Filter by Keywords

10 Production Schedule Templates for Production Planning
Praburam Srinivasan
Growth Marketing Manager
February 13, 2024
If you’re in the business of making something—a new app, a website, or even a multimedia project—you need to carefully plan, control, and execute your production to succeed. A good production schedule helps you to deliver your goods on time while optimizing your resources.
These blueprint plans keep everyone in the know and on track throughout every stage of the production process. These schedules specify who is responsible for each task, the completion date, and the next steps in the process .
In this guide, we’ll cover the benefits of a well-designed schedule and share 10 production schedule templates you can start using now. 🦄
What is a Production Planning Template?
Benefits of using a master production schedule template, what makes a good production planning template, 1. clickup production tracking template, 2. clickup production cost analysis template, 3. clickup daily production report template, 4. clickup manufacturing project plan template, 5. clickup manufacturing communication plan template, 6. clickup sprint planning template, 7. clickup development schedule template, 8. clickup build plan template, 9. clickup release planning template, 10. excel production schedule template by simple sheets.
A production planning template is a framework that creates a visual representation of production scheduling. The schedule establishes a production process and assigns a plan and budget, outlining the task sequence, timing, and allocation of necessary resources to create something or deliver services.
Production schedules usually include details on the production status, such as task description, start and end dates, role and responsibility assignments, and required materials for each step.
These resources are handy for optimizing workflows and minimizing obstacles that could delay production. They help project managers ensure on-time and on-budget delivery of goods and services.
A well-planned production schedule assists businesses in making intelligent, well-informed decisions and planning more efficiently.
Using a production schedule template improves your business’s efficiency and organization while contributing to the overall success of the production process. Some of the key advantages of using a production planning template include:
- More efficient resource allocation : A good production plan will help you allocate resources efficiently, including workforce, equipment, and materials. This helps reduce production costs and improve profitability
- Better time management : Production schedule templates help you create clear, reasonable timelines for each task, giving teams actionable deadlines and avoiding burnout or bottlenecks. You’ll also avoid unnecessary downtime
- Standardized processes : A production plan creates a framework for your operations and provides a consistent and replicable production process. This enhances quality control and reduces potential errors in production
- More transparency with accountability : Production schedules allow you to assign roles and responsibilities for each task, making it clear who’s responsible for each step. This makes the process transparent and holds team members accountable for their contributions
Some templates also allow you to run “what-if” scenarios. This helps you plan for different production scenarios and see how your team could overcome potential challenges. It’s a great way to build flexibility into your production schedule and keep things running smoothly, even when the unexpected happens.
A good production planning template helps make your production more efficient, flexible, and cost-efficient. The template must have an organized, logical layout and be easy to use, edit, and update.
Users need to identify tasks, timelines, and resources at a glance. Suitable templates should also have space for additional information, such as task descriptions and start and end dates. Production planning templates also benefit from built-in communication aids, including notes and comments sections, which promote collaboration within the team.
Excellent production schedule templates offer dependency indications for a smooth workflow and guide resource allocation. They typically incorporate visual elements, such as Gantt charts and milestone trackers, to mark progress within the project.
The best production planning templates are the ones that help you coordinate production tasks, minimize waste, and propel you to better on-time delivery. Experiment with several templates to see what works best for your team.
10 Production Planning Schedule Templates to Use in 2024
Here are 10 versatile and efficient production planning templates to try this year.
The ClickUp Production Tracking Template offers a comprehensive solution for any organization that needs to master production management. The template seamlessly integrates with the ClickUp ecosystem, so you can use the framework to streamline production tasks while taking advantage of the platform’s robust project planning tools .
The template allows you to meticulously map tasks, allocate resources, establish priorities, and identify dependencies by featuring an incredibly intuitive interface, complete with click-and-drag functionalities. The multiple views available let you create dynamic visualizations of the workflow to spot potential problems and remove them before they cause production issues.
ClickUp’s commitment to collaboration shines through in this template. It offers plenty of space for feedback, notes, and comments and informs teams with real-time updates. It’s a great way to avoid any issues with missed emails or poor version management because everything your team needs to stay on track is in one centralized hub.

Efficient production is vital for your bottom line, and the ClickUp Production Cost Analysis Template covers materials, labor, and overhead costs to help inform your decisions. You can gain insight into your production inefficiencies and forecast pricing impacts.
Product managers can leverage the template’s information to make better decisions and improve the production process. By gaining better cost visibility in your production process, you can optimize your resources and boost your long-term profitability and efficiency.
Let this template do the heavy lifting by collecting essential data and providing key actionable insights. It connects with the rest of the ClickUp platform, so it’s an excellent option if you already use the program as strategic planning software for your business.
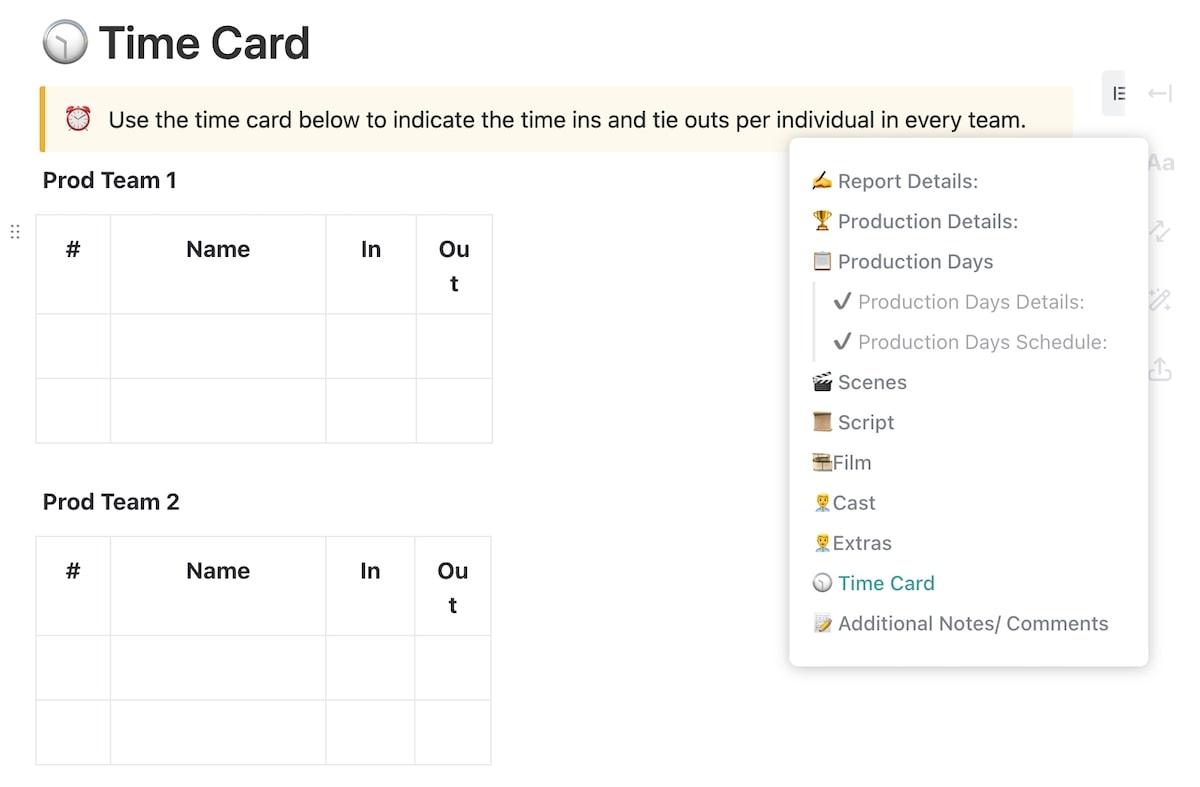
Production planning templates offer a high-level view of your process, but you must also know the daily details. The ClickUp Daily Production Report Template is an excellent addition to your product development process , giving your team space to update everyone on daily events.
Using the template within the ClickUp platform allows you to create real-time insights and progress tracking for more efficient reporting and better decision-making.
The Daily Production Report Template offers total customization, including status, fields, and multiple view options to incorporate it with your workflow. It’s a great way to maintain oversight, provide accountability, and create transparent collaboration with your production team.
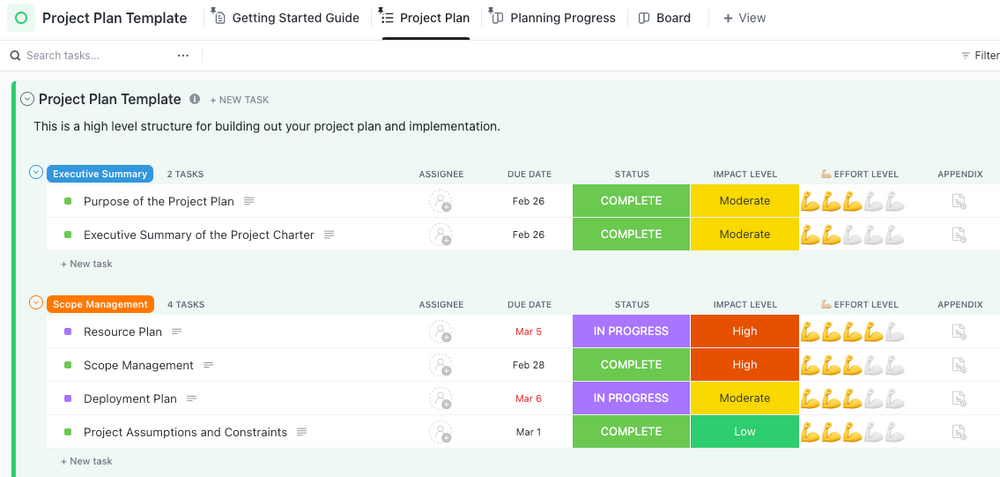
For those working specifically within the manufacturing industry, the ClickUp Manufacturing Project Plan Template will streamline the planning and organization process. The template has space for project objectives , manufacturing tasks, resource allocation, progress tracking, and more.
Execute your projects more effectively and efficiently while optimizing your budget and resources. With careful planning and this functional template, you’ll reduce operation costs and make your production line more profitable.
It’s a great addition to your ClickUp ecosystem and a perfect addition if you already use ClickUp as a CRM platform for manufacturers . Add this template to your current ClickUp lineup and see how it strengthens your manufacturing plans, making them faster and more cost-effective.
Learn about the best manufacturing schedule software !
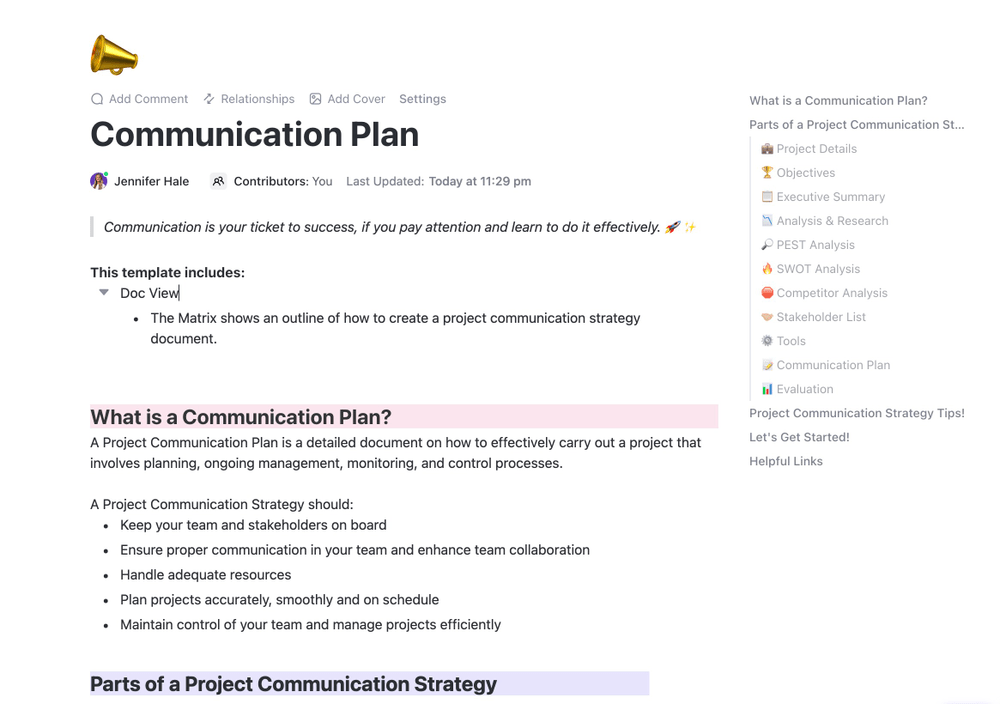
Our next free production schedule template is the ClickUp Manufacturing Communication Plan Template for better coordination and team collaboration, so you’ll avoid misunderstandings that may cause delays in the manufacturing processes.
This template helps you establish better communication paths between departments, suppliers, and stakeholders to keep information flowing and ensure everyone gets the same regular updates. Using this template, you’ll be able to document critical decisions and actions so everyone stays on the same page.
No matter the size of your operation, this template is a must-have in your collection of product management tools .

If your team operates on an Agile project management approach, sprint planning is a big part of your production plan. Make sprint planning more efficient with the ClickUp Sprint Planning Template . The template’s design makes it easier to plan each sprint, bringing clarity to a task regardless of complexity.
Use the platform’s many visualization features to create easy-to-read task planning and schedules because it plugs into ClickUp seamlessly. ClickUp’s collaborative features also make it easy for your team to keep the planning template current, so any project manager or team member can monitor progress throughout the sprint lifecycle and know where the team is at with every task on the list.

Are you looking for a way to keep your development team on track? The ClickUp Development Schedule Template is the resource you need, no matter what you’re working on and what stage of development you’re in.
The template streamlines creating a schedule with visual task management, collaborative features, real-time updates, and automated reminders. This keeps your team on track with tasks and ensures they meet deliverable deadlines.
The Development Schedule Template provides stakeholders with real-time updates. It’s a great way to update them on progress so they have the information they need at any time. With everything in one central hub, they can easily check progress while allowing the development team to continue working on their tasks.

You have an idea. Now, you need a plan to build it. The ClickUp Build Plan Template helps you organize your resources, timelines, and milestones to create a comprehensive plan for making your idea a reality.
From concept to launch, the build plan template becomes a roadmap where you can visualize tasks and progress while getting real-time updates from your team. It’s perfect for gaining clarity in each project development phase. It helps you set realistic deadlines while using internal and external resources wisely.
ClickUp’s free Build Plan Template offers plenty of customization options, including statuses, fields, and views, so you can tweak the template to suit the needs of your team. Use this template to create innovative plans for your next big idea.
This resource also works as a film production schedule template to align all departments and partners on development!

Are you trying to plan your next big software release? Keep your team on the same page with the ClickUp Release Planning Template . This is an alternative production planning template for those within the software development business. ClickUp designed the template to help oversee the launch of new software, giving you a way to organize your release plan strategically.
Start with plotting tasks, milestones, and dependencies to anticipate and remove potential bottlenecks. The template provides an insight into your team’s progress through each phase and helps you coach them to better performance.
From software inception to final deployment, the template creates a central hub for release planning, making it a seamless, collaborative effort. Take control over your release cycles and make them more efficient and effective for everyone involved.
If you’re looking for Excel templates, Simple Sheets has you covered. Its Excel Production Schedule template allows you to manage every aspect of your production process, from supply chain to operation rates, custom orders, and more.
Simple Sheets has carefully designed the spreadsheet with smart auto-population to save you from too much manual entry. Excel-savvy users can customize the spreadsheet to closely meet their team’s workflow process.
If you opt for this template, you’ll get all the benefits of working in the Excel environment, such as analyzing data and creating helpful charts to maximize efficiencies. The template is compatible with Google Sheets, too!
Track All the Production Activities and Resources in ClickUp
A great production schedule can be the backbone of your operation. It transforms the most complex processes into organized management steps. With a well-planned production schedule, you can oversee the timely delivery of goods and services while optimizing your resources and keeping everyone accountable for their responsibilities.
If you’re ready to take your production planning to the next level, check out ClickUp.
This productivity platform has a vast library of free templates to help you plan and organize your next project, whether refining an old project or developing something from the ground up. You can track tasks, allocate resources, and create timelines while working in a collaborative platform that puts communication and transparency first.
Revolutionize your production process on the ClickUp platform today!
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months

- Case Studies
- Free Coaching Session
Production Plan in Business Plan: A Comprehensive Guide to Success
Last Updated:
February 26, 2024

In any business venture, a solid production plan is crucial for success. A production plan serves as a roadmap that outlines the steps, resources, and strategies required to manufacture products or deliver services efficiently. By carefully crafting a production plan within a business plan, entrepreneurs can ensure optimal utilisation of resources, timely delivery, cost efficiency, and customer satisfaction. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of creating an effective production plan in a business plan , exploring its key components, strategies, and the importance of aligning it with overall business objectives .
Key Takeaways on Production Plans in Business Planning
- A production plan : a detailed outline that guides efficient product manufacturing or service delivery.
- Importance of a production plan : provides a roadmap for operations, optimises resource utilisation, and aligns with customer demand.
- Key components : demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, resource allocation, and quality assurance.
- Strategies : lean manufacturing, JIT inventory, automation and technology integration, supplier relationship management, and continuous improvement.
- Benefits of a well-executed production plan : improved efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced product quality, and increased profitability.

