- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions

- Web Stories

Saturday, October 23, 2021
Class 10 maths case study based questions chapter 15 probability cbse board term 1 with answer key.

Hello students, Welcome to Maths Easy Institute.
CASE STUDY 1:

0 comments:
Post a comment.
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.
Warning: Do Not Copy!
- Blog Archives

- Best Books for IIT JEE
- Best Colleges Of India
- class 10 Case Study Based questions
- Class 10 Maths MCQ
- Class 11 Maths Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Maths MCQ
- Class 12 Math Case Study questions
- Class 12 Maths MCQ
- JEE MAIN MCQ
- Maths Strategy JEE
- News for Students
Blog Archive
- ► April (3)
- ► March (2)
- ► February (1)
- ► January (5)
- ► December (9)
- ► November (5)
- Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Appl...
- Class 10 Maths Case Study Based Questions Chapter ...
- Class 11 Maths MCQ Chapter 5 Complex Numbers CBSE ...
- Class 11 MCQ type Questions Chapter 2 Relations an...
- ► September (5)
- ► April (4)
- ► March (3)
- ► October (2)
- ► September (7)
- ► August (2)
- ► July (4)


Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability
- Last modified on: 9 months ago
- Reading Time: 3 Minutes
Case Study Questions:
Question 1:
On a weekend Rani was playing cards with her family. The deck has 52 cards. If her brother drew one card.
(i) Find the probability of getting a king of red colour. (a) 1/26 (b) 1/13 (c) 1/52 (d) 1/4
(ii) Find the probability of getting a face card. (a) 1/26 (b) 1/13 (c) 2/13 (d) 3/13
(iii) Find the probability of getting a jack of hearts. (a) 1/26 (b) 1/52 (c) 3/52 (d) 3/26
(iv) Find the probability of getting a red face card. (a) 3/26 (b) 1/13 (c) 1/52 (d) 1/4
(v) Find the probability of getting a spade. (a) 1/26 (b) 1/13 (c) 1/52 (d) 1/4
✨ Free Quizzes, Test Series and Learning Videos for CBSE Class 10 Maths
You may also like:
Chapter 1 Real Numbers Chapter 2 Polynomials Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables C hapter 4 Quadratic Equations Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Chapter 6 Triangles Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry Chapter 10 Circles Chapter 11 Constructions Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Chapter 14 Statistics Chapter 15 Probability
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Probability Free PDF

Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Probability in order to fully complete your preparation . They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Case Study Based Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams!
I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams. To download the latest CBSE Case Study Questions , just click ‘ Download PDF ’.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Probability PDF
Checkout our case study questions for other chapters.
- Chapter 11: Construction Case Study Questions
- Chapter 12: Area Related to Circles Case Study Questions
- Chapter 13: Surface Area and Volumes Case Study Questions
- Chapter 14: Statistics Case Study Questions
How should I study for my upcoming exams?
First, learn to sit for at least 2 hours at a stretch
Solve every question of NCERT by hand, without looking at the solution.
Solve NCERT Exemplar (if available)
Sit through chapter wise FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS
Practice MCQ Questions (Very Important)
Practice Assertion Reason & Case Study Based Questions
Sit through FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS involving MCQs. Assertion reason & Case Study Based Questions
After Completing everything mentioned above, Sit for atleast 6 full syllabus TESTS.
Contact Form
Privacy Policy
UPSKILL MATH PLUS
Learn Mathematics through our AI based learning portal with the support of our Academic Experts!
- Mathematics CBSE
- Probability
28. Case study: Probability
Exercise condition:.

myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- Case Study Class 10...
Case Study Class 10 Maths Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Now, CBSE will ask only subjective questions in class 10 Maths case studies. But if you search over the internet or even check many books, you will get only MCQs in the class 10 Maths case study in the session 2022-23. It is not the correct pattern. Just beware of such misleading websites and books.
We advise you to visit CBSE official website ( cbseacademic.nic.in ) and go through class 10 model question papers . You will find that CBSE is asking only subjective questions under case study in class 10 Maths. We at myCBSEguide helping CBSE students for the past 15 years and are committed to providing the most authentic study material to our students.
Here, myCBSEguide is the only application that has the most relevant and updated study material for CBSE students as per the official curriculum document 2022 – 2023. You can download updated sample papers for class 10 maths .
First of all, we would like to clarify that class 10 maths case study questions are subjective and CBSE will not ask multiple-choice questions in case studies. So, you must download the myCBSEguide app to get updated model question papers having new pattern subjective case study questions for class 10 the mathematics year 2022-23.
Class 10 Maths has the following chapters.
- Real Numbers Case Study Question
- Polynomials Case Study Question
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Case Study Question
- Quadratic Equations Case Study Question
- Arithmetic Progressions Case Study Question
- Triangles Case Study Question
- Coordinate Geometry Case Study Question
- Introduction to Trigonometry Case Study Question
- Some Applications of Trigonometry Case Study Question
- Circles Case Study Question
- Area Related to Circles Case Study Question
- Surface Areas and Volumes Case Study Question
- Statistics Case Study Question
- Probability Case Study Question
Format of Maths Case-Based Questions
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions will have one passage and four questions. As you know, CBSE has introduced Case Study Questions in class 10 and class 12 this year, the annual examination will have case-based questions in almost all major subjects. This article will help you to find sample questions based on case studies and model question papers for CBSE class 10 Board Exams.
Maths Case Study Question Paper 2023
Here is the marks distribution of the CBSE class 10 maths board exam question paper. CBSE may ask case study questions from any of the following chapters. However, Mensuration, statistics, probability and Algebra are some important chapters in this regard.
Case Study Question in Mathematics
Here are some examples of case study-based questions for class 10 Mathematics. To get more questions and model question papers for the 2021 examination, download myCBSEguide Mobile App .
Case Study Question – 1
In the month of April to June 2022, the exports of passenger cars from India increased by 26% in the corresponding quarter of 2021–22, as per a report. A car manufacturing company planned to produce 1800 cars in 4th year and 2600 cars in 8th year. Assuming that the production increases uniformly by a fixed number every year.
- Find the production in the 1 st year.
- Find the production in the 12 th year.
- Find the total production in first 10 years. OR In which year the total production will reach to 15000 cars?
Case Study Question – 2
In a GPS, The lines that run east-west are known as lines of latitude, and the lines running north-south are known as lines of longitude. The latitude and the longitude of a place are its coordinates and the distance formula is used to find the distance between two places. The distance between two parallel lines is approximately 150 km. A family from Uttar Pradesh planned a round trip from Lucknow (L) to Puri (P) via Bhuj (B) and Nashik (N) as shown in the given figure below.
- Find the distance between Lucknow (L) to Bhuj(B).
- If Kota (K), internally divide the line segment joining Lucknow (L) to Bhuj (B) into 3 : 2 then find the coordinate of Kota (K).
- Name the type of triangle formed by the places Lucknow (L), Nashik (N) and Puri (P) OR Find a place (point) on the longitude (y-axis) which is equidistant from the points Lucknow (L) and Puri (P).
Case Study Question – 3
- Find the distance PA.
- Find the distance PB
- Find the width AB of the river. OR Find the height BQ if the angle of the elevation from P to Q be 30 o .
Case Study Question – 4
- What is the length of the line segment joining points B and F?
- The centre ‘Z’ of the figure will be the point of intersection of the diagonals of quadrilateral WXOP. Then what are the coordinates of Z?
- What are the coordinates of the point on y axis equidistant from A and G? OR What is the area of area of Trapezium AFGH?
Case Study Question – 5
The school auditorium was to be constructed to accommodate at least 1500 people. The chairs are to be placed in concentric circular arrangement in such a way that each succeeding circular row has 10 seats more than the previous one.
- If the first circular row has 30 seats, how many seats will be there in the 10th row?
- For 1500 seats in the auditorium, how many rows need to be there? OR If 1500 seats are to be arranged in the auditorium, how many seats are still left to be put after 10 th row?
- If there were 17 rows in the auditorium, how many seats will be there in the middle row?
Case Study Question – 6
- Draw a neat labelled figure to show the above situation diagrammatically.
- What is the speed of the plane in km/hr.
More Case Study Questions
We have class 10 maths case study questions in every chapter. You can download them as PDFs from the myCBSEguide App or from our free student dashboard .
As you know CBSE has reduced the syllabus this year, you should be careful while downloading these case study questions from the internet. You may get outdated or irrelevant questions there. It will not only be a waste of time but also lead to confusion.
Here, myCBSEguide is the most authentic learning app for CBSE students that is providing you up to date study material. You can download the myCBSEguide app and get access to 100+ case study questions for class 10 Maths.
How to Solve Case-Based Questions?
Questions based on a given case study are normally taken from real-life situations. These are certainly related to the concepts provided in the textbook but the plot of the question is always based on a day-to-day life problem. There will be all subjective-type questions in the case study. You should answer the case-based questions to the point.
What are Class 10 competency-based questions?
Competency-based questions are questions that are based on real-life situations. Case study questions are a type of competency-based questions. There may be multiple ways to assess the competencies. The case study is assumed to be one of the best methods to evaluate competencies. In class 10 maths, you will find 1-2 case study questions. We advise you to read the passage carefully before answering the questions.
Case Study Questions in Maths Question Paper
CBSE has released new model question papers for annual examinations. myCBSEguide App has also created many model papers based on the new format (reduced syllabus) for the current session and uploaded them to myCBSEguide App. We advise all the students to download the myCBSEguide app and practice case study questions for class 10 maths as much as possible.
Case Studies on CBSE’s Official Website
CBSE has uploaded many case study questions on class 10 maths. You can download them from CBSE Official Website for free. Here you will find around 40-50 case study questions in PDF format for CBSE 10th class.
10 Maths Case Studies in myCBSEguide App
You can also download chapter-wise case study questions for class 10 maths from the myCBSEguide app. These class 10 case-based questions are prepared by our team of expert teachers. We have kept the new reduced syllabus in mind while creating these case-based questions. So, you will get the updated questions only.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2020-21
- Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions
- CBSE Reduced Syllabus Class 10 (2020-21)
- Class 10 Maths Basic Sample Paper 2024
- How to Revise CBSE Class 10 Maths in 3 Days
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Maths Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions Chapter 15 Probability
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions in the Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 15 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions Chapter 15 Probability
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Maths Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Probability Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
Answer: (a) 18
(ii) If the probability of distributing dark chocolates is 4/9, then the number of dark chocolates Rohit has, is
Answer: (c) 24
(iii) The probability of distributing white chocolates is
Answer: (d) 2/9
(iv) The probability of distributing both milk and white chocolates is
Answer: (b) 5/9
(v) The probability of distributing all the chocolates is
Answer: (b) 1
Question 2:
Rahul and Ravi planned to play Business ( board game) in which they were supposed to use two dice.

