November 1, 2023
21 min read

Can We Save Every Species from Extinction?
The Endangered Species Act requires that every U.S. plant and animal be saved from extinction, but after 50 years, we have to do much more to prevent a biodiversity crisis
By Robert Kunzig
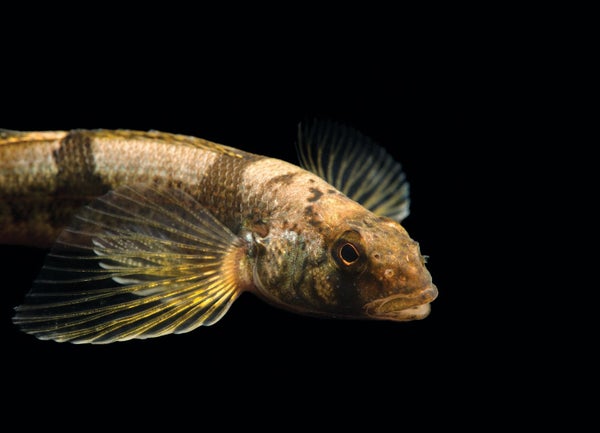

Snail Darter Percina tanasi. Listed as Endangered: 1975. Status: Delisted in 2022.
© Joel Sartore/National Geographic Photo Ark
A Bald Eagle disappeared into the trees on the far bank of the Tennessee River just as the two researchers at the bow of our modest motorboat began hauling in the trawl net. Eagles have rebounded so well that it's unusual not to see one here these days, Warren Stiles of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service told me as the net got closer. On an almost cloudless spring morning in the 50th year of the Endangered Species Act, only a third of a mile downstream from the Tennessee Valley Authority's big Nickajack Dam, we were searching for one of the ESA's more notorious beneficiaries: the Snail Darter. A few months earlier Stiles and the FWS had decided that, like the Bald Eagle, the little fish no longer belonged on the ESA's endangered species list. We were hoping to catch the first nonendangered specimen.
Dave Matthews, a TVA biologist, helped Stiles empty the trawl. Bits of wood and rock spilled onto the deck, along with a Common Logperch maybe six inches long. So did an even smaller fish; a hair over two inches, it had alternating vertical bands of dark and light brown, each flecked with the other color, a pattern that would have made it hard to see against the gravelly river bottom. It was a Snail Darter in its second year, Matthews said, not yet full-grown.
Everybody loves a Bald Eagle. There is much less consensus about the Snail Darter. Yet it epitomizes the main controversy still swirling around the ESA, signed into law on December 28, 1973, by President Richard Nixon: Can we save all the obscure species of this world, and should we even try, if they get in the way of human imperatives? The TVA didn't think so in the 1970s, when the plight of the Snail Darter—an early entry on the endangered species list—temporarily stopped the agency from completing a huge dam. When the U.S. attorney general argued the TVA's case before the Supreme Court with the aim of sidestepping the law, he waved a jar that held a dead, preserved Snail Darter in front of the nine judges in black robes, seeking to convey its insignificance.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Now I was looking at a living specimen. It darted around the bottom of a white bucket, bonking its nose against the side and delicately fluttering the translucent fins that swept back toward its tail.
“It's kind of cute,” I said.
Matthews laughed and slapped me on the shoulder. “I like this guy!” he said. “Most people are like, ‘Really? That's it?’ ” He took a picture of the fish and clipped a sliver off its tail fin for DNA analysis but left it otherwise unharmed. Then he had me pour it back into the river. The next trawl, a few miles downstream, brought up seven more specimens.
In the late 1970s the Snail Darter seemed confined to a single stretch of a single tributary of the Tennessee River, the Little Tennessee, and to be doomed by the TVA's ill-considered Tellico Dam, which was being built on the tributary. The first step on its twisting path to recovery came in 1978, when the U.S. Supreme Court ruled, surprisingly, that the ESA gave the darter priority even over an almost finished dam. “It was when the government stood up and said, ‘Every species matters, and we meant it when we said we're going to protect every species under the Endangered Species Act,’” says Tierra Curry, a senior scientist at the Center for Biological Diversity.
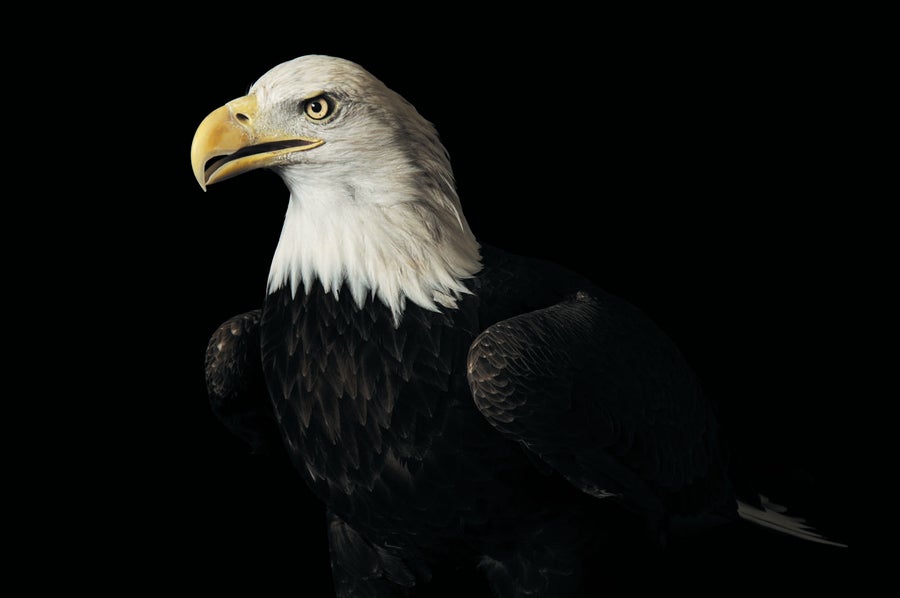

Bald Eagle Haliaeetus leucocephalus. Listed as Endangered: 1967. Status: Delisted in 2007. Credit: © Joel Sartore/National Geographic Photo Ark
Today the Snail Darter can be found along 400 miles of the river's main stem and multiple tributaries. ESA enforcement has saved dozens of other species from extinction. Bald Eagles, American Alligators and Peregrine Falcons are just a few of the roughly 60 species that had recovered enough to be “delisted” by late 2023.
And yet the U.S., like the planet as a whole, faces a growing biodiversity crisis. Less than 6 percent of the animals and plants ever placed on the list have been delisted; many of the rest have made scant progress toward recovery. What's more, the list is far from complete: roughly a third of all vertebrates and vascular plants in the U.S. are vulnerable to extinction, says Bruce Stein, chief scientist at the National Wildlife Federation. Populations are falling even for species that aren't yet in danger. “There are a third fewer birds flying around now than in the 1970s,” Stein says. We're much less likely to see a White-throated Sparrow or a Red-winged Blackbird, for example, even though neither species is yet endangered.
The U.S. is far emptier of wildlife sights and sounds than it was 50 years ago, primarily because habitat—forests, grasslands, rivers—has been relentlessly appropriated for human purposes. The ESA was never designed to stop that trend, any more than it is equipped to deal with the next massive threat to wildlife: climate change. Nevertheless, its many proponents say, it is a powerful, foresightful law that we could implement more wisely and effectively, perhaps especially to foster stewardship among private landowners. And modest new measures, such as the Recovering America's Wildlife Act—a bill with bipartisan support—could further protect flora and fauna.
That is, if special interests don't flout the law. After the 1978 Supreme Court decision, Congress passed a special exemption to the ESA allowing the TVA to complete the Tellico Dam. The Snail Darter managed to survive because the TVA transplanted some of the fish from the Little Tennessee, because remnant populations turned up elsewhere in the Tennessee Valley, and because local rivers and streams slowly became less polluted following the 1972 Clean Water Act, which helped fish rebound.
Under pressure from people enforcing the ESA, the TVA also changed the way it managed its dams throughout the valley. It started aerating the depths of its reservoirs, in some places by injecting oxygen. It began releasing water from the dams more regularly to maintain a minimum flow that sweeps silt off the river bottom, exposing the clean gravel that Snail Darters need to lay their eggs and feed on snails. The river system “is acting more like a real river,” Matthews says. Basically, the TVA started considering the needs of wildlife, which is really what the ESA requires. “The Endangered Species Act works,” Matthews says. “With just a little bit of help, [wildlife] can recover.”
The trouble is that many animals and plants aren't getting that help—because government resources are too limited, because private landowners are alienated by the ESA instead of engaged with it, and because as a nation the U.S. has never fully committed to the ESA's essence. Instead, for half a century, the law has been one more thing that polarizes people's thinking.
I t may seem impossible today to imagine the political consensus that prevailed on environmental matters in 1973. The U.S. Senate approved the ESA unanimously, and the House passed it by a vote of 390 to 12. “Some people have referred to it as almost a statement of religion coming out of the Congress,” says Gary Frazer, who as assistant director for ecological services at the FWS has been overseeing the act's implementation for nearly 25 years.
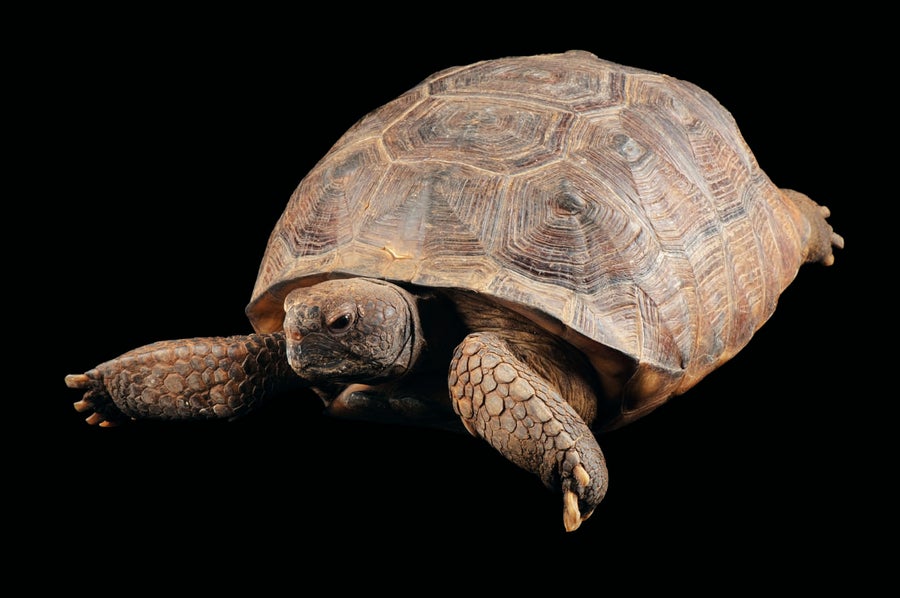

