- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- How to end a speech effectively

How to end a speech memorably
3 ways to close a speech effectively.
By: Susan Dugdale | Last modified: 09-05-2022
Knowing how, and when, to end a speech is just as important as knowing how to begin. Truly.
What's on this page:
- why closing well is important
- 3 effective speech conclusions with examples and audio
- 7 common ways people end their speeches badly - what happens when you fail to plan to end a speech memorably
- How to end a Maid Honor speech: 20 examples
- links to research showing the benefits of finishing a speech strongly

Why ending a speech well is important
Research * tells us people most commonly remember the first and last thing they hear when listening to a speech, seminar or lecture.
Therefore if you want the audience's attention and, your speech to create a lasting impression sliding out with: "Well, that's all I've got say. My time's up anyway. Yeah - so thanks for listening, I guess.", isn't going to do it.
So what will?
* See the foot of the page for links to studies and articles on what and how people remember : primacy and recency.
Three effective speech conclusions
Here are three of the best ways to end a speech. Each ensures your speech finishes strongly rather than limping sadly off to sure oblivion.
You'll need a summary of your most important key points followed by the ending of your choice:
- a powerful quotation
- a challenge
- a call back
To work out which of these to use, ask yourself what you want audience members to do or feel as a result of listening to your speech. For instance;
- Do you want to motivate them to work harder?
- Do you want them to join the cause you are promoting?
- Do you want them to remember a person and their unique qualities?
What you choose to do with your last words should support the overall purpose of your speech.
Let's look at three different scenarios showing each of these ways to end a speech.
To really get a feel for how they work try each of them out loud yourself and listen to the recordings.
1. How to end a speech with a powerful quotation

Your speech purpose is to inspire people to join your cause. Specifically you want their signatures on a petition lobbying for change and you have everything ready to enable them to sign as soon as you have stopped talking.
You've summarized the main points and want a closing statement at the end of your speech to propel the audience into action.
Borrowing words from a revered and respected leader aligns your cause with those they fought for, powerfully blending the past with the present.
For example:
"Martin Luther King, Jr said 'The ultimate measure of a man is not where he stands in moments of comfort, but where he stands at times of challenge and controversy.'
Now is the time to decide. Now is the time to act.
Here's the petition. Here's the pen. And here's the space for your signature.
Now, where do you stand?"
Try it out loud and listen to the audio
Try saying this out loud for yourself. Listen for the cumulative impact of: an inspirational quote, plus the rhythm and repetition (two lots of 'Now is the time to...', three of 'Here's the...', three repeats of the word 'now') along with a rhetorical question to finish.
Click the link to hear a recording of it: sample speech ending with a powerful quotation .
2. How to end a speech with a challenge

Your speech purpose is to motivate your sales force.
You've covered the main points in the body of it, including introducing an incentive: a holiday as a reward for the best sales figures over the next three weeks.
You've summarized the important points and have reached the end of your speech. The final words are a challenge, made even stronger by the use of those two extremely effective techniques: repetition and rhetorical questions.
"You have three weeks from the time you leave this hall to make that dream family holiday in New Zealand yours.
Can you do it?
Will you do it?
The kids will love it.
Your wife, or your husband, or your partner, will love it.
Do it now!"
Click the link to listen to a recording of it: sample speech ending with a challenge . And do give it a go yourself.
3. How to end a speech with a call back

Your speech purpose is to honor the memory of a dear friend who has passed away.
You've briefly revisited the main points of your speech and wish in your closing words to leave the members of the audience with a happy and comforting take-home message or image to dwell on.
Earlier in the speech you told a poignant short story. It's that you return to, or call back.
Here's an example of what you could say:
"Remember that idyllic picnic I told you about?
Every blue sky summer's day I'll see Amy in my mind.
Her red picnic rug will be spread on green grass under the shade of an old oak tree. There'll be food, friends and laughter.
I'll see her smile, her pleasure at sharing the simple good things of life, and I know what she'd say too. I can hear her.
"Come on, try a piece of pie. My passing is not the end of the world you know."
Click the link to hear a recording of it: sample speech ending with a call back . Try it out for yourself too. (For some reason, this one is a wee bit crackly. Apologies for that!)
When you don't plan how to end a speech...
That old cliché 'failing to plan is planning to fail' can bite and its teeth are sharp.
The 'Wing It' Department * delivers lessons learned the hard way. I know from personal experience and remember the pain!
How many of these traps have caught you?
- having no conclusion and whimpering out on a shrug of the shoulders followed by a weak, 'Yeah, well, that's all, I guess.', type of line.
- not practicing while timing yourself and running out of it long before getting to your prepared conclusion. (If you're in Toastmasters where speeches are timed you'll know when your allotted time is up, that means, finish. Stop talking now, and sit down. A few seconds over time can be the difference between winning and losing a speech competition.)
- ending with an apology undermining your credibility. For example: 'Sorry for going on so long. I know it can be a bit boring listening to someone like me.'
- adding new material just as you finish which confuses your audience. The introduction of information belongs in the body of your speech.
- making the ending too long in comparison to the rest of your speech.
- using a different style or tone that doesn't fit with what went before it which puzzles listeners.
- ending abruptly without preparing the audience for the conclusion. Without a transition, signal or indication you're coming to the end of your talk they're left waiting for more.
* Re The 'Wing It' Department
One of the most galling parts of ending a speech weakly is knowing it's avoidable. Ninety nine percent of the time it didn't have to happen that way. But that's the consequence of 'winging it', trying to do something without putting the necessary thought and effort in.
It's such a sod when there's no one to blame for the poor conclusion of your speech but yourself! ☺
How to end a Maid of Honor speech: 20 examples
More endings! These are for Maid of Honor speeches. There's twenty examples of varying types: funny, ones using Biblical and other quotations... Go to: how to end a Maid of Honor speech

How to write a speech introduction
Now that you know how to end a speech effectively, find out how to open one well. Discover the right hook to use to captivate your audience.
Find out more: How to write a speech introduction: 12 of the very best ways to open a speech .

More speech writing help

You do not need to flail around not knowing what to do, or where to start.
Visit this page to find out about structuring and writing a speech .
You'll find information on writing the body, opening and conclusion as well as those all important transitions. There's also links to pages to help you with preparing a speech outline, cue cards, rehearsal, and more.
Research on what, and how, people remember: primacy and recency
McLeod, S. A. (2008). Serial position effect . (Primacy and recency, first and last) Simply Psychology.
Hopper, Elizabeth. "What Is the Recency Effect in Psychology?" ThoughtCo, Feb. 29, 2020.
ScienceDirect: Recency Effect - an overview of articles from academic Journals & Books covering the topic.
- Back to top of how to end a speech page
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9 Closing a Speech: End with Power and Let Them Know It is Time to Clap

Open Your Speech With a Bang Close It With a Slam-Dunk Westside Toastmasters
“Great is the art of beginning, but greater is the art of ending,” according to poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow. The first few words of your speech make the audience want to listen and the last few sentences help them decide what they feel about you and your topic. In this chapter, I will explain the function of a conclusion, the format of a conclusion, and I will give you numerous examples of ways to end your speech. Most of this chapter is dedicated to showing you good examples of different types of speech closings. Let’s get started by talking about the purpose of the closing.
A Strong Closing Does Many Things
- Summarizes the points. By restating your points your audience is more likely to remember them.
- Tells the audience when to clap. Let’s face it, it is so awkward when you are done with your speech, and no one claps. Being clear the end is near, relieves the audience of the pressure of wondering if they are clapping at the right time.
- Provides resolution. Your speech should give the audience a sense of resolve or a sense of being challenged.
The Formula for Closing Most Speeches
- Transition statement to ending.
- Review the main points–repeat the thesis.
- If it is a persuasive speech, tell the audience what you want them to do or think.
- Provide a closing statement.
Restate the Thesis
Tell them what you are going to say, say it, tell them what you have said. This speech pattern is useful in most types of speeches because it helps the speaker to remember your key points. As you build your closing, make sure you restate the thesis. A good rule of thumb is to write it in such a way that if the audience were asked to restate the main points, their answer would match closely with your thesis.
EXAMPLE Watch as Stella Young gives her thesis and then restates her thesis at the end of the speech as she wraps up. The thesis of the talk in the introduction: We’ve been sold the lie that disability is a Bad Thing, capital B, capital T. It’s a bad thing, and to live with a disability makes you exceptional. It’s not a bad thing, and it doesn’t make you exceptional. Restates the thesis of the talk at the closing: Disability doesn’t make you exceptional but questioning what you think you know about it does.
Stella Young, I’m not your inspiration, thank you very much. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GtPGrLoU5Uk
This next example is from a student’s speech. It is easy to pull out one sentence that clearly summarizes the main points of her speech. Following her summary, she winds the speech down into a thoughtful conclusion and ends with three powerful words.
Now is the time to separate the war on drugs from the war on addiction. T oday you’ve heard the problems, impacts, and solutions of criminalizing addictions. Bruce Callis is 50 years old now. And he is still struggling with his addiction. while you all are sitting out there listening to this, I’m living with it. Bruce Callis is my father and for my entire life, I have watched our misguided system destroy him. The irony here is that we live in a society where we are told to recycle. We recycle paper, aluminum, and electronics. But why don’t we ever consider recycling them most precision think on Earth– the human life. Student Tunnette Powell, Winner of the 2012 Interstate Oratorical Association Contest.
Closing Phrases
After you restate your thesis, you should carefully deliver your closing phrases. Your closing should provide a resolution to your speech and/or it should challenge the audience. Frantically Speaking writer Hrideep Barot suggests “a conclusion is like tying a bow or ribbon to a box of your key ideas that your audience will be taking along with them.”
A speech closing is not just about the words you say, but it is also the way you say it. Change the pace near the end of your speech. Let your tone alone should signal the end is near. It is about deliberate voice control, don’t let your voice weakly away.
In the next section, I will cover these ways to end your speech:
End with powerful words End with a quote End with a graphic End with parallel construction End on a positive note End with a challenge End with a question End with inspiration End with well-wishing End with humor End with a call to action End with a feeling of resolve End with a prop
The best way to teach you about advanced closings is to show not tell. For this section, I will briefly explain each type of closing and then provide a video. Each video is queued so you can play the video and watch the closing statement. I included a transcript under each video if you want to follow along. It will be most beneficial for you to watch the clip and not just read the text. By watching, you will have a chance to hear the subtle changes in the speaker’s voice as they deliver their closing statements.
End with Powerful Words
As you design your closing, look at the last three to five words and examine them to see if they are strong words. Oftentimes, you can rearrange a sentence to end with a powerful word. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
Watch this clip for how BJ Miller ends with a powerful thought and a powerful word.
Parts of me died early on, and that’s something we can all say one way or another. I got to redesign my life around this fact, and I tell you it has been a liberation to realize you can always find a shock of beauty or meaning in what life you have left, like that snowball lasting for a perfect moment, all the while melting away. If we love such moments ferociously, then maybe we can learn to live well — not in spite of death, but because of it. Let death be what takes us, not lack of imagination. BJ Miller, What Really Matters at the End of Life
End by Circling Back to the Opening
Another type of ending is to circle back to what you said in the beginning. You can revisit a quote, share the end to an illustration that was begun in the beginning, or you can put away a prop you got out in the beginning.
Watch this clip for how Zubing Zhang begins and ends with the same quote to circle back around to the main idea.
She starts by telling a story of bungee jumping off the world’s highest platform and how she saw a sign with a quote that says, “Life begins at the edge of your comfort zone.” After telling her own story about pushing her emotional limits, she circles back around at the end by saying, “As the words said high on the bungee platform, “Life begins at the edge of your comfort zone.”
Yubing Zhang, Life Begins at the End of Your Comfort Zone.
End With Quote
If you end your speech with a quote, attend to the following.
- Always say the author of the quote before the quote for example, “I want to leave you with a leadership quote ‘What you do has far greater impact than what you say,’ Steven Covey.” The problem with this ending is that “Stephen Covey” are the last two words of the speech and that is boring. Consider instead this ending. “I think Robin Sharma said it best ‘Leadership is not about a title or a designation. It’s about impact, influence, and inspiration.'” In this arrangement, the last three words are powerful–influence and inspiration.
- Provided context for the quote before or after. Make sure the quote is meaningful and not just an easy way to end.
Watch this clip for how Sir Ken Robinson ends with a quote. Notice how he says the author and then the quote.
Also, notice how he then ties his speech to the quote with a final few sentences and ends with the powerful word–“revolution” and how he uses a strong vocal emphasis as he says his last word. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
There’s a wonderful quote from Benjamin Franklin. “There are three sorts of people in the world: Those who are immovable, people who don’t get it, or don’t want to do anything about it; there are people who are movable, people who see the need for change and are prepared to listen to it; and there are people who move, people who make things happen.” And if we can encourage more people, that will be a movement. And if the movement is strong enough, that’s, in the best sense of the word, a revolution. And that’s what we need.
Sir Ken Robinson, How to Escape Education’s Death Valley.
End with a Graphic
You might want to use a visual to make your final point. Bringing in a picture, graphic, or object, reengages the audience to pay attention to your final ideas.
Watch this clip for how Barry Schartz uses the magic words “so to conclude” and then he creatively uses a picture of a fishbowl to narrow in on his point. Notice how his final word is spoken with urgency as he says “disaster.” (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
So, to conclude. (He shows a picture of fish in a fishbowl) He says, “You can be anything you want to be — no limits.” You’re supposed to read this cartoon and, being a sophisticated person, say, “Ah! What does this fish know? Nothing is possible in this fishbowl.” Impoverished imagination, a myopic view of the world –that’s the way I read it at first. The more I thought about it, however, the more I came to the view that this fish knows something. Because the truth of the matter is, if you shatter the fishbowl so that everything is possible, you don’t have freedom. You have paralysis. If you shatter this fishbowl so that everything is possible, you decrease satisfaction. You increase paralysis, and you decrease satisfaction. Everybody needs a fishbowl. This one is almost certainly too limited –perhaps even for the fish, certainly for us. But the absence of some metaphorical fishbowl is a recipe for misery and, I suspect, disaster. Barry Schwartz, The Paradox of Choice
End with Parallel Construction
Parallel construction is a series of repeated phrases. It can be a powerful tool to use in a persuasive speech as it creates a feeling of importance.
Watch this clip for how Malala Yousafzai ends with a series of parallel statements to build momentum. Notice how her pace perfectly matches her words and you feel her strength when she ends with “education first.” (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
Dear brothers and sisters, we must not forget that millions of people are suffering from poverty, injustice, and ignorance. We must not forget that millions of children are out of schools. We must not forget that our sisters and brothers are waiting for a bright peaceful future. So let us wage a global struggle against illiteracy, poverty, and terrorism, and let us pick up our books and pens. They are our most powerful weapons. One child, one teacher, one pen, and one book can change the world. Education is the only solution. Education First.
Malala Yousafzai, United Nations Youth Assembly
End on a Positive Note
Audiences are constantly evaluating a speaker to determine their attitude and motivation. As you consider your speech closing, ask yourself what type of impression do you want to leave? Do you want to leave them with depression or hope? Sadness or promise? Most of the time, audiences will receive messages that end positively better than speeches that end negatively.
In this speech sample, Hans Rosling showed the audience some hard statistics and he even pointed fingers at the audience as part of the problem. To help them hear his main point, he wisely ends on a positive note.
Watch this clip for how Hans Rosling ends this thought-provoking talk on a positive note. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
Now, when thinking about where all this leaves us, I have just one little humble advice for you, besides everything else, look at the data. Look at the facts about the world and you will see where we are today and how we can move forwards with all these billions on our wonderful planet. The challenge of extreme poverty has been greatly reduced and it’s for the first time in history within our power to end it for good. The challenge of population growth is, in fact, already being solved, the number of children has stopped growing. And for the challenge for climate change, we can still avoid the worst, but that requires the richest, as soon as possible, find a way to use their set their use of resources and energy at a level that, step by step, can be shared by 10 billion or 11 billion by the end of this century. I’ve never called myself an optimist, but I do say I’m a possibilist and I also say the world is much better than many of you think.
Hans Rosling, Facts about the Population.
End with a Challenge
Leave the audience with a doable personal challenge. Help them mentally make sense of all the information that you shared by helping them know how to file it away and how to use it.
Watch this clip for how Melissa Butler ends with a challenge. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
So, I challenge each of you, when you go home today, look at yourself in the mirror, see all of you, look at all of your greatness that you embody, accept it, and love it. And finally, when you leave the house tomorrow, try to extend that same love and acceptance to someone who doesn’t look like you . Melissa Butler, Why You Think You’re Ugly.
Watch this clip as Darren LaCroix literally falls face down to anchor the point that when we fall, we “fall forward.” (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
Darren LaCroix talks about taking risks and falling down and getting back up, he literally and purposefully falls down during his speech and ends this way: What’s your next step… take it. I didn’t want to look back at my life and say you know I never did try that comedy thing, but I died debt-free. All of us are headed toward that goal we are going to teach a point where we get stuck and our feet are like in cement and we can’t move but we’re so afraid of that ouch but we forget that if we lean forward and take a risk–(He falls face down) and we fall on our face. When we get up, notice, you still made progress. So please, with me, go ahead and fall. But fall forward. Darren LaCroiz, Winning Speech delivered at National Speech Association
End with a Question
Asking a question at the end is one way to reengage the audience. It helps them think about what your topic might mean for them.
Watch this clip for how David Eagleman reminds us about why his topic is important and then ends with a question. Notice how he pauses before his final question and how he changes the pace of his speech for the final sentence. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
So I think there’s really no end to the possibilities on the horizon for human expansion. Just imagine an astronaut being able to feel the overall health of the International Space Station, or, for that matter, having you feel the invisible states of your own health, like your blood sugar and the state of your microbiome, or having 360-degree vision or seeing in infrared or ultraviolet. So the key is this: As we move into the future, we’re going to increasingly be able to choose our own peripheral devices. We no longer have to wait for Mother Nature’s sensory gifts on her timescales, but instead, like any good parent, she’s given us the tools that we need to go out and define our own trajectory. So the question now is, how do you want to go out and experience your universe?
David Eagleman, Can We Create New Senses for Humans?
Watch this clip for how Lera Boroditsky ends with a personal note and a powerful final question. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
I want to leave you with this final thought. I’ve told you about how speakers of different languages think differently, but of course, that’s not about how people elsewhere think. It’s about how you think. It’s how the language that you speak shapes the way that you think. And that gives you the opportunity to ask, “Why do I think the way that I do?” “How could I think differently?” And also, “What thoughts do I wish to create?” Lera Boroditsky, How Language Shapes the Way We Think
End with Inspiration
“Inspiring your audience is all about helping them see their own vision, not yours.”
You may want to end your speech with inspiring and encouraging words. Pick words that resonate with most of your audience and deliver them in such a way that your audience feels your lift in emotion.
Watch this clip for how Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie ends with an inspiring final note and a powerful last few words “regain a kind of paradise” (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
Stories matter. Many stories matter. Stories have been used to dispossess and to malign, but stories can also be used to empower and humanize. Stories can break the dignity of a people, but stories can also repair that broken dignity.
I would like to end with this thought: That when we reject the single-story, when we realize that there is never a single story about any place, we regain a kind of paradise.
Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie, The Danger of a Single Story
Watch this clip for how Dan Pink ends with an inspiring final note. (I have the video cued to play just the closing) Let me wrap up. There is a mismatch between what science knows and what business does. Here is what science knows. One: Those 20th century rewards, those motivators we think are a natural part of business, do work, but only in a surprisingly narrow band of circumstances. Two: Those if-then rewards often destroy creativity. Three: The secret to high performance isn’t rewards and punishments, but that unseen intrinsic drive– the drive to do things for their own sake. The drive to do things cause they matter.
And here’s the best part. We already know this. The science confirms what we know in our hearts. So, if we repair this mismatch between what science knows and what business does, if we bring our motivation, notions of motivation into the 21st century, if we get past this lazy, dangerous, ideology of carrots and sticks, we can strengthen our businesses, we can solve a lot of those candle problems, and maybe, maybe — we can change the world. I rest my case. Dan Pink, The Puzzle of Motivation
End with Well Wishing
There are several types of closings where the speaker wished the audience well.
The Benediction Close: M ay God bless and keep you…. The Presidential Close: God bless you and may God bless the USA The Congratulatory Close: I congratulate you on your accomplishment and wish you continued success.
End with Humor
You can end on a fun lighthearted note. It is important to always run your humor by a variety of people to make sure you are funny, and your humor is appropriate.
Watch this clip for how Andrew Dunham uses humor throughout his speech and ends with a funny one-liner. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
I wish you all the best as we begin this journey on our paths and I sincerely hope and pray that your time and success have proven to be as memorable and spiritually rewarding as mine. If not, there’s always summer school.
Andrew Dunham, Valedictorian Comes Out As Autistic During Speech
End with a Call to Action
If you are delivering a persuasive speech, let the audience know exactly what you want them to do.
End with a Feeling of Resolve
Paul Harvey made famous the line “And now you know…the rest of the story.” Your closing should allow us to know the rest of the story or to know how a situation was resolved.
Watch this clip for how Lucy Hone ends this tough but inspiring talk with a feeling of resolve (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
https://youtu.be/9-5SMpg7Q0k?t=913 If you ever find yourself in a situation where you think there’s no way I’m coming back from this, I urge you to lean into these strategies and think again. I won’t pretend that thinking this way is easy and it doesn’t remove all the pain. But if I’ve learned anything over the last five years, it is that thinking this way really does help. More than anything it has shown me that it is possible to live and grieve at the same time. And for that I will be always grateful. Lucy Hone, The Three Secrets of Resilient People
End with a Prop
Nancy Duarte says you should give your audience, SOMETHING THEY will ALWAYS REMEMBER–S.T.A.R. One way to do that is with an action or statement that will have the audience talking about it for a long time. President Obama did it with a mic drop.
Memorize Your Conclusion
End on time.
Do not diminish the effect of a great speech with a bloated, aimless conclusion. Dan Rothwell.
“Times about up.”
Don’t end with any references to time. It is like a giant stop sign saying, “stop listening.” Don’t highlight that you ran over time or that it is almost time for lunch. You want them to think about your speech, not the clock.
“Any Questions?”
You want them to feel a sense of closure for your speech. End with something powerful and let them applaud. After the applause, you can offer to answer questions. Similarly, projecting your last slide with the words, “Any Questions” is a weak ending.
“Let Me Add This Point I Missed”
If you forget something in the body of your speech, it is usually best to leave it out. Most of the time you are the only one who will miss it.
“Thank You to the Team”
There is a time to thank the organizers and those who helped you but it is not at the end of your speech. Your focus should be on your audience and what they need and what they need to hear is your idea. Send a thank you letter to the team if you want them to feel your appreciation.
“I’m Sorry”
“Sorry again for the technology issue,” “I apologize for going over time, ” “I regret I have no answer to this.” These are all negative phrases. Keep to your topic that is what they need to hear and stay focused.
“I’ll Close with this Video”
No, you should close with talking about the big idea.
If you don’t have a plan at the end, you will ramble. “Steer clear of meandering endings they kill a story,” according to the Moth Storytelling website. “Your last line should be clear in your head before you start. Yes, bring the audience along with you as you contemplate what transpires in your story, but remember, you are driving the story, and must know the final destination. Keep your hands on the wheel!”
To Thank or Not to Thank, That is the Question
There is a debate amongst speech professionals, speech teachers, and speech coaches about whether or not you should thank the audience. Here are their main arguments.
Why You Should Not Say Thank You
- You want to end with powerful words. “Thank you” are not strong words.
- The recency effect suggests they will remember the last words you spoke. You want them to remember more than just “thank you.”
- It is not a very creative way to end.
- It can be a sign of a lazy speaker, “I have no idea how to end this, I’ve run out of good things to say so I’ll say ‘Thank you’ so you will clap now.”
Why You Should Say Thank You
- It has come to be the expected ending in many settings. Violating their expectations can cause them to have a negative reaction.
- It clearly signals you are finished so the audience knows when to clap. The relieves the pressure from both you and the audience.
- It expresses gratitude.
I will leave it up to you to decide what works for you. As for me, I plan on trying to find more creative ways to end other than just saying “thank you.”
Maximizing the Primacy Recency Effect
If I were to read you a list of thirty things on my grocery list and then asked you to list all that you can remember, chances are you would remember the first times on the list and the last items on the list ( and any ones you found interesting from the middle). When people engage in listening, they tend to remember the first and last things they hear, it is called the primacy-recency effect. T his is just one more reason that your introduction and conclusion should be so well planned out. It is those first words and last words that the audience is going to remember.
The primacy recency effect influences, not only what people pay attention to in a speech, but also which speech we pay the most attention to in a series of speeches. For example, if there is a lineup of six speakers, the first and last speakers tend to get the most attention.
As a speaker, you can use this information to your advantage by volunteering to go first or last. If you are giving a long presentation, you can break it up by allowing the audience to move around or talk to a neighbor. When you come back from break, you have re-engaged that primacy effect and moved them back to a high state of attention.
Do You Have Everything You Need for a Strong Closing?
- Have I signaled my speech is coming to an end with my words or my voice?
- Have I restated my main points?
- If I am persuading my audience, do they know what I want them to do or think?
- Have I written the last three to five words in such a way that I end with powerful words?
- Have I memorized my closing?
Getting Off the Platform is Part of Your Closing
Plan on making a strong exit. Whether you are stepping off a stage or simply going to your seat, you should consider that the audience is watching you.
I have had students who finished their speech and then walked over to the trashcan and in a large, exaggerated movement, they threw their notecards in the trash. In our minds, we threw their message away with those cards. I’ve seen speakers, sit in their chairs and then announce, “I can’t believe my hands were shaking so much.” I’ve sat there and thought, “I didn’t notice.” I then realized that the comments they made influenced my perception of them and my perception of their topic.
You said your last word and the audience is applauding, now what? Look at your audience and smile and nod in appreciation before walking off the stage. If you will be answering questions, wait until after the applause stops to begin your question and answering period.
When practicing your speech, it is a good idea to start from your chair, walk up to a spot and then give your speech, and then walk back to your chair and sit down. Your “speech” impression begins and ends from your chair.
Key Takeaways
Remember This!
- A speech closing should include a review of the main points and a purposeful closing sentence.
- Persuasive speech endings should tell the audience specifically what they should do or think about.
- The recency effect suggests that people remember the most recent things they have heard which is one reason the closing is so important.
- Chance the pace of your speech and the tone of your voice to signal the end of the speech.
Please share your feedback, suggestions, corrections, and ideas.
I want to hear from you.
Do you have an activity to include? Did you notice a typo that I should correct? Are you planning to use this as a resource and do you want me to know about it? Do you want to tell me something that really helped you?
Click here to share your feedback.
Adichie, C.N. (2009). The danger of a single story. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D9Ihs241zeg Standard YouTube License.
Anderson, C. (2016). TED talks: The official TED guide to public speaking. Mariner Books.
Barot, H. Fifteen powerful speech ending lines (and tips to create your own). Frantically Speaking. https://franticallyspeaking.com/15-powerful-speech-ending-lines-and-tips-to-create-your-own/
Boroditsky, L. (2017). How language shapes the way we think. https://www.ted.com/talks/lera_boroditsky_how_language_shapes_the_way_we_think Standard Youtube License.
Butler, M. (2018). Why you think you’re ugly. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=imCBztvKgus Standard YouTube License.
Dunham. A. (2019). Valedictorian comes out as autistic during speech. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GtPGrLoU5Uk Standard Youtube License.
Eagleman, D. (2015). Can we create new senses for humans?[Video]. YouTube https://youtu.be/4c1lqFXHvqI Standard YouTube License.
Hone, L. (2019). The three secrets of resilient people. [Video]. YouTube https://youtu.be/NWH8N-BvhAw Standard YouTube License.
Jeff, P. (2009). Ten ways to end your speech with a bang. http://sixminutes.dlugan.com/10-ways-to-end-your-speech
Jobs, S. (2005). You’ve got to find what you love. https://news.stanford.edu/2005/06/14/jobs-061505/
Khanna, P. (2016). Let the head of TED show you how to end your speech with power. https://www.fastcompany.com/3059459/let-the-head-of-ted-show-you-how-to-end-your-speech-with-p
Karia, A. (2013). How to open and close a TED talk (or any other speech or presentation). https://akashkaria.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/HowtoOpenandCloseaTEDTalk.pdf
LaCroix, D. (2001). World champion of public speaking. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FUDCzbmLV-0 Standard YouTube License.
Mandela, N. (2011). Speech from the dock in the Rivonia trial.[Video]. YouTube https://www.nelsonmandela.org/news/entry/i-am-prepared-to-die Standard YouTube License.
Mandela, N. (1994). Presidential Inaugural Speech. [Video]. YouTube https://www.americanrhetoric.com/speeches/nelsonmandelainauguralspeech.htm Standard YouTube License.
Miller, B.J. (2015). What really matters at the end of life. [Video]. YouTube https://www.ted.com/talks/bj_miller_what_really_matters_at_the_end_of_life?language=en Standard YouTube License.
Moth. (2021). Storytelling tips and tricks: How to tell a successful story. https://themoth.org/share-your-story/storytelling-tips-tricks
Obama, B. (2016). White House correspondents dinner. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NxFkEj7KPC0 Standard YouTube License.
Pink, D. (2009). The puzzle of motivation. [Video]. YouTube https://www.ted.com/talks/dan_pink_the_puzzle_of_motivation Standard YouTube License.
Rothwell, D. (2014). Practically Speaking. Oxford University Press.Robinson, K. (2013). How to escape education’s death valley. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wX78iKhInsc Standard YouTube License.
Rosling, H. (2014). Don’t Panic-Hans Rosling showing the facts about population.[Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FACK2knC08E Standard YouTube License.
Schwartz, B. (2005). The paradox of choice. [Video]. YouTube https://www.ted.com/talks/barry_schwartz_the_paradox_of_choice Standard YouTube License.
Toastmasters International. (2016). Concluding your Speech. https://www.toastmasters.org/Resources/Concluding-Your-Speech
Young, S. (2014). I’m not your inspiration, thank you very much. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GtPGrLoU5Uk Standard YouTube License.
Yousafzai, M. (2013). Malala Yousafzai addresses United Nations Youth Assembly. [Video]. YouTube https://youtu.be/3rNhZu3ttIU Standard YouTube License.
Zhang, Y. (2015). Life begins at the end of your comfort zone. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cmN4xOGkxGo Standard YouTube License.
Media Attributions
- Audience clapping © Alex Motoc is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- jose-aragones-81QkOoPGahY-unsplash © Jose Aragones is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
Advanced Public Speaking Copyright © 2021 by Lynn Meade is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Different Ways to End a Presentation or Speech
November 6, 2017 - Dom Barnard
The beginning and ending of your presentation are the most important. The beginning is where you grab the audience’s attention and ensure they listen to the rest of your speech. The conclusion gives you a chance to leave a lasting impression that listeners take away with them.
Studies show that when people are tasked with recalling information, they “best performance at the beginning and end”. It’s therefore essential you leave an impact with your closing statement. A strong ending motivates, empowers and encourages people to take action.
The power of three
The rule of three is a simple yet powerful method of communication and we use it often in both written and verbal communication. Using information in patterns of three makes it more memorable for the audience.
Examples of the power of three being used:
- This is not the end. It is not even the beginning of the end. But it is, perhaps, the end of the beginning – Winston Churchill
- Blood, sweat and tears – General Patton
- I came, I saw, I conquered – Julius Caesar
A compelling story
Ending your presentation on a short story, especially if that story is personal or illustrates how the content presented affects others is the best way to conclude.
If you want to talk about a customer experience or successful case study, think about how you can turn it into a meaningful story which the audience will remember and even relate to. Creating empathy with your audience and tying the story back to points made throughout the presentation ensures your presentation will be well received by the audience.
A surprising fact
A surprising fact has the power to re-engage the audience’s attention, which is most likely to wane by the end of a presentation. Facts with statistical numbers in them work well – you can easily search online for facts related to your speech topic. Just make use you remember the source for the fact in case you are questioned about it.
A running clock
Marketing and advertising executive Dietmar Dahmen ends his Create Your Own Change talk with a running clock to accompany his last statement. “Users rule,” he says, “so stop waiting and start doing. And you have to do that now because time is running out.”
If you’re delivering a time-sensitive message, where you want to urge your listeners to move quickly, you can have a background slide with a running timer to add emphasis to your last statement.