1. Ravi got first chance to roll the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is 8?
Answer: b) 5/36
2. Rahul got next chance. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is 13?
Answer: d) 0
3. Now it was Ravi’s turn. He rolled the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is less than or equal to 12?
Answer: a) 1
4. Rahul got next chance. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is equal to 7?
Answer: c) 1/6
5. Now it was Ravi’s turn. He rolled the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is greater than 8?
Answer: d) 5/18
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Maths Probability Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like

CBSE Class 10 Previous Year Questions Papers PDF with Solutions

CBSE Class 10 Science Heredity & Evolution MCQ Quiz with Answers

Class 10 Social Science Civics Notes by Toppers – Download PDF
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Case Based Questions - Probability
Study case - 1.

Q2: The probability of drawing a ball of colour other than green colour is: (a) 0 (b) 4/25 (c) 21/25 (d) 17/25 Ans: (c) Explanation: From part (A), number of green balls = 4. ∴ Number of balls of colour other than = 25 − 4 = 21. ∴ Probability of drawing a ball of colour other than green colour = 21/25.
Q3: The probability of drawing either a green or white ball is: (a) 0 (b) 12/25 (c) 13/25 (d) 17/25 Ans: (b) Explanation: The number of green balls = 4 and number of white balls =8. Therefore, total number of green balls + white balls = 4 + 8 = 12.. ∴ Probability of drawing either a or a white ball = 12/25.
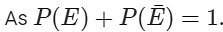
Study Case - 2

Q1: The probability of getting almost one tail is: (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 1/2 (d) 1/4 Ans: (c) Explanation: Sample space (S) = {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT} ⇒ n(S) = 8 Let A be the event of getting at most one tail. ∴ A = {HHH, HHT, HTH, THH} ⇒ n(A) = 4 ∴ Required probability = 4/8 = 1/2
Q2: The probability of getting exactly 1 head is: (a) 1/2 (b) 1/4 (c) 1/8 (d) 3/8 Ans: (d) Explanation: Let B be the event of getting exactly 1 head. ∴B = {HTT, THT, TTH} ⇒ n(B) = 3 ∴ Required probability = 3/8 Q3: The probability of getting exactly 3 tails is: (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 1/4 (d) 1/8 Ans: (d) Explanation: Let C be the event of getting exactly 3 tails. ∴ C = {TTT} ⇒ n(C) = 1 ∴ Required probability = 1/8 Q4: The probability of getting at most 3 heads is: (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 1/2 (d) 1/8 Ans: (b) Explanation: Let D be the event of getting atmost 3 heads. ∴ D = {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTT} ⇒ n(D) = 8 ∴ Required probability = 8/8 = 1.
Q5: The probability of getting at least two heads is: (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 1/2 (d) 1/4 Ans: (c) Explanation: Let E be the event of getting at least two heads. ∴E = {HHT, HTH, THH, HHH} ⇒ n(E) = 4 ∴ Required probability = n(E)/n(S) = 4/8 = 1/2.
Top Courses for Class 10
Semester notes, sample paper, study material, important questions, previous year questions with solutions, practice quizzes, viva questions, shortcuts and tricks, past year papers, objective type questions, video lectures, mock tests for examination, extra questions.

Case Based Questions: Probability Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: probability, case based questions: probability notes, case based questions: probability class 10, study case based questions: probability on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.

Class 10th Maths - Probability Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 10th Maths Subject - Probability, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Probability case study questions with answer key.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015

(ii) \(\begin{equation} ₹ \end{equation} \) 20 coin
(iii) not a \(\begin{equation} ₹ \end{equation} \) 10 coin
(iv) of denomination of atleast \(\begin{equation} ₹ \end{equation} \) 10.
(v) of denomination of atmost \(\begin{equation} ₹ \end{equation} \) 5.

(ii) a monkey
(iii) a teddy bear
(iv) not a monkey
(v) not a pokemon
(ii) If the probability of distributing dark chocolates is 4/9, then the number of dark chocolates Rohit has, is
(iii) The probability of distributing white chocolates is
(iv) The probability of distributing both milk and white chocolates is
(v) The probability of distributing all the chocolates is
In a party, some children decided to play musical chair game. In the game the person playing the music has been advised to stop the music at any time in the interval of 3 mins after he start the music in each turn. On the basis of the given information, answer the following questions. (i) What is the probability that the music will stop within first 30 sees after starting?
(ii) The probability that the music will stop within 45 sees after starting is
(iii) The probability that the music will stop after 2 mins after starting is
(iv) The probability that the music will not stop within first 60 sees after starting is
(v) The probability that the music will stop within first 82 sees after starting is

(ii) The probability of getting exactly 1 head is
(iii) The probability of getting exactly 3 tails is
(iv) The probability of getting atmost 3 heads is
(v) The probability of getting atleast two heads is
(ii) not of yellow colour
(iii) of green colour
(iv) of yellow colour
(v) not of blue colour
Rahul goes to a fete in Mussoorie. There he saw a game having prizes - wall clocks, power banks, puppets and water bottles. The game consists of a box having cards inside it, bearing the numbers 1 to 200, one on each card. A person has to select a card at random. Now, the winning of prizes has the following conditions:
- Wall clock - If the number on the selected card is a perfect square.
- Power bank - If the number on the selected card is multiple of 3.
- Puppet - If the number on selected card is divisible by 10.
- Water bottle - If the number on the selected card is a prime number more than 100 but less than 150.
- Better luck next time - If the number on the selected card is a perfect cube.

(ii) The probability of winning a water bottle is
(iii) The probability of winning a power bank is
(iv) The probability of winning a wall clock is
(v) The probability of getting 'Better Luck next time' is

(ii) The probability of selecting a flowerhorn fish is
(iii) The probability of not selecting a koi fish is
(iv) The probability of selecting neither angle fish nor flowerhorn fish is
(v) The probability of selecting a guppy fish is

(ii) The probability of getting the sum of numbers on two dice is 16, is
(iii) The probability that both the numbers are prime numbers, is
(iv) The probability that product of two numbers is odd, is|
(v) The probability that difference between numbers is zero, is

(ii) The probability of getting a black diamond is
(iii) The probability of getting a face card is
(iv) The probability of getting a club is
(v) The probability of getting a red card is
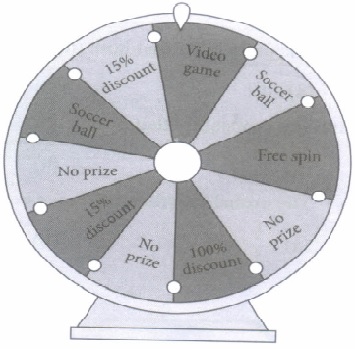
(ii) If Anita spins the wheel, then the probability of getting no prize is
(iii) Anshu spins the wheel, the probability that the wheel stops at soccer ball is
(iv) The probability that one customer wins 15% discount is
(v) The probability of getting a free spin is

(ii) A football is selected at random, the probability of selecting a non-defective football is
(iii) The total number of defective footballs produced in one day is
(iv) The total number of non-defective footballs produced in one day is
(v) If the probability of selecting a defective football is , then the number of non-defective footballs produced in one day, if everyday same number of footballs produced in the factory, is

(ii) The probability that Gupta's has atleast 1 boy is
(iii) The probability that Gupta's has atmost 1 girl is
(iv) The probability that Singhal's has no boy is
(v) The sum of probabilities that both families have exactly two girls is

(ii) The probability that the selected carton is not of orange juice is
(iii) The probability of selecting a carton of guava juice is
(iv) Vishal buys 4 cartons of apple juice, 3 cartons of orange juice and 3 cartons of guava juice. A customer comes to Vishal's shop and picks a tetrapack of juice at random. The probability that the customer picks a guava juice, if each carton has 10 tetrapacks of juice, is
(v) If the storekeeper bought 14 more cartons of apple juice, then the probability of selecting a tetrapack of apple juice from the store is
In the month of May, the weather forecast department gives the prediction of weather for the month of June, The given table shows the probabilities of forecast of different days:
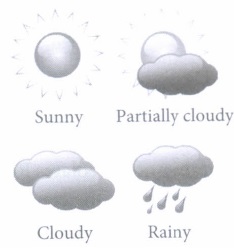
(ii) If the number of cloudy days in June is 5, then x =
(iii) The probability that the day is not rainy is
(iv) If the sum of x < and y is \(\begin{equation} \frac{3}{10} \end{equation}\) , then the number of rainy days in June is
(v) Find the number of partially cloudy days
*****************************************
Related 10th standard cbse maths materials, other 10th standard cbse materials.

