Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates

How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
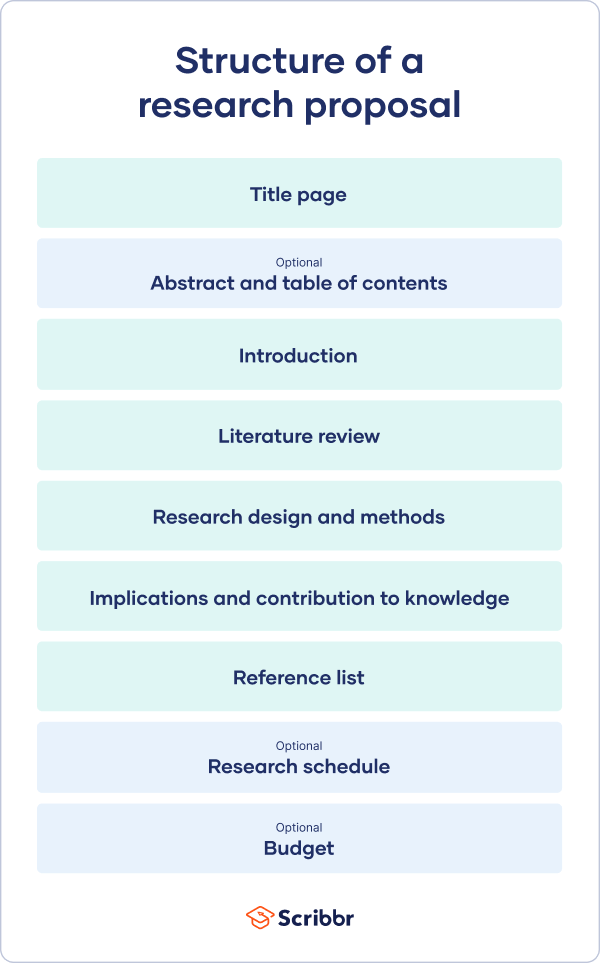
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 31 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a research proposal

What is a research proposal?
What is the purpose of a research proposal , how long should a research proposal be, what should be included in a research proposal, 1. the title page, 2. introduction, 3. literature review, 4. research design, 5. implications, 6. reference list, frequently asked questions about writing a research proposal, related articles.
If you’re in higher education, the term “research proposal” is something you’re likely to be familiar with. But what is it, exactly? You’ll normally come across the need to prepare a research proposal when you’re looking to secure Ph.D. funding.
When you’re trying to find someone to fund your Ph.D. research, a research proposal is essentially your “pitch.”
A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research.
You’ll need to set out the issues that are central to the topic area and how you intend to address them with your research. To do this, you’ll need to give the following:
- an outline of the general area of study within which your research falls
- an overview of how much is currently known about the topic
- a literature review that covers the recent scholarly debate or conversation around the topic
➡️ What is a literature review? Learn more in our guide.
Essentially, you are trying to persuade your institution that you and your project are worth investing their time and money into.
It is the opportunity for you to demonstrate that you have the aptitude for this level of research by showing that you can articulate complex ideas:
It also helps you to find the right supervisor to oversee your research. When you’re writing your research proposal, you should always have this in the back of your mind.
This is the document that potential supervisors will use in determining the legitimacy of your research and, consequently, whether they will invest in you or not. It is therefore incredibly important that you spend some time on getting it right.
Tip: While there may not always be length requirements for research proposals, you should strive to cover everything you need to in a concise way.
If your research proposal is for a bachelor’s or master’s degree, it may only be a few pages long. For a Ph.D., a proposal could be a pretty long document that spans a few dozen pages.
➡️ Research proposals are similar to grant proposals. Learn how to write a grant proposal in our guide.
When you’re writing your proposal, keep in mind its purpose and why you’re writing it. It, therefore, needs to clearly explain the relevance of your research and its context with other discussions on the topic. You need to then explain what approach you will take and why it is feasible.
Generally, your structure should look something like this:
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Research Design
- Implications
If you follow this structure, you’ll have a comprehensive and coherent proposal that looks and feels professional, without missing out on anything important. We’ll take a deep dive into each of these areas one by one next.
The title page might vary slightly per your area of study but, as a general point, your title page should contain the following:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- The name of your institution and your particular department
Tip: Keep in mind any departmental or institutional guidelines for a research proposal title page. Also, your supervisor may ask for specific details to be added to the page.
The introduction is crucial to your research proposal as it is your first opportunity to hook the reader in. A good introduction section will introduce your project and its relevance to the field of study.
You’ll want to use this space to demonstrate that you have carefully thought about how to present your project as interesting, original, and important research. A good place to start is by introducing the context of your research problem.
Think about answering these questions:
- What is it you want to research and why?
- How does this research relate to the respective field?
- How much is already known about this area?
- Who might find this research interesting?
- What are the key questions you aim to answer with your research?
- What will the findings of this project add to the topic area?
Your introduction aims to set yourself off on a great footing and illustrate to the reader that you are an expert in your field and that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge and theory.
The literature review section answers the question who else is talking about your proposed research topic.
You want to demonstrate that your research will contribute to conversations around the topic and that it will sit happily amongst experts in the field.
➡️ Read more about how to write a literature review .
There are lots of ways you can find relevant information for your literature review, including:
- Research relevant academic sources such as books and journals to find similar conversations around the topic.
- Read through abstracts and bibliographies of your academic sources to look for relevance and further additional resources without delving too deep into articles that are possibly not relevant to you.
- Watch out for heavily-cited works . This should help you to identify authoritative work that you need to read and document.
- Look for any research gaps , trends and patterns, common themes, debates, and contradictions.
- Consider any seminal studies on the topic area as it is likely anticipated that you will address these in your research proposal.
This is where you get down to the real meat of your research proposal. It should be a discussion about the overall approach you plan on taking, and the practical steps you’ll follow in answering the research questions you’ve posed.
So what should you discuss here? Some of the key things you will need to discuss at this point are:
- What form will your research take? Is it qualitative/quantitative/mixed? Will your research be primary or secondary?
- What sources will you use? Who or what will you be studying as part of your research.
- Document your research method. How are you practically going to carry out your research? What tools will you need? What procedures will you use?
- Any practicality issues you foresee. Do you think there will be any obstacles to your anticipated timescale? What resources will you require in carrying out your research?
Your research design should also discuss the potential implications of your research. For example, are you looking to confirm an existing theory or develop a new one?
If you intend to create a basis for further research, you should describe this here.
It is important to explain fully what you want the outcome of your research to look like and what you want to achieve by it. This will help those reading your research proposal to decide if it’s something the field needs and wants, and ultimately whether they will support you with it.
When you reach the end of your research proposal, you’ll have to compile a list of references for everything you’ve cited above. Ideally, you should keep track of everything from the beginning. Otherwise, this could be a mammoth and pretty laborious task to do.
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to format and organize your citations. Paperpile allows you to organize and save your citations for later use and cite them in thousands of citation styles directly in Google Docs, Microsoft Word, or LaTeX.
Your project may also require you to have a timeline, depending on the budget you are requesting. If you need one, you should include it here and explain both the timeline and the budget you need, documenting what should be done at each stage of the research and how much of the budget this will use.
This is the final step, but not one to be missed. You should make sure that you edit and proofread your document so that you can be sure there are no mistakes.
A good idea is to have another person proofread the document for you so that you get a fresh pair of eyes on it. You can even have a professional proofreader do this for you.
This is an important document and you don’t want spelling or grammatical mistakes to get in the way of you and your reader.
➡️ Working on a research proposal for a thesis? Take a look at our guide on how to come up with a topic for your thesis .
A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research. Generally, your research proposal will have a title page, introduction, literature review section, a section about research design and explaining the implications of your research, and a reference list.
A good research proposal is concise and coherent. It has a clear purpose, clearly explains the relevance of your research and its context with other discussions on the topic. A good research proposal explains what approach you will take and why it is feasible.
You need a research proposal to persuade your institution that you and your project are worth investing their time and money into. It is your opportunity to demonstrate your aptitude for this level or research by showing that you can articulate complex ideas clearly, concisely, and critically.
A research proposal is essentially your "pitch" when you're trying to find someone to fund your PhD. It is a clear and concise summary of your proposed research. It gives an outline of the general area of study within which your research falls, it elaborates how much is currently known about the topic, and it highlights any recent debate or conversation around the topic by other academics.
The general answer is: as long as it needs to be to cover everything. The length of your research proposal depends on the requirements from the institution that you are applying to. Make sure to carefully read all the instructions given, and if this specific information is not provided, you can always ask.

