- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities

What can QuickMath do?
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students.
- The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and cancelling common factors within a fraction.
- The equations section lets you solve an equation or system of equations. You can usually find the exact answer or, if necessary, a numerical answer to almost any accuracy you require.
- The inequalities section lets you solve an inequality or a system of inequalities for a single variable. You can also plot inequalities in two variables.
- The calculus section will carry out differentiation as well as definite and indefinite integration.
- The matrices section contains commands for the arithmetic manipulation of matrices.
- The graphs section contains commands for plotting equations and inequalities.
- The numbers section has a percentages command for explaining the most common types of percentage problems and a section for dealing with scientific notation.
Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions

Game Central
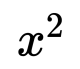
Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
Brainly: AI Homework Helper
About this app
Math answer scanner to solve math problems, get homework help from a community of experts, get 1:1 homework help with brainly plus or tutor, data safety.
Ratings and reviews
- Flag inappropriate
What's new
App support, similar apps.
- Number Charts
- Multiplication
- Long division
- Basic operations
- Telling time
- Place value
- Roman numerals
- Fractions & related
- Add, subtract, multiply, and divide fractions
- Mixed numbers vs. fractions
- Equivalent fractions
- Prime factorization & factors
- Fraction Calculator
- Decimals & Percent
- Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals
- Fractions to decimals
- Percents to decimals
- Percentage of a number
- Percent word problems
- Classify triangles
- Classify quadrilaterals
- Circle worksheets
- Area & perimeter of rectangles
- Area of triangles & polygons
- Coordinate grid, including moves & reflections
- Volume & surface area
- Pre-algebra
- Square Roots
- Order of operations
- Scientific notation
- Proportions
- Ratio word problems
- Write expressions
- Evaluate expressions
- Simplify expressions
- Linear equations
- Linear inequalities
- Graphing & slope
- Equation calculator
- Equation editor
- Elementary Math Games
- Addition and subtraction
- Math facts practice
- The four operations
- Factoring and number theory
- Geometry topics
- Middle/High School
- Statistics & Graphs
- Probability
- Trigonometry
- Logic and proof
- For all levels
- Favorite math puzzles
- Favorite challenging puzzles
- Math in real world
- Problem solving & projects
- For gifted children
- Math history
- Math games and fun websites
- Interactive math tutorials
- Math help & online tutoring
- Assessment, review & test prep
- Online math curricula
- Algebra Calculator
- Mobile App for iOS

Free Algebra Calculator
Step-by-step calculator and algebra solver.

Algebra Solver to Check Your Homework
- For Parents
- For Teachers
- Teaching Topics

- Kindergarten
- EM3/CCSS at Home
- Family Letters
- Student Gallery
- Understanding EM
- Algorithms/ Computation
- Student Links
EM4 at Home
Fraction and mixed-number computation; measurement.

Everyday Mathematics for Parents: What You Need to Know to Help Your Child Succeed
The University of Chicago School Mathematics Project
University of Chicago Press
Learn more >>
Related Links
Help with algorithms.
Access video tutorials, practice exercises, and information on the research basis and development of various algorithms.
Everyday Mathematics Online
With a login provided by your child's teacher, access resources to help your child with homework or brush up on your math skills.
Parent Connections on Publisher's site
McGraw-Hill Education offers many resources for parents, including tips, activities, and helpful links.
Parent Resources on EverydayMath.com
EverydayMath.com features activity ideas, literature lists, and family resources for the EM curriculum.
Understanding Everyday Mathematics for Parents
Learn more about the EM curriculum and how to assist your child.