Gopher Tortoise Gopherus polyphemus . Listed as Threatened: 1987. Status: Still threatened. Credit: ©Joel Sartore/National Geographic Photo Ark
But loss of faith began five years later with the Snail Darter case. Congresspeople who had been thinking of eagles, bears and Whooping Cranes when they passed the ESA, and had not fully appreciated the reach of the sweeping language they had approved, were disabused by the Supreme Court. It found that the legislation had created, “wisely or not ... an absolute duty to preserve all endangered species,” Chief Justice Warren E. Burger said after the Snail Darter case concluded. Even a recently discovered tiny fish had to be saved, “whatever the cost,” he wrote in the decision.
Was that wise? For both environmentalists such as Curry and many nonenvironmentalists, the answer has always been absolutely. The ESA “is the basic Bill of Rights for species other than ourselves,” says National Geographic photographer Joel Sartore, who is building a “photo ark” of every animal visible to the naked eye as a record against extinction. (He has taken studio portraits of 15,000 species so far.) But to critics, the Snail Darter decision always defied common sense. They thought it was “crazy,” says Michael Bean, a leading ESA expert, now retired from the Environmental Defense Fund. “That dichotomy of view has remained with us for the past 45 years.”
According to veteran Washington, D.C., environmental attorney Lowell E. Baier, author of a new history called The Codex of the Endangered Species Act, both the act itself and its early implementation reflected a top-down, federal “command-and-control mentality” that still breeds resentment. FWS field agents in the early days often saw themselves as combat biologists enforcing the act's prohibitions. After the Northern Spotted Owl's listing got tangled up in a bitter 1990s conflict over logging of old-growth forests in the Pacific Northwest, the FWS became more flexible in working out arrangements. “But the dark mythology of the first 20 years continues in the minds of much of America,” Baier says.
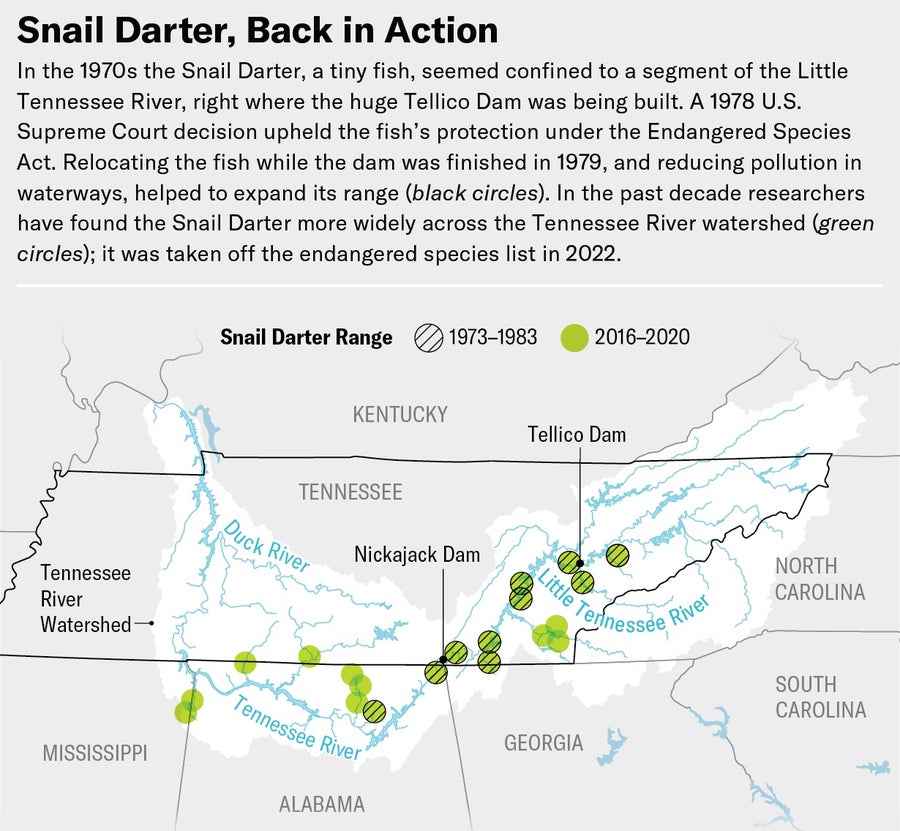
Credit: June Minju Kim ( map ); Source: David Matthews, Tennessee Valley Authority ( reference )
The law can impose real burdens on landowners. Before doing anything that might “harass” or “harm” an endangered species, including modifying its habitat, they need to get a permit from the FWS and present a “habitat conservation plan.” Prosecutions aren't common, because evidence can be elusive, but what Bean calls “the cloud of uncertainty” surrounding what landowners can and cannot do can be distressing.
Requirements the ESA places on federal agencies such as the Forest Service and the Bureau of Land Management—or on the TVA—can have large economic impacts. Section 7 of the act prohibits agencies from taking, permitting or funding any action that is likely to “jeopardize the continued existence” of a listed species. If jeopardy seems possible, the agency must consult with the FWS first (or the National Marine Fisheries Service for marine species) and seek alternative plans.
“When people talk about how the ESA stops projects, they've been talking about section 7,” says conservation biologist Jacob Malcom. The Northern Spotted Owl is a strong example: an economic analysis suggests the logging restrictions eliminated thousands of timber-industry jobs, fueling conservative arguments that the ESA harms humans and economic growth.
In recent decades, however, that view has been based “on anecdote, not evidence,” Malcom claims. At Defenders of Wildlife, where he worked until 2022 (he's now at the U.S. Department of the Interior), he and his colleagues analyzed 88,290 consultations between the FWS and other agencies from 2008 to 2015. “Zero projects were stopped,” Malcom says. His group also found that federal agencies were only rarely taking the active measures to recover a species that section 7 requires—like what the TVA did for the Snail Darter. For many listed species, the FWS does not even have recovery plans.
Endangered species also might not recover because “most species are not receiving protection until they have reached dangerously low population sizes,” according to a 2022 study by Erich K. Eberhard of Columbia University and his colleagues. Most listings occur only after the FWS has been petitioned or sued by an environmental group—often the Center for Biological Diversity, which claims credit for 742 listings. Years may go by between petition and listing, during which time the species' population dwindles. Noah Greenwald, the center's endangered species director, thinks the FWS avoids listings to avoid controversy—that it has internalized opposition to the ESA.
He and other experts also say that work regarding endangered species is drastically underfunded. As more species are listed, the funding per species declines. “Congress hasn't come to grips with the biodiversity crisis,” says Baier, who lobbies lawmakers regularly. “When you talk to them about biodiversity, their eyes glaze over.” Just this year federal lawmakers enacted a special provision exempting the Mountain Valley Pipeline from the ESA and other challenges, much as Congress had exempted the Tellico Dam. Environmentalists say the gas pipeline, running from West Virginia to Virginia, threatens the Candy Darter, a colorful small fish. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 provided a rare bit of good news: it granted the FWS $62.5 million to hire more biologists to prepare recovery plans.
The ESA is often likened to an emergency room for species: overcrowded and understaffed, it has somehow managed to keep patients alive, but it doesn't do much more. The law contains no mandate to restore ecosystems to health even though it recognizes such work as essential for thriving wildlife. “Its goal is to make things better, but its tools are designed to keep things from getting worse,” Bean says. Its ability to do even that will be severely tested in coming decades by threats it was never designed to confront.
T he ESA requires a species to be listed as “threatened” if it might be in danger of extinction in the “foreseeable future.” The foreseeable future will be warmer. Rising average temperatures are a problem, but higher heat extremes are a bigger threat, according to a 2020 study.
Scientists have named climate change as the main cause of only a few extinctions worldwide. But experts expect that number to surge. Climate change has been “a factor in almost every species we've listed in at least the past 15 years,” Frazer says. Yet scientists struggle to forecast whether individual species can “persist in place or shift in space”—as Stein and his co-authors put it in a recent paper—or will be unable to adapt at all and will go extinct. On June 30 the FWS issued a new rule that will make it easier to move species outside their historical range—a practice it once forbade except in extreme circumstances.
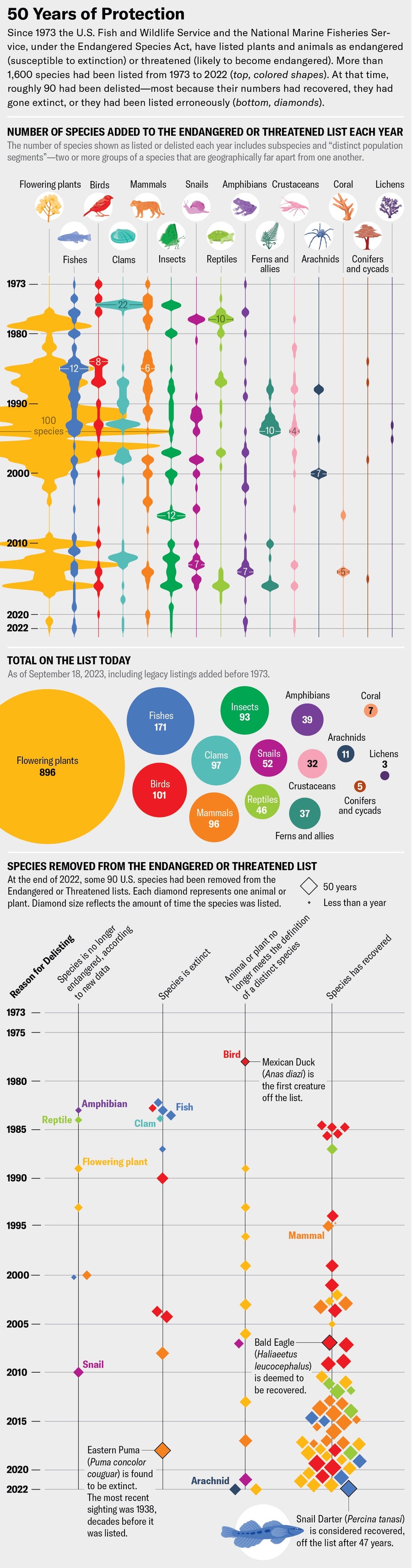
Credit: June Minju Kim ( graphic ); Brown Bird Design ( illustrations ); Sources: U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Environmental Conservation Online System; U.S. Federal Endangered and Threatened Species by Calendar Year https://ecos.fws.gov/ecp/report/species-listings-by-year-totals ( annual data through 2022 ); Listed Species Summary (Boxscore) https://ecos.fws.gov/ecp/report/boxscore ( cumulative data up to September 18, 2023, and annual data for coral ); Delisted Species https://ecos.fws.gov/ecp/report/species-delisted ( delisted data through 2022 )
Eventually, though, “climate change is going to swamp the ESA,” says J. B. Ruhl, a law professor at Vanderbilt University, who has been writing about the problem for decades. “As more and more species are threatened, I don't know what the agency does with that.” To offer a practical answer, in a 2008 paper he urged the FWS to aggressively identify the species most at risk and not waste resources on ones that seem sure to expire.
Yet when I asked Frazer which urgent issues were commanding his attention right now, his first thought wasn't climate; it was renewable energy. “Renewable energy is going to leave a big footprint on the planet and on our country,” he says, some of it threatening plants and animals if not implemented well. “The Inflation Reduction Act is going to lead to an explosion of more wind and solar across the landscape.
Long before President Joe Biden signed that landmark law, conflicts were proliferating: Desert Tortoise versus solar farms in the Mojave Desert, Golden Eagles versus wind farms in Wyoming, Tiehm's Buckwheat (a little desert flower) versus lithium mining in Nevada. The mine case is a close parallel to that of Snail Darters versus the Tellico Dam. The flower, listed as endangered just last year, grows on only a few acres of mountainside in western Nevada, right where a mining company wants to extract lithium. The Center for Biological Diversity has led the fight to save it. Elsewhere in Nevada people have used the ESA to stop, for the moment, a proposed geothermal plant that might threaten the two-inch Dixie Valley Toad, discovered in 2017 and also declared endangered last year.
Does an absolute duty to preserve all endangered species make sense in such places? In a recent essay entitled “A Time for Triage,” Columbia law professor Michael Gerrard argues that “the environmental community has trade-off denial. We don't recognize that it's too late to preserve everything we consider precious.” In his view, given the urgency of building the infrastructure to fight climate change, we need to be willing to let a species go after we've done our best to save it. Environmental lawyers adept at challenging fossil-fuel projects, using the ESA and other statutes, should consider holding their fire against renewable installations. “Just because you have bullets doesn't mean you shoot them in every direction,” Gerrard says. “You pick your targets.” In the long run, he and others argue, climate change poses a bigger threat to wildlife than wind turbines and solar farms do.
For now habitat loss remains the overwhelming threat. What's truly needed to preserve the U.S.'s wondrous biodiversity, both Stein and Ruhl say, is a national network of conserved ecosystems. That won't be built with our present politics. But two more practical initiatives might help.
The first is the Recovering America's Wildlife Act, which narrowly missed passage in 2022 and has been reintroduced this year. It builds on the success of the 1937 Pittman-Robertson Act, which funds state wildlife agencies through a federal excise tax on guns and ammunition. That law was adopted to address a decline in game species that had hunters alarmed. The state refuges and other programs it funded are why deer, ducks and Wild Turkeys are no longer scarce.
The recovery act would provide $1.3 billion a year to states and nearly $100 million to Native American tribes to conserve nongame species. It has bipartisan support, in part, Stein says, because it would help arrest the decline of a species before the ESA's “regulatory hammer” falls. Although it would be a large boost to state wildlife budgets, the funding would be a rounding error in federal spending. But last year Congress couldn't agree on how to pay for the measure. Passage “would be a really big deal for nature,” Curry says.
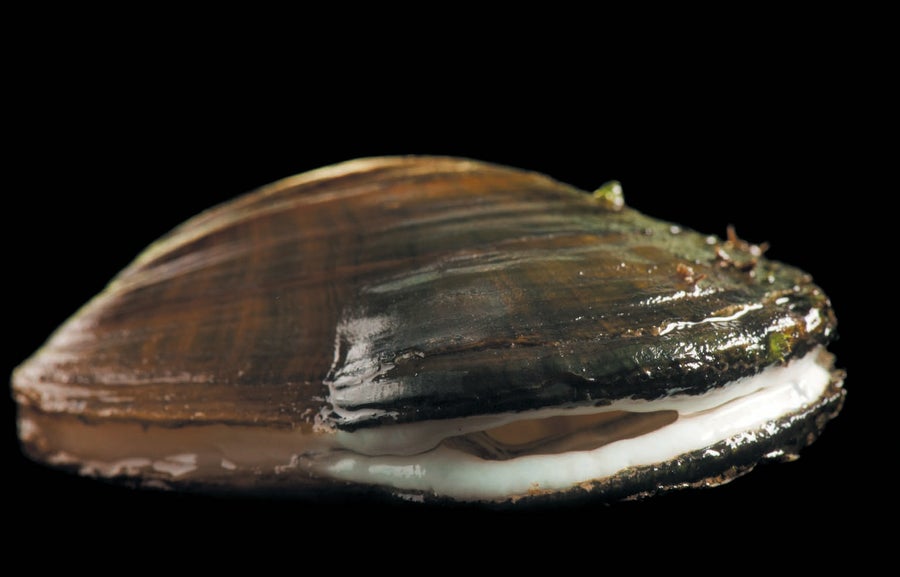