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
The goal of a research proposal is twofold: to present and justify the need to study a research problem and to present the practical ways in which the proposed study should be conducted. The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews. They must provide persuasive evidence that a need exists for the proposed study. In addition to providing a rationale, a proposal describes detailed methodology for conducting the research consistent with requirements of the professional or academic field and a statement on anticipated outcomes and benefits derived from the study's completion.
Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005.
How to Approach Writing a Research Proposal
Your professor may assign the task of writing a research proposal for the following reasons:
- Develop your skills in thinking about and designing a comprehensive research study;
- Learn how to conduct a comprehensive review of the literature to determine that the research problem has not been adequately addressed or has been answered ineffectively and, in so doing, become better at locating pertinent scholarship related to your topic;
- Improve your general research and writing skills;
- Practice identifying the logical steps that must be taken to accomplish one's research goals;
- Critically review, examine, and consider the use of different methods for gathering and analyzing data related to the research problem; and,
- Nurture a sense of inquisitiveness within yourself and to help see yourself as an active participant in the process of conducting scholarly research.
A proposal should contain all the key elements involved in designing a completed research study, with sufficient information that allows readers to assess the validity and usefulness of your proposed study. The only elements missing from a research proposal are the findings of the study and your analysis of those findings. Finally, an effective proposal is judged on the quality of your writing and, therefore, it is important that your proposal is coherent, clear, and compelling.
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions:
- What do you plan to accomplish? Be clear and succinct in defining the research problem and what it is you are proposing to investigate.
- Why do you want to do the research? In addition to detailing your research design, you also must conduct a thorough review of the literature and provide convincing evidence that it is a topic worthy of in-depth study. A successful research proposal must answer the "So What?" question.
- How are you going to conduct the research? Be sure that what you propose is doable. If you're having difficulty formulating a research problem to propose investigating, go here for strategies in developing a problem to study.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failure to be concise . A research proposal must be focused and not be "all over the map" or diverge into unrelated tangents without a clear sense of purpose.
- Failure to cite landmark works in your literature review . Proposals should be grounded in foundational research that lays a foundation for understanding the development and scope of the the topic and its relevance.
- Failure to delimit the contextual scope of your research [e.g., time, place, people, etc.]. As with any research paper, your proposed study must inform the reader how and in what ways the study will frame the problem.
- Failure to develop a coherent and persuasive argument for the proposed research . This is critical. In many workplace settings, the research proposal is a formal document intended to argue for why a study should be funded.
- Sloppy or imprecise writing, or poor grammar . Although a research proposal does not represent a completed research study, there is still an expectation that it is well-written and follows the style and rules of good academic writing.
- Too much detail on minor issues, but not enough detail on major issues . Your proposal should focus on only a few key research questions in order to support the argument that the research needs to be conducted. Minor issues, even if valid, can be mentioned but they should not dominate the overall narrative.
Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sanford, Keith. Information for Students: Writing a Research Proposal. Baylor University; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences, Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Structure and Writing Style
Beginning the Proposal Process
As with writing most college-level academic papers, research proposals are generally organized the same way throughout most social science disciplines. The text of proposals generally vary in length between ten and thirty-five pages, followed by the list of references. However, before you begin, read the assignment carefully and, if anything seems unclear, ask your professor whether there are any specific requirements for organizing and writing the proposal.
A good place to begin is to ask yourself a series of questions:
- What do I want to study?
- Why is the topic important?
- How is it significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
- What problems will it help solve?
- How does it build upon [and hopefully go beyond] research already conducted on the topic?
- What exactly should I plan to do, and can I get it done in the time available?
In general, a compelling research proposal should document your knowledge of the topic and demonstrate your enthusiasm for conducting the study. Approach it with the intention of leaving your readers feeling like, "Wow, that's an exciting idea and I can’t wait to see how it turns out!"
Most proposals should include the following sections:
I. Introduction
In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project or it's the first step in getting approval to write a doctoral dissertation. Even if this is just a course assignment, treat your introduction as the initial pitch of an idea based on a thorough examination of the significance of a research problem. After reading the introduction, your readers should not only have an understanding of what you want to do, but they should also be able to gain a sense of your passion for the topic and to be excited about the study's possible outcomes. Note that most proposals do not include an abstract [summary] before the introduction.
Think about your introduction as a narrative written in two to four paragraphs that succinctly answers the following four questions :
- What is the central research problem?
- What is the topic of study related to that research problem?
- What methods should be used to analyze the research problem?
- Answer the "So What?" question by explaining why this is important research, what is its significance, and why should someone reading the proposal care about the outcomes of the proposed study?
II. Background and Significance
This is where you explain the scope and context of your proposal and describe in detail why it's important. It can be melded into your introduction or you can create a separate section to help with the organization and narrative flow of your proposal. Approach writing this section with the thought that you can’t assume your readers will know as much about the research problem as you do. Note that this section is not an essay going over everything you have learned about the topic; instead, you must choose what is most relevant in explaining the aims of your research.
To that end, while there are no prescribed rules for establishing the significance of your proposed study, you should attempt to address some or all of the following:
- State the research problem and give a more detailed explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction. This is particularly important if the problem is complex or multifaceted .
- Present the rationale of your proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing; be sure to answer the "So What? question [i.e., why should anyone care?].
- Describe the major issues or problems examined by your research. This can be in the form of questions to be addressed. Be sure to note how your proposed study builds on previous assumptions about the research problem.
- Explain the methods you plan to use for conducting your research. Clearly identify the key sources you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Describe the boundaries of your proposed research in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you plan to study, but what aspects of the research problem will be excluded from the study.
- If necessary, provide definitions of key concepts, theories, or terms.
III. Literature Review
Connected to the background and significance of your study is a section of your proposal devoted to a more deliberate review and synthesis of prior studies related to the research problem under investigation . The purpose here is to place your project within the larger whole of what is currently being explored, while at the same time, demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methodological approaches they have used, and what is your understanding of their findings and, when stated, their recommendations. Also pay attention to any suggestions for further research.
Since a literature review is information dense, it is crucial that this section is intelligently structured to enable a reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your proposed study in relation to the arguments put forth by other researchers. A good strategy is to break the literature into "conceptual categories" [themes] rather than systematically or chronologically describing groups of materials one at a time. Note that conceptual categories generally reveal themselves after you have read most of the pertinent literature on your topic so adding new categories is an on-going process of discovery as you review more studies. How do you know you've covered the key conceptual categories underlying the research literature? Generally, you can have confidence that all of the significant conceptual categories have been identified if you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations that are being made.
NOTE: Do not shy away from challenging the conclusions made in prior research as a basis for supporting the need for your proposal. Assess what you believe is missing and state how previous research has failed to adequately examine the issue that your study addresses. Highlighting the problematic conclusions strengthens your proposal. For more information on writing literature reviews, GO HERE .
To help frame your proposal's review of prior research, consider the "five C’s" of writing a literature review:
- Cite , so as to keep the primary focus on the literature pertinent to your research problem.
- Compare the various arguments, theories, methodologies, and findings expressed in the literature: what do the authors agree on? Who applies similar approaches to analyzing the research problem?
- Contrast the various arguments, themes, methodologies, approaches, and controversies expressed in the literature: describe what are the major areas of disagreement, controversy, or debate among scholars?
- Critique the literature: Which arguments are more persuasive, and why? Which approaches, findings, and methodologies seem most reliable, valid, or appropriate, and why? Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what an author says/does [e.g., asserts, demonstrates, argues, etc.].
- Connect the literature to your own area of research and investigation: how does your own work draw upon, depart from, synthesize, or add a new perspective to what has been said in the literature?
IV. Research Design and Methods
This section must be well-written and logically organized because you are not actually doing the research, yet, your reader must have confidence that you have a plan worth pursuing . The reader will never have a study outcome from which to evaluate whether your methodological choices were the correct ones. Thus, the objective here is to convince the reader that your overall research design and proposed methods of analysis will correctly address the problem and that the methods will provide the means to effectively interpret the potential results. Your design and methods should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
Describe the overall research design by building upon and drawing examples from your review of the literature. Consider not only methods that other researchers have used, but methods of data gathering that have not been used but perhaps could be. Be specific about the methodological approaches you plan to undertake to obtain information, the techniques you would use to analyze the data, and the tests of external validity to which you commit yourself [i.e., the trustworthiness by which you can generalize from your study to other people, places, events, and/or periods of time].
When describing the methods you will use, be sure to cover the following:
- Specify the research process you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results obtained in relation to the research problem. Don't just describe what you intend to achieve from applying the methods you choose, but state how you will spend your time while applying these methods [e.g., coding text from interviews to find statements about the need to change school curriculum; running a regression to determine if there is a relationship between campaign advertising on social media sites and election outcomes in Europe ].
- Keep in mind that the methodology is not just a list of tasks; it is a deliberate argument as to why techniques for gathering information add up to the best way to investigate the research problem. This is an important point because the mere listing of tasks to be performed does not demonstrate that, collectively, they effectively address the research problem. Be sure you clearly explain this.
- Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers and pitfalls in carrying out your research design and explain how you plan to address them. No method applied to research in the social and behavioral sciences is perfect, so you need to describe where you believe challenges may exist in obtaining data or accessing information. It's always better to acknowledge this than to have it brought up by your professor!
V. Preliminary Suppositions and Implications
Just because you don't have to actually conduct the study and analyze the results, doesn't mean you can skip talking about the analytical process and potential implications . The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you believe your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the subject area under investigation. Depending on the aims and objectives of your study, describe how the anticipated results will impact future scholarly research, theory, practice, forms of interventions, or policy making. Note that such discussions may have either substantive [a potential new policy], theoretical [a potential new understanding], or methodological [a potential new way of analyzing] significance. When thinking about the potential implications of your study, ask the following questions:
- What might the results mean in regards to challenging the theoretical framework and underlying assumptions that support the study?
- What suggestions for subsequent research could arise from the potential outcomes of the study?
- What will the results mean to practitioners in the natural settings of their workplace, organization, or community?
- Will the results influence programs, methods, and/or forms of intervention?
- How might the results contribute to the solution of social, economic, or other types of problems?
- Will the results influence policy decisions?
- In what way do individuals or groups benefit should your study be pursued?
- What will be improved or changed as a result of the proposed research?
- How will the results of the study be implemented and what innovations or transformative insights could emerge from the process of implementation?
NOTE: This section should not delve into idle speculation, opinion, or be formulated on the basis of unclear evidence . The purpose is to reflect upon gaps or understudied areas of the current literature and describe how your proposed research contributes to a new understanding of the research problem should the study be implemented as designed.
ANOTHER NOTE : This section is also where you describe any potential limitations to your proposed study. While it is impossible to highlight all potential limitations because the study has yet to be conducted, you still must tell the reader where and in what form impediments may arise and how you plan to address them.
VI. Conclusion
The conclusion reiterates the importance or significance of your proposal and provides a brief summary of the entire study . This section should be only one or two paragraphs long, emphasizing why the research problem is worth investigating, why your research study is unique, and how it should advance existing knowledge.
Someone reading this section should come away with an understanding of:
- Why the study should be done;
- The specific purpose of the study and the research questions it attempts to answer;
- The decision for why the research design and methods used where chosen over other options;
- The potential implications emerging from your proposed study of the research problem; and
- A sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship about the research problem.
VII. Citations
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used . In a standard research proposal, this section can take two forms, so consult with your professor about which one is preferred.
- References -- a list of only the sources you actually used in creating your proposal.
- Bibliography -- a list of everything you used in creating your proposal, along with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem.
In either case, this section should testify to the fact that you did enough preparatory work to ensure the project will complement and not just duplicate the efforts of other researchers. It demonstrates to the reader that you have a thorough understanding of prior research on the topic.
Most proposal formats have you start a new page and use the heading "References" or "Bibliography" centered at the top of the page. Cited works should always use a standard format that follows the writing style advised by the discipline of your course [e.g., education=APA; history=Chicago] or that is preferred by your professor. This section normally does not count towards the total page length of your research proposal.
Develop a Research Proposal: Writing the Proposal. Office of Library Information Services. Baltimore County Public Schools; Heath, M. Teresa Pereira and Caroline Tynan. “Crafting a Research Proposal.” The Marketing Review 10 (Summer 2010): 147-168; Jones, Mark. “Writing a Research Proposal.” In MasterClass in Geography Education: Transforming Teaching and Learning . Graham Butt, editor. (New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2015), pp. 113-127; Juni, Muhamad Hanafiah. “Writing a Research Proposal.” International Journal of Public Health and Clinical Sciences 1 (September/October 2014): 229-240; Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005; Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Punch, Keith and Wayne McGowan. "Developing and Writing a Research Proposal." In From Postgraduate to Social Scientist: A Guide to Key Skills . Nigel Gilbert, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), 59-81; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences , Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- << Previous: Writing a Reflective Paper
- Next: Generative AI and Writing >>
- Last Updated: May 31, 2024 1:46 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
10 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 14: The Research Proposal
14.3 Components of a Research Proposal
Krathwohl (2005) suggests and describes a variety of components to include in a research proposal. The following sections – Introductions, Background and significance, Literature Review; Research design and methods, Preliminary suppositions and implications; and Conclusion present these components in a suggested template for you to follow in the preparation of your research proposal.
Introduction
The introduction sets the tone for what follows in your research proposal – treat it as the initial pitch of your idea. After reading the introduction your reader should:
- understand what it is you want to do;
- have a sense of your passion for the topic; and
- be excited about the study’s possible outcomes.
As you begin writing your research proposal, it is helpful to think of the introduction as a narrative of what it is you want to do, written in one to three paragraphs. Within those one to three paragraphs, it is important to briefly answer the following questions:
- What is the central research problem?
- How is the topic of your research proposal related to the problem?
- What methods will you utilize to analyze the research problem?
- Why is it important to undertake this research? What is the significance of your proposed research? Why are the outcomes of your proposed research important? Whom are they important?
Note : You may be asked by your instructor to include an abstract with your research proposal. In such cases, an abstract should provide an overview of what it is you plan to study, your main research question, a brief explanation of your methods to answer the research question, and your expected findings. All of this information must be carefully crafted in 150 to 250 words. A word of advice is to save the writing of your abstract until the very end of your research proposal preparation. If you are asked to provide an abstract, you should include 5 to 7 key words that are of most relevance to your study. List these in order of relevance.
Background and significance
The purpose of this section is to explain the context of your proposal and to describe, in detail, why it is important to undertake this research. Assume that the person or people who will read your research proposal know nothing or very little about the research problem. While you do not need to include all knowledge you have learned about your topic in this section, it is important to ensure that you include the most relevant material that will help to explain the goals of your research.
While there are no hard and fast rules, you should attempt to address some or all of the following key points:
- State the research problem and provide a more thorough explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction.
- Present the rationale for the proposed research study. Clearly indicate why this research is worth doing. Answer the “so what?” question.
- Describe the major issues or problems to be addressed by your research. Do not forget to explain how and in what ways your proposed research builds upon previous related research.
- Explain how you plan to go about conducting your research.
- Clearly identify the key or most relevant sources of research you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Set the boundaries of your proposed research, in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you will study, but what will be excluded from your study.
- Provide clear definitions of key concepts and terms. Since key concepts and terms often have numerous definitions, make sure you state which definition you will be utilizing in your research.
Literature review
This key component of the research proposal is the most time-consuming aspect in the preparation of your research proposal. As described in Chapter 5 , the literature review provides the background to your study and demonstrates the significance of the proposed research. Specifically, it is a review and synthesis of prior research that is related to the problem you are setting forth to investigate. Essentially, your goal in the literature review is to place your research study within the larger whole of what has been studied in the past, while demonstrating to your reader that your work is original, innovative, and adds to the larger whole.
As the literature review is information dense, it is essential that this section be intelligently structured to enable your reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your study. However, this can be easier to state and harder to do, simply due to the fact there is usually a plethora of related research to sift through. Consequently, a good strategy for writing the literature review is to break the literature into conceptual categories or themes, rather than attempting to describe various groups of literature you reviewed. Chapter 5 describes a variety of methods to help you organize the themes.
Here are some suggestions on how to approach the writing of your literature review:
- Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methods they used, what they found, and what they recommended based upon their findings.
- Do not be afraid to challenge previous related research findings and/or conclusions.
- Assess what you believe to be missing from previous research and explain how your research fills in this gap and/or extends previous research.
It is important to note that a significant challenge related to undertaking a literature review is knowing when to stop. As such, it is important to know when you have uncovered the key conceptual categories underlying your research topic. Generally, when you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations, you can have confidence that you have covered all of the significant conceptual categories in your literature review. However, it is also important to acknowledge that researchers often find themselves returning to the literature as they collect and analyze their data. For example, an unexpected finding may develop as you collect and/or analyze the data; in this case, it is important to take the time to step back and review the literature again, to ensure that no other researchers have found a similar finding. This may include looking to research outside your field.
This situation occurred with one of this textbook’s authors’ research related to community resilience. During the interviews, the researchers heard many participants discuss individual resilience factors and how they believed these individual factors helped make the community more resilient, overall. Sheppard and Williams (2016) had not discovered these individual factors in their original literature review on community and environmental resilience. However, when they returned to the literature to search for individual resilience factors, they discovered a small body of literature in the child and youth psychology field. Consequently, Sheppard and Williams had to go back and add a new section to their literature review on individual resilience factors. Interestingly, their research appeared to be the first research to link individual resilience factors with community resilience factors.
Research design and methods
The objective of this section of the research proposal is to convince the reader that your overall research design and methods of analysis will enable you to solve the research problem you have identified and also enable you to accurately and effectively interpret the results of your research. Consequently, it is critical that the research design and methods section is well-written, clear, and logically organized. This demonstrates to your reader that you know what you are going to do and how you are going to do it. Overall, you want to leave your reader feeling confident that you have what it takes to get this research study completed in a timely fashion.
Essentially, this section of the research proposal should be clearly tied to the specific objectives of your study; however, it is also important to draw upon and include examples from the literature review that relate to your design and intended methods. In other words, you must clearly demonstrate how your study utilizes and builds upon past studies, as it relates to the research design and intended methods. For example, what methods have been used by other researchers in similar studies?
While it is important to consider the methods that other researchers have employed, it is equally, if not more, important to consider what methods have not been but could be employed. Remember, the methods section is not simply a list of tasks to be undertaken. It is also an argument as to why and how the tasks you have outlined will help you investigate the research problem and answer your research question(s).
Tips for writing the research design and methods section:
Specify the methodological approaches you intend to employ to obtain information and the techniques you will use to analyze the data.
Specify the research operations you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results of those operations in relation to the research problem.
Go beyond stating what you hope to achieve through the methods you have chosen. State how you will actually implement the methods (i.e., coding interview text, running regression analysis, etc.).
Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers you may encounter when undertaking your research, and describe how you will address these barriers.
Explain where you believe you will find challenges related to data collection, including access to participants and information.
Preliminary suppositions and implications
The purpose of this section is to argue how you anticipate that your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the area of your study. Depending upon the aims and objectives of your study, you should also discuss how your anticipated findings may impact future research. For example, is it possible that your research may lead to a new policy, theoretical understanding, or method for analyzing data? How might your study influence future studies? What might your study mean for future practitioners working in the field? Who or what might benefit from your study? How might your study contribute to social, economic or environmental issues? While it is important to think about and discuss possibilities such as these, it is equally important to be realistic in stating your anticipated findings. In other words, you do not want to delve into idle speculation. Rather, the purpose here is to reflect upon gaps in the current body of literature and to describe how you anticipate your research will begin to fill in some or all of those gaps.
The conclusion reiterates the importance and significance of your research proposal, and provides a brief summary of the entire proposed study. Essentially, this section should only be one or two paragraphs in length. Here is a potential outline for your conclusion:
Discuss why the study should be done. Specifically discuss how you expect your study will advance existing knowledge and how your study is unique.
Explain the specific purpose of the study and the research questions that the study will answer.
Explain why the research design and methods chosen for this study are appropriate, and why other designs and methods were not chosen.
State the potential implications you expect to emerge from your proposed study,
Provide a sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship currently in existence, related to the research problem.
Citations and references
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your research proposal. In a research proposal, this can take two forms: a reference list or a bibliography. A reference list lists the literature you referenced in the body of your research proposal. All references in the reference list must appear in the body of the research proposal. Remember, it is not acceptable to say “as cited in …” As a researcher you must always go to the original source and check it for yourself. Many errors are made in referencing, even by top researchers, and so it is important not to perpetuate an error made by someone else. While this can be time consuming, it is the proper way to undertake a literature review.
In contrast, a bibliography , is a list of everything you used or cited in your research proposal, with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem. In other words, sources cited in your bibliography may not necessarily appear in the body of your research proposal. Make sure you check with your instructor to see which of the two you are expected to produce.
Overall, your list of citations should be a testament to the fact that you have done a sufficient level of preliminary research to ensure that your project will complement, but not duplicate, previous research efforts. For social sciences, the reference list or bibliography should be prepared in American Psychological Association (APA) referencing format. Usually, the reference list (or bibliography) is not included in the word count of the research proposal. Again, make sure you check with your instructor to confirm.
Research Methods for the Social Sciences: An Introduction Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
Table of Contents

