
- Spartanburg Community College Library
- SCC Research Guides
- Citing a Play
When you refer to lines from a play in-text, you need to cite these lines according to MLA. There are several ways to do in-text citations for plays. Depending on what information you have about your play will determine how you do your citations.
- Citing a Play (MLA Works Cited)
- In-Text Citations for Plays
- Help Resources

Citing a Play from Textbook
Format: Author. Title of Play in Italics . Title of Textbook, edited by Editor Name, edition, vol. #, Publisher, Year, Page Numbers.
Example: Hansberry, Lorraine. A Raisin in the Sun. The Norton Anthology of African American Literature , edited by Henry Louis Gates, Jr. and Valerie Smith, 3rd ed. vol. 2, W.W. Norton and Company, 2014, pp. 470-532.
Citing a Play in a Book
*Note: this citation should be used if you find your play in a book where the play is the entire book
Format: Author. Title of Play in Italics. Edition, Publisher, Year. Database Name in Italics (if electronic), URL.
Example: Sophocles. Antigone. Translated by David Mulroy, University of Wisconsin Press, 2013. ProQuest Ebook Central, ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/sccsc/detail.action?docID=3445283.
How you cite in-text depends on whether you are using line numbers or page numbers.
Using Line Numbers
Example: (Hansberry, 4.5. lines 171-9)
*Note: If the text of your play includes line numbers on the side of the page, then replace the page number with the act, scene, and line numbers.
*Notes: Once you establish you are using line numbers for your in-text citations, you no longer need to use the word "line" in your parenthetical citation.
*Note: If you have used the author's name or the play's title in the signal phrase before introducing a quote, you do not need to include it in your in-text citation.
Using Page Numbers
Example : (Wilson 200)
*Note: If lines in your play are not numbered, you can use the page number in your citation.
- Sample Drama Paper
- Sample Drama Paper with Line Number Citations This sample drama paper will show examples of in-text citations using line numbers.
- << Previous: Citing Artistic Works/Performances
- Next: Citing a Poem >>
- Online MLA Handbook This link opens in a new window
- Formatting the Author and Title
- Container Punctuation
- Citing a Book or Ebook
- Citing Part of a Book or Ebook
- Citing an Encyclopedia
- Citing a Journal Article
- Citing an Article Written for a Database
- Citing a Magazine or Newspaper Article
- Citing an Interview/Podcast
- Citing a Website
- Citing a Video
- Citing Social Media
- Citing Images in a Project
- Citing Artistic Works/Performances
- Citing a Poem
- In-text Citations
- Formatting Your Word Document
- MLA Handouts
- MLA Workshop (video, Feb. 2022)
- MLA - Getting Started (Basic Tutorial)
- Annotated Bibliography
- Last Updated: May 29, 2024 4:30 PM
- URL: https://libguides.sccsc.edu/MLA
Giles Campus | 864.592.4764 | Toll Free 866.542.2779 | Contact Us
Copyright © 2024 Spartanburg Community College. All rights reserved.
Info for Library Staff | Guide Search
Return to SCC Website

AP Style Composition Titles
Home » AP Style » AP Style Composition Titles
The following guidelines are rules set out in the AP Stylebook for AP style book titles, computer game titles, AP Style movie titles, opera titles, play titles, poem titles, album titles, AP Style song titles, radio and television titles, and the titles of lectures, speeches, and work of art.
In AP Style, magazines names and titles are governed by their own rules. See AP Style Magazine Names .
How to Capitalize Composition Titles
Capitalize the principal words, including prepositions and conjunctions of four or more letters.
Capitalize an article (a, an, the) or words of fewer than four letters if it is the first or last word in the title.
Put quotation marks around the names of all of the aforementioned types of works except the Bible and books that are primarily catalogs or reference materials. Items of reference include almanacs, directories, dictionaries, encyclopedias, gazetteers, handbooks, and other such similar publications. You should not include quotations around such software titles such as Adobe Photoshop or Windows.
You should translate a foreign title into an English one unless the specific word is commonly known by its foreign name. There is one exception to this and that is for reviews of musical performances. In such instances, you should generally refer to the work in the language that it was sung in, so as to differentiate it for your reader. However, musical compositions in Slavic languages are always referred to in their English translations.
For other classical music titles, use quotation marks around the composition’s nicknames but not compositions that are identified by their sequence. For example,
- Beethoven’s “New World Symphony,” but Beethoven’s Symphony No. 9.
Below are a number of examples for composition titles in AP Style,
AP Style Book Titles
- “To Kill a Mockingbird”
- “The Magician’s Nephew”
- “Of Mice and Men”
AP Style Movie Titles
- “Saving Private Ryan”
- “Trouble With the Curve”
- “The Dark Knight Rises”
AP Style Song Titles
- “Stairway to Heaven”
- “Good Vibrations
AP Style Videogame Titles
- “Call of Duty”
- “God of War”
- “Tom Clancy’s Splinter Cell”
AP Style Opera Titles
- “A Night in the Chinese Opera”
- “Nixon in China”
- “The Lighthouse”
AP Style Play Titles
- “The Sound of Music”
- “The Book of Mormon”
- “Fiddler on the Roof”
AP Style Poem Titles
- “The Road Not Taken”
- “A Pretty a Day”
- “Seeker of Truth”
AP Style Album Titles
- “Appetite for Destruction”
- “And Justice for All”
- “Sgt. Pepper’s Lonely Hearts Club Band”
AP Style Television Titles
- “How I Met Your Mother”
- “The Tonight Show”
- “Good Morning America”
AP Style Website Titles
Most websites and apps are capitalized without quotations. For example,
“Farmville” and similar computer games apps are an exception and should be in quotes.
For classical compositions, use quotation marks around the composition’s nicknames but not compositions identified by its sequence. For example,
- Dvorak’s “New World Symphony.”
- Dvorak’s Symphony No. 9.
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, quoting plays and poetry in mla.
- © 2023 by Angela Eward-Mangione - Hillsborough Community College
The rules for quoting drama and/or poetry in Modern Language Association (MLA) Style differ from those for quoting the genre of prose. This article discusses rules for using MLA style to format quotes from drama and poetry. Consult the MLA Handbook to learn more.
Quoting Poetry
The MLA Handbook offers specific guidelines for quoting poetry.
In addition to the amount quoted and line breaks, other factors that matter include stanza breaks, and unusual layouts.
Special Issues: Stanza Breaks, Unusual Layouts
Stanza Breaks: Mark stanza breaks that occur in a quotation with two forward slashes, with a space before and after them ( / / ) (78).
William Carlos Williams depicts a vivid image in “The Red Wheelbarrow”: “so much depends / / upon / / a red wheel / / barrow / / glazed with rain / / water / / beside the white / / chickens” (“Williams”).
Unusual Layouts: If the layout of the lines in the original text is unusual, reproduce it as accurately as you can (79).
The English metaphysical John Donne uses indentation in some of his poems to create unusual layouts, as the first stanza of including “A Valediction: of Weeping” demonstrates:
Let me pour forth My tears before they face, whilst I stay here, For thy face coins them, and thy stamp they bear, And by this mintage they are something worth, For thus they be Pregnant of thee; Fruits of much grief they are, emblems of more, When a tear falls, that thou falls which it bore, So thou and I are nothing then, when on a divers shore. (lines 1-9)
Quoting Plays
When you must quote dialogue from a play, adhere to these rules:
- Set the quotation off from your text.
- Indent each name half an inch from the left margin and write it in all capital letters.
- Follow the name with a period and then start the quotation.
- Indent all other lines in the character’s speech an additional amount.
- When the dialogue shifts to another character, start a new line indented half an inch.
- Maintain this pattern throughout the quotation (80).
Example: One of the flashbacks in Margaret Edson’s Wit suggests Vivian Bearing’s illness causes her to question some of her previous interactions with students:
STUDENT 1. Professor Bearing? Can I talk to you for a minute?
VIVIAN: You may.
STUDENT 1: I need to ask for an extension on my paper. I’m really sorry, and I know your policy, but see—
VIVIAN: Don’t tell me. Your grandmother died.
STUDENT 1: You knew.
VIVIAN: It was a guess.
STUDENT 1: I have to go home.
VIVIAN: Do what you will, but the paper is due when it is due. (63)
Special Issues
Omissions: Follow the rules for omissions in quotations of prose (83).
Although some of the rules for quoting plays and poetry in MLA differ than those for quoting prose, understanding the guidelines will help you apply them in any scenario.
Donne, John. “The Bait.” The Complete English Poems . Penguin Books, 1971, pp. 43-4.
—. “The Break of Day.” The Complete English Poems . Penguin Books, 1971, pp. 45-6. Edson, Margaret. Wit. Faber and Faber, 1993.
Shakespeare, William. Sonnet 39. The Pelican Shakespeare: The Sonnets . Penguin Books, 1970, p. 59.
Williams, William Carlos: “The Red Wheelbarrow.” Poetry Foundation. Poetry Foundation, www.poetryfoundation.org/resources/learning/core-poems/detail/45502 .
Yeats, William. “A Prayer for My Daughter.” The Collected Poems . Ed. Richard Finneran. Scribner, 1983, pp. 188-190.