Oyster Mussel. Epioblasma capsaeformis. Listed as Endangered: 1997. Status: Still endangered. Credit: © Joel Sartore/National Geographic Photo Ark
The second initiative that could promote species conservation is already underway: bringing landowners into the fold. Most wildlife habitat east of the Rocky Mountains is on private land. That's also where habitat loss is happening fastest. Some experts say conservation isn't likely to succeed unless the FWS works more collaboratively with landowners, adding carrots to the ESA's regulatory stick. Bean has long promoted the idea, including when he worked at the Interior Department from 2009 to early 2017. The approach started, he says, with the Red-cockaded Woodpecker.
When the ESA was passed, there were fewer than 10,000 Red-cockaded Woodpeckers left of the millions that had once lived in the Southeast. Humans had cut down the old pine trees, chiefly Longleaf Pine, that the birds excavate cavities in for roosting and nesting. An appropriate tree has to be large, at least 60 to 80 years old, and there aren't many like that left. The longleaf forest, which once carpeted up to 90 million acres from Virginia to Texas, has been reduced to less than three million acres of fragments.
In the 1980s the ESA wasn't helping because it provided little incentive to preserve forest on private land. In fact, Bean says, it did the opposite: landowners would sometimes clear-cut potential woodpecker habitat just to avoid the law's constraints. The woodpecker population continued to drop until the 1990s. That's when Bean and his Environmental Defense Fund colleagues persuaded the FWS to adopt “safe-harbor agreements” as a simple solution. An agreement promised landowners that if they let pines grow older or took other woodpecker-friendly measures, they wouldn't be punished; they remained free to decide later to cut the forest back to the baseline condition it had been in when the agreement was signed.
That modest carrot was inducement enough to quiet the chainsaws in some places. “The downward trends have been reversed,” Bean says. “In places like South Carolina, where they have literally hundreds of thousands of acres of privately owned forest enrolled, Red-cockaded Woodpecker numbers have shot up dramatically.”
The woodpecker is still endangered. It still needs help. Because there aren't enough old pines, land managers are inserting lined, artificial cavities into younger trees and sometimes moving birds into them to expand the population. They are also using prescribed fires or power tools to keep the longleaf understory open and grassy, the way fires set by lightning or Indigenous people once kept it and the way the woodpeckers like it. Most of this work is taking place, and most Red-cockaded Woodpeckers are still living, on state or federal land such as military bases. But a lot more longleaf must be restored to get the birds delisted, which means collaborating with private landowners, who own 80 percent of the habitat.
Leo Miranda-Castro, who retired last December as director of the FWS's southeast region, says the collaborative approach took hold at regional headquarters in Atlanta in 2010. The Center for Biological Diversity had dropped a “mega petition” demanding that the FWS consider 404 new species for listing. The volume would have been “overwhelming,” Miranda-Castro says. “That's when we decided, ‘Hey, we cannot do this in the traditional way.’ The fear of listing so many species was a catalyst” to look for cases where conservation work might make a listing unnecessary.
An agreement affecting the Gopher Tortoise shows what is possible. Like the woodpeckers, it is adapted to open-canopied longleaf forests, where it basks in the sun, feeds on herbaceous plants and digs deep burrows in the sandy soil. The tortoise is a keystone species: more than 300 other animals, including snakes, foxes and skunks, shelter in its burrows. But its numbers have been declining for decades.
Urbanization is the main threat to the tortoises, but timberland can be managed in a way that leaves room for them. Eager to keep the species off the list, timber companies, which own 20 million acres in its range, agreed to figure out how to do that—above all by returning fire to the landscape and keeping the canopy open. One timber company, Resource Management Service, said it would restore Longleaf Pine on about 3,700 acres in the Florida panhandle, perhaps expanding to 200,000 acres eventually. It even offered to bring other endangered species onto its land, which delighted Miranda-Castro: “I had never heard about that happening before.” Last fall the FWS announced that the tortoise didn't need to be listed in most of its range.
Miranda-Castro now directs Conservation Without Conflict, an organization that seeks to foster conversation and negotiation in settings where the ESA has more often generated litigation. “For the first 50 years the stick has been used the most,” Miranda-Castro says. “For the next 50 years we're going to be using the carrots way more.” On his own farm outside Fort Moore, Ga., he grows Longleaf Pine—and Gopher Tortoises are benefiting.
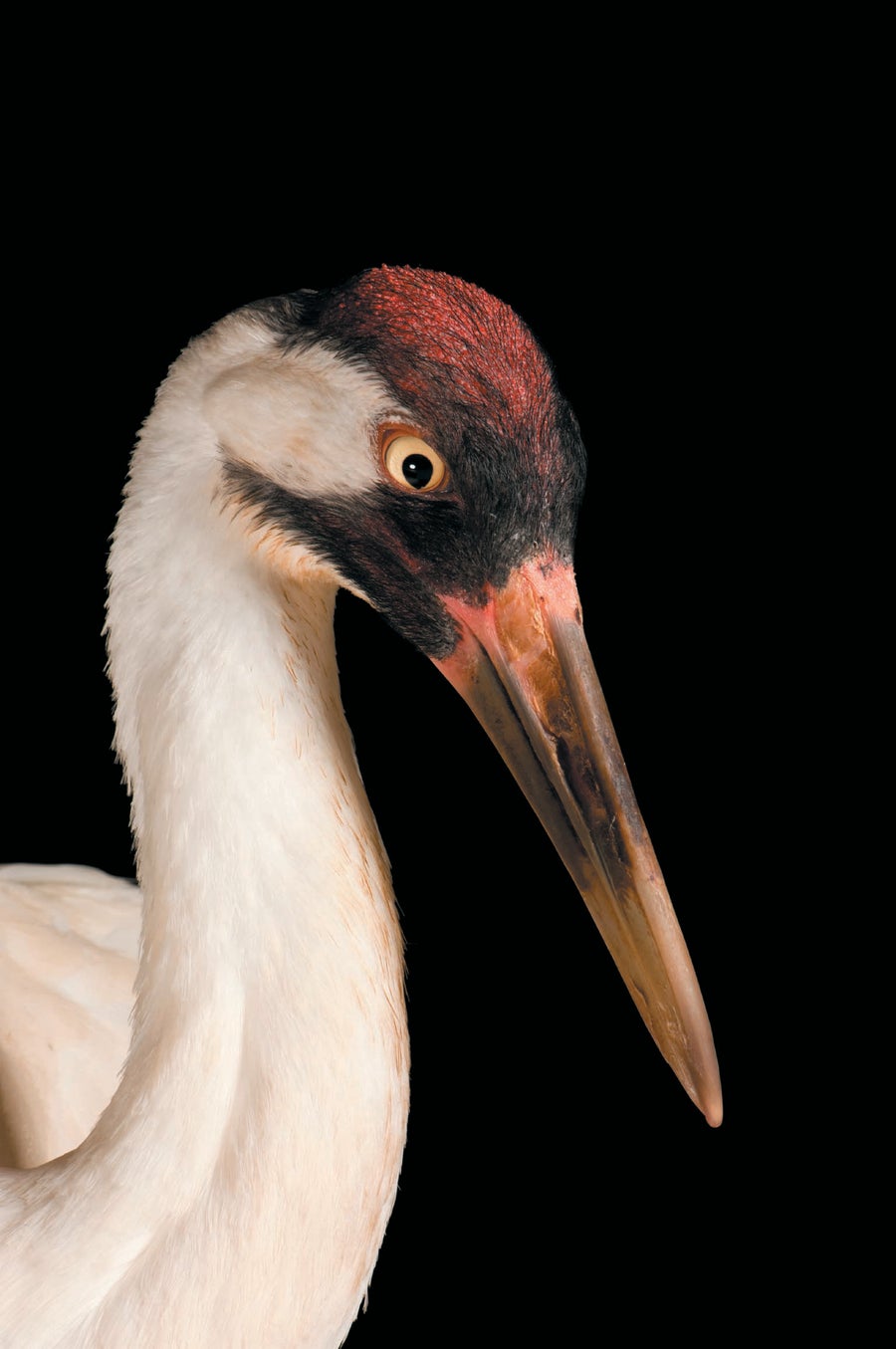

Whooping Crane. Grus americana. Listed as Endangered: 1967. Status: Still endangered. Credit: © Joel Sartore/National Geographic Photo Ark
The Center for Biological Diversity doubts that carrots alone will save the reptile. It points out that the FWS's own models show small subpopulations vanishing over the next few decades and the total population falling by nearly a third. In August 2023 it filed suit against the FWS, demanding the Gopher Tortoise be listed.
The FWS itself resorted to the stick this year when it listed the Lesser Prairie-Chicken, a bird whose grassland home in the Southern Plains has long been encroached on by agriculture and the energy industry. The Senate promptly voted to overturn that listing, but President Biden promised to veto that measure if it passes the House.
B ehind the debates over strategy lurks the vexing question: Can we save all species? The answer is no. Extinctions will keep happening. In 2021 the FWS proposed to delist 23 more species—not because they had recovered but because they hadn't been seen in decades and were presumed gone. There is a difference, though, between acknowledging the reality of extinction and deliberately deciding to let a species go. Some people are willing to do the latter; others are not. Bean thinks a person's view has a lot to do with how much they've been exposed to wildlife, especially as a child.
Zygmunt Plater, a professor emeritus at Boston College Law School, was the attorney in the 1978 Snail Darter case, fighting for hundreds of farmers whose land would be submerged by the Tellico Dam. At one point in the proceedings Justice Lewis F. Powell, Jr., asked him, “What purpose is served, if any, by these little darters? Are they used for food?” Plater thinks creatures such as the darter alert us to the threat our actions pose to them and to ourselves. They prompt us to consider alternatives.
The ESA aims to save species, but for that to happen, ecosystems have to be preserved. Protecting the Northern Spotted Owl has saved at least a small fraction of old-growth forest in the Pacific Northwest. Concern about the Red-cockaded Woodpecker and the Gopher Tortoise is aiding the preservation of longleaf forests in the Southeast. The Snail Darter wasn't enough to stop the Tellico Dam, which drowned historic Cherokee sites and 300 farms, mostly for real estate development. But after the controversy, the presence of a couple of endangered mussels did help dissuade the TVA from completing yet another dam, on the Duck River in central Tennessee. That river is now recognized as one of the most biodiverse in North America.
The ESA forced states to take stock of the wildlife they harbored, says Jim Williams, who as a young biologist with the FWS was responsible for listing both the Snail Darter and mussels in the Duck River. Williams grew up in Alabama, where I live. “We didn't know what the hell we had,” he says. “People started looking around and found all sorts of new species.” Many were mussels and little fish. In a 2002 survey, Stein found that Alabama ranked fifth among U.S. states in species diversity. It also ranks second-highest for extinctions; of the 23 extinct species the FWS recently proposed for delisting, eight were mussels, and seven of those were found in Alabama.
One morning this past spring, at a cabin on the banks of Shoal Creek in northern Alabama, I attended a kind of jamboree of local freshwater biologists. At the center of the action, in the shade of a second-floor deck, sat Sartore. He had come to board more species onto his photo ark, and the biologists—most of them from the TVA—were only too glad to help, fanning out to collect critters to be decanted into Sartore's narrow, flood-lit aquarium. He sat hunched before it, a black cloth draped over his head and camera, snapping away like a fashion photographer, occasionally directing whoever was available to prod whatever animal was in the tank into a more artful pose.
As I watched, he photographed a striated darter that didn't yet have a name, a Yellow Bass, an Orangefin Shiner and a giant crayfish discovered in 2011 in the very creek we were at. Sartore's goal is to help people who never meet such creatures feel the weight of extinction—and to have a worthy remembrance of the animals if they do vanish from Earth.
With TVA biologist Todd Amacker, I walked down to the creek and sat on the bank. Amacker is a mussel specialist, following in Williams's footsteps. As his colleagues waded in the shoals with nets, he gave me a quick primer on mussel reproduction. Their peculiar antics made me care even more about their survival.
There are hundreds of freshwater mussel species, Amacker explained, and almost every one tricks a particular species of fish into raising its larvae. The Wavy-rayed Lampmussel, for example, extrudes part of its flesh in the shape of a minnow to lure black bass—and then squirts larvae into the bass's open mouth so they can latch on to its gills and fatten on its blood. Another mussel dangles its larvae at the end of a yard-long fishing line of mucus. The Duck River Darter Snapper—a member of a genus that has already lost most of its species to extinction—lures and then clamps its shell shut on the head of a hapless fish, inoculating it with larvae. “You can't make this up,” Amacker said. Each relationship has evolved over the ages in a particular place.
The small band of biologists who are trying to cultivate the endangered mussels in labs must figure out which fish a particular mussel needs. It's the type of tedious trial-and-error work conservation biologists call “heroic,” the kind that helped to save California Condors and Whooping Cranes. Except these mussels are eyeless, brainless, little brown creatures that few people have ever heard of.
For most mussels, conditions are better now than half a century ago, Amacker said. But some are so rare it's hard to imagine they can be saved. I asked Amacker whether it was worth the effort or whether we just need to accept that we must let some species go. The catch in his voice almost made me regret the question.
“I'm not going to tell you it's not worth the effort,” he said. “It's more that there's no hope for them.” He paused, then collected himself. “Who are we to be the ones responsible for letting a species die?” he went on. “They've been around so long. That's not my answer as a biologist; that's my answer as a human. Who are we to make it happen?”
Robert Kunzig is a freelance writer in Birmingham, Ala., and a former senior editor at National Geographic, Discover and Scientific American .

- Protecting Endangered Species
- Wildlife Conservation
From majestic mammals like bison and grizzly bears to tiny desert wildflowers, America harbors a remarkable array of plant and animal species.
Unfortunately many of our species have not fared well over the past few decades, suffering from threats such as habitat loss and the spread of invasive species.
Scientists estimate that up to one-third of U.S. species are at increased risk of extinction , and more than 1,600 U.S. plants and animals already have been federally listed as threatened or endangered and protected under the Endangered Species Act.
The National Wildlife Federation has long has been focused on protecting the most vulnerable of our wild species.
Recovering America's Wildlife Act
Scientists estimate that one third of all U.S. wildlife species are already imperiled or are vulnerable. Habitat loss, invasive species, and severe weather have all taken a severe toll on birds, mammals, fish, amphibians, reptiles, butterflies, and bees. All types of wildlife are declining—in many cases dramatically. We need urgent action to protect vulnerable wildlife. The Recovering America’s Wildlife Act is the solution we need.
Our Approach
The National Wildlife Federation works to defend, strengthen, fund, and ensure effective implementation of the Endangered Species Act and other core wildlife protection laws.
- Defending and strengthening the Endangered Species Act , which provides an essential legal safety net to prevent the loss of plant and animal species to extinction.
- Holding federal agencies and others accountable for complying with laws protecting rare and endangered species using cooperation, persuasion, and—where necessary—litigation.
- Advocating for increased funding for federal and state conservation programs that benefit endangered species.
- Protecting, restoring, and connecting the habitats on which endangered species and other wildlife depend for their survival, and encouraging wildlife-friendly land management practices.
- Reducing threats to wildlife that can lead to their endangerment and extinction, such as loss of habitat, contamination of water and spread of invasive species.
State Wildlife Action Plans
One of the best ways to protect endangered species is to prevent their decline and deterioration in the first place. Toward that end, National Wildlife Federation works to maintain healthy populations of fish, wildlife, and plant species through promoting broad-based conservation efforts such as State Wildlife Action Plans. National Wildlife Federation is advocating for passage of the Recovering America’s Wildlife Act , which is a bold new approach for providing the funding needed to carry out these proactive conservation plans.
Climate Change
Climate change is making the protection of endangered species increasingly challenging. Climate change not only affects our plants and animals directly —through changes in temperature and precipitation for instance—but can worsen the impact on endangered species of traditional threats, such as invasive species, wildfires and diseases.
The National Wildlife Federation is playing a leadership role in developing and promoting innovative approaches for climate-smart conservation that can safeguard endangered species and other wildlife in the face of a changing climate.

Wildlife Success Stories
12 hopeful reminders that when we invest in wildlife conservation, wildlife wins

7 Reasons to Support the Recovering America’s Wildlife Act
Read the latest story from the National Wildlife Federation blog

Report: Reversing America's Wildlife Crisis
How the Recovering America's Wildlife Act can help species in trouble
Get Involved
Donate Today

Sign a Petition
Donate Monthly
Nearby Events

Sign Up for Updates
What's Trending

"Better" Chocolate for a Sweeter World
Chocolate is sweet but the bitter truth is that its industry is linked to harmful practices like forced labor and deforestation. Explore the ongoing efforts and find out how you can contribute to the movement for "better" chocolate.

Take the Pledge
Encourage your mayor to take the Mayors' Monarch Pledge and support monarch conservation before March 31!

UNNATURAL DISASTERS
A new storymap connects the dots between extreme weather and climate change and illustrates the harm these disasters inflict on communities and wildlife.

Creating Safe Spaces
Promoting more-inclusive outdoor experiences for all
Where We Work
More than one-third of U.S. fish and wildlife species are at risk of extinction in the coming decades. We're on the ground in seven regions across the country, collaborating with 52 state and territory affiliates to reverse the crisis and ensure wildlife thrive.

- ACTION FUND

PO Box 1583, Merrifield, VA 22116-1583
800.822.9919

Join Ranger Rick
Inspire a lifelong connection with wildlife and wild places through our children's publications, products, and activities
- Terms & Disclosures
- Privacy Policy
- Community Commitment

National Wildlife Federation is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization
You are now leaving nwf.org
In 4 seconds , you'll be redirected to our Action Center at www.nwfactionfund.org.
Why protect species
- Interactive map

The alarm has been raised repeatedly about the decline in biodiversity across the planet.
By allowing this decline to continue, we erode the very foundations of our traditions, economies, livelihoods, food security, health, and even the existence of life worldwide.
Why Are Species Important?
The millions of species on land, in freshwater and in the ocean have evolved over millennia and form the web of life that sustains the planet. Species and their populations are the building blocks of ecosystems, individually and collectively securing the conditions for life. They provide food, medicine and raw materials. They are the basis of soil formation, decomposition, water filtration and flow, pollination, pest control and climate regulation. They are the primary source of income and resources for hundreds of millions of people around the globe.
Species are an essential part of the history, culture, tradition and folklore of every culture on Earth and their aesthetic values and spiritual roles provide comfort and inspiration as well as recreation.

The Species Emergency
The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species™ reveals that a quarter of all species face high risk of extinction. Human activity has severely altered more than 75% of the Earth’s land and freshwater areas, and 66% of the oceans. Climate change and political instability are exacerbating this crisis at all levels.
Species loss at current rates will eliminate the vital ecological, economic and cultural roles that they fulfil. The crisis goes beyond species loss; human pressures mean that a vast array of species are experiencing dramatic population declines (often irreversible) to a level that affects their future and our resource base. It is beyond question that the current way of life is unsustainable and transformational change is vital.
The world’s people must accept responsibility for this emergency and act now to ensure we pass on a rich natural heritage to future generations.

