- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing

How to Write a History Essay
Last Updated: December 27, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 243,174 times.
Writing a history essay requires you to include a lot of details and historical information within a given number of words or required pages. It's important to provide all the needed information, but also to present it in a cohesive, intelligent way. Know how to write a history essay that demonstrates your writing skills and your understanding of the material.
Preparing to Write Your Essay

- The key words will often need to be defined at the start of your essay, and will serve as its boundaries. [2] X Research source
- For example, if the question was "To what extent was the First World War a Total War?", the key terms are "First World War", and "Total War".
- Do this before you begin conducting your research to ensure that your reading is closely focussed to the question and you don't waste time.

- Explain: provide an explanation of why something happened or didn't happen.
- Interpret: analyse information within a larger framework to contextualise it.
- Evaluate: present and support a value-judgement.
- Argue: take a clear position on a debate and justify it. [3] X Research source

- Your thesis statement should clearly address the essay prompt and provide supporting arguments. These supporting arguments will become body paragraphs in your essay, where you’ll elaborate and provide concrete evidence. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Your argument may change or become more nuanced as your write your essay, but having a clear thesis statement which you can refer back to is very helpful.
- For example, your summary could be something like "The First World War was a 'total war' because civilian populations were mobilized both in the battlefield and on the home front".

- Pick out some key quotes that make your argument precisely and persuasively. [5] X Research source
- When writing your plan, you should already be thinking about how your essay will flow, and how each point will connect together.
Doing Your Research

- Primary source material refers to any texts, films, pictures, or any other kind of evidence that was produced in the historical period, or by someone who participated in the events of the period, that you are writing about.
- Secondary material is the work by historians or other writers analysing events in the past. The body of historical work on a period or event is known as the historiography.
- It is not unusual to write a literature review or historiographical essay which does not directly draw on primary material.
- Typically a research essay would need significant primary material.

- Start with the core texts in your reading list or course bibliography. Your teacher will have carefully selected these so you should start there.
- Look in footnotes and bibliographies. When you are reading be sure to pay attention to the footnotes and bibliographies which can guide you to further sources a give you a clear picture of the important texts.
- Use the library. If you have access to a library at your school or college, be sure to make the most of it. Search online catalogues and speak to librarians.
- Access online journal databases. If you are in college it is likely that you will have access to academic journals online. These are an excellent and easy to navigate resources.
- Use online sources with discretion. Try using free scholarly databases, like Google Scholar, which offer quality academic sources, but avoid using the non-trustworthy websites that come up when you simply search your topic online.
- Avoid using crowd-sourced sites like Wikipedia as sources. However, you can look at the sources cited on a Wikipedia page and use them instead, if they seem credible.

- Who is the author? Is it written by an academic with a position at a University? Search for the author online.
- Who is the publisher? Is the book published by an established academic press? Look in the cover to check the publisher, if it is published by a University Press that is a good sign.
- If it's an article, where is published? If you are using an article check that it has been published in an academic journal. [8] X Research source
- If the article is online, what is the URL? Government sources with .gov addresses are good sources, as are .edu sites.

- Ask yourself why the author is making this argument. Evaluate the text by placing it into a broader intellectual context. Is it part of a certain tradition in historiography? Is it a response to a particular idea?
- Consider where there are weaknesses and limitations to the argument. Always keep a critical mindset and try to identify areas where you think the argument is overly stretched or the evidence doesn't match the author's claims. [9] X Research source

- Label all your notes with the page numbers and precise bibliographic information on the source.
- If you have a quote but can't remember where you found it, imagine trying to skip back through everything you have read to find that one line.
- If you use something and don't reference it fully you risk plagiarism. [10] X Research source
Writing the Introduction

- For example you could start by saying "In the First World War new technologies and the mass mobilization of populations meant that the war was not fought solely by standing armies".
- This first sentences introduces the topic of your essay in a broad way which you can start focus to in on more.

- This will lead to an outline of the structure of your essay and your argument.
- Here you will explain the particular approach you have taken to the essay.
- For example, if you are using case studies you should explain this and give a brief overview of which case studies you will be using and why.

Writing the Essay

- Try to include a sentence that concludes each paragraph and links it to the next paragraph.
- When you are organising your essay think of each paragraph as addressing one element of the essay question.
- Keeping a close focus like this will also help you avoid drifting away from the topic of the essay and will encourage you to write in precise and concise prose.
- Don't forget to write in the past tense when referring to something that has already happened.

- Don't drop a quote from a primary source into your prose without introducing it and discussing it, and try to avoid long quotations. Use only the quotes that best illustrate your point.
- If you are referring to a secondary source, you can usually summarise in your own words rather than quoting directly.
- Be sure to fully cite anything you refer to, including if you do not quote it directly.

- Think about the first and last sentence in every paragraph and how they connect to the previous and next paragraph.
- Try to avoid beginning paragraphs with simple phrases that make your essay appear more like a list. For example, limit your use of words like: "Additionally", "Moreover", "Furthermore".
- Give an indication of where your essay is going and how you are building on what you have already said. [15] X Research source

- Briefly outline the implications of your argument and it's significance in relation to the historiography, but avoid grand sweeping statements. [16] X Research source
- A conclusion also provides the opportunity to point to areas beyond the scope of your essay where the research could be developed in the future.
Proofreading and Evaluating Your Essay

- Try to cut down any overly long sentences or run-on sentences. Instead, try to write clear and accurate prose and avoid unnecessary words.
- Concentrate on developing a clear, simple and highly readable prose style first before you think about developing your writing further. [17] X Research source
- Reading your essay out load can help you get a clearer picture of awkward phrasing and overly long sentences. [18] X Research source

- When you read through your essay look at each paragraph and ask yourself, "what point this paragraph is making".
- You might have produced a nice piece of narrative writing, but if you are not directly answering the question it is not going to help your grade.

- A bibliography will typically have primary sources first, followed by secondary sources. [19] X Research source
- Double and triple check that you have included all the necessary references in the text. If you forgot to include a reference you risk being reported for plagiarism.
Sample Essay

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.historytoday.com/robert-pearce/how-write-good-history-essay
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/writing-a-good-history-paper
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/thesis_statement_tips.html
- ↑ http://history.rutgers.edu/component/content/article?id=106:writing-historical-essays-a-guide-for-undergraduates
- ↑ https://guides.lib.uw.edu/c.php?g=344285&p=2580599
- ↑ http://www.hamilton.edu/documents/writing-center/WritingGoodHistoryPaper.pdf
- ↑ http://www.bowdoin.edu/writing-guides/
- ↑ https://www.wgtn.ac.nz/hppi/publications/Writing-History-Essays.pdf
About This Article

To write a history essay, read the essay question carefully and use source materials to research the topic, taking thorough notes as you go. Next, formulate a thesis statement that summarizes your key argument in 1-2 concise sentences and create a structured outline to help you stay on topic. Open with a strong introduction that introduces your thesis, present your argument, and back it up with sourced material. Then, end with a succinct conclusion that restates and summarizes your position! For more tips on creating a thesis statement, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lea Fernandez
Nov 23, 2017
Did this article help you?

Matthew Sayers
Mar 31, 2019
Millie Jenkerinx
Nov 11, 2017
Oct 18, 2019
Shannon Harper
Mar 9, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How to Write a Good History Essay. A Sequence of Actions and Useful Tips
/rating_on.png)
Before you start writing your history essay, there is quite a lot of work that has to be done in order to gain success.
You may ask: what is history essay? What is the difference between it and other kinds of essays? Well, the main goal of a history essay is to measure your progress in learning history and test your range of skills (such as analysis, logic, planning, research, and writing), it is necessary to prepare yourself very well.
Your plan of action may look like this. First of all, you will have to explore the topic. If you are going to write about a certain historical event, think of its causes and premises, and analyze what its impact on history was. In case you are writing about a person, find out why and how he or she came to power and how they influenced society and historical situations.
The next step is to make research and collect all the available information about the person or event, and also find evidence.
Finally, you will have to compose a well-organized response.
During the research, make notes and excerpts of the most notable data, write out the important dates and personalities. And of course, write down all your thoughts and findings.
It all may seem complicated at first sight, but in fact, it is not so scary! To complete this task successfully and compose a good history essay, simply follow several easy steps provided below.
Detailed Writing Instruction for Students to Follow
If you want to successfully complete your essay, it would be better to organize the writing process. You will complete the assignment faster and more efficient if you divide the whole work into several sections or steps.
- Introduction
Writing a good and strong introduction part is important because this is the first thing your reader will see. It gives the first impression of your essay and induces people to reading (or not reading) it.
To make the introduction catchy and interesting, express the contention and address the main question of the essay. Be confident and clear as this is the moment when you define the direction your whole essay will take. And remember that introduction is not the right place for rambling! The best of all is, to begin with, a brief context summary, then go to addressing the question and express the content. Finally, mark the direction your essay about history will take.
Its quality depends on how clear you divided the whole essay into sections in the previous part. As long as you have provided a readable and understandable scheme, your readers will know exactly what to expect.
The body of your essay must give a clear vision of what question you are considering. In this section, you can develop your idea and support it with the evidence you have found. Use certain facts and quotations for that. When being judicial and analytical, they will help you to easily support your point of view and argument.
As long as your essay has a limited size, don’t be too precise. It is allowed to summarize the most essential background information, for example, instead of giving a precise list of all the issues that matter.
It is also good to keep in mind that each paragraph of your essay’s body must tell about only one issue. Don’t make a mess out of your paper!
It is not only essential to start your essay well. How you will end it also matters. A properly-written conclusion is the one that restates the whole paper’s content and gives a logical completion of the issue or question discussed above. Your conclusion must leave to chance for further discussion or arguments on the case. It’s time, to sum up, give a verdict.
That is why it is strongly forbidden to provide any new evidence or information here, as well as start a new discussion, etc.
After you finish writing, give yourself some time and put the paper away for a while. When you turn back to it will be easier to take a fresh look at it and find any mistakes or things to improve. Of course, remember to proofread your writing and check it for any grammar, spelling and punctuation errors. All these tips will help you to learn how to write a history essay.

How to Write a History Essay?
04 August, 2020
10 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
There are so many types of essays. It can be hard to know where to start. History papers aren’t just limited to history classes. These tasks can be assigned to examine any important historical event or a person. While they’re more common in history classes, you can find this type of assignment in sociology or political science course syllabus, or just get a history essay task for your scholarship. This is Handmadewriting History Essay Guide - let's start!

Purpose of a History Essay
Wondering how to write a history essay? First of all, it helps to understand its purpose. Secondly, this essay aims to examine the influences that lead to a historical event. Thirdly, it can explore the importance of an individual’s impact on history.
However, the goal isn’t to stay in the past. Specifically, a well-written history essay should discuss the relevance of the event or person to the “now”. After finishing this essay, a reader should have a fuller understanding of the lasting impact of an event or individual.
Need basic essay guidance? Find out what is an essay with this 101 essay guide: What is an Essay?
Elements for Success
Indeed, understanding how to write a history essay is crucial in creating a successful paper. Notably, these essays should never only outline successful historic events or list an individual’s achievements. Instead, they should focus on examining questions beginning with what , how , and why . Here’s a pro tip in how to write a history essay: brainstorm questions. Once you’ve got questions, you have an excellent starting point.
Preparing to Write

Evidently, a typical history essay format requires the writer to provide background on the event or person, examine major influences, and discuss the importance of the forces both then and now. In addition, when preparing to write, it’s helpful to organize the information you need to research into questions. For example:
- Who were the major contributors to this event?
- Who opposed or fought against this event?
- Who gained or lost from this event?
- Who benefits from this event today?
- What factors led up to this event?
- What changes occurred because of this event?
- What lasting impacts occurred locally, nationally, globally due to this event?
- What lessons (if any) were learned?
- Why did this event occur?
- Why did certain populations support it?
- Why did certain populations oppose it?
These questions exist as samples. Therefore, generate questions specific to your topic. Once you have a list of questions, it’s time to evaluate them.
Evaluating the Question

Seasoned writers approach writing history by examining the historic event or individual. Specifically, the goal is to assess the impact then and now. Accordingly, the writer needs to evaluate the importance of the main essay guiding the paper. For example, if the essay’s topic is the rise of American prohibition, a proper question may be “How did societal factors influence the rise of American prohibition during the 1920s? ”
This question is open-ended since it allows for insightful analysis, and limits the research to societal factors. Additionally, work to identify key terms in the question. In the example, key terms would be “societal factors” and “prohibition”.
Summarizing the Argument
The argument should answer the question. Use the thesis statement to clarify the argument and outline how you plan to make your case. In other words. the thesis should be sharp, clear, and multi-faceted. Consider the following tips when summarizing the case:
- The thesis should be a single sentence
- It should include a concise argument and a roadmap
- It’s always okay to revise the thesis as the paper develops
- Conduct a bit of research to ensure you have enough support for the ideas within the paper
Outlining a History Essay Plan