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
How To Cite A Play In MLA – Formatting & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

In academic writing , proper citation practices are essential to acknowledge the intellectual contributions of authors and to uphold the integrity of scholarly discourse. For scholars, students, and writers engaged in the study of drama and theater, understanding how to cite a play in MLA format is important. This guide delves into the intricacies of citing plays in MLA, providing a step-by-step elucidation of the citation process for various play types, including classic and contemporary works.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 How to cite a play in MLA – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: How to cite a play in MLA
- 3 How to cite a play in MLA: In-text citations
- 4 How to cite a play in MLA: Works Cited list
How to cite a play in MLA – In a Nutshell
- When quoting from a play in an essay, MLA style requires you to add an in-text citation indicating the source.
- Including quotes from a play in your work will vary based on whether you are quoting a single character or dialogue between numerous characters.
- In MLA format, an additional page is inserted after the last page of the academic essay to list all sources acknowledged within.
Definition: How to cite a play in MLA
An MLA parenthetical citation for a play with numbered lines should include the play’s title, author, act number, scene number, and line numbers. Without line numbers, refer to the page the text appears on. Capitalize, punctuate, and indent dialogue as necessary.
- Banquo: I’ll have it done.
- Macduff: What he hath lost, noble Macbeth hath won. (Shakespeare 1.2.94–95)
How to cite a play in MLA: In-text citations
An MLA in-text citation includes the author’s last name and page number:
- (Beckett 8)
Replace the page number with the act, scene, and line numbers, separated by periods if they’re included in the play:
- (Shakespeare 1.3.188–90)
If the text only employs lines, clarify what the numbers represent by including “lines” before the author’s name or title in the first citation of that piece. Subsequent references to the same play may omit “lines.”
- (Malcolm, lines 15–26)
- (Malcolm 35–40)
Multiple plays by the same author
In articles focusing on many works by a single playwright, italicize the play title instead of the writer’s name in each reference.
- ( Macbeth 1.3.188–90)
The MLA style manual suggests using abbreviations after the initial reference to avoid repeating play titles throughout your dissertation . If your study is on Shakespeare, you can utilize commonly accepted acronyms for play titles.
- ( Mac . 2.1.25)
Quoting dialogue
When quoting several dialogue lines from a play or film:
- Place the quotation on a new line with a half-inch left margin indent.
- The discourse should begin with the character’s name in capital letters and a period.
- If a character’s discourse extends beyond one line, indent the subsequent lines by a half inch.
- Add the citation following the punctuation mark.
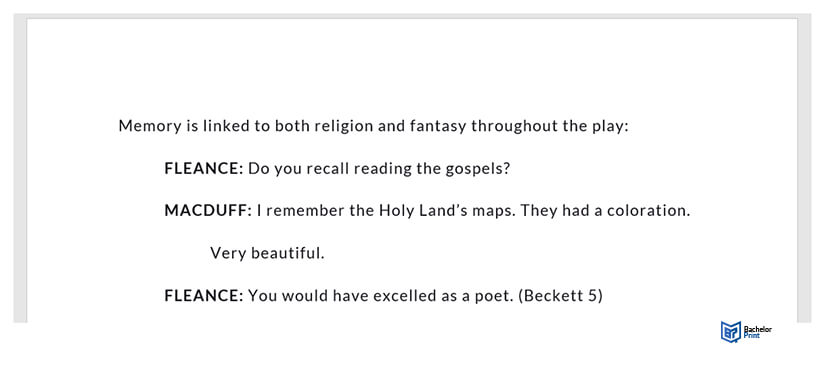
How to cite a play in MLA: Works Cited list
The Works Cited section contains the citation information used in the text. The citation format depends on whether it was published as a book, an anthology, or a live performance.
If the play is published as a book, the citation format is identical to the standard MLA format.
Collection or anthology
Put a period after the play’s title if published in a collection or anthology, and then give the complete details of the sourcebook.
If there is no editor listed, simply remove this section and proceed as illustrated above.
Live performance
To reference a live performance of a play, provide the date and location of the performance. Include the theater company as well.
- ✓ Post a picture on Instagram
- ✓ Get the most likes on your picture
- ✓ Receive up to $300 cash back
How to cite a play in MLA with a one-act play?
MLA style ensures that your reader knows the play being cited. Italicize the work’s title with the page number or scene, act , and lines and only use the full title in the initial citation.
How to cite a play in MLA with no author?
Use a shortened version of the work’s title when a source’s author is unknown. If the work is short, enclose the title in quotation marks ; if longer, italicize the title and include the page number.
How to cite a play in MLA with multiple lines
Quotes longer than four prose lines or three verse lines should be placed in a separate block of text without quotation marks. Begin the quotation on a new line, double-spacing throughout and indenting it by 1/2 inch from the left margin.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
Citation guides
All you need to know about citations
How to cite a play in APA

To cite a play in a reference entry in APA style 6th edition include the following elements:
- Author(s) of the play: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J. D.) of up to seven authors with the last name preceded by an ampersand (&). For eight or more authors include the first six names followed by an ellipsis (…) and add the last author's name.
- Year of publication: Give the year in brackets followed by a full stop.
- Title of the play: Only the first letter of the first word and proper nouns are capitalized.
- Place of publication: List the city and the US state using the two-letter abbreviation. Spell out country names if outside of the UK or the USA.
- Publisher: Give the name of the publisher but omit terms, such as Publishers, Co., and Inc. Retain the words Books and Press.
Here is the basic format for a reference list entry of a play in APA style 6th edition:
Author(s) of the play . ( Year of publication ). Title of the play . Place of publication : Publisher .
To cite a play in a reference entry in APA style 7th edition include the following elements:
- Author(s) of the play: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J. D.) of up to 20 authors with the last name preceded by an ampersand (&). For 21 or more authors include the first 19 names followed by an ellipsis (…) and add the last author's name.
Here is the basic format for a reference list entry of a play in APA style 7th edition:
Author(s) of the play . ( Year of publication ). Title of the play . Publisher .
APA reference list examples
Take a look at our reference list examples that demonstrate the APA style guidelines for a play citation in action:
A play with one author
Williams, T . ( 2009 ). Cat on a hot tin roof . London, England : Penguin Classics .
Williams, T . ( 2009 ). Cat on a hot tin roof . Penguin Classics .
A play with two authors
Manoussi, J., & Timmory, G . ( 1902 ). Un beau marriage . Paris, France : Librairie Théâtrale .
A book with two authors
Manoussi, J., & Timmory, G . ( 1902 ). Un beau marriage . Librairie Théâtrale .
APA in-text citations
APA-style in-text citations for plays follow the standard author-date format used for other mediums like books.
In practice, using one of the examples of plays from above, an in-text citation will look like this:
Similar to his other works, Cat on a hot tin roof explores the theme of the broken man (Williams, 2009) .
When citing plays, you can expand on the in-text citation by adding the act, scene, and line number at the end of the citation. Take a look at this example:
In-text citation of a play including act, scene and line numbers
This passage of Hamlet is essential to establishing the resolve in Gertrude's character (Shakespeare, trans. 1992, 1.2.70-72 ).

