
How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 11 min read

Getting to the Root of a Problem Quickly
By the Mind Tools Content Team
5 Whys Root-Cause Analysis
Have you ever had a problem that refused to go away? No matter what you did, sooner or later it would return, perhaps in another form.
Stubborn or recurrent problems are often symptoms of deeper issues. "Quick fixes" may seem convenient, but they often solve only the surface issues and waste resources that could otherwise be used to tackle the real cause.
In this article and in the video, below, we look at the 5 Whys technique (sometimes known as 5Y). This is a simple but powerful tool for cutting quickly through the outward symptoms of a problem to reveal its underlying causes – so that you can deal with it once and for all.
Origins of the 5 Whys Technique
Sakichi Toyoda, the Japanese industrialist, inventor, and founder of Toyota Industries, developed the 5 Whys technique in the 1930s. It became popular in the 1970s, and Toyota still uses it to solve problems today.
Toyota has a "go and see" philosophy. This means that its decision making is based on an in-depth understanding of what's actually happening on the shop floor , rather than on what someone in a boardroom thinks might be happening.
The 5 Whys technique is true to this tradition, and it is most effective when the answers come from people who have hands-on experience of the process or problem in question.
The method is remarkably simple: when a problem occurs, you drill down to its root cause by asking "Why?" five times. Then, when a counter-measure becomes apparent, you follow it through to prevent the issue from recurring.
The 5 Whys uses "counter-measures," rather than "solutions." A counter-measure is an action or set of actions that seeks to prevent the problem from arising again, while a solution may just seek to deal with the symptom. As such, counter-measures are more robust, and will more likely prevent the problem from recurring.
When to Use a 5 Whys Analysis
You can use 5 Whys for troubleshooting, quality improvement, and problem solving, but it is most effective when used to resolve simple or moderately difficult problems.
It may not be suitable if you need to tackle a complex or critical problem. This is because 5 Whys can lead you to pursue a single track, or a limited number of tracks, of inquiry when, in fact, there could be multiple causes. In cases like these, a wider-ranging method such as Cause and Effect Analysis or Failure Mode and Effects Analysis may b e more effective.
This simple 5 Whys technique, however, can often direct you quickly to the root cause of a problem. So, whenever a system or process isn't working properly, give it a try before you embark on a more in-depth approach – and certainly before you attempt to develop a solution.
The tool's simplicity gives it great flexibility, too, and 5 Whys combines well with other methods and techniques, such as Root Cause Analysis . It is often associated with Lean Manufacturing , where it is used to identify and eliminate wasteful practices. It is also used in the analysis phase of the Six Sigma quality improvement methodology.
How to Use the 5 Whys
The model follows a very simple seven-step process: [1]
1. Assemble a Team
Gather together people who are familiar with the specifics of the problem, and with the process that you're trying to fix. Include someone to act as a facilitator , who can keep the team focused on identifying effective counter-measures.
2. Define the Problem
If you can, observe the problem in action. Discuss it with your team and write a brief, clear problem statement that you all agree on. For example, "Team A isn't meeting its response time targets" or "Software release B resulted in too many rollback failures."
Then, write your statement on a whiteboard or sticky note, leaving enough space around it to add your answers to the repeated question, "Why?"
3. Ask the First "Why?"
Ask your team why the problem is occurring. (For example, "Why isn't Team A meeting its response time targets?")
Asking "Why?" sounds simple, but answering it requires serious thought. Search for answers that are grounded in fact: they must be accounts of things that have actually happened, not guesses at what might have happened.
This prevents 5 Whys from becoming just a process of deductive reasoning, which can generate a large number of possible causes and, sometimes, create more confusion as you chase down hypothetical problems.
Your team members may come up with one obvious reason why, or several plausible ones. Record their answers as succinct phrases, rather than as single words or lengthy statements, and write them below (or beside) your problem statement. For example, saying "volume of calls is too high" is better than a vague "overloaded."
4. Ask "Why?" Four More Times
For each of the answers that you generated in Step 3, ask four further "whys" in succession. Each time, frame the question in response to the answer you've just recorded.
What Is a 5 Whys Template?
The diagram, below, shows an example of 5 Whys in action, following a single lane of inquiry.
Figure 1: 5 Whys Example (Single Lane)
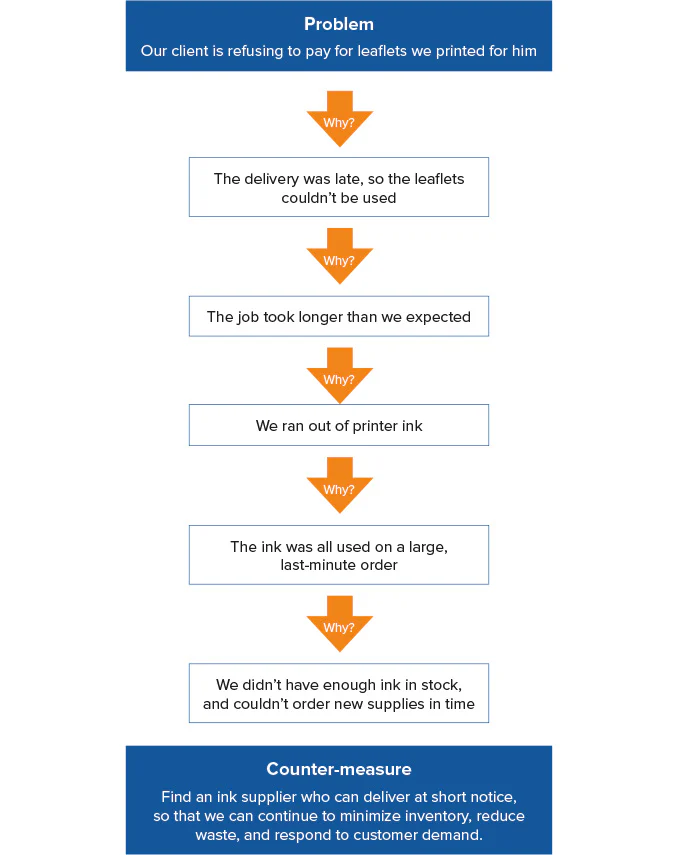
The 5 Whys method also allows you to follow multiple lanes of inquiry. An example of this is shown in Figure 2, below.
In our example, asking "Why was the delivery late?" produces a second answer (Reason 2). Asking "Why?" for that answer reveals a single reason (Reason 1), which you can address with a counter-measure.
Similarly, asking "Why did the job take longer than expected?" has a second answer (Reason 2), and asking "Why?" at this point reveals a single reason (Reason 1). Another "Why?" here identifies two possibilities (Reasons 1 and 2) before a possible counter-measure becomes evident.
There is also a second reason for "Why we ran out of printer ink" (Reason 2), and a single answer for the next "Why?" (Reason 1), which can then be addressed with a counter-measure.
Figure 2: 5 Whys Example (Multiple Lanes)

Step 5. Know When to Stop
You'll know that you've revealed the root cause of the problem when asking "why" produces no more useful responses, and you can go no further. An appropriate counter-measure or process change should then become evident. (As we said earlier, if you're not sure that you've uncovered the real root cause, consider using a more in-depth problem-solving technique like Cause and Effect Analysis , Root-Cause Analysis , or FMEA .)
If you identified more than one reason in Step 3, repeat this process for each of the different branches of your analysis until you reach a root cause for each one.
6. Address the Root Cause(s)
Now that you've identified at least one root cause, you need to discuss and agree on the counter-measures that will prevent the problem from recurring.
7. Monitor Your Measures
Keep a close watch on how effectively your counter-measures eliminate or minimize the initial problem. You may need to amend them, or replace them entirely. If this happens, it's a good idea to repeat the 5 Whys process to ensure that you've identified the correct root cause.
Appreciation
A similar question-based approach known as "appreciation" can help you to uncover factors in a situation that you might otherwise miss.
It was originally developed by the military to assist commanders in gaining a comprehensive understanding of any fact, problem or situation. But you can also apply it in the workplace.
Starting with a fact, you first ask the question, "So what?" – in other words, what are the implications of that fact? Why is this fact important?
You then continue asking that question until you've drawn all possible conclusions from it.
The major difference between this and the 5 Whys technique is that appreciation is often used to get the most information out of a simple fact or statement, while 5 Whys is designed to drill down to the root of a problem.
Tips for Using the 5 Whys Technique
- Try to move quickly from one question to the next. That way, you'll have the full picture before you jump to any conclusions.
- The "5" in 5 Whys is really just a " rule of thumb ." In some cases, you may need to ask "Why?" a few more times before you get to the root of the problem. In other cases, you may reach this point before you ask your fifth "Why?" If you do, make sure that you haven't stopped too soon, and that you're not simply accepting "knee-jerk" responses.
- Know when to stop! The important point is to stop asking "Why?" when you stop producing useful responses.
Frequently Asked Questions About 5 Whys
1. what is the 5 whys technique.
The 5 Whys Technique is a problem-solving method involving repeatedly asking "why?" It's a way of quickly getting to the root cause of a situation.
2. Who Invented 5 Whys?
The 5 Whys technique was invented in the 1930s by Sakichi Toyoda, the Japanese industrialist, inventor, and founder of Toyota Industries.
5 Whys Infographic
See our infographic on the 5 Whys and use it to get to the root of your problems!

Bear in mind that appreciation can restrict you to one line of thinking. For instance, once you've answered your first "So what?" question, you might follow a single line of inquiry to its conclusion. To avoid this, repeat the appreciation process several times over to make sure that you've covered all bases.
The 5 Whys strategy is a simple, effective tool for uncovering the root of a problem. You can use it in troubleshooting, problem-solving, and quality-improvement initiatives.
Start with a problem and ask why it is occurring. Make sure that your answer is grounded in fact, and then ask the question again. Continue the process until you reach the root cause of the problem, and you can identify a counter-measure that will prevent it from recurring.
Bear in mind that this questioning process is best suited to simple or moderately difficult problems. Complex problems may benefit from a more detailed approach, although using 5 Whys will still give you useful insights.
[1] Pojasek, R. (2000). 'Asking "Why?" Five Times,' Environmental Quality Management , Volume 10, Issue 1, 79–84. Available here . [Accessed July 1, 2022.]
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Using root cause analysis.
Find the Root of Your Problems
Root Cause Analysis
Tracing a Problem to Its Origins
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

7 Reasons Why Change Fails

Why Change Can Fail
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Top tips for tackling problem behavior.
Tips to tackle instances of problem behavior effectively
Defeat Procrastination for Good
Saying "goodbye" to procrastination
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
The iron triangle of project management.
Balancing Your Budget, Scope and Schedule
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- RCA 101 – 5-Why Analysis (Free Training)
- RCA 201 – Basic Failure Analysis
- RCA 301 – PROACT® RCA Certification
- RCA 401 – RCA Train The Trainer
- Other Trainings
- 5 Whys Root Cause Analysis Template
- RCA Template
- Chronic Failure Calculator
Root Cause Analysis with 5 Whys Technique (With Examples)

By Sebastian Traeger
Updated: April 23, 2024
Reading Time: 7 minutes
What Is the 5 Whys Technique?
Example of the 5 whys technique, how to conduct a 5 whys analysis in 5 steps, when to use a 5 whys analysis, using 5 whys template, tips for mastering the 5 whys technique, frequently asked questions about 5 whys.
With over two decades in business – spanning strategy consulting, tech startups and executive leadership – I am committed to helping your organization thrive.
At Reliability, we’re on a mission to help enhance strategic decision-making and operational excellence through the power of Root Cause Analysis, and I hope this article will be helpful!
Our goal is to help you better understand 5 whys techniques by offering insights and practical tips based on years of experience. Whether you’re new to doing RCAs or a seasoned pro, we trust this will be useful in your journey towards working hard and working smart.
The 5 Whys Technique is like peeling an onion – it helps you uncover the underlying reasons behind a problem, layer by layer. By repeatedly asking “why” at least five times, this method digs deep to reveal the root cause of an issue. It’s a simple yet powerful problem-solving approach that aims to get to the heart of the matter rather than just addressing surface-level symptoms.
5 Whys Technique: A method that involves iteratively asking “why” five times to unveil the fundamental cause of a problem.
In essence, the 5 Whys Technique is not just about fixing what’s broken on the surface; it’s about understanding and addressing the deeper issues that lead to problems in the first place.
The 5 Whys Technique is like a detective, uncovering the truth behind recurring problems. Let’s take a look at how this method works in two different scenarios.
Case Study: Manufacturing Defects
Imagine a company that keeps encountering the same manufacturing defects despite various attempts to fix them. By using the 5 Whys Technique, they discovered that the defects were not caused by faulty machinery, as previously assumed, but rather by human error due to unclear operating instructions. This realization led to improved training procedures and clear work guidelines, ultimately eliminating the defects.
Application in Service Industry
Now, consider a service industry struggling with frequent customer complaints and service failures. Through the 5 Whys Technique, it was revealed that these issues stemmed from inadequate staffing levels during peak hours. By addressing this root cause, such as hiring additional staff or adjusting schedules, the service quality can significantly improve, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
These examples illustrate how the 5 Whys Technique can be applied across different sectors to identify and address underlying issues effectively.
Step 1: Identify the Problem
Before diving into a 5 Whys analysis, it’s crucial to clearly identify the problem or issue at hand . This step sets the stage for the entire process and ensures that the focus remains on addressing the right concern. Take the time to gather relevant data, observe patterns, and consult with team members or stakeholders to gain a comprehensive understanding of the problem.
Step 2: Ask ‘Why’ Five Times
Once the problem is clearly defined, it’s time to start peeling back the layers. The process involves asking “why” five times, not necessarily limited to five questions but enough to delve deeper into the underlying causes of the problem . Each “why” serves as a gateway to uncovering additional factors contributing to the issue. This iterative approach helps in identifying not just one cause, but multiple interconnected elements that may be at play.
By consistently probing deeper with each “why,” you can reveal hidden complexities and nuances that may have been overlooked initially. This method allows for a more thorough understanding of the situation, paving the way for effective solutions that address root causes rather than surface-level symptoms.
This structured approach encourages critical thinking and enables teams to move beyond quick fixes towards sustainable improvements.
The 5 Whys Technique is a versatile problem-solving approach that can be applied in various scenarios to uncover root causes and drive continuous improvement. Here are two key situations where the 5 Whys Analysis can be particularly beneficial:
Recurring Issues
- The 5 Whys Technique is especially useful when dealing with recurring issues. Whether it’s a manufacturing defect that keeps resurfacing or a persistent customer complaint in the service industry, this method helps identify the underlying reasons behind these repetitive problems. By repeatedly asking “why,” it becomes possible to trace the issue back to its root cause, allowing for targeted solutions that prevent reoccurrence.
Process Improvement
- Organizations constantly strive to enhance their processes and workflows for increased efficiency and quality. When seeking to improve existing procedures, the 5 Whys Technique serves as a valuable tool. By systematically analyzing the factors contributing to inefficiencies or bottlenecks, teams can gain insights into how processes can be optimized at their core. This method enables organizations to make informed decisions about process improvements based on a deep understanding of the underlying issues.
In both cases, the 5 Whys Analysis offers a structured yet flexible approach to delve into complex problems, making it an indispensable tool for driving meaningful change and progress within organizations.
When it comes to conducting a 5 Whys analysis, utilizing a structured template can greatly facilitate the process and ensure a comprehensive investigation into the root cause identification. Using RCA software such as EasyRCA can benefit the team by streamlining your 5-why process. Here’s how organizations can benefit from using a template:
Benefits of Using a Template
- Streamlined Process: A well-designed 5 Whys template provides a clear framework for conducting the analysis, guiding teams through the iterative questioning process. This streamlines the investigation, making it easier to navigate and ensuring that no crucial aspects are overlooked.
- Thorough Investigation: By following a predefined template, teams are prompted to explore various facets of the problem systematically. This ensures that all relevant factors are considered, leading to a more thorough and insightful investigation into the underlying causes.
- Consistent Approach: Templates offer a standardized approach to conducting 5 Whys analyses within an organization. This consistency promotes uniformity in problem-solving methods across different teams or departments, enhancing overall efficiency and effectiveness.
Customizing the Template
Organizations have the flexibility to customize 5 Whys templates according to their specific needs and industry requirements. This adaptability allows for tailoring the template to address unique challenges and incorporate industry-specific considerations. Customization may include:
- Adding Industry-Specific Prompts: Tailoring the template by incorporating prompts or questions relevant to particular industries or types of issues being analyzed.
- Incorporating Visual Aids: Enhancing the template with visual aids such as flow charts or diagrams can help teams better understand and communicate complex causal relationships.
- Iterative Refinement: Regularly reviewing and refining the template based on feedback and evolving organizational needs ensures that it remains aligned with current processes and challenges.
Customizing the template empowers organizations to harness the full potential of the 5 Whys Technique in addressing diverse problems while aligning with their unique operational contexts.
Encouraging Open Communication
In mastering the 5 Whys Technique as a problem-solving method, creating an environment that fosters open communication is paramount. When team members feel comfortable expressing their perspectives and insights, it leads to a more comprehensive exploration of the underlying causes of a problem. Encouraging open communication allows for diverse viewpoints to be considered, providing a holistic understanding of the issue at hand.
By promoting an atmosphere where individuals are empowered to voice their observations and concerns, the 5 Whys analysis can benefit from a rich tapestry of ideas and experiences. This inclusive approach not only enhances the depth of the analysis but also cultivates a sense of ownership and collective responsibility for addressing root causes within the team or organization.
Continuous Improvement Mindset
A key aspect of mastering the 5 Whys Technique is embracing a continuous improvement mindset. Rather than viewing problems as isolated incidents, this approach encourages teams to see them as opportunities for growth and development. By instilling a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can leverage the insights gained from 5 Whys analyzes to drive positive change across various aspects of their operations.
Fostering a mindset focused on continuous improvement entails actively seeking feedback, evaluating processes, and implementing iterative enhancements based on the findings. It involves an ongoing commitment to learning from past experiences and leveraging that knowledge to proactively address potential issues before they escalate. Embracing this mindset ensures that the 5 Whys Technique becomes ingrained in the organizational ethos, leading to sustained progress and resilience in problem-solving efforts.
As we wrap up our exploration of the 5 Whys Technique, let’s address some common questions that may arise regarding this powerful problem-solving method.
What is the primary goal of the 5 Whys Technique?
The primary goal of the 5 Whys Technique is to uncover the root cause of a problem by iteratively asking “why” at least five times. This approach aims to move beyond surface-level symptoms and address the underlying issues that lead to recurring problems.
Is the 5 Whys Technique limited to specific industries or sectors?
No, the 5 Whys Technique is versatile and can be applied across various industries and sectors. Whether it’s manufacturing, healthcare, service, or technology, this method offers a structured yet flexible approach to identifying root causes and driving continuous improvement.
How does the 5 Whys Technique contribute to continuous improvement?
By delving into the fundamental reasons behind problems, the 5 Whys Technique provides organizations with valuable insights for driving continuous improvement. It not only helps in resolving immediate issues but also fosters a culture of ongoing enhancement and development within an organization.
Can the 5 Whys Technique be used for complex problems with multiple contributing factors?
Yes, while initially designed as a simple and straightforward method, the 5 Whys Technique can certainly be applied to complex problems with multiple interconnected factors. By systematically probing deeper into each layer of causality, this technique enables a comprehensive understanding of intricate issues.
I hope you found this guide to 5 whys technique insightful and actionable! Stay tuned for more thought-provoking articles as we continue to share our knowledge. Success is rooted in a thorough understanding and consistent application, and we hope this article was a step in unlocking the full potential of Root Cause Analysis for your organization.
Reliability runs initiatives such as an online learning center focused on the proprietary PROACT® RCA methodology and EasyRCA.com software. For additional resources, visit Reliability Resources .
- Root Cause Analysis /
Recent Posts
5 Root Cause Analysis Examples That Shed Light on Complex Issues
What Is Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)? Definition & Examples
Guide to Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Root Cause Analysis Software
Our RCA software mobilizes your team to complete standardized RCA’s while giving you the enterprise-wide data you need to increase asset performance and keep your team safe.
Root Cause Analysis Training
[email protected]
Tel: 1 (800) 457-0645
Share article with friends:

- Your Project
- 5 Whys Method
What is the Five Whys method?
The “ 5 Whys ” is a Problem-Solving method that identifies Root Causes of Problems by asking five consecutive times:
- “Why this happened?”.
It Starts with the most obvious “Symptom” (or Issue) and Forces the analyst to wonder Why it happened .
- Once the Analyst has a first Explanation, he/she has to repeat this cycle 4 more times.
5 Whys method Flowchart
Let’s see it with one example:
Five Whys example
Imagine that one day, your front-right tire suddenly bursts .
As we all would do, you call your car assistance company, that comes exactly where you are and replace it with a new tire.
Few weeks later, again, this same tire (the new one) bursts again .
And you start thinking that this is not normal (or shouldn’t be).
Then, you decide to apply the 5 Why methodology :
1. Why this happened?
- Why your tire burst in the first place?
You bring your car to the car shop.
There, they tell you that your rims are not aligned and that is causing your tires to burst.
Many people would settle for this explanation but you then, ask yourself again:
2. Why this happened?
- Why weren’t they aligned?

Your car is only 2 years old so, it shouldn’t be usual.
Your car assistant tells you this can happen if case you park on irregular terrain frequently .
You do it, but just once a month. It shouldn’t be enough.
3. Why this happens?
- Why parking once a month on irregular terrain misalign your wheels?

You decide to investigate about it, and you find out that you have a loose master screw that is causing this problem .
4. But how is this possible?
- Why is this screw loose? Is it a car problem?

You ask different same-car owners and you find out that this is only happening to you , so you start to suspect that in your last car revision somebody caused this problem.
You then ask in your car shop about what they did in your last revision and they confirm that they “manipulated” that piece .
5. Then, how is it possible that they forgot a loose screw?
- Should you take your car to another shop? Why this happened?

In the workshop, they confess that the last revision of your car, was developed by an external worker since the main mechanic was sick .
They assure you they won’t hire that external worker again since he didn’t know what he was doing.
- Moreover, they will give your money back (what you had to pay for your tires and the alignment).
Summarizing:
Imagine now, what would have happened if you had settled for the first explanation they gave you .
- You would have stopped parking on uneven terrains, but you would still have the problem.
We are not car-mechanic experts, so forgive us if we said something stupid.
We just wanted you to understand how the “five Whys” tool works.
Why is the 5 Whys method important?
By nature, we all tend to settle for the first explanation we have.
The 5 Whys method pushes you to see beyond and find the “root cause” of your problem.
But, can you always apply this method?
When can be used the 5 Whys method?
Whenever you need to find the root cause of a certain problem .
- Which Plugins may cause it and why?
- Which employee could do better and why?
- You can even use to improve your diet and find out why you are gaining weight!
Although it was originally designed for Industrial quality processes (where it is extremely useful) it can be used in practically all situations .
How should you develop a Five Whys analysis?
According to our experience, the simpler the better .
There are dozens of Flowcharts with crossed explanations, difficult algorithms…
We propose you to use the simplest approach possible.
It is better to use a simple yet useful approach instead of a difficult one that you would only use once.
What do you need for applying the 5 Whys method?
Some people recommend assembling a Team, but we don’t think that is necessary.
- If you develop this method at your Job you can do it without any problem.
You only need to feel like finding the Root Cause of your Problem .
Should you always find 5 Whys?
Sometimes, with just 3 “Whys” is enoug h .
- You should try to dig as deep as you can, but sometimes you get to “bedrock” with less than 5 Whys.
5 Whys Method Examples
Now, we’ll propose you two examples of different situations in which this method can be very useful.
Let’s begin:
YouTube Channel - 5 Whys Method Example

Let’s imagine you own a YouTube channel :
- You have been publishing new videos for a whole year on regular basis.
- Your videos have a higher than average quality (regarding image, sound, etc).
- All the people you’ve asked tell you that your videos are funny.
However, you just have half the audience of other similar channels .
1. Why do you have half the audience of your competitors?
Assuming you have approximately the same videos published; the obvious answer is this:
- YouTube is not showing your content as often as that of your competitors.
This statement is not as obvious as it may seem.
If your content is good, and you have “plenty” of it…
2. Why is YouTube not showing your content as often as that of your competitors?
If YouTube is not showing your content as much as you would like, must be because some of your metrics are not as good as you expected:
You then discover that:
- Your “Engagement” is not very high.
- Your “Audience retention” is limited.
- The “Average percentage viewed” is reduced.
- On the other hand, your “Click-Through rate” is elevated.
Some users devour your videos, but others just move on .
So far, you have concluded that:
- Your YouTube Title descriptions are better than average.
- Some of your users love your videos.
- Others don’t.
And this last fact is preventing your content from being better positioned.
3. Why some of your users don’t like your content?
You decide to investigate the average profile of your users:
- Where they come from.
- What they are interested about.
After a deep research, you conclude that users of your same country are much more engaged than those from other countries .
4. Why the users from your same country are much more engaged?
You start to look at your YouTube comments in order to figure out what is going on.
You find 3 different kinds of comments:
- Stupid meaningless comments.
- You suspect they are from your same country.
- Comments requesting for some explanations; they didn’t understand your video at all.
The people from your same country understood perfectly your content:
- Your Jokes.
- The references you made.
- The people you referred to.
While people from other countries, didn’t understood everything you said .
5. Why people from other countries don’t fully understand your videos?
So far, we have that:
- Your videos don’t have as good metrics as you thought and that is why YouTube is not showing your content as much as that of your competitors.
- Some of your users are very engaged while others are not.
- Those Engaged users are from your same country.
- They like your videos because it seems that they are the only ones that understand perfectly everything you say; your jokes, your references, etc…
And the reason some users don’t understand your videos is:
- You are publishing videos with local references for a global audience.
People from other countries don’t understand your jokes because what you think is very popular all over the world, is popular only in your country .
- That is why your publications don’t have as good metrics as they could.
Now, you’ll start introducing new and more international references in your videos.
We are not YouTube experts so please, forgive us if we said something wrong.
Since lots of our users are very interested in SEO, we’ll show a similar example, but focused on a Website:
Improving SEO - 5 Whys Method Example

Let’s imagine that you own a WordPress Site .
You have been writing interesting and high-quality content for a whole year.
- You have already published 60 interesting articles.
However, you barely have 1,000 pageviews per month . What is going on?
Let’s develop a “condensed” 5 Whys method:
1. Why you only have 1,000 pageviews per month?
Because your content isn’t Rankings very good .
2. Why is your content Ranking so poorly?
Because your metrics are terrible:
- You have a 0.3% CTR.
People do not Click on your content .
3. Why people don’t Click through your content?
You decide to look for some of your pages on Google and you find out that your Publications’ titles are not attractive at all .
While your competitors have nice Titles and Descriptions, your Posts have short boring titles.
4. Why do your Posts have boring Titles?
Because you didn’t know that you could edit them .
With this “5 Whys analysis” you found out that it is very important to edit your publications’ titles, so they are more attractive to your potential users .
Your content may be the best, but if it has a generic boring Title, nobody will Click through it.
* Believe or not, this is based on a true story.
Summarizing
The 5 Whys method is a simple iterative analysis that pushes you to find the root cause of your problems by asking yourself 5 consecutive times: Why this happens?
- Sometimes you’ll need less than 5 Whys, and other times 5 won’t be enough.
Although there are different approaches for developing a “5 Whys analysis”, the simpler the better .
Never underestimate this method : You have surely settled for the first explanation you’ve encountered several times without discovering the true root cause of your problem .
- Economies of Scale
- Business Plan for Beginners
- Business Plan Basics
- How to write a Business Plan
- Cash Flow Calculation
- Raising Funds for a Business
- 4 C’s of Credit
- Business Plan Templates
- Customer Insight
- Customer Experience
- Customer Pain Points
- 4C Marketing Model
- RATER Model
- Augmented Product
- Product Mix
- Unique Selling Proposition
- DAGMAR Model
- Marketing Storytelling
- Content Marketing
- Psychographics
- Barnum Effect
- Market Segmentation
- Market Research & Big Data
- Marketing to Generation Z
- 4P Marketing Mix
- 7P Marketing Mix
- Sales Funnel
- Loyalty Ladder
- RACE Planning
- Push and Pull Marketing
- Marketing Strategy
- Marketing Templates
- Starting your own business
- From Startup to a Business
- Entrepreneur FAQs
- Start your Business Idea
- Entrepreneur Golden Rules
- Innovate or Imitate?
- Design Thinking
- SCAMPER Model
- AAR Process
- Work From Home
- Growth strategies for Startups
- VMOST Analysis
- 3P Framework
- SOAR Analysis
- TELOS Analysis
- 5 C’s of Entrepreneurship
- Crowdfunding
- BATNA & ZOPA Negotiation
- Entrepreneur with no Money
- Entrepreneurship Templates
- Strategy vs Tactics
- Mission and Vision
- Business Values
- Value Chain
- Scenario Planning
- Porter 6 Forces
- Bowman’s Strategy Clock
- GE-McKinsey Matrix
- Delta Model
- PEST Analysis
- PESTEL Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- VRIO Framework
- Strategy Canvas
- Competitive Advantages
- Porter’s Four Corners
- 5 Ps of Strategy
- Porter’s Generic Strategies
- Porter’s Diamond Model
- Wardley Map
- Core Competencies
- Resource Based View
- Bridges Transition Model
- CAGE Distance Framework
- McKinsey’s 3 Horizons
- Vertical Integration
- Horizontal Integration
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Red Ocean Strategy
- Porter 5 Forces
- Ansoff Matrix
- McKinsey 7S Framework
- CATWOE Analysis
- Strategy Pyramid
- Bain’s RAPID Framework
- Balanced Scorecard
- Resources and Capabilities
- Strategy of Apple
- Strategy of Amazon
- Strategy of Starbucks
- Strategy Templates
- Communicate Effectively
- COIN Conversation Model
- SCARF Model
- SBI Feedback Model
- CEDAR Feedback Model
- How to behave at a meeting
- Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle
- Bloom’s Taxonomy
- 5E Learning Model
- 9-Box Performance Grid
- SEEDS Bias Model
- Halo Effect
- Pygmalion Rosenthal Effect
- Dunning-Kruger Effect
- How to be an Entrepreneur
- How to be a Leader
- Mintzberg Managerial Roles
- Cog’s Ladder
- The Peter Principle
- How to Negotiate
- Teamwork Skills and Profiles
- Gantt Chart
- RACI Matrix
- Eisenhower Matrix
- MoSCoW Method
- FMEA Process
- Problem Solving
- Ishikawa Fishbone diagram
- 8 Disciplines Method
- ADDIE Model
- ORAPAPA Method
- Cynefin Framework
- Just In Time
- SMART Goals
- KISS Principle
- Birkinshaw’s 4 Dimensions
- Parkinson’s Law
- OGSM Framework
- OKR Methodology
- APQP Framework
- Theory of Constraints
- Success through Organization
- ADKAR Model
- Lewin’s Change Model
- Kotter’s 8-Step Model
- The Greiner Curve
- GAP Analysis
- Planning Templates
- Mean, Median and Mode
- Define your Data
- Pareto Principle 80/20 Rule
- Decision Matrix
- Decision Tree
- TARA Framework
- Root Cause Analysis
- Simplex Process
- Forecasting Methods
- Product Life Cycle
- How to use Google Trends
- Correlation vs Causation
© 2024 - Consuunt .
We're not around right now. But you can send us an email and we'll get back to you, asap.
Log in with your credentials
Forgot your details.

The Simple Yet Powerful 5 Whys Method for Effective Problem-Solving
Updated: May 16, 2023 by Lori Kinney

