Solver Title

Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Expanded Form Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- Pre Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Conversions

Most Used Actions
Number line.
- x^{2}-x-6=0
- -x+3\gt 2x+1
- line\:(1,\:2),\:(3,\:1)
- prove\:\tan^2(x)-\sin^2(x)=\tan^2(x)\sin^2(x)
- \frac{d}{dx}(\frac{3x+9}{2-x})
- (\sin^2(\theta))'
- \lim _{x\to 0}(x\ln (x))
- \int e^x\cos (x)dx
- \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx
- \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n}
- Is there a step by step calculator for math?
- Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of math problems, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and linear algebra. It shows you the solution, graph, detailed steps and explanations for each problem.
- Is there a step by step calculator for physics?
- Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of physics problems, including mechanics, electricity and magnetism, and thermodynamics. It shows you the steps and explanations for each problem, so you can learn as you go.
- How to solve math problems step-by-step?
- To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem.
- My Notebook, the Symbolab way Math notebooks have been around for hundreds of years. You write down problems, solutions and notes to go back...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&
High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
Free ready-to-use math resources
Hundreds of free math resources created by experienced math teachers to save time, build engagement and accelerate growth
20 Effective Math Strategies To Approach Problem-Solving
Katie Keeton
Math strategies for problem-solving help students use a range of approaches to solve many different types of problems. It involves identifying the problem and carrying out a plan of action to find the answer to mathematical problems.
Problem-solving skills are essential to math in the general classroom and real-life. They require logical reasoning and critical thinking skills. students must be equipped with strategies to help them find solutions to problems.
This article explores mathematical problem solving strategies, logical reasoning and critical thinking skills to help learners with solving math word problems independently in real-life situations.
What are problem-solving strategies?
Problem-solving strategies in math are methods students can use to figure out solutions to math problems. Some problem-solving strategies:
- Draw a model
- Use different approaches
- Check the inverse to make sure the answer is correct
Students need to have a toolkit of math problem-solving strategies at their disposal to provide different ways to approach math problems. This makes it easier to find solutions and understand math better.
Strategies can help guide students to the solution when it is difficult ot know when to start.

The ultimate guide to problem solving techniques
Download these ready-to-go problem solving techniques that every student should know. Includes printable tasks for students including challenges, short explanations for teachers with questioning prompts.
20 Math Strategies For Problem-Solving
Different problem-solving math strategies are required for different parts of the problem. It is unlikely that students will use the same strategy to understand and solve the problem.
Here are 20 strategies to help students develop their problem-solving skills.
Strategies to understand the problem
Strategies that help students understand the problem before solving it helps ensure they understand:
- The context
- What the key information is
- How to form a plan to solve it
Following these steps leads students to the correct solution and makes the math word problem easier .
Here are five strategies to help students understand the content of the problem and identify key information.
1. Read the problem aloud
Read a word problem aloud to help understand it. Hearing the words engages auditory processing. This can make it easier to process and comprehend the context of the situation.
2. Highlight keywords
When keywords are highlighted in a word problem, it helps the student focus on the essential information needed to solve it. Some important keywords help determine which operation is needed. For example, if the word problem asks how many are left, the problem likely requires subtraction. Ensure students highlight the keywords carefully and do not highlight every number or keyword. There is likely irrelevant information in the word problem.
3. Summarize the information
Read the problem aloud, highlight the key information and then summarize the information. Students can do this in their heads or write down a quick summary. Summaries should include only the important information and be in simple terms that help contextualize the problem.
4. Determine the unknown
A common problem that students have when solving a word problem is misunderstanding what they are solving. Determine what the unknown information is before finding the answer. Often, a word problem contains a question where you can find the unknown information you need to solve. For example, in the question ‘How many apples are left?’ students need to find the number of apples left over.
5. Make a plan
Once students understand the context of the word problem, have dentified the important information and determined the unknown, they can make a plan to solve it. The plan will depend on the type of problem. Some problems involve more than one step to solve them as some require more than one answer. Encourage students to make a list of each step they need to take to solve the problem before getting started.
Strategies for solving the problem
1. draw a model or diagram.
Students may find it useful to draw a model, picture, diagram, or other visual aid to help with the problem solving process. It can help to visualize the problem to understand the relationships between the numbers in the problem. In turn, this helps students see the solution.
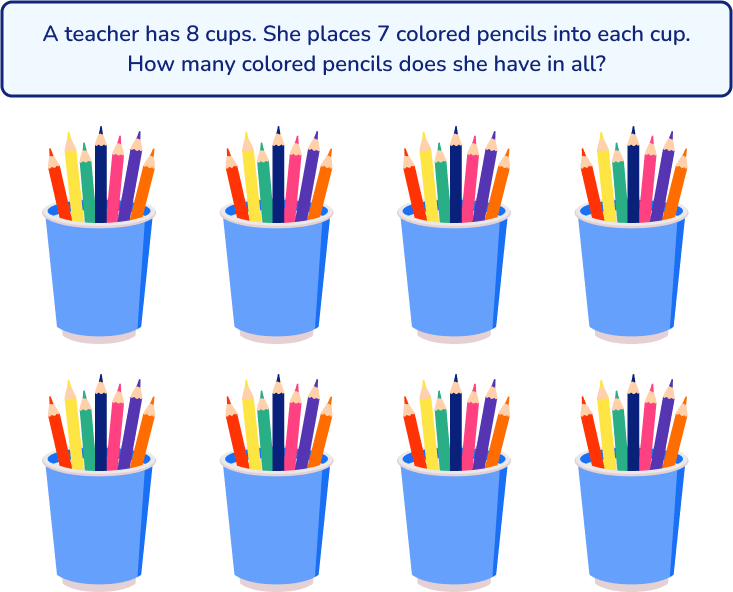
Similarly, you could draw a model to represent the objects in the problem:
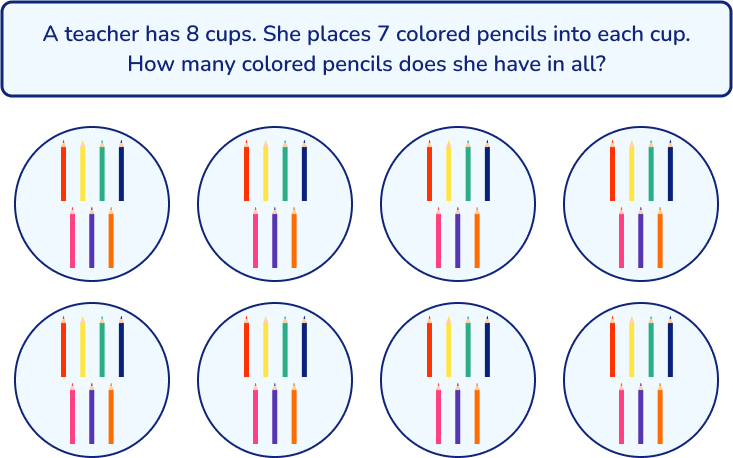
2. Act it out
This particular strategy is applicable at any grade level but is especially helpful in math investigation in elementary school . It involves a physical demonstration or students acting out the problem using movements, concrete resources and math manipulatives . When students act out a problem, they can visualize and contectualize the word problem in another way and secure an understanding of the math concepts. The examples below show how 1st-grade students could “act out” an addition and subtraction problem:
3. Work backwards
Working backwards is a popular problem-solving strategy. It involves starting with a possible solution and deciding what steps to take to arrive at that solution. This strategy can be particularly helpful when students solve math word problems involving multiple steps. They can start at the end and think carefully about each step taken as opposed to jumping to the end of the problem and missing steps in between.
For example,

To solve this problem working backwards, start with the final condition, which is Sam’s grandmother’s age (71) and work backwards to find Sam’s age. Subtract 20 from the grandmother’s age, which is 71. Then, divide the result by 3 to get Sam’s age. 71 – 20 = 51 51 ÷ 3 = 17 Sam is 17 years old.
4. Write a number sentence
When faced with a word problem, encourage students to write a number sentence based on the information. This helps translate the information in the word problem into a math equation or expression, which is more easily solved. It is important to fully understand the context of the word problem and what students need to solve before writing an equation to represent it.
5. Use a formula
Specific formulas help solve many math problems. For example, if a problem asks students to find the area of a rug, they would use the area formula (area = length × width) to solve. Make sure students know the important mathematical formulas they will need in tests and real-life. It can help to display these around the classroom or, for those who need more support, on students’ desks.
Strategies for checking the solution
Once the problem is solved using an appropriate strategy, it is equally important to check the solution to ensure it is correct and makes sense.
There are many strategies to check the solution. The strategy for a specific problem is dependent on the problem type and math content involved.
Here are five strategies to help students check their solutions.
1. Use the Inverse Operation
For simpler problems, a quick and easy problem solving strategy is to use the inverse operation. For example, if the operation to solve a word problem is 56 ÷ 8 = 7 students can check the answer is correct by multiplying 8 × 7. As good practice, encourage students to use the inverse operation routinely to check their work.
2. Estimate to check for reasonableness
Once students reach an answer, they can use estimation or rounding to see if the answer is reasonable. Round each number in the equation to a number that’s close and easy to work with, usually a multiple of ten. For example, if the question was 216 ÷ 18 and the quotient was 12, students might round 216 to 200 and round 18 to 20. Then use mental math to solve 200 ÷ 20, which is 10. When the estimate is clear the two numbers are close. This means your answer is reasonable.
3. Plug-In Method
This method is particularly useful for algebraic equations. Specifically when working with variables. To use the plug-in method, students solve the problem as asked and arrive at an answer. They can then plug the answer into the original equation to see if it works. If it does, the answer is correct.