Once you’ve refined your argument, it’s time to outline. Notably, many skip this step to regret it then. Nonetheless, the outline is a map that shows where you need to arrive historically and when. Specifically, taking the time to plan, placing the strongest argument last, and identifying your sources of research is a good use of time. When you’re ready to outline, do the following:
- Consider the necessary background the reader should know in the introduction paragraph
- Define any important terms and vocabulary
- Determine which ideas will need the cited support
- Identify how each idea supports the main argument
- Brainstorm key points to review in the conclusion
Gathering Sources
As a rule, history essays require both primary and secondary sources . Primary resources are those that were created during the historical period being analyzed. Secondary resources are those created by historians and scholars about the topic. It’s a good idea to know if the professor requires a specific number of sources, and what kind he or she prefers. Specifically, most tutors prefer primary over secondary sources.
Where to find sources? Great question! Check out bibliographies included in required class readings. In addition, ask a campus Librarian. Peruse online journal databases; In addition, most colleges provide students with free access. When in doubt, make an appointment and ask the professor for guidance.
Writing the Essay
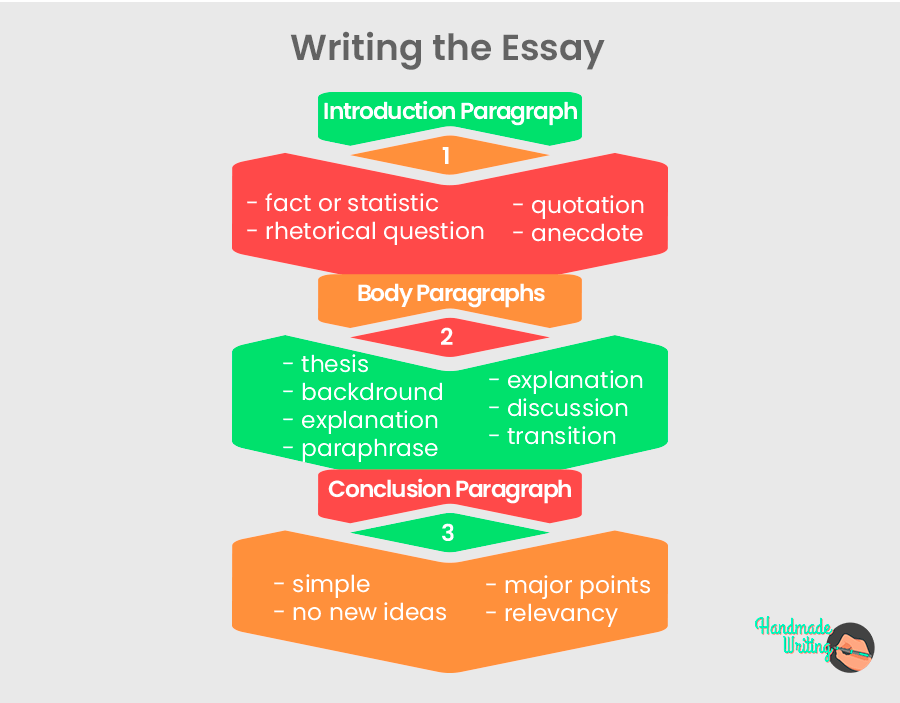
Now that you have prepared your questions, ideas, and arguments; composed the outline ; and gathered sources – it’s time to write your first draft. In particular, each section of your history essay must serve its purpose. Here is what you should include in essay paragraphs.
Introduction Paragraph
Unsure of how to start a history essay? Well, like most essays, the introduction should include an attention-getter (or hook):
- Relevant fact or statistic
- Rhetorical Question
- Interesting quotation
- Application anecdote if appropriate
Once you’ve captured the reader’s interest, introduce the topic. Similarly, present critical historic context. Namely, it is necessary to introduce any key individuals or events that will be discussed later in the essay. At last, end with a strong thesis which acts as a transition to the first argument.
Body Paragraphs
Indeed, each body paragraph should offer a single idea to support the argument. Then, after writing a strong topic sentence, the topic should be supported with correctly cited research. Consequently, a typical body paragraph is arranged as follows:
- Topic sentence linking to the thesis
- Background of the topic
- Research quotation or paraphrase #1
- Explanation and analysis of research
- Research quotation or paraphrase #2
- Transition to the next paragraph
Equally, the point of body paragraphs is to build the argument. Hence, present the weakest support first and end with the strongest. Admittedly, doing so leaves the reader with the best possible evidence.
Conclusion Paragraph
You’re almost there! Eventually, conclusion paragraphs should review the most important points in the paper. In them, you should prove that you’ve supported the argument proposed in the thesis. When writing a conclusion paragraph keep these tips in mind:
- Keep it simple
- Avoid introducing new information
- Review major points
- Discuss the relevance to today
Problems with writing Your History essay ? Try our Essay Writer Service!

Proofreading Your Essay
Once the draft is ready and polished, it’s time to proceed to final editing. What does this process imply? Specifically, it’s about removing impurities and making the essay look just perfect. Here’s what you need to do to improve the quality of your paper:
- Double check the content. In the first place, it’s recommended to get rid of long sentences, correct vague words. Also, make sure that all your paragrahps contain accurate sentences with transparent meaning.
- Pay attention to style. To make the process of digesting your essay easier, focus on crafting a paper with readable style, the one that is known to readers. Above all, the main mission here is to facilitate the perception of your essay. So, don’t forget about style accuracy.
- Practice reading the essay. Of course, the best practice before passing the paper is to read it out loud. Hence, this exercise will help you notice fragments that require rewriting or a complete removal.
History Essay Example
Did you want a history essay example? Take a look at one of our history essay papers.
Make it Shine
An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it’s achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine:
- Write a substantial introduction. Particularly, it’s the first impression the professor will have of the paper.
- State a clear thesis. A strong thesis is easier to support.
- Incorporate evidence critically. If while researching you find opposing arguments, include them and discuss their flaws.
- Cite all the research. Whether direct quotations or paraphrases, citing evidence is crucial to avoiding plagiarism, which can have serious academic consequences.
- Include primary and secondary resources. While primary resources may be harder to find, the professor will expect them—this is, after all, a history essay.
History Essay Sample
Ready to tackle the history essay format? Great! Check out this history essay sample from an upper-level history class. While the essay isn’t perfect, the professor points out its many strengths.
Remember: start early and revise, revise, revise . We can’t revise history, but you can revise your ideas until they’re perfect.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
How to Write a History Essay with Outline, Tips, Examples and More

Before we get into how to write a history essay, let's first understand what makes one good. Different people might have different ideas, but there are some basic rules that can help you do well in your studies. In this guide, we won't get into any fancy theories. Instead, we'll give you straightforward tips to help you with historical writing. So, if you're ready to sharpen your writing skills, let our history essay writing service explore how to craft an exceptional paper.
What is a History Essay?
A history essay is an academic assignment where we explore and analyze historical events from the past. We dig into historical stories, figures, and ideas to understand their importance and how they've shaped our world today. History essay writing involves researching, thinking critically, and presenting arguments based on evidence.
Moreover, history papers foster the development of writing proficiency and the ability to communicate complex ideas effectively. They also encourage students to engage with primary and secondary sources, enhancing their research skills and deepening their understanding of historical methodology.
History Essay Outline
.png)
The outline is there to guide you in organizing your thoughts and arguments in your essay about history. With a clear outline, you can explore and explain historical events better. Here's how to make one:
Introduction
- Hook: Start with an attention-grabbing opening sentence or anecdote related to your topic.
- Background Information: Provide context on the historical period, event, or theme you'll be discussing.
- Thesis Statement: Present your main argument or viewpoint, outlining the scope and purpose of your history essay.
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context
- Provide background information on the historical context of your topic.
- Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay.
Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence
- Each paragraph should focus on a specific argument or aspect of your thesis.
- Present evidence from primary and secondary sources to support each argument.
- Analyze the significance of the evidence and its relevance to your history paper thesis.
Counterarguments (optional)
- Address potential counterarguments or alternative perspectives on your topic.
- Refute opposing viewpoints with evidence and logical reasoning.
- Summary of Main Points: Recap the main arguments presented in the body paragraphs.
- Restate Thesis: Reinforce your thesis statement, emphasizing its significance in light of the evidence presented.
- Reflection: Reflect on the broader implications of your arguments for understanding history.
- Closing Thought: End your history paper with a thought-provoking statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
References/bibliography
- List all sources used in your research, formatted according to the citation style required by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include both primary and secondary sources, arranged alphabetically by the author's last name.
Notes (if applicable)
- Include footnotes or endnotes to provide additional explanations, citations, or commentary on specific points within your history essay.
History Essay Format
Adhering to a specific format is crucial for clarity, coherence, and academic integrity. Here are the key components of a typical history essay format:
Font and Size
- Use a legible font such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri.
- The recommended font size is usually 12 points. However, check your instructor's guidelines, as they may specify a different size.
- Set 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Double-space the entire essay, including the title, headings, body paragraphs, and references.
- Avoid extra spacing between paragraphs unless specified otherwise.
- Align text to the left margin; avoid justifying the text or using a centered alignment.
Title Page (if required):
- If your instructor requires a title page, include the essay title, your name, the course title, the instructor's name, and the date.
- Center-align this information vertically and horizontally on the page.
- Include a header on each page (excluding the title page if applicable) with your last name and the page number, flush right.
- Some instructors may require a shortened title in the header, usually in all capital letters.
- Center-align the essay title at the top of the first page (if a title page is not required).
- Use standard capitalization (capitalize the first letter of each major word).
- Avoid underlining, italicizing, or bolding the title unless necessary for emphasis.
Paragraph Indentation:
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches or use the tab key.
- Do not insert extra spaces between paragraphs unless instructed otherwise.
Citations and References:
- Follow the citation style specified by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include in-text citations whenever you use information or ideas from external sources.
- Provide a bibliography or list of references at the end of your history essay, formatted according to the citation style guidelines.
- Typically, history essays range from 1000 to 2500 words, but this can vary depending on the assignment.

How to Write a History Essay?
Historical writing can be an exciting journey through time, but it requires careful planning and organization. In this section, we'll break down the process into simple steps to help you craft a compelling and well-structured history paper.
Analyze the Question
Before diving headfirst into writing, take a moment to dissect the essay question. Read it carefully, and then read it again. You want to get to the core of what it's asking. Look out for keywords that indicate what aspects of the topic you need to focus on. If you're unsure about anything, don't hesitate to ask your instructor for clarification. Remember, understanding how to start a history essay is half the battle won!
Now, let's break this step down:
- Read the question carefully and identify keywords or phrases.
- Consider what the question is asking you to do – are you being asked to analyze, compare, contrast, or evaluate?
- Pay attention to any specific instructions or requirements provided in the question.
- Take note of the time period or historical events mentioned in the question – this will give you a clue about the scope of your history essay.
Develop a Strategy
With a clear understanding of the essay question, it's time to map out your approach. Here's how to develop your historical writing strategy:
- Brainstorm ideas : Take a moment to jot down any initial thoughts or ideas that come to mind in response to the history paper question. This can help you generate a list of potential arguments, themes, or points you want to explore in your history essay.
- Create an outline : Once you have a list of ideas, organize them into a logical structure. Start with a clear introduction that introduces your topic and presents your thesis statement – the main argument or point you'll be making in your history essay. Then, outline the key points or arguments you'll be discussing in each paragraph of the body, making sure they relate back to your thesis. Finally, plan a conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your history paper thesis.
- Research : Before diving into writing, gather evidence to support your arguments. Use reputable sources such as books, academic journals, and primary documents to gather historical evidence and examples. Take notes as you research, making sure to record the source of each piece of information for proper citation later on.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate potential counterarguments to your history paper thesis and think about how you'll address them in your essay. Acknowledging opposing viewpoints and refuting them strengthens your argument and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Set realistic goals : Be realistic about the scope of your history essay and the time you have available to complete it. Break down your writing process into manageable tasks, such as researching, drafting, and revising, and set deadlines for each stage to stay on track.

Start Your Research
Now that you've grasped the history essay topic and outlined your approach, it's time to dive into research. Here's how to start:
- Ask questions : What do you need to know? What are the key points to explore further? Write down your inquiries to guide your research.
- Explore diverse sources : Look beyond textbooks. Check academic journals, reliable websites, and primary sources like documents or artifacts.
- Consider perspectives : Think about different viewpoints on your topic. How have historians analyzed it? Are there controversies or differing interpretations?
- Take organized notes : Summarize key points, jot down quotes, and record your thoughts and questions. Stay organized using spreadsheets or note-taking apps.
- Evaluate sources : Consider the credibility and bias of each source. Are they peer-reviewed? Do they represent a particular viewpoint?
Establish a Viewpoint
By establishing a clear viewpoint and supporting arguments, you'll lay the foundation for your compelling historical writing:
- Review your research : Reflect on the information gathered. What patterns or themes emerge? Which perspectives resonate with you?
- Formulate a thesis statement : Based on your research, develop a clear and concise thesis that states your argument or interpretation of the topic.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate objections to your history paper thesis. Are there alternative viewpoints or evidence that you need to address?
- Craft supporting arguments : Outline the main points that support your thesis. Use evidence from your research to strengthen your arguments.
- Stay flexible : Be open to adjusting your viewpoint as you continue writing and researching. New information may challenge or refine your initial ideas.
Structure Your Essay
Now that you've delved into the depths of researching historical events and established your viewpoint, it's time to craft the skeleton of your essay: its structure. Think of your history essay outline as constructing a sturdy bridge between your ideas and your reader's understanding. How will you lead them from point A to point Z? Will you follow a chronological path through history or perhaps dissect themes that span across time periods?
And don't forget about the importance of your introduction and conclusion—are they framing your narrative effectively, enticing your audience to read your paper, and leaving them with lingering thoughts long after they've turned the final page? So, as you lay the bricks of your history essay's architecture, ask yourself: How can I best lead my audience through the maze of time and thought, leaving them enlightened and enriched on the other side?
Create an Engaging Introduction
Creating an engaging introduction is crucial for capturing your reader's interest right from the start. But how do you do it? Think about what makes your topic fascinating. Is there a surprising fact or a compelling story you can share? Maybe you could ask a thought-provoking question that gets people thinking. Consider why your topic matters—what lessons can we learn from history?
Also, remember to explain what your history essay will be about and why it's worth reading. What will grab your reader's attention and make them want to learn more? How can you make your essay relevant and intriguing right from the beginning?

Develop Coherent Paragraphs
Once you've established your introduction, the next step is to develop coherent paragraphs that effectively communicate your ideas. Each paragraph should focus on one main point or argument, supported by evidence or examples from your research. Start by introducing the main idea in a topic sentence, then provide supporting details or evidence to reinforce your point.
Make sure to use transition words and phrases to guide your reader smoothly from one idea to the next, creating a logical flow throughout your history essay. Additionally, consider the organization of your paragraphs—is there a clear progression of ideas that builds upon each other? Are your paragraphs unified around a central theme or argument?
Conclude Effectively
Concluding your history essay effectively is just as important as starting it off strong. In your conclusion, you want to wrap up your main points while leaving a lasting impression on your reader. Begin by summarizing the key points you've made throughout your history essay, reminding your reader of the main arguments and insights you've presented.
Then, consider the broader significance of your topic—what implications does it have for our understanding of history or for the world today? You might also want to reflect on any unanswered questions or areas for further exploration. Finally, end with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action that encourages your reader to continue thinking about the topic long after they've finished reading.
Reference Your Sources
Referencing your sources is essential for maintaining the integrity of your history essay and giving credit to the scholars and researchers who have contributed to your understanding of the topic. Depending on the citation style required (such as MLA, APA, or Chicago), you'll need to format your references accordingly. Start by compiling a list of all the sources you've consulted, including books, articles, websites, and any other materials used in your research.
Then, as you write your history essay, make sure to properly cite each source whenever you use information or ideas that are not your own. This includes direct quotations, paraphrases, and summaries. Remember to include all necessary information for each source, such as author names, publication dates, and page numbers, as required by your chosen citation style.
Review and Ask for Advice
As you near the completion of your history essay writing, it's crucial to take a step back and review your work with a critical eye. Reflect on the clarity and coherence of your arguments—are they logically organized and effectively supported by evidence? Consider the strength of your introduction and conclusion—do they effectively capture the reader's attention and leave a lasting impression? Take the time to carefully proofread your history essay for any grammatical errors or typos that may detract from your overall message.
Furthermore, seeking advice from peers, mentors, or instructors can provide valuable insights and help identify areas for improvement. Consider sharing your essay with someone whose feedback you trust and respect, and be open to constructive criticism. Ask specific questions about areas you're unsure about or where you feel your history essay may be lacking.
History Essay Example
In this section, we offer an example of a history essay examining the impact of the Industrial Revolution on society. This essay demonstrates how historical analysis and critical thinking are applied in academic writing. By exploring this specific event, you can observe how historical evidence is used to build a cohesive argument and draw meaningful conclusions.