The key threats that are driving population declines and extinctions include :
Habitat loss & degradation
Climate change

Invasive alien species
Human-wildlife conflict
Disruption of water flow
Over-exploitation of natural resources & prey depletion

Reduced genetic diversity
- Over the last few years, we have seen how the world has changed: from youth to business , the global community has now recognised the irreplaceable and vital role of biodiversity and its intrinsic link to the climate change crisis we are facing.
- Biodiversity is affected by climate change, with negative consequences for human health, but biodiversity , through the ecosystem services it supports, also makes an important contribution to both climate-change mitigation and adaptation: conserving and sustainably managing biodiversity is critical to addressing climate change (Secretariat on Convention on Biological Diversity, 2019).
- We cannot overcome climate change without the help of ecosystems: they provide up to 35% of the solutions that can help keep global warming below 2°C (Griscom et all, 2017).
- Yet, the current global response if insufficient: more than 1,000,000 species are threatened with extinction (IPBES, 2019).
- The current rate of species extinction has no precedent since the dinosaurs’ extinction 66 million years ago.

Make a difference
Help us bring threatened species back from the brink of extinction. Make a difference by donating today .
Search the site
Links to social media channels

Protecting Endangered Species
Still Only One Earth: Lessons from 50 years of UN sustainable development policy
Despite continued conservation efforts, the status of many endangered species remains unchanged. The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) and the Convention on Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS) are the primary treaties tasked with protection of endangered species. But moving forward, species conservation efforts should expand to include lesser known species that serve important ecosystem services. ( Download PDF ) ( See all policy briefs ) ( Subscribe to ENB )
The Persian leopard (Panthera pardus tulliana), the largest subspecies of leopards, used to roam widely across Central Asia and the Caucasus. They are large spotted cats—about five feet in length—with slender hindquarters and long, thick tails. Both male and female leopards lead solitary lives, though they come together during winter mating. They are very territorial, patrolling wide home ranges to scent-mark trees, shrubs, and rocks. The leopard inhabits a wide variety of habitats: from mountain crags up to 3,000 meters in elevation, to grasslands and cold desert ecosystems, with a preference for cliff and rocky areas, as well as juniper and pistachio woodlands that give them cover for hunting.
During the past century, human-wildlife conflict, indiscriminate killing of their prey, habitat loss, and bounties incentivizing their killing have reduced their historic range by 72-84% (Jacobson et al., 2016). Today, according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species—the world’s most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of species and subspecies, which uses a set of defined criteria to evaluate their extinction risk (Rodrigues et al., 2006)—the Persian leopard is endangered.
The story of the Persian leopard is the story of many species pushed by human action to the brink of extinction. Strong conservation measures can still reverse the course for some species. For many others, it is too late.
During the past century, human-wildlife conflict, indiscriminate killing of their prey, habitat loss, and bounties incentivizing their killing have reduced the leopard’s historic range by 72-84% JACOBSON ET AL., 2016
The foundations of global species conservation measures date back to the 1972 Stockholm Conference on the Human Environment . Principle 2 of the Stockholm Declaration says “the natural resources of the earth, including the air, water, land, flora and fauna and especially representative samples of natural ecosystems, must be safeguarded for the benefit of present and future generations.” Principle 4 reads “Man has a special responsibility to safeguard and wisely manage the heritage of wildlife and its habitat, which are now gravely imperilled by a combination of adverse factors.”
Among the 109 recommendations found in the Stockholm Action Plan , Recommendation 99 calls for the preparation and adoption of an international treaty to regulate international trade in certain species of wild plants and animals. This treaty, the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), had been drafted as a result of a resolution adopted in 1963 at a meeting of members of IUCN. As a result of the push provided by the Stockholm Conference, the Convention was finally adopted at a meeting of representatives of 80 countries in Washington, D.C. on 3 March 1973.

There are a few other relevant recommendations. Recommendation 29 draws attention to species of wildlife that may serve as indicators for future wide environmental disturbances. Recommendation 30 emphasizes drawing attention to the situation of animals endangered by their trade value. The Stockholm Declaration and Action Plan also legitimized the role of IUCN and especially the Red List, which had been established in 1964. In fact, IUCN was one of the few environmental organizations formally involved in the preparations of the Stockholm Conference and in the drafting and implementation of the three conventions that followed it: the Convention Concerning the Protection of World Cultural and Natural Heritage (1972), CITES, and the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance (1971).
What are Endangered Species: The Role of the IUCN Red List
Since its establishment, the IUCN Red List has been the key tool to assess the status of species and catalyze action for conservation and policy change. Through the List’s rigorous assessment processes, experts linked to the IUCN Species Survival Commission’s specialist groups collect information on a species’ range, population size, habitat and ecology, use and/or trade, threats, and conservation actions that inform necessary conservation decisions.
The assessments published in the IUCN Red List are used by governments, nongovernmental organizations (NGOs), and multilateral environmental agreements. The assessments drive conservation action and funding, albeit still in insufficient ways to always ensure saving species. In fact, Betts et al. (2020) noted that without successful communication between species experts, academics, policymakers, funders, and practitioners, IUCN Red List assessments may not lead to development and implementation of conservation action plans.

The IUCN Red List has nine categories to indicate how close a species is to becoming extinct. The closest to extinction is the “critically endangered” category, with a species example being the Asiatic cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus venaticus), a subspecies found only in Iran that has dwindled to fewer than 50 animals remaining in the wild. The least critical category is defined as “least concern.” For example, the global brown bear (Ursus arctos) population is considered to be of “least concern” because it is large and spread over three continents, even though there are some local populations that are under threat. The categories in the middle, i.e., “vulnerable” and “endangered,” are for species considered under threat.
In other words, if a species is either critically endangered, endangered, or vulnerable, it is in popular terms “endangered.”
This mismatch between the technical terms of the IUCN Red List and common language can lead to confusion. In 2016, a re-assessment of the snow leopard prompted an outcry from some members of the conservation community due the species’ being reclassified from endangered to vulnerable (McCarthy et al., 2016). Their anger was echoed by members of the public, in part because they did not understand “being vulnerable” under IUCN Red List criteria still means at high risk of extinction.
The way a species is assessed under the IUCN Red List can also determine whether such species deserve protection under two international treaties aimed at species conservation: CITES and the Convention on Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS). Listing an endangered species under either of these two conventions can catalyze further action and, possibly, save a species from extinction (Zahler & Rosen, 2013).
Without successful communication between species experts, academics, policy makers, funders, and practitioners, IUCN Red List assessment may not lead to development and implementation of conservation action plans. BETTS ET AL. (2020)

Regulating the Protection of Endangered Species
CITES and CMS are the key conventions tasked with regulating protection of endangered species.
CITES regulates international trade and therefore looks at the impact of trade on species conservation. Annually, international wildlife trade is estimated to be worth billions of dollars and to include hundreds of millions of plant and animal specimens. The trade is diverse, ranging from live animals and plants to an array of products derived from them, including food, exotic leather goods, wooden musical instruments, timber, tourist curios, and medicines. Since trade in wild animals and plants crosses borders between countries, the effort to regulate it requires international cooperation to safeguard certain species from over-exploitation. Today, CITES accords varying degrees of protection to more than 37,000 species of animals and plants, whether they are traded as live specimens, fur coats, or dried herbs (CITES, n.d.)
In the language of CITES, species listed under Appendix I are considered threatened with extinction and afforded the highest level of protection, including restrictions on commercial trade. Examples of the 931 species currently listed under Appendix 1 include gorillas (Gorilla sp.), tigers (Panthera tigris), and snow leopards (Panthera uncia). Appendix II includes species that, while currently not threatened with extinction, may become so without trade controls. It also includes species that resemble other listed species and must be regulated to effectively control the trade in those other listed species. Currently 34,419 species are listed under Appendix II, including saiga antelope (Saiga tatarica), wolf (Canis lupus), argali sheep (Ovis ammon), and kiang (Equus kiang). Appendix III includes a list of wildlife and plant species identified by particular CITES parties as being in need of international trade controls.
The purpose of CMS is conservation of migratory species, their habitats, and migration routes. “Migratory” is broadly defined as species that straddle international borders (Lewis & Trouwborst, 2019). Migratory species threatened with extinction are listed in Appendix I of the Convention. Appendix I listing is a mechanism to promote conservation measures called, in CMS terminology, “Concerted Action” among the range states of the listed species. CMS parties commit to ensure strict protections under national laws and conserving their habitats, mitigating obstacles to migration, among other threats. Migratory species viewed as benefiting from international cooperation are listed in Appendix II of the Convention (CMS, n.d.). To date, seven specialized regional agreements and 19 memoranda of understanding have been concluded for Appendix II species under the CMS.
Representative Frameworks for the Conservation of Endangered Species
The development of models tailored to conservation needs throughout migratory ranges is a unique feature of the CMS. Along these lines, there are two important initiatives benefiting endangered species in Africa and Central Asia under the CMS umbrella.
One is the Central Asian Mammals Initiative (CAMI) and its associated Programme of Work. Established in 2014, CAMI aims to strengthen the conservation of Central Asian migratory mammals through a common framework to coordinate conservation activities in the region and coherently address major threats to migratory species. By developing an initiative for Central Asian mammals, CMS is catalyzing collaboration between all stakeholders, with the aim of harmonizing and strengthening the implementation of the Convention (Rosen & Roettger, 2014). One of the most recent projects under CAMI is the proposed development of a regional strategy for the conservation of the Persian leopard.
The Joint CITES-CMS African Carnivores Initiative (ACI), established in 2017, stems from the recognition of the importance of synergies and coordination of measures toward species that are protected under both Conventions. Supported by IUCN Species Survival Commission ’s specialist groups, the Secretariats are tasked to drive effective conservation of African lion, leopard, cheetah, and wild dog, and help avoid duplicate activities and associated costs, and generate funding.
By developing an initiative for Central Asian mammals, CMS is catalyzing collaboration between all stakeholders, with the aim of harmonizing and strengthening the implementation of the Convention ROSEN & ROETTGER, 2014
There are also two other important frameworks, each focused on the conservation of single species. One is the Global Tiger Initiative Council (GTIC), and the other is the Global Snow Leopard Ecosystem Protection Program (GSLEP).
GTIC was originally set up as the Global Tiger Initiative (GTI), a global alliance of governments, international organizations, NGOs, and the private sector, with the goal to save tigers from extinction. Established by the World Bank, the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the Smithsonian Institution, Save the Tiger Fund, and International Tiger Coalition (representing more than 40 NGOs), the initiative is led by the 13 tiger range countries. The St. Petersburg Declaration , adopted in 2010 at the Tiger Summit in Russia, defines the priorities.
GSLEP, propelled by GTI and established in 2013, is driven by 12 snow leopard range states, NGOs, and international organizations, which sit on a steering committee. The foundation of the GSLEP is 12 individual National Snow Leopard and Ecosystems Priorities (NSLEPs). Under GSLEP, specific activities are grouped under broad themes that correspond to the commitments of the Bishkek Declaration adopted at the 2013 Global Snow Leopard Conservation Forum (Zakharenka et al., 2016).
Some of these initiatives have successfully catalyzed attention, resources, and conservation action. They have received a high level of political attention, especially GTI in Russia and GSLEP in Kyrgyzstan, as respective hosts of the Tiger Summit and Snow Leopard Forum. However, some conservationists argue, especially in relation to tigers, that results have fallen short, and lack of transparency and accountability is compromising progress in tiger conservation efforts. Slappendel (2021) writes that “tiger-range countries are responsible for making tiger conservation efforts and holding themselves accountable for their methods and results. There’s no authority above them, so they can do whatever they want.