As a child, you were always asking your parents “Why this?” “Why that?” “Why can’t I do this?” “Why can’t I do that?” Little did you know that you were preparing yourself to be a problem-solver looking for root causes when you would grow up.
This article will discuss what is the 5 Why method of looking for a problem’s root cause, how to correctly ask the questions, and what benefits and best practices there might be to help you do a better job of improving your processes.
Overview: What are the 5 Whys?
The 5 Whys technique was developed in the 1930s by Sakichi Toyoda, the Japanese industrialist, inventor, and founder of Toyota Industries. The 5 Whys technique is an iterative, team-driven process that interrogates the problem by asking Why(?) a number of times, usually 5, thus driving the search to uncover the root cause of a problem.
Rather than using the phrase “solutions” once the root cause is found, the 5 Whys uses the term “countermeasures.” A countermeasure is action-oriented and seeks to prevent the problem from happening again, whereas a solution may just seek to deal with the symptoms.
Here is the 5 Why technique in a nutshell:
First, you must have a defined problem. Put together a team to address the problem. Then:
- List: Using a white board, flip chart, butcher paper, or other visual display, list five potential reasons for your problem.
- Evaluate: Using data, subject matter experts, or experience, evaluate each of the five potential reasons.
- Select: Select the one reason that seems to be the most likely potential cause.
- List again: Now list five potential reasons for the potential cause that you selected.
- Evaluate again: Evaluate those five new potential reasons.
- Select again: Again, select the one reason that seems to have the most potential as a root cause.
Repeat the process of list, evaluate, and select as many times as needed until you feel that the root cause has been uncovered. The
Unfortunately, many organizations don’t do the 5 Whys the correct way. Often, they:
- Look at the problem
- Offer one potential cause
- Ask “Why?” for that one cause
- And continue one at a time
In the end, you will have only explored five potential causes. Doing it with the list, evaluate, and select approach, you will have assessed 25 potential causes by listing five for each iteration.
3 benefits of the 5 Whys
This technique has been around since the 1930s. It has been shown to work and can be successfully applied to many situations.
1. It is a simple yet powerful tool
With just the use of a flip chart and a few markers, a group of people can usually get to the root cause of a problem relatively quickly.
2. A sking “why” 5 times focuses the team on getting to the root cause
Using this approach in a disciplined fashion will get you to focus on the causes and prevent you from jumping to conclusions as to the solution.
3. Helps engage the people who deal with the problem
Getting input from the people who deal with the problem and making them part of the solution can result in better buy-in and engagement.
Why are the 5 Whys important to understand?
While the 5 Why technique is simple, you must understand the proper mechanics of the method so that you get the best results possible.
It encourages collaborative problem-solving
Getting the team to collaboratively work together is not only important for the 5 Why problem solving session but for any future activities that would improve the process.
You want to focus on improvement, not blame
Do not allow such causes as “ human error,” “employee attitude,” “communication,” and other generic and ill-defined reasons to be used as the root cause.
Understand the importance of having support from leadership
Hopefully, in the end, the team will come up with a number of countermeasures that will remove the root cause(s) of a problem. It will usually fall upon leadership to provide the resources to make the change. Avoid future frustration by having management on board with this technique from the beginning.
An example of the 5 Whys in use
An example is in order.
You are on your way home from work, and your car stops:
- Why did your car stop? Because it ran out of gas.
- Why did it run out of gas? Because I didn’t buy any gas on my way to work.
- Why didn’t you buy any gas this morning? Because I didn’t have any money.
- Why didn’t you have any money? Because I lost it all last night in a poker game.
This example should illustrate the importance of digging down beneath the most proximate cause of the problem. Failure to determine the root cause assures that you will be treating the symptoms of the problem instead of its cause, in which case, the disease will return — that is, you will continue to have the same problems over and over again.
Also note that the actual numbers of whys is not important as long as you get to the root cause. One might also ask, “Why did you lose all your money in the poker game last night?”
Here’s another example. The Washington Monument was disintegrating:
- Why? Use of harsh chemicals
- Why? To clean pigeon poop
- Why so many pigeons? They eat spiders and there are a lot of spiders at monument
- Why so many spiders? They eat gnats and lots of gnats at monument
- Why so many gnats? They are attracted to the light at dusk.
Countermeasure: Turn on the lights at a later time.
3 best practices when thinking about the 5 Whys
Doing the 5 Whys is simple, but not easy. Keep the team on task and take advantage of the team members’ knowledge, experience, and enthusiasm.
1. Don’t try to do this alone; use a group of people involved in the process
Five heads are better than one. Select a diverse group of team members to get the widest perspective.
2. Focus on counter measures rather than solutions
The solution to a headache is to take two aspirin. The countermeasure to a headache is to find out what is causing it and remove it.
3. Be open and respectful of everyone’s input and participation
Everyone’s idea has value. You never know who might hold the hidden gem. Listen and be respectful so people will feel comfortable offering their ideas — you’ll also have better buy-in once you find the root cause.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about the 5 Whys
Can i ask more than 5 whys .
Yes. You can ask more than five or less than five. The key is, how many questions does it take to get to what appears to be the root cause.
Can I use the computer to do the 5 Why exercise?
It’s recommended that you use something more tactile like flip charts. This way, you can tear them off and hang them on the wall for everyone to see. The more visual you make the work, the better.
Should my manager run the 5 Why session or someone else?
Since the manager often has a stake in the outcome of the process, it might be best to use a neutral facilitator who can help keep the team on task, ask the right questions, and not get defensive when the potential causes are mentioned.
The 5 Whys wrapped up
The 5 Whys is an iterative, team-based approach to asking questions about the potential causes of a problem. Once the problem is defined, the potential causes should be listed, evaluated, and selected, and then repeated as many times as necessary to get to the root cause.
Once the root cause(s) is identified, the team should recommend specific, action-oriented countermeasures to mitigate or eliminate the root cause of the problem. Remember, don’t just address the symptoms; you must find the underlying cause, otherwise the problem will resurface sometime in the future.
About the Author
Lori Kinney
- Professional Scrum Product Owner (PSPO)
- SAFe for Government
- Professional Scrum Master (PSM)
- Certified ScrumMaster
- PMI-ACP Exam Prep
- Leading SAFe® 6.0 Certification
- SAFe Scrum Master
- Certified Scrum Product Owner (CSPO)
- SAFe for Teams
- Agile Scrum Foundation
- AgilePM Foundation and Practitioner Certification
- Agile Scrum Master (ASM)
- Kanban Training
- Scrum Fundamentals
- PMP Certification
- Project Management Fundamentals
- CAPM Exam Prep
- Change Management Foundation and Practitioner Certification
- PRINCE2 Foundation & Practitioner Certification (7th Edition)
- PRINCE2 Agile Foundation & Practitioner Certification
- Business Analysis Foundation and Practitioner Certification
- Microsoft Project Training
- JIRA Certification Training
- Lean Project Management
- ITIL 4 Foundation
- VeriSM™ Foundation
- SIAM Foundation
- SIAM Professional
- 7 QC Tools Training
- Minitab Essentials
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt
- Six Sigma Awareness
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
- Design for Six Sigma
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
- Lean Fundamentals
- Value Stream Mapping
- Quality by Design
- Quality Function Deployment
- BPM and Six Sigma
- RCA through Six Sigma
- DevOps Foundation
- DevOps Master
- DevOps Professional
- Continuous Delivery Architecture
- COBIT 5 Certification
- Corporate Group Training
- 1-to-1 Training
- Join as a Trainer

- Top Blogs on Quality Management
5 Whys: Root Cause Analysis – What It Is and How to Use It

Have you ever experienced a problem that kept recurring? Addressing a problem or failure mode more than once is time-consuming and a waste of valuable resources. The issue is that the root cause isn’t being identified or addressed. If you’re not getting to the root cause, you are merely treating a symptom of the problem. In addition, if a permanent remedy is not determined and implemented, the problem will eventually repeat. However, an easy-use tool can assist in eliminating repeat problems. This tool is known as 5 Whys analysis. Unpredicted problems might occur in any team or process. However, issues are just symptoms of deeper issues. Fixing a problem faster may be a convenient solution. However, it does not protect your work process from recurring errors. This is why your team must concentrate on identifying the root cause and tackle it properly.
The 5 Whys analysis, often known as the root cause analysis, is one of the seven fundamentals used in Six Sigma . The principle idea behind the tool is that there is a cause for every effect. Therefore, the quality issue can be seen as having multiple causes. However, it is also known that there is a series of reactions called symptoms before the cause reaches its effect. Therefore pinpointing and solving the problem at its source would benefit management. Every team encounters roadblocks in its daily work. However, using the 5 Whys will assist you in finding the root cause of any issues and protect the process from recurring errors and failures.
So, to enhance your career in quality management, Design for Six Sigma certification is a perfect choice. This Design for Six Sigma training delivered by Invensis Learning is ideal for anybody looking to understand this complex process improvement methodology. In this blog, you’ll get to know the 5 whys analysis is a simple but powerful tool for cutting rapidly through the external symptoms of a problem to discover its underlying causes so that you can resolve it once and for all.

Origin of 5 Whys
The 5 Whys technique was created in the 1930s by Sakichi Toyoda, a Japanese manufacturer, inventor, and founder of Toyota Industries . It became very famous in the 1970s, and Toyota still uses it to solve problems today. One of the essential variables for the successful implementation of the technique is to make an informed decision. This implies that the decision-making process should be based on an insightful grasp of what is happening on the work floor. In other words, people with real-world experience should be involved in the root cause analysis process. Then, logically, they can provide you with the most valuable information regarding any problem that appears in their area of expertise.
The method is remarkably simple: you drill down to its root cause by asking “Why?” five times when a problem occurs. Then, when a countermeasure becomes evident, you follow it to prevent the recurring issue. A countermeasure is an action or set of actions that seek to prevent the problem from arising again, while a solution may seek to deal with the symptom. Countermeasures are more robust and will more likely prevent the problem from recurring.
Before going to the depth of the topic, first, we need to understand the definition of What is 5 Whys analysis?
What is 5 Whys Analysis?
Five whys (5 whys) is an iterative inquisitive technique used to explore the cause-and-effect relationships underlying a particular problem. The primary objective of the technique is to determine the root cause of a defect or issue by repeating the question “Why?”. Each answer frames the basis of the next question. The “five” in the name derives from a recounted observation of the number of iterations to resolve the problem. Not all problems have a solitary root cause. If one wishes to reveal multiple root causes, the method must be repeated, asking a different sequence of questions each time. The method provides no rigid and fast rules about what lines of questions to investigate or how long to proceed with the search for additional root causes.
We got the definition of 5 Whys. Now, let us try to understand why we need 5 whys analysis?
Why Do We Need 5 Whys Analysis?
The primary advantage of the Five Whys is that it is one of the most powerful assessment methods of all non-statistical analyses. It can uncover and trace back to problems that were not obvious.
When applying the 5 Whys technique, you need to get to the problem’s essence and fix it. The 5 Whys may demonstrate to you that the source of the problem is quite unpredictable. Often, issues considered a technical problem turns out to be human and process issues. Therefore finding and eliminating the root cause is crucial to avoid iteration of failures.
As we have discussed why we need 5 whys analysis, now will discuss how to use 5 why analysis
How to Use the 5 Whys Analysis?
The 5 Whys technique will help you achieve continuous improvement at any level of your organization. Though the core of 5 Whys problem-solving is only asking five questions, we recommend some additional steps to bring the mental ability of your team members together and take action on the root causes you find. Following are some of the fundamental steps you need to follow.
- Gather your team
- Define the issue
- Ask “Why?”
- Ask “Why?” four more times
- Know When to Stop
- Address the Root Cause
- Monitor Your Measures
Now will see the detailed description of using the 5 Whys analysis.
Step 1: Gather Your Team
The 5 Whys approach is not an individual-based activity. Attempt to gather a team of people from various departments. Each representative must be familiar with the process that will be investigated. By forming a cross-functional team, you will receive unique points of view. This will help you collect sufficient information to make an informed decision. Keep in mind that this is not an individual task, and it needs to be executed by the team.
Step 2: Define the Issue
Discuss the issue with the team and make a concise problem statement. It will help you characterize the scope of the issue you will investigate. This is important because it investigates a wide-scope problem with hazy boundaries. Try to be as concentrated as possible to find a dynamic solution in the end.
For example, “Team A isn’t reaching its response time goals” or “Software release B caused too many rollback failures.” Then, write your assertion on a whiteboard or sticky note, leaving sufficient space around it to add your answers to the repeated question, “Why?”
Step 3: Ask “Why?”
Now it’s time for your team to inquire why the problem is happening. These questions need to address concrete problems, not just theories. Asking “Why?” sounds easy, but answering it requires genuine thought. Look for answers that are based on facts: they must be records of things that have happened, not guesses at what might have occurred. This blocks 5 Whys from becoming just a process of deductive reasoning, generating many possible causes and, sometimes, creating more confusion as you chase down theoretical issues.
The facilitator should inquire “Why” as many times as needed until the team can figure out the root cause of the initial issue.
Advice 1: Don’t ask an excessive number of Whys. If you keep going, you might end up getting tons of unreasonable suggestions and complaints, which is not the purpose. Instead, focus on finding the root cause.
Advice 2: In some cases, there could be multiple root causes. The 5 Whys analysis will resemble a matrix with various branches in these circumstances. This may even help you identify and eliminate organizational issues that permanently negatively affect the overall performance.
Step 4: Ask “Why?” Four More Times
Ask why four times, using the previous answer to base your question on. You will have five reasons for each “why?” question whenever you have done this. As previously mentioned, you might need to ask why more times than five if you haven’t got to the root of the problem.
Step 5: Know When to Stop
You will know when to stop asking “why?” when asking that question no longer produces good responses. On the off chance that if you haven’t gotten to the root cause of the issue, you might need to consider a more in-depth problem-solving method like FMEA or cause-and-effect analysis. If you’ve found more than one cause in step three, repeat the 5 Whys technique for each branch until you find a single root cause for each one. It is also important to ensure you haven’t stopped too soon and aren’t just accepting a knee-jerk or gut reaction. Please take it to the point where the team produces no reasonable responses.
Finally, you may find the root cause of the problem is that someone failed to take the necessary action. Again, the 5 Whys method lets you bypass blame and ask why that happened. Often, you will discover an underlying organizational issue or an area where the process needs to be improved.
Step 6: Address the Root Cause
Whenever you have identified the root cause of the problem, the entire team should discuss a list of corrective actions or countermeasures to prevent the problem from recurring. The 5 Whys Master should then assign which team members should take responsibility for each item on the list.
Step 7: Monitor Your Measures
It’s very important to carefully monitor how successful your countermeasures are in stopping the problem. If they aren’t as effective as you need them to be, it means you may not have found the true root cause, and you should repeat the 5 Whys technique from the beginning. In conclusion, record your findings and distribute them throughout your organization so that everyone can learn from this particular case study. Again, if this happens, it’s a good idea to repeat the 5 Whys process to ensure that you’ve identified the correct root cause.

Now, let us grab some ideas on using the 5 whys analysis in the next segment.
When Should We Use the 5 Whys Analysis?
You can use 5 Whys for quality improvement, troubleshooting, and problem-solving, but it is most effective to resolve simple or moderately difficult problems. However, it may not be suitable to tackle complex or critical issues. This is because 5 Whys can lead you down a single track, or a finite number of tracks, of inquiry when, indeed, there could be multiple causes. An extensive method such as cause and effect analysis or failure mode and effects analysis may be more effective in cases like these.
However, this simple technique can often direct you quickly to the root cause. So, whenever a process or system is not working perfectly, give it a shot before you embark on a more in-depth approach and certainly before you try to develop a solution. The tool’s simplicity gives it high flexibility, too, and 5 Whys combines well with other methods and techniques, such as Root Cause Analysis . It is often analogous with Lean Manufacturing, identifying and eliminating wasteful practices.
Importance of 5 Whys Analysis
The 5 Whys technique is a simple and powerful tool for solving problems. Its main goal is to track down the exact reason that causes a given issue by asking a sequence of “Why” questions.
- The 5 Whys method assists your team focus on finding the root cause of any problem
- It encourages each team member to share thoughts for continuous improvement, rather than accusing others
- It gives your team the confidence so that it can eliminate any issue and prevent the process from recurring failures
Techniques Used in 5 Whys Analysis
Two main techniques are used to perform a 5 whys analysis:
- The Fishbone (or Ishikawa) Diagram
- A Tabular Format
The Fishbone Diagram
Fishbone diagrams (also known as Ishikawa diagrams, herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, or Fishikawa) are causal diagrams created by Kaoru Ishikawa that demonstrate the potential causes of a particular event. Common uses of the fishbone diagram are product design and quality defect prevention to identify potential elements causing an overall impact. Each cause or justification for imperfection is a source of variation. To identify and characterize various sources of variation, causes are frequently classified into primary categories.
A Tabular Format
A table is an arrangement of data, typically in rows and columns or possibly in a more complicated structure. Tables are widely used in communication, research, and data analysis. Tables appear in print media, handwritten notes, computer software, architectural ornamentation, traffic signs, and many other places. The specific conventions and terminology for describing tables vary depending on the context. Further, tables differ significantly in variety, structure, flexibility, notation, representation, and use. Information or data conveyed in table form is in tabular format.
These techniques enable the spread of analysis to reveal various root causes.
Next, we will move towards the rules of performing a 5 why analysis.
Rules of Performing a 5 Whys Analysis
The five whys system can be personalized based on the particular needs of a given facility. However, most companies implementing this type of strategy will use some general rules or guidelines that can help keep the strategy focused. The following rules of performing the five whys are generally a good place to start for most situations:
- It is important to engage the management in the five whys process in the company. For the analysis itself, think what is the right working group and consider bringing in a facilitator for more difficult topics
- Use a whiteboard or paper instead of computers
- Please write down the problem and make sure that all people understand it
- Distinguish between causes and symptoms
- Focus on the logic of the cause-and-effect relationship
- Ensure that root causes certainly led to the mistake by reversing the sentences created due to the analysis using the expression “and therefore.”
- Attempt to make answers more accurate
- Search for cause step by step, don’t make hasty judgments
- Base the statements on facts and knowledge
- Evaluate the process, not people
- Never leave “human error,” “blame John,” “worker’s inattention,” etc. as the root cause
- Establish an atmosphere of trust and authenticity
- When you structure the answer to the question “Why?” it should be according to the customer’s perspective
Criticism of the 5 Whys
Many companies for training and engineering services successfully utilize the 5 Why technique for fundamental incidents or failures. By utilizing the right placement of triggers, organizations can use the 5 Why for its fundamental problem solving and then progress to form a Cause and Effect analysis for more complicated problems like the Apollo Root Cause Analysis method.
A disciplined problem-solving strategy should push teams to think outside the box, identifying root causes and solutions that will prevent the recurrence of the problem instead of just treating the symptoms. There are various reasons for this criticism of the 5 Whys method:
- The inclination for investigators to stop at symptoms rather than going on to lower-level root causes
- Inability to look beyond the investigator’s present knowledge – cannot think of any new causes
- Inadequate of support to assist the investigator in asking the right “why” questions
- Results are not repeatable – different individuals using 5 Whys come up with various causes for the same problem
- A tendency to isolate a solitary root cause, whereas each question could elicit many various root causes
- Considered a linear method of communication for what is often a non-linear event
Now, we’ll discuss the benefits and limitations of a 5 Whys analysis.
Benefits of 5 Whys Analysis
Following are some of the benefits of 5 whys analysis:
- Helps identify the root cause of a problem
- It is a very powerful tool that is easy to use
- Understand how one process can cause a chain of problems
- Allocates time to fix the problems
- Improves decision making
- Determine the relationship between different root causes
- Highly effective without complicated evaluation techniques
Limitation of the 5 Whys Technique
The 5 Whys method is an incredible technique for getting to the root cause of a problem in a rather short period. However, its speed and convenience of use sometimes can lead to uneven results when it comes to a repeating failure if the 5 Whys fail to deliver the true root cause. The following are a few of the limitations of 5 Whys:
- It doesn’t continuously lead to the identification of the root cause when the cause is unknown to team members
- Different people may get different answers about the cause of the same problem. This raises a question about the authenticity of the technique
- Confirmation bias – The tendency to interpret new data as confirmation of one’s own existing ideas or theories tends to be a driving factor for some team members during analysis
- The technique can only be as good as the people who use its expertise and experience
- You may not dive deep enough to reveal the root cause of the issue entirely
- Team members tend to depend on deductive logic instead of observation when recognizing factors leading to the root cause, which can produce needy results
Example of 5 Whys Analysis
Jeff Bezos Amazon Example of Application of 5 Whys:
Jeff Bezos illustrated how the Five Whys could be used. He had gone to one of the shop floors at Amazon. During his visit, he saw that one of the employees fingers were caught in the conveyor belt, and the employee had been injured. The following is a record of the meeting where Mr. Bezos described this incident.
Question 1: What caused the associate to damage his thumb?
Answer: Because his thumb got trapped in the conveyor belt.
Question 2: Why did his thumb get trapped in the conveyor?
Answer: Because he was chasing his bag, which was moving along a conveyor.
Question 3: Why was he chasing after his bag?
Answer: Because he put his bag on the conveyor, but it then turned on by surprise
Question 4: What was the purpose of his bag being on the conveyor?
Answer: Because he used the conveyor as a table
Conclusion of the Case
So, the logical root cause of the associate’s damaged thumb is that he needed a table. Unfortunately, there wasn’t one around, so he used a conveyor as a table. To eliminate further safety incidents, we need to provide tables at the appropriate stations or give portable, light tables for the associates to utilize, update, and focus on safety training. Also, look into preventative maintenance standard work.
Conclusion Regarding the Methodology in General
The 5 Whys act as a powerful tool and help sift through the symptoms, which represent surface-level problems to the root cause of the real problem. Solving this root cause solves all the issues in between.
Subjectivity Involved
The 5 Whys process is only semi-structured. Therefore, if different people do it, they may come to very different results. In addition, the process is only as good as the person running it. This makes it important to ensure that the team is cross-functional and involved in obtaining the best results for the process.
Conclusion
The 5 Whys technique is a problem-solving method that relies on asking “why?” five times in a continuous sequence to find the root cause. Each time you inquire why a problem occurred, your answer turns into the reason for your next question, compelling you to dig deeper and deeper into the true cause of the issue. This informed decision-making technique investigates the cause-and-effect relationships hidden behind a specific problem. Rather than coming up with a solution that could only address a certain symptom, the 5 Whys process focuses on countermeasures that aim to prevent the problem from ever occurring again.
To learn more about 5 why analysis and, more importantly, a company that functions as an effective system, individuals and enterprise teams should get trained in widely-recognized quality management certification courses. Invensis Learning offers some of the popular quality management courses that individuals and enterprise teams can take up are: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification, Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Certification, RCA through Six Sigma Certification, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification, Lean Fundamentals Certification. Invensis Learning is one of the world’s leading and best professional certification training providers.
Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Certification Training
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification Training
Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification Training
Lean Fundamentals Certification Training
Lean IT Certification Training
RCA Through Six Sigma Certification Training
7QC Tools Certification Training
Value Stream Mapping Certification Training
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

What is Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)?