Acknowledging people or companies
There are times when it’s appropriate to thank people publicly for helping you – such as
- Presenting a research paper and want to thank people involved in the project
- Presenting data or information obtained from a company or a person
- When someone helped you build the presentation if it’s a particularly complex one
You can even use the PowerPoint credits feature for additional ‘wow’ factor.
A short, memorable sentence
A sound bite is an attention magnet. It cuts to the core of your central message and is one of the most memorable takeaways for today’s Twitter-sized attention spans. Consider Steve Jobs’ famous last line at his commencement address at Stanford University: “Stay hungry, stay foolish.”
Think about how you can distil your message down to a crisp, memorable statement. Does it represent your authentic voice? Does it accurately condense what your core message is about? Listeners, especially business audiences, have a radar that quickly spots an effort to impress rather than to genuinely communicate an important message.
An interesting quote
A relatively easy way to end your speech is by using a quote. For this to be effective, however, the quote needs to be one that has not been heard so often that it has become cliché.
To access fresh quotes, consider searching current personalities rather than historical figures. For example, a quote on failing from J.K. Rowling: “It is impossible to live without failing at something, unless you live so cautiously that you might as well not have lived at all – in which case, you fail by default.”
You need to figure out what resonates with your audience, and choose a quote that fits the presentation theme. If you’re up to it, you can round off the quote with your own thoughts as well.
A visual image
Make use of this power by ending your presentation with a riveting visual that ties to your take-home message. Leave this slide on when you finish your presentation to give the audience something to look at and think about for the next few minutes.
Use a summary slide instead of a ‘thank you’ slide
‘Thank You’ slides don’t really help the audience. You should be verbally saying ‘Thank you’, with a smile and with positive eye contact, putting it on a slide removes the sentiment.
Instead of a ‘Thank You’ slide, you can use a summary slide showing all the key points you have made along with your call to action. It can also show your name and contact details.
This slide is the only slide you use that can contain a lot of text, use bullet points to separate the text. Having all this information visible during the Q&A session will also help the audience think of questions to ask you. They may also choose to take photos of this slide with their phone to take home as a summary of your talk and to have your contact details.

Repeat something from the opening
Closing a presentation with a look back at the opening message is a popular technique. It’s a great way to round off your message, whilst simultaneously summing up the entire speech and creating a feeling of familiarity for the audience. Comedians do this well when they tie an earlier joke to a later one.
Doing this will signal to the audience that you are coming to the end of your talk. It completes the circle – you end up back where you started.
There are a few ways to approach this technique:
- Set up a question at the beginning of your speech and use your ending to answer it
- Finish a story you started, using the anecdote to demonstrate your message
- Close with the title of the presentation – this works best with a provocative, memorable title
Link the main points to the key message
At the beginning of your talk, it’s important to map out the main ideas you will talk about. An audience that doesn’t know the stages of the journey you are about to take them on will be less at ease than one that knows what lies ahead. At the end of your talk, take them back over what you’ve spoken about but don’t just list the different ideas you developed, show how they are related and how they support your main argument.
Finish with enthusiasm
It’s only natural that you’ll feel tired when you get to the end of your talk. The adrenaline that was racing through your body at the beginning has now worn off.
It’s crucial that the audience feels that you are enthusiastic and open for questions. If you’re not enthusiastic about the presentation, why should the audience be?
Practice Presentation Skills
Improve your public speaking and presentation skills by practicing them in realistic environments, with automated feedback on performance. Learn More
Don’t end with audience questions
When the Q&A session is over, stand up, get their attention and close the presentation. In your closing give your main argument again, your call to action and deal with any doubts or criticisms that out in the Q&A.
A closing is more or less a condensed version of your conclusions and an improvised summary of the Q&A. It’s important that the audience goes home remembering the key points of the speech, not with a memory of a Q&A that may or may not have gone well or may have been dominated by someone other than you.
If possible, try and take questions throughout your presentation so they remain pertinent to the content.
Getting rid of the “questions?” slide
To start, let’s talk about what you shouldn’t do. You shouldn’t end a presentation with a slide that asks “Questions?” Everyone does and there is nothing memorable about this approach.
Ideally, you should take questions throughout the presentation so that the question asked and the answer given is relevant to the content presented. If you choose to take questions at the end of your presentation, end instead with a strong image that relates to your presentation’s content.
Worried about no audience questions?
If you’re afraid of not getting any questions, then you can arrange for a friend in the audience to ask one. The ‘plant’ is a good way to get questions started if you fear silence.
Chances are that people do want to ask questions, but no one wants to be the first to ask a question. If you don’t have a ‘plant’, you might need to get the ball rolling yourself. A good way to do this is for you to ask am open question to the audience. Ask the most confident looking person in the room for their opinion, or get the audience to discuss the question with the person sitting beside them.
A cartoon or animation
In his TED talk on The Paradox of Choice , Barry Schwartz ends his presentation with a cartoon of a fishbowl with the caption, “You can be anything you want to be – no limits.” He says, “If you shatter the fishbowl, so that everything is possible, you don’t have freedom, you have paralysis… Everybody needs a fishbowl”. This is a brilliant ending that combines visuals, humour and a metaphor. Consider ending your presentation with a relevant cartoon to make your message memorable.
Ask a rhetoric question
So, for example, if you’re finishing up a talk on the future of engineering, you might say, “I’d like to end by asking you the future of manufacturing, will it be completely taken over by robots in the next 30 years?”
The minute you ask a question , listeners are generally drawn into thinking about an answer. It’s even more engaging when the question is provocative, or when it touches potentially sensitive areas of our lives
Thank the audience
The simplest way to end a speech, after you’ve finished delivering the content, is to say, “thank you.” That has the benefit of being understood by everyone.
It’s the great way for anyone to signal to the audience that it’s time to applaud and then head home.
Call your audience to action and make it clear
It’s not enough to assume your message will inspire people to take action. You need to actually tell them to take action. Your call to action should be clear and specific. Your audience should be left with no doubt about what it is you’re asking.
Use the last few minutes of the presentation to reinforce the call to action you seek. Examples of strong calls to actions include:
- Retain 25% more employees with our personal development solution
- Save your business 150% by using this framework
- Donate today to save millions around the world
Make it clear that you’ve finished
Nothing is more uncomfortable than the silence of an audience working out if you’ve finished or not.
Your closing words should make it very clear that it’s the end of the presentation. The audience should be able to read this immediately, and respond. As we mentioned previously, saying “thank you” is a good way to finish.
If the applause isn’t forthcoming, stand confidently and wait. Don’t fidget and certainly don’t eke out a half-hearted, ‘And that just about covers it. Thank you’.
How to End a Speech: The Best Tips and Examples
I like building and growing simple yet powerful products for the world and the worldwide web.
Published Date : February 16, 2024
Reading Time :
As the introduction sets the stage, your conclusion seals the deal. The question, “How do you end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ?” is an essential query that each presenter or speaker must ask, given the final words’ impact and weight on your audience.
Since your final words eventually have a lasting effect, you must make a striking thought to the people. Your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s ending is your last opportunity to reiterate the fundamental idea, inspire the listeners , motivate a group to take action, change an individual’s perspective, or make a final impression on them.
If you are still wondering how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that can appease your audience, then be worry-free because this guide can help you. Read this article to learn how to end a maid of honor Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , a graduation Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , and more because it contains the best tips and examples.
Why is a Conclusion Important?
The audience is more likely not to forget the latest thing a speaker said due to the “Recency Effect” in learning. Hence, the conclusion of a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech serves as a signal to the audience that it is nearing the end, helping them recall the entire topic’s essential points.
You can’t just suddenly stop speaking in front of your listeners because that will disappoint and confuse them. It is best to ensure they are left satisfied and knowledgeable about your speeches by closing them smoothly.
Additionally, it is vital always to link your conclusion back to your introduction. The most effective way to do this method is through going back to your attention grabber or “hook.”
At the end of your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , it is where most of your audience’s lasting impression of everything you have said will form. Thus, if you ask how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , use its conclusion to secure the necessary components in your listeners’ minds.
You might confuse, disappoint, or even leave the audience unconvinced without a satisfactory conclusion. With these thoughts, we can tell that it has a two-fold purpose: to signal the Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s end and reinforce the speaker’s message to the people.
The Key Elements of a Good Conclusion
When contemplating how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , remember that your introduction is the appetizer, while your conclusion is its dessert. Conclusions must round off the topic and make a strong impression on people’s minds.
To create a conclusion that will satisfy and sum up all the vital information from your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , consider these three key elements:
1. Reiterate the main idea
What is the central idea of your message? That is a secure place to start your conclusion.
Above all, you have directed each part of your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech to support your topic, subject, or information. To start your conclusion, by all means, reiterate your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s main idea.
Of course, making it different and fresh to the listeners would be best. You do not want to repeat it verbatim, making the audience feel like you are just redoing things.
Somewhat loosen it up as you prepare to remind your audience why they would be well-provided to adopt your viewpoint or follow your suggestion.
2. Summarize three primary points
Another vital element to answer your question on how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is summarizing. For your overall summary, getting three main points is a good benchmark.
You do not have to restate each argument or claim because you can eventually pick three that you think are the most remarkable. In regards to your main idea, do not be dry and monotonous.
Avoid merely repeating three points; show your audience how those points strengthened your claim or Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . Draw them together into a single special force, supplementing weight to your primary idea.
3. Close on a high note
Leave your audience pleased and satisfied but also wanting more. When you are closing your conclusion, consider ending it with a capturing, thought-provoking concept.
You may want to raise a rhetorical question or state a notable quote from your research. From time to time, good quotations serve as illustrations, stating what we want to mention with a bit of Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence and style.
Another method to add some “food for thought” to your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s conclusion is to connect your primary idea to a more in-depth scenario. Also, note that your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s closing line needs extra effort .
The portion acts as your last opportunity to make it stick, so never introduce new information in your ending. Additional information can confuse your listeners and take them away from the essential features of a conclusion, which are:
- Restatement of your primary idea
- Summary of three main points
- Remarkable closing line
What are the Considerations on How to End a Speech?
When you imagine how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation, there are several things to consider when it comes to their close, which include:
- Is your ending engaging?
- Does your conclusion restate your message?
- Have you identified the next step you want your listeners to take clearly?
Too often, speakers or presenters believe that people will infer what they should act next. The reality or truth is that even the most talented speaker can benefit from setting off a clear call to action to their audience.
When it is particular, uncomplicated to perform, and aligns with the audience’s concerns, needs, and wants, they are more likely to take upon your persuasion , especially if you are making a persuasive speech.
Always consider that an impactful ending encourages, empowers, and motivates people. See the best tips in the next part to learn how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech .
What are some Good Ways to End a Speech?
A study shows that when they need to recall information, they best remember the beginning and the end. Therefore, impacting your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s closing is essential because people will mostly think of that part.
Here are seven different ways to choose and make an unforgettable ending for your audience if you still doubt how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech most appealingly.
1. The Summary Close
This method on how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is about the most direct, specific, and straightforward one on the list. The history of how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation also refers to this as a “recap” close.
If you end your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with a summary, clarify your most significant idea and convey to the listeners that it is what you want them to take. However, that does not imply that your summary close is not engaging.
2. The Surprise Close
Several of the best movie endings of all time were surprising conclusions, outright shockers, and wicked twists. Why do you think they are so memorable?
It is because the viewers or the audience did not expect that ending. When we experience something we did not anticipate, it turns out that our brains are more active.
In other cases, we might have also expected a different or another scenario for the conclusion. Hence, we become notably accustomed to what occurs when a pattern breaks.
Closing a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with a hint of surprise at its ending is like signaling your audience to listen to you.
3. The Illustrative Close
Another method to close your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is to do it in this way. The artistry in an illustrative close comes from your skill to correct the following:
- first or third-person anecdote
It can also refer to another storytelling device representing your illustration of the primary points you created during your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . Many speakers use this manner at the start and end of their talks.
4. The Forward-looking Close
This method of closing a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is a better option if you discuss suggestions for future trends that could bear your topic. To help your audience visualize what you desire to accomplish, make a vibrant and vivid picture of it because it is essential.
For example, you are a financial consultant talking to a crowd 15 years away from retirement. During your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , share your company’s approach to investment or a portfolio of your products.
5. The Backward-looking Close
Besides the forward-looking close, there is also a backward-looking close. This way, you move away from the future and go into the past instead.
Let’s say you are wondering how to end a maid of honor Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech as the bride’s sister and has spent so many years and memories with her. During your message, you can recall those moments. Then, from those past happenings, close your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech by wishing her a happy future with her husband.
6. The Metaphor Close
You might feel like you are drowning in options regarding how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . However, if you carefully look at your topic or subject and what you must convey, you will eventually find it easy as pie.
Welcome to the metaphor close. Yes, I just used some metaphors in the earlier part. Perhaps you had noticed them already before I pointed it out.
Metaphors are figures of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that indirectly compare two figuratively similar things but are distinct. You do not take it in a literal sense that you are drowning in options, but you can feel that way.
If you still don’t know how to end a graduation Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , this method may be one of your best options.
7. The Provocative Close
Provocative refers to the tendency to provoke, stimulate, or excite. Of course, as the speaker or presenter, you hope to encourage your audience, but using a provocative close snaps them to attention.
Check the table for some examples of how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech provocatively.
How to End a PowerPoint Presentation?
When you provide cluttered visual presentations , instead of an illustration that draws the people in, you can use PowerPoint to make a memorable close.
You can encourage and bring out their curiosity through powerful visualization. To help you with this matter, we have provided options for ending a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with a PowerPoint slide.
Here are a couple of samples of what you can project:
- A humorous image but has a profound significance.
- A photo that is supposedly unrelated to your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech subject or topic needs your explanation.
- A line graph shows two possible outcomes in which the audience may get involved.
How Should You End a Presentation Slideshow?
Since you have learned what you can project in your PowerPoint presentation and how useful it is to end your talk, let us get into several essential tips on finishing a formal presentation slideshow.
Here are ways you can do to make it memorable and impactful to your audience:
- Have a clear and concise message
To close your formal presentation slideshow, bring your fundamental message to the forefront and align it with your objectives. You must give your final message down to a notable point so that your audience can walk away remembering what you have said.
- Utilize the best final PowerPoint slide.
Your final slide will differ according to the type of presentation you are delivering.
For example, if you are still having second thoughts regarding how to end a maid of honor Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech uniquely, maybe you can opt to make a slideshow presentation for your sister’s wedding. There are creative ways to give your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , especially when you are too nervous about Public Speaking <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking refers to any live presentation or speech. It can cover a variety of topics on various fields and careers (you can find out more about public speaking careers here: https://orai.com/blog/public-speaking-careers/. Public speaking can inform, entertain, or educate an audience and sometimes has visual aids.</p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking is done live, so the speakers need to consider certain factors to deliver a successful speech. No matter how good the speech is, if the audience doesn't connect with the speaker, then it may fall flat. Therefore, speakers have to use a lot more nonverbal communication techniques to deliver their message. </p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:heading --> <h2>Tips for public speaking</h2> <!-- /wp:heading --><br /><!-- wp:list --> <ul> <li>Have a sense of humor.</li> <li>Tell personal stories that relate to the speech you're giving.</li> <li>Dress appropriately for the event. Formal and business casual outfits work best.</li> <li>Project a confident and expressive voice.</li> <li>Always try to use simple language that everyone can understand.</li> <li>Stick to the time given to you.</li> <li>Maintain eye contact with members of your audience and try to connect with them.</li> </ul> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/public-speaking/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">public speaking .
You only have to ensure that you are using a powerful final PowerPoint graphic slide to showcase your concluding information. Of course, you should fit its theme at the event.
- Use animation to highlight something.
Adding a hint of animation in your presentation or slideshow is one of the best ways to bring the significant element onto your slide at the perfect period. A program like PowerPoint has features, such as built-in animations, that you can efficiently utilize.
How to End a Speech Dos and Don’ts
After discussing the key elements of ending a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech and ways to close your presentation, we should tackle how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s dos and don’ts.
We have compiled a few things that you must consider. See them in this table:
How to End Your Speech Examples (video examples)
We have made your work easier if you seek the best examples of closing a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . Be worry-free about how to end a maid of honor Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , graduation address, and other presentations.
How to End a Graduation Speech
Here are four tips on how to end a graduation Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that would give you big applause from the crowd:
- Plan every word of your closing remarks.
- Close it with a story.
- Insert a little humor and make the audience laugh.
- Close your graduation Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with inspiration.
How to End a Maid of Honor Speech
Are you worried about how to end a maid of honor Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ? The following are the typical phrases used for the maid of honor speech ending:
- Let us all toast for the happiness of the newly married couple!
- Best wishes to the happy and lovely couple!
- Please raise your glasses in honor of the bride and groom.
- Cheers to the newlyweds!
- Wishing years of bliss to the bride and groom!
- What a beautiful wedding day, so let us toast wherever their lives may lead.
How to Close a Sales Presentation
Another example of how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech we have is closing a Sales Pitch <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:394">A <strong>sales pitch</strong> is a persuasive presentation, often concise and direct, to convince a potential customer to purchase a product, service, or idea. While <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> can present a hurdle, effective communication remains critical. Consider exploring resources like <strong>speaking coaches</strong> to overcome anxiety and deliver pitches that resonate with confidence.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:134"><strong>Compelling value proposition:</strong> Communicate the unique benefits of your offering and how it solves the customer's problem.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:94"><strong>Targeted message:</strong> Tailor your pitch to the specific needs and interests of the customer.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:85"><strong>Strong opening:</strong> Grab attention with a catchy introduction or relevant question.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:102"><strong>Social proof:</strong> Leverage testimonials, statistics, or case studies to build trust and credibility.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Call to action:</strong> Clearly state your desired outcome, whether a purchase, investment or further discussion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:39"><strong>Benefits of a Powerful Sales Pitch:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:88"><strong>Increases sales and conversions:</strong> Converts interest into action and drives revenue.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:107"><strong>Builds rapport and trust:</strong> Connects with the customer personally and establishes credibility.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:104"><strong>Differentiates from competitors:</strong> Highlights the unique value proposition compared to alternatives.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:94"><strong>Educates and informs:</strong> Explain how your offering solves the customer's problem.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Generates leads and interest:</strong> Captures attention and encourages further conversation or consideration.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:35"><strong>Crafting a Winning Sales Pitch:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:92"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Research the customer's needs, challenges, and buying preferences.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:95"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Hone your delivery, timing, and responses to potential objections.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:106"><strong>Focus on benefits, not features:</strong> Explain how your offering improves the customer's life or business.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:95"><strong>Use storytelling:</strong> Weave a narrative that showcases the impact of your product or service.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Be enthusiastic and passionate:</strong> Convey your belief in the value you offer.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:56"><strong>Overcoming Fear of Public Speaking in Sales Pitches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:113"><strong>Focus on the customer's needs:</strong> Shift your focus away from your anxieties and onto helping the customer.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:102"><strong>Deep breathing exercises:</strong> Calm your nerves and improve oxygen flow before and during your pitch.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:98"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Replace negative thoughts with affirmations and focus on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:91"><strong>Join a public speaking group:</strong> Practice and gain feedback in a supportive environment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Consider a speaking coach:</strong> They can provide personalized techniques to manage anxiety and improve delivery.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:464"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:464">A <strong>sales pitch</strong> is a conversation, not a monologue. By understanding the key elements, tailoring your message to the customer, and overcoming any <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>, you can deliver pitches that resonate, connect, and drive successful sales conversions. Consider exploring resources like <strong>speaking coaches</strong> for further support refining your communication skills and building the confidence to deliver winning sales pitches.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/sales-pitch/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">sales pitch . An outstanding presentation turns off if you do not try to create a great closing. To make your customers eager to purchase, try the tips we recommend.
- Go back to your opening idea.
- Close it with a challenge to your audience.
- Indulge your listeners into a metaphorical mission.
- Share a story.
- End your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with a quote.
To get additional sales presentation tips, you can check this video:
How can you effectively call your audience to action?
To ignite action, be crystal clear with your desired action, use persuasive language to spark urgency, and highlight the benefits they’ll reap. Back it up with evidence, repeat it for impact, and remove any hurdles that stand in their way. Finally, it tugs at their heartstrings to connect and motivate them to follow through. This winning formula fuels effective calls to action!
What are some creative ways to end a presentation?
Spice up your presentation ending! Ditch the boring summary and opt for storytelling, metaphors, inspiring quotes, actionable steps, thought-provoking questions, surprising elements, laughter, or genuine gratitude. Choose what fits your style and leave your audience with a bang, not a whimper!
What should you not do when ending a presentation?
When concluding a presentation, it is important to avoid certain practices. One thing you should not do is end your presentation with a slide that simply asks “Questions?” This approach is commonplace and lacks originality, making it forgettable for your audience. Instead, it is crucial to consider alternative techniques for concluding your presentation on a strong and memorable note.
How can something from the opening be repeated to close a presentation?
Start strong, end strong! Bookend your presentation by repeating a thought-provoking question, concluding a captivating story, or tying back to your title. This creates a unified message, satisfying closure, and a lasting impression on your audience. They’ll leave remembering “the answer,” “the ending,” or “the meaning,” solidifying your impact.
What can be used instead of a “thank you” slide?
Ditch the “thank you” slide! Show gratitude verbally and utilize a summary slide with key points, a call to action, and your contact details. More text is okay here; use bullet points for Clarity <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:269">In <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>clarity</strong> refers to the quality of your message being readily understood and interpreted by your audience. It encompasses both the content and delivery of your speech, ensuring your message resonates and leaves a lasting impact.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:133"><strong>Conciseness:</strong> Avoid unnecessary details, digressions, or excessive complexity. Focus on delivering the core message efficiently.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:149"><strong>Simple language:</strong> Choose words and phrases your audience understands readily, avoiding jargon or technical terms unless you define them clearly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:145"><strong>Logical structure:</strong> Organize your thoughts and ideas logically, using transitions and signposts to guide your audience through your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:136"><strong>Effective visuals:</strong> If using visuals, ensure they are clear, contribute to your message, and don't distract from your spoken words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:144"><strong>Confident delivery:</strong> Speak clearly and articulately, avoiding mumbling or rushing your words. Maintain good eye contact with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Active voice:</strong> Emphasize active voice for better flow and avoid passive constructions that can be less engaging.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:24"><strong>Benefits of Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:123"><strong>Enhanced audience engagement:</strong> A clear message keeps your audience interested and helps them grasp your points easily.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:123"><strong>Increased credibility:</strong> Clear communication projects professionalism and expertise, building trust with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:111"><strong>Improved persuasiveness:</strong> A well-understood message is more likely to resonate and win over your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Reduced confusion:</strong> Eliminating ambiguity minimizes misinterpretations and ensures your message arrives as intended.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-27:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:129"><strong>Condensing complex information:</strong> Simplifying complex topics without sacrificing crucial details requires skill and practice.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:128"><strong>Understanding your audience:</strong> Tailoring your language and structure to resonate with a diverse audience can be challenging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:85"><strong>Managing nerves:</strong> Nerves can impact your delivery, making it unclear or rushed.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-27:0"><strong>Avoiding jargon:</strong> Breaking technical habits and simplifying language requires constant awareness.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="28:1-28:22"><strong>Improving Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="30:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:117"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> The more you rehearse your speech, the more natural and clear your delivery will become.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:107"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech with others and ask for feedback on clarity and comprehension.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:161"><strong>Consider a public speaking coach:</strong> A coach can provide personalized guidance on structuring your message, simplifying language, and improving your delivery.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:128"><strong>Join a public speaking group:</strong> Practicing in a supportive environment can help you gain confidence and refine your clarity.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Listen to effective speakers:</strong> Analyze how clear and impactful others achieve communication.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Clarity</strong> is a cornerstone of impactful <strong>public speaking</strong>. By honing your message, focusing on delivery, and actively seeking feedback, you can ensure your audience receives your message clearly and leaves a lasting impression.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/clarity/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">clarity . It helps during Q&A; attendees might even snap a picture for a handy takeaway.
How can a running clock be used to emphasize the urgency of a message?
Tick-tock! Adding a running clock to your time-sensitive message visually screams urgency. It shows limited time, fuels action, grabs attention, and boosts your message’s credibility. Don’t let your audience miss out – let the clock do the talking!
How can a surprising fact re-engage the audience’s attention?
Attention fading? Drop a surprising fact with stats! It jolts your audience awake, adds credibility, and keeps them hooked. Find it online, but cite your source to be extra legitimate. Facts rock; use them to rule your presentation!
How can the rule of three be used in communication?
Group in threes! This communication rule makes your message stick. Break down ideas, stories, or anything you say into triplets. It’s easy to remember, catchy and keeps your audience engaged with your message long after you’re done. So go forth and conquer with the power of three!
How can the main points be linked to the key message in the conclusion?
Ditch the swim, find the gem! Your conclusion reflects your whole Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . Summarize key points, deliver a lasting impact, and tie it all together. Don’t leave it as an afterthought – make it resonate, leaving your audience nodding, satisfied, and remembering your message long after you’re done.
How can a visual image be used to end a presentation?
Don’t bore your audience with text! Ditch the cluttered slides and use a powerful image to end your presentation. Funny, thought-provoking, or a line graph with a choice – pick one to intrigue and make them think. Leave it on the screen for impact, let them ponder; your message will stick long after you’re done. Just remember, image and message go hand in hand!
How can a compelling story be used to conclude a presentation?
Forget jokes and platitudes. Close with a powerful story! Not just any story, one that makes them laugh, feel your message and remember it all. Your article mentions this, but their article goes deeper. They say to make it personal, relatable, and tied to your key points. This creates empathy, connection, and an unforgettable ending that leaves your audience wanting more. Go beyond the basics and tell a story they’ll remember long after the presentation.
What are the different ways to end a presentation or speech?
Ditch the panic. Pick your closing! Consider metaphors to leave a deep impression, challenge your audience with a “what if” scenario, or use visuals to stimulate their minds. Summarize key points, deliver a powerful message, and practice your ending for polish. Do avoid rambling, awkward gestures, or rushing out. Remember, a strong closing leaves a lasting mark. Now go captivate them!
In making your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s ending, do not make your conclusion only an afterthought. It should support everything you have said in your talk and remind the audience why your topic matters.
Leave the people nodding in agreement or satisfied by ending your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech remarkably. Yes, you can’t win everybody over your talk, but you can significantly make them pause and think.
We hope this article has imparted enough knowledge and answered your question about ending a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . Download the Orai Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech app for an AI-powered Speech Coach <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:411">A <strong>speech coach</strong> is a trained professional who provides personalized guidance and support to individuals seeking to improve their <strong>public speaking</strong> skills. Whether you aim to <strong>master public speaking</strong> for professional presentations, overcome stage fright, or simply hone your everyday communication, a <strong>speech coach</strong> can tailor their expertise to meet your needs and goals.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:32"><strong>What Does a Speech Coach Do?</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:124"><strong>Conduct assessments:</strong> Analyze your strengths, weaknesses, and communication style through evaluations and observations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:149"><strong>Develop personalized plans:</strong> Create a customized roadmap with exercises, techniques, and feedback to address your specific areas of improvement.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:167"><strong>Offer expert instruction:</strong> We will guide you through various aspects of public speaking, including vocal control, body language, content delivery, and overcoming anxiety.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:168"><strong>Provide practice opportunities:</strong> Facilitate mock presentations, simulations, and role-playing scenarios to refine your skills in a safe and supportive environment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:114"><strong>Offer constructive feedback:</strong> Identify areas for improvement and suggest strategies for achieving your goals.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Boost confidence and motivation:</strong> Encourage and support you throughout your journey, empowering you to become a confident and impactful communicator.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:40"><strong>Who Can Benefit from a Speech Coach?</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:174"><strong>Professionals:</strong> Refining public speaking skills can benefit executives, entrepreneurs, salespeople, leaders, and anyone who presents in professional settings.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:160"><strong>Students:</strong> Teachers, public speakers, debaters, and students wanting to excel in presentations or classroom settings can gain valuable skills with a coach.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:176"><strong>Individuals who fear public speaking:</strong> Coaching can help those who experience anxiety or nervousness when speaking in public develop strategies and gain confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Anyone seeking to improve communication:</strong> A coach can provide guidance to individuals seeking to enhance their communication skills for personal or professional development.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:28"><strong>Types of Speech Coaches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:110"><strong>Private coaches:</strong> Work one-on-one with individuals to provide highly personalized attention and feedback.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:130"><strong>Group coaches:</strong> Offer workshops or classes in group settings, often at a lower cost but with less individualized attention.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Specialization coaches:</strong> Some coaches specialize in executive communication, storytelling, or presentation design.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:35"><strong>Finding the Right Speech Coach:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-33:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:91"><strong>Identify your goals:</strong> What areas do you want to improve? What are your specific needs?</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:109"><strong>Research credentials and experience:</strong> Look for qualified coaches with relevant experience and expertise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:122"><strong>Consider availability and budget:</strong> Set a budget and explore options that fit your schedule and financial constraints.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-33:0"><strong>Schedule consultations:</strong> Talk to potential coaches to assess their personality, approach, and compatibility with your needs.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="34:1-34:418"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="34:1-34:418">Investing in a <strong>speech coach</strong> can be a transformative experience, enhancing your communication skills, boosting your confidence, and empowering you to achieve your communication goals. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting your journey, consider exploring the potential of working with a <strong>speech coach</strong> to unlock your full potential as a communicator and <strong>master public speaking</strong>.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech-coach/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech coach for interactive and fun lessons!
Good luck with your presentation!
You might also like
How many words is a 5-minute speech, good attention getters for speeches with 10+ examples, quick links.
- Presentation Topics
Useful Links
- Start free trial
- The art of public speaking
- improve public speaking
- mastering public speaking
- public speaking coach
- professional speaking
- public speaking classes - Courses
- public speaking anxiety
- © Orai 2023
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