While the reach and influence of CAMI and ACI are more limited compared to GTI and GSLEP, they have also generated important resources for conservation and could likely have a stronger policy-driving role in the future.
Generally, these four frameworks serve as important examples for directing donor resources.
The Role of UN Agencies and Donors
The GEF, established in 1992, is the largest multilateral fund focused on enabling developing countries to invest in nature. It supports the implementation of major international environmental conventions including on biodiversity, climate change, chemicals, and desertification. Endangered species prioritized under CITES and CMS, such as GTI and GSLEP, are also prioritized for GEF funding.
In 2010, the GEF indicated it would provide up to USD 50 million in grants to save the tiger through contributions to be invested by developing countries using their GEF allocations in biodiversity, supplemented by investments from its REDD+ Program (reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation in developing countries, and the role of conservation, sustainable use of forests, and enhancement of carbon stocks) (GEF, 2010). Since 1991, the GEF has invested nearly USD 100 million toward snow leopard projects implemented by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). The GSLEP Forum in 2013 catalyzed nine further GEF-financed, UNDP-implemented projects, representing an investment of about USD 45 million to support snow leopard range countries. These nine projects also leveraged over USD 200 million in co-financing from national and international partners (UNDP, 2016).
UNDP has emerged as one of the key implementing UN agencies when it comes to endangered species and conservation projects more broadly. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has also spearheaded initiatives for the conservation of endangered species, such as Vanishing Treasures . This EUR 9 million project, funded by the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, seeks to better understand the vulnerability to climate change of the snow leopard, tiger, and gorilla and the ecosystems being affected.
Why Do Many Species Continue to be Endangered?
The Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) warned in its Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services that “nature is declining globally at rates unprecedented in human history—and the rate of species extinctions is accelerating” (IPBES, 2019).
Despite continued conservation efforts, the status of many endangered species remains unchanged—including tigers, lions, and cheetahs. The question is: Why? With our growing knowledge of the fragility of the planet’s ecosystems, why are we pushing entire species out of existence?
The limited amount of funding benefiting species research and conservation is one reason. Often these funds are short term, whereas to really see progress and results, a longer funding commitment is necessary. Some projects are also too narrowly focused on protection and enforcement, without seeking ways local communities can be part of the solution. Likewise, some projects do not address root causes of decline.
But there are also issues of capacity. In many countries that provide habitat for endangered species, there is limited technical capacity to protect such species. Local and national conservation organizations also would benefit from greater capacity building.
At the national level, species conservation may not be prioritized. This is often reflected in ministries tasked with both environment and agriculture or economic and mining issues—with the latter issues prioritized over conservation. Species conservation also does not operate in a vacuum, but must be considered alongside mechanisms to address threats to their survival, which may be exacerbated by conflicting development goals. For example, a development project aimed at improving access to water, through building dams and irrigation channels, may hurt access by salmon species to spawning grounds or damage riparian habitat. Finally, conservation organizations—with their own agendas and issues of competition for funding that leads to lack of cooperation—sometimes fail to create better synergies for conservation.
There are also many other endangered species that are not as well known or do not have the appeal of more popular endangered species, such as snow leopards or tigers. Some of these species have disappeared from large swaths of their range, including the striped hyaena (Hyaena hyaena), which can no longer be found in parts of Central Asia and Caucasus regions. The lesser-known Saint Lucia racer (Erythrolamprus ornatus), listed as Critically Endangered, numbers fewer than 20 individuals and is considered one of the rarest snakes in the world. Similarly, the Daguo Mulian tree (Magnolia grandis) is listed as critically endangered due to habitat loss for agricultural expansion and logging.
Moving Forward
Protecting iconic endangered species is still important for promoting policies and measures that can benefit entire ecosystems and many other endangered species. Nevertheless, species conservation efforts must expand to include many more species that are lesser known and serve important ecosystem services. Such efforts should also create incentives for local communities to conserve them, including through sustainable use when that is recognized as the only or the most effective measure. Finally, greater financial resources have to be allocated. Many hope the post-2020 global biodiversity framework will help guide the most pressing actions to keep entire species from being erased from our shared world.
Works Consulted
Betts, J., Young, R. P., Hilton-Taylor, C., Hoffmann, M., Rodríguez, J. P., Stuart, S. N., & Milner-Gulland, E. J. (2020). A framework for evaluating the impact of the IUCN Red List of threatened species. Conservation Biology: The Journal of the Society for Conservation Biology, 34(3), 632–643. doi.org/10.1111/cobi.13454
Convention on International Trade of Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora. (n.d.). What is CITES? cites.org/eng/disc/what.php
Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals. (n.d.). CMS. cms.int/en/legalinstrument/cms
Global Environment Facility. (2010). Global Environment Facility to support $50 million in grants to save the tiger. thegef.org/newsroom/news/global-environmentfacility-support-50-million-grants-save-tiger
Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. (2019). Global assessment report on biodiversity and ecosystem services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3831673
Jacobson, A.P., Gerngross, P., Lemeris, Jr., J.R., Schoonover, R.F., Anco, C., Breitenmoser-Würsten, C., Durant, S.M., Farhadinia, M.S., Henschel, P., Kamler, J.F., Laguardia, A., Rostro-García, S., Stein, A.B., & Dollar, L. (2016). Leopard (Panthera pardus) status, distribution, and the research efforts across its range. PeerJ 4:e1974. doi.org/10.7717/peerj.1974
Lewis, M., & Trouwborst, A. (2019). Large carnivores and the Convention on Migratory Species (CMS)—definitions, sustainable use, added value, and other emerging issues. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 7. frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fevo.2019.00491
McCarthy, T., Mallon, D., Jackson, R., Zahler, P., & McCarthy, K. (2017). Panthera uncia. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017. Panthera uncia (Snow Leopard) (iucnredlist.org)
Rodrigues, A.S.L., Pilgrim, J.D., Lamoreux, J.F., Hoffmann, M., & Brooks, T.M. (2006). The value of the IUCN Red List for conservation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 21(2), 71-76. doi.org/10.1016/j. tree.2005.10.010
Rosen, T., & Roettger, C. (2014). Central Asian Mammals Initiative: Saving the last migrations. CMS. cms.int/sites/default/files/publication/Central_Asian_Mammals_Initiative.pdf
Slappendel, C. (2021). What’s stopping some countries from keeping up with tiger conservation promises? Commentary. Mongabay news.mongabay.com/2021/11/whats-stopping-some-countries-from-keeping-up-with-tiger-conservationpromises-commentary/
UNDP. (2016). Silent Roar - UNDP and GEF in the snow leopard landscape. undp.org/publications/silent-roar-undpand-gef-snow-leopard-landscape
Zahler, P., & Rosen, T. (2013). Endangered mammals. Encyclopedia of Biodiversity. Elsevier.
Zakharenka, A., Sharma, K., Kochorov, C., Rutherford, B., Varma, K., Seth, A., Kushlin, A., Lumpkin, S., Seidensticker, J., Laporte, B., Tichomirow, B., Jackson, R. M., Mishra, C., Abdiev, B., Modaqiq, A. W., Wangchuk, S., Zhongtian, Z., Khanduri, S. K., Duisekeyev, B., … Yunusov, N. (2016). The Global Snow Leopard and Ecosystem Protection Program. Snow Leopards, 559–573. doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-802213-9.00045-6
Additional downloads

Government of Norway, Ministry of Foreign Affairs

Government of Sweden, Ministry of Environment

Government of Canada, Global Affairs Canada
Deep dive details, you might also be interested in, web of resilience.
Pakistan's development model has still not recognised the limits of the natural environment and the damage it would cause, if violated, to the sustainability of development and to the health and well-being of its population. Pakistan’s environment journey began with Stockholm Declaration in 1972. A delegation led by Nusrat Bhutto represented the country at the Stockholm meeting, resulting in the establishment of the Urban Affairs Division (UAD), the precursor of today’s Ministry of Climate Change. In setting the country’s environmental agenda, we were inspired by the Stockholm Principles, but in reality, we have mostly ignored them for the last five decades.
IISD in the news
June 5, 2022
The Legacies of the Stockholm Conference
Fifty years after Stockholm, we face a triple planetary crisis of climate change, nature and biodiversity loss, and pollution.
June 1, 2022
The Roots of Forest Loss and Forest Governance
If lessons from past failures on deforestation are learned, forest protection could play a major role in reversing both climate change and biodiversity loss.
May 9, 2022
Pathways to Sustainable Cities
Urban planning needs to be inclusive and responsive to the needs of local communities and build on participatory approaches that foster the engagement of marginalized actors.
April 28, 2022
/
Conservation
In defense of biodiversity: why protecting species from extinction matters.
By Carl Safina • February 12, 2018
A number of biologists have recently made the argument that extinction is part of evolution and that saving species need not be a conservation priority. But this revisionist thinking shows a lack of understanding of evolution and an ignorance of the natural world.
A few years ago, I helped lead a ship-based expedition along south Alaska during which several scientists and noted artists documented and made art from the voluminous plastic trash that washes ashore even there. At Katmai National Park, we packed off several tons of trash from as distant as South Asia. But what made Katmai most memorable was: huge brown bears. Mothers and cubs were out on the flats digging clams. Others were snoozing on dunes. Others were patrolling.
During a rest, several of us were sitting on an enormous drift-log, watching one mother who’d been clamming with three cubs. As the tide flooded the flat, we watched in disbelief as she brought her cubs up to where we were sitting — and stepped up on the log we were on. There was no aggression, no tension; she was relaxed. We gave her some room as she paused on the log, and then she took her cubs past us into a sedge meadow. Because she was so calm, I felt no fear. I felt the gift.
In this protected refuge, bears could afford a generous view of humans. Whoever protected this land certainly had my gratitude.
In the early 20th century, a botanist named Robert F. Griggs discovered Katmai’s volcanic “Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes.” In love with the area, he spearheaded efforts to preserve the region’s wonders and wildlife. In 1918, President Woodrow Wilson established Katmai National Monument (now Katmai National Park and Preserve ), protecting 1,700 square miles, thus ensuring a home for bear cubs born a century later, and making possible my indelible experience that day. As a legacy for Griggs’ proclivity to share his love of living things, George Washington University later established the Robert F. Griggs Chair in Biology.
That chair is now occupied by a young professor whose recent writing probably has Griggs spinning in his grave. He is R. Alexander Pyron . A few months ago, The Washington Post published a “ Perspective” piece by Pyron that is an extreme example of a growing minority opinion in the conservation community, one that might be summarized as, “Humans are profoundly altering the planet, so let’s just make peace with the degradation of the natural world.”
No biologist is entitled to butcher the scientific fundamentals on which they hang their opinions.
Pyron’s essay – with lines such as, “The only reason we should conserve biodiversity is for ourselves, to create a stable future for human beings” and “[T]he impulse to conserve for conservation’s sake has taken on an unthinking, unsupported, unnecessary urgency” – left the impression that it was written in a conservative think tank, perhaps by one of the anti-regulatory zealots now filling posts throughout the Trump administration. Pyron’s sentiments weren’t merely oddly out of keeping with the legacy of the man whose name graces his job title. Much of what Pyron wrote is scientifically inaccurate. And where he stepped out of his field into ethics, what he wrote was conceptually confused.
Pyron has since posted, on his website and Facebook page, 1,100 words of frantic backpedaling that land somewhere between apology and retraction, including mea culpas that he “sensationalized” parts of his own argument and “cavalierly glossed over several complex issues.” But Pyron’s original essay and his muddled apology do not change the fact that the beliefs he expressed reflect a disturbing trend that has taken hold among segments of the conservation community. And his article comes at a time when conservation is being assailed from other quarters, with a half-century of federal protections of land being rolled back, the Endangered Species Act now more endangered than ever, and the relationship between extinction and evolution being subjected to confused, book-length mistreatment.
Pyron’s original opinion piece, so clear and unequivocal in its assertions, is a good place to unpack and disentangle accelerating misconceptions about the “desirability” of extinction that are starting to pop up like hallucinogenic mushrooms.
In recent years, some biologists and writers have been distancing themselves from conservation’s bedrock idea that in an increasingly human-dominated world we must find ways to protect and perpetuate natural beauty, wild places, and the living endowment of the planet. In their stead, we are offered visions of human-dominated landscapes in which the stresses of destruction and fragmentation spur evolution.
White rhinoceros ( Ceratotherium simum ). Source: Herman Pijpers/ Flickr
Conservation International ditched its exuberant tropical forest graphic for a new corporate logo whose circle and line were designed to suggest a human head and outstretched arms. A few years ago, Peter Kareiva, then chief scientist for The Nature Conservancy, said , “conservationists will have to jettison their idealized notions of nature, parks, and wilderness,” for “a more optimistic, human-friendly vision.” Human annihilation of the passenger pigeon, he wrote, caused “no catastrophic or even measurable effects,” characterizing the total extinction of the hemisphere’s most abundant bird — whose population went from billions to zero inside a century (certainly a “measurable effect” in itself) — as an example of nature’s “resilience.”
British ecologist Chris Thomas’s recent book, Inheritors of the Earth: How Nature is Thriving in an Age of Extinction, argues that the destruction of nature creates opportunities for evolution of new lifeforms that counterbalance any losses we create, an idea that is certainly optimistic considering the burgeoning lists of endangered species. Are we really ready to consider that disappearing rhinos are somehow counterbalanced by a new subspecies of daisy in a railroad track? Maybe it would be simpler if Thomas and his comrades just said, “We don’t care about nature.’’
Enter Pyron, who — at least in his initial essay — basically said he doesn’t. He’s entitled to his apathy, but no biologist is entitled to butcher the scientific fundamentals on which they hang their opinions.
Pyron began with a resonant story about his nocturnal rediscovery of a South American frog that had been thought recently extinct. He and colleagues collected several that, he reassured us, “are now breeding safely in captivity.” As we breathed a sigh of relief, Pyron added, “But they will go extinct one day, and the world will be none the poorer for it.”
The conviction that today’s slides toward mass extinction are not inevitable spurred the founding of the conservation movement.
I happen to be writing this in the Peruvian Amazon, having just returned from a night walk to a light-trap where I helped a biologist collect moths. No one yet knows how many species live here. Moths are important pollinators. Knowing them helps detangle a little bit of how this rainforest works. So it’s a good night to mention that the number of species in an area carries the technical term “species richness.” More is richer, and fewer is, indeed, poorer. Pyron’s view lies outside scientific consensus and societal values.
Pyron wasn’t concerned about his frogs going extinct, because, “Eventually, they will be replaced by a dozen or a hundred new species that evolve later.” But the timescale would be millennia at best — meaningless in human terms — and perhaps never; hundreds of amphibians worldwide are suffering declines and extinctions, raising the possibility that major lineages and whole groups of species will vanish. Pyron seemed to have no concerns about that possibility, writing, “Mass extinctions periodically wipe out up to 95 percent of all species in one fell swoop; these come every 50 million to 100 million years.”
But that’s misleading. “Periodically” implies regularity. There’s no regularity to mass extinctions. Not in their timing, nor in their causes. The mass extinctions are not related. Three causes of mass extinctions — prolonged worldwide atmosphere-altering volcanic eruptions; a dinosaur-snuffing asteroid hit; and the spreading agriculture, settlement, and sheer human appetite driving extinctions today — are unrelated.
Rio Pescado stubfoot toad ( Atelopus balios ). Source: De Investigación y Conservación de Anfibios/ Flickr
The conviction that today’s slides toward mass extinction are not inevitable, and could be lessened or avoided, spurred the founding of the conservation movement and created the discipline of conservation biology.
But Pyron seems unmoved. “Extinction is the engine of evolution, the mechanism by which natural selection prunes the poorly adapted and allows the hardiest to flourish,” he declared. “Species constantly go extinct, and every species that is alive today will one day follow suit. There is no such thing as an ‘endangered species,’ except for all species.”
Let us unpack. Extinction is not evolution’s driver; survival is. The engine of evolution is survival amidst competition. It’s a little like what drives innovation in business. To see this, let’s simply compare the species diversity of the Northern Hemisphere, where periodic ice sheets largely wiped the slate clean, with those of the tropics, where the evolutionary time clock continued running throughout. A couple of acres in eastern temperate North America might have a dozen tree species or fewer. In the Amazon a similar area can have 300 tree species. All of North American has 1,400 species of trees; Brazil has 8,800. All of North America has just over 900 birds; Colombia has 1,900 species. All of North America has 722 butterfly species. Where I am right now, along the Tambopata River in Peru, biologists have tallied around 1,200 butterfly species.
Competition among living species drives proliferation into diversified specialties. Specialists increasingly exploit narrowing niches. We can think of this as a marketplace of life, where little competition necessitates little specialization, thus little proliferation. An area with many types of trees, for instance, directly causes the evolution of many types of highly specialized pollinating insects, hummingbirds, and pollinating bats, who visit only the “right” trees. Many flowering plants are pollinated by just one specialized species.
Pyron muddles several kinds of extinctions, then serves up further misunderstanding of how evolution works. So let’s clarify. Mass extinctions are global; they involve the whole planet. There have been five mass extinctions and we’ve created a sixth . Past mass extinctions happened when the entire planet became more hostile. Regional wipeouts, as occurred during the ice ages, are not considered mass extinctions, even though many species can go extinct. Even without these major upheavals there are always a few species blinking out due to environmental changes or new competitors. And there are pseudo-extinctions where old forms no longer exist, but only because their descendants have changed through time.
New species do not suddenly “arise,” nor are they really new. They evolve from existing species, as population gene pools change.
Crucially for understanding the relationship between extinction and evolution is this: New species do not suddenly “arise,” nor are they really new. New species evolve from existing species, as population gene pools change. Many “extinct” species never really died out; they just changed into what lives now. Not all the dinosaurs went extinct; theropod dinosaurs survived. They no longer exist because they evolved into what we call birds. Australopithecines no longer exist, but they did not all go extinct. Their children morphed into the genus Homo, and the tool- and fire-making Homo erectus may well have survived to become us. If they indeed are our direct ancestor — as some species was — they are gone now, but no more “extinct” than our own childhood. All species come from ancestors, in lineages that have survived.
Pyron’s contention that the “hardiest” flourish is a common misconception. A sloth needs to be slow; a faster sloth is going to wind up as dinner in a harpy eagle nest. A white bear is not “hardier” than a brown one; the same white fur that provides camouflage in a snowy place will scare away prey in green meadow. Bears with genes for white fur flourished in the Arctic, while brown bears did well amidst tundra and forests. Polar bears evolved from brown bears of the tundra; they got so specialized that they separated, then specialized further. Becoming a species is a process, not an event. “New” species are simply specialized descendants of old species.
True extinctions beget nothing. Humans have recently sped the extinction rate by about a thousand times compared to the fossil record. The fact that the extinction of dinosaurs was followed, over tens of millions of years, by a proliferation of mammals, is irrelevant to present-day decisions about rhinos, elephant populations, or monarch butterflies. Pyron’s statement, “There is no such thing as an ‘endangered species,’ except for all species,” is like saying there are no endangered children except for all children. It’s like answering “Black lives matter” with “All lives matter.” It’s a way of intentionally missing the point.
Chestnut-sided warbler ( Setophaga pensylvanica ). Source: Francesco Veronesi/ Wikimedia
Here’s the point: All life today represents non-extinctions; each species, every living individual, is part of a lineage that has not gone extinct in a billion years.
Pyron also expressed the opinion that “the only reason we should conserve biodiversity is for ourselves …” I don’t know of another biologist who shares this opinion. Pyron’s statement makes little practical sense, because reducing the diversity and abundance of the living world will rob human generations of choices, as values change. Save the passenger pigeon? Too late for that. Whales? A few people acted in time to keep most of them. Elephants? Our descendants will either revile or revere us for what we do while we have the planet’s reins in our hands for a few minutes. We are each newly arrived and temporary tourists on this planet, yet we find ourselves custodians of the world for all people yet unborn. A little humility, and forbearance, might comport.
Thus Pyron’s most jarring assertion: “Extinction does not carry moral significance, even when we have caused it.” That statement is a stranger to thousands of years of philosophy on moral agency and reveals an ignorance of human moral thinking. Moral agency issues from an ability to consider consequences. Humans are the species most capable of such consideration. Thus many philosophers consider humans the only creatures capable of acting as moral agents. An asteroid strike, despite its consequences, has no moral significance. Protecting bears by declaring Katmai National Monument, or un-protecting Bears Ears National Monument, are acts of moral agency. Ending genetic lineages millions of years old, either actively or by the willful neglect that Pyron advocates, certainly qualifies as morally significant.
Do we really wish a world with only what we “rely on for food and shelter?” Do animals have no value if we don’t eat them?
How can we even decide which species we “directly depend’’ upon? We don’t directly depend on peacocks or housecats, leopards or leopard frogs, humpback whales or hummingbirds or chestnut-sided warblers or millions of others. Do we really wish a world with only what we “rely on for food and shelter,” as Pyron seemed to advocate? Do animals have no value if we don’t eat them? I happen not to view my dogs as food, for instance. Things we “rely on” make life possible, sure, but the things we don’t need make life worthwhile.
When Pyron wrote, “Conservation is needed for ourselves and only ourselves… If this means fewer dazzling species, fewer unspoiled forests, less untamed wilderness, so be it,” he expressed a dereliction of the love, fascination, and perspective that motivates the practice of biology.
Here is a real biologist, Alfred Russell Wallace, co-discoverer of evolution by natural selection:
I thought of the long ages of the past during which the successive generations of these things of beauty had run their course … with no intelligent eye to gaze upon their loveliness, to all appearances such a wanton waste of beauty… . This consideration must surely tell us that all living things were not made for man… . Their happiness and enjoyments, their loves and hates, their struggles for existence, their vigorous life and early death, would seem to be immediately related to their own well-being and perpetuation alone. —The Malay Archipelago, 1869
At the opposite pole of Wallace’s human insight and wonder, Pyron asked us to become complicit in extinction. “The goals of species conservation have to be aligned with the acceptance that large numbers of animals will go extinct,” he asserted. “Thirty to 40 percent of species may be threatened with extinction in the near future, and their loss may be inevitable. But both the planet and humanity can probably survive or even thrive in a world with fewer species … The species that we rely on for food and shelter are a tiny proportion of total biodiversity, and most humans live in — and rely on — areas of only moderate biodiversity, not the Amazon or the Congo Basin.”
African elephant ( Loxodonta africana ). Source: Flowcomm/ Flickr
Right now, in the Amazon as I type, listening to nocturnal birds and bugs and frogs in this towering emerald cathedral of life, thinking such as Pyron’s strikes me as failing to grasp both the living world and the human spirit.
The massive destruction that Pyron seems to so cavalierly accept isn’t necessary. When I was a kid, there were no ospreys, no bald eagles, no peregrine falcons left around New York City and Long Island where I lived. DDT and other hard pesticides were erasing them from the world. A small handful of passionate people sued to get those pesticides banned, others began breeding captive falcons for later release, and one biologist brought osprey eggs to nests of toxically infertile parents to keep faltering populations on life support. These projects succeeded. All three of these species have recovered spectacularly and now again nest near my Long Island home. Extinction wasn’t a cost of progress; it was an unnecessary cost of carelessness. Humans could work around the needs of these birds, and these creatures could exist around development. But it took some thinking, some hard work, and some tinkering.
It’s not that anyone thinks humans have not greatly changed the world, or will stop changing it. Rather, as the great wildlife ecologist Aldo Leopold wrote in his 1949 classic A Sand County Almanac , “To keep every cog and wheel is the first precaution of intelligent tinkering.”
Related Articles
As flooding increases on the mississippi, forests are drowning.
By Richard Mertens
Rain Comes to the Arctic, With a Cascade of Troubling Changes
By Ed Struzik
How DNA from the Dead Is Helping Boost Species on the Brink
By Aisling Irwin
More From E360
Nations are undercounting emissions, putting un goals at risk, as carbon air capture ramps up, major hurdles remain, how china became the world’s leader on renewable energy, biodiversity, in mongolia, a killer winter is ravaging herds and a way of life, in rush for lithium, miners turn to the oil fields of arkansas, food & agriculture, how a solar revolution in farming is depleting world’s groundwater, what will it take to save our cities from a scorching future, plastics reckoning: pvc is ubiquitous, but maybe not for long, how a legal loophole allows gas leaks to keep on flowing, flying green: the pursuit of carbon-neutral aviation revs up.
Campaign to Save Endangered Species
Become a family of environmental leaders with these ideas on the process of designing a social action campaign to educate your community about the plight of endangered species and actions they can take to help ensure Earth is a healthy place for all living things.
Conservation