If students use the equation 20m+80=300 to solve this problem and find that m = 11, they can plug that value back into the equation to see if it is correct. 20m + 80 = 300 20 (11) + 80 = 300 220 + 80 = 300 300 = 300 ✓
4. Peer Review
Peer review is a great tool to use at any grade level as it promotes critical thinking and collaboration between students. The reviewers can look at the problem from a different view as they check to see if the problem was solved correctly. Problem solvers receive immediate feedback and the opportunity to discuss their thinking with their peers. This strategy is effective with mixed-ability partners or similar-ability partners. In mixed-ability groups, the partner with stronger skills provides guidance and support to the partner with weaker skills, while reinforcing their own understanding of the content and communication skills. If partners have comparable ability levels and problem-solving skills, they may find that they approach problems differently or have unique insights to offer each other about the problem-solving process.
5. Use a Calculator
A calculator can be introduced at any grade level but may be best for older students who already have a foundational understanding of basic math operations. Provide students with a calculator to allow them to check their solutions independently, accurately, and quickly. Since calculators are so readily available on smartphones and tablets, they allow students to develop practical skills that apply to real-world situations.
Step-by-step problem-solving processes for your classroom
In his book, How to Solve It , published in 1945, mathematician George Polya introduced a 4-step process to solve problems.
Polya’s 4 steps include:
- Understand the problem
- Devise a plan
- Carry out the plan
Today, in the style of George Polya, many problem-solving strategies use various acronyms and steps to help students recall.
Many teachers create posters and anchor charts of their chosen process to display in their classrooms. They can be implemented in any elementary, middle school or high school classroom.
Here are 5 problem-solving strategies to introduce to students and use in the classroom.
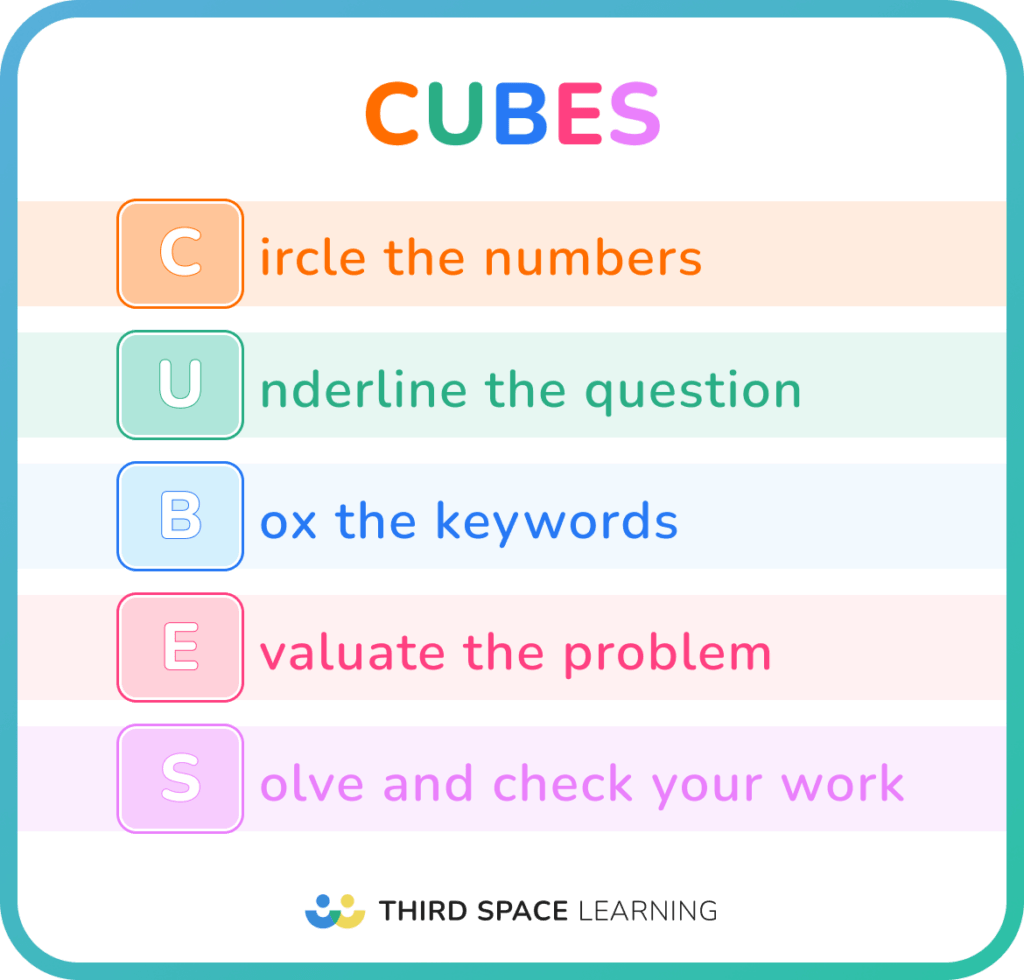
How Third Space Learning improves problem-solving
Resources .
Third Space Learning offers a free resource library is filled with hundreds of high-quality resources. A team of experienced math experts carefully created each resource to develop students mental arithmetic, problem solving and critical thinking.
Explore the range of problem solving resources for 2nd to 8th grade students.
One-on-one tutoring
Third Space Learning offers one-on-one math tutoring to help students improve their math skills. Highly qualified tutors deliver high-quality lessons aligned to state standards.
Former teachers and math experts write all of Third Space Learning’s tutoring lessons. Expertly designed lessons follow a “my turn, follow me, your turn” pedagogy to help students move from guided instruction and problem-solving to independent practice.
Throughout each lesson, tutors ask higher-level thinking questions to promote critical thinking and ensure students are developing a deep understanding of the content and problem-solving skills.
Problem-solving
Educators can use many different strategies to teach problem-solving and help students develop and carry out a plan when solving math problems. Incorporate these math strategies into any math program and use them with a variety of math concepts, from whole numbers and fractions to algebra.
Teaching students how to choose and implement problem-solving strategies helps them develop mathematical reasoning skills and critical thinking they can apply to real-life problem-solving.
READ MORE : 8 Common Core math examples
There are many different strategies for problem-solving; Here are 5 problem-solving strategies: • draw a model • act it out • work backwards • write a number sentence • use a formula
Here are 10 strategies of problem-solving: • Read the problem aloud • Highlight keywords • Summarize the information • Determine the unknown • Make a plan • Draw a model • Act it out • Work backwards • Write a number sentence • Use a formula
1. Understand the problem 2. Devise a plan 3. Carry out the plan 4. Look back
Some strategies you can use to solve challenging math problems are: breaking the problem into smaller parts, using diagrams or models, applying logical reasoning, and trying different approaches.
Related articles

Why Student Centered Learning Is Important: A Guide For Educators

13 Effective Learning Strategies: A Guide to Using them in your Math Classroom

Differentiated Instruction: 9 Differentiated Curriculum And Instruction Strategies For Teachers

5 Math Mastery Strategies To Incorporate Into Your 4th and 5th Grade Classrooms
Ultimate Guide to Metacognition [FREE]
Looking for a summary on metacognition in relation to math teaching and learning?
Check out this guide featuring practical examples, tips and strategies to successfully embed metacognition across your school to accelerate math growth.
Privacy Overview
- Problem Generator
- Mobile Apps
- All Products
- Preferences
- My Apps (API)

Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems
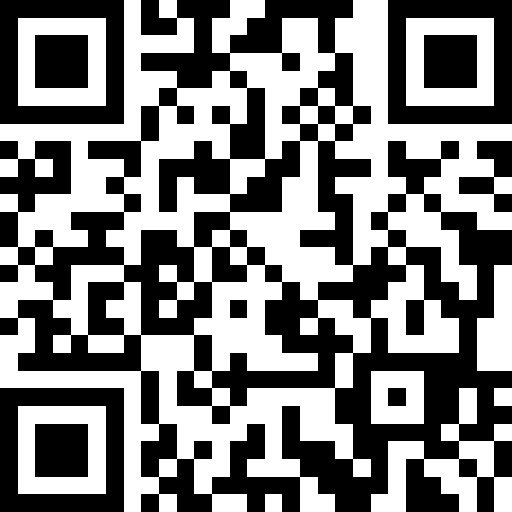

Try Math Solver

Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities
What can QuickMath do?
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students.
- The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and cancelling common factors within a fraction.
- The equations section lets you solve an equation or system of equations. You can usually find the exact answer or, if necessary, a numerical answer to almost any accuracy you require.
- The inequalities section lets you solve an inequality or a system of inequalities for a single variable. You can also plot inequalities in two variables.
- The calculus section will carry out differentiation as well as definite and indefinite integration.
- The matrices section contains commands for the arithmetic manipulation of matrices.
- The graphs section contains commands for plotting equations and inequalities.
- The numbers section has a percentages command for explaining the most common types of percentage problems and a section for dealing with scientific notation.
Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions

Game Central
- Try for free
Problem Solving: Make a Table Math Strategy

Math Problem Solving: Make a Table
In this introductory guide, we will explore the Make a Table math strategy, a valuable tool for solving problems by organizing information in a logical format.
This problem-solving strategy encourages students to identify patterns and relationships within data. We’ll explain the strategy using an example and explain how it can be used effectively in mathematical problem-solving.

