Students & Educators —Menu
- Educational Resources
- Educators & Faculty
- College Planning
- ACS ChemClub
- Project SEED
- U.S. National Chemistry Olympiad
- Student Chapters
- ACS Meeting Information
- Undergraduate Research
- Internships, Summer Jobs & Coops
- Study Abroad Programs
- Finding a Mentor
- Two Year/Community College Students
- Social Distancing Socials
- Planning for Graduate School
- Grants & Fellowships
- Career Planning
- International Students
- Planning for Graduate Work in Chemistry
- ACS Bridge Project
- Graduate Student Organizations (GSOs)
- Schedule-at-a-Glance
- Standards & Guidelines
- Explore Chemistry
- Science Outreach
- Publications
- ACS Student Communities
- You are here:
- American Chemical Society
- Students & Educators

Writing the Research Plan for Your Academic Job Application
By Jason G. Gillmore, Ph.D., Associate Professor, Department of Chemistry, Hope College, Holland, MI
A research plan is more than a to-do list for this week in lab, or a manila folder full of ideas for maybe someday—at least if you are thinking of a tenure-track academic career in chemistry at virtually any bachelor’s or higher degree–granting institution in the country. A perusal of the academic job ads in C&EN every August–October will quickly reveal that most schools expect a cover letter (whether they say so or not), a CV, a teaching statement, and a research plan, along with reference letters and transcripts. So what is this document supposed to be, and why worry about it now when those job ads are still months away?
What Is a Research Plan?
A research plan is a thoughtful, compelling, well-written document that outlines your exciting, unique research ideas that you and your students will pursue over the next half decade or so to advance knowledge in your discipline and earn you grants, papers, speaking invitations, tenure, promotion, and a national reputation. It must be a document that people at the department you hope to join will (a) read, and (b) be suitably excited about to invite you for an interview.
That much I knew when I was asked to write this article. More specifics I only really knew for my own institution, Hope College (a research intensive undergraduate liberal arts college with no graduate program), and even there you might get a dozen nuanced opinions among my dozen colleagues. So I polled a broad cross-section of my network, spanning chemical subdisciplines at institutions ranging from small, teaching-centered liberal arts colleges to our nation’s elite research programs, such as Scripps and MIT. The responses certainly varied, but they did center on a few main themes, or illustrate a trend across institution types. In this article I’ll share those commonalities, while also encouraging you to be unafraid to contact a search committee chair with a few specific questions, especially for the institutions you are particularly excited about and feel might be the best fit for you.
How Many Projects Should You Have?

While more senior advisors and members of search committees may have gotten their jobs with a single research project, conventional wisdom these days is that you need two to three distinct but related projects. How closely related to one another they should be is a matter of debate, but almost everyone I asked felt that there should be some unifying technique, problem or theme to them. However, the projects should be sufficiently disparate that a failure of one key idea, strategy, or technique will not hamstring your other projects.
For this reason, many applicants wisely choose to identify:
- One project that is a safe bet—doable, fundable, publishable, good but not earthshaking science.
- A second project that is pie-in-the-sky with high risks and rewards.
- A third project that fits somewhere in the middle.
Having more than three projects is probably unrealistic. But even the safest project must be worth doing, and even the riskiest must appear to have a reasonable chance of working.
How Closely Connected Should Your Research Be with Your Past?
Your proposed research must do more than extend what you have already done. In most subdisciplines, you must be sufficiently removed from your postdoctoral or graduate work that you will not be lambasted for clinging to an advisor’s apron strings. After all, if it is such a good idea in their immediate area of interest, why aren’t they pursuing it?!?
But you also must be able to make the case for why your training makes this a good problem for you to study—how you bring a unique skill set as well as unique ideas to this research. The five years you will have to do, fund, and publish the research before crafting your tenure package will go by too fast for you to break into something entirely outside your realm of expertise.
Biochemistry is a partial exception to this advice—in this subdiscipline it is quite common to bring a project with you from a postdoc (or more rarely your Ph.D.) to start your independent career. However, you should still articulate your original contribution to, and unique angle on the work. It is also wise to be sure your advisor tells that same story in his or her letter and articulates support of your pursuing this research in your career as a genuinely independent scientist (and not merely someone who could be perceived as his or her latest "flunky" of a collaborator.)
Should You Discuss Potential Collaborators?
Regarding collaboration, tread lightly as a young scientist seeking or starting an independent career. Being someone with whom others can collaborate in the future is great. Relying on collaborators for the success of your projects is unwise. Be cautious about proposing to continue collaborations you already have (especially with past advisors) and about starting new ones where you might not be perceived as the lead PI. Also beware of presuming you can help advance the research of someone already in a department. Are they still there? Are they still doing that research? Do they actually want that help—or will they feel like you are criticizing or condescending to them, trying to scoop them, or seeking to ride their coattails? Some places will view collaboration very favorably, but the safest route is to cautiously float such ideas during interviews while presenting research plans that are exciting and achievable on your own.
How Do You Show Your Fit?
Some faculty advise tailoring every application packet document to every institution to which you apply, while others suggest tweaking only the cover letter. Certainly the cover letter is the document most suited to introducing yourself and making the case for how you are the perfect fit for the advertised position at that institution. So save your greatest degree of tailoring for your cover letter. It is nice if you can tweak a few sentences of other documents to highlight your fit to a specific school, so long as it is not contrived.
Now, if you are applying to widely different types of institutions, a few different sets of documents will certainly be necessary. The research plan that you target in the middle to get you a job at both Harvard University and Hope College will not get you an interview at either! There are different realities of resources, scope, scale, and timeline. Not that my colleagues and I at Hope cannot tackle research that is just as exciting as Harvard’s. However, we need to have enough of a niche or a unique angle both to endure the longer timeframe necessitated by smaller groups of undergraduate researchers and to ensure that we still stand out. Furthermore, we generally need to be able to do it with more limited resources. If you do not demonstrate that understanding, you will be dismissed out of hand. But at many large Ph.D. programs, any consideration of "niche" can be inferred as a lack of confidence or ambition.
Also, be aware that department Web pages (especially those several pages deep in the site, or maintained by individual faculty) can be woefully out-of-date. If something you are planning to say is contingent on something you read on their Web site, find a way to confirm it!
While the research plan is not the place to articulate start-up needs, you should consider instrumentation and other resources that will be necessary to get started, and where you will go for funding or resources down the road. This will come up in interviews, and hopefully you will eventually need these details to negotiate a start-up package.
Who Is Your Audience?
Your research plan should show the big picture clearly and excite a broad audience of chemists across your sub-discipline. At many educational institutions, everyone in the department will read the proposal critically, at least if you make the short list to interview. Even at departments that leave it all to a committee of the subdiscipline, subdisciplines can be broad and might even still have an outside member on the committee. And the committee needs to justify their actions to the department at large, as well as to deans, provosts, and others. So having at least the introduction and executive summaries of your projects comprehensible and compelling to those outside your discipline is highly advantageous.
Good science, written well, makes a good research plan. As you craft and refine your research plan, keep the following strategies, as well as your audience in mind:
- Begin the document with an abstract or executive summary that engages a broad audience and shows synergies among your projects. This should be one page or less, and you should probably write it last. This page is something you could manageably consider tailoring to each institution.
- Provide sufficient details and references to convince the experts you know your stuff and actually have a plan for what your group will be doing in the lab. Give details of first and key experiments, and backup plans or fallback positions for their riskiest aspects.
- Hook your readers with your own ideas fairly early in the document, then strike a balance between your own new ideas and the necessary well referenced background, precedents, and justification throughout. Propose a reasonable tentative timeline, if you can do so in no more than a paragraph or two, which shows how you envision spacing out the experiments within and among your projects. This may fit well into your executive summary
- Show how you will involve students (whether undergraduates, graduate students, an eventual postdoc or two, possibly even high schoolers if the school has that sort of outreach, depending on the institutions to which you are applying) and divide the projects among students.
- Highlight how your work will contribute to the education of these students. While this is especially important at schools with greater teaching missions, it can help set you apart even at research intensive institutions. After all, we all have to demonstrate “broader impacts” to our funding agencies!
- Include where you will pursue funding, as well as publication, if you can smoothly work it in. This is especially true if there is doubt about how you plan to target or "market" your research. Otherwise, it is appropriate to hold off until the interview to discuss this strategy.
So, How Long Should Your Research Plan Be?

Learn more on the Blog
Here is where the answers diverged the most and without a unifying trend across institutions. Bottom line, you need space to make your case, but even more, you need people to read what you write.
A single page abstract or executive summary of all your projects together provides you an opportunity to make the case for unifying themes yet distinct projects. It may also provide space to articulate a timeline. Indeed, many readers will only read this single page in each application, at least until winnowing down to a more manageable list of potential candidates. At the most elite institutions, there may be literally hundreds of applicants, scores of them entirely well-suited to the job.
While three to five pages per proposal was a common response (single spaced, in 11-point Arial or 12-point Times with one inch margins), including references (which should be accurate, appropriate, and current!), some of my busiest colleagues have said they will not read more than about three pages total. Only a few actually indicated they would read up to 12-15 pages for three projects. In my opinion, ten pages total for your research plans should be a fairly firm upper limit unless you are specifically told otherwise by a search committee, and then only if you have two to three distinct proposals.
Why Start Now?
Hopefully, this question has answered itself already! Your research plan needs to be a well thought out document that is an integrated part of applications tailored to each institution to which you apply. It must represent mature ideas that you have had time to refine through multiple revisions and a great deal of critical review from everyone you can get to read them. Moreover, you may need a few different sets of these, especially if you will be applying to a broad range of institutions. So add “write research plans” to this week’s to do list (and every week’s for the next few months) and start writing up the ideas in that manila folder into some genuine research plans. See which ones survive the process and rise to the top and you should be well prepared when the job ads begin to appear in C&EN in August!

Jason G. Gillmore , Ph.D., is an Associate Professor of Chemistry at Hope College in Holland, MI. A native of New Jersey, he earned his B.S. (’96) and M.S. (’98) degrees in chemistry from Virginia Tech, and his Ph.D. (’03) in organic chemistry from the University of Rochester. After a short postdoctoral traineeship at Vanderbilt University, he joined the faculty at Hope in 2004. He has received the Dreyfus Start-up Award, Research Corporation Cottrell College Science Award, and NSF CAREER Award, and is currently on sabbatical as a Visiting Research Professor at Arizona State University. Professor Gillmore is the organizer of the Biennial Midwest Postdoc to PUI Professor (P3) Workshop co-sponsored by ACS, and a frequent panelist at the annual ACS Postdoc to Faculty (P2F) Workshops.
Other tips to help engage (or at least not turn off) your readers include:
- Avoid two-column formats.
- Avoid too-small fonts that hinder readability, especially as many will view the documents online rather than in print!
- Use good figures that are readable and broadly understandable!
- Use color as necessary but not gratuitously.
Accept & Close The ACS takes your privacy seriously as it relates to cookies. We use cookies to remember users, better understand ways to serve them, improve our value proposition, and optimize their experience. Learn more about managing your cookies at Cookies Policy .
1155 Sixteenth Street, NW, Washington, DC 20036, USA | service@acs.org | 1-800-333-9511 (US and Canada) | 614-447-3776 (outside North America)
- Terms of Use
- Accessibility
Copyright © 2024 American Chemical Society

- Appointments

- Resume Reviews

- Undergraduates
- PhDs & Postdocs
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- Online Students
- Career Champions
- I’m Exploring
- Architecture & Design
- Education & Academia
- Engineering
- Fashion, Retail & Consumer Products
- Fellowships & Gap Year
- Fine Arts, Performing Arts, & Music
- Government, Law & Public Policy
- Healthcare & Public Health
- International Relations & NGOs
- Life & Physical Sciences
- Marketing, Advertising & Public Relations
- Media, Journalism & Entertainment
- Non-Profits
- Pre-Health, Pre-Law and Pre-Grad
- Real Estate, Accounting, & Insurance
- Social Work & Human Services
- Sports & Hospitality
- Startups, Entrepreneurship & Freelancing
- Sustainability, Energy & Conservation
- Technology, Data & Analytics
- DACA and Undocumented Students
- First Generation and Low Income Students
- International Students
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Transfer Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Explore Careers & Industries
- Make Connections & Network
- Search for a Job or Internship
- Write a Resume/CV
- Write a Cover Letter
- Engage with Employers
- Research Salaries & Negotiate Offers
- Find Funding
- Develop Professional and Leadership Skills
- Apply to Graduate School
- Apply to Health Professions School
- Apply to Law School
- Self-Assessment
- Experiences
- Post-Graduate
- Jobs & Internships
- Career Fairs
- For Employers
- Meet the Team
- Peer Career Advisors
- Social Media
- Career Services Policies
- Walk-Ins & Pop-Ins
- Strategic Plan 2022-2025
Research statements for faculty job applications
The purpose of a research statement.
The main goal of a research statement is to walk the search committee through the evolution of your research, to highlight your research accomplishments, and to show where your research will be taking you next. To a certain extent, the next steps that you identify within your statement will also need to touch on how your research could benefit the institution to which you are applying. This might be in terms of grant money, faculty collaborations, involving students in your research, or developing new courses. Your CV will usually show a search committee where you have done your research, who your mentors have been, the titles of your various research projects, a list of your papers, and it may provide a very brief summary of what some of this research involves. However, there can be certain points of interest that a CV may not always address in enough detail.
- What got you interested in this research?
- What was the burning question that you set out to answer?
- What challenges did you encounter along the way, and how did you overcome these challenges?
- How can your research be applied?
- Why is your research important within your field?
- What direction will your research take you in next, and what new questions do you have?
While you may not have a good sense of where your research will ultimately lead you, you should have a sense of some of the possible destinations along the way. You want to be able to show a search committee that your research is moving forward and that you are moving forward along with it in terms of developing new skills and knowledge. Ultimately, your research statement should complement your cover letter, CV, and teaching philosophy to illustrate what makes you an ideal candidate for the job. The more clearly you can articulate the path your research has taken, and where it will take you in the future, the more convincing and interesting it will be to read.
Separate research statements are usually requested from researchers in engineering, social, physical, and life sciences, but can also be requested for researchers in the humanities. In many cases, however, the same information that is covered in the research statement is often integrated into the cover letter for many disciplines within the humanities and no separate research statement is requested within the job advertisement. Seek advice from current faculty and new hires about the conventions of your discipline if you are in doubt.
Timeline: Getting Started with your Research Statement
You can think of a research statement as having three distinct parts. The first part will focus on your past research, and can include the reasons you started your research, an explanation as to why the questions you originally asked are important in your field, and a summary some of the work you did to answer some of these early questions.
The middle part of the research statement focuses on your current research. How is this research different from previous work you have done, and what brought you to where you are today? You should still explain the questions you are trying to ask, and it is very important that you focus on some of the findings that you have (and cite some of the publications associated with these findings). In other words, do not talk about your research in abstract terms, make sure that you explain your actual results and findings (even if these may not be entirely complete when you are applying for faculty positions), and mention why these results are significant.
The final part of your research statement should build on the first two parts. Yes, you have asked good questions, and used good methods to find some answers, but how will you now use this foundation to take you into your future? Since you are hoping that your future will be at one of the institutions to which you are applying, you should provide some convincing reasons why your future research will be possible at each institution, and why it will be beneficial to that institution, or to the students at that institution.
While you are focusing on the past, present, and future or your research, and tailoring it to each institution, you should also think about the length of your statement and how detailed or specific you make the descriptions of your research. Think about who will be reading it. Will they all understand the jargon you are using? Are they experts in the subject, or experts in a range of related subjects? Can you go into very specific detail, or do you need to talk about your research in broader terms that make sense to people outside of your research field focusing on the common ground that might exist? Additionally, you should make sure that your future research plans differ from those of your PI or advisor, as you need to be seen as an independent researcher. Identify 4-5 specific aims that can be divided into short-term and long-term goals. You can give some idea of a 5-year research plan that includes the studies you want to perform, but also mention your long-term plans, so that the search committee knows that this is not a finite project.
Another important consideration when writing about your research is realizing that you do not perform research in a vacuum. When doing your research you may have worked within a team environment at some point, or sought out specific collaborations. You may have faced some serious challenges that required some creative problem-solving to overcome. While these aspects are not necessarily as important as your results and your papers or patents, they can help paint a picture of you as a well-rounded researcher who is likely to be successful in the future even if new problems arise, for example.
Follow these general steps to begin developing an effective research statement:
Step 1: Think about how and why you got started with your research. What motivated you to spend so much time on answering the questions you developed? If you can illustrate some of the enthusiasm you have for your subject, the search committee will likely assume that students and other faculty members will see this in you as well. People like to work with passionate and enthusiastic colleagues. Remember to focus on what you found, what questions you answered, and why your findings are significant. The research you completed in the past will have brought you to where you are today; also be sure to show how your research past and research present are connected. Explore some of the techniques and approaches you have successfully used in your research, and describe some of the challenges you overcame. What makes people interested in what you do, and how have you used your research as a tool for teaching or mentoring students? Integrating students into your research may be an important part of your future research at your target institutions. Conclude describing your current research by focusing on your findings, their importance, and what new questions they generate.
Step 2: Think about how you can tailor your research statement for each application. Familiarize yourself with the faculty at each institution, and explore the research that they have been performing. You should think about your future research in terms of the students at the institution. What opportunities can you imagine that would allow students to get involved in what you do to serve as a tool for teaching and training them, and to get them excited about your subject? Do not talk about your desire to work with graduate students if the institution only has undergraduates! You will also need to think about what equipment or resources that you might need to do your future research. Again, mention any resources that specific institutions have that you would be interested in utilizing (e.g., print materials, super electron microscopes, archived artwork). You can also mention what you hope to do with your current and future research in terms of publication (whether in journals or as a book), try to be as specific and honest as possible. Finally, be prepared to talk about how your future research can help bring in grants and other sources of funding, especially if you have a good track record of receiving awards and fellowships. Mention some grants that you know have been awarded to similar research, and state your intention to seek this type of funding.
Step 3: Ask faculty in your department if they are willing to share their own research statements with you. To a certain extent, there will be some subject-specific differences in what is expected from a research statement, and so it is always a good idea to see how others in your field have done it. You should try to draft your own research statement first before you review any statements shared with you. Your goal is to create a unique research statement that clearly highlights your abilities as a researcher.
Step 4: The research statement is typically a few (2-3) pages in length, depending on the number of images, illustrations, or graphs included. Once you have completed the steps above, schedule an appointment with a career advisor to get feedback on your draft. You should also try to get faculty in your department to review your document if they are willing to do so.
Explore other application documents:

/images/cornell/logo35pt_cornell_white.svg" alt="how to write a research plan for academic job"> Cornell University --> Graduate School
Research statement, what is a research statement.
The research statement (or statement of research interests) is a common component of academic job applications. It is a summary of your research accomplishments, current work, and future direction and potential of your work.
The statement can discuss specific issues such as:
- funding history and potential
- requirements for laboratory equipment and space and other resources
- potential research and industrial collaborations
- how your research contributes to your field
- future direction of your research
The research statement should be technical, but should be intelligible to all members of the department, including those outside your subdiscipline. So keep the “big picture” in mind. The strongest research statements present a readable, compelling, and realistic research agenda that fits well with the needs, facilities, and goals of the department.
Research statements can be weakened by:
- overly ambitious proposals
- lack of clear direction
- lack of big-picture focus
- inadequate attention to the needs and facilities of the department or position
Why a Research Statement?
- It conveys to search committees the pieces of your professional identity and charts the course of your scholarly journey.
- It communicates a sense that your research will follow logically from what you have done and that it will be different, important, and innovative.
- It gives a context for your research interests—Why does your research matter? The so what?
- It combines your achievements and current work with the proposal for upcoming research.
- areas of specialty and expertise
- potential to get funding
- academic strengths and abilities
- compatibility with the department or school
- ability to think and communicate like a serious scholar and/or scientist
Formatting of Research Statements
The goal of the research statement is to introduce yourself to a search committee, which will probably contain scientists both in and outside your field, and get them excited about your research. To encourage people to read it:
- make it one or two pages, three at most
- use informative section headings and subheadings
- use bullets
- use an easily readable font size
- make the margins a reasonable size
Organization of Research Statements
Think of the overarching theme guiding your main research subject area. Write an essay that lays out:
- The main theme(s) and why it is important and what specific skills you use to attack the problem.
- A few specific examples of problems you have already solved with success to build credibility and inform people outside your field about what you do.
- A discussion of the future direction of your research. This section should be really exciting to people both in and outside your field. Don’t sell yourself short; if you think your research could lead to answers for big important questions, say so!
- A final paragraph that gives a good overall impression of your research.
Writing Research Statements
- Avoid jargon. Make sure that you describe your research in language that many people outside your specific subject area can understand. Ask people both in and outside your field to read it before you send your application. A search committee won’t get excited about something they can’t understand.
- Write as clearly, concisely, and concretely as you can.
- Keep it at a summary level; give more detail in the job talk.
- Ask others to proofread it. Be sure there are no spelling errors.
- Convince the search committee not only that you are knowledgeable, but that you are the right person to carry out the research.
- Include information that sets you apart (e.g., publication in Science, Nature, or a prestigious journal in your field).
- What excites you about your research? Sound fresh.
- Include preliminary results and how to build on results.
- Point out how current faculty may become future partners.
- Acknowledge the work of others.
- Use language that shows you are an independent researcher.
- BUT focus on your research work, not yourself.
- Include potential funding partners and industrial collaborations. Be creative!
- Provide a summary of your research.
- Put in background material to give the context/relevance/significance of your research.
- List major findings, outcomes, and implications.
- Describe both current and planned (future) research.
- Communicate a sense that your research will follow logically from what you have done and that it will be unique, significant, and innovative (and easy to fund).
Describe Your Future Goals or Research Plans
- Major problem(s) you want to focus on in your research.
- The problem’s relevance and significance to the field.
- Your specific goals for the next three to five years, including potential impact and outcomes.
- If you know what a particular agency funds, you can name the agency and briefly outline a proposal.
- Give broad enough goals so that if one area doesn’t get funded, you can pursue other research goals and funding.
Identify Potential Funding Sources
- Almost every institution wants to know whether you’ll be able to get external funding for research.
- Try to provide some possible sources of funding for the research, such as NIH, NSF, foundations, private agencies.
- Mention past funding, if appropriate.
Be Realistic
There is a delicate balance between a realistic research statement where you promise to work on problems you really think you can solve and over-reaching or dabbling in too many subject areas. Select an over-arching theme for your research statement and leave miscellaneous ideas or projects out. Everyone knows that you will work on more than what you mention in this statement.
Consider Also Preparing a Longer Version
- A longer version (five–15 pages) can be brought to your interview. (Check with your advisor to see if this is necessary.)
- You may be asked to describe research plans and budget in detail at the campus interview. Be prepared.
- Include laboratory needs (how much budget you need for equipment, how many grad assistants, etc.) to start up the research.
Samples of Research Statements
To find sample research statements with content specific to your discipline, search on the internet for your discipline + “Research Statement.”
- University of Pennsylvania Sample Research Statement
- Advice on writing a Research Statement (Plan) from the journal Science
- Publications
ACS NETWORK
Chemistry community online.
- ACS Community
- Special Interest
- Career Development
- Writing the Research Plan for your Academic Job Ap...
Writing the Research Plan for your Academic Job Application
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content

- application
- chemistry research
- college graduates
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
This website uses cookies to improve your user experience. By continuing to use the site, you are accepting our use of cookies. Read the ACS privacy policy.
- ACS Publications
Writing the Research Plan for Your Academic Job Application
- Sep 8, 2017
Want to get that academic faculty job you’ve been dreaming about? Are you stressed about writing a lengthy research plan as part of the application process? Do not fear. ACS can provide you with guidance on writing a remarkable research plan needed for your academic job application so that you can stand out among other […]

Want to get that academic faculty job you’ve been dreaming about? Are you stressed about writing a lengthy research plan as part of the application process? Do not fear. ACS can provide you with guidance on writing a remarkable research plan needed for your academic job application so that you can stand out among other job applicants.
The mobile-friendly eBook entitled “ Writing the Research Plan for Your Academic Job Application ” includes tips on how to:
- Tailor your application for each school: Make sure you look at the guidelines that your university requires for the application. If your application matches the qualities of the type of candidate they want, the more likely you will be selected for the desired position. (i.e. Shania is applying to a university and sees that their “Desired Qualifications” list says they want someone who has a Bachelor of Science degree in Chemistry and knowledge using a certain type of equipment. When she includes this experience on her application, the recruiter will prioritize her as one of the top candidates.)
- Craft your research plan with your audience in mind: The audience reading your research plan will make or break your fate in getting your dream job. If the research plan grabs their attention, it will increase your chances of being hired. (i.e., Britney is starting to write her research plan and begins it with an engaging introduction and provides sufficient details that demonstrate her expertise in the field. If her goal and plan of execution intrigues the audience, she will become a standout candidate.)
- Determine the length of your plan: The recommended length for a research plan is ten pages. Additionally, you should have a proposal that is 3-5 pages long, which would serve as a summary of your roles and responsibilities if/when hired.
Want to show hiring managers that you’re the most qualified candidate? Download your free eBook to learn what it takes to write an effective research plan for your academic job application!
Want the latest stories delivered to your inbox each month?
Understanding and solving intractable resource governance problems.
- In the Press
- Conferences and Talks
- Exploring models of electronic wastes governance in the United States and Mexico: Recycling, risk and environmental justice
- The Collaborative Resource Governance Lab (CoReGovLab)
- Water Conflicts in Mexico: A Multi-Method Approach
- Past projects
- Publications and scholarly output
- Research Interests
- Higher education and academia
- Public administration, public policy and public management research
- Research-oriented blog posts
- Stuff about research methods
- Research trajectory
- Publications
- Developing a Writing Practice
- Outlining Papers
- Publishing strategies
- Writing a book manuscript
- Writing a research paper, book chapter or dissertation/thesis chapter
- Everything Notebook
- Literature Reviews
- Note-Taking Techniques
- Organization and Time Management
- Planning Methods and Approaches
- Qualitative Methods, Qualitative Research, Qualitative Analysis
- Reading Notes of Books
- Reading Strategies
- Teaching Public Policy, Public Administration and Public Management
- My Reading Notes of Books on How to Write a Doctoral Dissertation/How to Conduct PhD Research
- Writing a Thesis (Undergraduate or Masters) or a Dissertation (PhD)
- Reading strategies for undergraduates
- Social Media in Academia
- Resources for Job Seekers in the Academic Market
- Writing Groups and Retreats
- Regional Development (Fall 2015)
- State and Local Government (Fall 2015)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2016)
- Regional Development (Fall 2016)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2018)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2019)
- Public Policy Analysis (Spring 2016)
- POLI 351 Environmental Policy and Politics (Summer Session 2011)
- POLI 352 Comparative Politics of Public Policy (Term 2)
- POLI 375A Global Environmental Politics (Term 2)
- POLI 350A Public Policy (Term 2)
- POLI 351 Environmental Policy and Politics (Term 1)
- POLI 332 Latin American Environmental Politics (Term 2, Spring 2012)
- POLI 350A Public Policy (Term 1, Sep-Dec 2011)
- POLI 375A Global Environmental Politics (Term 1, Sep-Dec 2011)
Preparing a research statement for an academic job application
This is not my first blog post on research statements (this one on research statements and research trajectories and this other on research pipelines, research trajectories and research programmes are quite related), but this is perhaps the first time I write about and address the Research Statement as a key component of job applications for tenure-track or post-doctoral positions. We all know how angry and upset I feel about the dismal state of the academic job market(s). However, let us assume that you still want to apply for tenure-track (TT) jobs. I do have some experience applying for (and landing) TT jobs, as well as chairing search committees for these positions. I have also sat on search committees, and have read hundreds of applications. These are thus a few pointers that I think might help potential applicants write their statements.