Math Expressions Answer Key for Grade 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, and Kindergarten K | Math Expressions Common Core Grades K-5
Houghton mifflin math expressions common core answer key for grade 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, and kindergarten k.
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Homework and Remembering Answer Key
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Homework and Remembering Answer Key
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Homework and Remembering Answer Key
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Homework and Remembering Answer Key
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Homework and Remembering Answer Key
- Math Expressions Kindergarten Homework and Remembering Answer Key
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Student Activity Book Answer Key
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Student Activity Book Answer Key
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Student Activity Book Answer Key
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Student Activity Book Answer Key
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Student Activity Book Answer Key
- Math Expressions Kindergarten Student Activity Book Answer Key
Math Expressions Common Core Grade 5 Homework and Remembering Answer Key
Math Expressions Grade 5 Homework and Remembering Volume 1 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade 5 Volume 1 Answer Key
Unit 1 Addition and Subtraction with Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 1 Answer Key Introducing the MathBoard
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 2 Answer Key Explain Equivalent Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 3 Answer Key Equivalent Fractions and Multipliers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 4 Answer Key Strategies for Comparing Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 5 Answer Key Fractions Greater Than One
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 6 Answer Key Add and Subtract Like Mixed Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 7 Answer Key Add Unlike Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 8 Answer Key Subtract Unlike Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 9 Answer Key Solve with Unlike Mixed Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 10 Answer Key Practice with Unlike Mixed Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 11 Answer Key Reasonable Answers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 12 Answer Key Real-World Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 1 Lesson 13 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 2 Addition and Subtraction with Decimals
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 2 Lesson 1 Answer Key Decimals as Equal Divisions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 2 Lesson 2 Answer Key Thousands to Thousandths
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 2 Lesson 3 Answer Key Equate and Compare Thousandths
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 2 Lesson 4 Answer Key Adding and Subtracting Decimals
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 2 Lesson 5 Answer Key Add Whole Numbers and Decimals
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 2 Lesson 6 Answer Key Subtract Whole and Decimal Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 2 Lesson 7 Answer Key Properties and Strategies
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 2 Lesson 8 Answer Key Round and Estimate with Decimals
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 2 Lesson 9 Answer Key Graph with Decimal Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 2 Lesson 10 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 3 Multiplication and Division with Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Answer Key Basic Multiplication Concepts
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 2 Answer Key Multiplication with Non-Unit Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 3 Answer Key Multiplication with Fractional Solutions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 4 Answer Key Multiply a Fraction by a Fraction
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 5 Answer Key Multiplication Strategies
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 6 Answer Key Multiply Mixed Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 7 Answer Key Relate Fraction Operations
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 8 Answer Key Solve Real-World Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 9 Answer Key Make Generalizations
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 10 Answer Key When Dividing is Also Multiplying
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 11 Answer Key Solve Division Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 12 Answer Key Distinguish Multiplication from Division
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 13 Answer Key Review Operations with Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 3 Lesson 14 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 4 Multiplication with Whole Numbers and Decimals
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 1 Answer Key Shift Patterns in Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 2 Answer Key Patterns with Fives and Zeros
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 3 Answer Key Sharing Methods for Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 4 Answer Key Multiply Two-Digit Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 5 Answer Key Practice Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 6 Answer Key Multiply Decimals by Whole Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 7 Answer Key Multiply by Decimals
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 8 Answer Key Multiply with Decimals Greater Than 1
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 9 Answer Key Compare Shift Patterns
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 10 Answer Key Estimate Products
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 11 Answer Key Multiplication Practice
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 4 Lesson 12 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Grade 5 Homework and Remembering Volume 2 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade 5 Volume 2 Answer Key
Math Expressions Common Core Grade 5 Answer Key Unit 5 Division with Whole Numbers and Decimals
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 1 Answer Key Divide Whole Numbers by One Digit
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 2 Answer Key Explore Dividing by Two-Digit Whole Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 3 Answer Key Too Large, Too Small, or Just Right?
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 4 Answer Key Interpret Remainders
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 5 Answer Key Division Practice
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 6 Answer Key Divide Decimal Numbers by Whole Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 7 Answer Key Divide Whole Numbers by Decimal Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 8 Answer Key Divide with Two Decimal Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 9 Answer Key Division Practice
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 10 Answer Key Distinguish Between Multiplication and Division
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 5 Lesson 11 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Math Expressions Grade 5 Answer Key Unit 6 Operations and Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 6 Lesson 1 Answer Key Situation and Solution Equations for Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 6 Lesson 2 Answer Key Situation and Solution Equations for Multiplication and Division
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 6 Lesson 3 Answer Key Write Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 6 Lesson 4 Answer Key Determine Reasonable Answers
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 6 Lesson 5 Answer Key Language of Comparison Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 6 Lesson 6 Answer Key Multiplicative Comparison Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 6 Lesson 7 Answer Key Types of Comparison Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 6 Lesson 8 Answer Key Equations and Parentheses
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 6 Lesson 9 Answer Key Multistep Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 6 Lesson 10 Answer Key Practice Problem Solving
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 6 Lesson 11 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Common Core Grade 5 Volume 2 Answer Key Unit 7 Algebra, Patterns, and Coordinate Graphs
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 7 Lesson 1 Answer Key Read and Write Expressions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 7 Lesson 2 Answer Key Simplify Expressions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 7 Lesson 3 Answer Key Evaluate Expressions
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 7 Lesson 4 Answer Key Patterns and Relationships
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 7 Lesson 5 Answer Key The Coordinate Plane
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 7 Lesson 6 Answer Key Graph Ordered Pairs
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 7 Lesson 7 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Grade 5 Homework and Remembering Volume 2 Answer Key Unit 8 Measurement and Geometry
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 1 Answer Key Convert Metric Units of Length
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 2 Answer Key Metric Units of Liquid Volume
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 3 Answer Key Metric Units of Mass
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 4 Answer Key Customary Units of Length
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 5 Answer Key Customary Measures of Liquid Volume
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 6 Answer Key Customary Units of Weight
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 7 Answer Key Read and Make Line Plots
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 8 Answer Key Perimeter and Area of Rectangles
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 9 Answer Key Cubic Units and Volume
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 10 Answer Key Visualize Volume
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 11 Answer Key Introduce Volume Formulas
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 12 Answer Key Relate Length, Area, and Volume
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 13 Answer Key Volume of Composite Solid Figures
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 14 Answer Key Attributes of Quadrilaterals
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 15 Answer Key Attributes of Triangles
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 16 Answer Key Attributes of Two-Dimensional Shapes
- Math Expressions Grade 5 Unit 8 Lesson 17 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Common Core Grade 4 Homework and Remembering Answer Key
Math Expressions Grade 4 Homework and Remembering Volume 1 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade 4 Volume 1 Answer Key
Unit 1 Place Value and Multidigit Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 1 Answer Key Place Value to Thousands
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 2 Answer Key Place Value Patterns
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 3 Answer Key Round Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 4 Answer Key Numbers to One Million
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 5 Answer Key Compare and Round Greater Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 6 Answer Key Make New Groups for Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 7 Answer Key Add Greater Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 8 Answer Key Estimation and Mental Math
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 9 Answer Key Subtract from Thousands
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 10 Answer Key Subtraction Undoes Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 11 Answer Key Subtract Greater Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 12 Answer Key Practice Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 13 Answer Key Problem Solving with Greater Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 1 Lesson 14 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 2 Multiplication with Whole Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 1 Answer Key Arrays and Area Models
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 2 Answer Key Connect Place Value and Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 3 Answer Key Mental Math and Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 4 Answer Key Model One-Digit by Two-Digit Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 5 Answer Key Estimate Products
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 6 Answer Key Use Place Value to Multiply
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 7 Answer Key Algebraic Notation Method
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 8 Answer Key Compare Methods of One-Digit by Two-Digit Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 9 Answer Key Discuss Different Methods
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 10 Answer Key One-Digit by Three-Digit Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 11 Answer Key Multistep Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 12 Answer Key Two-Digit by Two-Digit Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 13 Answer Key Different Methods for Two-Digit Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 14 Answer Key Check Products of Two-Digit Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 15 Answer Key Practice Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 16 Answer Key Multiply One-Digit and Four-Digit Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 17 Answer Key Use the Shortcut Method
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 18 Answer Key Practice Multiplying
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 2 Lesson 19 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 3 Division with Whole Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Answer Key Divide with Remainders
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 2 Answer Key Relate 3-Digit Multiplication to Division
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 3 Answer Key Discuss 2-Digit and 4-Digit Quotients
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 4 Answer Key Digit-by-Digit Method
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 5 Answer Key Relate Three Methods
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 6 Answer Key Divide by Any Method
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 7 Answer Key Just-Under Quotient Digits
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 8 Answer Key Estimate to Check Quotients
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 9 Answer Key Make Sense of Remainders
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 10 Answer Key Mixed Problem Solving
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 11 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 4 Equations and Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 1 Answer Key Properties and Algebraic Notation
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 2 Answer Key Situation and Solution Equations for Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 3 Answer Key Situation and Solution Equations for Multiplication and Division
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 4 Answer Key Multiplication Comparisons
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 5 Answer Key Discuss Comparison Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 6 Answer Key Graphs and Comparison Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 7 Answer Key Solve Two-Step Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 8 Answer Key Solve Multistep Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 9 Answer Key Practice with Multistep Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 10 Answer Key Factors and Prime Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 11 Answer Key Analyze Patterns
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 4 Lesson 12 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Grade 4 Homework and Remembering Volume 2 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade 4 Volume 2 Answer Key
Grade 4 Answer Key Unit 5 Measurement
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 5 Lesson 1 Answer Key Measure Length
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 5 Lesson 2 Answer Key Metric Measures of Liquid Volume and Mass
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 5 Lesson 3 Answer Key Units of Time
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 5 Lesson 4 Answer Key Customary Measures of Length
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 5 Lesson 5 Answer Key Customary Units of Weight and Liquid Volume
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 5 Lesson 6 Answer Key Perimeter and Area of Rectangles
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 5 Lesson 7 Answer Key Solve Measurement Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 5 Lesson 8 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 6 Fraction Concepts and Operations
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 6 Lesson 1 Answer Key Understand Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 6 Lesson 2 Answer Key Fractions That Add to One
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 6 Lesson 3 Answer Key Add and Subtract Fractions with Like Denominators
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 6 Lesson 4 Answer Key Mixed Numbers and Fractions Greater Than 1
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 6 Lesson 5 Answer Key Add and Subtract Mixed Numbers with Like Denominators
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 6 Lesson 6 Answer Key Practice with Fractions and Mixed Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 6 Lesson 7 Answer Key Multiply a Fraction by a Whole Number
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 6 Lesson 8 Answer Key Practice Multiplying a Fraction by a Whole Number
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 6 Lesson 9 Answer Key Mixed Practice
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 6 Lesson 10 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 7 Fractions and Decimals
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 1 Answer Key Compare Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 2 Answer Key Fractions on the Number Line
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 3 Answer Key Fractions of Different-Size Wholes
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 4 Answer Key Equivalent Fractions Using Multiplication
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 5 Answer Key Equivalent Fractions Using Division
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 6 Answer Key Compare Fractions with Unlike Denominators
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 7 Answer Key Fractions and Line Plots
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 8 Answer Key Relate Fractions and Decimals
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 9 Answer Key Explore Decimal Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 10 Answer Key Compare Decimals to Hundredths
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 11 Answer Key Decimals Greater Than 1
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 12 Answer Key Compare Decimals Greater Than 1
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 7 Lesson 13 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 8 Geometry
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 1 Answer Key Points, Rays, and Angles
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 2 Answer Key Measuring Angles
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 3 Answer Key Circles and Angles
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 4 Answer Key Name Triangles
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 5 Answer Key Compose and Decompose Angles
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 6 Answer Key Real World Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 7 Answer Key Parallel and Perpendicular Lines and Line Segments
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 8 Answer Key Classifying Quadrilaterals
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 9 Answer Key Decompose Quadrilaterals and Triangles
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 10 Answer Key Classify Polygons
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 11 Answer Key Line Symmetry
- Math Expressions Grade 4 Unit 8 Lesson 12 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Common Core Grade 3 Homework and Remembering Answer Key
Math Expressions Grade 3 Homework and Remembering Volume 1 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade 3 Volume 1 Answer Key
Unit 1 Multiplication and Division with 0-5, 9 and 10
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 1 Answer Key Multiply with 5
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 2 Answer Key Multiplication as Equal Groups
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 3 Answer Key Multiplication and Arrays
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 4 Answer Key The Meaning of Division
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 5 Answer Key Multiply and Divide with 2
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 6 Answer Key Building Fluency with 2s and 5s
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 7 Answer Key Multiply and Divide with 10
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 8 Answer Key Multiply and Divide with 9
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 9 Answer Key Building Fluency with 2s, 5s, 9s, and 10s
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 10 Answer Key Multiply and Divide with 3
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 11 Answer Key Multiplication and Area
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 12 Answer Key Multiply and Divide with 4
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 13 Answer Key Use the Strategy Cards
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 14 Answer Key Building Fluency with 2s, 3s, 4s, 5s, 9s, and 10s
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 15 Answer Key Multiply and Divide with 1 and 0
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 16 Answer Key Solve and create Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 17 Answer Key Play Multiplication and Division Games
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 18 Answer Key Building Fluency with 0s, 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s, 5s, 9s, 10s
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 19 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 2 Multiplication and Division with 6, 7, and 8, Multiply with Multiples of 10, and Problem Solving
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 1 Answer Key Multiply and Divide with 6
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 2 Answer Key Solve Area Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 3 Answer Key Multiply and Divide with 8
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 4 Answer Key Write Word Problems and Equations
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 5 Answer Key Multiply and Divide with 7
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 6 Answer Key Square Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 7 Answer Key Practice with 6s, 7s, and 8s
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 8 Answer Key Building Fluency with 0s – 10s
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 9 Answer Key Equations and Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 10 Answer Key Write First Step Questions for Two-Step Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 11 Answer Key Make Sense of Two-Step Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 12 Answer Key Multiply with Multiples of 10
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 13 Answer Key Play Multiplication and Division Games
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 14 Answer Key Building Fluency with 0s – 10s
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 2 Lesson 15 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 3 Measurement, Time, and Graphs
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Answer Key Customary Units of Length
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 2 Answer Key Customary Units of Liquid Volume
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 3 Answer Key Metric Units of Liquid Volume
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 4 Answer Key Customary Units of Weight and Metric Units of Mass
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 5 Answer Key Solve Word Problems Involving Liquid Volume and Mass
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 6 Answer Key Tell Time
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 7 Answer Key Before and After the Hour
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 8 Answer Key Elapsed Time
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 9 Answer Key Add and Subtract Time
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 10 Answer Key Solve Word Problems Involving Time
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 11 Answer Key Read and Create Pictographs and Bar Graphs
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 12 Answer Key Read and Create Bar Graphs with Multidigit Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 13 Answer Key Represent and Organize Data
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 14 Answer Key Use Graphs to Solve Time and Measurement Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 3 Lesson 15 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Grade 3 Homework and Remembering Volume 3 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade 3 Volume 2 Answer Key
Unit 4 Multidigit Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 1 Answer Key Make Place Value Drawings
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 2 Answer Key Build Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 3 Answer Key Place Value in Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 4 Answer Key Practice with Place Value
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 5 Answer Key Round to the Nearest Hundred
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 6 Answer Key Round to the Nearest Ten
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 7 Answer Key Explore Multidigit Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 8 Answer Key Discuss Addition Methods
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 9 Answer Key The Grouping Concept in Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 10 Answer Key Practice Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 11 Answer Key Ungroup to Subtract
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 12 Answer Key Subtract Across Zeros
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 13 Answer Key Discuss Methods of Subtracting
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 14 Answer Key Relate Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 15 Answer Key Subtraction Practice
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 16 Answer Key Addition and Subtraction Practice
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 17 Answer Key Solve Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 4 Lesson 18 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 5 Write Equations to Solve Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 5 Lesson 1 Answer Key Addition and Subtraction Situations
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 5 Lesson 2 Answer Key Word Problems with Unknown Addends or Unknown factors
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 5 Lesson 3 Answer Key Word Problems with Unknown Starts
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 5 Lesson 4 Answer Key Comparison Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 5 Lesson 5 Answer Key Comparison Problems with Misleading Language
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 5 Lesson 6 Answer Key Word Problems with Extra, Hidden, or Not Enough Information
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 5 Lesson 7 Answer Key Write First Step Questions for Two-Step Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 5 Lesson 8 Answer Key Solve Two-Step Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 5 Lesson 9 Answer Key Equations and Two-Step Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 5 Lesson 10 Answer Key Practice with Two-Step Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 5 Lesson 11 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 6 Polygons, Perimeter, and Area
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 6 Lesson 1 Answer Key Triangles
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 6 Lesson 2 Answer Key Parallelograms, Rectangles, Squares, and Rhombuses
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 6 Lesson 3 Answer Key Draw Quadrilaterals
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 6 Lesson 4 Answer Key Classify Quadrilaterals
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 6 Lesson 5 Answer Key Perimeter and Area
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 6 Lesson 6 Answer Key Side Lengths with Area and Perimeter
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 6 Lesson 7 Answer Key Compare Areas and Perimeters
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 6 Lesson 8 Answer Key Area of Rectilinear Figures
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 6 Lesson 9 Answer Key Solve Perimeter and Area Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 6 Lesson 10 Answer Key Tangram Shapes and Area
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 6 Lesson 11 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 7 Explore Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 7 Lesson 1 Answer Key Understand Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 7 Lesson 2 Answer Key Model Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 7 Lesson 3 Answer Key Locate Fractions on the Number Line
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 7 Lesson 4 Answer Key Compare Unit Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 7 Lesson 5 Answer Key Compare Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 7 Lesson 6 Answer Key Introduce Equivalence
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 7 Lesson 7 Answer Key Equivalent Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 7 Lesson 8 Answer Key Problem Solving with Fractions
- Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 7 Lesson 9 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Common Core Grade 2 Homework and Remembering Answer Key
Math Expressions Grade 2 Homework and Remembering Volume 1 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade 2 Volume 1 Answer Key
Unit 1 Addition and Subtraction Within 20
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 1 Answer Key Represent Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 2 Answer Key Relate Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 3 Answer Key Make-a-Ten Strategies
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 4 Answer Key Relate Unknown Addends and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 5 Answer Key More Practice with Unknown Addends and Teen Totals
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 6 Answer Key Odd and Even Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 7 Answer Key Strategies Using Doubles
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 8 Answer Key Equations, Equation Chains, and Vertical Form
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 9 Answer Key Add Three or Four Addends
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 10 Answer Key Add To and Take From Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 11 Answer Key Add To and Take From Problems – Unknown in All Positions
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 12 Answer Key Put Together/Take Apart Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 13 Answer Key Special Put Together/Take Apart Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 14 Answer Key Compare Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 15 Answer Key More Compare Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 16 Answer Key Mixed Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 17 Answer Key Problems with Not Enough, Extra, or Hidden Information
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 18 Answer Key More Complex Compare Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 19 Answer Key Two-Step Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 20 Answer Key Mixed Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 1 Lesson 21 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 2 Addition Within 200
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 1 Answer Key Ones, Tens, and Hundreds
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 2 Answer Key Draw Quick Tens and Quick Hundreds
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 3 Answer Key Represent Numbers in Different Ways
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 4 Answer Key Combine Ones, Tens, and Hundreds
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 5 Answer Key Compare Numbers within 200
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 6 Answer Key Explore 2-Digit Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 7 Answer Key Addition – Show All Totals Method
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 8 Answer Key Addition – New Groups Below Method
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 9 Answer Key Practice Addition with Sums over 100
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 10 Answer Key Choose an Addition Method
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 11 Answer Key Buy with Pennies and Dimes
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 12 Answer Key Pennies, Nickels, and Dimes
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 13 Answer Key Fluency: Addition Within 100
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 14 Answer Key Add Three or Four 2-Digit Addends
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 2 Lesson 15 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 3 Length and Shapes
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Answer Key Measure Length
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 3 Lesson 2 Answer Key Recognize and Draw Shapes
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 3 Lesson 3 Answer Key Estimate and Measure
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 3 Lesson 4 Answer Key Draw, Estimate, and Measure
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 3 Lesson 5 Answer Key Draw Using Faces
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 3 Lesson 6 Answer Key Estimate and Measure with Centimeters
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 3 Lesson 7 Answer Key Estimate and Measure with Inches
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 3 Lesson 8 Answer Key Measure for and Make Line Plots
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 3 Lesson 9 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Grade 2 Homework and Remembering Volume 3 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade 2 Volume 2 Answer Key
Unit 4 Subtract 2-Digit Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 1 Answer Key Explore Quarters
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 2 Answer Key Explore Dollars
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 3 Answer Key Addends and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 4 Answer Key Subtraction Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 5 Answer Key Two Methods of Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 6 Answer Key Practice and Explain a Method
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 7 Answer Key Subtract from 200
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 8 Answer Key Ungroup from the Left or from the Right
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 9 Answer Key Zero in the Ones or Tens Place
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 10 Answer Key Model Subtraction with Money
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 11 Answer Key Fluency: Subtraction Within 100
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 12 Answer Key Word Problems with Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 13 Answer Key Equations with Greater Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 14 Answer Key Practice Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 15 Answer Key Buy and Sell with One Dollar
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 16 Answer Key Word Problems with Unknown Addends
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 17 Answer Key More Word Problems with Unknown Addends
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 18 Answer Key Start Unknown Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 19 Answer Key Compare Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 20 Answer Key Mixed Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 21 Answer Key Two-Step Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 22 Answer Key More Two-Step Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 4 Lesson 23 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 5 Time, Graphs, and Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 5 Lesson 1 Answer Key Hours and A.M. or P.M
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 5 Lesson 2 Answer Key Hours and Minutes
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 5 Lesson 3 Answer Key Discuss Picture Graphs
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 5 Lesson 4 Answer Key Read Picture Graphs
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 5 Lesson 5 Answer Key Introduce Bar Graphs
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 5 Lesson 6 Answer Key Read Bar Graphs
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 5 Lesson 7 Answer Key Solve Problems Using a Bar Graph
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 5 Lesson 8 Answer Key Collect and Graph Data
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 5 Lesson 9 Answer Key Make Graphs and Interpret Data
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 5 Lesson 10 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
3-Digit Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 1 Answer Key Count Numbers to 1,000
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 2 Answer Key Place Value
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 3 Answer Key Compare Numbers Within 999
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 4 Answer Key Count by Ones and by Tens
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 5 Answer Key Add Ones, Tens, and Hundreds
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 6 Answer Key 3-Digit Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 7 Answer Key Discuss 3-Digit Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 8 Answer Key Word Problems: Unknown Addends
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 9 Answer Key Subtract from Hundreds Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 10 Answer Key Subtract from Numbers with Zeros
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 11 Answer Key Subtract from Any 3-Digit Number
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 12 Answer Key Practice Ungrouping
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 13 Answer Key Relationships Between Addition and Subtraction Methods
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 14 Answer Key Mixed Addition and Subtraction Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 6 Lesson 15 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 7 Arrays, Equal Shares, and Adding or Subtracting
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 7 Lesson 1 Answer Key Arrays, Partitioned Rectangles, and Equal Shares
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 7 Lesson 2 Answer Key Find Equal Shares
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 7 Lesson 3 Answer Key Length Word Problems and Number Line Diagrams
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 7 Lesson 4 Answer Key Add Three and Four Lengths
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 7 Lesson 5 Answer Key More Length Word Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 2 Unit 7 Lesson 6 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Common Core Grade 1 Homework and Remembering Answer Key
Math Expressions Grade 1 Homework and Remembering Volume 1 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade 1 Volume 1 Answer Key
Unit 1 Partners and Number Patterns Through 10
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 1 Lesson 1 Answer Key Discuss Numbers 1 – 10
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 1 Lesson 2 Answer Key Visualize Numbers as a 5-Group and Ones
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 1 Lesson 3 Answer Key Partners of 2 Through 5
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 1 Lesson 4 Answer Key Partners of 6
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 1 Lesson 5 Answer Key Partners of 7
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 1 Lesson 6 Answer Key Partners of 8
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 1 Lesson 7 Answer Key Partners of 9
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 1 Lesson 8 Answer Key Partners of 10
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 1 Lesson 9 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 2 Addition and Subtraction Strategies
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 1 Answer Key Represent Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 2 Answer Key Addition with Circle Drawings
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 3 Answer Key Addition Equations
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 4 Answer Key Addition Equations and Stories
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 5 Answer Key Explore Solution Methods
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 6 Answer Key Addition Strategies: Counting On
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 7 Answer Key Count On from the Greater Number
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 8 Answer Key Addition Game: Unknown Totals
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 9 Answer Key Practice Counting On
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 10 Answer Key Represent Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 11 Answer Key Subtraction with Drawings and Equations
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 12 Answer Key Practice with Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 13 Answer Key Generate Subtraction Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 14 Answer Key Relate Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 15 Answer Key Mixed Practice with Equations
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 2 Lesson 16 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 3 Unknown Numbers in Addition and Subtraction
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Answer Key Explore Unknowns
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 2 Answer Key Problems with Unknown Partners
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 3 Answer Key Solve Equations with Unknown Partners
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 4 Answer Key Addition Game: Unknown Partners
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 5 Answer Key Practice with Unknown Partners
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 6 Answer Key Subtraction Strategies
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 7 Answer Key Subtraction Stories and Games
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 8 Answer Key Practice with Subtraction Stories
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 9 Answer Key Relate Addition and Subtraction Situations
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 10 Answer Key Solve Mixed Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 11 Answer Key Practice with Mixed Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 3 Lesson 12 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 4 Place Value Concepts
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 1 Answer Key Introduction to Tens Groupings
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 2 Answer Key Explore Teen Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 3 Answer Key Represent and Compare Teen Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 4 Answer Key Visualize Teen Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 5 Answer Key Teen Addition Strategies
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 6 Answer Key Investigate Doubles
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 7 Answer Key Understand Tens and Ones
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 8 Answer Key Integrate Tens and Ones
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 9 Answer Key Practice Grouping Ones into Tens
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 10 Answer Key Add with Groups of Ten
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 11 Answer Key Practice with Tens and Ones
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 12 Answer Key Use Place Value to Compare Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 13 Answer Key Add Tens or Ones
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 14 Answer Key Mixed Addition with Tens and Ones
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 15 Answer Key Counting On Strategy: 2-Digit Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 16 Answer Key Practice with 2-Digit Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 17 Answer Key 2-Digit Addition Games
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 4 Lesson 18 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Grade 1 Homework and Remembering Volume 3 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade 1 Volume 2 Answer Key
Unit 5 Place Value Situations
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 5 Lesson 1 Answer Key Unknown Partners with Teen Totals
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 5 Lesson 2 Answer Key Subtraction with Teen Numbers
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 5 Lesson 3 Answer Key Mixed Practice with Teen Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 5 Lesson 4 Answer Key Small Group Practice with Teen Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 5 Lesson 5 Answer Key Teen Problems with Various Unknowns
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 5 Lesson 6 Answer Key Problems with Three Addends
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 5 Lesson 7 Answer Key Count with Groups of 10
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 5 Lesson 8 Answer Key Numbers Through 120
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 5 Lesson 9 Answer Key Add and Subtract Tens
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 5 Lesson 10 Answer Key Add and Subtract Multiples of 10
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 5 Lesson 11 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 6 Comparisons and Data
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 6 Lesson 1 Answer Key Explore Representing Data
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 6 Lesson 2 Answer Key Organize Categorical Data
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 6 Lesson 3 Answer Key Use Stair Steps to Represent Data
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 6 Lesson 4 Answer Key Data Sets with Three Categories
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 6 Lesson 5 Answer Key Data Collecting
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 6 Lesson 6 Answer Key Introduce Comparison Bars
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 6 Lesson 7 Answer Key Comparison Bars and Comparing Language
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 6 Lesson 8 Answer Key Solve Compare Problems
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 6 Lesson 9 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 7 Geometry, Measurement, and Equal Shares
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 1 Answer Key Introduction to Time
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 2 Answer Key Tell and Write Time in Hours
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 3 Answer Key Time in Our Day
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 4 Answer Key Tell and Write Time in Half-Hours
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 5 Answer Key Practice Telling and Writing Time
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 6 Answer Key Squares and Other Rectangles
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 7 Answer Key Triangles and Circles
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 8 Answer Key Equal Shares
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 9 Answer Key Compose 2-Dimensional Shapes
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 10 Answer Key 3-Dimensional Shapes
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 11 Answer Key Compose 3-Dimensional Shapes
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 12 Answer Key Order by Length
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 13 Answer Key Measure with Length Units
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 7 Lesson 14 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Unit 8 Two-Digit Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 8 Lesson 1 Answer Key Explore 2-Digit Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 8 Lesson 2 Answer Key Methods of 2-Digit Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 8 Lesson 3 Answer Key Addition of Tens and Ones
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 8 Lesson 4 Answer Key Discuss Solution Methods
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 8 Lesson 5 Answer Key Practice 2-Digit Addition
- Math Expressions Grade 1 Unit 8 Lesson 6 Answer Key Focus on Mathematical Practices
Math Expressions Common Core Kindergarten Homework and Remembering Answer Key
Math Expressions Kindergarten Homework and Remembering Volume 1 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade K Volume 1 Answer Key
- Math Expressions Grade K Unit 1 Answer Key Understand Numbers 1 – 10
- Math Expressions Grade K Unit 2 Answer Key 5-Groups in Numbers 6 – 10
- Math Expressions Grade K Unit 3 Answer Key Teen Numbers as Tens and Ones
Math Expressions Kindergarten Homework and Remembering Volume 3 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade K Volume 2 Answer Key
- Math Expressions Grade K Unit 4 Answer Key Partners, Problem Drawings, and Tens
- Math Expressions Grade K Unit 5 Answer Key Consolidation of Concepts

