexed as the father mentioned one “Satyam” answering 120 questions as the UPSC Prelims exams have only 100 questions. Reacting to it, a user wrote, “Questions to sirf 100 the, 120 kahan sahi kar diya bhai (There were only 100 questions, how come he can correctly mark 120 questions).”
Another user commented, “Such parenting results in neither professionally successful nor socially well-adjusted individuals.”
“The tone is familiar but reading this feels so bad for the son reading this. I hope he stays strong and keeps his morale high,” said another X user.
- UPSC Civil Services

IMD extends yellow alert for Mumbai till Thursday due to moderate to heavy rainfall. Island city and suburban belt woke up to rain, with Santacruz recording 20mm and Colaba recording 55mm in past 24 hours. Scientist predicts continued rainfall on Thursday and receding intensity starting Friday. Earlier forecast predicted surplus rainfall this year.
- KEAM Result 2024 Live Updates: How to check scorecard at cee.kerala.gov.in 27 mins ago
- Weather Today Live Updates (June 20): IMD expects light to moderate rainfall in Delhi, nearby districts 1 hour ago
- NEET UG 2024 Row Live Updates: NEET controversy reaches Amit Shah’s table 1 hour ago
- Mumbai News Live Updates: City braces for rains for next 24 hours as IMD sounds ‘yellow’ alert 1 hour ago

Best of Express

Buzzing Now

Jun 20: Latest News
- 01 The Trump rallying cry that’s also a math problem
- 02 Shinde: Sena UBT abandoned Hindutva for Congress vote bank
- 03 My Hindutva is reformist, not jaded like yours: Uddhav to BJP
- 04 Russia and North Korea sign partnership deal that appears to be the strongest since the Cold War
- 05 T20 World Cup: Middle-order six-hitting a worry for India
- Elections 2024
- Political Pulse
- Entertainment
- Movie Review
- Newsletters
- Web Stories

- OUR CENTERS Bangalore Delhi Lucknow Mysuru Srinagar Dharwad Hyderabad
Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

UPSC Mains Answer Writing Practice – Insights SECURE: 19 June 2024

The Insights IAS Secure Initiative for UPSC Mains Answer Writing practice enables you to practice daily answer writing, enhancing your skills and boosting your scores with regular feedback, expert tips, and strategies. Let consistency be the hallmark of your preparation and utilize UPSC Mains Answer Writing practice initiative wisely