We all know the huge role that luck, connections, institutional “pedigree” and other factors play, but for purposes of helping those who want to apply, some ideas that you all may want to consider in crafting your Research Statements. This blog post started as a Twitter thread so I’ve pulled from there too.
One way to write your research statement is to follow a similar model to the blog post I wrote here https://t.co/A3FaGQkeCU DO NOTE: In this post, I wrote about writing a Research Statement and crafting a Research Trajectory. This was not by chance. There’s a logic to this. — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) July 25, 2020
Personally, I think that when departments and universities hire you, they want to see how you develop your work through time . In that sense, the Research Statement that you arrive with (at the time of application) is STATIC . You present a SNAPSHOT of what you’ve done so far.
In my personal view (please don’t take my suggestions as dogma or guidelines!), I think that there is value in developing both a Research Statement and a Research Trajectory (this one is worth considering in both ex-ante and ex-post modes)
A Research Trajectory can one (or both) of two things:
1) it can present a narrative in timeline form of how your thinking has evolved.
2) it can present your Research Plan for the next 5-6 years (pandemics and life will obviously derail that plan!)
So what I have done with my own Research Statements is to present how my research interests have evolved through time. In that sense, my Research Statement is a STATIC snapshot at a certain point in time (at the time of writing, of course!) of how my different research strands have evolved through time (that is, of my Research Trajectory ). Below is an example of how I have done self-reflection about my own Research Statement.
Last year I was invited to participate in a global workshop of a few selected scholars on the future of environmental policy, which surprised a couple of people. Well, here’s the thing: at the beginning of my career, I *was* a specialist in environmental policy instruments.
Now, my own thinking about the importance, value, structure and content of the Research Plan, Research Trajectory, Research Pipeline and Research Statement has evolved (most recent iteration can be found here https://t.co/nNMDnKa3Gm ) What must be clear from my blog is that… — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) July 25, 2020
… to observe and read many Research Statements (or research narratives, as you may want to call them), but I recently came across @paullagunes ‘ revamped website, and I really, really liked how he narrates his work https://t.co/dWdYJbHjvT Paul explains his projects through time — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) July 25, 2020
Paul also explains very well how his work contributes to theoretical debates and the empirical literature. Paul is an excellent writer and you may consider reading through his website and published work to see how he crafts his narratives.
If people want to learn more about how to craft a Research Statement, I think one strategy would be to poke around and read the “Research” pages of various scholars’ websites to find patterns. That is how I have learned much of what I now write about, by looking at many scholars’ strategies, distilling them and adapting them into something that works FOR ME.
I said I had two pieces of advice. But in reality, I think it’s just that one: for me, a Research Statement of a candidate tells me what they’ve done, if/where it is published or under review, and how those pieces of work fit a coherent, cohesive narrative of their research .
As someone with interdisciplinary training who continues to do interdisciplinary work, I often struggle when people want to categorize me (am I a geographer, a political scientist, a public administration scholar, a sociologist?). Truth be told, the way I have made peace with this challenge of being interdisciplinary when being in disciplinary departments (who say they want interdisciplinarity but judge you by their disciplinary norms) is to show how my work speaks to the debates of their discipline.
Also, my work (though it cuts through different disciplines and methods), is centred around ONE key question that has puzzled me my entire life: what drives agents to cooperate and collaborate? ?
Studying collaborative behaviour has led me to write on environmental activism and transnational coalitions.
And yes, I study cooperation and collaboration, but often times there are factors that preclude these and lead to disputes, which is why I ALSO study protests, activist mobilization and conflict: https://t.co/cwOJ6mkrcO Studying water conflict has led me to study this resource. — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) July 25, 2020
… the study of cooperation and conflict for the governance of orthodox and unorthodox commons (or common pool resources). Anyhow, just my two cents in hopes this thread may help those crafting their research statements. </end thread> — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) July 25, 2020
You can share this blog post on the following social networks by clicking on their icon.
Posted in academia .
Tagged with research pipeline , research plan , research statement , research trajectory .
No comments
By Raul Pacheco-Vega – July 31, 2020
0 Responses
Stay in touch with the conversation, subscribe to the RSS feed for comments on this post .
Leave a Reply Cancel Some HTML is OK
Name (required)
Email (required, but never shared)
or, reply to this post via trackback .
About Raul Pacheco-Vega, PhD
Find me online.
My Research Output
- Google Scholar Profile
- Academia.Edu
- ResearchGate
My Social Networks
- Polycentricity Network
Recent Posts
- “State-Sponsored Activism: Bureaucrats and Social Movements in Brazil” – Jessica Rich – my reading notes
- Reading Like a Writer – Francine Prose – my reading notes
- Using the Pacheco-Vega workflows and frameworks to write and/or revise a scholarly book
- On framing, the value of narrative and storytelling in scholarly research, and the importance of asking the “what is this a story of” question
- The Abstract Decomposition Matrix Technique to find a gap in the literature
Follow me on Twitter:
Proudly powered by WordPress and Carrington .
Carrington Theme by Crowd Favorite
- DACA/Undocumented
- First Generation, Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with disabilities
- Undergraduate Students
- Master’s Students
- PhD Students
- Faculty/Staff
- Family/Supporters
- Career Fairs
- Post Jobs, Internships, Fellowships
- Build your Brand at MIT
- Recruiting Guidelines and Resources
- Connect with Us
- Career Advising
- Distinguished Fellowships
- Employer Relations
- Graduate Student Professional Development
- Prehealth Advising
- Student Leadership Opportunities
- Academia & Education
- Architecture, Planning, & Design
- Arts, Communications, & Media
- Business, Finance, & Fintech
- Computing & Computer Technology
- Data Science
- Energy, Environment, & Sustainability
- Life Sciences, Biotech, & Pharma
- Manufacturing & Transportation
- Health & Medical Professions
- Social Impact, Policy, & Law
- Getting Started & Handshake 101
- Exploring careers
- Networking & Informational Interviews
- Connecting with employers
- Resumes, cover letters, portfolios, & CVs
- Finding a Job or Internship
- Post-Graduate and Summer Outcomes
- Professional Development Competencies
- Preparing for Graduate & Professional Schools
- Preparing for Medical / Health Profession Schools
- Interviewing
- New jobs & career transitions
- Career Prep and Development Programs
- Employer Events
- Outside Events for Career and Professional Development
- Events Calendar
- Career Services Workshop Requests
- Early Career Advisory Board
- Peer Career Advisors
- Student Staff
- Mission, Vision, Values and Diversity Commitments
- News and Reports
Application Materials for a Faculty Job Search
- Share This: Share Application Materials for a Faculty Job Search on Facebook Share Application Materials for a Faculty Job Search on LinkedIn Share Application Materials for a Faculty Job Search on X
The following materials are commonly requested. We encourage you to schedule an appointment with a career advisor to review your documents and discuss your plan. Get additional feedback on your materials from your faculty advisor and other mentors.
1) CV (curriculum vitae) : comprehensive scholarly record, including your research experience, teaching and mentoring experience, publication record, and more. See more details on preparing a CV .
2) Cover letter : 1-2 page letter, addressed to search committee. Include a brief summary of your academic background, highlights of past and future research, summary of teaching experiences and interests, and your fit with the department and school (why are you interested in that position? How does your experience match the position ad?)
3) Research Statement: A summary of your past research accomplishments, and a proposal for your future research plan as a faculty member. Include both your long-term vision, as well as concrete projects for your research group for the first 3-5 years. Length varies, but typically 3-6 pages. See more advice on writing research statements .
4) Teaching Statement : A statement of your approaches and philosophy regarding teaching and learning. Include specific examples to illustrate your approaches from your past teaching experience, or propose specific ideas for how you would teach future courses. Include a statement of the broad courses you are qualified to teach, as well as any courses you would like to develop. Usually 1-2 pages. See more advice on writing teaching statements .
5) Diversity Statement : A discussion of your past, present and future contributions to promoting equity, inclusion and diversity in your professional career. Typically 1-2 pages. See sample guidelines for writing a diversity statement .

RESOURCES FOR: Job Seekers Faculty Employers
RESOURCES FOR:
Job Seekers Faculty Employers
How to Write a Research Statement
By Sarah Hildebrand

Photo by Nick Youngson on Alpha Stock Images
Research statements have become a core component of faculty job applications. A research statement is a map for your career as a researcher, expanding on how you describe your research in your cover letter. A research statement should document a three- to five-year plan that lays out attainable goals. It should explain your past, present, and future research projects, as well as any major accomplishments. Make sure to highlight your strengths and the importance of your future work, but be realistic about what you can achieve—search committees will know the difference.
Tips and Considerations for Writing an Effective Research Statement
The length of a research statement varies by discipline. Although the average is three pages, it may be slightly shorter (1-2 pages) in the humanities or slightly longer (3-4 pages) in the social sciences and STEM fields.
Organization
Research statements begin with an introductory paragraph that describes your overall work and field, followed by body paragraphs that narrow down into your specific area of expertise and projects.
While some research statements are organized topically by project, most are ordered chronologically. Begin by discussing any past work, such as your dissertation; next describe any current research projects; end with ideas you have for the future. Some applicants may choose to use headings to further delineate among projects or clarify whether certain paragraphs focus on past, present, or future work.
Depending on your discipline, you may choose to include an executive summary at the end of your statement, which summarizes your main research goals, methodology, and qualifications for the position. STEM students may also incorporate relevant graphics that help clearly demonstrate results at a glance.
Research statements should be written for generalists who would make up a search committee. Contextualize your work within your field, avoid jargon, and make sure your work can be understood across your discipline.
Avoid long paragraphs. Paragraphs should never take up more than half a page and may be even shorter. If you have a lot to say about one particular project, that section might be broken up into 2-3 paragraphs to help keep your reader engaged.
Research statements should be written in the first-person and in the active voice. Both of these rhetorical strategies will ensure that you remain the focus of the statement. Your writing should be clear, concise, and assertive.
Example of passive vs. active voice:
Passive voice: The data was collected over a series of three experiments.
Active voice: I collected the data over a series of three experiments.
Topics to Cover in Your Research Statement
The subject and importance of your research.
Describe your general interest area, specific areas of expertise, and methodologies. Explain exactly what your research is and why it matters. How is your work innovative? What contribution does it make to existing bodies of knowledge? What major problems will you solve?
Past, Current, and Future Research Projects
Search committees expect you to discuss multiple projects. While you will certainly spend a paragraph or two on your dissertation, you should also have additional works-in-progress, as well as two or three defined projects you will conduct in the future. You can also describe any projects you’ve completed in the past. Be sure to draw connections between projects and demonstrate how your future work will build off the work you’ve already done. This will help prove that the project is feasible and that you are qualified to lead it.
Major Accomplishments
Describe any publications you have in a sentence or two by explaining what knowledge they contribute to the field. You should also acknowledge any major grants received, sources of funding secured, or awards won.
Additional Considerations for STEM Applicants
In a research statement, STEM applicants must demonstrate that their work is independent from the work of their PI. It may be helpful to describe how you will involve students of your own in your lab. If you require lab equipment and/or support staff, make sure all of your planned research can be accommodated by the institution as is, or identify how you will secure funding to obtain additional resources. Identify potential sources of external funding for your work, as well as potential collaborators within the department, school, or industry. Try to be as specific as possible by naming particular organizations or researchers.

This entry is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International license.
Related Posts
- How to Write a Diversity Statement
- How to Write a Teaching Statement
Need help with the Commons?
Email us at [email protected] so we can respond to your questions and requests. Please email from your CUNY email address if possible. Or visit our help site for more information:

- Terms of Service
- Accessibility
- Creative Commons (CC) license unless otherwise noted


Faculty Application: Research Statement
Criteria for success.
- Clearly articulate your brand.
- Demonstrate the impact of your past work.
- Show that you are credible to carry out your proposed future research.
- Articulate the importance of your research vision.
- Match the standards within the department to which you are applying.
- Show that you are a good fit for the position.
- Polish. Avoid typos.
Structure Diagram
The typical structure and length of research statements vary widely across fields. If you are unsure of what is typical in the field where you are applying, be sure to check with someone who is familiar with the standards.
In electrical engineering and computer science, research statements are usually around three pages long with a focus on past and current work, often following the structure in the diagram below.
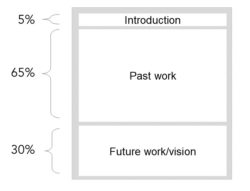
Identify Your Purpose
Your cover letter and CV outline your past work and hint at a general direction of your future work but do not go into detail. Therefore, the purpose of a research statement is to emphasize the importance of your past work and describe your research vision. Both your past/current work and future work presented in the research statement should reflect your branding statement .
In EECS, faculty research statements focus on past/current work. However, it is important to also include your vision for the future, which should build on your previous work. This statement should convince the committee that your future work is important, relevant, and feasible. The future work section should go beyond direct extensions of your doctoral or postdoctoral work; it should cover a 5-10 year span. Proposed future work should show scientific growth and convince the committee that you propose strong research directions for your future group. Your research statement can also include possible funding sources and collaborations.
Analyze Your Audience
Your audience is a faculty search committee, which is made up of professors from across the department, not just the ones in your research area. A typical search committee member is probably very busy reviewing lots of applications, and hence may not read your statement in depth until you make it to later rounds of the hiring process.
Knowing details of the job posting and what the faculty search committee is looking for will help you tailor your statement. If the call is for a specific research area (e.g., language processing, bioinformatics, algorithms, machine learning, systems), it is beneficial to motivate and emphasize the importance of your work in the language of that area whenever possible.
Structure your statement
Although there is usually no mandated structure for a research statement, it can be very helpful to a reader if the content flows naturally.
Use the hourglass concept. It makes a compelling introduction if a research statement presents motivation starting from the high-level picture and then zooms in to the main topic(s) of research. This is helpful for two reasons. First, a research statement is typically read by committee members from several research areas, so starting with a high-level picture gives members a gentle guidance to the meat of a work. Second, providing general motivation helps in showing how different pieces of research fit in a big puzzle.
After talking about specific results, the story typically zooms back out by discussing impact and future directions. It is best if future work has some concrete research directions and also widens up to touch on a broader perspective of research plans.
The diagram below summarizes the hourglass concept and provides one potential flow of content.
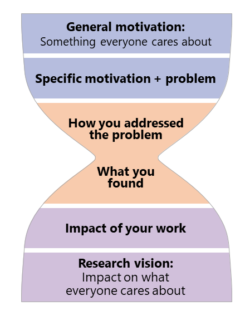
Use good formatting to help retain focus . A successful research statement is typically organized into three main parts: Introduction and motivation; past work/achievements; and vision/future work. Each of these parts can be divided into subsections.
In addition, you can help a reader focus their attention on the important content by:
- making each section/paragraph title tell a message;
- using bullet points and itemization while listing;
- using bold or italics to emphasize important keywords or sentences.
Some institutions set constraints on the format of research statements, primarily constraints on length . Make sure that your research statement is tailored to the guidelines. It is helpful to prepare two versions of your statement — a long one and a short one. The short version is usually the long one stripped of many details with the emphasis on high-level pictures and ideas.
Say who you are
Your research statement tells a story about you. Think who you want to be in the eyes of committee members (e.g., a programming languages person, a machine learning expert, a theory professor) and which of your achievements you want them to remember.
Make your research statement echo your branding one . A successful research statement builds a story around the author’s branding statement. A strong point is made if past and future work are echoes of the same brand.
Successful candidates outline their research agenda before stating actual results and after providing a background. Sometimes this is done even before giving background and motivation. In the latter case, the research agenda is typically stated briefly, and then reiterated with more context after providing the background.
Show credibility for your future work by your past work
Your past work is an excellent way to illustrate that you are fit for the future work you are proposing. Refer to some of your past work when outlining feasibility of your proposed future directions. Even if you aim to change your field of research, your past experience should still serve as a justification for why you are well suited for the new line of work.
Dedicate space to your strongest results . Describe your strongest results in the most detail. If you want to mention many papers, organize them into several themes. A successful statement communicates how obtained results affect a field or a research community. Impact of papers can be shown by awards, high number of citations, or follow up papers by other research groups. A reader will have limited time to go over your statement, so make sure that the reader’s attention is spent on your most impactful work. Note that your strongest results do not necessarily have to be your most recent ones; they can even be several years old. Nevertheless, it is still a good idea to also mention some of your recent work as it shows that you have been active lately as well.
Importantly, a research statement should be a coherent story about ideas and impact, not only an overview of published articles. Hence, it is often the case that a research statement does not discuss all papers published or all work done by the applicant.
Use figures to support important claims . Consider including figures . They can be used to support your claims about your results and/or in the future work section to illustrate your research plans. A well-made figure can help the reader quickly understand your work, but figures also take up a large amount of space. Use figures carefully, only to draw attention to the most important points.
Devote time!
Getting out a job application package takes an indefinitely long time (writing, addressing feedback, polishing, addressing feedback … aaaand polishing)! Start early and invest time.
Get feedback . Your application package will be read by committee members that are not necessarily in your research area. It is thus important to get feedback about your research statement from colleagues with different backgrounds and seniority. Note that it might take time for other people to share their feedback (remember, others are busy as well!), so plan ahead.
MIT EECS affiliates can also make an appointment with a Communication Fellow to obtain additional feedback on their statements.
Resources and Annotated Examples
Amy zhang research statement.
Submitted in 2018-2019 by Amy Zhang, now faculty at University of Washington 1 MB
Elena Glassman Research Statement
Submitted in 2017-2018 by Elena Glassman, now faculty at Harvard University 2 MB

JHM Professional Development and Career Office Awareness. Preparation. Development.
Academic | research statements, research statements.
The research statement requires you to think actively about your future career as a research scientist by charting out long-term research goals for both yourself and your proposed laboratory. The research statement should answer three questions: 1) What is your research to date? 2) Why is your research important? and 3) What is your proposed research agenda at your new institution? Highlight your most important scientific findings and describe promising future directions. Provide the search committee with a convincing and realistic plan of your future goals, using your academic history as an indicator for your potential success as an emerging research scientist in your field. Key Piece of Advice: Research statements are more effective if they are structured around research problems or focus areas, rather than strictly chronologically. Start with the current state of research in your field, then progress to what is and is not known, your research idea, your research, work planned for new ideas, potential funding opportunities, and your ‘fit’ with the institution. Be sure the reader understands what your most surprising scientific finding was and why they should care about it.
- How will you be able to adapt your research to your new institution?
- What resources does the university have that you will be able to utilize for your future projects?
- What resources does the university lack that you require in order to complete your research? You can propose to secure external funding for new laboratory equipment, where applicable.
- Which faculty members would you plan to collaborate with on research projects and grant proposals?
- How will you incorporate opportunities for undergraduate and graduate research in your laboratory (particularly at teaching-focused institutions)?
- Avoid jargon that faculty outside of your immediate subfield will have difficulty understanding. Try to pitch your research statement to a broad, but informed scientific audience.
- Keep your research statement clear and concise. Eliminate any miscellaneous threads that will distract your reader from your primary narrative. The research statement should aim to get search committees excited about your research.
General tips for formatting your research statement
- Research Statements are typically between 2-5 pages in length. The exact statement length may be specified in the job advertisement. For more guidance on formatting, read the detailed PDF.
- Begin your statement with a paragraph about the overarching theme of your past research and how it connects with your future research plans.
- What specific research methods did you use?
- What did you discover? What were your conclusions?
- What were your most important conceptual advances and your most significant contributions to your field? Reference high impact publications, where applicable.
- Include figures and diagrams to make your statement more visually appealing and more accessible to non-specialists.
- Outline 2-3 potential projects for future research, both for you and your proposed laboratory, and include any preliminary data.
- Indicate potential sources of funding for your proposed laboratory, referencing funding you have successfully applied for in the past or plans to write new grant applications.
- Cite current publication productivity to estimate future publication productivity.
‘Writing a Research Plan’ - Science ‘Writing a Research Statement’ Cornell University, Office of Postdoctoral Studies Duke University – Dr. Mohamed Noor
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is your plagiarism score.