CBSE 10th Social Science The Making Of A Global World Chapter Case Study Question with Answers
Cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers.

CBSE 10th Science Metals And Non Metals Chapter Case Study Question with Answers
Cbse 10th science acids, bases and salts chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th science chemical reactions and equations chapter case study question with answers, class 10th science - our environment case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - magnetic effects of electric current case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - electricity case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - human eye and the colourful world case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - light reflection and refraction case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - heredity and evolution case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - how do organisms reproduce case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - life processes case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - periodic classification of elements case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, tamilnadu stateboard 10th standard cbse study materials.

Tamilnadu Stateboard 10th Standard CBSE Subjects

- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 14 Class 10 Probability
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Updated for new NCERT Books - for 2024 Boards.
Get NCERT Solutions for Chapter 14 Class 10 free at teachoo. Solutions to all exercise questions, examples and optional is available with detailed explanations.
In Class 9 , we studied about Empirical or Experimental Probability.
In this chapter, we will study
- Theoretical Probability , that is, P(E) = Number of outcomes with E / Total possible outcomes
- Probability of complementary event, i.e., P(not E)
- Probability of Impossible and sure events
- Probability of questions where die is thrown twice
- Probability of card questions
- Finding Probability using distance and area
Click on an exercise or a topic link below to get started.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Ap inter results.
- AP Board Results 2024
- UP Board Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 - Probability (Published by CBSE)
Cbse class 10 maths case study questions for chapter 15 - probability are published by the cbse board itself to help students understand the new format of questions. these questions are important for the cbse class 10 maths 2022 board exam preparations..

CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 - Probability are provided here. These questions are quite useful to understand how real-life problems can be put in the form of questions. These case study questions are published by the CBSE board. Solve all these questions to prepare for your exams and score the desired marks.
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 - Probability:
CASE STUDY 1:
On a weekend Rani was playing cards with her family. The deck has 52 cards. If her brother drew one card.

1. Find the probability of getting a king of red colour.
Answer: a) 1/26
2. Find the probability of getting a face card.
Answer: d) 3/13
3. Find the probability of getting a jack of hearts.
4. Find the probability of getting a jack of hearts.
Answer: a) 3/13
5. Find the probability of getting a jack of hearts.
Answer: d) 1/4
CASE STUDY 2:
Rahul and Ravi planned to play Business ( board game) in which they were supposed to use two dice.

1. Ravi got first chance to roll the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is 8?
Answer: b) 5/36
2. Rahul got next chance. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is 13?
Answer: d) 0
3. Now it was Ravi’s turn. He rolled the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is less than or equal to 12?
Answer: a) 1
4. Rahul got next chance. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is equal to 7?
Answer: c) 1/6
5. Now it was Ravi’s turn. He rolled the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is greater than 8?
Answer: d) 5/18
Also Check:
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths - All Chapters
Tips to Solve Case Study Based Questions Accurately
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- NDA 1 Admit Card 2024
- TSPSC AE Answer Key 2024
- NDA Admit Card 2024
- CTET Correction Window 2024
- NTA NITTT Result 2024
- APPSC Group 2 Result 2024
- CUET PG Answer Key 2024
- TN SET Application Form 2024
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
Board Result 2024 Date LIVE: UP, MP, JAC, CGBSE, UK और CBSE बोर्ड के परिणामों पर लेटेस्ट अपडेट
NDA Admit Card 2024 Live Updates: UPSC NDA 1 Hall Ticket Download Link on upsc.gov.in Soon
BPSSC SI PET Schedule 2024 Out on bpssc.nih.nic.in, Admit Card to be released on 29 May
JKSSB Junior Assistant Typing Test Admit Card 2024 OUT: SSBJK JA Call Letter Direct Link at jkssb.nic.in
Current Affairs One Liners: 09 April 2024- Wipro's New CEO and MD
Karnataka Board Result 2024: KSEAB SSLC, 2nd PUC Result Date and Time at karresults.nic.in
Karnataka Board 2nd PUC Result 2024: KSEAB 2nd PUC Result Date and Time at karresults.nic.in
IB ACIO Cut Off 2024: Category-wise Previous Year Cutoff Marks
SSC CHSL 2024 Notification Out: एसएससी सीएचएसएल अधिसूचना जारी, देखें आवेदन प्रक्रिया, योग्यता
IB ACIO Salary 2024: Per Month In Hand Salary, Allowances and Promotion
Eid 2024: Is Eid al-Fitr on April 10 or 11 in India? Check the Date and Moon Sighting Timings Here
Current Affairs Quiz: 09 April 2024- TSAT-1A Satellite
RSMSSB Junior Instructor 2024 Registration Ends Soon, Direct Apply Online Link Here
UPPSC PCS Syllabus 2024: जानें कैसा आता है यूपीपीसीएस का पेपर और क्या है एग्जाम पैटर्न ?
MJPRU Result 2024 Out: रोहिलखंड यूनिवर्सिटी रिजल्ट mjpruiums.in पर घोषित, इस लिंक से करें चेक
ICSI CS June Exam 2024 Registration with Late Fee Closes Today; Check Full Details Here
SSC CHSL Notification 2024 Released for 3712 Vacancies, Registration Begins at ssc.gov.in, Check Eligibility
UPSC NDA Exam Date 2024: Check Written Exam Shift Timing
GUJCET 2024 Answer Key PDF (Final) Released at gsebeservice.com, Download Here
JEE Main Session 2 (April 8) Aakash Answer Key 2024: Download Shift 1 and Shift 2 Answer Key FREE PDF
CBSE Expert
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions PDF
Download Case Study Questions for Class 10 Mathematics to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 10 Final Exam. These Case Study and Passage Based questions are published by the experts of CBSE Experts for the students of CBSE Class 10 so that they can score 100% on Boards.

CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Exam 2024 will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. The CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends.
Table of Contents
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 10 Mathematics
Inboard exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
The above Case studies for Class 10 Maths will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of cbseexpert.com for the benefit of Class 10 students.
- Class 10th Science Case Study Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions of Class 10th Science
- Assertion and Reason Questions of Class 10th Social Science
Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2024
Chapter-1 real numbers.
Starting with an introduction to real numbers, properties of real numbers, Euclid’s division lemma, fundamentals of arithmetic, Euclid’s division algorithm, revisiting irrational numbers, revisiting rational numbers and their decimal expansions followed by a bunch of problems for a thorough and better understanding.
Chapter-2 Polynomials
This chapter is quite important and marks securing topics in the syllabus. As this chapter is repeated almost every year, students find this a very easy and simple subject to understand. Topics like the geometrical meaning of the zeroes of a polynomial, the relationship between zeroes and coefficients of a polynomial, division algorithm for polynomials followed with exercises and solved examples for thorough understanding.
Chapter-3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
This chapter is very intriguing and the topics covered here are explained very clearly and perfectly using examples and exercises for each topic. Starting with the introduction, pair of linear equations in two variables, graphical method of solution of a pair of linear equations, algebraic methods of solving a pair of linear equations, substitution method, elimination method, cross-multiplication method, equations reducible to a pair of linear equations in two variables, etc are a few topics that are discussed in this chapter.
Chapter-4 Quadratic Equations
The Quadratic Equations chapter is a very important and high priority subject in terms of examination, and securing as well as the problems are very simple and easy. Problems like finding the value of X from a given equation, comparing and solving two equations to find X, Y values, proving the given equation is quadratic or not by knowing the highest power, from the given statement deriving the required quadratic equation, etc are few topics covered in this chapter and also an ample set of problems are provided for better practice purposes.