Click on EACH question to post/upload you answers.
How to Follow Secure Initiative?
How to self-evaluate your answer , mission – 2024: yearlong timetable, join ipm 4.0 to get an assured review of 2 secure answers everyday, general studies – 1.
Topic: political philosophies like communism, capitalism, socialism etc.— their forms and effect on the society.
1. The major political philosophies of the world, including liberalism, socialism, and communism, have shaped the world order through their ideologies and have had a wide range of impacts. Analyse. (250 words)
Difficulty level: Tough
Reference: Insights on India
Why the question: The question is part of the static syllabus of General studies paper – 1. Key Demand of the question: To critically analyse the major political philosophies of modern world history and their impact on world order. Directive: Analyse – When asked to analyse, you must examine methodically the structure or nature of the topic by separating it into component parts and present them in a summary. Structure of the answer: Introduction: Begin by giving context regarding the major political philosophies of twentieth and twenty first century. Body: First, write about the achievements as well as shortcomings of major political philosophies – communism, capitalism, socialism, colonialism, liberalism etc. Next, write about the various ways in which the above shaped the global world order in the present times – governance, economics, and international relations. Substantiate with examples. Conclusion: Conclude by summarising.
Topic: Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India; Social empowerment.
2. Caste inequality remains a critical determinant of social and economic disparities, requiring targeted policies and inclusive growth efforts to address systemic discrimination and historical injustices. Examine. (250 words)
Difficulty level: Moderate
Reference: Indian Express , Insights on India
Why the question: A recent working paper of the World Inequality Lab has reignited discussion on the widening gap between the rich and poor. Inequality in India, however, transcends the dichotomy between the haves and the have-nots, as caste-based inequalities are among the defining features of the country’s socioeconomic framework. Key Demand of the question: To write about the ill effects of caste discrimination, reasons for its prevalence and ways to overcome it. Directive: Examine – When asked to ‘Examine’, we must investigate the topic (content words) in detail, inspect it, investigate it and establish the key facts and issues related to the topic in question. While doing so we should explain why these facts and issues are important and their implications. Structure of the answer: Introduction: Begin by giving background about the caste discrimination in modern India. Body: First, write about the reasons for the prevalence of caste discrimination in India and factors behind it. Next, mention the impact of caste discrimination and how it is affecting contemporary society. Substantiate with facts and examples. Next, write about the steps that are needed to overcome the above issues and empower weaker sections. Conclusion: Conclude by writing a way forward.
General Studies – 2
Topic: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
3. Delayed census data stalls progress towards sustainable development and exacerbates inequalities. Analyse. (250 words)
Reference: The Hindu , Insights on India
Why the question: Census data are essential for many purposes, including the implementation of welfare schemes. Key Demand of the question: To write about benefits of collecting census data and impact of delayed census. Directive word: Analyse – When asked to analyse, you must examine methodically the structure or nature of the topic by separating it into component parts and present them in a summary. Structure of the answer: Introduction: Begin by giving context of census in India. Body: In the first part, discuss the advantages of census – essential for planning the provision of health care, education, employment, etc, helpful in the debate related to reservation policy, targeted poverty reduction programmes etc Next, Discuss the limitations of not conducting census – inefficient resource allocation, outdated policies, inadequate urban planning, overlooked vulnerable populations, and compromised public health and emergency responses etc. Conclusion: Conclude with a way forward.
Topic: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
4. The G-7 (Group of Seven), faces an evolving landscape that necessitates a reassessment of its purpose and must adapt to contemporary global challenges. Examine. (150 words)
Reference: The Hindu
Why the question: Welcoming leaders of 10 countries including Prime Minister Narendra Modi to the “G-7 Outreach” Summit, Italy’s Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni said it was important to step away from the old trope of the “West vs the Rest”. Key Demand of the question: To write about the various changes needed in G7 to adapt to changing geopolitics of the current times. Directive word: Examine – When asked to ‘Examine’, we must investigate the topic (content words) in detail, inspect it, investigate it and establish the key facts and issues related to the topic in question. While doing so we should explain why these facts and issues are important and their implications. Structure of the answer: Introduction: Begin by giving context. Body: First, in brief, write about aims and objectives of G-7. Next, write about the major challenges G-7 faces in the current times – global instability, Geopolitical tensions, non-traditional security threats, rise of emerging economies like China and India, Climate Change etc. Next, write about the steps that G-7 should take in this regard. Conclusion: Conclude by writing a way forward.
General Studies – 3
Topic: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment
5. Debt instruments play a crucial role in the global financial system by providing various entities with access to capital markets to finance their operations and investments. Discuss. (150 words)
Difficulty level: Easy
Why the question: The question is part of the static syllabus of General studies paper – 3. Key Demand of the question: To write about various types of debt instruments available in the Indian market. Directive word: Discuss – This is an all-encompassing directive – you must debate on paper by going through the details of the issues concerned by examining each one of them. You must give reasons for both for and against arguments. Structure of the answer: Introduction: Begin by defining a debt instrument. Body: Write about the various type of debt instruments – government securities, corporate bonds, debentures, commercial papers, certificates of deposit, and money market instruments. Explain them in brief with suitable examples and the role they play in the economy. Conclusion: Conclude by summarising their importance.
Topic: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
6. India’s progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030 shows positive strides, yet requires targeted actions to address the shortcomings in the efforts. Critically analyse.
Reference: Down to Earth
Why the question: The world is significantly behind schedule in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations in 2015, according to a new UN report. Key Demand of the question: To write about India’s performance with respect to SDG’s and changes required to achieve the target. Directive word: Critically analyze – When asked to analyse, you must examine methodically the structure or nature of the topic by separating it into component parts and present them in a summary. When ‘critically’ is suffixed or prefixed to a directive, one needs to look at the good and bad of the topic and give a balanced judgment on the topic. Structure of the answer: Introduction: Begin by giving context about 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) that are to be achieved by 2030. Body: First, mention the important SDGs in brief and write about the various measures taken in order to achieve them. Next, evaluate India’s performance toward achieving various SDGs by 2030 and mention the shortfalls. Next, write about the various course corrections that are required in order to ensure that SGDs are achieved by 2030. Conclusion: Conclude with a way forward.
General Studies – 4
Topic: Human Values – lessons from the lives and teachings of great leaders, reformers and administrators;
7. What does this quote means to you? (150 words)
“Courage is not simply one of the virtues, but the form of every virtue at the testing point.” – C.S. Lewis
Why the question: The question is part of the static syllabus of General studies paper – 4. Structure of the answer: Introduction: Begin by explaining the literal meaning of the quote. Body: Write about how courage is not just a virtue, but rather the expression of all virtues when put to the test. It suggests that courage is the foundation that enables individuals to live virtuously in challenging circumstances by allowing them to act in accordance with their values. Cite examples to substantiate. Conclusion: Summarise by highlighting the importance of the quote in the present day.
Click here to Download the SECURE Questions in PDF Format
Join our Official Telegram Channel HERE
Please subscribe to Our podcast channel HERE
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel HERE
Follow our Twitter Account HERE
Follow our Instagram ID HERE
Follow us on LinkedIn : HERE