FAQs about History Essay Writing
How to write a history essay introduction, how to write a conclusion for a history essay, how to write a good history essay.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support
A guide to writing history essays
This guide has been prepared for students at all undergraduate university levels. Some points are specifically aimed at 100-level students, and may seem basic to those in upper levels. Similarly, some of the advice is aimed at upper-level students, and new arrivals should not be put off by it.
The key point is that learning to write good essays is a long process. We hope that students will refer to this guide frequently, whatever their level of study.
Why do history students write essays?
Essays are an essential educational tool in disciplines like history because they help you to develop your research skills, critical thinking, and writing abilities. The best essays are based on strong research, in-depth analysis, and are logically structured and well written.
An essay should answer a question with a clear, persuasive argument. In a history essay, this will inevitably involve a degree of narrative (storytelling), but this should be kept to the minimum necessary to support the argument – do your best to avoid the trap of substituting narrative for analytical argument. Instead, focus on the key elements of your argument, making sure they are well supported by evidence. As a historian, this evidence will come from your sources, whether primary and secondary.
The following guide is designed to help you research and write your essays, and you will almost certainly earn better grades if you can follow this advice. You should also look at the essay-marking criteria set out in your course guide, as this will give you a more specific idea of what the person marking your work is looking for.
Where to start
First, take time to understand the question. Underline the key words and consider very carefully what you need to do to provide a persuasive answer. For example, if the question asks you to compare and contrast two or more things, you need to do more than define these things – what are the similarities and differences between them? If a question asks you to 'assess' or 'explore', it is calling for you to weigh up an issue by considering the evidence put forward by scholars, then present your argument on the matter in hand.
A history essay must be based on research. If the topic is covered by lectures, you might begin with lecture and tutorial notes and readings. However, the lecturer does not want you simply to echo or reproduce the lecture content or point of view, nor use their lectures as sources in your footnotes. They want you to develop your own argument. To do this you will need to look closely at secondary sources, such as academic books and journal articles, to find out what other scholars have written about the topic. Often your lecturer will have suggested some key texts, and these are usually listed near the essay questions in your course guide. But you should not rely solely on these suggestions.
Tip : Start the research with more general works to get an overview of your topic, then move on to look at more specialised work.
Crafting a strong essay
Before you begin writing, make an essay plan. Identify the two-to-four key points you want to make. Organize your ideas into an argument which flows logically and coherently. Work out which examples you will use to make the strongest case. You may need to use an initial paragraph (or two) to bring in some context or to define key terms and events, or provide brief identifying detail about key people – but avoid simply telling the story.
An essay is really a series of paragraphs that advance an argument and build towards your conclusion. Each paragraph should focus on one central idea. Introduce this idea at the start of the paragraph with a 'topic sentence', then expand on it with evidence or examples from your research. Some paragraphs should finish with a concluding sentence that reiterates a main point or links your argument back to the essay question.
A good length for a paragraph is 150-200 words. When you want to move to a new idea or angle, start a new paragraph. While each paragraph deals with its own idea, paragraphs should flow logically, and work together as a greater whole. Try using linking phrases at the start of your paragraphs, such as 'An additional factor that explains', 'Further', or 'Similarly'.
We discourage using subheadings for a history essay (unless they are over 5000 words in length). Instead, throughout your essay use 'signposts'. This means clearly explaining what your essay will cover, how an example demonstrates your point, or reiterating what a particular section has added to your overall argument.
Remember that a history essay isn't necessarily about getting the 'right' answer – it's about putting forward a strong case that is well supported by evidence from academic sources. You don't have to cover everything – focus on your key points.
In your introduction or opening paragraph you could indicate that while there are a number of other explanations or factors that apply to your topic, you have chosen to focus on the selected ones (and say why). This demonstrates to your marker that while your argument will focus on selected elements, you do understand the bigger picture.
The classic sections of an essay
Introduction.
- Establishes what your argument will be, and outlines how the essay will develop it
- A good formula to follow is to lay out about 3 key reasons that support the answer you plan to give (these points will provide a road-map for your essay and will become the ideas behind each paragraph)
- If you are focusing on selected aspects of a topic or particular sources and case studies, you should state that in your introduction
- Define any key terms that are essential to your argument
- Keep your introduction relatively concise – aim for about 10% of the word count
- Consists of a series of paragraphs that systematically develop the argument outlined in your introduction
- Each paragraph should focus on one central idea, building towards your conclusion
- Paragraphs should flow logically. Tie them together with 'bridge' sentences – e.g. you might use a word or words from the end of the previous paragraph and build it into the opening sentence of the next, to form a bridge
- Also be sure to link each paragraph to the question/topic/argument in some way (e.g. use a key word from the question or your introductory points) so the reader does not lose the thread of your argument
- Ties up the main points of your discussion
- Should link back to the essay question, and clearly summarise your answer to that question
- May draw out or reflect on any greater themes or observations, but you should avoid introducing new material
- If you have suggested several explanations, evaluate which one is strongest
Using scholarly sources: books, journal articles, chapters from edited volumes
Try to read critically: do not take what you read as the only truth, and try to weigh up the arguments presented by scholars. Read several books, chapters, or articles, so that you understand the historical debates about your topic before deciding which viewpoint you support. The best sources for your history essays are those written by experts, and may include books, journal articles, and chapters in edited volumes. The marking criteria in your course guide may state a minimum number of academic sources you should consult when writing your essay. A good essay considers a range of evidence, so aim to use more than this minimum number of sources.
Tip : Pick one of the books or journal articles suggested in your course guide and look at the author's first few footnotes – these will direct you to other prominent sources on this topic.
Don't overlook journal articles as a source. They contain the most in-depth research on a particular topic. Often the first pages will summarise the prior research into this topic, so articles can be a good way to familiarise yourself with what else has 'been done'.
Edited volumes can also be a useful source. These are books on a particular theme, topic or question, with each chapter written by a different expert.
One way to assess the reliability of a source is to check the footnotes or endnotes. When the author makes a claim, is this supported by primary or secondary sources? If there are very few footnotes, then this may not be a credible scholarly source. Also check the date of publication, and prioritise more recent scholarship. Aim to use a variety of sources, but focus most of your attention on academic books and journal articles.
Paraphrasing and quotations
A good essay is about your ability to interpret and analyse sources, and to establish your own informed opinion with a persuasive argument that uses sources as supporting evidence. You should express most of your ideas and arguments in your own words. Cutting and pasting together the words of other scholars, or simply changing a few words in quotations taken from the work of others, will prevent you from getting a good grade, and may be regarded as academic dishonesty (see more below).
Direct quotations can be useful tools if they provide authority and colour. For maximum effect though, use direct quotations sparingly – where possible, paraphrase most material into your own words. Save direct quotations for phrases that are interesting, contentious, or especially well-phrased.
A good writing practice is to introduce and follow up every direct quotation you use with one or two sentences of your own words, clearly explaining the relevance of the quote, and putting it in context with the rest of your paragraph. Tell the reader who you are quoting, why this quote is here, and what it demonstrates. Avoid simply plonking a quotation into the middle of your own prose. This can be quite off-putting for a reader.
- Only include punctuation in your quote if it was in the original text. Otherwise, punctuation should come after the quotation marks. If you cut out words from a quotation, put in three dots (an ellipsis [ . . .]) to indicate where material has been cut
- If your quote is longer than 50 words, it should be indented and does not need quotation marks. This is called a block quote (use these sparingly: remember you have a limited word count and it is your analysis that is most significant)
- Quotations should not be italicised
Referencing, plagiarism and Turnitin
When writing essays or assignments, it is very important to acknowledge the sources you have used. You risk the charge of academic dishonesty (or plagiarism) if you copy or paraphrase words written by another person without providing a proper acknowledgment (a 'reference'). In your essay, whenever you refer to ideas from elsewhere, statistics, direct quotations, or information from primary source material, you must give details of where this information has come from in footnotes and a bibliography.
Your assignment may be checked through Turnitin, a type of plagiarism-detecting software which checks assignments for evidence of copied material. If you have used a wide variety of primary and secondary sources, you may receive a high Turnitin percentage score. This is nothing to be alarmed about if you have referenced those sources. Any matches with other written material that are not referenced may be interpreted as plagiarism – for which there are penalties. You can find full information about all of this in the History Programme's Quick Guide Referencing Guide contained in all course booklets.
Final suggestions
Remember that the easier it is to read your essay, the more likely you are to get full credit for your ideas and work. If the person marking your work has difficulty reading it, either because of poor writing or poor presentation, they will find it harder to grasp your points. Try reading your work aloud, or to a friend/flatmate. This should expose any issues with flow or structure, which you can then rectify.
Make sure that major and controversial points in your argument are clearly stated and well- supported by evidence and footnotes. Aspire to understand – rather than judge – the past. A historian's job is to think about people, patterns, and events in the context of the time, though you can also reflect on changing perceptions of these over time.
Things to remember
- Write history essays in the past tense
- Generally, avoid sub-headings in your essays
- Avoid using the word 'bias' or 'biased' too freely when discussing your research materials. Almost any text could be said to be 'biased'. Your task is to attempt to explain why an author might argue or interpret the past as they do, and what the potential limitations of their conclusions might be
- Use the passive voice judiciously. Active sentences are better!
- Be cautious about using websites as sources of information. The internet has its uses, particularly for primary sources, but the best sources are academic books and articles. You may use websites maintained by legitimate academic and government authorities, such as those with domain suffixes like .gov .govt .ac or .edu
- Keep an eye on word count – aim to be within 10% of the required length. If your essay is substantially over the limit, revisit your argument and overall structure, and see if you are trying to fit in too much information. If it falls considerably short, look into adding another paragraph or two
- Leave time for a final edit and spell-check, go through your footnotes and bibliography to check that your references are correctly formatted, and don't forget to back up your work as you go!
Other useful strategies and sources
- Student Learning Development , which offers peer support and one-on-one writing advice (located near the central library)
- Harvard College's guide to writing history essays (PDF)
- Harvard College's advice on essay structure
- Victoria University's comprehensive essay writing guide (PDF)

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
18 Preparing to Write: Organizing and Outlines
One of the most important—and perhaps the more difficult—parts of writing a good history research paper is deciding what to say and in what order to say it. A good outline can limit a student’s anxiety about writing a big paper as it may help break the writing process down into manageable chunk. A good outline also helps ensure that you’re approaching your argument in a logical way.
How you go about organizing your thoughts and creating an outline, however, depends a good deal on how your brain works best. Effective writers do not all use the same method. But here are few steps to follow to avoid the dreaded blank page (or monitor) and the essay that meanders and never really makes an argument (or repeats elements of the same argument unnecessarily).
Before you begin the outlining process, keep in mind that the basic form of analytical writing usually utilizes the “Rule of Three.” Simply, there should be at least three key points/pieces of evidence in a piece of writing introduced by a strong clear thesis. As you deliberate about possible thesis statements and debate what points are major elements of your argument and which ones are minor, or supporting, pieces of evidence, keep in mind that your argument will convince your readers when it has at least three supporting points.
STRATEGIES FOR DEVELOPING AN OUTLINE:
Use the terms you found helpful for organizing notes to start your outline:.
The words or tags you used to organize your notes can help in a couple of ways. First, for the “brain dump” process described next, these terms can be the first entries. Second, these terms could form the basis of main elements of your outline. Keywords that appear most frequently in your note-taking process could translate into major elements of your outline.
“Dump” the contents of your brain:
- Before attempting a formal outline, compile a list of all the interesting facts, ideas, concepts, individuals, and events that you’ve uncovered in your research. Keep an open mind, and don’t limit this list to just what you assumed would be the focus of your paper when you wrote your proposal. For example, what were the arguments of the secondary sources you read? What ideas or phrases came up again and again? Who were the main historical actors and what surprises did you encounter in the primary sources they produced (or were produced about them)? Can you construct a rough timeline without looking at your notes? The unofficial term for this compilation is a “brain dump,” because you are recording all the ideas that have occurred to you without regard to whether they are Big and Important Ideas or smaller, secondary points. Write down as much as you can, without worrying where it fits in the paper or even knowing for sure that it does fit in the paper.
Making sense of the results of the “brain dump”
- Visual learners often benefit from hand-writing the terms around a physical sheet of paper, and then using a spider-web concept map. In such a concept map, once you have all the terms on the page, you draw lines between related items. The terms that have multiple lines coming to or from them are the nodal points that should serve as main elements in your outline. The items that have just one or two connections are minor explanatory points in your formal outline.
- Natural list-makers think hierarchically (from most to least important) as a matter of course. If you’re a hierarchical thinker, you might think you already know your outline without drawing lines. But before you jump straight to a formal outline, let yourself think creatively. Try creating multiple lists, with perhaps different items and different orders for the compiled “brain dump” terms and phrases. In this process, some items will appear in multiple lists. Once you have several, think through the pros and cons of each one. Choose the best one and convert it into a formal outline.
Here is a detailed description of how to create a concept map from the University of West Florida and here you can find three examples of different types of concept maps .
Mind Maps are another form of concept mapping that uses a visual hierachy with associated information branching out from that concept.
Just as there’s not one way to organize your thoughts, there’s not a single form of an outline. Some writers do best with heavily detailed outlines, while others need only “bare bones.” Likewise, the necessity of maintaining an accurate outline is also a matter of personal preference. Some writers continually revise their outline as their thinking about their topic evolves with their writing, while others use an outline only to launch their writing and to prevent the intimidation of a blank screen, then abandon it once they’ve begun writing. Still, it’s extraordinarily helpful to make a plan before you begin. Below what you’ll see are some templates that work for a few common types of arguments. You may find one that works for you, perhaps with a bit of adapting.
Option 1: Chronological
Many history essays have a natural chronological focus. Arguments that seek to explain what happened at a place and time, or demonstrate what led up to an event, as well as essays that focus on an individual’s importance, can be organized chronologically.
- Early phase or antecedents
- Middle years or main event
- Later years or impact
Option 2: Revision
If your main argument centers on suggesting a correction to a currently accepted explanation of the past—perhaps you want to establish a new periodization, or make a case for an additional influence or outcome to what historians have argued—then you might consider this sort of organization.
- Summaries of what several historians have written
- with three examples/supporting points
Option 3: Topical/thematic approach
When your argument does not fall into one of the above traditional formats, you’ll need to uncover the patterns within evidence, and align them into to (at least) 2-3 explanatory aspects. Research that is not following political or military events often is organizes topically. There are several variations on this format, but at its most basic, consider this format.
How History is Made: A Student’s Guide to Reading, Writing, and Thinking in the Discipline Copyright © 2022 by Stephanie Cole; Kimberly Breuer; Scott W. Palmer; and Brandon Blakeslee is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Tips from my first year - essay writing
This is the third of a three part series giving advice on the essay writing process, focusing in this case on essay writing.
Daniel is a first year BA History and Politics student at Magdalen College . He is a disabled student and the first in his immediate family to go to university. Daniel is also a Trustee of Potential Plus UK , a Founding Ambassador and Expert Panel Member for Zero Gravity , and a History Faculty Ambassador. Before coming to university, Daniel studied at a non-selective state school, and was a participant on the UNIQ , Sutton Trust , and Social Mobility Foundation APP Reach programmes, as well as being part of the inaugural Opportunity Oxford cohort. Daniel is passionate about outreach and social mobility and ensuring all students have the best opportunity to succeed.