Research Proposal
Research proposal is a document that outlines a proposed research project . It is typically written by researchers, scholars, or students who intend to conduct research to address a specific research question or problem.
Types of Research Proposal
Research proposals can vary depending on the nature of the research project and the specific requirements of the funding agency, academic institution, or research program. Here are some common types of research proposals:
Academic Research Proposal
This is the most common type of research proposal, which is prepared by students, scholars, or researchers to seek approval and funding for an academic research project. It includes all the essential components mentioned earlier, such as the introduction, literature review , methodology , and expected outcomes.
Grant Proposal
A grant proposal is specifically designed to secure funding from external sources, such as government agencies, foundations, or private organizations. It typically includes additional sections, such as a detailed budget, project timeline, evaluation plan, and a description of the project’s alignment with the funding agency’s priorities and objectives.
Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
Students pursuing a master’s or doctoral degree often need to submit a proposal outlining their intended research for their dissertation or thesis. These proposals are usually more extensive and comprehensive, including an in-depth literature review, theoretical framework, research questions or hypotheses, and a detailed methodology.
Research Project Proposal
This type of proposal is often prepared by researchers or research teams within an organization or institution. It outlines a specific research project that aims to address a particular problem, explore a specific area of interest, or provide insights for decision-making. Research project proposals may include sections on project management, collaboration, and dissemination of results.
Research Fellowship Proposal
Researchers or scholars applying for research fellowships may be required to submit a proposal outlining their proposed research project. These proposals often emphasize the novelty and significance of the research and its alignment with the goals and objectives of the fellowship program.
Collaborative Research Proposal
In cases where researchers from multiple institutions or disciplines collaborate on a research project, a collaborative research proposal is prepared. This proposal highlights the objectives, responsibilities, and contributions of each collaborator, as well as the overall research plan and coordination mechanisms.
Research Proposal Outline
A research proposal typically follows a standard outline that helps structure the document and ensure all essential components are included. While the specific headings and subheadings may vary slightly depending on the requirements of your institution or funding agency, the following outline provides a general structure for a research proposal:
- Title of the research proposal
- Name of the researcher(s) or principal investigator(s)
- Affiliation or institution
- Date of submission
- A concise summary of the research proposal, typically limited to 200-300 words.
- Briefly introduce the research problem or question, state the objectives, summarize the methodology, and highlight the expected outcomes or significance of the research.
- Provide an overview of the subject area and the specific research problem or question.
- Present relevant background information, theories, or concepts to establish the need for the research.
- Clearly state the research objectives or research questions that the study aims to address.
- Indicate the significance or potential contributions of the research.
- Summarize and analyze relevant studies, theories, or scholarly works.
- Identify research gaps or unresolved issues that your study intends to address.
- Highlight the novelty or uniqueness of your research.
- Describe the overall approach or research design that will be used (e.g., experimental, qualitative, quantitative).
- Justify the chosen approach based on the research objectives and question.
- Explain how data will be collected (e.g., surveys, interviews, experiments).
- Describe the sampling strategy and sample size, if applicable.
- Address any ethical considerations related to data collection.
- Outline the data analysis techniques or statistical methods that will be applied.
- Explain how the data will be interpreted and analyzed to answer the research question(s).
- Provide a detailed schedule or timeline that outlines the various stages of the research project.
- Specify the estimated duration for each stage, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
- State the potential outcomes or results of the research.
- Discuss the potential significance or contributions of the study to the field.
- Address any potential limitations or challenges that may be encountered.
- Identify the resources required to conduct the research, such as funding, equipment, or access to data.
- Specify any collaborations or partnerships necessary for the successful completion of the study.
- Include a list of cited references in the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
———————————————————————————————–
Research Proposal Example Template
Here’s an example of a research proposal to give you an idea of how it can be structured:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Well-being: A Mixed-Methods Study
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of social media on the well-being of adolescents. The study will employ a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews to gather comprehensive data. The research objectives include examining the relationship between social media use and mental health, exploring the role of peer influence in shaping online behaviors, and identifying strategies for promoting healthy social media use among adolescents. The findings of this study will contribute to the understanding of the effects of social media on adolescent well-being and inform the development of targeted interventions.
1. Introduction
1.1 Background and Context:
Adolescents today are immersed in social media platforms, which have become integral to their daily lives. However, concerns have been raised about the potential negative impact of social media on their well-being, including increased rates of depression, anxiety, and body dissatisfaction. It is crucial to investigate this phenomenon further and understand the underlying mechanisms to develop effective strategies for promoting healthy social media use among adolescents.
1.2 Research Objectives:
The main objectives of this study are:
- To examine the association between social media use and mental health outcomes among adolescents.
- To explore the influence of peer relationships and social comparison on online behaviors.
- To identify strategies and interventions to foster positive social media use and enhance adolescent well-being.
2. Literature Review
Extensive research has been conducted on the impact of social media on adolescents. Existing literature suggests that excessive social media use can contribute to negative outcomes, such as low self-esteem, cyberbullying, and addictive behaviors. However, some studies have also highlighted the positive aspects of social media, such as providing opportunities for self-expression and social support. This study will build upon this literature by incorporating both quantitative and qualitative approaches to gain a more nuanced understanding of the relationship between social media and adolescent well-being.
3. Methodology
3.1 Research Design:
This study will adopt a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. The quantitative phase will involve administering standardized questionnaires to a representative sample of adolescents to assess their social media use, mental health indicators, and perceived social support. The qualitative phase will include in-depth interviews with a subset of participants to explore their experiences, motivations, and perceptions related to social media use.
3.2 Data Collection Methods:
Quantitative data will be collected through an online survey distributed to schools in the target region. The survey will include validated scales to measure social media use, mental health outcomes, and perceived social support. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a purposive sample of participants. The interviews will be audio-recorded and transcribed for thematic analysis.
3.3 Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis to examine the relationships between variables. Qualitative data will be analyzed thematically to identify common themes and patterns within participants’ narratives. Integration of quantitative and qualitative findings will provide a comprehensive understanding of the research questions.
4. Timeline
The research project will be conducted over a period of 12 months, divided into specific phases, including literature review, study design, data collection, analysis, and report writing. A detailed timeline outlining the key milestones and activities is provided in Appendix A.
5. Expected Outcomes and Significance
This study aims to contribute to the existing literature on the impact of social media on adolescent well-being by employing a mixed-methods approach. The findings will inform the development of evidence-based interventions and guidelines to promote healthy social media use among adolescents. This research has the potential to benefit adolescents, parents, educators, and policymakers by providing insights into the complex relationship between social media and well-being and offering strategies for fostering positive online experiences.
6. Resources
The resources required for this research include access to a representative sample of adolescents, research assistants for data collection, statistical software for data analysis, and funding to cover survey administration and participant incentives. Ethical considerations will be taken into account, ensuring participant confidentiality and obtaining informed consent.
7. References
Research Proposal Writing Guide
Writing a research proposal can be a complex task, but with proper guidance and organization, you can create a compelling and well-structured proposal. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Understand the requirements: Familiarize yourself with the guidelines and requirements provided by your institution, funding agency, or program. Pay attention to formatting, page limits, specific sections or headings, and any other instructions.
- Identify your research topic: Choose a research topic that aligns with your interests, expertise, and the goals of your program or funding opportunity. Ensure that your topic is specific, focused, and relevant to the field of study.
- Conduct a literature review : Review existing literature and research relevant to your topic. Identify key theories, concepts, methodologies, and findings related to your research question. This will help you establish the context, identify research gaps, and demonstrate the significance of your proposed study.
- Define your research objectives and research question(s): Clearly state the objectives you aim to achieve with your research. Formulate research questions that address the gaps identified in the literature review. Your research objectives and questions should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Develop a research methodology: Determine the most appropriate research design and methodology for your study. Consider whether quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods approaches will best address your research question(s). Describe the data collection methods, sampling strategy, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations associated with your research.
- Create a research plan and timeline: Outline the various stages of your research project, including tasks, milestones, and deadlines. Develop a realistic timeline that considers factors such as data collection, analysis, and report writing. This plan will help you stay organized and manage your time effectively throughout the research process.
- A. Introduction: Provide background information on the research problem, highlight its significance, and introduce your research objectives and questions.
- B. Literature review: Summarize relevant literature, identify gaps, and justify the need for your proposed research.
- C . Methodology: Describe your research design, data collection methods, sampling strategy, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
- D . Expected outcomes and significance: Explain the potential outcomes, contributions, and implications of your research.
- E. Resources: Identify the resources required to conduct your research, such as funding, equipment, or access to data.
- F . References: Include a list of cited references in the appropriate citation style.
- Revise and proofread: Review your proposal for clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Check for grammar and spelling errors. Seek feedback from mentors, colleagues, or advisors to refine and improve your proposal.
- Finalize and submit: Make any necessary revisions based on feedback and finalize your research proposal. Ensure that you have met all the requirements and formatting guidelines. Submit your proposal within the specified deadline.
Research Proposal Length
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the specific guidelines provided by your institution or funding agency. However, research proposals typically range from 1,500 to 3,000 words, excluding references and any additional supporting documents.
Purpose of Research Proposal
The purpose of a research proposal is to outline and communicate your research project to others, such as academic institutions, funding agencies, or potential collaborators. It serves several important purposes:
- Demonstrate the significance of the research: A research proposal explains the importance and relevance of your research project. It outlines the research problem or question, highlights the gaps in existing knowledge, and explains how your study will contribute to the field. By clearly articulating the significance of your research, you can convince others of its value and potential impact.
- Provide a clear research plan: A research proposal outlines the methodology, design, and approach you will use to conduct your study. It describes the research objectives, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and potential outcomes. By presenting a clear research plan, you demonstrate that your study is well-thought-out, feasible, and likely to produce meaningful results.
- Secure funding or support: For researchers seeking funding or support for their projects, a research proposal is essential. It allows you to make a persuasive case for why your research is deserving of financial resources or institutional backing. The proposal explains the budgetary requirements, resources needed, and potential benefits of the research, helping you secure the necessary funding or support.
- Seek feedback and guidance: Presenting a research proposal provides an opportunity to receive feedback and guidance from experts in your field. It allows you to engage in discussions and receive suggestions for refining your research plan, improving the methodology, or addressing any potential limitations. This feedback can enhance the quality of your study and increase its chances of success.
- Establish ethical considerations: A research proposal also addresses ethical considerations associated with your study. It outlines how you will ensure participant confidentiality, obtain informed consent, and adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations. By demonstrating your awareness and commitment to ethical research practices, you build trust and credibility in your proposed study.
Importance of Research Proposal
The research proposal holds significant importance in the research process. Here are some key reasons why research proposals are important:
- Planning and organization: A research proposal requires careful planning and organization of your research project. It forces you to think through the research objectives, research questions, methodology, and potential outcomes before embarking on the actual study. This planning phase helps you establish a clear direction and framework for your research, ensuring that your efforts are focused and purposeful.
- Demonstrating the significance of the research: A research proposal allows you to articulate the significance and relevance of your study. By providing a thorough literature review and clearly defining the research problem or question, you can showcase the gaps in existing knowledge that your research aims to address. This demonstrates to others, such as funding agencies or academic institutions, why your research is important and deserving of support.
- Obtaining funding and resources: Research proposals are often required to secure funding for your research project. Funding agencies and organizations need to evaluate the feasibility and potential impact of the proposed research before allocating resources. A well-crafted research proposal helps convince funders of the value of your research and increases the likelihood of securing financial support, grants, or scholarships.
- Receiving feedback and guidance: Presenting a research proposal provides an opportunity to seek feedback and guidance from experts in your field. By sharing your research plan and objectives with others, you can benefit from their insights and suggestions. This feedback can help refine your research design, strengthen your methodology, and ensure that your study is rigorous and well-informed.
- Ethical considerations: A research proposal addresses ethical considerations associated with your study. It outlines how you will protect the rights and welfare of participants, maintain confidentiality, obtain informed consent, and adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations. This emphasis on ethical practices ensures that your research is conducted responsibly and with integrity.
- Enhancing collaboration and partnerships: A research proposal can facilitate collaborations and partnerships with other researchers, institutions, or organizations. When presenting your research plan, you may attract the interest of potential collaborators who share similar research interests or possess complementary expertise. Collaborative partnerships can enrich your study, expand your resources, and foster knowledge exchange.
- Establishing a research trajectory: A research proposal serves as a foundation for your research project. Once approved, it becomes a roadmap that guides your study’s implementation, data collection, analysis, and reporting. It helps maintain focus and ensures that your research stays on track and aligned with the initial objectives.
When to Write Research Proposal
The timing of when to write a research proposal can vary depending on the specific requirements and circumstances. However, here are a few common situations when it is appropriate to write a research proposal:
- Academic research: If you are a student pursuing a research degree, such as a Ph.D. or Master’s by research, you will typically be required to write a research proposal as part of the application process. This is usually done before starting the research program to outline your proposed study and seek approval from the academic institution.
- Funding applications: When applying for research grants, scholarships, or funding from organizations or institutions, you will often need to submit a research proposal. Funding agencies require a detailed description of your research project, including its objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. Writing a research proposal in this context is necessary to secure financial support for your study.
- Research collaborations: When collaborating with other researchers, institutions, or organizations on a research project, it is common to prepare a research proposal. This helps outline the research objectives, roles and responsibilities, and expected contributions from each party. Writing a research proposal in this case allows all collaborators to align their efforts and ensure a shared understanding of the project.
- Research project within an organization: If you are conducting research within an organization, such as a company or government agency, you may be required to write a research proposal to gain approval and support for your study. This proposal outlines the research objectives, methodology, resources needed, and expected outcomes, ensuring that the project aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives.
- Independent research projects: Even if you are not required to write a research proposal, it can still be beneficial to develop one for your independent research projects. Writing a research proposal helps you plan and structure your study, clarify your research objectives, and anticipate potential challenges or limitations. It also allows you to communicate your research plans effectively to supervisors, mentors, or collaborators.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