Chapter-5 Arithmetic Progressions
This chapter is another interesting and simpler topic where the problems here are mostly based on a single formula and the rest are derivations of the original one. Beginning with a basic brief introduction, definitions of arithmetic progressions, nth term of an AP, the sum of first n terms of an AP are a few important and priority topics covered under this chapter. Apart from that, there are many problems and exercises followed with each topic for good understanding.
Chapter-6 Triangles
This chapter Triangle is an interesting and easy chapter and students often like this very much and a securing unit as well. Here beginning with the introduction to triangles followed by other topics like similar figures, the similarity of triangles, criteria for similarity of triangles, areas of similar triangles, Pythagoras theorem, along with a page summary for revision purposes are discussed in this chapter with examples and exercises for practice purposes.
Chapter-7 Coordinate Geometry
Here starting with a general introduction, distance formula, section formula, area of the triangle are a few topics covered in this chapter followed with examples and exercises for better and thorough practice purposes.
Chapter-8 Introduction to Trigonometry
As trigonometry is a very important and vast subject, this topic is divided into two parts where one chapter is Introduction to Trigonometry and another part is Applications of Trigonometry. This Introduction to Trigonometry chapter is started with a general introduction, trigonometric ratios, trigonometric ratios of some specific angles, trigonometric ratios of complementary angles, trigonometric identities, etc are a few important topics covered in this chapter.
Chapter-9 Applications of Trigonometry
This chapter is the continuation of the previous chapter, where the various modeled applications are discussed here with examples and exercises for better understanding. Topics like heights and distances are covered here and at the end, a summary is provided with all the important and frequently used formulas used in this chapter for solving the problems.
Chapter-10 Circle
Beginning with the introduction to circles, tangent to a circle, several tangents from a point on a circle are some of the important topics covered in this chapter. This chapter being practical, there are an ample number of problems and solved examples for better understanding and practice purposes.
Chapter-11 Constructions
This chapter has more practical problems than theory-based definitions. Beginning with a general introduction to constructions, tools used, etc, the topics like division of a line segment, construction of tangents to a circle, and followed with few solved examples that help in solving the exercises provided after each topic.
Chapter-12 Areas related to Circles
This chapter problem is exclusively formula based wherein topics like perimeter and area of a circle- A Review, areas of sector and segment of a circle, areas of combinations of plane figures, and a page summary is provided just as a revision of the topics and formulas covered in the entire chapter and also there are many exercises and solved examples for practice purposes.
Chapter-13 Surface Areas and Volumes
Starting with the introduction, the surface area of a combination of solids, the volume of a combination of solids, conversion of solid from one shape to another, frustum of a cone, etc are to name a few topics explained in detail provided with a set of examples for a better comprehension of the concepts.
Chapter-14 Statistics
In this chapter starting with an introduction, topics like mean of grouped data, mode of grouped data, a median of grouped, graphical representation of cumulative frequency distribution are explained in detail with exercises for practice purposes. This chapter being a simple and easy subject, securing the marks is not difficult for students.
Chapter-15 Probability
Probability is another simple and important chapter in examination point of view and as seeking knowledge purposes as well. Beginning with an introduction to probability, an important topic called A theoretical approach is explained here. Since this chapter is one of the smallest in the syllabus and problems are also quite easy, students often like this chapter
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability are provided here to help the students of CBSE class 10. Our expert teachers prepared all these solutions as per the latest CBSE syllabus and guidelines. In this chapter, we have discussed the theoretical approach of probability in details. CBSE Class 10 Maths solutions provide a detailed and step-wise explanation of each answer to the questions given in the exercises of NCERT books.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability Solutions
Below we have given the answers to all the questions present in Probability in our NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths chapter 15. In this lesson, students are introduced to a lot of important concepts that will be useful for those who wish to pursue mathematics as a subject in their future classes. Based on these solutions, students can prepare for their upcoming Board Exams. These solutions are helpful as the syllabus covered here follows NCERT guidelines.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Exercise 15.1

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Exercise 15.2

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- DK Goel Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
- STATE WISE BOOKS
- ENGINEERING EXAM
- SCHOLARSHIP OLYMPIAD
- STATE BOOKS
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study
CBSE Board has introduced the case study questions for the ongoing academic session 2021-22. The board will ask the paper on the basis of a different exam pattern which has been introduced this year where 50% syllabus is occupied for MCQ for Term 1 exam. Selfstudys has provided below the chapter-wise questions for CBSE Class 10 Maths. Students must solve these case study based problems as soon as they are done with their syllabus.
These case studies are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions where students need to answer them as asked in the exam. The MCQs are not that difficult but having a deep and thorough understanding of NCERT Maths textbooks are required to answer these. Furthermore, we have provided the PDF File of CBSE Class 10 maths case study 2021-2022.
Class 10 Maths (Formula, Case Based, MCQ, Assertion Reason Question with Solutions)
In order to score good marks in the term 1 exam students must be aware of the Important formulas, Case Based Questions, MCQ and Assertion Reasons with solutions. Solving these types of questions is important because the board will ask them in the Term 1 exam as per the changed exam pattern of CBSE Class 10th.
Important formulas should be necessarily learned by the students because the case studies are solved with the help of important formulas. Apart from that there are assertion reason based questions that are important too.
Assertion Reasoning is a kind of question in which one statement (Assertion) is given and its reason is given (Explanation of statement). Students need to decide whether both the statement and reason are correct or not. If both are correct then they have to decide whether the given reason supports the statement or not. In such ways, assertion reasoning questions are being solved. However, for doing so and getting rid of confusions while solving. Students are advised to practice these as much as possible.
For doing so we have given the PDF that has a bunch of MCQs questions based on case based, assertion, important formulas, etc. All the Multiple Choice problems are given with detailed explanations.
CBSE Class 10th Case study Questions
Recently CBSE Board has the exam pattern and included case study questions to make the final paper a little easier. However, Many students are nervous after hearing about the case based questions. They should not be nervous because case study are easy and given in the board papers to ease the Class 10th board exam papers. However to answer them a thorough understanding of the basic concepts are important. For which students can refer to the NCERT textbook.
Basically, case study are the types of questions which are developed from the given data. In these types of problems, a paragraph or passage is given followed by the 5 questions that are given to answer . These types of problems are generally easy to answer because the data are given in the passage and students have to just analyse and find those data to answer the questions.
CBSE Class 10th Assertion Reasoning Questions
These types of questions are solved by reading the statement, and given reason. Sometimes these types of problems can make students confused. To understand the assertion and reason, students need to know that there will be one statement that is known as assertion and another one will be the reason, which is supposed to be the reason for the given statement. However, it is students duty to determine whether the statement and reason are correct or not. If both are correct then it becomes important to check, does reason support the statement?
Moreover, to solve the problem they need to look at the given options and then answer them.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Based MCQ
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Based MCQ are either Multiple Choice Questions or assertion reasons. To solve such types of problems it is ideal to use elimination methods. Doing so will save time and answering the questions will be much easier. Students preparing for the board exams should definitely solve these types of problems on a daily basis.
Also, the CBSE Class 10 Maths MCQ Based Questions are provided to us to download in PDF file format. All are developed as per the latest syllabus of CBSE Class Xth.
Class 10th Mathematics Multiple Choice Questions
Class 10 Mathematics Multiple Choice Questions for all the chapters helps students to quickly revise their learnings, and complete their syllabus multiple times. MCQs are in the form of objective types of questions whose 4 different options are given and one of them is a true answer to that problem. Such types of problems also aid in self assessment.
Case Study Based Questions of class 10th Maths are in the form of passage. In these types of questions the paragraphs are given and students need to find out the given data from the paragraph to answer the questions. The problems are generally in Multiple Choice Questions.
The Best Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions are available on Selfstudys.com. Click here to download for free.
To solve Class 10 Maths Case Studies Questions you need to read the passage and questions very carefully. Once you are done with reading you can begin to solve the questions one by one. While solving the problems you have to look at the data and clues mentioned in the passage.
In Class 10 Mathematics the assertion and reasoning questions are a kind of Multiple Choice Questions where a statement is given and a reason is given for that individual statement. Now, to answer the questions you need to verify the statement (assertion) and reason too. If both are true then the last step is to see whether the given reason support=rts the statement or not.

CBSE Class 10 Exams Finish, When Can You Expect Results? Details Here

CBSE Board Class 10 Information Technology Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs

CBSE Board Class 10 Computer Applications Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs

CBSE Class 10 Information Technology Exam 2024 : Most Important Questions Answers for Last-Minute Revision

CBSE Class 10 Computer Applications Exam 2024 : Most Important Questions Answers for Last-Minute Revision

CBSE Board Class 10 Maths Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- Math Article
- Probability For Class 10
Probability Class 10 Notes Chapter 15
According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 14.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Probability Notes:- Download PDF Here
Class 10 maths chapter 15 probability notes.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability Notes are provided here in detail. In this article, we are going to learn the definition of probability, experimental probability, theoretical probability and the different terminologies used in probability with complete explanations.
Students can refer to the short notes and MCQ questions along with separate solution pdf of this chapter for quick revision from the links below:
- Probability Short Notes
- Probability MCQ Practice Questions
- Probability MCQ Practice Solutions
What Is Probability?
The branch of mathematics that measures the uncertainty of the occurrence of an event using numbers is called probability. The chance that an event will or will not occur is expressed on a scale ranging from 0-1. It can also be represented as a percentage, where 0% denotes an impossible event and 100 % implies a certain event. Probability of an Event E is represented by P(E). For example, the probability of getting a head when a coin is tossed is equal to 1/2. Similarly, the probability of getting a tail when a coin is tossed is also equal to 1/2. Hence, the total probability will be: P(E) = 1/2 + 1/2 = 1 Know more about probability by clicking here .
Event and outcome
An Outcome is a result of a random experiment. For example, when we roll a dice getting six is an outcome. An Event is a set of outcomes. For example, when we roll dice, the probability of getting a number less than five is an event. Note: An event can have a single outcome.
To know more about Types of Events, visit here .
Experimental Probability
Experimental probability can be applied to any event associated with an experiment that is repeated a large number of times. A trial is when the experiment is performed once. It is also known as empirical probability . Experimental or empirical probability: P(E) =Number of trials where the event occurred/Total Number of Trials Example: In a day, a shopkeeper is able to sell 15 balls, out of which 6 were red balls. Find the probability of selling red balls on the next day of his sales. Given, the total number of balls sold = 15 Number of red balls sold = 6 Probability of red balls = 6/15 = 2/5
To know more about Experimental Probability, visit here .
Theoretical Probability
Theoretical Probability, P(E) = Number of Outcomes Favourable to E / Number of all possible outcomes of the experiment
Here we assume that the outcomes of the experiment are equally likely . Example: Find the probability of picking up a red ball from a basket that contains 5 red and 7 blue balls. Solution: Number of possible outcomes = Total number of balls = 5+7 = 12 Number of favourable outcomes = Number of red balls = 5 Hence, Probability, P(red) = 5/12
For more information on Probability, watch the below video