What is the Make a Table Math Strategy?
Making a table is a math problem-solving strategy that students can use to solve word problems by writing information in a more organized format.
Example of a problem that can be solved by making a table:
Juanita checked a book out of the library, and it is now 7 days overdue. If a book is 1 day overdue, the fine is 10¢, 2 days overdue, 20¢, 3 days overdue, 30¢, and so on. How much is her fine?
Why is the Make a Table Math Strategy Important?
This problem-solving strategy allows students to discover relationships and patterns among data. It encourages students to organize information logically and to look critically at the data to find patterns and develop a solution.
How to Make a Table to Solve a Math Problem
To help you learn to teach the Make a Table Math strategy, we will use the following word problem as an example:
How many hours will a car traveling at 65 miles per hour take to catch up with a car traveling at 55 miles per hour if the slower car starts one hour before the faster car?
Step 1: Understand the Problem
Demonstrate that the first step is understanding the problem. This involves identifying the key pieces of information needed to find the answer. This may require students to read the problem several times or put the problem into their own words.
In this problem, students need to understand that there is a slower car going 55 miles per hour and a faster car going 65 miles per hour. The slower car starts one hour before the faster car. Students need to find how many hours it will take the faster car to catch up to the slower car.
Step 2: Choose a Strategy
Because there are three sets of data to organize, you should use the Make a Table strategy. Generally, if there is data associated with a certain category, it can be organized easily by making a table. This strategy also overlaps with the Find a Pattern strategy because it is often easier to find a pattern when the data is organized in a table.
Step 3: Solve the Problem
Make a table to organize the data. For this example, create a row for the slower car, a row for the faster car, and a column for each hour. Find the distance traveled during each hour by looking at the distances listed in each column.
The distance of the faster car was more than the distance of the slower car in hour seven. The faster car took six hours to catch up to the slower car.
Step 3: Check Your Work
Reread the problem to be sure the question was answered.
Did you find the number of hours it took for the faster car to catch up?
Yes, it took 6 hours.
Check the math to be sure it is correct.
55 x 2 = 110, 55 x 3 = 165, 55 x 4 = 220, 55 x 5 = 275, 55 x 6 = 330, 55 x 7 = 385 65 x 2 = 130, 65 x 3 = 195, 65 x 4 = 260, 65 x 5 = 325, 65 x 6 = 390
Determine if the best strategy was chosen for this problem or if there was another way to solve the problem.
Making a table was a good way to solve this problem.
Step 4: Explain Your Work
The last step is explaining how you found the answer. Demonstrate how to write a paragraph describing the steps you took and how you made decisions throughout the process.
I set up a table for the miles each car had gone during each hour. I kept adding columns until the faster car caught up to the slower car. At the end of the seventh hour, the faster car had gone 390 miles, which was more than the distance traveled by the slower car, 385 miles. Because the faster car didn't start traveling in the first hour, it traveled for six hours.
Step 5: Guided Practice
Have students try solving the following problem using the strategy Make a Table.
The printer in the media center can print 1 page every 30 seconds. The printer in the office can print 4 pages every 30 seconds. If both printers are printing, how many pages will the office printer have printed by the time the media center printer prints 5 pages?
Have students work in pairs, groups, or individually to solve this problem. They should be able to tell or write about how they found the answer and justify their reasoning.
How Can You Stretch Students’ Thinking?
The Make a Table math strategy can be stretched when combined with other strategies, such as looking for patterns or drawing a picture. By combining this strategy with others, students can analyze the data that is given to find more complex relationships.
Featured Middle School Resources

Related Resources
About the author.

Digital Content Manager & Editor
About haley.


Or search by topic
Number and algebra
- The Number System and Place Value
- Calculations and Numerical Methods
- Fractions, Decimals, Percentages, Ratio and Proportion
- Properties of Numbers
- Patterns, Sequences and Structure
- Algebraic expressions, equations and formulae
- Coordinates, Functions and Graphs
Geometry and measure
- Angles, Polygons, and Geometrical Proof
- 3D Geometry, Shape and Space
- Measuring and calculating with units
- Transformations and constructions
- Pythagoras and Trigonometry
- Vectors and Matrices
Probability and statistics
- Handling, Processing and Representing Data
- Probability
Working mathematically
- Thinking mathematically
- Mathematical mindsets
- Cross-curricular contexts
- Physical and digital manipulatives
For younger learners
- Early Years Foundation Stage
Advanced mathematics
- Decision Mathematics and Combinatorics
- Advanced Probability and Statistics
Published 2018
The Problem-solving Classroom
- Visualising
- Working backwards
- Reasoning logically
- Conjecturing
- Working systematically
- Looking for patterns
- Trial and improvement.
- stage of the lesson
- level of thinking
- mathematical skill.
- The length of student response increases (300-700%)
- More responses are supported by logical argument.
- An increased number of speculative responses.
- The number of questions asked by students increases.
- Student - student exchanges increase (volleyball).
- Failures to respond decrease.
- 'Disciplinary moves' decrease.
- The variety of students participating increases. As does the number of unsolicited, but appropriate contributions.
- Student confidence increases.
- conceptual understanding
- procedural fluency
- strategic competence
- adaptive reasoning
- productive disposition

Upload a screenshot and solve any math problem instantly with MathGPT!
Drag & drop an image file here, or click to select an image.

Problem Solving Activities: 7 Strategies
- Critical Thinking

Problem solving can be a daunting aspect of effective mathematics teaching, but it does not have to be! In this post, I share seven strategic ways to integrate problem solving into your everyday math program.
In the middle of our problem solving lesson, my district math coordinator stopped by for a surprise walkthrough.
I was so excited!
We were in the middle of what I thought was the most brilliant math lesson– teaching my students how to solve problem solving tasks using specific problem solving strategies.
It was a proud moment for me!
Each week, I presented a new problem solving strategy and the students completed problems that emphasized the strategy.
Genius right?
After observing my class, my district coordinator pulled me aside to chat. I was excited to talk to her about my brilliant plan, but she told me I should provide the tasks and let my students come up with ways to solve the problems. Then, as students shared their work, I could revoice the student’s strategies and give them an official name.
What a crushing blow! Just when I thought I did something special, I find out I did it all wrong.
I took some time to consider her advice. Once I acknowledged she was right, I was able to make BIG changes to the way I taught problem solving in the classroom.
When I Finally Saw the Light
To give my students an opportunity to engage in more authentic problem solving which would lead them to use a larger variety of problem solving strategies, I decided to vary the activities and the way I approached problem solving with my students.
Problem Solving Activities
Here are seven ways to strategically reinforce problem solving skills in your classroom.

Seasonal Problem Solving
Many teachers use word problems as problem solving tasks. Instead, try engaging your students with non-routine tasks that look like word problems but require more than the use of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to complete. Seasonal problem solving tasks and daily challenges are a perfect way to celebrate the season and have a little fun too!
Cooperative Problem Solving Tasks
Go cooperative! If you’ve got a few extra minutes, have students work on problem solving tasks in small groups. After working through the task, students create a poster to help explain their solution process and then post their poster around the classroom. Students then complete a gallery walk of the posters in the classroom and provide feedback via sticky notes or during a math talk session.
Notice and Wonder
Before beginning a problem solving task, such as a seasonal problem solving task, conduct a Notice and Wonder session. To do this, ask students what they notice about the problem. Then, ask them what they wonder about the problem. This will give students an opportunity to highlight the unique characteristics and conditions of the problem as they try to make sense of it.
Want a better experience? Remove the stimulus, or question, and allow students to wonder about the problem. Try it! You’ll gain some great insight into how your students think about a problem.

Math Starters
Start your math block with a math starter, critical thinking activities designed to get your students thinking about math and provide opportunities to “sneak” in grade-level content and skills in a fun and engaging way. These tasks are quick, designed to take no more than five minutes, and provide a great way to turn-on your students’ brains. Read more about math starters here !
Create your own puzzle box! The puzzle box is a set of puzzles and math challenges I use as fast finisher tasks for my students when they finish an assignment or need an extra challenge. The box can be a file box, file crate, or even a wall chart. It includes a variety of activities so all students can find a challenge that suits their interests and ability level.
Calculators
Use calculators! For some reason, this tool is not one many students get to use frequently; however, it’s important students have a chance to practice using it in the classroom. After all, almost everyone has access to a calculator on their cell phones. There are also some standardized tests that allow students to use them, so it’s important for us to practice using calculators in the classroom. Plus, calculators can be fun learning tools all by themselves!
Three-Act Math Tasks
Use a three-act math task to engage students with a content-focused, real-world problem! These math tasks were created with math modeling in mind– students are presented with a scenario and then given clues and hints to help them solve the problem. There are several sites where you can find these awesome math tasks, including Dan Meyer’s Three-Act Math Tasks and Graham Fletcher’s 3-Acts Lessons .
Getting the Most from Each of the Problem Solving Activities
When students participate in problem solving activities, it is important to ask guiding, not leading, questions. This provides students with the support necessary to move forward in their thinking and it provides teachers with a more in-depth understanding of student thinking. Selecting an initial question and then analyzing a student’s response tells teachers where to go next.
Ready to jump in? Grab a free set of problem solving challenges like the ones pictured using the form below.
Which of the problem solving activities will you try first? Respond in the comments below.

Shametria Routt Banks
- Assessment Tools
- Content and Standards
- Differentiation
- Math & Literature
- Math & Technology
- Math Routines
- Math Stations
- Virtual Learning
- Writing in Math
You may also like...
2 Responses
This is a very cool site. I hope it takes off and is well received by teachers. I work in mathematical problem solving and help prepare pre-service teachers in mathematics.
Thank you, Scott! Best wishes to you and your pre-service teachers this year!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

©2024 The Routty Math Teacher. All Rights Reserved. Designed by Ashley Hughes.
Privacy overview.

5 Ways to Build Math Problem Solving Skills (based on brain research)
Whether talking about state tests or meeting with your team to plan the next math unit, the conversation inevitably turns to word problems. But knowing how to build math problem-solving skills without resorting to pages of boring story problem practice can be hard.
These days word problems aren’t the basic one-step wonders that many of us dealt with as students. Instead, multi-step story problems that require students to apply multiple concepts and skills are incorporated into instruction and state assessments.
Understanding brain research can help simply the process of teaching this challenging format of math problem-solving to students, including those who struggle.

