Words, Phrases, and Arguments to Use in Persuasive Writing
PhotoAlto / Sigrid Olsson / Getty Images
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- University of Maine
Persuasive writing is tough for kids to get used to, especially if they’re not argumentative by nature. A few tools and shortcuts can help your child learn how to write well enough to convince someone (even you!) to change his mind about an issue that really matters to him or her.

Persuasive Strategies and Devices
ONOKY - Fabrice LEROUGE / Brand X Pictures / Getty Images
There are common persuasion techniques sometimes referred to as persuasive devices that can be used to back up an argument in writing . Knowing the names of the strategies and how they work can make it easier to remember them when it’s time to write. The five common persuasive strategies are:
- Pathos: Pathos involves using emotional language that is designed to draw the reader in and make them feel for you. For example: "If my allowance isn’t increased, I won’t be able to go out with my friends and do everything they do."
- Big Names: The big names strategy involves using the names of experts or well-known people who support your position. For example: "Dad agrees that increasing my allowance will..."
- Research and Logos: These strategies involve using studies, data, charts , illustrations, and logic to back up her position and points. For example: "As you can see in the pie chart, at my age the average child’s allowance is..."
- Ethos: The ethos strategy of persuasion involves using language that shows that the writer is trustworthy and believable. For example: "As you may recall, I’ve always been willing to put ten percent of my allowance in my bank account, thus..."
- Kairos: This type of argument creates a sense of urgency about how this is the right moment to act. For example: "If I don’t get an increase in my allowance today, I will miss out on the chance to..."
Phrases and Words to Use in Persuasive Writing
Camille Tokerud / Getty Images
Once your child has figured out the techniques she can use in her persuasive writing, she will need to find some words and phrases that help her to be convincing. Using phrases like "I think" or "It seems that" don’t convey a sense of confidence in her position. Instead, she needs to use word combinations that show how much she believes in what she is writing.
- Phrases to Illustrate a Point: For instance, for example, specifically, in particular, namely, such as, like
- Phrases to Introduce an Example: For example, thus, as an example, in the instance of, in other words, to illustrate
- Phrases to Make Suggestions: To this end, keeping this in mind, for this purpose, therefore
- Phrases to Transition Between Information: Also, furthermore, additionally, besides that, equally as important, similarly, likewise, as a result, otherwise, however
- Phrases to Contrast Points: On the other hand, nevertheless, despite, in spite of, yet, conversely, instead, by the same token
- Phrases for Conclusions and Summarizing: With this in mind, as a result of, because of this, for this reason, so, due to, since, finally, in short, in conclusion
Other Handy Phrases for Persuasive Writing
John Howard / Getty Images
Some phrases don’t easily fit into a category and are just good for general use in persuasive writing. Here are a few to remember:
- I am certain. . .
- I’m sure that you can see that . . .
- What needs to be done/what we need to do. . .
- I ask you to think about . . .
- I am writing in order to . . .
- Nevertheless . . .
- On the other hand . . .
- It has come to my attention that . . .
- If you move forward with . . .
- Obviously. . .
- Surely . . .
- Regardless . . .
- If [ ] were to happen, then . . .
- This can be fixed by . . .
- Although it may seem...
- Convince Me: A Persuasive Writing Activity
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- Writing Prompt (Composition)
- Use Social Media to Teach Ethos, Pathos and Logos
- Persuasive Writing: For and Against
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- What Is a Rhetorical Device? Definition, List, Examples
- Persuasion and Rhetorical Definition
- AP English Exam: 101 Key Terms
- Concession Used in Rhetoric
- Artistic Proofs: Definitions and Examples
- What Is Phronesis?
- Definition and Examples of Ethos in Classical Rhetoric
- Argument (Rhetoric and Composition)
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.
General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument . Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.
Get 25% OFF new yearly plans in our Spring Sale
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: Tips and Tricks

Allison Bressmer

Most composition classes you’ll take will teach the art of persuasive writing. That’s a good thing.
Knowing where you stand on issues and knowing how to argue for or against something is a skill that will serve you well both inside and outside of the classroom.
Persuasion is the art of using logic to prompt audiences to change their mind or take action , and is generally seen as accomplishing that goal by appealing to emotions and feelings.
A persuasive essay is one that attempts to get a reader to agree with your perspective.

Ready for some tips on how to produce a well-written, well-rounded, well-structured persuasive essay? Just say yes. I don’t want to have to write another essay to convince you!
How Do I Write a Persuasive Essay?
What are some good topics for a persuasive essay, how do i identify an audience for my persuasive essay, how do you create an effective persuasive essay, how should i edit my persuasive essay.
Your persuasive essay needs to have the three components required of any essay: the introduction , body , and conclusion .
That is essay structure. However, there is flexibility in that structure.
There is no rule (unless the assignment has specific rules) for how many paragraphs any of those sections need.
Although the components should be proportional; the body paragraphs will comprise most of your persuasive essay.

How Do I Start a Persuasive Essay?
As with any essay introduction, this paragraph is where you grab your audience’s attention, provide context for the topic of discussion, and present your thesis statement.
TIP 1: Some writers find it easier to write their introductions last. As long as you have your working thesis, this is a perfectly acceptable approach. From that thesis, you can plan your body paragraphs and then go back and write your introduction.
TIP 2: Avoid “announcing” your thesis. Don’t include statements like this:
- “In my essay I will show why extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
- “The purpose of my essay is to argue that extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
Announcements take away from the originality, authority, and sophistication of your writing.
Instead, write a convincing thesis statement that answers the question "so what?" Why is the topic important, what do you think about it, and why do you think that? Be specific.
How Many Paragraphs Should a Persuasive Essay Have?
This body of your persuasive essay is the section in which you develop the arguments that support your thesis. Consider these questions as you plan this section of your essay:
- What arguments support your thesis?
- What is the best order for your arguments?
- What evidence do you have?
- Will you address the opposing argument to your own?
- How can you conclude convincingly?

TIP: Brainstorm and do your research before you decide which arguments you’ll focus on in your discussion. Make a list of possibilities and go with the ones that are strongest, that you can discuss with the most confidence, and that help you balance your rhetorical triangle .
What Should I Put in the Conclusion of a Persuasive Essay?
The conclusion is your “mic-drop” moment. Think about how you can leave your audience with a strong final comment.
And while a conclusion often re-emphasizes the main points of a discussion, it shouldn’t simply repeat them.
TIP 1: Be careful not to introduce a new argument in the conclusion—there’s no time to develop it now that you’ve reached the end of your discussion!
TIP 2 : As with your thesis, avoid announcing your conclusion. Don’t start your conclusion with “in conclusion” or “to conclude” or “to end my essay” type statements. Your audience should be able to see that you are bringing the discussion to a close without those overused, less sophisticated signals.

If your instructor has assigned you a topic, then you’ve already got your issue; you’ll just have to determine where you stand on the issue. Where you stand on your topic is your position on that topic.
Your position will ultimately become the thesis of your persuasive essay: the statement the rest of the essay argues for and supports, intending to convince your audience to consider your point of view.
If you have to choose your own topic, use these guidelines to help you make your selection:
- Choose an issue you truly care about
- Choose an issue that is actually debatable
Simple “tastes” (likes and dislikes) can’t really be argued. No matter how many ways someone tries to convince me that milk chocolate rules, I just won’t agree.
It’s dark chocolate or nothing as far as my tastes are concerned.
Similarly, you can’t convince a person to “like” one film more than another in an essay.
You could argue that one movie has superior qualities than another: cinematography, acting, directing, etc. but you can’t convince a person that the film really appeals to them.

Once you’ve selected your issue, determine your position just as you would for an assigned topic. That position will ultimately become your thesis.
Until you’ve finalized your work, consider your thesis a “working thesis.”
This means that your statement represents your position, but you might change its phrasing or structure for that final version.
When you’re writing an essay for a class, it can seem strange to identify an audience—isn’t the audience the instructor?
Your instructor will read and evaluate your essay, and may be part of your greater audience, but you shouldn’t just write for your teacher.
Think about who your intended audience is.
For an argument essay, think of your audience as the people who disagree with you—the people who need convincing.
That population could be quite broad, for example, if you’re arguing a political issue, or narrow, if you’re trying to convince your parents to extend your curfew.
Once you’ve got a sense of your audience, it’s time to consult with Aristotle. Aristotle’s teaching on persuasion has shaped communication since about 330 BC. Apparently, it works.

Aristotle taught that in order to convince an audience of something, the communicator needs to balance the three elements of the rhetorical triangle to achieve the best results.
Those three elements are ethos , logos , and pathos .
Ethos relates to credibility and trustworthiness. How can you, as the writer, demonstrate your credibility as a source of information to your audience?
How will you show them you are worthy of their trust?

- You show you’ve done your research: you understand the issue, both sides
- You show respect for the opposing side: if you disrespect your audience, they won’t respect you or your ideas
Logos relates to logic. How will you convince your audience that your arguments and ideas are reasonable?

You provide facts or other supporting evidence to support your claims.
That evidence may take the form of studies or expert input or reasonable examples or a combination of all of those things, depending on the specific requirements of your assignment.
Remember: if you use someone else’s ideas or words in your essay, you need to give them credit.
ProWritingAid's Plagiarism Checker checks your work against over a billion web-pages, published works, and academic papers so you can be sure of its originality.
Find out more about ProWritingAid’s Plagiarism checks.
Pathos relates to emotion. Audiences are people and people are emotional beings. We respond to emotional prompts. How will you engage your audience with your arguments on an emotional level?

- You make strategic word choices : words have denotations (dictionary meanings) and also connotations, or emotional values. Use words whose connotations will help prompt the feelings you want your audience to experience.
- You use emotionally engaging examples to support your claims or make a point, prompting your audience to be moved by your discussion.
Be mindful as you lean into elements of the triangle. Too much pathos and your audience might end up feeling manipulated, roll their eyes and move on.
An “all logos” approach will leave your essay dry and without a sense of voice; it will probably bore your audience rather than make them care.
Once you’ve got your essay planned, start writing! Don’t worry about perfection, just get your ideas out of your head and off your list and into a rough essay format.
After you’ve written your draft, evaluate your work. What works and what doesn’t? For help with evaluating and revising your work, check out this ProWritingAid post on manuscript revision .
After you’ve evaluated your draft, revise it. Repeat that process as many times as you need to make your work the best it can be.
When you’re satisfied with the content and structure of the essay, take it through the editing process .
Grammatical or sentence-level errors can distract your audience or even detract from the ethos—the authority—of your work.
You don’t have to edit alone! ProWritingAid’s Realtime Report will find errors and make suggestions for improvements.
You can even use it on emails to your professors:
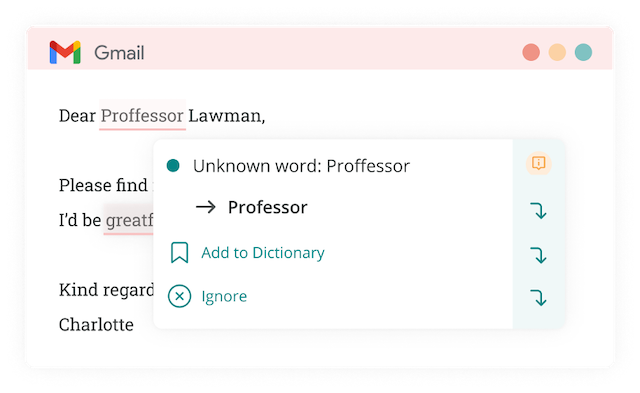
Try ProWritingAid with a free account.
How Can I Improve My Persuasion Skills?
You can develop your powers of persuasion every day just by observing what’s around you.
- How is that advertisement working to convince you to buy a product?
- How is a political candidate arguing for you to vote for them?
- How do you “argue” with friends about what to do over the weekend, or convince your boss to give you a raise?
- How are your parents working to convince you to follow a certain academic or career path?
As you observe these arguments in action, evaluate them. Why are they effective or why do they fail?
How could an argument be strengthened with more (or less) emphasis on ethos, logos, and pathos?
Every argument is an opportunity to learn! Observe them, evaluate them, and use them to perfect your own powers of persuasion.
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Allison Bressmer is a professor of freshman composition and critical reading at a community college and a freelance writer. If she isn’t writing or teaching, you’ll likely find her reading a book or listening to a podcast while happily sipping a semi-sweet iced tea or happy-houring with friends. She lives in New York with her family. Connect at linkedin.com/in/allisonbressmer.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
How to Write a Persuasive Essay (This Convinced My Professor!)
.png)
Table of contents

Meredith Sell
You can make your essay more persuasive by getting straight to the point.
In fact, that's exactly what we did here, and that's just the first tip of this guide. Throughout this guide, we share the steps needed to prove an argument and create a persuasive essay.
This AI tool helps you improve your essay > This AI tool helps you improve your essay >