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 5 best homework help websites (free and paid).
Other High School , General Education

Listen: we know homework isn’t fun, but it is a good way to reinforce the ideas and concepts you’ve learned in class. But what if you’re really struggling with your homework assignments?
If you’ve looked online for a little extra help with your take-home assignments, you’ve probably stumbled across websites claiming to provide the homework help and answers students need to succeed . But can homework help sites really make a difference? And if so, which are the best homework help websites you can use?
Below, we answer these questions and more about homework help websites–free and paid. We’ll go over:
- The basics of homework help websites
- The cost of homework help websites
- The five best homework websites out there
- The pros and cons of using these websites for homework help
- The line between “learning” and “cheating” when using online homework help
- Tips for getting the most out of a homework help website
So let’s get started!

The Basics About Homework Help Websites–Free and Paid
Homework help websites are designed to help you complete your homework assignments, plain and simple.
What Makes a Homework Help Site Worth Using
Most of the best sites allow users to ask questions and then provide an answer (or multiple possible answers) and explanation in seconds. In some instances, you can even send a photo of a particular assignment or problem instead of typing the whole thing out!
Homework help sites also offer more than just help answering homework questions. Common services provided are Q&A with experts, educational videos, lectures, practice tests and quizzes, learning modules, math solving tools, and proofreading help. Homework help sites can also provide textbook solutions (i.e. answers to problems in tons of different textbooks your school might be using), one-on-one tutoring, and peer-to-peer platforms that allow you to discuss subjects you’re learning about with your fellow students.
And best of all, nearly all of them offer their services 24/7, including tutoring!
What You Should Should Look Out For
When it comes to homework help, there are lots–and we mean lots –of scam sites out there willing to prey on desperate students. Before you sign up for any service, make sure you read reviews to ensure you’re working with a legitimate company.
A word to the wise: the more a company advertises help that veers into the territory of cheating, the more likely it is to be a scam. The best homework help websites are going to help you learn the concepts you’ll need to successfully complete your homework on your own. (We’ll go over the difference between “homework help” and “cheating” a little later!)

You don't need a golden piggy bank to use homework help websites. Some provide low or no cost help for students like you!
How Expensive Are the Best Homework Help Websites?
First of all, just because a homework help site costs money doesn’t mean it’s a good service. Likewise, just because a homework help website is free doesn’t mean the help isn’t high quality. To find the best websites, you have to take a close look at the quality and types of information they provide!
When it comes to paid homework help services, the prices vary pretty widely depending on the amount of services you want to subscribe to. Subscriptions can cost anywhere from $2 to $150 dollars per month, with the most expensive services offering several hours of one-on-one tutoring with a subject expert per month.
The 5 Best Homework Help Websites
So, what is the best homework help website you can use? The answer is that it depends on what you need help with.
The best homework help websites are the ones that are reliable and help you learn the material. They don’t just provide answers to homework questions–they actually help you learn the material.
That’s why we’ve broken down our favorite websites into categories based on who they’re best for . For instance, the best website for people struggling with math might not work for someone who needs a little extra help with science, and vice versa.
Keep reading to find the best homework help website for you!
Best Free Homework Help Site: Khan Academy
- Price: Free!
- Best for: Practicing tough material
Not only is Khan Academy free, but it’s full of information and can be personalized to suit your needs. When you set up your account , you choose which courses you need to study, and Khan Academy sets up a personal dashboard of instructional videos, practice exercises, and quizzes –with both correct and incorrect answer explanations–so you can learn at your own pace.
As an added bonus, it covers more course topics than many other homework help sites, including several AP classes.
Runner Up: Brainly.com offers a free service that allows you to type in questions and get answers and explanations from experts. The downside is that you’re limited to two answers per question and have to watch ads.
Best Paid Homework Help Site: Chegg
- Price: $14.95 to $19.95 per month
- Best for: 24/7 homework assistance
This service has three main parts . The first is Chegg Study, which includes textbook solutions, Q&A with subject experts, flashcards, video explanations, a math solver, and writing help. The resources are thorough, and reviewers state that Chegg answers homework questions quickly and accurately no matter when you submit them.
Chegg also offers textbook rentals for students who need access to textbooks outside of their classroom. Finally, Chegg offers Internship and Career Advice for students who are preparing to graduate and may need a little extra help with the transition out of high school.
Another great feature Chegg provides is a selection of free articles geared towards helping with general life skills, like coping with stress and saving money. Chegg’s learning modules are comprehensive, and they feature solutions to the problems in tons of different textbooks in a wide variety of subjects.
Runner Up: Bartleby offers basically the same services as Chegg for $14.99 per month. The reason it didn’t rank as the best is based on customer reviews that say user questions aren’t answered quite as quickly on this site as on Chegg. Otherwise, this is also a solid choice!

Best Site for Math Homework Help: Photomath
- Price: Free (or $59.99 per year for premium services)
- Best for: Explaining solutions to math problems
This site allows you to t ake a picture of a math problem, and instantly pulls up a step-by-step solution, as well as a detailed explanation of the concept. Photomath also includes animated videos that break down mathematical concepts to help you better understand and remember them.
The basic service is free, but for an additional fee you can get extra study tools and learn additional strategies for solving common math problems.
Runner Up: KhanAcademy offers in-depth tutorials that cover complex math topics for free, but you won’t get the same tailored help (and answers!) that Photomath offers.
Best Site for English Homework Help: Princeton Review Academic Tutoring
- Price: $40 to $153 per month, depending on how many hours of tutoring you want
- Best for: Comprehensive and personalized reading and writing help
While sites like Grammarly and Sparknotes help you by either proofreading what you write via an algorithm or providing book summaries, Princeton Review’s tutors provide in-depth help with vocabulary, literature, essay writing and development, proofreading, and reading comprehension. And unlike other services, you’ll have the chance to work with a real person to get help.
The best part is that you can get on-demand English (and ESL) tutoring from experts 24/7. That means you can get help whenever you need it, even if you’re pulling an all-nighter!
This is by far the most expensive homework site on this list, so you’ll need to really think about what you need out of a homework help website before you commit. One added benefit is that the subscription covers over 80 other subjects, including AP classes, which can make it a good value if you need lots of help!

Best Site for STEM Homework Help: Studypool
- Best for: Science homework help
- Price: Varies; you’ll pay for each question you submit
When it comes to science homework help, there aren’t a ton of great resources out there. The best of the bunch is Studypool, and while it has great reviews, there are some downsides as well.
Let’s start with the good stuff. Studypool offers an interesting twist on the homework help formula. After you create a free account, you can submit your homework help questions, and tutors will submit bids to answer your questions. You’ll be able to select the tutor–and price point–that works for you, then you’ll pay to have your homework question answered. You can also pay a small fee to access notes, lectures, and other documents that top tutors have uploaded.
The downside to Studypool is that the pricing is not transparent . There’s no way to plan for how much your homework help will cost, especially if you have lots of questions! Additionally, it’s not clear how tutors are selected, so you’ll need to be cautious when you choose who you’d like to answer your homework questions.

What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Homework Help Sites?
Homework help websites can be a great resource if you’re struggling in a subject, or even if you just want to make sure that you’re really learning and understanding topics and ideas that you’re interested in. But, there are some possible drawbacks if you don’t use these sites responsibly.
We’ll go over the good–and the not-so-good–aspects of getting online homework help below.
3 Pros of Using Homework Help Websites
First, let’s take a look at the benefits.
#1: Better Grades Beyond Homework
This is a big one! Getting outside help with your studies can improve your understanding of concepts that you’re learning, which translates into better grades when you take tests or write essays.
Remember: homework is designed to help reinforce the concepts you learned in class. If you just get easy answers without learning the material behind the problems, you may not have the tools you need to be successful on your class exams…or even standardized tests you’ll need to take for college.
#2: Convenience
One of the main reasons that online homework help is appealing is because it’s flexible and convenient. You don’t have to go to a specific tutoring center while they’re open or stay after school to speak with your teacher. Instead, you can access helpful resources wherever you can access the internet, whenever you need them.
This is especially true if you tend to study at off hours because of your extracurriculars, work schedule, or family obligations. Sites that offer 24/7 tutoring can give you the extra help you need if you can’t access the free resources that are available at your school.
#3: Variety
Not everyone learns the same way. Maybe you’re more of a visual learner, but your teacher mostly does lectures. Or maybe you learn best by listening and taking notes, but you’re expected to learn something just from reading the textbook .
One of the best things about online homework help is that it comes in a variety of forms. The best homework help sites offer resources for all types of learners, including videos, practice activities, and even one-on-one discussions with real-life experts.
This variety can also be a good thing if you just don’t really resonate with the way a concept is being explained (looking at you, math textbooks!).

Not so fast. There are cons to homework help websites, too. Get to know them below!
3 Cons of Using Homework Help Websites
Now, let’s take a look at the drawbacks of online homework help.
#1: Unreliable Info
This can be a real problem. In addition to all the really good homework help sites, there are a whole lot of disreputable or unreliable sites out there. The fact of the matter is that some homework help sites don’t necessarily hire people who are experts in the subjects they’re talking about. In those cases, you may not be getting the accurate, up-to-date, and thorough information you need.
Additionally, even the great sites may not be able to answer all of your homework questions. This is especially true if the site uses an algorithm or chatbot to help students…or if you’re enrolled in an advanced or college-level course. In these cases, working with your teacher or school-provided tutors are probably your best option.
#2: No Clarification
This depends on the service you use, of course. But the majority of them provide free or low-cost help through pre-recorded videos. Watching videos or reading info online can definitely help you with your homework… but you can’t ask questions or get immediate feedback if you need it .
#3: Potential For Scamming
Like we mentioned earlier, there are a lot of homework help websites out there, and lots of them are scams. The review comments we read covered everything from outdated or wrong information, to misleading claims about the help provided, to not allowing people to cancel their service after signing up.
No matter which site you choose to use, make sure you research and read reviews before you sign up–especially if it’s a paid service!

When Does “Help” Become “Cheating”?
Admittedly, whether using homework help websites constitutes cheating is a bit of a grey area. For instance, is it “help” when a friend reads your essay for history class and corrects your grammar, or is it “cheating”? The truth is, not everyone agrees on when “help” crosses the line into “cheating .” When in doubt, it can be a good idea to check with your teacher to see what they think about a particular type of help you want to get.
That said, a general rule of thumb to keep in mind is to make sure that the assignment you turn in for credit is authentically yours . It needs to demonstrate your own thoughts and your own current abilities. Remember: the point of every homework assignment is to 1) help you learn something, and 2) show what you’ve learned.
So if a service answers questions or writes essays for you, there’s a good chance using it constitutes cheating.
Here’s an example that might help clarify the difference for you. Brainstorming essay ideas with others or looking online for inspiration is “help” as long as you write the essay yourself. Having someone read it and give you feedback about what you need to change is also help, provided you’re the one that makes the changes later.
But copying all or part of an essay you find online or having someone write (or rewrite) the whole thing for you would be “cheating.” The same is true for other subjects. Ultimately, if you’re not generating your own work or your own answers, it’s probably cheating.

5 Tips for Finding the Best Homework Help Websites for You
Now that you know some of our favorite homework help websites, free and paid, you can start doing some additional research on your own to decide which services might work best for you! Here are some top tips for choosing a homework help website.
Tip 1: Decide How You Learn Best
Before you decide which site or sites you’re going to use for homework help, y ou should figure out what kind of learning style works for you the most. Are you a visual learner? Then choose a site that uses lots of videos to help explain concepts. If you know you learn best by actually doing tasks, choose a site that provides lots of practice exercises.
Tip 2: Determine Which Subjects You Need Help With
Just because a homework help site is good overall doesn’t mean that it’s equally good for every subject. If you only need help in math, choose a site that specializes in that area. But if history is where you’re struggling, a site that specializes in math won’t be much help. So make sure to choose a site that you know provides high-quality help in the areas you need it most.