How to End a Speech: The 15 Best Tips and Examples To Elevate Your Speech Closing
When it comes to giving a speech, the conclusion is just as important as the introduction and body. It’s the final impression you leave on your audience, and it can make or break your entire presentation. A powerful and memorable conclusion can leave your audience inspired, informed, and engaged.
Crafting a Memorable Conclusion

1. Summarize Your Key Points
One of the best ways to conclude a speech is to focus on the key points you’ve made throughout your presentation. This helps highlight your message and ensures that your audience remembers the most important takeaways.
For example, if you were giving a speech on the importance of environmental conservation, you could conclude by summarizing the key actions individuals can take, such as reducing waste and conserving energy.
Before that, it is crucial to memorize the speech , and each detail of it in the right order. That will help you to act like a pro in your presentation.
2. End with a Powerful Quote
Quotes can be a powerful tool to end a speech, as they can encapsulate your message and leave a lasting impression. Choose a quote that relates to your topic and resonates with your audience.
For instance, if you were giving a motivational speech, you could end with a quote like, “Success is not final, failure is not fatal: It is the courage to continue that counts,” by Winston Churchill.
Engaging Your Audience

3. Ask a Thought-Provoking Question
Engage your audience by asking a thought-provoking question in your conclusion. This can encourage them to reflect on the topic and even initiate discussions after your speech.
If you were delivering a speech on the future of technology, you could ask, “What do you envision for the future of human-technology interaction?” This prompts your audience to consider the possibilities.
4. Tell a Personal Anecdote
Sharing a personal anecdote related to your speech topic can humanize you as a speaker and make a deep connection with your audience . This can be particularly effective when giving a persuasive or motivational speech.
In case you were speaking about overcoming adversity, you could share a personal story of a challenging experience you faced and how you persevered. This personal touch can leave a lasting impact on your audience.
Creating a Memorable Conclusion

5. End with a Call to Action
If your speech is meant to inspire action, a strong call to action in your conclusion is essential. Clearly state what you want your audience to do or how you want them to apply the information you’ve provided.
If your speech is about volunteer opportunities in your community, conclude by encouraging your audience to sign up for a specific event or join a local organization.
6. Use Visual Aids
Visual aids can be a compelling way to conclude your speech, especially if you’ve used them throughout your presentation . You can end with a powerful image, graph, or chart that reinforces your message.
For example, if you were giving a speech on the effects of deforestation, you could conclude by displaying a before-and-after image of a deforested area that has been restored.
Captivating Your Audience

7. Employ Humor
Ending your speech with a touch of humor can be a great way to leave your audience with a smile. A well-timed joke or witty remark related to your topic can help lighten the mood and make your conclusion more memorable.
However, be cautious with humor , as it should be appropriate and inoffensive to your audience.
8. Use a Visual Metaphor
Visual metaphors are a creative way to conclude your speech. They involve using a physical object or action that symbolizes your message. For instance, if your speech is about the power of unity, you could conclude by bringing two puzzle pieces together to illustrate how unity can solve complex problems.
Demonstrating Confidence and Gratitude

9. Express Gratitude
Showing appreciation to your audience is a gracious way to conclude your speech. Thank your listeners for their time, attention, and engagement. Expressing gratitude not only leaves a positive impression but also reinforces the connection you’ve established with your audience.
You can say, “I want to express my sincere gratitude to each of you for being here today and for your dedication to our cause.”
10. Maintain Eye Contact
Maintaining eye contact with your audience during the conclusion is crucial. It conveys confidence and sincerity, making your message more impactful. Avoid looking down at your notes or staring at a distant point. Instead, connect with individual members of your audience as you wrap up your speech.
Inspiring and Motivating

11. End with a Vision
Paint a vivid picture of the future in your conclusion. Share a vision that inspires and motivates your audience. This approach works well in speeches related to goals, aspirations, or change.
When you are speaking about the future of renewable energy, describe a world where clean energy sources power our cities and protect our environment.
12. Leave a Rhetorical Question
A rhetorical question in your conclusion can leave your audience pondering your message long after your speech has ended. It encourages reflection and engages your listeners on a deeper level.
Moreover, if you’re delivering a speech on the importance of education, you could conclude with a rhetorical question like, “Can we afford to neglect the potential of the next generation?”
Achieving Impactful Closure

13. Connect to Your Opening
A powerful technique for closing a speech is to circle back to your opening statement or anecdote. This creates a sense of closure and reinforces the theme or message you introduced at the beginning.
If you began your speech with a personal story, bringing that story full circle in your conclusion can be particularly impactful.
14. Use a Poignant Quote or Poem
Consider ending your speech with a meaningful quote or a short poem that encapsulates your message. Poetry, in particular, can evoke strong emotions and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
Choose a quote or poem that resonates with your speech’s theme and delivers a profound message.
Practice and Feedback
15. rehearse and seek feedback.
Lastly, practice and feedback are essential for a successful conclusion . Rehearse your ending multiple times to ensure that your delivery is confident and polished. Seek feedback from trusted individuals who can provide constructive suggestions to help you refine your conclusion further.
Should I memorize my conclusion word-for-word, or is it okay to improvise?
Memorizing your conclusion word-for-word is generally not recommended. While it’s crucial to know the key points and structure of your conclusion, sounding too rehearsed can come across as insincere. Instead, aim to understand the main ideas and transitions in your conclusion, allowing for some flexibility in your delivery. This approach can make your conclusion feel more authentic and engaging.
Can I use multiple techniques in a single conclusion?
The key is to maintain coherence and relevance. For instance, you can end with a powerful quote followed by a call to action or a thought-provoking question, as long as they flow naturally and support your speech’s objectives.
Is it acceptable to use humor in the conclusion of a serious or formal speech?
It can be acceptable to use humor in the conclusion of a serious or formal speech, but it should be used judiciously and in a way that is contextually appropriate. Humor can help break the tension or lighten the mood, but it should not detract from the overall message or tone of your speech. Ensure that your humor is respectful and relevant to your audience and topic.
The Bottom Line
Ending a speech effectively is a skill that can be honed with practice and attention to detail. Remember that the conclusion is your final opportunity to connect with your audience, so make it count by crafting a memorable and impactful ending.
Related Posts:
- 7 Must-Watch TED Talks for Students in 2023 - #4…
- 5 Inspiring TED Talks That'll Boost Your Self-Confidence
- How to Write a Demonstrative Speech? - Guide for…
- 8 Steps To Memorize a Speech: Present Like a Pro

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8 Effective Introductions and Powerful Conclusions
Learning objectives.
- Identify the functions of introductions and conclusions.
- Understand the key parts of an introduction and a conclusion.
- Explore techniques to create your own effective introductions and conclusions.

Introductions and conclusions can be challenging. One of the most common complaints novice public speakers have is that they simply don’t know how to start or end a speech. It may feel natural to start crafting a speech at the beginning, but it can be difficult to craft an introduction for something which doesn’t yet exist. Many times, creative and effective ideas for how to begin a speech will come to speakers as they go through the process of researching and organizing ideas. Similarly, a conclusion needs to be well considered and leave audience members with a sense of satisfaction.
In this chapter, we will explore why introductions and conclusions are important, and we will identify various ways speakers can create impactful beginnings and endings. There is not a “right” way to start or end a speech, but we can provide some helpful guidelines that will make your introductions and conclusions much easier for you as a speaker and more effective for your audience.
The Importance of an Introduction

The introduction of a speech is incredibly important because it needs to establish the topic and purpose, set up the reason your audience should listen to you and set a precedent for the rest of the speech. Imagine the first day of a semester long class. You will have a different perception of the course if the teacher is excited, creative and clear about what is to come then if the teacher recites to you what the class is about and is confused or disorganized about the rest of the semester. The same thing goes for a speech. The introduction is an important opportunity for the speaker to gain the interest and trust of the audience.
Overall, an effective introduction serves five functions. Let’s examine each of these.
Gain Audience Attention and Interest
The first major purpose of an introduction is to gain your audience’s attention and get them interested in what you have to say. While your audience may know you, this is your speeches’ first impression! One common incorrect assumption beginning speakers make that people will naturally listen because the speaker is speaking. While many audiences may be polite and not talk while you’re speaking, actually getting them to listen and care about what you are saying is a completely different challenge. Think to a time when you’ve tuned out a speaker because you were not interested in what they had to say or how they were saying it. However, I’m sure you can also think of a time someone engaged you in a topic you wouldn’t have thought was interesting, but because of how they presented it or their energy about the subject, you were fascinated. As the speaker, you have the ability to engage the audience right away.
State the Purpose of Your Speech
The second major function of an introduction is to reveal the purpose of your speech to your audience. Have you ever sat through a speech wondering what the basic point was? Have you ever come away after a speech and had no idea what the speaker was talking about? An introduction is critical for explaining the topic to the audience and justifying why they should care about it. The speaker needs to have an in-depth understanding of the specific focus of their topic and the goals they have for their speech. Robert Cavett, the founder of the National Speaker’s Association, used the analogy of a preacher giving a sermon when he noted, “When it’s foggy in the pulpit, it’s cloudy in the pews.” The specific purpose is the one idea you want your audience to remember when you are finished with your speech. Your specific purpose is the rudder that guides your research, organization, and development of main points. The more clearly focused your purpose is, the easier it will be both for you to develop your speech and your audience to understand your core point. To make sure you are developing a specific purpose, you should be able to complete the sentence: “I want my audience to understand…” Notice that your specific speech purpose is phrased in terms of expected audience responses, not in terms of your own perspective.
Establish Credibility
One of the most researched areas within the field of communication has been Aristotle’s concept of ethos or credibility. First, and foremost, the idea of credibility relates directly to audience perception. You may be the most competent, caring, and trustworthy speaker in the world on a given topic, but if your audience does not perceive you as credible, then your expertise and passion will not matter to them. As public speakers, we need to communicate to our audiences why we are credible speakers on a given topic. James C. McCroskey and Jason J. Teven have conducted extensive research on credibility and have determined that an individual’s credibility is composed of three factors: competence, trustworthiness, and caring/goodwill (McCroskey & Teven, 1999). Competence is the degree to which a speaker is perceived to be knowledgeable or expert in a given subject by an audience member.
The second factor of credibility noted by McCroskey and Teven is trustworthiness or the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as honest. Nothing will turn an audience against a speaker faster than if the audience believes the speaker is lying. When the audience does not perceive a speaker as trustworthy, the information coming out of the speaker’s mouth is automatically perceived as deceitful.
Finally, caring/goodwill is the last factor of credibility noted by McCroskey and Teven. Caring/goodwill refers to the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as caring about the audience member. As indicated by Wrench, McCroskey, and Richmond, “If a receiver does not believe that a source has the best intentions in mind for the receiver, the receiver will not see the source as credible. Simply put, we are going to listen to people who we think truly care for us and are looking out for our welfare” (Wrench, McCroskey & Richmond, 2008). As a speaker, then, you need to establish that your information is being presented because you care about your audience and are not just trying to manipulate them. We should note that research has indicated that caring/goodwill is the most important factor of credibility. This understanding means that if an audience believes that a speaker truly cares about the audience’s best interests, the audience may overlook some competence and trust issues.
Credibility relates directly to audience perception. You may be the most competent, caring, and trustworthy speaker in the world on a given topic, but if your audience does not perceive you as credible, then your expertise and passion will not matter to them.
Trustworthiness is the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as honest.
Caring/goodwill is the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as caring about the audience member.
Provide Reasons to Listen
The fourth major function of an introduction is to establish a connection between the speaker and the audience, and one of the most effective means of establishing a connection with your audience is to provide them with reasons why they should listen to your speech. The idea of establishing a connection is an extension of the notion of caring/goodwill. In the chapters on Language and Speech Delivery, we’ll spend a lot more time talking about how you can establish a good relationship with your audience. This relationship starts the moment you step to the front of the room to start speaking.
Instead of assuming the audience will make their own connections to your material, you should explicitly state how your information might be useful to your audience. Tell them directly how they might use your information themselves. It is not enough for you alone to be interested in your topic. You need to build a bridge to the audience by explicitly connecting your topic to their possible needs.
Preview Main Ideas
The last major function of an introduction is to preview the main ideas that your speech will discuss. A preview establishes the direction your speech will take. We sometimes call this process signposting because you’re establishing signs for audience members to look for while you’re speaking. In the most basic speech format, speakers generally have three to five major points they plan on making. During the preview, a speaker outlines what these points will be, which demonstrates to the audience that the speaker is organized.
A study by Baker found that individuals who were unorganized while speaking were perceived as less credible than those individuals who were organized (Baker, 1965). Having a solid preview of the information contained within one’s speech and then following that preview will help a speaker’s credibility. It also helps your audience keep track of where you are if they momentarily daydream or get distracted.
Putting Together a Strong Introduction

Now that we have an understanding of the functions of an introduction, let’s explore the details of putting one together. As with all aspects of a speech, these may change based on your audience, circumstance, and topic. But this will give you a basic understanding of the important parts of an intro, what they do, and how they work together.
Attention Getting Device
An attention-getter is the device a speaker uses at the beginning of a speech to capture an audience’s interest and make them interested in the speech’s topic. Typically, there are four things to consider in choosing a specific attention-getting device:
- Topic and purpose of the speech
- Appropriateness or relevance to the audience
First, when selecting an attention-getting device is considering your speech topic and purpose. Ideally, your attention-getting device should have a relevant connection to your speech. Imagine if a speaker pulled condoms out of his pocket, yelled “Free sex!” and threw the condoms at the audience. This act might gain everyone’s attention, but would probably not be a great way to begin a speech about the economy. Thinking about your topic because the interest you want to create needs to be specific to your subject. More specifically, you want to consider the basic purpose of your speech. When selecting an attention getter, you want to make sure that you select one that corresponds with your basic purpose. If your goal is to entertain an audience, starting a speech with a quotation about how many people are dying in Africa each day from malnutrition may not be the best way to get your audience’s attention. Remember, one of the goals of an introduction is to prepare your audience for your speech . If your attention-getter differs drastically in tone from the rest of your speech the disjointedness may cause your audience to become confused or tune you out completely.
Possible Attention Getters
These will help you start brainstorming ideas for how to begin your speech. While not a complete list, these are some of the most common forms of attention-getters:
- Reference to Current Events
- Historical Reference
- Startling Fact
- Rhetorical Question
- Hypothetical Situation
- Demonstration
- Personal Reference
- Reference to Audience
- Reference to Occasion
Second, when selecting an attention-getting device, you want to make sure you are being appropriate and relevant to your specific audience. Different audiences will have different backgrounds and knowledge, so you should keep your audience in mind when determining how to get their attention. For example, if you’re giving a speech on family units to a group of individuals over the age of sixty-five, starting your speech with a reference to the television show Gossip Girl may not be the best idea because the television show may not be relevant to that audience.
Finally, the last consideration involves the speech occasion. Different occasions will necessitate different tones or particular styles or manners of speaking. For example, giving a eulogy at a funeral will have a very different feel than a business presentation. This understanding doesn’t mean certain situations are always the same, but rather taking into account the details of your circumstances will help you craft an effective beginning to your speech. When selecting an attention-getter, you want to make sure that the attention-getter sets the tone for the speech and situation.
Tones are particular styles or manners of speaking determined by the speech’s occasion.
Link to Topic
The link to the topic occurs when a speaker demonstrates how an attention-getting device relates to the topic of a speech. This presentation of the relationship works to transition your audience from the attention getter to the larger issue you are discussing. Often the attention-getter and the link to the topic are very clear. But other times, there may need to be a more obvious connection between how you began your attention-getting device and the specific subject you are discussing. You may have an amazing attention-getter, but if you can’t connect it to the main topic and purpose of your speech, it will not be as effective.
Significance
Once you have linked an attention-getter to the topic of your speech, you need to explain to your audience why your topic is important and why they should care about what you have to say. Sometimes you can include the significance of your topic in the same sentence as your link to the topic, but other times you may need to spell out in one or two sentences why your specific topic is important to this audience.
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. A strong, clear thesis statement is very valuable within an introduction because it lays out the basic goal of the entire speech. We strongly believe that it is worthwhile to invest some time in framing and writing a good thesis statement. You may even want to write a version of your thesis statement before you even begin conducting research for your speech in order to guide you. While you may end up rewriting your thesis statement later, having a clear idea of your purpose, intent, or main idea before you start searching for research will help you focus on the most appropriate material.
Preview of Speech
The final part of an introduction contains a preview of the major points to be covered by your speech. I’m sure we’ve all seen signs that have three cities listed on them with the mileage to reach each city. This mileage sign is an indication of what is to come. A preview works the same way. A preview foreshadows what the main body points will be in the speech. For example, to preview a speech on bullying in the workplace, one could say, “To understand the nature of bullying in the modern workplace, I will first define what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying, I will then discuss the common characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets, and lastly, I will explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.” In this case, each of the phrases mentioned in the preview would be a single distinct point made in the speech itself. In other words, the first major body point in this speech would examine what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying; the second major body point in this speech would discuss the characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets; and lastly, the third body point in this speech would explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.
Putting it all together
The importance of introductions often leads speakers to work on them first, attending to every detail. While it is good to have some ideas and notes about the intro, specifically the thesis statement, it is often best to wait until the majority of the speech is crafted before really digging into the crafting of the introduction. This timeline may not seem intuitive, but remember, the intro is meant to introduce your speech and set up what is to come. It is difficult to introduce something that you haven’t made yet. This is why working on your main points first can help lead to an even stronger introduction.
Why Conclusions Matter
Willi Heidelbach – Puzzle2 – CC BY 2.0.
As public speaking professors and authors, we have seen many students give otherwise good speeches that seem to fall apart at the end. We’ve seen students end their three main points by saying things such as “OK, I’m done”; “Thank God that’s over!”; or “Thanks. Now what? Do I just sit down?” It’s understandable to feel relief at the end of a speech, but remember that as a speaker, your conclusion is the last chance you have to drive home your ideas. When a speaker opts to end the speech with an ineffective conclusion, or no conclusion at all, the speech loses the energy that’s been created, and the audience is left confused and disappointed. Instead of falling prey to emotional exhaustion, remind yourself to keep your energy up as you approach the end of your speech, and plan ahead so that your conclusion will be an effective one.
Of course, a good conclusion will not rescue a poorly prepared speech. Thinking again of the chapters in a novel, if one bypasses all the content in the middle, the ending often isn’t very meaningful or helpful. So to take advantage of the advice in this chapter, you need to keep in mind the importance of developing a speech with an effective introduction and an effective body. If you have these elements, you will have the foundation you need to be able to conclude effectively. Just as a good introduction helps bring an audience member into the world of your speech, and a good speech body holds the audience in that world, a good conclusion helps bring that audience member back to the reality outside of your speech.
In this section, we’re going to examine the functions fulfilled by the conclusion of a speech. A strong conclusion serves to signal the end of the speech and helps your listeners remember your speech.
Signals the End
The first thing a good conclusion can do is to signal the end of a speech. You may be thinking that showing an audience that you’re about to stop speaking is a “no brainer,” but many speakers don’t prepare their audience for the end. When a speaker just suddenly stops speaking, the audience is left confused and disappointed. Instead, we want to make sure that audiences are left knowledgeable and satisfied with our speeches. In the next section, we’ll explain in great detail about how to ensure that you signal the end of your speech in a manner that is both effective and powerful.
Aids Audience’s Memory of Your Speech
The second reason for a good conclusion stems out of some research reported by the German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus back in 1885 in his book Memory: A Contribution to Experimental Psychology (Ebbinghaus, 1885). Ebbinghaus proposed that humans remember information in a linear fashion, which he called the serial position effect. He found an individual’s ability to remember information in a list (e.g. a grocery list, a chores list, or a to-do list) depends on the location of an item on the list. Specifically, he found that items toward the top of the list and items toward the bottom of the list tended to have the highest recall rates. The serial position effect finds that information at the beginning of a list (primacy) and information at the end of the list (recency) are easier to recall than information in the middle of the list.
So what does this have to do with conclusions? A lot! Ray Ehrensberger wanted to test Ebbinghaus’ serial position effect in public speaking. Ehrensberger created an experiment that rearranged the ordering of a speech to determine the recall of information (Ehrensberger, 1945). Ehrensberger’s study reaffirmed the importance of primacy and recency when listening to speeches. In fact, Ehrensberger found that the information delivered during the conclusion (recency) had the highest level of recall overall.
Steps of a Conclusion