History and its related disciplines mainly rely on essay writing with most term-time work centring on this, so it’s a good idea to be prepared. The blessing of the Oxford system though is you get plenty of opportunity to practice, and your tutors usually provide lots of feedback (both through comments on essays and in tutorials) to help you improve. Here are my tips from my first year as an Oxford Undergraduate:
- Plan for success – a good plan really sets your essay in a positive direction, so try to collect your thoughts if you can. I find a great way to start my planning process is to go outside for a walk as it helps to clear my head of the detail, it allows me to focus on the key themes, and it allows me to explore ideas without having to commit anything to paper. Do keep in mind your question throughout the reading and notetaking process, though equally look to the wider themes covered so that when you get to planning you are in the right frame of mind.
- Use what works for you – if you try to use a method you aren’t happy with, it won’t work. That doesn’t mean you shouldn’t experiment; to the contrary I highly encourage it as it can be good to change up methods and see what really helps you deliver a strong essay. However, don’t feel pressured into using one set method, as long as it is time-efficient and it gets you ready for the next stage of the essay process it is fine!
- Focus on the general ideas – summarise in a sentence what each author argues, see what links there are between authors and subject areas, and possibly group your ideas into core themes or paragraph headers. Choose the single piece of evidence you believe supports each point best.
- Make something revision-ready – try to make something which you can come back to in a few months’ time which makes sense and will really get your head back to when you were preparing for your essay.
- Consider what is most important – no doubt if you spoke about everything covered on the reading list you would have far more words than the average essay word count (which is usually advised around 1,500-2,000 words - it does depend on your tutor.) You have a limited amount of time, focus, and words, so choose what stands out to you as the most important issues for discussion. Focus on the important issues well rather than covering several points in a less-focused manner.
- Make it your voice – your tutors want to hear from you about what you think and what your argument is, not lots of quotes of what others have said. Therefore, when planning and writing consider what your opinion is and make sure to state it. Use authors to support your viewpoint, or to challenge it, but make sure you are doing the talking and driving the analysis. At the same time, avoid slang, and ensure the language you use is easy to digest.
- Make sure you can understand it - don’t feel you have to use big fancy words you don’t understand unless they happen to be relevant subject-specific terminology, and don’t swallow the Thesaurus. If you use a technical term, make sure to provide a definition. You most probably won’t have time to go into it fully, but if it is an important concept hint at the wider historical debate. State where you stand and why briefly you believe what you are stating before focusing on your main points. You need to treat the reader as both an alien from another planet, and a very intelligent person at the same time – make sure your sentences make sense, but equally make sure to pitch it right. As you can possibly tell, it is a fine balancing act so my advice is to read through your essay and ask yourself ‘why’ about every statement or argument you make. If you haven’t answered why, you likely require a little more explanation. Simple writing doesn’t mean a boring or basic argument, it just means every point you make lands and has impact on the reader, supporting them every step of the way.
- Keep introductions and conclusions short – there is no need for massive amounts of setting the scene in the introduction, or an exact repeat of every single thing you have said in the essay appearing in the conclusion. Instead, in the first sentence of your introduction provide a direct answer to the question. If the question is suitable, it is perfectly fine to say yes, no, or it is a little more complicated. Whatever the answer is, it should be simple enough to fit in one reasonable length sentence. The next three sentences should state what each of your three main body paragraphs are going to argue, and then dive straight into it. With your conclusion, pick up what you said about the key points. Suggest how they possibly link, maybe do some comparison between factors and see if you can leave us with a lasting thought which links to the question in your final sentence.
- Say what you are going to say, say it, say it again – this is a general essay structure; an introduction which clearly states your argument; a main body which explains why you believe that argument; and a conclusion which summarises the key points to be drawn from your essay. Keep your messaging clear as it is so important the reader can grasp everything you are trying to say to have maximum impact. This applies in paragraphs as well – each paragraph should in one sentence outline what is to be said, it should then be said, and in the final sentence summarise what you have just argued. Somebody should be able to quickly glance over your essay using the first and last sentences and be able to put together the core points.
- Make sure your main body paragraphs are focused – if you have come across PEE (Point, Evidence, Explain – in my case the acronym I could not avoid at secondary school!) before, then nothing has changed. Make your point in around a sentence, clearly stating your argument. Then use the best single piece of evidence available to support your point, trying to keep that to a sentence or two if you can. The vast majority of your words should be explaining why this is important, and how it supports your argument, or how it links to something else. You don’t need to ‘stack’ examples where you provide multiple instances of the same thing – if you have used one piece of evidence that is enough, you can move on and make a new point. Try to keep everything as short as possible while communicating your core messages, directly responding to the question. You also don’t need to cover every article or book you read, rather pick out the most convincing examples.
- It works, it doesn’t work, it is a little more complicated – this is a structure I developed for writing main body paragraphs, though it is worth noting it may not work for every question. It works; start your paragraph with a piece of evidence that supports your argument fully. It doesn’t work; see if there is an example which seems to contradict your argument, but suggest why you still believe your argument is correct. Then, and only if you can, see if there is an example which possibly doesn’t quite work fully with your argument, and suggest why possibly your argument cannot wholly explain this point or why your argument is incomplete but still has the most explanatory power. See each paragraph as a mini-debate, and ensure different viewpoints have an opportunity to be heard.
- Take your opponents at their best – essays are a form of rational dialogue, interacting with writing on this topic from the past, so if you are going to ‘win’ (or more likely just make a convincing argument as you don’t need to demolish all opposition in sight) then you need to treat your opponents fairly by choosing challenging examples, and by fairly characterising their arguments. It should not be a slinging match of personal insults or using incredibly weak examples, as this will undermine your argument. While I have never attacked historians personally (though you may find in a few readings they do attack each other!), I have sometimes chosen the easier arguments to try to tackle, and it is definitely better to try to include some arguments which are themselves convincing and contradictory to your view.
- Don’t stress about referencing – yes referencing is important, but it shouldn’t take too long. Unless your tutor specifies a method, choose a method which you find simple to use as well as being an efficient method. For example, when referencing books I usually only include the author, book title, and year of publication – the test I always use for referencing is to ask myself if I have enough information to buy the book from a retailer. While this wouldn’t suffice if you were writing for a journal, you aren’t writing for a journal so focus on your argument instead and ensure you are really developing your writing skills.
- Don’t be afraid of the first person – in my Sixth Form I was told not to use ‘I’ as it weakened my argument, however that isn’t the advice I have received at Oxford; in fact I have been encouraged to use it as it forces me to take a side. So if you struggle with making your argument clear, use phrases like ‘I believe’ and ‘I argue’.
I hope this will help as a toolkit to get you started, but my last piece of advice is don’t worry! As you get so much practice at Oxford you get plenty of opportunity to perfect your essay writing skills, so don’t think you need to be amazing at everything straight away. Take your first term to try new methods out and see what works for you – don’t put too much pressure on yourself. Good luck!


Subscription Offers
Give a Gift

How to Write Your First Undergraduate Essay
Jeremy Black prepares readers for the rigours of university history.
Well done! You have got into university to read history, one of the most interesting subjects on offer. One reason it is very interesting is that there is a clear progression from the challenges at A level to the requirements of a degree. And that is your problem. You have been set your first essay and you are not clear about these requirements.
The first rule is a simple one. The questions may look the same but your answers must be different. One can be set the identical question, say ‘Why did the French Revolution occur?’, at ages 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 or, if you are an academic writing a paper, 50 or 60, but a different type of answer is required.
In what way different? Not primarily in terms of more facts, because university history degrees are not essentially a test of knowledge, not a question of remembering dates or quotes. It is certainly appropriate to support arguments with relevant information, the emphasis being on relevant not information, and, when you deploy facts, do get them right. To get your facts wrong risks undermining the impression you create because it suggests that you do not really know the subject.
Save 35% with a student subscription to History Today
But history is what you remember when you forget the facts. It is a habit of thought, an attitude of critical scrutiny and exposition, a method of enquiry. These should underlie your reading for your essay and should guide your preparation, and it is in their light that facts are to be assessed. They must contribute to the critical argument, and that requires an ability to engage with three elements if the essay is to be a good one:
Conceptualisation
Methodology
- Historiography.
I will go through all three, but do not worry. At this stage, for most students, these are an aspiration and not an achievement; but the aspiration is important as it shows you, first, how your degree course is different from A level and, secondly, what you will be expected to be able to do by the end of your university career. To do well, you should make an effort to begin including each of these elements in your essays.
Many questions relate to key concepts in history. For example, if you are asked ‘What were the causes of the French Revolution?’, the key concepts are causes and revolution. What do you mean by the French Revolution? Is it primarily the violent challenge to royal authority in 1789, the creation of a new political order, a marked ideological discontinuity, the process of socio-economic change, or, if a combination of all of these, which takes precedence and requires most explanation? What do you understand by causes? Are we talking primarily about long-term, ‘structural’ factors that caused problems, or about precipitants that led to a breakdown of the existing situation? These issues need discussing explicitly, out-in-the-open. That is key to a good essay at university level. They should not be left unspoken and unaddressed; and your discussion of them should reflect your awareness that issues are involved in the analysis, and that you are capable of addressing them. You also need to be aware that there will be different answers and this should guide your handling of the concepts. This leads into Methodology.
In this section, you should explicitly address the issue of how scholars, including yourself, can handle the conceptual questions. This follows the previous point closely. What sources should scholars use and how should they use them? Do you put a preference in studying the French Revolution on the declarations made by revolutionaries, on their public debates, or on what happened ‘on the ground’, including the violent opposition they aroused? If you discuss the latter, you underline the fact that the Revolution led to civil war, and that the causes of what you present as the Revolution were not a mass rejection of the existing system. You also point out that in 1789 few people envisaged what they were expected to support in 1792 (a republic and the trial of the king) let alone 1793 (the Reign of Terror). The Revolution is thus presented and studied as a dynamic, changing process, which requires different explanations at particular stages.
Historiography
A key feature of university work is that you need to address explicitly the degree to which historians hold different views, and why, and to show that you understand that these views change, and can locate your own essay in their debates. For the French Revolution, we see a tendency among French scholars to stress socio-economic causes, among American academics to emphasise the conceptual inconsistencies of the French ancien régime , and among British writers to underline short-term political issues.
Ten Key Things To Do
- Read the question and understand what it is asking.
- Work out your approach.
- Write a detailed essay plan, with different points per paragraph.
- Have an introduction in which you reveal your understanding of the current debate in interpretations.
- Remember to handle the concepts in the question and in your answer clearly.
- Remember to introduce the relevant historical methods explicitly.
- Engage with the historiography, the views of different historians.
- In doing so, show how your work is part of the debate.
- Have a clear conclusion that brings out the relevance of the topic and your answer for wider historical issues.
- Include a reading list and a word count.
Sounds difficult? Well, these approaches add interest and understanding, and help make your degree a worthwhile process of education and exposition.
Jeremy Black is Professor of History at the University of Exeter. He is the author, with Donald M. MacRaild, of Studying History (Palgrave, 3rd edition, 2007).
Popular articles

When Nostalgia Was Deadly

Why Were the Jews Persecuted?

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Undergraduate courses
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Postgraduate events
- Fees and funding
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Term dates and calendars
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
- Give to Cambridge
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges & departments
- Email & phone search
- Museums & collections
- Student information
Department of History and Philosophy of Science
- About the Department overview
- How to find the Department
- Annual Report
- Video and audio
- HPS Discussion email list
- Becoming a Visiting Scholar or Visiting Student overview
- Visitor fee payment
- Becoming an Affiliate
- Applying for research grants and post-doctoral fellowships
- Administration overview
- Information for new staff
- Information for examiners and assessors overview
- Operation of the HPS plagiarism policy
- Information for supervisors overview
- Supervising Part IB and Part II students
- Supervising MPhil and Part III students
- Supervising PhD students
- People overview
- Teaching Officers
- Research Fellows and Teaching Associates
- Professional Services Staff
- PhD Students
- Research overview
- Research projects overview
- Natural History in the Age of Revolutions, 1776–1848
- In the Shadow of the Tree: The Diagrammatics of Relatedness as Scientific, Scholarly and Popular Practice
- The Many Births of the Test-Tube Baby
- Culture at the Macro-Scale: Boundaries, Barriers and Endogenous Change
- Making Climate History overview
- Project summary
- Workstreams
- Works cited and project literature
- Research and teaching fellowships
- Histories of Artificial Intelligence: A Genealogy of Power overview
- From Collection to Cultivation: Historical Perspectives on Crop Diversity and Food Security overview
- Call for papers
- How Collections End: Objects, Meaning and Loss in Laboratories and Museums
- Tools in Materials Research
- Epsilon: A Collaborative Digital Framework for Nineteenth-Century Letters of Science
- Contingency in the History and Philosophy of Science
- Industrial Patronage and the Cold War University
- FlyBase: Communicating Drosophila Genetics on Paper and Online, 1970–2000
- The Lost Museums of Cambridge Science, 1865–1936
- From Hansa to Lufthansa: Transportation Technologies and the Mobility of Knowledge in Germanic Lands and Beyond, 1300–2018
- Medical Publishers, Obscenity Law and the Business of Sexual Knowledge in Victorian Britain
- Kinds of Intelligence
- Varieties of Social Knowledge
- The Vesalius Census
- Histories of Biodiversity and Agriculture
- Investigating Fake Scientific Instruments in the Whipple Museum Collection
- Before HIV: Homosex and Venereal Disease, c.1939–1984
- The Casebooks Project
- Generation to Reproduction
- The Darwin Correspondence Project
- History of Medicine overview
- Events overview
- Past events
- Philosophy of Science overview
- Study HPS overview
- Undergraduate study overview
- Introducing History and Philosophy of Science
- Frequently asked questions
- Routes into History and Philosophy of Science
- Part II overview
- Distribution of Part II marks
- BBS options
- Postgraduate study overview
- Why study HPS at Cambridge?
- MPhil in History and Philosophy of Science and Medicine overview
- A typical day for an MPhil student
- MPhil in Health, Medicine and Society
- PhD in History and Philosophy of Science overview
- Part-time PhD
PhD placement record
- Funding for postgraduate students
- Student information overview
- Timetable overview
- Primary source seminars
- Research methods seminars
- Writing support seminars
- Dissertation seminars
- BBS Part II overview
- Early Medicine
- Modern Medicine and Biomedical Sciences
- Philosophy of Science and Medicine
- Ethics of Medicine
- Philosophy and Ethics of Medicine
- Part III and MPhil
- Single-paper options
- Part IB students' guide overview
- About the course
- Supervisions
- Libraries and readings
- Scheme of examination
- Part II students' guide overview
- Primary sources
- Dissertation
- Key dates and deadlines
- Advice overview
- Examination advice
- Learning strategies and exam skills
- Advice from students
- Part III students' guide overview
- Essays and dissertation
- Subject areas
- MPhil students' guide overview
- PhD students' guide overview
- Welcome to new PhDs
- Registration exercise and annual reviews
- Your supervisor and advisor
- Progress log
- Intermission and working away from Cambridge
- The PhD thesis
- Submitting your thesis
- Examination
- News and events overview
- Seminars and reading groups overview
- Departmental Seminars
- Coffee with Scientists
- Cabinet of Natural History overview
- Publications
- History of Medicine Seminars
- The Anthropocene
- Calculating People
- Measurement Reading Group
- Teaching Global HPSTM
- Pragmatism Reading Group
- Foundations of Physics Reading Group
- Atmospheric Humanities Reading Group
- Values in Science Reading Group
- HPS Workshop
- Postgraduate Seminars overview
- Images of Science
- Language Groups overview
- Latin Therapy overview
- Bibliography of Latin language resources
- Fun with Latin
- Archive overview
- Lent Term 2024
- Michaelmas Term 2023
- Easter Term 2023
- Lent Term 2023
- Michaelmas Term 2022
- Easter Term 2022
- Lent Term 2022
- Michaelmas Term 2021
- Easter Term 2021
- Lent Term 2021
- Michaelmas Term 2020
- Easter Term 2020
- Lent Term 2020
- Michaelmas Term 2019
- Easter Term 2019
- Lent Term 2019
- Michaelmas Term 2018
- Easter Term 2018
- Lent Term 2018
- Michaelmas Term 2017
- Easter Term 2017
- Lent Term 2017
- Michaelmas Term 2016
- Easter Term 2016
- Lent Term 2016
- Michaelmas Term 2015
- Postgraduate and postdoc training overview
- Induction sessions
- Academic skills and career development
- Print & Material Sources
- Other events and resources
How to organise a history essay or dissertation
- About the Department
- News and events