What is a Production Plan?
A production Seamless Searches plan is a detailed outline that specifies the processes, resources, timelines, and strategies required to convert raw materials into finished goods or deliver services. It serves as a blueprint for the entire production cycle, guiding decision-making and resource allocation. The production plan considers factors such as demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, and quality assurance to ensure efficient operations and optimal customer satisfaction.
Why is a Production Plan Important in a Business Plan?
The inclusion of a production plan in a business plan is vital for several reasons. First and foremost, it provides a clear roadmap for business operations, helping entrepreneurs and managers make informed decisions related to production processes. A well-developed production plan ensures that resources are utilised efficiently, minimising wastage and optimising productivity.
Additionally, a production plan allows businesses to align their production capabilities with customer demand. By forecasting market trends and analysing customer needs, businesses can develop a production plan that caters to current and future demands, thus avoiding overstocking or understocking situations.
Furthermore, a production plan helps businesses enhance their competitive advantage. By implementing strategies such as lean manufacturing and automation, companies can streamline their production processes, reduce costs, improve product quality, and ultimately outperform competitors.
Key Components of a Production Plan
To create an effective production plan, it is crucial to consider several key components. These components work together to ensure efficient operations and successful fulfilment of customer demands. Let's explore each component in detail.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is a critical aspect of production planning. By analysing historical data, market trends, and customer behaviour, businesses can predict future demand for their products or services. Accurate demand forecasting allows companies to optimise inventory levels, plan production capacity, and ensure timely delivery to customers.
One approach to demand forecasting is quantitative analysis, which involves analysing historical sales data to identify patterns and make predictions. Another approach is qualitative analysis, which incorporates market research, customer surveys, and expert opinions to gauge demand fluctuations. By combining both methods, businesses can develop a robust demand forecast, minimising the risk of underproduction or overproduction. Utilising a free notion template for demand forecasting can further streamline this process, allowing businesses to organise and analyse both quantitative and qualitative data efficiently in one centralised location.
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning involves determining the optimal production capacity required to meet projected demand. This includes assessing the production capabilities of existing resources, such as machinery, equipment, and labour, and identifying any gaps that need to be addressed. By conducting a thorough capacity analysis, businesses can ensure that their production capacity aligns with customer demand, avoiding bottlenecks or excess capacity.
An effective capacity plan takes into account factors such as production cycle times, labour availability, equipment maintenance, and production lead times. It helps businesses allocate resources efficiently, minimise production delays, and maintain a consistent level of output to meet customer expectations.
Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management is crucial for a successful production plan. It involves balancing the cost of holding inventory with the risk of stockouts. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, businesses can reduce carrying costs while ensuring that sufficient stock is available to fulfil customer orders.
Inventory management techniques, such as the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model and Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory system, help businesses strike the right balance between inventory investment and customer demand. These methods consider factors such as order frequency, lead time, and carrying costs to optimise inventory levels and minimise the risk of excess or insufficient stock.
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation plays a pivotal role in a production plan. It involves assigning available resources, such as labour, materials, and equipment, to specific production tasks or projects. Effective resource allocation ensures that resources are utilised optimally, avoiding underutilisation or overutilisation.
To allocate resources efficiently, businesses must consider factors such as skill requirements, resource availability, project timelines, and cost constraints. By conducting a thorough resource analysis and implementing resource allocation strategies, businesses can streamline production processes, minimise bottlenecks, and maximise productivity.
Quality Assurance
Maintaining high-quality standards is essential for any production plan. Quality assurance involves implementing measures to monitor and control the quality of products or services throughout the production process. By adhering to quality standards and conducting regular inspections, businesses can minimise defects, ensure customer satisfaction, and build a positive brand reputation.
Quality assurance techniques, such as Total Quality Management (TQM) and Six Sigma , help businesses identify and rectify any quality-related issues. These methodologies involve continuous monitoring, process improvement, and employee training to enhance product quality and overall operational efficiency.
In addition to the core components of a production plan, it's also important for businesses to consider the broader aspects of their business strategy, including marketing and advertising. Understanding the costs and returns of different marketing approaches is crucial for comprehensive business planning. For instance, direct response advertising costs can vary significantly, but they offer the advantage of measurable responses from potential customers. This type of advertising can be a valuable strategy for businesses looking to directly engage with their target audience and track the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
Strategies for Developing an Effective Production Plan
Developing an effective production plan requires implementing various strategies and best practices. By incorporating these strategies into the production planning process, businesses can optimise operations and drive success. Let's explore some key strategies in detail.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a systematic Seamless Searches approach aimed at eliminating waste and improving efficiency in production processes. It emphasises the concept of continuous improvement and focuses on creating value for the customer while minimising non-value-added activities.
By adopting lean manufacturing principles, such as just-in-time production, standardised work processes, and visual management, businesses can streamline operations, reduce lead times, and eliminate unnecessary costs. Lean manufacturing not only improves productivity but also enhances product quality and customer satisfaction.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory is a strategy that aims to minimise inventory levels by receiving goods or materials just when they are needed for production. This strategy eliminates the need for excess inventory storage, reducing carrying costs and the risk of obsolete inventory.
By implementing a JIT inventory system, businesses can optimise cash flow, reduce storage space requirements, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. However, it requires robust coordination with suppliers, accurate demand forecasting, and efficient logistics management to ensure timely delivery of materials.
Automation and Technology Integration
Automation and technology integration play a crucial role in modern production planning. By leveraging technology, businesses can streamline processes, enhance productivity, and reduce human error. Automation can be implemented in various aspects of production, including material handling, assembly, testing, and quality control.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a fundamental principle of effective production planning. It involves regularly evaluating production processes, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes to enhance efficiency and quality.
By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, businesses can drive innovation, optimise resource utilisation, and stay ahead of competitors. Techniques such as Kaizen, Six Sigma, and value stream mapping can help businesses identify inefficiencies, eliminate waste, and streamline production workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the role of a production plan in business planning.
A1: A production plan plays a crucial role in business planning by providing a roadmap for efficient production processes. It helps align production capabilities with customer demand, optimise resource utilisation, and ensure timely delivery of products or services.
How does a production plan affect overall business profitability?
A2: A well-developed production plan can significantly impact business profitability. By optimising production processes, reducing costs, and enhancing product quality, businesses can improve their profit margins and gain a competitive edge in the market.
What are the common challenges faced in production planning?
A3: Production planning can present various challenges, such as inaccurate demand forecasting, capacity constraints, supply chain disruptions, and quality control issues. Overcoming these challenges requires robust planning, effective communication, and the implementation of appropriate strategies and technologies.
What is the difference between short-term and long-term production planning?
A4: Short-term production planning focuses on immediate production requirements, such as daily or weekly schedules. Long-term production planning, on the other hand, involves strategic decisions related to capacity expansion, technology investments, and market expansion, spanning months or even years.
How can a production plan be adjusted to accommodate changes in demand?
A5: To accommodate changes in demand, businesses can adopt flexible production strategies such as agile manufacturing or dynamic scheduling. These approaches allow for quick adjustments to production levels, resource allocation, and inventory management based on fluctuating customer demand.
In conclusion, a well-crafted production plan is essential for business success. By incorporating a production plan into a comprehensive business plan, entrepreneurs can optimise resource utilisation, meet customer demands, enhance product quality, and drive profitability. Through effective demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, resource allocation, and quality assurance, businesses can streamline production processes and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Related Articles:
Client Success!! Watch THIS >>>
Client Success - Case Study