What research says about building master problem solvers in math
Have you seen how many math skills we must teach these days? No teacher has enough time to build critical math skills AND effectively teach problem-solving…or do they?
Research would argue we are going about these tasks all wrong. They say there are many reasons students struggle with math word problems , but one big one is that we aren’t doing what’s best for the brain. Instead, here’s what the brain research says about the must-have elements for building step-by-step math problem-solving mastery.
Finding #1: Becoming a master problem solver requires repetition.
Duh, right? Any good teacher knows this…but what’s the best recipe for repetition if you want students to master math word problems? How much practice? How often?
Let’s start with the concept of mastery.
How do you develop math problem solving skills?
In the 1990’s, Anders Ericsson studied experts to explore what made some people excel. Findings showed a positive correlation between the amount of deliberate practice (activities that require a high level of concentration and aren’t necessarily inherently fun) and skill level.
In other words, the more practice someone gets, the more they improve. This became the basis of Malcolm Gladwell’s 10,000-hour rule, which stated that it takes 10,000 hours to make you an expert in a field.
But what should that practice look like for students who struggle with word problems? Is it better to have a deep dive into story problems, or do short bursts of practice do more for long-term understanding?
Designing Better Word Problem Activities: Building Step-by-step Math Problem-Solving Practice
We can look at Ebbinghaus’ work on memory & retention to answer that. He found spacing practice over time decreased the number of exposures needed. In other words, small amounts of practice over several days, weeks, or even months actually means you need LESS practice than if you try to cram it all in at once.
For over 80 years, this finding has stood the test of time. While research has shown that students who engage in mass practice (lots of practice all at once) might do better on an assessment that takes place tomorrow, students who engage in repeated practice over a period of time retain more skills long-term (Bloom & Shuell, 1981; Rea & Modigliani, 1985).
And how long does the research say you should spend reviewing?

How long should problem-solving practice really be?
Shorter is better. As discussed earlier, peak attention required for deliberate practice can only be maintained for so long. And the majority of research supports 8-10 minutes as the ideal lesson length (Robertson, 2010).
This means practice needs to be focused so that during those minutes of discussion, you can dive deep – breaking down the word problem and discussing methods to solve it.
Teacher Tip: Applying this finding to your classroom
Less is actually more as long as you plan to practice regularly. While students who struggle with word problems may need a great deal of practice to master word problems, ideally, this practice should be provided in short, regular intervals with no more than 8-10 minutes spent in whole group discussion.
Here are a few simple steps to apply these findings to your math classroom:
- Find 8-12 minutes in your daily schedule to focus on problem-solving – consider this time sacred & only for problem-solving.
- Select only 1-2 word problems per day. Target step-by-step math problem-solving to build math problem-solving skills through a less-is-more approach using Problem of the Day .
Finding #2: Students who are challenged & supported have better outcomes.
Productive struggle, as it is called in the research, focuses on the effortful practice that builds long-term understanding.
Important to this process are opportunities for choice, collaboration, and the use of materials or topics of interest (which will be discussed later).
This productive struggle also helps students build flexible thinking so that they can apply previously learned skills to new or unfamiliar tasks (Bransford, Brown, & Cocking, 2000).
“Meaningful learning tasks need to challenge ever student in some way. It is crucial that no student be able to coast to success time after time; this experience can create the belief that you are smart only if you can succeed without effort.” -Carol Dweck
It is also critical to provide support and feedback during the challenging task (Cimpian, Arce, Markman, & Dweck, 2007). This prevents frustration and fear of failure when the goal seems out of reach or when a particularly challenging task arises.
Simple ways to build productive struggle into your math classroom
Giving students who struggle with word problems a chance to struggle with challenging word problems is critical to building confidence and skills. However, this challenge must be reasonable, or the learner’s self-esteem will falter, and students need support and regular feedback to achieve their potential.
Here are a few simple things to try:
- Select problems that are just at the edge of students’ Zone of Proximal Development.
- Scaffold or model with more challenging problems to support risk-taking.
- Give regular feedback & support – go over the work and discuss daily.
Finding #3: Novelty & variation are keys to engagement.
When it comes to standardized testing (and life in general), problems that arise aren’t labeled with the skills and strategies required to solve them.
This makes it important to provide mixed practice opportunities so students are focused on asking themselves questions about what the problem is asking and what they are trying to find.
This type of variation not only supports a deeper level of engagement, it also supports the metacognitive strategies needed to analyze and develop a strategy to solve (Rohrer & Taylor, 2014).
The benefits of novelty in learning
A 2013 study also supports the importance of novelty in supporting reinforcement learning (aka review). The findings suggested that when task variation was provided for an already familiar skill, it offered the following benefits:
- reduced errors due to lack of focus
- helped learners maintain attention to task
- motivated and engaged student
Using variety to build connections & deepen understanding
In addition, by providing variations in practice, we can also help learners understand the skills and strategies they are using on a deeper level.
When students who struggle with word problems are forced to apply their toolbox of strategies to novel problem formats, they begin to analyze and observe patterns in how problems are structured and the meaning they bring.
This requires much more engagement than being handed a sheet full of multiplication story problems, where students can pull the numbers and compute with little focus on understanding.
Designing word problems that incorporate variety & novelty
Don’t be afraid to shake things up!
Giving students practice opportunities with different skills or problem formats mixed in is a great way to boost engagement and develop meta-cognitive skills.
Here are a few tips for trying it out in the classroom:
- Change it up! Word problem practice doesn’t have to match the day’s math lesson.
- Give opportunities to practice the same skill or strategy in via different formats.
- Adjust the wording and/or topic in word problems to help students generalize skills.
Finding #4: Interest and emotion increase retention and skill development.
Attention and emotion are huge for learning. We’ve all seen it in our classroom.
Those magical lessons that hook learners are the ones that stick with them for years to come, but what does the research say?

The Science Behind Emotion & Learning
Neuroscientists have shown that emotions create connections among different sections of the brain (Immordino-Yang, 2016) . This supports long-term retrieval of the skills taught and a deeper connection to the learning.
This means if you can connect problem-solving with a scenario or a feeling, your students will be more likely to internalize the skills being practiced. Whether this is by “wowing” them with a little-known fact or solving real-world problems, the emotional trigger can be huge for learning.
What about incorporating student interests?
As for student interests, a long line of research supports the benefits of using these to increase educational outcomes and student motivation, including for students who struggle with word problems (Chen, 2001; Chen & Ennis, 2004; Solomon, 1996).
Connecting classwork with student interests has increased students’ intentions to participate in future learning endeavors (Chen, 2001).
And interests don’t just mean that love of Pokemon!
It means allowing social butterflies to work collaboratively. Providing students with opportunities to manipulate real objects or create models. Allowing kids to be authentic while digging in and developing the skills they need to master their learning objectives.
What this looks like in a math class
Evoke emotion and use student interests to engage the brain in deep, long-lasting learning whenever possible.
This will help with today’s learning and promote long-term engagement, even when later practice might not be as interesting for students who struggle with word problems.
Here’s how to start applying this research today:
- Find word problems that match student interests.
- Connect real-life situations and emotions to story problem practice.
- Consider a weekly theme to connect practice throughout the week.
Finding #5: Student autonomy builds confidence & independence.
Autonomy is a student’s ability to be in control of their learning. In other words, it is their ability to take ownership over the learning process and how they demonstrate mastery.
Why students need to control their learning
Research shows that providing students a sense of control and supporting their choices is way to help engage learners and build independent thinking. It also increased intrinsic motivation (Reeve, Nix, & Hamm, 2003).
However, this doesn’t mean we just let kids learn independently. Clearly, some things require repeated guidance and modeling. Finding small ways that students can take control of the learning process is much better in these instances.
We know that giving at least partial autonomy has been linked to numerous positive student learning outcomes (Wielenga-Meijer, Taris, Widboldus, & Kompier, 2011).
But how can we foster this independence and autonomy, especially with those students who struggle to self-regulate behavior?
Fostering independence in students who struggle to stay on task
Well, the research says several conditions support building toward independence.
The first (and often neglected) is to explain unappealing choices and why they are one of the options.
When it comes to word problems, this might include explaining the rationale behind one of the strategies that appears to be a lot more work than the others.
It is also important to acknowledge students’ negative feelings about a task or their ability to complete it. While we want them to be able to build independence, we don’t want them to drown in overwhelm.
By providing emotional support, we can help determine whether a student is stuck with the learning or with the emotions from the cognitive challenge.
Finally, giving choices is recommended. Identifying choices you and your students who struggle with word problems can live with is an important step.
Whether this is working in partners, trying an alternative method, or skipping a problem and coming back, students need to feel like they have some ownership over the challenge they are working through.
By building in opportunities for autonomy, and choice, teachers help students build a sense of self-efficacy and confidence in their ability to be successful learners across various contexts (McCombs, 2002,2006).
We know this leads to numerous positive outcomes and has even been linked to drop-out prevention (Christenson & Thurlow, 2004).
Fostering autonomy in your classroom
You’re not going to be able to hold their hands forever.
Giving opportunities to work through challenges independently and to feel ownership for their choices will help build both confidence and skills.
Here’s how to get started letting go:
- Give students time to tackle the problem independently (or in partners).
- Don’t get hyper-focused on a single method to solve – give opportunities to share & learn together.
- Provide appropriate support (where needed) to build autonomy for all learners – like reading the problem orally.
Finding #6: Students need to be taught how to fail & recover from it.
Despite Ericsson’s findings discussed early on in this post, talent does matter, and it is important to teach students to recover from failure because those are the moments when they learn the most.
A 2014 study by Brooke Macnamara analyzed 88 studies to determine how talent factored into deliberate practice.
Her findings show what we (as teachers) already know, students may require different amounts of practice to reach the same skill level…but how do we keep those struggling students from keeping up?