Sachiko Kusukawa
There are many ways of writing history and no fixed formula for a 'good' essay or dissertation. Before you start, you may find it helpful to have a look at some sample dissertations and essays from the past: ask at the Whipple Library.
Some people have a clear idea already of what they are going to write about; others find it more difficult to choose or focus on a topic. It may be obvious, but it is worth pointing out that you should choose a topic you find interesting and engaging. Ask a potential supervisor for a list of appropriate readings, chase up any further sources that look interesting or promising from the footnotes, or seek further help. Try to define your topic as specifically as possible as soon as possible. Sometimes, it helps to formulate a question (in the spirit of a Tripos question), which could then be developed, refined, or re-formulated. A good topic should allow you to engage closely with a primary source (text, image, object, etc.) and develop a historiographical point – e.g. adding to, or qualifying historians' current debates or received opinion on the topic. Specific controversies (either historically or historiographically) are often a great place to start looking. Many dissertations and essays turn out to be overambitious in scope, but underambition is a rare defect!
Both essays and dissertations have an introduction and a conclusion . Between the introduction and the conclusion there is an argument or narrative (or mixture of argument and narrative).
An introduction introduces your topic, giving reasons why it is interesting and anticipating (in order) the steps of your argument. Hence many find that it is a good idea to write the introduction last. A conclusion summarises your arguments and claims. This is also the place to draw out the implications of your claims; and remember that it is often appropriate to indicate in your conclusion further profitable lines of research, inquiry, speculation, etc.
An argument or narrative should be coherent and presented in order. Divide your text into paragraphs which make clear points. Paragraphs should be ordered so that they are easy to follow. Always give reasons for your assertions and assessments: simply stating that something or somebody is right or wrong does not constitute an argument. When you describe or narrate an event, spell out why it is important for your overall argument. Put in chapter or section headings whenever you make a major new step in your argument of narrative.
It is a very good idea to include relevant pictures and diagrams . These should be captioned, and their relevance should be fully explained. If images are taken from a source, this should be included in the captions or list of illustrations.
The extent to which it is appropriate to use direct quotations varies according to topic and approach. Always make it clear why each quotation is pertinent to your argument. If you quote from non-English sources say if the translation is your own; if it isn't give the source. At least in the case of primary sources include the original in a note if it is your own translation, or if the precise details of wording are important. Check your quotations for accuracy. If there is archaic spelling make sure it isn't eliminated by a spell-check. Don't use words without knowing what they mean.
An essay or a dissertation has three components: the main text , the notes , and the bibliography .
The main text is where you put in the substance of your argument, and is meant to be longer than the notes. For quotes from elsewhere, up to about thirty words, use quotation marks ("...", or '...'). If you quote anything longer, it is better to indent the whole quotation without quotation marks.
Notes may either be at the bottom of the page (footnotes) or at the end of the main text, but before the bibliography (endnotes). Use notes for references and other supplementary material which does not constitute the substance of your argument. Whenever you quote directly from other works, you must give the exact reference in your notes. A reference means the exact location in a book or article which you have read , so that others can find it also – it should include author, title of the book, place and date of publication, page number. (There are many different ways to refer to scholarly works: see below.) . If you cite a primary source from a secondary source and you yourself have not read or checked the primary source, you must acknowledge the secondary source from which the citation was taken. Whenever you paraphrase material from somebody else's work, you must acknowledge that fact. There is no excuse for plagiarism. It is important to note that generous and full acknowledgement of the work of others does not undermine your originality.
Your bibliography must contain all the books and articles you have referred to (do not include works that you did not use). It lists works alphabetically by the last name of the author. There are different conventions to set out a bibliography, but at the very least a bibliographic entry should include for a book the last name and initials/first name of the author, the title of the book in italics or underlined, and the place, (publisher optional) and date of publication; or, for an article, the last name and initials/first name of the author, the title in inverted commas, and the name of the journal in italics or underlined, followed by volume number, date of publication, and page numbers. Names of editors of volumes of collected articles and names of translators should also be included, whenever applicable.
- M. MacDonald, Mystical Bedlam: Madness, Anxiety, and Healing in Seventeenth-Century England , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1981.
- William Clark, 'Narratology and the History of Science', Studies in History and Philosophy of Science 26 (1995), 1–72.
- M. F. Burnyeat, 'The Sceptic in His Place and Time', in R. Rorty, J. B. Schneewind and Q. Skinner (eds), Philosophy in History , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1984, pp. 225–54.
Alternatively, if you have many works to refer to, it may be easier to use an author-date system in notes, e.g.:
- MacDonald [1981], p. 89; Clark [1995a], p. 65; Clark [1995b], pp. 19–99.
In this case your bibliography should also start with the author-date, e.g.:
- MacDonald, Michael [1981], Mystical Bedlam: Madness, Anxiety, and Healing in Seventeenth-Century England , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Clark, William [1995a], 'Narratology and the History of Science', Studies in History and Philosophy of Science 26, 1–72.
This system has the advantage of making your foot- or endnotes shorter, and many choose it to save words (the bibliography is not included in the word limit). It is the system commonly used in scientific publications. Many feel however that something is historically amiss when you find in a footnote something like 'Plato [1996b]' or 'Locke [1975]'. In some fields of research there are standard systems of reference: you will find that this is the case if, for example, you write an essay/dissertation on classical history or philosophy of science. In such cases it is a good idea to take a standard secondary source as your model (e.g. in the case of classics, see G.E.R. Lloyd's The Revolutions of Wisdom: Studies in the Claims and Practices of Ancient Greek Science , Berkeley 1987).
Whatever system you decide to follow for your footnotes, what matters most is that the end-product is consistent.
Keep accurate records of all the relevant bibliographic information as you do your reading for your essay/dissertation. (If you don't you may waste days trying to trace references when you are close to submission deadlines.)
Consistency of style throughout the essay/dissertation is encouraged. There are many professional guides to thesis writing which give you more information on the style and format of theses – for example the MLS handbook (British) and the Chicago Manual of Style (American), both in the Whipple, and a booklet, H. Teitelbaum, How to Write a Thesis: A Guide to the Research Paper , 3rd ed., 126 pp., New York: Macmillan (& Arco), 1994 (in the UL: 1996.8.2620). But don't try to follow everything they say!
Every now and then you should read through a printout of your whole essay/dissertation, to ensure that your argument flows throughout the piece: otherwise there is a danger that your arguments become compartmentalised to the size of the screen. When reading drafts, ask yourself if it would be comprehensible to an intelligent reader who was not an expert on the specific topic.
It is imperative that you save your work on disk regularly – never be caught out without a back-up.
Before you submit:
- remember to run a spell-check (and remember that a spell check will not notice if you have written, for example, 'pheasant' instead of 'peasant', or, even trickier, 'for' instead of 'from', 'it' instead of 'is', etc.);
- prepare a table of contents, with titles for each chapter of your essay/dissertation, page numbers and all;
- prepare a cover page with the title, your name and college;
- prepare a page with the required statement about length, originality etc.
Email search
Privacy and cookie policies
Study History and Philosophy of Science
Undergraduate study
Postgraduate study
Library and Museum
Whipple Library
Whipple Museum
Museum Collections Portal
Research projects
History of Medicine
Philosophy of Science
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- Terms and conditions
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...
- Solar Eclipse 2024
What the World Has Learned From Past Eclipses
C louds scudded over the small volcanic island of Principe, off the western coast of Africa, on the afternoon of May 29, 1919. Arthur Eddington, director of the Cambridge Observatory in the U.K., waited for the Sun to emerge. The remains of a morning thunderstorm could ruin everything.
The island was about to experience the rare and overwhelming sight of a total solar eclipse. For six minutes, the longest eclipse since 1416, the Moon would completely block the face of the Sun, pulling a curtain of darkness over a thin stripe of Earth. Eddington traveled into the eclipse path to try and prove one of the most consequential ideas of his age: Albert Einstein’s new theory of general relativity.
Eddington, a physicist, was one of the few people at the time who understood the theory, which Einstein proposed in 1915. But many other scientists were stymied by the bizarre idea that gravity is not a mutual attraction, but a warping of spacetime. Light itself would be subject to this warping, too. So an eclipse would be the best way to prove whether the theory was true, because with the Sun’s light blocked by the Moon, astronomers would be able to see whether the Sun’s gravity bent the light of distant stars behind it.
Two teams of astronomers boarded ships steaming from Liverpool, England, in March 1919 to watch the eclipse and take the measure of the stars. Eddington and his team went to Principe, and another team led by Frank Dyson of the Greenwich Observatory went to Sobral, Brazil.
Totality, the complete obscuration of the Sun, would be at 2:13 local time in Principe. Moments before the Moon slid in front of the Sun, the clouds finally began breaking up. For a moment, it was totally clear. Eddington and his group hastily captured images of a star cluster found near the Sun that day, called the Hyades, found in the constellation of Taurus. The astronomers were using the best astronomical technology of the time, photographic plates, which are large exposures taken on glass instead of film. Stars appeared on seven of the plates, and solar “prominences,” filaments of gas streaming from the Sun, appeared on others.
Eddington wanted to stay in Principe to measure the Hyades when there was no eclipse, but a ship workers’ strike made him leave early. Later, Eddington and Dyson both compared the glass plates taken during the eclipse to other glass plates captured of the Hyades in a different part of the sky, when there was no eclipse. On the images from Eddington’s and Dyson’s expeditions, the stars were not aligned. The 40-year-old Einstein was right.
“Lights All Askew In the Heavens,” the New York Times proclaimed when the scientific papers were published. The eclipse was the key to the discovery—as so many solar eclipses before and since have illuminated new findings about our universe.
To understand why Eddington and Dyson traveled such distances to watch the eclipse, we need to talk about gravity.
Since at least the days of Isaac Newton, who wrote in 1687, scientists thought gravity was a simple force of mutual attraction. Newton proposed that every object in the universe attracts every other object in the universe, and that the strength of this attraction is related to the size of the objects and the distances among them. This is mostly true, actually, but it’s a little more nuanced than that.
On much larger scales, like among black holes or galaxy clusters, Newtonian gravity falls short. It also can’t accurately account for the movement of large objects that are close together, such as how the orbit of Mercury is affected by its proximity the Sun.
Albert Einstein’s most consequential breakthrough solved these problems. General relativity holds that gravity is not really an invisible force of mutual attraction, but a distortion. Rather than some kind of mutual tug-of-war, large objects like the Sun and other stars respond relative to each other because the space they are in has been altered. Their mass is so great that they bend the fabric of space and time around themselves.
Read More: 10 Surprising Facts About the 2024 Solar Eclipse
This was a weird concept, and many scientists thought Einstein’s ideas and equations were ridiculous. But others thought it sounded reasonable. Einstein and others knew that if the theory was correct, and the fabric of reality is bending around large objects, then light itself would have to follow that bend. The light of a star in the great distance, for instance, would seem to curve around a large object in front of it, nearer to us—like our Sun. But normally, it’s impossible to study stars behind the Sun to measure this effect. Enter an eclipse.
Einstein’s theory gives an equation for how much the Sun’s gravity would displace the images of background stars. Newton’s theory predicts only half that amount of displacement.
Eddington and Dyson measured the Hyades cluster because it contains many stars; the more stars to distort, the better the comparison. Both teams of scientists encountered strange political and natural obstacles in making the discovery, which are chronicled beautifully in the book No Shadow of a Doubt: The 1919 Eclipse That Confirmed Einstein's Theory of Relativity , by the physicist Daniel Kennefick. But the confirmation of Einstein’s ideas was worth it. Eddington said as much in a letter to his mother: “The one good plate that I measured gave a result agreeing with Einstein,” he wrote , “and I think I have got a little confirmation from a second plate.”
The Eddington-Dyson experiments were hardly the first time scientists used eclipses to make profound new discoveries. The idea dates to the beginnings of human civilization.
Careful records of lunar and solar eclipses are one of the greatest legacies of ancient Babylon. Astronomers—or astrologers, really, but the goal was the same—were able to predict both lunar and solar eclipses with impressive accuracy. They worked out what we now call the Saros Cycle, a repeating period of 18 years, 11 days, and 8 hours in which eclipses appear to repeat. One Saros cycle is equal to 223 synodic months, which is the time it takes the Moon to return to the same phase as seen from Earth. They also figured out, though may not have understood it completely, the geometry that enables eclipses to happen.
The path we trace around the Sun is called the ecliptic. Our planet’s axis is tilted with respect to the ecliptic plane, which is why we have seasons, and why the other celestial bodies seem to cross the same general path in our sky.
As the Moon goes around Earth, it, too, crosses the plane of the ecliptic twice in a year. The ascending node is where the Moon moves into the northern ecliptic. The descending node is where the Moon enters the southern ecliptic. When the Moon crosses a node, a total solar eclipse can happen. Ancient astronomers were aware of these points in the sky, and by the apex of Babylonian civilization, they were very good at predicting when eclipses would occur.
Two and a half millennia later, in 2016, astronomers used these same ancient records to measure the change in the rate at which Earth’s rotation is slowing—which is to say, the amount by which are days are lengthening, over thousands of years.
By the middle of the 19 th century, scientific discoveries came at a frenetic pace, and eclipses powered many of them. In October 1868, two astronomers, Pierre Jules César Janssen and Joseph Norman Lockyer, separately measured the colors of sunlight during a total eclipse. Each found evidence of an unknown element, indicating a new discovery: Helium, named for the Greek god of the Sun. In another eclipse in 1869, astronomers found convincing evidence of another new element, which they nicknamed coronium—before learning a few decades later that it was not a new element, but highly ionized iron, indicating that the Sun’s atmosphere is exceptionally, bizarrely hot. This oddity led to the prediction, in the 1950s, of a continual outflow that we now call the solar wind.
And during solar eclipses between 1878 and 1908, astronomers searched in vain for a proposed extra planet within the orbit of Mercury. Provisionally named Vulcan, this planet was thought to exist because Newtonian gravity could not fully describe Mercury’s strange orbit. The matter of the innermost planet’s path was settled, finally, in 1915, when Einstein used general relativity equations to explain it.
Many eclipse expeditions were intended to learn something new, or to prove an idea right—or wrong. But many of these discoveries have major practical effects on us. Understanding the Sun, and why its atmosphere gets so hot, can help us predict solar outbursts that could disrupt the power grid and communications satellites. Understanding gravity, at all scales, allows us to know and to navigate the cosmos.
GPS satellites, for instance, provide accurate measurements down to inches on Earth. Relativity equations account for the effects of the Earth’s gravity and the distances between the satellites and their receivers on the ground. Special relativity holds that the clocks on satellites, which experience weaker gravity, seem to run slower than clocks under the stronger force of gravity on Earth. From the point of view of the satellite, Earth clocks seem to run faster. We can use different satellites in different positions, and different ground stations, to accurately triangulate our positions on Earth down to inches. Without those calculations, GPS satellites would be far less precise.
This year, scientists fanned out across North America and in the skies above it will continue the legacy of eclipse science. Scientists from NASA and several universities and other research institutions will study Earth’s atmosphere; the Sun’s atmosphere; the Sun’s magnetic fields; and the Sun’s atmospheric outbursts, called coronal mass ejections.
When you look up at the Sun and Moon on the eclipse , the Moon’s day — or just observe its shadow darkening the ground beneath the clouds, which seems more likely — think about all the discoveries still yet waiting to happen, just behind the shadow of the Moon.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- Dua Lipa Manifested All of This
- Exclusive: Google Workers Revolt Over $1.2 Billion Contract With Israel
- Stop Looking for Your Forever Home
- The Sympathizer Counters 50 Years of Hollywood Vietnam War Narratives
- The Bliss of Seeing the Eclipse From Cleveland
- Hormonal Birth Control Doesn’t Deserve Its Bad Reputation
- The Best TV Shows to Watch on Peacock
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]