© 2016 - 2024 Robin Waite. All rights reserved.
- HR & Payroll

Production Planning and Scheduling: The Complete Guide

Has your company expanded from a one-person gig to a large team? You may be in-charge of a busy workshop and want to increase productivity there. Whatever the reason, you'll need a solution to make your production planning and scheduling as efficient as possible.
The overall adequate use of resources has always been a focus of production planning and scheduling. Production planning's main objective is to ensure that the supply chain process moves smoothly. The more smoothly your production and supply chains move, the less money you'll spend and the more you make.
One of the most crucial elements and indicators of the health of your supply chain is the flow. You're on the right track if your production process moves smoothly.
Various possibilities are available today for your growing manufacturing company to locate production planning software. These softwares have been created especially for contemporary manufacturers.
You will learn everything you need to know about using production scheduling and planning to organize your resources in this guide. Continue reading to learn how to enhance production scheduling in your expanding manufacturing company.
The following are the topics covered:
What is Production Planning?
What is production scheduling, difference between production planning and scheduling, importance of production planning and scheduling processes, 4 benefits of using a production schedule, how do you optimize production scheduling, the right production plan for you, key takeaways.
Production planning involves scheduling processes, raw materials, and resources to produce goods for consumers within predetermined time frames. Production scheduling specifies who will conduct the operations and when.
- Production planning determines what and how much work needs to be done. Production planning and scheduling help your manufacturing process run as smoothly as possible.
- It is done by combining your production needs with your available resources in the most cost-effective way.
- It ensures that your orders are processed as quickly, smoothly, and stress-free as possible. Do you think that's just a dream? All your production planning flow requires are a few minor adjustments.
In any case, effective production planning and scheduling are essential. For manufacturers, production planning is crucial since it has an impact on other critical parts of their business, such as
- Capacity Planning
- Supply Chain Management
- Production Lead Time
- Production Scheduling
- Material Requirements Planning
Production Planning Process
Production planning is a key process in any manufacturing organization. It helps to ensure that the right products are produced in the right quantities, at the right times, and with the right resources. The following are the five key steps of the production planning process:
- Calculate product demand
It will provide a general idea of how many products need to be produced at a specific time. A combination of analysis of current market trends and historical production trends is used to create this estimate.
This involves estimating the number of products that must be produced to meet customer demand. This step also involves forecasting future demand and understanding customer needs to ensure the right amount of product is produced.
- Evaluate production alternatives
It entails assessing the available resources and determining how to use them best. It is done in light of anticipated demand estimations.
This includes evaluating different production methods, such as batch production, continuous production, and job shop production, as well as different production locations, such as on-site or off-site production. This step helps to identify the most efficient and cost-effective production alternative.
- Select the most effective solution
After evaluating the different production alternatives, the next step is to select the most effective solution. This involves considering factors such as cost, time, quality, and efficiency. It is important to select the solution that will provide the best results for the organization.
- Monitoring and evaluation
As the plan is implemented, businesses keep an eye on what is occurring. They compare it to what should be happening as per the plan. They then assess how well the two line up.
Once the production plan is in place, it is important to monitor and evaluate its progress. This involves tracking the production plan's progress and ensuring that it meets the organization’s objectives. Additionally, it is important to evaluate the effectiveness of the plan in order to identify areas that need to be improved.
- Adjust plan
This may involve making changes to the production process or adjusting the production schedule in order to accommodate changes in demand or other factors. This step helps to ensure that the production plan remains effective.
Types of Production Planning
There are numerous varieties of production planning that concentrate on different aspects of the production process. Here are a few of them:
- Master Production Schedule (MPS)
These are production schedules for specific commodities that must be manufactured one at a time. They are frequently produced by software and subsequently modified by users.
- Material requirements planning (MRP)
MRP is a system for inventory management, production scheduling, and planning. Raw material availability is guaranteed by MRP, which also maintains internal material and product levels as low as feasible.
MRP also schedules manufacturing and purchase activities. Although software frequently partially automates it, it can also be done by hand.
It is the process of figuring out how well-equipped a company is to handle shifting demands.
- Level Production Planning
Level Production Planning is a type of production planning that focuses on the production of a constant rate of output over a given period of time. This means that the same amount of raw materials and resources are used throughout the production period, resulting in consistent and predictable output.
The goal of this type of planning is to achieve high efficiency and reduce costs by ensuring that resources are used in the most efficient way possible.
- Lean Production Planning
Lean Production Planning is a type of production planning that focuses on minimizing waste and optimizing the use of resources. This type of planning emphasizes the use of small batches and the elimination of overproduction. The goal of lean production planning is to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Kaizen Production Planning
Kaizen Production Planning is a type of production planning that focuses on continuous improvement and process optimization. This type of planning emphasizes the use of data and feedback to identify areas for improvement and to make changes that will increase efficiency and reduce costs.
- Agile Production Planning
Agile Production Planning is a type of production planning that focuses on making quick and effective decisions. This type of planning emphasizes the use of data and feedback to make decisions quickly and to adapt to changing conditions quickly.
Agile production planning is used to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and increase customer satisfaction.
- Workflow Planning
Workflow planning refers to scheduling a series of tasks to be carried out by a single employee or group of employees. Several planning kinds use the logic of production planning in adjacent or unrelated fields to manufacturing.
For instance, optimizing hiring and talent management processes is a component of human resources planning. Other illustrations include:
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a business process combining primary corporate operations into a single, cohesive system. It is often accompanied by software.
- Sales and operations planning (S&OP)
This procedure helps manufacturers more precisely match their supply with market demand.
Types of Production Planning Methods
The same production plan is only appropriate for some operations because every business is different. You must choose the approach that works best for your manufacturing process. It is to maximize the benefits of project planning. Having stated that, here is a brief introduction to the various production planning methods.
When producing a single product for which a particular production plan is made, the task approach is frequently utilized. This method of production planning can be employed in more extensive manufacturing facilities. It is typically used in smaller enterprises. The work technique is beneficial when a good or service needs precise adjustments.
Batch Production Method
In contrast to individual or continuous production, a batch production is a form of production. Batch production involves producing things in groups. When delivering goods on a vast scale, this strategy is helpful.
Flow Method
By accelerating the production line, the flow method is a demand-based manufacturing strategy. It reduces the length of the production lead time. Based on work orders, the production process begins and ends once all finished goods are produced.
Continuous manufacturing is what is accomplished by employing machinery and minimum human intervention. It is done to reduce waiting time.
Process Method
The process method is essentially an assembly line, which is what most people envision when they think of production. The process method often assembles the finished goods with various types of machinery doing different jobs.
Mass Production Method
The main goal of the mass production method is to produce an endless stream of identical goods. Like the flow method, it reduces production costs by operating on a much larger scale.
When efficiency and uniformity are equally important, "standardized processes" must be used. It ensures that all products have the same appearance.
How to Make a Production Plan
Follow these five steps to ensure that your production plan is as robust as it can be when you set out to construct one.
1. Project/Estimate Product Demand The easiest way to choose which product planning strategy is ideal for your operation is to understand product demand planning. The first step is to understand product demand planning.
Then you may determine which resources are necessary and how they will be utilized during the manufacturing process.
2. Access Inventory
Making an inventory management plan will help you avoid experiencing shortages or letting items go to waste. Accessing inventory involves more than just taking stock. To handle inventory as efficiently as possible, concentrate on the inventory control and management strategies you might use in this stage.
3. Resource Planning
Knowing the specifics of resource planning for the manufacturing process is necessary for a successful production plan. Keep in mind the bare minimum of laborers and supplies needed to complete a task (producing a good or providing a service).
Additionally, think about the equipment and systems necessary for your manufacturing plan.
4. Monitor Production
Keep an eye on how the output stacks up against the production schedule and resource allocation forecasts as production progresses. Throughout the production process, this should be ongoing and documented.
5. Modify the Strategy to Improve Production Efficiency in the future
Reflecting on the knowledge, you obtained in step four and making plans for improving the production plan are the final steps in production planning. It is the final step in production planning.
However, production planning aims to manufacture a good or service. It should also serve as a learning opportunity to improve production plans in the future.
Components of Production Planning
Making a proper production plan requires the following inputs:
- Bill of Materials: The Bill of Materials (BOM) is an important document in production planning, as it provides a detailed list of all the components and parts needed to manufacture a product. It is commonly used to track the cost of materials, labor and overhead used to manufacture the product. The BOM also provides a means of tracking the status of each component, from initial procurement to final assembly.
- Stock Levels: Production planning also requires the tracking of stock levels. This is because having too much stock can lead to expensive storage costs, while too little stock can lead to production delays. By monitoring stock levels, production planners can ensure that the right amount of stock is available at the right time.
- Price of Materials: The price of materials is an important factor in production planning. Knowing the cost of materials helps production planners to accurately estimate the cost of producing a product. Additionally, by regularly comparing the current price of materials with the market price, production planners can make sure that they are getting the best value for their money.
- Lot Sizes: Lot sizes are another important factor in production planning. Lot sizes are the number of items produced in a single production run. Lot sizes are determined based on the demand for the product, the cost of production, and the availability of materials.
- Manufacturing Lead Time: Manufacturing lead time is the amount of time that it takes for a product to be manufactured from start to finish. This includes the amount of time required for the procurement of materials, assembly, testing, and packaging. Knowing the lead time can help production planners accurately estimate the time required for production and plan accordingly.
Assigning various raw materials, resources, or production processes to multiple products is the process of product production scheduling. The goal is to produce goods on schedule while making your production process as effective and economical as possible. It is possible in terms of labor and material costs.
All parts of the supply chain depend on the production schedule. In fact, the supply chain as a whole depends on it for some of the most significant key performance indicators (KPIs) . A few typical KPIs for production schedules are listed below:
- Order management
- Daily performance
- Cost reduction
- Production time
- Production service rate
- Inventory turns
Production Scheduling involves planning out how many units need to be produced and when they should be produced. This includes allocating resources (labor, materials, and equipment) to each component of the production process, as well as determining the sequence in which they should be used. To streamline this process and enhance precision in scheduling, consider incorporating a reliable schedule maker for work that caters to your unique production requirements.
Production Scheduling also entails setting deadlines for each step of the process and monitoring the progress of the project to ensure that all tasks are completed on time. It is essential for ensuring that production costs are kept to a minimum, as well as allowing organizations to meet customer demand in a timely manner.
We will need to establish an acceptable timetable and create a plan for accomplishing our objectives. We will need to develop a proper timetable for the KPIs mentioned above.
Types of Schedules
- Master Schedules
The completion dates for significant production items are specified in this timetable. Each product's production requirements were divided into separate columns in this schedule.
Before entering any order into the master schedule, we always consider resource availability when receiving an order. As it includes information on the product's quantities and delivery schedules. The master schedule is beneficial for in-depth planning.
- Manufacturing Schedule
When the master schedule has been created, the manufacturing schedule will be ready. A manufacturing schedule will then be created.
Here, we give a particular store a set amount of time to produce the goods that must be prepared. As well as the deadline, which should be a day or a week from now.
Types of Scheduling
- Forward Scheduling: This scheduling starts on a fixed date. The last operation comes before the first operation, as well. It is made easier to find the date the final product was completed.
The goal of advanced scheduling is to accomplish mass production at a low cost while also maximizing the usage of the plant's capacity.
- Backward Scheduling: To determine the needed start date and ensure that the finished product is produced by the due date, it starts with a due date that has been established. It works backward from there.
- Chase: This type of scheduling is used when the production process is quite simple and does not require a lot of resources. It is used to plan the production order for each stage, starting from the demand for the finished product and moving forward until the production process is completed.
This type of scheduling is mainly used when the production process is quite simple and does not require a lot of resources.
- Infinite Capacity Planning: This type of scheduling is used when the production process has no limitations in terms of resources. It is used to plan the production order for each stage, starting from the demand for the finished product and moving forward until the production process is completed.
This type of scheduling is mainly used when the production process has no limitations in terms of resources.
- Finite Capacity Planning: This type of scheduling is used when the production process has limited resources. It is used to plan the production order for each stage, starting from the demand for the finished product and moving forward until the production process is completed.
This type of scheduling is mainly used when the production process has limited resources.
- Make-To-Stock: This type of scheduling is used when the production process is used to produce a certain number of products in advance, without any specific customer orders. It is used to plan the production order for each stage, starting from the demand for the finished product and moving forward until the production process is completed.
This type of scheduling is mainly used when the production process is used to produce a certain number of products in advance, without any specific customer orders.
- Make-To-Order: This type of scheduling is used when the production process is used to produce a certain number of products based on specific customer orders. It is used to plan the production order for each stage, starting from the demand for the finished product and moving forward until the production process is completed.
This type of scheduling is mainly used when the production process is used to produce a certain number of products based on specific customer orders.
What Is a Production Schedule Used For?
The production schedule is a flexible and significant document for organizing, predicting, and satisfying demand. It helps you maintain the timeliness and affordability of your operations. It supports you in upholding your obligation to your clients. Let's look more closely at its primary functions.
- Planning: Predicting demand and balancing it with available labor, supplies, and equipment.
- Scheduling Resources: A production schedule is used to plan and schedule resources for the production process. This includes personnel, equipment, materials, and other resources. By scheduling resources, producers can ensure that the production process can be completed efficiently and on time.
- Preventing stock-outs: Planning to maintain output even if supplies are delayed or demand surges due to increased orders.
- Improved efficiency: Increased effectiveness in identifying bottlenecks and seeking out areas for development is essential. It leads to shorter lead times and more fluid demand flows. By tracking the progress of production, producers can identify areas where production can be improved and make adjustments accordingly. This helps to ensure that production is as efficient as possible.
- Tracking Progress: A production schedule is also used to track the progress of production. Producers can monitor how the production is progressing, identify problems, and make adjustments as needed. This helps to keep the production on track and ensure that it is completed on time and within budget.
- Improved communication: Communication has been improved because there is now a single document that contains information on every step of the production workflow.
Overall, a production schedule is an important tool used to plan, organize, and track the progress of a production process. It helps to ensure that the production process is completed efficiently and on time, and that all resources are allocated correctly.
Components of Production Scheduling
The following steps are involved in production scheduling:
- Identifying and assigning the correct number of employees;
- Identifying and allocating suitable raw materials;
- Identifying and allocating the right machinery and equipment, and
- Synchronizing all the resources to establish priorities and meet customer needs.
As you can see, it is crucial to recognize that resources are limited at both stages. Combining the scarce resources in the best possible method will enable the creation of the finished goods.
Production scheduling focuses on how and when something will be manufactured. Production planning outlines the potential dates when something could be made generally.
Factors to Consider While Scheduling Production
Production scheduling is an essential element of production planning and is a key factor in determining how well the production process runs. It is important to consider many factors when scheduling production, such as customer demand, resource availability, and cost considerations.
Below are some key factors to consider when scheduling production.
- Raw Material Availability: One of the most important factors to consider while scheduling production is the availability of raw materials. This includes the required components' availability, the materials' quality, and their cost. The availability of materials should be checked in terms of quantity and time to ensure that production can be completed within the desired timeline.
- Production Capacity: The plant's production capacity should also be considered when scheduling production. This includes the number of machines, the work hours available, and the number of workers available. Having enough capacity will ensure that the production is completed according to the desired timeline and that the quality of the products is not compromised.
- Customer Demand: Customer demand is another important factor to consider when scheduling production. Knowing the demand for the product, the number of orders and the time of delivery will help to determine the timeline for the completion of the production. This will help to ensure that production is completed on time and that customer expectations are met.
- Quality Assurance: Quality assurance is another important factor to consider while scheduling production. Quality assurance should be taken into consideration when determining the timeline for production and should be monitored throughout the entire process. This will help to ensure that the products are up to the desired standard and that the customer is satisfied with the final product.
- Labour Efficiency: Labour efficiency is also an important factor to consider when scheduling production. The number of workers available and their skill levels should be taken into account when determining the timeline for production. Having enough skilled workers will ensure that the production is completed within the desired timeframe and that the desired quality is maintained.
- Cost Control: Cost control is another essential factor to consider when scheduling production. This includes the cost of raw materials, labor, energy, and other resources used in the production process. It is important to keep costs in check in order to ensure that production is completed within the desired timeline and that the desired quality is maintained.
Stages of Production Scheduling
The number of orders to be filled, the availability of employees and resources, and the production schedule are all considered. In essence, you want to strike a balance between the demands of your clients and the resources at your disposal. The following seven steps are used to design and carry out the production schedule:
Static and dynamic planning are both options. Production planning can be divided into two categories: static planning and dynamic planning.
Static Planning: The premise behind static production planning is that a process's phases can be specified and won't change. Retail clothing is one instance of this when manufacturing volumes are chosen up to a year in advance.
Dynamic Planning: With this alternative approach to production planning, it is assumed that process stages will vary. As a result, plans are made when demand is observed. A floral store may have a few arrangements on display and available for purchase.
The main emphasis is on making custom arrangements once an order is received. It is an example of dynamic planning in action. Dynamic assume anything could change. Static believes nothing will change during the production process. Both include gathering and examining the available resources. These include financial plans, schedules, and staffing levels.
Manufacturing production planning ensures you have enough labor, raw materials, and other resources to produce completed goods on schedule. It is an important stage in the planning and management of production. Complete production planning necessitates the precise monitoring of the following:
Raw materials
- Team members
- Workstations
Knowing numbers and measurements is insufficient. You must comprehend how each step of your manufacturing process interacts with one another and functions best as a whole.
The route raw materials take to become final goods is called routing. Production routing should pinpoint the manufacturing process steps that are economical and effective.
The manufacturing pathway outlines the process from procuring raw materials to creating a final good. If everything is done correctly, you can determine your item's stage and the machine, tool, or work center it needs to go to next.
3. Scheduling
This is the process of determining (with time and date) when each step must be finished to fill a manufacturing order on schedule. You can build a variety of schedules throughout this procedure, including
- Master schedule: master production scheduling considers resources, routing procedures, and personnel.
- Operations or Manufacturing schedule: The manufacturing or operations schedule covers the routing phases.
- Scheduling for retail operations: For the retail industry, this refers to product routing procedures. Products are different because they are produced to be placed on a shelf or in a queue for e-commerce rather than delivered directly to the customer.
You have "the knowledge" — the recipe for everything your company makes — at your disposal. So you don't need to estimate or guess when a sizeable order will arrive. This recipe is a critical component of your master production schedule (MPS) and is included in your bill of materials (BOM).
4. Communicating
Make sure everyone involved knows the production timeline and understands it.
5. Dispatching
Dispatching involves putting the procedures that schedulers have created into action. Production schedulers ensure all resources are on hand and prepared to start production. They also give directions to production team members. It is so that they know their specific responsibilities within the production schedule.
6. Execution
Realizing the plans of the schedule is the last phase in the production scheduling process. Schedulers ensure the following:
- Every process runs smoothly.
- The production is completed by the deadline.
- Every consumer gets their order quickly and effectively.
7. Maintenance
Production schedulers may need to make changes to the plan due to changes that arise during the production process. These changes have an impact on the initial schedule. Production managers may ensure the plan is always current by keeping an eye on the schedule and revising it as necessary.
To ensure that all team members know the revised expectations and strategy, they must distribute the updated schedule to everyone involved.
An effective calendar necessitates several components, as we've seen above, and it can occasionally feel daunting to know where to begin. We won't abandon you in the cold; learn about our go-to method for controlling production scheduling.
The two scheduling procedures—production planning and detailed scheduling—are frequently complementary, but businesses can only employ one in some circumstances. The decision is mainly based on the type of production. Check out how the two processes differ from one another.
- The main distinction is that scheduling transforms orders planned by the MRP into fixed-planned orders with the MPS.
- These are converted into work orders once they enter the production time window or within the cumulative lead time.
- At the same time, production planning works with orders planned by the MRP and fixed orders designed by the MPS.
- The MRP can plan orders outside the cumulative lead time window.
Planning Horizon
The planning horizon is a term used in the manufacturing sector. It is a time in the future (often a business year) during which production-supporting departments arrange production activities. The planning horizon is used to decide how much material is required. Planning scopes are separated into periods where specific actions occur:
- Execution window: the number of days or weeks during which work orders are issued as per the production schedule;
- Scheduling window: the cumulative lead time established minus the execution interval.
- Schedule window: all days/weeks outside the cumulative lead-time window.
Planning focuses on the tasks and how we must complete them. Compared to scheduling, which deals with who will carry out the functions and when they will be completed.
Time Fences
There are various time fences kinds, and they vary depending on the organization and the ERP system being used. The demand time fence and the planning time fence are the two main ones.
- Only customer orders are taken into account during this period. That is when the forecast is no longer considered in the calculations of total demand and predicted inventory.
- Beyond this time frame, depending on the consumption forecasting method selected, the total demand will be made up of both actual orders and forecasts.
- Due to the planning time fence, changes to the timetable are not permitted during MRP regeneration. It is done without determining if the change is feasible and getting the support of executive decision-makers.
- In fact, altering plans during this time can cost the business money. It may result in delays or shortages in customer shipments, disrupt the supply of raw materials, and amplify a domino effect throughout the entire supply chain.
- Stabilizing production loads and ensuring uninterrupted product flow into and out of manufacturing enterprises' facilities are two of their top priorities.
- A solid demand management strategy, a well-balanced production plan, competent schedulers, a statistically calculated security stock, and buffer/kanban are all necessary.
Even though the term "production planning and scheduling" can be a bit vague. It is important to remember that the main objective is the effective use of resources. This phrase refers to all facets of the business, from employee activities to product deliveries.
This idea is primarily applied in manufacturing settings. Many service-oriented organizations use different production planning strategies.
Problems inevitably arise if your order fulfillment process needs to be addressed. Small inefficiencies might be apparent later. But if you let them go on, the problem will become significant.
Your production process becomes congested as a result of this. Bottlenecks are areas of your production line that move slowly. They may seriously disrupt the way your production process operates. These problems impact your entire company:
- Customers will become irate if orders are delayed.
- Crew members will experience tension and demotivation as they struggle to keep up.
A production manager needs to be effective in identifying and treating the reasons for bottlenecks. These are resources and time that could be used in other ways. After that, precautions must be taken to ensure that nothing similar happens again.
- Using production planning tools, you may simplify this process by breaking it down into manageable steps.
- Finding methods to optimize the production flow saves time for operation managers. You can maintain control over your management at the floor level. Some people believe that you can skip management or gloss over strategy.
- Production scheduling is one of the most challenging yet crucial aspects of manufacturing. There will be delays if any aspect of your work needs to be fixed.
Making sure there are no finished goods or dissatisfied consumers. It is what manufacturing process optimization entails. A solid production strategy typically includes the following:
- Using the most logical and simple manufacturing process possible.
- Planning and foreseeing circumstances such as excessive demand, shortages, and bottlenecks.
- Finding areas of the production chain that are inefficient.
- Choosing the best strategy for delivering orders on time.
A production schedule is a document that establishes a timeline and workflow for the production process. It helps to ensure the production process runs smoothly and efficiently, and it can be used to manage resources, personnel, and costs. Here are four key benefits of using a production schedule.
- Improved Efficiency: A production schedule can help to maximize the efficiency of the production process. It can be used to identify bottlenecks in the process, manage resources, and optimize workflow. By utilizing a production schedule, production times can be minimized and production output can be maximized.
- Reduced Costs: A production schedule can help to reduce costs associated with the production process. It can be used to identify areas where costs can be reduced and to ensure that resources are being used efficiently.
- Increased Productivity: A production schedule can help to increase the productivity of the production process. By scheduling tasks in a logical order, it can help to ensure that tasks are completed in a timely manner, and it can help to reduce the amount of time wasted on non-essential tasks.
- Improved Communication: A production schedule can help to improve communication between production personnel. By providing a clear timeline and workflow, everyone involved in the production process can be kept informed of the progress of the project. This can help to ensure that tasks are being completed in a timely manner and can help to reduce the potential for misunderstandings.
Demand planning, supply planning, and the shifting demands of your consumers will all benefit from your production scheduling. Then you can start to plan your production schedule. It should give you a better sense of how work will fluctuate and a structure to fall back on when things don't go according to plan. Here is a list of what your production schedule accomplishes:
- It lets HR know how many employees you'll need at any given time.
- It provides a list of your goods so that you always know what you have and where to restock them.
- It will help you navigate risks and stop problems from halting production.
- Knowing how much raw material you have on hand, how long production will take, and how much you'll need helps you avoid stock-outs.
There are several methods for streamlining the production scheduling process. Yet, Agile scheduling is the best. Consider how the shop floor may take control of manufacturing operations when things inevitably go wrong. Rather than imposing due deadlines on projects instead of forcing them. A flexible production schedule can be created as follows:
- Create a dynamic timetable: When something goes wrong, you must be ready to react quickly. It requires allocating resources, calling in reinforcements, and assessing worker capability.
- Manage the work-in-progress (WIP) that is being done: If everything is WIP, nothing is a priority. Use the WIP label only for tasks that need to be finished immediately.
- Place on-time delivery as a higher priority than setting due dates for tasks: Your manufacturing schedule might give tomorrow's order deadline priority. However, the order won't arrive by the deadline in five days if nothing is done today. You can give the latter more priority using a dynamic schedule.
- Use project management tools: You can use a Gantt chart to make your timetable utilizing a project management application. It essentially functions as a virtual diagram that aids work and resource scheduling across a timeline. Individuals can submit their data as the project develops.
The chart automatically changes in real time, so everyone is simultaneously on the same page. The team can change it if raw material delays or staff absences occur. The new data will be transformed into an updated schedule with revised timings, costs, and other metrics. No more manual changes or emails with updates—the entire team operates as smoothly as possible.
With the appropriate planning and scheduling tools, it is possible to create a dynamic timetable and workflow. It should enable you to
- Meet demand and plan for change.
- Avoid downtime in your workshop.
- Significantly lessen scheduling mistakes.
- Create precise, realistic deadlines.
- Reduce the price of moving and storing inventory.
- Identify inefficiencies that can result in production bottlenecks.
- Ships goods promptly and delivers them to clients.
While most technologies bind you to a single deadline, some offer the flexible assistance an operations team needs. It is essential to manage a production schedule at peak performance.
Planning your production is essential for any manufacturing or handicraft enterprise. A precise and regulated flow is required to transform even simple products from raw materials into high-quality finished goods. If this is done, the quality of your items will undoubtedly improve.
Your standardized procedures are sure to be forgotten without a robust approach. So what are the main things to consider while scheduling product production?
Team management
Effective team use. Your company's most significant resource is its workforce. They are crucial to the improvement of the manufacturing process.
- Knowing your employees' talents and limitations should be a priority. You can assign each team member the duties and equipment best fitting them.
- You have the additional capacity to make up for the temporary loss if someone gets sick or takes a vacation.
- You can maximize the performance of both your employees and equipment by using effective production planning.
- Each team member is aware of the tasks they have been given and the results they should anticipate producing. Monitoring this process enables you to compensate for shortcomings and meet strong demand.
Full capacity
Is your workshop consistently producing at full capacity? Things can come to a complete stop with just a tiny bump. A solid rule of thumb is to always calculate your capacity planning so that your maximum production is more significant than what you are now producing.
You will be happy you were prepared if you get one or two abnormally large orders. The same is true for your crew, who has all the tools necessary to finish their work on schedule.
Production planning delays frequently require paying workers and equipment to sit on standby. MRP can now be integrated into industrial process planning software. It implies that you can always have the necessary raw materials on hand. Production will never need to be delayed due to stock-outs or delayed supply orders.
Due to a lack of supplies, priority dates can be completed on time. It's unnecessary to walk on extra raw materials on your shop floor constantly. If done correctly, storing and shipping costs will stay the same because of an excess product. Additionally, each team member always has something to do as they utilize your resources.
Workshop logistics
Each step in your manufacturing process's logistical flow needs to be considered. You might not think this is significant, but you would be wrong. As a result of one weak link being placed on the incorrect stage, numerous production lines have come to a complete stop. Efficiency can suffer if people and machinery are pushed into inappropriate spaces. Even basic sense can sometimes be detrimental to your flow.
Determining the flow of materials, resources, people, and supplies on your shop floor requires rigorous investigation. A design or arrangement might be more effective for your company. Sometimes a simple adjustment to your production plan might have a significant impact.
Problem-solving
Your company loses money on each failed attempt when you solve problems via trial and error. A temporary fix is to over-order or overproduce, as this results in additional expenses or employee stress.
Get to the bottom of a problem by tracking your flow and identifying production schedule problems. Identify production schedule problems with effective production planning software.
Learn about your manufacturing techniques.
You can manage your manufacturing methodically and quickly resolve production challenges by understanding production planning and scheduling.
Effectively manage and track everything, and everything should go well. Effective production scheduling makes it simpler to follow the rules. It is laid out clearly for your entire team and is accessible around the clock.
How Can Scaling Firms Achieve Optimal Production Efficiency?
Finding the appropriate instruments is a simple solution. It requires sound management and the right software for production planning and scheduling. If you do this well, the order fulfillment process will function as it should.
- Determine the Production Capacity: The first step in achieving optimal production efficiency is to determine the capacity of the production facility. This means understanding the maximum amount of products that the firm can produce in a given period of time.
- Evaluate Current Production Processes: The second step is to evaluate the current production processes and identify areas for improvement. This includes examining the efficiency of the equipment, labor, materials, and other resources being used in the production process.
- Implement Lean Manufacturing Techniques: Lean manufacturing techniques can help firms achieve optimal production efficiency by reducing waste and improving efficiency. This includes streamlining processes and eliminating unnecessary steps.
- Invest in Quality Control: Quality control is essential for achieving optimal production efficiency. Investing in quality control measures can help identify and address any problems before they become serious.
- Utilize Automation: Automation can help reduce labor costs and improve efficiency. Automation can also help reduce errors and improve quality control.
- Monitor Production Performance: Regularly monitoring production performance can help ensure that the firm is achieving optimal production efficiency. Implementing a performance tracking system can help identify areas of improvement.
- Take Advantage of Technology: Technology can help firms achieve optimal production efficiency. Investing in the right technology can help streamline processes and improve accuracy.
- Utilize Data Analysis: Analyzing data can help identify areas of improvement and help the firm make better decisions. Utilizing data analysis tools can help firms achieve optimal production efficiency.
- Invest in Training: Investing in training can help ensure that employees are properly trained and knowledgeable about the production process. This can help reduce errors and improve efficiency.
- Invest in Research and Development: Investing in research and development can help firms identify new technologies and processes to improve production efficiency. Research and development can also help firms stay ahead of the competition.
Why Do Some Scheduling Projects Fail?
A project with thorough scheduling can fail for two primary reasons. One is about the systems' underlying technologies, and the other is about the input data.
System technology for scheduling
The first justification has to do with the technology of the current scheduling system. Most planning systems in use today are built on operations research methods.
- It is sufficient to click the "execute" command, wait, and find the best course of action.
- When the operations research-based scheduler is used, it produces a production plan near the ideal one. However, you must be careful because this only holds true for a short period.
- These results degrade rapidly with time, the introduction of new items and processes, variations in mix and demand, and so on. As a result of the numerous hazards involved with this tool, planners are eventually forced to return to Excel.
- The quality of the created plan needs to be better. It is because operations research-based schedulers must be modeled and optimized for the particular scenario. It is in order to provide a high-quality result while preserving an acceptable computing time.
- The model needs to be adjusted whenever anything in the production environment changes. It is impossible to predict when a system will need to be tuned. A qualified operations researcher must work with the system to make the necessary adjustments.
As a result, there is a systematic delay in realigning the model with production because the plan cannot be issued after a few days or weeks. It explains why there are few operations research-based programmers used for discrete production.
Schedule input
The scheduler uses the aim established by planning to guide and optimize the plan. This issue relates to the plan received and communicated by the scheduler. The scheduler cannot produce a viable program if the goals are impractical, unclear, or lacking in resources.
In fact, the scheduler plans with a "blind horizon" if the plan is not connected with the detailed schedule. The plan needs to be more balanced over the medium-long period. The strategy, in this instance, is repeatedly modified the following day, changing virtually all together.
Excel usage
Many manufacturers have had to make do with spreadsheets due to a lack of or the high cost of production planning software for businesses. The three primary issues with this strategy are as follows:
- Spreadsheets are slow; Excel may be faster than using a pen and paper, but it still requires too much work.
- Spreadsheets are prone to errors. It can result in confusion, production delays, and issues that disrupt the company.
- Spreadsheets do not automatically update; they are static. The failure to convey changes, may cause delays.
- Excel is the only alternative available to many contemporary producers. They don't perceive any other options. It is comprehensible.
Most manufacturers do not require the massive Gantt charts and flow diagrams found in business applications. Excel, a program that can be purchased, appears like a simple and quick solution. However, it needs more power to use production management well.
Production planning varies depending on the type of production method being used. Such as single-item manufacturing, batch production, mass production, continuous production, etc. Creating a production plan for a predetermined time frame is known as the planning horizon.
The planning horizon is short-term, medium-term, long-term, etc. A successful planning system will do the following to generate a comprehensive and adaptable production plan:
- Choose the actual work to begin in the manufacturing facility and schedule it;
- Match the required level of production to the available resources;
- Determine the necessary product mix and factory load to meet customer expectations.
Accurately estimating the productive potential of the resources at hand is a crucial component of production planning.
- The availability of raw materials, the availability of resources, and knowledge of future demand should constantly be considered during production planning.
- Plans for production must also be adaptable and quick to adjust to meet the demands of the industry and the markets.
- Digital production planning solutions are rarely separate systems, however, they can be.
- To better oversee order execution and maintain ongoing alignment with customer demand and sales. They are frequently integrated with ERP and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES).
Production Planning Best Practices
No matter what kind of goods or services are produced, several tried-and-true best practices position your business for success. Be sure to have these two in mind while drafting a production strategy.
- Make Reliable Predictions
Developing a thorough production strategy is possible if you correctly estimate your good or service demand. Demand forecasting is never constant. You must consider past purchasing patterns, population shifts, resource availability, and other factors. The basis for expert production planning is these projections for demand planning.
- Identify Resources Needed
Before production planning can begin, businesses must have a clear understanding of the resources that will be needed. This includes both human and material resources, and will vary depending on the production process. Companies should have a list of all the resources they need, such as machinery, equipment, personnel, and supplies, as well as an estimate of the cost required to acquire them.
- Establish Goals
It’s important to set clear and achievable goals when planning production. Companies should identify specific objectives and performance metrics that will help them measure their progress and guide their decision-making. This includes setting targets for output, quality, cost, and delivery times.
- Analyze Processes
Companies should take the time to analyze their production processes to identify any areas that need improvement. This includes looking for potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies and deciding how to address them. They should also look for opportunities to streamline processes and reduce costs.
- Monitor Performance
Once production planning is complete, companies should monitor their performance to ensure they are meeting their goals. This includes tracking output, quality, cost, and delivery times and making adjustments if needed. This will help ensure that the production process is running smoothly and that goals are being achieved.
- Know Your Capacity
Knowing your operation's total capacity—the most goods or services it can provide at any given time—is the first step in capacity planning. The only method to calculate how much of each resource you will need to produce X number of items is in this way. The planning of your production is equivalent to shooting a blind shot when you don't know the manufacturing capacity.
- Organize with Gantt charts
Utilize our Gantt chart view to plan and manage the production of your products across time. To make sure you're never overspending, you can monitor your resources (like raw materials) tracked by cost with it. Then, you can connect any related tasks to prevent manufacturing bottlenecks.
What Is Production Scheduling Software?
You may create and maintain your production schedule using software that is specifically designed for that purpose.
- Production scheduling software is a type of software used to optimize and manage the production process. It is an important tool for production managers to manage resources, production orders and staff in the most efficient way possible.
- Production scheduling software can be used to plan and manage the production process from start to finish. It can be used to track the production of each product and also to manage the number of parts and materials required for each product.
- The software can also be used to track the cost of production, analyze production efficiency and identify areas for improvement.
The best of the lot, also known as advanced planning and scheduling (APS) software, can interface with your enterprise resource planning (ERP) or manufacturing resource planning (MRP) program. It means that data is automatically updated throughout all tools.
How Can Deskera Help You?
As a manufacturer, you must keep track of your inventory stock. The condition of your inventory has a direct impact on production planning. It also has a direct impact on people and machinery use and capacity utilization.
Deskera MRP is the one tool that lets you do all of the above. With Deskera, you can:
- Control production schedules
- Compile a Bill of Materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your dashboard
Deskera ERP is a complete solution that allows you to manage suppliers and track supply chain activity in real-time. It also allows you to streamline a range of other company functions.
Deskera Books allows you to manage your accounts and finances better. It helps maintain good accounting standards by automating billing, invoicing, and payment processing tasks.
Deskera CRM is a powerful tool that organizes your sales and helps you close deals rapidly. It enables you to perform crucial tasks like lead generation via email and gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a straightforward application for centralizing your human resource management activities. Not only does the technology expedite payroll processing, but it also helps you to handle all other operations such as overtime, benefits, bonuses, training programs, and much more.
It is crucial to note that a well-organized manufacturing company can only function with both production planning and production scheduling. The logical first stage in every production process is production planning. Production scheduling is the more in-depth extension of that.
These procedures make it feasible to produce precise production schedules. It allows for effective production control. The statistics can be used to optimize both processes further. Production activity will ultimately deliver the actual volumes and results.
A variety of persons and duties are involved in production scheduling, making it a difficult process. Then there are factors like the unpredictable nature of supply and demand, the transportation of resources, and the intricate production process. All of which have the potential to ruin your previously thought-out plan.
The entire process could come to a standstill if one of those objects deviates from its intended course. Dynamic production schedules are crucial for this reason.
- Production planning's function is to use the business's resources to keep the production flow steady. By doing this, production is maximized by lowering downtime and mitigating bottlenecks.
- When planning dynamically, it is assumed that the order of the phases in the process will alter. Materials must therefore be prepared, but production cannot begin until the demand has been established.
- Scheduling is the process of producing items from parts or raw materials using the defined planning level. It must meet the demand set at the planning level and is time-based.
- Master production schedules are used to define product timelines at the highest level. Sub-schedules for sub-assemblies or mixes and blends may be department-specific.
- The process of assigning the order of tasks to be completed next from a subset of tasks in the production queue is known as dispatching. Making decisions for immediate action is done through dispatching.
- To guarantee that all operations are completed correctly and in the order, they are supposed to be produced. Production scheduling must rely on proper execution.
- The process of creating your production strategy could reveal waste sources. To reduce waste, speed up processes, and enhance deliveries and costs. Operational efficiency and value-added manufacturing concepts can be applied.
Related Articles
Will the Dog Days of Summer Slow Down US Manufacturing in 2024?