Growth mindset research gives us insight into ways to support students who struggle with word problems, encourage all students in math problem-solving, and harness the power of failure through “yet.”
You might not be able to do something yet, but if you keep trying, you will. This opens the door for multiple practice opportunities where students learn from each other.

And what about the advanced students?
Many of these students have not experienced failure, but they may have met their match when it comes to complex word problems.
To support these students, who may be experiencing their first true challenge, we need to have high standards and provide constructive, supportive feedback on how to grow.
Then we need to give them space to try again.
There is great power in allowing students to revise and try again, but our grading system often discourages being comfortable with failure.
Building the confidence to fail in your classroom
Many students feel the pressure always to have the right answer. Allowing students to fail safely means you can help them learn from these failures so they don’t make the same mistake twice.
Here’s how you can safely foster growth and build math problem solving skills through failure in your classroom:
- Build in time to analyze errors & reflect.
- Reward effort & growth as much as, if not more than, accuracy.
- At least initially, skip the grading so students aren’t afraid to be wrong.
Getting started with brain-based problem solving
The brain research is clear.
Spending 45 minutes focused on a sheet of word problems following the same format isn’t the answer.
By implementing this research, you can save yourself time and the frustration from a disengaged class.

Based on this research, I’ve created Daily Problem Solving bundles to save you time and build math problem-solving skills. You can get each month separately or buy the full-year bundle at a major discount.
Currently, I offer these bundles for several grade levels, including:
Try Daily Problem Solving with your Learners
Of course, you do! Start working to build step-by-step math problem-solving skills today by clicking the button below to sign up for a free set of Daily Problem Solving.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Teaching Problem Solving in Math
- Freebies , Math , Planning

Every year my students can be fantastic at math…until they start to see math with words. For some reason, once math gets translated into reading, even my best readers start to panic. There is just something about word problems, or problem-solving, that causes children to think they don’t know how to complete them.
Every year in math, I start off by teaching my students problem-solving skills and strategies. Every year they moan and groan that they know them. Every year – paragraph one above. It was a vicious cycle. I needed something new.

I put together a problem-solving unit that would focus a bit more on strategies and steps in hopes that that would create problem-solving stars.
The Problem Solving Strategies
First, I wanted to make sure my students all learned the different strategies to solve problems, such as guess-and-check, using visuals (draw a picture, act it out, and modeling it), working backward, and organizational methods (tables, charts, and lists). In the past, I had used worksheet pages that would introduce one and provide the students with plenty of problems practicing that one strategy. I did like that because students could focus more on practicing the strategy itself, but I also wanted students to know when to use it, too, so I made sure they had both to practice.
I provided students with plenty of practice of the strategies, such as in this guess-and-check game.

There’s also this visuals strategy wheel practice.
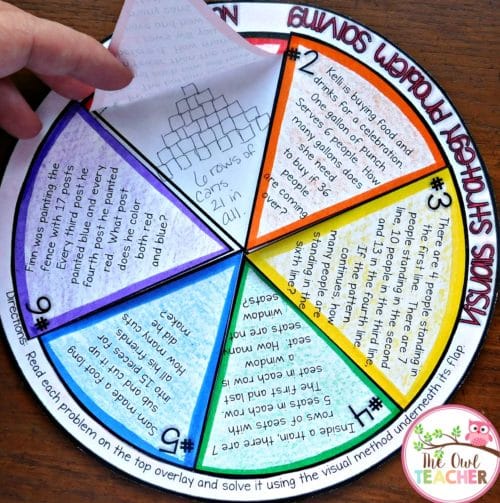

I also provided them with paper dolls and a variety of clothing to create an organized list to determine just how many outfits their “friend” would have.

Then, as I said above, we practiced in a variety of ways to make sure we knew exactly when to use them. I really wanted to make sure they had this down!

Anyway, after I knew they had down the various strategies and when to use them, then we went into the actual problem-solving steps.
The Problem Solving Steps
I wanted students to understand that when they see a story problem, it isn’t scary. Really, it’s just the equation written out in words in a real-life situation. Then, I provided them with the “keys to success.”
S tep 1 – Understand the Problem. To help students understand the problem, I provided them with sample problems, and together we did five important things:
- read the problem carefully
- restated the problem in our own words
- crossed out unimportant information
- circled any important information
- stated the goal or question to be solved
We did this over and over with example problems.

Once I felt the students had it down, we practiced it in a game of problem-solving relay. Students raced one another to see how quickly they could get down to the nitty-gritty of the word problems. We weren’t solving the problems – yet.

Then, we were on to Step 2 – Make a Plan . We talked about how this was where we were going to choose which strategy we were going to use. We also discussed how this was where we were going to figure out what operation to use. I taught the students Sheila Melton’s operation concept map.

We talked about how if you know the total and know if it is equal or not, that will determine what operation you are doing. So, we took an example problem, such as:
Sheldon wants to make a cupcake for each of his 28 classmates. He can make 7 cupcakes with one box of cupcake mix. How many boxes will he need to buy?
We started off by asking ourselves, “Do we know the total?” We know there are a total of 28 classmates. So, yes, we are separating. Then, we ask, “Is it equal?” Yes, he wants to make a cupcake for EACH of his classmates. So, we are dividing: 28 divided by 7 = 4. He will need to buy 4 boxes. (I actually went ahead and solved it here – which is the next step, too.)
Step 3 – Solving the problem . We talked about how solving the problem involves the following:
- taking our time
- working the problem out
- showing all our work
- estimating the answer
- using thinking strategies
We talked specifically about thinking strategies. Just like in reading, there are thinking strategies in math. I wanted students to be aware that sometimes when we are working on a problem, a particular strategy may not be working, and we may need to switch strategies. We also discussed that sometimes we may need to rethink the problem, to think of related content, or to even start over. We discussed these thinking strategies:
- switch strategies or try a different one
- rethink the problem
- think of related content
- decide if you need to make changes
- check your work
- but most important…don’t give up!
To make sure they were getting in practice utilizing these thinking strategies, I gave each group chart paper with a letter from a fellow “student” (not a real student), and they had to give advice on how to help them solve their problem using the thinking strategies above.

Finally, Step 4 – Check It. This is the step that students often miss. I wanted to emphasize just how important it is! I went over it with them, discussing that when they check their problems, they should always look for these things:
- compare your answer to your estimate
- check for reasonableness
- check your calculations
- add the units
- restate the question in the answer
- explain how you solved the problem
Then, I gave students practice cards. I provided them with example cards of “students” who had completed their assignments already, and I wanted them to be the teacher. They needed to check the work and make sure it was completed correctly. If it wasn’t, then they needed to tell what they missed and correct it.

To demonstrate their understanding of the entire unit, we completed an adorable lap book (my first time ever putting together one or even creating one – I was surprised how well it turned out, actually). It was a great way to put everything we discussed in there.

Once we were all done, students were officially Problem Solving S.T.A.R.S. I just reminded students frequently of this acronym.
Stop – Don’t rush with any solution; just take your time and look everything over.
Think – Take your time to think about the problem and solution.
Act – Act on a strategy and try it out.
Review – Look it over and see if you got all the parts.

Wow, you are a true trooper sticking it out in this lengthy post! To sum up the majority of what I have written here, I have some problem-solving bookmarks FREE to help you remember and to help your students!
You can grab these problem-solving bookmarks for FREE by clicking here .
You can do any of these ideas without having to purchase anything. However, if you are looking to save some time and energy, then they are all found in my Math Workshop Problem Solving Unit . The unit is for grade three, but it may work for other grade levels. The practice problems are all for the early third-grade level.
- freebie , Math Workshop , Problem Solving
FIND IT NOW!
Check me out on tpt.

CHECK THESE OUT

Three Types of Rocks and Minerals with Rock Cycle Circle Book
Partitioning Shapes Equal Share Fractions Halves, Thirds, Fourths Math Puzzles
Want to save time?
COPYRIGHT © 2016-2024. The Owl Teacher | Privacy page | Disclosure Page | Shipping | Returns/Refunds
BOGO on EVERYTHING!
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
5 Teaching Mathematics Through Problem Solving
Janet Stramel