5 Simple Tips for Writing a Good Research Statement for a Faculty Position
Completed your Ph.D.? What next?
Traditionally, most sought-after jobs after completing Ph.D. are university professors and industry R&D labs professionals. While industrial jobs have seen a surge in applicants to various positions, academia has prominently been the most considered field by Ph.Ds. As a part of the job application for faculty positions in academia, applicants are required to present a research statement that outlines the research they have already completed.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Statement?
A research statement is a document that summarizes your research interests, accomplishments, current research, and future research conduction plans. Furthermore, it outlines how your work contributes to the field. It allows applicants to present the importance and impact of their past, current, and future research to their potential future colleagues. However, throughout your academic career, you may be asked to prepare similar documents for annual reviews, tenure packages, or promotion.
What is the Purpose of a Research Statement?
The purpose of a research statement isn’t just about exhibiting your research interests, achievement, or other academic feats. In fact, its purpose is to make a persuasive case about the importance of your completed work and the potential impact of your future trajectory in research. In other words, researchers must coherently write about their past and current research efforts and articulately present their future research plans.
Furthermore, a research statement’s purpose is to allow the search committee to envision the applicant’s research evolution, productivity, and potential contributions over the coming years. Your research statement must promisingly convey the benefits you bring to the position. In other words, these benefits could be in terms of grant money, faculty collaborations, student involvement in research, or development of new courses.
Three key purposes of a research statement are:
- Clear presentation of your academic feats.
- Description of your research in a broader context, both scientifically and societally.
- Laying out a clear road map for future endeavors concerning the newly applied position.
How is a Research Statement Different from a CV?
While your CV gives an overview of your past research projects, it does not address the details of conducted research or future research interests. Furthermore, a CV fails to answer some questions that can be easily answered through a research statement.
- Why are you interested in a particular research topic?
- Why is your research important?
- What techniques do you use?
- How have you contributed to your field?
- How can your research be applied commercially or academically?
- Does your research have an impact on allied fields?
- Is your research directing you to newer questions?
- How do you plan to develop new skills and knowledge?
What Should You Include in a Research Statement for Faculty Position?
With over hundreds of applications being received at various departments, your research statement must stand out from the crowd and address all points concerning the target position. Expectations for research statements may vary across disciplines. However, certain key elements must be included in a research statement, irrespective of the field.
- Academic specialty and interests.
- Dedication for research.
- Compatibility with departmental or university research efforts.
- Ideas about potential funding sources, collaborative partners, etc.
- Ability to work as a professional scholar.
- Capability to work as an independent researcher.
- Writing proficiency.
- Relevance of your research and its contribution to the field.
- Significant recognition received by your research such as publications, presentations, grants, awards, etc.
- Appropriate acknowledgment of other scholars’ work in your field by giving them credits where due.
- Degree of specificity for future research.
- Long-term and short-term research goals
How to Write a Research statement for Faculty Position?
An effective research statement must present a clear narrative of the relation between your past and current research. Additionally, it should clearly state how your research aligns with the goals, resources, and needs of the institution to which you are applying.
Here we discuss 5 simple tips for writing a good research statement:

As stated earlier, a faculty position may easily receive over a couple of hundred applications. Consequently, the search committee may just glance through some applications. Therefore, you must make your research statement reader-friendly.
Following tips will allow readers to quickly determine why should they select you over other applicants:
- Organize your ideas by using headings and sub-headings.
- Space out different sections properly.
- Additionally, include figures and diagrams to illustrate key findings or concepts.
- Avoid writing long paragraphs in your research statement. Moreover, a concise yet thoughtfully laid out research statement demonstrates your ability to organize ideas in a coherent and easy-to-understand manner.
2. Ensure to Present Your Focus on Research
- Discuss feasible research ideas that interest you.
- Explain how your goals are related to your recent work.
- Additionally, mention your short-term (2-5 years) and long-term (5+ years) research goals.
- Discuss your ideas about potential funding sources, collaborative partners, facilities, etc.
- Specifically mention how your research goals align with your department’s goals.

3. Tailor Your Research Statement
- It is imperative to mention how you will contribute to the research at the institution you are applying to.
- Mention how will you use core facilities or resources at the institution.
- Furthermore, you should mention particular research infrastructure present at the target institution that you may need to do your work.
4. Write for Each Audience
- Even at top-most institutions, not all members of the search committee may be aware of the intricacies of your research work. Therefore, you should avoid jargon and describe your research work in a detailed yet lucid manner.
- Your motive must be to instill a sense of belief in the reader that you are a dedicated researcher and not overwhelm them with finer details.
- Moreover, focus on conveying the importance of your work and its contribution to the field.
5. Be Yourself
In an attempt to impress the search committee, applicants are often seen to go overboard and come out as boastful.
- Emphasize your major academic achievements.
- Be realistic and do not present research goals that are too ambitious.
- Finally, avoid comparing your research statement with other applicants.
Did you decide on the faculty position you want to apply for? How do you plan to go ahead with your research statement? Follow these tips while writing your research statement to acquire your most desired faculty position .
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Simplifying the Literature Review Journey — A comparative analysis of 6 AI summarization tools
Imagine having to skim through and read mountains of research papers and books, only to…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

8 Effective Strategies to Write Argumentative Essays
In a bustling university town, there lived a student named Alex. Popular for creativity and…

- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- PhDs & Postdocs
Mentoring for Change: Creating an inclusive academic landscape through support programs
Imagine stepping into a world where everyone’s unique talents and backgrounds are not only recognized…
Mentoring for Change: Creating an inclusive academic landscape through support…
Reviving Your Research Career: Overcoming the roadblocks of resuming research after a…
Aiming for Academic Tenure? – 5 Things You Should Know Before Applying!
Statement of Purpose Vs. Personal Statement – A Guide for Early Career…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

- CREd Library , Planning, Managing, and Publishing Research
Developing a Five-Year Research Plan
Cathy binger and lizbeth finestack, doi: 10.1044/cred-pvd-path006.
The following is a transcript of the presentation videos, edited for clarity.
What Is a Research Plan, and Why Do You Need One?
Presented by Cathy Binger

First we’re going to talk about what a research plan is, why it’s important to write one, and why five years—why not one year, why not ten years. So we’ll do some of those basic things, then Liza is going to get down and dirty into the nitty-gritty of “now what” how do I go about writing that research plan.

First of all, what is a research plan? I’m sure some of you have taken a stab at these already. In case you haven’t, this is a real personalized map that relates your projects to goals. It’s exactly what it sounds like, it’s a plan of how you’re going to go about doing your research. It doesn’t necessarily just include research.
It’s something that you need to put a little time and effort into in the beginning. And then, if you don’t revisit it, it’s really a useless document. It’s something that you need to come back to repeatedly, at least annually, and you need to make it visible. So it’s not a document that sits around and once a year you pull it out and look at it.
It can and should be designed, especially initially, with the help of a mentor or colleague. And it does serve multiple purposes, with different lengths and different amounts of detail.
I forgot to say, too, getting started, the slides for this talk were started using as a jumping off point Ray Kent’s talk from last year. So some of the slides we’ve borrowed from him, so many thanks to him for that.

But why do we want to do a research plan? Well, to me the big thing is the vision. Dr. Barlow talked this morning about your line of research and really knowing where you want to go, and this is where that shows up with all the nuts and bolts in place.
What do you want to accomplish? What do you want to contribute? Most of you are at the stage in your career where maybe you have started out with that you want to change the world scenario and realized that whatever you wanted your first research project to be, really, is your entire career. You need to get that down to the point where it is manageable projects that you can do—this is where you map out what those projects are and set reasonable timelines for that.
You want to really demonstrate your independent thinking and your own creativity, whatever that is that you then establish as a PhD student, postdoc, and beyond—this is where you come back to, okay, here’s how I’m going to go about achieving all of that.
This next point, learning to realistically gauge how long it takes to achieve each goal, this for most of us is a phenomenally challenging thing to do. Most of us really overestimate what we can do in a certain amount of time, and we learn the hard way that you can’t, and that’s another reason why you keep coming back to these plans repeatedly and learning over time what’s really manageable, what’s really doable, so we can still reach our goals and be very strategic about how we do that.
When you’re not strategic, you just don’t meet the goals. Your time gets sucked into so many different things. We need to be really practical and strategic.
Everything we do is going to take longer than we think.
I think this last one is something that maybe we don’t talk about enough. Really being honest with ourselves about the role of research in our lives. Not all of you are at very high-level research universities. Some of you have chosen to go elsewhere, where research maybe isn’t going to be playing the same role as it is for other people. The research plan for someone at an R One research intensive university is going to look quite different from someone who is at a primary teaching university. We need to be open and practical about that.

Getting sidetracked. I love this picture, I just found this picture the other day. This feels like my life. You can get pulled in so many different directions once you are a professor. You will get asked to do a thousand different things. There are lots of great opportunities that are out there. Especially initially, it’s tempting to say yes to all of them. But if you’re going to be productive, you have to be very strategic. I’m going to be a little bit sexist against my own sex here for a minute, but my observation has been that women tend to fall into this a little bit more than men do in wanting to say yes and be people pleasers for everything that comes down the pike.
It is a professional skill to learn how to say no. And to do that in such a way that you are not burning bridges as you go down the path. That is a critical skill if you are going to be a successful researcher. I can’t tell you how many countless people I’ve seen who are very bright, very dedicated, have the skills that it takes in terms of doing the work—but then they are not successful because they’ve gotten sidetracked and they try to be too much of a good citizen, give too much service to the department, too much “sure I’ll take on that extra class” or whatever else comes down the line.
I just spoke with a professor recently who had something like five hours a week of office hours scheduled every single week for one class. Margaret is shaking her head like “are you kidding?” That’s crazy stuff. But he wanted to really support his students. His students loved him, but he was not going to get tenure. That’s the story.
So we have to be very thoughtful and strategic, and what can help you with this, and ASHA very firmly recognizes which is why we’re here—is that your mentors in your life should be there to help you learn these skills and learn what to say yes to, and learn what to say no to. I’ve learned to say things like, “Let me check with my mentor before I agree to that.” And it gives you a way out of that. The line that I use a lot is, “Let me check with my department head” or, I just said this to somebody last week, “I just promised my department head two weeks ago that I would only do X number of external workshops this year, so I’m going to have to turn this one down.” Those are really important skills to develop.
And having that research plan in place that you can go back to and say, know what, it’s not on my plan I can’t do it. If I do it—I have to go back to my research plan and figure out what I’m going to kick off in order to review this extra paper, in order to take on this extra task. The plan also helps me to know exactly what to say no to. And to be very direct and have a very strong visual.
I actually have my research plan up on a giant whiteboard in my office, so I can always go back to that and see where I am, and I can say, “Okay, what am I going to kick off of here? Nothing. Okay, I have to say no to whatever comes up.” Just be strategic. This is where I see most beginning professors really end up taking that wrong fork in the road—taking that right instead of that left, and ending up not being the successful researcher that they wanted to be.

What evidence supports research planning? This was something Ray Kent had found. That a recent analysis had found that postdoc scholars who developed a written plan with their postdoc advisers were much more productive than those who didn’t. And your performance during a postdoc—and I know many of you have either finished your postdoc or decided not to—so more simply, just during those first six years, the decisions you make really do establish the foundation for the rest of your professional life. It’s very important to get started and get off on the right foot.

I love this quote, I just found it the other day: “Productivity is never an accident. It is always the result of a commitment to excellence, intelligent planning, and focused effort.”

What we see with productivity is that postdoc scholars who developed written productivity expectations with their advisers were more productive than those who didn’t. You see 23% more papers submitted, 30% more first-author papers, and more grant proposals as well.

So why five years? I’m going to start with number 5. It’s long enough to build a program of research, but short enough to deal with changing circumstances. That’s really the long and the short of the matter. As well as these other things as well that I won’t take the time to go through point by point.
What Should a Five-Year Plan Include?
Presented by Lizbeth Finestack

So, thinking about a five-year research plan, I like to think about it like your major “To Do List.” It’s what you’re going to accomplish in five years. Start thinking: What is going to be on my to do list?

You can also think about it like: Okay, I have research. I’ve got to do research. Maybe think about this as one big bucket, or maybe one humongous silo. I have some farm themes going on. Cathy was just on a farm, so I thought I’d tie that in.
So here’s your big silo. You can call that your research silo.

But more realistically, you need to think about it like separate buckets, separate silos, where research is just one of those. Just like Cathy indicated, there’s going to be lots of other things coming up that you’re going to have to manage. They are going to have to be on your to do list, you need to figure out how to fit everything in.
What all those other buckets or silos are, are really going to depend on your job. And maybe the size of the silos, and the size of the buckets are going to vary depending on where you are, what the expectations are at your institution.
That’s important to keep in mind, and Cathy said this too, it’s not going to be the same for everyone. The five-year plan has to be your plan, your to do list.

Here are some buckets or some silos that I have on my list and the way that I break it up, this is just one example, take it or leave it.
The first three are all very closely related, right? Thinking about grants, thinking about research, thinking about publications. I’m going to define grants as actual writing, getting the grant, getting the money.
Research is what you’re going to do once you get that money. Steps you need to take before you are getting the money. Any sorts of projects, the lab work, that’s why I have the lab picture there. Of course, publications are part of the product—what’s coming out of the research—but it also cycles in because you need publications to support that you are a researcher to apply for funding and show you have this line of research that you’ve established and you’ll be able to continue. So, those first three are really closely related. And that’s where I’ll go next. And then have teaching and service you see here at the bottom.