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A bad bank is a financial entity set up to buy Non-Performing Assets (NPAs), or Bad Loans, from banks. The aim of setting up a bad bank is to help ease the burden on banks by taking bad loans off their balance sheets and get them to lend again to customers without constraints. After the purchase of a bad loan from a bank, the bad bank may later ...
Why in News. Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Governor has agreed to look at a proposal for creating a Bad Bank.. Key Points. About: A bad bank conveys the impression that it will function as a bank but has bad assets to start with.; Technically, a bad bank is an Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) or an Asset Management Company (AMC) that takes over the bad loans of commercial banks ...
A Bad Bank is a financial institution created to hold and manage toxic or NPAs of troubled banks or financial institutions.. This topic of the "Bad Bank" is important from the perspective of the UPSC IAS Examination which falls under General Studies Paper 3 (Mains) and General Studies Paper 1 (Prelims) and particularly in the Economy. In this article, we shall discuss Bad Banks, the ...
The remaining 51% stake will be with private-sector lenders. The NARCL-IDRCL structure is the new bad bank structure. Existing ARCs have been helpful in the resolution of stressed assets, especially for smaller value loans. Various available resolution mechanisms, including Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), have proved to be useful.
Bad bank: Context: The Indian Banks' Association (IBA) has begun identifying bad loans which can be transferred to the Centre's proposed bad bank. The IBA has written to banks asking them for a list of all bad loans worth Rs 500 crore and above to "identify magnitude of the problem" and "get clarity over initial capital required for ...
The idea of Bad Bank is not new. Currently, this is in the news due to the problem caused by COVID-19. Earlier the topic of Bad Bank was a matter of debate in the banking and finance circles when former Interim Finance Minister Piyush Goyal had put forward the idea when a committee headed by Sunil Mehta was formed to study the feasibility of ...
This means that about 10% of loans are never paid back, resulting in substantial loss of money to the banks. When restructured and unrecognised assets are added the total stress would be 15-20% of total loans. NPA crisis in India is set to worsen. Restructuring norms are being misused.
Introduction . Bad banks, formally called Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARC), are specialized financial institutions that buy the stressed and non-performing assets (NPA) of the bank to help clean up their balance sheet.; Establishment and Regulations of ARC; Incorporated under the Companies Act and registered with RBI under the Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and ...
A bad bank is simply an entity which specialises in handling bad loans or NPAs. It is basically an entity which buys the NPAs of commercial banks and tries to recover at least a part of the value of such NPAs. Usually, banks discount the book value of NPAs when they are transferred to a bad bank. After that, whatever recovery is possible from ...
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE Topic: GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment. GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation. Bad Bank Context: With commercial banks set to witness a spike in NPAs, or bad loans, in the…
Context: Budget 2021-22 recommended for setting up an Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) Ltd and an Asset Management Company (AMC) for dealing with stressed debt, signals a green light for 'Bad Bank' Arguments favouring setting up of 'Bad Banks' It benefits Commercial banks: by transferring their bad loans to bad banks and thereby reducing loan book risks and provisioning losses and ...
The Genesis of the Idea of Bad Bank. The troubled asset relief program, also known as TARP, implemented by the U.S. Treasury in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, was modelled around the idea of a bad bank.; Under the program, the U.S. Treasury bought troubled assets such as mortgage-backed securities from U.S. banks at the peak of the crisis and later resold it when market conditions ...