Photograph by NurPhoto / Getty Images
A social action campaign is a positive, organized, and active effort to educate others about an issue and ask them to take action. Effective campaigns not only inform but evoke the passion campaigners have for something they want to change. Social action campaigns have led to action in a variety of fields, including wildlife conservation. One example is the yellow-shouldered Amazon parrot ( Amazona barbadensis ), whose population rose on the island of Bonaire after a social action campaign, reforestation efforts, and efforts to educate the public, were initiated.

Design a Campaign Poster
Work together as a family to create a social action campaign poster to raise awareness about the plight of an endangered species that encourages the viewer to take a specific action. Start by selecting an endangered species to build your campaign poster around. As a family, research examples of campaign posters for inspiration. Decide on a catchy phrase for your poster to grab your audience’s attention and quickly make your point. Then create a rough sketch on scrap paper of the poster’s design to ensure that the text and image of your species is placed the way you want it. Make notes about what colors you want to use and the style of lettering. After completing your poster, plan to place it where it can be displayed for maximum reach.

Research, Research, Research
Great, effective campaigns are built on facts. As a family, vote on an endangered species to research. Then work together to find five to ten facts about that species. Your facts might cover the species’ physical characteristics, habitat, food, the threats it faces to survival, and any existing efforts underway to protect that species and its habitat.

Research Existing Campaigns
Select an endangered species your family would like to help. Then research groups and individuals who are working to protect those species. Make notes as you go. What actions do these individuals or organizations take to protect that species? What can you do in your area to help? How can you help them raise awareness and encourage others to take action?
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Last Updated
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .

Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
- Invertebrates
- Best Dog Collar
- Best Smart Dog Collar
- Halo Dog Collar
- Spoton vs Halo Collar
- Wagz Freedom Dog Collar
- SpotOn Dog Collar
- Best Dog Fence
- Best Invisible Dog Fence
- Dog Accessories
- Dog Training
- Dog Harness
- Dog Leashes
- Dog Grooming
- CBD for Dogs
- Dog Age Calculator
- Dog BMI Calculator
- Dog Chocolate Toxicity Calculator
- Dog Food Calculator
- Dog Harness Size Calculator
- Dog Life Expectancy Calculator
- Puppy Weight Calculator
- Dog Water Intake Calculator
- Dog Crate Size Calculator
- Dog Onion Toxicity Calculator
- Dog Raisin Toxicity Calculator
- Pet Sitter Rates Calculator
- Dog Groomer Tip Calculator
- Dog Quality of Life Calculator
- Cost of Owning a Dog Calculator
- Raw Dog Food Calculator
- Dog Dad Shirts
- Dog Mom Shirts
- Automatic Litter Box
- Cat Accessories
- Cat Collars
- Cat Grooming
- Cat Mom Shirts
- Animal Abuse
- Animal Laws
- Animal Rights
- Animal Testing
- How to Help
- Facts & Stats
- Our Campaigns
How To Help Endangered Species? Take Action to Conserve Wildlife!
Emma Davies
January 27, 2023.

WorldAnimalFoundation.org is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn More
Look we are all very aware that we can not continue to destroy not only our planet but the animals and plants that inhabit it. After all, our survival depends on us being able to share this amazing planet with all its inhabitants.
There are loads of simple ways that we can all help endangered species even in our everyday lives.
Most of us can’t welcome an endangered species into our homes, although who wouldn’t want to snuggle up with a furry lion? But there are still things that we can do!
We can all spread awareness of the wild animals that are in danger and help to protect endangered species.
Here’s the best part, most of this protection work can be done at home from your backyard, or via the internet. This means it won’t cost you a thing to make these simple changes that can help with the protection and survival of millions of animal species.
11 Ways To Help Endangered Species From Extinction

It’s hard to ignore the frightening endangered animal statistics that show just how many animals and plants are facing habitat destruction, poaching , and illegal wildlife trade. And the sad fact is that this comes down to the actions of one species – us humans!
But are there ways that we, the general public, can really help?
Check out the 11 ways we can all help save animals and plants. Such as making your local area wildlife-friendly and supporting organizations to ensure we preserve the natural world for future generations.
1. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle!
I know this one may seem far too obvious, but one of the first steps we can take to help protect native species is by making a difference in our local area.
Start by reducing our household waste by making a conscious decision to choose products that have recyclable or compostable packaging – this is so easy, and we can get the whole family involved.
Reducing the amount of plastic we all use by utilizing reusable bags when shopping and even choosing refillable household products like hand soap and shower gel. And we all use disposable bottled water, how about opting for a reusable one instead?
It might not seem like we are making groundbreaking changes, but even small ones mean that as a household we can all contribute towards the protection of some of the most amazing creatures. You could also help by using sustainable products like bamboo and recycled paper instead of plastic.
2. Learn About Endangered Species In Your Area

It’s important to work on saving native species in our local area, and also a great way to get other committed volunteers involved in conservation efforts.
Teach anyone who will listen about the ways they can help support the local native wildlife population by maintaining natural habitats and not interrupting native plant species growth.
Get the local schools involved, after all the younger we teach our children about what they can do to protect this planet and animals the more likely we all are to survive!
3. Limit Your Consumption of Factory
Our world has undergone a huge population increase and this in itself has brought about a crisis as the consumption and demand for food, especially meat and seafood, skyrockets. Sadly, this means there is an overwhelming amount of factory-farmed meat that will have come from poaching and illegal animal trafficking.
We live in a world where there are a thousand different options for everything we could ever buy. But this makes it difficult to identify the best products to purchase so that we can help to protect endangered species.
Certifications from organizations such as Animal Welfare Approved by AGW can help us all make informed choices. These organizations are independent and nonprofit, meaning their conservation efforts are committed to supporting animal welfare and have no hidden agenda.
4. Make Your Home Wildlife Friendly
Another one of the ways we can all help endangered species thrive in our community is through simply being responsible and thinking before we do things.
For example, instead of planting invasive species in your next garden makeover, use native plants. These will not only look fantastic but also attract wildlife and avoid damaging the food source of other animals.
In well-developed areas, it can be hard for local wildlife species to thrive, especially with the threat of cats, dogs, and other domesticated animals.
Making changes such as feeding pets indoors, locking our pet doors, and even securing our trash can lids can be a step towards protecting them.
If like me you’re a fan of feathered friends, then you need to regularly disinfect bird baths and feeders to prevent cross-contamination risks, and maybe consider using window stickers to deter the little guys from a collision and concussion combo.
All these small changes can help turn our gardens into a wildlife-safe haven. Helping our local wildlife to blossom and still be around for generations to come.

5. Reduce Your Impact on the Environment
This may seem like a really obvious point to make and one that every climate activist is shouting about – but reducing the impact on the environment is one of the most important things we can all do!
Start researching the ways you can help by buying sustainable products, recycling all your old technology such as phones and laptops, and even being aware of the energy that you consume can help.
Small changes like changing your lightbulbs to energy-saving ones and turning off devices when they aren’t being used can help our environment and in turn, the animals that are being displaced.
Two of the biggest causes of our ever-growing list of endangered species are deforestation and climate change, and the vast majority of this is caused by global warming and us infringing on animal habitats. We can all help even in small ways by putting our planet first!
6. Never Purchase Products Made With Ivory, Real Tortoise Shell, or Coral.
Even though the government has made this practice illegal, sadly an estimated 20,000 elephants were harmed or killed last year.
The ivory industry is worth a lot of money, so the important and necessary work of companies such as Coalition Wildlife Trafficking Online works to protect endangered species from being sold online and keep native wildlife where they belong – in their native lands!
Thank goodness you are less likely to find products made of these threatened species, thanks to the Endangered Species Act that restricts the importation and exportation of exotic plants and native wildlife species.
But unfortunately, there is still big money in ivory, coral , and turtle shells. And while there are people willing to pay big bucks for these things, our precious animals will always live in fear.

7. Help Endangered Species When You Travel
Whether you’re going on a road trip or traveling halfway across the world, there are ways to save endangered species whilst still having a great time.
Endangered animals can be found almost anywhere, so educate yourself about the best ways for protecting endangered species and maybe read up on protected lands and any national wildlife refuge that you can support.
If you’re buying gifts for yourself or people back at home, make sure they are made from sustainable products that will protect and help endangered species instead of driving them to the brink of extinction.
As we mentioned previously, purchasing products made from things such as tortoise shells and ivory is not only illegal, but it won’t help these animals to survive in the wild. Instead, all it does is cram the pockets of these poachers and increase the demand for such products.
8. Donate To Organizations Created To Help Zoo Animals And Wildlife
There are a huge number of organizations that specialize in Endangered species conservation such as the Wild Animal Health Fund. Their sole purpose is to ensure the protection of any species whether it be an animal or plant that is endangered.
They work tirelessly researching the causes of native landscape decline and help endangered animals to get back to living in their natural habitat. These types of organizations allow nature to survive its greatest threat- Us!
The International Union for the Conservation of Nature shows that as of March 2019, there were 7,510 endangered or critically endangered animal species globally. And this is just animals, it doesn’t include plants or insect species that are also nearing extinction levels.
This is why we need to be increasing our support for these organizations and educating our children.