So thinking about research, in that broad sense. As you’re writing your five-year plan you’re going to want to think of, “What’s my long-term goal?” There’s lots of ways to think of long-term goals. You could think, before I die, this is what I want to accomplish. For me I kind of have that. My long-term goal is that I’m going to find the most effective and efficient interventions for kids with language impairment. Huge broad goal. But within that I can start narrowing it down.
Where am I within that? Within the next five years or maybe the next ten years, what is it I want to accomplish towards that goal. Then start thinking about: In order to accomplish that goal, what are the steps I need to take? Starting to break it down a little bit. Then it’s also going to be really important to think: where are you going to start? Where are you now? What do you need to have happen? And is it reasonable to accomplish this goal within five years? Is it going to take longer? Maybe you could do it in a couple years? Start thinking about the timeline that’s going to work for you.
Then thinking about your goals—and everyone’s program is going to be different, like I said, there’s going to be a lot of individual needs, preferences. So it might be the case that you have this one long-term goal that you’re aiming for. Long-term goal in the sense of, maybe, what you want to study in your R01, perhaps something like that. But in order to get to that point, you’re going to have several short-term goals that need to be accomplished.
Or maybe it’s the case that you have two long-term goals. And with each of those you’re going to have multiple short-term goals that you’re working on. Maybe the scope of each of these long-term goals is a little bit less than in that first scenario.
Start thinking about my research, what I want to do, and how it might fit into these different circumstances.

Also thinking about your goals, this is a slide from Ray Kent from last year, was thinking about the different types of projects you might want to pursue, and thinking about ones that are definitely well on your way. They are safe bets. You have some funding. They are going to lead directly into your longer-term plan.
Those are going to be your front burner—things you can easily focus on. That said, don’t put everything there.
You can also have things on the back burner. Things that really excite you, might have huge benefits, big pay. But you don’t want to spend all of your time there because they could be pretty risky.
Start thinking about where you’re putting your time. Are you putting it all on this high-risk thing that if it doesn’t pan out you’re going to be in big trouble? Or balancing that somewhat with your front burner. Making that steady progress that will lead directly to help fund an R01 or whatever the mechanism that you’re looking for.

Then, thinking about your goals—if you have multiple long-term goals, or thinking about your short-term goals, you could think about your process. Is it something where you need to do study 1 then study 2, then study 3—each of those building on each other, that’s leading to that long-term goal. In many cases, that is the case, where you have to get information from the first study which is going to lead directly to the second study and so forth.

Or is it the case that you can be working on these three short-term goals simultaneously? Spreading your resources at the same time. Maybe it will take longer for any one study, but across a longer period of time you’ll get the information that you need to reach that long-term goal.
Lots and lots of different ways to go about it. The important thing is to think about what your needs are and what makes the most sense for you.
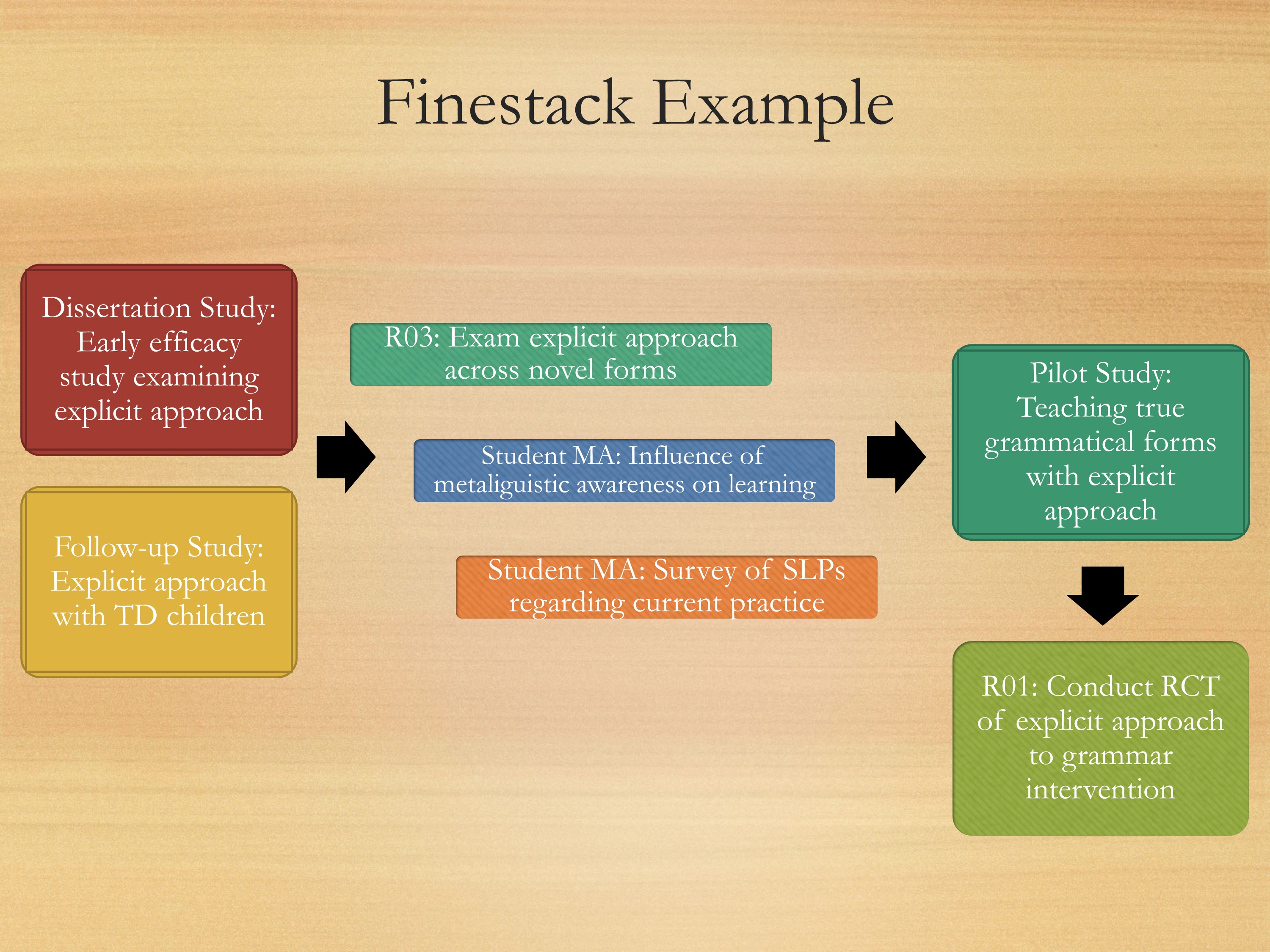
Here’s my own little personal example. Starting over here, I have my dissertation study. My dissertation study was this early efficacy study looking at one treatment approach using novel forms that really can’t generalize to anything too useful, but it was important.
Then I did a follow up study, where I was taking that same paradigm, looking to see where kids with typical development perform on the task. So I have these two studies, and they served as my preliminary studies for an R03. So I just finished an R03 where I was looking at different treatment approaching for kids with primary language impairment. At the same time, while conducting my R03, I’m also looking at some different approaches that might help with language development. Also conducting surveys to see what current practices are.
I have these three projects going on simultaneously, that are going to lead to a bigger pilot study that are going to feed directly into my R01. All of this will serve as preliminary data to go into an R01.
Start thinking about your projects, what you have. Maybe starting with your dissertation project or work that you’re doing as a postdoc as seeing how that can feed into your long-term goal. And really utilizing it, building on it, to your benefit.