- Research Process

Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal
- 5 minute read
- 104.7K views
Table of Contents
The importance of a well-written research proposal cannot be underestimated. Your research really is only as good as your proposal. A poorly written, or poorly conceived research proposal will doom even an otherwise worthy project. On the other hand, a well-written, high-quality proposal will increase your chances for success.
In this article, we’ll outline the basics of writing an effective scientific research proposal, including the differences between research proposals, grants and cover letters. We’ll also touch on common mistakes made when submitting research proposals, as well as a simple example or template that you can follow.
What is a scientific research proposal?
The main purpose of a scientific research proposal is to convince your audience that your project is worthwhile, and that you have the expertise and wherewithal to complete it. The elements of an effective research proposal mirror those of the research process itself, which we’ll outline below. Essentially, the research proposal should include enough information for the reader to determine if your proposed study is worth pursuing.
It is not an uncommon misunderstanding to think that a research proposal and a cover letter are the same things. However, they are different. The main difference between a research proposal vs cover letter content is distinct. Whereas the research proposal summarizes the proposal for future research, the cover letter connects you to the research, and how you are the right person to complete the proposed research.
There is also sometimes confusion around a research proposal vs grant application. Whereas a research proposal is a statement of intent, related to answering a research question, a grant application is a specific request for funding to complete the research proposed. Of course, there are elements of overlap between the two documents; it’s the purpose of the document that defines one or the other.
Scientific Research Proposal Format
Although there is no one way to write a scientific research proposal, there are specific guidelines. A lot depends on which journal you’re submitting your research proposal to, so you may need to follow their scientific research proposal template.
In general, however, there are fairly universal sections to every scientific research proposal. These include:
- Title: Make sure the title of your proposal is descriptive and concise. Make it catch and informative at the same time, avoiding dry phrases like, “An investigation…” Your title should pique the interest of the reader.
- Abstract: This is a brief (300-500 words) summary that includes the research question, your rationale for the study, and any applicable hypothesis. You should also include a brief description of your methodology, including procedures, samples, instruments, etc.
- Introduction: The opening paragraph of your research proposal is, perhaps, the most important. Here you want to introduce the research problem in a creative way, and demonstrate your understanding of the need for the research. You want the reader to think that your proposed research is current, important and relevant.
- Background: Include a brief history of the topic and link it to a contemporary context to show its relevance for today. Identify key researchers and institutions also looking at the problem
- Literature Review: This is the section that may take the longest amount of time to assemble. Here you want to synthesize prior research, and place your proposed research into the larger picture of what’s been studied in the past. You want to show your reader that your work is original, and adds to the current knowledge.
- Research Design and Methodology: This section should be very clearly and logically written and organized. You are letting your reader know that you know what you are going to do, and how. The reader should feel confident that you have the skills and knowledge needed to get the project done.
- Preliminary Implications: Here you’ll be outlining how you anticipate your research will extend current knowledge in your field. You might also want to discuss how your findings will impact future research needs.
- Conclusion: This section reinforces the significance and importance of your proposed research, and summarizes the entire proposal.
- References/Citations: Of course, you need to include a full and accurate list of any and all sources you used to write your research proposal.
Common Mistakes in Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal
Remember, the best research proposal can be rejected if it’s not well written or is ill-conceived. The most common mistakes made include:
- Not providing the proper context for your research question or the problem
- Failing to reference landmark/key studies
- Losing focus of the research question or problem
- Not accurately presenting contributions by other researchers and institutions
- Incompletely developing a persuasive argument for the research that is being proposed
- Misplaced attention on minor points and/or not enough detail on major issues
- Sloppy, low-quality writing without effective logic and flow
- Incorrect or lapses in references and citations, and/or references not in proper format
- The proposal is too long – or too short
Scientific Research Proposal Example
There are countless examples that you can find for successful research proposals. In addition, you can also find examples of unsuccessful research proposals. Search for successful research proposals in your field, and even for your target journal, to get a good idea on what specifically your audience may be looking for.
While there’s no one example that will show you everything you need to know, looking at a few will give you a good idea of what you need to include in your own research proposal. Talk, also, to colleagues in your field, especially if you are a student or a new researcher. We can often learn from the mistakes of others. The more prepared and knowledgeable you are prior to writing your research proposal, the more likely you are to succeed.
Language Editing Services
One of the top reasons scientific research proposals are rejected is due to poor logic and flow. Check out our Language Editing Services to ensure a great proposal , that’s clear and concise, and properly referenced. Check our video for more information, and get started today.

- Manuscript Review
Research Fraud: Falsification and Fabrication in Research Data

Research Team Structure
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.23(2); 2008 Apr

How to prepare a Research Proposal
Health research, medical education and clinical practice form the three pillars of modern day medical practice. As one authority rightly put it: ‘Health research is not a luxury, but an essential need that no nation can afford to ignore’. Health research can and should be pursued by a broad range of people. Even if they do not conduct research themselves, they need to grasp the principles of the scientific method to understand the value and limitations of science and to be able to assess and evaluate results of research before applying them. This review paper aims to highlight the essential concepts to the students and beginning researchers and sensitize and motivate the readers to access the vast literature available on research methodologies.
Most students and beginning researchers do not fully understand what a research proposal means, nor do they understand its importance. 1 A research proposal is a detailed description of a proposed study designed to investigate a given problem. 2
A research proposal is intended to convince others that you have a worthwhile research project and that you have the competence and the work-plan to complete it. Broadly the research proposal must address the following questions regardless of your research area and the methodology you choose: What you plan to accomplish, why do you want to do it and how are you going to do it. 1 The aim of this article is to highlight the essential concepts and not to provide extensive details about this topic.
The elements of a research proposal are highlighted below:
1. Title: It should be concise and descriptive. It must be informative and catchy. An effective title not only prick’s the readers interest, but also predisposes him/her favorably towards the proposal. Often titles are stated in terms of a functional relationship, because such titles clearly indicate the independent and dependent variables. 1 The title may need to be revised after completion of writing of the protocol to reflect more closely the sense of the study. 3
2. Abstract: It is a brief summary of approximately 300 words. It should include the main research question, the rationale for the study, the hypothesis (if any) and the method. Descriptions of the method may include the design, procedures, the sample and any instruments that will be used. 1 It should stand on its own, and not refer the reader to points in the project description. 3
3. Introduction: The introduction provides the readers with the background information. Its purpose is to establish a framework for the research, so that readers can understand how it relates to other research. 4 It should answer the question of why the research needs to be done and what will be its relevance. It puts the proposal in context. 3
The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1
The importance of the statement of the research problem 5 : The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology, work plan and budget etc). It is an integral part of selecting a research topic. It will guide and put into sharper focus the research design being considered for solving the problem. It allows the investigator to describe the problem systematically, to reflect on its importance, its priority in the country and region and to point out why the proposed research on the problem should be undertaken. It also facilitates peer review of the research proposal by the funding agencies.
Then it is necessary to provide the context and set the stage for the research question in such a way as to show its necessity and importance. 1 This step is necessary for the investigators to familiarize themselves with existing knowledge about the research problem and to find out whether or not others have investigated the same or similar problems. This step is accomplished by a thorough and critical review of the literature and by personal communication with experts. 5 It helps further understanding of the problem proposed for research and may lead to refining the statement of the problem, to identify the study variables and conceptualize their relationships, and in formulation and selection of a research hypothesis. 5 It ensures that you are not "re-inventing the wheel" and demonstrates your understanding of the research problem. It gives due credit to those who have laid the groundwork for your proposed research. 1 In a proposal, the literature review is generally brief and to the point. The literature selected should be pertinent and relevant. 6
Against this background, you then present the rationale of the proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing.
4. Objectives: Research objectives are the goals to be achieved by conducting the research. 5 They may be stated as ‘general’ and ‘specific’.
The general objective of the research is what is to be accomplished by the research project, for example, to determine whether or not a new vaccine should be incorporated in a public health program.
The specific objectives relate to the specific research questions the investigator wants to answer through the proposed study and may be presented as primary and secondary objectives, for example, primary: To determine the degree of protection that is attributable to the new vaccine in a study population by comparing the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups. 5 Secondary: To study the cost-effectiveness of this programme.
Young investigators are advised to resist the temptation to put too many objectives or over-ambitious objectives that cannot be adequately achieved by the implementation of the protocol. 3
5. Variables: During the planning stage, it is necessary to identify the key variables of the study and their method of measurement and unit of measurement must be clearly indicated. Four types of variables are important in research 5 :
a. Independent variables: variables that are manipulated or treated in a study in order to see what effect differences in them will have on those variables proposed as being dependent on them. The different synonyms for the term ‘independent variable’ which are used in literature are: cause, input, predisposing factor, risk factor, determinant, antecedent, characteristic and attribute.
b. Dependent variables: variables in which changes are results of the level or amount of the independent variable or variables.
Synonyms: effect, outcome, consequence, result, condition, disease.
c. Confounding or intervening variables: variables that should be studied because they may influence or ‘mix’ the effect of the independent variables. For instance, in a study of the effect of measles (independent variable) on child mortality (dependent variable), the nutritional status of the child may play an intervening (confounding) role.
d. Background variables: variables that are so often of relevance in investigations of groups or populations that they should be considered for possible inclusion in the study. For example sex, age, ethnic origin, education, marital status, social status etc.
The objective of research is usually to determine the effect of changes in one or more independent variables on one or more dependent variables. For example, a study may ask "Will alcohol intake (independent variable) have an effect on development of gastric ulcer (dependent variable)?"
Certain variables may not be easy to identify. The characteristics that define these variables must be clearly identified for the purpose of the study.
6. Questions and/ or hypotheses: If you as a researcher know enough to make prediction concerning what you are studying, then the hypothesis may be formulated. A hypothesis can be defined as a tentative prediction or explanation of the relationship between two or more variables. In other words, the hypothesis translates the problem statement into a precise, unambiguous prediction of expected outcomes. Hypotheses are not meant to be haphazard guesses, but should reflect the depth of knowledge, imagination and experience of the investigator. 5 In the process of formulating the hypotheses, all variables relevant to the study must be identified. For example: "Health education involving active participation by mothers will produce more positive changes in child feeding than health education based on lectures". Here the independent variable is types of health education and the dependent variable is changes in child feeding.
A research question poses a relationship between two or more variables but phrases the relationship as a question; a hypothesis represents a declarative statement of the relations between two or more variables. 7
For exploratory or phenomenological research, you may not have any hypothesis (please do not confuse the hypothesis with the statistical null hypothesis). 1 Questions are relevant to normative or census type research (How many of them are there? Is there a relationship between them?). Deciding whether to use questions or hypotheses depends on factors such as the purpose of the study, the nature of the design and methodology, and the audience of the research (at times even the outlook and preference of the committee members, particularly the Chair). 6
7. Methodology: The method section is very important because it tells your research Committee how you plan to tackle your research problem. The guiding principle for writing the Methods section is that it should contain sufficient information for the reader to determine whether the methodology is sound. Some even argue that a good proposal should contain sufficient details for another qualified researcher to implement the study. 1 Indicate the methodological steps you will take to answer every question or to test every hypothesis illustrated in the Questions/hypotheses section. 6 It is vital that you consult a biostatistician during the planning stage of your study, 8 to resolve the methodological issues before submitting the proposal.
This section should include:
Research design: The selection of the research strategy is the core of research design and is probably the single most important decision the investigator has to make. The choice of the strategy, whether descriptive, analytical, experimental, operational or a combination of these depend on a number of considerations, 5 but this choice must be explained in relation to the study objectives. 3
Research subjects or participants: Depending on the type of your study, the following questions should be answered 3 , 5
- - What are the criteria for inclusion or selection?
- - What are the criteria for exclusion?
- - What is the sampling procedure you will use so as to ensure representativeness and reliability of the sample and to minimize sampling errors? The key reason for being concerned with sampling is the issue of validity-both internal and external of the study results. 9
- - Will there be use of controls in your study? Controls or comparison groups are used in scientific research in order to increase the validity of the conclusions. Control groups are necessary in all analytical epidemiological studies, in experimental studies of drug trials, in research on effects of intervention programmes and disease control measures and in many other investigations. Some descriptive studies (studies of existing data, surveys) may not require control groups.
- - What are the criteria for discontinuation?
Sample size: The proposal should provide information and justification (basis on which the sample size is calculated) about sample size in the methodology section. 3 A larger sample size than needed to test the research hypothesis increases the cost and duration of the study and will be unethical if it exposes human subjects to any potential unnecessary risk without additional benefit. A smaller sample size than needed can also be unethical as it exposes human subjects to risk with no benefit to scientific knowledge. Calculation of sample size has been made easy by computer software programmes, but the principles underlying the estimation should be well understood.
Interventions: If an intervention is introduced, a description must be given of the drugs or devices (proprietary names, manufacturer, chemical composition, dose, frequency of administration) if they are already commercially available. If they are in phases of experimentation or are already commercially available but used for other indications, information must be provided on available pre-clinical investigations in animals and/or results of studies already conducted in humans (in such cases, approval of the drug regulatory agency in the country is needed before the study). 3
Ethical issues 3 : Ethical considerations apply to all types of health research. Before the proposal is submitted to the Ethics Committee for approval, two important documents mentioned below (where appropriate) must be appended to the proposal. In additions, there is another vital issue of Conflict of Interest, wherein the researchers should furnish a statement regarding the same.
The Informed consent form (informed decision-making): A consent form, where appropriate, must be developed and attached to the proposal. It should be written in the prospective subjects’ mother tongue and in simple language which can be easily understood by the subject. The use of medical terminology should be avoided as far as possible. Special care is needed when subjects are illiterate. It should explain why the study is being done and why the subject has been asked to participate. It should describe, in sequence, what will happen in the course of the study, giving enough detail for the subject to gain a clear idea of what to expect. It should clarify whether or not the study procedures offer any benefits to the subject or to others, and explain the nature, likelihood and treatment of anticipated discomfort or adverse effects, including psychological and social risks, if any. Where relevant, a comparison with risks posed by standard drugs or treatment must be included. If the risks are unknown or a comparative risk cannot be given it should be so stated. It should indicate that the subject has the right to withdraw from the study at any time without, in any way, affecting his/her further medical care. It should assure the participant of confidentiality of the findings.
Ethics checklist: The proposal must describe the measures that will be undertaken to ensure that the proposed research is carried out in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki on Ethical Principles for Medical research involving Human Subjects. 10 It must answer the following questions:
- • Is the research design adequate to provide answers to the research question? It is unethical to expose subjects to research that will have no value.
- • Is the method of selection of research subjects justified? The use of vulnerable subjects as research participants needs special justification. Vulnerable subjects include those in prison, minors and persons with mental disability. In international research it is important to mention that the population in which the study is conducted will benefit from any potential outcome of the research and the research is not being conducted solely for the benefit of some other population. Justification is needed for any inducement, financial or otherwise, for the participants to be enrolled in the study.
- • Are the interventions justified, in terms of risk/benefit ratio? Risks are not limited to physical harm. Psychological and social risks must also be considered.
- • For observations made, have measures been taken to ensure confidentiality?
Research setting 5 : The research setting includes all the pertinent facets of the study, such as the population to be studied (sampling frame), the place and time of study.
Study instruments 3 , 5 : Instruments are the tools by which the data are collected. For validated questionnaires/interview schedules, reference to published work should be given and the instrument appended to the proposal. For new a questionnaire which is being designed specifically for your study the details about preparing, precoding and pretesting of questionnaire should be furnished and the document appended to the proposal. Descriptions of other methods of observations like medical examination, laboratory tests and screening procedures is necessary- for established procedures, reference of published work cited but for new or modified procedure, an adequate description is necessary with justification for the same.
Collection of data: A short description of the protocol of data collection. For example, in a study on blood pressure measurement: time of participant arrival, rest for 5p. 10 minutes, which apparatus (standard calibrated) to be used, in which room to take measurement, measurement in sitting or lying down position, how many measurements, measurement in which arm first (whether this is going to be randomized), details of cuff and its placement, who will take the measurement. This minimizes the possibility of confusion, delays and errors.
Data analysis: The description should include the design of the analysis form, plans for processing and coding the data and the choice of the statistical method to be applied to each data. What will be the procedures for accounting for missing, unused or spurious data?
Monitoring, supervision and quality control: Detailed statement about the all logistical issues to satisfy the requirements of Good Clinical Practices (GCP), protocol procedures, responsibilities of each member of the research team, training of study investigators, steps taken to assure quality control (laboratory procedures, equipment calibration etc)
Gantt chart: A Gantt chart is an overview of tasks/proposed activities and a time frame for the same. You put weeks, days or months at one side, and the tasks at the other. You draw fat lines to indicate the period the task will be performed to give a timeline for your research study (take help of tutorial on youtube). 11
Significance of the study: Indicate how your research will refine, revise or extend existing knowledge in the area under investigation. How will it benefit the concerned stakeholders? What could be the larger implications of your research study?
Dissemination of the study results: How do you propose to share the findings of your study with professional peers, practitioners, participants and the funding agency?
Budget: A proposal budget with item wise/activity wise breakdown and justification for the same. Indicate how will the study be financed.
References: The proposal should end with relevant references on the subject. For web based search include the date of access for the cited website, for example: add the sentence "accessed on June 10, 2008".
Appendixes: Include the appropriate appendixes in the proposal. For example: Interview protocols, sample of informed consent forms, cover letters sent to appropriate stakeholders, official letters for permission to conduct research. Regarding original scales or questionnaires, if the instrument is copyrighted then permission in writing to reproduce the instrument from the copyright holder or proof of purchase of the instrument must be submitted.