How to write a conclusion for a history essay

Every essay needs to end with a concluding paragraph. It is the last paragraph the marker reads, and this will typically be the last paragraph that you write.
What is a ‘concluding paragraph?
The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay that reminds the reader about the points you have made and how it proves the argument which you stated in your hypothesis .
By the time your marker reads your conclusion, they have read all the evidence you have presented in your body paragraphs . This is your last opportunity to show that you have proven your points.
While your conclusion will talk about the same points you made in your introduction , it should not read exactly the same. Instead, it should state the same information in a more developed form and bring the essay to an end.
In general, you should never use quotes from sources in your conclusion.
Concluding paragraph structure
While the concluding paragraph will normally be shorter than your introductory and body paragraphs , it still has a specific role to fulfil.
A well-written concluding paragraph has the following three-part structure:
- Restate your key points
- Restate your hypothesis
- Concluding sentence
Each element of this structure is explained further, with examples, below:
1. Restate your key points
In one or two sentences, restate each of the topic sentences from your body paragraphs . This is to remind the marker about how you proved your argument.
This information will be similar to your elaboration sentences in your introduction , but will be much briefer.
Since this is a summary of your entire essay’s argument, you will often want to start your conclusion with a phrase to highlight this. For example: “In conclusion”, “In summary”, “To briefly summarise”, or “Overall”.
Example restatements of key points:
Middle Ages (Year 8 Level)
In conclusion, feudal lords had initially spent vast sums of money on elaborate castle construction projects but ceased to do so as a result of the advances in gunpowder technology which rendered stone defences obsolete.
WWI (Year 9 Level)
To briefly summarise, the initially flood of Australian volunteers were encouraged by imperial propaganda but as a result of the stories harsh battlefield experience which filtered back to the home front, enlistment numbers quickly declined.
Civil Rights (Year 10 Level)
In summary, the efforts of important First Nations leaders and activist organisations to spread the idea of indigenous political equality had a significant effect on sway public opinion in favour of a ‘yes’ vote.
Ancient Rome (Year 11/12 Level)
Overall, the Marian military reforms directly changed Roman political campaigns and the role of public opinion in military command assignments across a variety of Roman societal practices.
2. Restate your hypothesis
This is a single sentence that restates the hypothesis from your introductory paragraph .
Don’t simply copy it word-for-word. It should be restated in a different way, but still clearly saying what you have been arguing for the whole of your essay.
Make it clear to your marker that you are clearly restating you argument by beginning this sentence a phrase to highlight this. For example: “Therefore”, “This proves that”, “Consequently”, or “Ultimately”.
Example restated hypotheses:
Therefore, it is clear that while castles were initially intended to dominate infantry-dominated siege scenarios, they were abandoned in favour of financial investment in canon technologies.
This proves that the change in Australian soldiers' morale during World War One was the consequence of the mass slaughter produced by mass-produced weaponry and combat doctrine.
Consequently, the 1967 Referendum considered a public relations success because of the targeted strategies implemented by Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders.
Ultimately, it can be safely argued that Gaius Marius was instrumental in revolutionising the republican political, military and social structures in the 1 st century BC.
3. Concluding sentence
This is the final sentence of your conclusion that provides a final statement about the implications of your arguments for modern understandings of the topic. Alternatively, it could make a statement about what the effect of this historical person or event had on history.
Example concluding sentences:
While these medieval structures fell into disuse centuries ago, they continue to fascinate people to this day.
The implications of the war-weariness produced by these experiences continued to shape opinions about war for the rest of the 20 th century.
Despite this, the Indigenous Peoples had to lobby successive Australian governments for further political equality, which still continues today.
Ancient Rome (Year 11/12 Level)
The impact of these changes effectively prepared the way for other political figures, like Pompey, Julius Caesar and Octavian, who would ultimately transform the Roman republic into an empire.
Putting it all together
Once you have written all three parts of, you should have a completed concluding paragraph. In the examples above, we have shown each part separately. Below you will see the completed paragraphs so that you can appreciate what a conclusion should look like.
Example conclusion paragraphs:
In conclusion, feudal lords had initially spent vast sums of money on elaborate castle construction projects but ceased to do so as a result of the advances in gunpowder technology which rendered stone defences obsolete. Therefore, it is clear that while castles were initially intended to dominate infantry-dominated siege scenarios, they were abandoned in favour of financial investment in canon technologies. While these medieval structures fell into disuse centuries ago, they continue to fascinate people to this day.
To briefly summarise, the initially flood of Australian volunteers were encouraged by imperial propaganda, but as a result of the stories harsh battlefield experience which filtered back to the home front, enlistment numbers quickly declined. This proves that the change in Australian soldiers' morale during World War One was the consequence of the mass slaughter produced by mass-produced weaponry and combat doctrine. The implications of the war-weariness produced by these experiences continued to shape opinions about war for the rest of the 20th century.
In summary, the efforts of important indigenous leaders and activist organisations to spread the idea of indigenous political equality had a significant effect on sway public opinion in favour of a ‘yes’ vote. Consequently, the 1967 Referendum considered a public relations success because of the targeted strategies implemented by Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders. Despite this, the Indigenous Peoples had to lobby successive Australian governments for further political equality, which still continues today.
Overall, the Marian military reforms directly changed Roman political campaigns and the role of public opinion in military command assignments across a variety of Roman societal practices. Ultimately, it can be safely argued that Gaius Marius was instrumental in revolutionising the republican political, military and social structures in the 1st century BC. The impact of these changes effectively prepared the way for other political figures, like Pompey, Julius Caesar and Octavian, who would ultimately transform the Roman republic into an empire.
Additional resources

What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
Find anything you save across the site in your account
So You Think You’ve Been Gaslit
By Leslie Jamison

When Leah started dating her first serious boyfriend, as a nineteen-year-old sophomore at Ohio State, she had very little sense that sex was supposed to feel good. (Leah is not her real name.) In the small town in central Ohio where she grew up, sex ed was basically like the version she remembered from the movie “Mean Girls”: “Don’t have sex, because you will get pregnant and die.”
With her college boyfriend, the sex was rough from the beginning. There was lots of choking and hitting; he would toss her around the bed “like a rag doll,” she told me, and then assure her, “This is how everyone has sex.” Because Leah had absorbed an understanding of sex in which the woman was supposed to be largely passive, she told herself that her role was to be “strong enough” to endure everything that felt painful and scary. When she was with other people, she found herself explaining away bruises and other marks on her body as the results of accidents. Once, she said to her boyfriend, “I guess you like it rough,” and he said, “No, all women like it like this.” And she thought, “O.K., then I guess I don’t know shit about myself.”
Her boyfriend was popular on campus. “If you brought up his name,” she told me, “people would say, ‘Oh, my God, I love that guy.’ ” This unanimous social endorsement made it harder for her to doubt anything he said. But, in private, she saw glimpses of a darker side—stray comments barbed with cruelty, a certain cunning. He never drank, and, though in public he cited vague life-style reasons, in private he told her that he loved being fully in control around other people as they unravelled, grew messy, came undone. Girls, especially.
Sometimes, when they were having sex, Leah would get a strong gut feeling that what was happening wasn’t right. In these moments, she would feel overwhelmed by a self-protective impulse that drove her out of bed, naked and crying, to shut herself in the bathroom. What she remembers most clearly is not the fleeing, however, but the return: walking back to bed, still naked, and embarrassed about having “made a scene.” When she got back, her boyfriend would tell her, “You have to get it together. Maybe you should see someone.”
A few months after they broke up—not because of the sex but for “stupid normal relationship reasons”—Leah found herself chatting with a girl who was sitting next to her in a science lecture. It emerged that this girl had gone to the same high school as her ex, and when Leah asked if she knew him the girl looked horrified. “That guy’s a psycho,” she said. Leah had never heard anyone speak about him like this. The girl said that, in high school, he’d had a reputation for sexual assault. Some of what she described sounded eerily familiar. “The idea that he would want to have power over a girl while she was asleep was as easy for me to believe as the idea that he needed air to breathe,” she said. “It reminded me of every sexual experience I had with him, where he had all of the power and I was only a vessel to accept it.”
Leah went back to her dorm room and lay in bed for almost two days straight. She kept revisiting memories from the relationship, understanding them in a new way. Evidently, what she’d understood as “normal” sex had been something more aggressive. And her ex’s attempts to convince her otherwise—implying that she was crazy for having any problem with it—were a kind of controlling behavior so fundamental that she did not have a name for it. Now, six years later, as a social worker at a university, she calls it “gaslighting.”
These days, it seems as if everyone’s talking about gaslighting. In 2022, it was Merriam-Webster’s Word of the Year, on the basis of a seventeen-hundred-and-forty-per-cent increase in searches for the term. In the past decade, the word and the concept have come to saturate the public sphere. In the run-up to the 2016 election, Teen Vogue ran a viral op-ed with the title “Donald Trump Is Gaslighting America.” Its author, Lauren Duca, wrote, “He lied to us over and over again, then took all accusations of his falsehoods and spun them into evidence of bias.” In 2020, the album “Gaslighter,” by the Chicks (formerly known as the Dixie Chicks), débuted at No. 1 on the Billboard country chart, offering an indignant anthem on behalf of the gaslit: “Gaslighter, denier . . . you know exactly what you did on my boat.” (What happened on the boat is revealed a few songs later: “And you can tell the girl who left her tights on my boat / That she can have you now.”) The TV series “Gaslit” (2022) follows a socialite, played by Julia Roberts, who becomes a whistle-blower in the Watergate scandal, having previously been manipulated into thinking she had seen no wrongdoing. The Harvard Business Review has been publishing a steady stream of articles with titles like “What Should I Do if My Boss Is Gaslighting Me?”
The popularity of the term testifies to a widespread hunger to name a certain kind of harm. But what are the implications of diagnosing it everywhere? When I put out a call on X (formerly known as Twitter) for experiences of gaslighting, I immediately received a flood of responses, Leah’s among them. The stories offered proof of the term’s broad resonance, but they also suggested the ways in which it has effectively become an umbrella that shelters a wide variety of experiences under the same name. Webster’s dictionary defines the term as “psychological manipulation of a person usually over an extended period of time that causes the victim to question the validity of their own thoughts, perception of reality, or memories and typically leads to confusion, loss of confidence and self-esteem, uncertainty of one’s emotional or mental stability, and a dependency on the perpetrator.” Leah’s own experience of gaslighting offers a quintessential example—coercive, long-term, and carried out by an intimate partner—but as a clinician she has witnessed the rise of the phrase with both relief and skepticism. Her current job gives her the chance to offer college students the language and the knowledge that she didn’t have at their age. “I love consent education,” she told me. “I wish someone had told me it was O.K. to say no.” But she also sees the word “gaslighting” as being used so broadly that it has begun to lose its meaning. “It’s not just disagreement,” she said. It’s something much more invasive: the gaslighter “scoops out what you know to be true and replaces it with something else.”
The term “gaslighting” comes from the title of George Cukor’s film “Gaslight,” from 1944, a noirish drama that tracks the psychological trickery of a man, Gregory, who spends every night searching for a set of lost jewels in the attic of a town house he shares with his wife, Paula, played by Ingrid Bergman. (The jewels are her inheritance, and we come to understand that he has married her in order to steal them.) Based on Patrick Hamilton’s 1938 play of the same name, the film is set in London in the eighteen-eighties, which gives rise to its crucial dramatic trick: during his nighttime rummaging, Gregory turns on the gas lamps in the attic, causing all the other lamps in the house to flicker. But, when Paula wonders why they are flickering, he convinces her that she must have imagined it. Filmed in black-and-white, with interior shots full of shadows and exterior shots full of swirling London fog, the film offers a clever inversion of the primal trope of light as a symbol of knowledge. Here, light becomes an agent of confusion and deception, an emblem of Gregory’s manipulation.
Gregory gradually makes Paula doubt herself in every way imaginable. He convinces her that she has stolen his watch and hidden one of their paintings, and that she is too fragile and unwell to appear in public. When Paula reads a novel by the fire, she can’t even focus on the words; all she can hear is Gregory’s voice inside her head. The house in which she is now confined becomes a physical manifestation of the claustrophobia of gaslighting and the ways in which it can feel like being trapped inside another person’s narrative—dimly aware of a world outside but lacking any idea of how to reach it.