This citation style guide is based on the official Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association ( 6 th edition).
More useful guides
- APA citation guide on plays
- Santa Monica College APA guide for theatre arts
More great BibGuru guides
- Harvard: how to cite a film
- Chicago: how to cite an annual report
- AMA: how to cite a Khan academy video
Automatic citations in seconds
Citation generators
Alternative to.
- NoodleTools
- Getting started
From our blog
- 📚 How to write a book report
- 📝 APA Running Head
- 📑 How to study for a test
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Guidelines for referring to the works of others in your text using MLA style are covered throughout the MLA Handbook and in chapter 7 of the MLA Style Manual . Both books provide extensive examples, so it's a good idea to consult them if you want to become even more familiar with MLA guidelines or if you have a particular reference question.
Basic in-text citation rules
In MLA Style, referring to the works of others in your text is done using parenthetical citations . This method involves providing relevant source information in parentheses whenever a sentence uses a quotation or paraphrase. Usually, the simplest way to do this is to put all of the source information in parentheses at the end of the sentence (i.e., just before the period). However, as the examples below will illustrate, there are situations where it makes sense to put the parenthetical elsewhere in the sentence, or even to leave information out.
General Guidelines
- The source information required in a parenthetical citation depends (1) upon the source medium (e.g. print, web, DVD) and (2) upon the source’s entry on the Works Cited page.
- Any source information that you provide in-text must correspond to the source information on the Works Cited page. More specifically, whatever signal word or phrase you provide to your readers in the text must be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of the corresponding entry on the Works Cited page.
In-text citations: Author-page style
MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the sentence itself or in parentheses following the quotation or paraphrase, but the page number(s) should always appear in the parentheses, not in the text of your sentence. For example:
Both citations in the examples above, (263) and (Wordsworth 263), tell readers that the information in the sentence can be located on page 263 of a work by an author named Wordsworth. If readers want more information about this source, they can turn to the Works Cited page, where, under the name of Wordsworth, they would find the following information:
Wordsworth, William. Lyrical Ballads . Oxford UP, 1967.
In-text citations for print sources with known author
For print sources like books, magazines, scholarly journal articles, and newspapers, provide a signal word or phrase (usually the author’s last name) and a page number. If you provide the signal word/phrase in the sentence, you do not need to include it in the parenthetical citation.
These examples must correspond to an entry that begins with Burke, which will be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of an entry on the Works Cited page:
Burke, Kenneth. Language as Symbolic Action: Essays on Life, Literature, and Method . University of California Press, 1966.
In-text citations for print sources by a corporate author
When a source has a corporate author, it is acceptable to use the name of the corporation followed by the page number for the in-text citation. You should also use abbreviations (e.g., nat'l for national) where appropriate, so as to avoid interrupting the flow of reading with overly long parenthetical citations.
In-text citations for sources with non-standard labeling systems
If a source uses a labeling or numbering system other than page numbers, such as a script or poetry, precede the citation with said label. When citing a poem, for instance, the parenthetical would begin with the word “line”, and then the line number or range. For example, the examination of William Blake’s poem “The Tyger” would be cited as such:
The speaker makes an ardent call for the exploration of the connection between the violence of nature and the divinity of creation. “In what distant deeps or skies. / Burnt the fire of thine eyes," they ask in reference to the tiger as they attempt to reconcile their intimidation with their relationship to creationism (lines 5-6).
Longer labels, such as chapters (ch.) and scenes (sc.), should be abbreviated.
In-text citations for print sources with no known author
When a source has no known author, use a shortened title of the work instead of an author name, following these guidelines.
Place the title in quotation marks if it's a short work (such as an article) or italicize it if it's a longer work (e.g. plays, books, television shows, entire Web sites) and provide a page number if it is available.
Titles longer than a standard noun phrase should be shortened into a noun phrase by excluding articles. For example, To the Lighthouse would be shortened to Lighthouse .
If the title cannot be easily shortened into a noun phrase, the title should be cut after the first clause, phrase, or punctuation:
In this example, since the reader does not know the author of the article, an abbreviated title appears in the parenthetical citation, and the full title of the article appears first at the left-hand margin of its respective entry on the Works Cited page. Thus, the writer includes the title in quotation marks as the signal phrase in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader directly to the source on the Works Cited page. The Works Cited entry appears as follows:
"The Impact of Global Warming in North America." Global Warming: Early Signs . 1999. www.climatehotmap.org/. Accessed 23 Mar. 2009.
If the title of the work begins with a quotation mark, such as a title that refers to another work, that quote or quoted title can be used as the shortened title. The single quotation marks must be included in the parenthetical, rather than the double quotation.
Parenthetical citations and Works Cited pages, used in conjunction, allow readers to know which sources you consulted in writing your essay, so that they can either verify your interpretation of the sources or use them in their own scholarly work.
Author-page citation for classic and literary works with multiple editions
Page numbers are always required, but additional citation information can help literary scholars, who may have a different edition of a classic work, like Marx and Engels's The Communist Manifesto . In such cases, give the page number of your edition (making sure the edition is listed in your Works Cited page, of course) followed by a semicolon, and then the appropriate abbreviations for volume (vol.), book (bk.), part (pt.), chapter (ch.), section (sec.), or paragraph (par.). For example:

Author-page citation for works in an anthology, periodical, or collection
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write something like this:
See also our page on documenting periodicals in the Works Cited .
Citing authors with same last names
Sometimes more information is necessary to identify the source from which a quotation is taken. For instance, if two or more authors have the same last name, provide both authors' first initials (or even the authors' full name if different authors share initials) in your citation. For example:
Citing a work by multiple authors
For a source with two authors, list the authors’ last names in the text or in the parenthetical citation:
Corresponding Works Cited entry:
Best, David, and Sharon Marcus. “Surface Reading: An Introduction.” Representations , vol. 108, no. 1, Fall 2009, pp. 1-21. JSTOR, doi:10.1525/rep.2009.108.1.1
For a source with three or more authors, list only the first author’s last name, and replace the additional names with et al.
Franck, Caroline, et al. “Agricultural Subsidies and the American Obesity Epidemic.” American Journal of Preventative Medicine , vol. 45, no. 3, Sept. 2013, pp. 327-333.
Citing multiple works by the same author
If you cite more than one work by an author, include a shortened title for the particular work from which you are quoting to distinguish it from the others. Put short titles of books in italics and short titles of articles in quotation marks.
Citing two articles by the same author :
Citing two books by the same author :
Additionally, if the author's name is not mentioned in the sentence, format your citation with the author's name followed by a comma, followed by a shortened title of the work, and, when appropriate, the page number(s):
Citing multivolume works
If you cite from different volumes of a multivolume work, always include the volume number followed by a colon. Put a space after the colon, then provide the page number(s). (If you only cite from one volume, provide only the page number in parentheses.)
Citing the Bible
In your first parenthetical citation, you want to make clear which Bible you're using (and underline or italicize the title), as each version varies in its translation, followed by book (do not italicize or underline), chapter, and verse. For example:
If future references employ the same edition of the Bible you’re using, list only the book, chapter, and verse in the parenthetical citation:
John of Patmos echoes this passage when describing his vision (Rev. 4.6-8).
Citing indirect sources
Sometimes you may have to use an indirect source. An indirect source is a source cited within another source. For such indirect quotations, use "qtd. in" to indicate the source you actually consulted. For example:
Note that, in most cases, a responsible researcher will attempt to find the original source, rather than citing an indirect source.
Citing transcripts, plays, or screenplays
Sources that take the form of a dialogue involving two or more participants have special guidelines for their quotation and citation. Each line of dialogue should begin with the speaker's name written in all capitals and indented half an inch. A period follows the name (e.g., JAMES.) . After the period, write the dialogue. Each successive line after the first should receive an additional indentation. When another person begins speaking, start a new line with that person's name indented only half an inch. Repeat this pattern each time the speaker changes. You can include stage directions in the quote if they appear in the original source.
Conclude with a parenthetical that explains where to find the excerpt in the source. Usually, the author and title of the source can be given in a signal phrase before quoting the excerpt, so the concluding parenthetical will often just contain location information like page numbers or act/scene indicators.
Here is an example from O'Neill's The Iceman Cometh.
WILLIE. (Pleadingly) Give me a drink, Rocky. Harry said it was all right. God, I need a drink.
ROCKY. Den grab it. It's right under your nose.
WILLIE. (Avidly) Thanks. (He takes the bottle with both twitching hands and tilts it to his lips and gulps down the whiskey in big swallows.) (1.1)
Citing non-print or sources from the Internet
With more and more scholarly work published on the Internet, you may have to cite sources you found in digital environments. While many sources on the Internet should not be used for scholarly work (reference the OWL's Evaluating Sources of Information resource), some Web sources are perfectly acceptable for research. When creating in-text citations for electronic, film, or Internet sources, remember that your citation must reference the source on your Works Cited page.
Sometimes writers are confused with how to craft parenthetical citations for electronic sources because of the absence of page numbers. However, these sorts of entries often do not require a page number in the parenthetical citation. For electronic and Internet sources, follow the following guidelines:
- Include in the text the first item that appears in the Work Cited entry that corresponds to the citation (e.g. author name, article name, website name, film name).
- Do not provide paragraph numbers or page numbers based on your Web browser’s print preview function.
- Unless you must list the Web site name in the signal phrase in order to get the reader to the appropriate entry, do not include URLs in-text. Only provide partial URLs such as when the name of the site includes, for example, a domain name, like CNN.com or Forbes.com, as opposed to writing out http://www.cnn.com or http://www.forbes.com.
Miscellaneous non-print sources
Two types of non-print sources you may encounter are films and lectures/presentations:
In the two examples above “Herzog” (a film’s director) and “Yates” (a presentor) lead the reader to the first item in each citation’s respective entry on the Works Cited page:
Herzog, Werner, dir. Fitzcarraldo . Perf. Klaus Kinski. Filmverlag der Autoren, 1982.
Yates, Jane. "Invention in Rhetoric and Composition." Gaps Addressed: Future Work in Rhetoric and Composition, CCCC, Palmer House Hilton, 2002. Address.
Electronic sources
Electronic sources may include web pages and online news or magazine articles:
In the first example (an online magazine article), the writer has chosen not to include the author name in-text; however, two entries from the same author appear in the Works Cited. Thus, the writer includes both the author’s last name and the article title in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader to the appropriate entry on the Works Cited page (see below).
In the second example (a web page), a parenthetical citation is not necessary because the page does not list an author, and the title of the article, “MLA Formatting and Style Guide,” is used as a signal phrase within the sentence. If the title of the article was not named in the sentence, an abbreviated version would appear in a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence. Both corresponding Works Cited entries are as follows:
Taylor, Rumsey. "Fitzcarraldo." Slant , 13 Jun. 2003, www.slantmagazine.com/film/review/fitzcarraldo/. Accessed 29 Sep. 2009.
"MLA Formatting and Style Guide." The Purdue OWL , 2 Aug. 2016, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/01/. Accessed 2 April 2018.
Multiple citations
To cite multiple sources in the same parenthetical reference, separate the citations by a semi-colon:
Time-based media sources
When creating in-text citations for media that has a runtime, such as a movie or podcast, include the range of hours, minutes and seconds you plan to reference. For example: (00:02:15-00:02:35).
When a citation is not needed
Common sense and ethics should determine your need for documenting sources. You do not need to give sources for familiar proverbs, well-known quotations, or common knowledge (For example, it is expected that U.S. citizens know that George Washington was the first President.). Remember that citing sources is a rhetorical task, and, as such, can vary based on your audience. If you’re writing for an expert audience of a scholarly journal, for example, you may need to deal with expectations of what constitutes “common knowledge” that differ from common norms.
Other Sources
The MLA Handbook describes how to cite many different kinds of authors and content creators. However, you may occasionally encounter a source or author category that the handbook does not describe, making the best way to proceed can be unclear.
In these cases, it's typically acceptable to apply the general principles of MLA citation to the new kind of source in a way that's consistent and sensible. A good way to do this is to simply use the standard MLA directions for a type of source that resembles the source you want to cite.
You may also want to investigate whether a third-party organization has provided directions for how to cite this kind of source. For example, Norquest College provides guidelines for citing Indigenous Elders and Knowledge Keepers —an author category that does not appear in the MLA Handbook . In cases like this, however, it's a good idea to ask your instructor or supervisor whether using third-party citation guidelines might present problems.
- Craft and Criticism
- Fiction and Poetry
- News and Culture
- Lit Hub Radio
- Reading Lists