Key takeaways: - Proven process to make any argument persuasive - 5-step process to structure arguments - How to use AI to formulate and optimize your essay
Why is being persuasive so difficult?
"Write an essay that persuades the reader of your opinion on a topic of your choice."
You might be staring at an assignment description just like this 👆from your professor. Your computer is open to a blank document, the cursor blinking impatiently. Do I even have opinions?
The persuasive essay can be one of the most intimidating academic papers to write: not only do you need to identify a narrow topic and research it, but you also have to come up with a position on that topic that you can back up with research while simultaneously addressing different viewpoints.
That’s a big ask. And let’s be real: most opinion pieces in major news publications don’t fulfill these requirements.
The upside? By researching and writing your own opinion, you can learn how to better formulate not only an argument but the actual positions you decide to hold.
Here, we break down exactly how to write a persuasive essay. We’ll start by taking a step that’s key for every piece of writing—defining the terms.
What Is a Persuasive Essay?
A persuasive essay is exactly what it sounds like: an essay that persuades . Over the course of several paragraphs or pages, you’ll use researched facts and logic to convince the reader of your opinion on a particular topic and discredit opposing opinions.
While you’ll spend some time explaining the topic or issue in question, most of your essay will flesh out your viewpoint and the evidence that supports it.
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay
If you’re intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place.
1. A topic or issue to argue
This is probably the hardest step. You need to identify a topic or issue that is narrow enough to cover in the length of your piece—and is also arguable from more than one position. Your topic must call for an opinion , and not be a simple fact .
It might be helpful to walk through this process:
- Identify a random topic
- Ask a question about the topic that involves a value claim or analysis to answer
- Answer the question
That answer is your opinion.
Let’s consider some examples, from silly to serious:
Topic: Dolphins and mermaids
Question: In a mythical match, who would win: a dolphin or a mermaid?
Answer/Opinion: The mermaid would win in a match against a dolphin.
Topic: Autumn
Question: Which has a better fall: New England or Colorado?
Answer/Opinion: Fall is better in New England than Colorado.
Topic: Electric transportation options
Question: Would it be better for an urban dweller to buy an electric bike or an electric car?
Answer/Opinion: An electric bike is a better investment than an electric car.
Your turn: Walk through the three-step process described above to identify your topic and your tentative opinion. You may want to start by brainstorming a list of topics you find interesting and then going use the three-step process to find the opinion that would make the best essay topic.
2. An unequivocal thesis statement
If you walked through our three-step process above, you already have some semblance of a thesis—but don’t get attached too soon!
A solid essay thesis is best developed through the research process. You shouldn’t land on an opinion before you know the facts. So press pause. Take a step back. And dive into your research.
You’ll want to learn:
- The basic facts of your topic. How long does fall last in New England vs. Colorado? What trees do they have? What colors do those trees turn?
- The facts specifically relevant to your question. Is there any science on how the varying colors of fall influence human brains and moods?
- What experts or other noteworthy and valid sources say about the question you’re considering. Has a well-known arborist waxed eloquent on the beauty of New England falls?
As you learn the different viewpoints people have on your topic, pay attention to the strengths and weaknesses of existing arguments. Is anyone arguing the perspective you’re leaning toward? Do you find their arguments convincing? What do you find unsatisfying about the various arguments?
Allow the research process to change your mind and/or refine your thinking on the topic. Your opinion may change entirely or become more specific based on what you learn.
Once you’ve done enough research to feel confident in your understanding of the topic and your opinion on it, craft your thesis.
Your thesis statement should be clear and concise. It should directly state your viewpoint on the topic, as well as the basic case for your thesis.
Thesis 1: In a mythical match, the mermaid would overcome the dolphin due to one distinct advantage: her ability to breathe underwater.
Thesis 2: The full spectrum of color displayed on New England hillsides is just one reason why fall in the northeast is better than in Colorado.
Thesis 3: In addition to not adding to vehicle traffic, electric bikes are a better investment than electric cars because they’re cheaper and require less energy to accomplish the same function of getting the rider from point A to point B.
Your turn: Dive into the research process with a radar up for the arguments your sources are making about your topic. What are the most convincing cases? Should you stick with your initial opinion or change it up? Write your fleshed-out thesis statement.
3. Evidence to back up your thesis
This is a typical place for everyone from undergrads to politicians to get stuck, but the good news is, if you developed your thesis from research, you already have a good bit of evidence to make your case.
Go back through your research notes and compile a list of every …
… or other piece of information that supports your thesis.
This info can come from research studies you found in scholarly journals, government publications, news sources, encyclopedias, or other credible sources (as long as they fit your professor’s standards).
As you put this list together, watch for any gaps or weak points. Are you missing information on how electric cars versus electric bicycles charge or how long their batteries last? Did you verify that dolphins are, in fact, mammals and can’t breathe underwater like totally-real-and-not-at-all-fake 😉mermaids can? Track down that information.
Next, organize your list. Group the entries so that similar or closely related information is together, and as you do that, start thinking through how to articulate the individual arguments to support your case.
Depending on the length of your essay, each argument may get only a paragraph or two of space. As you think through those specific arguments, consider what order to put them in. You’ll probably want to start with the simplest argument and work up to more complicated ones so that the arguments can build on each other.
Your turn: Organize your evidence and write a rough draft of your arguments. Play around with the order to find the most compelling way to argue your case.
4. Rebuttals to disprove opposing theses
You can’t just present the evidence to support your case and totally ignore other viewpoints. To persuade your readers, you’ll need to address any opposing ideas they may hold about your topic.
You probably found some holes in the opposing views during your research process. Now’s your chance to expose those holes.
Take some time (and space) to: describe the opposing views and show why those views don’t hold up. You can accomplish this using both logic and facts.
Is a perspective based on a faulty assumption or misconception of the truth? Shoot it down by providing the facts that disprove the opinion.
Is another opinion drawn from bad or unsound reasoning? Show how that argument falls apart.
Some cases may truly be only a matter of opinion, but you still need to articulate why you don’t find the opposing perspective convincing.
Yes, a dolphin might be stronger than a mermaid, but as a mammal, the dolphin must continually return to the surface for air. A mermaid can breathe both underwater and above water, which gives her a distinct advantage in this mythical battle.
While the Rocky Mountain views are stunning, their limited colors—yellow from aspen trees and green from various evergreens—leaves the autumn-lover less than thrilled. The rich reds and oranges and yellows of the New England fall are more satisfying and awe-inspiring.
But what about longer trips that go beyond the city center into the suburbs and beyond? An electric bike wouldn’t be great for those excursions. Wouldn’t an electric car be the better choice then?
Certainly, an electric car would be better in these cases than a gas-powered car, but if most of a person’s trips are in their hyper-local area, the electric bicycle is a more environmentally friendly option for those day-to-day outings. That person could then participate in a carshare or use public transit, a ride-sharing app, or even a gas-powered car for longer trips—and still use less energy overall than if they drove an electric car for hyper-local and longer area trips.
Your turn: Organize your rebuttal research and write a draft of each one.
5. A convincing conclusion
You have your arguments and rebuttals. You’ve proven your thesis is rock-solid. Now all you have to do is sum up your overall case and give your final word on the subject.
Don’t repeat everything you’ve already said. Instead, your conclusion should logically draw from the arguments you’ve made to show how they coherently prove your thesis. You’re pulling everything together and zooming back out with a better understanding of the what and why of your thesis.
A dolphin may never encounter a mermaid in the wild, but if it were to happen, we know how we’d place our bets. Long hair and fish tail, for the win.
For those of us who relish 50-degree days, sharp air, and the vibrant colors of fall, New England offers a season that’s cozier, longer-lasting, and more aesthetically pleasing than “colorful” Colorado. A leaf-peeper’s paradise.
When most of your trips from day to day are within five miles, the more energy-efficient—and yes, cost-efficient—choice is undoubtedly the electric bike. So strap on your helmet, fire up your pedals, and two-wheel away to your next destination with full confidence that you made the right decision for your wallet and the environment.
3 Quick Tips for Writing a Strong Argument
Once you have a draft to work with, use these tips to refine your argument and make sure you’re not losing readers for avoidable reasons.
1. Choose your words thoughtfully.
If you want to win people over to your side, don’t write in a way that shuts your opponents down. Avoid making abrasive or offensive statements. Instead, use a measured, reasonable tone. Appeal to shared values, and let your facts and logic do the hard work of changing people’s minds.
Choose words with AI

You can use AI to turn your general point into a readable argument. Then, you can paraphrase each sentence and choose between competing arguments generated by the AI, until your argument is well-articulated and concise.
2. Prioritize accuracy (and avoid fallacies).
Make sure the facts you use are actually factual. You don’t want to build your argument on false or disproven information. Use the most recent, respected research. Make sure you don’t misconstrue study findings. And when you’re building your case, avoid logical fallacies that undercut your argument.
A few common fallacies to watch out for:
- Strawman: Misrepresenting or oversimplifying an opposing argument to make it easier to refute.
- Appeal to ignorance: Arguing that a certain claim must be true because it hasn’t been proven false.
- Bandwagon: Assumes that if a group of people, experts, etc., agree with a claim, it must be true.
- Hasty generalization: Using a few examples, rather than substantial evidence, to make a sweeping claim.
- Appeal to authority: Overly relying on opinions of people who have authority of some kind.
The strongest arguments rely on trustworthy information and sound logic.
Research and add citations with AI

We recently wrote a three part piece on researching using AI, so be sure to check it out . Going through an organized process of researching and noting your sources correctly will make sure your written text is more accurate.
3. Persuasive essay structure

If you’re building a house, you start with the foundation and go from there. It’s the same with an argument. You want to build from the ground up: provide necessary background information, then your thesis. Then, start with the simplest part of your argument and build up in terms of complexity and the aspect of your thesis that the argument is tackling.
A consistent, internal logic will make it easier for the reader to follow your argument. Plus, you’ll avoid confusing your reader and you won’t be unnecessarily redundant.
The essay structure usually includes the following parts:
- Intro - Hook, Background information, Thesis statement
- Topic sentence #1 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence
- Topic sentence #2 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence Topic sentence #3 , with supporting facts or stats
- Conclusion - Thesis and main points restated, call to action, thought provoking ending
Are You Ready to Write?
Persuasive essays are a great way to hone your research, writing, and critical thinking skills. Approach this assignment well, and you’ll learn how to form opinions based on information (not just ideas) and make arguments that—if they don’t change minds—at least win readers’ respect.
Share This Article:

Preparing for Graduate School: 8 Tips to Know
How to Master Concise Writing: 9 Tips to Write Clear and Crisp Content

Title Case vs. Sentence Case: How to Capitalize Your Titles
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Paper Types / How to Write a Persuasive Essay
How to Write a Persuasive Essay
The entire point of a persuasive essay is to persuade or convince the reader to agree with your perspective on the topic. In this type of essay, you’re not limited to facts. It’s completely acceptable to include your opinions and back them up with facts, where necessary.
Guide Overview
- Be assertive
- Use words that evoke emotion
- Make it personal
- Topic selection hints
Tricks for Writing a Persuasive Essay
In this type of writing, you’ll find it is particularly helpful to focus on the emotional side of things. Make your reader feel what you feel and bring them into your way of thinking. There are a few ways to do that.
Be Assertive
A persuasive essay doesn’t have to be gentle in how it presents your opinion. You really want people to agree with you, so focus on making that happen, even if it means pushing the envelope a little. You’ll tend to get higher grades for this, because the essay is more likely to convince the reader to agree. Consider using an Persuasive Essay Template to understand the key elements of the essay.
Use Words that Evoke Emotion
It’s easier to get people to see things your way when they feel an emotional connection. As you describe your topic, make sure to incorporate words that cause people to feel an emotion. For example, instead of saying, “children are taken from their parents” you might say, “children are torn from the loving arms of their parents, kicking and screaming.” Dramatic? Yes, but it gets the point across and helps your reader experience the
Make it Personal
By using first person, you make the reader feel like they know you. Talking about the reader in second person can help them feel included and begin to imagine themselves in your shoes. Telling someone “many people are affected by this” and telling them “you are affected by this every day” will have very different results.
While each of these tips can help improve your essay, there’s no rule that you have to actually persuade for your own point of view. If you feel the essay would be more interesting if you take the opposite stance, why not write it that way? This will require more research and thinking, but you could end up with a very unique essay that will catch the teacher’s eye.
Topic Selection Hints
A persuasive essay requires a topic that has multiple points of view. In most cases, topics like the moon being made of rock would be difficult to argue, since this is a solid fact. This means you’ll need to choose something that has more than one reasonable opinion related to it.
A good topic for a persuasive essay would be something that you could persuade for or against.
Some examples include:
- Should children be required to use booster seats until age 12?
- Should schools allow the sale of sugary desserts and candy?
- Should marijuana use be legal?
- Should high school students be confined to school grounds during school hours?
- Should GMO food be labeled by law?
- Should police be required to undergo sensitivity training?
- Should the United States withdraw troops from overseas?
Some topics are more controversial than others, but any of these could be argued from either point of view . . . some even allow for multiple points of view.
As you write your persuasive essay, remember that your goal is to get the reader to nod their head and agree with you. Each section of the essay should bring you closer to this goal. If you write the essay with this in mind, you’ll end up with a paper that will receive high grades.
Finally, if you’re ever facing writer’s block for your college paper, consider WriteWell’s template gallery to help you get started.
EasyBib Writing Resources
Writing a paper.
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Research Paper
- Thesis Statement
- Writing a Conclusion
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing an Outline
- Writing a Summary
EasyBib Plus Features
- Citation Generator
- Essay Checker
- Expert Check Proofreader
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tools
Plagiarism Checker
- Spell Checker
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Persuasive Essay: A Guide for Writing