Introduction A bad bank is a business that trades in risky and illiquid assets owned by banks, other financial institutions, or a collection of banks. By moving subpar loans, it is meant to help banks balance their books and free them up to concentrate on their main activities of accepting deposits and lending money. Let's look at the definition of a "bad bank," the need for one ...
Government's Guarantee: The GoI Guarantee of up to Rs 30,600 crore will back Security Receipts (SRs) issued by NARCL. The guarantee will be valid for 5 years. If the bad bank is unable to sell the bad loan, or has to sell it at a loss, then the government guarantee will be invoked. The guarantee shall cover the shortfall between the face ...
A bad bank is technically an asset reconstruction company that buys bad loans (NPAs) from the commercial banks at a discount and tries to recover the money from the defaulter by providing a systematic solution over a period of time. The idea of a bad bank seeks to reduce the NPAs in the banking sector and then revive lending and credit growth.
List out the objectives behind setting up 'Bad Bank'? Login. Study Materials. NCERT Solutions. NCERT Solutions For Class 12. NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics; ... UPSC Previous Question Papers. UPSC 2022 Question Papers. Prelims 2022 Question Papers; UPSC 2021 Question Papers ; UPSC 2020 Question Papers. Prelims 2020 Question Papers;
Bad Bank Concept UPSC The topic of bad banks is important for the UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) examination as it is relevant to several areas of the UPSC Syllabus, such as economics, banking, and governance. Understanding the concept of bad banks, their pros and cons, and their role in resolving the issue of bad loans in the banking ...
Climate. Bratsk has a subarctic climate ( Köppen climate classification Dfc ). Winters are very cold and long with average temperatures from −23.4 °C (−10.1 °F) to −15.7 °C (3.7 °F) in January, while summers are mild to warm with average temperatures from +13.3 °C (55.9 °F) to +23.8 °C (74.8 °F) in July.
Irkutsk Oblast is a large subject of the Russian Federation that is almost equal to the territory of Turkey. It is the largest region of Russia that has no outlet to the sea. From north to south the region stretches for about 1,450 km, from west to east - for 1,318 km. The distance from Irkutsk to Moscow by rail - 5,192 km, to Vladivostok ...
Presentation of the largest kraftliner production site in Russia took place at the 27th International Exhibition of the Packaging Industry RosUpack. The presentation of the Big Ust-Ilimsk Project, involving the construction of Russia's one-of-a-kind pulp and board (KLB) mill in the Irkutsk Oblast, was one of the key events at RosUpack 2023.
Setting up of NARCL, the proposed bad bank for taking over stressed assets of lenders, was announced in the Budget for 2021-22. The plan is to create a bad bank to house bad loans of ₹500 crore and above, in a structure that will contain an asset reconstruction company (ARC) and an asset management company (AMC) to manage and recover dud assets.
Providing Lending Leverage to Banks: The benefits of bad bank include the recovered value, and significant lending leverage because of three factors: Capital being freed up from less than fully provisioned bad assets. Capital freed up from security receipts because of a sovereign guarantee. Cash receipts that come back to the banks and can be ...
Price trend information excludes taxes and fees and is based on base rates for a nightly stay for 2 adults found in the last 7 days on our site and averaged for commonly viewed hotels in Bratsk.Select dates and complete search for nightly totals inclusive of taxes and fees.
The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) Civil Services Exam is considered one of the toughest examinations in India. Approximately 10 lakh candidates appear yearly in the UPSC exams, out of which only 180 candidates become IAS officers. A post showing an angry father bashing his son expected to ...
The Insights IAS Secure Initiative for UPSC Mains Answer Writing practice enables you to practice daily answer writing, enhancing your skills. ... one needs to look at the good and bad of the topic and give a balanced judgment on the topic. ... 1st floor above Punjab National Bank , Ashoknagar X roads, Ashoknagar Hyderabad 500020. About Us.