- Literary Criticism
- Craft and Advice
- In Conversation
- On Translation
- Short Story
- From the Novel
- Bookstores and Libraries
- Film and TV
- Art and Photography
- Freeman’s
- The Virtual Book Channel
- Behind the Mic
- Beyond the Page
- The Cosmic Library
- The Critic and Her Publics
- Emergence Magazine
- Fiction/Non/Fiction
- First Draft: A Dialogue on Writing
- The History of Literature
- I’m a Writer But
- Lit Century
- Tor Presents: Voyage Into Genre
- Windham-Campbell Prizes Podcast
- Write-minded
- The Best of the Decade
- Best Reviewed Books
- BookMarks Daily Giveaway
- The Daily Thrill
- CrimeReads Daily Giveaway

The Importance of Play: On Finding Joy in your Writing Practice
How to approach your work with open hands, not closed fists.
This article originally appeared in Issue #62, Winter 2017 issue of Creative Nonfiction .
On the last morning of a writers’ retreat I went to a year ago, there was a tiny bell lying on the seat of every chair in the spacious conference center. The weekend was unlike any gathering of writers I’d ever been to: for two days, we attendees had listened, enthralled, to one heresy after another. “Find a hobby that isn’t writing,” one speaker said. “Take walks. Do yoga. Don’t be literary. Be a human being.” Another went further. “It doesn’t take that much time to get writing done,” she said, and a gasp rippled through the audience. Here were writers who took their art seriously, but not themselves—at least, not all the time.
I was charmed to find the little trinket on my seat. What was it for? While the auditorium began to fill, people traded them, pocketed them, bounced them from hand to hand.
One of the workshop leaders took the microphone. He asked us to take our bells, hold them as tightly as we could, and give them a shake. Nothing happened, although several faces turned red with exertion.
“Now take your bell,” he said, “hold it loosely in your hand, and shake it.”
Lovely tinkling music filled the giant room up to its vaulted ceiling.
“That’s how you need to approach writing,” he told us—not with clenched fists, but with open hands.
Relaxed. Playful. Open to possibility.
I returned home from the weekend, set the bell on my desk, and told myself the next hour or two was just for fun. Then I started to write—with results that surprised me. I began to wonder if other writers knew something I didn’t. Could writing be as enjoyable at the outset as at the conclusion? Could it be—dare I say it?—something close to play?
I interviewed four of my favorite writers to find out, and, although they didn’t all use (or even like) the word play , some clear themes began to emerge. Themes like surprise, laughter, and a willingness to let go of self-consciousness and convention. These writers have discovered ways to bring joy into their work, so perhaps it’s no surprise that their writing is a delight to read.
Brenda Miller
One of the workshop leaders at the retreat was Brenda Miller. As she walked us through the steps of writing short, powerful pieces, like her much-anthologized apologia “Swerve” and the sensory-rich “What I Could Eat,” she couldn’t stop smiling. On the last day of the conference, I asked her about her generative writing group, which meets every week to do a series of unusual exercises: first, five minutes of subject-verb-object sentences; then, ten minutes of linking sentences; and finally, one long, continuous run-on sentence for twenty minutes. I was puzzled by so much prescription.
“It’s an interesting paradox,” she said.
Sometimes, the more constraints we give ourselves, the more fun we can have. Think about the rules of a sport or a game: while a free-for-all may sound like fun, we often prefer to have rules and guidelines, and to see how much creativity and mastery we can accomplish within those guidelines. For these particular exercises (which were taught to me by the artist and writer Nancy Canyon), the rules give your intellectual mind something to concentrate on, and then your subconscious mind can come out to play. The time limit quiets the inner censor and forces you to keep writing whatever comes out.
Miller said she also plays in her writing practice by trying pieces as “hermit crab” essays:
In a hermit crab piece, you are adopting already existing forms to tell your story, such as a recipe, a how-to article, etc. I’ve written pieces in the forms of rejection notes, field guides, a table of figures, and how-to pieces. I end up having so much fun developing and playing with the voices of these forms that the writing barely seems like work. In the rejection note piece, titled, “We Regret to Inform You,” I begin by cataloging all the rejections one receives from grade school on, so it starts on a lighthearted note and gets progressively more serious as the chronology goes along, including my experiences with two miscarriages in my early twenties.
Miller has talked about seasons in her writing life—writing in solitude, writing in community, and, most recently, writing in collaboration:
I’ve been doing two different collaborations over the last year: one with my colleague and friend Lee Gulyas and one with my friend Julie Marie Wade. With Lee, we’ve been trading photographs and writing to the images, sometimes together and sometimes individually. You never know what the image will trigger, how our two perspectives will either mesh or diverge.
With Julie, we’ve written many different kinds of essays, usually with one of us starting on a specific topic and lobbing the essay back to the other. In this way, the essay builds bit by bit, shifting directions, always surprising us. Sometimes, it feels like a conversation with each section referring directly to something that came before (such as the essay “Toys” in CNF #60); sometimes, it feels more like parallel play.
I asked if she had always approached writing with this attitude of play.
I can say that after writing for more than thirty years, and teaching for almost twenty, I had to find some new ways to approach the writing process, or I would have stopped writing altogether. As a creative nonfiction writer, it can be easy to feel like you’ve used up your material, so the emphasis becomes finding new perspectives and forms. And yes, this approach makes me very happy to write. I get that thrill of writing something new and unexpected almost every time I come out to play.
Brian Doyle
I first met Brian Doyle at a writers’ workshop fifteen years ago and have been a fan ever since. He had a handout that suggested writers think sideways: What does grass mean? How does winter smell? In “Playfulnessness: A Note,” Doyle argues that the essay is “the most playful of forms, liable to hilarity and free association and startlement.” I recently asked him if he thinks he brings those qualities to his own writing.
Hmm—I do think it’s true, and immediately think of my sister saying I am congenitally wonder-addled because I got spectacles at age seven and have never recovered from that wash of wonder. I suppose I am also sort of addicted to the salt and swing and song of the American language, which is a bruised dusty lewd brave vibrant language, and trammeling it carefully seems disrespectful to me, as long as I am clear. I set out with an idea and try to hammer sentences that have loose ends; does that make sense? I never know where a story or an essay or a proem is going to end up, or even go, quite. . . . I just start, and I have in mind that I want to write like people talk and think, in loose-limbed, free, piercing, entertaining ways, and things go from there—sometimes utterly to the dogs.
I had to ask: what does it mean to hammer sentences that have loose ends?
I am trying to stay open to surprise, to spin, to swerve, to deepen—I want to start and then see what happens. I suspect that if you know exactly what you want to say, or exactly how a piece should end, then you have put yourself in a polite jail cell. I have the utmost respect for op-eds and editorials and reports and journalism, but I also love and am much more deeply moved by pieces that are open to surprise. An example for me is a long essay called “The Meteorites,” which started out simply as a list of all the weird summer jobs I’d had, and morphed into a piece about being a counselor at a summer day camp, and finally into a piece very much about the spangle and spatter of light and love.
Language isn’t the only thing Doyle doesn’t “trammel carefully.” He also plays with form, and I asked him about his proems —the word he uses to describe his box-shaped pieces that are part poem, part prose, part prayer.
With the proems, I want to get to some place between prose and poems, because while poems at their best are the form closest to music and swing and rhythm and cadence, at their worst, they are artsy-fartsy selfish elusive self-absorbed muddles; can you make a thing that’s alert to music but also clear as a bell, in unadorned conversational lines? And as regarding forms, there are so many: the story that’s all one voice; a paragraph in which two stories are being told alternately, as happens in my novel Mink River; the essay that is clearly wildly hyperbolic but also totally true because you waved the hyperbole flag, somehow. . .
Doyle has advised new writers to “type fast and tell a story with your fingers.”