Link copied
The first recorded use of “gaslight” as a verb is from 1961, according to the Oxford English Dictionary, and its first mention in clinical literature came in the British medical journal The Lancet , in a 1969 article titled “The Gas-Light Phenomenon.” Written by two British doctors, the article summarizes the plot of the original play and then examines three real-life cases in which something similar occurred. Two of the cases feature devious wives, flipping the gender dynamic usually assumed today; in one, a woman tried to convince her husband that he was insane, so that he would be committed to a mental hospital and she could divorce him without penalty. The article is ultimately less concerned with gaslighting itself than with safeguards around admitting patients to mental hospitals. The actual psychology of gaslighting emerged as an object of study a decade later. The authors of a 1981 article in The Psychoanalytic Quarterly interpreted it as a version of a phenomenon known as “projective identification,” in which a person projects onto someone else some part of himself that he finds intolerable. Gaslighting involves a “special kind of ‘transfer,’ ” they write, in which the victimizer, “disavowing his or her own mental disturbance, tries to make the victim feel he or she is going crazy, and the victim more or less complies.”
On its way from niche clinical concept to ubiquitous cultural diagnosis, gaslighting has, of course, passed through the realm of pop psychology. In the 2007 book “The Gaslight Effect,” the psychotherapist Robin Stern mines the metaphor to the fullest, advising her readers to “Turn Up Your Gaslight Radar,” “Develop Your Own ‘Gaslight Barometer,’ ” and “Gasproof Your Life.” Stern anchors the phenomenon in a relationship pattern that she noticed during her twenty years of therapeutic work: “Confident, high-achieving women were being caught in demoralizing, destructive, and bewildering relationships” that in each case caused the woman “to question her own sense of reality.” Stern offers a series of taxonomies for the stages (Disbelief, Defense, Depression) and the perpetrators (Glamour Gaslighters, Good-Guy Gaslighters, and Intimidators). She understands gaslighting as a dynamic that “plays on our worst fears, our most anxious thoughts, our deepest wishes to be understood, appreciated, and loved.”
In the past decade, philosophy has turned its gaze to the phenomenon, too. In 2014, Kate Abramson, a philosophy professor at the University of Indiana, published an essay called “Turning Up the Lights on Gaslighting,” which she has now expanded into a rigorous and passionately argued book-length study, “On Gaslighting.” Early in the book, she describes giving talks and having conversations about gaslighting in the decade since publishing her original article: “I still remember the sense of revelation I had when first introduced to the notion of gaslighting. I’ve now seen that look of stunned discovery on a great many faces.”
The core of Abramson’s argument is that gaslighting is an act of grievous moral wrongdoing which inflicts “a kind of existential silencing.” “Agreement isn’t the endpoint of successful gaslighting,” she writes. “Gaslighters aim to fundamentally undermine their targets as deliberators and moral agents.” Abramson catalogues the ways in which gaslighters leverage their authority, cultivating isolation in the victim and leaning on social tropes (for example, the “hysterical woman”) to achieve their aims. Outlining the various forms of suffering that gaslighting causes, Abramson stresses the tautological bind in which it places the victim—“charging someone not simply with being wrong or mistaken, but being in no condition to judge whether she is wrong or mistaken.” Gaslighting essentially turns its targets against themselves, she writes, by harnessing “the very same capacities through which we create lives that have meaning to us as individuals,” such as the capacities to love, to trust, to empathize with others, and to recognize the fallibility of our perceptions and beliefs. This last point has always struck me as one of gaslighting’s keenest betrayals: it takes what is essentially an ethically productive form of humility, the awareness that one might be wrong, and turns it into a liability. Any argument in which two people remember the same thing in different ways can feel like a terrible game of chicken: the “winner” of the argument is the one less willing to doubt their own memories—arguably the more flawed moral position—whereas the one who swerves first looks weaker but is often driven by a more conscientious commitment to self-doubt.
Being a philosopher, Abramson spends a good deal of time defining the phenomenon by specifying what it isn’t. Gaslighting is not the same as brainwashing, for example, because it involves not simply convincing someone of something that isn’t true but, rather, convincing that person to distrust their own capacity to distinguish truth from falsehood. It is also not the same as guilt-tripping, because someone can be aware of being guilt-tripped while still effectively being guilt-tripped. At the same time—and although Abramson recognizes that “concept creep” threatens to dilute the meaning and the utility of the term—her own examples of gaslighting sometimes grow uncomfortably expansive. (And her decision to use male pronouns for gaslighters and female pronouns for the gaslit also reinforces a reductive notion of its gender patterns.) Both the book and her original essay open with a list of more than a dozen “things gaslighters say,” ranging from “Don’t be so sensitive” to “If you’re going to be like this, I can’t talk to you” to “I’m worried; I think you’re not well.” It’s hard to imagine a person who hasn’t heard at least one of these. The quotations function as a kind of net, drawing readers into the force field of the book’s argument with an implicit suggestion: Perhaps this has happened to you.
Growing up in Bangladesh as the daughter of two literature professors, a woman I’ll call Adaya often had difficulty understanding what other people were saying. She felt stupid because it seemed so much harder for her to comprehend things others understood easily, but over time she began to suspect that her hearing was physically impaired. Her parents told her that she was just seeking attention, and when they finally took her to the family doctor he confirmed that her hearing was fine. She was just exaggerating, he said, as teen-age girls are prone to do.
Adaya believed what her parents had said, though she kept encountering situations where she couldn’t hear things. It wasn’t until her mid-thirties, in 2011, that she finally went to see another specialist. This was in Iowa, where she’d moved for a graduate program in writing after her first marriage, in Bangladesh, fell apart. The clinician told her that her middle-ear bone was calcifying; it was a congenital problem that had almost certainly affected her hearing for at least twenty-five years. Waiting for a bus home from the hospital—in the middle of winter, with a foot of snow all around her—Adaya called her mother to tell her. She responded without apology (“You’re old enough to take care of yourself, so take care of yourself”), and let another six years pass before casually disclosing that the family doctor had found something wrong with Adaya’s hearing, all those years before. When Adaya asked why they had kept this from her, her mother replied, “I didn’t want to tell you because I didn’t want you to be weak about it.”
Of all the people who approached me on X with testimonies of gaslighting, I found Adaya and her story particularly compelling because her diagnosis eventually offered her a kind of irrefutable confirmation—something the gaslit crave, but often never receive—that allowed her to confront the dynamic directly. For Adaya, the damage of her parents’ deception went beyond the hardships of her medical condition. “It made me feel that what I was experiencing in my body was not real,” she told me. “All my life I was told I was lying and exaggerating. . . . In those years when my sense of self was being formed, I was being given a deficient version of myself.” It was part of a broader pattern. From an early age, Adaya told me, she felt that she didn’t fit in with her family without quite knowing why. Eventually, she realized that this sense of falling short had arisen from things her mother said. She thought of herself as ugly because her mother said so, disparaging her dark skin; when she got a skin infection, she was made to believe it was because she didn’t keep herself clean enough. “If your mother cannot see the grace and beauty in you, who can?” Adaya said. That sense of shame and worthlessness propelled her toward an abusive marriage (“The first boy who told me I was worth loving, I moved toward him”) and kept her in it for years.
The idea of gaslighting first began to resonate with Adaya when she finally went to therapy, in her forties. She had gone in order to understand the dynamics of her failed marriage, but came to see that the problems went deeper. As she wrote in one of her first messages to me, she found it easier to talk about surviving domestic violence than about the emotional violence she experienced in her childhood. The things her mother had said about her “dislodged and disoriented and to some extent destroyed my sense of self.” Adaya has come to divide her life into three parts: her youth, when she believed in the version of herself shaped by her mother’s narrative; the period of adulthood when the hearing diagnosis caused her to wrestle with that narrative; and the current era, in which she has a stronger self-conception and is in a stable romantic relationship. She was able to arrive at this point in part because her therapist helped her identify her relationship with her parents as one of gaslighting. Looking back on herself when she was young, she says, “I almost feel like it’s a different person—like she is my child, and I want to take care of her.”
The psychoanalyst and historian Ben Kafka, who is working on a book about how other people drive us crazy, told me that he thinks our most familiar tropes about gaslighting are slightly misleading. He believes that, although romantic relationships dominate our cultural narratives of gaslighting, the parent-child dynamic is a far more useful frame. When I visited Kafka in the cozy Greenwich Village office where he sees his patients, he pointed out that, for one thing, the power imbalance between parents and their children is intrinsically conducive to this form of manipulation. Indeed, it often happens unwittingly: if a child receives her version of reality from her parents, then she may feel that she has to consent to it as a way to insure that she continues to be loved and cared for. (And what other sense of reality do we have at first, besides what our parents tell us to be true?) Additionally, gaslighting later in life almost always involves some degree of infantilization and regression, insofar as it creates an enforced dependence. Lastly, and crucially, Kafka’s orientation toward parent-child bonds stems from an essentially Freudian belief that the dynamics at play in our adult relationships can usually be traced back to those we grew familiar with in childhood.
There are many memoirs that recount experiences one might call gaslighting—indeed, the very act of writing personal narrative often involves an attempt to “reclaim” a story that’s already been told another way—but few trace the lasting residue of parental gaslighting as deftly as Lily Dunn’s “Sins of My Father.” When Dunn was six, her father left the family to join a cult who called themselves the sannyasins and preached a doctrine of radical emotional autonomy. At thirteen, Dunn went to spend the summer at her father’s villa, in Tuscany, where he lived with a much younger wife (they’d got together when he was thirty-seven and she was eighteen) and a rotating crew of fellow cult members. In the entrancing but unsettling paradise of the villa—with its marble floors and grand staircases, shoddy electricity, and plentiful vats of wine—one of her father’s middle-aged friends began trying to seduce her. After kissing her in the kitchen, his skin leathery and his breath stale from cigarette smoke, he whispered, “I want to have sex with you,” and invited her back to his camper van to listen to his poems.
When Dunn told her father how anxious these sexual advances made her, he replied that she shouldn’t be worried. “You could learn something,” he told her. “He’s a good man. He’ll be gentle.” (He changed his mind once he learned that his friend had gonorrhea.) For Dunn, her father’s failure to affirm her sense of being preyed upon was far more damaging than the other man’s predation. Years later, whenever she asked her father to acknowledge that his behaviors had affected her, he would gaslight her even more. Echoing the teachings of his sannyasin guru, he acted as if it were inappropriate for her to blame him for any emotional damage: “ ‘You can choose how you feel,’ he said, again and again. ‘It has nothing to do with me.’ ”
For years after that incident, Dunn told me, “I could never trust that what I was feeling was quite right,” because she’d been consistently told by her father that she felt too much, and that she needed to deal with these feelings on her own rather than foisting them onto others. At fifteen, she began her first serious romantic relationship, with a much older man (he was thirty-two), and found it almost impossible to trust her suspicions about him. Looking back, it’s clear to her that he was living with his female partner, but he said that the woman was just a roommate, and Dunn didn’t have the confidence to disbelieve him. Instead, she told me, she got lost in obsessive thought patterns, trying to figure out whether this man was lying or if she was being paranoid; she couldn’t concentrate properly because she was so consumed by this circular thinking. “I thought I had to work it out myself,” she said. Looking back, she sees herself frantically trying to play two roles at once: she was the anxious child, who knew something was wrong but couldn’t figure out what, and the adult who was attempting—but not yet able—to take care of things, to make them right.
Sitting in Kafka’s office thinking of Dunn and Adaya, I found myself swelling with indignation on behalf of these gaslit children, taught to feel responsible for the pain their parents had caused them. But beneath that indignation lurked something else—a nagging anxiety coaxed into sharper visibility by the therapeutic aura of Kafka’s sleek analytic couch. I eventually told him that, as I worked on this piece, I had started to wonder about the ways I might be unintentionally gaslighting my daughter—telling her that she is “just fine” when she clearly isn’t, or giving her a hard time for making us late for school by demanding to wear a different pair of tights, when it is clearly my own fault for not starting our morning routine ten minutes earlier. In these interactions, I can see the distinct mechanisms of gaslighting at work, albeit in a much milder form: taking a difficult feeling—my latent sense of culpability whenever she is unhappy, or my guilt for running behind schedule—and placing it onto her. Part of me hoped that Kafka would disagree with me, but instead he started nodding vehemently. “Yes!” he said. “Within a two-block range of any elementary school, just before the bell rings, you can find countless parents gaslighting their children, off-loading their anxiety.”
We both laughed. In the moment, this jolt of recognition seemed incidental, a brief diversion into daily life as we crawled through the darker trenches of human manipulation. But, after I’d left Kafka’s office, it started to feel like a crucial acknowledgment: that gaslighting is neither as exotic nor as categorically distinct as we’d like to believe.
Gila Ashtor, a psychoanalyst and a professor at Columbia University, told me she often sees patients experience a profound sense of relief when it occurs to them that they may have been gaslit. As she put it, “It’s like light at the end of the tunnel.” But Ashtor worries that such relief may be deceptive, in that it risks effacing the particular (often unconscious) reasons they may have been drawn to the dynamic. Ashtor defines gaslighting as “the voluntary relinquishing of one’s narrative to another person,” and the word “voluntary” is crucial—that’s what makes it a dynamic rather than just a unilateral act of violence. For Ashtor, it’s not a question of blaming the victim but of examining their susceptibility: what makes someone ready to accept another person’s narrative of their own experience? What might they have been seeking?
In addition to working as a psychoanalyst, Ashtor has studied and taught in Columbia’s M.F.A. program in creative nonfiction (where I also teach), and she thinks a lot about the connections between gaslighting and personal narrative. I asked her how patients tend to narrate their gaslighting experiences: how often they come to her with the idea already in their minds, and how often she is the one to bring it up. Ashtor said that, if she introduces the term, she tries to use it as a placeholder, a first step in figuring out what was at play in a relationship. When patients introduce it—and sometimes she can sense a patient wanting her to use it first—she may be skeptical, not because they are wrong but because they usually haven’t fully reckoned with their own role in the dynamic yet. It’s as if they are trying to close something by invoking the word—to mark it as settled, figured out—whereas she wants to open it up. Ashtor says it frequently becomes clear that patients are very attached to the term “gaslighting,” and fear something will be taken away from them if she disputes it. The question of what would be taken away is an illuminating one, and it raises an even trickier question: what did the dynamic give them in the first place?
The issue of susceptibility gets thorny quickly; it can appear to veer dangerously close to victim-blaming. Ashtor doesn’t believe in the old psychoanalytic idea that everything that happens to us is somehow desired, but she does think that it’s worthwhile to investigate why people find themselves in certain toxic dynamics. Without discounting the genuine suffering involved, she finds it useful to ask what her patients were seeking. Ashtor wondered aloud to me whether there could be something “good” about gaslighting, and why it feels so transgressive even to suggest that this might be the case. “There’s a real appeal in adopting someone else’s view of the world and escaping our own,” she told me. “There are very few acceptable outlets in our lives for this hunger for difference.”
Ashtor thinks that therapeutic examination of a gaslighting dynamic can bring you closer to understanding something crucial about yourself: a complicated relationship to motherhood, say, or the effects of certain imbalances or conflicts in your parents’ marriage. The work is to “understand what’s getting enacted and why.” One doesn’t necessarily emerge from this type of examination with a self that is entirely “cured” or integrated, but it can, as she says, allow one to “live in closer proximity to the questions and struggles that animate the self.” In working with patients to better understand their experiences of being gaslit, Ashtor is hoping to give them a different way to engage with the impulses that led them there.
Although most accounts of gaslighting focus on interpersonal dynamics, Pragya Agarwal, a behavioral scientist and a writer based between Ireland and the U.K., believes that it’s more useful to consider the phenomenon from a sociological perspective. “People who have less power because of their status in society, whether it be gender, race, class, and so on, are more susceptible to being gaslighted,” she told me. “Their inferior status is used as leverage to invalidate their experiences and testimonies.” She spoke of instances in medicine in which genuinely ill patients are repeatedly told that their symptoms are psychosomatic. Endometriosis, for example, is an underdiagnosed condition, she said, because women’s pain is often discounted. Similarly, in the workplace, minorities who report microaggressions may be told that they are being “too sensitive” or that the offending colleague “didn’t mean it like that.”
In this view of gaslighting, it becomes harder to see the utility of susceptibility as a framing concept. When I asked Agarwal about what role the gaslit party might play in the dynamic, she replied, “I don’t believe that it is the responsibility of the oppressed to create conditions where they wouldn’t be oppressed.”
What does the gaslighter want? In the 1944 film, the gaslighter’s motivation (to steal Paula’s jewels) is so cartoonishly superficial that it seems like a stand-in for something larger—a metaphor for the desire to undermine a woman’s self-confidence, perhaps, in order to keep her dependent. In real life, casting the gaslighter as a two-dimensional villain seems insufficient, another way of avoiding a reckoning with complicity and desire.
The question of the gaslighter’s motivation often becomes a chicken-or-egg dilemma: whether their impulse to destabilize another person’s sense of reality stems primarily from wanting to harm that person or from wanting to corroborate their own truth. Think of the college boyfriend who convinces his girlfriend that all sex involves violence—is his fundamental investment in controlling her or in somehow justifying his own desires? Abramson writes that both goals can be at play simultaneously, such that a gaslighter may be “trying to radically undermine his target” and also, “in a perfectly ordinary way, trying to tell himself a story about why there’s nothing that happened with which he needs to deal.” (Indeed, as she points out, gaslighters “are often not consciously trying to drive their targets crazy,” so they may not always be self-aware enough to distinguish between these reasons.) If the need to affirm one’s own version of reality is pretty much universal, it makes sense that a desire to attack someone else’s competing version is universal, too. Yet, in the popular discourse, it can seem as if everyone has been gaslit but no one will admit to doing the gaslighting.
Kristin Dombek, in her 2014 book, “The Selfishness of Others: An Essay on the Fear of Narcissism,” discusses how narcissism, once solely a clinical diagnosis, became an all-purpose buzzword. In her view, we hurl the accusation of pathological selfishness at others as a way of making sense of the feeling of being ignored or slighted. Gaslighting is not a clinical diagnosis, but, as with narcissism, less precise applications of the term can be a way to take an inevitable source of pain—the fact of disagreement, or the fact that we are not the center of other people’s lives—and turn it into an act of wrongdoing. This is not to say that narcissism or gaslighting don’t exist, but that, in seeing them everywhere, we risk not just diluting the concepts but also attributing natural human friction to the malevolence of others. Although “gaslighting” is a term that many members of Gen Z have grown up with, one teen-ager I know expresses its perils in this vein succinctly: “Every time someone gets criticized or called out, they just say, ‘Oh, you’re gaslighting me,’ and it makes the other person the bad guy.”
It doesn’t help that the accusation is essentially unanswerable: “No, I’m not” is exactly what a gaslighter would say. Even a third party who disputes someone’s account of being gaslit is threatening to inflict the same harm as the gaslighter. No wonder the issue of proof is crucial in many accounts of gaslighting: the tights on the boat, the charts that show decades of hearing loss, the other women who were assaulted. These are empirical life preservers that pull us out of the epistemic whirlpool. In proving that our past perceptions were correct after all, they also seem to guarantee that we are correct now in our feeling of having been hurt.
Such certainty is possible only in retrospect, however. Inside the experience of gaslighting, Abramson writes, “the gaslit find themselves tossed between trust and distrust, unstably occupying a world between the two.” Which is to say, the more adamant you are that you’re being gaslit, the more probable it is that you’re not. On Reddit, a man laments, “My last GF loved to tell me I was ‘gaslighting’ her every time I simply had a different opinion than hers. Infuriating.” Has he been gaslit into thinking he’s a gaslighter?
Part of the tremendously broad traction of the concept, I suspect, has to do with the fact that gaslighting is adjacent to so many common relationship dynamics: not only disagreeing on a shared version of reality but feeling that you are in a contest over which version prevails. It would be nearly impossible to find someone who hasn’t experienced the pain and frustration—utterly ordinary, but often unbearable—that comes when your own sense of reality diverges from someone else’s. Because this gap can feel so maddening and wounding, it can be a relief to attribute it to villainy.
At the climax of Cukor’s film, Paula confronts her husband with the truth of his manipulations. (He has been tied to a chair by a helpful detective. She is brandishing a knife.) He doubles down on his old tricks, trying to convince her that she has misinterpreted the evidence and should cut him free. But Paula turns his own game against him: “Are you suggesting that this is a knife I hold in my hand? Have you gone mad, my husband?” In a further twist, she inhabits the role of madwoman as a repurposed costume:
How can a madwoman help her husband to escape? . . . If I were not mad, I could have helped you. . . . But because I am mad, I hate you. Because I am mad, I have betrayed you. And because I’m mad, I’m rejoicing in my heart, without a shred of pity, without a shred of regret, watching you go with glory in my heart!
On its surface, this final scene offers us a clear, happy ending. The gaslit party triumphs and objective truth prevails. But deeper down it gestures toward a more complex vision of gaslighting: as a reciprocal exchange in which both parties take turns as gaslit and gaslighter. This is a version of gaslighting that psychoanalysis is more congenial to. In the Psychoanalytic Quarterly article from 1981, the authors describe a “gaslighting partnership” whose participants may “oscillate” between roles: “Not infrequently, each of the participants is convinced that he or she is the victim.”
In this sense, gaslighting is both more and less common than we think. Extreme cases undoubtedly occur, and deserve recognition as such, but to understand the phenomenon exclusively in light of these dire examples allows us to avoid the more uncomfortable notion that something similar takes place in many intimate relationships. One doesn’t have to dilute the definition of gaslighting to recognize that it happens on many scales, from extremely toxic to undeniably commonplace.
Ben Kafka told me that he thinks one of the key insights of psychoanalysis is that people respond to anxiety by dividing the world into good and bad, a tendency known as “splitting.” It strikes me that some version of this splitting is at play not only in gaslighting itself—taking an undesirable “bad” emotion or quality and projecting it onto someone else, so that the self can remain “good”—but also in the widespread invocation of the term, the impulse to split the world into innocent and culpable parties. If the capacity to gaslight is more widely distributed than its most extreme iterations would lead us to believe, perhaps we’ve all done more of it than we care to admit. Each of us has been the one making our way back into bed, vulnerable and naked, and each of us has been the one saying, Come back into this bed I made for you. ♦
New Yorker Favorites
Why facts don’t change our minds .
The tricks rich people use to avoid taxes .
The man who spent forty-two years at the Beverly Hills Hotel pool .
How did polyamory get so popular ?
The ghostwriter who regrets working for Donald Trump .
Snoozers are, in fact, losers .
Fiction by Jamaica Kincaid: “Girl”
Sign up for our daily newsletter to receive the best stories from The New Yorker .
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Margaret Talbot