Ever found yourself wrestling with the challenge of convincing others through your writing? Look no further – our guide is your go-to roadmap for mastering the art of persuasion. In a world where effective communication is key, this article unveils practical tips and techniques to help you produce compelling arguments that captivate your audience. Say goodbye to the struggles of conveying your message – let's learn how to make your persuasive essay informative and truly convincing.
What Is a Persuasive Essay
Persuasive essays are a form of writing that aims to sway the reader's viewpoint or prompt them to take a specific action. In this genre, the author employs logical reasoning and compelling arguments to convince the audience of a particular perspective or stance on a given topic. The persuasive essay typically presents a clear thesis statement, followed by well-structured paragraphs that provide evidence and examples supporting the author's position. The ultimate goal is to inform and influence the reader's beliefs or behavior by appealing to their emotions, logic, and sense of reason. If you need urgent help with this assignment, use our persuasive essay writing service without hesitation.
Which Three Strategies Are Elements of a Persuasive Essay
Working on a persuasive essay is like building a solid argument with three friends: ethos, pathos, and logos. Ethos is about trustworthiness, like when someone vouches for your credibility before making a point. Picture it as your introduction, earning trust from the get-go. Then comes pathos, your emotional storyteller. It's all about making your readers feel something, turning your essay into an experience rather than just a bunch of words. Lastly, logos is your logical thinker, using facts and solid reasoning to beef up your argument. These three work together to engage both the heart and mind of your audience. So, let's see how this trio can take your arguments from so-so to memorable.
In a persuasive essay, ethos functions much like introducing your friend as the go-to expert in their field before they share their insights with a new group. It's about showcasing the writer's credibility, expertise, and trustworthiness through a mix of personal experience, professional background, and perhaps even endorsements. Readers are more likely to buy into an argument when they believe the person presenting it knows their stuff and has a solid ethical standing, creating a foundation of trust. Does this information seem a bit confusing? Then simply type, ‘ write my paper ,’ and our writers will help you immediately.
Now, let's consider pathos – the emotional connection element. Imagine a movie that entertains and makes you laugh, cry, or feel a rush of excitement. Pathos in a persuasive essay aims to tap into your emotions to make you feel something. It's the storyteller in the essay weaving narratives that resonate personally. By sharing relatable anecdotes, vivid imagery, or emotionally charged language, writers can create a powerful connection with readers, turning a dry argument into a compelling human experience that leaves a lasting impression.
Lastly, logos is the cool-headed, logical friend who always has the facts straight. In a persuasive essay, logos presents a strong, well-reasoned argument supported by evidence, data, and solid reasoning. The backbone holds the essay together, appealing to the reader's sense of logic and reason. This might include citing research studies, providing statistical evidence, or employing deductive reasoning to build a solid case. So, think of ethos as your trustworthy friend, pathos as the emotional storyteller, and logos as the rational thinker – together, they create a persuasive essay that speaks to the heart and stands up to critical scrutiny. Choose the persuasive essay format accordingly, depending on how you’d like to approach your readers.
.webp)
Persuasive Essay Outline
Creating an outline for persuasive essay is like sketching a plan for your argument, which is the GPS to help your readers follow along smoothly. Start with an engaging intro that grabs attention and states your main point. Then, organize your body paragraphs, each focusing on one important aspect or evidence backing up your main idea. Mix in ethos (credibility), pathos (emotion), and logos (logic) throughout to make your argument strong. Don't forget to address opposing views and show why your stance is the way to go. Finally, wrap things up with a strong conclusion that reinforces your main points. Here’s a general outline for a persuasive essay:
How to start a persuasive essay? Introduction.
- Hook. Start with a captivating anecdote, surprising fact, or thought-provoking question to grab the reader's attention.
- Background. Provide context for the issue or topic you're addressing.
- Thesis Statement. Clearly state your main argument or position.
Body Paragraphs
Paragraph 1
- Topic Sentence. Introduce the first key point supporting your thesis.
- Supporting Evidence. Include facts, statistics, or examples that back up your point.
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos. Incorporate elements of persuasion to strengthen your argument.
Paragraph 2
- Topic Sentence. Introduce the second key point supporting your thesis.
- Supporting Evidence. Provide relevant information or examples to bolster your argument.
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos. Continue integrating persuasive elements for a well-rounded appeal.
Paragraph 3
- Topic Sentence. Introduce the third key point supporting your thesis.
- Supporting Evidence. Present compelling evidence or examples.
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos. Ensure a balanced use of persuasive strategies.
Counterargument
- Address opposing views. Acknowledge and counter opposing arguments.
- Refutation. Explain why the counterargument is invalid or less convincing.
- Summarize main points. Recap the key arguments from the body paragraphs.
- Call to Action. Encourage readers to take a specific stance, consider your perspective, or engage in further discussion.
Closing Statement
- Leave a lasting impression. End with a powerful statement that reinforces your thesis and strongly impacts the reader.
We recommend you study our guide on how to write an argumentative essay as well, as these two types of assignments are the most common in school and college.
.webp)
Take Your Persuasive Writing to the Next Level!
Give us your task to amaze your readers with our tried-and-true methods
How to WritHow to Write a Persuasive Essay
Writing a persuasive essay typically follows a structured format that begins with a compelling introduction, where the writer captures the reader's attention with a hook, provides background information on the topic, and presents a clear thesis statement outlining the main argument. The body paragraphs delve into supporting evidence and key points, each focusing on a specific aspect of the argument and incorporating persuasive elements such as ethos, pathos, and logos. Counterarguments are addressed and refuted to strengthen the overall stance. The conclusion briefly summarizes the main points, reiterates the thesis, and often includes a call to action or a thought-provoking statement to leave a lasting impression on the reader. Follow these tips if you want to learn how to write a good persuasive essay up to the mark:

Choose a Strong Topic
Selecting a compelling topic is crucial for a persuasive essay. Consider issues that matter to your audience and elicit strong emotions. A well-chosen topic captures your readers' interest and provides a solid foundation for building a persuasive argument. If you’re low on ideas, check out a collection of persuasive essay topics from our experts.
Research Thoroughly
Thorough research is the backbone of a persuasive essay. Dive into various sources, including academic journals, reputable websites, and books. Ensure that your information is current and reliable. Understanding the counterarguments will help you anticipate objections and strengthen your position.
Brainstorm a Solid Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement serves as the central point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and specific, outlining your stance. Consider it a guideline for your readers, guiding them through your argument. A strong thesis statement sets the tone for the entire essay and helps maintain focus.
Organize Your Thoughts
A rigid persuasive essay structure is key to creating a desired effect on readers. Begin with an engaging introduction that introduces your topic, provides context, and ends with a clear thesis statement. The body paragraphs should each focus on a single point that supports your thesis, providing evidence and examples. Transition smoothly between paragraphs to ensure a cohesive flow. Conclude with a powerful summary that reinforces your main points and leaves a lasting impression.
Develop Compelling Arguments
Each body paragraph should present a persuasive argument supported by evidence. Clearly articulate your main points and use examples, statistics, or expert opinions to strengthen your claims. Make sure to address potential counterarguments and refute them, demonstrating the robustness of your position.
- Use Persuasive Language
Employ language that is strong, clear, and persuasive. Be mindful of your tone, avoiding overly aggressive or confrontational language. Appeal to your audience's emotions, logic, and credibility. Use rhetorical devices like anecdotes or powerful metaphors to make your writing more engaging and memorable.
Revise and Edit
The final step is revising and editing your essay. Take the time to review your work for clarity, coherence, and grammar. Ensure that your arguments flow logically and eliminate any unnecessary repetition. Consider seeking feedback from peers or mentors to gain valuable perspectives on the strength of your persuasive essay. You should also explore the guide on how to write a synthesis essay , as you’ll be dealing with it quite often as a student.
Tips for Writing a Persuasive Essay
The most important aspect of writing a persuasive essay is constructing a compelling and well-supported argument. A persuasive essay's strength hinges on the clarity and persuasiveness of the main argument, encapsulated in a robust thesis statement. This central claim should be clearly articulated and supported by compelling evidence, logical reasoning, and an understanding of the target audience. Here are more tips for you to consider:
- Write a Compelling Hook
Begin your essay with a captivating hook that grabs the reader's attention. This could be a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote. A strong opening sets the tone for the rest of the essay.
- Establish Credibility
Build your credibility by demonstrating your expertise on the topic. Incorporate well-researched facts, statistics, or expert opinions that support your argument. Establishing credibility enhances the persuasiveness of your essay.
- Clearly Articulate Your Thesis
Craft a clear and concise thesis statement that outlines your main argument. This statement should convey your position on the issue and provide a path for the reader to follow throughout the essay. Note that if you use custom essay writing services , a thesis is automatically included in the assignment.
- Organize Your Arguments Effectively
Structure your essay with a logical flow. Each paragraph should focus on a single point that supports your thesis. Use transitional phrases to guide the reader smoothly from one idea to the next. This organizational clarity enhances the persuasive impact of your essay.
- Address Counterarguments
Anticipate and address potential counterarguments to strengthen your position. Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and provide compelling reasons why your stance is more valid. This demonstrates a thorough understanding of the topic and reinforces the credibility of your argument.
Choose words and phrases that evoke emotion and engage your reader. Employ rhetorical devices, such as metaphors, similes, or vivid language, to make your argument more compelling. Pay attention to tone, maintaining a respectful and persuasive demeanor.
- Appeal to Emotions and Logic
Strike a balance between emotional appeal and logical reasoning. Use real-life examples, personal stories, or emotional anecdotes to connect with your audience. Simultaneously, support your arguments with logical reasoning and evidence to build a robust case.
- Create a Strong Conclusion
Summarize your main points in the conclusion and restate the significance of your thesis. End with a powerful call to action or a thought-provoking statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. A strong conclusion reinforces the persuasive impact of your essay.
Persuasive Essay Examples
Explore the persuasive essay examples provided below to gain a deeper comprehension of crafting this type of document.
Persuasive Essay Example: Are Women Weaker Than Men Today?
Students should explore persuasive essay examples as they provide valuable insights into effective argumentation, organizational structure, and the art of persuasion. Examining well-crafted samples allows students to grasp various writing techniques, understand how to present compelling evidence, and observe the nuanced ways in which authors address counterarguments. Additionally, exposure to diverse examples helps students refine their own writing style and encourages critical thinking by showcasing the diversity of perspectives and strategies. Here are two excellent persuasive essay examples pdf for your inspiration. If you enjoy the work of our writers, buy essay paper from them and receive an equally quality document prepared individually for you.
Example 1: “The Importance of Incorporating Financial Literacy Education in High School Curriculum”
This essay advocates for the imperative inclusion of financial literacy education in the high school curriculum. It emphasizes the critical role that early exposure to financial concepts plays in empowering students for lifelong success, preventing cycles of debt, fostering responsible citizenship, adapting to technological advancements, and building a more inclusive society. By arguing that financial literacy is a practical necessity and a crucial step towards developing informed and responsible citizens, the essay underscores the long-term societal benefits of equipping high school students with essential financial knowledge and skills.
Example 2: “Renewable Energy: A Call to Action for a Sustainable Future”
This persuasive essay argues for the urgent adoption of renewable energy sources as a moral imperative and a strategic move towards mitigating climate change, fostering economic growth, achieving energy independence, and driving technological innovation. The essay emphasizes the environmental, economic, and societal benefits of transitioning from conventional energy to renewable alternatives, asserting that such a shift is not just an environmentally conscious choice but a responsible investment in the sustainability and well-being of the planet for current and future generations.
Knowing how to write a persuasive essay is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it cultivates critical thinking and analytical skills, requiring students to evaluate and organize information effectively to support their arguments. This process enhances their ability to assess different perspectives and make informed decisions. The persuasive essay format also equips students with valuable communication skills, teaching them to articulate ideas clearly and convincingly. As effective communicators, students can advocate for their viewpoints, contributing to a more engaged and informed society. This proficiency extends beyond academic settings, proving crucial in various professional and personal scenarios. If you’d like to expedite the process, consider using our essay service , which saves time and brings positive grades.
Want to Easily Influence Your Readers?
Buy your persuasive essay right away to start using words to change the world!
What are the 7 Tips for Persuasive Essays?
How do i make a persuasive essay, related articles.
%20(2).webp)

The 108 Most Persuasive Words In The English Language
Home » Blog » The 108 Most Persuasive Words In The English Language

THE 108 MOST PERSUASIVE WORDS IN THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE
It’s a long known fact that the secret to persuasive writing isn’t in the adjectives, it’s in the verbs.
Copywriters know power verbs sell and convince.
Internally, we have a list of 108 verbs that we’ve been using for a good decade, and we recently thought we should share it with proper credit to the original author.
We found that although the list is being recirculated (and in many cases claimed as original by several different authors!), the original author is, in fact, nowhere to be found.
So, if anyone knows who wrote this, we’d love to know!
With or without the original author, it’s still a great list…here it is!

According to legendary advertising man, Leo Burnet, “Dull and exaggerated ad copy is due to the excess use of adjectives.”
To prove it, he asked his staff to compare the number of adjectives in 62 ads that failed to the number of adjectives in Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address, and other age-old classics.
Here’s what he discovered:
Of the 12,758 words in the 62 failed ads, 24.1% were adjectives.
By direct comparison, Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address contains only 35 adjectives out of 268 immortal words – only 13.1% adjective-to-total-word ratio.
Winston Churchill’s famous “Blood, Sweat and Tears” speech rates even lower and has a 12.1% adjective ratio (81 adjectives from 667 words).
Burnett found that similar ratios applied to great works such as The Lord’s Prayer, the Ten Commandments, and the Preamble to the U.S. Constitution. Conclusion: Use more verbs, not adjectives.
Verbs increase the pulling-power and believability of ad copy.
That’s why it makes sense to keep this 108-VERB “CHEAT-SHEET” close-by whenever you begin to draft your next space ad, sales letter, Website, or email campaign.

Still unsure how to incorporate these verbs into your marketing campaign? Or, perhaps, you just don’t have the time?
Then consider hiring a team of professional copywriters to do it for you! Talented advertising and marketing writers can take mediocre content and use power verbs to turn it into engaging copy that meets goals and produces results.
Related Content

3 thoughts on “ The 108 Most Persuasive Words In The English Language ”
It is remarkable, very amusing piece
Hi there, love your website. I am a teacher and my kids love using your amazing verbs you have provided us with in their writing. Email me and I could send you some drafts of their writing – you’ll be blown away!
Catch up soon 🙂
Thanks, Hope Brown
Hi Hope! We are so happy to hear that our blog has helped you and your students. We would love to see some of their writing!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe to Newsletter
- The Abilities and Limitations of AI in Content Creation
- How to Use AI to Power Up Your Marketing Communication Strategy
- The Impact of AI-Generated Content on SEO Rankings
- Top Tools for Harnessing AI for Your Content
- 5 Ways to Make Your Content Marketing Campaign About Your Customers, Not You
- Copywriting & PR
- Editing & Proofreading
- Writer's Resources
- Training & HR Material
- Ghostwriting & Books
- Social Content
- Web Content
- Corporate & Stakeholder Communications
- Technical Writing
- Medical Copy
- O&G Copy
- Thought Leadership Content
- RFPs & Proposals
- Speeches & Presentations
- Watercooler
Which of these “Power Verbs” do you find most persuasive?
Persuasive Essay Writing

How to Write a Persuasive Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide
13 min read
Published on: Jan 3, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 29, 2024