Naval Research Program
Research proposal guide - naval research program, research proposal guide.
Once an Initial Research Estimate Form (IREF) is validated and selected for funding, the next step is to complete a Research Proposal. Proposals must be completed and approved before funding can be authorized and released.
Faculty that have an IREF validated and selected for funding are required to complete the following steps before funding will be authorized and established. More details for each step are provided below; this list can be used as a checklist if desired.
Please notify NRP at [email protected] if you have any reservations about accepting your funded project (e.g. impending retirement, emergent obligations, etc.).
Jump to section
Eligibility, annual pi training, acknowledgment of terms.
- Technical Proposal/Narrative
Proposal tab
Nps personnel tab, proposal questions tab, proposal data tab, abstracts and attachments tab, proposal budget tab, review process, proposal amendments, troubleshooting.
More events
Events & Deadlines
Quick links, principal investigators.
The Principal Investigator (PI) is the researcher who has primary responsibility for the design, execution, and management of a sponsored research project and is named on the proposal to the sponsoring agency. The PI has the primary responsibility for the fulfillment of the Statement of Work. Even when collaborating with one or more Co-PIs, the PI has the ultimate responsibility for the project and remains the sole individual responsible for managing expenditures in support of the project.
Only eligible Naval Postgraduate School faculty participating in the mission of NPS may submit proposals and act as a PI/PD/Co-I/Co-PD for sponsored projects. Individuals in a faculty or staff category other than those listed in the SPPGM-22 require a waiver to be eligible. Sponsored Program Policy/Guidance Memo 22 (SPPGM-22): Who can be a PI/PD/Co-I/Co-PD? (PDF, 4 January 2023) PI/PD/Co-I/Co-PD Justification Memorandum (Waiver Form) (PDF)
^ Back to top
Training is required for anyone who functions as a PI/PD or has direct access to funds on sponsored projects. Annual PI Training is completed within Sakai, and includes four modules:
- Accountability/Fiscal Law: 13/14 required to pass
- Protection of Human Subjects: 7/8 required to pass
- OPSEC for the PI/PD: pass/fail
- Stewardship: 18/20 required to pass
PIs must pass all modules for training to be complete. Please visit Sponsored Programs Related Annual Online Trainings to begin.
Please send a screenshot or export of your passing scores to NRP upon successful completion of your Annual PI Training.
All PIs and Co-PIs must digitally sign the Acknowledgment of Terms form . This form must then be uploaded as an attachment to your Research Proposal.
To digitally sign the form, you may need to download and save it to your computer, and open in Adobe Reader. Opening it in your web browser doesn't reliably activate the signature fields.
When uploading as an attachment, go to the Abstracts and Attachments tab in Coeus, and upload the form using the "Supplementary Documentation" category.
Please do not email any documents directly to NRP unless requested to do so.
PDF, 142KB. Last updated November 2023
All PIs must complete a Technical Proposal/Narrative, using the official NRP template. These documents must be submitted as attachments to your Research Proposal.
- Read all template guidance prior to starting your proposal
- Complete all required template elements
- Supporting TASKS section must include direct correlation/justification for all budget expenses
- Coeus is approved for CUI, but please mark all documents accordingly if applicable
- Remove the first page containing template guidance before submitting to Coeus
Topic Advocate signatures are no longer required. Research Proposals will be routed through the chain for approval by NPS personnel and teams using Coeus. For efficiency purposes and to prevent delays, please do not bypass this process.
Word, 57KB. Last updated October 2023
Coeus Proposal Package
Koali Coeus is the system NRP uses to manage and review Research Proposals. To submit a Research Proposal, you will use a Proposal Development Document (PDD).
NRP creates empty PDD shells within Coeus, to pre-populate required information and simplify setup. Each PI will receive a Coeus-generated, automated email prompting you to begin your proposal.
Please email the NRP office at [email protected] with any questions, or if you don't receive your Coeus access email.
- Period of performance and milestone dates, in all proposal documents, must match.
- Proposals are only accepted through Coeus. Incomplete proposal packages will be rejected.
- Spend plans must be realistic as you will be required to execute as scheduled (burn rate).
- Expenses must include direct correlation/justification to the TASKS in your technical proposal.
- If someone is assisting you in preparing your proposal package, give them a link to this page.
This tab will be completed by NRP. Please do not make any changes to the fields present on this tab.
At minimum, you must include the PI and any Co-PIs. You can be a PI on no more than two concurrent NRP projects across all Cycle Years, and no more than one NRP project per Cycle Year.
- Enter the last name, email address, etc. of the person you wish to add. You only need to fill out one field, and the search is not case-sensitive. Click search .
- Click return value on the far left of the row containing the correct personnel record.
- The top section of the page will now have the person's name, as well as a Proposal Role section. Select the appropriate role, then click add person below that.
If additional staff/faculty are expected to participate but have yet to be identified, input their positions in your project using To be named instead of Employee Search .

Please answer all Proposal Questions, including any sub-questions that may appear. If you have any questions about this tab, please contact NRP .
Please fill out all Proposal Data. If you have any questions about this tab, please contact NRP .
To select multiple items in a "select all that apply" list, use Ctrl on Windows, or Cmd on Mac.
Upload your required attachments including your Acknowledgment of Terms form and your Technical Proposal/Narrative under the categories below:
- Acknowledgment of Terms: "Supplementary Documentation"
- Technical Proposal/Narrative: "Technical Proposal/Narrative"
- Budget Justification: "Budget Justification"
- Equipment Justification: "Equipment"
- You must upload a waiver for each person requiring one
Copy-paste the abstract from your Technical Proposal/Narrative into the Publicly Releasable Abstract section, under Enter Abstract . Make sure to click add or it will not save to your PDD correctly.
When entering keywords, please enter one keyword per line, not a comma-separated list. Keywords are used by other integrated systems and comma-separating them can cause errors in the data integrations.
The quarterly spend plan you enter into Coeus generates your required burn rate schedule. This data is reported to the Budget Submission Office (BSO) and the burn rate must be executed as input into Coeus. PIs are expected to plan for salary adjustments within their budget. The authorized project amount is not increased due to promotions or Cost of Living Allowance increases.
Ensure your quarterly spend plan is realistic by accounting for:
- Cost-of-living adjustments
- Raises and promotions
- Reasonable flexibility
Official research proposal budgets must be submitted using the Coeus budget proposal tool. The FY24 NRP Budget Spreadsheet is used for budget/spend plan updates during the PoP. The spreadsheet can be used for general offline proposal budget planning purposes but it is highly recommended that you use the Coeus training instance to draft your proposal budget.
Your proposal budget is an embedded document within your PDD, and has tabs of its own. NRP has created a quarterly budget shell for you to fill out; open this budget by using the open button on the far right of the page.
Using your IREF budget allocations, enter quarterly expenses in the NPS Labor and Other Direct Costs (Non-Labor) tabs. Your PDD's budget must be equal to or less than the budget proposed in your IREF.
If financial expenditure questions arise during budget development or execution, PIs should consult with the NRP SPFA .
How can the money be spent?
- NRP funds are RDT&E BA 6.6 and are appropriated solely for specific selected NRP projects. There must be a direct relationship between funds spent and the selected NRP research project.
- This money cannot be used for academic/curriculum support.
- This money cannot be used for office supplies, printers or cell phones.
- This money cannot be used to hire administrative personnel.
Financial Terms
- Indirect Costs: The NRP uses NR&DE funds, and indirect cost are not collected. The indirect rate is 0%.
- Fringe (aka Acceleration or Fully Burdened Rate): Fringe is always included in the cost of payroll regardless of how your payroll is being charged. Fringe addresses the actual cost of benefits paid by the government for each employee (TSP, FERS, Medicare, FEGLI, TSP Matching, Annual Leave, Sick Leave, Vacation). NPS recommends using 52.5% for projection purposes.
- Overhead: The NRP takes a small percentage off the top of the annual budget to run the program. Therefore, no overhead cost needs to be factored into each individual project budget.
Spend Plan Justification
The Description & Purpose field(s) in Coeus for all expenses (Other Direct Costs/Non-Labor) must include a direct correlation/justification to the TASKS in your Technical Proposal/Narrative. Do not use blanket terms.
If your budget includes costs that exceed the NRP allowances, attach a Budget Justification document. Alternatively, you can include line-item Budget Justification notes in your PDD's budget.
- Ensure that quarters with proposed travel include appropriate corresponding labor hours
- People who are not listed in the specific NRP project are not allowed to utilize these funds. Travel percentage and total cap may change in FY25.
- Unique business such as project kick-off meetings, mid-year progress review meetings, final projects delivery meetings, data collection, and/or one conference attendance that are directly tied to the project can be conducted via travel, but all “regular business” should be conducted on Teams. Virtual/online conferences are preferred and encouraged. Labor must be charged to the project at the same time you are on travel.
- Ensure travel and labor expenses align with research completion timelines, to include any travel for the purpose of final debriefing/delivering the final product(s)
- Students: Student participation is allowed; however, travel requests must state how the travel applies to the associated NRP research.
- DTS form justification box must include: NRP project number, PI Name, detailed purpose of the travel i.e., how the travel is directly related to the NRP project, travel is/is not included in the original proposal.
- All travelers are required to submit a Travel Report after each trip.
- Academic purposes
- Thesis development
- Student graduations
- Other research projects
- List all known project personnel. List additional planned but unidentified individuals under "To be named." Notify the NRP SPFA of project personnel changes immediately to avoid a payroll approval delay.
- Labor is charged using actual benefits and varies per individual. Rates are updated/calculated in Coeus routinely. Consult your SPFA for individual rates. NRP is exempt from other Indirect Costs.
- NRP funds are not appropriate for employee cash awards. All awards using NRP funds will be reversed upon detection.
- The fully burdened amount is listed in Coeus. PIs are expected to plan for salary adjustments within their budget. The authorized project amount is not increased due to promotions or Cost of Living Allowance increases .
External Support
If you are intending/planning to outsource labor/skills that cannot be performed by NPS personnel you must obtain approval from your department chair.
NRP funds cannot be used to hire administrative personnel.
Acquisitions
All purchases must align with the tasks and deliverables cited in your proposal and require a detailed justification to be submitted in ERP. As per the Annual PI Training, purchasing for "the greater good" is not allowed.
Provide an explanation, in plain language, detailing how each purchase contributes to the tasks and deliverables of the project. Blanket terms such as "Mission Essential / Critical" are not a valid justification.
Total purchasing exceeding 25% of your project's total budget will require additional justification.
- Orders should be submitted early in order to contribute to the project deliverable(s), and must be acquired within the project's Period of Performance.
- Acquisitions for computers, equipment, contracts, and MIPRS are only approved for the benefit of the selected NRP project. Therefore, each item must be ordered soon enough that it arrives early enough to contribute to the project deliverables.
- PIs may be allowed to purchase equipment with justification (e.g., computers) once every three years, however purchasing peripheral equipment that is considered office equipment is not allowed.
- All equipment must be shipped directly to the warehouse and registered in the NPS property accounting system prior to receipt under the PI’s name. The PI is accountable to produce records during an audit.
- Cell phones & cell phone services
- Computer peripherals: monitors, keyboards, mice, headsets, etc.
- Printers, ink, and toner
- Office supplies
- Publications (Please contact NRP for NRP-related publication expenses)
- Items considered to be for general purposes
- Checklist of OSHE Related Hazards to Consider
- Include labor, time, and costs for safety controls.
- Include safety and environmental planning and training hours.
- Include funds for safety assessments if needed, protective equipment and physical controls.
- Critical to plan ahead for off-campus activities, UUVs, lithium batteries, RF emitter, hazmat, lasers, etc.
Review Safety Information Needed from PIs for Project Descriptions
For safety questions or concerns email [email protected] or visit the Safety Review and Planning page on the Safety website.
Finalizing your budget
Once your budget is complete, save it with the button at the bottom, and use the blue Return to Proposal button at the top right. Check the Final box for your budget in the Proposal Budget tab.
- Coeus User Guide
- Contact NRP
- Contact Coeus Ombudsman
- Contact NRP SPFA for financial expenditure questions
- Budget Spreadsheet
Submit Your Proposal
Once your PDD is completed, run Data Validation .
- Go to the Proposal Actions tab
- On the Data Validation section, click the show button to expand it
- Click turn on validation
- Go through each of the Validation Errors and Warnings , and fix them
- Reach out to NRP at [email protected] if you need any help
Once your PDD passes validation, please use the Submit button at the bottom of the Proposal Actions tab to submit it for approval. NRP will receive an automated email from Coeus letting us know when your PDD is ready to review.
See the Troubleshooting guide below for help resolving errors. NRP is also happy to assist; contact us at [email protected] .
Once your PDD is successfully submitted, it goes through several stages of review:
- Your department chair reviews and approves your PDD. If you have Co-PIs listed, their department chairs must review and approve your PDD as well.
- NRP reviews your PDD for completeness, accuracy, and adherence to requirements and guidance.
- NRP's Financial Manager reviews your budget and spending allocations.
- NRP's Program Manager reviews and approves your PDD.
- The Vice Provost for Research and Innovation reviews and approves your PDD.
Once the VPR has approved your PDD, NRP double-checks a few more requirements:
- Completion of your annual PI training
- Completion and submission of all previous Cycle Years' required research deliverables
- Successful approval from the Human Research Protection Program Office & Institutional Review Board (IRB) , if required
Once these are complete, NRP then issues funding for you to begin your research.
To check your proposal's current status in the review process:
- Log in to Coeus
- In the Proposals section of the Coeus homepage, click "Search Proposals"
- In the Document ID field, enter the five-digit Document ID of your proposal. If you don't know the Document ID, please reach out to NRP and we can provide that to you.
- Click the Search button
- Click "view" on the left of the row your proposal shows up in, in the search results
- Go to the Proposal Actions tab
- Open the Route Log section by clicking the "show" button on it
- In Action List to Complete: Approval is required
- In Action List to FYI: Approval is not required; the person was notified for their situational awareness
- If multiple people are listed within the same approval line, only one of them is required to approve
To make amendments to an approved and finalized PDD, email the Coeus Ombudsman with your amendment request.
The types of changes that require an amendment through Coeus are:
- Changes to the Period of Performance
- Budget increases
- Changes to the PI or Co-PI(s)
- Topic Advocate changes
- Statement of Work changes
Here are solutions to common problems encountered through the Research Proposal process.
If you're still having trouble, please reach out to NRP . We're happy to help!
PDDs are "checked out" when someone opens them to edit them, and locked until the person editing clicks the close button to "check in" the proposal. Closing the browser tab will not check in the PDD.
If your proposal was locked by someone else, Coeus will display their name at the top of the PDD. Simply email them and request that they open the proposal and close it using the close button at the bottom of the page rather than just closing the browser tab.
If you're not able to get a hold of the person your PDD is checked out to, email the Coeus Ombudsman to request an administrator to unlock your PDD.
Reach out to NRP and let us know; we can add them as an authorized user to your PDD.
Opening the PDF in your browser doesn't always activate the signature fields. Download it to your computer and open it in Adobe Reader or Adobe Acrobat. The fields should show up.
- Essay Editor
Proposal Essay Examples: Convincing Ideas for Your Research Paper or Essay