Quality Control and Assurance in Contract Manufacturing

Sustainability and Green Practices in Contract Manufacturing
Hey! Try Deskera Now!
Everything to Run Your Business
Get Accounting, CRM & Payroll in one integrated package with Deskera All-in-One .
What Is Production Scheduling and Why Is It Important?
By Joe Weller | March 9, 2023
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
If you walk into a store and see that your favorite brand of frozen pizza is out of stock, you’ll probably be disappointed and choose a different item. Customers often opt for convenience, especially with so many different product variations available.
Companies shouldn’t lose revenue and let customers slip through the cracks by underestimating demand and resources or failing to meet deadlines. Production scheduling helps you anticipate demand, stock resources, manage labor, and prioritize on-time production in order to avoid these crucial business objectives.
In this guide, you’ll learn the importance of production scheduling , the steps for creating a schedule , and optimization practices to help keep your company on track .
What Is Production Scheduling?
Production scheduling is the process of determining when products will be manufactured to maximize efficiency while limiting stockouts and unbalanced inputs and outputs. This process includes optimizing where, when, how, and what materials you will use to manufacture your products.
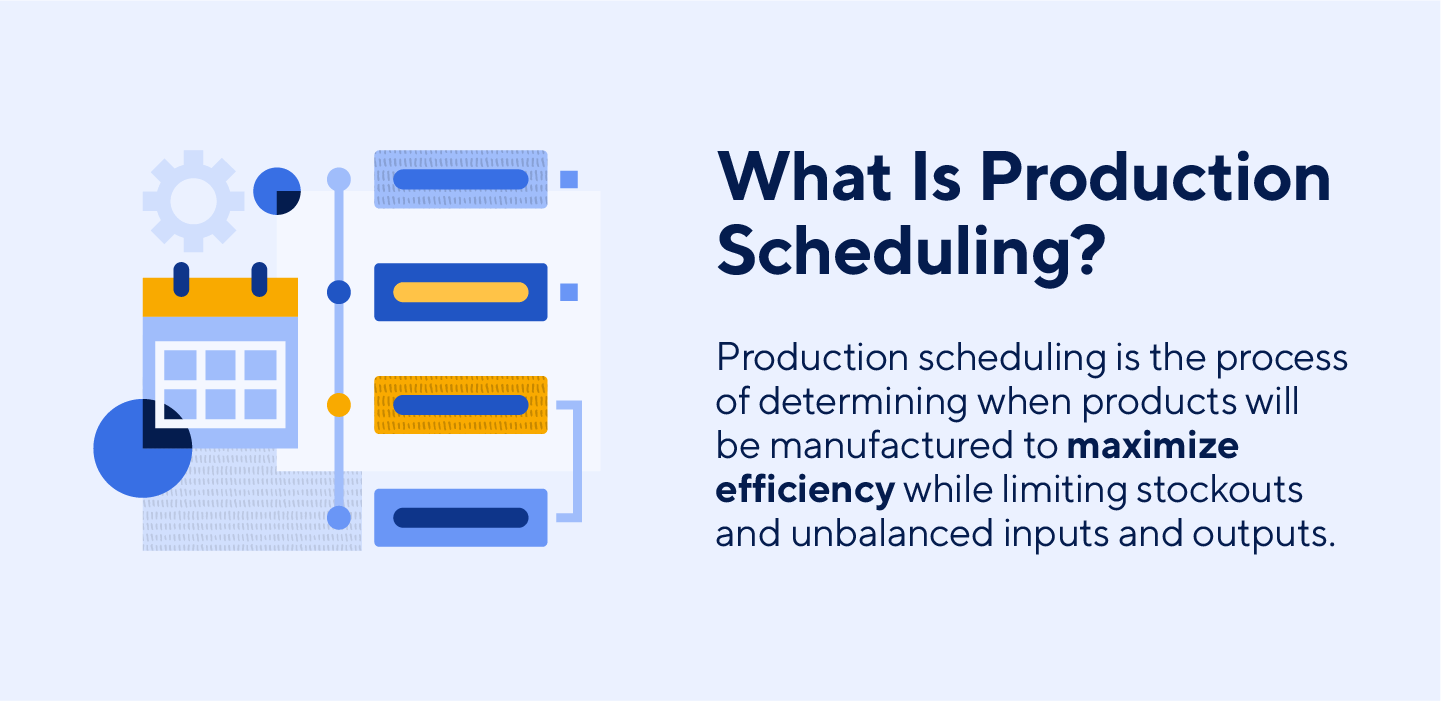
A successful production schedule will help you do the following:
- Plan for changing supply and demand
- Organize workers and contingency plans
- Maintain stock , even with delays
- Refine efficiency and note areas of possible improvement
- Standardize communication across a company
- Determine costs for parts and labor
- Identify opportunities for improvement
- Eliminate disruptions to workflow
- Establish relationships with vendors and other third parties
- Improve visibility across all company platforms
These schedules are flexible documents, and may include different variables relevant to the current production period. A successful production schedule will also report on critical supply chain key performance indicators (KPIs), including the following:
- Performance, daily or otherwise
- Reductions in cost
- Service rates
- Production times
- Cycle times
- Order management