Tip 3: Decide How Much One-On-One Help You Need
This is really about cost-effectiveness. If you learn well on your own by reading and watching videos, a free site like Khan Academy is a good choice. But if you need actual tutoring, or to be able to ask questions and get personalized answers from experts, a paid site that provides that kind of service may be a better option.
Tip 4: Set a Budget
If you decide you want to go with a paid homework help website, set a budget first . The prices for sites vary wildly, and the cost to use them can add up quick.
Tip 5: Read the Reviews
Finally, it’s always a good idea to read actual reviews written by the people using these homework sites. You’ll learn the good, the bad, and the ugly of what the users’ experiences have been. This is especially true if you intend to subscribe to a paid service. You’ll want to make sure that users think it’s worth the price overall!

What’s Next?
If you want to get good grades on your homework, it’s a good idea to learn how to tackle it strategically. Our expert tips will help you get the most out of each assignment…and boost your grades in the process.
Doing well on homework assignments is just one part of getting good grades. We’ll teach you everything you need to know about getting great grades in high school in this article.
Of course, test grades can make or break your GPA, too. Here are 17 expert tips that’ll help you get the most out of your study prep before you take an exam.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
5.1 Quadratic Functions
The path passes through the origin and has vertex at ( − 4 , 7 ) , ( − 4 , 7 ) , so h ( x ) = – 7 16 ( x + 4 ) 2 + 7. h ( x ) = – 7 16 ( x + 4 ) 2 + 7. To make the shot, h ( − 7.5 ) h ( − 7.5 ) would need to be about 4 but h ( – 7.5 ) ≈ 1.64 ; h ( – 7.5 ) ≈ 1.64 ; he doesn’t make it.
g ( x ) = x 2 − 6 x + 13 g ( x ) = x 2 − 6 x + 13 in general form; g ( x ) = ( x − 3 ) 2 + 4 g ( x ) = ( x − 3 ) 2 + 4 in standard form
The domain is all real numbers. The range is f ( x ) ≥ 8 11 , f ( x ) ≥ 8 11 , or [ 8 11 , ∞ ) . [ 8 11 , ∞ ) .
y -intercept at (0, 13), No x - x - intercepts
- ⓐ 3 seconds
- ⓒ 7 seconds
5.2 Power Functions and Polynomial Functions
f ( x ) f ( x ) is a power function because it can be written as f ( x ) = 8 x 5 . f ( x ) = 8 x 5 . The other functions are not power functions.
As x x approaches positive or negative infinity, f ( x ) f ( x ) decreases without bound: as x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ because of the negative coefficient.
The degree is 6. The leading term is − x 6 . − x 6 . The leading coefficient is − 1. − 1.
As x → ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ ; a s x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ . x → ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ ; a s x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ . It has the shape of an even degree power function with a negative coefficient.
The leading term is 0.2 x 3 , 0.2 x 3 , so it is a degree 3 polynomial. As x x approaches positive infinity, f ( x ) f ( x ) increases without bound; as x x approaches negative infinity, f ( x ) f ( x ) decreases without bound.
y -intercept ( 0 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , 0 ) ; x -intercepts ( 0 , 0 ) , ( – 2 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 0 ) , ( – 2 , 0 ) , and ( 5 , 0 ) ( 5 , 0 )
There are at most 12 x - x - intercepts and at most 11 turning points.
The end behavior indicates an odd-degree polynomial function; there are 3 x - x - intercepts and 2 turning points, so the degree is odd and at least 3. Because of the end behavior, we know that the lead coefficient must be negative.
The x - x - intercepts are ( 2 , 0 ) , ( − 1 , 0 ) , ( 2 , 0 ) , ( − 1 , 0 ) , and ( 5 , 0 ) , ( 5 , 0 ) , the y- intercept is ( 0 , 2 ) , ( 0 , 2 ) , and the graph has at most 2 turning points.
5.3 Graphs of Polynomial Functions
y -intercept ( 0 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , 0 ) ; x -intercepts ( 0 , 0 ) , ( – 5 , 0 ) , ( 2 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 0 ) , ( – 5 , 0 ) , ( 2 , 0 ) , and ( 3 , 0 ) ( 3 , 0 )
The graph has a zero of –5 with multiplicity 3, a zero of -1 with multiplicity 2, and a zero of 3 with multiplicity 4.
Because f f is a polynomial function and since f ( 1 ) f ( 1 ) is negative and f ( 2 ) f ( 2 ) is positive, there is at least one real zero between x = 1 x = 1 and x = 2. x = 2.
f ( x ) = − 1 8 ( x − 2 ) 3 ( x + 1 ) 2 ( x − 4 ) f ( x ) = − 1 8 ( x − 2 ) 3 ( x + 1 ) 2 ( x − 4 )
The minimum occurs at approximately the point ( 0 , − 6.5 ) , ( 0 , − 6.5 ) , and the maximum occurs at approximately the point ( 3.5 , 7 ) . ( 3.5 , 7 ) .
5.4 Dividing Polynomials
4 x 2 − 8 x + 15 − 78 4 x + 5 4 x 2 − 8 x + 15 − 78 4 x + 5
3 x 3 − 3 x 2 + 21 x − 150 + 1 , 090 x + 7 3 x 3 − 3 x 2 + 21 x − 150 + 1 , 090 x + 7
3 x 2 − 4 x + 1 3 x 2 − 4 x + 1
5.5 Zeros of Polynomial Functions
f ( − 3 ) = − 412 f ( − 3 ) = − 412
The zeros are 2, –2, and –4.
There are no rational zeros.
The zeros are –4, 1 2 , and 1 . –4, 1 2 , and 1 .
f ( x ) = − 1 2 x 3 + 5 2 x 2 − 2 x + 10 f ( x ) = − 1 2 x 3 + 5 2 x 2 − 2 x + 10
There must be 4, 2, or 0 positive real roots and 0 negative real roots. The graph shows that there are 2 positive real zeros and 0 negative real zeros.
3 meters by 4 meters by 7 meters
5.6 Rational Functions
End behavior: as x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → 0 ; x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → 0 ; Local behavior: as x → 0 , f ( x ) → ∞ x → 0 , f ( x ) → ∞ (there are no x - or y -intercepts)
The function and the asymptotes are shifted 3 units right and 4 units down. As x → 3 , f ( x ) → ∞ , x → 3 , f ( x ) → ∞ , and as x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → − 4. x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → − 4.
The function is f ( x ) = 1 ( x − 3 ) 2 − 4. f ( x ) = 1 ( x − 3 ) 2 − 4.
12 11 12 11
The domain is all real numbers except x = 1 x = 1 and x = 5. x = 5.
Removable discontinuity at x = 5. x = 5. Vertical asymptotes: x = 0 , x = 1. x = 0 , x = 1.
Vertical asymptotes at x = 2 x = 2 and x = – 3 ; x = – 3 ; horizontal asymptote at y = 4. y = 4.
For the transformed reciprocal squared function, we find the rational form. f ( x ) = 1 ( x − 3 ) 2 − 4 = 1 − 4 ( x − 3 ) 2 ( x − 3 ) 2 = 1 − 4 ( x 2 − 6 x + 9 ) ( x − 3 ) ( x − 3 ) = − 4 x 2 + 24 x − 35 x 2 − 6 x + 9 f ( x ) = 1 ( x − 3 ) 2 − 4 = 1 − 4 ( x − 3 ) 2 ( x − 3 ) 2 = 1 − 4 ( x 2 − 6 x + 9 ) ( x − 3 ) ( x − 3 ) = − 4 x 2 + 24 x − 35 x 2 − 6 x + 9
Because the numerator is the same degree as the denominator we know that as x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → − 4 ; so y = – 4 x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → − 4 ; so y = – 4 is the horizontal asymptote. Next, we set the denominator equal to zero, and find that the vertical asymptote is x = 3 , x = 3 , because as x → 3 , f ( x ) → ∞ . x → 3 , f ( x ) → ∞ . We then set the numerator equal to 0 and find the x -intercepts are at ( 2.5 , 0 ) ( 2.5 , 0 ) and ( 3.5 , 0 ) . ( 3.5 , 0 ) . Finally, we evaluate the function at 0 and find the y -intercept to be at ( 0 , − 35 9 ) . ( 0 , − 35 9 ) .
Horizontal asymptote at y = 1 2 . y = 1 2 . Vertical asymptotes at x = 1 and x = 3. x = 1 and x = 3. y -intercept at ( 0 , 4 3 . ) ( 0 , 4 3 . )
x -intercepts at ( 2 , 0 ) and ( – 2 , 0 ) . ( 2 , 0 ) and ( – 2 , 0 ) . ( – 2 , 0 ) ( – 2 , 0 ) is a zero with multiplicity 2, and the graph bounces off the x -axis at this point. ( 2 , 0 ) ( 2 , 0 ) is a single zero and the graph crosses the axis at this point.
5.7 Inverses and Radical Functions
f − 1 ( f ( x ) ) = f − 1 ( x + 5 3 ) = 3 ( x + 5 3 ) − 5 = ( x − 5 ) + 5 = x f − 1 ( f ( x ) ) = f − 1 ( x + 5 3 ) = 3 ( x + 5 3 ) − 5 = ( x − 5 ) + 5 = x and f ( f − 1 ( x ) ) = f ( 3 x − 5 ) = ( 3 x − 5 ) + 5 3 = 3 x 3 = x f ( f − 1 ( x ) ) = f ( 3 x − 5 ) = ( 3 x − 5 ) + 5 3 = 3 x 3 = x
f − 1 ( x ) = x 3 − 4 f − 1 ( x ) = x 3 − 4
f − 1 ( x ) = x − 1 f − 1 ( x ) = x − 1
f − 1 ( x ) = x 2 − 3 2 , x ≥ 0 f − 1 ( x ) = x 2 − 3 2 , x ≥ 0
f − 1 ( x ) = 2 x + 3 x − 1 f − 1 ( x ) = 2 x + 3 x − 1
5.8 Modeling Using Variation
128 3 128 3
x = 20 x = 20
5.1 Section Exercises
When written in that form, the vertex can be easily identified.
If a = 0 a = 0 then the function becomes a linear function.
If possible, we can use factoring. Otherwise, we can use the quadratic formula.
g ( x ) = ( x + 1 ) 2 − 4 , g ( x ) = ( x + 1 ) 2 − 4 , Vertex ( − 1 , − 4 ) ( − 1 , − 4 )
f ( x ) = ( x + 5 2 ) 2 − 33 4 , f ( x ) = ( x + 5 2 ) 2 − 33 4 , Vertex ( − 5 2 , − 33 4 ) ( − 5 2 , − 33 4 )
f ( x ) = 3 ( x − 1 ) 2 − 12 , f ( x ) = 3 ( x − 1 ) 2 − 12 , Vertex ( 1 , − 12 ) ( 1 , − 12 )
f ( x ) = 3 ( x − 5 6 ) 2 − 37 12 , f ( x ) = 3 ( x − 5 6 ) 2 − 37 12 , Vertex ( 5 6 , − 37 12 ) ( 5 6 , − 37 12 )
Minimum is − 17 2 − 17 2 and occurs at 5 2 . 5 2 . Axis of symmetry is x = 5 2 . x = 5 2 .
Minimum is − 17 16 − 17 16 and occurs at − 1 8 . − 1 8 . Axis of symmetry is x = − 1 8 . x = − 1 8 .
Minimum is − 7 2 − 7 2 and occurs at −3. −3. Axis of symmetry is x = −3. x = −3.
Domain is ( − ∞ , ∞ ) . ( − ∞ , ∞ ) . Range is [ 2 , ∞ ) . [ 2 , ∞ ) .
Domain is ( − ∞ , ∞ ) . ( − ∞ , ∞ ) . Range is [ −5 , ∞ ) . [ −5 , ∞ ) .
Domain is ( − ∞ , ∞ ) . ( − ∞ , ∞ ) . Range is [ −12 , ∞ ) . [ −12 , ∞ ) .
f ( x ) = x 2 + 4 x + 3 f ( x ) = x 2 + 4 x + 3
f ( x ) = x 2 - 4 x + 7 f ( x ) = x 2 - 4 x + 7
f ( x ) = - 1 49 x 2 + 6 49 x + 89 49 f ( x ) = - 1 49 x 2 + 6 49 x + 89 49
f ( x ) = x 2 - 2 x + 1 f ( x ) = x 2 - 2 x + 1
Vertex: (3, −10), axis of symmetry: x = 3, intercepts: ( 3 + 10 , 0 ) ( 3 + 10 , 0 ) and ( 3 - 10 , 0 ) ( 3 - 10 , 0 )
Vertex: ( 3 2 , - 12 ) ( 3 2 , - 12 ) , axis of symmetry: x = 3 2 x = 3 2 , intercept: ( 3 + 2 3 2 , 0 ) ( 3 + 2 3 2 , 0 ) and ( 3 - 2 3 2 , 0 ) ( 3 - 2 3 2 , 0 )
f ( x ) = x 2 + 2 x + 3 f ( x ) = x 2 + 2 x + 3
f ( x ) = - 3 x 2 − 6 x − 1 f ( x ) = - 3 x 2 − 6 x − 1
f ( x ) = - 1 4 x 2 − x + 2 f ( x ) = - 1 4 x 2 − x + 2
f ( x ) = x 2 + 2 x + 1 f ( x ) = x 2 + 2 x + 1
f ( x ) = - x 2 + 2 x f ( x ) = - x 2 + 2 x
f ( x ) = 2 x 2 f ( x ) = 2 x 2
The graph is shifted to the right or left (a horizontal shift).
The suspension bridge has 1,000 feet distance from the center.
Domain is ( − ∞ , ∞ ) . ( − ∞ , ∞ ) . Range is ( - ∞ , 2 ] . ( - ∞ , 2 ] .
Domain: ( - ∞ , ∞ ) ( - ∞ , ∞ ) ; range: [ 100 , ∞ ) [ 100 , ∞ )
f ( x ) = 2 x 2 + 2 f ( x ) = 2 x 2 + 2
f ( x ) = - x 2 − 2 f ( x ) = - x 2 − 2
f ( x ) = 3 x 2 + 6 x - 15 f ( x ) = 3 x 2 + 6 x - 15
75 feet by 50 feet
3 and 3; product is 9
The revenue reaches the maximum value when 1800 thousand phones are produced.
2.449 seconds
41 trees per acre
5.2 Section Exercises
The coefficient of the power function is the real number that is multiplied by the variable raised to a power. The degree is the highest power appearing in the function.
As x x decreases without bound, so does f ( x ) . f ( x ) . As x x increases without bound, so does f ( x ) . f ( x ) .