Matthew Culnane – Steps – CC BY-SA 2.0.
In the previous sections, we discussed the importance a conclusion has on a speech. In this section, we’re going to examine the three steps to building an effective conclusion.
Restatement of the Thesis
Restating a thesis statement is the first step to a powerful conclusion. As we explained earlier, a thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. When we restate the thesis statement at the conclusion of our speech, we’re attempting to reemphasize what the overarching main idea of the speech has been. Suppose your thesis statement was, “I will analyze Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his July 2008 speech, ‘A World That Stands as One.’” You could restate the thesis in this fashion at the conclusion of your speech: “In the past few minutes, I have analyzed Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his July 2008 speech, ‘A World That Stands as One.’” Notice the shift in tense. The statement has gone from the future tense (this is what I will speak about) to the past tense (this is what I have spoken about). Restating the thesis in your conclusion reminds the audience of the main purpose or goal of your speech, helping them remember it better.
Review of Main Points
After restating the speech’s thesis, the second step in a powerful conclusion is to review the main points from your speech. One of the biggest differences between written and oral communication is the necessity of repetition in oral communication. When we preview our main points in the introduction, effectively discuss and make transitions to our main points during the body of the speech, and review the main points in the conclusion, we increase the likelihood that the audience will retain our main points after the speech is over.
In the introduction of a speech, we deliver a preview of our main body points, and in the conclusion, we deliver a review . Let’s look at a sample preview:
In order to understand the field of gender and communication, I will first differentiate between the terms biological sex and gender. I will then explain the history of gender research in communication. Lastly, I will examine a series of important findings related to gender and communication.
In this preview, we have three clear main points. Let’s see how we can review them at the conclusion of our speech:
Today, we have differentiated between the terms biological sex and gender, examined the history of gender research in communication, and analyzed a series of research findings on the topic.
In the past few minutes, I have explained the difference between the terms “biological sex” and “gender,” discussed the rise of gender research in the field of communication, and examined a series of groundbreaking studies in the field.
Notice that both of these conclusions review the main points initially set forth. Both variations are equally effective reviews of the main points, but you might like the linguistic turn of one over the other. Remember, while there is a lot of science to help us understand public speaking, there’s also a lot of art as well. You are always encouraged to choose the wording that you think will be most effective for your audience.
Concluding Device
The final part of a powerful conclusion is the concluding device. A concluding device is a final thought you want your audience members to have when you stop speaking. It also provides a definitive sense of closure to your speech. One of the authors of this text often makes an analogy between a gymnastics dismount and the concluding device in a speech. Just as a gymnast dismounting the parallel bars or balance beam wants to stick the landing and avoid taking two or three steps, a speaker wants to “stick” the ending of the presentation by ending with a concluding device instead of with, “Well, umm, I guess I’m done.” Miller observed that speakers tend to use one of ten concluding devices when ending a speech (Miller, 1946). The rest of this section is going to examine these ten concluding devices and one additional device that we have added.
Conclude with a Challenge
The first way that Miller found that some speakers end their speeches is with a challenge. A challenge is a call to engage in some activity that requires a special effort. In a speech on the necessity of fund-raising, a speaker could conclude by challenging the audience to raise 10 percent more than their original projections. In a speech on eating more vegetables, you could challenge your audience to increase their current intake of vegetables by two portions daily. In both of these challenges, audience members are being asked to go out of their way to do something different that involves effort on their part.
Conclude with a Quotation
A second way you can conclude a speech is by reciting a quotation relevant to the speech topic. When using a quotation, you need to think about whether your goal is to end on a persuasive note or an informative note. Some quotations will have a clear call to action, while other quotations summarize or provoke thought. For example, let’s say you are delivering an informative speech about dissident writers in the former Soviet Union. You could end by citing this quotation from Alexander Solzhenitsyn: “A great writer is, so to speak, a second government in his country. And for that reason, no regime has ever loved great writers” (Solzhenitsyn, 1964). Notice that this quotation underscores the idea of writers as dissidents, but it doesn’t ask listeners to put forth the effort to engage in any specific thought process or behavior. If, on the other hand, you were delivering a persuasive speech urging your audience to participate in a very risky political demonstration, you might use this quotation from Martin Luther King Jr.: “If a man hasn’t discovered something that he will die for, he isn’t fit to live” (King, 1963). In this case, the quotation leaves the audience with the message that great risks are worth taking, that they make our lives worthwhile, and that the right thing to do is to go ahead and take that great risk.
Conclude with a Summary
When a speaker ends with a summary, they are simply elongating the review of the main points. While this may not be the most exciting concluding device, it can be useful for information that was highly technical or complex or for speeches lasting longer than thirty minutes. Typically, for short speeches (like those in your class), this summary device should be avoided.
Conclude by Visualizing the Future
The purpose of a conclusion that refers to the future is to help your audience imagine the future you believe can occur. If you are giving a speech on the development of video games for learning, you could conclude by depicting the classroom of the future where video games are perceived as true learning tools and how those tools could be utilized. More often, speakers use visualization of the future to depict how society would be, or how individual listeners’ lives would be different if the speaker’s persuasive attempt worked. For example, if a speaker proposes that a solution to illiteracy is hiring more reading specialists in public schools, the speaker could ask her or his audience to imagine a world without illiteracy. In this use of visualization, the goal is to persuade people to adopt the speaker’s point of view. By showing that the speaker’s vision of the future is a positive one, the conclusion should help to persuade the audience to help create this future.
Conclude with an Appeal for Action
Probably the most common persuasive concluding device is the appeal for action or the call to action. In essence, the appeal for action occurs when a speaker asks their audience to engage in a specific behavior or change in thinking. When a speaker concludes by asking the audience “to do” or “to think” in a specific manner, the speaker wants to see an actual change. Whether the speaker appeals for people to eat more fruit, buy a car, vote for a candidate, oppose the death penalty, or sing more in the shower, the speaker is asking the audience to engage in action.
One specific type of appeal for action is the immediate call to action. Whereas some appeals ask for people to engage in behavior in the future, an immediate call to action asks people to engage in behavior right now. If a speaker wants to see a new traffic light placed at a dangerous intersection, he or she may conclude by asking all the audience members to sign a digital petition right then and there, using a computer the speaker has made available ( http://www.petitiononline.com ). Here are some more examples of immediate calls to action:
- In a speech on eating more vegetables, pass out raw veggies and dip at the conclusion of the speech.
- In a speech on petitioning a lawmaker for a new law, provide audience members with a prewritten e-mail they can send to the lawmaker.
- In a speech on the importance of using hand sanitizer, hand out little bottles of hand sanitizer and show audience members how to correctly apply the sanitizer.
- In a speech asking for donations for a charity, send a box around the room asking for donations.
These are just a handful of different examples we’ve seen students use in our classrooms to elicit an immediate change in behavior. These immediate calls to action may not lead to long-term change, but they can be very effective at increasing the likelihood that an audience will change behavior in the short term.
Conclude by Inspiration
By definition, the word inspire means to affect or connect with someone emotionally. Both affect and arouse have strong emotional connotations. The ultimate goal of an inspiration concluding device is similar to an “appeal for action,” but the ultimate goal is more lofty or ambiguous. The goal is to stir someone’s emotions in a specific manner. Maybe a speaker is giving an informative speech about the prevalence of domestic violence in our society today. That speaker could end the speech by reading Paulette Kelly’s powerful poem “I Got Flowers Today.” “I Got Flowers Today” is a poem that evokes strong emotions because it’s about an abuse victim who received flowers from her abuser every time she was victimized. The poem ends by saying, “I got flowers today… Today was a special day. It was the day of my funeral. Last night he killed me” (Kelly, 1994).
Conclude with Advice
The next concluding device is one that should be used primarily by speakers who are recognized as expert authorities on a given subject. Advice is a speaker’s opinion about what should or should not be done. The problem with opinions is that everyone has one, and one person’s opinion is not necessarily any more correct than another’s. There needs to be a really good reason for your opinion. Your advice should matter to your audience. If, for example, you are an expert in nuclear physics, you might conclude a speech on energy by giving advice about the benefits of nuclear energy.
Conclude by Proposing a Solution
Another way a speaker can conclude a speech powerfully is to offer a solution to the problem discussed within a speech. For example, perhaps a speaker has been discussing the problems associated with the disappearance of art education in the United States. The speaker could then propose a solution for creating more community-based art experiences for school children as a way to fill this gap. Although this can be a compelling conclusion, a speaker must ask themselves whether the solution should be discussed in more depth as a stand-alone main point within the body of the speech so that audience concerns about the proposed solution may be addressed.
Conclude with a Question
Another way you can end a speech is to ask a rhetorical question that forces the audience to ponder an idea. Maybe you are giving a speech on the importance of the environment, so you end the speech by saying, “Think about your children’s future. What kind of world do you want them raised in? A world that is clean, vibrant, and beautiful—or one that is filled with smog, pollution, filth, and disease?” Notice that you aren’t asking the audience to verbally or nonverbally answer the question. The goal of this question is to force the audience into thinking about what kind of world they want for their children.
Conclude with a Reference to Audience
The last concluding device discussed by Miller (1946) was a reference to one’s audience. This concluding device is when a speaker attempts to answer the audience question, “What’s in it for me?” The goal of this concluding device is to spell out the direct benefits a behavior or thought change has for audience members. For example, a speaker talking about stress reduction techniques could conclude by listing all the physical health benefits stress reduction offers (e.g. improved reflexes, improved immune system, improved hearing, reduction in blood pressure). In this case, the speaker is spelling out why audience members should care. They’re telling the audience what’s in it for them!
Connect to your Introduction
Finally, one tactic a speaker often uses is to link the introduction of the speech to the conclusion. For example, if you began your speech with a quotation, your conclusion may refer back to that person’s words in respect to what your audience has learned throughout your speech. While not always necessary, linking back to your introduction can provide a feeling of coming full circle for your audience. The repetitive nature can also help aid in remembering your speech and topic. However, you don’t want to just repeat. Instead, you want to utilize similar aspects of your attention getter to illustrate growth or movement from the beginning of your speech to the end.
A concluding device is a final thought you want your audience members to have when you stop speaking.
A challenge is a call to engage in some activity that requires special effort.
An appeal for action occurs when a speaker asks their audience to engage in a specific behavior or change in thinking.
An immediate call to action asks people to engage in behavior right now.
Inspire means to affect or connect with someone emotionally.
Advice is a speaker’s opinion about what should or should not be done.
Informative versus Persuasive Conclusions
As you read through the ten possible ways to conclude a speech, hopefully, you noticed that some of the methods are more appropriate for persuasive speeches and others are more appropriate for informative speeches. To help you choose appropriate conclusions for informative, persuasive, or entertaining speeches, we’ve created a table to help you quickly identify suitable concluding devices.
Your Speech Purpose and Concluding Devices
Ebbinghaus, H. (1885). Memory: A contribution to experimental psychology [Online version]. Retrieved from http://psychclassics.yorku.ca/Ebbinghaus/index.htm .
Ehrensberger, R. (1945). An experimental study of the relative effectiveness of certain forms of emphasis in public speaking. Speech Monographs, 12 , 94–111. doi: 10.1080/03637754509390108.
Kelly, P. (1994). I got flowers today. In C. J. Palmer & J. Palmer, Fire from within . Painted Post, NY: Creative Arts & Science Enterprises.
King, M. L. (1963, June 23). Speech in Detroit. Cited in Bartlett, J., & Kaplan, J. (Eds.), Bartlett’s familiar quotations (6th ed.). Boston, MA: Little, Brown & Co., p. 760.
Miller, E. (1946). Speech introductions and conclusions. Quarterly Journal of Speech, 32 , 181–183.
Solzhenitsyn, A. (1964). The first circle. New York: Harper & Row. Cited in Bartlett, J., & Kaplan, J. (Eds.), Bartlett’s familiar quotations (6th ed.). Boston, MA: Little, Brown & Co., p. 746.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2017 by Josh Miller; Marnie Lawler-Mcdonough; Megan Orcholski; Kristin Woodward; Lisa Roth; and Emily Mueller is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Methodology
- Specialized
- Train-the-Trainer
- Build Your Own Program
How To End A Speech

Putting together and delivering an effective speech takes time and the right strategy. One of the most challenging aspects is figuring out how to end a speech effectively. You might have prepared a fantastic opening and delivered a compelling message, but if you fail to wrap up your speech in a powerful and memorable way, your audience may leave feeling unsatisfied or even forget what you said altogether.
Many speakers struggle with their closing words, whether it’s because they run out of time, they lose their train of thought, or they simply don’t know how to bring everything together in a cohesive and impactful way. This can lead to a lack of confidence, anxiety, and even embarrassment, all of which can significantly hinder your ability to communicate your message effectively.
In this article we’ll explore some proven tips and strategies, show you three simple techniques that summarize your message and key ideas, and explain how to get your audience members to take action. You’ll start delivering the final words of your speeches with confidence and know you’re leaving a lasting impression on your audience. Whether you’re a seasoned speaker looking to polish your skills or a newcomer to public speaking , this article will help you overcome the hurdles of ending a great speech so you can deliver a powerful and memorable message every time. Your last words will be your most impactful words.
Why is a Conclusion Important?

“Great is the art of beginning, but greater is the art of the ending.” Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
The conclusion of your speech is arguably the most critical part. It’s the pinnacle of your persuasion, the culmination of everything you’ve talked about so far, and it’s the moment when you state your final call to action. This is why it’s crucial to devote sufficient time and attention to crafting your last inspiring words and final point.
Your conclusion is where you’ll leave your audience with the most significant take away from your speech. These closing words are the last impression they’ll have of you and your key message, and it’s where you can reinforce the key message points you’ve made throughout your presentation. By reiterating your main message and summarizing your key arguments, you can ensure that your audience remembers your message long after your speech is over in such a way that inspires them to take action.
The conclusion is also where you summarize your entire speech and make your final call to action. Whether it’s encouraging your audience to remember and take specific actions, supporting a particular cause, or adopting a new way of thinking, your conclusion is the time to motivate your audience to act. This is where you can challenge them to make a difference, do something, or think differently about a particular issue.
Most importantly, your conclusion can make or break your speech. A weak or ineffective ending can leave your audience feeling unimpressed or even confused, undermining the impact of your entire presentation up to that point. Conversely, a strong and impactful conclusion can leave a lasting impression on your audience, motivating them to take action and inspiring them to share your message with others. It even has the potential to turn an average persuasive speech into an unforgettable speech.
Because the conclusion of your speech is so important, it’s worth taking the time to ensure that your final words are as effective as possible. By crafting a strong and impactful conclusion, you can leave your audience with a lasting impression, and ensure that your message is remembered long after your closing statement.
BE AN EFFECTIVE COMMUNICATOR Suasive Presentation Coaching
What is a good closing message?

A good closing is a bookend to your opening, but is much more concise. It should resolve the entire presentation. In the beginning you grab your audience’s attention. Next you navigate them through all the parts. Finally you introduce your call to action so the audience knows what to expect. Your speech’s closing message should fulfill the classical requirements of any story: a strong beginning, a solid middle, and a decisive end.
To fully understand how your closing message connects with your opening you’ll need to first understand the three parts of your opening and how to think about them: Opening Gambit, USP, and Point B.
Opening Gambit
The Opening Gambit is a series of short sentences to get the audience engaged and establish a need for your idea, concept, or solution. Suasive recommends the following seven Opening Gambits .
- Rhetorical question Get your audience thinking about your message by posing a meaningful question that is relevant to them. Scott Cook, the founding CEO of Intuit, used a rhetorical phrase when making a presentation at the Robertson, Stephens, and Company Technology Investment Conference in San Francisco. He began with: “Let me begin today’s presentation with a question. How many of you balance your checkbooks? May I see a show of hands?” Almost everyone’s hand went up. “Okay. Now how many of you like doing it?” Everyone’s hand went down. He had their focus because he got them moving their body and used an easy question that would resonate with everyone. If he had launched into his presentation with a detailed description of Quicken accounting software, he likely would have lost them. Instead, he engaged the audience with a personal question and got them focused on thinking about their checkbooks.
- Factoid You can convert any question to a simple, striking statistic or factual statement to capture your audience’s attention. For instance, instead of asking, “How many iPhones are sold each year?” (which cedes control of the floor), turn it into a Factoid: “185 million iPhones are sold every year.” The Factoid you choose should be related to the main theme of your presentation and not just dropped in for shock value. We’ve all heard off-the-wall statements that only serve to throw the audience off track all the while never coming back to the main point thread or thesis.
- Retrospective/Prospective A Retrospective (backward) or Prospective (forward) look allows you to grab your audience’s attention by moving them in one direction or another, away from their present, immediate concerns. Consider this technique as a flashback or flashforward, or “That was then, this is now.” For instance, you could refer to the way things used to be done, the way they are done now, and the way you project them being done in the future. Technology companies often choose to start their presentations with a look back to earlier functions to contrast how their new technology disrupts the same functionality: library search before the internet, cassette tapes before digital music, brick and mortar shopping before e-commerce, a rat’s nest of tangled wiring before Bluetooth, and keypad entry before facial recognition.
- Anecdote An anecdote is a brief human interest story. “Personal stories” have recently become the holy grail of storytelling . A tsunami of consultants, courseware, workshops , seminars, blogs, and publications are now advising individuals and businesses to develop their great speeches and presentations by reaching deep inside themselves for a heartwarming opening anecdote. People naturally identify with other people, and a personal story can create empathy.
- Quotation You can also use a relevant quotation from a well-known, reliable source such as William Shakespeare, Winston Churchill , John F. Kennedy, Tom Peters or, as many businesspeople do, Sun Tzu’s The Art of War . Yet the best famous quotation is something from a third party that credentializes you, your idea, or your company. Whichever you use, be sure to tie the quotation closely to your content.
- Aphorism An aphorism is a well-known saying, maxim, or idiom. Because of its familiarity, as soon as you state an Aphorism, it rings a bell in your audience’s minds. They may not even recognize the source, but it brings them to attention.
- Analogy Analogies help explain complex subjects. If your business involves highly technical or specialized products, services, or systems, a simple analogous comparison can help clarify. During the early days of the internet, companies developing networking products analogized the web to highways: with main roads to represent carriers, interchanges to represent routing and switching equipment, on-ramps and off-ramps to represent local carriers, and tolls to represent revenues.
COMMUNICATION WITH PURPOSE
Unique Selling Proposition
Once you’ve stated your Opening Gambit, it’s time for your Unique Selling Proposition (USP). The USP is a succinct summary of your business, describing the basic premise that describes what your company, product, or service does. One of the most common complaints about presentations is “I listened to them for 30 minutes, and I still don’t know what they do!” The USP is what they do.
The Opening Gambit grabbed your viewer’s attention and established need, and your USP demonstrates your solution to that need with maximum clarity. It summarizes the body or middle part of your speech. The best USPs are short and are communicated in one sentence.
Which company’s USP is “Melt in your mouth, not in your hand?”
Did you guess it? M&Ms of course.
Point B is your call to action. It’s how you end your speech with a bang and plan to bring your audience to action. The Opening Gambit, USP, and Point B are all connected in a sequence that feeds into one another.
Here’s an example of a full sequence from Opening Gambit to Point B.
- Opening Gambit (Anecdote): Last year, one of Acme’s customers had a flood in their home. The sprinkler system broke and damaged all the furniture, carpets, and other possessions. Not only did they lose their home, they took a big financial hit.
- Link: This customer is like many customers who purchase a basic policy not customized to their individual needs. That means being just one step away from disaster.
- USP: Acme Insurance has a solution. We can provide you with a customized, value-added package of insurance that provides for your Individual needs to protect you against serious financial loss.
- Proof of Concept (POC)–evidence that your USP is worthy: That’s why Acme is one of the fastest-growing insurance brokers in the state.
- Link: I know that you’ll want to take advantage of this opportunity…
- Point B: …and sign up for this important coverage today.
You can see how all three elements feed into each other. One can’t effectively exist without the other. What’s great about the three steps is they compromise your entire speech outline on a macro level, and you can also use them again on a micro level within the closing section of your presentation.
Three Ways to Close a Speech Effectively

“Tell ’em what you’ve told ’em” is a classic closing technique that involves summarizing your main points and reiterating your message in a clear and concise way. This technique helps to reinforce your key ideas and ensure that your audience remembers them long after your speech is over. By summarizing your main points and restating your message, you can drive home the key takeaways and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
“Tell ‘em what you’ve told ‘em” is your closing, a bookend to your opening, and includes three key elements: a Bookend Gambit (like the Opening Gambit but more concise), Recap (of the agenda and your main points), and Point B (call to action).
The Bookend Gambit is a powerful technique that involves referencing your Opening Gambit in your closing remarks. This technique creates a sense of closure and brings your presentation full circle, leaving your audience feeling satisfied and fulfilled.
A brief Recap of your agenda is the second element of the closing technique. By summarizing what you’ve covered you can reinforce the key points you’ve made and drive home your message in a powerful and impactful way.
Point B is the third element and involves making a clear and compelling call to action in your closing remarks. This technique encourages your audience to take specific actions based on the message you’ve delivered, whether it’s signing a petition, making a donation, or simply changing their behavior. By providing a clear and actionable next step, you can motivate your audience to take action and make a difference.
What is a Strong Concluding Statement?
A strong concluding statement is critical for leaving a long-term impression on your audience and motivating them to take action. You want to end your speech with your audience thinking about your objective, willing to do what you want them to do. It’s the last thing they hear you say at the end of your speech, and for many leading speakers it holds the most weight.
One of the most effective ways to close your speech with a bang is with a clear and concise call to action, also known as Point B as discussed above. This final remark should be a short and powerful statement that encapsulates the central message of your presentation and inspires your audience to act.
For example, let’s suppose that in your opening statement you said, “So that we can control our own destiny, I’m seeking your approval and a budget to start this unit.” In your closing statement, you might shorten this message to “All we need is your approval.” This statement is short, clear, and to the point, emphasizing the importance of your request.