9. Support Local Accredited Zoos And Aquariums
Some of the most at-risk wildlife are often in captivity. So make sure you research any zoos or aquariums you plan to visit beforehand so you can make sure they are accredited by the ZAA or AZA.
Breeding programs in an accredited zoo can make an unbelievable difference in conserving threatened species, and even prevent animals from reaching extinction levels. By breeding them in captivity, we can give them a fighting chance by removing the dangers that are found in their natural habitat.
10. Protect Wildlife Habitats
Scientists have been warning us for decades that widespread deforestation will lead to the destruction of our planet. Not only is it destroying the natural habitat of many native animals but it will also be key in the destruction of many native plants.
And without these forests, our air quality will reach a point where it is no longer breathable.
These habitats are crucial in order to help bees, butterflies , and other pollinating insects to do what they were born to do in these threatened areas – and that’s to pollinate!
Wildlife, forests, and native plants need to be conserved there’s no question there. But in highly developed areas, it’s common to find housing projects either built or in the process of being built.

11. Harassing Wildlife Is Cruel and Illegal
Millions of animals have been disgustingly killed for souvenirs, and when people purchase these products this only further increases the cruel and destructive demand for them.
It’s a vicious circle that is found all across the world and that we are all a part of.
We are forcing animals to extinction for the sake of a cool pair of sunglasses made from turtle shell, or a unique ornament that is made from the tusk of an elephant – is it really worth it?
If we treat all animals with the love and respect they deserve, these issues would never have reared their ugly heads in the first place.
Next time you are near wetlands or in a forest, think about how you can enjoy these amazing places without leaving any sign that you were actually there.
Why Are Both Habitats and Animals Important?
You may be wondering why a habitat and animals are so important. Well, one can not survive without the other, and the truth is without animals, we can’t survive either.
Good habitats provide everything an animal, insect , or plant needs to not just survive but thrive. This includes things like clean air, shelter, a good food source, and the right environment.
But each animal’s habitat differs even if only slightly. Our planet is made up of a vast range of different habitats from forests, glaciers, oceans, and even microhabitats. These all play a crucial part in our survival and the survival of this planet.
Final Verdict
Look we all know that we have an enormous number of endangered wildlife or species with rapidly declining populations that need our help, not in 2 years or even 6 months’ time – they need it now!
By supporting conservation organizations, and doing your bit at home by recycling, we can all make a real difference in the fight to save our animals, our homes, and our world!
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest Posts

Top 10 Quiet Guard Dog Breeds That Offer Peaceful Protection

10 Best Dog Breeds To Protect Against Hyenas & Wild Predators

7 Most Active Guard Dog Breeds to Help Protect Your Family

7 Best Guard Dog Breeds for Veterans

9 Guard Dog Breeds for Off-Grid Living

9 Guard Dog Breeds with the Best Sense of Danger Awareness

7 Best Dog Breeds To Protect Against Wild Boars

7 Best Travel-Ready Guard Dog Breeds for Nomads and Adventurers

7 Best Guard Dog Breeds for Homes With Multiple Pets

10 Guard Dog Breeds that are Natural Intruder Detectors
Get updates on the latest posts and more from World Animal Foundation straight to your inbox.

What can we do to protect biodiversity?
Loss of natural habitats has been taking place over thousands of years, but scientists are confident that we have ways to help biodiversity recover. Global efforts so far have been insufficient. We must produce food much more efficiently using less land and with less waste. We must also change how and where we urbanise and industrialise landscape and the ocean, and how we produce energy. Paying more attention to the multiple values of nature, including placing a financial value on nature, might also help us to avoid losing more biodiversity.
The world’s nations could improve the situation at the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity Fifteenth Conference of the Parties (COP15) to be held in Kunming, China. Ours is the first generation that understands in detail the damage that it is causing to biodiversity – and the last with the time to make a difference.
Growing populations and the even faster growing rates of consumption are a major threat to biodiversity. Half of the Earth’s ice free and otherwise habitable land is now occupied by cropland and pastures, and it is estimated that half of the species at risk are threatened by agriculture. We need new ways of farming, using land for different purposes. Exactly how we do that is currently much debated.
Deforestation, often linked to agriculture, is also a major problem, bringing about the destruction of habitats. It is essential to protect forests. A growing threat is climate change, which is both driven by and drives biodiversity loss. Reducing emissions and absorbing carbon will be an essential route to reducing biodiversity loss. Nature-based solutions for climate change include methods which could enhance biodiversity at the same time as tackling climate change.
We will also need new ways to value and account for nature that put a price on its destruction so that we take this into account when assessing the overall cost and value of what we produce. We also need a global monitoring network that allows us to hold countries to account for failures to tackle biodiversity loss.
And finally, we need to do more to support the Indigenous peoples and local communities on whose land biodiversity is thriving, but who are struggling to protect it against the pressures of external developers and extractive industries. Strengthening their land rights will help protect them as well as protecting biodiversity.
To find out more; Preserving global biodiversity requires rapid agricultural improvements | Royal Society ; Plural valuation of nature matters for environmental sustainability and justice | Royal Society ; The economics of biodiversity: The Dasgupta Review | Royal Society
Climate change and biodiversity
Human activities are changing the climate. Science can help us understand what we are doing to habitats and the climate, but also find solutions.
Email updates
We promote excellence in science so that, together, we can benefit humanity and tackle the biggest challenges of our time.
Subscribe to our newsletters to be updated with the latest news on innovation, events, articles and reports.
What subscription are you interested in receiving? (Choose at least one subject)

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
113 Endangered Species Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Endangered species are a critical issue facing our planet today. With habitat destruction, climate change, pollution, and illegal hunting threatening the survival of countless species, it is more important than ever to raise awareness and take action to protect these vulnerable creatures.
If you are looking for essay topic ideas on endangered species, look no further. Here are 113 examples to inspire your writing:
- The impact of climate change on polar bears
- The illegal trade of rhino horns
- The conservation efforts to save the black rhinoceros
- The decline of the African elephant population
- The role of zoos in endangered species conservation
- The threats facing the Sumatran tiger
- The conservation status of the Amur leopard
- The effects of deforestation on orangutan populations
- The decline of the vaquita porpoise
- The conservation efforts to save the Javan rhinoceros
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine turtles
- The decline of the North Atlantic right whale population
- The conservation status of the saola
- The role of ecotourism in endangered species conservation
- The decline of the pangolin population
- The conservation efforts to save the African wild dog
- The impact of habitat destruction on the red panda
- The decline of the Western lowland gorilla population
- The conservation status of the Philippine eagle
- The effects of overfishing on the bluefin tuna population
- The decline of the mountain gorilla population
- The conservation efforts to save the snow leopard
- The impact of pollution on the beluga whale
- The decline of the black-footed ferret population
- The conservation status of the golden lion tamarin
- The role of captive breeding in endangered species conservation
- The decline of the giant panda population
- The conservation efforts to save the tigers in India
- The impact of climate change on the Adélie penguin
- The decline of the African penguin population
- The conservation status of the sea otter
- The effects of habitat destruction on the California condor
- The decline of the hawksbill sea turtle population
- The conservation efforts to save the cheetah
- The impact of pollution on the vaquita porpoise
- The decline of the orangutan population
- The conservation status of the black rhinoceros
- The role of wildlife corridors in endangered species conservation
- The decline of the Amur leopard population
- The conservation efforts to save the Sumatran tiger
- The impact of climate change on the African elephant
- The decline of the Javan rhinoceros population
- The conservation status of the black-footed ferret
- The effects of overfishing on the North Atlantic right whale population
- The decline of the saola population
- The conservation efforts to save the pangolin
- The impact of habitat destruction on the Philippine eagle
- The decline of the bluefin tuna population
- The conservation status of the red panda
- The role of genetic diversity in endangered species conservation
- The decline of the African wild dog population
- The conservation efforts to save the vaquita porpoise
- The impact of pollution on the Amur leopard
- The decline of the snow leopard population
- The conservation status of the beluga whale
- The effects of habitat destruction on the golden lion tamarin
- The conservation efforts to save the North Atlantic right whale
- The impact of climate change on the pangolin
- The decline of the black rhinoceros population
- The conservation status of the Sumatran tiger
- The role of community-based conservation in endangered species conservation
- The conservation efforts to save the sea otter
- The impact of pollution on the California condor
- The conservation status of the cheetah
- The effects of habitat destruction on the vaquita porpoise
- The conservation efforts to save the golden lion tamarin
- The impact of climate change on the black-footed ferret
- The decline of the Adélie penguin population
- The conservation status of the African elephant
- The role of habitat restoration in endangered species conservation
- The conservation efforts to save the saola 77
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade

Essay on Save Endangered Animals
Students are often asked to write an essay on Save Endangered Animals in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Save Endangered Animals
Why save endangered animals.
Many animals are in danger of disappearing forever. Saving them is important because they are part of our world. Each animal has a role in nature. Losing one can harm the environment and other living things.
Causes of Danger
Animals become endangered for many reasons. Some include losing their homes, pollution, and hunting. People’s actions often cause these problems. By changing how we live, we can help save these animals.
What Can We Do?
Everyone can help save endangered animals. Planting trees, cleaning up areas, and learning more about wildlife are good steps. By working together, we can protect these animals for the future.
250 Words Essay on Save Endangered Animals
Why saving endangered animals is important.
Many animals around the world are in danger of disappearing forever. These animals are called endangered animals. Saving them is important for many reasons. First, every animal has a role in nature. They help keep the environment healthy. For example, bees help flowers grow by moving pollen. If we lose one animal, it can upset the balance of nature.
Reasons Animals Become Endangered
Animals become endangered for several reasons. One big reason is that their homes are being destroyed. When forests are cut down or waters are polluted, animals lose their homes. Another reason is hunting. Some animals are hunted for their fur, tusks, or other parts. This can reduce their numbers very quickly. Also, when the climate changes, it can make it hard for animals to survive.
How We Can Help
Everyone can help save endangered animals. One way is by taking care of the environment. This means not littering and recycling when you can. Another way is by learning about endangered animals and telling others. The more people know, the more they can help. Also, supporting parks and places that protect animals is a good way to help.
Saving endangered animals is very important. It keeps the environment healthy and balanced. There are many reasons animals become endangered, but there are also many ways we can help. By doing our part, we can make sure these animals are around for future generations to enjoy.
500 Words Essay on Save Endangered Animals
Many animals around the world are in danger of disappearing forever. This is a big problem because every animal plays a special role in nature. Some animals help to keep the environment clean, while others are food for different animals. If we lose one animal, it can cause problems for other animals and even people. This is why we need to protect animals that are in danger.
There are many reasons why animals become endangered. One big reason is that their homes are being destroyed. When forests are cut down or wetlands are filled in, animals lose the places where they live, find food, and raise their babies. Another reason is pollution. Water and air pollution can make it hard for animals to survive. Also, some animals are in danger because people hunt them for their fur, tusks, or other parts. Lastly, climate change is making it harder for many animals to live in their natural habitats.
What We Can Do to Help
Everyone, including kids, can help save endangered animals. One way to help is by learning about endangered animals and telling others about them. The more people know about the problem, the more they can help. You can also help by raising money for groups that work to protect animals. Even small amounts of money can help buy land for animal homes or pay for people to take care of the animals.
Another way to help is by taking care of the environment. This means recycling, using less water, and not littering. When we keep our environment clean, we help all animals, not just the endangered ones. Also, when you or your family buy things, you can choose products that are good for the environment and don’t harm animals’ homes.
Success Stories
There are some happy stories about animals that were once in big trouble but are now doing better because people helped them. For example, the giant panda was once very close to disappearing. But, thanks to a lot of hard work from people all over the world, there are now more giant pandas than there were 20 years ago. Another success story is the American bald eagle. It was almost gone because of pollution, but laws that protect the air and water helped the eagles to come back. These stories show that when people work together, they can save animals.
Saving endangered animals is very important. Every animal has a role in nature, and losing one can cause problems for other animals and people. There are many reasons animals become endangered, but there are also many ways we can help. By learning, sharing, raising money, and taking care of our environment, we can make a big difference. Remember, every small action counts. Let’s all do our part to protect our animal friends and keep them safe for future generations.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Scary Experience
- Essay on School Camping
- Essay on Scientist
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Environment: Endangered Species Essay
Globally, over 14,000 animal species face a risk of extinction. The reasons for the near extinction include poaching, habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, pollution, diseases, climate change, and low birth rates (IUCN, 2021). Some of the most endangered species include the Javan rhino, African elephants, black rhino, snow leopards, orangutans, the vaquita, Amur leopards, and the eastern lowland gorillas. With the appropriate conservation measure, endangered animals may increase over time.
Captive breeding and reintroduction are among the most effective conservation approaches. They involve capturing, breeding, and rearing endangered animals in wildlife reserves, zoos, or aquariums to help increase their numbers. After a significant number is raised, the animals can then be released back to their natural habitats. For example, in 1982, only 22 California condors existed in the wild; however, captive breeding increased the number to 425 in 2014 (Association of Zoos & Aquarium, n.d). Thus, when threats are reduced, the rare species can improve in numbers.
Habitat protection is critical in ensuring the safety of endangered animals. Protected areas where endangered species can be placed include nature reserves, national parks, and wildlife refuges. There are various marine reserves and protected areas that prohibit fishing, thus safeguarding the marine species. In this case, New Zealand has several marine reserves that protect sea turtles, aquatic mammals, and some fish species such as manta rays and white pointer sharks (Ministry for Primary Industries, n.d). Additionally, some laws and regulations safeguard wildlife at state, national, and global levels to prevent animal extinction. In this case, CITES or the Washington convention significantly regulates the global trade of wild animals. This treaty restricts and controls any trade involving endangered species to ensure they do not become extinct
In conclusion, human activity and climate change continually threaten some wild animals’ survival. Nonetheless, appropriate conservation methods such as captive breeding and habitat protection can ensure the continuous reproduction of these species. The enactment of state, national and global laws that safeguard wild animals also promotes the survival of these species. Human beings have a responsibility to ensure the protection of wild animals and their habitats.
Global warming is one of the biggest threats to animal and plant survival. The accumulation of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, deforestation, and increased agricultural activities are major contributors to this phenomenon. The increased earth temperature associated with global warming has led to climate change resulting in several natural calamities. However, the threat of global warming can be reduced by using renewable energy, recycling, planting more trees, and lowering the emission of greenhouse gases.
Global warming has significant adverse impacts on human beings and the environment. The extreme heat associated with climate change increases complications from underlying respiratory and heart diseases such as renal failure and asthma and may cause other heat-related disorders. Global warming also increases the risk of storms and drought, affecting food supply, which may cause death to both humans and animals (Global Climate Change, 2021). It has also been linked to ocean acidification, increased ocean temperature, and rising sea levels. Such occurrences have led to the death of a significant number of marine life.
Rather than human actions, global warming may result from natural forces. Human activities such as deforestation, industrial processes, and agricultural activities have long been attributed to climate change. However, there are claims that complex gravitational interactions, particularly alterations in the earth’s orbit, torque, and axial tilt, may also influence climate change resulting in increased temperature (Neaves, 2017). Gradual shifts in the earth’s orbit combined with its axial tilt places the south and north poles more directly to the sun resulting in temperature extremes.
In conclusion, global warming has adverse effects on humans and nature. It exposes humans to heat-related diseases and increases complications of respiratory illnesses such as asthma. Climate change depletes vegetation causing food shortage and death to humans and animals. Similarly, it causes ocean warming and acidification, which destroys marine life. Although some natural forces such as shifts in the earth’s orbit and axis may trigger temperature changes, human activities are the greatest contributors to global warming.
Association of Zoos & Aquarium (n.d). Reintroduction programs . Web.
Ministry for Primary Industries. (n.d). Protecting marine life . Web.
Neaves, T., T. (2017). The climate is changing, but not just because of humans. Here’s why that matters . NBC News . Web.
International Union for Conservation of Nature. (2021). African elephant species now endangered and critically endangered – IUCN Red List . Web.
Global Climate Change. (2021). The effects of climate change . Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, November 16). Environment: Endangered Species. https://ivypanda.com/essays/environment-endangered-species/
"Environment: Endangered Species." IvyPanda , 16 Nov. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/environment-endangered-species/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Environment: Endangered Species'. 16 November.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Environment: Endangered Species." November 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/environment-endangered-species/.
1. IvyPanda . "Environment: Endangered Species." November 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/environment-endangered-species/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Environment: Endangered Species." November 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/environment-endangered-species/.
- Javan Rhinos: Wildlife Trading of Endangered Animals
- "Save the Rhino, Save the Plant" Summary
- Global Climate Change and Environmental Conservation
- Summary of the Rhino Hunter Podcast
- Conservation Status of Poached Species in Africa: A Case of Rhinos, Elephants, and Gorillas
- Climate Change Effects on Ocean Acidification
- Ocean Acidification Impact on the Sea Urchin Larval Growth
- The Axial Age and World Religions
- Axial age thinkers
- Ocean Acidification: Marine Calcification Process
- Human Impact on Seismic Activity
- Is Fashion Destroying the Planet?
- Reducing Personal Impact on the Environment
- Poor Waste Disposal and Pollution in California
- Food Production and The Environment
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Biden Administration Moves to Protect the Sage Grouse
A new proposal lays out six possible plans, singling out one compromise approach as the preferred option.