Struggling to craft a captivating and well-built proposal essay? Many students find it challenging to compose a proposal-based essay and struggle to generate convincing ideas. If this sounds familiar, read on. In this comprehensive guide, we streamline the process of brainstorming and composing work, offering resources like suggestions on how to write a proposal essay, suggested steps when writing, useful examples, and efficient essay-crafting tips.
Developed through several years of expertise in scholarly writing, our article is meticulously tailored to help you excel in your academic assignments. Join us as we explore crafting an exceptional proposal paper. With the right tools and assistance, you'll move from ambiguity to self-assurance, ready to write an impressive work. Let's master the art of creating an attention-grabbing essay.
What is a Proposal Essay?
A proposal essay succinctly outlines the key content and aim of your intended study, summarizing its primary points and overall intent. Unlike a thesis, which presents the main idea of your academic study, a proposal-focused assignment acts as a detailed plan addressing a specific problem. As a proposal writer, you identify an issue, suggest a possible solution, and then provide persuasive evidence for the audience to have them support your viewpoint. Your goal is to convince them that this view is exceptional and deserves implementation. When writing such an essay, consider it as a chance to immerse in practical issues and showcase analytical and creative thinking skills. These papers serve as strategic tools, allowing an author to present their ideas or beliefs compellingly. Beyond business or economics, they encourage solution-seeking and reasoning skills across a variety of disciplines.
In a nutshell, a proposal-driven assignment allows you to demonstrate your ability to think innovatively and critically, addressing real-life issues with practical solutions. Now that you understand what is a proposal essay, join us in exploring its specifics and revealing your writer’s potential.
How to Write a Proposal Essay
Creating a successful proposal-related paper necessitates thorough preparation and an understanding of your audience's needs. To write such an essay, observe these stages:
- Extensively investigate your assignment’s topic to identify a chosen problem.
- Develop a compelling thesis statement summarizing your suggested solution.
- Make a solid proposal essay outline to logically organize all your ideas and ensure unity and cohesion.
- Present solid proof to support your viewpoints and anticipate any objections.
- Refine your writing carefully to enhance content clarity and logic.
When you are occupied with thoughts on how to write a paper proposal, handy tools like the AI essay generator Aithor have become indispensable helpers. Aithor, our intuitive assistant, empowers writers by utilizing advanced technology to generate ideas, check accuracy, and offer alternative words, improving the piece of writing. Explore the innovative capabilities of our AI tool by visiting https://aithor.com/ai-essay-generator and let it assist you with your assignment.
Check out some additional tips to enhance your overall essay quality:
- Get to know your audience and tailor your planned proposal to its interests.
- Use convincing language to involve your audience to advocate for your notion.
- Incorporate relevant data, instances, and statistics to reinforce your position.
- Address possible counterarguments to demonstrate thorough consideration.
- Use a powerful summary to conclude and inspire to act, urging support for your concepts.
To wrap up, writing a decent proposal-based essay requires in-depth investigation, persuasive argumentation, and attention to detail. By following the mentioned guidelines and additional tips, you can smoothly write a solid solution-focused writing that inspires action.
Prewriting Stage
Setting for a journey of composing a proposal-related assignment can be overwhelming. How to start a proposal essay? To ease this process, academic writers advocate for a systematic approach to craft a captivating piece of writing.
Here's a full guide to guarantee your assignment paper stands out. Know Your Reader
Being sympathetic to your prospective listeners is paramount when writing a persuasive paper. Who will you write for? Identify their key roles, preferences, and concerns to efficiently customize your message. This ensures mutual resonance in your views and addresses their specific needs and expectations.
Research Academic investigation forms the foundation of a robust convincing paper. Even with a prior understanding of the material, delving deeper yields new insights and perspectives. Revising scholarly literature enhances arguments, lending authority and credibility to your message.
Set an Issue
State the topic and challenges precisely and clearly. Use evidence to accentuate its significance and establish your grasp of the matter. That step is pivotal in gaining the audience's sympathy and support.
Define a Solution
Offer a straightforward and practical way out to the identified problem. Ensure its clarity and usefulness, aligning with indicated requirements. Frame your resolution in terms of objectives, delineating primary goals and additional benefits your project will provide.
Write an Essay Proposal Outline
Crafting an outline for your persuasive paper is essential. This helps put your ideas in order and create a logical flow. When structuring your paper, begin with a catchy introduction that describes the problem. Outline your suggested resolution with strong evidence, facts, and illustrations. Finally, summarize the noteworthy aspects and emphasize the relevance of your proposal. This structured approach enhances coherence and persuasiveness.
Ø For executive proposals, add organizational data and budget analysis, maintaining clear and direct language, devoid of unnecessary jargon.
Structure of a Proposal Essay
Generating a credible proposal-focused essay involves several main components, each serving a definite purpose to efficiently convey your key idea. Here's a full breakdown of how to write an essay proposal:
Introduction
- Captivating Intro
Capture the readers' attention with an eye-catching hook. Precisely state your essay’s thesis statement, conveying your message succinctly and convincingly.
- Context and Background
Provide a solid background for your proposed idea, thus setting a stage for the topic matter and its validity.
- Research Relevance
State why your investigation is essential, drawing upon the background info provided.
- Problem Statement
Dive deeper into the presented issue, delineating its relevance and impact to deliver a captivating context for your written work.
- Proposal Statement
State your projected way out to the mentioned challenges. Emphasize its paybacks and mention potential shortcomings to showcase its viability.
- Implementation Plan
Clarify in detail how you wish to put your words into effect, addressing practical considerations and potential obstacles.
- Expected Outcome
Talk about the positive effects that you expect from executing your solution proposal, conveying distinctly its probable impact.
- Evaluation of Feasibility
Consider the proposal’s practicability considering the essential resources and would-be objections.
- Resource Management and Timeline
Indicate the demanded resources and generate a timeline for implementation if applicable.
- Research Queries and Objectives
List the goals of your inquiry and say how will addressing the challenges impact your audience. Utilize credible sources and data to reinforce your arguments.
- Study Design and Methodology
Explain your methodology for addressing the challenge, illustrating the rationale behind your selected approach, and predicting the anticipated outcomes.
- Key Points Summary
Recap the main points from the intro, background, and topic relevance, along with the hypotheses/research questions sections.
- Importance and Potential Impact
Accentuate how your investigation can hypothetically contribute to addressing the mentioned issue and consider potential consequences if the proposal is not implemented.
- Call to Action and Close
Restate the proposal’s relevance, leaving the audience with a convincing call to action. Express gratitude for the committee's consideration and leave readers with a sense of anticipation for the proposed research.
- Bibliography (Optional)
Include a literature list that references the materials used and displays the work’s contents to demonstrate the depth of the investigation. It is usually placed at the end of the whole text as a separate section.
Remember to refine your final draft for clarity and conciseness, testing if the paper proposal format is well-constructed. Consider seeking some feedback from others to enhance the presentation and proposal actuality. Additionally, ensure each paragraph flows smoothly and plausibly and supports your general argument. This ensures content clarity and cohesion throughout your text.
Academic Research Study Proposal Sample 2024
Here is a sample idea for an interesting proposal paper:
- The proposed research study will investigate the risks of sending messages while driving and explore measures to mitigate this hazardous behavior.
- Texting when driving continues to be a widespread issue despite various awareness campaigns and legal restrictions.
- The study will focus on examining the mental and physical distractions caused by this activity. Also, the proposal will delve into the increased likelihood of mishaps and fatalities associated with such behavior.
- Utilizing a mixed-methods approach, the investigation will gather data through surveys, interviews, and driving simulations from a diverse sample of drivers across different age groups and regions.
- Data analysis will include statistical analysis of accident rates, qualitative coding of interview responses, and thematic analysis of driving simulation outcomes.
- The essay's findings aim to raise awareness among policymakers, law enforcement agencies, and the public about the grave dangers of texting when driving.
- Additionally, the investigation will propose recommendations for interventions such as stricter enforcement of existing regulations, educational programs targeting drivers of all ages, and the creation of technological solutions to prevent distraction-related cases.
- Ultimately, this study seeks to add to the lessening of crashes and fatalities caused by texting in a car and encourage safer driving habits in society.
Final Remarks
In composing a robust proposal essay, the journey from beginning to culmination is marked by strategic planning and scrupulous work. If you embrace a methodical approach, a captivating paper will emerge. Such vital details as understanding the audience, conducting in-depth research, describing the challenges, proposing possible way-outs, and structuring your arguments are vital elements of a successfully written work. Each phase of this process contributes to the clarity and persuasiveness of the text, ensuring resonance with readers. Using illustrative examples adds depth and relatability to the proposal.
Ultimately, the proposal paper showcases not only analytical prowess and solution-seeking acumen but also adept communication of intricate concepts. With unwavering dedication and meticulous focus on details, the proposal essay becomes a testament to effective persuasion and insightful discourse.
Related articles
Ace your graduation speech with aithor.
Hello, Aithors! Can you feel it? That's the buzz of graduation season in the air:) And while we're all about the caps flying and the proud smiles, we also know that being asked to write a graduation speech can feel a bit like being handed a mountain to climb. Crafting a graduation speech is all about capturing the spirit of the journey you've been on, from the triumphs to the trials, and everything in between. It's a reflection of where you've been, and a beacon of light pointing towards where ...
Will I Get Caught Using Chat GPT?
ChatGPT has been around for a little over a year but already found popularity among all groups of users. School and college students have taken a particular liking to it. However, many students avoid using the chatbot for fear that their teacher might catch them. Read this article to learn more about ChatGPT, its features, and whether your teacher can actually find out if you use it for your homework. What is Chat GPT? ChatGPT was first introduced to the world in November 2022. At the time, ...
Create a Perfect Essay Structure
Hello Aithors! We're back again with another feature highlight. Today, we want to talk about a tool that can be a game-changer for your essay writing process - our Table of Contents tool. Writing an essay isn't just about getting your ideas down on paper. It's about presenting them in a clear, structured way that makes sense to your reader. However, figuring out the best structure for your essay can sometimes be a tough nut to crack. That's why we developed the Table of Contents feature. The b ...
How To Write Reflection Essays
How often do you contemplate how the tapestry of your experiences shapes your thoughts? A reflection paper lets you explore that. It's like deep diving into your life’s precious moments, examining how stories, books, events, or even lectures have influenced your views. This type of academic essay integrates a personal perspective, allowing you to openly express your opinions. In this guide, we will delve into the specifics of reflective writing, share some tips, and show some self-reflection es ...
APA or MLA: Choosing the Right Citation Style for Your Paper
When it comes to academic writing, properly citing your sources is crucial. It not only helps you avoid plagiarism but also adds credibility to your work by showing that you've done your research. However, with various citation styles out there, it can be tricky to know which one to use. Two of the most common styles are APA (American Psychological Association) and MLA (Modern Language Association). In this article, we'll take a closer look at the APA vs MLA format to help you decide which is ri ...
How to Write an Evaluation Essay That Engages and Persuades: Helpful Tips and Inspiring Examples
Are you feeling unsure about how to effectively evaluate a subject from your own perspective in an evaluation essay? If you're struggling to understand how to present a balanced assessment, don't worry! We're here to guide you through the process of writing an evaluation that showcases your critical thinking skills. What Is an Evaluation Essay? An evaluation essay is a type of writing in which the writer gives their opinion on a topic. You look at something carefully and think about how good ...
Literary Analysis Essay Example: Discover How to Analyze Literature and Improve Your Writing Skills
Creating a literary analysis essay is one of the most interesting assignments during college and high school studies. It needs both good text interpreting and analytical skills. The number of proper forms is great, including short stories and novels, poems and ballads, comedies and dramas. Any literary work may be analyzed. In brief, when writing this paper a student should give a summary of the text and a detailed review of the language, structure, and other stuff the author used to express hi ...
Biographical Essay: Tips and Tricks for Writing a Perfect Biography
Biographical essays are some of the most common texts you can find on the Internet. When you browse a Wiki article about your favorite singer, you are basically reading a biography paper. However, in academia, there are certain rules students need to follow to get perfect marks for their papers. In this article, we will explore what a biographical essay is, why it matters, and how to write an essay about a person. What is a biographical essay? A biographical essay is a paper that focuses on ...
Human-in-the-Loop for Personality Dynamics: Proposal of a New Research Approach
- Conference paper
- First Online: 31 May 2024
- Cite this conference paper