The polynomial function is of even degree and leading coefficient is negative.
Power function
Degree = 2, Coefficient = –2
Degree =4, Coefficient = –2
As x → ∞ x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞
As x → − ∞ x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞
As x → ∞ x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞
y -intercept is ( 0 , 12 ) , ( 0 , 12 ) , t -intercepts are ( 1 , 0 ) ; ( – 2 , 0 ) ; and ( 3 , 0 ) . ( 1 , 0 ) ; ( – 2 , 0 ) ; and ( 3 , 0 ) .
y -intercept is ( 0 , − 16 ) . ( 0 , − 16 ) . x -intercepts are ( 2 , 0 ) ( 2 , 0 ) and ( − 2 , 0 ) . ( − 2 , 0 ) .
y -intercept is ( 0 , 0 ) . ( 0 , 0 ) . x -intercepts are ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 4 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 4 , 0 ) , and ( − 2 , 0 ) . ( − 2 , 0 ) .
Yes. Number of turning points is 2. Least possible degree is 3.
Yes. Number of turning points is 1. Least possible degree is 2.
Yes. Number of turning points is 0. Least possible degree is 1.
As x → − ∞ x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞
As x → − ∞ x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞
The y - y - intercept is ( 0 , 0 ) . ( 0 , 0 ) . The x - x - intercepts are ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 2 , 0 ) . ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 2 , 0 ) . As x → − ∞ x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞
The y - y - intercept is ( 0 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) . The x - x - intercepts are ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 5 , 0 ) , ( 7 , 0 ) . ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 5 , 0 ) , ( 7 , 0 ) . As x → − ∞ x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞
The y - y - intercept is ( 0 , 0 ) . ( 0 , 0 ) . The x - x - intercept is ( − 4 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 4 , 0 ) . ( − 4 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 4 , 0 ) . A s x → − ∞ A s x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞
The y - y - intercept is ( 0 , − 81 ) . ( 0 , − 81 ) . The x - x - intercept are ( 3 , 0 ) , ( − 3 , 0 ) . ( 3 , 0 ) , ( − 3 , 0 ) . As x → − ∞ x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞
The y - y - intercept is ( 0 , 0 ) . ( 0 , 0 ) . The x - x - intercepts are ( − 3 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 5 , 0 ) . ( − 3 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 5 , 0 ) . As x → − ∞ x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞
f ( x ) = x 2 − 4 f ( x ) = x 2 − 4
f ( x ) = x 3 − 4 x 2 + 4 x f ( x ) = x 3 − 4 x 2 + 4 x
f ( x ) = x 4 + 1 f ( x ) = x 4 + 1
V ( m ) = 8 m 3 + 36 m 2 + 54 m + 27 V ( m ) = 8 m 3 + 36 m 2 + 54 m + 27
V ( x ) = 4 x 3 − 32 x 2 + 64 x V ( x ) = 4 x 3 − 32 x 2 + 64 x
5.3 Section Exercises
The x - x - intercept is where the graph of the function crosses the x - x - axis, and the zero of the function is the input value for which f ( x ) = 0. f ( x ) = 0.
If we evaluate the function at a a and at b b and the sign of the function value changes, then we know a zero exists between a a and b . b .
There will be a factor raised to an even power.
( − 2 , 0 ) , ( 3 , 0 ) , ( − 5 , 0 ) ( − 2 , 0 ) , ( 3 , 0 ) , ( − 5 , 0 )
( 3 , 0 ) , ( − 1 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 0 ) ( 3 , 0 ) , ( − 1 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 0 )
( 0 , 0 ) , ( − 5 , 0 ) , ( 2 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) , ( − 5 , 0 ) , ( 2 , 0 )
( 0 , 0 ) , ( − 5 , 0 ) , ( 4 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) , ( − 5 , 0 ) , ( 4 , 0 )
( 2 , 0 ) , ( − 2 , 0 ) , ( − 1 , 0 ) ( 2 , 0 ) , ( − 2 , 0 ) , ( − 1 , 0 )
( − 2 , 0 ) , ( 2 , 0 ) , ( 1 2 , 0 ) ( − 2 , 0 ) , ( 2 , 0 ) , ( 1 2 , 0 )
( 1 , 0 ) , ( − 1 , 0 ) ( 1 , 0 ) , ( − 1 , 0 )
( 0 , 0 ) , ( 3 , 0 ) , ( − 3 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 3 , 0 ) , ( − 3 , 0 )
( 0 , 0 ) , ( 1 , 0 ) , ( − 1 , 0 ) , ( 2 , 0 ) , ( − 2 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) , ( 1 , 0 ) , ( − 1 , 0 ) , ( 2 , 0 ) , ( − 2 , 0 )
f ( 2 ) = – 10 f ( 2 ) = – 10 and f ( 4 ) = 28. f ( 4 ) = 28. Sign change confirms.
f ( 1 ) = 3 f ( 1 ) = 3 and f ( 3 ) = – 77. f ( 3 ) = – 77. Sign change confirms.
f ( 0.01 ) = 1.000001 f ( 0.01 ) = 1.000001 and f ( 0.1 ) = – 7.999. f ( 0.1 ) = – 7.999. Sign change confirms.
0 with multiplicity 2, − 3 2 − 3 2 with multiplicity 5, 4 with multiplicity 2
0 with multiplicity 2, –2 with multiplicity 2
− 2 3 − 2 3 with multiplicity 5, 5 with multiplicity 2
0 with multiplicity 4, 2 with multiplicity 1, −1 with multiplicity 1
3 2 3 2 with multiplicity 2, 0 with multiplicity 3
0 with multiplicity 6 , 2 3 with multiplicity 2 0 with multiplicity 6 , 2 3 with multiplicity 2
x -intercepts, ( 1, 0 ) ( 1, 0 ) with multiplicity 2, ( – 4 , 0 ) ( – 4 , 0 ) with multiplicity 1, y - y - intercept ( 0 , 4 ). ( 0 , 4 ). As x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ . x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ .
x -intercepts ( 3 , 0 ) ( 3 , 0 ) with multiplicity 3, ( 2 , 0 ) ( 2 , 0 ) with multiplicity 2, y - y - intercept ( 0 , – 108 ) . ( 0 , – 108 ) . As x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ . x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ .
x -intercepts ( 0 , 0 ) , ( – 2 , 0 ) , ( 4 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) , ( – 2 , 0 ) , ( 4 , 0 ) with multiplicity 1, y - y - intercept ( 0 , 0 ) . ( 0 , 0 ) . As x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ . x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ .
f ( x ) = − 2 9 ( x − 3 ) ( x + 1 ) ( x + 3 ) f ( x ) = − 2 9 ( x − 3 ) ( x + 1 ) ( x + 3 )
f ( x ) = 1 4 ( x + 2 ) 2 ( x − 3 ) f ( x ) = 1 4 ( x + 2 ) 2 ( x − 3 )
–4, –2, 1, 3 with multiplicity 1
–2, 3 each with multiplicity 2
f ( x ) = − 2 3 ( x + 2 ) ( x − 1 ) ( x − 3 ) f ( x ) = − 2 3 ( x + 2 ) ( x − 1 ) ( x − 3 )
f ( x ) = 1 3 ( x − 3 ) 2 ( x − 1 ) 2 ( x + 3 ) f ( x ) = 1 3 ( x − 3 ) 2 ( x − 1 ) 2 ( x + 3 )
f ( x ) = −15 ( x − 1 ) 2 ( x − 3 ) 3 f ( x ) = −15 ( x − 1 ) 2 ( x − 3 ) 3
f ( x ) = − 2 ( x + 3 ) ( x + 2 ) ( x − 1 ) f ( x ) = − 2 ( x + 3 ) ( x + 2 ) ( x − 1 )
f ( x ) = − 3 2 ( 2 x − 1 ) 2 ( x − 6 ) ( x + 2 ) f ( x ) = − 3 2 ( 2 x − 1 ) 2 ( x − 6 ) ( x + 2 )
local max ( – .58, – .62 ) , ( – .58, – .62 ) , local min ( .58, –1 .38 ) ( .58, –1 .38 )
global min ( – .63, – .47 ) ( – .63, – .47 )
global min ( .75, .89) ( .75, .89)
f ( x ) = ( x − 500 ) 2 ( x + 200 ) f ( x ) = ( x − 500 ) 2 ( x + 200 )
f ( x ) = 4 x 3 − 36 x 2 + 80 x f ( x ) = 4 x 3 − 36 x 2 + 80 x
f ( x ) = 4 x 3 − 36 x 2 + 60 x + 100 f ( x ) = 4 x 3 − 36 x 2 + 60 x + 100
f ( x ) = 9 π ( x 3 + 5 x 2 + 8 x + 4 ) f ( x ) = 9 π ( x 3 + 5 x 2 + 8 x + 4 )
5.4 Section Exercises
The binomial is a factor of the polynomial.
x + 6 + 5 x - 1 , quotient: x + 6 , remainder: 5 x + 6 + 5 x - 1 , quotient: x + 6 , remainder: 5
3 x + 2 , quotient: 3 x + 2 , remainder: 0 3 x + 2 , quotient: 3 x + 2 , remainder: 0
x − 5 , quotient: x − 5 , remainder: 0 x − 5 , quotient: x − 5 , remainder: 0
2 x − 7 + 16 x + 2 , quotient: 2 x − 7 , remainder: 16 2 x − 7 + 16 x + 2 , quotient: 2 x − 7 , remainder: 16
x − 2 + 6 3 x + 1 , quotient: x − 2 , remainder: 6 x − 2 + 6 3 x + 1 , quotient: x − 2 , remainder: 6
2 x 2 − 3 x + 5 , quotient: 2 x 2 − 3 x + 5 , remainder: 0 2 x 2 − 3 x + 5 , quotient: 2 x 2 − 3 x + 5 , remainder: 0
2 x 2 + 2 x + 1 + 10 x − 4 2 x 2 + 2 x + 1 + 10 x − 4
2 x 2 − 7 x + 1 − 2 2 x + 1 2 x 2 − 7 x + 1 − 2 2 x + 1
3 x 2 − 11 x + 34 − 106 x + 3 3 x 2 − 11 x + 34 − 106 x + 3
x 2 + 5 x + 1 x 2 + 5 x + 1
4 x 2 − 21 x + 84 − 323 x + 4 4 x 2 − 21 x + 84 − 323 x + 4
x 2 − 14 x + 49 x 2 − 14 x + 49
3 x 2 + x + 2 3 x − 1 3 x 2 + x + 2 3 x − 1
x 3 − 3 x + 1 x 3 − 3 x + 1
x 3 − x 2 + 2 x 3 − x 2 + 2
x 3 − 6 x 2 + 12 x − 8 x 3 − 6 x 2 + 12 x − 8
x 3 − 9 x 2 + 27 x − 27 x 3 − 9 x 2 + 27 x − 27
2 x 3 − 2 x + 2 2 x 3 − 2 x + 2
Yes ( x − 2 ) ( 3 x 3 − 5 ) ( x − 2 ) ( 3 x 3 − 5 )
Yes ( x − 2 ) ( 4 x 3 + 8 x 2 + x + 2 ) ( x − 2 ) ( 4 x 3 + 8 x 2 + x + 2 )
( x − 1 ) ( x 2 + 2 x + 4 ) ( x − 1 ) ( x 2 + 2 x + 4 )
( x − 5 ) ( x 2 + x + 1 ) ( x − 5 ) ( x 2 + x + 1 )
Quotient: 4 x 2 + 8 x + 16 , remainder: − 1 Quotient: 4 x 2 + 8 x + 16 , remainder: − 1
Quotient: 3 x 2 + 3 x + 5 , remainder: 0 Quotient: 3 x 2 + 3 x + 5 , remainder: 0
Quotient: x 3 − 2 x 2 + 4 x − 8 , remainder: − 6 Quotient: x 3 − 2 x 2 + 4 x − 8 , remainder: − 6
x 6 − x 5 + x 4 − x 3 + x 2 − x + 1 x 6 − x 5 + x 4 − x 3 + x 2 − x + 1
x 3 − x 2 + x − 1 + 1 x + 1 x 3 − x 2 + x − 1 + 1 x + 1
1 + 1 + i x − i 1 + 1 + i x − i
1 + 1 − i x + i 1 + 1 − i x + i
x 2 − i x − 1 + 1 − i x − i x 2 − i x − 1 + 1 − i x − i
2 x 2 + 3 2 x 2 + 3
2 x + 3 2 x + 3
x + 2 x + 2
x − 3 x − 3
3 x 2 − 2 3 x 2 − 2
5.5 Section Exercises
The theorem can be used to evaluate a polynomial.
Rational zeros can be expressed as fractions whereas real zeros include irrational numbers.
Polynomial functions can have repeated zeros, so the fact that number is a zero doesn’t preclude it being a zero again.
− 106 − 106
− 2 , 1 , 1 2 − 2 , 1 , 1 2
− 5 2 , 6 , − 6 − 5 2 , 6 , − 6
2 , − 4 , − 3 2 2 , − 4 , − 3 2
4 , − 4 , − 5 4 , − 4 , − 5
5 , − 3 , − 1 2 5 , − 3 , − 1 2
1 2 , 1 + 5 2 , 1 − 5 2 1 2 , 1 + 5 2 , 1 − 5 2
2 , 3 , − 1 , − 2 2 , 3 , − 1 , − 2
1 2 , − 1 2 , 2 , − 3 1 2 , − 1 2 , 2 , − 3
− 1 , − 1 , 5 , − 5 − 1 , − 1 , 5 , − 5
− 3 4 , − 1 2 − 3 4 , − 1 2
2 , 3 + 2 i , 3 − 2 i 2 , 3 + 2 i , 3 − 2 i
− 2 3 , 1 + 2 i , 1 − 2 i − 2 3 , 1 + 2 i , 1 − 2 i
− 1 2 , 1 + 4 i , 1 − 4 i − 1 2 , 1 + 4 i , 1 − 4 i
1 positive, 1 negative
3 or 1 positive, 0 negative
0 positive, 3 or 1 negative
2 or 0 positive, 2 or 0 negative
± 5 , ± 1 , ± 5 2 , ± 1 2 ± 5 , ± 1 , ± 5 2 , ± 1 2
± 1 , ± 1 2 , ± 1 3 , ± 1 6 ± 1 , ± 1 2 , ± 1 3 , ± 1 6
1 , 1 2 , − 1 3 1 , 1 2 , − 1 3
2 , 1 4 , − 3 2 2 , 1 4 , − 3 2
f ( x ) = 4 9 ( x 3 + x 2 − x − 1 ) f ( x ) = 4 9 ( x 3 + x 2 − x − 1 )
f ( x ) = − 1 5 ( 4 x 3 − x ) f ( x ) = − 1 5 ( 4 x 3 − x )
8 by 4 by 6 inches
5.5 by 4.5 by 3.5 inches
8 by 5 by 3 inches
Radius = 6 meters, Height = 2 meters
Radius = 2.5 meters, Height = 4.5 meters
5.6 Section Exercises
The rational function will be represented by a quotient of polynomial functions.
The numerator and denominator must have a common factor.
Yes. The numerator of the formula of the functions would have only complex roots and/or factors common to both the numerator and denominator.
All reals x ≠ – 1 , 1 All reals x ≠ – 1 , 1
All reals x ≠ – 1 , – 2 , 1 , 2 All reals x ≠ – 1 , – 2 , 1 , 2
V.A. at x = – 2 5 ; x = – 2 5 ; H.A. at y = 0 ; y = 0 ; Domain is all reals x ≠ – 2 5 x ≠ – 2 5
V.A. at x = 4 , – 9 ; x = 4 , – 9 ; H.A. at y = 0 ; y = 0 ; Domain is all reals x ≠ 4 , – 9 x ≠ 4 , – 9
V.A. at x = 0 , 4 , − 4 ; x = 0 , 4 , − 4 ; H.A. at y = 0 ; y = 0 ; Domain is all reals x ≠ 0 , 4 , – 4 x ≠ 0 , 4 , – 4
V.A. at x = 5 ; x = 5 ; H.A. at y = 0 ; y = 0 ; Domain is all reals x ≠ 5 , − 5 x ≠ 5 , − 5
V.A. at x = 1 3 ; x = 1 3 ; H.A. at y = − 2 3 ; y = − 2 3 ; Domain is all reals x ≠ 1 3 . x ≠ 1 3 .