Need Help Closing Your Speech?
Putting all the pieces of your speech or presentation together takes know how. The good news is because it’s more science than art, anyone can learn how to do it with the right training. A good presentation has all the parts of a good compelling story – a beginning, middle, and end. The only difference is the pacing and delivery techniques, but story is still at the heart. With practice and preparation, you can improve your speech writing and delivering skills, and make sure your ideas are heard and considered.
So whether you are preparing for a job interview, a presentation at work, or an entire speech in front of a large audience, remember to believe in yourself, focus on your key points, and prepare to the best of your ability. When it’s time to deliver your closing remarks, be sure to incorporate the three techniques you learned in this article and we’re confident you’ll make an impact.
How to tell your story so the audience feels it’s their story.
Suasive, Inc. is a Silicon Valley-based communication consulting company that offers public speaking classes for organizations and individuals. To date, we’ve coached over 600 CEOs and helped individuals in some of the world’s largest companies including Netflix , eBay , Sonos , Lyft , and Freshworks .
Start Your public speaking Training
Privacy Overview

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.3 Putting It Together: Steps to Complete Your Introduction
Learning objectives.
- Clearly identify why an audience should listen to a speaker.
- Discuss how you can build your credibility during a speech.
- Understand how to write a clear thesis statement.
- Design an effective preview of your speech’s content for your audience.
Erin Brown-John – puzzle – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Once you have captured your audience’s attention, it’s important to make the rest of your introduction interesting, and use it to lay out the rest of the speech. In this section, we are going to explore the five remaining parts of an effective introduction: linking to your topic, reasons to listen, stating credibility, thesis statement, and preview.
Link to Topic
After the attention-getter, the second major part of an introduction is called the link to topic. The link to topic is the shortest part of an introduction and occurs when a speaker demonstrates how an attention-getting device relates to the topic of a speech. Often the attention-getter and the link to topic are very clear. For example, if you look at the attention-getting device example under historical reference above, you’ll see that the first sentence brings up the history of the Vietnam War and then shows us how that war can help us understand the Iraq War. In this case, the attention-getter clearly flows directly to the topic. However, some attention-getters need further explanation to get to the topic of the speech. For example, both of the anecdote examples (the girl falling into the manhole while texting and the boy and the filberts) need further explanation to connect clearly to the speech topic (i.e., problems of multitasking in today’s society).
Let’s look at the first anecdote example to demonstrate how we could go from the attention-getter to the topic.
In July 2009, a high school girl named Alexa Longueira was walking along a main boulevard near her home on Staten Island, New York, typing in a message on her cell phone. Not paying attention to the world around her, she took a step and fell right into an open manhole. This anecdote illustrates the problem that many people are facing in today’s world. We are so wired into our technology that we forget to see what’s going on around us—like a big hole in front of us.
In this example, the third sentence here explains that the attention-getter was an anecdote that illustrates a real issue. The fourth sentence then introduces the actual topic of the speech.
Let’s now examine how we can make the transition from the parable or fable attention-getter to the topic:
The ancient Greek writer Aesop told a fable about a boy who put his hand into a pitcher of filberts. The boy grabbed as many of the delicious nuts as he possibly could. But when he tried to pull them out, his hand wouldn’t fit through the neck of the pitcher because he was grasping so many filberts. Instead of dropping some of them so that his hand would fit, he burst into tears and cried about his predicament. The moral of the story? “Don’t try to do too much at once.” In today’s world, many of us are us are just like the boy putting his hand into the pitcher. We are constantly trying to grab so much or do so much that it prevents us from accomplishing our goals. I would like to show you three simple techniques to manage your time so that you don’t try to pull too many filberts from your pitcher.
In this example, we added three new sentences to the attention-getter to connect it to the speech topic.
Reasons to Listen
Once you have linked an attention-getter to the topic of your speech, you need to explain to your audience why your topic is important. We call this the “why should I care?” part of your speech because it tells your audience why the topic is directly important to them. Sometimes you can include the significance of your topic in the same sentence as your link to the topic, but other times you may need to spell out in one or two sentences why your specific topic is important.
People in today’s world are very busy, and they do not like their time wasted. Nothing is worse than having to sit through a speech that has nothing to do with you. Imagine sitting through a speech about a new software package you don’t own and you will never hear of again. How would you react to the speaker? Most of us would be pretty annoyed at having had our time wasted in this way. Obviously, this particular speaker didn’t do a great job of analyzing her or his audience if the audience isn’t going to use the software package—but even when speaking on a topic that is highly relevant to the audience, speakers often totally forget to explain how and why it is important.
Appearing Credible
The next part of a speech is not so much a specific “part” as an important characteristic that needs to be pervasive throughout your introduction and your entire speech. As a speaker, you want to be seen as credible (competent, trustworthy, and caring/having goodwill). As mentioned earlier in this chapter, credibility is ultimately a perception that is made by your audience. While your audience determines whether they perceive you as competent, trustworthy, and caring/having goodwill, there are some strategies you can employ to make yourself appear more credible.
First, to make yourself appear competent, you can either clearly explain to your audience why you are competent about a given subject or demonstrate your competence by showing that you have thoroughly researched a topic by including relevant references within your introduction. The first method of demonstrating competence—saying it directly—is only effective if you are actually a competent person on a given subject. If you are an undergraduate student and you are delivering a speech about the importance of string theory in physics, unless you are a prodigy of some kind, you are probably not a recognized expert on the subject. Conversely, if your number one hobby in life is collecting memorabilia about the Three Stooges, then you may be an expert about the Three Stooges. However, you would need to explain to your audience your passion for collecting Three Stooges memorabilia and how this has made you an expert on the topic.
If, on the other hand, you are not actually a recognized expert on a topic, you need to demonstrate that you have done your homework to become more knowledgeable than your audience about your topic. The easiest way to demonstrate your competence is through the use of appropriate references from leading thinkers and researchers on your topic. When you demonstrate to your audience that you have done your homework, they are more likely to view you as competent.
The second characteristic of credibility, trustworthiness, is a little more complicated than competence, for it ultimately relies on audience perceptions. One way to increase the likelihood that a speaker will be perceived as trustworthy is to use reputable sources. If you’re quoting Dr. John Smith, you need to explain who Dr. John Smith is so your audience will see the quotation as being more trustworthy. As speakers we can easily manipulate our sources into appearing more credible than they actually are, which would be unethical. When you are honest about your sources with your audience, they will trust you and your information more so than when you are ambiguous. The worst thing you can do is to out-and-out lie about information during your speech. Not only is lying highly unethical, but if you are caught lying, your audience will deem you untrustworthy and perceive everything you are saying as untrustworthy. Many speakers have attempted to lie to an audience because it will serve their own purposes or even because they believe their message is in their audience’s best interest, but lying is one of the fastest ways to turn off an audience and get them to distrust both the speaker and the message.
The third characteristic of credibility to establish during the introduction is the sense of caring/goodwill. While some unethical speakers can attempt to manipulate an audience’s perception that the speaker cares, ethical speakers truly do care about their audiences and have their audience’s best interests in mind while speaking. Often speakers must speak in front of audiences that may be hostile toward the speaker’s message. In these cases, it is very important for the speaker to explain that he or she really does believe her or his message is in the audience’s best interest. One way to show that you have your audience’s best interests in mind is to acknowledge disagreement from the start:
Today I’m going to talk about why I believe we should enforce stricter immigration laws in the United States. I realize that many of you will disagree with me on this topic. I used to believe that open immigration was a necessity for the United States to survive and thrive, but after researching this topic, I’ve changed my mind. While I may not change all of your minds today, I do ask that you listen with an open mind, set your personal feelings on this topic aside, and judge my arguments on their merits.
While clearly not all audience members will be open or receptive to opening their minds and listening to your arguments, by establishing that there is known disagreement, you are telling the audience that you understand their possible views and are not trying to attack their intellect or their opinions.
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. A strong, clear thesis statement is very valuable within an introduction because it lays out the basic goal of the entire speech. We strongly believe that it is worthwhile to invest some time in framing and writing a good thesis statement. You may even want to write your thesis statement before you even begin conducting research for your speech. While you may end up rewriting your thesis statement later, having a clear idea of your purpose, intent, or main idea before you start searching for research will help you focus on the most appropriate material. To help us understand thesis statements, we will first explore their basic functions and then discuss how to write a thesis statement.
Basic Functions of a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement helps your audience by letting them know “in a nutshell” what you are going to talk about. With a good thesis statement you will fulfill four basic functions: you express your specific purpose, provide a way to organize your main points, make your research more effective, and enhance your delivery.
Express Your Specific Purpose
To orient your audience, you need to be as clear as possible about your meaning. A strong thesis will prepare your audience effectively for the points that will follow. Here are two examples:
- “Today, I want to discuss academic cheating.” (weak example)
- “Today, I will clarify exactly what plagiarism is and give examples of its different types so that you can see how it leads to a loss of creative learning interaction.” (strong example)
The weak statement will probably give the impression that you have no clear position about your topic because you haven’t said what that position is. Additionally, the term “academic cheating” can refer to many behaviors—acquiring test questions ahead of time, copying answers, changing grades, or allowing others to do your coursework—so the specific topic of the speech is still not clear to the audience.
The strong statement not only specifies plagiarism but also states your specific concern (loss of creative learning interaction).
Provide a Way to Organize Your Main Points
A thesis statement should appear, almost verbatim, toward the end of the introduction to a speech. A thesis statement helps the audience get ready to listen to the arrangement of points that follow. Many speakers say that if they can create a strong thesis sentence, the rest of the speech tends to develop with relative ease. On the other hand, when the thesis statement is not very clear, creating a speech is an uphill battle.
When your thesis statement is sufficiently clear and decisive, you will know where you stand about your topic and where you intend to go with your speech. Having a clear thesis statement is especially important if you know a great deal about your topic or you have strong feelings about it. If this is the case for you, you need to know exactly what you are planning on talking about in order to fit within specified time limitations. Knowing where you are and where you are going is the entire point in establishing a thesis statement; it makes your speech much easier to prepare and to present.
Let’s say you have a fairly strong thesis statement, and that you’ve already brainstormed a list of information that you know about the topic. Chances are your list is too long and has no focus. Using your thesis statement, you can select only the information that (1) is directly related to the thesis and (2) can be arranged in a sequence that will make sense to the audience and will support the thesis. In essence, a strong thesis statement helps you keep useful information and weed out less useful information.
Make Your Research More Effective
If you begin your research with only a general topic in mind, you run the risk of spending hours reading mountains of excellent literature about your topic. However, mountains of literature do not always make coherent speeches. You may have little or no idea of how to tie your research all together, or even whether you should tie it together. If, on the other hand, you conduct your research with a clear thesis statement in mind, you will be better able to zero in only on material that directly relates to your chosen thesis statement. Let’s look at an example that illustrates this point:
Many traffic accidents involve drivers older than fifty-five.
While this statement may be true, you could find industrial, medical, insurance literature that can drone on ad infinitum about the details of all such accidents in just one year. Instead, focusing your thesis statement will help you narrow the scope of information you will be searching for while gathering information. Here’s an example of a more focused thesis statement:
Three factors contribute to most accidents involving drivers over fifty-five years of age: failing eyesight, slower reflexes, and rapidly changing traffic conditions.
This framing is somewhat better. This thesis statement at least provides three possible main points and some keywords for your electronic catalog search. However, if you want your audience to understand the context of older people at the wheel, consider something like:
Mature drivers over fifty-five years of age must cope with more challenging driving conditions than existed only one generation ago: more traffic moving at higher speeds, the increased imperative for quick driving decisions, and rapidly changing ramp and cloverleaf systems. Because of these challenges, I want my audience to believe that drivers over the age of sixty-five should be required to pass a driving test every five years.
This framing of the thesis provides some interesting choices. First, several terms need to be defined, and these definitions might function surprisingly well in setting the tone of the speech. Your definitions of words like “generation,” “quick driving decisions,” and “cloverleaf systems” could jolt your audience out of assumptions they have taken for granted as truth.
Second, the framing of the thesis provides you with a way to describe the specific changes as they have occurred between, say, 1970 and 2010. How much, and in what ways, have the volume and speed of traffic changed? Why are quick decisions more critical now? What is a “cloverleaf,” and how does any driver deal cognitively with exiting in the direction seemingly opposite to the desired one? Questions like this, suggested by your own thesis statement, can lead to a strong, memorable speech.
Enhance Your Delivery
When your thesis is not clear to you, your listeners will be even more clueless than you are—but if you have a good clear thesis statement, your speech becomes clear to your listeners. When you stand in front of your audience presenting your introduction, you can vocally emphasize the essence of your speech, expressed as your thesis statement. Many speakers pause for a half second, lower their vocal pitch slightly, slow down a little, and deliberately present the thesis statement, the one sentence that encapsulates its purpose. When this is done effectively, the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech is driven home for an audience.
How to Write a Thesis Statement
Now that we’ve looked at why a thesis statement is crucial in a speech, let’s switch gears and talk about how we go about writing a solid thesis statement. A thesis statement is related to the general and specific purposes of a speech as we discussed them in Chapter 6 “Finding a Purpose and Selecting a Topic” .
Choose Your Topic
The first step in writing a good thesis statement was originally discussed in Chapter 6 “Finding a Purpose and Selecting a Topic” when we discussed how to find topics. Once you have a general topic, you are ready to go to the second step of creating a thesis statement.
Narrow Your Topic
One of the hardest parts of writing a thesis statement is narrowing a speech from a broad topic to one that can be easily covered during a five- to ten-minute speech. While five to ten minutes may sound like a long time to new public speakers, the time flies by very quickly when you are speaking. You can easily run out of time if your topic is too broad. To ascertain if your topic is narrow enough for a specific time frame, ask yourself three questions.
First, is your thesis statement narrow or is it a broad overgeneralization of a topic? An overgeneralization occurs when we classify everyone in a specific group as having a specific characteristic. For example, a speaker’s thesis statement that “all members of the National Council of La Raza are militant” is an overgeneralization of all members of the organization. Furthermore, a speaker would have to correctly demonstrate that all members of the organization are militant for the thesis statement to be proven, which is a very difficult task since the National Council of La Raza consists of millions of Hispanic Americans. A more appropriate thesis related to this topic could be, “Since the creation of the National Council of La Raza [NCLR] in 1968, the NCLR has become increasingly militant in addressing the causes of Hispanics in the United States.”
The second question to ask yourself when narrowing a topic is whether your speech’s topic is one clear topic or multiple topics. A strong thesis statement consists of only a single topic. The following is an example of a thesis statement that contains too many topics: “Medical marijuana, prostitution, and gay marriage should all be legalized in the United States.” Not only are all three fairly broad, but you also have three completely unrelated topics thrown into a single thesis statement. Instead of a thesis statement that has multiple topics, limit yourself to only one topic. Here’s an example of a thesis statement examining only one topic: “Today we’re going to examine the legalization and regulation of the oldest profession in the state of Nevada.” In this case, we’re focusing our topic to how one state has handled the legalization and regulation of prostitution.
The last question a speaker should ask when making sure a topic is sufficiently narrow is whether the topic has direction. If your basic topic is too broad, you will never have a solid thesis statement or a coherent speech. For example, if you start off with the topic “Barack Obama is a role model for everyone,” what do you mean by this statement? Do you think President Obama is a role model because of his dedication to civic service? Do you think he’s a role model because he’s a good basketball player? Do you think he’s a good role model because he’s an excellent public speaker? When your topic is too broad, almost anything can become part of the topic. This ultimately leads to a lack of direction and coherence within the speech itself. To make a cleaner topic, a speaker needs to narrow her or his topic to one specific area. For example, you may want to examine why President Obama is a good speaker.
Put Your Topic into a Sentence
Once you’ve narrowed your topic to something that is reasonably manageable given the constraints placed on your speech, you can then formalize that topic as a complete sentence. For example, you could turn the topic of President Obama’s public speaking skills into the following sentence: “Because of his unique sense of lyricism and his well-developed presentational skills, President Barack Obama is a modern symbol of the power of public speaking.” Once you have a clear topic sentence, you can start tweaking the thesis statement to help set up the purpose of your speech.
Add Your Argument, Viewpoint, or Opinion
This function only applies if you are giving a speech to persuade. If your topic is informative, your job is to make sure that the thesis statement is nonargumentative and focuses on facts. For example, in the preceding thesis statement we have a couple of opinion-oriented terms that should be avoided for informative speeches: “unique sense,” “well-developed,” and “power.” All three of these terms are laced with an individual’s opinion, which is fine for a persuasive speech but not for an informative speech. For informative speeches, the goal of a thesis statement is to explain what the speech will be informing the audience about, not attempting to add the speaker’s opinion about the speech’s topic. For an informative speech, you could rewrite the thesis statement to read, “This speech is going to analyze Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his speech, ‘A World That Stands as One,’ delivered July 2008 in Berlin.”
On the other hand, if your topic is persuasive, you want to make sure that your argument, viewpoint, or opinion is clearly indicated within the thesis statement. If you are going to argue that Barack Obama is a great speaker, then you should set up this argument within your thesis statement.
Use the Thesis Checklist
Once you have written a first draft of your thesis statement, you’re probably going to end up revising your thesis statement a number of times prior to delivering your actual speech. A thesis statement is something that is constantly tweaked until the speech is given. As your speech develops, often your thesis will need to be rewritten to whatever direction the speech itself has taken. We often start with a speech going in one direction, and find out through our research that we should have gone in a different direction. When you think you finally have a thesis statement that is good to go for your speech, take a second and make sure it adheres to the criteria shown in Table 9.1 “Thesis Checklist”
Table 9.1 Thesis Checklist
Preview of Speech
The final part of an introduction contains a preview of the major points to be covered within your speech. I’m sure we’ve all seen signs that have three cities listed on them with the mileage to reach each city. This mileage sign is an indication of what is to come. A preview works the same way. A preview foreshadows what the main body points will be in the speech. For example, to preview a speech on bullying in the workplace, one could say, “To understand the nature of bullying in the modern workplace, I will first define what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying, I will then discuss the common characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets, and lastly, I will explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.” In this case, each of the phrases mentioned in the preview would be a single distinct point made in the speech itself. In other words, the first major body point in this speech would examine what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying; the second major body point in this speech would discuss the common characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets; and lastly, the third body point in this speech would explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.
Key Takeaways
- Linking the attention-getter to the speech topic is essential so that you maintain audience attention and so that the relevance of the attention-getter is clear to your audience.
- Establishing how your speech topic is relevant and important shows the audience why they should listen to your speech.
- To be an effective speaker, you should convey all three components of credibility, competence, trustworthiness, and caring/goodwill, by the content and delivery of your introduction.
- A clear thesis statement is essential to provide structure for a speaker and clarity for an audience.
- An effective preview identifies the specific main points that will be present in the speech body.
- Make a list of the attention-getting devices you might use to give a speech on the importance of recycling. Which do you think would be most effective? Why?
- Create a thesis statement for a speech related to the topic of collegiate athletics. Make sure that your thesis statement is narrow enough to be adequately covered in a five- to six-minute speech.
- Discuss with a partner three possible body points you could utilize for the speech on the topic of volunteerism.
- Fill out the introduction worksheet to help work through your introduction for your next speech. Please make sure that you answer all the questions clearly and concisely.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
How to Conclude a Speech
Last Updated: May 15, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Gale McCreary . Gale McCreary is the Founder and Chief Coordinator of SpeechStory, a nonprofit organization focused on improving communication skills in youth. She was previously a Silicon Valley CEO and President of a Toastmasters International chapter. She has been recognized as Santa Barbara Entrepreneurial Woman of the Year and received Congressional recognition for providing a Family-Friendly work environment. She has a BS in Biology from Stanford University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 114,888 times.
The last moments are where a good speech can be made. If you want to leave your audience stunned, you can learn the basics needs of a good conclusion, as well as some tactics for ending creatively. You can also learn what techniques to avoid.
Things You Should Know
- Summarize the main points of your speech to remind listeners what they've learned.
- Recall something from the introduction so your speech comes full circle.
- Thank your audience for attending and listening.
Concluding Your Speech

- Use the chance to repeat your thesis a final time, if necessary. What's the one thing you hope someone remembers from your speech? What's the one thing that needs to be learned?
- In informal speeches, repeating the main points won't be necessary. If you're giving a toast at a wedding, you don't need to run back through a list of the great things about the groom.

- If you started the speech by drawing a sad portrait of a recently returned veteran who couldn't get work, or health insurance, and ended up in dire straits, that can be a heart-breaking intro. Pick back up with the story in conclusion to let you know where that vet is now.
- Any kind of reference can work. If you started a speech with a quote by Thomas Paine, end with more about Thomas Paine. The bookend technique is an excellent way of signaling the end for the audience.

- Put a face on things. Case studies and personal examples are extremely effective in helping an audience connect with a complicated issue or topic.
- Some people like to use this technique for the introduction, but it can be unexpected and even more effective to wait and use it at the conclusion, especially for speeches that are a little bit shorter.

- "We can turn back the oceans and stop the warming of our planet. It's not too late, as the title of my speech promises. It's not too late for any of us."

- It's also appropriate to use a "thank you" as the very last thing that you say: "We must continue fighting the good fight on climate change, for our children, for our economy, and for ourselves. Thank you." Cue applause.
- Sometimes, it's also appropriate to ask for questions if the occasion calls for it. People should be sure your speech is over, but if people seem hesitant, it's ok to say, "I'd be happy to take questions, if anyone has them."
Nailing the Ending

- "The fight for climate change (pause ) is a fight (pause) that we must (pause) win. Our children (pause). Our children's children (pause). Demand it."

- Return to the story of the veteran struggling to find work. With the sorts of infrastructure you're calling for in your speech, maybe he could be working a specific job, and getting into his own house, and even starting to plant a garden in the yard, something he always wanted to do. Dream a little, and let your audience do the same.

- "We must do this for our children, we must do this for our neighbors, we must do this for America, we must do this for the world, we must do this for the oceans, we must do this for the forests..."
- "Politicians can't legislate this. Architects can't build this. Artists can't dream this. Developers can't innovate this. Only you can do this."

- Address the audience specifically. Start using "you" toward the end of the speech, or address an individual in the audience to help bring it home.
Avoiding Common Mistakes

- "Well, that's pretty much it."
- "That's it."
- "I'm done."

- When the speech is over, don't keep talking. Even if you just remembered a point you forgot to make a few minutes ago, don't launch back into the speech when people are clapping, or once they're finished. When the speech is over, let it be over. If there's a chance for Q & A, then get to it then.

- Some speeches can be leavened with a bit of humor in the ending. If you've just given a particularly touching toast at a wedding, it might be good to release a bit of the tension with a well-placed gag. Probably not so much for a professional presentation.
Community Q&A
- Don't overwrite it. After your first few drafts, sit back and let it rest a few days. Then come back to your ending with new perspective. Pretend that you are listening to someone else say it for the first time. Read it like you will at the event. Then go back to editing. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0
- Catch your audience's attention. Use a shocking fact, or statistic that will leave the listeners thinking and will urge them to action. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/oralcommunication/guides/introductions-and-conclusions
- ↑ https://westsidetoastmasters.com/article_reference/12_ways_to_end_your_speech.html
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-conclude-a-presentation
- ↑ https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-communications/chapter/conclusion/
- ↑ https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/best-call-action-speech-examples-mitch-carson?trk=public_profile_article_view
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/oralcommunication/guides/avoid-these-common-speech-mistakes-1
About This Article

To conclude a speech, try summarizing the main points you made throughout it so you can remind the listener what you want them to learn or take away. In some cases, you can use the conclusion to recall the introduction, showing how the speech comes full circle. Or, if you have a catchy title, work it into the conclusion to grab your audience's attention. You can also signal the ending by thanking the audience for listening or simply stating “In conclusion” to let your listeners know it’s time to wrap up. To put extra emphasis on your ending, slow your speech to get people to perk up and really hear your final points. To learn how to use your conclusion as a call to action, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Gaukhu Bankar
Aug 14, 2019
Did this article help you?
Oct 18, 2017
Yasar Arfath
Aug 23, 2018
Nov 26, 2017
Sep 18, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Speech Writing
Introduction Speech
Introduction Speech - A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
11 min read

People also read
The 10 Key Steps for Perfect Speech Writing
Understanding the Speech Format - Detailed Guide & Examples
How to Start A Speech - 13 Interesting Ideas & Examples
20+ Outstanding Speech Examples for Your Help
Common Types of Speeches that Every Speechwriter Should Know
Good Impromptu Speech Topics for Students
Entertaining Speech Topics for Your Next Debate
How to Write a Special Occasion Speech: Types, Tips, and Examples
How to Write the Best Acceptance Speech for Your Audience?
Presentation Speech - An Ultimate Writing Guide
Commemorative Speech - Writing Guide, Outline & Examples
Farewell Speech - Writing Tips & Examples
How to Write an Extemporaneous Speech? A Step-by-Step Guide
Crafting the Perfect Graduation Speech: A Guide with Examples
Introduction speeches are all around us. Whenever we meet a new group of people in formal settings, we have to introduce ourselves. That’s what an introduction speech is all about.
When you're facing a formal audience, your ability to deliver a compelling introductory speech can make a lot of difference. With the correct approach, you can build credibility and connections.
In this blog, we'll take you through the steps to craft an impactful introduction speech. You’ll also get examples and valuable tips to ensure you leave a lasting impression.
So, let's dive in!
- 1. What is an Introduction Speech?
- 2. How to Write an Introduction Speech?
- 3. Introduction Speech Outline
- 4. 7 Ways to Open an Introduction Speech
- 5. Introduction Speech Example
- 6. Introduction Speech Ideas
- 7. Tips for Delivering the Best Introduction Speech
What is an Introduction Speech?
An introduction speech, or introductory address, is a brief presentation at the beginning of an event or public speaking engagement. Its primary purpose is to establish a connection with the audience and to introduce yourself or the main speaker.
This type of speech is commonly used in a variety of situations, including:
- Public Speaking: When you step onto a stage to address a large crowd, you start with an introduction to establish your presence and engage the audience.
- Networking Events: When meeting new people in professional or social settings, an effective introduction speech can help you make a memorable first impression.
- Formal Gatherings: From weddings to conferences, introductions set the tone for the event and create a warm and welcoming atmosphere.
In other words, an introduction speech is simply a way to introduce yourself to a crowd of people.
How to Write an Introduction Speech?
Before you can just go and deliver your speech, you need to prepare for it. Writing a speech helps you organize your ideas and prepare your speech effectively.
Here is how to introduce yourself in a speech.
- Know Your Audience
Understanding your audience is crucial. Consider their interests, backgrounds, and expectations to tailor your introduction accordingly.
For instance, the audience members could be your colleagues, new classmates, or various guests depending on the occasion. Understanding your audience will help you decide what they are expecting from you as a speaker.
- Start with a Hook
Begin with a captivating opening line that grabs your audience's attention. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a thought-provoking question about yourself or the occasion.
- Introduce Yourself
Introduce yourself to the audience. State your name, occupation, or other details relevant to the occasion. You should mention the reason for your speech clearly. It will build your credibility and give the readers reasons to stay with you and read your speech.
- Keep It Concise
So how long is an introduction speech?
Introduction speeches should be brief and to the point. Aim for around 1-2 minutes in most cases. Avoid overloading the introduction with excessive details.
- Highlight Key Points
Mention the most important information that establishes the speaker's credibility or your own qualifications. Write down any relevant achievements, expertise, or credentials to include in your speech. Encourage the audience to connect with you using relatable anecdotes or common interests.
- Rehearse and Edit
Practice your introduction speech to ensure it flows smoothly and stays within the time frame. Edit out any unnecessary information, ensuring it's concise and impactful.
- Tailor for the Occasion
Adjust the tone and content of your introduction speech to match the formality and purpose of the event. What works for a business conference may not be suitable for a casual gathering.
Introduction Speech Outline
To assist you in creating a structured and effective introduction speech, here's a simple outline that you can follow:
Here is an example outline for a self-introduction speech.
Outline for Self-Introduction Speech
7 Ways to Open an Introduction Speech
You can start your introduction speech as most people do:
“Hello everyone, my name is _____. I will talk about _____. Thank you so much for having me. So first of all _______”
However, this is the fastest way to make your audience lose interest. Instead, you should start by captivating your audience’s interest. Here are 7 ways to do that:
- Quote
Start with a thought-provoking quote that relates to your topic or the occasion. E.g. "Mahatma Gandhi once said, 'You must be the change you want to see in the world."
- Anecdote or Story
Begin with a brief, relevant anecdote or story that draws the audience in. It could be a story about yourself or any catchy anecdote to begin the flow of your speech.
Pose a rhetorical question to engage the audience's curiosity and involvement. For example, "Have you ever wondered what it would be like to travel back in time, to experience a moment in history?”
- Statistic or Fact
Share a surprising statistic or interesting fact that underscores the significance of your speech. E.g. “Did you know that as of today, over 60% of the world's population has access to the internet?”
- “What If” Scenario
Paint a vivid "What if" scenario that relates to your topic, sparking the audience's imagination and curiosity. For example, "What if I told you that a single decision today could change the course of your life forever?"
- Ignite Imagination
Encourage the audience to envision a scenario related to your topic. For instance, "Imagine a world where clean energy powers everything around us, reducing our carbon footprint to almost zero."
Start your introduction speech with a moment of silence, allowing the audience to focus and anticipate your message. This can be especially powerful in creating a sense of suspense and intrigue.
Introduction Speech Example
To help you understand how to put these ideas into practice, here are the introduction speech examples for different scenarios.
Introduction Speech Writing Sample
Short Introduction Speech Sample
Self Introduction Speech for College Students
Introduction Speech about Yourself
Student Presentation Introduction Speech Script
Teacher Introduction Speech
New Employee Self Introduction Speech
Introduction Speech for Chief Guest
Moreover, here is a video example of a self introduction. Watch it to understand how you should deliver your speech:
Want to read examples for other kinds of speeches? Find the best speeches at our blog about speech examples !
Introduction Speech Ideas
So now that you’ve understood what an introduction speech is, you may want to write one of your own. So what should you talk about?
The following are some ideas to start an introduction speech for a presentation, meeting, or social gathering in an engaging way.
- Personal Story: Share a brief personal story or an experience that has shaped you, introducing yourself on a deeper level.
- Professional Background: Introduce yourself by highlighting your professional background, including your career achievements and expertise.
- Hobby or Passion: Discuss a hobby or passion that you're enthusiastic about, offering insights into your interests and what drives you.
- Volunteer Work: Introduce yourself by discussing your involvement in volunteer work or community service, demonstrating your commitment to making a difference.
- Travel Adventures: Share anecdotes from your travel adventures, giving the audience a glimpse into your love for exploring new places and cultures.
- Books or Literature: Provide an introduction related to a favorite book, author, or literary work, revealing your literary interests.
- Achievements and Milestones: Highlight significant achievements and milestones in your life or career to introduce yourself with an impressive track record.
- Cultural Heritage: Explore your cultural heritage and its influence on your identity, fostering a sense of cultural understanding.
- Social or Environmental Cause: Discuss your dedication to a particular social or environmental cause, inviting the audience to join you in your mission.
- Future Aspirations: Share your future goals and aspirations, offering a glimpse into what you hope to achieve in your personal or professional life.
You can deliver engaging speeches on all kinds of topics. Here is a list of entertaining speech topics to get inspiration.
Tips for Delivering the Best Introduction Speech
Here are some tips for you to write a perfect introduction speech in no time.
Now that you know how to write an effective introduction speech, let's focus on the delivery. The way you present your introduction is just as important as the content itself.
Here are some valuable tips to ensure you deliver a better introduction speech:
- Maintain Eye Contact
Make eye contact with the audience to establish a connection. This shows confidence and engages your listeners.
- Use Appropriate Body Language
Your body language should convey confidence and warmth. Stand or sit up straight, use open gestures, and avoid fidgeting.
- Mind Your Pace
Speak at a moderate pace, avoiding rapid speech. A well-paced speech is easier to follow and more engaging.
- Avoid Filler Words
Minimize the use of filler words such as "um," "uh," and "like." They can be distracting and detract from your message.
- Be Enthusiastic
Convey enthusiasm about the topic or the speaker. Your energy can be contagious and inspire the audience's interest.
- Practice, Practice, Practice
Rehearse your speech multiple times. Practice in front of a mirror, record yourself, or seek feedback from others.
- Be Mindful of Time
Stay within the allocated time for your introduction. Going too long can make your speech too boring for the audience.
- Engage the Audience
Encourage the audience's participation. You could do that by asking rhetorical questions, involving them in a brief activity, or sharing relatable anecdotes.
Mistakes to Avoid in an Introduction Speech
While crafting and delivering an introduction speech, it's important to be aware of common pitfalls that can diminish its effectiveness. Avoiding these mistakes will help you create a more engaging and memorable introduction.
Here are some key mistakes to steer clear of:
- Rambling On
One of the most common mistakes is making the introduction too long. Keep it concise and to the point. The purpose is to set the stage, not steal the spotlight.
- Lack of Preparation
Failing to prepare adequately can lead to stumbling, awkward pauses, or losing your train of thought. Rehearse your introduction to build confidence.
- Using Jargon or Complex Language
Avoid using technical jargon or complex language that may confuse the audience. Your introduction should be easily understood by everyone.
- Being Too Generic
A generic or uninspiring introduction can set a lackluster tone. Ensure your introduction is tailored to the event and speaker, making it more engaging.
- Using Inappropriate Humor
Be cautious with humor, as it can easily backfire. Avoid inappropriate or potentially offensive jokes that could alienate the audience.
- Not Tailoring to the Occasion
An introduction should be tailored to the specific event's formality and purpose. A one-size-fits-all approach may not work in all situations.
To Conclude,
An introduction speech is more than just a formality. It's an opportunity to engage, inspire, and connect with your audience in a meaningful way.
With the help of this blog, you're well-equipped to shine in various contexts. So, step onto that stage, speak confidently, and captivate your audience from the very first word.
Moreover, you’re not alone in your journey to becoming a confident introducer. If you ever need assistance in preparing your speech, let the experts help you out.
MyPerfectWords.com offers a reputable essay writing service with experienced professionals who can craft tailored introductions, ensuring your speech makes a lasting impact.
Don't hesitate; hire our professional speech writing service to deliver top-quality speeches at your deadline!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