Top 6 Quality Management Trends to Follow in 2024

What is the Plan Do Check Act (PDCA) Cycle?
Leave a reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 14,521 Likes
- 444 Followers
- 96,000 Subscribers
- 2,170 Followers
Related Articles

Agile Definition – Introduction to Agile Values, Principles and Benefits

The Agile Development Cycle

Top Risk Management Certifications for Enterprise Teams

ITIL Certification Vs. Scrum Master Certification – Key Differences

The Values & Principles of DevOps
Popular posts.

The Project Management Life Cycle Explained

Roles and Responsibilities of a Quality Control Inspector

7 Cs of Effective Communication with Example

Top 5 Factors for Project Success

Quality Analyst Job Role and Responsibilities- Explained!
Suggested posts.
- 7 Cs of Effective Communication with Examples
- Project Management Lifecycle
- Project Success Factors
- Quality Control Inspector Job Description
- Risk Management Examples
- QA Manager Job Description
- Quality Management Team Roles and Responsibilities
- Risk Management Tools & Techniques
- Quality Analyst Job Description
- What is Business Value
- Who are Project Stakeholders
- Importance of Project Management
- What is Project Management
- Project Management Skills
- Project Manager Job Description
- Agile Project Manager Interview Questions
- Risk and Compliance Manager Job Description
- Risk Management Process
- Project Scope Management
- Healthcare Project Manager Job Description
- Six Sigma Project Examples
- Risk Analysis Methods
- ITIL Service Lifecycle
- Risk Manager Job Description
POPULAR CATEGORIES
- Best Project Management Blogs 254
- Top Agile Blog Posts 158
- Top Blogs on Quality Management 126
- Latest IT Service Management Blogs 108
- Trending Articles on DevOps 65
- Popular Blogs on IT Security and Governance 55
- Top Blogs on Professional Development 33
- Top Infographics Collection 8
Download E-book Blog
Thank You for submitting your enquiry. One of our training consultants will get in touch with you shortly.
50+ Training and Certification Programs - Upskill Today Learn more about our training programs.

5 Whys: Examples, explanations, and how to find the causes of problems

At some point, we’ve all experienced a problem with a process or strategy at work. But figuring out why the problem exists can be a daunting task. When you sit your teammates down for a discussion, emotions run high and miscommunication is common.
The 5 Whys is a powerful, easy-to-use technique for getting at the root of a problem. It empowers you and your team to understand why a problem persists and to decide on a path forward.
- What is the 5 Whys framework?
The 5 Whys is a popular problem-solving method that individuals and teams use to understand the potential causes of a specific issue. Years ago, Toyota developed the approach to help them get at the heart of complex mechanical issues, so you know it’s legitimate! The technique is easy to use: you ask why a problem happened, and then you ask four more times. By asking “why” on a step-by-step basis, you can get to the root cause of a defect, failure, challenge, or malfunction.
- When and Why the 5 Whys Analysis is Used
The 5 Whys framework is useful in a variety of situations. People love it because it helps you have a focused discussion and avoid getting distracted by other topics. You just start with a problem statement, ask why the problem exists, and keep moving through the exercise until you’ve uncovered the problem.
Here are some scenarios where you might find the 5 Whys approach to be useful.
Working on complex products
Remember, the 5 Whys technique was originally developed by Toyota. The car manufacturer needed a clear-cut way of dealing with a product that has thousands of parts. But that doesn’t mean the technique only works for large physical goods. Many organizations use the 5 Whys approach when software malfunctions, when a key deliverable with many moving parts doesn’t work properly, or when a multi-step process breaks down.
Solving complex problems
When a problem is so complex that engineers, designers, or decision-makers are scratching their heads, the 5 Whys approach may serve you well. Maybe your complicated marketing strategy didn’t hit your targets, or an important API isn’t working. Instead of getting overwhelmed, the 5 Whys framework helps you wrap your head around the problem.
Dealing with consistent problems
Maybe the problem doesn’t seem complex, but it keeps coming up. Or maybe you’ve tried multiple solutions and none seem to work. Rather than burning precious time and money on yet another risky bandaid, try the 5 Whys to finally discover what’s going on.
- How to conduct a 5 Whys analysis in 6 steps
One of the great things about the 5 Whys framework is that it’s easy to understand. Unlike many other problem-solving techniques, which can be difficult to grasp, you can explain the 5 Whys to your team in minutes. Follow these guidelines any time you need to use the approach.
Step 1 – Form your problem statement.
Start by asking your team what problem you’re about to analyze. Everyone should get a chance to articulate the problem so you’re all on the same page. Sometimes, you might find yourself using the 5 Whys approach to uncover the root of a difficult or charged obstacle. If that’s the case, give your team the time and space to be honest with each other and to have difficult conversations. Write down the problem statement for everyone to reference.
Step 2 – Ask “why has this happened?” 5 times.
Don’t be too literal with it. Feel free to amend the “why” statement to something like “Why does this keep happening?” or “Why are we having this problem?” Keep going until you’ve asked “why” five or more times. It might feel unnatural, but eventually, you’ll push through any awkwardness to uncover the root of the problem.
Step 3 – Jot down logical causes.
Okay, now you have a pretty good handle on your problem. Write down any logical causes that have followed from your 5 Whys analysis. Regardless of whether those causes came from your first “why” or your fifth, make a detailed note of them. Discuss the causes with your team and make sure you’re all agreed.
Step 4 – Hypothesize an answer.
Now that you have your logical cause, it’s time to come up with some potential solutions. At this stage, you’re just having a conversation. You don’t need to come up with the perfect solution in this meeting. Have everyone go around the room and say (or write down) a possible solution. Ask everyone to vote on the most actionable one.
Step 5 – Test your hypothesis.
Put your solution to the test with some experiments. If you’ve decided that a marketing campaign failed because you didn’t choose the correct target audience, then maybe you can come up with some A/B tests to vet possible solutions. Aim for low-stakes tests that you can use to draw meaningful conclusions.
Step 6 – Repeat until solved.
Iterate until you’ve solved the problem! Don’t be discouraged if it doesn’t happen right away. Sometimes, it might take multiple rounds of “whys” followed by many rounds of testing to uncover a solution. Keep an open line of communication among your teammates and don’t give up.
Try Miro today
- A simple 5 Whys example
The 5 Whys is an adaptable, easy-to-use framework for uncovering the root of a problem. Organizations and teams of all sizes use the framework to overcome complex, high-stakes challenges. Here’s a quick example to help you bring this method of analysis to your own team.
Let’s say your team has been working on an app for many months. You rolled out a beta version late last quarter. You were supposed to ship the app to the rest of your users at the beginning of this quarter, but a problem arose: a bunch of your early users complained of a fatal error that caused the app to crash. As a result, you couldn’t ship it, and your customers were disappointed.
Step 1 — Write down your problem statement.
As we mentioned above, the first step in following the 5 Whys framework is to clearly and succinctly define what problem you’re trying to solve. The entire group should be clear about this issue. In this case, the problem statement is: your app wasn’t ready to ship to your customers.
Step 2 — Start with the broadest possible question.
Start with the broadest possible question. Then aim to answer it. Why wasn’t the app ready for your customers? It wasn’t ready because there was a bug in the code that caused it to crash.
Drill down into that question. Why was there a bug in the code that caused it to crash? There was a bug in the code because the engineers didn’t get user feedback in time to fix it.
Keep drilling down. Why didn’t the engineers get that user feedback? They didn’t get the feedback because the development team didn’t provide an easy way for users to submit their feedback.
Continue drilling down, asking more and more precise questions as you get closer to the answer. Why didn’t the development team provide an easy way for users to leave feedback? They didn’t provide an easy way for users to leave feedback because they weren’t clear on deadlines for the project.
Ask “why” at least one more time. Why wasn’t the development team clear on deadlines for the project? They weren’t clear on deadlines because they weren’t meeting with stakeholders often enough to know when the timeline changed.
Step 3 – Write down logical issues.
Now you have enough information to write down logical causes. It seems that this problem stemmed from a lack of communication between stakeholders. That caused the development team and engineering team to become misaligned.
Step 4 – Once you’re ready, you can come up with a possible solution to this problem.
Once you’re ready, you can come up with a possible solution to this problem. In the future, internal stakeholders will hold weekly check-ins to make sure they’re aligned on where the project is headed.
Step 5 – Put that hypothesis into action.
Here’s where you get to test out your hypothesis and see what effects it has. Moving forward, start holding weekly check-ins and see what happens. If miscommunication and confusion goes down, you’ll know you’re on the right track.Step 6 – Adjust your strategy, if needed
Resist the urge to consider a problem “solved” and move on immediately. It’s important to revisit how the solution is functioning in the weeks ahead, continually checking in with everyone on the team to see how they’re feeling about it. You may need to tweak your strategy over time.
- How 5 Whys helped solve the problem
This example clearly showcases the power of the 5 Whys. What looked like a problem with code turned out to be a symptom of miscommunication.
Although this is just a hypothetical, we all know stuff like this happens every day. But it’s often difficult to uncover the root causes of a problem without months and months of exploration. With the 5 Whys, you can overcome costly challenges in a much shorter amount of time.
- Try the 5 Whys template for free
Clearly, asking “why?” isn’t just a technique used by persistent 4-year-olds – it’s actually a quick and easy way to identify a root cause. Countless teams across different industries have had great results using this framework. Save time, collaborate with your team, and solve hard problems with Miro’s free 5 Whys template .
- How Miro helps distributed teams collaborate
Working with a remote team can be challenging — but it also offers unparalleled opportunities for creativity and collaboration. Miro’s online whiteboard helps teams overcome cultural divides, communication silos, geographic barriers, and micro-cultures to empower you to stay connected and do great things.
Miro has a variety of templates and tools for teams to help you and your team:
- Create a mind map
- Manage a scrum board
- Create user story maps and customer journey maps
- Work with sticky notes, even if you aren’t in the same room
- Generate flow charts and diagrams
- Run brainstorming sessions
And lots more… try Miro for remote collaboration today!
Miro is your team's visual platform to connect, collaborate, and create — together.
Join millions of users that collaborate from all over the planet using Miro.
Keep reading
Agile beyond software development: how to empower non-tech teams.

Achieve continuous improvement with as-is and to-be process mapping
How to build resilient teams with Agile expert Diana Larsen

Five Whys Method

Five Whys is an effective problem-solving approach that constitutes a questioning process designed to drill down into the details of a problem and peel away the layers of symptoms.
The technique was originally developed by Sakichi Toyoda and was used during the evolution of manufacturing methodologies at Toyota Motor Corporation. It is a critical component of problem-solving training, delivered as part of the induction into the Toyota Production System. [1], [2]
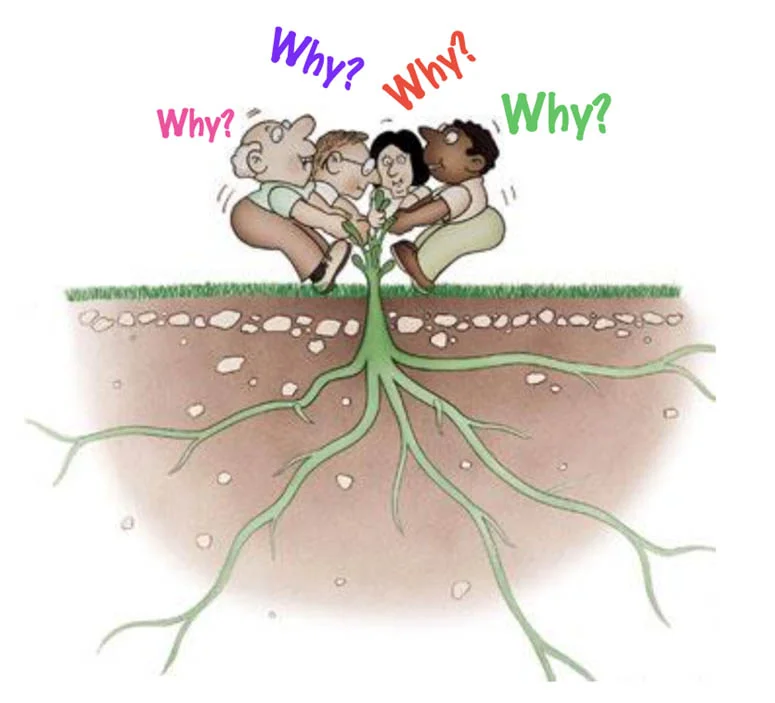
5 Whys analysis can be used to develop a better and more detailed understanding of the problem, to implement solutions that don’t just address the symptoms but have a lasting, more permanent impact and to get to the Root Cause.
The technique works on the premise that for every effect, there is a root cause, but the resulting chain between the two can be fairly long and difficult to establish. When a problem appears, the temptation is strong to blame it on what is easily evident while ignoring the hidden root cause(s).
This tendency frequently results in suboptimal or temporary solutions, and the problem resurfaces shortly after.
Five Whys works by providing a simple question-asking technique that explores the cause-and-effect relationships and the underlying problems.
There are three key elements to effective use of the Five Whys technique:
- Accurate and complete problem statement
- Honesty in answering the questions
- The determination to get to the bottom of the problem
How to Use the Five Whys Technique
The Five Whys technique promotes deep thinking through questioning and can be applied to most problems. It is more effective when used in a team (preferably cross-functional) and has five basic steps:
1. Forming the Team and defining the problem statement
Gather the team and develop the problem statement in agreement. Decide whether additional individuals are needed to resolve the problem.
It is important to involve those responsible for the process and those who carried out the activity that presented the problem. Including individuals with varied experiences brings unique viewpoints, leading to effective analysis.
The specific problem must then be written down as it helps formalize the issue and ensures team focus. The problem statement must describe the current condition as it is known and not as it “could be” or “thought to be”.
The situation must be supported by data wherever possible, for example: “Overall customer complaints are up 50%”.
Data may come from reports, staff or stakeholder qualitative surveys, experiences, or by observing the problem occurring in multiple situations while taking notes.
2. Asking the first Why
Answering why requires genuine thought. As far as possible, teams must stick to answers that are based on facts: there must be records of events that have happened, not guesses at what might have occurred.
Asking the first “why” could generate three or four sensible answers. They must then be recorded on a flip chart or whiteboard.
3. Successive Whys
The team then continues asking more (typically four) successive “whys,” repeating the process for every statement on the flip chart or whiteboard.
Answers to each of these ‘whys’ must be posted near its “parent.”
All plausible answers must then be followed up. Eventually, the team will reach a point where there are no more “Whys” and the question that remains is the root cause.