x -intercepts none, y -intercept ( 0 , 1 4 ) x -intercepts none, y -intercept ( 0 , 1 4 )
Local behavior: x → − 1 2 + , f ( x ) → − ∞ , x → − 1 2 − , f ( x ) → ∞ x → − 1 2 + , f ( x ) → − ∞ , x → − 1 2 − , f ( x ) → ∞
End behavior: x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → 1 2 x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → 1 2
Local behavior: x → 6 + , f ( x ) → − ∞ , x → 6 − , f ( x ) → ∞ , x → 6 + , f ( x ) → − ∞ , x → 6 − , f ( x ) → ∞ , End behavior: x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → − 2 x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → − 2
Local behavior: x → − 1 3 + , f ( x ) → ∞ , x → − 1 3 − , x → − 1 3 + , f ( x ) → ∞ , x → − 1 3 − , f ( x ) → − ∞ , x → 5 2 − , f ( x ) → ∞ , x → 5 2 + , f ( x ) → − ∞ f ( x ) → − ∞ , x → 5 2 − , f ( x ) → ∞ , x → 5 2 + , f ( x ) → − ∞
End behavior: x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → 1 3 x → ± ∞ , f ( x ) → 1 3
y = 2 x + 4 y = 2 x + 4
y = 2 x y = 2 x
V . A . x = 0 , H . A . y = 2 V . A . x = 0 , H . A . y = 2
V . A . x = 2 , H . A . y = 0 V . A . x = 2 , H . A . y = 0
V . A . x = − 4 , H . A . y = 2 ; ( 3 2 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , − 3 4 ) V . A . x = − 4 , H . A . y = 2 ; ( 3 2 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , − 3 4 )
V . A . x = 2 , H . A . y = 0 , ( 0 , 1 ) V . A . x = 2 , H . A . y = 0 , ( 0 , 1 )
V . A . x = − 4 , x = 4 3 , H . A . y = 1 ; ( 5 , 0 ) ; ( − 1 3 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , 5 16 ) V . A . x = − 4 , x = 4 3 , H . A . y = 1 ; ( 5 , 0 ) ; ( − 1 3 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , 5 16 )
V . A . x = − 1 , H . A . y = 1 ; ( − 3 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , 3 ) V . A . x = − 1 , H . A . y = 1 ; ( − 3 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , 3 )
V . A . x = 4 , S . A . y = 2 x + 9 ; ( − 1 , 0 ) ; ( 1 2 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , 1 4 ) V . A . x = 4 , S . A . y = 2 x + 9 ; ( − 1 , 0 ) ; ( 1 2 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , 1 4 )
V . A . x = − 2 , x = 4 , H . A . y = 1 , ( 1 , 0 ) ; ( 5 , 0 ) ; ( − 3 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , − 15 16 ) V . A . x = − 2 , x = 4 , H . A . y = 1 , ( 1 , 0 ) ; ( 5 , 0 ) ; ( − 3 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , − 15 16 )
y = 50 x 2 − x − 2 x 2 − 25 y = 50 x 2 − x − 2 x 2 − 25
y = 7 x 2 + 2 x − 24 x 2 + 9 x + 20 y = 7 x 2 + 2 x − 24 x 2 + 9 x + 20
y = 1 2 x 2 − 4 x + 4 x + 1 y = 1 2 x 2 − 4 x + 4 x + 1
y = 4 x − 3 x 2 − x − 12 y = 4 x − 3 x 2 − x − 12
y = 27 ( x − 2 ) ( x + 3 ) ( x – 3 ) 2 y = 27 ( x − 2 ) ( x + 3 ) ( x – 3 ) 2
y = 1 3 x 2 + x − 6 x − 1 y = 1 3 x 2 + x − 6 x − 1
y = − 6 ( x − 1 ) 2 ( x + 3 ) ( x − 2 ) 2 y = − 6 ( x − 1 ) 2 ( x + 3 ) ( x − 2 ) 2
Vertical asymptote x = 2 , x = 2 , Horizontal asymptote y = 0 y = 0
Vertical asymptote x = − 4 , x = − 4 , Horizontal asymptote y = 2 y = 2
Vertical asymptote x = − 1 , x = − 1 , Horizontal asymptote y = 1 y = 1
( 3 2 , ∞ ) ( 3 2 , ∞ )
( − 2 , 1 ) ∪ ( 4 , ∞ ) ( − 2 , 1 ) ∪ ( 4 , ∞ )
( 2 , 4 ) ( 2 , 4 )
( 2 , 5 ) ( 2 , 5 )
( – 1 , 1 ) ( – 1 , 1 )
C ( t ) = 8 + 2 t 300 + 20 t C ( t ) = 8 + 2 t 300 + 20 t
After about 6.12 hours.
A ( x ) = 50 x 2 + 800 x . A ( x ) = 50 x 2 + 800 x . 2 by 2 by 5 feet.
A ( x ) = π x 2 + 100 x . A ( x ) = π x 2 + 100 x . Radius = 2.52 meters.
5.7 Section Exercises
It can be too difficult or impossible to solve for x x in terms of y . y .
We will need a restriction on the domain of the answer.
f − 1 ( x ) = x + 4 f − 1 ( x ) = x + 4
f − 1 ( x ) = x + 3 − 1 f − 1 ( x ) = x + 3 − 1
f − 1 ( x ) = 12 − x f − 1 ( x ) = 12 − x
f − 1 ( x ) = ± x − 4 2 f − 1 ( x ) = ± x − 4 2
f − 1 ( x ) = x − 1 3 3 f − 1 ( x ) = x − 1 3 3
f − 1 ( x ) = 4 − x 2 3 f − 1 ( x ) = 4 − x 2 3
f −1 ( x ) = 3 − x 2 4 , [ 0 , ∞ ) f −1 ( x ) = 3 − x 2 4 , [ 0 , ∞ )
f −1 ( x ) = ( x - 5 ) 2 + 8 6 f −1 ( x ) = ( x - 5 ) 2 + 8 6
f −1 ( x ) = ( 3 - x ) 2 f −1 ( x ) = ( 3 - x ) 2
f −1 ( x ) = 4 x + 3 x f −1 ( x ) = 4 x + 3 x
f −1 ( x ) = 7 x − 3 1 − x f −1 ( x ) = 7 x − 3 1 − x
f −1 ( x ) = 2 x - 1 5 x + 5 f −1 ( x ) = 2 x - 1 5 x + 5
f −1 ( x ) = x + 3 − 2 f −1 ( x ) = x + 3 − 2
f − 1 ( x ) = x − 2 f − 1 ( x ) = x − 2
f − 1 ( x ) = x − 3 f − 1 ( x ) = x − 3
f − 1 ( x ) = x − 3 3 f − 1 ( x ) = x − 3 3
f − 1 ( x ) = x + 4 - 2 f − 1 ( x ) = x + 4 - 2
[ - 1 , 0 ) ∪ [ 1 , ∞ ) [ - 1 , 0 ) ∪ [ 1 , ∞ )
[ - 3 , 0 ] ∪ ( 4 , ∞ ) [ - 3 , 0 ] ∪ ( 4 , ∞ )
[ - ∞ , - 4 ] ⋅ [ - 3 , 3 ] [ - ∞ , - 4 ] ⋅ [ - 3 , 3 ]
( – 2 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 1 ) , ( 8 , 2 ) ( – 2 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 1 ) , ( 8 , 2 )
( – 13 , – 1 ) , ( – 4 , 0 ) , ( 5 , 1 ) ( – 13 , – 1 ) , ( – 4 , 0 ) , ( 5 , 1 )
f − 1 ( x ) = x − b a 3 f − 1 ( x ) = x − b a 3
f − 1 ( x ) = x 2 - b a f − 1 ( x ) = x 2 - b a
f − 1 ( x ) = c x - b a - x f − 1 ( x ) = c x - b a - x
t ( h ) = 600 - h 16 t ( h ) = 600 - h 16 , 3.54 seconds
r ( A ) = A 4 π , ≈ r ( A ) = A 4 π , ≈ 8.92 in.
l ( T ) = 32.2 ( T 2 π ) , ≈ l ( T ) = 32.2 ( T 2 π ) , ≈ 3.26 ft
r ( A ) = A + 2 π 8 π , r ( A ) = A + 2 π 8 π , -2, 3.99 ft
r ( V ) = V 10 π , r ( V ) = V 10 π , ≈ 5.64 ft
5.8 Section Exercises
The graph will have the appearance of a power function.
No. Multiple variables may jointly vary.
y = 5 x 2 y = 5 x 2
y = 1 1944 x 3 y = 1 1944 x 3
y = 6 x 4 y = 6 x 4
y = 18 x 2 y = 18 x 2
y = 81 x 4 y = 81 x 4
y = 20 x 3 y = 20 x 3
y = 10 x z w y = 10 x z w
y = 10 x z y = 10 x z
y = 4 x z w y = 4 x z w
y = 40 x z w t 2 y = 40 x z w t 2
y = 256 y = 256
y = 6 y = 6
y = 27 y = 27
y = 3 y = 3
y = 18 y = 18
y = 90 y = 90
y = 81 2 y = 81 2
y = 3 4 x 2 y = 3 4 x 2
y = 1 3 x y = 1 3 x
y = 4 x 2 y = 4 x 2
49.75 pounds
33.33 amperes
2.88 inches
Review Exercises
f ( x ) = ( x − 2 ) 2 − 9 vertex ( 2 , –9 ) , intercepts ( 5 , 0 ) ; ( –1 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , –5 ) f ( x ) = ( x − 2 ) 2 − 9 vertex ( 2 , –9 ) , intercepts ( 5 , 0 ) ; ( –1 , 0 ) ; ( 0 , –5 )
f ( x ) = 3 25 ( x + 2 ) 2 + 3 f ( x ) = 3 25 ( x + 2 ) 2 + 3
300 meters by 150 meters, the longer side parallel to river.
Yes, degree = 5, leading coefficient = 4
Yes, degree = 4, leading coefficient = 1
As x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ As x → − ∞ , f ( x ) → − ∞ , as x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞
–3 with multiplicity 2, − 1 2 − 1 2 with multiplicity 1, –1 with multiplicity 3
4 with multiplicity 1
1 2 1 2 with multiplicity 1, 3 with multiplicity 3
x 2 + 4 x 2 + 4 with remainder 12
x 2 − 5 x + 20 − 61 x + 3 x 2 − 5 x + 20 − 61 x + 3
2 x 2 − 2 x − 3 2 x 2 − 2 x − 3 , so factored form is ( x + 4 ) ( 2 x 2 − 2 x − 3 ) ( x + 4 ) ( 2 x 2 − 2 x − 3 )
{ − 2 , 4 , − 1 2 } { − 2 , 4 , − 1 2 }
{ 1 , 3 , 4 , 1 2 } { 1 , 3 , 4 , 1 2 }
0 or 2 positive, 1 negative
Intercepts ( –2 , 0 ) and ( 0 , − 2 5 ) ( –2 , 0 ) and ( 0 , − 2 5 ) , Asymptotes x = 5 x = 5 and y = 1. y = 1.
Intercepts (3, 0), (-3, 0), and ( 0 , 27 2 ) ( 0 , 27 2 ) , Asymptotes x = 1 , x = – 2 , y = 3. x = 1 , x = – 2 , y = 3.
y = x − 2 y = x − 2
f − 1 ( x ) = x + 2 f − 1 ( x ) = x + 2
f − 1 ( x ) = x + 11 − 3 f − 1 ( x ) = x + 11 − 3
f − 1 ( x ) = ( x + 3 ) 2 − 5 4 , x ≥ − 3 f − 1 ( x ) = ( x + 3 ) 2 − 5 4 , x ≥ − 3
y = 64 y = 64
y = 72 y = 72
148.5 pounds
Practice Test
Degree: 5, leading coefficient: −2
As x → −∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ , As x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ As x → −∞ , f ( x ) → ∞ , As x → ∞ , f ( x ) → ∞
f ( x ) = 3 ( x - 2 ) 2 f ( x ) = 3 ( x - 2 ) 2
3 with multiplicity 3, 1 3 1 3 with multiplicity 1, 1 with multiplicity 2
- 1 2 - 1 2 with multiplicity 3, 2 with multiplicity 2
x 3 + 2 x 2 + 7 x + 14 + 26 x - 2 x 3 + 2 x 2 + 7 x + 14 + 26 x - 2
{ –3 , –1 , 3 2 } { –3 , –1 , 3 2 }
1, −2, and − 3 2 3 2 (multiplicity 2)
f ( x ) = - 2 3 ( x - 3 ) 2 ( x - 1 ) ( x + 2 ) f ( x ) = - 2 3 ( x - 3 ) 2 ( x - 1 ) ( x + 2 )
2 or 0 positive, 1 negative
( - 3 , 0 ) ( 1 , 0 ) ( 0 , 3 4 ) ( - 3 , 0 ) ( 1 , 0 ) ( 0 , 3 4 )
f − 1 ( x ) = ( x - 4 ) 2 + 2 , x ≥ 4 f − 1 ( x ) = ( x - 4 ) 2 + 2 , x ≥ 4
f − 1 ( x ) = x + 3 3 x - 2 f − 1 ( x ) = x + 3 3 x - 2
y = 20 y = 20
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/college-algebra/pages/1-introduction-to-prerequisites
- Authors: Jay Abramson
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: College Algebra
- Publication date: Feb 13, 2015
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-algebra/pages/1-introduction-to-prerequisites
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-algebra/pages/chapter-5
© Dec 8, 2021 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- 888-309-8227
- 732-384-0146
New User Registration
Forgot Password
Go Math! 5 Student Edition, Grade: 5 Publisher: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Go math 5 student edition, title : go math 5 student edition, publisher : houghton mifflin harcourt, isbn : 547352042, isbn-13 : 9780547352046, use the table below to find videos, mobile apps, worksheets and lessons that supplement go math 5 student edition., textbook resources.
- Call us toll-free
- FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
- Contact Lumos Learning – Proven Study Programs by Expert Teachers
Follow us: Lumos Learning -->
- 2024 © Lumos Learning
- Privacy Policy - Terms of Service - Disclaimers
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc... Read More
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc., the Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any state of the Union. Neither PARCC, Inc., nor The Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any member state has endorsed this product. No portion of any fees or charges paid for any products or services Lumos Learning offers will be paid or inure to the benefit of PARCC, Inc., or any state of the Union
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not aff... Read More
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC, was not... Read More
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC,was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved... Read More
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the prod... Read More
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved... Read More
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved... Read More
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved... Read More
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved... Read More
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 13 Answer Key
Engage ny eureka math 5th grade module 3 lesson 13 answer key, eureka math grade 5 module 3 lesson 13 problem set answer key.
Question 1. Are the following expressions greater than or less than 1? Circle the correct answer. a. \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{2}{7}\) greater than 1 less than 1
b. \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) greater than 1 less than 1
c. 1\(\frac{1}{4}\) – \(\frac{1}{3}\) greater than 1 less than 1