Newer writers very often sit down with expectations and plans and programs and outlines and assumptions as to form, and I think all those things are little jail cells. You shut off so much possible when you insist on what must be. And so much poor writing is just news and memory and explanation and persuasion and report and data and airy opinion; whereas stories are bigger deeper wilder unforgettabler. For me, I think it was years as a journalist on magazines and papers in Boston and Chicago that made me yearn for what was under mere reporting and accounting. Could I catch and share moments, images, the deeper story? Could you use one tiny story to carry a thousand bigger stories on its shoulders?
David Quammen
I met David Quammen a year ago when I interviewed him about his book Ebola in the wake of the 2014 outbreak. A literary journalist who specializes in ecology and evolutionary biology, Quammen told me, then, that his purposes “are divided about halfway between education and vaudeville” as he tries to make science writing accessible to a broad audience. When I recently asked him about approaching writing with an attitude of playfulness, he made it clear he didn’t like that word:
First thing I want to say is that I distrust programmatic approaches to writing. It can’t be taught. A person is funny or playful if he or she has that capacity. Or not. It’s not a recipe. I love humor. I love surprise. I tend to be a smart aleck. “Playfulness”? Meh.
I pressed him. While playfulness may not be the right word in every case, how writers escape “programmatic” approaches to writing to keep returning and delighting in their work was exactly what I was interested in. How, for instance, does he find moments of relief while writing about infectious disease? He acknowledged the challenge:
The world right now is grim. Problems are dire. It’s rotten, catastrophic. But also filled with wonders, joys, amazing places and things, heroic behaviors. Pratfalls and ridiculosity. It’s always important to be able to laugh in the face of gloom, and in the face of time. I’ve learned that from some of the masters—Samuel Beckett; Faulkner; Ed Abbey; Dorothy Parker; my Irish mother, Mary Egan Quammen.
Quammen noted his humor can be dry and oblique. In Spillover , about the growing incidence of zoonotic diseases (infections that spread from animals to humans), he recounts an instance in which a Texas lab euthanized forty-nine monkeys as a precaution because they shared the same room as one that died and tested positive for Reston virus. Most of the monkeys, later screened posthumously for the virus, tested negative. Without missing a beat, Quammen writes, “Ten employees who had helped unload and handle the monkeys were also screened for infection, and they also tested negative, but none of them were euthanized.”
Gallows humor is helpful, too, if you’re writing about something like Ebola or HIV or herpes B. There’s always room, if it’s done with irony about the brutality of life and with sympathy for the victims’ side. Why not laugh darkly? We need laughter as much as we need pharmaceuticals.
Surprise is something Quammen said he relishes in his work. For him, it comes not from plumbing the depths of memory, but from the people he interviews.
I get interested, immediately, in their whole lives, their whole stories. I wait and hope for them to surprise me. I never ever ever say to a source, “Give me a quote on yadda yadda.” I ask genuine questions. I wait and hope for them to tell me a story because they suddenly feel they can trust me with something they have never told any other person—or, at least, any other writer. Jack Horner did that with me, 35 years ago: dyslexia led him to dinosaur bones. Kelly Warfield did it more recently: working in a 7-Eleven at Fort Detrick led her to Ebola research.
Abigail Thomas
At the writing retreat, Brenda Miller introduced me to Thomas’s first memoir, Safekeeping . She presented it as an example of memoir that—with its tiny micro-chapters, third-person accounts, and soliloquies from Thomas’s sister who comes in now and again to explain the action (a move Miller likened to a Greek chorus)—doesn’t follow convention. It’s a memoir about loss, and yet there are moments when it’s impossible not to laugh. I asked Thomas about the book’s playful tone.
Well, lots of my memories were hilarious, as were the conversations with my sister. Life is full of loss but also a lot of laughs, thank god. And yeah, probably because I had no set plan, no outline, no nothing, anything and everything came marching in. Or slithering. Life is so very funny, right in the middle of everything awful. That’s how we survive, I think.
The way I wrote Safekeeping was determined by the way my memory works (or doesn’t). My memory is terrible, but what I do remember, I remember well. There usually isn’t any interstitial material. After [my second husband] Quin died, these hundreds of little pieces came more or less flying out of me. It wasn’t a plan. I really didn’t know why I was doing what I was doing, didn’t for a long time think it would be a book. I was writing down moments, mostly—moments and feelings I remembered well.
I do think that if you have a memory, and you get it right, you leave it alone. You don’t need to put in the weather report or whatever else is lying around on the grass. Hit it, hit it as best as you can, and move on. And I couldn’t have done it without my sister. Wonderful, the Greek chorus description. Perfect.
Thomas is known for assigning her students “two pages” exercises as a way into a story “they may be staring too directly in the face,” she writes in her book Thinking about Memoir . She recalled a workshop in which she asked students to write two pages about a time they were dressed inappropriately for the occasion:
One woman described what had happened to her first husband. He had been helping load a truck for a neighbor, someone he barely knew, but that was the kind of generous man he was. The truck moved unexpectedly, and her husband was thrown to the ground. By the time they got him to the hospital, he was declared brain-dead. She remembered walking back and forth on the roof of the hospital with her husband’s brother, trying to decide whether or not to take him off life support, and thinking she was wearing the wrong clothes to be making such a decision: cutoffs, a T-shirt, sandals. It was the first time she’d ever written about this, and it was the assignment that gave her a side door. Extremely moving.
Two pages makes it less intimidating. If it goes longer, fine. But it doesn’t have to. We’re not on guard.
There’s a line in Thinking about Memoir that reminds me of the object lesson at the writers’ retreat with the bell: “We do better when we’re not trying too hard,” Thomas writes. “There is nothing more deadening to creativity than the grim determination to write.” How does she avoid the writerly tendency toward grim determination?
Doing absolutely nothing helps. Keep quiet. Take note of what you notice. See what happens. Get out of the way. Stop thinking. Wait for the unlikely pair to couple. Take naps. Especially take naps. If something strikes you while you’re beginning to drift off (and it will), get up immediately and write it down. For me, painting is a wonderful way of using a different part of what’s left of my brain. I just wait for the accident, wait for the thing to reveal itself to me. I’m NOT in charge.
What’s the most fun you’ve ever had writing?
Brenda Miller:
The most fun I’ve ever had writing was when I wrote my first hermit crab piece, “How to Meditate.” I loved poking fun at both myself and the earnestness of the meditation community while still getting at the heart of some essential experiences. It was the first time I felt so immersed in a voice not my own, and I wrote the entire piece in one twelve-hour writing day on retreat at the Ucross Foundation in Wyoming.
Brian Doyle:
Oh man, a nonfiction book about a year in a vineyard: The Grail . That was fun for all sorts of reasons, not just the wine. To write loose and free about a real place and people and science, to write a fun book about wine in a world filled with so many somber, lugubrious books about wine. . . .
David Quammen:
In Spillover, I used the techniques of fiction (which I had once used in writing novels) to give the reader an imagined (truth in advertising) version of how the fateful passage of HIV from a forest-dwelling chimpanzee to the big cities of Central Africa may have happened. It was risky, this movement in a nonfiction book from carefully reported scientific fact into a mythic mode—and it was liberating, and maybe a bit provocative. I can still remember the thrill as my hypothetical story of that event, featuring a character I called the Voyager, unfolded for me each day on the page. It was great fun, in roughly the same way that running a Class V stretch of whitewater in a kayak is fun—dangerous, exhilarating, worth-the-risk fun.
Abigail Thomas:
Well, I had a lot of fun with “Sixteen Again,” the account of a date where I feel madly in love with the guy who did not return the compliment, and got over it very quickly. The essay changed in the course of the writing from a lament to a sort of triumph, and I wound up laughing.
- Share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Google+ (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)

Susan Bruns Rowe
Previous article, next article, support lit hub..

Join our community of readers.
to the Lithub Daily
Popular posts.