People also read
Easy and Unique Persuasive Essay Topics with Tips
The Basics of Crafting an Outstanding Persuasive Essay Outline
Ace Your Next Essay With These Persuasive Essay Examples!
Persuasive Essay About Gun Control - Best Examples for Students
Top Examples of Persuasive Essay about Covid-19
Learn How To Write An Impressive Persuasive Essay About Business
Learn How to Craft a Compelling Persuasive Essay About Abortion With Examples!
Make Your Point: Tips and Examples for Writing a Persuasive Essay About Online Education
Learn How To Craft a Powerful Persuasive Essay About Bullying
Craft an Engaging Persuasive Essay About Smoking: Examples & Tips
Learn How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Social Media With Examples
Craft an Effective Argument: Examples of Persuasive Essay About Death Penalty
Share this article
It's the night before the essay is due, and you haven't even started. Your mind is blank, and you have no idea what words will persuade your teacher.
The good news is that some tips and tricks can make the process of writing a persuasive essay much easier.
In this blog, we'll break down the components of a persuasive essay and provide helpful tips and examples along the way. By the end, you should have all the guidelines to create a winning essay that will persuade your readers to see things your way.
Let's take a closer look at all these steps.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Persuasive Essay?
A persuasive essay presents logical arguments with emotional appeal.
Typically, persuasive essays begin with a question that the writer spends the essay arguing in favor of or opposition to.
For example: should kids be allowed to play video games on weekdays?
The writer would then spend the rest of the essay backing up their claim with reasons and evidence.
Persuasive essays often include counterarguments. These arguments oppose the writer's position.
By including counterarguments, persuasive essays become more interesting. They also force the writer to think critically about their position.
For example, an opponent of the previous argument might say that playing video games leads to poor grades.
The original writer could deny this claim by pointing to studies that show no correlation between bad grades and playing video games.
The best persuasive essays are well-researched and use data to support their claims.
However, persuasive essays are not just about logic. They also need to include emotional appeal.
After all, people are more likely to be persuaded by an argument that speaks to their feelings.
Elements of a Persuasive Essay
When a persuasive essay is a task, you must keep these three greek terms in mind. They are:
- Ethos (appeal to ethics)
- Pathos (appeal to emotion)
- Logos (appeal to logic)
A good essay will use all of these elements to convince the reader that the argument presented is valid.
Let's take a closer look at each one.
Ethos - the Credibility Element
The persuasive power of ethos lies in the character or credibility of the person making the argument.
For an argument to be persuasive, the person presenting it must be someone that the audience trusts.
This could be because they are an expert on the subject or because they have first-hand experience with it. Either way, ethos establishes the speaker's credibility and makes the audience more likely to trust what they have to say.
Pathos -the Emotional Element
While ethos deals with the character of the person making the argument, pathos has to do with the audience's emotions. A persuasive argument will tap into the audience's emotions and use them to sway their opinion.
This could be done through stories or anecdotes that evoke an emotional response or by using language that stirs certain feelings.
Logos - the Logical Element
The final element of persuasion is logos, which appeals to logic. A persuasive argument will use sound reasoning and evidence to convince the audience that it is valid. This could be done through data or using persuasive techniques like cause and effect.
Using all these elements of a persuasive essay can make your argument much more effective.
How To Write a Persuasive Essay
Writing persuasive essays can be challenging, but they don't have to be.
With the following simple steps, you can quickly turn an ordinary essay into one that will make a lasting impression.
Tough Essay Due? Hire a Writer!

How To Start a Persuasive Essay
Here is a complete guide on how to start a persuasive essay. Follow them to compose a perfect essay every time.
Brainstorm All Possible Angles
The first step in writing a persuasive essay is brainstorming. You need to develop an angle for your essay that will make it unique and interesting.
For example, let's say you're writing about the death penalty. A lot has been said on this topic, so it might be hard to find an angle that hasn't been covered already.
But if you think about it, there are many different ways to approach the issue.
Maybe you could write about the personal experiences of someone affected by the death penalty. Or maybe you could write about the economic costs of the death penalty.
There are many possibilities here - it's all about thinking creatively.
Select Your Topic
Once you've brainstormed a few ideas, it's time to choose your topic. Pick the angle you think will most effectively persuade your reader.
Once you've chosen your topic, it's time to research. Use statistics, expert opinions, and real-life examples to support your position.
Choose Your Side
Now that you've researched, it's time to take a side in the debate. Remember, you must take a strong stance on one side of the issue.
After deciding your stance, research and support it with evidence.
Appeal to Human Emotions
One of the most effective ways to persuade someone is by appealing to their emotions.
After all, we're not robots - we're human beings and always make decisions based on our feelings.
Make your reader feel something, whether it's anger, sadness, empathy, or even amusement. You'll be well on convincing them of your point of view.
Anticipate Possible Objections.
Of course, not everyone will agree, and that's okay!
The important thing is that you anticipate some of those objections and address them head-on in your essay.
This shows that you take your reader's objections seriously and are confident in your position.
Organize Your Evidence
Once you have all of your evidence collected, it's time to start organizing it into an outline for your essay.
Organizing your essay is a key step in the writing process. It helps you keep track of all the evidence you've gathered and structure your argument in an organized way.
What Are The Steps To Write Your Persuasive Essay?
Now that you have your topic essay outline, it's time to move on to the actual writing.
Here are the steps you need to take:
Step 1: Create a Compelling Introduction
You want to hook your readers with a great opening for your persuasive essay, so they'll want to keep reading.
Here are 3 tips for writing an attention-grabbing introduction for your next essay.
- Use a strong hook statement
Your hook statement should immediately draw the reader in and make them want to learn more.
A good hook statement will vary depending on whether you're writing for an academic or more casual audience.
Still, some good options include a quote, an interesting statistic, or a rhetorical question.
- Make sure your thesis statement is clear and concise
Your thesis statement is the main argument of your essay, so it needs to be stated clearly and concisely in your introduction.
A good thesis statement will be specific and limit the scope of your argument so that it can be fully addressed in the body of your paper.
- Use a transition
Transitions are important in writing for academic and non-academic audiences because they help guide the reader through your argument.
A good transition will introduce the main point of your next paragraph while still maintaining the connection to the previous one.
Step 2: Write The Body Paragraphs
Here is a formula for structuring your body paragraphs in a persuasive essay.
This formula will ensure that each body paragraph is packed with evidence and examples while still being concise and easy to read.
- The Topic Sentence
Every body paragraph should start with a topic sentence. A topic sentence is a key sentence that sums up the paragraph's main point.
It should be clear, concise, and direct.
For example, if you were writing a paragraph about the importance of exercise, your topic sentence might be this:
"Regular exercise is essential for good physical and mental health."
See how that sentence gives a clear overview of what the rest of the paragraph will be about.
- Relevant Supporting Sentences
Once your topic sentence is down, it's time to fill the rest of the paragraph with relevant supporting sentences.
These sentences should provide evidence to support the claims made in the topic sentence.
For the exercise example, we might use sentences like this:
"Exercise has been shown to improve heart health, reduce stress levels, and boost brain power."
"A sedentary lifestyle has been linked to an increased risk of obesity, heart disease, and type II diabetes."
See how each sentence ties back to the paragraph's main point. That's what you want your supporting sentences to do.
- Closing Sentence
Last but not least, every body paragraph should end with a closing (or transition) sentence. This sentence should briefly summarize the main points of the paragraph and introduce the next point that will be discussed in the following paragraph.
For the exercise example, the closing sentence might look like this:
"So, as you can see, there are many compelling reasons to make exercise a regular part of your routine."
How to End a Persuasive Essay
The end of your essay is just as important as the introduction. You must leave your readers with a lasting impression and ensure your argument convinces them.
To do this, you'll want to craft a persuasive conclusion that ties together all the points you have made in the essay.
Here is a video explaining the body paragraphs in a persuasive essay. Check it out for more information.
Step 1: Write a Persuasive Conclusion
Here are a few tips to help make sure your persuasive essay conclusion is as effective and persuasive as possible.
- Restate Your Thesis
Begin your essay conclusion by restating the thesis statement you began within your introduction. Doing so will remind readers of what you set out to prove and provide a sense of closure.
- Summarize Your Arguments
You can also use your conclusion to summarize the main points of your argument. This will help readers recall the evidence you presented and reinforce why it supports your thesis.
- Offer a Call to Action
Lastly, don't forget to include a call to action in your essay conclusion. This can be anything from a persuasive plea to a persuasive suggestion.
Step 2: Polish Up Your Essay
After youâre done with the essay, take a few minutes to read through it. Ensure that your persuasive points and evidence are clear, concise, and persuasive.
Also, double-check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation mistakes. Ensure that all of your persuasive points are properly explained and make sense to the reader.
If youâre not confident in your persuasive writing skills, you can enlist a friend or family member to read through it and provide feedback.
You can follow a proofreading checklist after completing your essay to ensure you are on track.
By following these steps, youâll end up with a persuasive essay that will impress anyone who reads it!
Format Of A Persuasive Essay
Once you have your persuasive essay topic, it's time to craft an essay structure. Crafting the perfect persuasive essay format is essential for ensuring your paper has maximum persuasive power.
Here are some tips for formatting an effective persuasive essay.
- Increase the Readability of Your Text
Ensure that you have adhered to all the paragraphing requirements of your instructor.
Double-check that your margins are set properly. A margin of 1 inch (2.5 cm) on all sides is the standard for most written documents.
This makes it easier for readers to focus and extract important information quickly.
- Use Easy-to-Read Font
Choose a font that is easy to read and professional. Stay away from script fonts or anything too fancy or difficult to read. Stick with basic fonts like Times New Roman, Arial, and Calibri.
- Keep a Defined Alignment
Align your persuasive essay to the left margin. This makes it easier for readers to follow along with your argument without having to do too much extra scrolling.
By following these simple tips, you'll be able to craft the perfect persuasive essay format.
Persuasive Essay Examples
Here are some examples of persuasive essays that can help you get the gist of essay writing.
Persuasive essay on the preservation of nature
Persuasive essay examples pdf
Example of a persuasive essay about covid-19
Check out some more persuasive essay examples here for more inspiration.
Good Persuasive Essay Topics
The right persuasive essay topics can make or break your essay. Here are a few examples of persuasive essay topics that can help you.
- Should the government increase taxes on sugary foods to reduce obesity?
- Do standardized tests accurately measure student intelligence and aptitude?
- Should studying a foreign language be mandatory in schools?
- Should all high school students complete community service hours before graduating?
- Are video games affecting the concentration and cognitive development of children?
- Should genetically modified foods be labeled as such in stores?
- Are the current copyright laws protecting artists and content creators enough?
- Should college tuition be reduced for all students?
- Is the use of animals in medical research ethical?
- Should the use of drones be regulated by the government?
- Should college athletes receive payment for their performance?
- Should students be allowed to have cell phones in school?
- Is drug testing in schools an effective way to prevent substance abuse?
- Does social media promote a healthy lifestyle or contribute to cyber bullying?
- Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
If youâre stuck with choosing topics, these are great persuasive essay topics to get you started!
Pick one of these and craft an essay that will leave your readers thinking.
Tips to Write a Compelling Persuasive Essay
Here are a few tips and tricks to help you make a lasting impression on your reader:
Pick A Topic You're Passionate About
First, you need to choose a topic you're passionate about. It will be easier to write about the topic if you care about the essay.
This will make it easier to develop persuasive arguments, and you'll be more motivated to do research.
Research Your Topic Thoroughly
After picking a persuasive essay topic, you need thorough research. This will help you gain a better understanding of the issue, which in turn will make your essay stronger. This will also ensure that you fully grasp all counterarguments on your topic.
Know Your Audience
Knowing your audience before writing is important. Are you writing to your classmates? Your teacher? The general public? Once you know your audience, you can tailor your argument to them.
Knowing your audience will help determine the tone and approach of your essay.
Hook The Reader's Attention
The first few sentences of your essay are crucial - they must grab the reader's attention and make them want to keep reading.
One way to do this is by starting with a shocking statistic or an interesting story. The reader will be instantly hooked and will be enticed to read more.
Research Both Sides
A good persuasive essay will consider both sides of an issue and present a well-rounded view. This means researching both sides of the argument before taking a stance.
Make sure to consider all the evidence before making up your mind - otherwise, your argument won't be as strong as it could be.
Ask Rhetorical Questions
Rhetorical questions are not meant to be answered but rather to make the reader think about the issue.
For example, "How can we expect our children to succeed in school if they don't have enough resources?"
Questions like this can help engage readers and get them thinking about solutions rather than just complaining about problems.
Emphasize Your Point
It's important to reiterate your main points throughout the essay so that readers don't forget what they are supposed to argue for or against by the time they reach the end of the paper.
Persuasive essays can be difficult to write, but following simple tips can help make the process easier.
In this blog, we've outlined the components of a persuasive essay and provided some tips on how to write one. We also shared examples of persuasive essays that scored high marks on standardized tests.
If you are looking for an essay writing service , look no further than CollegeEssay.org! Our experienced essay writer can provide the assistance you need to produce an essay that meets the highest standards.
Let our persuasive essay writer handle the hard work and get you started on your path to success.
Try our AI essay writer and elevate your writing to new heights today!
Frequently Asked Questions About Persuasive Essays
How long should a persuasive essay be.
Generally speaking, persuasive essays should be between 500-750 words. However, the length of your essay will depend on the instructions given by your teacher or professor.
What Techniques Are Used In Persuasive Essays?
Persuasive techniques include facts and statistics, emotion and logic, personal stories, analogies and metaphors, pathos, ethos, and logos.
How Do I Make My Persuasive Essay More Convincing?
To make your essay more convincing, cite reliable sources, use persuasive language, and provide strong evidence and arguments.
How Is Persuasive Writing Different From Argumentative Writing?
The main difference between persuasive and argumentative writing is that persuasive writing seeks to convince or persuade the reader. On the other hand, argumentative writing seeks to debate an issue.
Cathy A. (Literature, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Willow Tenny
- Writing Prompts
- Writing Tools
- Shop For Articles