By Lisa Friedman and Catrin Einhorn
The Biden administration on Thursday proposed plans to save the greater sage grouse, a move that could tighten restrictions on drilling, mining and other commercial activities on public lands in the West.
The sage grouse, a ground-nesting bird that is known for the males’ flamboyant mating dance, has been at the center of a decade-long battle between industry and conservationists. The new plan, issued by the Bureau of Land Management, is expected to set off a new round of debate and legal challenges.
The bureau controls the country’s largest single share of sage grouse habitat, nearly 70 million acres across 11 Western states. That amounts to almost half of the bird’s habitat.
Over the past decades, the sage grouse population has declined precipitously because of habitat loss exacerbated by wildfires fueled by climate change.
Across their entire range, greater sage grouse populations have declined about 80 percent since 1965, and nearly 40 percent since 2002, according to a report by the U.S. Geological Survey .
The proposal, which offers six alternatives, is an effort to keep the sage grouse off the endangered species list. That would trigger much greater restrictions on activities within the bird’s range, while balancing the use of public lands for energy development, mining and grazing.
“The majesty of the West and its way of life are at stake,” Tracy Stone-Manning, the director of the Bureau of Land Management, said in a statement.
She noted that states and the federal government had worked together on conservation efforts for the bird, and said the new plan built on that work.
The six alternatives will now be open for public comment. Each would bring some restrictions on commercial activities, with varying amounts of land affected. The agency’s preference is No. 5 on the list, a compromise between more restrictive and permissive propositions from previous administrations.
Compared with the status quo, for example, it would place an additional 2.5 million acres under the most restrictive sage grouse protections, bringing that total to almost 35 million acres, agency officials said. It would also ensure that renewable energy was sited away from sensitive sage grouse habitat and streamline management of the birds across state borders.
Immediate reaction from conservation groups was mixed.
“This plan represents the last, best hope to save the sage grouse and avoid a listing under the Endangered Species Act,” Aaron Weiss, deputy director of the Center for Western Priorities, an environmental group, said in a statement.
Other conservation groups sounded the alarm.
“The draft proposal just doesn’t cut it for the sage grouse,” said Vera Smith, senior federal lands policy analyst with Defenders of Wildlife. “The draft proposal still allows for oil and gas drilling, mining, and other activities — some of the biggest threats to the bird’s habitat.”
Oil industry executives, who have been anxious about the plan, took a cautious approach. Kathleen Sgamma, president of Western Energy Alliance, an association of independent oil and gas companies, said she worried that the Biden administration was taking a “one-size-fits-all” approach to states with different needs.
But, Ms. Sgamma said in a statement, “It’s positive that the preferred alternative seems to be a blend between the other approaches and prior plans.” She added that this indicated that the Bureau of Land Management “is trying to find a workable balance.”
The federal battle over the greater sage grouse began when the Obama administration issued a land-use plan to shield the bird’s habitat from mining and energy development. That plan was considered strong enough to keep the sage grouse off the endangered species list.
But it was sharply criticized by the oil and gas industry, and, in 2017, the Trump administration issued a new plan that weakened protections and made it easier for states to approve drilling, pipelines and other activities in sage grouse breeding areas.
A federal court in 2019 blocked the Trump plan from moving forward, and the bureau consequently never put in place any of the proposed management plans.
According to the bureau, the birds rely on sagebrush to meet their food and reproduction needs, and a local population could need as much as 40 square miles of intact landscape to stay healthy. Other Western species also rely on healthy sagebrush, including mule deer, pronghorn and pygmy rabbits.
Lisa Friedman is a Times reporter who writes about how governments are addressing climate change and the effects of those policies on communities. More about Lisa Friedman
Catrin Einhorn covers biodiversity, climate and the environment for The Times. More about Catrin Einhorn
Home — Essay Samples — Environment — Endangered Species — Ways of Protection Endangered Species
Ways of Protection Endangered Species
- Categories: Animal Welfare Endangered Species
About this sample

Words: 791 |
Published: Apr 29, 2022
Words: 791 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
The petition filed to protect giraffes
What you can do to help protect endangered species.
- Reduce your plastic consumption. Instead of getting new plastic bags every time you buy groceries, bring reusable ones when you can. Reusable straws are also becoming a trend recently, and they are not difficult to carry around because of their small size. Plastic products are not biodegradable so they can possibly end up somewhere they shouldn’t be in the ecosystem, like in the stomach of a fish or around the neck of a turtle.
- Conserve water. Water is very important for every living creature. Just because we seem to have an abundance of potable water, that doesn’t mean it is the same everywhere else. Little things matter, like turning off the faucet while you are brushing your teeth or reusing the towels in your hotel room.
- Reduce your carbon footprint. Habitat loss is often driven by the expansion of cities and logging. Instead of driving alone, you can opt to walk, bike, or carpool. Conserve energy and consider if the appliances you are purchasing are energy efficient.
- Have an effective trash system. Help preserve the animals’ natural habitat by protecting the environment from too much garbage. Reduce, reuse, and recycle.
- Learn about the endangered species around where you live.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Environment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 737 words
3 pages / 1250 words
2 pages / 668 words
4 pages / 1827 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Endangered Species
Imagine you are an animal. You’ve been wandering the wastelands, which used to be a lush green forest, what used to be your home. Its late spring, right about time for mating season. Normally, you’d be out calling for a mate, [...]
The job of a marine biologist is to study and conserve the ocean, and all the creatures within it. While their main focus is the water, a lot of their work is conducted on dry land, as they fight for regional laws, fisherman [...]
Giant pandas, or Ailuropoda, are one of the most beloved and iconic animals in the world. Their distinctive black and white fur, gentle demeanor, and unique diet of bamboo have captivated people around the globe. However, the [...]
Red pandas are “raccoon-like” animals with fluffy fur ranging from orange, brown, black, and white. The red panda is found in Central China, Nepal, Burma, and other places in the surrounding area. They live in isolated mountain [...]
Endangerment is a bigger issue, one of them that include the animals as well as the atmosphere where they interact with each other and live. To solve or elevate this problem every aspect related to this need to be studied. So, [...]
The African elephant, one of the planet's most majestic and iconic creatures, stands at the precipice of extinction. This essay delves into the critical issue of endangered species, focusing on the plight of the African [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Endangered Species Act requires that every U.S. plant and animal be saved from extinction, but after 50 years, we have to do much more to prevent a biodiversity crisis. By Robert Kunzig. Snail ...
2. Visit a national wildlife refuge, park or other open space . These protected lands provide habitat to many native wildlife, birds, fish and plants. Scientists tell us the best way to protect endangered species is to protect the places where they live. Get involved by volunteering at your local nature center or wildlife refuge.
Defending and strengthening the Endangered Species Act, which provides an essential legal safety net to prevent the loss of plant and animal species to extinction. Holding federal agencies and others accountable for complying with laws protecting rare and endangered species using cooperation, persuasion, and—where necessary—litigation.
The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species™ reveals that a quarter of all species face high risk of extinction. Human activity has severely altered more than 75% of the Earth's land and freshwater areas, and 66% of the oceans. Climate change and political instability are exacerbating this crisis at all levels. Species loss at current rates ...
An endangered species is a type of organism that is threatened by extinction.Species become endangered for two main reasons: loss of habitat and loss of genetic variation. Loss of Habitat A loss of habitat can happen naturally. Nonavian dinosaurs, for instance, lost their habitat about 65 million years ago.The hot, dry climate of the Cretaceous period changed very quickly, most likely because ...
The way a species is assessed under the IUCN Red List can also determine whether such species deserve protection under two international treaties aimed at species conservation: CITES and the Convention on Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS). Listing an endangered species under either of these two conventions can catalyze further action and ...
Make a symbolic animal adoption to help save some of the world's most endangered animals from extinction and support WWF's conservation efforts. From elephants to polar bears, WWF fights to secure a future for animals on the planet we all share. WWF helped bring back the Amur tiger and Africa's black rhinos from the edge of extinction.
One possible entry point to this discussion is through the vivid, often disturbing pictures in the photo essay "A Mausoleum for Endangered Species."You could select one image to show students ...
Pyron seemed to have no concerns about that possibility, writing, "Mass extinctions periodically wipe out up to 95 percent of all species in one fell swoop; these come every 50 million to 100 million years.". But that's misleading. "Periodically" implies regularity. There's no regularity to mass extinctions.
Work together as a family to create a social action campaign poster to raise awareness about the plight of an endangered species that encourages the viewer to take a specific action. Start by selecting an endangered species to build your campaign poster around. As a family, research examples of campaign posters for inspiration.
Published: Dec 16, 2021. From 41,415 animal species, 16,306 of them are facing extinction according to IUCN's Red List. Some of these animals are the Amur Leopard, the Orangutan, the Hawksbill Turtle, the African Wild Dog, and many more. It is our job to protect these animals because of their vital roles in our ecosystem.
4. Make Your Home Wildlife Friendly. Another one of the ways we can all help endangered species thrive in our community is through simply being responsible and thinking before we do things. For example, instead of planting invasive species in your next garden makeover, use native plants.
Spread Awareness: Another way to protect endangered animals is to create awareness about them. You can create local community groups that work for this cause. Having seminars is another way of creating awareness. Also, inculcating lessons in student's academics on how to protect animals will go a long way.
It is essential to protect forests. A growing threat is climate change, which is both driven by and drives biodiversity loss. Reducing emissions and absorbing carbon will be an essential route to reducing biodiversity loss. Nature-based solutions for climate change include methods which could enhance biodiversity at the same time as tackling ...
Endangered Species: The African Elephant. 2 pages / 1011 words. Introduction The African elephant, one of the planet's most majestic and iconic creatures, stands at the precipice of extinction. This essay delves into the critical issue of endangered species, focusing on the plight of the African elephant.
The conservation efforts to save the snow leopard; The impact of pollution on the beluga whale; The decline of the black-footed ferret population; The conservation status of the golden lion tamarin; The role of captive breeding in endangered species conservation; The decline of the giant panda population; The conservation efforts to save the ...
For more information about endangered species, visit endangered.fws.gov. 2) Create a backyard wildlife habitat. Put bird feeders and other wildlife attractants, such as bird houses and baths. 3) Establish a pollinator garden with native vegetation in your yard. Native plants provide food and shelter for native wildlife.
As of 2020, they reported that more than 37,400 species are threatened with extinction. This includes 41% of amphibians, 34% of conifers, 33% of reef-building corals, 25% of mammals, and 14% of birds. The reasons for the endangerment of these animals range from habitat loss and climate change to overexploitation and pollution.
Idaho still proposes to kill wolves. Throughout the history of our species, we have played a role—often the starring role—in driving species to extinction. Sailors killed dodos and harvested their eggs, and sailing ships introduced predators to the dodos' habitat. People hunted passenger pigeons and deforested their habitats until the ...
One of the most effective ways to protect endangered species is through legislation. Laws like the Endangered Species Act in the United States and the Wildlife Protection Act in India aim to protect threatened species and their habitats. However, laws are only effective if they are enforced. Therefore, governments should invest in training and ...
Javan Rhinos: Wildlife Trading of Endangered Animals. Out of the five rhino species, Javan rhinoceros is the most threatened species despite being in the ecosystem for millions of years, playing a crucial role in shaping the landscape by its feeding style. Australia's Endangered Diverse Marine Ecosystem.
Students are often asked to write an essay on Save Endangered Animals in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. ... Everyone, including kids, can help save endangered animals. One way to help is by learning about endangered animals and telling ...
This essay aims to present a compelling argument for the conservation and protection of endangered animals. By examining the ecological, ethical, and economic implications of their extinction, it becomes evident that urgent action is necessary to prevent further loss of biodiversity.
Globally, over 14,000 animal species face a risk of extinction. The reasons for the near extinction include poaching, habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, pollution, diseases, climate change, and low birth rates (IUCN, 2021). Some of the most endangered species include the Javan rhino, African elephants, black rhino, snow leopards, orangutans ...
Endangered Species Coalition's Pollinator Protectors campaign helps to create habitat for pollinating species of each of these animals. So far in 2024, the Endangered Species Coalition has funded restoration work for a greenhouse propagating agave for native pollinating bats in Texas, the purchase of a locally rare native pollinator plant for ...
"This plan represents the last, best hope to save the sage grouse and avoid a listing under the Endangered Species Act," Aaron Weiss, deputy director of the Center for Western Priorities, an ...
Ways of Protection Endangered Species. A species is categorized as "endangered" if it has a high possibility of being extinct in the near future. It is second in severity in the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)'s conservation status system, following only those labeled "critically endangered.".