Follow us on Twitter

Reclaiming Of Mice and Men from Parody
- RSS - Posts
Literary Hub
Created by Grove Atlantic and Electric Literature
Sign Up For Our Newsletters
How to Pitch Lit Hub
Advertisers: Contact Us
Privacy Policy
Support Lit Hub - Become A Member
Become a Lit Hub Supporting Member : Because Books Matter
For the past decade, Literary Hub has brought you the best of the book world for free—no paywall. But our future relies on you. In return for a donation, you’ll get an ad-free reading experience , exclusive editors’ picks, book giveaways, and our coveted Joan Didion Lit Hub tote bag . Most importantly, you’ll keep independent book coverage alive and thriving on the internet.

Become a member for as low as $5/month
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Book Name in an Essay
Last Updated: February 14, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Noah Taxis and by wikiHow staff writer, Danielle Blinka, MA, MPA . Noah Taxis is an English Teacher based in San Francisco, California. He has taught as a credentialed teacher for over four years: first at Mountain View High School as a 9th- and 11th-grade English Teacher, then at UISA (Ukiah Independent Study Academy) as a Middle School Independent Study Teacher. He is now a high school English teacher at St. Ignatius College Preparatory School in San Francisco. He received an MA in Secondary Education and Teaching from Stanford University’s Graduate School of Education. He also received an MA in Comparative and World Literature from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and a BA in International Literary & Visual Studies and English from Tufts University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 63,573 times.
When you’re writing an essay that includes a book title, it can be confusing to write the title correctly. However, it’s really easy once you know the rules. How you write the title will vary a little bit depending on the style your instructor assigns and if you are typing or handwriting the essay. Luckily, it's easy to follow the rules for writing a book name in an essay.
Writing Help

Typing an Essay in MLA or Chicago Style Format

- For example, you would write To Kill a Mockingbird , The Lord of the Rings , or Wuthering Heights .

- If you have the book name in front of you, you can just copy it down as it is printed.
- Articles include a, an, and the.
- Prepositions include at, in, on, of, about, since, from, for, until, during, over, above, under, underneath, below, beneath, near, by, next to, between, among, and opposite.
- Coordinating conjunctions include the FANBOYS, which are for, and, not, but, or, yet, and

- For example, you would write the name of William Faulkner’s novel Absalom, Absalom! with both the comma and the exclamation point in italics.

- If the highlight bar goes away, try again, making sure that you don’t click anywhere on the page after you highlight the book name.

- Alternatively, you can press the italicize icon before you type the title.
- If you’re using Microsoft Word to type your essay, the italicize key may appear if you hover over the highlighted book name.

- If the next word after your title appears italicized when you resume typing, simply highlight it and click the italicize icon to remove the formatting.

- For example, The Lord of the Rings trilogy is sometimes published in one volume. In this case, you could write the name of the first novel as "The Fellowship of the Ring" when citing it in an essay.
Typing an Essay in APA Format

- Capitalize the first letter of the words, not the entire word.
- If the word is a two-part hyphenated word in the title, you should capitalize both words. For example, you would write Blue River: The Trial of a Mayor-Elect .
- If there is a dash or colon in the title, you should capitalize the word after the punctuation, regardless of how long the word is. As above, you would write Blue River: The Trial of a Mayor-Elect .

- For example, you would write Philip K. Dick’s Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep? with the question mark italicized.

- If the book name is not highlighted, left click and drag your cursor again, making sure that you don’t click again anywhere on the page.

- If you are using Microsoft Word, the italics icon may appear when you hover over the highlighted book title. It’s okay to click this key.

Handwriting an Essay

- For MLA and Chicago style essays, capitalize the first word of the book name and every word other than articles, prepositions, or coordinating conjunctions. For example, write The Lord of the Rings .
- If you’re using APA style, capitalize the first word and all words longer than 4 letters. [9] X Research source This means you would write Public Policy in Local Government .

- If you’re writing on lined paper, it may help to follow along the line of the paper. However, make sure your line is dark enough so that your instructor will see that you properly underlined the book name.

- For example, you would write Judy Blume’s Are You There, God? It’s Me, Margaret by underlining the punctuation marks as well as the words.
Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about academic writing, check out our in-depth interview with Noah Taxis .
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_general_format.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/subject_specific_writing/writing_in_literature/writing_about_literature/formatting.html
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/underline-or-italicize-book-titles/
- ↑ https://askus.library.wwu.edu/faq/116757
- ↑ https://libguides.up.edu/apa/books_ebooks
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/italics-quotations/italics
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Writing A Book Title In Your Essay – The Right Way
Table of contents
- 1 APA Style: How to Write Book Titles in Essays
- 2 APA Style Essay: Writing The Name of The Author
- 3 MLA Style Essay: Citing a Book Title
- 4 Chicago Style Essay: Writing the Book Title
- 5 Writing Various Types of Titles
- 6 Should We Underline or Italicize Book Titles?
When you are writing an academic essay , the book title and author’s name should be written in italics. However, if the book title is part of a larger work (such as a journal article), it should be underlined instead. So, you’re wondering how to write a book title in an essay?
Writing an essay with a book title can be tricky, particularly because each style guide has its own formatting rules for including titles in the main text. Whether you are using MLA, APA, Chicago, or Harvard referencing styles, you will need to consider how to properly format the book title. For more complicated literature-based assignments, seeking assistance from an admission essay writing service may be wise, as they specialize in writing essays that incorporate academic sources.
In this article, we will explore how to write both titles in an essay properly so that you avoid any mistakes!
APA Style: How to Write Book Titles in Essays
When writing an essay, you must follow the style guide provided by your professor. Some teachers may require you to use APA style and others MLA style. There are some rules on how to quote a book title in an essay. You should use italics and quotation marks when writing book titles in essays. For example: “ The Rape of Nanking: The Forgotten Holocaust of World War II. “
When writing a book title in APA Style , you should be aware of these rules:
Write the book title in italics and place it after the author’s name, which is presented in reverse order (last name first).
Use quotation marks around the headline of a chapter or article.
Capitalize proper names that are not common nouns (names of people, places, organizations), but do not capitalize words such as “and,” “or,” “to,” or “and/or.”
Do not capitalize prepositions that appear at the beginning of titles if they are followed by an article (e.g., “A,” “An”), but do capitalize prepositions at the beginning of titles if they are not followed by articles (“Of”).
The first word of the headline should be capitalized, as well as any other words after a colon or hyphen. For example, “The Elements of Style: Grammar for Everyone” or “Theories of Personality: Critical Perspectives.”
Capitalize proper names and words derived from them (e.g., the names of people, places, organizations), except proper nouns used generically (e.g., ‘a bed’).
APA Style Essay: Writing The Name of The Author
You should always use the full name and surname of the author in your APA essay because this will give proper credit to the writer. If you do not mention the author’s full name, people may not know who wrote what and will think you copied it from somewhere else. This will cause lots of problems for you and your reputation as well.
Make sure that all authors’ names appear in the same format in each entry. For example, if one person’s surname is Smith and another’s is Jones, both have first names starting with “J.” It may seem like they are being cited as different people when they’re actually written differently from each other on separate pages in your paper.
To write an APA essay without any issues, there are certain rules that you need to follow while writing an author’s name in APA essay:
- Use only one author’s name in your paper unless there are multiple authors
- If there are multiple authors, then use both their last names followed by the initials of their first names
- Only use initials of first names when there are three or more authors; otherwise, use full names with their last names
Example: Johnson, M.C., Carlson, M., Smith, J. N., & Hanover, L. E.
MLA Style Essay: Citing a Book Title
Now let’s discuss how to mention a book in an essay. The MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers, 7th edition, published by the Modern Language Association (2014), contains detailed rules about how to cite a book title in an essay.
The following guidelines will instruct you on how to refer to a book in an essay in MLA style :
- List your sources at the end of your paper, before the works cited page or bibliography.
- Use italics for titles of books, magazines, and newspapers, but not for articles within those publications, which should be placed in quotation marks.
- Include all relevant book information under two categories: “title” and “author.” In the former category, include the work’s title and its subtitle if there is one; do this even if neither appears on your title page (see below). In the latter category, include only primary authors who have written or edited an entire book; if there are multiple contributors, you should cite them separately under each.
The general format for citing the title of the book in an essay is as follows:
Author’s last name, first initial (Date). Title of Book with Subtitle if there is one. Publisher Name/Location of Publisher; Year Published
Chicago Style Essay: Writing the Book Title
One of the most important things to remember when writing in Chicago style is how to write the title of a book in an essay. To write a good book title in an essay, you should follow these steps:
- Write it at the beginning of your sentence.
- Capitalize it just like any other noun or proper noun.
- Put a comma after the title unless it’s an introductory clause or phrase. For example: “The Firm,” by John Grisham (not “by”) and “The Catcher in the Rye,” by J.D Salinger (not “and”).
- In addition to the book’s name, punctuation marks should also be italicized.
For example: Harry Potter and the Half-blood Prince: Children’s Edition
Writing Various Types of Titles
Now that we covered how to write a book title and author in an essay, it’s time to look at some different types of titles. When you write a book title in an essay, several things must be considered. Whether it’s a book, series, chapter title, editor’s name, or author’s name, how you write it depends on where it appears in your paper.
Here are some key rules for writing headings for novels:
- Use capital letters to write the title of the novel. For example, The Secret Garden by Frances Hodgson Burnett .
- Use italics and capital letters to write the name of the author and his/her other works mentioned in a book title—for example, Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice (1813) .
You should use quotation marks when writing headings of short title poems, articles, and stories.
However, before deciding which format to use, it is important to understand the main idea you want to express in your essay. Additionally, you could use essay papers for sale to help you accomplish your goal of writing an essay effectively.