Production Scheduling vs. Production Planning
While a production schedule is determined by short-term factors, production planning takes a longer time frame into consideration. Production plans are determined by the ideal times to produce products for on-time deliveries, capacity plans, and material requirements.
Production schedules are relatively flexible and adapt to changes in manufacturing operations, but production plans are required to stick to predetermined timelines. Production planning also considers the following:
- Type and amount of necessary product
- Raw materials
- Required workstations
The Importance of Production Scheduling
Production scheduling is a crucial part of the manufacturing process that helps to ensure efficient production times, decrease costs and product shortages, and eliminate interruptions, delays, and waste.
Production scheduling also concerns the following eight elements:
- Parts Distribution: Production schedules reduce bottlenecks and downtime by distributing the correct type and number of parts to workers throughout the production timeline.
- Stock Levels: Scheduling helps guarantee that you maintain stock levels, keep warehouses organized, and can account for all outputs.
- Labor Distribution: A production schedule can help you record and maintain working hours, overtime, and the number of workers needed during a shift or production period.
- Equipment Performance: Equipment analysis and scheduling allow manufacturers to optimize workstations and equipment usage, which reduces the need to purchase extra or overuse equipment.
- Finance Optimization: Schedules help companies allocate resources efficiently and optimally, which decreases financial emergencies and increases the reliability of available funds.
- Product Quality: Optimally planned production schedules can increase the quality of products across a shorter time frame.
- Customer Relationships: Production schedules help keep customer orders fulfilled on time, and can help increase satisfaction, trust, and brand loyalty.
- Company Reputation: Companies that optimize manufacturing schedules are known for being timely, economical, and considerate of both their workers and customers.
Production templates can help you keep these priorities in mind while creating a top-notch schedule personalized for your organization.
Six Production Scheduling Steps
Creating a production schedule requires you to balance customer needs with your organization’s available time and resources. Whether you’re creating a product or producing a video , your production schedule should consider or include steps for planning, routing, scheduling, dispatching, executing, and maintaining.
These six steps are outlined in more detail below.
1. Planning
During the first step, a company will analyze resources, budgets, staff, stock, and timelines to evaluate the status of the production processes. There are two types of planning methodologies:
- Static Planning: This type of planning assumes nothing will change during the production process.
- Dynamic Planning: This type of planning assumes anything could change during the production process.
At this stage, you should also set strategic goals and calculate labor and capacity.
In the routing step, a company will determine the path that raw materials must take from their original form to a finished product. This also includes determining the most efficient, cost-effective steps in the manufacturing processes.
3. Scheduling
This step is used to officially determine the dates and times for a project using a company’s specific methodology. You can create different types of schedules, including the following:
- Master Schedules: Full-scale, summary-level schedules that include breakdowns for labor, routing, resources, and more.
- Manufacturing Schedules: These are more limited schedules that only include the routing steps.
- Retail Operations Schedules: These are retail-focused schedules that include routing steps for retail and e-commerce products.
4. Dispatching
Dispatching refers to issuing orders concerning the locations of people, parts, and products. In this step, a company determines how these items will reach their designated locations during the entire scheduling process.
5. Executing
This is when the company actually carries out the production schedule from beginning to end — and thus, sinks or swims. If researched and created effectively, the schedule should create a smooth production process.
6. Maintaining
After a company executes the production schedule, two-way communication between management and workers begins. This step can help a company determine areas for improvement, which it can then take action on.

Production Scheduling Methods
While there are six main steps to the production scheduling process, there are different methods companies can use to optimize their own systems. Capacity planning and forward and backward scheduling are the most common methods used to create production schedules.
Capacity Planning
If client satisfaction is a main concern for your company, consider capacity planning as your main scheduling method. Capacity planning is mainly concerned with resource availability, service delivery, and customer satisfaction.
There are two main types of capacity planning:
- Infinite Capacity: This method assumes there are no resource limitations — including workers, workstations, parts, and stock.
- Finite Capacity: This method assumes there are predefined limitations for working hours, resources, equipment availability, labor, and other factors.
Companies with a few larger, simultaneous projects should consider an infinite capacity methodology, while those with many simultaneous complex projects will likely benefit from finite capacity. If you are considering using this methodology for your production scheduling, capacity planning templates can help you quickly produce schedules specific to your company’s resources.
Forward and Backward Scheduling
You can also use forward and backward scheduling to determine a project’s production order. This method bases the project timeline on either the first step or the due date, as described below:
- Forward Scheduling: In this method, you determine the timeline by first looking at the time of the earliest step and scheduling the following steps one by one.
- Backward Scheduling: In this method, you base the project timeline off the due date and schedule and work backward from there.
Backward scheduling is also known as a workback schedule and is best suited for a project with a hard deadline. If you’re using a forward and backward scheduling methodology, first determine if your project depends on strict due dates or tight schedules.
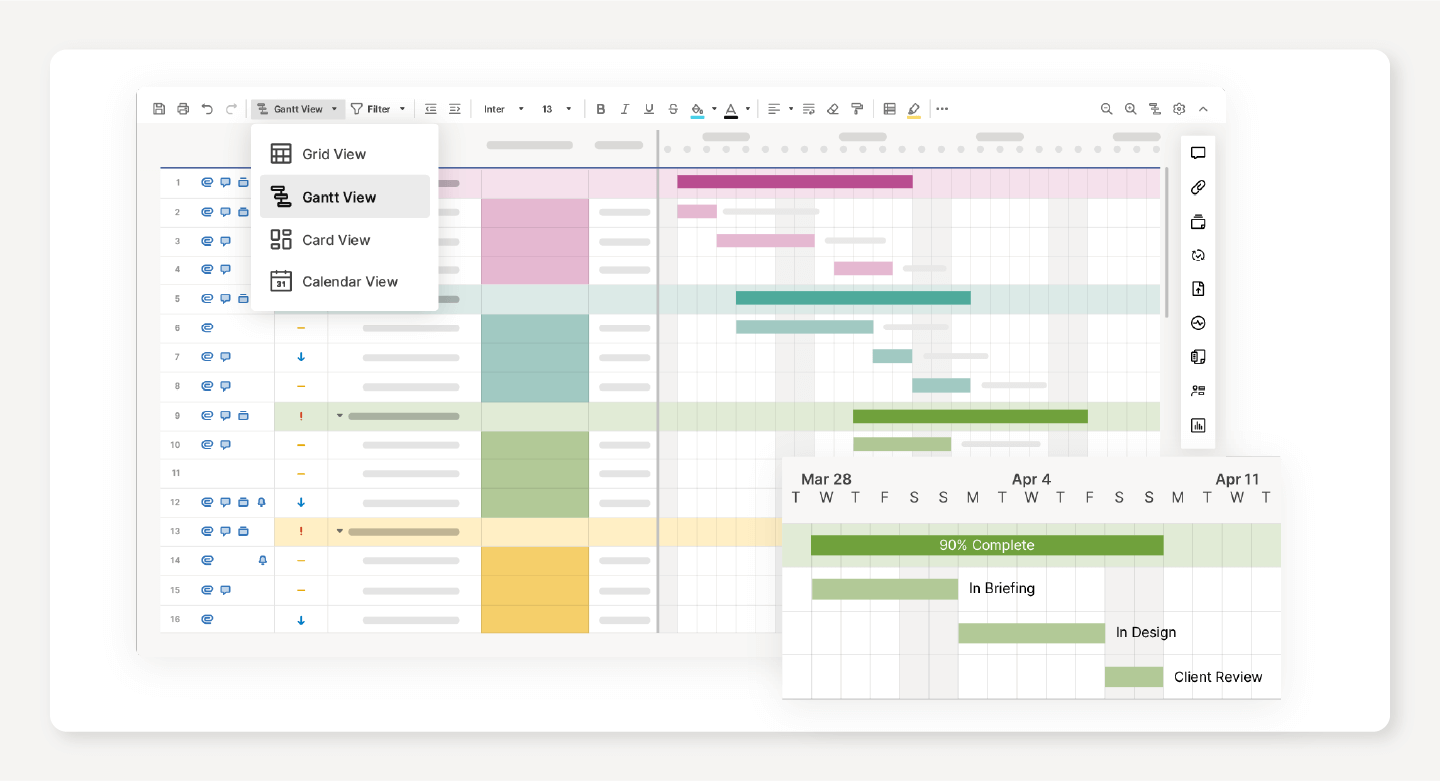
How to Optimize Production Scheduling
Since there are different methodologies, contributors, and factors that either change or depend on an up-to-date production schedule, it’s crucial to continually optimize. One of the best ways to do this is to incorporate agile planning into your scheduling process.
To do this, consider the following:
- Dynamic Scheduling: Prepare for changes in distribution, resource allocation, labor usage, worker capacity, and more by developing an adaptable schedule.
- Work-in-Progress Control: Determine a priority schedule and label projects by importance to keep urgent and significant projects on track.
- Prioritized On-Time Deliveries: Determine priority based on need and resources, rather than on the due date.
- Inventory and Supply Management: Coordinate resource arrivals and availability to ensure projects can continue on schedule with minimal product loss or confusion.
- Maintained Equipment and Facility: Working equipment and machinery allow workers to produce products on time, while also keeping laborers safe and protected.
- Production Scheduling Software: You can also use project scheduling software to efficiently and effectively manage orders, track inventory, organize laborers, and more.
What Is Production Scheduling Software?
Production scheduling software allows you to determine, build, and manage your production schedule from one platform. This type of software — also known as Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) software — allows you to create dynamic, up-to-date schedules across diverse teams.
Many companies use simplified tools for scaled-down operations schedules. However, there are some downsides, as tools like Excel and Google Sheets can:
- Create bulky files
- Lack integration and functionality options
- Increase human error possibilities
For companies with larger-scale scheduling or enterprise resource planning needs, production scheduling software can be an incredibly powerful tool with a variety of benefits and capabilities.
If you’re considering a software program, evaluate your options by examining the following:
- Integration possibilities with current enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing resource planning (MRP) software
- Central database capabilities
- Possible data formations
- User and worker access
- Available tools , including calendars, charts, and item tracking