50 Power Words To Use In Persuasive Writing

Certain words pack a powerful punch. When used correctly, they can grab attention, convey emotion, and motivate people to take action. Using power words in persuasive writing can be incredibly effective and help lead to conversions.
Some of the most commonly used power words include:
1. “You” – This word is a powerful way to get someone’s attention. It personalizes the message and makes the recipient feel like you are speaking directly to them.
2. “New” – This word is eye-catching and creates a sense of urgency. It implies that there is something fresh and exciting to be experienced.
3. “Free” – This word is a great way to get people’s attention. It conveys the message that no risk or cost is associated with taking advantage of what you are offering.
4. ” because ” – This phrase is a great way to justify or explain why someone should take action. It shows that you have thought through the situation and have a logical reason for why someone should comply with your request.
5. ” now ” – This word creates a sense of urgency and encourages people to take action immediately. It suggests they may miss out on a great opportunity if they delay.
6. ” instantly ” – This word is similar to “now” because it creates a sense of urgency. However, it takes things one step further by implying that the results will be immediate.
7. ” save ” – This word is often used to get people’s attention and encourage them to take action. It suggests they can reduce costs or time by taking advantage of your offer.
8. ” increase ” – This word is typically used to show how someone will benefit from taking action. It suggests that they will be able to improve or enhance something by doing what you are suggesting.
9. ” discover ” – This word piques curiosity and encourages people to want to learn more. It suggests that there is something new and exciting to be found by taking the recommended action.
10. ” create ” – It implies that the individual has the power to make something happen by taking the recommended course of action.
11. ” prevent ” – This word is a great way to get people’s attention and show them how your suggestion can help them avoid a negative outcome.
12. ” eliminate ” – Similar to “prevent,” this word also highlights how taking action can help people steer clear of undesirable consequences.
13. ” gain ” – This word is typically used to show how someone will benefit from taking action. It suggests that they will be able to acquire something desirable by doing what you are suggesting.
14. ” improve ” – It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something better by doing what you are suggesting.
15. ” reduce ” – This word is a great way to get people’s attention and show them how your suggestion can help them save money or time.
16. ” simplify ” – It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something easier by doing what you are suggesting.
17. ” accelerate ” -. It suggests that they will be able to achieve their goals more quickly by doing what you are suggesting.
18. ” award ” – This word suggests they can receive something desirable (such as recognition or a prize) by doing what you suggest.
19. ” authorize ” – It suggests that the individual has the ability to give permission or approval by doing what you are suggesting.
20. ” boost ” – It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something better or more effective by doing what you are suggesting.
21. ” complete ” suggests that they can finish or accomplish something by doing what you suggest.
22. ” double ” – This word is a great way to get people’s attention and show them how your suggestion can help them improve or enhance something.
23. ” enable ” – It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something possible by doing what you are suggesting.
24. ” encourage ” -. It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something more likely or probable by doing what you are suggesting.
25. ” expand ” – It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something larger or greater by doing what you are suggesting.
26. ” extend ” – It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something longer or last longer by doing what you are suggesting.
27. ” facilitate ” – It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something easier or more likely by doing what you are suggesting.
28. ” finance ” – This word is a great way to get people’s attention and show them how your suggestion can help them obtain money or funding.
29. ” generate ” – It suggests that the individual has the ability to create or produce something by doing what you are suggesting.
30. ” implement ” suggests that they can put something into effect or make it happen
31. ” increase ” – It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something greater or larger.
32. ” influence ” – This word is a great way to get people’s attention and show them how your suggestion can help them change or affect something.
33. ” launch ” -. It suggests that the individual has the ability to start or initiate something by doing what you are suggesting.
34. ” maximize ” – This word is a great way to get people’s attention and show them how your suggestion can help them make something as large or great as possible.
35. ” motivate ” – it suggests that the individual has the ability to encourage or inspire someone to do something by doing what you are suggesting.
36. ” optimize ” – This word is a great way to get people’s attention and show them how your suggestion can help them make something as effective or efficient as possible.
37. ” outline ” – It suggests that the individual has the ability to describe or summarize something by doing what you are suggesting.
38. ” promote ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something more widely known or accepted by doing what you are suggesting.
39. ” provide ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something available or accessible by doing what you are suggesting.
40. ” recommend ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to suggest or endorse something by doing what you are suggesting.
41. ” reduce ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something smaller or less by doing what you are suggesting.
42. ” register ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to record or officially sign up for something by doing what you are suggesting.
43. ” reinforce ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something stronger or more effective by doing what you are suggesting.
44. ” represent ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to stand for or act on behalf of something by doing what you are suggesting.
45. ” simplify ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something easier or less complicated by doing what you are suggesting.
46. ” stimulate ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to encourage or motivate someone to do something by doing what you are suggesting.
47. ” strengthen ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something stronger or more effective by doing what you are suggesting.
48. ” support ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to provide assistance or help to something by doing what you are suggesting.
49. ” test ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to see if something works or not by doing what you are suggesting.
50. ” validate ”- It suggests that the individual has the ability to confirm or verify something by doing what you are suggesting.
Using these power words in your content will help increase the persuasiveness of your writing and make it more likely that people will take action on what you are suggesting. So don’t hesitate to incorporate them into your next piece!
Direct Response Copywriting: 5 Tips to Writing Copy That Sells
Unleashing your inner writer: a guide to using chatgpt to create a comprehensive blog outline.
When it comes to writing, Willow Tenny is a true pro. She has a wealth of experience in SEO copywriting and creative writing, and she knows exactly what it takes to produce quality content. On her blog, Willow Writes, Willow shares top writing strategies with both beginners and experienced writers.
Related Posts

Sharper Words, Bigger Impact: A Writer’s Guide to Pointed Copywriting

Crafting Poems with an Allusion: Enhance Your Verse

Protagonist vs Antagonist: Story Roles Explained

Novel vs Book: Key Differences Explained

Exploring Situational Archetypes in Literature

Authority Content: Boost Your Brand’s Trust
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- AI Writing (7)
- Angel Numbers (1)
- Publishing (3)
- Spirituality (1)
- Writing Jobs (6)
- Writing Prompts (4)
- Writing Tips (43)
- Writing Tools (3)

So Mote It Be: A deeper look into the meaning and usage of this phrase.

How to Write in 3rd Person About Yourself

Conversational Style Writing Examples

How to Write a Personal Narrative [in 10 Easy Steps]
- Writing Tips
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Copyblogger
Most Persuasive Words and Phrases for Copywriting (and How to Use Them)
When it comes to assembling persuasive words for copywriting, like any other construction job, you need to rely on your skills, experience, and toolbox .
The toolbox of the writer is filled with words.
In defining what I believe is a critical element of effective copywriting , I’ll make my case by amending the famous quote from Animal Farm:
“All words are equal, but some words are more equal than others.”
And there are certain power words that hold more sway over our decision-making process than others. You might be surprised to find that these “power words” don’t seem … well, all that powerful.
This speaks to just how damned efficient they are. Simple language is crystal-clear, as we’ve learned from Brian’s article How to Write like Hemingway . And these compelling words make just what you want your reader to do clear.
Warning: I can’t stress enough, though — just as in the application of writing headlines that work — you must understand why these words are persuasive. You can’t forget to use them in the contexts that make sense for your audience and your business. If you just start slapping them on every piece of content you create for no apparent reason, you’ll quickly see just how unpersuasive they can be.
There, you’ve been warned. Now, let’s get on with the show …
How do you make a sentence more persuasive?
Before you can make a sentence more persuasive, you have to intimately know who you’re talking to in your content and copy. That’s why these words don’t work if you just blindly start using them. You’ll actually combine them with your research about your prospects.
Making a sentence more compelling is all about adding persuasive language to otherwise vague sentences. The more specific you can be, the more the reader will feel like you’ve written your content specifically for them. Then you sprinkle in known persuasive words to keep your reader hooked.
Ready to check out top persuasive words and sentences?
The 5 most persuasive words in the English language for copywriting
You might be surprised to learn that the most persuasive words in the English language are actually quite simple. Simple, but highly effective.
The persuading words list below (along with studies related to their power) will show you how to speak more persuasively to your audience.
There’s an often-cited study in the copywriting world. It’s about a piece of Yale research that reveals “You” to be the #1 power word out of a supposed 12.
Despite the fact that the study likely never happened , I have some actual research that reveals the power of invoking the self.
As it turns out, while people might like the word “you,” it is guaranteed that they love reading their own name much more.
According to research examining brain activation , few things light us up quite like seeing our own names in print or on the screen. Our names are intrinsically tied to our self-perception and make up a massive part of our identity. No surprise then, that we become more engaged and even more trusting of a message in which our name appears.
Research has shown that we will gladly pay more for personalization . So, isn’t it about time you start getting personal with your customers?
However, there is one small problem with this finding …
Writing general web copy with name utilization in mind isn’t usually possible. But by capitalizing on the power of permission marketing, you can adapt this strategy easily. Emails are greatly enhanced when they start off messages with a customer’s name.
If you maintain a variety of separate lists for your products (and you should), make sure you’re grabbing the first name. This way, your broadcasts can trigger that personal aspect with customers.
Want us to scale your traffic?
For the first time, The Copyblogger methodology is now available to a select few clients. We know it works. We’ve been doing it since 2006.
Everybody loves free.
People love free stuff so much they’ll actually make different choices, even when the respective value of the item or service remains the same.
Dan Ariely revealed this startling fact in his book Predictably Irrational . He examined a very unusual “battle” between Lindt chocolate truffles and Hershey’s Kisses.
To test the power of the word “free” in relation to concrete value, the study first asked people to choose between a 1-cent Hershey Kiss or a 15-cent Lindt truffle. (That’s about half of the truffle’s actual value, and Lindt is generally considered a richer, superior chocolate).
Here were the results:
In other words, tastes were found to be very much in favor for the truffle. I mean, who’s going to pass up a deal, right?
Later though, another random group of subjects seemingly flipped on their opinion of these two treats. Ariely revealed that when the price was reduced by one cent for both brands (meaning the Kiss was now free), people altered their choices drastically.
With the new prices, here were the results:

Although in the first test it appears we simply can’t pass up a deal, as it turns out, we really can’t pass up a steal . Although the relation in prices remained the same (a 14 cent difference between the two), people chose the Kiss far more often when it was free.
Ariely points to loss aversion (our disdain for losing out on things) and our natural instinct to go after “low hanging fruit” as the reasons why we are so susceptible to snatching up free stuff.
Use free only when it makes sense, and only in the right context
There’s a certain inherent danger in trumpeting free things. Having something for free will attract more people. But that will most certainly include a fair share of “bargain hunters” who aren’t likely to turn into the superstar customers who really grow your business.
Emphasizing the “freeness” of your free guides, courses, information, support, etc., can go a long way in attracting attention. On Sparring Mind , I emphasize the fact that my newsletter is “free to join,” because although most marketers understand this, many folks don’t quite understand what it means to subscribe.
Conversely, you should use minimal pricing to keep out those barnacle customers who aren’t ideal long-term buyers, or who aren’t truly suited for your flagship offerings.
In a study from the classic book Influence by Robert Cialdini, tests were conducted on requests from a person in a hurry to use an in-office copy machine. The tests examined how different requests might affect people’s willingness to allow this person to “cut” in line.
In the first test, the participant simply stated:
“Excuse me, I have 5 pages. May I use the Xerox machine?”
In this scenario, around 60% of people allowed him to cut in line and use the machine first.
In the next scenario, the request was slightly tweaked. This time the participant said:
“I have 5 pages. May I use the Xerox machine, because I am in a rush?”
Did you see the ever-so-subtle difference between the two?
Let’s break down this experiment with one of the most persuasive words.
Not only was the request only minimally changed, but the “because” (his reason) was barely a reason at all! “Because I’m in a rush” wouldn’t stand up as a good excuse for most of us, right? Isn’t a majority of the working world in a rush?
Despite what we might like to believe, around 94% of people allowed him to cut in line this time! If you think that’s strange, check out the request used in the 3rd and final test:
“Excuse me, I have 5 pages. May I use the Xerox machine because I have to make copies?”
That went from having a barely passable reason to absolutely no reason at all for letting the man cut. In spite of this, 93% of people let him cut on this third trial. That’s only a 1% drop from when he had a weak reason (“I’m in a rush”) and a 33% improvement vs. the first test.
According to Cialdini:
“A well-known principle of human behavior says that when we ask someone to do us a favor we will be more successful if we provide a reason. People simply like to have reasons for what they do.”
Here’s the bottom line
Many companies are proud of the features that their product (or service) can offer. That’s fine, but you have to remember that when you’re focusing on writing persuasive copy, it all comes down to answering your customer’s #1 question:
What’s in it for me?
Although “because” may appear to have some sort of brainwashing effect on people at Xerox machines, it’s only really a matter of reasoning. Even giving weak reasons have been shown to be more persuasive than giving no reason at all.
Only trumpet features and product traits you’re proud of when they help make your point. Use them to create an incentive for customers to take action. And use “because” when pointing out these compelling reasons, but don’t rely on it as a crutch.
4. Instantly
Delayed gratification is an important subject among neuroscientists. Many famous studies (such as the Stanford marshmallow experiment ) showcase how being able to delay rewards to a later date is a skill needed to become successful. (I know very few entrepreneurs who would argue against that.)
This interests us as marketers because it reveals an interesting aspect of human nature …
We want things yesterday!
Several MRI studies have shown just how fired up our mid-brain gets when we envision instant rewards. It’s our frontal cortex that’s activated when it comes to waiting for something (that’s a no-no for sales).
Words like “instant,” “immediately,” or even “fast” are triggers for flipping the switch on that mid-brain activity.
If you are in the business of selling web-based software, you already have an advantage here. “Instant access” isn’t a vague promise; it’s often the reality.
For those in the physical products or services business, using persuasive words and phrases to remind customers that they’ll receive their product quickly (or someone will get in touch with them ASAP) can go a long way. It can be the gentle push they need to buy.
We’ve seen how even “tightwad customers” can be swayed. These subtle changes in language to create persuasion sentences insinuate fast pain removal. It’s a reliable tactic for converting more prospects into customers as long as you follow the one golden rule …
Always deliver on your promises
And, whenever possible, overdeliver .
This is an area where many business get too optimistic. Although it’s smart to emphasis these instant rewards, it’s also always a good idea to under-promise and over-deliver. Be sure you can actually follow through on your promises, or you may end up with a “tribe” that hates your guts.
This one almost seems paradoxical.
According to neuroimaging research , we actually respond more favorably to recognized brands, and can have a hefty amount of disdain for any drastic changes. (Remember New Coke? Oh, the horror …)
On the other hand, it’s long been known that novelty plays an incredibly important role in activating our brains’ reward centers and in keeping us content with our products.
“Newness” is important to products, especially because research has shown that they age far more quickly than “experiential” purchases. (In other words, you’ll hate your new headphones in two years, but that concert you went to five years ago probably aged in your mind like a fine wine.)
How can you achieve a zen-like balance against these two contradictory sides of the same word?
The important things to consider here are which parts of your business generate trust, and which parts generate utility. It’s your brand that creates trust. And as the saying goes, if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it.
Your products however are what customers get utility out of. Stagnant offerings are your first class ticket to an abysmally bored user base.
Your core brand elements like your unique selling proposition , dazzling customer service , and quality offering in the marketplace should be approached with excessive caution if things are going well.
With your products, it’s far easier to excite customers with new features and polish. Even if things don’t work out perfectly, a majority of customers will appreciate innovation attempts over no progression at all.
New fixes to old problems, new features and improvements, a fresh new design, or even new ways of getting your message out there are all essential. They keep customers “on their toes,” without losing the trust that has cemented you as an awesome brand in their mind.
Powerful, persuasive phrases and sentences
We just covered a lot, so take all the time you need to study those lessons.
When you’re ready to keep going, here are 20 more trigger words and phrases to supercharge your copy at the exact right moment when you need to connect with your reader.
To introduce your topic
- Picture this …
- Although it’s commonly believed …
- When was the last time you …?
- I’m sure you’ve heard of [blank], but …
- Ready to discover a new way to …?
To make a point
- Also …
- In other words …
- Therefore …
- Supporting evidence shows …
- I reached this conclusion after finding …
To support your point
- For example …
- Especially in this case …
- In fact …
- According to this study …
- Independent test results show …
To end your case
- In conclusion …
- To wrap things up …
- As you understand by now …
- Try [blank] for yourself, if you want to see similar results.
Now it’s your turn to experiment with persuasive copywriting words …
You know your audience better than anyone else. So, what type of persuasive language strikes a chord with your prospects?
Keep digging deeper and experimenting to find out how to connect with more people who are the perfect fit for your products or services.
Gregory Ciotti
Gregory Ciotti is the marketing strategist at Help Scout , the invisible email support software for small businesses who love taking care of customers. Get more data-driven content from Greg by visiting the Help Scout blog .
- Copyblogger Academy - The Copyblogger Academy is a premier membership program that gives you the tools and skillset to turn your writing into income. Join 1300+ members inside.
- Content Marketing - We're Digital Commerce Partners, Copyblogger's Content Marketing & SEO Agency. Fill out this form to apply for our program.
- Promote yourself to 100,000+ subscribers by sponsoring our newsletter.
Reader Interactions
Reader comments (182).
December 6, 2012 at 6:58 am
I often listen when the the word “Appreciate” is used. It’s a word often used by Mr. Nelson Mandela.
December 6, 2012 at 10:16 am
Meet you out the back.
December 9, 2012 at 1:37 pm
Interesting… why do you think that is? I would imagine that “appreciate” has some really meaningful connections to our ego.
December 9, 2012 at 6:08 pm
Not too sure if your prescriptions (which do make sense to me) are universally applicable, especially as regards the words ‘free’ and ‘new’. For some audiences in the UK and Ireland these two words can have negative connotations. ‘Free’, for example can be associated with ‘shoddy’ or ‘valueless’ or ‘they wouldn’t be giving it away for free if it was any good’; while ‘new’ can give the impression that the product is ‘untested’.
December 22, 2012 at 5:01 pm
I wouldn’t have agreed with you but last year a friend put an ad for free poodle puppies in the paper and didn’t get one response. She then put in an ad to sell them for $100 each and they were gone in a week.
May 30, 2013 at 10:48 am
Lisa, that goes back to the piece on understanding why these words work and using them in the right situations. For example, a free ebook is a nice benefit that captivates my attention. However, free puppies makes me think there’s probably something heinously wrong with them. A dog is such a long term valued investment that it almost doesn’t seem right to acquire one for free, which sparks suspicion and mistrust
July 23, 2013 at 10:26 am
Lisa – free, for some, means too good to be true. By having a value people can understand response is bound to be higher.
December 6, 2012 at 7:23 am
You presented some interesting research here because it is fascinating to learn how we are converted.
I don’t write persuasive copy, but I will start using some these words more often in my blogging.
Perhaps I can use this type of language to help persuade more people to comment.
December 6, 2012 at 8:30 am
I’m in the same boat as you, lacking persuasive copy. I also enjoyed seeing the psychology behind how we make decisions and are converted to the message.
December 6, 2012 at 9:34 am
Thanks Iain!
I would also add that you ARE writing persuasive copy, even if you don’t write sales pages, because any business related writing will at *least* have the simple goals of getting people to read all the way through and then take some sort of action when they’re finished.
So give yourself some credit. 😉
December 6, 2012 at 5:54 pm
Thanks for the support.
You are right. Business writing is persuasive writing, It revolves around persuading your boss, or persuading a colleague, and not selling a product per se. Selling your boss on an idea is converting a lead I guess.
Perhaps I feel am not writing persuasive copy, but in reality I am.
Again, great work.
December 9, 2012 at 1:39 pm
Definitely! Persuasion is really in all aspects of our lives, including how we persuade ourselves. 🙂
December 6, 2012 at 8:28 am
A surprising piece that is nicely done, and I notice that you model the strategies nicely in your own writing, with “you need,” for example. “You” in the number one position was especially surprising since it counters everything we’ve been taught in other types of writing. Teachers always scold when if you adopt the second person, but what you say makes perfect sense in engaging the reader. As a university English professor, unfortunately, I still have to teach this because all of the other professors while criticize the use of “you.” I guess it all depends on your purpose in writing, the audience’s needs and expectations.
The others were less surprising except “because,” which struck me as unusual at first. However, you make clear how the word establishes the significance of the message for the reader. These are all things that we are not normally conscious of, and therefore very helpful to consider. Thank you.
December 6, 2012 at 11:34 am
I don’t remember where or explicitly what, but I recently read an article that commented on writing as taught in school as being suitable only for the academic community. The gist was that this ‘formal’ writing didn’t actually communicate with the world outside academia and that an ‘informal’ style that used contractions and other speech-like forms did a better job with sales, instructional material, etc.
December 6, 2012 at 3:52 pm
I do not doubt it, and the battle is often fought between the sciences and humanities in higher education. The sciences tend to be prescriptive with language and writing, wanting to freeze academic language in time while the humanities lean towards the descriptive (a little bit), believing that languages change over time. The main objective is to communicate your purpose and message to an audience effectively.
The real difficulty lies in determining where the boundaries are drawn. With too much freedom, communication is hindered, but with excessive restriction comes the scene as you describe it. I like the approach taken in Gregory’s article where he focuses strictly on his purpose, message, and reader.
Thanks for your insight , Amki,
December 9, 2012 at 1:42 pm
Great points Darin, really appreciate your thoughts.
I would clarify on “You” just a bit: it obviously isn’t appropriate for certain styles of writing, but in this instance I actually use “You” in reference to the self, that is, your *name* is actually one of the most important words in your own mind.
December 9, 2012 at 6:00 pm
Hey, thank you for the follow up and clarification, Gregory. It’s great when bloggers participate in the conversation! Looking forward to reading more of your writing.
December 6, 2012 at 10:35 am
I thought I was all high and mighty because I read Cialdini (by the way – it’s the first time I’ve seen him being mentioned on a blog, you have my respect for this one). But I was only using the first three words, so thanks for the help. I always enjoy the down-to-earth, no-bull**** way in which you write articles. It makes it much easier to remember the pieces of information you give out. Keep it up! 🙂
December 6, 2012 at 11:04 am
If you like Cialdini, check out this series of posts I wrote in 2006, when Copyblogger was only 3 months old. 😉
https://copyblogger.com/blog-triggers/
December 7, 2012 at 3:30 am
Hey, thanks a lot Brian! I can’t wait to read it:) And of course, I’ll give feedback. Cheers!
December 9, 2012 at 1:44 pm
This is a great segment, Cialdini’s is almost a *must* reference in these sorts of articles, and Brian covers his book really well here on CB. 🙂
I’m flattered! (And flattery goes a long way with me! ;))
December 6, 2012 at 10:45 am
Great stuff! I’d like to nominate a sixth word: SAVE. When people are buying something, they’re often more interested in getting a good deal than paying a low price, and SAVE implies that they are indeed getting a deal. People also like to save things other than money, like time and effort. Do you have any research supporting the power of SAVE?
Thanks for a very insightful post!
December 9, 2012 at 1:46 pm
Really like this one John.
I like it so much that I think I’ll have to look around for some research on the subject!
That’s the best part about citing research in my opinion, not to break new ground, but to verify things we already suspect, a la:
“Normal science does not aim at novelty but at clearing up the status quo. It discovers what it expects to discover.” – Thomas Kuhn
I”ll get back to you if I find anything. 🙂
December 6, 2012 at 11:01 am
Good stuff Gregory. Interesting point on the danger of free attracting the wrong kind of customer. I’m sure the 80/20 rule applies here.
I also like the words “check”, “how”, “why”, “try” and “value”. They can certainly be persuasive.
December 9, 2012 at 1:47 pm
Why do you consider “check” and “why” to be persuasive words? Curious about those two choices…
I agree with John Pohl that “save” is a good word. I also like “now”, “hurry”, & “limited”. I enjoyed this article and look forward to more.
December 9, 2012 at 1:48 pm
This is very true, in fact in our e-Book I cover the importance of urgency (and follow-up instructions) that cites some interesting research on the matter. You should check it out 😉
December 6, 2012 at 11:16 am
Just expanding on the word ‘you’ a bit further, it is particularly effective when used with certain simple (but also powerful) verbs, e.g. you’ll have you’ll get you’ll save (as mentioned in the comment above) you’ll find you’ll discover
December 6, 2012 at 11:48 am
Kevin –
I might add that from a sub-conscious perspective, the contraction you’ll implies you will have in the future…
A better word would be to put them into the present tense, such as “you have” or “you get”… present tense will allow themselves to visualize already owning the product, and mentally they will already own the proverbial set of keys to the car, making it that much easier for them to plop down money
December 6, 2012 at 11:37 am
FREE I’m starting to get suspicious of that word. I’ve jumped through hoops only to determine that “free” meant: – Free 7-day limited trial – Free to register and look at titles but accessing anything costs money – EXTREMELY limited access. I wanted to convert a 166-page PDF and went to a “free” site. After giving all of my contact info and doing the confirmation email, I converted the file and … oops … “free” means 3 pages. My other 163 pages would have cost me about $10. I was irritated by then that I left the site and blocked the domain fomr ever coming up in future Google searches.
I don’t chase free things because I’m cheap. Often I have legit interest in something and the marketing just irritates me because they’re being slimy.
Marketers need to be judicious about what they call “free” because consumers are learning to put bogus or even offensive data into online forms just to peek over the wall and see if the marketer is really delivering what they are touting. Now, what good is the data that’s been collected?
December 6, 2012 at 3:05 pm
Absolutely agree — it all has to be in context. If you’re in a context of providing solid value with content + you’re getting good word of mouth over social platforms, “Free” is something your audience will feel they can trust. But all of these classic persuasive power words are used extensively by businesses that are dodgy or spammy, as well.
“Free” will feel trustworthy to your audience when they know they can trust you, in other words. 🙂
December 7, 2012 at 8:29 am
Developing trust! YESSSSS! I think this is more important than the 5 Most Persuasive Words. So many marketers are abusing these words. Yes, there are studies showing that the words work. But will they work in the long run?
If you look up ‘banner blindness’ is shows a habit that people have for consciously and subconsciously being blind to ads. We’ve been trained. Ads not only try to sell to us, they also have a history of being associated with malware, pop-up storms, endless redirects, etc.
SImilarly, we can be trained to be suspicious of words like free and instantly. We might be “persuaded” but then we can be “trained” to click on something and stay there long enough to determine there’s something useful or just bait to build their list and load users into an auto-responder.
Marketers are going to have to do more to cultivate trust. This will ensure that the persuasive words remain persuasive or, they can turn into warning flags.
December 8, 2012 at 9:09 am
Also, it wasn’t brought up that maybe the reason the $.15 sold over the $.01 is perceived value.
What would happen if Hershey raised their prices to $.15 or even $.30? Some people, like myself, like to pay extra for the good stuff. So if something is more expensive there can be more perceived value…
December 10, 2012 at 10:53 am
Perhaps the word “Free” would create less suspicion if it came with a “Because”.
December 6, 2012 at 11:42 am
Gregory –
A well formed story, and your final 2 points highlight my own – that you made this an interesting exercise to practice putting these words together into a sentence or two, which is exactly what I did as I posted this to facebook… I used all 5 words in two sentences, that will become clear to my friends after they read it.
As I started your article, the first book I thought of was “How to win friends and Influence people”, our names are our most important power word, and your tie in with mailing lists was spot on with that.
Thanks for sharing such a succinct and insightful article.
December 6, 2012 at 11:52 am
Something positive about a negative…not exactly what you asked for:
It always intrigues me that ‘need’ is NOT a trigger word. While it is always emphasized that buying is an emotional process based on desire and not logic, it seems to me that need would be at least equally motivational emotionally.
I can’t exactly put my finger on it, but I think that says something about my own logical processes. 😉
December 6, 2012 at 12:01 pm
I’d like to nominate ‘GET’. Because everybody wants something. As always, a very helpful post, Brian. Happy Holidays!
December 6, 2012 at 4:47 pm
Heh, “everybody wants something”, maybe the understatement of the century. 🙂
December 6, 2012 at 12:32 pm
Great article You & Your – such powerful words, but how many websites talk about them?
December 6, 2012 at 2:28 pm
The analysis around the word free was really interesting. I’d like to think that I’m smart enough to see through the marketing when it comes to free stuff, but either I’m really naive about how I really think, or I’m in the minority. I don’t tend to offer free stuff because I think that people tend to see through it. but maybe it’s just me! Might make me reconsider making free offers in future.
January 9, 2013 at 11:49 am
Good points Dave, but I think we become susceptible to these words during situations where they aren’t directly on our minds.
For instance, reading this post, these words seem “too obvious” to be effective, but out and about in the real world when we aren’t consciously thinking about them, they’re able to influence us.
December 6, 2012 at 2:55 pm
A surprisingly short post for you, Greg, but just as excellent as ever!
We recently started using customer names in our email blasts. I don’t have any numbers yet, but we are definitely seeing more conversions. Getting intimate works, plain and simple.
Personally, I like using “right now” in my copy. I use it mostly because I know it usually gets me to buy, so hey, it should work for others! And based on the psychology behind “instantly,” it all makes more sense. 🙂
December 6, 2012 at 4:46 pm
Agree 100%, I always try to attach some form of “time limit” to actions I’d like for people to take. Given people’s reluctance to come back to things a second time, any language that urges action within the next few minutes is key. 🙂
December 6, 2012 at 3:04 pm
I’m not sure I agree with the use of a person’s name – in advertising copy, it seems manipulative to me when I see it. Especially if it’s in an email from someone who I know has no idea who the hell I am (and that goes double if they’ve spelled my name wrong). But then, I’m in marketing, so I’m probably a tougher audience. People in general are more cynical and aware of marketing “tricks” than they used to be, though. It’d be interesting to see how some of those stats have changed over time!
December 6, 2012 at 3:08 pm
Laurie, that’s why we don’t personalize the emails at Copyblogger — our audience of marketers sees that and thinks, “Ad.” Normal people are less likely to do that. 🙂
September 11, 2013 at 3:07 pm
Our target audience are mechanics, and used to be video store owners (still is, but less these days).
We’ve had people respond to our emails as if we’d sent them directly, so I agree marketers are more skeptical. We also noticed (and we never figured out why), that the mechanics (or their assistants) tend to post correct info including the phone number, whereas the video store people gave us bogus info. Perhaps we’re saying something wrong on the download page. I’ll be checking into that after this article, Thanks.
December 6, 2012 at 3:10 pm
Hi Gregory, great post. I’m a huge fan of using “you” in copy. Why? Because it’s the equivalent of using someone’s first name in a mass communication. Yes, actually using their first name would provide a better result, but using “you” as a first name alternative gets nearly the same results.
December 6, 2012 at 4:44 pm
Thanks Joe, I’d agree that on a large scale, it’s the best way to go, I was just tired of that fake “study” getting passed around the web 😉
December 6, 2012 at 3:15 pm