Should We Underline or Italicize Book Titles?
It depends on which style guide you use. The Modern Language Association and Chicago Manual of Style both suggest using italics, while the American Psychological Association suggests using quotation marks with a few exceptions.
The way you write the title of a book in an essay is different depending on the instructions you were given. For example, if you’re writing an essay in APA style, use quotation marks around the book’s name. If you’re writing for MLA or Chicago style , however, italicize the book’s name instead. If you’re writing a handwritten essay instead of using a computer, capitalize and underline the book’s name.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / How to Cite Sources
How to Cite Sources
Here is a complete list for how to cite sources. Most of these guides present citation guidance and examples in MLA, APA, and Chicago.
If you’re looking for general information on MLA or APA citations , the EasyBib Writing Center was designed for you! It has articles on what’s needed in an MLA in-text citation , how to format an APA paper, what an MLA annotated bibliography is, making an MLA works cited page, and much more!
MLA Format Citation Examples
The Modern Language Association created the MLA Style, currently in its 9th edition, to provide researchers with guidelines for writing and documenting scholarly borrowings. Most often used in the humanities, MLA style (or MLA format ) has been adopted and used by numerous other disciplines, in multiple parts of the world.
MLA provides standard rules to follow so that most research papers are formatted in a similar manner. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the information. The MLA in-text citation guidelines, MLA works cited standards, and MLA annotated bibliography instructions provide scholars with the information they need to properly cite sources in their research papers, articles, and assignments.
- Book Chapter
- Conference Paper
- Documentary
- Encyclopedia
- Google Images
- Kindle Book
- Memorial Inscription
- Museum Exhibit
- Painting or Artwork
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Sheet Music
- Thesis or Dissertation
- YouTube Video
APA Format Citation Examples
The American Psychological Association created the APA citation style in 1929 as a way to help psychologists, anthropologists, and even business managers establish one common way to cite sources and present content.
APA is used when citing sources for academic articles such as journals, and is intended to help readers better comprehend content, and to avoid language bias wherever possible. The APA style (or APA format ) is now in its 7th edition, and provides citation style guides for virtually any type of resource.
Chicago Style Citation Examples
The Chicago/Turabian style of citing sources is generally used when citing sources for humanities papers, and is best known for its requirement that writers place bibliographic citations at the bottom of a page (in Chicago-format footnotes ) or at the end of a paper (endnotes).
The Turabian and Chicago citation styles are almost identical, but the Turabian style is geared towards student published papers such as theses and dissertations, while the Chicago style provides guidelines for all types of publications. This is why you’ll commonly see Chicago style and Turabian style presented together. The Chicago Manual of Style is currently in its 17th edition, and Turabian’s A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations is in its 8th edition.
Citing Specific Sources or Events
- Declaration of Independence
- Gettysburg Address
- Martin Luther King Jr. Speech
- President Obama’s Farewell Address
- President Trump’s Inauguration Speech
- White House Press Briefing
Additional FAQs
- Citing Archived Contributors
- Citing a Blog
- Citing a Book Chapter
- Citing a Source in a Foreign Language
- Citing an Image
- Citing a Song
- Citing Special Contributors
- Citing a Translated Article
- Citing a Tweet
6 Interesting Citation Facts
The world of citations may seem cut and dry, but there’s more to them than just specific capitalization rules, MLA in-text citations , and other formatting specifications. Citations have been helping researches document their sources for hundreds of years, and are a great way to learn more about a particular subject area.
Ever wonder what sets all the different styles apart, or how they came to be in the first place? Read on for some interesting facts about citations!
1. There are Over 7,000 Different Citation Styles
You may be familiar with MLA and APA citation styles, but there are actually thousands of citation styles used for all different academic disciplines all across the world. Deciding which one to use can be difficult, so be sure to ask you instructor which one you should be using for your next paper.
2. Some Citation Styles are Named After People
While a majority of citation styles are named for the specific organizations that publish them (i.e. APA is published by the American Psychological Association, and MLA format is named for the Modern Language Association), some are actually named after individuals. The most well-known example of this is perhaps Turabian style, named for Kate L. Turabian, an American educator and writer. She developed this style as a condensed version of the Chicago Manual of Style in order to present a more concise set of rules to students.
3. There are Some Really Specific and Uniquely Named Citation Styles
How specific can citation styles get? The answer is very. For example, the “Flavour and Fragrance Journal” style is based on a bimonthly, peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1985 by John Wiley & Sons. It publishes original research articles, reviews and special reports on all aspects of flavor and fragrance. Another example is “Nordic Pulp and Paper Research,” a style used by an international scientific magazine covering science and technology for the areas of wood or bio-mass constituents.
4. More citations were created on EasyBib.com in the first quarter of 2018 than there are people in California.
The US Census Bureau estimates that approximately 39.5 million people live in the state of California. Meanwhile, about 43 million citations were made on EasyBib from January to March of 2018. That’s a lot of citations.
5. “Citations” is a Word With a Long History
The word “citations” can be traced back literally thousands of years to the Latin word “citare” meaning “to summon, urge, call; put in sudden motion, call forward; rouse, excite.” The word then took on its more modern meaning and relevance to writing papers in the 1600s, where it became known as the “act of citing or quoting a passage from a book, etc.”
6. Citation Styles are Always Changing
The concept of citations always stays the same. It is a means of preventing plagiarism and demonstrating where you relied on outside sources. The specific style rules, however, can and do change regularly. For example, in 2018 alone, 46 new citation styles were introduced , and 106 updates were made to exiting styles. At EasyBib, we are always on the lookout for ways to improve our styles and opportunities to add new ones to our list.
Why Citations Matter
Here are the ways accurate citations can help your students achieve academic success, and how you can answer the dreaded question, “why should I cite my sources?”
They Give Credit to the Right People
Citing their sources makes sure that the reader can differentiate the student’s original thoughts from those of other researchers. Not only does this make sure that the sources they use receive proper credit for their work, it ensures that the student receives deserved recognition for their unique contributions to the topic. Whether the student is citing in MLA format , APA format , or any other style, citations serve as a natural way to place a student’s work in the broader context of the subject area, and serve as an easy way to gauge their commitment to the project.
They Provide Hard Evidence of Ideas
Having many citations from a wide variety of sources related to their idea means that the student is working on a well-researched and respected subject. Citing sources that back up their claim creates room for fact-checking and further research . And, if they can cite a few sources that have the converse opinion or idea, and then demonstrate to the reader why they believe that that viewpoint is wrong by again citing credible sources, the student is well on their way to winning over the reader and cementing their point of view.
They Promote Originality and Prevent Plagiarism
The point of research projects is not to regurgitate information that can already be found elsewhere. We have Google for that! What the student’s project should aim to do is promote an original idea or a spin on an existing idea, and use reliable sources to promote that idea. Copying or directly referencing a source without proper citation can lead to not only a poor grade, but accusations of academic dishonesty. By citing their sources regularly and accurately, students can easily avoid the trap of plagiarism , and promote further research on their topic.
They Create Better Researchers
By researching sources to back up and promote their ideas, students are becoming better researchers without even knowing it! Each time a new source is read or researched, the student is becoming more engaged with the project and is developing a deeper understanding of the subject area. Proper citations demonstrate a breadth of the student’s reading and dedication to the project itself. By creating citations, students are compelled to make connections between their sources and discern research patterns. Each time they complete this process, they are helping themselves become better researchers and writers overall.
When is the Right Time to Start Making Citations?
Make in-text/parenthetical citations as you need them.
As you are writing your paper, be sure to include references within the text that correspond with references in a works cited or bibliography. These are usually called in-text citations or parenthetical citations in MLA and APA formats. The most effective time to complete these is directly after you have made your reference to another source. For instance, after writing the line from Charles Dickens’ A Tale of Two Cities : “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times…,” you would include a citation like this (depending on your chosen citation style):
(Dickens 11).
This signals to the reader that you have referenced an outside source. What’s great about this system is that the in-text citations serve as a natural list for all of the citations you have made in your paper, which will make completing the works cited page a whole lot easier. After you are done writing, all that will be left for you to do is scan your paper for these references, and then build a works cited page that includes a citation for each one.
Need help creating an MLA works cited page ? Try the MLA format generator on EasyBib.com! We also have a guide on how to format an APA reference page .
2. Understand the General Formatting Rules of Your Citation Style Before You Start Writing
While reading up on paper formatting may not sound exciting, being aware of how your paper should look early on in the paper writing process is super important. Citation styles can dictate more than just the appearance of the citations themselves, but rather can impact the layout of your paper as a whole, with specific guidelines concerning margin width, title treatment, and even font size and spacing. Knowing how to organize your paper before you start writing will ensure that you do not receive a low grade for something as trivial as forgetting a hanging indent.
Don’t know where to start? Here’s a formatting guide on APA format .
3. Double-check All of Your Outside Sources for Relevance and Trustworthiness First
Collecting outside sources that support your research and specific topic is a critical step in writing an effective paper. But before you run to the library and grab the first 20 books you can lay your hands on, keep in mind that selecting a source to include in your paper should not be taken lightly. Before you proceed with using it to backup your ideas, run a quick Internet search for it and see if other scholars in your field have written about it as well. Check to see if there are book reviews about it or peer accolades. If you spot something that seems off to you, you may want to consider leaving it out of your work. Doing this before your start making citations can save you a ton of time in the long run.
Finished with your paper? It may be time to run it through a grammar and plagiarism checker , like the one offered by EasyBib Plus. If you’re just looking to brush up on the basics, our grammar guides are ready anytime you are.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
- Irresistible Tech Gifts for That Special Dad
- Killer Smartphone Deals We Love
Proper Formatting of Song Titles in Written Documents
Learn when to use italics and quotation marks to write clearly
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/WorkBadgePhoto-61c0b98ef5a74e4a85851a8f706dbd65.jpg)
- Animation & Video
What to Know
- Refer to the style guide specified by your employer, client, or teacher.
- In the absence of a style guide, the general rule is to use quotation marks for song titles and italicize CD or album titles.
- Don't use underlining in place of italics unless you are using a typewriter or writing titles by hand.
This article explains the proper formatting of song titles in written documents and includes examples.
How to Format Song Titles in Written Documents
For matters of style when punctuating and formatting titles of any kind, turn first to the style guide prescribed by your employer, client, or teacher. In the absence of a style guide, use the following guidelines:
- Put quotation marks around song titles : For best appearance in professionally typeset material, use proper typographical quote marks and apostrophes ( curly quotes ).
- Set CD/album titles in italics : In typeset material, watch out for fake italics . That's not a grammar rule but it is a good design and printing rule.
- Do not use underlining (in place of italics) unless you're using a typewriter or writing titles by hand.
In desktop publishing and word processing software, create character styles to quickly format song titles and other types of titles used throughout a document.
Example References to Song Titles and Albums
Here are two examples of text that includes song titles and album titles:
- Trace Adkins' first #1 single “(This Ain’t) No Thinkin’ Thing” is from his 1997 CD Dreamin’ Out Loud .
- The title cut from Toby Keith’s How Do You Like Me Now? was the most-played country song of 2000. Other favorites from the same album include “You Shouldn’t Kiss Me Like That” and “Country Comes to Town.”
When the song/album is the same : In the second example, although “ How Do You Like Me Now? ” is the song title, it is also the album title and in that context is treated as the album title, using italics. It would be just as correct to write: My favorite song on the How Do You Like Me Now? album is “How Do You Like Me Now?”
Punctuation in titles : When a song title ends in a question mark, exclamation point, or other punctuation, that punctuation goes inside the quotation marks because it's part of the song title. The beginning portion of the Adkins song title in parentheses is contained in the quotation marks the same as the other part of the song title.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- The 18 Best Tips and Tricks For Spotify
- Why Is Song Metadata Important?
- Underlining in a Plain Text Email
- How to Use APA Format in Google Docs
- How to Use the IF-THEN Function in Excel
- Writing in All Caps Is Like Shouting
- How to Do a Block Quote in Google Docs
- How to Type Curly Quotes and Curly Apostrophes
- Using Markdown in Email to Send Plain Text Messages
- How to Highlight Text in Yahoo Mail Messages
- How to Use Quotation Marks on Search Engines
- Changing the Appearance of Quotation Marks in Microsoft Word
- How to Put iTunes Playlist Songs in the Right Order
- How to Edit Your iPhone or iPad Email Signature
- How to Identify Songs in YouTube Videos
- How to Convert Text to Upper, Lower, or Proper Case in Excel