Make A Speech Introduction That Grabs Audience Attention

The speech introduction is the first part of a speech and the first opportunity to grab the audience’s attention. The speaker should state the topic, make it relatable to the audience, establish credibility and preview the main points. You should write or finalize your introduction at the end so that it reflects what you actually said.
Listen up, audience!
No matter whether you are giving an informative speech to enlighten an audience about a certain topic or a persuasive speech aims to convince the crowd to adopt a particular viewpoint. But whichever type of speech you’re writing or delivering, one thing is true: You must create an attention-grabbing speech introduction.
Table of Contents
What Is The Best Way To Start A Speech?
Whether in speech writing or public speaking, the role of a good intro cannot be understated. It is your best chance to captivate your audience’s attention and entice them to be with you until the rest of your speech.
It’s also your opportunity to introduce the topic and thesis statement and set up the points you’ll discuss later. So, keep in mind that you emphasize the relevance of your subject matter to the audience and contextualize it properly.
These are some of the best ways to make a compelling introduction speech.
- State a quote or use a historical event reference. Analyze your target audience and look for a powerful quote from a relevant figure or a historical event that will resonate with listeners and relate it to your topic. A notable quotation can immediately establish a strong connection. On the other hand, an important event will help you illustrate your point or paint a scenario better.
- Share a personal story. Sometimes, you don’t have to search far and wide to demonstrate a point. You can tap into your personal experience and share something about yourself. Generally, audience members enjoy hearing stories as they pique their interest and get a glimpse of who the speaker is. Your anecdotes will also make you more human and accessible.
- Start with an “Imagine” or “What if?” scenario. Want to make your audience engaged? Let their imagination run. In many speeches over the years, some of the most successful ones used this technique. Speakers transport the audience to the future or a scenario wherein their proposed idea or belief reigns. For example, “What if we live in a world where everyone can access healthcare?”
- Count on a video or any other visual aids. If you’re a public speaker keen to use technology, you may also want to commence your speech with visual aids. For instance, you can show a pre-prepared video to draw the crowd’s attention right before you speak. If you’re talking about hunger and food security, you can show footage of how such issues take a toll in many third-world countries.
- Tell surprising statistics. One of the most effective ways to shock — and, ultimately, grab your audience’s attention is by telling real, hard facts. If you’re looking for a good attention-getter, you can rely on surprising statistics about your topic. For instance, if your topic is bullying, you can mention that in the US, around 3 million students are victims of bullying.
- Ask the audience a question. Another way to hook your audience is by asking them a question. It can be a direct one (e.g., “Who among here are…” then ask for a show of hands). It can also be a rhetorical question (e.g., “What is the meaning of life?”). The key is interacting with the crowd to get their attention and effectively introducing your subject matter.

What Should You Include In the Introduction?
When you look at intro samples and templates on the web, you’ll find that effective speech introductions contain key elements. And one of the most important is your attention-grabber, which will compel your audience to listen to your speech and narrative.
You must also introduce your speech topic and indicate why it matters to your audience. You should also share something about yourself, especially your credibility, to discuss a particular subject matter.
Once you’ve laid out these foundations, state your central idea or thesis statement. Tell the audience members the point of view you want them to adopt, and give them a preview of the main points you’re discussing if you’re giving a persuasive speech. If you’re writing or delivering an informative one, you can provide them with a brief speech outline or the key points you’ll touch upon throughout the body of the speech.
What Are The Best Lines To Introduce A Speech?
One of the most common public speaking tips you’ll encounter is to have a good introduction. To help you capture the audience’s attention, here are some ideas you can use in your speech.
- A famous quote (For example, “Innovation distinguishes between a leader and a follower” by Steve Jobs)
- A song lyric (“Imagine there’s no countries/ It isn’t hard to do/ Nothing to kill or die for/ And no religion, too,” from “Imagine by John Lennon)
- A line from a poem (“You may write me down in history With your bitter, twisted lies, You may trod me in the very dirt But still, like dust, I’ll rise,” from “Still I Rise” by Maya Angelou)
- A line from a movie (“Greed, for a lack of a better word, is good,” from “Wall Street”)
- Reference to a historical event (“Two hundred years ago, one of the most important proclamations was made. Through the Emancipation Proclamation issued by President Abraham Lincoln, the enslaved Black people were given freedom.”
- Reference to a notable figure (“Stan Lee, the man behind iconic Marvel characters, was hired as an editorial assistant at a comics company after graduating high school.”).
- A bold statement (“Prostitution must be legalized.”)
- A serious statement (“Climate change is a pressing issue.”)
- A humorous line (“Don’t underestimate me. That’s the job of my mom.”)
- A shocking statistic (“If you’re consuming too much fast food and baked goods, did you know that you are 51% more likely to be depressed?”)
- A direct question (“Who among here plays violent video games?”)
- A rhetorical question (“Is there a more powerful feeling than love?”)
- A personal story (“Back when I was a fresh college graduate, I busied myself applying to the top multi-national companies.”)
- An anecdote (“Long ago, there was a man — an old but healthy man — who dared climb Mount Everest. He was 80, and he succeeded.”)
- A what-if scenario (“What if there were no poor people?”)
How Do You Introduce Yourself In A Speech?
Whether you’re a first-time speaker or a veteran, how you approach introducing yourself in a speech is important in establishing your credibility. To avoid getting called boring, you might want to shy away from the usual “Hi, everyone. I’m (your name). I (your credentials), and today I will be talking about (points of the speech).”
Usually, someone else may have given your name and background. This gives you the liberty to begin your speech more interestingly.
You can start by stating any of the introduction lines listed above, then transition to why listening to you will matter to them. For example, if you’re talking about mental health and depression, you can follow up a surprising statistic with something like, “I know because I was a part of that statistic. Now, I’ve studied to become a therapist myself.”
To further create an air of authority, you must be mindful of your body language (taking a deep breath before speaking can help you shake off your nervousness and tension). Additionally, you must make eye contact and speak words clearly.
How Do You Introduce A Speaker?
Now, if you’re tasked to introduce the one who will deliver the speech, it’s your responsibility to set the right atmosphere and build excitement.
One of the first things to do is know how to pronounce the speaker’s name and ensure that what you’ll say about the speaker’s credibility is factual. Since you’re only introducing the speaker, keep things simple and concise. If you want to enrich your introduction, you can ask the speaker what they want to be highlighted (Do they have a new book? Which prestigious groups are they affiliated with?).
Like what the speaker would do, you must also make eye contact to engage the audience. Practice and have a run-through before you take the stage to guarantee a smooth delivery.

What Is An Example Of A Speech Introduction?
Speakers and speech writers know how challenging it is to grab an audience’s attention. Here’s a good example of an introductory speech that uses statistics. This is from English restaurateur Jamie Oliver who delivered a TED Talk about food:
“Sadly, in the next 18 minutes when I do our chat, four Americans that are alive will be dead from the food that they eat.
My name’s Jamie Oliver. I’m 34 years old. I’m from Essex in England, and for the last seven years, I’ve worked fairly tirelessly to save lives in my own way. I’m not a doctor; I’m a chef, I don’t have expensive equipment or medicine. I use information, education.”
What Is The Introduction For A Speech On Bully
Looking for inspiration for a good introduction where your topic is bullying? Check out this sample intro from actress and UNICEF Goodwill Ambassador Millie Bobby Brown during World Children’s Day in 2019:
“In world capitals — in buildings like this — adults talk about children’s rights. But today, young people don’t want to be talked about. They want to do the talking.
Millions of people responded to UNICEF surveys and petitions about what the Convention on the Rights of the Child meant to them. In the words of one young person: ‘Be an active voice. Don’t let things go unnoticed. So today, I want to talk about an issue that is very personal to me. Something that so often goes unnoticed — but causes real suffering. Bullying.”
What Are Some Other Examples Of Speech Introductions?
Below are some more speech introduction examples you can take inspiration from.
- “Three things I learned while my plane crashed” by Ric Elias : “Imagine a big explosion as you climb through 3,000 ft. Imagine a plane full of smoke. Imagine an engine going clack, clack, clack, clack, clack, clack, clack. It sounds scary. Well, I had a unique seat that day. I was sitting in 1D.”
- “How to find and do work you love” by Scott Dinsmore : “8 years ago, I got the worst career advice of my life.”
“How great leaders inspire action” by Simon Sinek : “How do you explain when things don’t go as we assume? Or better, how do you explain when others are able to achieve things that seem to defy all of the assumptions?”
Recent Posts
Active Listening Absorbs The Whole Message, Not Just The Words
Active listening goes beyond hearing the words someone is saying to you and understanding the message they are conveying. Many only hear a small percentage of what is being said as they are...
Counteracting Fear Of Public Speaking With Coaching And Therapy
Nearly 75% of people experience the social phobia of fear of public speaking. The result may be nervousness before speaking or a full-blown panic attack. Practicing public speaking may lessen the...
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
How to End a Speech of Introduction
Public speaking can be challenging, especially when at an important event. Speaking in front of an audience can be even more difficult when introducing an important or notable guest. Guest speakers often bring some sort of expertise or unique perspective on a topic. Introductory speeches are your opportunity to build excitement for the speaker and provide the audience with background information. To properly conclude an introductory speech, give the speaker’s name and title.
Give an overview of the speaker’s achievements and accolades. Describe the speaker’s expertise in his subject. For example, say, "I now want to introduce you to award-winning environmentalist John Smith, who has written more than 10 books on green energy in California."
Present a summary of what the guest will discuss. For example, you might say, “I would now like to introduce the intelligible Nancy Green, who will present on how upcoming policy changes will affect green energy and what we can do to address these changes.”
Give the reason the organization selected the speaker. Say, for example, “I would like to introduce Bryan Frazier, who is an expert in all areas of the field and we are thankful he is here to share his knowledge this evening.”
State the speaker's title. “I now introduce to you Karen Smith, environmental activist and professor of urban planning at UCLA.”
- Speech Topics Help: Introductory Speeches
Christina Whitaker began her writing career in 2005 in newspaper journalism. She holds a Bachelor of Arts in English from UCLA and a law degree. Her legal experience includes work in Federal Court, and civil and criminal litigation. She also maintains a blog on social, pop-culture and cultural matters.
Self Introduction Speech – How To Write With Examples
First impressions are very important. Whether it is at school, work, or organization, your introduction is an audience’s first real chance to know you. It will have a huge impact on how they perceive you.
But the good news is: You get to control that narrative.
The key to a good self-introduction speech is balance. You want to present your accomplishments but without coming off as bragging. Typically, this type of speech is known as an “icebreaker” as it aims to break the ice and let others know you. This is your chance to establish good credibility.
Fear not! We will help you craft the best introduction speech with our outline, tips, as well as self-introduction speech samples.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Self-introduction Speech Outline
Sample introduction speech topics, sample self introduction speech objectives, write the outline, including hobbies and interests, sell yourself, use short, simple sentences..
What exactly do you need to cover in your introduction speech? You might choose to include a wide variety of information but there are some things you should not miss. Some of them are as follows:
- What is your name?
- Where are you from?
- What are some of your main interests and hobbies?
- What has been your passion in life?
- Who has been your role model?
- Any fun facts that make you stand out.
- Your credibility or job title.
Tip: If possible you should definitely include a visual aid in the form of pictures to compliment your speech. Pictures of you, your travels, family, or pets are always endearing!

Writing a self-introduction speech always seems easy at first. Besides, you definitely know yourself the best. However, once you begin writing you can find yourself getting lost. What do you want to include in this speech? So, grab a pen and scan through the topics in the list below. Circle any of the ones that speak to you so that you have a better grasp of what direction you’d like to take with your speech.
- What event has played an important part in shaping your life? Tell the story and the lesson you’ve learned.
- What is your goal in life?
- Where are you from? Is there anything about your culture or traditions that you’d like to share?
- How do you like to spend your time?
- What are some of your pet peeves?
- Do you have any special skills that you’re proud of?
- What does a day in your shoes feel like?
- What have been some of the most important milestones in your life?
- Have there been any difficult times that guided your life?
- What is a topic you could talk about for hours?
- What is an object that is dearest to you?
- What quirks make you the individual you are?
Now that you have an idea on how to draft your outline, here are some objectives for you to tick off.
- First off, grab their attention. Just because it is your introduction does not mean that your opening has to be plain. Find something catchy and concise.
- Start with some background. Set up the stage and introduce who you are. Try to present it in chronological order.
- Build a story. The speech is about you but make sure you build a relatable story to keep the audience’s attention.
- Show, don’t tell. Instead of saying how reliable you are, tell a story that shows it.
- For conclusion, try to leave your audience with a takeaway. Whether from your experiences or from a relatable standpoint. Either that or you can build the story leading up to who you are right now and leave the stage on an inspirational note.
How to write a self-introduction speech?
Are you ready to write your self-introduction speech? We’ve got just the steps for you:
The outline of your speech is simply a skeletal draft of your speech. It can initially simply take the form of bullet points. What matters is you figure out what elements are going into the speech. Similarly, figure out what order you will be presenting these elements. Typically icebreakers follow a chronological order so that you can build up to the current you.
It is common to start with your roots. Pick out some childhood traits that are relatable or that make you stand out. You can build on this with stories, talk about your education, and go on to talk about how you got to where you are currently.
If you are introducing yourself in a work setting, make sure you link your interest to your ambition. It will project you in a good light to your superiors and will also make your hobbies a lot more relevant. This is also a great idea to keep your speech concise and to the point. From a professional standpoint, you should follow your hobbies with the steps you are taking to reach the goal. For example, “I’ve always been into sketching, but now I’m taking illustrator courses to put my designing skills to use.”
Your hobbies are a great insight into who you are in your free time. If you’re into a particular niche hobby like bird-watching or pottery, you might even end up finding others in the crowd with similar interests. Similarly, it is a great way to gain credibility on a certain subject.
When people talk about their passion, there is a certain twinkle in their eyes. This is such an endearing quality that is sure to get your audience to respond. Try to give a short insight into you pursuing the hobby or how you came about to discover it in the first place. It is much more effective than simply listing out your interests. Talk about what aspects of the hobby draw you to it. It can help the audience get the bigger picture in getting to know you.
If the icebreaker is being delivered in a much more formal setting, you might want to focus more on your personal skills than your hobbies. The audience there might be more interested in your soft skills than your love of photography.
It might help to list out all your hobbies, interests, and skills along with why you are drawn to those interests. It can help you draw a parallel between them and deliver a much more well-rounded speech.
Knowing a person is an endless process. We’re sure you must have gone through your own journey with highs, lows, milestones and learnings that could be their own feature movies. It can be difficult to decide what exactly gets to make it to the speech when all of it made you who you are. But the longer you pad your introduction, the less are the chances of people actually listening to it.
This is why your self-introduction speech needs to spend a good amount of time on the cutting floor as well. Assess your audience and try to think of it from their perspective. What is relevant? Also, think of the location and if your stories are appropriate for the setting. Make sure you respect the time by picking only the most relevant information and keeping it short.
Even if your usual style is something like self-deprecating humor, for this occasion try to present yourself in a much more positive light. You want to project confidence. This is the impression that most of these people are likely to remember, so make it a good one. Pick your traits and stories well.
A self-introduction speech is almost always a great floor to pitch yourself. When else will you get this open invitation to present yourself to potential clients? Remember, the aim is to boost yourself and not boast about yourself. If you talk too much about what you can do and have done, it is easy to sound pompous and turn people off.
Try to stick to the truth. Instead of listing accomplishments by the dozens, talk about a passion you had and how you turned it into an accomplishment. Stay humble when speaking of future aspirations. And most of all, be grateful. Show appreciation to the people who have helped you so far.
How you sell yourself is not just dependent on the words you speak but also on your delivery. All the words in the world won’t be able to make up for a meek delivery. So make sure you write from your heart as that will be the easiest to deliver. Work on your build-up so that the ending is satisfying. Don’t just give an account for accomplishments by the year. For example: talk about how curious you were about animals from early on, how you got into photography because it lets you keep a moment with you forever, and eventually you got into animal photography. This way, it feels like a complete story.
In a more professional setting, you’d say, “As a freelance photographer, I used my marketing background to promote myself and stayed active in networking. I learned that creativity is wonderful but paired with due diligence, it can get you to much greater heights.” It showcases your skills, your traits, as well as shows you as an individual that is constantly reflecting, learning, and growing. This is the sweet spot you are aiming for.
While we’ve stressed the importance of relatability and humility, it is also important to create your own place on stage. You cannot be yet another person with only music and travel as their interests. Think of things that make you unique.
Put your humble hat aside for a bit. If you’ve assisted in making a big project happen, mention it. Talk about how you’ve led a team through a crisis. Discuss your learning experiences. Present a before and after of a milestone to show how much a role has impacted who you are today. Even if the project wasn’t successful, you can talk about how you’d approach it differently in the present day.
Even for relatively common interests like travel, you can pick unique memories and what aspects of travel have changed you for the better. Take every opportunity to spin a story to showcase a trait or talent. Think of the unique things that make you, you.
It can be easy to get lost in your stories. Try not to ramble too much and stick to the point. When writing your script, use varied sentence structures to keep things interesting. It will help if you read it out loud or record yourself so you can track how you’re doing. Try not to use too much jargon. Keep it simple and clear.
- Personal Development
- Sales Training
- Business Training
- Time Management
- Leadership Training
- Book Writing
- Public Speaking
- Live Speaker Training With Brian
- See Brian Speak
- Coaching Programs
- Become a Coach
- Personal Success
- Sales Success
- Business Success
- Leadership Success
15 Ways to Start a Speech + Bonus Tips
You have heard the saying “First impressions are lasting; you never get a second chance to create a good first impression.”
The same is true when talking about how to start a speech…
The truth is, when you start your speech, you must focus everything on making a positive first impression on your audience members (especially if you are doing the presentation virtually ). The introduction is basically the formal greetings for speeches, so let’s be sure to get this right to really hook the audience.
Here are 15 different ways to start a speech as well as 2 extra BONUS tips at the end.
1) Thank the Organizers and Audience
You can start by thanking the audience for coming and thanking the organization for inviting you to speak.
Refer to the person who introduced you or to one or more of the senior people in the organization in the audience.
This compliments them, makes them feel proud and happy about your presence, and connects you to the audience like an electrical plug in a socket.
2) Start With a Positive Statement
A presentation tip at the start is to tell the audience members how much they will like and enjoy what you have to say.
For example, you might say:
“You’re really going to enjoy the time we spend together this evening. I’m going to share with you some of the most important ideas that have ever been discovered in this area.”
Remember that speaking is an art, so be an artist and take complete control of your performance,
3) Compliment the Audience
You can begin by complimenting the audience members sincerely and with great respect.
Smile as if you are really glad to see them as if they are all old friends of yours that you have not seen for quite a while.
You can tell them that it is a great honor for you to be here, that they are some of the most important people in this business or industry, and that you are looking forward to sharing some key ideas with them.
You could say something like:
“It is an honor to be here with you today. You are the elite, the top 10 percent of people in this industry. Only the very best people in any field will take the time and make the sacrifice to come so far for a conference like this.”
4) Start Your Speech By Referring to Current Events
Use a current event front-page news story to transition into your subject and to illustrate or prove your point. You can bring a copy of the newspaper and hold it up as you refer to it in your introduction.
This visual image of you holding the paper and reciting or reading a key point rivets the audience’s attention and causes people to lean forward to hear what you have to say.
5) Refer to a Historical Event
For many years, I studied military history…
Especially the lives and campaigns of the great generals and the decisive battles they won. One of my favorites was Alexander the Great.
One day, I was asked to give a talk on leadership principles to a roomful of managers for a Fortune 500 company.
I decided that the campaign of Alexander the Great against Darius of Persia would make an excellent story that would illustrate the leadership qualities of one of the great commanders in history.
I opened my talk with these words:
“Once upon a time there was a young man named Alex who grew up in a poor country. But Alex was a little bit ambitious. From an early age, he decided that he wanted to conquer the entire known world. But there was a small problem. Most of the known world was under the control of a huge multinational called the Persian Empire, headed by King Darius II. To fulfill his ambition, Alex was going to have to take the market share away from the market leader, who was very determined to hold on to it.
This is the same situation that exists between you and your major competitors in the market today. You are going to have to use all your leadership skills to win the great marketing battles of the future.”
6) Refer to a Well Known Person
You can start by quoting a well-known person or publication that recently made an important statement.
One of the subjects I touch upon regularly is the importance of continual personal development.
I will say something like:
“In the twenty-first century, knowledge and know-how are the keys to success. As basketball coach Pat Riley said, ‘If you are not getting better, you are getting worse.’”
7) Refer to a Recent Conversation
Start by telling a story about a recent conversation with someone in attendance.
For instance, I might say:
“A few minutes ago, I was talking with Tom Robinson in the lobby. He told me that this is one of the very best times to be working in this industry, and I agree.”
8) Make a Shocking Statement
You can start your talk by making a shocking statement of some kind.
For example, you might say something like:
“According to a recent study, there will be more change, more competition, and more opportunities in this industry in the next year than ever before. And 72 percent of the people in this room will be doing something different within two years if they do not rapidly adapt top these changes.”
Click here If you want to learn more techniques to wow your audience.
9) Quote From Recent Research
You can start by quoting a recent research report.
One example is:
“According to a story in a recent issue of Businessweek, there were almost 11 million millionaires in America in 2018, most of them self-made.”
10) Start Your Speech By Giving Them Hope
The French philosopher Gustav Le Bon once wrote, “The only religion of mankind is, and always has been hope.”
When you speak effectively, you give people hope of some kind.
Remember, the ultimate purpose of speaking is to inspire people to do things that they would not have done in the absence of your comments.
Everything you say should relate to the actions you want people to take and the reasons that they should take those actions.
11) Be Entertaining
Bill Gove used to walk onto the stage after his introduction if he had just finished talking to someone on the side and was breaking off to give his talk to the group.
The audience got the feeling that his entire talk was one continuous conversation, devoid of meaningless filler words .
Bill would often go to the edge of the stage and then drop his voice in a conspiratorial way, open his arms, and beckon the audience members to come a little closer.
He would say, “Come here, let me tell you something,” and then he would wave them forward as though he was about to tell a secret to the entire room.
The amazing thing was that everyone in the room would lean forward to hear this “secret” that he was about to share. People would all suddenly realize what they were doing and break out in laughter. It was a wonderful device to get the audience into the palm of his hands.
12) Ask a Question
You can open by making a positive statement and then ask a question requiring a show of hands.
Try something like this:
“This is a great time to be alive and in business in America. By the way how many people here are self-employed?”
Raise your hand to indicate what you want people to do. I have used this line, and after a number of hands go up, I then say to someone who raised their hand in the front, “How many people here are really self-employed?”
Invariably, someone will say, “We all are!”
I then compliment and affirm the answer: “You’re right! We are all self-employed, from the time we take our first jobs to the day that we retire; we all work for ourselves, no matter who signs our paychecks.”
13) Open With a Problem
You can start with a problem that must be solved. If it is a problem that almost everyone has in common, you will immediately have the audience’s complete and undivided attention.
For example, you could say:
“Fully 63 percent of baby boomers are moving toward retirement without enough money put aside to provide for themselves for as long as they are going to live. We must address this problem and take action immediately to ensure that each person who retires will be able to live comfortably for the rest of his or her natural life.”
14) Make a Strong Statement, Then Ask a Question
You can start by making a strong statement and then ask a question. You then follow with an answer and ask another question. This gets people immediately involved and listening to your every word.
Here’s an example:
“Twenty percent of the people in our society make 80 percent of the money. Are you a member of the top 20 percent? If not, would you like to join the top 20 percent or even the top 10 percent? Well, in the next few minutes, I am going to give you some ideas to help you become some of the highest-paid people in our society. Would that be a good goal for our time together today?”
15) Tell a Story
You can start your talk with a story. Some of the most powerful words grab the complete attention of the audience are, “Once upon a time…”
From infancy and early childhood, people love stories of any kind. When you start off with the words, “Once upon a time…” you tell the audience that a story is coming. People immediately settle down, become quiet, and lean forward like kids around a campfire.
When I conduct full-day seminars and I want to bring people back to their seats after a break, I will say loudly, “Once upon a time there was a man, right here in this city…”
As soon as I say these words, people hurry back to their seats and begin to listen attentively to the rest of the story.
The story technique is very effective.
In fact, its probably one of the best public speaking tips I’ve learned to this day.
Bonus Tip: Tell Them About Yourself
Very often, I will start a speech to a business, sales, or entrepreneurial group by saying:
“I started off without graduating from high school. My family had no money. Everything I accomplished in life I had to do on my own with very little help from anyone else.”
It is amazing how many people come up to me after a talk that began with those words and tells me that was their experience as well.
They tell me that they could immediately identify with me because they too had started with poor grades and limited funds, as most people do. As a result, they were open to the rest of my talk, even a full-day seminar, and felt that everything I said was more valid and authentic than if I had been a person who started off with a successful background.
Building a bridge like this is very helpful in bringing the audience onto your side.
Bonus Tip: Get Them Talking to One Another
You can ask people to turn to the person next to them to discuss a particular point.
For instance, you could say:
“Tell the person next to you what you would like to learn from this seminar.”
Whatever you ask your audience members to do, within reason, they will do it for you. Your commands and your thought leadership will easily influence them, as long as you ask them with confidence.
By following any one of these tips for starting your speech, you are sure to grab your audience’s attention every time. How do you start a speech? Let me know in the comments.
« Previous Post 9 Tips to End a Speech With a Bang Next Post » 15 Ways to Overcome Your Fears of Writing a Book
About Brian Tracy — Brian is recognized as the top sales training and personal success authority in the world today. He has authored more than 60 books and has produced more than 500 audio and video learning programs on sales, management, business success and personal development, including worldwide bestseller The Psychology of Achievement. Brian's goal is to help you achieve your personal and business goals faster and easier than you ever imagined. You can follow him on Twitter , Facebook , Pinterest , Linkedin and Youtube .
- Most Recent
- The Art of Business Success: A Blueprint for Entrepreneurs
- How to Develop a Habit That Will Last
- How to Write an Author Bio (Examples Included)
- Personal Development Plan Templates for Success
- How to Sell and Become a Master Salesperson
- Free Webinar: How To Write a Book and Become a Published Author
- Free Video Series: 3-Part Sales Mastery Training Series
- Free Assessment: The Confidence Factor
- Free Assessment: Discovering Your Talents
Browse Categories
- Financial Success
Follow Brian & Join the Discussion
- Free Resources
- Best Sellers
- Knowledge Base
- Shipping & Returns
- Privacy Policy
- About Brian
- Brian Recommends
Your Privacy is Guaranteed. We will never give, lease or sell your personal information. Period!
© Copyright 2001-2024 Brian Tracy International. All Rights Reserved.