The team will know they have arrived at the root cause when asking “why” yields no further useful information. (The team might need to continue to ask questions beyond the arbitrary five layers to get to the root cause)
4. Look for systemic causes
Among the dozen or so answers to the last asked “why”, look for systemic causes of the problem. Discuss these and settle on the most likely systemic cause.
Follow the team session with a debriefing and show the results to others to confirm that they see logic in the analysis.
5. Develop Corrective action
After settling on the most probable root cause of the problem and obtaining confirmation of the logic behind the analysis, develop appropriate corrective actions to remove the root cause from the system. The actions can (as the case demands) be undertaken by others but planning and implementation will benefit from team inputs.
Five Whys – Working Templates
Teams can make use of the below worksheet while conducting the Five Whys Analysis:
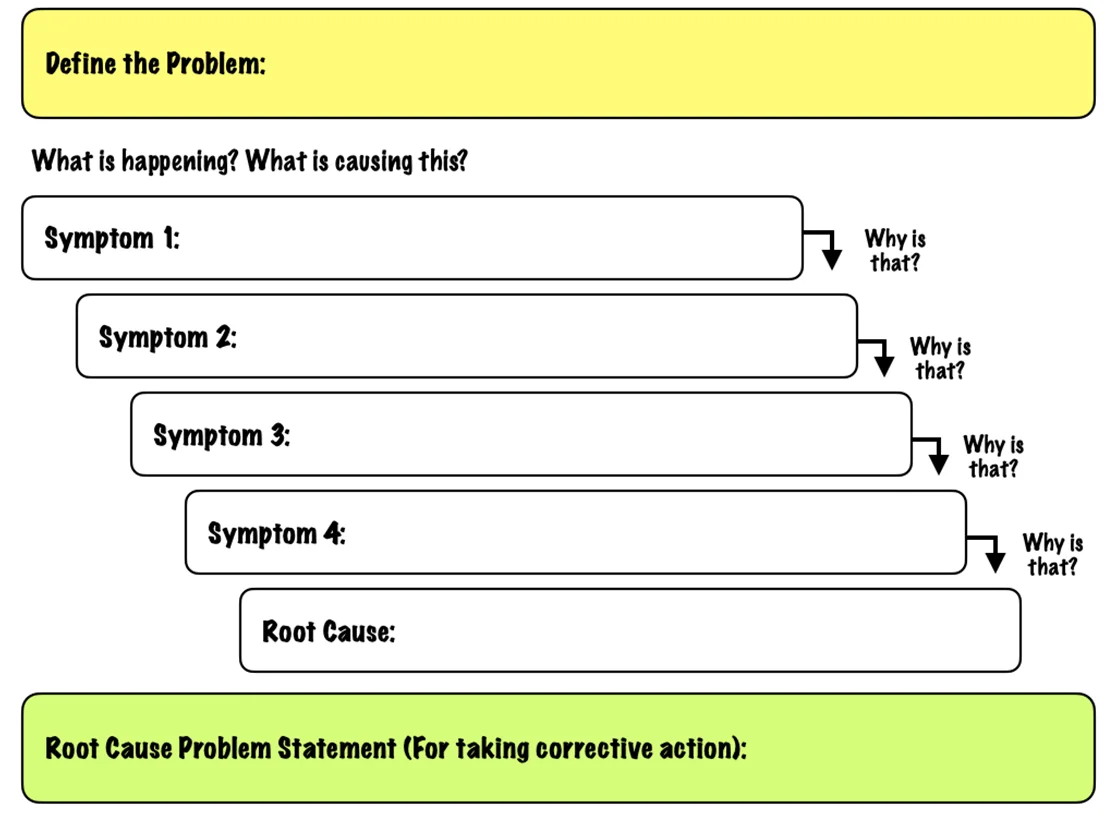
In some cases, there could be more than one root cause, in which case, the analysis will follow the “Why Tree Framework” as shown:
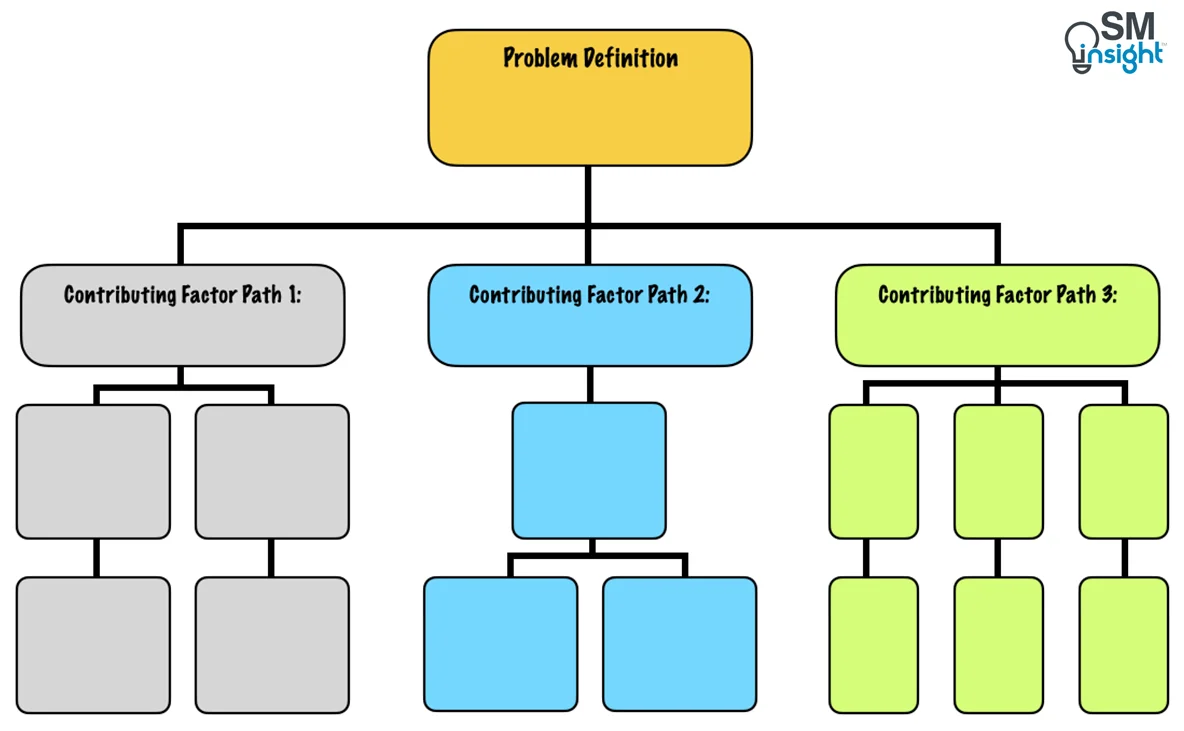
Example of Five Whys Analysis
Five Whys Analysis is a flexible tool and can be applied to varied situations and conditions, from manufacturing to business to organization design. Some of the example applications are as follows:
Five Whys in Manufacturing
Suppose a machine in an assembly line has stopped functioning. Five Whys analysis of the situation would proceed as follows:
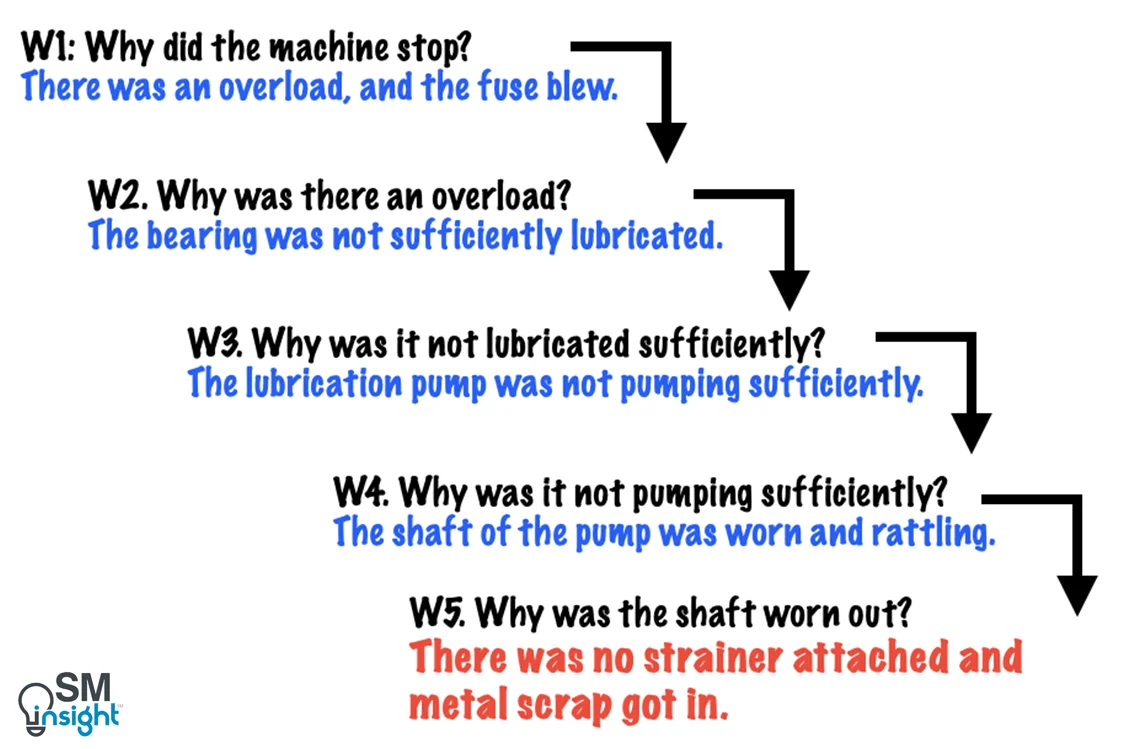
The example demonstrates how repeating why five times helps uncover the root problem and thus correct it. If this procedure were not carried out, one could simply replace the fuse or the pump shaft. In such case, the problem would recur within a few months, or in the worst case cause permanent damage.
Five Whys in Diagnosing System Usage
The Harford County Health Department (HCHD) noticed very low usage of a newly introduced translation service meant to help the Limited English Proficiency (LEP) populations residing in the County.
HCHD decided to perform a Five Whys analysis to understand the underlying reasons. The resulting analysis is as shown:
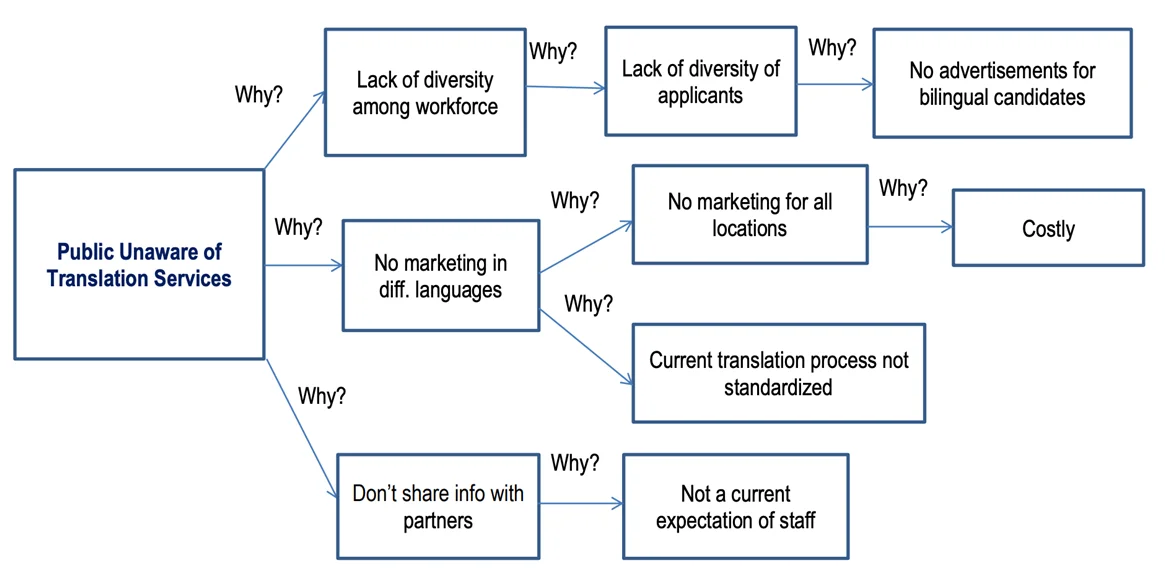
It can be seen how the analysis reveals more than one branch of causes and drills down to the fundamental reasons.
5-Whys Criticisms
Five Whys has been criticized as a poor tool for root cause analysis. Its critics include Teruyuki Minoura, former managing director of global purchasing for Toyota [7] and Medical professor Alan J. Card. [8]
Some of the reasons for this criticism are:
- The tendency to stop at symptoms rather than going on to lower-level root causes.
- Inability to go beyond the investigator’s current knowledge.
- Lack of support to help the investigator provide the right answer to “why” questions.
- Results may not be repeatable – different people may come up with different causes.
- Tendency to isolate a single root cause, whereas each question could have many different root causes.
However, in his article [9] , author, Mark Galley defends the tool and concludes that while Five Whys is not a complete method, it helps bring structure, clarity, and simplicity to problem-solving.
1. “Toyota Production System”. Toyota, https://global.toyota/en/company/vision-and-philosophy/production-system/ . Accessed 26 Aug 2023
2. “Toyota Production System: Beyond Large-Scale Production”. Taiichi Ohno, https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0B3FY1MT5?ref_=cm_sw_r_cp_ud_dp_799G30M0SS0RW9ANSEH4 . Accessed 27 Aug 2023
3. “The 5 Whys – What is it?”. County of Los Angeles Public Health, http://publichealth.lacounty.gov/qiap/docs/Topic3-Fishbone.pdf . Accessed 27 Aug 2023
4. “5 Whys Exercise”. University of Wisconsin, https://media.wcwpds.wisc.edu/PDSA%20Online%20Toolkit/Plan_Problem%20Exploration_Test%20Selection/5%20Whys%20Exercise.pdf . Accessed 27 Aug 2023
5. “The Five Whys Technique”. Olivier Serrat (Asian Development Bank), https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/27641/five-whys-technique.pdf . Accessed 27 Aug 2023
6. “Improving Communication with Limited English Proficiency (LEP) Populations”. Harford County Health Department, http://publichealth.lacounty.gov/qiap/docs/Topic3-StoryboardWhys.pdf . Accessed 28 Aug 2023
7. “THE “THINKING” PRODUCTION SYSTEM: TPS AS A WINNING STRATEGY FOR DEVELOPING PEOPLE IN THE GLOBAL MANUFACTURING ENVIRONMENT”. Toyota, https://web.archive.org/web/20201121032113/https://media.toyota.co.uk/wp-content/files_mf/1323862732essenceTPS.pdf . Accessed 28 Aug 2023
8. “The problem with ‘5 whys’”. Dr Alan J Card, https://qualitysafety.bmj.com/content/26/8/671 . Accessed 28 Aug 2023
9. “What the critics don’t understand”. Mark Galley, https://blog.thinkreliability.com/top-criticisms-of-the-5-why-approach . Accessed 28 Aug 2023
- Porter's Five Forces
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Explore the Platform
- Integrations
- Governance & Change Management
- Common Data Model
- Integrated Validation
- Data & Analytics
- Computer Vision
- Frontline Copilot™️
- Automations
- Edge Connectivity
- Machine Connectivity
- Edge Devices
- Machine Kit
- Device Library
- Composable MES
- Digital Guidance
- Production Management
- Traceability and Compliance
- Digital Work Instructions
- Manufacturing Training Software
- Kitting Software
- Production Tracking Software
- Manufacturing Dashboards
- Inline Quality Inspection
- Non-Conformance Management
- Visual Quality Inspection
- Electronic Batch Records
- Device History Records
- Genealogy & Traceability
- Equipment Logbooks
- Industrial Products
- Consumer Products
- Luxury Goods
- Electronics
- Automotive & Specialty Vehicle
- Aerospace & Defense
- Food & Beverage
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- Biotech Manufacturing
- Cell & Gene Therapy
- Medical Devices & Diagnostics
- High-Mix Discrete Assembly
- Additive Manufacturing
- Batch and Hybrid Batch
- Contract Manufacturing
- New Product Introduction (NPI)
- Case Studies
- Augmented Ops Podcast
- Augmented Lean
- 30-Day Free Trial
- Tulip University
- Knowledge Base
- Attend Operations Calling 2024
- Tulip Experience Center
- Trust Center
- Website Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Support Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
What are the Five Whys? A Tool For Root Cause Analysis
What are the five whys.
Five whys (5 whys) is a problem-solving method that explores the underlying cause-and-effect of particular problems.
The primary goal is to determine the root cause of a defect or a problem by successively asking the question “Why?”. The number ‘5’ here comes from the anecdotal observation that five iterations of asking why is usually sufficient enough to reveal the root cause.
In some cases, it may take more or fewer whys, depending on the depth of the root cause.
Why The Five Whys?
The main benefit of the Five Whys is that it is one of the most powerful assessment methods of all non-statistical analyses. It can uncover and trace back to problems that were not very clear or obvious.
It is simple, and it works.
The Benefits of Five Whys
- Helps identify the root cause of a problem
- Understand how one process can cause a chain of problems
- Determine the relationship between different root causes
- Highly effective without complicated evaluation techniques
When Should You Use This Method?
- For simple to moderately difficult problems
- More complex problems may require this method in combination with some others
- When problems involve human factors or interactions. So any time human error is involved in the process.
How to Complete a Five Whys Root Cause Analysis
- Begin with a specific problem. What is it that you are having an issue with? This can also help the team focus on the same problem.
- Ask why the problem happened and write the answer down below the specific problem you listed in step one.
- Keep asking “ why” to each of the successive answers you write down until you reach the root cause of the problem.
- Again, this may take more or less than five “ why”s . Make sure your team sees eye-to-eye with each of the questions being answered as well as the final root cause.
Key Things to Keep in Mind
- Distinguish causes from symptoms or causal factors
- To make sure that you are attributing the correct answer to each “ why” , try working backwards. (Answer to the “ Why?” + “and therefore” + the Problem Identified for that Question)
- You can break down your answers as much as you like. The more the better.
- Answers should always be based on facts and data
- Last but not least, assess the process, not the people.
Toyota Five Whys
The Five Whys method was originally developed by Sakichi Toyoda , the founder of Toyota Industries. This method became widely used in Toyota Motor Corporation and is still used frequently to this day. Taiichi Ohno, the architect of the Toyota Production System, describes the five whys as “the basis of Toyota’s scientific approach.”
Along with their other “go and see” philosophies, the five whys method is used along with other famous concepts such as kaizen , poka-yoke , and jidoka .
Five Whys Example
Here’s an example of how this works:
The Root Cause reveals the source of the problem. By coming up with a solution for the root cause, there is a high chance that all of the whys leading up to the final answer will naturally get resolved.
Five Whys Tools
The simplest way of conducting the Five Whys test is to simply write it down on a piece of paper. However, the fishbone, or the Ishikawa diagram , can help during the initial process of identifying problems. The diagram can reveal problems that may need the five whys for a deeper look. Then, you can gather all of the root-cause-effect relationships and evaluate which of them had the greatest impact on the original problem.
Enable continuous improvement with Tulip's Frontline Operations Platform
Learn how a system of apps can digitize your lean manufacturing practices, collect and analyze data in real-time, and reduce human errors with a 30-day free trial.
- Professional Services
- Creative & Design
- See all teams
- Project Management
- Workflow Management
- Task Management
- Resource Management
- See all use cases
Apps & Integrations
- Microsoft Teams
- See all integrations
Explore Wrike
- Book a Demo
- Take a Product Tour
- Start With Templates
- Customer Stories
- ROI Calculator
- Find a Reseller
- Mobile & Desktop Apps
- Cross-Tagging
- Kanban Boards
- Project Resource Planning
- Gantt Charts
- Custom Item Types
- Dynamic Request Forms
- Integrations
- See all features
Learn and connect
- Resource Hub
- Educational Guides
Become Wrike Pro
- Submit A Ticket
- Help Center
- Premium Support
- Community Topics
- Training Courses
- Facilitated Services
Introducing the 5 Whys Technique of Problem Solving
February 3, 2021 - 7 min read
What do you do when you and your team run into a problem?
Do you try to find the quickest fix to keep things moving? Get through and assume it was a fluke that won’t happen again? Shift blame to circumstances that were beyond your control?
There’s a better way to diagnose and even solve your problems. It’s called the five whys.
What is the five whys method?
The five whys method is a problem-solving technique that helps you get to the root cause of a problem. Using this technique, you’ll uncover cause and effect relationships and ultimately uncover how processes and projects can be improved in the future.
The premise of the five whys is fairly straightforward: You’ll ask “why?” five times in a row.
Maybe your team didn’t complete a major project by the deadline. Why? Because a team member was late submitting their piece of the project. Why? Because the end client was delayed in getting her the feedback she needed. Why? ...and so on.
Sound like overkill? Or maybe something a curious toddler would do? We get it. However, this technique is surprisingly beneficial.
When you and your team are brainstorming or problem-solving, it’s tempting to jump right into identifying solutions — without realizing you don’t quite understand the extent of the problem yet. The five whys technique keeps you and your team zoned in on the challenge so you can identify the most impactful solution.
A five whys analysis is helpful for understanding the inner workings of problems, but it’s not without its flaws. Let’s cover a few pros and cons of this approach.
Benefits of the five whys method
- It’s simple to use : As far as problem-solving tools and analyses go, the five whys technique is one of the most straightforward and intuitive.
- It uncovers the root cause : It pushes teams to go beyond their gut feeling or their first answer to think critically about the real source of their issues.
- It encourages conversation : “Why?” is an open-ended question , which can encourage candid and valuable discussions between your team members. It can also expose them to roadblocks or areas of confusion they didn’t realize others were experiencing.
Challenges of the five whys method
- It’s subjective : One team member might think your project was delayed because a colleague dropped the ball, while another thinks it’s because the original deadline was unrealistic. Conflicting opinions are common, which can present some roadblocks for the effectiveness of this technique.
- It’s limiting : Despite the name, you might need to ask “why?” more than five times to get to the heart of a problem. Additionally, there may be more than one root cause for an issue, which this technique doesn’t easily address or accommodate.
- It requires visibility : Your team is smart, but they don’t know everything. When asking “why?” you might run into some instances where the only answer you can come up with is, “I don’t know.” That means this technique is at a standstill.
Why does the five whys technique benefit project management?
Ask yourself this: When’s the last time you had a project go off without a hitch? Everything went exactly according to plan, and you didn’t experience a single hiccup along the way.
Has it been a while? That’s normal. Collaboration is complicated, and even the most successful project managers will admit that even the most carefully-planned projects sometimes run off course. In one report from the Project Management Institute ( PMI ), respondents said that only 69% of their project s met their original goals—implying that 31% of projects fell short.
When that happens, it’s tempting to grit your teeth, get through the muck, and then move on. However, the best thing to do is to reflect on those project problems , drill down to their root causes, and identify how you can fix those for future projects.
That’s why the five whys technique is important for project management: It will help you and your project team identify how you can collaborate more effectively, proactively navigate risks and problems, and deliver more winning projects.
The five whys example: How it applies to project management
Want to see a five whys analysis in action? Let’s continue with the example that we set up at the beginning:
The Problem: Our team was two weeks late in finalizing a client’s keyword research report.
- Why? Maggie was late in delivering the section on keyword opportunities.
- Why? The end client took too long to get the audience personas she requested.
- Why? We didn’t get the information we needed at the start of the project.
- Why? We don’t have a streamlined process for collecting the client information we need.
- Why? We haven’t created a work intake form.
Now you know what you need to do to ensure you don’t hit the same snag on your next projects: You need to create an intake form so that your team is equipped with the must-have information they need from your clients — before they even start any work.
See how it works? By doing nothing more than asking, “Why?” five times in a row, you identified a relatively simple fix (particularly if you’re using a project management platform like Wrike that has dynamic request forms ) that will yield huge results for your team and your projects.
And you owe all of that to the five whys technique—proof that problem-solving methods don’t need to be complicated to be effective.
Wrike gives you and your team visibility into your work processes so that you have an easier time leveraging the five whys method. Start your two-week free trial now .
Kat Boogaard
Kat is a Midwest-based contributing writer. She covers topics related to careers, self-development, and the freelance life. She is also a columnist for Inc., writes for The Muse, is Career Editor for The Everygirl, and a contributor all over the web.
Related articles