In his book “How to Solve It,” George Pólya (1945) said, “One of the most important tasks of the teacher is to help his students. This task is not quite easy; it demands time, practice, devotion, and sound principles. The student should acquire as much experience of independent work as possible. But if he is left alone with his problem without any help, he may make no progress at all. If the teacher helps too much, nothing is left to the student. The teacher should help, but not too much and not too little, so that the student shall have a reasonable share of the work.” (page 1)
What is a problem in mathematics? A problem is “any task or activity for which the students have no prescribed or memorized rules or methods, nor is there a perception by students that there is a specific ‘correct’ solution method” (Hiebert, et. al., 1997). Problem solving in mathematics is one of the most important topics to teach; learning to problem solve helps students develop a sense of solving real-life problems and apply mathematics to real world situations. It is also used for a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts. Learning “math facts” is not enough; students must also learn how to use these facts to develop their thinking skills.
According to NCTM (2010), the term “problem solving” refers to mathematical tasks that have the potential to provide intellectual challenges for enhancing students’ mathematical understanding and development. When you first hear “problem solving,” what do you think about? Story problems or word problems? Story problems may be limited to and not “problematic” enough. For example, you may ask students to find the area of a rectangle, given the length and width. This type of problem is an exercise in computation and can be completed mindlessly without understanding the concept of area. Worthwhile problems includes problems that are truly problematic and have the potential to provide contexts for students’ mathematical development.
There are three ways to solve problems: teaching for problem solving, teaching about problem solving, and teaching through problem solving.
Teaching for problem solving begins with learning a skill. For example, students are learning how to multiply a two-digit number by a one-digit number, and the story problems you select are multiplication problems. Be sure when you are teaching for problem solving, you select or develop tasks that can promote the development of mathematical understanding.
Teaching about problem solving begins with suggested strategies to solve a problem. For example, “draw a picture,” “make a table,” etc. You may see posters in teachers’ classrooms of the “Problem Solving Method” such as: 1) Read the problem, 2) Devise a plan, 3) Solve the problem, and 4) Check your work. There is little or no evidence that students’ problem-solving abilities are improved when teaching about problem solving. Students will see a word problem as a separate endeavor and focus on the steps to follow rather than the mathematics. In addition, students will tend to use trial and error instead of focusing on sense making.
Teaching through problem solving focuses students’ attention on ideas and sense making and develops mathematical practices. Teaching through problem solving also develops a student’s confidence and builds on their strengths. It allows for collaboration among students and engages students in their own learning.
Consider the following worthwhile-problem criteria developed by Lappan and Phillips (1998):
- The problem has important, useful mathematics embedded in it.
- The problem requires high-level thinking and problem solving.
- The problem contributes to the conceptual development of students.
- The problem creates an opportunity for the teacher to assess what his or her students are learning and where they are experiencing difficulty.
- The problem can be approached by students in multiple ways using different solution strategies.
- The problem has various solutions or allows different decisions or positions to be taken and defended.
- The problem encourages student engagement and discourse.
- The problem connects to other important mathematical ideas.
- The problem promotes the skillful use of mathematics.
- The problem provides an opportunity to practice important skills.
Of course, not every problem will include all of the above. Sometimes, you will choose a problem because your students need an opportunity to practice a certain skill.
Key features of a good mathematics problem includes:
- It must begin where the students are mathematically.
- The feature of the problem must be the mathematics that students are to learn.
- It must require justifications and explanations for both answers and methods of solving.

Problem solving is not a neat and orderly process. Think about needlework. On the front side, it is neat and perfect and pretty.

But look at the b ack.
It is messy and full of knots and loops. Problem solving in mathematics is also like this and we need to help our students be “messy” with problem solving; they need to go through those knots and loops and learn how to solve problems with the teacher’s guidance.
When you teach through problem solving , your students are focused on ideas and sense-making and they develop confidence in mathematics!
Mathematics Tasks and Activities that Promote Teaching through Problem Solving

Choosing the Right Task
Selecting activities and/or tasks is the most significant decision teachers make that will affect students’ learning. Consider the following questions:
- Teachers must do the activity first. What is problematic about the activity? What will you need to do BEFORE the activity and AFTER the activity? Additionally, think how your students would do the activity.
- What mathematical ideas will the activity develop? Are there connections to other related mathematics topics, or other content areas?
- Can the activity accomplish your learning objective/goals?

Low Floor High Ceiling Tasks
By definition, a “ low floor/high ceiling task ” is a mathematical activity where everyone in the group can begin and then work on at their own level of engagement. Low Floor High Ceiling Tasks are activities that everyone can begin and work on based on their own level, and have many possibilities for students to do more challenging mathematics. One gauge of knowing whether an activity is a Low Floor High Ceiling Task is when the work on the problems becomes more important than the answer itself, and leads to rich mathematical discourse [Hover: ways of representing, thinking, talking, agreeing, and disagreeing; the way ideas are exchanged and what the ideas entail; and as being shaped by the tasks in which students engage as well as by the nature of the learning environment].
The strengths of using Low Floor High Ceiling Tasks:
- Allows students to show what they can do, not what they can’t.
- Provides differentiation to all students.
- Promotes a positive classroom environment.
- Advances a growth mindset in students
- Aligns with the Standards for Mathematical Practice
Examples of some Low Floor High Ceiling Tasks can be found at the following sites:
- YouCubed – under grades choose Low Floor High Ceiling
- NRICH Creating a Low Threshold High Ceiling Classroom
- Inside Mathematics Problems of the Month
Math in 3-Acts
Math in 3-Acts was developed by Dan Meyer to spark an interest in and engage students in thought-provoking mathematical inquiry. Math in 3-Acts is a whole-group mathematics task consisting of three distinct parts:
Act One is about noticing and wondering. The teacher shares with students an image, video, or other situation that is engaging and perplexing. Students then generate questions about the situation.
In Act Two , the teacher offers some information for the students to use as they find the solutions to the problem.
Act Three is the “reveal.” Students share their thinking as well as their solutions.
“Math in 3 Acts” is a fun way to engage your students, there is a low entry point that gives students confidence, there are multiple paths to a solution, and it encourages students to work in groups to solve the problem. Some examples of Math in 3-Acts can be found at the following websites:
- Dan Meyer’s Three-Act Math Tasks
- Graham Fletcher3-Act Tasks ]
- Math in 3-Acts: Real World Math Problems to Make Math Contextual, Visual and Concrete
Number Talks
Number talks are brief, 5-15 minute discussions that focus on student solutions for a mental math computation problem. Students share their different mental math processes aloud while the teacher records their thinking visually on a chart or board. In addition, students learn from each other’s strategies as they question, critique, or build on the strategies that are shared.. To use a “number talk,” you would include the following steps:
- The teacher presents a problem for students to solve mentally.
- Provide adequate “ wait time .”
- The teacher calls on a students and asks, “What were you thinking?” and “Explain your thinking.”
- For each student who volunteers to share their strategy, write their thinking on the board. Make sure to accurately record their thinking; do not correct their responses.
- Invite students to question each other about their strategies, compare and contrast the strategies, and ask for clarification about strategies that are confusing.
“Number Talks” can be used as an introduction, a warm up to a lesson, or an extension. Some examples of Number Talks can be found at the following websites:
- Inside Mathematics Number Talks
- Number Talks Build Numerical Reasoning

Saying “This is Easy”
“This is easy.” Three little words that can have a big impact on students. What may be “easy” for one person, may be more “difficult” for someone else. And saying “this is easy” defeats the purpose of a growth mindset classroom, where students are comfortable making mistakes.
When the teacher says, “this is easy,” students may think,
- “Everyone else understands and I don’t. I can’t do this!”
- Students may just give up and surrender the mathematics to their classmates.
- Students may shut down.
Instead, you and your students could say the following:
- “I think I can do this.”
- “I have an idea I want to try.”
- “I’ve seen this kind of problem before.”
Tracy Zager wrote a short article, “This is easy”: The Little Phrase That Causes Big Problems” that can give you more information. Read Tracy Zager’s article here.
Using “Worksheets”
Do you want your students to memorize concepts, or do you want them to understand and apply the mathematics for different situations?
What is a “worksheet” in mathematics? It is a paper and pencil assignment when no other materials are used. A worksheet does not allow your students to use hands-on materials/manipulatives [Hover: physical objects that are used as teaching tools to engage students in the hands-on learning of mathematics]; and worksheets are many times “naked number” with no context. And a worksheet should not be used to enhance a hands-on activity.
Students need time to explore and manipulate materials in order to learn the mathematics concept. Worksheets are just a test of rote memory. Students need to develop those higher-order thinking skills, and worksheets will not allow them to do that.
One productive belief from the NCTM publication, Principles to Action (2014), states, “Students at all grade levels can benefit from the use of physical and virtual manipulative materials to provide visual models of a range of mathematical ideas.”
You may need an “activity sheet,” a “graphic organizer,” etc. as you plan your mathematics activities/lessons, but be sure to include hands-on manipulatives. Using manipulatives can
- Provide your students a bridge between the concrete and abstract
- Serve as models that support students’ thinking
- Provide another representation
- Support student engagement
- Give students ownership of their own learning.
Adapted from “ The Top 5 Reasons for Using Manipulatives in the Classroom ”.
any task or activity for which the students have no prescribed or memorized rules or methods, nor is there a perception by students that there is a specific ‘correct’ solution method
should be intriguing and contain a level of challenge that invites speculation and hard work, and directs students to investigate important mathematical ideas and ways of thinking toward the learning
involves teaching a skill so that a student can later solve a story problem
when we teach students how to problem solve
teaching mathematics content through real contexts, problems, situations, and models
a mathematical activity where everyone in the group can begin and then work on at their own level of engagement
20 seconds to 2 minutes for students to make sense of questions
Mathematics Methods for Early Childhood Copyright © 2021 by Janet Stramel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Question Generator
Enjoy using the site, become a member and enjoy access to all the resources on the site ad-free.
- My Storyboards
Problem Solving Worksheets
Customize problem solving worksheets.