b. \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) lcm of 8 and 5 is 40. \(\frac{25}{40}\) + \(\frac{24}{40}\) = \(\frac{49}{40}\) = 1\(\frac{9}{40}\)
c. 1\(\frac{1}{4}\) – \(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{5}{4}\) – \(\frac{1}{3}\) lcm of 4 and 3 is 12. \(\frac{15}{12}\) – \(\frac{4}{12}\) = \(\frac{11}{12}\)
d. 3\(\frac{5}{8}\) – 2\(\frac{5}{9}\) = \(\frac{29}{8}\) – \(\frac{23}{9}\) lcm of 8 and 9 is 72 . \(\frac{261}{72}\) – \(\frac{184}{72}\) = \(\frac{77}{72}\) = 1\(\frac{5}{72}\) .
Question 2. Are the following expressions greater than or less than \(\frac{1}{2}\) ? Circle the correct answer. a. \(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{2}{3}\) greater than \(\frac{1}{2}\) less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
b.\(\frac{3}{7}\) – \(\frac{1}{8}\) greater than \(\frac{1}{2}\) less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
c. 1\(\frac{1}{7}\) – \(\frac{7}{8}\) greater than \(\frac{1}{2}\) less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)

b.\(\frac{3}{7}\) – \(\frac{1}{8}\) lcm of 7 and 8 is 56. \(\frac{24}{56}\) – \(\frac{7}{56}\) = \(\frac{17}{56}\) less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
c. 1\(\frac{1}{7}\) – \(\frac{7}{8}\) = \(\frac{8}{7}\) – \(\frac{7}{8}\) lcm of 7 and 8 is 56. \(\frac{64}{56}\) – \(\frac{49}{56}\) = \(\frac{15}{56}\) less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
d. \(\frac{3}{7}\) + \(\frac{2}{6}\) lcm of 7 and 6 is 42. \(\frac{18}{42}\) + \(\frac{14}{42}\) = \(\frac{32}{42}\) = \(\frac{16}{21}\) greater than \(\frac{1}{2}\) .
Question 3. Use > , < , or = to make the following statements true. a. 5\(\frac{2}{3}\) + 3\(\frac{3}{4}\) _______ 8\(\frac{2}{3}\) b. 4\(\frac{5}{8}\) – 3\(\frac{2}{5}\) _______ 1\(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) c. 5\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 1\(\frac{3}{7}\) _______ 6 + \(\frac{13}{14}\) d. 15\(\frac{4}{7}\) – 11\(\frac{2}{5}\) _______ 4\(\frac{4}{7}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) Answer: a. 5\(\frac{2}{3}\) + 3\(\frac{3}{4}\) = 8\(\frac{2}{3}\) b. 4\(\frac{5}{8}\) – 3\(\frac{2}{5}\) < 1\(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) c. 5\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 1\(\frac{3}{7}\) = 6 + \(\frac{13}{14}\) d. 15\(\frac{4}{7}\) – 11\(\frac{2}{5}\) > 4\(\frac{4}{7}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) Explanation : a. 5\(\frac{2}{3}\) + 3\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{17}{3}\) + \(\frac{12}{4}\) lcm of 3 and 4 is 12. \(\frac{68}{12}\) + \(\frac{36}{12}\) = \(\frac{104}{12}\) = \(\frac{26}{3}\) =8\(\frac{2}{3} \)
b. 4\(\frac{5}{8}\) – 3\(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{37}{8}\) – \(\frac{17}{5}\) lcm of 8 and 5 is 40 . \(\frac{185}{40}\) – \(\frac{136}{40}\) = \(\frac{49}{40}\) =1\(\frac{9}{40}\) 1\(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{13}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) lcm of 8 and 5 is 40 . \(\frac{65}{40}\) + \(\frac{16}{5}\) = \(\frac{81}{40}\) = 2\(\frac{1}{40}\)
c. 5\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 1\(\frac{3}{7}\) = \(\frac{11}{2}\) + \(\frac{10}{7}\) lcm of 2 and 7 is 14. \(\frac{77}{14}\) + \(\frac{20}{14}\) = \(\frac{97}{14}\) = 6 \(\frac{13}{14}\) 6 + \(\frac{13}{14}\) =\(\frac{84}{14}\) + \(\frac{13}{14}\) = \(\frac{97}{14}\) = 6 \(\frac{13}{14}\)
d. 15\(\frac{4}{7}\) – 11\(\frac{2}{5}\) =\(\frac{109}{7}\) – \(\frac{57}{5}\) lcm of 7 and 5 is 35 . \(\frac{545}{35}\) – \(\frac{399}{35}\) = \(\frac{944}{35}\) = 26\(\frac{34}{35}\) . 4\(\frac{4}{7}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{32}{7}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) lcm of 7 and 5 is 35 . \(\frac{160}{35}\) + \(\frac{14}{35}\) = \(\frac{174}{35}\)= 4\(\frac{34}{35}\)
Question 4. Is it true that 4\(\frac{3}{5}\) – 3\(\frac{2}{3}\) = 1 + \(\frac{3}{5}\) + \(\frac{2}{3}\)? Prove your answer. Answer: No it is wrong 4\(\frac{3}{5}\) – 3\(\frac{2}{3}\) < 1 + \(\frac{3}{5}\) + \(\frac{2}{3}\) Explanation : 4\(\frac{3}{5}\) – 3\(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{23}{5}\) – \(\frac{11}{3}\) lcm of 5 and 3 is 15 . \(\frac{69}{15}\) – \(\frac{55}{15}\) = \(\frac{14}{15}\)
1 + \(\frac{3}{5}\) + \(\frac{2}{3}\) lcm of 5 and 3 is 15 . \(\frac{15}{15}\) + \(\frac{9}{15}\) + \(\frac{10}{15}\) = latex]\frac{34}{15}[/latex] = 2latex]\frac{4}{15}[/latex] .
Question 5. Jackson needs to be 1\(\frac{3}{4}\) inches taller in order to ride the roller coaster. Since he can’t wait, he puts on a pair of boots that add 1\(\frac{1}{6}\) inches to his height and slips an insole inside to add another \(\frac{1}{8}\) inch to his height. Will this make Jackson appear tall enough to ride the roller coaster? Answer: Fraction of Height required to ride a roller coaster for Jackson = 1\(\frac{3}{4}\) inches. Fraction of his height = 1\(\frac{1}{6}\) inches = \(\frac{7}{6}\) Fraction of his boots length = \(\frac{1}{8}\) inches Total fraction of his height with boots = \(\frac{7}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{8}\) = \(\frac{28}{24}\) + \(\frac{3}{24}\) = \(\frac{31}{24}\) = 1\(\frac{7}{24}\) . 1\(\frac{3}{4}\) = multiply by 6 both numerator and denominator = 1\(\frac{18}{24}\) therefore, 1\(\frac{18}{24}\) > is greater than 1\(\frac{7}{24}\) So, he is not taller enough to ride roller coaster . So, he cant ride the roller coaster .
Question 6. A baker needs 5 lb of butter for a recipe. She found 2 portions that each weigh 1\(\frac{1}{6}\) lb and a portion that weighs 2\(\frac{2}{7}\) lb. Does she have enough butter for her recipe? Answer: Fraction of butter required for a recipe = 5 lb Fraction of 2 portions that weigh = 2 × \(\frac{7}{6}\) lb = \(\frac{7}{3}\) Fraction of portions that weighs = 2\(\frac{2}{7}\) lb. = \(\frac{16}{7}\) lb. Fraction of butter of portions = \(\frac{7}{3}\) + \(\frac{16}{7}\) = \(\frac{49}{21}\) + \(\frac{48}{21}\) = \(\frac{97}{21}\) = 4\(\frac{13}{21}\) Therefore, she doesnot have enough butter for the recipe = 4\(\frac{13}{21}\)
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 13 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Question 1. Circle the correct answer. a. \(\frac{1}{2}\) +\(\frac{5}{12}\) greater than 1 less than 1
b. 2\(\frac{7}{8}\) – 1\(\frac{7}{9}\) greater than 1 less than 1
c. 1\(\frac{1}{12}\) – \(\frac{7}{10}\) greater than \(\frac{1}{2}\) less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
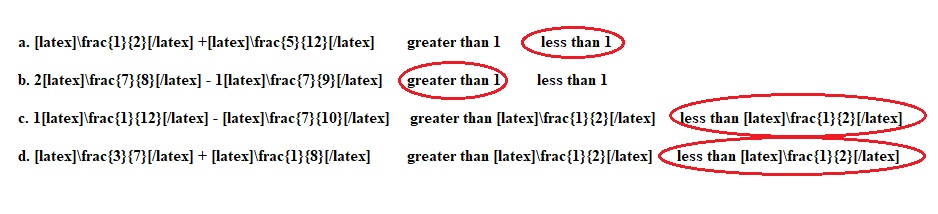
Question 2. Use > , < , or = to make the following statement true. 4\(\frac{4}{5}\) + 3\(\frac{2}{3}\) < 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) Answer: 4\(\frac{4}{5}\) + 3\(\frac{2}{3}\) < 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : 4\(\frac{4}{5}\) + 3\(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{24}{5}\) + \(\frac{11}{3}\) lcm of 5 and 3 is 15 . \(\frac{72}{15}\) + \(\frac{55}{15}\) = \(\frac{127}{15}\) = 8 \(\frac{7}{15}\)
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 13 Homework Answer Key
Question 1. Are the following expressions greater than or less than 1? Circle the correct answer. a. \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{4}{9}\) greater than 1 less than 1
b. \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) greater than 1 less than 1
c. 1\(\frac{1}{5}\) – \(\frac{1}{3}\) greater than 1 less than 1
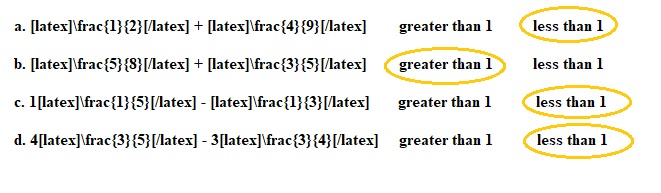
Question 2. Are the following expressions greater than or less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)? Circle the correct answer. a. \(\frac{1}{5}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) greater than \(\frac{1}{2}\) less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
b. \(\frac{6}{7}\) – \(\frac{1}{6}\) greater than \(\frac{1}{2}\) less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
c. 1\(\frac{1}{7}\) – \(\frac{5}{6}\) greater than \(\frac{1}{2}\) less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 3. Use > , < , or = to make the following statements true. a. 5\(\frac{4}{5}\) + 2\(\frac{2}{3}\) _______ 8\(\frac{3}{4}\) b. 3\(\frac{4}{7}\) – 2\(\frac{3}{5}\) _______ 1\(\frac{4}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) c. 4\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 1\(\frac{4}{9}\) _______ 5 + \(\frac{13}{18}\) d. 10\(\frac{3}{8}\) – 7\(\frac{3}{5}\) _______ 3\(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) Answer: a. 5\(\frac{4}{5}\) + 2\(\frac{2}{3}\) < 8\(\frac{3}{4}\) b. 3\(\frac{4}{7}\) – 2\(\frac{3}{5}\) < 1\(\frac{4}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) c. 4\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 1\(\frac{4}{9}\) < 5 + \(\frac{13}{18}\) d. 10\(\frac{3}{8}\) – 7\(\frac{3}{5}\) > 3\(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) Explanation : a. 5\(\frac{4}{5}\) + 2\(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{29}{5}\) + \(\frac{8}{3}\) lcm of 5 and 3 is 15 . \(\frac{57}{15}\) + \(\frac{40}{15}\) = \(\frac{97}{15}\) = 6\(\frac{7}{15}\) .
b. 3\(\frac{4}{7}\) – 2\(\frac{3}{5}\) = \(\frac{25}{7}\) – \(\frac{13}{5}\) . lcm of 7 and 5 is 35 . \(\frac{125}{35}\) – \(\frac{91}{35}\) = \(\frac{34}{35}\) 1\(\frac{4}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) = \(\frac{11}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) lcm of 5 and 7 is 35 . \(\frac{55}{35}\) + \(\frac{21}{35}\) = \(\frac{76}{35}\) = 2 \(\frac{6}{35}\)
c. 4\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 1\(\frac{4}{9}\) = \(\frac{9}{2}\) + \(\frac{13}{9}\) lcm of 2 and 9 is 18 . 4\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 1\(\frac{4}{9}\) 5 + \(\frac{13}{18}\) = \(\frac{90}{18}\) + \(\frac{13}{18}\) = \(\frac{103}{18}\) = 5\(\frac{13}{18}\)
d. 10\(\frac{3}{8}\) – 7\(\frac{3}{5}\) = \(\frac{83}{8}\) – \(\frac{38}{5}\) lcm of 8 and 5 is 40 . \(\frac{415}{40}\) – \(\frac{304}{40}\) = \(\frac{311}{40}\) = 7\(\frac{31}{40}\) 3\(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) = \(\frac{27}{8}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) lcm of 8 and 5 is 40 . \(\frac{135}{40}\) + \(\frac{24}{40}\) = \(\frac{159}{40}\)= 3\(\frac{39}{40}\)
Question 4. Is it true that 5\(\frac{2}{3}\) – 3\(\frac{3}{4}\) = 1 + \(\frac{2}{3}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)? Prove your answer. Answer: It is not true . 5\(\frac{2}{3}\) – 3\(\frac{3}{4}\) < 1 + \(\frac{2}{3}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\) Explanation : 5\(\frac{2}{3}\) – 3\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{17}{3}\) – \(\frac{15}{4}\) lcm of 3 and 4 is 12. \(\frac{68}{12}\) – \(\frac{45}{12}\) = \(\frac{23}{12}\) = 1\(\frac{11}{12}\)
1 + \(\frac{2}{3}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\) lcm of 3 and 4 is 12 . \(\frac{12}{12}\) + \(\frac{8}{12}\) + \(\frac{9}{12}\) = \(\frac{29}{12}\) = 2\(\frac{5}{12}\) .
Question 5. A tree limb hangs 5\(\frac{1}{4}\) feet from a telephone wire. The city trims back the branch before it grows within 2 \(\frac{1}{2}\) feet of the wire. Will the city allow the tree to grow 2\(\frac{3}{4}\) more feet? Answer: Fraction of height at which telephone wire is hung = 5\(\frac{1}{4}\) =\(\frac{21}{4}\) feet Fraction of height city allow the tree to grow = 2\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{11}{4}\) feet . Fraction of height city trims back the branch before it grows = 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{5}{2}\) feet Fraction of height of telephone wire can be hang = \(\frac{21}{4}\) – \(\frac{11}{4}\) = \(\frac{10}{4}\) = \(\frac{5}{2}\) both are equal that means the tree will be trim back .
Question 6. Mr. Kreider wants to paint two doors and several shutters. It takes 2\(\frac{1}{8}\) gallons of paint to coat each door and 1\(\frac{3}{5}\) gallons of paint to coat all of his shutters. If Mr. Kreider buys three 2-gallon cans of paint, does he have enough to complete the job? Answer: Fraction of cost of paint to coat each door = 2\(\frac{1}{8}\) gallons = \(\frac{17}{8}\) Fraction of cost of paint to coat all his shutters = 1\(\frac{3}{5}\) gallons = \(\frac{8}{5}\) Fraction of cost to paint 2 doors and shutters = 2 × \(\frac{17}{8}\) + \(\frac{8}{5}\) = \(\frac{17}{4}\) + \(\frac{8}{5}\) = \(\frac{85}{20}\) + \(\frac{32}{20}\) = \(\frac{117}{20}\) = 5latex]\frac{17}{20}[/latex] Total paint = three 2-gallon cans of paint = 3 × 2 = 6 gallons. Therefore Kreider doesn’t have sufficient amount of paint .
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
MATH 1324 Homework 12 Answers
- Mathematics
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
55 Coast Guard Academy cadets disciplined over homework cheating accusations
FILE - The United States Coast Guard Academy is seen, Sept. 14, 2020, in New London, Conn. Fifty-five U.S. Coast Guard Academy cadets have been disciplined for sharing homework answers in violation of academy policy, Coast Guard officials announced. (AP Photo/Jessica Hill, File)
- Copy Link copied
NEW LONDON, Conn. (AP) — Fifty-five U.S. Coast Guard Academy cadets have been disciplined for sharing homework answers in violation of academy policy, Coast Guard officials announced.
After a series of disciplinary hearings, six of the cadets failed the course and 48 got lowered grades, officials said Wednesday.
The cadets were accused of cheating by sharing answers for two separate homework assignments electronically.
“The U.S. Coast Guard Academy is committed to upholding the highest standards of integrity, honor, and accountability,” said Capt. Edward Hernaez, commandant of the academy. “Misconduct like this undermines trust and those found to have violated our principles were held accountable for their actions.”
The cadets will be provided the opportunity to appeal the disciplinary actions, officials said.
10 Surprising Facts About Earth Day