The Ultimate Guide to Sprint Retrospectives
Plan your next sprint retrospective with these tips and best practices. Use this guide to enable your Scrum team to look back and optimize processes.

The Ultimate Guide to Implementation Plans
Achieve better outcomes and stronger results by creating implementation plans that help you turn concepts into real world action. Learn more with Wrike.

What Is a Bottleneck in Project Management?
What is a bottleneck in project management? Here’s how to perform a bottleneck analysis to identify project roadblocks before they spiral out of control.

Get weekly updates in your inbox!
You are now subscribed to wrike news and updates.
Let us know what marketing emails you are interested in by updating your email preferences here .
Sorry, this content is unavailable due to your privacy settings. To view this content, click the “Cookie Preferences” button and accept Advertising Cookies there.
- Join Mind Tools

Getting to the Root of a Problem Quickly
Have you ever had a problem that refused to go away? No matter what you did, sooner or later it would return, perhaps in another form.
Stubborn or recurrent problems are often symptoms of deeper issues. "Quick fixes" may seem convenient, but they often solve only the surface issues and waste resources that could otherwise be used to tackle the real cause.
In this article and in the video, below, we look at the 5 Whys technique (sometimes known as 5Y). This is a simple but powerful tool for cutting quickly through the outward symptoms of a problem to reveal its underlying causes, so that you can deal with it once and for all.
Click here to view a transcript of this video.
Origins of the 5 Whys Technique
Sakichi Toyoda, the Japanese industrialist, inventor, and founder of Toyota Industries, developed the 5 Whys technique in the 1930s. It became popular in the 1970s, and Toyota still uses it to solve problems today.
Toyota has a "go and see" philosophy. This means that its decision making is based on an in-depth understanding of what's actually happening on the shop floor , rather than on what someone in a boardroom thinks might be happening.
The 5 Whys technique is true to this tradition, and it is most effective when the answers come from people who have hands-on experience of the process or problem in question.
The method is remarkably simple: when a problem occurs, you drill down to its root cause by asking "Why?" five times. Then, when a counter-measure becomes apparent, you follow it through to prevent the issue from recurring.
The 5 Whys uses "counter-measures," rather than "solutions." A counter-measure is an action or set of actions that seeks to prevent the problem from arising again, while a solution may just seek to deal with the symptom. As such, counter-measures are more robust, and will more likely prevent the problem from recurring.
When to Use a 5 Whys Analysis
You can use 5 Whys for troubleshooting, quality improvement, and problem solving, but it is most effective when used to resolve simple or moderately difficult problems.
It may not be suitable if you need to tackle a complex or critical problem. This is because 5 Whys can lead you to pursue a single track, or a limited number of tracks, of inquiry when, in fact, there could be multiple causes. In cases like these, a wider-ranging method such as Cause and Effect Analysis or Failure Mode and Effects Analysis may be more effective.
This simple technique, however, can often direct you quickly to the root cause of a problem. So, whenever a system or process isn't working properly, give it a try before you embark on a more in-depth approach – and certainly before you attempt to develop a solution.
The tool's simplicity gives it great flexibility, too, and 5 Whys combines well with other methods and techniques, such as Root Cause Analysis . It is often associated with Lean Manufacturing , where it is used to identify and eliminate wasteful practices. It is also used in the analysis phase of the Six Sigma quality improvement methodology.
How to Use the 5 Whys
The model follows a very simple seven-step process:
1. Assemble a Team
Gather together people who are familiar with the specifics of the problem, and with the process that you're trying to fix. Include someone to act as a facilitator , who can keep the team focused on identifying effective counter-measures.
2. Define the Problem
If you can, observe the problem in action. Discuss it with your team and write a brief, clear problem statement that you all agree on. For example, "Team A isn't meeting its response time targets" or "Software release B resulted in too many rollback failures."
Then, write your statement on a whiteboard or sticky note, leaving enough space around it to add your answers to the repeated question, "Why?"
3. Ask the First "Why?"
Ask your team why the problem is occurring. (For example, "Why isn't Team A meeting its response time targets?")
Asking "Why?" sounds simple, but answering it requires serious thought. Search for answers that are grounded in fact: they must be accounts of things that have actually happened, not guesses at what might have happened.
This prevents 5 Whys from becoming just a process of deductive reasoning, which can generate a large number of possible causes and, sometimes, create more confusion as you chase down hypothetical problems.
Finding This Article Useful?
You can learn another 44 problem-solving skills, like this, by joining the Mind Tools Club.

Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Receive new career skills every week, plus get our latest offers and a free downloadable Personal Development Plan workbook.
Your team members may come up with one obvious reason why, or several plausible ones. Record their answers as succinct phrases, rather than as single words or lengthy statements, and write them below (or beside) your problem statement. For example, saying "volume of calls is too high" is better than a vague "overloaded."
4. Ask "Why?" Four More Times
For each of the answers that you generated in Step 3, ask four further "whys" in succession. Each time, frame the question in response to the answer you've just recorded.
Try to move quickly from one question to the next, so that you have the full picture before you jump to any conclusions.
The diagram, below, shows an example of 5 Whys in action, following a single lane of inquiry.
Figure 1: 5 Whys Example (Single Lane)
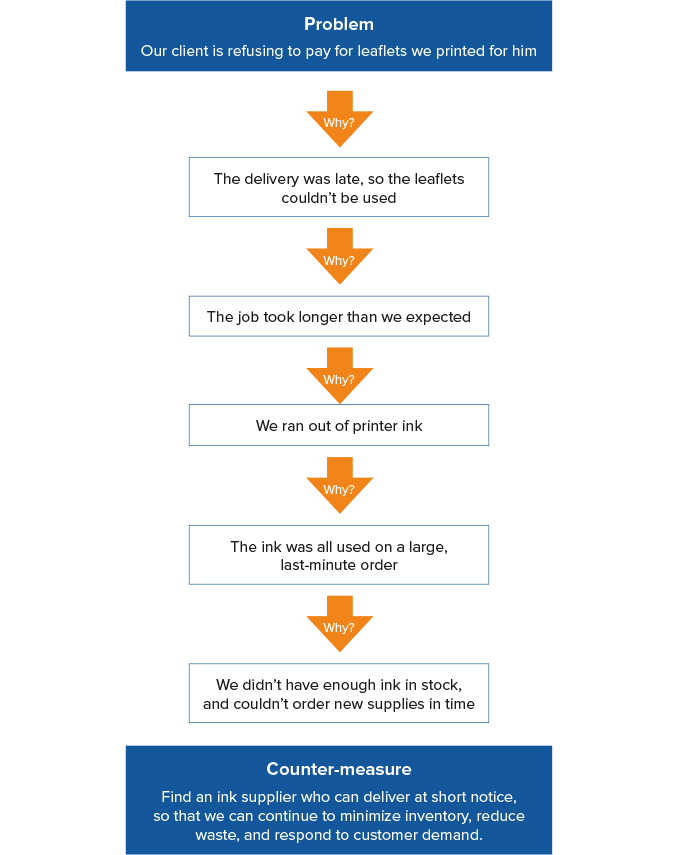
The 5 Whys method also allows you to follow multiple lanes of inquiry. An example of this is shown in Figure 2, below.
In our example, asking "Why was the delivery late?" produces a second answer (Reason 2). Asking "Why?" for that answer reveals a single reason (Reason 1), which you can address with a counter-measure.
Similarly, asking "Why did the job take longer than expected?" has a second answer (Reason 2), and asking "Why?" at this point reveals a single reason (Reason 1). Another "Why?" here identifies two possibilities (Reasons 1 and 2) before a possible counter-measure becomes evident.
There is also a second reason for "Why we ran out of printer ink" (Reason 2), and a single answer for the next "Why?" (Reason 1), which can then be addressed with a counter-measure.
Figure 2: 5 Whys Example (Multiple Lanes)
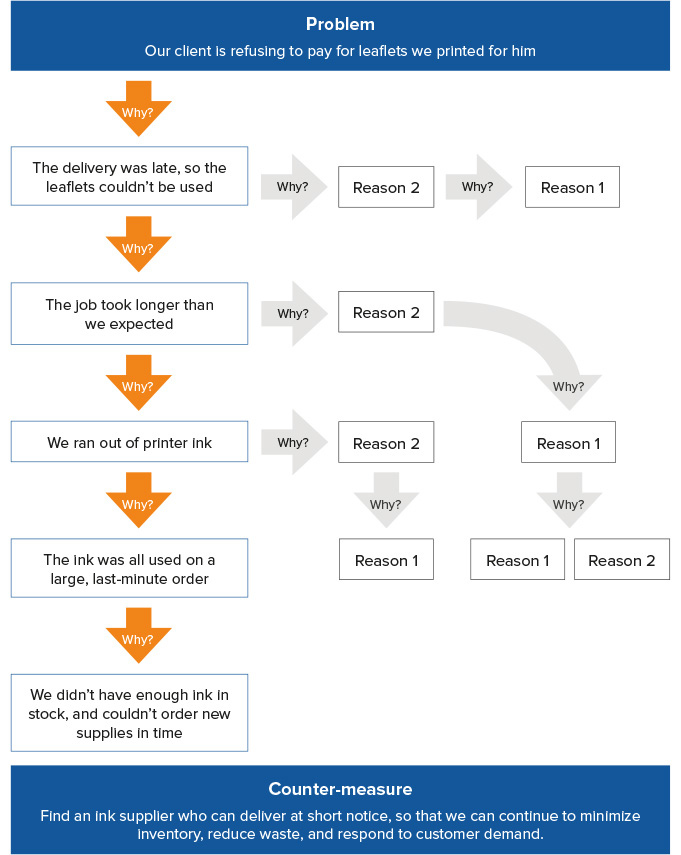
Step 5. Know When to Stop
You'll know that you've revealed the root cause of the problem when asking "why" produces no more useful responses, and you can go no further. An appropriate counter-measure or process change should then become evident. (As we said earlier, if you're not sure that you've uncovered the real root cause, consider using a more in-depth problem-solving technique like Cause and Effect Analysis , Root Cause Analysis , or FMEA .)
If you identified more than one reason in Step 3, repeat this process for each of the different branches of your analysis until you reach a root cause for each one.
The "5" in 5 Whys is really just a " rule of thumb ." In some cases, you may need to ask "Why?" a few more times before you get to the root of the problem.
In other cases, you may reach this point before you ask your fifth "Why?" If you do, make sure that you haven't stopped too soon, and that you're not simply accepting "knee-jerk" responses.
The important point is to stop asking "Why?" when you stop producing useful responses.
As you work through your chain of questions, you may find that someone has failed to take a necessary action. The great thing about 5 Whys is that it prompts you to go further than just assigning blame , and to ask why that happened. This often points to organizational issues or areas where processes need to be improved.
6. Address the Root Cause(s)
Now that you've identified at least one root cause, you need to discuss and agree on the counter-measures that will prevent the problem from recurring.
7. Monitor Your Measures
Keep a close watch on how effectively your counter-measures eliminate or minimize the initial problem. You may need to amend them, or replace them entirely. If this happens, it's a good idea to repeat the 5 Whys process to ensure that you've identified the correct root cause.
Appreciation
A similar question-based approach known as "appreciation" can help you to uncover factors in a situation that you might otherwise miss.
It was originally developed by the military to assist commanders in gaining a comprehensive understanding of any fact, problem or situation. But you can also apply it in the workplace.
Starting with a fact, you first ask the question, "So what?" – in other words, what are the implications of that fact? Why is this fact important?
You then continue asking that question until you've drawn all possible conclusions from it.
The major difference between this and the 5 Whys technique is that appreciation is often used to get the most information out of a simple fact or statement, while 5 Whys is designed to drill down to the root of a problem.
Bear in mind that appreciation can restrict you to one line of thinking. For instance, once you've answered your first "So what?" question, you might follow a single line of inquiry to its conclusion. To avoid this, repeat the appreciation process several times over to make sure that you've covered all bases.
The 5 Whys strategy is a simple, effective tool for uncovering the root of a problem. You can use it in troubleshooting, problem-solving, and quality-improvement initiatives.
Start with a problem and ask why it is occurring. Make sure that your answer is grounded in fact, and then ask the question again. Continue the process until you reach the root cause of the problem, and you can identify a counter-measure that will prevent it from recurring.
Bear in mind that this questioning process is best suited to simple or moderately difficult problems. Complex problems may benefit from a more detailed approach, although using 5 Whys will still give you useful insights.
Infographic
You can see our infographic on the 5 Whys method here:

This site teaches you the skills you need for a happy and successful career; and this is just one of many tools and resources that you'll find here at Mind Tools. Subscribe to our free newsletter , or join the Mind Tools Club and really supercharge your career!
Rate this resource
The Mind Tools Club gives you exclusive tips and tools to boost your career - plus a friendly community and support from our career coaches!