What is Problem Solving?
It is the cognitive process of identifying, analyzing, and finding solutions to challenges or issues. It involves using logical and creative thinking to address obstacles that occur, make decisions, and achieve goals. Consider the five problem-solving steps: identifying the problem, generating possible solutions, evaluating options, selecting the best solution, and implementing it. Understanding the steps is crucial for navigating complex challenges with clarity and efficiency.
What are Problem Solving Worksheets?
These worksheets are structured in such a way that encourages solution-based thinking. Engaging in interactive problem-solving activities can help develop critical thinking skills and creative approaches to overcoming obstacles. While these skills are used in a variety of aspects of life, our worksheets focus on problem solving in mathematics. Printable worksheets provide practice for any child who is learning to master new skills they are taught in class. They are perfect for any level, and can be applied to any type of mathematical problem or unit of study.
Why are They Important and How are They Best Used?
They are great for ensuring that students practice what they have yet to master, since they can be customized by the teacher to meet the class and individual needs. They can be used to practice all kinds of word problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and so much more.
In a world where challenges are inevitable, the ability to tackle problems effectively is a valuable skill that can be applied across all subjects and age groups. Problem-solving skills are the generator of success. They empower individuals to navigate complex situations, identify triggers, and develop plans to overcome obstacles. From the classroom to the boardroom, these skills are in high demand.
Tailoring Problem-Solving Worksheets for Different Subjects
Mathematics.
Math problem-solving worksheets can be a playground for nurturing critical thinking. Through word problem worksheets, students not only practice calculations but also apply math concepts to real-world scenarios.
Scientific problem-solving worksheets ignite curiosity. They prompt students to hypothesize, design experiments, collect data, and draw conclusions, fostering a scientific mindset.
Language Arts
Language skills and critical thinking intertwine in language arts problem-solving worksheets. Analyzing literature, engaging in creative writing prompts, and correcting grammar offer a holistic approach.
Social Studies
History comes to life through problem-solving worksheets. Encourage students to ponder over historical dilemmas and global challenges, nurturing their ability to think beyond the surface.
Math Worksheet Activity Ideas
- "Math Detective" Challenge: Create a set of worksheets featuring a fictional mystery storyline. Each worksheet presents a clue that requires students to solve a math problem to unveil the next piece of the puzzle. This engaging activity encourages critical and sequential thinking.
- "Math Menu" Project: Design a menu-style worksheet with various math problems categorized by difficulty levels. Allow students to choose a certain number of problems from each category to complete, giving them autonomy and catering to their individual skill levels.
- "Design Your Dream House" Activity: Provide a worksheet that guides students through designing their dream house layout. They need to calculate room dimensions, total area, and even budget constraints. This hands-on activity integrates math into real-life scenarios.
- "Math Art Gallery" Exhibition: Assign each student a famous artwork and create a worksheet that involves geometric calculations related to the art's dimensions and shapes. Students can then present their findings in a "Math Art Gallery" exhibition.
- "Math in the News" Analysis: Collect recent news articles that involve math-related concepts, such as statistics, percentages, or data analysis. Provide worksheets that require students to analyze the math behind the news and discuss its implications.
- "Budgeting for Vacation" Project: Design a project-based worksheet where students plan a vacation, considering expenses like transportation, accommodations, and activities. They must budget and calculate costs while staying within a specified budget.
- "Math Around the World" Exploration: Create a worksheet that presents math problems related to different countries' cultures, currencies, and measurements. Students solve problems like converting currencies or calculating time zone differences.
- "Mathopoly" Board Game: Design a problem-solving board game where players move through spaces by solving math problems. This interactive approach adds an element of fun while reinforcing math skills.
- "Math Olympiad Simulation" Practice: Prepare a set of challenging math problems similar to those in Math Olympiad competitions. Have students work on these problems individually or in teams to sharpen their skills.
- "Math Interview" Project: Assign each student a famous mathematician or scientist and provide a worksheet that guides them to research and create interview-style questions. This encourages exploration of math history and its relevance.
- "Math Escape Room" Challenge: Develop a series of interconnected math problems that lead students through a virtual "escape room." They must solve each problem correctly to advance to the next step and eventually "escape."
- "Data Analysis Report" Assignment: Provide students with a dataset related to a topic of interest, such as sports statistics or environmental data. They must analyze the data, create graphs, and present their findings in a structured report.
- "Math and Music Fusion" Project: Combine math with music by providing a worksheet that explores concepts like rhythm, frequency, and ratios in music. Students can calculate beats per minute, analyze musical patterns, and even compose their own melodies.
- "Math Recipe Creation" Challenge: Ask students to create a new recipe by adjusting ingredient quantities based on serving sizes. They must calculate ratios, proportions, and conversions to ensure the recipe's success.
Designing Effective Problem-Solving Worksheets
Creating successful problem-solving worksheets involves careful planning. Here are some ideas to consider:
- Define the Learning Objective: Clarify the specific mathematical concept you want to reinforce with the worksheet. Outline the steps involved and determine how this worksheet will contribute to improving their skills.
- Select a Problem Type: Choose a math problem type that aligns with the learning objective. It could involve algebraic equations, geometry calculations, or even practical scenarios related to everyday life.
- Structure the Steps: Break down the problem-solving process into logical steps. Ensure that each step reflects the problem solving steps you want students to follow, such as understanding the problem, planning, solving, and verifying.
- Incorporate Interactive Elements: Integrate interactive elements like multiple-choice questions, fill-in-the-blanks, or even drawing areas to encourage problem solving exercises within the worksheet.
- Utilize Graphic Organizers: Introduce a visual problem solving graphic organizer to help students map out their thinking. This can include spaces for writing down given information, variables, and equations.
- Provide a Problem Solving Template: Offer a structured template that guides students through the problem-solving process. Include prompts and placeholders for each step to provide clear direction.
- Encourage Exploration: Inspire students to explore different types of techniques to arrive at solutions. Encourage them to think critically and try various strategies before settling on an approach.
By incorporating these elements, you can create a comprehensive problem solving worksheet for kids that not only teaches mathematical concepts but also equips them with transferable skills. Whether you're focusing on basic arithmetic or more advanced mathematical principles, this approach ensures an engaging and educational experience for young learners.
More Storyboardthat Resources and Free Printables
- Multiplication Worksheets
- Subtraction Worksheets
- Game Worksheets
- Task Card Maker
How to Make a Problem Solving Worksheet
Choose one of the premade templates.
We have lots of templates to choose from. Take a look at our example for inspiration!
Click on “Copy Template”
Once you do this, you will be directed to the storyboard creator.
Give Your Worksheet a Name!
Be sure to call it something related to the topic so that you can easily find it in the future.
Edit Your Worksheet
This is where you will include directions, specific images, and make any aesthetic changes that you would like. The options are endless!
Click "Save and Exit"
When you are finished, click this button in the lower right hand corner to exit your storyboard.
From here you can print, download as a PDF, attach it to an assignment and use it digitally, and more!
Happy Creating!
Frequently Asked Questions About Problem Solving Worksheets
How can math problem-solving worksheets show students how to improve problem-solving skills.
They provide structured exercises that guide students through real-world scenarios. By actively engaging in these worksheets and activities, children can practice the problem solving process, enhancing their critical thinking and logical reasoning abilities.
What strategies can I use to teach problem-solving skills using math worksheets?
Incorporate helpful math problem solving worksheets for kids into your lessons. Support and encourage students to work through the problem-solving steps: understanding the problem, devising strategies, making calculations, and verifying their solutions. Provide examples, guidance, and feedback to nurture their problem-solving skills.
How can I ensure that students grasp the problem-solving process effectively?
Provide clear instructions in your math problem-solving worksheets that guide students through each step of the process. Offer examples and encourage them to discuss their approaches. By nurturing a supportive and collaborative environment, you can help both younger kids and older kids build confidence in their problem solving skills.
What are specific examples of how to teach problem-solving skills in math using pre-answered solution worksheets?
Teaching problem-solving skills in math using pre-answered solution worksheets can be exemplified through scenarios like quadratic equations. Present the class with a quadratic equation and a pre-answered solution that breaks down the steps of factoring or using the quadratic formula. This guides them to understand the process, identify key components, and apply appropriate methods. Similarly, for geometry, offer a challenging problem involving angles or area calculations, along with a pre-answered solution that demonstrates the application of relevant geometric principles. As students work through the problem and compare their reasoning with the pre-answered solution, they grasp problem-solving strategies, logical sequences, and the importance of meticulous calculations. In both cases, these worksheets instill confidence, reinforce systematic approaches, and enhance students' problem-solving skills while navigating mathematical complexities.
Try 1 Month For
30 Day Money Back Guarantee New Customers Only Full Price After Introductory Offer
Learn more about our Department, School, and District packages

- Thousands of images
- Custom layouts, scenes, characters
- And so much more!!
Create a Storyboard
3 Ways to Strengthen Math Instruction

- Share article
Students’ math scores have plummeted, national assessments show , and educators are working hard to turn math outcomes around.
But it’s a challenge, made harder by factors like math anxiety , students’ feelings of deep ambivalence about how math is taught, and learning gaps that were exacerbated by the pandemic’s disruption of schools.
This week, three educators offered solutions on how districts can turn around poor math scores in a conversation moderated by Peter DeWitt, an opinion blogger for Education Week.
Here are three takeaways from the discussion. For more, watch the recording on demand .
1. Intervention is key
Research shows that early math skills are a key predictor of later academic success.
“Children who know more do better, and math is cumulative—so if you don’t grasp some of the earlier concepts, math gets increasingly harder,” said Nancy Jordan, a professor of education at the University of Delaware.
For example, many students struggle with the concept of fractions, she said. Her research has found that by 6th grade, some students still don’t really understand what a fraction is, which makes it harder for them to master more advanced concepts, like adding or subtracting fractions with unlike denominators.
At that point, though, teachers don’t always have the time in class to re-teach those basic or fundamental concepts, she said, which is why targeted intervention is so important.

Still, Jordan’s research revealed that in some middle schools, intervention time is not a priority: “If there’s an assembly, or if there is a special event or whatever, it takes place during intervention time,” she said. “Or ... the children might sit on computers, and they’re not getting any really explicit instruction.”
2. ‘Gamify’ math class
Students today need new modes of instruction that meet them where they are, said Gerilyn Williams, a math teacher at Pinelands Regional Junior High School in Little Egg Harbor Township, N.J.
“Most of them learn through things like TikTok or YouTube videos,” she said. “They like to play games, they like to interact. So how can I bring those same attributes into my lesson?”
Part of her solution is gamifying instruction. Williams avoids worksheets. Instead, she provides opportunities for students to practice skills that incorporate elements of game design.
That includes digital tools, which provide students with the instant feedback they crave, she said.
But not all the games are digital. Williams’ students sometimes play “trashketball,” a game in which they work in teams to answer math questions. If they get the question right, they can crumble the piece of paper and throw it into a trash can from across the room.
“The kids love this,” she said.