Very interesting article and well researched. Here’s a tip to make your chocolate graphics even better: 15 cents should be $.15 or 15¢ (.15¢ means 15/100 or 3/20 of 1 cent). Ditto for the other amounts. Thanks!
December 6, 2012 at 3:25 pm
While using certain words is important I think its more important if you speak with conviction as people will pay more attention to what you say.
January 9, 2013 at 11:52 am
Very true! In fact there is research on things like confidence + persuasion, and many studies point to conviction playing a HUGE role in persuasive speaking and arguments.
December 6, 2012 at 4:38 pm
Ian, Thanks! I found this article to be helpful with the work I need to do on a daily basis. Writing persuasively is so difficult because you don’t get the chance to listen before making your argument.
Oh, how I fought the “you need” in a Tweet the other day.
Days went by and that hashtag my name and what I needed to do rolled around in my head. Finally and against my will my curiosity got the best of me. I clicked the website. When the “you need” is hard wired to my core interest and there is not even the slightest whiff of spam anywhere to be found, I was a goner. You’ve got to hate that. Or, you’ve got to figure out how to use it. Your call.
P.S. The person blew it though. You get to the site and it is miles away from the implication and someone just burned a bridge. The one that leads me to take ” you need” seriously. It is like a vaccination. Next time the bug has a harder time. Or, no shot at all.
December 6, 2012 at 4:59 pm
I agree with your list of words if our goal is to sell. I’ve taught advertsing and understand the basics of writing great headlines and copy. As a blogger, I’m creative and try to be sincere. I shudder to feel like I have to use advertising tactics to simply get more traffic, but I guess it comes with the territory.
January 9, 2013 at 11:50 am
I think it’s very possible to be persuasive and sincere at the same time Dan. It’s sometimes tough when we feel like we may be going “too far”, but as long as everything is honest, it’s okay to utilize this information to get people to take action.
December 6, 2012 at 5:05 pm
All good ideas and reminders. I too am suspicious of “free” yet really like “because” as folks like an explanation.
December 6, 2012 at 5:06 pm
persuasive indeed….how about words like “essential” or ‘vital” and “now”
December 6, 2012 at 7:22 pm
Thanks Greg. Great post. I saw four of the five coming but I have to admit I would never have picked ‘Because’. But it makes sense. Now to make sure that I keep these words in the back of my mind when writing. Cheers!
December 6, 2012 at 10:08 pm
One of my new power words is “Quickly”. I borrowed it from an ad for a competing hypnosis firm. 😉
December 7, 2012 at 12:58 am
The most powerful 3 letter word in the the English language is YET http://www.nylaw2law.blogspot.com/search/label/Power%20of%20Yet
December 7, 2012 at 3:01 am
Your piece is not just full of persuasive copy; it has a very persuasive headline too. I spotted it in Twitter and immediately wanted to know what those 5 words were – and I read right through to the end. In fact, I have even forgotten why I went to Twitter in the first case. Nice article 😉
December 7, 2012 at 11:37 am
Why thank ya! I actually can’t take credit for the headline this time around, the CB team came up with that gem. 🙂
December 7, 2012 at 5:00 am
Amazon once ran a promotion – free delivery when you make a 2nd book purchase. This was very successful in every country apart from France. The marketing department looked into it and found that the program had been slightly altered in France. The French offer charged 20 cents for shipping when customers made a 2nd purchase. Monetarily, the promotions are almost indistinguishable but the 20c offer did not perform…it just doesn’t have the power of FREE. http://www.webcontentwriter.co.uk/website-copywriter-reveals-2-most-powerful-web-words/
Very familiar with this study and I’ve written about it before too! Great minds must think alike 😉
December 7, 2012 at 5:28 am
Indivdually, each of these words appeals to a certain kind of person. If we use the Eisenberg Modes of Persuasion as a guide, we can assign each to a different mode.
“You” – Humanists are relationship oriented. When your voice shifts from “We” and “our company” and you speak to them in the first person, it feels more human — and more Humanistic.
“Free” – This word appeals to the Spontaneous reader. These visitors are just looking for an excuse to take action.
“Because” – Methodicals want to understand the details. They make decisions deliberately and logically. Credible proof is important.
“Instantly” – This also appeals to our Spontaneous reader, who wants immmediate gratification.
“New” – This appeals to the Competitive, who wants to know what will make them better. New technologies, new versions, new looks get their attention.
So, two of the words are very Spontaneous, and we tend to act spontaneously when we’ve decided to buy something. So, “Free” and “Instantly” are probably good “bottom of the funnel” words.
December 7, 2012 at 10:53 am
I’m going to start using “because” more when I’m in a rush. I think I’ll still get scolded, especially in the grocery store line in Philly.
December 7, 2012 at 3:49 pm
Thanks Greg (can I call ya Greg?)
It’s cool to read WHY those words we use in our copy actually work – and why sometimes they can be used incorrectly.
December 7, 2012 at 6:38 pm
Great article and great feedback.
I liked your action items at the end, asking for comments as well as offering your “10 Ways…” with a great reason. I’m going to use this reason with some of my offers. (Hope that’s OK)
A number of months ago I felt that I was writing too much copy with “you” in it and decided to switch to “we” instead.
Based on your article, I think I will go back to these articles and compare my reader engagement. It will be interesting to see if there is a difference.
December 7, 2012 at 9:16 pm
When you’re venturing into “because” land, try also using “so that” so that you can easily describe cause/effect relationships that enhance the persuasiveness of a message.
I’ve heard this discussed before, placing the connection between action and outcome more clearly… will have to look into that a little more…
December 7, 2012 at 9:43 pm
These are really interesting. I love that because is on the list.
December 8, 2012 at 1:13 am
I would like to politely disagree Gregory my man.
Five more persuasive words:
– Freeze! – Bomb! – Duck! – Run! – Three! (after dad had already said “….1…. 2…..”)
Great post bro. Always enjoy your research.
December 8, 2012 at 11:21 am
Good one! And you know what? You point to the fact that the context is really what’s important. The words happen inside a context. Do I want to see “free” at a plastic surgeon’s website? Oh, Lord!
December 9, 2012 at 1:53 pm
Ehhhh… a “free” consultation might be persuasive… but I definitely get what you’re saying. 🙂
December 9, 2012 at 1:52 pm
This guy right here…
That was a roller-coaster of a comment, I was initially so distraught that his royal highness didn’t agree with my post 😉
For more flavor, I’d add “BANZAI!”, heh.
December 9, 2012 at 10:58 pm
Ha ha you clown.
December 8, 2012 at 1:26 am
You can also use the word ESPECIALLY to justify a call to action. Unlike because,you can use ESPECIALLY to confirm your reader’s justification for wanting a particular product or service. Thank you for the practical advice and theory,especially the referenced academic studies.
December 8, 2012 at 2:29 am
You nailed it! A very good blog on the subject of writing persuasive texts. I would like to add that these words, in combination ith the three modalities that people perceive the wworld surrounding them is even more powerful. So like for people who think (mostly) in terms of pictures: Imaging yourself being… For those who act based upon their (gut?) feelings: You can feel yourself … For those that think in terms of words: You can hear the apraisal from your friends now that you…
Of course, combining these makes a post for all readers interesting
December 8, 2012 at 3:08 am
Thank you! A fan of words, I enjoyed this post very much; very interesting and inspiring.
December 8, 2012 at 9:21 am
Hello, my two cents, or should I say my $.02? … 🙂
Great article. Way to put 5 great topics into one short and to-the-point blog.
One phrase I’m trying is “CLICK HERE” and seeing if that works. From what I have learned, some people like to be told what to do. You lead them through the process while giving the impression that all choices are made by YOU. I thought it was a great comment about how in English class we are taught not to use “You” or “I” but to write academically. I guess it really depends on your audience and the search criteria they are using.
I know one word that really helps. When I was reading, I thought the word “Warning” was one of those words you were talking about, but it wasn’t even part of the article.
Another word is “Help”. People like to help. “Please help me”, “Could you help me?”
And as far as “Free” goes, I’ve heard that “Free” can be a bad thing too because it lowers the perceived value. Yeah someone wants something free, but when the person has to spend money, are they going to buy the Hershey Kisses or the other kind? I would have liked to see the conversions of the people after the test, whether or not they became customers or bought anything afterwards.
Another thing I would personally like to see is if someone is telling me to click on a link, I want to know exactly what I’m getting myself into. If not, I assume they are hiding something because they won’t tell me what the hell is going to happen once I click that link.
As one person says, “Free” usually means “Free for 7 days, then it’s $39.99 a month” and they don’t mention how difficult it is to get through to customer service to cancel. Or all the other assortment of not-so-free sites.
December 9, 2012 at 1:55 pm
I agree with “Click Here” when it comes to the web, I’ve tested that on multiple occasions and an “action phrase” like that almost always outperforms other words.
December 8, 2012 at 4:37 pm
Imagine, Extend, Expand, Value, Reach, Grow
December 9, 2012 at 2:15 pm
Are you being cheeky?
December 12, 2012 at 1:27 am
I asked at the bottom of the article to suggest more persuasive words, I didn’t require any research. 🙂
December 8, 2012 at 8:06 pm
I’m going to experiment with this, and make an effort to notice when I used these words and what effect they have.
December 9, 2012 at 9:20 pm
Report back! Where will you be testing these words?
December 9, 2012 at 3:15 am
Well-researched article. Using simple language is the way to write. Now I agree more with #5 because before I always replace it with the word “improved”. But then it’s the right timing that makes these words most persuasive. Great article.
December 9, 2012 at 1:56 pm
Eh, I would say they go hand-in-hand on many occasions. The persuasive element here is the *novelty* of whatever you’re describing, and “improved” often implies that something about the product is new.
December 9, 2012 at 1:20 pm
Found this really interesting. Most of them I can see how they work. For me the first one can be a complete turn off!! If my name is anywhere other than in the titles then I switch off. My Mum used to put my name in a sentence as a put down or to let me know I was in the wrong – it still has the same connotation!!
December 9, 2012 at 4:14 pm
True, but a lot of testing with personal communication (read: email marketing) has shown that names often increase open-rates and engagement in many instances. I remember a MailChimp article that showed exactly that, so it’s something to consider.
December 9, 2012 at 3:05 pm
Your title totally drew me in because I wanted to instantly know those five words that would be new to me . . . for free!! Aren’t I clever? I used all five words in that sentence! Seriously, great and helpful post with terrific research and backing added in. Can’t wait to grab that free report too. 🙂
December 9, 2012 at 4:13 pm
I see what you did there 😉
You’ll definitely enjoy the report if you liked this post! 🙂
December 10, 2012 at 12:00 am
awesome and informative stuff here.. Love to read it.. Normally, i will incorporate this word in my article: I, me, you etc.. and it is worked, my blog looks more alive..
December 10, 2012 at 3:32 am
I imagined the word “FREE” would be at the top. I also knew about “because” and “you”. The word “instantly” is a new idea. I’ll try and fit that into my writing…
December 10, 2012 at 11:00 am
It’s definitely a great way to promote action immediately, and on the web, you rarely get a second chance if you lose someone the first time.
December 11, 2012 at 2:11 am
But be careful. Using these words to draw people in, and then not delivering anything, that can hurt a person’s reputation and train people on what to ignore.
Yes. We get one chance to make an impression. Don’t miss an opportunity, but don’t ruin the experience either.
Awesome information for a newbie like me to get his hands on. Thanks!
December 11, 2012 at 8:49 am
Very welcome!
December 10, 2012 at 9:52 pm
Who amongst us can resist the alluring nature of the word “FREE”? Posts like this are why I love Copy Blogger. The info on here is great and has really helped me improve my writing over the years. No matter how long you’ve been writing, there’s always something new to learn.
December 11, 2012 at 2:16 am
Lots of us can resist the word “free.” We’re being trained to be suspicious. See some of the earlier conversation.
Free can get someone’s attention. “Free” can also be the first step toward “I should have known it was too good to be true. Lots of “free” software is revealed to be packaged with adware and hijacks your homepage, and claims “in order to provide this to you for free, we have to pull these shenanigans.”
December 11, 2012 at 8:50 am
I think it was a given here that honesty needs to accompany every form of persuasion that you implement. 🙂
December 11, 2012 at 2:05 am
“Free”, “New” and “You” were quite obvious but didn’t expect “Because” and “Instantly” in the top 5 list. I expected “Now” word.
December 11, 2012 at 10:52 am
If I had to go with a 6th “bonus word”, I’d definitely envision it being something like “Now”, I should look to see if there is any solid research on that! 🙂
December 11, 2012 at 11:17 am
These are specially great for writing ads, where you have so little time to grab someone’s attention, not to mention the million other ads competing for those same eyeballs. Great, useful article. Anyone looking to improve their copywriting skills should spend some time learning all the “power” words that can dramatically improve engagement and clickthrough rates.
December 12, 2012 at 1:24 am
Very true, advertisements are a medium where you have a very limited time span to catch attention.
December 14, 2012 at 5:01 pm
I hardly ever write copy. Most often I just correct it. Coincidentally however, I just helped someone write copy for an advertorial of sorts today. I think it’s important to say “we will” as opposed to “we can.” “We can” just sounds too much like “we may,” while “we will” sounds more certain. Agree? Loved the information….thank you!
December 16, 2012 at 8:46 pm
I agree 100% Joline, in fact, I’d go even further and say that great copy should eliminate any phrases that showcases an alternative (“I think that…”, etc.)
December 16, 2012 at 1:15 am
About 20 years ago i was working for a bank selling balance transfers, which basically is trying to get people to switch all of their debt to us for a lower interest rate. I was doing a terrible job up until the guy next to me said to start using the phrase. It’s a no brainer. To my shock and amazement I more than doubled my closing rate with this stupid phrase. I guess no one wants to feel like they have no brain…LOL
December 16, 2012 at 8:45 pm
Ha! Wow, that’s a story I almost feel guilty laughing about…
December 18, 2012 at 4:13 am
The world will be pleased to know I’ve ordered that Cialdini book.
Everywhere I go recently that book is recommended. Can’t wait!
Great post – I loved the Chocolate study, that’s fascinating.
December 22, 2012 at 10:43 am
Thanks, I now have the title of my next headline…
“I am giving YOU a FREE eBook BECAUSE I INSTANTLY want a NEW Fan” 🙂
December 23, 2012 at 1:06 pm
Gregory – YOU did a great job with this article BECAUSE it INSTANTLY helped me idetify specific ways to make my copy more persuasive. I hope I can reciprocate in the near future with NEW ideas for you in my next blog post on Harvard Business Review. Thank you. I find thank you and reciprocity to be attractive words as well.
January 3, 2013 at 11:31 pm
I do agree that FREE is a great in attracting attention. But over the years, I do notice that FREE attracts the wrong prospects as well. Now I actually charge a nominal fee for all the workshops to capture a better qualified audience.
February 7, 2013 at 12:43 am
From my media training – “Actually” is very powerful. It’s a good word to use instead of “yes” or “no” to pivot questioning
February 8, 2013 at 3:52 pm
I’m not sure about the “because” but You, free, instantly and New are difintely words that gets my heart racing. Like most people, I like to hear my name and see my name in big lites. Who doesn’t love free? Only thing about free is that it can sometimes devalue valuable things. We take things for granted when they’re free. Like mostly people today, we want everything and we want it now. Instantly ain’t fast enough sometimes. Definitely love new. Been buying used stuff so long only new will due for me now.
February 10, 2013 at 6:24 pm
Thanks for the information! I’m writing a sales letter for my ebook so you already know I turned to copyblogger for advice ?.
February 12, 2013 at 11:44 am
I read a blog a year ago where the writer had done tests to his “follow me on Twitter” link to see what compelled the most people to follow him. He ended up with “You should follow me on Twitter”. I wonder how much the “You” had to do with that being the most compelling version.
Now I also wonder how much more compelling it would have been if he had had a “because” in there.
March 19, 2013 at 5:50 am
I have always loved that Cialdini experiment example.thanks for the reminder….I’m in the middle of sending out some postcards and I think I will use this great article as the basis to do some testing…thanx
March 20, 2013 at 4:36 pm
Two words keep popping up in my mind: “please” and “thanks”. What strikes me is that I believe these two words are very powerful, but mostly when spoken! In writing, these are overused or expected. Interesting the difference between both ways of communicating
March 25, 2013 at 3:47 am
A word I keep thinking of is “beta”. Many people like the idea of being the first one to try something new. I know I do. Giving people access to something prior to the “general public” makes them feel special and will likely lead to brand loyalty and engagement.
April 1, 2013 at 7:41 pm
Wow, this list was put together well. I still can’t believe because is that persuasive, but the logic behind it makes sense. I could have guessed the other 4. Great post keep up the good work, Daniel
April 3, 2013 at 9:36 am
I always think when I see things like: “These are selling like hotcakes. Only 5 left. Hurry. Don’t miss out!”. This makes me think: “If they’re selling so fast and furious, why are they so bent on urging us to buy?”. They don’t need to!
April 13, 2013 at 12:17 pm
Not for headlines, but within copy, it is important for me to use the word LIKE somewhere in there for two reasons. The first is such usage almost always is in an analogy, and anologies work well in persuasive writing. Analogies are like pictures, they convey more than the words they are comprised of. The second is that within the analogy, I always try and put the word like in front of what I am persuading about. For example, if the new “what-a-car-mobile” is something I am trying to pursuade some to take interest in, I could say “Seeing a double rainbow is for visual pleasure much like the what-a-car-mobile is for driving pleasure. The embedded secondary statement that speaks to the subconscious is ‘like the what-a-car-mobile”.
May 15, 2013 at 10:09 am
As a Public Speaking Coach and Trainer, I teach 4 of these to my students! I have started Copywriting more and more to learn more about persuasive speaking! Thank you for the tips!
May 24, 2013 at 3:06 pm
This is a fabulous blog post.
‘You’ is a very powerful word that stands out to me above all others. ‘You’ creates a personal relationship between a reader and the content that they are reading.
Content writing often misses out in creating a relationship with the reader.
Without that relationship there will be no engagement and your content will not be valuable
May 28, 2013 at 7:58 am
I use superlatives to make products and services seem more attractive. Saying something is lovely or beautiful, amazing or remarkable, is powerful stuff.
June 8, 2013 at 8:51 am
The word “because” is definitely an important word to implement when using persuasive language. Especially when you’re trying to get your kids to do stuff like clean up their room and things like that. Great post by the way!
June 17, 2013 at 9:23 pm
yup, those are 5 very persuasive words!
July 11, 2013 at 6:25 pm
I can’t help but feeling a little sleezball knowing these psychological tricks and using them to get conversions.
I keep reminding myself that I am offering something really valuable, something that I would like to give away for free. And, even am giving away for free to a certain extent, or at least will be when I publish my free report “Busy People Get Healthy (In Half the Time)”
You should check out my site and let me know how your brain reacts because, I would really value your opinion. (There’s a real reason!)
Thanks for a great article,
July 18, 2013 at 5:53 am
From my experience, while “You” is indeed deserving its spot, an even better one is a person’s own name. We all hear our name from the very first days of our lives – we are conditioned to pay attention whenever that word is used.
Even when walking on the street, if you hear someone saying out loud your name: “Gregory!” … “you” would turn your head “instantly”, not “because” it is something “new” but simply “because” you are trained to do so from way back, during your childhood.
The attention-grabbing word “free” is an acquired taste, though; it comes in your life almost at the same time (parents provide you with anything in “free” mode) but you come to value it properly only much later… 🙂
Cheers, ~Steve
July 18, 2013 at 10:37 am
Thank you for making me smile in a VERY hectic week. Of course, you are right. But I write historical fiction and while ultimately I’m selling a product, something in me rebels/resists using outright marketing strategies such as those outlined here.
BUT I do want to reach my audience. So I’ve got my toe in and appreciate very much this NEW and FREE information you’ve made so INSTANTLY available BECAUSE you have helped me. Thank YOU!
July 19, 2013 at 7:12 pm
because you asked me to I’m going to instantly give you my new opinion, for free!
When I started blogging about yoga I quickly realized that my average competitor was writing a lot of blah blah blah posting photos of themselves in insanely difficult yoga poses, talking about their “beautiful” kids and supportive spouse. yawn. Even I don’t want to read about that, and I’m a professional yoga teacher!
So I started talking about “you” and things that might be of interest to “you”. Assuming that the average yoga practitioner is smart, green conscious, politically savvy I started instantly started blogging on new topics like big pharma, organic foods, and relationships because, you know, people like to read about interesting things – not just “me” and how my day went when I worked out.
My readership really grew! Stop by and read me some day, would love to meet you
July 22, 2013 at 7:04 pm
Thank You Gregory,
Simple and definitely meaningful tips. As Dale Carnegie said many years ago “the most important sound to a person is the sound of their own name”. A challenge though with digital communication, eg. communicating with parents via Facebook to help one another, the hardest job in the world with little to no prior preparation and loaded with exhaustion, frustration and loneliness.
I took a few great tips from your article, any others would be greatly appreciated by this parent and others ?
Thank you again all the way from Down Under.
August 6, 2013 at 8:09 pm
Persuasion is written and verbal and I think it’s true people like seeing their name in print, hearing it called. Persuading the brain in advertising is an awesome process when you see it unfold.
August 31, 2013 at 11:29 am
I like to use the word “imagine”. I think it is a way to get people involved in the content being discussed. I suppose it is a way to try to force them to think.
Once they are doing that, it may be possible to lead them in a certain direction by providing compelling arguments, research results, and information.
What do you think to this approach?
August 31, 2013 at 1:18 pm
That’s called “invoking the mind’s eye.” Very powerful.
August 31, 2013 at 3:07 pm
I should have mentioned it in the previous post, what an excellent and informative article that was. Certainly some food for thought there. I will keep this in mind when writing content for my site.
Thanks so much.
September 7, 2013 at 3:18 pm
Love this article. I’ve bought so many marketing tools, plugins, themes, etc. and most, if not all of these persuasive words were in the copy that sold me.
October 15, 2013 at 11:29 am
Great article really helpful for getting into your customers head and there thought processes. Very interesting and helpful. Thank you,
November 19, 2013 at 10:16 am
The word, “Please” is also very persuasive!
This article's comments are closed.
Get free access to proven marketing training.