To know more about Theoretical Probability, visit here .
Elementary Event
An event having only one outcome of the experiment is called an elementary event . Example: Take the experiment of tossing a coin n number of times. One trial of this experiment has two possible outcomes: Heads(H) or Tails(T). So for an individual toss, it has only one outcome, i.e. Heads or Tails.
Sum of Probabilities
The sum of the probabilities of all the elementary events of an experiment is one . Example: take the coin-tossing experiment. P(Heads) + P(Tails )
= (1/2)+ (1/2) =1
Impossible Event

An event that has a 100% probability of occurrence is called a sure event . The probability of occurrence of a sure event is one . E.g., What is the probability that a number obtained after throwing a die is less than 7? So, P(E) = P(Getting a number less than 7) = 6/6= 1
Range of Probability of an event
Probability can range between 0 and 1, where 0 probability means the event to be an impossible one and probability of 1 indicates a certain event i.e. 0 ≤P (E) ≤ 1.
Geometric Probability

Complementary Events
Complementary events are two outcomes of an event that are the only two possible outcomes. This is like flipping a coin and getting heads or tails.
The best example of complementary events is flipping a coin, where ‘getting a head’ complement the event of ‘getting a tail’. To know more about Complementary Events, visit here .
Probability for Class 10 Examples
A bag contains only lemon-flavoured candies. Arjun takes out one candy without looking into the bag. What is the probability that he takes out an orange-flavoured candy?
Let us take the number of candies in the bag to be 100.
Hence, the probability that he takes out an orange-flavoured candy is:
P (Taking orange-flavoured candy) = Number of orange-flavoured candies / Total number of candies.
= 0/100 = 0
Hence, the probability that Arjun takes out an orange-flavoured candy is 0.
This proves that the probability of an impossible event is 0.
A game of chance consists of spinning an arrow that comes to rest, pointing at any one of the numbers such as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, or 8, and these are equally likely outcomes. What is the probability that it will point at? (i)8 (ii) Number greater than 2 (iii) Odd numbers
Sample Space = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
Total Numbers = 8
(i) Probability that the arrow will point at 8:
Number of times we can get 8 = 1
P (Getting 8) = 1/8.
(ii) Probability that the arrow will point at a number greater than 2:
Number greater than 2 = 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8.
No. of numbers greater than 2 = 6
P (Getting numbers greater than 2) = 6/8 = 3/4.
(iii) Probability that the arrow will point at the odd numbers:
Odd number of outcomes = 1, 3, 5, 7
Number of odd numbers = 4.
P (Getting odd numbers) = 4/8 = ½.
Related Articles:
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability MCQs
- Important Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability
Stay tuned with BYJU’S – The Learning App and download the app to learn all Maths-related concepts easily by exploring more videos.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Maths related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Thank you byjus
thank u very much really helped for my exam preparation
Thank you so much it helped me out in my exams
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability
Class 10 maths chapter 15 probability.
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability, in this step-by-step answer guide. In some of State Boards and CBSE schools, students are taught thru NCERT books. As the chapter comes to an end, students are requested few questions in an exercising to evaluate their expertise of the chapter. Students regularly want guidance managing those NCERT Solutions.
It’s most effective natural to get stuck withinside the exercises while solving them so that you can assist students score higher marks, we’ve provided step by step NCERT answers for all exercises of Class ten Mathematics Probability so you can be looking for assist from them. Students should solve those exercises carefully as questions withinside the final exams are requested from those, so these exercises immediately have an impact on students’ final score. Find all NCERT Solutions for Class ten Mathematics Probability below and prepare in your tests easily.
Exercise: 15.1
Page No: 308
1. Complete the following statements:
(i) Probability of an event E + Probability of the event ‘not E’ = ___________.
(ii) The probability of an event that cannot happen is __________. Such an event is called ________.
(iii) The probability of an event that is certain to happen is _________. Such an event is called _________.
(iv) The sum of the probabilities of all the elementary events of an experiment is __________.
(v) The probability of an event is greater than or equal to and less than or equal to __________.
(i) Probability of an event E + Probability of the event ‘not E’ = 1 .
(ii) The probability of an event that cannot happen is 0 . Such an event is called an impossible event .
(iii) The probability of an event that is certain to happen is 1 . Such an event is called a sure or certain event .
(iv) The sum of the probabilities of all the elementary events of an experiment is 1 .
(v) The probability of an event is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1 .
2. Which of the following experiments have equally likely outcomes? Explain.
(i) A driver attempts to start a car. The car starts or does not start.
(ii) A player attempts to shoot a basketball. She/he shoots or misses the shot.
(iii) A trial is made to Solution: a true-false question. The Solution: is right or wrong.
(iv) A baby is born. It is a boy or a girl.
(i) This statement does not have equally likely outcomes as the car may or may not start depending upon various factors like fuel, etc.
(ii) Even this statement does not have equally likely outcomes as the player may shoot or miss the shot.
(iii) This statement has equally likely outcomes as it is known that the solution is either right or wrong.
(iv) This statement also has equally likely outcomes as it is known that the newly born baby can either be a boy or a girl.
3. Why is tossing a coin considered to be a fair way of deciding which team should get the ball at the beginning of a football game?
Tossing of a coin is a fair way of deciding because the number of possible outcomes are only 2 i.e. either head or tail. Since these two outcomes are an equally likely outcome, tossing is unpredictable and is considered to be completely unbiased.
4. Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
(A) 2/3 (B) -1.5 (C) 15% (D) 0.7
The probability of any event (E) always lies between 0 and 1 i.e. 0 ≤ P(E) ≤ 1. So, from the above options, option (B) -1.5 cannot be the probability of an event.
5. If P(E) = 0.05, what is the probability of ‘not E’?
We know that,
P(E)+P(not E) = 1
It is given that, P(E) = 0.05
So, P(not E) = 1-P(E)
Or, P(not E) = 1-0.05
∴ P(not E) = 0.95
6. A bag contains lemon flavored candies only. Malini takes out one candy without looking into the bag. What is the probability that she takes out
(i) an orange flavored candy?
(ii) a lemon flavored candy?
(i) We know that the bag only contains lemon-flavored candies.
So, The no. of orange flavored candies = 0
∴ The probability of taking out orange flavored candies = 0/1 = 0
(ii) As there are only lemon flavored candies, P(lemon flavored candies) = 1 (or 100%)
7. It is given that in a group of 3 students, the probability of 2 students not having the same birthday is 0.992. What is the probability that the 2 students have the same birthday?
Let the event wherein 2 students having the same birthday be E
Given, P(E) = 0.992
Or, P(not E) = 1–0.992 = 0.008
∴ The probability that the 2 students have the same birthday is 0.008
8. A bag contains 3 red balls and 5 black balls. A ball is drawn at random from the bag. What is the probability that the ball drawn is
(ii) not red?
The total number of balls = No. of red balls + No. of black balls
So, the total no. of balls = 5+3 = 8
We know that the probability of an event is the ratio between the no. of favourable outcomes and the total number of outcomes.
P(E) = (Number of favourable outcomes/ Total number of outcomes)
(i) Probability of drawing red balls = P (red balls) = (no. of red balls/total no. of balls) = 3/8
(ii) Probability of drawing black balls = P (black balls) = (no. of black balls/total no. of balls) = 5/8
9. A box contains 5 red marbles, 8 white marbles and 4 green marbles. One marble is taken out of the box at random. What is the probability that the marble taken out will be
(ii) white?
(iii) not green?
The Total no. of balls = 5+8+4 = 17
(i) Total number of red balls = 5
P (red ball) = 5/17 = 0.29
(ii) Total number of white balls = 8
P (white ball) = 8/17 = 0.47
(iii) Total number of green balls = 4
P (green ball) = 4/17 = 0.23
∴ P (not green) = 1-P(green ball) = 1-(4/7) = 0.77
10. A piggy bank contains hundred 50p coins, fifty ₹1 coins, twenty ₹2 coins and ten ₹5 coins. If it is equally likely that one of the coins will fall out when the bank is turned upside down, what is the probability that the coin
(i) will be a 50 p coin?
(ii) will not be a ₹5 coin?
Total no. of coins = 100+50+20+10 = 180
(i) Total number of 50 p coin = 100
P (50 p coin) = 100/180 = 5/9 = 0.55
(ii) Total number of ₹5 coin = 10
P (₹5 coin) = 10/180 = 1/18 = 0.055
∴ P (not ₹5 coin) = 1-P (₹5 coin) = 1-0.055 = 0.945
11. Gopi buys a fish from a shop for his aquarium. The shopkeeper takes out one fish at random from a tank containing 5 male fish and 8 female fish (see Fig. 15.4). What is the probability that the fish taken out is a male fish?