- Krzysztof Kutt ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5453-9763 27 ,
- Marzena Kutt ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5343-8925 28 ,
- Bartosz Kawa ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1277-2580 27 &
- Grzegorz J. Nalepa ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8182-4225 27
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Computer Science ((LNCS,volume 14674))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Work-Conference on the Interplay Between Natural and Artificial Computation
In recent years, one can observe an increasing interest in dynamic models in the personality psychology research. Opposed to the traditional paradigm—in which personality is recognized as a set of several permanent dispositions called traits—dynamic approaches treat it as a complex system based on feedback loops between individual and the environment. The growing attention to dynamic models entails the need for appropriate modelling tools. In this conceptual paper we address this demand by proposing a new approach called personality-in-the-loop, which combines state-of-the-art psychological models with the human-in-the-loop approach used in the design of intelligent systems. This new approach has a potential to open new research directions including the development of new experimental frameworks for research in personality psychology, based on simulations and methods used in the design of intelligent systems. It will also enable the development of new dynamic models of personality in silico. Finally, the proposed approach extends the field of intelligent systems design with new possibilities for processing personality-related data in these systems.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Cassimatis, N.L., Bello, P., Langley, P.: Ability, breadth, and parsimony in computational models of higher-order cognition. Cogn. Sci. 32 (8), 1304–1322 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/03640210802455175
Article Google Scholar
Costa, P.T., McCrae, R.R.: Trait theories of personality. In: Barone, D.F., Hersen, M., Van Hasselt, V.B. (eds.) Advanced Personality, pp. 103–121. Springer, Boston (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8580-4_5
Crupi, V., Nelson, J.D., Meder, B., Cevolani, G., Tentori, K.: Generalized information theory meets human cognition: introducing a unified framework to model uncertainty and information search. Cogn. Sci. 42 (5), 1410–1456 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/cogs.12613
Dzedzickis, A., Kaklauskas, A., Bucinskas, V.: Human emotion recognition: review of sensors and methods. Sensors 20 (3), 592 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030592
Feher, A., Vernon, P.A.: Looking beyond the big five: a selective review of alternatives to the big five model of personality. Personality Individ. Differ. 169 , 110002 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2020.110002
Friedman, S., Forbus, K., Sherin, B.: Representing, running, and revising mental models: a computational model. Cogn. Sci. 42 (4), 1110–1145 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/cogs.12574
Hopwood, C.J., Wright, A.G.C., Bleidorn, W.: Person-environment transactions differentiate personality and psychopathology. Nat. Rev. Psychol. 1 (1), 55–63 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44159-021-00004-0
Kelly, M.A., Arora, N., West, R.L., Reitter, D.: Holographic declarative memory: distributional semantics as the architecture of memory. Cogn. Sci. 44 (11) (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/cogs.12904
Kostromina, S.N., Grishina, N.V.: The dynamic personality: ‘continuity amid change’. Psychol. Russia State Art 12 (2), 34–45 (2020). https://doi.org/10.11621/pir.2019.0203
Kutt, K., Drążyk, D., Bobek, S., Nalepa, G.J.: Personality-based affective adaptation methods for intelligent systems. Sensors 21 (1), 163 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010163
Lara-Cabrera, R., Camacho, D.: A taxonomy and state of the art revision on affective games. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 92 , 516–525 (2019)
Matz, S., Chan, Y.W.F., Kosinski, M.: Models of personality. In: Tkalcic, M., Carolis, B.D., de Gemmis, M., Odic, A., Kosir, A. (eds.) Emotions and Personality in Personalized Services - Models, Evaluation and Applications. Human-Computer Interaction Series, pp. 35–54. Springer, Heidelberg (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31413-6_3
Mayer, J.D.: Asserting the definition of personality. Online Newslett. Pers. Sci. (1), 1–4 (2007). http://www.personality-arp.org/html/newsletter01/page5d.html
McCrae, R.R., Costa, P.T.: Personality in Adulthood. Taylor & Francis, Abingdon (2003). https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203428412
Mõttus, R., et al.: Descriptive, predictive and explanatory personality research: different goals, different approaches, but a shared need to move beyond the big few traits. Eur. J. Pers. 34 (6), 1175–1201 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/per.2311
Nalepa, G.J., Kutt, K., Bobek, S.: Mobile platform for affective context-aware systems. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 92 , 490–503 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.02.033
Neff, G., Nagy, P.: Talking to bots: symbiotic agency and the case of tay. Int. J. Commun. 10 , 4915–4931 (2016)
Google Scholar
Nunes, D.S.S., Zhang, P., Silva, J.S.: A survey on human-in-the-loop applications towards an internet of all. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 17 (2), 944–965 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2015.2398816
Phan, L.V., Rauthmann, J.F.: Personality computing: new frontiers in personality assessment. Soc. Pers. Psychol. Compass 15 (7) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/spc3.12624
Quirin, M., et al.: The dynamics of personality approach (DPA): 20 tenets for uncovering the causal mechanisms of personality. Eur. J. Pers. 34 (6), 947–968 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/per.2295
Rauthmann, J.F.: Motivational factors in the perception of psychological situation characteristics. Soc. Pers. Psychol. Compass 10 (2), 92–108 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/spc3.12239
Rauthmann, J.F.: Capturing interactions, correlations, fits, and transactions: a person-environment relations model. In: The Handbook of Personality Dynamics and Processes, pp. 427–522. Elsevier (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813995-0.00018-2
Rauthmann, J.F. (ed.): The Handbook of Personality Dynamics and Processes. Elsevier (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/C2017-0-00935-7
Roads, B.D., Mozer, M.C.: Improving human-machine cooperative classification via cognitive theories of similarity. Cogn. Sci. 41 (5), 1394–1411 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/cogs.12400
Tkalcic, M., Carolis, B.D., de Gemmis, M., Odic, A., Kosir, A. (eds.): Emotions and Personality in Personalized Services - Models, Evaluation and Applications. Human-Computer Interaction Series. Springer, Heidelberg (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31413-6
Valdez, A.C., Ziefle, M.: Human factors in the age of algorithms. understanding the human-in-the-loop using agent-based modeling. In: Meiselwitz, G. (ed.) Social Computing and Social Media: Technologies and Analytics (Part II). LNCS, vol. 10914, pp. 357–371. Springer, Heidelberg (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91485-5_27
Varma, S.: Criteria for the design and evaluation of cognitive architectures. Cogn. Sci. 35 (7), 1329–1351 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-6709.2011.01190.x
Wiener, N.: Cybernetics. Sci. Am. 179 (5), 14–19 (1948)
Download references
Acknowledgments
The research for this publication has been supported by a grant from the Priority Research Area DigiWorld under the Strategic Programme Excellence Initiative at Jagiellonian University. The research has been supported by a grant from the Faculty of Physics, Astronomy and Applied Computer Science under the Strategic Programme Excellence Initiative at Jagiellonian University.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Jagiellonian Human-Centered AI Lab, Mark Kac Center for Complex Systems Research, Institute of Applied Computer Science, Faculty of Physics, Astronomy and Applied Computer Science, Jagiellonian University, Kraków, Poland
Krzysztof Kutt, Bartosz Kawa & Grzegorz J. Nalepa
Institute of Psychology, University of the National Education Commission, Kraków, Poland
Marzena Kutt
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Krzysztof Kutt .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena, Cartagena, Spain
José Manuel Ferrández Vicente
Polytechnic University of Valencia, Valencia, Spain
Mikel Val Calvo
Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
Hojjat Adeli
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of interests.
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Kutt, K., Kutt, M., Kawa, B., Nalepa, G.J. (2024). Human-in-the-Loop for Personality Dynamics: Proposal of a New Research Approach. In: Ferrández Vicente, J.M., Val Calvo, M., Adeli, H. (eds) Artificial Intelligence for Neuroscience and Emotional Systems. IWINAC 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14674. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61140-7_43
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61140-7_43
Published : 31 May 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-61139-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-61140-7
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- My View My View
- Following Following
- Saved Saved
Hamas says it 'positively' views Gaza ceasefire proposal set out by Biden
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Nidal Al Mughrabi and Ahmed Tolba; Writing by Adam Makary; editing by Deepa Babington
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab
An Israeli pilotless plane was shot down over Lebanese territory by a surface-to-air missile on Saturday, Israel's military said, and Hezbollah claimed responsibility for the interception.

World Chevron

Boeing Starliner capsule's first crewed test flight postponed minutes before launch
Boeing, whose commercial plane operations are in disarray, badly needs a win in space for its Starliner venture, a program several years behind schedule with more than $1.5 billion in cost overruns.

Yemen's Houthis conducted six operations targeting a U.S. aircraft carrier, a U.S. destroyer and three vessels in the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean, the Iranian-backed group's military spokesperson Yahya Saree said on Saturday.

Israel describes a permanent cease-fire in Gaza as a ‘nonstarter,’ undermining Biden’s proposal