By Jia Tolentino

By Rebecca Mead

By Amanda Petrusich

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
the History Paper The Challenges of Writing About (a.k.a., Making) History At first glance, writing about history can seem like an overwhelming task. History's subject matter is immense, encompassing all of human affairs in the recorded past — up until the moment, that is, that you started reading this guide.
1. Background sentences. The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis, your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about. Background sentences explain the important historical ...
Download Article. 1. Have a clear structure. When you come to write the body of the essay it is important that you have a clear structure to your argument and to your prose. If your essay drifts, loses focus, or becomes a narrative of events then you will find your grade dropping.
Writing a history essay requires a lot of work and experience. A student needs to show a high level of knowledge and understanding of historical events, as well analytical and research skills. No wonder many students find it challenging to compose a well-written essay! To achieve success, use the following tips to level-up your writing abilities
To write an effective essay, students should examine the question, understand its focus and requirements, acquire information and evidence through research, then construct a clear and well-organised response. Writing a good history essay should be rigorous and challenging, even for stronger students. As with other skills, essay writing develops ...
Step 1: Understand the History Paper Format. You may be assigned one of several types of history papers. The most common are persuasive essays and research papers. History professors might also ask you to write an analytical paper focused on a particular source or an essay that reviews secondary sources.
If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece. Most essays will require you to write: 1 Introduction Paragraph. 3 Body Paragraphs. 1 Concluding Paragraph.
Historical essay writing is based upon the thesis. A thesis is a statement, an argument which will be presented by the writer. The thesis is in effect, your position, your particular interpretation, your way of seeing a problem. Resist the temptation, which many students have, to think of a thesis as simply "restating" an instructor's question.
Make it Shine. An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it's achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine: Write a substantial introduction.
Write in the past tense when discussing history. If a historical event took place in the past, write about it in the past. Be precise. Focus on your thesis and only provide information that is needed to support or develop your argument. Be formal. Try not to use casual language, and avoid using phrases like "I think.".
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context. Provide background information on the historical context of your topic. Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay. Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence.
The second is to write a narrative of events - often beginning with the birth of an individual - with a half-hearted attempt at answering the question in the final paragraph. Middle Paragraphs. Philip Larkin once said that the modern novel consists of a beginning, a muddle and an end. The same is, alas, all too true of many history essays.
Essays are an essential educational tool in disciplines like history because they help you to develop your research skills, critical thinking, and writing abilities. The best essays are based on strong research, in-depth analysis, and are logically structured and well written. An essay should answer a question with a clear, persuasive argument.
Many history essays have a natural chronological focus. Arguments that seek to explain what happened at a place and time, or demonstrate what led up to an event, as well as essays that focus on an individual's importance, can be organized chronologically. Intro; Early phase or antecedents; Middle years or main event; Later years or impact ...
Here are my tips from my first year as an Oxford Undergraduate: Planning. Plan for success - a good plan really sets your essay in a positive direction, so try to collect your thoughts if you can. I find a great way to start my planning process is to go outside for a walk as it helps to clear my head of the detail, it allows me to focus on ...
Rather, it requires explication. It requires, as well, that you connect it to your thesis. Remember that you bring evidence in support of your thesis and evidence that's evidence that does not serve that purpose should be excluded. (4) Weave your thesis throughout the body of your essay - Once delineated in your introduction, be sure to weave ...
Remember to introduce the relevant historical methods explicitly. Engage with the historiography, the views of different historians. In doing so, show how your work is part of the debate. Have a clear conclusion that brings out the relevance of the topic and your answer for wider historical issues. Include a reading list and a word count.
Many feel however that something is historically amiss when you find in a footnote something like 'Plato [1996b]' or 'Locke [1975]'. In some fields of research there are standard systems of reference: you will find that this is the case if, for example, you write an essay/dissertation on classical history or philosophy of science.
Check Out Typed (https://bit.ly/3EG1lVL) for a seamless workflow! #ad #typed.do_____ How to Write a History E...
The entire process I have outlined may take as much as three or four lessons. If you have this amount of time, here is a potential approach: Lesson 1: Example 'real world' essay construction. Lesson 2: Deconstruct a pre-written History essay. Lesson 3-4: Plan and write a class History essay.
Dr Nicholas Morton's advice on how to form an essay introduction.
The essay will answer the question(s) clearly and concisely. 2. The essay will argue using scholarly evidence (secondary sources) and ancient sources (sources written at the time) or commonly known as "primary sources". 3. The essay will "stick to the point" i.e. discuss the question and not go off topic.
On February 25, 2020, a top official at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention decided it was time to level with the U.S. public about the COVID-19 outbreak. At the time, there were just 57 people in the country confirmed to have the infection, all but 14 having been repatriated from Hubei province in China and the Diamond Princess cruise ship, docked off Yokohama, Japan.
"Lights All Askew In the Heavens," the New York Times proclaimed when the scientific papers were published. The eclipse was the key to the discovery—as so many solar eclipses before and ...
1. Restate your key points. In one or two sentences, restate each of the topic sentences from your body paragraphs. This is to remind the marker about how you proved your argument. This information will be similar to your elaboration sentences in your introduction, but will be much briefer. Since this is a summary of your entire essay's ...
The impetuous and reckless decision led to the death of both Romeo and Juliet, even though it could've been avoided. Bloom writes, "However, Seward maintains Shakespeare is making a statement regarding the inherent danger of playing with passion and the consequences of what the lovers might do as a result of these intense emotions." (Bloom ...
Both the book and her original essay open with a list of more than a dozen "things gaslighters say," ranging from "Don't be so sensitive" to "If you're going to be like this, I can ...