That’s all fine and dandy. You can draw these great pictures. But you still have to break it down some more. It’s not like, “Oh, I’m just going to do this project.” There are other steps involved, and lots of the time these steps are going to be just as time consuming.
Starting to think about: well, if you have the funding. Saying, “I want to do this study, but I have no money to do it.” What are the steps in order to get the money to do it? Do you have a pilot study? What do you need?
Start thinking about the resources? Do you need to develop stimuli, protocols, procedures? Start working on that. All of these can be very time consuming, and if you don’t jump on that immediately, it’s going to delay when you can start that project.
Thinking about IRB. Relationships for recruitment, if you’re working with special populations especially? Do you have necessary personnel, grad students, people to help you with the project? Do you need to train them? What’s the timeline of the study?
Start thinking about all these pieces, and how they are going to fit in that timeline.
This is one way that might help you start thinking about the resources that you need. This is online—Ray Kent had it in his talk, and when I was doing my searches I came across it too and I have the website at the end. Just different ways to think about the resources you might need.
Let’s talk about mapping it out. You have your long-term goal. You have your short-term goals. You’re breaking it down thinking about all those little steps that you need to accomplish. We gotta put it on a calendar. When is it going to happen?
This is an example—you might have your five years. Each month plugging in what are you going to accomplish by that time. Maybe it’s when are grant applications due? It’s going to be important to put those on there to go what do I need to do to make that deadline. Maybe it’s putting when you’re going to get publications out. Things like that.
Honestly, looking at this drives me a little bit crazy, it seems a bit overwhelming. But it’s important to get to these details.
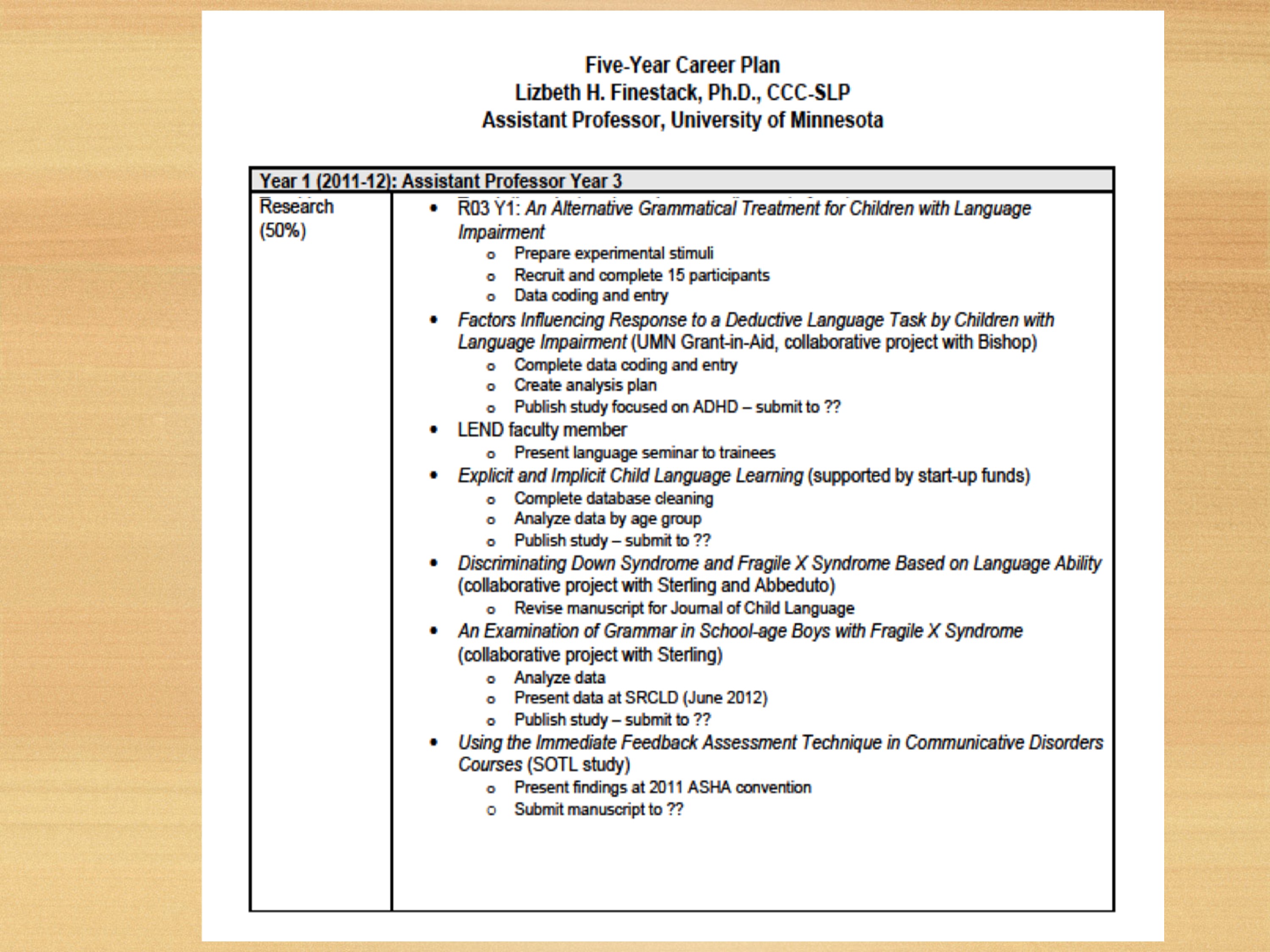
This is an example from, I did Lessons for Success a few years ago and they had their format for doing your plan. I wrote out all my projects, started thinking about all the different aspects. So if something like this works for you, by all means you could use that type of procedure.
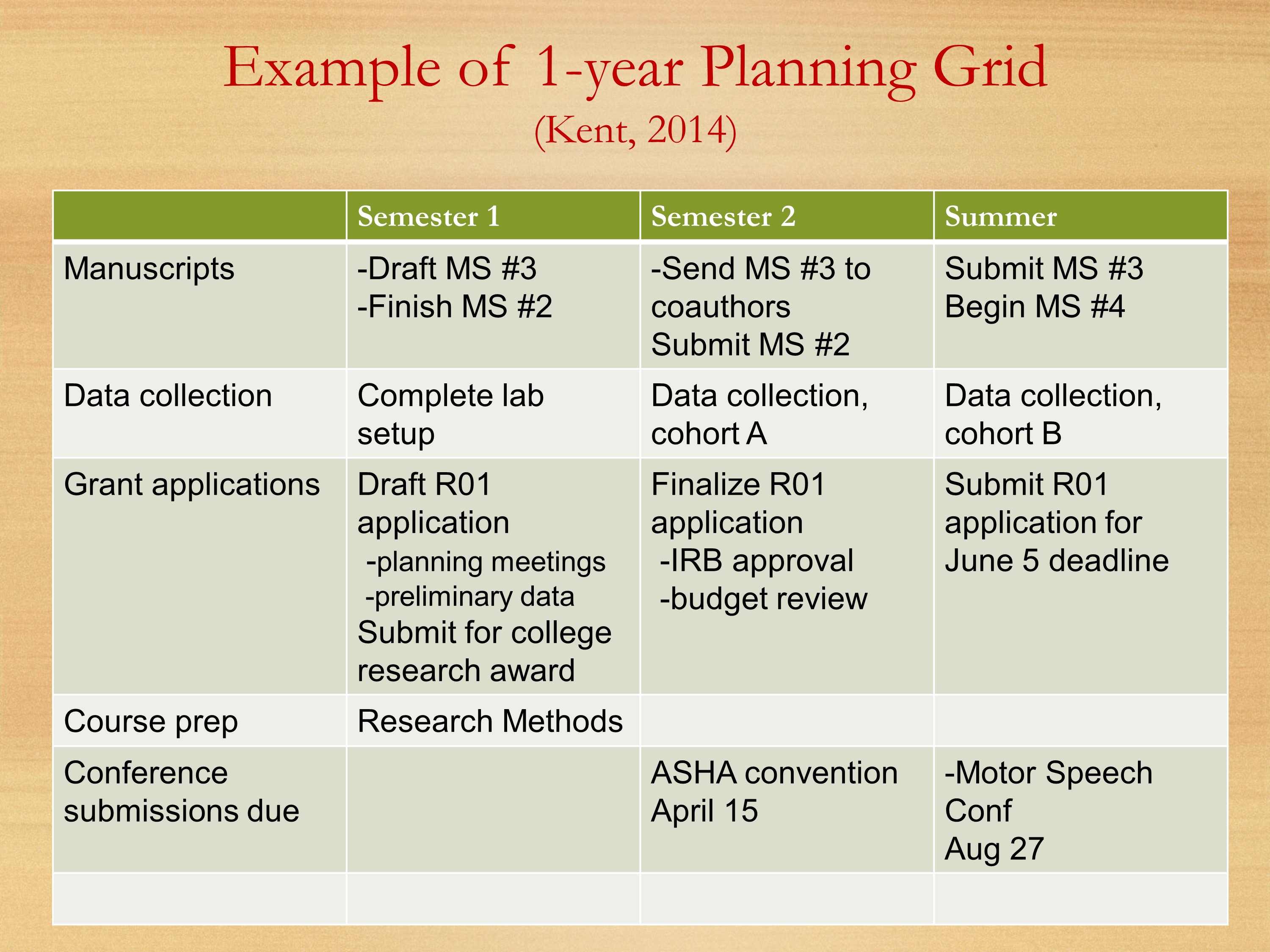
Here’s a grid that Ray Kent showed last year. We’re breaking it down by semester. Thinking about each of your semesters, what manuscripts you’re going to be working on, what data collection, your grant applications. Starting to get into some of those other buckets: course preparation, conference submissions.
We also need to include teaching and service.
You probably can’t see this very well. This is similar to that last slide Ray Kent had used last year.
I have my five year plan: what studies I want to accomplish, start thinking about breaking it down.
Then at the beginning of each semester, I fill in a grid like this. Where at the top, I have each of my buckets. I have my grant bucket, my writing bucket which is going to include publications. I also include doing article reviews in my writing bucket, because that’s my writing time. My teaching bucket, my research bucket. Then at the end, my service bucket.
At the beginning of the semester, I think about the big things I want to accomplish. I list those at the top. Then at the beginning of each month, I say, okay what are the things I’m going to accomplish this month, write those in. Then at the beginning of each week, I start looking at whether I’m dedicating any time to the things I said I was going to do that month. I start listing those out saying, this is the amount of time I’m going to spend on that. Of course, I have to take data on what I actually do, so I plug in how much time I’m spending on each of the tasks. Then I graph it, because that’s rewarding to see how much time you’re spending on things, and I get a little side-tracked sometimes.
Think about a system that will help you keep on track, to make sure you’re meeting the goals that you want to meet in terms of your research. But also getting the other things done that you need to get done in terms of teaching and service.
Discussion and Questions
Compiled from comments made during the Pathways 2014 and 2015 conferences. (Video unavailable.)
Building Flexibility into Your Five-Year Plan Comments by Ray Kent, University of Wisconsin-Madison
The five-year plan is not a contract. It’s a map or a compass. A general set of directions to help you plan ahead. It’s not even a contract with yourself, because it will inevitably be revised in some ways.
Sometimes cool things land in your lap. Very often it turns out that through serendipity or whatever else, you find opportunities that are very enticing. Some of those can be path to an entirely new line of research. Some of them can be a huge distraction and a waste of time. It’s a really cool part of science that new things come along. If we put on blinders and say, “I’m committed to my research plan,” and we don’t look to the left or the right, we’re really robbing ourselves of much of the richness of the scientific life. Science is full of surprises, and sometimes those surprises are going to appear as research projects. The problem is you don’t want to redirect all your time and resources to those until you’re really sure they are going to pay off. I personally believe, some of those high risk but really appealing projects are things you can nurse along. You can devote some time and build some collaborations – far enough to determine how realistic and viable they are. That’s important because those things can be the core of your next research program.
It’s very easy to get overcommitted. We all know people who always say “yes”—and we know those people, and they are often disappointing because they can’t get things done. It’s important to have new directions, but limit them. Don’t say, “I’m going to have 12 new directions this year.” Maybe one or two. Weigh them carefully. Talk about them with other people to get a judgment about how difficult it might be to implement them. It enriches science: not only our knowledge, but the way we acquire new knowledge. A psychologist, George Miller—this is the guy with the magic number 7 +- 2—when we interviewed him years ago at Boystown, he said, “My conviction is that everybody should be able to learn a new area of study within three months.” That’s what he thought for a scientist was a goal.
The idea is that you can learn new things. And that’s very important because when you think of it in terms of a 30-year career, how likely is it that the project that you’re undertaking at age 28 is the same project you’ll be working on at age 68? Not very likely. You’re going to be reinventing yourself as a scientist. And reinventing yourself is one of the most important things you can do, because otherwise you’re going to be dead wood. Some projects aren’t worth carrying beyond five or ten years. They have an expiration date.
Building Risk into Your Five-Year Plan Comments by Ray Kent, University of Wisconsin-Madison
Your doctoral study should generally be low-risk research. As you move into a postdoctoral fellowship, think about having two studies—one low-risk, one high-risk with a potential for high impact. At this time you can begin to play the risk factor a little bit differently.
When you are tenure-track you can have a mix of significance with low-risk and high-risk studies. And when you are tenured, then you can go for high risk, clinical trials, and collaborations. Because you have established your independence, so you do not need to worry about losing your visibility. You can be recognized as a legitimate member of the team.
As you plan your career, you should take risk into account. Just as you manage your money taking risk into account, we should manage our careers taking risk into account. I have met people who did not really think about that, and they embarked on some very risky procedures and wasted a lot of time and resources with very little to show for it. For example, don’t put everything into an untested technology basket. You want to be using state of the art technology, but you want to be sure it is going to give you what you need.
Other Formats and Uses of Your Research Plan Audience Comments
- If you do your job right with your job talk, there’s a lot of cross-pollination between your job talk and your research plan. Ideally your job talk tells your colleagues that this is the long-term plan that you have. And they shouldn’t be surprised when you submit a more detailed research plan. They should say, “okay this is very consistent with the job talk.” In my view, the job talk should be a crystal summary of the major aspects of that research program. Of course, much of the talk will be about a specific project or two—but it should always be embedded within the larger program. That helps the audience keep sight of the fact that you are looking at the program. You can say that this is one project that I’ve done, and I plan to do more of these, and this is how they are conceptually related. That’s a good example of why the research plan has multiple purposes – it can be a research statement, it can be the core of your job talk, it can be the nature of your elevator message, and it can be a version of your research plan for a K award application or R01 application or anything else of that nature.
- I think what’s useful is to actually draft your NIH biosketch. The new biosketch has a section called “contributions to science.” It’s really helpful to think about all your projects. It’s hard to start with a blank sheet of paper. But to have it in the format of a biosketch can be really helpful.
Avoiding Overcommitment Audience Comments
- One of the things that is amazing about planning is that if you put an estimate on the level of effort for each part of your plan, you’ll quickly find that you are living three or four lives. Some 300% of your time is spent. It’s helpful for those of us who might share my lack of ability to see constraints or limitations to reel it back and say, “I have a lot on my plate.” Which allows you to say no—which is not something we all do very well when it comes to those nice colleagues and those people you want to impress nationally and connect with. But it allows you to look at what’s planned and go, “I don’t know where I’d find the time to do that.” Which will hopefully help you stay on track.
- I keep a to do list, but I also keep a “to not do” list. One of the things I will keep on my plan is the maximum number of papers I will review in a year. If I hit that number in March, that’s it. I say no to every other paper that comes down the pike. That’s something to work out with your mentor as far as what’s realistic and what’s okay for you. Every time I get a request, I think, “That’s my reading and writing time, so what am I willing to give up. If it means I won’t be able to write on my own paper this week, am I willing to do this?”
Staying on Schedule with Reading, Writing, and Reviewing Audience Comments
- You have to do what works for you. Some people do wait for big blocks of time for writing—which are hard to come by. But the most important thing is to block off your time. Put it on your schedule, or it is the first thing that will get pushed aside.
- Another thing I’ve done with some of my colleagues is writing retreats. So maybe once a year, twice a year, we’ll get together. Usually we’ll go to a hotel or somewhere, and we’re just writing. It’s a great way to get a jumpstart on a project. Like, I need to sit down and start this manuscript, and you can keep going once you’ve got that momentum.
- My input would be that you really have to write all the time, every day. It’s a skill. I’ve found that if I take time off, my writing deteriorates. It’s something you need to keep up with.
- I would look at it like a savings account that you put money into on a daily, weekly, monthly basis. The flip side of writing is reading. I would read constantly, widely, and not just in the discipline. That will give you not only a breadth in terms of your understanding of your field and the world around you, but it will also give you an incentive to make your own contributions. I think we don’t talk enough about the comprehensive side to this, and being receptive to the reading. I have a book, or something, by my bedside every night. And I read that until I fall asleep every night. And it’s done me in good stead over the years.
- Reviewing articles can help advance your career, but it is something you need to weigh carefully as a draw on your time. You get a lot from it. You get to see what’s out there. You get to see what’s coming down the pipe before publication. To me that’s a huge benefit. You get to learn from other people’s writing, and that’s part of your reading you get to do. But it is time consuming. And it depends on the kinds of papers you get. Sometimes you’re lucky and sometimes you’re not.
- If someone else is reviewing your grants and your articles, at some point you owe it back. You should at least be in break-even mode. Now, pre-tenure or postdoc your mentor should be doing that or senior faculty in the department. But there are so many articles to review. I review so many articles, but I am also at the tail end of my career. The bottom line is, if you don’t put on your schedule that if you don’t put time on your schedule for reading, reviewing articles forces you to look at and think about the literature, so you can be accomplishing what you owe back to the field—and at the same time, staying one step ahead knowledge wise. It forces you to do what you should be doing all along, which is keeping up with the literature.
Further Reading: Web Resources
Golash-Boza, T. (2014). In Response to Popular Demand, More on the 5-Year Plan. The Professor Is In . Available at http://theprofessorisin.com/2014/05/09/in-response-to-popular-demand-more-on-the-5-year-plan
Kelsky, K. (2010). The Five-Year Plan for Tenure-Track Professors. Get a life, PhD . Available at http://getalifephd.blogspot.com/2010/07/five-year-plan-for-tenure-track.html
National Association of Geoscience Teachers (NAGT). (2012). Planning Worksheets . Planning your Research Program (Available from the Science Education Resource Center at Carelton College Website at http://serc.carleton.edu/).
Pfirman, S., Bell, R., Culligan, P., Balsam, P. & Laird, J. (2008) . Maximizing Productivity and Recognition , Part 3: Developing a Research Plan. Science Careers. Available at http://sciencecareers.sciencemag.org/career_magazine/previous_issues/articles/2008_10_10/caredit.a0800148
Cathy Binger University of New Mexico
Lizbeth Finestack University of Minnesota
Based on a presentation and slides originally developed by Ray Kent, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Presented at Pathways (2015). Hosted by the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association Research Mentoring Network.
Pathways is sponsored by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through a U24 grant awarded to ASHA.
Copyrighted Material. Reproduced by the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association in the Clinical Research Education Library with permission from the author or presenter.

Clinical Research Education
More from the cred library, innovative treatments for persons with dementia, implementation science resources for crisp, when the ears interact with the brain, follow asha journals on twitter.

© 1997-2024 American Speech-Language-Hearing Association Privacy Notice Terms of Use
- Utility Menu
Amanda Claybaugh, Dean of Undergraduate Education
Samuel zemurray jr. and doris zemurray stone radcliffe professor of english and harvard college professor.

How to Apply for Academic Jobs
1) a cover letter : The cover letter is the single most important part of your application. It is the first document that the hiring committee reads, and it determines whether they will read the rest: it should therefore capture everything that makes you a compelling candidate. Cover letters most often consist of five paragraphs:
an introduction that highlights the ways in which you're suited for this particular job a paragraph summarizing the argument of your dissertation as a whole a paragraph describing your other research interests, such as a second project or an article that is not part of your dissertation a paragraph describing your teaching, both the courses you have taught and the courses you would like to teach a boilerplate conclusion
Some cover letters may depart from the five-paragraph model, but none go over two pages: excessive length is seen as the mark of a madman, and overly small font also seems a bit crazed.
2) a cv : The cv performs the same function as the cover letter, but in a more abbreviated form. Formats vary, and you may pick the one you prefer. Whichever format you choose, make sure you mention the following:
your education, including the dates of all your degrees (either received or expected) your dissertation, including title, advisors, and a 2- to 3-sentence summary your publications, including those that are forthcoming or under review your conference talks your teaching experience your prizes and fellowships
3) a dissertation abstract : The dissertation abstract expands upon the cover letter, and it tends to do so in the following two ways. First, by elaborating the significance of your argument. In your cover letter, you summarize an argument; in your dissertation abstract, you explain why this argument matters (how does it change our understanding of your topic? how does it change our reading of the works you are focusing on?). And second, by explaining how the various parts of your dissertation connect to one another. In your cover letter, you name the authors or works you’re considering; in your dissertation abstract, you explain the distinctive role that each plays in your argument. The conventions of the dissertation abstract vary a bit, but most devote roughly a page to discussing the dissertation as a whole and roughly a page to summarizing the individual chapters. Some abstracts do depart from this structure, though, and you should think about what organization would make the most sense for your project.
4) a writing sample : The writing sample demonstrates that you can actually make the argument that you’ve so far been simply asserting. It should therefore be made up of two parts: an extended case study, drawn from one of your dissertation chapters; and a substantial opening section, drawn from your introduction, in which you frame this case study in a discussion of your argument as a whole. The more closely your writing sample resembles a journal article, the more successful it will be: dissertations tend to get bogged down in close reading and distracted by unrelated points, but a writing sample must move confidently through an array of examples in the course of making a sustained argument. You might find it helpful to model your writing sample on articles published in a journal you admire (look, in particular, for articles taken from projects that would later be published as books: these will likely have the right mix of framing and case study). Once you finish writing this article-like writing sample, you should send it to the journal you admire, so that you’ll have a(nother) publication under review for your cv. Different committees will request writing samples of different lengths, and you should draft your sample with that in mind, constructing it out of discrete units that you can include or leave out as the length requirements demand.
5) a job talk : The job talk does the same thing as the writing sample, but in oral form. It, too, should be made up of two parts: a substantial opening section that lays out your argument, followed by an extended case study (different from the one you offered in your writing sample). Different committees will ask for different things: some will want talks of thirty minutes (absolutely no more than 15 pages); others, talks of forty-five minutes (absolutely no more than 20 pages). Some may ask you to give a standard academic presentation; others, to present your research to undergrads.
But while these documents are fairly straightforward, they often prove to be very difficult to write. Writing them will require that you step back from the specific chapters and courses in which you’re now immersed and think about your scholarship and teaching more generally. You can do so by reflecting on the following topics:
1) your field : Some of you will find that your dissertation falls straightforwardly into a single hiring field (twentieth-century US, eighteenth-century English, Renaissance); your task, in that case, will be to persuade hiring committees that you have mastery of the entire field—not just that part of it that is covered by your dissertation. You will, of course, claim that you do, but it is best if you back up this claim in your descriptions of courses you might teach and other research interests you might pursue. That is, if your dissertation focuses on the Victorian novel, you should describe a survey course that focuses on poetry, drama, and prose as well, and you should also propose an additional research project that touches on topics and works that you do not cover in your dissertation.
Others will find that their dissertations fall into more than one field, crossing period or national boundaries. In this case, you will prepare two sets of materials, one for each field, and your task will be to persuade hiring committees that you are committed to whatever field they are hiring in. You should not try to conceal the fact that your dissertation crosses field boundaries; on the contrary, you should make a case for why it is necessary that it do so. But you should emphasize the field the department is hiring in when proposing courses and describing research interests. Still others of you will have written interdisciplinary dissertations, combining history and literature or literature and philosophy or touching on visual culture as well. In this case, your task is to persuade the hiring committee that your primary commitment is to literature. Once again, you should not try to conceal the interdisciplinary nature of your project, but rather make a case for it. But you should also take care to emphasize the literary in the courses and research projects you propose.
2) your dissertation :
a) What is the topic of your dissertation? It’s helpful to have a vivid word or phrase that you use consistently when describing your work; it’s also helpful to have a brief example of your topic that will be immediately familiar to others. And be prepared to explain where you set the limits of your topic: what doesn’t count as x , and why?
b) What is the argument of your dissertation?
c) How do the parts of your dissertation contribute to the argument of the whole? Some dissertations are organized chronologically (the pre-history of topic x , the height of topic x , the aftermath of topic x ); others are organized as a taxonomy.
d) What is the significance of your argument? More specifically, how does it change our understanding of your topic? and how does your focus on this topic change our reading of the works you are considering?
e) Why did you delimit your project in this way? How would it be different if you had focused on another period, another nation, another genre, different authors? Is there any work you’ve left out that you should be able to account for in some way?
f) What is the most significant change you’ll want to make as you turn this dissertation into a book?
g) How did you come to write this dissertation? What is the narrative of its development?
3) your teaching :
a) You will need to prepare an array of courses you’d like to teach. You might find it useful to sketch out a syllabus for each, but listing the readings you’d assign is less important than providing a rationale for the course as a whole. You should be able to describe, in two or three sentences, what you’d want your students to learn. You’ll tailor your course offerings to specific schools, but for now you should prepare courses in the following categories:
a multi-genre survey of your field (Renaissance Literature) a single-genre survey of your field (Twentieth-Century Poetry) an introductory survey course: usually either British literature to 1800, British literature after 1800, or US literature several undergraduate seminars in your field, organized in different ways (interdisciplinary, single-author, thematic) several graduate seminars in your field a first-year seminar or other intro to the major course a writing-intensive class
b) You should also gather anecdotes about your teaching: your greatest success; the skill you’ve struggled most to master; your most innovative assignment; your most unusual group of students.
3) your scholarship :
a) What other research interests are you pursuing or do you intend to pursue?
b) What do you think is the most significant recent development in your field? How does your work relate to it?
c) Who is the critic you most admire? Your most important intellectual influence?
d) How does your work differ from the work of your advisors?
Join thousands of product people at Insight Out Conf on April 11. Register free.
Insights hub solutions
Analyze data
Uncover deep customer insights with fast, powerful features, store insights, curate and manage insights in one searchable platform, scale research, unlock the potential of customer insights at enterprise scale.
Featured reads