Benefits of Production Scheduling Software
Production scheduling software can be expensive, and new programs can take time and resources to implement. However, the following seven benefits often outweigh the costs and setup times:
- Increased utilization of resources, workstations, and laborers
- Reduced inventory waste
- Prioritized on-time deliveries
- Synchronized manufacturing processes
- Visibility of projects across all teams
- Improved project management capabilities
- Better customer service and satisfaction
Optimize Production Scheduling With Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
inventory management
A Guide to Production Planning & Scheduling for Small Manufacturers
This ultimate guide to the art of production planning and scheduling will show you everything you need to know to implement into your small manufacturing business.
As a small manufacturing company, it’s extremely common to face challenges regarding production planning and scheduling.
Coordinating all the raw materials, equipment, and staff that create your products, and then - on top of it all - also ensuring timely delivery to customers can be a daunting and almost impossible task.
Implementing efficient production planning and scheduling for your small business can save time and money, reduce wastage and errors, increase productivity and profits, and improve customer satisfaction.
In this guide, we will explore production planning and scheduling best practices for small manufacturers.
☞ Need to get your raw material and product inventory under control?
Try Craftybase - the inventory and manufacturing solution for DTC sellers . Track raw materials and product stock levels (in real time!), COGS, shop floor assignment and much more. It's your new production central.
What is production planning?
Production planning is the process of creating a detailed roadmap for producing goods or services. It involves determining what needs to be produced, when it needs to be produced, and how it will be produced.
This includes identifying raw materials needed, estimating production time and costs, and coordinating all resources involved in the production process.
Effective production planning helps manufacturers stay on top of their operations by ensuring that production is aligned with customer demand, inventory levels are optimized, and resources are utilized efficiently.
Free Download: Production planning template for Excel and Numbers
What is production scheduling?
Production Scheduling involves creating a timetable for production activities based on the production plan (known as a Master Production Schedule or MPS).
It includes assigning tasks to specific machines or employees and setting start and end times for each task.
A well-defined schedule helps manufacturers meet deadlines, track progress, and make adjustments as needed to avoid delays and bottlenecks.
Now that we better understand the concepts behind production scheduling and planning, let’s take a look at how best to implement them in a small manufacturing company via several best practices.
Make to order production planning vs. batch production planning
There are slightly different considerations when production planning for make-to-order situations.
This type of planning involves producing goods based on specific customer orders rather than forecasting future demand. Make-to-order production requires a flexible and customizable approach to ensure that customer’s needs are met efficiently. Software solutions are typically the best approach to take as orders can be imported from multiple sales channels and matched to manufacture records.
Read more: Make to Order Production Planning: Making It Work for your Small Business
Production Planning & Scheduling Best Practices
Analyze demand and capacity.
The first step in production planning and scheduling is to analyze demand and capacity. This includes forecasting demand, evaluating available resources, determining lead time, and identifying constraints.
A demand forecast helps you to estimate the production volumes needed to fulfill customer orders. Evaluating available resources such as raw materials, equipment, and personnel helps you to confirm your ability to meet customer demands.
Determining lead times is essential to ensure that you meet customer requirements within the promised delivery time. Identifying constraints such as time, cost, and resource availability can help you to identify areas where operational improvements are needed.
Set your production planning metrics / KPIs
Production planning metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential for monitoring and improving production processes.
These can differ based on your particular business structure and market, so it’s wise to take some time to consider the KPIs that will represent your production process.
Some common metrics used in production planning include on-time delivery, cycle time, lead time, and inventory turnover rate.
Read more 10 Production Planning Metrics and KPIs You Need To Know
Create a production schedule
Once you have analyzed demand and capacity, you are ready to create a production schedule. As we discussed earlier, a production schedule details the sequence of activities, resources required, and timelines for each operation involved in producing a product.
It is important to consider lead times, available resources, machine time, and personnel availability when creating a production schedule.
You should also consider the critical path, which is the longest sequence of dependent activities that must be completed within a given timeframe to meet customer demands.
How to create a production schedule
- Identify all operations involved in producing the product - this includes creating a bill of materials for the product , and also any documentation on how to produce the product (i.e. SOPs or guides )
- Determine the sequence of operations based on any dependencies and constraints - this involves mapping out any sub-assemblies you have in your production process and ensuring that these sub-steps are completed in a timely manner to ensure the final product can be delivered.
- Estimate the time required for each operation, taking into account setup times, processing times, and downtime. Analysing manufacturing logs and averaging the labor time can be a good way of generating this information.
- Allocate resources such as team members and equipment to each operation based on availability and capability. Create or use a system that can assign team members to specific manufactures to see them through to either sub-assembly or finished production completion.
- Create a timeline for each manufacture, taking into account lead times and any potential bottlenecks
- Continuously monitor and update the production schedule as needed, based on changes in demand or resources.
Create ownership of your production schedule
While it can feel great to have a series of well designed production plans and schedules done and dusted, assigning a dedicated person or team to own the production schedule is crucial in ensuring its success. This person should have good communication skills, be detail-oriented, and able to prioritize tasks effectively.
Their responsibilities may include coordinating with different departments, tracking progress against plans, and addressing issues that may arise during production. This role is usually called a Production Planning Manager ,however can also be referred to as a Production Manager, Operations Manager or Warehouse Manager.
In smaller manufacturing situations this role may be performed by a responsible member of the shop floor or (in the very early days) the founder of the business.
Communicate and collaborate
Effective communication and collaboration between different departments is essential for successful production planning and scheduling. This includes regular meetings to discuss priorities, progress updates, and addressing any issues or bottlenecks that may arise during production.
Having open communication channels can help ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
Collaboration also extends to involving employees in the production planning process, as they often have valuable insights and suggestions for improving processes.
Create a realistic schedule
When creating a production schedule, it’s essential to be realistic.
Avoid overloading your production schedule and setting unrealistic deadlines for tasks, as it can lower team morale due to the production team’s inability to meet or deliver these objectives.
An accurate understanding of your capacity, lead times, and constraints will help you create a feasible schedule that can be consistently met.
Implementing Production Planning and Scheduling Software
Small manufacturers often rely on manual methods or simple spreadsheets for production planning and scheduling when getting started. However, as the business grows, managing production using these methods may become more challenging, so it’s wise to investigate a software solution as early as possible.
A production planning and scheduling software (PPS) solution helps small manufacturers to streamline their production planning and scheduling processes. A PPS automates repetitive tasks such as data collection, demand forecasting, production scheduling, and inventory management.
It enables real-time monitoring, alerts, and updates of your production progress, inventory levels, and resource utilization.
Using a PPS can help small businesses to reduce time, errors, and costs associated with manual processes and increase efficiency, accuracy, and profitability.
Read more: Production Planning Tools You Need for your Maker Business ->
A PPS can be either a standalone product or, in most cases, a suite of tools available in either an MRP or ERP product .
Investing in a production planning tool can help streamline your processes and provide visibility into your operations. There are many affordable options available that cater specifically to small businesses.
Craftybase is a cost-effective small business production planning tool tailored toward small-scale manufacturers and offers a full suite of reports and data to set KPIs and monitor their progress. Try us for free today!
Monitor and review progress
Monitoring and reviewing progress are essential to ensure that your production planning and scheduling processes are on track. Real-time monitoring using software like the ones we discussed above enables you to detect and address issues before they become major problems.
Regular reviews also allow you to identify areas for improvement, measure performance, and adjust your plans as needed.
Why is production planning important?
Production planning is crucial for small manufacturers to meet customer demands, optimize resources, reduce costs, and improve efficiency and quality. It enables businesses to balance supply with demand by creating realistic schedules that can be consistently met.
Small manufacturers who invest in production planning tools or software can gain a competitive advantage by streamlining their processes and improving overall performance.
By implementing lean principles and utilizing production planning best practices, small manufacturers can achieve their goals and grow their businesses successfully.
What is MPS in Production Planning?
MPS stands for “Master Production Schedule” and is a key component of production planning. It details the specific quantities and schedule for each product to be manufactured, taking into account factors such as lead times, available resources, and customer demand. The MPS serves as a guideline for creating the production schedule and helps manufacturers prioritize production tasks to meet customer requirements effectively.
Production planning and scheduling is a critical activity for small manufacturers who want to be competitive, profitable, and customer-centric.
By analyzing demand and capacity, creating a production schedule, using production planning and scheduling software, implementing lean manufacturing principles, and monitoring progress, small manufacturers can optimize their resources, reduce errors, and improve efficiency.
Remember that production planning and scheduling is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement and adaptation to changing customer demands and market conditions. With the right approach and tools, small manufacturers can excel in production planning and scheduling and achieve their business objectives.
Nicole Pascoe Written by Nicole Pascoe Nicole is the co-founder of Craftybase, inventory and manufacturing software designed for small manufacturers. She has been working with, and writing articles for, small manufacturing businesses for the last 12 years. Her passion is to help makers to become more successful with their online endeavors by empowering them with the knowledge they need to take their business to the next level.
Starting a Pottery Business: Tips and Tricks to Get You Started
Reorder Points: Why You Need Them
Browse Topics
- Inventory Management
- Bookkeeping & Tax
- Compliance & Traceability
- Maker Success
- What's New?
Sign up for our newsletter
We ♥ to help makers just like you to become more successful. Please join our newsletter to receive regular updates and actionable tips on how to take your maker business to the next level!
We care about the protection of your data. Read our Privacy Policy.
Learn how other ambitious makers are growing their businesses
Join the Craftybase email community to get regular tips and recommendations by and for small makers like you! (Emails come just once a week — we know you’re busy ❤️)
* We hate spam as much as you do!
- Send a message
- Partnering with Unleashed
- (NA) +1 888 813 6691
- (GB) +44 117 205 1394
- (AU) +61 3 7003 6819
- (NZ) +64 9 801 6337
- +64 9 801 6337
- General Enquiries
- Product Feedback
- Get Support
- Help Articles & How-tos
- Community Forum
- Company News

- Contact Sales
- Start a free trial
- Benefits of Unleashed
- The ROI of Unleashed
- Support & Onboarding
- Customer Success Stories
- Purchase Costs
- Purchase Orders
- Purchase Order Recosting
- Supplier Management
- Supplier Returns
- Receipt Purchases
- Purchase Order Management
- Batch Tracking
- Product Management
- Serial Number Tracking
- Barcode Scanning
- Inventory Optimization Software
- Demand Planning Software
- Disassembly
- Bill of Materials
- Sales Orders
- Sales Quotes
- Freight and Charges
- Order Management
- Customer Pricing
- Quantity Discounts
- Business Intelligence
- Advanced Inventory Manager
- Integrations
- Manufacturing
- Distribution
- Food Manufacturing
- Health Supplements
- Coffee Roasters
- Solar and electronics
- Medical Devices
- The Unleashed Basics
- Advanced Unleashed Training
- Business Insights and Advice
- Supply Chain Podcast
- Inventory Calculators
- The Backorder Newsletter
- Inventory Management Guide
- Inventory Accounting Guide
- Modern Manufacturing Guide
- Supply Chain Management Guide
- Manufacturing Productivity Guide
- Send a Message
How to Create a Production Schedule (with Example & Tips)
- Oliver Munro
- 6 months ago

- November 3, 2023
A production schedule can help you bring down manufacturing costs and maximise efficiency during the production process. Effective production scheduling can mean the difference between a happy customer and a job that was cancelled because it wasn’t completed on time.
Keep reading to learn what a production schedule is, how to create one, and the actionable tips that’ll help you maximise success and improve productivity in your production scheduling process.
In this production schedule guide:
What is a production schedule.
A production schedule is a project plan detailing the scheduled timeline for goods to be manufactured. It may contain key information about the items being produced and the manufacturing process itself, including any raw materials, labour, and equipment – along with the scheduled dates for executing each stage of the production process.
Simply put, a production schedule acts as a calendar that shows each step required to produce a finished good.
Production schedules help manufacturers avoid stockouts and bring costs down while increasing manufacturing efficiency. For the customer, production schedules aim to shorten lead times and improve the quality of goods produced. This means better products, faster order fulfilment, and happier customers.

The role of a production scheduler
A production scheduler is the person who is responsible for creating your production schedule. They might be the production manager involved in all tasks related to production, or a dedicated person employed solely for this task.
The role of a production scheduler includes:
- Analysing your manufacturing capacities
- Identifying deadlines and detailing how you’ll meet them
- Consulting the production plan and preparing contingencies within the schedule to mitigate any challenges
- Liaising with relevant stakeholders to ensure the right expertise has been taken into account
- Creating processes that will improve manufacturing efficiency and reduce costs
- Producing the production schedule document
It is also the responsibility of the production scheduler to make any necessary adjustments to the schedule once production has begun. This is an important task, as unforeseen disruptions may force a complete rescheduling of certain processes.
Production scheduling vs production planning
Production scheduling is the process of determining when products will be manufactured and setting a timeline for production. Its goal is to ensure goods are manufactured with maximum efficiency, on time and within budget.
Production planning precedes production scheduling. It is the process of determining future demand for products, how those products will be manufactured to meet that demand, and the manufacturing metrics that will measure success. Production planning also involves mapping out the required materials, labour, and equipment for a future production job.
Here’s the difference between a production plan and a production schedule:
- A production plan is a document containing a top-down view of manufacturing processes, requirements, and forecasted demand for a product.
- A production schedule is a document that tells manufacturers which goods need to be produced, when they need to be produced, and the production methods.
You can think of a production plan as the ingredients list for a product. The production schedule acts as the recipe for building that product.
Why is a manufacturing production schedule important?
A production schedule helps significantly in reducing manufacturing costs and improving the efficiency of your manufacturing inventory management .
But that’s not all.
A production schedule also helps to:
- Prevent stockouts – Forecasting demand and planning contingencies for disruptions to production means you’re better able to maintain production throughout the year.
- Improve efficiency – A production schedule can improve productivity by putting steps in place to mitigate any risks or bottlenecks identified during the production planning process.
- Identify opportunities – Addressing inefficiencies also provides the data you need to find opportunities for optimisation.
- Increase visibility – A production schedule creates a paper trail for your manufacturing activities. This facilitates better communication and ensures clarity around project requirements and timelines.
- Manage production costs – By increasing manufacturing process efficiencies, a production schedule simultaneously helps to minimise the cost of inventory and production.
To summarise, a manufacturing schedule is important because it ensures your business is operating at maximum efficiency while keeping costs as low as possible. The reduced production costs directly translate into wider profit margins for your products.
Production schedule example
Production schedules can be highly complex documents produced by manufacturing software that go into detail about each stage of production, or they can be simple spreadsheets that just list out the start times and deadlines for each process.
The production schedule example below demonstrates how the latter might look:

As you can see, specific cells from each row have been blocked out. These cells reflect the period during which each stage of production is expected to take place.
Creating a production schedule
We can break down the process of creating a production schedule into five elements:
- Production planning
- Production scheduling
- Dispatch and execution
- Maintenance
Here’s what to expect from each stage.
1. Production planning
Production planning is the process of developing a strategy for achieving your manufacturing goals. It can also include determining what those goals should be.
The purpose of production planning is to create a document – the production plan – that describes which goods are to be manufactured, how you’ll manufacture them, and any resources such as raw materials or labour required to produce those goods.
The information captured during the production planning stage may be communicated via the production schedule or in a separate document.
Routing refers to the path taken by raw materials and components as they pass through the production line and are eventually used to create a finished good.
When it comes to creating a production schedule, routing optimisation is how you make your production process efficient. It involves mapping out each step required to build a product, identifying the optimal sequence of operations, and looking for ways to improve efficiency within each step.
3. Production scheduling
Production scheduling is when you use the information you’ve gathered in the earlier steps to create a calendar-format document – your production schedule.
The production scheduling process focuses on creating 1–3 types of schedules:
- Master production schedule: A planned timeline of the entire production process.
- Manufacturing production schedule: A planned timeline for the conversion of raw materials into a finished product.
- Retail operations schedule: A planned timeline for transporting finished goods to your store.
When each schedule is ready, it should be shared with the relevant stakeholders so they may review it and offer any feedback.
Once approved by the necessary parties, the production schedule should be communicated to all employees who will be involved in the manufacturing process.
4. Dispatch
Dispatching is the process of assigning people to tasks. Now that you know what work needs to be done and when it needs to be done, communicate with your team to determine how they will manage their roles. This can include breaking down any manufacturing methods, parts-picking strategies, and processes for moving goods along each stage of the production line.
5. Maintenance
Once you’re confident in your approach, it’s time to execute the tasks in your production schedule.
Because things can often go awry in manufacturing, you’ll need to keep an eye on the progress of your production activities. There’s a good chance that your production schedule will need some adjusting: Customer demand could change, supply chain disruptions could slow down production, or equipment failure may prevent goods from being produced on time.
Update the production schedule to account for unexpected interruptions as necessary. Make sure your staff are informed of any changes made to the original schedule.

Production scheduling best practices
Are you ready to dive into the production scheduling process for your next project? Here are some actionable tips and production scheduling best practices to help you along.
1. Stay flexible
Plans often change, so a production schedule needs to be dynamic. When you create your production schedule, allow flexibility for changes to dates, tasks, and resources. Make a plan around how you’ll communicate any changes to the original production schedule to your staff.
2. Implement production scheduling software
Spreadsheets are helpful, but they can be limiting. If production scheduling is a regular activity in your business, you may benefit from investing in specialised production management software . Cloud-based tools can automate repetitive production scheduling tasks, allowing you to complete more tasks in less time.
3. Prioritise based on need
You might be tempted to prioritise tasks based on their deadline or how demanding a certain customer is. However, this strategy can be risky. Consider the master production schedule and each task’s requirements and focus on those with the highest need or highest risk first.
4. Optimise your inventory management
Improve your inventory management processes to boost inventory accuracy and prevent stockouts that could affect production times. When your goods are tracked and managed efficiently, you’ll be in a better position to forecast inventory requirements and adjust your purchasing processes accordingly.
5. Don’t forget equipment maintenance
The last thing you need is for something to unexpectedly break while you’re in full swing. Equipment maintenance can slow down processes, feeling like a chore you want to avoid rather than encourage. But preventative maintenance can mean the difference between a small amount of regularly scheduled downtime and a lot of downtime spent fixing or replacing broken equipment.
Production scheduling software
Production scheduling software refers to digital tools designed to streamline the process of creating, updating, and distributing a production schedule.
Many production planning and production scheduling software come as a complete package. This is good news for small businesses, as it means you’ll have fewer licences to purchase. For businesses with large or complex production processes , production scheduling can also be found as a module inside ERP and MRP software.
In addition to these options, there are other software tools that are useful for specific stages in the production scheduling process.
These include:
- Demand forecasting software – to help you accurately predict future demand for specific products so you can plan and schedule production activities accordingly.
- Inventory management software – to help you optimise your inventory levels so that there is always sufficient stock available to meet your production needs.
- Procurement and purchasing software – to facilitate better supplier sourcing and communications, shorten raw materials lead times, and reduce the risk of supply chain disruptions.

Article by Oliver Munro in collaboration with our team of specialists. Oliver's background is in inventory management and content marketing. He's visited over 50 countries, lived aboard a circus ship, and once completed a Sudoku in under 3 minutes (allegedly).
Today’s manufacturing sector is being shaped by large scale economic forces, technological change, rising costs, and supply chain disruptions. D...
3D printing technology is now used for a vast array of products – from rocket parts to food, face coverings, medical products, rubbish bins and buil...
UK electronics manufacturers have seen a sales revenue lift of 30% in 2021 vs 2020, outpacing the average performance of manufacturers of 24%, accordi...

- (Global) +64 9 801 6337
- B2B eCommerce
- Unleashed Integrations
- Integrate with Us
- Health and Supplements
- Help Center
- Learning Academy
Please wait while you are redirected to the right page...

What Is a Production Schedule, and What Should It Include?
Discover the importance of a production schedule and its main components. Use Motion to create a comprehensive production schedule that meets deadlines.