The total number of fish in the tank = 5+8 = 13
Total number of male fish = 5
P (male fish) = 5/13 = 0.38
12. A game of chance consists of spinning an arrow which comes to rest pointing at one of the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 (see Fig. 15.5), and these are equally likely outcomes. What is the probability that it will point at
(ii) an odd number?
(iii) a number greater than 2?
(iv) a number less than 9?

Total number of possible outcomes = 8
(i) Total number of favourable events (i.e. 8) = 1
∴ P (pointing at 8) = ⅛ = 0.125
(ii) Total number of odd numbers = 4 (1, 3, 5 and 7)
P (pointing at an odd number) = 4/8 = ½ = 0.5
(iii) Total numbers greater than 2 = 6 (3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8)
P (pointing at a number greater than 4) = 6/8 = ¾ = 0.75
(iv) Total numbers less than 9 = 8 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8)
P (pointing at a number less than 9) = 8/8 = 1
13. A die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting
(i) a prime number;
(ii) a number lying between 2 and 6;
(iii) an odd number.
Total possible events when a dice is thrown = 6 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6)
(i) Total number of prime numbers = 3 (2, 3 and 5)
P (getting a prime number) = 3/6 = ½ = 0.5
(ii) Total numbers lying between 2 and 6 = 3 (3, 4 and 5)
P (getting a number between 2 and 6) = 3/6 = ½ = 0.5
(iii) Total number of odd numbers = 3 (1, 3 and 5)
P (getting an odd number) = 3/6 = ½ = 0.5
14. One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting
(i) a king of red colour
(ii) a face card
(iii) a red face card
(iv) the jack of hearts
(v) a spade
(vi) the queen of diamonds
Total number of possible outcomes = 52
(i) Total numbers of king of red colour = 2
P (getting a king of red colour) = 2/52 = 1/26 = 0.038
(ii) Total numbers of face cards = 12
P (getting a face card) = 12/52 = 3/13 = 0.23
(iii) Total numbers of red face cards = 6
P (getting a king of red colour) = 6/52 = 3/26 = 0.11
(iv) Total numbers of jack of hearts = 1
P (getting a king of red colour) = 1/52 = 0.019
(v) Total numbers of king of spade = 13
P (getting a king of red colour) = 13/52 = ¼ = 0.25
(vi) Total numbers of queen of diamonds = 1
15. Five cards the ten, jack, queen, king and ace of diamonds, are well-shuffled with their face downwards. One card is then picked up at random.
(i) What is the probability that the card is the queen?
(ii) If the queen is drawn and put aside, what is the probability that the second card picked up is (a) an ace? (b) a queen?
Total numbers of cards = 5
(i) Numbers of queen = 1
P (picking a queen) = ⅕ = 0.2
(ii) If the queen is drawn and put aside, the total numbers of cards left is (5-4) = 4
(a) Total numbers of ace = 1
P (picking an ace) = ¼ = 0.25
(b) Total numbers of queen = 0
P (picking a queen) = 0/4 = 0
16. 12 defective pens are accidentally mixed with 132 good ones. It is not possible to just look at a pen and tell whether or not it is defective. One pen is taken out at random from this lot. Determine the probability that the pen taken out is a good one.
Numbers of pens = Numbers of defective pens + Numbers of good pens
∴ Total number of pens = 132+12 = 144 pens
P(picking a good pen) = 132/144 = 11/12 = 0.916
17. (i) A lot of 20 bulbs contain 4 defective ones. One bulb is drawn at random from the lot. What is the probability that this bulb is defective?
(ii) Suppose the bulb drawn in (i) is not defective and is not replaced. Now one bulb is drawn at random from the rest. What is the probability that this bulb is not defective?
(i) Numbers of defective bulbs = 4
The total numbers of bulbs = 20
∴ Probability of getting a defective bulb = P (defective bulb) = 4/20 = ⅕ = 0.2
(ii) Since 1 non-defective bulb is drawn, then the total numbers of bulbs left are 19
So, the total numbers of events (or outcomes) = 19
Numbers of defective bulbs = 19-4 = 15
So, the probability that the bulb is not defective = 15/19 = 0.789
18. A box contains 90 discs which are numbered from 1 to 90. If one disc is drawn at random from the box, find the probability that it bears
(i) a two-digit number
(ii) a perfect square number
(iii) a number divisible by 5.
The total numbers of discs = 50
(i) Total number of discs having two digit numbers = 81
(Since 1 to 9 are single digit numbers and so, total 2 digit numbers are 90-9 = 81)
P (bearing a two-digit number) = 81/90 = 9/10 = 0.9
(ii) Total number of perfect square numbers = 9 (1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64 and 81)
P (getting a perfect square number) = 9/90 = 1/10 = 0.1
(iii) Total numbers which are divisible by 5 = 18 (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60, 65, 70, 75, 80, 85 and 90)
P (getting a number divisible by 5) = 18/90 = ⅕ = 0.2
19. A child has a die whose six faces show the letters as given below:
The die is thrown once. What is the probability of getting
The total number of possible outcomes (or events) = 6
(i) The total number of faces having A on it = 2
P (getting A) = 2/6 = ⅓ = 0.33
(ii) The total number of faces having D on it = 1
P (getting D) = ⅙ = 0.166
20. Suppose you drop a die at random on the rectangular region shown in Fig. 15.6. What is the probability that it will land inside the circle with diameter 1m?

First, calculate the area of the rectangle and the area of the circle. Here, the area of the rectangle is the possible outcome and the area of the circle will be the favourable outcome.
So, the area of the rectangle = (3×2) m 2 = 6 m 2
The area of the circle = πr 2 = π(½) 2 m 2 = π/4 m 2 = 0.78
∴ The probability that die will land inside the circle = [(π/4)/6] = π/24 or, 0.78/6 = 0.13
21. A lot consists of 144 ball pens of which 20 are defective and the others are good. Nuri will buy a pen if it is good, but will not buy if it is defective. The shopkeeper draws one pen at random and gives it to her. What is the probability that
(i) She will buy it?
(ii) She will not buy it?
The total numbers of outcomes i.e. pens = 144
Given, numbers of defective pens = 20
∴ The numbers of non defective pens = 144-20 = 124
(i) Total numbers events in which she will buy them = 124
So, P (buying) = 124/144 = 31/36 = 0.86
(ii) Total numbers events in which she will not buy them = 20
So, P (not buying) = 20/144 = 5/36 = 0.138
22. Refer to Example 13. (i) Complete the following table:

(ii) A student argues that ‘there are 11 possible outcomes 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12. Therefore, each of them has a probability 1/11. Do you agree with this argument? Justify your Solution:.
If 2 dices are thrown, the possible events are:
(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6)
(2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6)
(3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6)
(4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6)
(5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6)
(6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)
So, the total numbers of events: 6×6 = 36
(i) It is given that to get the sum as 2, the probability is 1/36 as the only possible outcomes = (1,1)
For getting the sum as 3, the possible events (or outcomes) = E (sum 3) = (1,2) and (2,1)
So, P(sum 3) = 2/36
E (sum 4) = (1,3), (3,1), and (2,2)
So, P (sum 4) = 3/36
E (sum 5) = (1,4), (4,1), (2,3), and (3,2)
So, P (sum 5) = 4/36
E (sum 6) = (1,5), (5,1), (2,4), (4,2), and (3,3)
So, P (sum 6) = 5/36
E (sum 7) = (1,6), (6,1), (5,2), (2,5), (4,3), and (3,4)
So, P (sum 7) = 6/36
E (sum 8) = (2,6), (6,2), (3,5), (5,3), and (4,4)
So, P (sum 8) = 5/36
E (sum 9) = (3,6), (6,3), (4,5), and (5,4)
So, P (sum 9) = 4/36
E (sum 10) = (4,6), (6,4), and (5,5)
So, P (sum 10) = 3/36
E (sum 11) = (5,6), and (6,5)
So, P (sum 11) = 2/36
E (sum 12) = (6,6)
So, P (sum 12) = 1/36
So, the table will be as:
(ii) The argument is not correct as it is already justified in (i) that the number of all possible outcomes is 36 and not 11.
23. A game consists of tossing a one rupee coin 3 times and noting its outcome each time. Hanif wins if all the tosses give the same result i.e., three heads or three tails, and loses otherwise. Calculate the probability that Hanif will lose the game.
The total number of outcomes = 8 (HHH, HHT, HTH, THH, TTH, HTT, THT, TTT)
Total outcomes in which Hanif will lose the game = 6 (HHT, HTH, THH, TTH, HTT, THT)
P (losing the game) = 6/8 = ¾ = 0.75
24. A die is thrown twice. What is the probability that
(i) 5 will not come up either time?
(ii) 5 will come up at least once?
[Hint : Throwing a die twice and throwing two dice simultaneously are treated as the same experiment]
Outcomes are:
So, the total number of outcome = 6×6 = 36
(i) Method 1:
Consider the following events.
A = 5 comes in first throw,
B = 5 comes in second throw
P(A) = 6/36,
P(B) = 6/36 and
P(not B) = 5/6
So, P(not A) = 1-(6/36) = 5/6
∴ The required probability = (5/6)×(5/6) = 25/36
Let E be the event in which 5 does not come up either time.
So, the favourable outcomes are [36–(5+6)] = 25
∴ P(E) = 25/36
(ii) Number of events when 5 comes at least once = 11(5+6)
∴ The required probability = 11/36
25. Which of the following arguments are correct and which are not correct? Give reasons for your Solution:.
(i) If two coins are tossed simultaneously there are three possible outcomes—two heads, two tails or one of each. Therefore, for each of these outcomes, the probability is 1/3
(ii) If a die is thrown, there are two possible outcomes—an odd number or an even number. Therefore, the probability of getting an odd number is 1/2
(i) All the possible events are (H,H); (H,T); (T,H) and (T,T)
So, P (getting two heads) = ¼
and, P (getting one of the each) = 2/4 = ½
∴ This statement is incorrect.
(ii) Since the two outcomes are equally likely, this statement is correct.
Exercise: 15.2
Page No: 311
1. Two customers Shyam and Ekta are visiting a particular shop in the same week (Tuesday to Saturday). Each is equally likely to visit the shop on any day as on another day. What is the probability that both will visit the shop on
(i) the same day?
(ii) consecutive days?
(iii) different days?
Since there are 5 days and both can go to the shop in 5 ways each so,
The total number of possible outcomes = 5×5 = 25
(i) The number of favourable events = 5 (Tue., Tue.), (Wed., Wed.), (Thu., Thu.), (Fri., Fri.), (Sat., Sat.)
So, P (both visiting on the same day) = 5/25 = ⅕
(ii) The number of favourable events = 8 (Tue., Wed.), (Wed., Thu.), (Thu., Fri.), (Fri., Sat.), (Sat., Fri.), (Fri., Thu.), (Thu., Wed.), and (Wed., Tue.)
So, P(both visiting on the consecutive days) = 8/25
(iii) P (both visiting on the different days) = 1-P (both visiting on the same day)
So, P (both visiting on the different days) = 1-(⅕) = ⅘
2. A die is numbered in such a way that its faces show the numbers 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 6. It is thrown two times and the total score in two throws is noted. Complete the following table which gives a few values of the total score on the two throws:

What is the probability that the total score is
(iii) at least 6?
The table will be as follows:
So, the total number of outcomes = 6×6 = 36
(i) E (Even) = 18
P (Even) = 18/36 = ½
(ii) E (sum is 6) = 4
P (sum is 6) = 4/36 = 1/9
(iii) E (sum is atleast 6) = 15
P (sum is atleast 6) = 15/36 = 5/12
3. A bag contains 5 red balls and some blue balls. If the probability of drawing a blue ball
is double that of a red ball, determine the number of blue balls in the bag.
It is given that the total number of red balls = 5
Let the total number of blue balls = x
So, the total no. of balls = x+5
∴ P (drawing a blue ball) = [x/(x+5)] ——–(i)
P (drawing a red ball) = [5/(x+5)] ——–(i)
From equation (i) and (ii)
So, the total number of blue balls = 10
4. A box contains 12 balls out of which x are black. If one ball is drawn at random from the
box, what is the probability that it will be a black ball?
If 6 more black balls are put in the box, the probability of drawing a black ball is now
double of what it was before. Find x
Total number of black balls = x
Total number of balls = 12
P (getting black balls) = x/12 ——————-(i)
Now, when 6 more black balls are added,
Total balls become = 18
∴ Total number of black balls = x+6
Now, P (getting black balls) = (x+6)/18 ——————-(ii)
It’s given that, the probability of drawing a black ball now is double of what it was before
(ii) = 2 × (i)
(x+6)/18 = 2 × (x/12)
5. A jar contains 24 marbles, some are green and others are blue. If a marble is drawn at
random from the jar, the probability that it is green is ⅔. Find the number of blue balls
in the jar.
Total marbles = 24
Let the total green marbles = x
So, the total blue marbles = 24-x
P(getting green marble) = x/24
From the question, x/24 = ⅔
So, the total green marbles = 16
And, the total blue marbles = 24-x = 8
Benefits of NCERT Solutions
NCERT’s Class 10 solution contains extremely important points, and for each chapter, each concept has been simplified to make it easier to remember and increase your chances of achieving excellent exam results. Exam Preparation References Here are some tips on how these solutions can help you prepare for the exam.
- This helps students solve many of the problems in each chapter and encourages them to make their concepts more meaningful.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 solutions encourage you to update your knowledge and refine your concepts so that you can get good results in the exam.
- These solutions are the best exam materials, allowing you to learn more about your week and your strengths. To get good results in the exam, it is important to overcome your weaknesses.
- Most of the questions in the exam are formulated in a similar way to NCERT textbooks. Therefore, students should review the solutions in each chapter in order to better understand the topic.
- It is free of cost
Tips & Strategies for Class 10 Exam Preparation
- Plan your course and syllabus and make time for revision
- Please refer to the NCERT solution available on the cbsestudyguru website to clarify your concepts every time you prepare for the exam.
- Use the cbsestudyguru learning app to start learning to successfully pass the exam. Provide complete teaching materials, including resolved and unresolved tasks.
- It is important to clear all your doubts before the exam with your teachers or Alex (an Al study Bot).
- When you read or study a chapter, write down algorithm formulas, theorems, etc., and review them quickly before the exam.
- Practice an ample number of question papers to make your concepts stronger.
- Take rest and a proper meal. Don’t stress too much.
Why opt for cbsestudyguru NCERT Solutions for Class 10 ?
- cbsestudyguru provide NCERT Solutions for all subjects at your fingertips.
- These solutions are designed by subject matter experts and provide solutions to every NCERT textbook questions.
- cbsestudyguru especially focuses on making learning interactive, effective and for all classes.
- We provide free NCERT Solutions for class 10 and all other classes.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Study on Target Reliability of Mine Rock Slopes by Grey Fixed Weight Clustering and Analogy Method—Case Study of the Jinbao Iron Mine
- Published: 08 April 2024
Cite this article
- Axin Zheng 1 &
- Jianping Pan 1
The target reliability of mine rock slopes must be scientifically determined, which can fully reflect the safety level of slope stability and plays an essential role in establishing slope reliability design guidelines. Since the design guidelines based on reliability methods have not been established for mine rock slopes, the suggested target reliability values are proposed based on the grey fixed weight clustering and analogy method. Firstly, a new evaluation method of slope safety grade is proposed by considering more influencing factors of slopes. Secondly, the grey fixed weight clustering is used to quantitatively processes the slope reliability data, and the slope safety grade is judged. Then, the target reliability of each grade is obtained by the analogy method. Finally, the equal difference method is applied to set the threshold of allowable failure probability for the minimum service life of slopes, and the reliability of other service life is processed by linear interpolation. The results show that, the target reliability of the maximum service life for grade I, II, III ductile failure is 3.25, 2.75, 2.25, and brittle failure is 3.75, 3.25, 2.75, respectively. the allowable failure probability of the minimum service life for each grade shows that the ductile failure is 1%, 3%, 5% and brittle failure is 0.5%, 1%, 3%, respectively. In addition, the suggested values of Inter-ramp and Bench slopes are also improved, and a case study is conducted in the Jinbao iron mine to illustrate the feasibility of the method and results in this paper.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Data availability
The data can be made available upon request.
Abdellah, W. R., Hirohama, C., Sainoki, A., et al. (2022). Estimating the optimal overall slope angle of open-pit mines with probabilistic analysis. Applied Sciences, 12 , 4746.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Amoushahi, S., Grenon, M., Locat, J., et al. (2018). Deterministic and probabilistic stability analysis of a mining rock slope in the vicinity of a major public road—case study of the LAB Chrysotile mine in Canada. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 55 (10), 1391–1404.
Deng, J. L. (1989). Introduction to Grey system theory. The Journal of Grey System, 1 (1), 1–24.
Google Scholar
Department of minerals and energy (1999) Guideline of geotechnical considerations in open-pit mines (1st ed., pp. 24-25). Western Australia.
Du, S. G. (2018). Method of equal accuracy assessment for the stability analysis of large open-pit mine slopes. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 37 (6), 1301–1331.
Du, S. G., Saroglou, C., Chen, Y. F., et al. (2022). A new approach for evaluation of slope stability in large open-pit mines: a case study at the dexing copper mine China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 81 (3), 102.
Article Google Scholar
Du, S. G., Yong, R., Chen, J. Q., et al. (2017). Graded analysis for slope stability assessment of large open-pit mines. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 36 (11), 2601–2611.
Fang, Y. S. (2015). Application and division of safety levels of slope projects. Chongqing Architecture, 14 (8), 40–45.
Fang, Q. C., & Shang, L. (2019). Analysis of the rock slope stability for the open-pit mine based on the game theory and the cloud model. Journal of Safety and Environment, 19 (1), 8–13.
GB 50153–2008. (2008). Unified standard for reliability design of engineering structures . China Architecture and Building Press.
GB 51016–2014. (2014). Technical code for con-coal open-pit mine slope engineering . China Planning Press.
He, M. C. (2009). Real-time remote monitoring and forecasting system for geological disasters of landslides and its engineering application. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 28 (6), 1081–1090.
Huang, D. X., Dong, X., Wang, J. X., et al. (2020). Study on the sensitivity of joint parameters and slope stability analysis of open-pit mine. Metal Mine, 2020 (3), 64–70.
Liu, S. F., Yang, Y. J., Wu, L. F., et al. (2014). Grey system theory and its applications. Grey cluster evaluation model (7th ed., pp. 113–139). Science Press.
Pine, R. J. (1992). Risk analysis design applications in mining geomechanics. Transactions of the Institution of Mining and Metallurgy., 101(Sec A) , 149–158.
Priest, S. D., & Brown, E. T. (1983). Probabilistic stability analysis of variable rock slopes. Transactions of the Institution of Mining and Metallurgy., 92 (Sec A) , 1–12.
Qiu, X. D., Gao, X. L., Yuan, S. D., et al. (1998). Research on the reliability analysis for the slope of open pit. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 27 (1), 2–5.
Read, J., & Stacey, P. (2009). Guidelines for open-pit slope design . CSIRO.
Book Google Scholar
Safe Work Australia (2011) Ground control in open-pit mines (pp. 18-19). Australia.
Sjöberg J (1999) Analysis of large scale rock slopes. Dissertation, Luleå tekniska universitet.
Song, Z. H., Li, X. F., Qi, F. F., et al. (2021). Analysis of the triggering factors for dangerous rockfall accident in open pit mine. Journal of Guangxi University (natural Science Edition), 46 (1), 159–165.
Su, P. D., Qiu, P., Liu, B., et al. (2022). Stability prediction and optimal angle of high slope in open-pit mine based on two-dimension limit equilibrium method and three-dimension numerical simulation. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts a/b/c, 127 , 103151.
Wang, L. D., Hou, K. P., Sun, H. F., & Sun, W. (2021). Evaluation of slope stability based on improved game theory-variable weight extension model. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 11 (9), 100–106.