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2. Use Quotation Marks. Place the titles of one-act plays in quotation marks. MLA calls for titles of short works, such as articles and short poems, to be put in quotation marks. One-act plays fall in this category. 3. Italicize the Title. Italicize the title of longer plays. MLA calls for the title of longer works, such as books and films, to ...
2. Cite the author's name. Note the author's full last name first in the citation. [3] For example, you may write: " (Albee…)" or " (Hansberry…)". 3. Note the title of the play. After the author's last name, put in a comma. Then, write the title of the play you are quoting in italics.
Also, most of the names of works in the works cited section are italicized, articles and sections being the big exception. I also remember finding some works-cited example pages at .edu websites doing a keyword search for +hamlet site: .edu or something similar. I found a site that told how to cite a "live play". This is a quote from that site ...
In-text citation with abbreviated play title (Mac. 2.1.25) How to quote dialogue from a play. When quoting multiple lines of dialogue from a play or screenplay: Set the quote on a new line, indented half an inch from the left margin. Start the dialogue with the character's name in capital letters, followed by a period.
Citing a Play in a Book. *Note: this citation should be used if you find your play in a book where the play is the entire book. Format: Author. Title of Play in Italics. Edition, Publisher, Year. Database Name in Italics (if electronic), URL. Example: Sophocles. Antigone.
Analyzing Plays. When you are writing an analysis of a play, remember that it may combine aspects of both prose and poetry. You might want to refer to the UWC's handouts on analyzing poetry, novels, and short stories, since they contain ideas that also apply to analyzing a play. The main distinction, of course, is that a play is meant to be ...
In AP Style, magazines names and titles are governed by their own rules. See AP Style Magazine Names. How to Capitalize Composition Titles. Capitalize the principal words, including prepositions and conjunctions of four or more letters. Capitalize an article (a, an, the) or words of fewer than four letters if it is the first or last word in the ...
Use quotation marks around the title if it is part of a larger work (e.g. a chapter of a book, an article in a journal, or a page on a website). All major words in a title are capitalized. The same format is used in the Works Cited list and in the text itself. When you use the Scribbr MLA Citation Generator, the correct formatting and ...
Quoting Plays. When you must quote dialogue from a play, adhere to these rules: Set the quotation off from your text. Begin each part of the dialogue with the appropriate character's name. Indent each name half an inch from the left margin and write it in all capital letters. Follow the name with a period and then start the quotation.
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Whether you dream of becoming a great dramatic writer or simply want to express yourself in a new way, writing a play is a rewarding creative exercise. Read on to learn how to write a play and turn your words into a live performance.
Collection or anthology. Put a period after the play's title if published in a collection or anthology, and then give the complete details of the sourcebook. Example. MLA format. Author last name, First name. Title of Play. Collection/Anthology Title, edited by Editor first name Last name, Publisher, Year, Page range. MLA format.
2 — The titles of parts within a book should go in quotation marks: chapter titles, titles of poems inside a collection, acts or scenes in a play, and so on. For example: The Great Gatsby's "Chapter 5: The Meeting". "The Mirror of Erised" from Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone.
Harvard College Writing Center 5 Asking Analytical Questions When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a
APA 7 Format. If you're merely paraphrasing or discussing a play in general terms, you're not required to use a page number or other locator. But if you directly quote a play script, you must include a location for the relevant passage. For plays, this often means including a page number (s). However, some plays use books, chapters, verses ...
To cite a play in a reference entry in APA style 7th edition include the following elements: Author (s) of the play: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J. D.) of up to 20 authors with the last name preceded by an ampersand (&). For 21 or more authors include the first 19 names followed by an ellipsis (…) and add the last author's ...
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...
Themes like surprise, laughter, and a willingness to let go of self-consciousness and convention. These writers have discovered ways to bring joy into their work, so perhaps it's no surprise that their writing is a delight to read. Brenda Miller. One of the workshop leaders at the retreat was Brenda Miller.
For example, you would write the name of William Faulkner's novel Absalom, Absalom! with both the comma and the exclamation point in italics. 4. Highlight the book name. Hover your cursor at the beginning of the book name and left click your mouse. Hold the key down and drag your cursor over the title of the book.
Write it at the beginning of your sentence. Capitalize it just like any other noun or proper noun. Put a comma after the title unless it's an introductory clause or phrase. For example: "The Firm," by John Grisham (not "by") and "The Catcher in the Rye," by J.D Salinger (not "and"). In addition to the book's name ...
The Chicago/Turabian style of citing sources is generally used when citing sources for humanities papers, and is best known for its requirement that writers place bibliographic citations at the bottom of a page (in Chicago-format footnotes) or at the end of a paper (endnotes). The Turabian and Chicago citation styles are almost identical, but ...
In the absence of a style guide, the general rule is to use quotation marks for song titles and italicize CD or album titles. Don't use underlining in place of italics unless you are using a typewriter or writing titles by hand. This article explains the proper formatting of song titles in written documents and includes examples.