Inspiration
Three things to look forward to at Insight Out
Tips and tricks
Make magic with your customer data in Dovetail

Four ways Dovetail helps Product Managers master continuous product discovery
Events and videos
© Dovetail Research Pty. Ltd.
How to write a research plan: Step-by-step guide
Last updated
30 January 2024
Reviewed by
Today’s businesses and institutions rely on data and analytics to inform their product and service decisions. These metrics influence how organizations stay competitive and inspire innovation. However, gathering data and insights requires carefully constructed research, and every research project needs a roadmap. This is where a research plan comes into play.
There’s general research planning; then there’s an official, well-executed research plan. Whatever data-driven research project you’re gearing up for, the research plan will be your framework for execution. The plan should also be detailed and thorough, with a diligent set of criteria to formulate your research efforts. Not including these key elements in your plan can be just as harmful as having no plan at all.
Read this step-by-step guide for writing a detailed research plan that can apply to any project, whether it’s scientific, educational, or business-related.
- What is a research plan?
A research plan is a documented overview of a project in its entirety, from end to end. It details the research efforts, participants, and methods needed, along with any anticipated results. It also outlines the project’s goals and mission, creating layers of steps to achieve those goals within a specified timeline.
Without a research plan, you and your team are flying blind, potentially wasting time and resources to pursue research without structured guidance.
The principal investigator, or PI, is responsible for facilitating the research oversight. They will create the research plan and inform team members and stakeholders of every detail relating to the project. The PI will also use the research plan to inform decision-making throughout the project.
- Why do you need a research plan?
Create a research plan before starting any official research to maximize every effort in pursuing and collecting the research data. Crucially, the plan will model the activities needed at each phase of the research project.
Like any roadmap, a research plan serves as a valuable tool providing direction for those involved in the project—both internally and externally. It will keep you and your immediate team organized and task-focused while also providing necessary definitions and timelines so you can execute your project initiatives with full understanding and transparency.
External stakeholders appreciate a working research plan because it’s a great communication tool, documenting progress and changing dynamics as they arise. Any participants of your planned research sessions will be informed about the purpose of your study, while the exercises will be based on the key messaging outlined in the official plan.
Here are some of the benefits of creating a research plan document for every project:
Project organization and structure
Well-informed participants
All stakeholders and teams align in support of the project
Clearly defined project definitions and purposes
Distractions are eliminated, prioritizing task focus
Timely management of individual task schedules and roles
Costly reworks are avoided
- What should a research plan include?
The different aspects of your research plan will depend on the nature of the project. However, most official research plan documents will include the core elements below. Each aims to define the problem statement, devising an official plan for seeking a solution.
Specific project goals and individual objectives
Ideal strategies or methods for reaching those goals
Required resources
Descriptions of the target audience, sample sizes, demographics, and scopes
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Project background
Research and testing support
Preliminary studies and progress reporting mechanisms
Cost estimates and change order processes
Depending on the research project’s size and scope, your research plan could be brief—perhaps only a few pages of documented plans. Alternatively, it could be a fully comprehensive report. Either way, it’s an essential first step in dictating your project’s facilitation in the most efficient and effective way.
- How to write a research plan for your project
When you start writing your research plan, aim to be detailed about each step, requirement, and idea. The more time you spend curating your research plan, the more precise your research execution efforts will be.
Account for every potential scenario, and be sure to address each and every aspect of the research.
Consider following this flow to develop a great research plan for your project:
Define your project’s purpose
Start by defining your project’s purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language.
Thinking about the project’s purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities. These individual tasks will be your stepping stones to reach your overarching goal.
Additionally, you’ll want to identify the specific problem, the usability metrics needed, and the intended solutions.
Know the following three things about your project’s purpose before you outline anything else:
What you’re doing
Why you’re doing it
What you expect from it
Identify individual objectives
With your overarching project objectives in place, you can identify any individual goals or steps needed to reach those objectives. Break them down into phases or steps. You can work backward from the project goal and identify every process required to facilitate it.
Be mindful to identify each unique task so that you can assign responsibilities to various team members. At this point in your research plan development, you’ll also want to assign priority to those smaller, more manageable steps and phases that require more immediate or dedicated attention.
Select research methods
Research methods might include any of the following:
User interviews: this is a qualitative research method where researchers engage with participants in one-on-one or group conversations. The aim is to gather insights into their experiences, preferences, and opinions to uncover patterns, trends, and data.
Field studies: this approach allows for a contextual understanding of behaviors, interactions, and processes in real-world settings. It involves the researcher immersing themselves in the field, conducting observations, interviews, or experiments to gather in-depth insights.
Card sorting: participants categorize information by sorting content cards into groups based on their perceived similarities. You might use this process to gain insights into participants’ mental models and preferences when navigating or organizing information on websites, apps, or other systems.
Focus groups: use organized discussions among select groups of participants to provide relevant views and experiences about a particular topic.
Diary studies: ask participants to record their experiences, thoughts, and activities in a diary over a specified period. This method provides a deeper understanding of user experiences, uncovers patterns, and identifies areas for improvement.
Five-second testing: participants are shown a design, such as a web page or interface, for just five seconds. They then answer questions about their initial impressions and recall, allowing you to evaluate the design’s effectiveness.
Surveys: get feedback from participant groups with structured surveys. You can use online forms, telephone interviews, or paper questionnaires to reveal trends, patterns, and correlations.
Tree testing: tree testing involves researching web assets through the lens of findability and navigability. Participants are given a textual representation of the site’s hierarchy (the “tree”) and asked to locate specific information or complete tasks by selecting paths.
Usability testing: ask participants to interact with a product, website, or application to evaluate its ease of use. This method enables you to uncover areas for improvement in digital key feature functionality by observing participants using the product.
Live website testing: research and collect analytics that outlines the design, usability, and performance efficiencies of a website in real time.
There are no limits to the number of research methods you could use within your project. Just make sure your research methods help you determine the following:
What do you plan to do with the research findings?
What decisions will this research inform? How can your stakeholders leverage the research data and results?
Recruit participants and allocate tasks
Next, identify the participants needed to complete the research and the resources required to complete the tasks. Different people will be proficient at different tasks, and having a task allocation plan will allow everything to run smoothly.
Prepare a thorough project summary
Every well-designed research plan will feature a project summary. This official summary will guide your research alongside its communications or messaging. You’ll use the summary while recruiting participants and during stakeholder meetings. It can also be useful when conducting field studies.
Ensure this summary includes all the elements of your research project. Separate the steps into an easily explainable piece of text that includes the following:
An introduction: the message you’ll deliver to participants about the interview, pre-planned questioning, and testing tasks.
Interview questions: prepare questions you intend to ask participants as part of your research study, guiding the sessions from start to finish.
An exit message: draft messaging your teams will use to conclude testing or survey sessions. These should include the next steps and express gratitude for the participant’s time.
Create a realistic timeline
While your project might already have a deadline or a results timeline in place, you’ll need to consider the time needed to execute it effectively.
Realistically outline the time needed to properly execute each supporting phase of research and implementation. And, as you evaluate the necessary schedules, be sure to include additional time for achieving each milestone in case any changes or unexpected delays arise.
For this part of your research plan, you might find it helpful to create visuals to ensure your research team and stakeholders fully understand the information.
Determine how to present your results
A research plan must also describe how you intend to present your results. Depending on the nature of your project and its goals, you might dedicate one team member (the PI) or assume responsibility for communicating the findings yourself.
In this part of the research plan, you’ll articulate how you’ll share the results. Detail any materials you’ll use, such as:
Presentations and slides
A project report booklet
A project findings pamphlet
Documents with key takeaways and statistics
Graphic visuals to support your findings
- Format your research plan
As you create your research plan, you can enjoy a little creative freedom. A plan can assume many forms, so format it how you see fit. Determine the best layout based on your specific project, intended communications, and the preferences of your teams and stakeholders.
Find format inspiration among the following layouts:
Written outlines
Narrative storytelling
Visual mapping
Graphic timelines
Remember, the research plan format you choose will be subject to change and adaptation as your research and findings unfold. However, your final format should ideally outline questions, problems, opportunities, and expectations.
- Research plan example
Imagine you’ve been tasked with finding out how to get more customers to order takeout from an online food delivery platform. The goal is to improve satisfaction and retain existing customers. You set out to discover why more people aren’t ordering and what it is they do want to order or experience.
You identify the need for a research project that helps you understand what drives customer loyalty. But before you jump in and start calling past customers, you need to develop a research plan—the roadmap that provides focus, clarity, and realistic details to the project.
Here’s an example outline of a research plan you might put together:
Project title
Project members involved in the research plan
Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan’s intent)
Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective)
Objective 2
Objective 3
Proposed timeline
Audience (detail the group you want to research, such as customers or non-customers)
Budget (how much you think it might cost to do the research)
Risk factors/contingencies (any potential risk factors that may impact the project’s success)
Remember, your research plan doesn’t have to reinvent the wheel—it just needs to fit your project’s unique needs and aims.
Customizing a research plan template
Some companies offer research plan templates to help get you started. However, it may make more sense to develop your own customized plan template. Be sure to include the core elements of a great research plan with your template layout, including the following:
Introductions to participants and stakeholders
Background problems and needs statement
Significance, ethics, and purpose
Research methods, questions, and designs
Preliminary beliefs and expectations
Implications and intended outcomes
Realistic timelines for each phase
Conclusion and presentations
How many pages should a research plan be?
Generally, a research plan can vary in length between 500 to 1,500 words. This is roughly three pages of content. More substantial projects will be 2,000 to 3,500 words, taking up four to seven pages of planning documents.
What is the difference between a research plan and a research proposal?
A research plan is a roadmap to success for research teams. A research proposal, on the other hand, is a dissertation aimed at convincing or earning the support of others. Both are relevant in creating a guide to follow to complete a project goal.
What are the seven steps to developing a research plan?
While each research project is different, it’s best to follow these seven general steps to create your research plan:
Defining the problem
Identifying goals
Choosing research methods
Recruiting participants
Preparing the brief or summary
Establishing task timelines
Defining how you will present the findings
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 17 February 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

Scientific Writing Resources / Career Development / Research Statement
General Guidelines in Scientific Writing
- Academic Integrity
- Building an Argument
- Critical Reading
- Critical Writing
- Figures and Tables
- Paragraphs
- Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing
- Peer-review
- Response to Reviewers’ Critiques
- Writing Tips and Tools
- Types or Styles of Writing
- How to evaluate online information resources
- Miscellaneous
Preparing Scholarly Work
- Dissertation/ Thesis
- Journal Article
- Original (Research) Article
- Review Article
- Editorial, Opinion, and Perspectives Articles
Preparing for a Publication
- Deciding on Authorship
- Cover letter for a journal manuscript submission
- Reference Management
Career Development
- Statement of Purpose (SOP)
Research Statement
- Teaching Statement
- Cover letter for a job application
A research statement may form a part of an application for college admission, a fellowship program, or a scholarship. It is typically required for an academic position (e.g., a postdoctoral or a faculty position) in a research-intensive institute/university. A research statement highlights the prior research experiences and future plans of the candidate. Importantly, a research statement helps the evaluation committee assess the suitability of the candidate and potential for success in a specific position or program. Furthermore, the presentation of the research statement demonstrates the candidate’s ability to think critically and communicate effectively.
A research statement typically includes information about the following:
- Broad description of the candidate’s research area
- Candidate’s academic research trajectory
- Short-term and long-term research vision and goals
- Resources required to achieve research goals
The evaluation committee may provide instructions on what to include in the research statement. Carefully read these instructions and create an outline of your research statement. Thereafter, expand your outline into descriptive paragraphs. It is important to also write within the word/page limits, if these instructions have been provided. It is also recommended to request your colleagues or faculty mentors to review your research statement. They may provide valuable insights that can help support your application.
The following are resources on writing a research statement for positions at different career stages, i.e., for post-graduate school or an academic (postdoctoral and faculty) position.
For Post-Graduate School
- Carnegie Mellon University, Global Communication Center, Writing a Research Statement
- Cornell University, Graduate School, Writing Your Research Statement
- Purdue Online Writing Lab, Graduate School Applications: Writing a Research Statement
For an Academic Position
- Austin, J. (2002). Writing a Research Plan , Sciencemag.org
- Ball, C.E. (2014). Research Statements . Inside Higher Ed.
- Gillmore, J.G. (n.d.). Writing the Research Plan for Your Academic Job Application. American Chemical Society.
- Taylor, C. (2020). How to Write a Research Statement , WikiHow.
- University of Pennsylvania (n.d.). Research Statements for Faculty Job Applications.
- Boothroyd, J. (2020). How to Prepare a Compelling Research Statement for R1 Faculty Applications , Stanford University.
- Hadjiargyrou, M. (2012). How to Write a Research Statement, Stony Brook University.
- White, A., and zue Loye, H-C. (2015). How to Write your Research Statement , University of South Carolina.

- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to secondary sidebar
- Skip to footer
career-advice.jobs.ac.uk
Making A Five Year Research Plan

Many academics will be asked by their institutions to produce a research plan that will take them up to the date of the next REF-style audit. In this exercise universities want their researchers to conduct ‘blue skies’ thinking that will fulfil their institutional strategic needs. However, scholars have their own agendas too. Here’s some advice on how to make your five-year research plan work for you.
Thinking backwards:
Preparing a five-year plan is a good opportunity for you to tie up loose ends. Doing your PhD you will have come across numerous avenues of research that did not make the final draft. So you will probably have several half-started projects or ideas that have a lot of potential. You might now be able to schedule time to complete these projects. If they are worthwhile to the development of your discipline, enhancing your own scholarly identity and furthering your career, then they are definitely worth pursuing.
Thinking forwards:
This is also an exciting opportunity to plan and develop new projects. It is vital to think big and to show your current employers or any future employers that you can deliver significant research projects. However, be realistic. Take into account the teaching commitments that will distract you from research and the competitive nature of funding and publication opportunities.
Planning ahead – career and research:
Using this method of five-year planning, you can tie your research profile to your developing career. Do you want to move to another institution or gain promotion in your current one? If so, think of ways in which your research plan can improve your chances of doing just that. Undertaking an audit of your progress so far and your future plans is a perfect activity for the new year!
Institutional needs:
Your university (and future employers) will want to see that you’ve thought about three major areas: internationalisation, third stream income and impact . They may also have their own particular areas of focus that you can refer to.
Your research mentor will want to see that any projects are realistically costed. Do not just imagine what you want to research but how you will pay for it. If you suggest a piece of research that can be accomplished without teaching relief, practical resources, or travel costs then you can complete it when you like, but some funding will be required for most projects. Try to achieve a balance between internal funding from your institution and external funding from other sources.
Collaborations:
You don’t always have to design, undertake and complete a research project alone. Scientists are much better at collaborative work than their humanities counterparts. Not only can collaborations be personally rewarding through developing connections and even friendships with like-minded individuals, but also much larger projects can be considered.
When thinking of your research plans, focus on the output that you will produce. This might be a traditional publication, a monograph, edited collection or journal, but could be something different such as a documentary, a museum exhibition, a website, a series of public lectures or a database. These outputs can be tied to the strategic agenda of your university, and to your career development ambitions.
Share this article
Reader Interactions
You may also like:, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please enter an answer in digits: 17 − nine =
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
4 Examples of Academic Writing
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
The best way to understand what effective academic writing looks like is to review academic writing examples.
Let's begin with four of the most common types of academic writing: research proposals, dissertations, abstracts, and academic articles. We'll be examining each type of writing and providing academic writing samples of each.
Whether you aim to earn funding for a passion project or are stymied by how to format an abstract, these academic writing examples will help you nail your next undertaking.
Academic Writing Example 1: Research Proposals
A research proposal is an outline of the proposed research of a PhD candidate, a private researcher, or someone hoping to obtain a research grant .
Your proposal should put your best foot forward: It details your intended research question and how it relates to existing research, makes an argument for why your research should be chosen for advancement or funding, and explains the deliverables you hope to achieve with your research.
A more detailed look at what proposal writing is and what goes into a research proposal may also be beneficial. Every proposal is different because every project is different. Proposal requirements also differ according to the university or funding agency that reviews the proposal.
Research Proposal Structure
A cover letter summarizing your proposal and showcasing why you should be chosen
An introduction or abstract
An explanation of the background, purpose, and significance of your research
A research plan or methodology that includes a timeline (a Gantt chart may be beneficial)
A projected budget, if applicable
Academic Writing Sample: Research Proposal Excerpt
Building on the work of the three foundational sociological theorists—Marx, Weber, and Durkheim—and Mark Traugott's theory of the "insurgent barricade," this proposed research will analyze the appearance, use, and disappearance of barricade warfare as an effective battle strategy.
Focusing on these three theorists, this research will determine which theory or theories best explain the life cycle of barricade warfare, focusing in particular on its disappearance. A brief but comprehensive history of barricade warfare will be provided in addition to the theoretical explanations of barricade warfare's utility.
Research Proposal Writing Tips
Before you format your proposal, contact your targeted university, private organization, or funding agency to confirm what they require for proposals. Then, try to follow this format as closely as possible.
Be detailed when outlining your goals and your funding needs. Connect the objectives of the research to the resources you're requesting.
Be realistic in what you ask for as far as resources—don't ask for more or less than you need, and show evidence to justify your choices.
Don't dedicate too much text in your proposal to describing past research. A summary of key points, arguments, theories, and how your research will build on them should suffice.
Remember that no matter how good your proposal is, it might be rejected. You're likely up against dozens or even hundreds of other candidates who have equally sound proposals. Don't be discouraged if this happens. See it as a learning opportunity for your next proposal.
Academic Writing Example 2: Dissertations
A dissertation is a body of writing that represents original research and is generally written as part of a PhD or master's program.
Typically, it builds on previous research in the field to make a significant contribution or advancement. You may benefit from more detailed information on what a dissertation is , how to write a dissertation , and how to edit a dissertation .
Dissertation Structure
Introduction/background and the significance of the study
Literature review
Methodology
Results/findings
Conclusion/contribution to the body of research
Academic Writing Sample: Dissertation Excerpt
There are two options for choosing a unit of analysis for this phenomenon: the social artifact (erected barricades) or the social interaction (the collaboration of insurgents engaged in barricade warfare). The best choice is social interaction.
Most individual occurrences of barricade warfare involve the construction of more than one barricade, and the number of barricades is not necessarily a valid indicator of the sociological magnitude of an insurgence. The most relevant choice is an insurgence, the event of a conflict involving barricade warfare.
Dissertation Writing Tips
Remember to bear in mind the significance of your study. It doesn't have to be paradigm shifting, but you want to infuse the dissertation with reminders of why your research is important.
Don't get bogged down in trying to show that your research is one of a kind or uniquely contributive to the body of research. It likely isn't, and it's more effective to show how you are building on previous research .
Remember to check with your college or university to ensure that you're formatting your dissertation according to the school's expectations.
Ask your advisor questions when you need to.
Be prepared to make alterations to your dissertation according to your thesis committee's suggestions. This doesn't mean you did a bad job—it just means there's room for improvement.
Academic Writing Example 3: Abstracts
The abstract is actually a component of other forms of academic writing, such as scholarly articles and dissertations. The abstract acts as a comprehensive outline of your paper in paragraph form.
Abstract Structure
Results
You may want to read more about what abstracts are and why they are important in preparing yourself for writing one.
Academic Writing Sample: Abstract
Barricade warfare has occurred across several spectra, but most notably, it occurred almost exclusively in a 300-year period between the 16th and 19th centuries. Each instance had an inciting incident, but a common thread was the culture of revolution: a revolutionary tradition based on the belief that injustice was being carried out and that, in this case, barricade insurgence was the way to resolve it.
This study uses the theories of Karl Marx and Emile Durkheim to analyze barricade warfare, its appearance, and its disappearance. Ultimately, neither theory can independently explain this phenomenon.
Marx offers a reasonable explanation for why barricade warfare may have died, but his theory is difficult to test empirically and fails to explain the absence of recurrences. Conversely, Durkheim's theory is much easier to observe and can explain why barricade warfare has not experienced a renaissance. However, he offered no reason as to why it died in the first place.
These two theoretical orientations complement each other nicely and, ultimately, neither can stand alone.
Notice that this abstract comes in at under 200 words (a common limit) but nevertheless covers the background of the study, how it was approached, and the results and conclusions of the research.
If you are struggling to meet a word count, check out 10 Academic Phrases Your Writing Doesn't Need .
Abstract Writing Tips
Be conscious of your word count. Stay under the limit.
Check with your school or target journal to make sure special formatting is not required.
Don't use abbreviations or citations in the abstract.
Don't simply restate your thesis or copy your introduction. Neither of these is an abstract.
Remember that your abstract often gives readers their first impressions of your work. Despite its short length, it deserves a lot of attention.
Academic Writing Example 4: Articles
Academic articles are pieces of writing intended for publication in academic journals or other scholarly sources. They may be original research studies, literature analyses, critiques , or other forms of scholarly writing.
Article Structure
Abstract and keywords
Introduction
Materials and methods
References and appendices
Academic Writing Sample: Article Excerpt
"Those great revolutionary barricades were places where heroes came together" (Hugo, 2008). This description by Victor Hugo of the 1832 June Rebellion in Paris comes from his seminal work of fiction, Les Miserables.
Although the account is fictionalized, it is deeply representative of what historian Mark Traugott (2010, p. 225) terms the "culture of revolution." This spirit of heroic response to social injustice swept across Europe during the second half of the millennium and was characterized in part by barricade warfare.
The phenomenon of the insurgent barricade has essentially disappeared, however, leaving no trace of its short-lived but intense epoch, and the question of why this happened remains a mystery. The theories of Karl Marx and Emile Durkheim, when taken together, provide a compelling explanation for the disappearance of barricade warfare, and the tenets of each theory will be examined to explain this phenomenon.
Article Writing Tips
Follow these detailed steps for writing an article and publishing it in a journal .
Make sure that you follow all of your target journal's guidelines.
Have a second set of educated eyes look over your article to correct typos, confusing language, and unclear arguments.
Don't be discouraged if your article is not chosen for publication. As with proposal writing, you are up against countless others with equally compelling research.
Don't be discouraged if the journal asks you to make changes to your article. This is common. It means they see value in your article, as well as room for improvement.
Whether you're applying for funding, earning an advanced degree, aiming to publish in a journal, or just trying to cram your 4,000-word study into a 150-word abstract, hopefully these academic writing examples have helped get your creative juices flowing.
Go out there and write! With these academic writing samples at your side, you are sure to model your academic writing appropriately.
Achieve Your Academic Goals
Hire an expert academic editor , or get a free sample, about the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

10 Academic Phrases Your Writing Doesn't Need

21 Legit Research Databases for Free Journal Articles in 2022

Grant Writing Basics
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).


COMMENTS
Good science, written well, makes a good research plan. As you craft and refine your research plan, keep the following strategies, as well as your audience in mind: Begin the document with an abstract or executive summary that engages a broad audience and shows synergies among your projects. This should be one page or less, and you should ...
Step 4: The research statement is typically a few (2-3) pages in length, depending on the number of images, illustrations, or graphs included. Once you have completed the steps above, schedule an appointment with a career advisor to get feedback on your draft. You should also try to get faculty in your department to review your document if they ...
The research statement (or statement of research interests) is a common component of academic job applications. It is a summary of your research accomplishments, current work, and future direction and potential of your work. The statement can discuss specific issues such as: The research statement should be technical, but should be intelligible ...
Many post-doc and faculty job postings - in a variety of disciplines and in an array of institutions - require that candidates send a Research Statement. Being able to write coherently about your past/current research efforts and articulately about your future research plans is very important. DEFINITION
If her goal and plan of execution intrigues the audience, she will become a standout candidate.) Determine the length of your plan: It is recommended for a research plan to be 10 pages in length. Additionally, you should have a proposal that is 3-5 pages long, which would serve as a summary of your roles and responsibilities if/when hired.
The mobile-friendly eBook entitled " Writing the Research Plan for Your Academic Job Application " includes tips on how to: Tailor your application for each school: Make sure you look at the guidelines that your university requires for the application. If your application matches the qualities of the type of candidate they want, the more ...
If you want to learn how to write your own plan for your research project, consider the following seven steps: 1. Define the project purpose. The first step to creating a research plan for your project is to define why and what you're researching. Regardless of whether you're working with a team or alone, understanding the project's purpose can ...
Nearly every applicant for a tenure-track faculty job is expected to include a research plan. Exceptions are rare. Just as rare are programs designed to help doctoral students and postdocs learn how to create a research plan. Which is too bad: Writing an effective research plan is tricky. And until now, there was little advice to be found.
A Research Trajectory can one (or both) of two things: 1) it can present a narrative in timeline form of how your thinking has evolved. 2) it can present your Research Plan for the next 5-6 years (pandemics and life will obviously derail that plan!) So what I have done with my own Research Statements is to present how my research interests have ...
Research agenda: The research agenda seems the most distant for most graduate students, and yet it might be the easiest document to write because it is speculative in many ways. This document — sometimes called a research statement or plan — is basically a one- to two-page, single-spaced text that outlines how you plan to get tenure.
Get additional feedback on your materials from your faculty advisor and other mentors. 1) CV (curriculum vitae) : comprehensive scholarly record, including your research experience, teaching and mentoring experience, publication record, and more. See more details on preparing a CV. 2) Cover letter : 1-2 page letter, addressed to search committee.
Style. Avoid long paragraphs. Paragraphs should never take up more than half a page and may be even shorter. If you have a lot to say about one particular project, that section might be broken up into 2-3 paragraphs to help keep your reader engaged. Research statements should be written in the first-person and in the active voice.
A research statement is a one to three page document that may be required to apply for an . academic job or (less frequently) graduate school. The purpose of a research statement is to describe the trajectory of your research to a selection/search committee. A research statement allows you to • show that you can take on independent research •
In EECS, faculty research statements focus on past/current work. However, it is important to also include your vision for the future, which should build on your previous work. This statement should convince the committee that your future work is important, relevant, and feasible. The future work section should go beyond direct extensions of ...
Research Statements are typically between 2-5 pages in length. The exact statement length may be specified in the job advertisement. For more guidance on formatting, read the detailed PDF. Begin your statement with a paragraph about the overarching theme of your past research and how it connects with your future research plans.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use" Title page
You only get about 40% of your time allocated to research as faculty in the UK. So, the actual goal of the presentation was to say stuff like: "for research idea A, I will aim to fund it from the agency B, which will allow me to hire a postdoctoral researcher for X years to work on A". Consequently, the research plan takes a much different ...
Here we discuss 5 simple tips for writing a good research statement: 1. Make Your Research Statement Reader-Friendly. As stated earlier, a faculty position may easily receive over a couple of hundred applications. Consequently, the search committee may just glance through some applications.
Presented by Cathy Binger. First we're going to talk about what a research plan is, why it's important to write one, and why five years—why not one year, why not ten years. So we'll do some of those basic things, then Liza is going to get down and dirty into the nitty-gritty of "now what" how do I go about writing that research plan.
In one sense, applying for academic jobs is a straightforward process, requiring only that you produce a small set of relatively brief documents according to fairly standard conventions: 1) a cover letter: The cover letter is the single most important part of your application. It is the first document that the hiring committee reads, and it ...
Start by defining your project's purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language. Thinking about the project's purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities.
Carefully read these instructions and create an outline of your research statement. Thereafter, expand your outline into descriptive paragraphs. It is important to also write within the word/page limits, if these instructions have been provided. It is also recommended to request your colleagues or faculty mentors to review your research statement.
This paper describes, for none major employer of recent Ph.D. graduates, (1) the nature of industrial employment; (2) how the hiring process works, including the major differences from academic ...
Preparing a five-year plan is a good opportunity for you to tie up loose ends. Doing your PhD you will have come across numerous avenues of research that did not make the final draft. So you will probably have several half-started projects or ideas that have a lot of potential. You might now be able to schedule time to complete these projects.
Academic Writing Sample: Research Proposal Excerpt Building on the work of the three foundational sociological theorists—Marx, Weber, and Durkheim—and Mark Traugott's theory of the "insurgent barricade," this proposed research will analyze the appearance, use, and disappearance of barricade warfare as an effective battle strategy.
How to Write a Research Statement. For a research statement to get its message across, a good format is required, poor formatting may have you lose structure and deliver your points in a disorderly fashion. A great statement should follow the following format: Introduction. As any other academic document, a research statement needs a good ...