CAS Google Scholar
Wang, S. W., Liu, H. D., & Wan, L. H. (2004). Research of safety standard of pit slope. Journal of North China Institute of Water Conservancy and Hydroelectric Power, 25 (1), 54–57.
Wu, S. C., He, P. B., Cheng, H. Y., et al. (2022). Discussion on the stability evaluation standard of a rock slope in a noncoal open-pit mine. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 44 (5), 876–885.
Wu, S. C., Zhang, H. J., Xiao, S., et al. (2019). Study on time-varying target reliability of open-pit slope considering service life. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 36 (03), 542–548.
Yan XM (2013) Risk Analysis on Open-Pit Slope Based on Reliability Theory. Dissertation, Central South University.
Yang, T. H., Zhang, F. C., Yu, Q. L., et al. (2011). Research situation of open-pit mining high and steep slope stability and its developing trend. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 32 (5), 1437–1451.
Zeng, S., Yang, S. J., Sun, B., et al. (2006). Reliability analysis of open-pit slope based on ABAQUS and ANFIS. Journal of China Coal Society, 31 (4), 437–441.
Zeng, X. N., Cheng, Y. C., Yang, H. Y., et al. (2009). Research and application of reliability analysis method in mine slope. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 29 (1), 23–26.
Zhao, B. (2022). The combination weighting model of game theory and cloud matter-element for slope stability evaluation. Mining Research and Development, 42 (6), 60–67.
Zhu, Y. X. (1993). Slope reliability analysis . Metallurgical Industry Press.
Download references
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support was received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Civil and Surveying Engineering, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou, 341000, Jiangxi Province, China
Axin Zheng & Jianping Pan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The first author (Axin Zheng) wrote the article. And the second author (Professor, Pan) provided some necessary suggestions.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jianping Pan .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Zheng, A., Pan, J. Study on Target Reliability of Mine Rock Slopes by Grey Fixed Weight Clustering and Analogy Method—Case Study of the Jinbao Iron Mine. Pure Appl. Geophys. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-024-03471-7
Download citation
Received : 28 May 2023
Revised : 09 March 2024
Accepted : 17 March 2024
Published : 08 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-024-03471-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mine rock slope
- grey fixed weight clustering
- analogy method
- target reliability
- service life
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 - Probability. CASE STUDY 1: On a weekend Rani was playing cards with her family . The deck has 52 cards. If her brother drew one card. 1. Find ...
CBSE 10th Standard Maths Subject Probability Case Study Questions 2021. 10th Standard CBSE. Reg.No. : Maths. Time : 01:00:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 25. Case Study Questions. In a play zone, Nishtha is playing claw crane game which consists of 58 teddy bears, 42 pokemons, 36 tigers and 64 monkeys. Nishtha picks a puppet at random.
Class 10 Case Study Based Questions Chapter 15 Probability CBSE Board Term 1 with Answer Key, ... (Probability) of Class 10th. These Case study Questions are based on the Latest Syllabus for 2021- 22 of the CBSE Board. Chapter 15 (Probability) ...
The case study on Probability Class 10 Maths with solutions in PDF helps students tackle questions that appear confusing or difficult to answer. The answers to the Probability case study questions are very easy to grasp from the PDF - download links are given on this page.
Probability Case Study Questions With answers. Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: Rohit wants to distribute chocolates in his class on his birthday. The chocolates are of three types: Milk chocolate, White chocolate and Dark chocolate.
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability Case Study Questions: Question 1: On a weekend Rani was playing cards with her family. The deck has 52 cards. If her brother drew one card. (i) Find the probability of getting a king of red colour.(a) 1/26(b) 1/13(c) 1/52(d) 1/4 … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter ...
Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Probability in order to fully complete your preparation.They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Case Study Based Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams!. I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams.
1. If Neha plays first, then the probability that she successfully sinks the ball numbered 10 is. 2. If Sneha plays secondly without replacing the ball 10, then the probability that Sneha sink the ball numbered 13 is. 3. The probability that Neha sinks a ball is an odd number is. 4.
Probability Case Study Question; Format of Maths Case-Based Questions. CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions will have one passage and four questions. As you know, CBSE has introduced Case Study Questions in class 10 and class 12 this year, the annual examination will have case-based questions in almost all major subjects.
Probability Case Study Questions With Answers. Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: Rohit wants to distribute chocolates in his class on his birthday. The chocolates are of three types: Milk chocolate, White chocolate and Dark chocolate.
The Case Based Questions: Probability is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 10 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
By QB365. QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 10th Maths Subject - Probability, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
Get NCERT Solutions for Chapter 14 Class 10 free at teachoo. Solutions to all exercise questions, examples and optional is available with detailed explanations. In Class 9, we studied about Empirical or Experimental Probability. In this chapter, we will study. Theoretical Probability, that is, P (E) = Number of outcomes with E / Total possible ...
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 - Probability: CASE STUDY 1: On a weekend Rani was playing cards with her family. The deck has 52 cards. If her brother drew one card. 1. Find ...
Download Case Study Questions for Class 10 Mathematics to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 10 Final Exam of 2022-23. These Case Study and Passage Based questions are published by the experts of CBSE Experts for the students of CBSE Class 10 so that they can score 100% on Boards. ... Probability is another simple and important chapter in ...
Important Questions & Answers For Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability. Q. 1: Two dice are thrown at the same time. Find the probability of getting. (i) the same number on both dice. (ii) different numbers on both dice. Solution: Given that, Two dice are thrown at the same time. So, the total number of possible outcomes n (S) = 6 2 = 36.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 - CBSE Free PDF Download *According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 14. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability is undoubtedly an essential study material for the students studying in CBSE Class 10.NCERT Solutions, along with the downloadable PDF provided in this article, can help ...
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability are provided here to help the students of CBSE class 10. Our expert teachers prepared all these solutions as per the latest CBSE syllabus and guidelines. In this chapter, we have discussed the theoretical approach of probability in details. CBSE Class 10 Maths solutions provide a detailed ...
Chapters for Case Study Questions. My Class Videos Tests ₹ Plans Ask a Doubt. TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 students. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving skills with expert advice.
CBSE Board has introduced the case study questions for the ongoing academic session 2021-22. The board will ask the paper on the basis of a different exam pattern which has been introduced this year where 50% syllabus is occupied for MCQ for Term 1 exam. Selfstudys has provided below the chapter-wise questions for CBSE Class 10 Maths.
No. of numbers greater than 2 = 6. P (Getting numbers greater than 2) = 6/8 = 3/4. (iii) Probability that the arrow will point at the odd numbers: Odd number of outcomes = 1, 3, 5, 7. Number of odd numbers = 4. P (Getting odd numbers) = 4/8 = ½. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability. Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability MCQs.
Determine the probability that the pen taken out is a good one. Solution: Numbers of pens = Numbers of defective pens + Numbers of good pens. ∴ Total number of pens = 132+12 = 144 pens. P (E) = (Number of favourable outcomes/ Total number of outcomes) P (picking a good pen) = 132/144 = 11/12 = 0.916.
The maximum failure probability of the Bench slope is 25%. Here, the equal difference method is used, and the allowable failure probability of the Inter-ramp slope of grades I and II, grade III is set to 5%, and 10% respectively, with 10% and 15% as the allowable failure probability of Bench slope of grades I and II, and grade III.
Nearly 50 million km2 of global land experiences seasonal transitions from predominantly frozen to thawed conditions, significantly impacting various ecosystems and hydrologic processes. In this study, we assessed the capability to retrieve surface freeze-thaw (FT) conditions using Sentinel-1 synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data time series at two agro-forested study sites, St-Marthe and St ...