TEL AVIV, Israel — Israel’s prime minister on Saturday called a permanent cease-fire in Gaza a “nonstarter” until long-standing conditions for ending the war are met, appearing to undermine a proposal that U.S. President Joe Biden had announced as an Israeli one.
The statement from Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s office came a day after Biden outlined the plan , and as families of Israeli hostages held by Hamas called for all parties to immediately accept the proposal. A major demonstration in Israel on Saturday night urged the government to act now.
And a joint statement by mediators the U.S., Egypt and Qatar pressed Israel and Hamas, saying the proposed deal “offers a road map for a permanent cease-fire and ending the crisis” and gives immediate relief to both the hostages and Gaza residents.
But Netanyahu’s statement said that “Israel’s conditions for ending the war have not changed: the destruction of Hamas’ military and governing capabilities, the freeing of all hostages and ensuring that Gaza no longer poses a threat to Israel. Under the proposal, Israel will continue to insist these conditions are met before a permanent cease-fire is put in place.”
In a separate statement, Netanyahu accepted an invitation from U.S. congressional leaders to deliver an address at the Capitol, a show of wartime support for Israel. No date has been set.
Biden on Friday asserted that Hamas is “no longer capable” of carrying out a large-scale attack on Israel like the one by the militant group in October that started the war. He urged Israel and Hamas to reach an agreement to release about 100 remaining hostages, along with the bodies of around 30 more, for an extended cease-fire.
Cease-fire talks halted last month after a push by the U.S. and other mediators to secure a deal in hopes of averting a full-scale Israeli invasion of Gaza’s southern city of Rafah. Israel says the Rafah operation is key to uprooting Hamas fighters responsible for the Oct. 7 attack.
Israel on Friday confirmed its troops were operating in central parts of the city . The ground assault has led around 1 million Palestinians to leave Rafah and thrown humanitarian operations into turmoil. The World Food Program has called living conditions “horrific and apocalyptic” as hunger grows.
Families of hostages said that time was running out.
“This might be the last chance to save lives,” Gili Roman told The Associated Press. His sister, Yarden Roman-Gat, was freed during a weeklong cease-fire in November, but sister-in-law Carmel is still held. “Our leadership must not disappoint us. But mostly, all eyes should be on Hamas,” Roman said.
Families described an aggressive meeting Thursday with Israel’s national security adviser, Tzachi Hanegbi, who told them the government wasn’t ready to sign a deal to bring all hostages home and there was no plan B.
Hanegbi said this week he expects the war to continue another seven months to destroy Hamas’ military and governing capabilities.
Many hostages’ families accuse the government of a lack of will.
“We know that the government of Israel has done an awful lot to delay reaching a deal, and that has cost the lives of many people who survived in captivity for weeks and weeks and months and months,” Sharone Lifschitz said. Her mother, Yocheved, was freed in November but her father, Oded, is still held.
The first phase of the deal proposed by Biden would last for six weeks and include a “full and complete cease-fire,” a withdrawal of Israeli forces from all densely populated areas of Gaza and the release of a number of hostages, including women, older people and the wounded, in exchange for the release of hundreds of Palestinian prisoners.
The second phase would include the release of all remaining living hostages, including male soldiers, and the withdrawal of Israeli forces from Gaza. The third phase calls for the start of a major reconstruction of Gaza, which faces decades of rebuilding from the war’s devastation.
Biden acknowledged that keeping the proposal on track would be difficult, with “details to negotiate” to move from the first phase to the second. Biden said if Hamas fails to fulfil its commitment under the deal, Israel can resume military operations.
Hamas has said it viewed the proposal “positively” and called on Israel to declare an explicit commitment to an agreement that includes a permanent cease-fire, a complete withdrawal of Israeli troops from Gaza, a prisoner exchange and other conditions.
In Deir al-Balah, where many Palestinians have fled following Israel’s assault on Rafah, there was some hope.
“This proposal came late, but better late than never,” said Akram Abu Al-Hasan.
The main difference from previous proposals is the readiness to stop the war for an undefined period, according to analysts. It leaves Israel the option to renew the war and diminish Hamas’ ability to govern, but over time, said Michael Milshtein, head of the Palestinian Studies Forum in Dayan Center at Tel Aviv University.
“It was a very good speech ... it seems that Biden is trying to force it on the Israeli government. He was clearly speaking directly to the Israeli people,” said Gershon Baskin, director for the Middle East at the International Communities Organization.
Also on Saturday, Egypt’s state-run Al-Qahera News said officials from Egypt, the United States and Israel would meet in Cairo over the weekend about the Rafah crossing, which has been closed since Israel took over the Palestinian side in May.
The crossing is a main way for aid to enter Gaza. Egypt has refused to open its side, fearing the Israeli control will remain permanent. Egypt wants Palestinians to be in charge again.
Hamas’ attack on Oct. 7 killed around 1,200 people — mostly civilians — and abducted about 250. More than 36,370 Palestinians have been killed in Gaza by Israel’s campaign of bombardment and offensives, according to Gaza’s Health Ministry. Its count doesn’t differentiate between civilians and combatants.
The Associated Press
Texas education leaders unveil Bible-infused elementary school curriculum
Elementary school curriculum proposed this week would infuse new state reading and language arts lessons with teachings on the Bible, marking the latest push by Texas Republicans to put more Christianity in public schools.
The Texas Education Agency released thousands of pages of educational materials this week. They have been made available for public viewing and feedback and, if approved by the State Board of Education in November, will be available for public schools to roll out in August of 2025. Districts will have the option of whether to use the materials but will be incentivized to do so with up to $60 per student in additional funding.
TEA Commissioner Mike Morath said the materials are based on extensive cognitive science research and will help improve students' reading and math scores. In 2019, less than half of students met grade-level standards for reading, and that percentage has declined since the pandemic , based on state standardized test scores.
The new materials have prompted criticism, though. The education news site, The 74 , first reported the redesign on Wednesday and included excerpts of lesson plans with biblical references. They also reported that a New York-based curriculum vendor, Amplify, opted out of bidding on a contract after the state sought to insert biblical materials, but not other religious texts, into the curriculum. The state education agency rejected those claims, saying multiple religions are included throughout the curriculum. Because of Texas' size, textbooks that are developed for its schools are often used in other states.
On Thursday, Morath told The Texas Tribune that religious materials are a "small piece of the content pie." His office could not quantify what percentage of each grade's textbook would be devoted to biblical references. The Tribune has not reviewed all materials, which include the state-designed textbooks as well as proposals from 25 different vendors.
But an initial review of the proposed state textbooks shows that religious materials feature prominently, with texts sourced from the Bible as the most heavily used.
"It's a tiny fraction of the overall fraction - it's just where it makes sense to do that," Morath said. "It's a very small but appropriate fraction."
The textbooks mark a shift toward a "classical, broad-based liberal arts education," from a more skills-based curriculum, Morath said.
"You're trying to build vocabulary, build background knowledge so that when kids are reading Steinbeck in high school, they get the references," Morath said.
The instructional materials were unveiled amid a broader movement by Republicans to further infuse conservative Christianity into public life. At last week's Texas GOP convention - which was replete with calls for "spiritual warfare" against their political opponents - delegates voted on a new platform that calls on lawmakers and the SBOE to "require instruction on the Bible, servant leadership and Christian self-governance."
Throughout the three-day convention, Republican leaders and attendees frequently claimed that Democrats sought to indoctrinate schoolchildren as part of a war on Christianity . SBOE Chair Aaron Kinsey, of Midland, echoed those claims in a speech to delegates, promising to use his position to advance Republican beliefs and oppose Critical Race Theory, "diversity, equity and inclusion" initiatives or "whatever acronym the left comes up with next."
"You have a chairman," Kinsey said, "who will fight for these three-letter words: G-O-D, G-O-P, and U-S-A."
Mark Chancey, a Southern Methodist University religious studies professor who focuses on movements to put the Bible in public schools, said there is "nothing inherently inappropriate" with teaching the Bible or other religious texts, so long as it's done neutrally. But he's concerned by some of the proposed curriculum, including lessons that he said seem to treat biblical stories as "straightforward historical accounts."
"It serves a civic good for students to be taught about religion," he said. "But that's different from giving students religious instruction. The question is going to be whether these materials teach about religion, or whether they cross the line into giving religious instruction."
For example: The curriculum promotes lessons on Leonardo Da Vinci's "The Last Supper" alongside the Gospel of Matthew, which centers on Jesus' crucifixion and its atonement for human sin. "These are very strong, central claims of Christian theology," Chancey said. "And students will have questions about that. How are teachers supposed to respond to those questions?"
It's not unforeseeable, he said, for those conversations to lead to even thornier areas that are still divisive even among Christians.
If the state education board approves the materials in November, schools will not be required to use them. But a measure approved by lawmakers last year will offer more money to public school districts that do choose to adopt any of the materials.
Some of that content includes a first-grade lesson stating the Liberty Bell "reminded [ the Founding Fathers ] of how God helped free the Hebrew people in the Bible" as well as a fifth-grade poetry lesson on "A Psalm of David," described as "one of the most popular poems ever written."
Other religions are also included. A second-grade lesson highlights the Jewish celebration of Purim. A fourth-grade poetry unit includes Kshemendra, a poet from India who "studied Buddhism and Hinduism."
Some State Board of Education members told the Tribune they had not yet read through the materials and would decide whether or not to approve the content based on standards they've already established.
Keven Ellis , a Republican state school board member who lives in Lufkin, said the role of the board is to make sure the materials are appropriate for each grade level and that they align with the state's curriculum standards, known as the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills.
"My focus will remain on approving instructional materials that improve outcomes in phonics, language arts, and math," Ellis said.
State curriculum guidelines spell out that "the instructional material should recognize and not contradict that parents have the right to 'direct the moral and religious training' of their children and the duty to support their children's education.'" Ellis did not respond to inquiries about the religious material.
Staci Childs , a Houston Democrat who sits on the SBOE, said she believes it's okay to include Biblical references as long as other religions are also introduced to students.
"As a Christian, I think it is okay [ to teach the Bible ] as long as you're normalizing the introduction of all religions and all types of mythologies so students have a varied and robust and true depiction of the materials in the text of our past," Childs said. "To only infuse Bible verses and teachings of the Bible is completely insensitive to all the different types of students we have in Texas and a disrespect to the faiths they may acknowledge."
Last year, the state directed the TEA to create its own textbooks when the Legislature passed House Bill 1605 . Lawmakers said the purpose of the policy was to give teachers access to high-quality instructional materials.
A teacher vacancy task force that had convened in 2022 found that teachers spend significant time creating and looking for lesson plans. Lawmakers said the new state textbooks will save teachers time.
In an op-ed published in the Dallas Morning News this week, state Rep. Brad Buckley , R-Killeen, and state Sen. Brandon Creighton , R-Conroe, said the new materials "will provide much-needed relief to teachers by eliminating the need to spend dozens of hours outside of the classroom developing curriculum."
Morath said the materials are designed for Texas students, with references to the state's geography and industries, as well as Texas-based historical figures like Clara Driscoll, known for her historic preservation work rescuing the Alamo from destruction, decades after the pivotal battle at the former Catholic mission in San Antonio.
"We've tried to make it as tightly based on the needs of Texas students as possible," Morath said.
Soon after the materials were released on Wednesday morning, Gov. Greg Abbott released a statement saying he supported the curriculum.
"The materials will also allow our students to better understand the connection of history, art, community, literature, and religion on pivotal events like the signing of the U.S. Constitution, the Civil Rights Movement, and the American Revolution," Abbott said in a statement.
When asked directly if Abbott had any role in developing the new content, Morath answered: "I'm not sure any. This was entirely a project of TEA." Morath added that the governor is keenly attentive to the subject of public education.
"The governor has been very interested in getting back to fundamentals of education for a long time," Morath said, "and so this is some of the lens that we think about, but he's not alone in that perspective."
Before HB 1605's passage, the Texas Education Agency was creating new instructional materials in order to help improve students' reading and math scores. Those materials were piloted in about 400 districts, a TEA spokesperson said. Some had full-scale, district-wide implementation while others tested the materials in a few grade levels.
Morath cited pilot studies in districts like Temple and Lubbock, where students' reading scores increased by as much as 16 points after adopting the newer reading and language arts program.
About 300 people, most of whom are educators, are reviewing all of the instructional materials and will present their feedback to the State Board of Education. TEA did not provide a list of the reviewers but said they were selected by the SBOE.
Members of the public can also weigh in and offer feedback on the materials until August 16 and from there, the materials will go before the state board in November for final approval. If approved, the materials will immediately be available for download.
Chancey, the Southern Methodist University religion professor, said teaching the Bible in any public setting immediately prompts a variety of complicated questions. First among them: Which of the many Bible translations should be used? "The choice of translation brought into the public school has at times proven controversial," he said.
Meanwhile, Chancey said, the proposed instructions on religious liberty in the original colonies seem to be a "tremendous oversimplification," failing to note the persecution faced by other religious groups, namely Quakers and early Baptists. Omitting that, he said, misses the real lesson to be learned from studying America's early settlers: "The dangers of religious favoritism."
The proposed state textbook calls for excerpts of Martin Luther King Jr.'s "Letter From a Birmingham Jail" to be paired with the Biblical story of Shadrach, Meshach and Abednego, whose defiance of the Babylonian leader Nebuchadnezzar is cited by King as an example of civil disobedience. And yet, the proposed curriculum does not appear to include any excerpts on the intended audience or a core theme of King's letter: White moderates and clergy, whom King chastised for critiquing his civil disobedience while remaining "silent behind the anesthetizing security of stained glass windows."
Morath said the excerpt chosen is the one that would be appropriate for a fifth grader, based on their vocabulary and knowledge level.
"We would expect students to return to it in deeper and deeper ways," Morath said. "You have to give him bits of knowledge that build on prior bits of knowledge, and you're steadily giving them more and more and more exposure."
This instructional redesign for public schools comes amid an ongoing embrace on the right of Christian nationalism, which claims that the United States founding was ordained by God, and that its laws and institutions should thus favor their conservative, Christian views. Recent polling from the Public Religion Research Institute found that more than half of Republicans adhere to or sympathize with pillars of Christian nationalism, including beliefs that the U.S. should be a strictly Christian nation. Of those respondents, PRRI found, roughly half supported having an authoritarian leader who maintains Christian dominance in society.
The Texas Tribune is a nonprofit, nonpartisan media organization that informs Texans - and engages with them - about public policy, politics, government, and statewide issues.
Related Topics
- REPUBLICANS
- RELIGION & SPIRITUALITY
- SCHOOL FUNDING
- TEXAS TRIBUNE

Houston ISD seeks feedback on $4.4 billion bond proposal

Man diagnosed with muscular dystrophy graduates from Rice University

Pearland ISD may see a tax decrease after surplus of nearly $4.1M

A fifth grader's fundraiser cleared his school of meal debt
Top stories.

Another chance for scattered storms Sunday... some strong
- 4 minutes ago

Man killed during dice game in NE Harris Co. by robbery suspects: HCSO

Several cruise passengers fly into Houston with flu-like symptoms: HFD

Teen left paralyzed after driver allegedly shot him in neck after prom

HPD looking for suspect in Westheimer Road sexual assault case
- 2 hours ago
2024 Tropical Weather Update: First day of hurricane season is quiet
SE Harris County kicks off hurricane season with preparedness workshop
- 31 minutes ago
Former Houston Public Works employee charged with bribery: Records

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
A research proposal outline's content typically varies in length, from 3 to 35 pages, with references (and appendices, if necessary). But like any academic activity, start the research proposal template writing process by first carefully reading the instructions. Make sure to clarify anything that needs clarification and only proceed once ...
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
1. Research Proposal Format Example. Following is a general outline of the material that should be included in your project proposal. I. Title Page II. Introduction and Literature Review (Chapters 2 and 3) A. Identification of specific problem area (e.g., what is it, why it is important). B. Prevalence, scope of problem.
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
Research proposal aims. Relevance. Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. Context. Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. Approach. Make a case for your methodology. Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the ...
Look for any research gaps, trends and patterns, common themes, debates, and contradictions. Consider any seminal studies on the topic area as it is likely anticipated that you will address these in your research proposal. 4. Research Design. This is where you get down to the real meat of your research proposal.
Content and style of your research proposal What to put in your proposal? Application processes can vary by subject area and discipline, so make sure you follow the relevant guidelines provided by your chosen PhD programme at the University of Edinburgh. If a School/Deanery template is available, you should use
The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews.
In general, the proposal components include: Introduction: Provides reader with a broad overview of problem in context. Statement of problem: Answers the question, "What research problem are you going to investigate?" Literature review: Shows how your approach builds on existing research; helps you identify methodological and design issues in studies similar to your own; introduces you to ...
We walk you through two successful research proposals (Master's PhD-level), as well as our free research proposal. Download PDF or Word. About Us; Services. 1-On-1 Coaching. Topic Ideation; ... All content copyright Grad Coach 2024 · The Grad Coach logo is a registered trade mark: UK00003956375 · Tutors' Association ID: 55870609
Develop an Outline. Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content. Consider the typical structure of a proposal: Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution. Background/Context: Offer relevant ...
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution. In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators ...
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let's look at the explanation for each of the steps here: Step 1: Title and Abstract. Step 2: Introduction. Step 3: Research objectives. Step 4: Literature review.
Literature review. This key component of the research proposal is the most time-consuming aspect in the preparation of your research proposal. As described in Chapter 5, the literature review provides the background to your study and demonstrates the significance of the proposed research.Specifically, it is a review and synthesis of prior research that is related to the problem you are setting ...
Academic Research Proposal. This is the most common type of research proposal, which is prepared by students, scholars, or researchers to seek approval and funding for an academic research project. It includes all the essential components mentioned earlier, such as the introduction, literature review, methodology, and expected outcomes.
Abstract: This is a brief (300-500 words) summary that includes the research question, your rationale for the study, and any applicable hypothesis. You should also include a brief description of your methodology, including procedures, samples, instruments, etc. Introduction: The opening paragraph of your research proposal is, perhaps, the most ...
It puts the proposal in context. 3. The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1. The importance of the statement of the research problem 5: The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology ...
Components of a Proposal. For each of the descriptions below, identify which component of the research proposal applies (title, abstract, table of contents, introduction, literature review, method ...
A research proposal aims to persuade the reader, usually a funding agency or a research committee, that the proposed research is worthwhile and deserves support. To create a research proposal in Visme, use premade templates, write the content, visualize important data, customize your research proposal, download it and share it with relevant ...
A research proposal is a roadmap that brings the researcher closer to the objectives, takes the research topic from a purely subjective mind, and manifests an objective plan. It shows us what steps we need to take to reach the objective, what questions we should answer, and how much time we need. It is a framework based on which you can perform ...
Research Proposal Guide. Once an Initial Research Estimate Form (IREF) is validated and selected for funding, the next step is to complete a Research Proposal. Proposals must be completed and approved before funding can be authorized and released. Faculty that have an IREF validated and selected for funding are required to complete the ...
This ensures content clarity and cohesion throughout your text. Academic Research Study Proposal Sample 2024. Here is a sample idea for an interesting proposal paper: The proposed research study will investigate the risks of sending messages while driving and explore measures to mitigate this hazardous behavior.
The personality models are summarized in Sect. 2. Then, in Sect. 3, the human-in-the-loop approach used as a basis for designing personalized systems is presented. The proposed personality-in-the-loop approach is outlined in Sect. 4. It is followed by a discussion of possible applications in Sect. 5.
Applications are invited from eligible graduate students to serve on the Student -Led Research, Scholarship, and Creative Activities Program Proposal Review Committee. The committee will read and review project proposals from Montclair undergraduate and graduate students and make funding recommendations to the Vice Provost for Research.
Palestinian Islamist group Hamas on Friday said it had a positive view of the contents of a three-phase ceasefire proposal announced by U.S. President Joe Biden for a permanent ceasefire in Gaza.
• Facilitate in-house education on research and analytic techniques using open source data. • Develop a curriculum of OSINT research, analysis, and production courses, leveraging existing IC and private sector offerings. • Establish guidelines to distinguish between OSINT and open source research. 3.2. Provide Training and Guidance
Israel's prime minister on Saturday called a permanent cease-fire in Gaza a "nonstarter" until long-standing conditions for ending the war are met, appearing to undermine a proposal that U.S.
The proposed curriculum overhaul was released a week after the Texas GOP proposed requiring the Bible to be taught in public schools. School districts that opt to use them will get more funding.