M ore than 8 billion people inhabit Earth, and soon a springtime holiday will remind them of the need to take care of their home.
Earth Day, which takes place on April 22, dates back to 1970, when U.S.-based organizers were hoping to bring awareness to the environmental degradation they were witnessing across the country. Since then, recognition of the holiday has expanded to more than 190 countries who have added Earth Day to their calendar.
The holiday is both a grim reminder of the work that must be done and a celebration of the progress that has been made when it comes to climate change efforts. It's also been the catalyst for actions including the creation of international climate agreements and environmental agencies.
This year’s theme is Planet vs. Plastics, which calls on government leaders, businesses, and everyday people to reduce plastic production by 60% by 2040. It is also calling for the full elimination of single use plastics by the end of this decade.
“The word environment means what surrounds you. In the case of plastics we have become the product itself—it flows through our blood stream, adheres to our internal organs, and carries with it heavy metals known to cause cancer and disease,” said Kathleen Rogers, President of earthday.org. “The Planet vs. Plastics campaign is a call to arms, a demand that we act now to end the scourge of plastics and safeguard the health of every living being upon our planet.”
Here are 10 interesting facts about Earth Day.
Earth Day was created by a senator
Gaylord Nelson, a Democratic senator from Wisconsin, was growing increasingly concerned over the state of the U.S. environment in the 1960s. After a massive oil spill in Santa Barbara, Calif. in January 1969, he had the idea to launch a nationwide, environmentally-focused teach-in on college campuses, drawing inspiration from the anti-war movements against the Vietnam War occurring on campuses around the country. Nelson recruited Denis Hayes, a young activist, to help bring the idea to the public.
The idea for Earth Day came after a series of environmental catastrophes
Hayes, one of the organizers behind the first Earth Day, previously told TIME that the idea behind the holiday came following a number of events that drew attention to the environment, including the release of Rachel Carson’s book Silent Spring in 1962 and the 1969 Cuyahoga River fire . Hayes said that while there were a number of groups in the U.S. working on different environmental issues—to reduce air pollution, bring attention to the impact of pesticides on farm workers, and more—they had never worked in conjunction.
“What we did was take all of those myriad strands, including wildlife protection issues, and wove them all together. It sounds strange today, but back then, the folks involved with those various causes didn’t think of themselves as having anything in common with one another,” he told TIME in 2019. “No one was asking that question at the end of the 1970s.”
More than 20 million people participated in the first Earth Day
Millions of people participated in the first Earth Day celebration on April 22, 1970. The event shut down Manhattan’s Fifth Avenue, as people demonstrated and participated in street clean-ups.
“The holiday mood on Fifth Avenue was exemplified by members of the architectural firm of Warner, Burns, Toan & Lunde, who spread a yellow and‐white quilt on the asphalt near 57th Street, put a tulip in a wine bottle for a centerpiece and enjoyed a picnic in the sun. A laughing crowd gathered around them and sang, ‘Happy Earth Day to You,’” the New York Times reported that day.
Earth Day is on April 22 because of college schedules
The date for Earth Day was largely dictated by the schedules of the college students Hayes and Nelson were hoping to attract. April 22 fell on a weekday during the school year—nestled between spring break and final exams, when the weather was mild enough to allow people to be outside.
The Environmental Protection Agency was created after the first Earth Day
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which regulates mechanisms to protect the environment, was created on Dec. 2, 1970 as a direct response to the first Earth Day. Congress formed the agency after witnessing the huge participation in Earth Day demonstrations across the country, the EPA says .
“Last year some said there would never be another Earth Day. They saw concern for our environment as a fad, and claimed that the instant enthusiasm of an activist generation would soon flow elsewhere,” said William D. Ruckelshaus, the EPA’s first administrator during the second Earth Day in 1971. “I believe they were wrong.”
Earth Day went global in 1990
Millions of people participated in the first Earth Day movement, which led to the passage of key environmental laws, including the National Environmental Education Act, the Occupational Safety and Health Act, and the Clean Air Act in the U.S. later that year.
“Earth Day 1970 achieved a rare political alignment, enlisting support from Republicans and Democrats, rich and poor, urban dwellers and farmers, business and labor leaders,” says the earthday.org history page .
But its impact spans larger than just one country. The movement went global in 1990, after a group of environmental leaders approached Hayes to organize another major campaign for the planet, which mobilized 200 million people in 141 countries.
In the new millennium, the movement switched its focus to campaign against global warming, and as recently as 2020, over 1 billion people worldwide participated in Earth Day actions.
The Paris Agreement opened for signature on Earth Day
The Paris Agreement , the most significant international climate accord in history, was opened for signature on Earth Day in 2016. The treaty has more than 190 signatories, all of whom agreed to reduce carbon emissions and carry out other actions to reduce climate change.
United Automobile Workers union played a role in making Earth Day possible
The former head of the United Automobile Workers (UAW) union was one of the biggest contributors to the original Earth Day, donating $2,000 in 1970 (the equivalent of more than $15,500 today).
“The UAW was by far the largest contributor to the first Earth Day, and its support went beyond the merely financial. It printed and mailed all our materials at its expense — even those critical of pollution-belching cars,” Hayes told Grist in 2010. “Its organizers turned out workers in every city where it has a presence. And, of course, Walter then endorsed the Clear Air Act that the Big Four were doing their damnedest to kill or gut.”
Organizers are trying to have the biggest Earth Day cleanup event in history in 2024
For this year’s Earth Day celebration, earthday.org is working with Malaysian organizations to host the largest cleanup in Earth Day history. Penang Island, the country’s main island, has been impacted by plastic pollution due to tourism. At least 100,000 volunteers will be cleaning up the beaches and forests in the country, according to organizers. They will also plant more than 1 million trees.
Tens of millions of trees have been planted on Earth Day
Some 18 million acres of forest are lost every year due to deforestation, per the United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization. To combat this, earthday.org founded the Canopy Project in 2010 and says it has since planted tens of millions of trees around the world.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- The Revolution of Yulia Navalnaya
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- What's the Deal With the Bitcoin Halving?
- If You're Dating Right Now , You're Brave: Column
- The AI That Could Heal a Divided Internet
- Fallout Is a Brilliant Model for the Future of Video Game Adaptations
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Simmone Shah at [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app ... Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Algebra. Basic Math. Pre-Algebra. Algebra. Trigonometry. Precalculus. Calculus. Statistics. Finite Math. Linear ...
What can QuickMath do? QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students. The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several ...
Get math help in your language. Works in Spanish, Hindi, German, and more. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
Brainly Community Q&A allows students to post their questions and get expert-verified answers. You'll be able to find solutions quickly since students, subject-matter experts, and teachers are available 24/7. Users can also: • Assist each other with exam preparation. • View step-by-step explanations for math problems.
A) MEAN: μ = 2.11. math: In order to find the mean (expectation) of the given distribution, we will use the following formula: μ = ∑x • P (x) So, first we need to multiply each value of X by each probability P (X), then add these results together. In this example we have: μ = 0 multiplied by .05 = 0.
Get Expert-Verified Homework Help and explanations personalized with AI. Understand faster with 24/7 personalized learning. Score higher with practice tests included in Study Sets. New. Learning, your way. ... "I struggled with math, but Brainly helped me overcome it by providing .
Brainly, the AI Learning Companion. Brainly is a powerful Math solver app that can help you with your school doubts. Solve Math problems in Algebra, Trigonometry, & Geometry with correct & expert-verified answers instantly. With Brainly, you can find solutions to your math homework. Math answers have never been easier to find!
This is a comprehensive collection of free printable math worksheets for grade 5, organized by topics such as addition, subtraction, algebraic thinking, place value, multiplication, division, prime factorization, decimals, fractions, measurement, coordinate grid, and geometry. They are randomly generated, printable from your browser, and ...
Algebra Calculator is a step-by-step calculator and algebra solver. It's an easy way to check your homework problems online. Click any of the examples below to see the algebra solver in action. Or read the Calculator Tutorial to learn more. Try Algebra Calculator >.
Welcome to MathHomeworkAnswers.org, where students, teachers and math enthusiasts can ask and answer any math question. Get help and answers to any math problem including algebra, trigonometry, geometry, calculus, trigonometry, fractions, solving expression, simplifying expressions and more. Get answers to math questions. Help is always 100% free!
Selected Answers. 3-5. Open Response: Game Strategies. Home Link 3-5 English Español Selected Answers ... With a login provided by your child's teacher, access resources to help your child with homework or brush up on your math skills. Understanding Everyday Mathematics for Parents.
Do you need help with math problems? Chegg.com offers a math problem solver tool and calculator that can guide you step by step to the solution. Whether you are studying algebra, calculus, geometry, or statistics, you can find flashcards, quizzes, and tips to improve your skills. Try it for free and see how Chegg.com can make math easy for you.
Selected Answers. 5-3. Adding Fractions. like denominators. Home Link 5-3 English Español Selected Answers. 5-4. Adding Mixed Numbers. Home Link 5 ... With a login provided by your child's teacher, access resources to help your child with homework or brush up on your math skills.
Problem Solving . Title: Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5 Created Date: 3/29/2016 4:07:11 PM
Math Expressions Common Core Grade 3 Homework and Remembering Answer Key. Math Expressions Grade 3 Homework and Remembering Volume 1 Answer Key | Math Expressions Common Core Grade 3 Volume 1 Answer Key. Unit 1 Multiplication and Division with 0-5, 9 and 10. Math Expressions Grade 3 Unit 1 Lesson 1 Answer Key Multiply with 5
Best Paid Homework Help Site: Chegg. Price: $14.95 to $19.95 per month. Best for: 24/7 homework assistance. This service has three main parts. The first is Chegg Study, which includes textbook solutions, Q&A with subject experts, flashcards, video explanations, a math solver, and writing help.
The graph has a zero of -5 with multiplicity 3, a zero of -1 with multiplicity 2, and a zero of 3 with multiplicity 4. 3. 4. Because f f is a polynomial function and since f (1) f (1) is negative and f (2) f (2) is positive, there is at least one real zero between x = 1 x = 1 and x = 2. x = 2. 5. ... We will need a restriction on the domain ...
Go Math! 5 Student Edition grade 5 workbook & answers help online. Grade: 5, Title: Go Math! 5 Student Edition, Publisher: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, ISBN: 547352042 ... worksheets and lessons that supplement Go Math! 5 Student Edition. Chapter 1: Whole Number Operations: Apps Videos Practice Now; Lesson 1: Place Value and Expanded Notation ...
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 13 Problem Set Answer Key. Question 1. Are the following expressions greater than or less than 1? Circle the correct answer. a. 12 + 27 greater than 1 less than 1. b. 58 + 35 greater than 1 less than 1. c. 1 14 - 13 greater than 1 less than 1. d. 3 58 - 2 59 greater than1 less than 1.
-5 + (5 + 3) which property do you use. property; asked Nov 25, 2012 in Pre-Algebra Answers by anonymous. answer comment ... 3 answers. Explain how usung partial quotients is similar to using the distributive property to multiply ... 2013 in Other Math Topics by Megan | 4.1k views. distributive; property; partial; quotient ...
Problem 1AYU. Chapter. CH5.3. Problem. 1AYU. Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 1. Two evens E and F are "Independent" if the occurrence of event E in a probability experiment does not affect the probability of even F. Back to top.
Free math problem solver answers your homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app ... Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Basic Math. Basic Math. Pre-Algebra. Algebra. Trigonometry. Precalculus. Calculus. Statistics. Finite Math. Linear ...
Mathematics document from University of Houston, 10 pages, 1 MATH 1324 - Finite Math with Applications Homework 12 (Untimed, 1 Attempt) DUE November 25, 2022 11:59:00 PM! Q1. The choices for problem number 8 part b, from Section 7.3 in the book are given below. A. 6.9676 B. 2.6396 C. 4.5727 D. 4.8776 E. 8.0278 F.
1. take the even number that is closest to half the 5 (2) 2. add the numerator and the denominator (3+4=7) this becomes the new numerator (7) 3. double the denominator (2X4=8) this becomes the new denominator. so half of 5 3/8 (in your head) becomes 2 7/8 this works with any odd number and a fraction. now you try it with 7 1/4 3 5 8 = 3 5/8.
NEW LONDON, Conn. (AP) — Fifty-five U.S. Coast Guard Academy cadets have been disciplined for sharing homework answers in violation of academy policy, Coast Guard officials announced. After a series of disciplinary hearings, six of the cadets failed the course and 48 got lowered grades, officials said Wednesday. The cadets were accused of ...
More than 20 million people participated in the first Earth Day. Millions of people participated in the first Earth Day celebration on April 22, 1970. The event shut down Manhattan's Fifth ...