Chapter 11: Introductions, Conclusions, and Transitions
Ada agreed to listen to the presentation her roommate is preparing for an Ancient History class. The topic is on the history of storytelling. Ada likes all kinds of books and stories. She enjoys reading novels and watching movies, and she knows her roommate spent a lot of time researching and writing this presentation, so she is happy to listen. Her roommate begins by providing a list of ten particularly ancient stories and telling how old each of them is and where it was written. Near the end of the list, when her roommate mentions how old The Odyssey is, Ada is reminded that she has a book report due in her own history class. As her roommate mentions that we still like stories today, Ada remembers that one of her favorite books is being released as a movie this weekend. She is hoping to go see it in the theater with a couple of friends who also liked the book. She should probably message them to figure out a good time. Right then, she feels her phone buzz in her bag. She does not want to be rude to her roommate, so she ignores it. But it keeps buzzing, and she finds herself wondering if that is one of the friends she is hoping will go to the movie with her. She starts mentally writing the message she will send once she is done listening to her roommate. And then Ada notices the silence; her roommate had reached the end of her presentation. “So,” her roommate asks, “do you think it is good?”
Have you ever tried to focus on something, only to realize that your attention had drifted? Take a moment to consider how many demands you have on your attention at any moment. You might be thinking about an upcoming exam, preparing for a challenging conversation at work, figuring out plans for tonight. Perhaps you are feeling hungry or tired. And you likely have a phone in reach that allows you to be constantly communicating with friends and family or getting updates on a topic that interests you. Even when you are trying to focus, it may be buzzing in your pocket or bag to let you know that there is something else that demands your attention. All of this is true for most of the people around you, as well. We live in a world with an immense number of distractions, and our attention is a limited resource.
This is important to remember when crafting a presentation, and it is why the introduction of any presentation is the most important part: A good opening captures the attention of listeners and makes them want to listen to the rest. It connects them to the topic and helps your audience understand why the topic matters to them. No matter how insightful, persuasive, or well-crafted the body of a presentation is, it cannot accomplish its purpose if the intended audience has already tuned it out and shifted their attention elsewhere. Think about the opening example. This is what happens when a speech begins with a poor introduction. Even a committed audience member who is interested in your topic might have a lot of other things competing for their attention. Would opening with a long list cut through those distractions? Unlikely. Would a generic connection to the topic, such as “everyone likes stories,” hold their interest? Probably not. And, if you start with a weak introduction that loses your audience’s attention at the start, it is very difficult to get it back.
Beyond gaining your audience’s attention, a well-designed introduction also provides an opportunity to set your audience’s expectations. If you have ever listened to a presentation that you thought would teach you about a topic that you were really interested in, only to have that topic never come up, you know the importance of setting audience expectations. You probably left that presentation disappointed. Even if the content of the presentation was well-researched and well-delivered, if you had been led to expect something else, you likely felt let-down because it failed to align with your expectations. Overall, the goal of an introduction is to create a desire in your audience to hear what you have to say. You can then end your speech with a conclusion that helps your audience see how you have met those expectations and remember what is most important from your presentation.
This chapter will teach you how to write good introductions and conclusions.
Introductions
So what makes for a good introduction? A good introduction should typically accomplish each of the following tasks: 1) Capture an audience’s attention, 2) Demonstrate the relevance of the presentation to the specific audience, 3) Establish the credibility of the speaker, 4) Clearly articulate the thesis of the presentation, 5) Provide a preview of the main points of the presentation. There are a variety of ways to accomplish each of these tasks, and the following section provides guidance on how to effectively accomplish each.
Attention Getter
The role of an attention getter is just what it sounds like—getting the audience to pay attention to what you are saying and interested in hearing more. There are many ways to accomplish this. You might ask a question. You might start with a statistic. You might tell a very brief story to get your audience invested. You might open with a famous quotation that connects to your speech in some important way. Whatever you choose to do, the first sentence of your presentation is incredibly important. Consider the following two attention getters:
Option 1: Sixty-three percent of college students report feeling stress about the transition to college. Option 2: People consistently rank public speaking ahead of death in terms of what they most fear.
Both of these technically meet the expectations described above, but the second is much stronger. Why? Because you probably already knew that transitioning to college is stressful. But learning that people are more afraid of public speaking than death surprises most people. In the context of a class that is going to ask everyone in the room to engage in public speaking, this surprising fact makes a good attention getter.
Relevance Statement
A Relevance Statement answers the question: Why should I care about this topic? If an Attention Getter is aimed at getting an audience member to briefly stop thinking about other things and momentarily give you their attention, a relevance statement is aimed at convincing audience members to listen to the rest of the presentation. A relevance statement should tell audience members why the topic of your presentation is important to them. A good relevance statement will make the connection between the topic and the audience as specific and personal as possible. Consider the following two relevance statements:
Option 1: Everyone experiences stress, and meditation can help reduce it. Option 2: We are all in a class that requires public speaking, which means each one of us will experience the stress of standing in front of a crowd and speaking. Meditation offers an effective way to manage that stress, on a budget any college student can afford.
What makes Option 2 the stronger relevance statement? It offers specific connections to the experience of the audience. In contrast to Option 1, which makes a more general connection to stress being a human experience, Option 2 connects the presentation to the specific activity—public speaking— that everyone in the class is engaging in. It also notes the financial limitations facing many college students, which makes low-cost solutions like meditation particularly relevant.
Credibility Statement
A Credibility Statement answers the question: Why should I listen to this person? The internet gives us access to lots of people venting their thoughts on virtually every topic imaginable; why should audience members trust you? A credibility statement is a chance to explain to your audience why your knowledge of and connection to a topic makes you a reliable source of information. In professional settings, you will likely be called upon to speak about topics on which you are professionally knowledgeable. You may be able to point to years of professional experience to establish your expertise. This is not always the case in college. You may be giving a speech on a topic that you just started researching within a few weeks of the presentation. In situations where you lack formal expertise, training, or experience on a topic, establishing a personal connection to the topic can help establish your credibility. Compare the following two relevance statements:
Option 1: I have been researching meditation for two weeks. Option 2: As someone who personally experiences anxiety when giving speeches, I have been researching meditation for this assignment, and I have already started using what I’ve learned to help me feel more comfortable and confident when speaking.
Option 2 is clearly stronger here. Why? The speaker has just started learning about the topic and has very little expertise. Both of these credibility statements clearly acknowledge this limitation. But Option 2 demonstrates the speaker has a real connection to the topic. They become more credible because they likely share a challenging experience with the audience (anxiety when giving speeches), and have learned enough about meditation to have a solution that is effective in addressing that problem.
Thesis Statement
A Thesis Statement answers the question: What is the central point of this presentation? A thesis statement condenses the main point/argument of your presentation into a single sentence. The rest of the presentation is aimed at supporting or accomplishing your thesis statement. For an informative presentation, a thesis statement will provide a specific articulation of what the audience will learn. For a persuasive presentation, a thesis will provide a specific articulation of what should be done in response to the presentation. Compare the following two thesis statements:
Option 1: My presentation will teach you about meditation. Option 2: Meditation offers an effective tool to manage stress and increase happiness that you can start using today.
What makes Option 2 better? Both are accurate, but Option 2 is much more specific. Because of this, it provides the listener a clearer understanding of what will be covered in the presentation.
Preview Statement
A Preview Statement answers the question: What are the main parts of this presentation? By telling audience members what the main parts of the presentation will be, it offers a roadmap of sorts. If the thesis tells audience members where the presentation is going, a preview statement tells them how it is going to get there. As we will cover later in this chapter, most presentations for a class will have 2-4 main points. A preview statement simply tells the audience what those points are and in what order they will be discussed. This helps audience members understand how your ideas fit together. Although it is possible to be creative with how you word a preview statement, it is usually best to be simple and clear. Consider the following preview statement:
My presentation today will describe what meditation is, how it affects the brain, and some simple meditation practices that anyone can use to improve their lives in a variety of ways.
Now, let’s combine the previous examples to see the introductions created by each. Our option 1 examples lead to the following introduction:
Sixty-three percent of college students report feeling stress about the transition to college. Everyone experiences stress, and meditation can help reduce it. I have been researching meditation for two weeks. My presentation will teach you about meditation. My presentation today will describe what meditation is, how it affects the brain, and some simple meditation practices that anyone can use to improve their lives in a variety of ways.
This introduction has all of the essential elements. But because it is too general and lacks any specific connection to the audience or speaker, it is unlikely to draw and hold the attention of audience members. Compare that to the introduction created from our option 2 examples:
People consistently rank public speaking ahead of death in terms of what they most fear. We are all in a class that requires public speaking, which means each one of us will experience the stress of standing in front of a crowd and speaking. Meditation offers an effective way to manage that stress, on a budget any student can afford. As someone who personally experiences anxiety when giving speeches, I have been researching meditation for this assignment, and I have already started using what I’ve learned to help me feel more comfortable and confident when speaking. Meditation offers an effective tool to manage stress and increase happiness that you can start using today. My presentation today will describe what meditation is, how it affects the brain, and some simple meditation practices that anyone can use to improve their lives in a variety of ways.
This introduction is far stronger It is constructed of the same parts as the previous introduction. However, because those parts are much better– the opening statistic is striking, there is a direct connection to the experiences of the specific audience, and it provides a clear articulation of what the audience will learn from the speech—they make for a much more engaging introduction. You will find that an introduction that does each of these five parts well is effective in almost any speaking situation.
Conclusions
Just as you should have a thoughtful and well-constructed introduction to start any presentation, you should also carefully construct the conclusion of your presentation. You have probably heard speeches in past classes or other settings in which the speaker ends abruptly by saying something like “that’s all” or “thank you.” You may have even experienced the awkward silence if a speaker simply stopped talking as they reach the end of their material, but the audience was unsure if the speaker was finished. An effective conclusion prepares an audience for the end of the presentation and takes advantage of the recency effect by ensuring the final moments of the speech review key information.
In many ways, effective conclusions mirror effective introductions. A conclusion should have the following parts: a review statement, a restatement of relevance, a restatement of the thesis, and a strong close. The first three can be taken, with minor modifications, from the introduction.
Review Statement
A Review Statement quickly reminds the audience of the main points covered in the speech. This serves two purposes: first, it gives the audience one more overview to see how the main ideas connect. Second, it provides a clear transition into the conclusion. When your audience hears you transition from the final point of your presentation to reviewing your main points, it cues them that the presentation is nearing its end. Based on the introduction we just created, you might modify the preview statement to create a review statement such as:
Today I discussed what meditation is, how it affects the brain, and some simple practices that anyone can use to reduce their own stress.
Restate Relevance
Your conclusion should restate relevance to provide a final reminder of the connection between this topic and your specific audience members. Hopefully your audience will already be convinced of the importance of your topic by the time you reach your conclusion. However, given that we are constantly competing for audience attention and interest, it is worth providing a final reminder of why your topic matters to your audience. For the speech we just created, you might say:
As we all deal with the stresses of having to give speeches, and of being college students, meditation is one way to reduce stress that we can all afford.
Restate Credibility (optional)
Hopefully, by the time you reach the end of your speech, your credibility on the topic will be clear. You can decide if you wish to take the time to remind the audience of your credibility based on how important them remembering that is to the goal of the speech. If your goal is to establish the importance of some problem so that your audience will hire you to solve it (imagine an entrepreneur pitching their service to a potential client), reminding them why they can trust you is a good idea. If your own expertise in the topic is not a key takeaway for your audience (such as you informing your class about the benefits of meditation), you do not need to include it in your conclusion.
Restate Thesis
Once you have reviewed your points and the relevance of your topic, it is time to restate your thesis and close the speech. A well-written thesis statement typically requires little revision from the introduction to the conclusion. In this case, the same exact sentence works nicely:
Meditation offers an effective tool to manage stress and increase happiness that you can start using today.
Strong Close
A Strong Close is a last sentence or sentences that alert your audience that the presentation is over and conclude it in a powerful way. As we mentioned, you have probably seen presentations with abrupt endings that leave the audience unsure if the presentation is over. This is easy to avoid if you carefully plan your final sentences. As with attention getters, there are many ways to craft a strong close to your presentation. In fact, linking your attention getter and conclusion is often an excellent way to craft a strong close. If you opened with a quotation or statistic, you might make a reference back to it. If you opened with a story, briefly return to that story in a way that ties your presentation together.
Sometimes a return to the attention getter may not work well or feel natural in a speech. In such situations, there are other ways to conclude. If you are advocating for your audience to act in a certain way, you might close with a call to action. For example, in a TEDx presentation challenging societal beauty norms, Melissa Butler (2017) closes with “So I challenge each of you: when you go home today, look at yourself in the mirror. See all of you. Look at all of your greatness that you embody. Accept it and love it. And finally, when you leave the house tomorrow, try to extend that same love and acceptance to someone who doesn’t look like you.” This strong close emphasizes the central ideas of the presentation and provides the audience with one final, memorable, call to action.
If your presentation does not lend itself to a powerful call to action, you might simply close with a provocative question that leaves your audience with something to think about. For example, in a fascinating Ted Talk about the power of language in shaping our thoughts, Cognitive Scientist Lera Boroditsky (2017) concludes, “I want to leave you with this final thought. I’ve told you about how speakers of different languages think differently, but of course that’s not about how people elsewhere think. It’s about how you think. It’s how the language that you speak shapes how you think. And that gives you the opportunity to ask yourself: Why do I think the way that I do? How could I think differently? And, also, what thoughts do I wish to create?” This strong close reconnects the topic and the audience. It reminds them that the presentation was not just scientific data on language, but rather an invitation for each listener to reflect more fully on their own words and thoughts.
Because our speech on meditation opened with particularly striking fact, it would make sense to return to it when closing the speech:
While the majority of people fear public speaking more than death, you don’t have to. You will be able to calmly and confidently speak in any situation now that you know what to do: meditate.
Combined, these elements lead to a strong conclusion to the speech:
Today I discussed what meditation is, how it affects the brain, and some simple practices that anyone can use to reduce their own stress. As we all deal with the stresses of having to give speeches, and of being college students, meditation is one way to reduce stress that we can all afford. Meditation offers an effective tool to manage stress and increase happiness that you can start using today. While the majority of people fear public speaking more than death, you don’t have to. You will be able to calmly and confidently speak in any situation now that you know what to do: meditate.
This chapter provides you the information you need to write effective introductions and conclusions. These parts of introductions and conclusions are applicable in most speaking situations, ranging from your in-class speeches to most professional presentations you may be asked to give. They also work for many types of writing. If you can get your audience’s attention, convince them of why the topic is important to them and why they should listen to you, and provide a clear thesis and preview your speech, you will have gone a long way toward getting your audience to listen. By briefly revisiting those elements in the conclusion, you help your audience remember the key ideas of your speech. The start and end of your speech are the parts your audience will remember most; make them count!
Works Cited
Boroditsky, L. (2017). How language shapes the way we think. TedWomen Conference https://www.ted.com/talks/lera_boroditsky_how_language_shapes_the_way_we_think
Butler, M. (2017). Why you think you’re ugly [Video]. TEDxDetroit Conference. https://www.ted.com/talks/melissa_butler_why_you_think_you_re_ugly
Communication for College, Career, and Civic Life Copyright © by Ryan McGeough; C. Kyle Rudick; Danielle Dick McGeough; and Kathryn B. Golsan is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Home » College Of William & Mary » How Do I End My Self Introduction?
How Do I End My Self Introduction?
Table of Contents
Keep your introduction short and conclude it by leading into what you’d like to happen next . For a presentation, you would summarize what you plan to discuss. In an interview, mention why you’re the best person for the job.
How do you end an introduction?
Therefore, ending your introductory paragraph means providing the thesis of your paper.
- Write exactly what you will argue for in the main body paragraphs.
- Link the thesis statement to the contents of introductory paragraph; do not just present your statement out of the blue.
How do you end a self-introduction speech?
The conclusion of a self-introduction speech should reiterate and summarize the most important parts of your speech, the main details about yourself that you shared .
How do I end my self?
How to Answer “Tell Me About Yourself” in an Interview:
- Choose the Right Starting Point for Your Story (IMPORTANT)
- Highlight Impressive Experience and Accomplishments.
- Conclude by Explaining Your Current Situation.
- Keep Your Answer Work-Related.
- Be Concise When Answering (2 Minutes or Less!)
How do I start and end my self-introduction?
Just sit back and note down the following pointers on how to ace self-introduction.
- Dress Appropriately.
- Prepare what to say.
- Begin by Greeting the Interviewer.
- Include your Educational Qualifications.
- Elaborate on Professional Experience (if any)
- Mention your Hobbies and Interests.
- Be Prepared for Follow Up Questions.
What should the last sentence of an introduction be?
The thesis The thesis is usually the last sentence of your intro paragraph. Whether it’s making a claim, outlining key points, or stating a hypothesis, your thesis statement will tell your reader exactly what idea(s) are going to be addressed in your essay.
How do you end an essay about yourself?
To end an essay, start your conclusion with a phrase that makes it clear your essay is coming to a close, like “In summary,” or “All things considered.” Then, use a few sentences to briefly summarize the main points of your essay by rephrasing the topic sentences of your body paragraphs.
What to say to end a speech?
As you approach the end of your talk, say something like, “ Let me briefly restate these main points …” You then list your key points, one by one, and repeat them to the audience, showing how each of them links to the other points. Audiences appreciate a linear repetition of what they have just heard.
What to say in a closing remarks?
Here are some dos which will help the speaker in concluding his speech.
- Indicate that the speech is close to the end.
- Give a rundown of your speech/presentation.
- Make eye-contact.
- Don’t make the closing remarks lengthy.
- Don’t end with a simple ‘Thank You”
- Don’t add new material out of no where.
- The fitting remark.
How do you conclude a speech?
Summarize the main points you made throughout the speech . If the introduction tells the audience what they will learn, and the body tells the audience the content they should be learning, the conclusion should repeat those main ideas one final time. Use the chance to repeat your thesis a final time, if necessary.
How do I tell about myself?
Every good answer to “tell me about yourself” should consist of: Work – This should make up about 80% of your answer. Focus on your previous experience and accomplishments here. Academic – 10-15% of your answer should then be about your academic background (university, academic achievements, etc.).
What to say in introduce yourself?
Here are some examples:
- Morning! I don’t think we’ve met before, I’m Aryan.
- Hey there! I’m Surya. I’m new—I just moved to the building a couple of days ago.
- Hi Amy. I heard it’s your first day so I thought I could reach out and introduce myself. We haven’t officially met but I’ll be working with you on this project.
How do I write about me?
Tips for writing an “about me” resume section
- Be brief. It is important to make sure you are not rambling in your “about me” section.
- Be honest. It is very important to be truthful in your “about me” section.
- Proofread and read aloud.
- Keep your “about me” section updated.
- Tie it into the job description.
What is a good closing sentence?
– Restate the topic sentence using synonyms . – Restate the topic sentence using a different kind of sentence. – Wrap up your paragraph. – Consider using transition words to signify the end of your paragraph.
What do you write in a closing paragraph?
The conclusion paragraph should restate your thesis, summarize the key supporting ideas you discussed throughout the work, and offer your final impression on the central idea . This final summation should also contain the moral of your story or a revelation of a deeper truth.
What is a good hook sentence?
A strong statement hook is a sentence that makes an assertive claim about your topic . It connects to the thesis statement and shows the importance of your essay or paper. A strong statement is a great technique because it doesn’t matter if your reader agrees or disagrees with your statement.
How do you end an essay example?
Summarize all the key points you made throughout the body of the paper (things that proved your thesis statement). Write about why this paper and topic are important, and leave the reader with ideas for additional research or maybe some questions that didn’t get answered.
How do you write the last sentence of an essay?
The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay. A strong conclusion aims to: Tie together the essay’s main points. Your essay’s conclusion should contain:
- A rephrased version of your overall thesis.
- A brief review of the key points you made in the main body.
- An indication of why your argument matters.
How do you end a paper?
Conclude an essay with one or more of the following:
- Include a brief summary of the paper’s main points.
- Ask a provocative question.
- Use a quotation.
- Evoke a vivid image.
- Call for some sort of action.
- End with a warning.
- Universalize (compare to other situations).
- Suggest results or consequences.
How do you say thank you after a speech?
Include your gratitude and how much it means to you with these alternative phrases.
- “Thank you for finding the words.”
- “Thank you for helping me through this grief.”
- “Thank you for making me smile during this sad time.”
- “Thank you for your beautiful words.”
- “I appreciate your help during this tough time.”
Do you say thank you at the end of a speech?
Official TM stand on thanking the audience after the speech: “ Don’t end by saying “Thank you.” The audience should thank you for the information you’ve shared. Instead, just close with your prepared ending, nod at the Toastmaster of the meeting, and say, ‘Mr. [or Madam] Toastmaster’ – then enjoy the applause. ‘”

By Edmund Duncan
Edmund Duncan is an education expert and thought leader in the field of learning. He has dedicated his life to helping students achieve their full potential in the classroom and beyond.
Edmund's work as a teacher, administrator, and researcher has given him a unique perspective on how students learn and what educators can do to foster a love of learning in their students. He is passionate about sharing this knowledge with others, and he frequently speaks at education conferences around the world.
When Edmund isn't working or speaking, he enjoys spending time with his family and friends. He loves traveling and exploring new places, and he is an avid reader who loves learning about new cultures and customs.
You might also like:
Is william and mary a dry campus, is william and mary for rich kids, is william and mary the oldest college in america.
Everything You Need to Know About Introducing a Speaker
Hrideep barot.
- Presentation