As a business owner or manager, you know that time is money. That’s why having a well-planned production schedule is crucial to the success of your business, whether you’re producing cars, cakes, or content.
Often overlooked, this behind-the-scenes process is the heart of any production operation, orchestrating the seamless coordination between resources, tasks, and timelines.
While production scheduling has always been important, technological advancements and data-driven approaches have changed the game.
The old days of static spreadsheets and disjointed workflows are fading away. Now, a wave of innovation is empowering businesses to streamline their operations, minimize their downtime, and increase their productivity.
Ready to maximize output like never before? We’ll tell you how to create and implement a production schedule — and how Motion can help.
What is a production schedule?
A production schedule is a detailed plan that outlines the specific activities and timeline for producing goods or services. It is a crucial component of production management, helping businesses efficiently allocate resources and meet production targets.
In simple terms, a production schedule is like a to-do list for a business to make things. It is a plan that shows what needs to be done, when it should be done, and how long it will take to complete each task.
Imagine you have a bakery, and you want to make and sell different types of cakes. A production schedule would outline the specific steps and timings for making each cake.
For example, it might say that on Monday morning, you need to gather all the ingredients, and in the afternoon, you mix the batter. You bake the cakes on Tuesday, and on Wednesday, you decorate them. The schedule also includes when the cakes will be ready for sale.
A production schedule helps you organize your work and ensure everything happens smoothly. It helps you know what needs to be done next and how long it will take so that you can plan your resources accordingly.
That way, you can avoid running out of supplies, manage your time effectively, and deliver your project on time — satisfying your customers.
Considerations to make when creating a production schedule
There are a few factors you should consider when crafting a production schedule. Here are just a few of them:
Production capacity
How much can you produce within the given timeframe?
Production capacity is the maximum number of goods that you can produce within a given timeframe. Establishing this number before creating your schedule is important, as it will affect the timeline for each production run.
Demand forecast
How much demand do you think there will be for your product or service?
Estimating how much demand there will be for your product or service will help you to plan how much to produce at each step of the process. You can use past sales data, market research, and other information to make an educated guess.
How long will the process take, from the raw material procurement to the final product delivery?
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from when you order raw materials to when you deliver the final product. This factor can have a big impact on how long it takes to complete each run, so make sure to factor it in when creating your schedule.
Material availability
Do you have all the raw materials, components, and supplies you need?
Having all the items you need is vital to completing a run successfully. Unfortunately, only 22% of companies have a proactive supply chain, which means that most businesses struggle with material availability. So be sure to plan ahead before starting a new production run.
Equipment and machinery
Do you have the right equipment to manufacture your goods?
Make sure you have the correct tools and other equipment throughout the production schedule. Be sure to check that all of your equipment is functioning properly and that you have backups in case of breakdowns.
Labor availability and skills
Do you have the right number of people, and do they have the correct skills?
Having enough workers with the right skills helps ensure that production will run smoothly and finish on time.
What goes into a production schedule?
Creating a production schedule takes a bit of time and effort, but it’s worth it to ensure that you meet your long-term goals . Here is a list of information to include in your production schedule for timely delivery and quality outcomes:
Tasks and activities
This is the first and most crucial step in creating a production schedule. List all the tasks involved in the production process, from procuring the raw materials to shipping and packaging. That way, everyone involved in the process can understand what’s expected of them.
A good task manager can help you keep track of everything as you go along. Check out Motion’s Task Manager to help you stay on top of your tasks.
Sequence of operations
Next, determine the order in which you need to execute your tasks. Arranging the tasks in a logical sequence helps keep the production process moving smoothly and delays at bay.
Set start and end dates for each task or activity in the production schedule to keep everything on track. This allows everyone involved to keep the expected delivery date in mind and work to ensure that all tasks are completed on time.
Resource allocation
This part of creating a production schedule is about making sure the right people have the necessary resources at each stage. Ensure that everyone can do their tasks efficiently through either skilled labor or productivity tools .
Constraints and considerations
It’s highly unlikely that your production schedule will go off without a hitch. Even the most comprehensive plan can encounter hurdles, including unforeseen challenges or delays, at any time.
Make a list of constraints and considerations that could potentially derail your production schedule. These could relate to budget, legal requirements, customer demand, or market conditions. It’s a good idea to incorporate extra time to account for any unexpected events.
Benefits of creating a production schedule
Creating a production schedule has many benefits. Planning ahead lets your team accomplish more in less time.
Efficient use of resources
Up to 20% of every dollar spent in the manufacturing industry is wasted.
A well-designed production schedule can help you efficiently allocate resources, thus reducing wastage and overall costs.
Improved productivity
A production schedule acts as a kind of product roadmap that everyone on the team can follow in pursuit of a common work goal . With clearly defined roles and deadlines, team members know what’s expected of them and can work more efficiently and productively.
Delivering products on time
With a work schedule in place, your team will know exactly when each product will be ready for market. This can help you set realistic and achievable deadlines.
Team alignment
When every team member has access to a production schedule, they’re aware of each other’s workloads and can plan their work accordingly. This can help prevent confusion and optimize team productivity.
Using Motion to create a production schedule enhances team collaboration and coordination among team members. A centralized platform for task and deadline management is a great way to keep everyone aligned throughout the production process.

Continuous improvement
Your production schedule can provide insights into what’s working and what isn’t. You can use this information to make adjustments and improve the process in the future. This helps your team remain nimble and responsive to change, improving your organization’s resilience in the face of competitors.
One concrete example of continuous improvement in manufacturing comes from The Raymond Corporation . They implemented lean management techniques, such as defect reduction, visual management, and active quality control circles. Because of these initiatives, the company was able to double its production volume and increase overall quality by 35% over three years. Such remarkable growth in production efficiency could not have been achieved without a culture of continuous improvement.
More satisfied customers
Delivering quality goods on time and in full helps you build a good reputation among your customers. This can translate to repeat business and more referrals. When you prioritize quality and delivery, you give customers a reason to come back for more.
5 stages of production scheduling
Creating a clear and robust production schedule is easier when you break the process down into stages. The five stages of production scheduling are as follows:
1. Planning
Set production goals and assess the availability of resources to achieve them. You can then create a plan that outlines the specific steps you need to take to meet those goals.
Production planning is vital to ensuring that your team knows the direction in which they’re heading and that everyone is on the same page.
Routing involves identifying the operations required to produce each product and the most efficient production path. Carefully analyze every step in the production process, from gathering the raw materials to the product’s completion.
The goal here is to come up with a streamlined production process that minimizes waste, maximizes output, and meets the quality standards you set.
3. Scheduling
Essentially, this step involves creating a timeline to ensure that each stage of production is completed on time.
Assign start and end dates for each operation. Assess the production capacity needed for them, and ensure that resources are available as necessary.
4. Dispatching
Next, issue work orders to the production team and assign tasks to individual workers.
At this stage, it’s essential to ensure that each worker knows what they’re supposed to do during the process. Clear communication between team members is crucial to ensuring that everyone works effectively.
5. Execution
The fifth and final stage is execution.
At this stage, the team follows the production plan according to the schedule and work orders. You monitor progress and adjust the manufacturing schedule as needed to ensure that everything runs smoothly. The goal is to run an efficient production process, meet the quality standards you set, and produce output on time.
Keep your production schedule on track with Motion
A production schedule can make or break the success of any project. Luckily, there’s an easy and effective way to streamline the production scheduling process: Motion.
Motion automates the process of production scheduling, eliminating the tedious and time-consuming aspects of the job. With it, you can easily keep your team members informed and on track, ensuring that each step of the production process is completed on time and within budget.
Whether you’re new to project management or a seasoned professional, Motion can help take your operations to the next level. So why not give it a try today? Sign up for a free 7-day trial .

Related articles
6 Best AI Calendar Assistants for Easy Organization

What Are Long-Term Goals? (+50 Examples & Tips to Achieve Them)

Understand Project Blockers & How to Transform Them Into Success
Put motion to the test., tech and media companies are talking about motion.

- See all articles
- Business tips
- Inventory management
- Manufacturing
- Product updates
What is a master production schedule? The complete guide
James humphreys.
Senior Content Manager
Here it is — A path to mastery over your day-to-day manufacturing challenges .
It’s called a master production schedule .
It’s an essential supporting document for your entire production planning and scheduling.
In short, it’s a big deal. It’s one of those secret ingredients that takes your business from a good earner to a truly outstanding enterprise. But how can something like a master production schedule do this?
Imagine you’re following a complex recipe from your favorite celebrity chef cookbook.
How would it turn out if the instructions did not give you any information about the amount of each ingredient or the time it takes to prepare and cook? You would spend a long time figuring out how to produce the finished product by looking at videos and pictures. Maybe you’d get it somewhat right, but along the way there would be a lot of thinking time and uncertainty.
This is the difference between having a master production schedule and making do without one.
A small change makes all the difference. That’s why investing time in master scheduling boosts your business’s power and capabilities.
It’s a force multiplier.
In this article, we will look into the master production schedule, its benefits, and the tools you can use to piece your master schedule together.
Table of contents
What is a master production schedule, what are the main functions of a master production schedule, the components of a master production schedule, 9 reasons your business needs a master production schedule, a master production schedule example in manufacturing, how manufacturers use a master production schedule, the difference between the master production schedule and production scheduling, cloud inventory software for your master production schedule, now it’s time to implement your master production schedule.
A master production schedule (MPS) is the overall plan to assess the production of your finished goods, detailing what you need to produce, how much you need to produce, and when you need to produce it.
In short, it contains any relevant information related to production, including time frames, such as your manufacturing lead time . Here is a quick overview of the master production schedule process steps you’ll need to follow when putting this together:
- Map your demand and make a demand plan .
- Work out the raw materials you need and get your supply chain up and running with production planning processes .
- Now you’re ready to develop a master production schedule proposal. This is like a rough draft to see if your production schedule is achievable.
- Use a rough-cut capacity planning technique to calculate if you can meet your proposed MPS manufacturing. Continue using this technique to continuously assess if your capacity can meet demand when your master production schedule is in action.
- If your master production schedule proposal is doable, you then evaluate it with regard to customer service, effective use of resources, and inventory investment.
Once you’ve implemented your master schedule, every employee on your shop floor is clear about what needs to be produced each week. Your master production schedule ensures everyone in your business is working towards the same goal. The master scheduler — the MPS architect — can then forecast relationships between demand and supply so you know when to increase or decrease production.
The master production schedule is a crucial input into the aggregate operations plan, giving an overview of everything your business needs to do for 100% order fulfillment.
This is producing sales orders and delivering them on time, without any problems or defects. This is known as a perfect order — which is what every business should strive for on all their sales channels.
The purpose of a master production schedule is to save you time by making the hours you spend managing your production flow much more efficient, giving you more space to scale your manufacturing business. Once you understand this ultimate goal of the master schedule, you can make sure that the other objectives are all aligned toward achieving this goal. Here are the other functions of a master production schedule.
1. Translating production plans
How will you manage operations to balance demand, labor requirements, and equipment capability? MPS in operations management will help you determine how many items you need to produce within a specific period.
2. Evaluating alternative schedules
A master production schedule should consider multiple manufacturing routes to determine the most efficient and consider any problems that might occur along a production line.
3. Produce capacity requirements
Rough-cut capacity planning with your master production schedule helps you figure out the realistic capacity you need to meet demand, increase profits, and minimize your costs.
4. Facilitating information processing
The master schedule helps you set your reorder points to make deliveries that need to be placed. You can coordinate different management information systems such as marketing, finance, etc.
5. Utilization of capacity
Finally, a master production schedule will help you establish the loads and utilization requirements for machines and equipment.
The other master production schedule objectives are:
- Makes your demand flow smoother
- Keeps your lead-time low
- Standardizes communication across your business
- Helps you to prioritize requirements
- Helps keep production stable
- Generates workable plans for your manufacturing orders
- Assists in making accurate purchases and transfer orders
Those are the desired outcomes of your master schedule. Now let’s look at the ingredients of the ideal master production schedule.
You’ll need a demand plan when you put together your production calendar. You need up-to-date and accurate historical sales data to generate said demand plan. You can use this to determine your projected demand for the upcoming weeks.
Just make sure that you adjust this on a week-to-week basis.
Keeping some safety stock around is good in case you receive an unusually large or uncommon order. If your demand grows, you need to increase your order policy so it does not frequently eat into your safety stock.
So as each week passes, you update your demand plan to create a more accurate production calendar. Your MPS manufacturing may be a work-in-progress, but you will fine-tune it, making it a valuable tool for your business’ order fulfillment .
The correct procedure for developing a master production schedule is to include the following elements:
- Product list — All product models you produce. After you have completed your ABC analysis , you can order them by popularity, so the items you produce the most are at the top of the list.
- Variation sub-lists for each product — Have a field for each product variation — one for each SKU . For example, you can split backpacks into S, M, and L for size. You can further split these into other variations like color.
- Year, month, and week — This is useful for planning and keeping records, which is necessary for accurate demand forecasting. Split up your schedule into months and weeks. The aim is to have a solid plan of what you will produce for the next few months. You can reassess your projected demand every few months. Don’t be afraid to make adjustments sooner if the demand calls for it.
- Production quantities — This is the number of units you decide to manufacture each week. Say, after analyzing your demand plan, you decide to manufacture 200 units of product in a week. You then add the number 200 to the bottom of each weekly column. But don’t stop there, as you need to allocate how many of each product variation will make up the 200 total. This depends on what you already have in stock and the projected demand. For example, in one week, all 200 units could be of one SKU, whereas the following production run could be evenly distributed across product models.
What benefits can you expect to reap once you implement a master production schedule into your business planning?
- You can build, optimize, and track your demand planning more efficiently since you’ll have a better understanding of your production runs.
- You can determine what your ideal inventory level is with an overview of the production requirements.
- Your HR department can see the requirements ahead of production in advance.
- You can optimize your capacity of materials and be sure to avoid stockouts.
- You can estimate the total amount of necessary labor for upcoming production runs.
- Knowing ahead of time how much production that’ll be taking place allows you to perform predictive maintenance along your manufacturing lines.
- You can ensure high-quality standards by scheduling time to go over your production quality control checklist.
- Your master production schedule helps you calculate how much inventory you’ll need in the future, improving your procurement process.
- Your finance department can also benefit from a master production schedule by using this document to create a cash flow forecast for the company.
Let’s review a master production example for a leather manufacturer selling bags.
To simplify this production schedule example, let’s look at just two products, with two variations each, making four SKUs:
- Their on-hand inventory is displayed at the top
- The projected demand is added below
- The production quantity is then calculated based on current inventory, demand, and capacity
First, let’s see how this looks in a run-of-the-mill master production schedule that thousands of businesses currently use.
Hard on the eyes, right? Apart from being hard on the eyes, one downside to this approach is that the master production schedule is not dynamic.
It doesn’t change based on actual orders and capacity. You have to update it yourself as it is based on a spreadsheet program. Excel is inefficient and vulnerable to business-harming errors.
That’s why manufacturers, especially scaling ones, turn to tools such as MES software to help them put together a more visually appealing and dynamic master production schedule.
But before we look into a master production schedule being used within a cloud-based inventory system, let’s quickly look into the difference between master production scheduling and production scheduling, both very important steps in manufacturing.
So, what kind of manufacturers use a master production schedule?
Well, no matter the size or type of your manufacturing business , the sooner you start, the better. This is because it fosters good business habits , so things like creating and managing a master schedule become second nature when you finally scale up. Your business habits are a key predictor of long-term success.
The master production schedule is compatible with different production workflows:
- Make-to-stock (MTS)
- Make-to-order (MTO)
- Assemble-to-order (ATO)
Master production scheduling focuses on producing finished goods or components (if you have an ATO workflow).
The most profitable goods for your business will likely make up most of the resources needed for production. Ultimately, manufacturers use their master production schedule to help them:
- Understand what needs to be produced
- How big should a batch be
- When should they be scheduled
- The manufacturing route should their products follow
So, when you’re putting together your master production schedule, you also need to consider these other important variants when utilizing your MPS:
- What are your batch criteria ?
- What are your sequence constraints?
- What are your set-up times?
- What’s the capacity over-saturation?
Create a master production schedule automatically
There can be confusion between a master production schedule and a production schedule since the processes to develop the two can be similar.
So, to tell them apart, here is the difference between an MPS and a production schedule:
Master production schedule
The continuous optimization process that businesses need to carry out determines the number of finished goods they need to produce based on the inputs and constraints of their production.
Production planning
On the other hand, production planning is the early stages of your manufacturing process , where you’ll define the production levels with limited and fewer details. Production planning aims to determine the production of items in terms of families or groups.
Now you’re updated on what is a master production schedule and the difference between production planning, you might realize that putting together an MPS is a lot of work.
Fortunately, software on the market can automate this process for you , so you can put together your master production schedule in no time and get right back to growing your business.
Katana is a platform for companies looking to centralize their entire business, from master production planning to manufacturing and even sales.
Katana comes with a master production schedule or real-time master planner, which automates the tasks associated with your master schedule and streamlines the entire process. So, using the earlier example, let’s take another look at a master production schedule in Katana.
This is the “Make” screen in Katana.
All the information you require from a master production schedule is here – amounts, production time, and deadlines. You can access the bill of materials for any manufacturing order by clicking on the row you want to access. Every staff member also has their own personalized schedule.
Pro tip: Click on “All Dates” below the “Production Deadline” (4th column from the right) to change the date range. You can review your schedule for the current day and the next seven days. In fact, you can set “Custom Dates” to customize your master production schedule as much as you need.
See how subtle changes can make all the difference?
But what about your raw materials planning ? Easy. Click on an MO (manufacturing order) field to open up a detailed breakdown of its production schedule.
This is the manufacturing order (MO) card in Katana. It is the part of the master production schedule that contains the bill of materials (BOM) and product recipe. It is very useful as it contains all your quantities and process, so you or your staff are never lost for how to produce something.
The product is split up into every part and component, which is given its own deadline for completion.
This advanced tool ensures you never slip up on the details, keeping you on schedule. Finally, you can review your staff members’ schedules. Do this by clicking on “Tasks” in the “Make” screen (the make screen is the central hub for your master production schedule).
The production schedule for each person in your team is laid out clearly.
Everyone has a job to do every minute of every day. You just need to decide when to break for lunch. When no time is wasted or lost, you’ll get your orders done much quicker.
This is the “Tasks” screen in Katana which shows you all the necessary operations for open MOs. You can assign and reassign tasks in a matter of seconds using a drag-and-drop system. All processes and sub-processes are scheduled so you know how long production will take, and hit your deadlines.
Pro tip: Katana gives manufacturers access to the Shop Floor Control App , perfect for managers with multiple employees who need a clear communication channel with their shop floor, available on the Advanced plan .
The trick is to find master production scheduling software that doesn’t make you shudder with dread when you open it. Seriously — the better you feel about your software, the more motivated you will feel to learn it thoroughly, and the more likely you are to use it effectively.
And there, you have everything you need to know about the master production schedule and how you can put yours together.
However, it’s one thing to know, but without using cloud inventory software to manage your master production schedule, you’re going to be stuck with a system like using inefficient Excel spreadsheets. This is why manufacturers turn to cloud-based inventory software to help them automate the process of making their master production schedule automated and easy to understand. Why not try out an automated master production schedule within your business? Request a demo today and see how much it can improve the efficiency of your production lines.
We hope you found this article useful, and if you have any questions, feel free to message us here or over on our social media channels, and until next time, happy manufacturing.
The main functions of an MPS are as follows:
Production planning
The MPS helps plan the production process by providing a detailed schedule of what products will be produced, how much will be produced, and when production will occur.
Resource planning
The MPS helps to ensure that the necessary resources, such as raw materials, labor, and equipment, are available to meet the production schedule.
Inventory control
The MPS helps to control inventory levels by determining the quantity of finished products that should be produced and when they should be produced.
Customer service
The MPS helps improve customer service by ensuring products are produced on time and delivered to customers as promised.
Capacity planning
The MPS helps to plan and optimize the capacity of the production process to ensure that it can meet the demand for products.
Performance evaluation
The MPS provides a basis for evaluating the performance of the production process by comparing actual production against the planned schedule.
Material requirements planning (MRP) and master production schedule (MPS) are two different but related manufacturing planning tools. The main differences between MRP and MPS are:
MRP is concerned with managing the materials required for production, whereas MPS is concerned with managing the overall production plan.
Time horizon
MRP focuses on the short-term, typically covering the next few weeks or months, while MPS is a longer-term plan, usually covering a period of several months to a year.
MRP relies on inputs such as the bill of materials, inventory levels, and customer orders, while MPS relies on inputs such as sales forecasts, production capacity, and inventory policies.
The main output of MRP is a list of materials and quantities required for production, while the main output of MPS is a detailed production schedule that outlines what will be produced, how much, and when.
In summary, MRP is a material-focused planning tool that calculates material requirements to meet the production schedule, while MPS is a production-focused planning tool that outlines the production plan and schedules required to meet demand.
The main difference between a master schedule and a production schedule is their level of detail and time horizon.
A master schedule is a high-level plan that outlines the overall production plan for a specified period, typically several months to a year. It provides a general overview of what products will be produced, the quantities to be produced, and when production will occur. The master schedule considers factors such as production capacity, inventory levels, and customer demand to ensure the production plan is realistic and achievable.
On the other hand, a production schedule is a more detailed plan that breaks down the master schedule into specific production units, typically a day or a week. It specifies the quantity of each product to be produced, the start and end dates of production, and the resources required to produce each item. The production schedule considers factors such as machine and labor availability, setup time, and lead time to ensure that the production plan is executed efficiently.
In summary, a master schedule is a high-level plan that provides an overview of the production plan for a specified period. In contrast, a production schedule is a detailed plan that breaks down the master schedule into specific production units, typically a day or a week.
James Humphreys has produced content on manufacturing and inventory management practices for 5+ years. He began his journey into writing via the creative industry, writing and producing plays, some of which toured the UK and Europe.
Related Articles
Manufacturing throughput time: fast-forwarding production, shop floor planning and control in production planning, intermittent production: making sense of the irregularity, production management: definition and solution, craft production: how to make it in the craft business, taking your fair slice of the food production pie, how to master bottleneck management in production process, the ultimate guide on how to outsource manufacturing, trending articles, electronic components inventory: how to do it right, sustainable manufacturing: the why, the how, and the who, how to know when it’s time for better clothing warehouse organization, untangle the complex web of pharma supply chain and logistics, 11 warehouse mistakes and how to fix them, erp vs. wms: which one is right for your business, inventory liquidation: why, when, and how to do it, woocommerce inventory sync solutions for your business.