Williams also incorporates game-based vocabulary into her instruction, drawing on terms from video games.
For example, “instead of calling them quizzes and tests, I call them boss battles,” she said. “It’s less frightening. It reduces that math anxiety, and it makes them more engaging.
“We normalize things like failure, because when they play video games, think about what they’re doing,” Williams continued. “They fail—they try again and again and again and again until they achieve success.”
3. Strengthen teacher expertise
To turn around math outcomes, districts need to invest in teacher professional development and curriculum support, said Chaunté Garrett, the CEO of ELLE Education, which partners with schools and districts to support student learning.
“You’re not going to be able to replace the value of a well-supported and well-equipped mathematics teacher,” she said. “We also want to make sure that that teacher has a math curriculum that’s grounded in the standards and conceptually based.”
Students will develop more critical thinking skills and better understand math concepts if teachers are able to relate instruction to real life, Garrett said—so that “kids have relationships that they can pull on, and math has some type of meaning and context to them outside of just numbers and procedures.”

It’s important for math curriculum to be both culturally responsive and relevant, she added. And teachers might need training on how to offer opportunities for students to analyze and solve real-world problems.
“So often, [in math problems], we want to go back to soccer and basketball and all of those things that we lived through, and it’s not that [current students] don’t enjoy those, but our students live social media—they literally live it,” Garrett said. “Those are the things that have to live out in classrooms right now, and if we’re not doing those things, we are doing a disservice.”
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

Ai Math Solver ◦ 4+
Instant answers, explained, designed for ipad.
- 4.7 • 106 Ratings
- Offers In-App Purchases
Screenshots
Description.
Introducing "AI Math Solver" - your ultimate academic sidekick! Say goodbye to math headaches and hello to instant solutions at your fingertips. Why Choose AI Math Solver? - Instant Math Magic: Snap a pic of any math problem, and watch our AI work its magic with lightning-fast solutions! - All-Subject AI Chat: Stuck on science or tangled up in literature? No worries! Our AI chat is here to give you personalized guidance whenever you need it. - Learning, Simplified: We're not just about answers; we're all about making complex concepts easy to understand! - Super Easy to Use: Our app is designed to be super intuitive and fun for learners of all ages! Key Features: - Snap & Solve: Snap a pic of any problem, and our AI will crack it in seconds! - Live Chat Help: Get instant explanations and study tips through interactive chat! - Covers Everything: From math mysteries to literary puzzles, we've got every subject covered! Your Ultimate Study Buddy: - Always Improving: We're constantly updating with the latest AI advancements and feedback from users like you! - Perfect for Everyone: Whether you're a student, teacher, or just curious, our app is tailor-made for all learners! Don't let homework stress you out any longer. With "AI Math Solver" by your side, acing assignments has never been easier! Download now and unleash your academic superpowers! Privacy policy: https://www.netsun.tech/privacy-policy Terms of use: https://www.netsun.tech/terms-and-conditions
Version 1.7
This update fixes bugs and makes your experience smoother and faster.
Ratings and Reviews
106 Ratings
When can I join Chinese?
Great in solving math problems, but very biased in AI writing
The software was able to calculate some math problems that I tried very quickly. I tested the AI writer, it was very biased in favor of Israel and Jews, and did not want to go to atrocities caused by Israel in Gaza and West Bank
Amazing App
Thanks for the most amazing and wonderful app
App Privacy
The developer, NETSUN LLC , indicated that the app’s privacy practices may include handling of data as described below. For more information, see the developer’s privacy policy .
Data Not Collected
The developer does not collect any data from this app.
Privacy practices may vary, for example, based on the features you use or your age. Learn More
Information
- Lifetime Access $0.00
- Weekly Access $6.99
- Yearly Access $39.99
- App Support
- Privacy Policy
More By This Developer
Smart Printer App ®
Phone Cleaner: AI Clean Up
Chat AI : AI Chatbot Assistant
You Might Also Like
WordSnap - AI Flashcards Maker
Spanish Learning App - Fluency
Homework Planner: Recitation
Science Answers
Coding game: Python Java Learn
Nihongo Lessons

Boston College Libraries

The Answer Wall
Answering questions at Boston College O’Neill Library
Could we solve the 3-body problem if we had a different system of math?


COMMENTS
To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem. Show more; en. Related Symbolab blog posts.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Algebra. Basic Math. Pre-Algebra. Algebra. Trigonometry. Precalculus.
Here are two solutions. How Not to Write the Solution 1: Let the line through A parallel to BC meet line BM at J. Let the line through J parallel to AB meet line BC at K. Let MN hit AB at X and AC at Y . Since JK \parallel AB and AJ \parallel BK, JKBA is a parallelogram. Since \angle {ABM} = (\angle A + \angle C)/2.
Math strategies for problem-solving help students use a range of approaches to solve many different types of problems. It involves identifying the problem and carrying out a plan of action to find the answer to mathematical problems. ... Many teachers create posters and anchor charts of their chosen process to display in their classrooms. They ...
Wolfram for Education. Wolfram Demonstrations. Mathematica. MathWorld. Online practice problems with answers for students and teachers. Pick a topic and start practicing, or print a worksheet for study sessions or quizzes.
Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students. The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and ...
Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more.
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
Step 3: Solve the Problem. Make a table to organize the data. For this example, create a row for the slower car, a row for the faster car, and a column for each hour. Find the distance traveled during each hour by looking at the distances listed in each column. The distance of the faster car was more than the distance of the slower car in hour ...
The Problem-solving Classroom. This article forms part of our Problem-solving Classroom Feature, exploring how to create a space in which mathematical problem solving can flourish. At NRICH, we believe that there are four main aspects to consider: • Highlighting key problem-solving skills. • Examining the teacher's role.
MathGPT. MathGPT Vision. MathGPT can solve word problems, write explanations, and provide quick responses. Drag & drop an image file here, or click to select an image. or. MathGPT is an AI-powered math problem solver, integral calculator, derivative cacluator, polynomial calculator, and more! Try it out now and solve your math homework!
Getting the Most from Each of the Problem Solving Activities. When students participate in problem solving activities, it is important to ask guiding, not leading, questions. This provides students with the support necessary to move forward in their thinking and it provides teachers with a more in-depth understanding of student thinking.
Find 8-12 minutes in your daily schedule to focus on problem-solving - consider this time sacred & only for problem-solving. Select only 1-2 word problems per day. Target step-by-step math problem-solving to build math problem-solving skills through a less-is-more approach using Problem of the Day.
I put together a problem-solving unit that would focus a bit more on strategies and steps in hopes that that would create problem-solving stars. The Problem Solving Strategies. First, I wanted to make sure my students all learned the different strategies to solve problems, such as guess-and-check, using visuals (draw a picture, act it out, and ...
Chat with your data, create graphs, build forecasting models, and more. Scan-and-solve math problems for free with the first AI-powered math equation solver. Perform calculations, solve equations, and get step-by-step solutions in seconds. Julius is a powerful AI data analyst that helps you analyze and visualize your data. ...
Teaching about problem solving begins with suggested strategies to solve a problem. For example, "draw a picture," "make a table," etc. You may see posters in teachers' classrooms of the "Problem Solving Method" such as: 1) Read the problem, 2) Devise a plan, 3) Solve the problem, and 4) Check your work. There is little or no ...
Difficulty. Min: Max: Fully customisable Maths Question Generator. Create up to 9 different groups of randomly generated questions, each testing a specific topic and level of difficulty.
Math problems are not just equations to solve or numbers to crunch, they are innovative puzzles designed to spark curiosity and foster critical thinking abilities. ... The math problem provides a way for individuals to apply their knowledge of mathematical theories and theorems, creating a process for critical thinking, logical reasoning, and ...
Math problem-solving worksheets can be a playground for nurturing critical thinking. Through word problem worksheets, students not only practice calculations but also apply math concepts to real-world scenarios. ... Creating successful problem-solving worksheets involves careful planning. Here are some ideas to consider: Define the Learning ...
Mixed Operations. Multiplication. Number Charts and Graphs. Pre-Algebra. Subtraction. Time. Word Problems. Create Your Own Math Worksheets With The Math Worksheet Generator. Choose A Main Topic To Create Custom Math Worksheets.
Here are three takeaways from the discussion. For more, watch the recording on demand. 1. Intervention is key. Research shows that early math skills are a key predictor of later academic success.
Small live classes for advanced math and language arts learners in grades 2-12. Visit AoPS Academy ‚ ... Art of Problem Solving is an ACS WASC Accredited School. aops programs. AoPS Online. Beast Academy. AoPS Academy. About. About AoPS. Our Team. Our History. Jobs. AoPS Blog. Site Info. Terms.
Great in solving math problems, but very biased in AI writing The software was able to calculate some math problems that I tried very quickly. I tested the AI writer, it was very biased in favor of Israel and Jews, and did not want to go to atrocities caused by Israel in Gaza and West Bank.
Could we solve the 3-body problem if we had a different system of math? April 23, 2024; What is the most dangerous threat to humanity? What is the best ice cream flavor? April 23, 2024 [crossed out] I have the best GF! April 23, 2024; If a BC student I know wrote and published a book. Can I submit it to the BC library to be added to the library?