Introducing a speaker is an art, a blend of etiquette and eloquence, a choreography of words and respect. It’s the crucial bridge between an audience eagerly waiting to absorb knowledge and the speaker about to impart it. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll uncover everything you need to know about introducing a speaker with finesse and impact. Whether you’re the host of a grand conference, a school assembly, or even a family gathering, these insights will help you set the stage for a successful speech. Let’s dive into the art of introductions.
What Are the key points to Include when Introducing a Speaker?
Speaker’s name and title: .
Clearly stating the speaker’s name and professional title is essential as it provides immediate identification. This introduction is often the first impression, so ensure you pronounce their name correctly. Use the full title and any honorifics if applicable, which enhances their credibility. For instance, “Ladies and gentlemen, please welcome Dr. Sarah Williams, a renowned climate scientist who holds a Ph.D. in Environmental Science.”
Relevance:
Explaining the speaker’s relevance is crucial. This is your opportunity to set the context. You can touch on the event’s main theme and why this speaker was chosen to address it. “Dr. Williams’ expertise is invaluable to us today as we are gathered to discuss climate change, an issue of global concern. Her insights will provide a fresh perspective on the topic.”
Brief Background:
When providing a brief background, focus on key milestones in the speaker’s career or life. It helps the audience connect with the speaker as a person and not just as a presenter. “Dr. Williams’ journey in climate science began as a passionate environmentalist. She earned her Ph.D. in Environmental Science from Stanford University and has since contributed significantly to this field.”
Topic and Objective:
It’s important to give the audience a preview of what to expect. Mention the main topic and the specific goals of the presentation. “Today, she will delve into the impact of climate change on coastal regions. Her objective is to present actionable solutions that can help us adapt to these challenges.”
Engaging Anecdote:
A personal or professional anecdote adds a human touch to the introduction. Sharing a story about the speaker’s journey or a moment of inspiration can captivate the audience’s attention. “One memorable incident from Dr. Williams’ career was when she spent several months in the Arctic, facing extreme conditions to gather crucial data. Her unwavering dedication was truly inspiring.”
Credibility Boosters:
Highlighting awards, publications, and recognitions helps establish the speaker’s credibility. Mention the significance of these achievements and how they contribute to their expertise. “Dr. Williams’ remarkable contributions have not gone unnoticed. She received the Nobel Prize in Environmental Science in 2020, recognizing her outstanding work.”
Audience Connection:
Relate the speaker’s expertise to the audience’s interests or current challenges. This connection makes the introduction more engaging. “Considering the pressing challenges posed by climate change, Dr. Williams’ insights will provide us with valuable knowledge to make informed decisions and contribute to a sustainable future.”
Upcoming Events or Acknowledgments:
If there are any upcoming events or achievements on the horizon, share them. It builds excitement and anticipation. “Dr. Williams is preparing to launch her latest book on climate resilience next month, and it has already generated substantial anticipation in academic and environmental circles.”
End with a Warm Welcome:
Conclude the introduction with a warm welcome. Encourage the audience to join you in showing appreciation for the speaker’s presence. “Ladies and gentlemen, it is with great pleasure that we invite Dr. Sarah Williams to the stage. Please join me in giving her a warm welcome and showing our gratitude for sharing her expertise with us.”
Brief Pause:
After introducing the speaker, a brief pause is essential. It allows the audience to applaud and transitions smoothly to the speaker’s presentation. This moment of pause adds a touch of professionalism to the introduction and keeps the event flowing seamlessly.
Incorporating these elaborations will make the speaker’s introduction not only informative but also engaging, setting the stage for a successful presentation.
How do you properly Introduce a speaker?
Establish a Personal Connection:
Building a personal connection with the audience begins with you. Share an anecdote or personal observation that relates to the speaker or the event. This could be a moment when you first learned about the speaker’s work, met them, or experienced the impact of their expertise. It creates an immediate bond with the audience, making the introduction more relatable and engaging.
Highlight Shared Values:
Emphasizing shared values between the speaker, the event, and the audience is a powerful way to foster unity. Consider mentioning common values, such as a commitment to education, innovation, or social change, and how the speaker embodies these values. It signals alignment, fostering a sense of shared purpose and goals.
Interactive Elements:
To make the introduction memorable, consider incorporating interactive elements. For instance, you might pose a thought-provoking question about the speaker’s topic and ask the audience to reflect on it. Alternatively, you could conduct a brief activity that serves as a teaser for the presentation. This interactivity not only engages the audience but also sets the tone for active participation throughout the event.
Emphasize the Speaker’s Enthusiasm:
Express the speaker’s genuine enthusiasm for their topic and their eagerness to share it with the audience. You can mention how passionate they are about their subject matter and how their enthusiasm is bound to be infectious. This approach creates an optimistic atmosphere from the very beginning.
Audience’s Role:
Outline the audience’s role in the presentation. Explain what they can expect from the speaker and how their participation can enhance the experience. Encourage active listening and interaction by specifying ways in which the audience can engage with the speaker, such as asking questions or sharing their thoughts.
Visual Aids:
Visual aids can be a valuable addition to the introduction. These aids should be relevant to the speaker or their topic and can range from impactful images to significant props. Visual elements enhance the introduction by providing a visual focus for the audience, making it more engaging and memorable.
Comparisons and Metaphors:
Utilize creative language to draw comparisons or metaphors that vividly illustrate the speaker’s significance. For example, you could liken the speaker to a guiding star in the field, someone who lights the way with their insights. Using such metaphors adds a creative and memorable dimension to the introduction, making it unique and thought-provoking.
Unique Contributions:
Highlight the speaker’s unique contributions to their field. Explain how their work stands out and the innovative approaches or ideas they’ve brought. This sets them apart from others and demonstrates the value of their insights.
Current Relevance:
Connect the speaker’s topic to current events or trends. Explain how their insights are particularly pertinent in the present moment. You can touch on ongoing discussions, recent developments, or issues of concern that align with the speaker’s area of expertise. This contextualization enhances the introduction’s timeliness and its connection to real-world issues.
End with an Anticipation-Building Statement:
Conclude the introduction with a statement that sparks curiosity and anticipation. Offer a tantalizing glimpse of a fascinating aspect of the speaker’s presentation without revealing too much. This leaves the audience eager to hear more, ensuring that they are actively engaged from the outset.
By implementing these elaborations, your introduction of a speaker will not only inform but also captivate the audience, setting the stage for a dynamic and interactive presentation.
What is the best line to Introduce Someone?
– the captivating teaser:.
The art of public speaking often begins with intrigue. A captivating teaser serves as the literary equivalent of a magician’s opening act. Just as a magician engages the audience with an exciting trick, you, as the introducer, can engage your audience’s curiosity with a teaser. In this approach, you introduce the speaker by offering a tantalizing tidbit of information or a thought-provoking question. This stirs curiosity and sets the stage for the exciting content the speaker is about to deliver.
Imagine you’re introducing a renowned historian, Dr. Eleanor Bennett. To captivate your audience, you could begin with a teaser: “Ladies and gentlemen, prepare to embark on a journey through time with a historian whose research unveiled hidden secrets of the past. Do you know what connects Cleopatra’s makeup and the fall of the Roman Empire? Get ready to be amazed!”
– The Enthusiastic Acclaim:
A burst of enthusiasm can work like magic in the world of introductions. This approach is akin to a standing ovation before the play even starts. The enthusiastic acclaim is about expressing your genuine admiration and excitement for the speaker. You highlight their exceptional qualities and achievements, essentially “pumping up” the audience before the main event. The speaker is welcomed with an energetic and fervent introduction, making them feel appreciated and valued.
Suppose you’re introducing an Olympic gold medalist, such as Michael Johnson. In this case, an enthusiastic acclaim could sound like: “Ladies and gentlemen, it’s not every day that we have the honor of welcoming a true legend. The man we’re about to introduce has not only redefined the world of athletics but has inspired generations. Please join me in an ecstatic round of applause for the phenomenal Michael Johnson!”
-The Relatable Remark:
Laughter and relatability are fantastic tools for capturing your audience’s attention. Starting with a relatable and light-hearted remark can help create an instant connection. Your remark can be humorous, touching, or a simple observation that the audience can connect with. By sharing a moment of common experience or offering a humorous insight, you create an immediate bond with the audience. It’s like sharing a knowing smile before diving into the main presentation.
For instance, if you’re introducing a speaker on the topic of work-life balance, you could start with a relatable remark: “Ladies and gentlemen, we’ve all been there, juggling our work commitments with our personal lives. Sometimes, it feels like trying to catch a falling star. Our next speaker is here to shed light on this universal challenge, and perhaps, to help us finally catch that elusive star.”
-The Empathetic Connection:
Imagine an introduction that tugs at the heartstrings of your audience, one that makes them feel understood and appreciated. The empathetic connection does just that. This approach is about crafting an introduction that emotionally connects the audience to the speaker. You share a relatable experience or challenge that the speaker and the audience have in common, fostering a deep sense of unity and understanding.
Suppose you’re introducing a mental health advocate, someone who has been through personal struggles. Your empathetic connection could be: “Ladies and gentlemen, many of us have faced moments of darkness in our lives, times when hope seemed distant. Our next speaker, John Parker, understands this all too well. He’s not just a mental health advocate; he’s someone who’s walked through the shadows and emerged with a message of hope that he’s here to share.”
By using these four distinct introduction styles, you can engage your audience and set the stage for a captivating presentation. Each approach creates a unique atmosphere, drawing the audience into the world of the speaker and making their message all the more impactful.
How to not Introduce a Speaker?
Monotone monologue:.
One surefire way to not introduce a speaker is to deliver a monotonous, uninspiring monologue. In this scenario, you step up to the podium and begin a long, tedious speech about the speaker’s credentials, achievements, and perhaps even their childhood stories. The audience is left in a daze, struggling to maintain focus. A monotone monologue can quickly drain any enthusiasm from the room, making it the antithesis of an engaging introduction.
Exaggerated Hyperbole:
While genuine enthusiasm is essential, exaggerating the speaker’s qualities to a comical extent is a definite no-go. Introducing a speaker as the “greatest genius of all time” or the “most extraordinary person to ever walk the Earth” can be perceived as insincere and over the top. It not only fails to make the speaker look good but also makes you, the introducer, appear insincere and inauthentic.
Lack of Preparation:
An introduction riddled with mistakes, mispronunciations, and a general lack of preparation can be a significant blunder. It’s akin to showing up unprepared for a critical presentation. Fumbling over the speaker’s name, stumbling through a disorganized introduction, or not providing essential context can leave a negative impression on the audience and the speaker. It reflects a lack of professionalism and care.
Inappropriate Humor:
Incorporating humor can be a valuable tool in an introduction. However, using inappropriate or offensive humor can quickly backfire. Cracking jokes that touch on sensitive topics, offensive stereotypes, or embarrassing personal anecdotes about the speaker can lead to awkwardness and discomfort. It’s crucial to choose humor carefully and ensure it aligns with the event’s tone and values.
Excessive Length:
Going on and on in the introduction without a clear endpoint is another pitfall to avoid. An overly lengthy introduction can be tiresome for the audience, delaying the main presentation and sapping their enthusiasm. It’s essential to keep introductions concise and to the point, saving detailed biographies and extended storytelling for more appropriate moments.
Overlooking the Audience:
Neglecting to connect with the audience is a common mistake. Some introducers focus solely on the speaker, providing a one-sided introduction that doesn’t engage the listeners. The audience’s role in the introduction is just as critical. Ignoring their presence and not addressing their interests can lead to a lack of engagement.
Scripted Formality:
Reading a pre-written introduction verbatim can strip away authenticity. It can make you sound robotic and disconnected from the audience. While preparation is vital, it’s equally important to maintain a conversational and engaging tone. Rigidly adhering to a script without adapting to the audience’s energy and needs can hinder a successful introduction.
Inadequate Research:
A lack of research about the speaker, event, or audience can lead to a subpar introduction. Providing inaccurate or irrelevant information can not only confuse the audience but also undermine the credibility of the introducer. It’s crucial to thoroughly research the speaker and align the introduction with the context of the event.
These are some of the pitfalls to avoid when introducing a speaker. By steering clear of these missteps, you can ensure that the introduction serves its purpose, setting a positive tone for the presentation and engaging the audience effectively.
How long should a Speaker’s Introduction Be?
The length of a speaker’s introduction is a subtle yet crucial aspect of any event. It’s akin to the opening scene of a movie, setting the tone and expectations for what follows. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to determining the perfect length. Instead, it’s a delicate dance influenced by various factors. The nature of the event plays a pivotal role, as grand galas and corporate gatherings might warrant more extensive introductions, while casual gatherings among friends require shorter, more relaxed ones. The audience’s familiarity with the speaker is another key consideration; well-known figures may benefit from shorter introductions, whereas lesser-known speakers may require more context. The relevance to the event’s theme, adherence to the schedule, and respecting the speaker’s preferences all contribute to finding that sweet spot. Above all, it’s about engaging the audience while respecting their time and maintaining their curiosity—a true art form in event planning.
Introducing a speaker in different settings:
A) introducing a speaker at an event:.
Introducing a speaker at an event is a multifaceted task that sets the stage for a successful presentation. In a formal setting, such as a corporate conference or an awards ceremony, the introduction should be distinguished and eloquent. It must incorporate the speaker’s credentials, accolades, and the relevance of their topic to the event. It’s also an opportunity to infuse the audience with anticipation and convey the significance of the upcoming speech. Striking a balance between professionalism and engagement is key, ensuring the audience is both informed and excited.
Introducing A speaker at a group Event
B) Introducing a Speaker at Church:
Introducing a speaker at a church event carries a distinct tone of reverence and spirituality. The introduction should align with the themes and values of the congregation, reflecting the spiritual significance of the gathering. It may include a brief background on the speaker, emphasizing their connection to the faith or community. Sharing personal anecdotes that highlight the speaker’s dedication to their faith can resonate deeply with the congregation. This type of introduction is not just about qualifications but also the shared spiritual journey, making it a heartfelt and spiritually uplifting experience.
C) Introducing a Speaker at Graduation:
Introducing a speaker at a graduation ceremony is a momentous task, marking the culmination of academic achievements. The introduction should emphasize the speaker’s connection to the graduates, potentially an alumnus, respected faculty member, or renowned figure in the academic world. It’s an opportunity to inspire the graduates and instill a sense of pride in their accomplishments. The introduction typically includes highlights of the speaker’s distinguished career or contributions to the field. It sets the stage for a motivational and memorable address, encapsulating the hopes and aspirations of the graduating class.
D) Introducing a Speaker in a Zoom Meeting:
Introducing a speaker in a virtual setting, such as a Zoom meeting, requires adaptability and conciseness. Given the digital platform’s unique dynamics, the introduction should be brief, focusing on the speaker’s qualifications and the topic’s relevance to the online audience. In a virtual environment, it’s essential to maintain engagement and capture attention swiftly. Including a fun fact or a relatable connection can also add a personal touch to the introduction, combating the potential for distractions in the online realm.
Each setting demands a tailored approach, considering the audience’s expectations, the formality of the event, and the unique nuances of the context. Adhering to these distinctions ensures that the speaker is introduced effectively and in a manner that resonates with the audience.
Introducing a Speaker sample Script:
Ladies and gentlemen, we are honored to introduce our next speaker. This individual needs no grand introduction, but we’ll certainly provide one deserving of their stature.
Allow us to present [Speaker’s Full Name], a visionary in their own right, whose accomplishments have left an indelible mark on [relevant field]. With a career spanning [number of years], they have achieved remarkable success in areas from [mention key areas], making them an indisputable authority in their domain.
[Speaker’s Name] has a track record that speaks for itself, having [specific accomplishments or awards] that exemplify their dedication to excellence. Their contributions have touched the lives of countless individuals, and today, we have the privilege of benefiting from their insights and wisdom.
But [Speaker’s Name] isn’t just a luminary in their professional sphere; they are also a compassionate soul dedicated to [mention any social or humanitarian causes they support]. This commitment reflects their character, making them not only a leader but also a role model for all of us.
Today, [Speaker’s Name] will delve into the [mention topic], shedding light on a subject that holds the power to transform our perspectives and actions. Their objective is clear: to inspire, to educate, and to spark change. It’s a mission that aligns seamlessly with our event’s theme of [mention the event’s theme].
So, fasten your seatbelts, ladies and gentlemen, for we’re about to embark on a journey of insight and enlightenment. Please join me in extending the warmest welcome to [Speaker’s Full Name].
Conclusion:
In conclusion, introducing a speaker is an art. Whether you’re introducing someone at a grand event, in a spiritual setting, at a graduation ceremony, or even virtually through a Zoom meeting, the principles of a captivating introduction remain the same. A well-crafted introduction engages the audience’s curiosity, evokes empathy, and fosters enthusiasm. It should be of an appropriate length, striking the balance between being informative and keeping the audience’s interest intact. Lastly, the sample script provided serves as a guideline, demonstrating how you can encapsulate the essence of the speaker while building anticipation. Always personalize your introductions, ensuring they reflect the tone and objectives of the event. Mastering the art of introducing a speaker can be a valuable skill that enriches every audience’s experience.
To learn more about effective introductions or even delivering speeches and presentations as a whole you can reach out to us here.
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

10 Hand Gestures That Will Make You More Confident and Efficient

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.

Introduction Speech
Discover the art of crafting compelling introduction speeches through our comprehensive guide. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned speaker, our step-by-step approach simplifies the process. Explore a rich collection of speech examples , tailored to inspire and improve your public speaking skills. Master the nuances of delivering impactful introductions that captivate your audience, using our expertly curated speech examples as your roadmap to success.
Download Introduction Speech Buncle
A speech can be of any form and used for various functions. It can be a thank-you speech to show one’s gratitude or even an introduction speech to introduce a person (even oneself), product, company, or the like. In these examples, let’s look at different speech examples that seek to introduce.
Introduction Speech Example

Free Download
Introduction Speech for Students

Introduction Speech for School

Self-Introduction Sample

Size: 143 KB
Short Introduction Speech

Size: 110 KB
Introduction Speech for Employee

Size: 47 KB
What to Include in an Introduction Speech
An introduction speech may also work as a welcome speech . You introduce yourself to an audience and provide the audience with the gist of a meeting or program. This would include providing recognition to significant individuals or even starting a brief discussion on a topic.
But of course, this would solely depend on what you’re trying to introduce. You can also use various speech templates for you to know what other information may be included in your speech.
How to Write a Introduction Speech?
In writing an introduction speech, it’s wise to familiarize the flow of a program.
Think about what your goal is and how you could attain it. You need to be able to capture the attention and interest of your listeners. If you’re giving a speech to introduce the president of your company, be sure to make it grand. Share significant details that are sure to receive a wow factor from the audience as an introduction speech can also be an informative speech . Keep in mind that it’s always best to start with an outline or draft so it will be easier for you to edit.
Introduction Speech for Chairman

Size: 281 KB
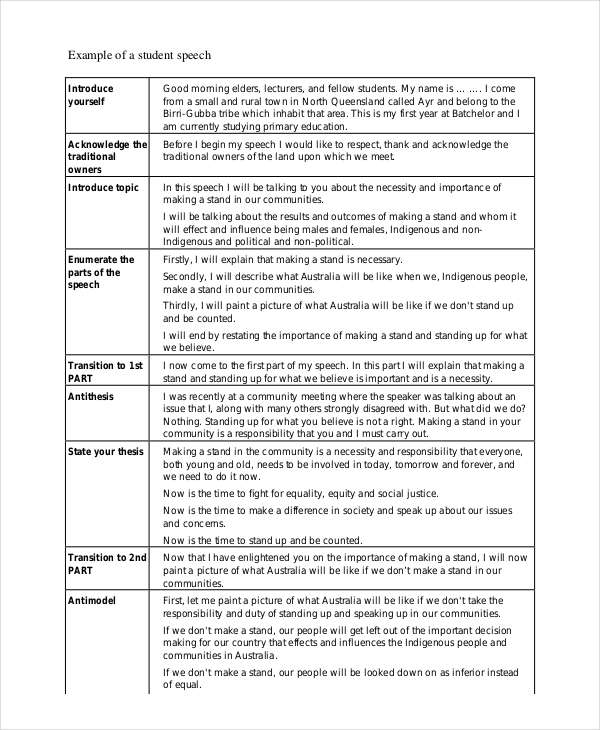
waalc.org.au
Size: 13 KB
Formal Introduction Sample

Size: 223 KB
Tips on Writing an Introduction Speech
1. Keep it short. When you try to self introduction speech to a person you just met, you don’t tell them paragraphs of information that aren’t even relevant. You would want to entice an audience, not bore them out. You don’t need to make it lengthy for it to be good. A few wise words and a touch of class will be enough for your listeners.
2. Make an outline. Introductions are meant to give an audience a quick run through of what they must know. Create a speech outline that will state the purpose of your speech and provide a preview of main ideas that are to be discussed. This is sure to give your audience a reason to listen.
3. Create an icebreaker. Speeches can be quite awkward, especially since they’re usually made formal. Craft a speech that will leave a good impact. Allow others to feel comfortable with the environment they are in and allow them to feel valued. You may also see orientation speech examples & samples
4. Read it out loud. The thing is, some things sound better in our heads than being said aloud. It’s possible that your speech in pdf may contain words that don’t sound good together or that it might give a different interpretation on a matter.
How to Conclude an Introduction Speech
Just as an essay can be conclude speech in different ways, an introduction speech may end in various ways.
You can close it in a challenging, congratulatory, suggestive or even inviting matter. It’s best to keep it as brief as possible to let your listeners know that you’re ending your speech in word . All you need to make sure of is that you don’t abruptly end your speech, leaving your audience hanging.
In the realm of public speaking, the introduction speech serves as a crucial gateway, opening the door to deeper engagement and understanding. Whether it’s for a corporate event, educational purpose, or a personal introduction, the essence of a good introduction speech lies in its ability to connect the speaker with the audience on a meaningful level. To further enhance your skills in crafting and delivering effective introduction speeches, exploring resources from esteemed institutions can be immensely beneficial. Websites like Harvard’s Public Speaking Resources offer a treasure trove of tips, techniques, and examples that can inspire and guide speakers to refine their approach.
Introduction Speech Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write an Introduction Speech for a guest speaker at a conference.
Create an Introduction Speech for a new teacher at school.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
5. Melissa Butler. Speech Ending: When you go home today, see yourself in the mirror, see all of you, look at all your greatness that you embody, accept it, love it and finally, when you leave the house tomorrow, try to extend that same love and acceptance to someone who doesn't look like you. 6.
Three effective speech conclusions. Here are three of the best ways to end a speech. Each ensures your speech finishes strongly rather than limping sadly off to sure oblivion. You'll need a summary of your most important key points followed by the ending of your choice: a powerful quotation. a challenge. a call back.
The Formula for Closing Most Speeches. Transition statement to ending. Review the main points-repeat the thesis. If it is a persuasive speech, tell the audience what you want them to do or think. Provide a closing statement. Restate the Thesis. Tell them what you are going to say, say it, tell them what you have said.
Select a friendly face in the audience and look straight at that person. If it is appropriate, smile warmly at that person to signal that your speech has come to an end. Resist the temptation to: Shuffle papers. Fidget with your clothes or microphone. Move forward, backward, or sideways.
There are a few ways to approach this technique: Set up a question at the beginning of your speech and use your ending to answer it. Finish a story you started, using the anecdote to demonstrate your message. Close with the title of the presentation - this works best with a provocative, memorable title.
As the introduction sets the stage, your conclusion seals the deal. The question, "How do you end a speech?" is an essential query that each presenter or speaker must ask, given the final words' impact and weight on your audience.. Since your final words eventually have a lasting effect, you must make a striking thought to the people.
That will help you to act like a pro in your presentation. 2. End with a Powerful Quote. Quotes can be a powerful tool to end a speech, as they can encapsulate your message and leave a lasting impression. Choose a quote that relates to your topic and resonates with your audience. For instance, if you were giving a motivational speech, you could ...
2) Simon Sinek. Speech ending line: "Listen to politicians now, with their comprehensive 12-point plans. They're not inspiring anybody. Because there are leaders and there are those who lead. Leaders hold a position of power or authority, but those who lead inspire us.
The first way that Miller found that some speakers end their speeches is with a challenge. A challenge is a call to engage in some activity that requires a special effort. In a speech on the necessity of fund-raising, a speaker could conclude by challenging the audience to raise 10 percent more than their original projections.
Conversely, a strong and impactful conclusion can leave a lasting impression on your audience, motivating them to take action and inspiring them to share your message with others. It even has the potential to turn an average persuasive speech into an unforgettable speech. Because the conclusion of your speech is so important, it's worth ...
A thesis statement should appear, almost verbatim, toward the end of the introduction to a speech. A thesis statement helps the audience get ready to listen to the arrangement of points that follow. Many speakers say that if they can create a strong thesis sentence, the rest of the speech tends to develop with relative ease.
Don't say "Thank you". Most speakers end their speech with a simple "Thank you". While this does become a clear way to end a speech, it's been done to death. The audience will appreciate it if an ending is different and truly impactful. Saying "Thank you" just doesn't do that. Here are some different ways you can use to end ...
4. Repeat a certain phrase to make it memorable. If there's a main point you want the audience to remember, repeat it throughout your speech. Then when you get to the end of your speech, make it your final line for a stronger impact. Keep the line short so that it's easy to remember. [4]
Dream a little, and let your audience do the same. 3. Try repetition. Repeating a phrase or a couple of lines can be a great way to hammer home a couple of points and let your speech end with a bang. You can repeat whole phrases, or use parallel sentence structure to end your speech with repetition.
An introduction speech, or introductory address, is a brief presentation at the beginning of an event or public speaking engagement. ... Optionally, you can end with a final thought, reflection, or a call to action related to the event or topic. Here is an example outline for a self-introduction speech. Outline for Self-Introduction Speech.
The speech introduction is the first part of a speech and the first opportunity to grab the audience's attention. The speaker should state the topic, make it relatable to the audience, establish credibility and preview the main points. You should write or finalize your introduction at the end so that it reflects what you actually said.
To properly conclude an introductory speech, give the speaker's name and title. Give an overview of the speaker's achievements and accolades. Describe the speaker's expertise in his subject. For example, say, "I now want to introduce you to award-winning environmentalist John Smith, who has written more than 10 books on green energy in ...
The key to a good self-introduction speech is balance. You want to present your accomplishments but without coming off as bragging. Typically, this type of speech is known as an "icebreaker" as it aims to break the ice and let others know you. This is your chance to establish good credibility. Fear not!
1) Thank the Organizers and Audience. You can start by thanking the audience for coming and thanking the organization for inviting you to speak. Refer to the person who introduced you or to one or more of the senior people in the organization in the audience. This compliments them, makes them feel proud and happy about your presence, and ...
An effective conclusion prepares an audience for the end of the presentation and takes advantage of the recency effect by ensuring the final moments of the speech review key information. In many ways, effective conclusions mirror effective introductions.
Here are some dos which will help the speaker in concluding his speech. Indicate that the speech is close to the end. Give a rundown of your speech/presentation. Make eye-contact. Don't make the closing remarks lengthy. Don't end with a simple 'Thank You". Don't add new material out of no where. The fitting remark.
Introducing a speaker is an art, a blend of etiquette and eloquence, a choreography of words and respect. It's the crucial bridge between an audience eagerly waiting to absorb knowledge and the speaker about to impart it. In this comprehensive guide, we'll uncover everything you need to know about introducing a speaker with finesse and impact.
Introductions are meant to give an audience a quick run through of what they must know. Create a speech outline that will state the purpose of your speech and provide a preview of main ideas that are to be discussed. This is sure to give your audience a reason to listen. 3. Create an icebreaker.
Catch the top stories of the day on ANC's 'Top Story' (18 April 2024)