Comments (77)
- Over a month ago BillT wrote Hi hunyakvera, Thanks for your observant feedback. Sakichi Toyoda died in October of 1930, and is the creator of the 5 Whys. Also, he is stated as the founder of Toyota as he challenged his son to start a business that applied the principles of Lean and the 5 Whys. His son Kiichiro first continued with the loom company, and then decided he could do the same for any company, primarily a car company that he called Toyota. BillT Mind Tools Team
- Over a month ago hunyakvera wrote Hi! Great article. However Sakichi Toyoda died in the year 1930, so i don't see how he could have developed this technique in the 1930s. Either 1930 in his last year of life, or the date is wrong. Also, he wasn't the founder of Toyota. His son was. However, he was the founder of Toyoda companies, but not Toyota
- Over a month ago Midgie wrote Hi MGlasscock, Welcome to the Club! Indeed this 5 Whys approach is a great technique to get to the bottom of things! It would be great to meet you so come on over to the Forums and introduce yourself. Also if you have any questions, just let us know and we will be happy to help. Midgie Mind Tools Team
Please wait...

Worawut/Adobe Stock
By Jill Babcock Leaders Staff
Jill Babcock
Personal Development Writer
Jillian Babcock is a personal development writer for Leaders Media. Previously, she was a senior content writer at Ancient Nutrition,...
Learn about our editorial policy
Aug 8, 2023
Reviewed by Hannah L. Miller
Hannah L. Miller
Senior Editor
Hannah L. Miller, MA, is the senior editor for Leaders Media. Since graduating with her Master of Arts in 2015,...
The Power of the Five Whys: Drilling Down to Effectively Problem-Solve
What is the “5 whys” method, the power of asking “why”, when the 5 whys should be used, how to utilize the 5 whys technique, five whys examples, other ways of improving problem-solving.
It’s a fact of life that things don’t always go according to plan. When facing mistakes or challenges, asking “why”—especially if you do it repeatedly—can help uncover deeper layers of understanding so you can identify potential solutions.
The question “why” can be used in problem-solving as a powerful technique that helps us dig deeper, challenge assumptions, and think critically. After all, if you’re not sure why a problem exists in the first place, it’s very difficult to solve it.
The “Five Whys” method (also called “5 Whys Root Cause Analysis”) can specifically help in examining beliefs, behaviors, and patterns to shine a light on areas for improvement. The Five Whys have other benefits too, including encouraging collaboration and communication since this strategy promotes open dialogue among team members or partners. It also helps generate effective and lasting solutions that can prevent similar issues from resurfacing in the future.
In this article, learn how to use the Five Whys to save yourself or your company from wasting time and money and to address important issues at their source before they escalate.
The “Five Whys” is a technique commonly used in problem-solving to find the root causes of problems . This type of analysis can be applied to various situations, including within companies and relationships, to gain deeper insights and understandings of challenges and obstacles. The method involves “drilling down” by repeatedly asking “why”—typically five times or more—to get to the underlying causes or motivations behind a particular issue. Overall, it’s a way to figure out causes and effects related to a situation so that solutions can be uncovered.
“Effective problem solving can help organizations improve in every area of their business, including product quality, client satisfaction, and finances.” Jamie Birt , Career Coach
Here are a few reasons why asking “why,” or practicing the Five Whys, is important in problem-solving:
- Identifies underlying issues and root causes: Repeatedly asking “why” helps peel back the layers of a problem to get closer to the heart of what’s not working well. The goal is to define the real issue at hand to address its underlying causes. Understanding root causes is crucial because it enables you to address issues at their source rather than simply dealing with surface-level effects.
- Promotes critical thinking: Critical thinking refers to the process of objectively and analytically evaluating information, arguments, or situations. To engage in critical thinking and analysis, we need to ask “why,” usually over and over again. This encourages us to develop a more nuanced understanding of a problem by evaluating different factors, examining relationships, and considering different perspectives. Doing so helps lead to well-reasoned judgments and informed decisions.
- Uncovers assumptions: The opposite of assuming something is remaining open-minded and curious about it. Albert Einstein once said , “The important thing is not to stop questioning. Curiosity has its own reason for existing.” Asking “why” prompts you to challenge preconceived notions you may not even realize you have. Often, we make assumptions about a problem or its causes without having all the information we need. By gaining a fresh perspective, we can consider alternative solutions.
- Generates insights: The Five Whys can lead to valuable discoveries and potential fixes by uncovering hidden connections. These insights can guide us toward innovative solutions that prevent similar problems from worsening or happening again.
“Curiosity has been identified as a characteristic of high-performing salespeople, and having a tool and system that fosters curiosity in your team is extremely helpful.” Alexander Young, Forbes
Any time a problem needs to be clarified and solved, the Five Whys can help. This flexible technique can be adapted to different situations, including personal and professional ones. For example, it’s useful when there are complications within businesses that are causing a loss of profits or when arguments occur among family members or partners. Eric Ries from Harvard Business Review points out that start-ups can especially benefit from the Five Whys to test and refine procedures, ideas, products, and processes.
To get the most out of the Five Whys, include people with personal knowledge of the problem, processes, and systems involved in the analysis, such as employees and customers. This means that if a leadership team, for example, wants to use the Five Whys to improve customer engagement, actual customers and customer service representatives would be ideal people to include in the discussion.
Here are examples of situations in which the Five Whys can be utilized:
- Troubleshooting business processes or operations issues, such as delivery or customer service concerns.
- Identifying the reasons behind personal challenges or recurring problems, such as disputes between bosses and employees.
- Analyzing project failures or setbacks, such as missed deadlines, to find underlying causes.
- Understanding customer complaints or dissatisfaction to improve products or services.
- Improving communication, teamwork, and client relationships.
Sakichi Toyoda (1867–1930) was a Japanese inventor and industrialist known for his business ventures, including founding the Toyota Motor Corporation. Toyoda is credited with developing the Five Whys method in the 1930s, which he used to support continuous improvement within his companies .
For example, within Toyota Production System (TPS), key goals included eliminating waste, improving efficiency, and ensuring quality. Toyoda used the Five Whys to identify problems within his company and to find ways to resolve them to improve production and customer satisfaction. He once stated , “By repeating why five times, the nature of the problem as well as its solution becomes clear.”
“The beauty of the [Five Whys] tool is in its simplicity. Not only is it universally applicable, it also ensures that you don’t move to action straight away without fully considering whether the reason you’ve identified really is the cause of the problem.” Think Design
The Five Whys works by drilling down to a main underlying cause. The answer to the first “why” should prompt another “why,” and then the answer to the second “why” should continue to prompt more “whys” until a root cause is identified.
Follow these steps to implement the Five Whys:
1. Identify the Initial Problem: Clearly define the problem you want to address. Be specific, such as by including details that help with the analysis. Make sure to clearly articulate the issue by breaking it down into smaller components to ensure everyone involved has a thorough understanding of the situation.
2. Ask “Why?”: Start by asking why the problem occurred. Answer your own question. The answer becomes the basis for the next “why” question.
3. Repeat the Process Five or More Times: Continue asking “why” about the previous answer, iterating at least five times or until you reach a point where the root cause of the problem becomes apparent.
4. Analyze and Take Action: Once you have identified the root cause, analyze potential solutions and take appropriate action.
Here’s a template that you can use to make the process simple:
Problem Statement: (One sentence description of the main problem)
- Why is the problem happening? (Insert answer)
- Why is the answer above happening? (Insert answer)
Root Cause(s)
To test if the root cause is correct, ask yourself the following: “If you removed this root cause, would this problem be resolved?”
Potential Solutions:
List one or more ways you can resolve the root cause of the problem.
The Five Whys method is not a rigid rule but rather a flexible framework that can be adjusted based on the complexity of the problem. You may need to ask “why” only three times or more than five times, such as 7 to 9 times, to nail down the main underlying cause. It’s not the exact amount of “whys” you ask that matters, more so that you’re really investigating the situation and getting to the root of the issue.
Here are two examples of how the Five Whys technique can be used to problem-solve:
Example 1: Machine Breakdown
- Problem Statement: A machine in a manufacturing facility keeps breaking down.
- Why did the machine break down? The motor overheated.
- Why did the motor overheat? The cooling system failed.
- Why did the cooling system fail? The coolant pump malfunctioned.
- Why did the coolant pump malfunction? It wasn’t properly maintained.
- Why wasn’t the coolant pump properly maintained? There was no regular maintenance schedule in place.
- Root Cause: The lack of a regular maintenance schedule led to the coolant pump malfunction and subsequent machine breakdown.
- Solution: Implement a scheduled maintenance program for all machines to ensure proper upkeep and prevent breakdowns.
Example 2: Orders Not Being Fulfilled On Time
- Problem Statement: The order fulfillment process in an e-commerce company is experiencing delays.
- Why are there delays in the order fulfillment process? The warehouse staff is spending excessive time searching for products.
- Why are they spending excessive time searching for products? The products are not organized efficiently in the warehouse.
- Why are the products not organized efficiently? There is no standardized labeling system for product placement.
- Why is there no standardized labeling system? The inventory management software does not support it.
- Why doesn’t the inventory management software support a labeling system? The current software version is outdated and lacks the necessary features.
- Root Cause: The use of outdated inventory management software lacking labeling functionality leads to inefficient product organization and delays in the order fulfillment process.
- Solution: Upgrade the inventory management software to a newer version that supports a standardized labeling system, improving product organization and streamlining the order fulfillment process.
“Great leaders are, at their core, great problem-solvers. They take proactive measures to avoid conflicts and address issues when they arise.” Alison Griswold , Business and Economics Writer
Problem-solving is a skill that can be developed and improved over time. The Five Whys method is most effective when used in conjunction with other problem-solving tools and when utilized in a collaborative environment that encourages open communication and a willingness to honestly explore underlying causes. For the method to work well, “radical candor” needs to be utilized, and constructive feedback needs to be accepted.
Here are other strategies to assist in problem-solving, most of which can be used alongside the Five Whys:
- Gather and analyze information: Collect relevant data, facts, and information related to the problem. This could involve conducting research, talking to experts, or analyzing past experiences. Examine the information you’ve gathered and identify patterns, connections, and potential causes of the problem. Look for underlying factors and consider both the immediate and long-term implications.
- Have a brainstorming session: Collaborate with colleagues, seek advice from experts, or gather input from stakeholders. Different perspectives can bring fresh ideas. Gather a group of teammates and get out a whiteboard and a marker. Create a list of opportunities or problems and potential solutions. Encourage creativity and think outside the box. Consider different perspectives and approaches.
- Draw a cause-and-effect diagram: Make a chart with three columns, one each for challenges, causes, and effects. Use this to come up with solutions, then assess the pros and cons of each potential solution by considering the feasibility, potential risks, and benefits associated with each option.
- Develop an action plan: Once you’ve selected the best solution(s), create a detailed action plan. Define the steps required to implement the solution, set timelines, and then track your progress.
Want to learn more about problem-solving using critical thinking? Check out this article:
Use Critical Thinking Skills to Excel at Problem-Solving
Leaders Media has established sourcing guidelines and relies on relevant, and credible sources for the data, facts, and expert insights and analysis we reference. You can learn more about our mission, ethics, and how we cite sources in our editorial policy .
- American Institute of Physics. Albert Einstein Image and Impact . History Exhibit. https://history.aip.org/exhibits/einstein/ae77.htm
- Indeed. 5 Whys Example: A Powerful Problem-Solving Tool for Career Development. Indeed Career Guide. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/5-whys-example
- Entrepreneur. 3 Steps to Creating a Culture of Problem Solvers . Entrepreneur – Leadership. https://www.entrepreneur.com/leadership/3-steps-to-creating-a-culture-of-problem-solvers/436071
- Harvard Business Review. (2010, April). The Five Whys for Startups. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2010/04/the-five-whys-for-startups
- Forbes. (2021, June 7). Understanding The Five Whys: How To Successfully Integrate This Tool Into Your Business . Forbes – Entrepreneurs. https://www.forbes.com/sites/theyec/2021/06/07/understanding-the-five-whys-how-to-successfully-integrate-this-tool-into-your-business/?sh=5eda43675c18
- Think Design. Five Whys: Get to the Root of Any Problem Quickly. Think Design – User Design Research. https://think.design/user-design-research/five-whys
- Business Insider. (2013, November). The Problem-Solving Tactics of Great Leaders. Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/problem-solving-tactics-of-great-leaders-2013-11
Search Leaders.com