Customer Reviews
Laura V. Svendsen

Finished Papers
Service Is a Study Guide
Our cheap essay writing service aims to help you achieve your desired academic excellence. We know the road to straight A's isn't always smooth, so contact us whenever you feel challenged by any kind of task and have an original assignment done according to your requirements.

Finished Papers

Customer Reviews
Still not convinced? Check out the best features of our service:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Once your child has figured out the techniques she can use in her persuasive writing, she will need to find some words and phrases that help her to be convincing. Using phrases like "I think" or "It seems that" don't convey a sense of confidence in her position. Instead, she needs to use word combinations that show how much she believes in ...
4. That is to say. Usage: "That is" and "that is to say" can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: "Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.". 5. To that end. Usage: Use "to that end" or "to this end" in a similar way to "in order to" or "so".
TIP 1: Some writers find it easier to write their introductions last. As long as you have your working thesis, this is a perfectly acceptable approach. From that thesis, you can plan your body paragraphs and then go back and write your introduction. TIP 2: Avoid "announcing" your thesis.
Persuasive essays that effectively use pathos include emotional language. The emotional language captivates the reader, which may convince the reader that your argument is worth considering.
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay. If you're intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place. 1. A topic or ...
The last time you wrote a persuasive essay may have been in high school or college, but the skill of writing a strong persuasive argument is always a useful one to have. Persuasive writing begins with a writer forming their own opinion on a topic, which they then attempt to convince their reader of this opinion by walking them through a number of logical and ethical arguments.
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: The Main Components. 1. Introduction: Capturing Attention and Stating the Thesis. The introduction serves as the gateway to your persuasive essay. Begin by grabbing the reader's attention with a compelling hook—an anecdote, a surprising fact, or a thought-provoking question.
Consider using an Persuasive Essay Template to understand the key elements of the essay. Use Words that Evoke Emotion. It's easier to get people to see things your way when they feel an emotional connection. As you describe your topic, make sure to incorporate words that cause people to feel an emotion. For example, instead of saying ...
Atrocious, Confusing, Cruel, Harmful, Inferior Dreadful, Outrageous, Shocking, Shameful, Offensive, Horrible, Unstable, Severe, No: - These negative words can be used to great effect when pulling apart the opposition. Persuasion is a useful tool in the business world, the educational sector, and in everyday life.
The persuasive essay typically presents a clear thesis statement, followed by well-structured paragraphs that provide evidence and examples supporting the author's position. The ultimate goal is to inform and influence the reader's beliefs or behavior by appealing to their emotions, logic, and sense of reason.
Of the 12,758 words in the 62 failed ads, 24.1% were adjectives. By direct comparison, Lincoln's Gettysburg Address contains only 35 adjectives out of 268 immortal words - only 13.1% adjective-to-total-word ratio. Winston Churchill's famous "Blood, Sweat and Tears" speech rates even lower and has a 12.1% adjective ratio (81 adjectives ...
7. Call to Action: End with powerful action-oriented words, urging the reader to take the desired step. Balancing emotional and logical appeal in sentence construction is key. Too much emotion can undermine the credibility of your argument, while too much logic can fail to connect on a human level.
Here are the steps you need to take: Step 1: Create a Compelling Introduction. You want to hook your readers with a great opening for your persuasive essay, so they'll want to keep reading. Here are 3 tips for writing an attention-grabbing introduction for your next essay. Use a strong hook statement.
TRANSITIONAL PHRASES. INTRODUCTORY PHRASES. In my opinion. There is no doubt that. I question whether. I believe. From my point of view. I (dis) agree with. It is my belief that.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
22. " double " - This word is a great way to get people's attention and show them how your suggestion can help them improve or enhance something. 23. " enable " - It suggests that the individual has the ability to make something possible by doing what you are suggesting. 24. " encourage " -.
Begin planning your response to the prompt by first looking for the key words. Verbs (write, explain, discuss) tell you what to do, but the prompt will also include clues about how to do it (e.g., "use specific reasons and examples"; "support your answer with appropriate evidence"; and "explain your answer").
8. When it comes to assembling persuasive words for copywriting, like any other construction job, you need to rely on your skills, experience, and toolbox. The toolbox of the writer is filled with words. In defining what I believe is a critical element of effective copywriting, I'll make my case by amending the famous quote from Animal Farm:
Keywords To Use In A Persuasive Essay, Teacher Ups Application Letter, Dissertation Results Writer Websites, Popular Dissertation Results Writer Sites For Masters, Essay Detail In Writing Definition, Book Report Information, Importance Of Forest Essay In Nepali Language
Keywords To Use In A Persuasive Essay | Best Writing Service. Success rate. Hire a Writer. (sq ft) 928Orders prepared. Why choose Us? We are inclined to write as per the instructions given to you along with our understanding and background research related to the given topic. The topic is well-researched first and then the draft is being written.
Referral program. Johan Wideroos. #17 in Global Rating. $ 24.99. Once your essay writing help request has reached our writers, they will place bids. To make the best choice for your particular task, analyze the reviews, bio, and order statistics of our writers. Once you select your writer, put the needed funds on your balance and we'll get started.