Root Cause Analysis – The 5 Whys Technique
This elementary and often effective approach to problem-solving promotes deep thinking through questioning, and can be adapted quickly and applied to most problems. For example, asking “Why?” may be a favorite technique of your three-year-old child in driving you crazy, but it could teach you a valuable problem-solving technique.
“If you don’t ask the right questions, you don’t get the right answers. A question asked in the right way often points to its answer. Asking questions is the ABC of diagnosis. Only the inquiring mind solves problems.” – Edward Hodnett
The “5 Whys” is a simple problem-solving technique that helps you to get to the root of a problem quickly, which was originally developed by Sakichi Toyota. It was used within the Toyota Motor Corporation during the evolution of its manufacturing methodologies. It is a critical component of problem-solving training, delivered as part of the induction into the Toyota Production System.
How to Conduct 5 Whys Analysis?
When you’re looking to solve a problem, start at the result and work backward (toward the root cause), continually asking: “Why?” You’ll need to repeat this over and over until the root cause of the problem becomes apparent.
The 5 Whys strategy involves looking at any problem and asking: “Why?” and “What caused this problem?” Very often, the answer to the first “why” will prompt another “why” and the answer to the second “why” will prompt another and so on; hence the name the 5 Whys strategy.
The 5 Whys exercise is vastly improved when applied by a team and there are five basic steps to conducting it:
- Write down the specific problem. Writing the issue helps you formalize the problem and describe it completely. It also helps a team focus on the same problem.
- Ask “Why” the problem happens and write the answer down below the problem.
- If the answer you just provided doesn’t identify the root cause of the problem that you wrote down in Step 1, ask “Why” again and write that answer down.
- Loopback to step 3 until the team is in agreement that the problem’s root cause is identified. Again, this may take fewer or more times than five Whys.
- After settling on the most probable root cause of the problem and obtaining confirmation of the logic behind the analysis, develop appropriate corrective actions to remove the root cause from the system.
Edit this Diagram
5 Whys Example
The vehicle will not start. (The problem)
- Why? – The battery is dead. (First why)
- Why? – The alternator is not functioning. (Second why)
- Why? – The alternator belt has broken. (Third why)
- Why? – The alternator belt was well beyond its useful service life and not replaced. (Fourth why)
- Why? – The vehicle was not maintained according to the recommended service schedule. (Fifth why, a root cause)
Note: A 5 Whys analysis sometime could be taken further to a sixth, seventh, or higher level, but five iterations of asking why are generally sufficient to get to a root cause.
5-Whys Criticisms
Here are each of the criticisms as listed on the Wikipedia:
- Stopping at symptoms, not the root cause
- Limited by the investigator’s knowledge.
- Not asking the right Why questions.
- Not repeatable – Different people build different 5 Whys.
- The tendency to isolate a single root cause
©2024 by Visual Paradigm. All rights reserved.
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Security Overview
- Guide: 5 Whys
Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is an experienced continuous improvement manager with a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt and a Bachelor's degree in Business Management. With more than ten years of experience applying his skills across various industries, Daniel specializes in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. His approach combines practical experience with a deep understanding of business fundamentals to drive meaningful change.
- Last Updated: May 9, 2023
- Learn Lean Sigma
5 Whys is a problem-solving technique used to get to the root cause of problems by asking the question of Why multiple times, but often 5 times giving it the name “5 Whys”. This allows people to address the root cause of issues instead of the symptoms of the root causes which is often what is seen as the problem.
Like a doctor diagnosing an issue such as neck pain, a painkiller will only address the symptoms of the neck pain and not the root cause of the pain. By getting to the root cause you can ensure a long-term fix to the root cause of the neck pain which could be caused by seating positions and not taking painkillers which is a short-term fix.
Table of Contents
What is the 5 whys.
The 5 Whys is a root cause analysis problem-solving technique that aims to identify the root cause of a problem by repeatedly asking the question “Why?” five times or until the core issue is unveiled. Developed within the Toyota Production System , it’s one of fundamental tools in the Lean Six Sigma methodology.
Here’s how it works:
- Begin with a clear and concise problem statement.
- Ask “Why?” the problem occurred. Document the answer.
- If this answer doesn’t identify the root cause, ask “Why?” again and document the subsequent answer.
- Continue this process until you’ve either asked “Why?” five times or the root cause has been identified.
Lets go through an example, let’s say a machine stopped working:
- Why? – The machine’s fuse blew.
- Why? – The machine was overloaded.
- Why? – There wasn’t adequate training on machine capacity.
- Why? – Training materials were outdated.
- Why? – There’s no review process for updating training materials.
In this case, the root cause is the lack of a review process for training materials, and addressing this will prevent similar issues in the future. Only treating the symptom in this situation would have been to change the fuse, for it then to regularly blow and cause additional downtime.
This is a good example where a machine stopping working’s root cause is cause by an issue what would not be obvious is first glace at the symptom of the problem and provides a clear example that root cause analysis is important to ensure that solutions are not jumped to before a through root cause analysis is conducted.
Why is the 5 Whys Important?
Understanding the 5 Whys is important because identifying symptoms of a problem is not the same as uncovering its root cause. If you only address symptoms this provides only temporary solution to the problem. However, understanding and resolving the root cause can prevent the issue from reoccurring.
The 5 Whys Problem-Solving technique is also useful for:
- Problem Prevention: By identifying the root cause of the problem, businesses can implement long-term solutions, leading to more robust systems and processes and prevent the problem reoccurring.
- Cost-Efficiency: Addressing root causes is often more cost-effective in the long run as it prevents recurrence and the associated costs of repeated problem-solving which usually involves the same people constantly firefighting the same issues such as repeated machine breakdowns.
- Improved Processes: Regular use of the 5 Whys to identify the root causes of problems can highlight weaknesses in processes, leading to continuous improvement and optimization processes.
- Empowerment: The use of 5 Whys by individuals a positive culture that promotes a deeper understanding of systems and processes, empowering teams to take ownership and responsibility in addressing issues.
How to Conduct a 5 Whys Root Cause Analysis?
Step 1: define the problem.
This is an important step as if the problem is not defined effectively it could result in focusing in the wrong problem. A good method for this could be to use the 5W1H Is/Is Not Problem solving technique to gain a common understanding of that the problem is.
When stating the problem you are going to conduct a 5 Whys on it is important to be specific about the issue and avoid ambiguous descriptions. Additionally, where data and information is available this should be collected and used as evidence that points to the actual problem rather than opinions of the problem.
Step 2: Ask the First “Why?”
Now you have a clear problem definition you should ask the question “Why did that happen?” This should be done to understand the problem without making assumptions and should be done with supporting facts and data that backs up the initial answer to the question.
Step 3: Continue to Ask Why?
Now you should have an answer to the first why. This should form the next step and ask why did that happen. This ensures you dont settle for the inisital surface-level answer or symptoms of the real problem and pushes you to understand the underlying issues.
When you continue to ask why you should:
- Continuously question the previous answer
- Challenge answer that seem like assumptions and lack evidence to support them to avoid going down the wrong route.
Step 4: Continue the Process
- Keep the questioning focused on the problem
- If you feel the questioning is going off track revert back to what the initial problem definition.
- Ensure each answer provided logically leads to the next “Why?”
- The 5 Whys process then concludes when further questions leads to no further valuable answers are given or the when the root cause of the issues becomes clear.
Step 5 Implement Solutions
Once you have identified the root cause the you need to address it by implementing a solution to prevent the problem reoccuring.
This should be a case of developing an actionable solution that address the root cause of the issue and not preventing the symptoms as addressing the symptom will likely cause the issue to reappear elsewhere.
Make sure you test the solutions to ensure they are effective in addressing the root cause, you should then continue to monitor the process over time to confirm the problem did not reappear in the same place or elsewhere.
If the problem does not re appear congratulations you have solved the problem!
An Example of 5 Whys Analysis
Below is a good example of a 5 Whys analysis done in a situation where there was a production downtime.
To summarize, the 5 Whys process is an effective problem-solving tool that can assist businesses in identifying the root cause of a problem and developing effective solutions. Teams can delve deep into underlying issues and develop targeted solutions that address the root cause of the problem by asking “why” multiple times.
The five steps of the 5 Whys process – defining the problem, asking “why” once, asking “why” more times, developing a solution, implementing the solution, provide a clear framework for problem-solving and can help ensure that the problem is effectively resolved. The 5 Whys process encourages teams to think critically and systematically, resulting in long-term solutions that are effective, targeted, and sustainable.
- Benjamin, S.J., Marathamuthu, M.S. and Murugaiah, U., 2015. The use of 5-WHYs technique to eliminate OEE’s speed loss in a manufacturing firm. Journal of Quality in Maintenance Engineering , 21 (4), pp.419-435.
A: The 5 Whys technique is a problem-solving method that involves asking “why” multiple times to uncover the root cause of a problem or issue.
A: The 5 Whys technique involves repeatedly asking “why” to identify the underlying cause of a problem. After asking “why” five times or until the root cause is revealed, you can develop effective solutions to address the issue.
A: The primary purpose of the 5 Whys technique is to identify and address the root cause of a problem. It helps organizations and individuals go beyond surface-level symptoms and understand the deeper issues affecting their processes or systems.
A: The 5 Whys technique is best used when you encounter a problem or issue that needs to be resolved. It is particularly useful for complex problems, recurring issues, or situations where multiple factors contribute to the problem.
A: Yes, the 5 Whys technique can be applied to any industry or field. It is commonly used in manufacturing, engineering, healthcare, software development, project management, and various other sectors.
A: While the technique is called the “5 Whys,” the number of “whys” you need to ask may vary. The goal is to keep asking “why” until you reach the root cause of the problem, which may require more or fewer than five iterations.
A: Yes, there are a few limitations to consider when using the 5 Whys technique. It relies on the skill and knowledge of the people involved, and it may oversimplify complex problems. Additionally, it assumes a linear cause-and-effect relationship, which may not always be accurate.
A: Yes, the 5 Whys technique can be used in a group setting. In fact, involving multiple perspectives can enhance the effectiveness of the technique and lead to more comprehensive problem-solving.
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Download Template
Free lean six sigma templates.
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.
Other Guides

5 Whys is the practice of asking why repeatedly whenever a problem is encountered in order to get beyond the obvious symptoms to discover the root cause.
For instance, Taiichi Ohno gives this example about a machine that stopped working (Ohno 1988, p. 17):
- Why did the machine stop? There was an overload and the fuse blew.
- Why was there an overload? The bearing was not sufficiently lubricated.
- Why was it not lubricated? The lubrication pump was not pumping sufficiently.
- Why was it not pumping sufficiently? The shaft of the pump was worn and rattling.
- Why was the shaft worn out? There was no strainer attached and metal scraps got in.
Without repeatedly asking why, managers would simply replace the fuse or pump and the failure would recur. The specific number five is not the point. Rather it is to keep asking until the root cause is reached and eliminated.
5 Whys Illustrated
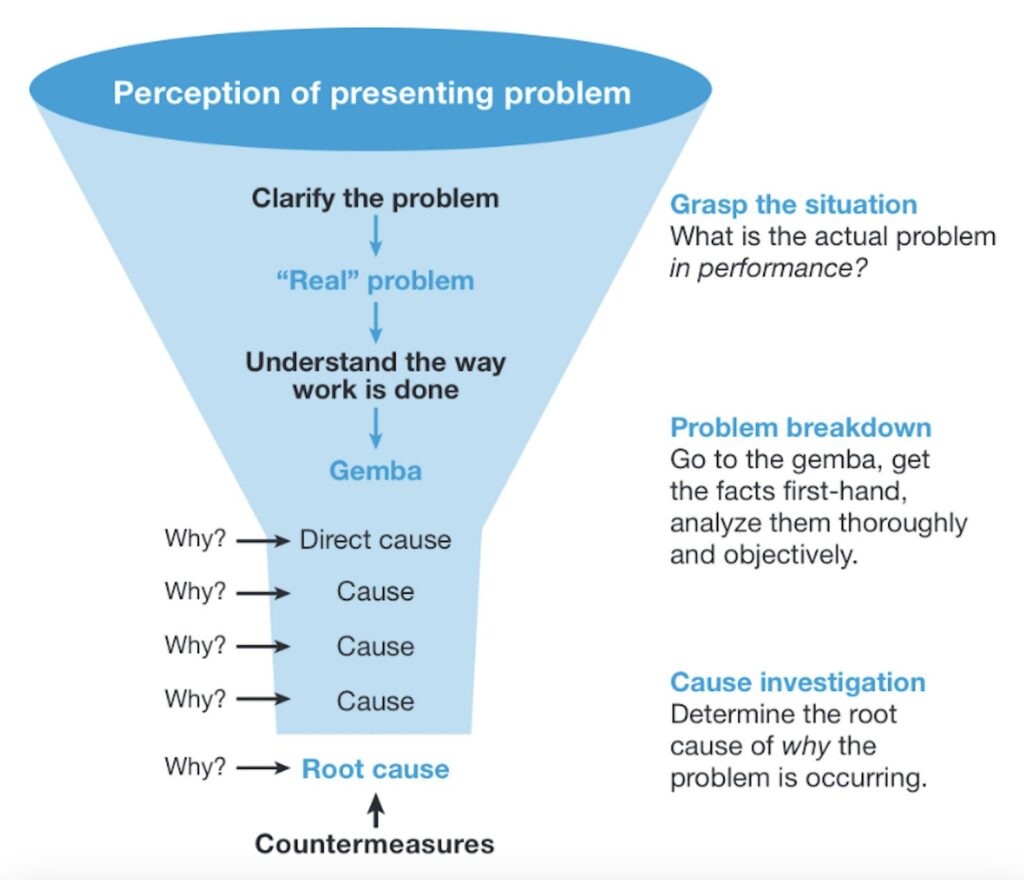
When to Use the 5 Whys
Management should use the 5 Why problem-solving method with Gap from Standard problems. This is problem-solving that focuses on:
- specific problem definition
- setting goals
- root cause analysis
- establishment of countermeasures
- checks, standards, and follow-up activities
The aim is to prevent the problem from recurring by eliminating its underlying causes.
In general, there are three types of root-cause analysis:
- One-variable-at-a-time (OVAT)
- Multivariate-at-a-time (MVAT)
No advanced math skills are required for logic-based analysis such as 5 Whys. However, the ability to think critically, especially in terms of inductive logic (broad generalization from specific observation), deductive logic (general premise to specific conclusion), and abductive logic (general observation to hypothesis), is necessary.
Art of Lean on Problem-Solving Video Series with Art Smalley

Take a deep dive into problem-solving in this eight-part video series by expert Art Smalley.
- Coaching Problem-Solving
- Lessons from NBA Coaches
- Lessons from Martial-Arts
- Military and Science Leadership
- Tuckman’s Model of Team Formation
- Team-Building Tools and Practices
- Dreyfus Model and Stages of Learning
- Toyota Coaching Practices
Additional Resources
- Gemba Coach: 5 Whys
- Approaching Problem-Solving More Effectively
- Change Your “Pet” Problem-Solving Method
See: Kaizen ; Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA)
Privacy Overview
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The 5 Whys strategy is a simple, effective tool for uncovering the root of a problem. You can use it in troubleshooting, problem-solving, and quality-improvement initiatives. Start with a problem and ask why it is occurring. Make sure that your answer is grounded in fact, and then ask the question again.
Tips for Mastering the 5 Whys Technique Encouraging Open Communication. In mastering the 5 Whys Technique as a problem-solving method, creating an environment that fosters open communication is paramount. When team members feel comfortable expressing their perspectives and insights, it leads to a more comprehensive exploration of the underlying ...
Five whys (or 5 whys) is an iterative interrogative technique used to explore the cause-and-effect relationships underlying a particular problem. The primary goal of the technique is to determine the root cause of a defect or problem by repeating the question "Why?" five times. The answer to the fifth why should reveal the root cause of the problem.
An in-depth look at the 5 Whys, a simple problem-solving exercise designed to unearth the root of any problem or unexpected situation. ... Here's an example Toyota offers of a potential 5 Whys that might be used at one of their plants. Today, the method is used far beyond Toyota, and it's particularly popular in the world of lean ...
The 5 Whys is a problem-solving technique used to explore the cause-and-effect relationship that leads to a particular problem. The name derives from the method's frequent utilization of the question "Why?" This repeating question is used to determine the root cause of a problem by repeating why the problem occurs five times.
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a common process for discovering the origin of a business problem. While there are many RCA problem-solving techniques, one popular and easy technique is the 5 Whys method. Performing a 5 Whys analysis is one of the most efficient ways to both discover the root cause of a problem and ensure that steps are taken to ...
The 5 Whys framework is a problem-solving technique used to identify the root cause of a problem. It's a simple but powerful way to uncover the underlying reasons behind a problem by asking the question "why" repeatedly. By doing so, you can delve beyond the symptoms and surface-level causes of a problem and reach the fundamental cause ...
The " 5 Whys " is a Problem-Solving method that identifies Root Causes of Problems by asking five consecutive times: "Why this happened?". It Starts with the most obvious "Symptom" (or Issue) and Forces the analyst to wonder Why it happened. Once the Analyst has a first Explanation, he/she has to repeat this cycle 4 more times.
3 benefits of the 5 Whys. This technique has been around since the 1930s. It has been shown to work and can be successfully applied to many situations. 1. It is a simple yet powerful tool. With just the use of a flip chart and a few markers, a group of people can usually get to the root cause of a problem relatively quickly. 2. Asking "why ...
Importance of 5 Whys Analysis. The 5 Whys technique is a simple and powerful tool for solving problems. Its main goal is to track down the exact reason that causes a given issue by asking a sequence of "Why" questions. The 5 Whys method assists your team focus on finding the root cause of any problem.
The 5 Whys is a popular problem-solving method that individuals and teams use to understand the potential causes of a specific issue. Years ago, Toyota developed the approach to help them get at the heart of complex mechanical issues, so you know it's legitimate! The technique is easy to use: you ask why a problem happened, and then you ask ...
The Five Whys technique promotes deep thinking through questioning and can be applied to most problems. It is more effective when used in a team (preferably cross-functional) and has five basic steps: 1. Forming the Team and defining the problem statement. Gather the team and develop the problem statement in agreement.
Five whys (5 whys) is a problem-solving method that explores the underlying cause-and-effect of particular problems. The primary goal is to determine the root cause of a defect or a problem by successively asking the question "Why?". The number '5' here comes from the anecdotal observation that five iterations of asking why is usually sufficient enough to reveal the root cause.
The five whys method is a problem-solving technique that helps you get to the root cause of a problem. Using this technique, you'll uncover cause and effect relationships and ultimately uncover how processes and projects can be improved in the future. The premise of the five whys is fairly straightforward: You'll ask "why?" five times ...
The 5 Whys strategy is a simple, effective tool for uncovering the root of a problem. You can use it in troubleshooting, problem-solving, and quality-improvement initiatives. Start with a problem and ask why it is occurring. Make sure that your answer is grounded in fact, and then ask the question again. Continue the process until you reach the ...
The five whys and five hows techniques constitute a questioning process designed to drill down into the details of a problem or a solution and peel away the layers of symptoms. The technique was originally developed by Sakichi Toyoda who stated that "by repeating why five times, the nature of the problem as well as its solution becomes clear ...
The "Five Whys" is a technique commonly used in problem-solving to find the root causes of problems. This type of analysis can be applied to various situations, including within companies and relationships, to gain deeper insights and understandings of challenges and obstacles. The method involves "drilling down" by repeatedly asking ...
The "5 Whys" is a simple problem-solving technique that helps you to get to the root of a problem quickly, which was originally developed by Sakichi Toyota. It was used within the Toyota Motor Corporation during the evolution of its manufacturing methodologies. It is a critical component of problem-solving training, delivered as part of the ...
The 5 Whys Problem-Solving technique is also useful for: Problem Prevention: By identifying the root cause of the problem, businesses can implement long-term solutions, leading to more robust systems and processes and prevent the problem reoccurring. Cost-Efficiency: Addressing root causes is often more cost-effective in the long run as it prevents recurrence and the associated costs of ...
Management should use the 5 Why problem-solving method with Gap from Standard problems. This is problem-solving that focuses on: specific problem definition. setting goals. root cause analysis. establishment of countermeasures. checks, standards, and follow-up activities. The aim is to prevent the problem from recurring by eliminating its ...
The 5 Whys technique is a simple method aiming to get to the root cause of various issues. Knowing how to apply the 5 Whys technique can enable you to address problems more effectively and find lasting solutions. In this article, we show you how to use the 5 Whys technique for more efficient problem solving and provide an example line of ...
Effective problem solving can help organizations improve in every area of their business, including product quality, client satisfaction and finances. The five whys method offers a simple, focused strategy for finding the root cause of a problem with minimal cost. In this article, we discuss what the five whys technique is and how to use it, plus share examples of businesses using the five ...
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective tool. The method "5 Whys" is named as such because it involves asking "why" repeatedly to delve deeper into the layers of a problem or issue to uncover its root cause. By asking "why" multiple times (typically five times), the method aims to encourage deeper investigation beyond the symptoms or ...
The 5 Whys. byHyper Island. # hyperisland # innovation. 30 - 602 - 10Low. This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question "why" five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem ...
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results. By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
DMAIC is an acronym that stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It represents the five phases that make up the process: Define the problem, improvement activity, opportunity for improvement, the project goals, and customer (internal and external) requirements.