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Production Schedule Templates with Samples And Examples [Free PDF Attached]
![production schedule for business plan Top 10 Production Schedule Templates with Samples And Examples [Free PDF Attached]](https://www.slideteam.net/wp/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Production-Schedule-Example-Templates-1-1013x441.png)
Dikshita Sharma
“Productivity is never an accident. It is always the result of a commitment to excellence, intelligent planning, and focused efforts,” Paul J. Meyer, the pioneer of the self-improvement industry, has enunciated.
It's possible that at some point, you may have come across someone asking these questions: “Is it important for an engineering manager to have a project schedule?” Or “Is a shooting schedule needed in a film or TV show plan?” Most will probably answer, “You must be kidding. A good schedule is a must-have."
A good schedule acts as a blueprint not only for a successful day-to-day life, but also for organizations and start-ups, helping managers keep tabs on tasks, processes, and more.
Are you eager to keep track of your tasks and priorities? Go through our exclusive weekly schedule PPT Template and manage your tasks with ease.
Production Schedule: An Overview
In any production and manufacturing unit, scheduling plays a crucial role. Production scheduling is the allocation of resources, operations, and processes required to create goods and services. It is an organized plan used in businesses to balance the needs of customers with available products.
Sometimes, production planning and production scheduling are used interchangeably. But, in business operations, planning and scheduling aren’t two peas in a pod. Planning deals with choosing the right procedures to furnish the goals of the project, scheduling assigns time, tasks, resources, and machinery to the objectives of your marketing plan.
Are you a project manager looking for a tool to take your production facility to the next level? Then check out our comprehensive blog on project schedule and take your first step towards better project execution.
Need to prioritize your projects? Explore our well-designed Top 10 Production Scheduling Example Templates with Samples and maintain a balance among the tasks that pertain to your production. Manage your production schedules and manufacturing tasks well with these customized production schedule templates, and keep track of day-to-day production-related activities with ease and confidence.
Let’s explore now!
Template 1: Work Plan Schedule Production Proposal Template
Clarify your business operations with the use of this production proposal PPT Template. Use this presentation template to schedule your strategic planning, production services, advertising campaign development, strategic partnership, and much more. Download it to create interactive slides with icons and bold colors to engage your audience.
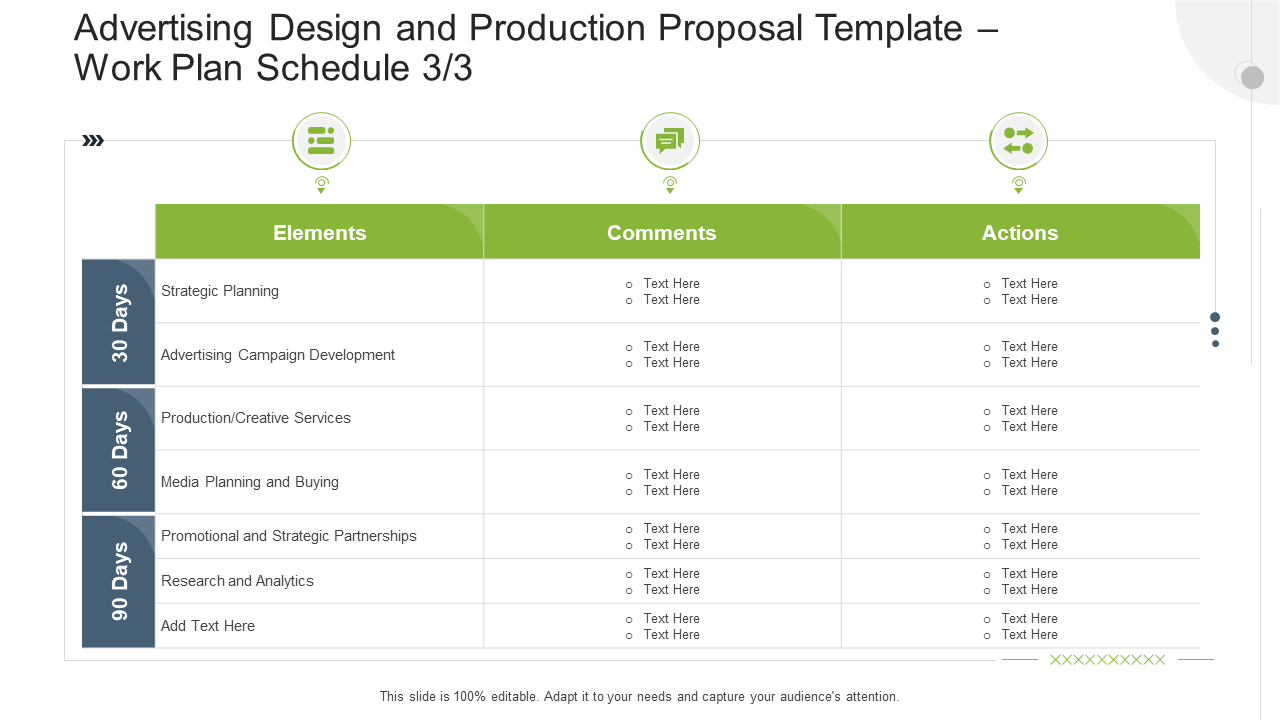
Template 2: Market Activity Schedule Plan for Production Promotion PPT Slides
Are you worried about presenting a product promotion-related activity to your boss? This market activity schedule plan PowerPoint Template will do the needful. Showcase your promotion schedule plan by portraying the promotion’s ideas, description, objectives, and designated employees with estimated cost and budget.
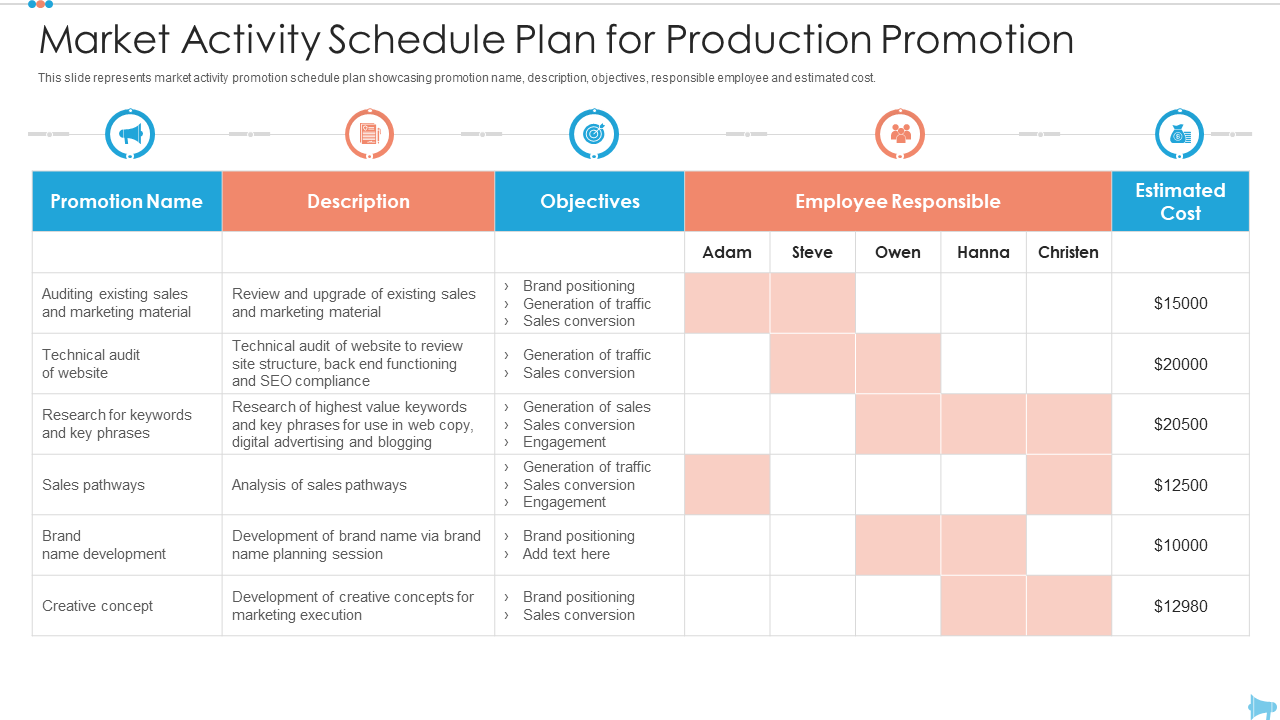
Template 3: One-Pager Production Schedule Sheet Template
Bored of long and massive marketing plans? Use our one-pager production schedule sheet template and pitch your production report with precision. With this presentation template, cover your upcoming production plan for the manufacturing plant focusing on launching stock, sales forecast, quantity to produce, current status (in terms of order fulfilment and production cost), order status, and product categories sold. Optimize the production scheduling sheet and make your team members aware of the process and their own tasks.
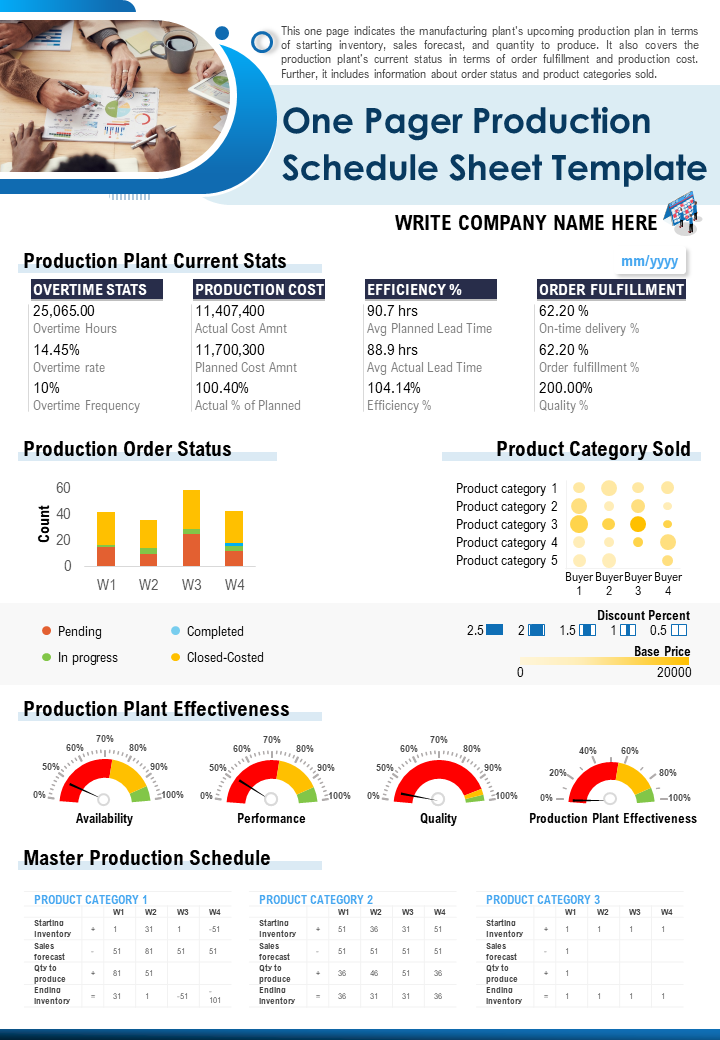
Template 4: Production Schedule Order Amendment Presentation Slides
Manage your production needs with the help of this production schedule PowerPoint Template. It allows you to cover planning and allocation processes, and create a well-organized schedule for your company's functioning prerequisites (proper routing, dispatching, and follow-up). Deploy this template at the earliest to convey your plan, and increase your company’s profitability and productivity.

Template 5: One-Pager Production Schedule Sheet Template Fit for Army Standards
Do you feel preparing a One-Pager data sheet from scratch can be a mammoth task? Deploy our top-notch one-pager army production schedule sheet PPT Template to provide a comprehensive view of the product or service details. This template is divided into Sections: Introduction of your company and its achievements, client requirements, production cost details, production schedule, and project team management. Customize this A4-size template now and present your product details to potential clients.
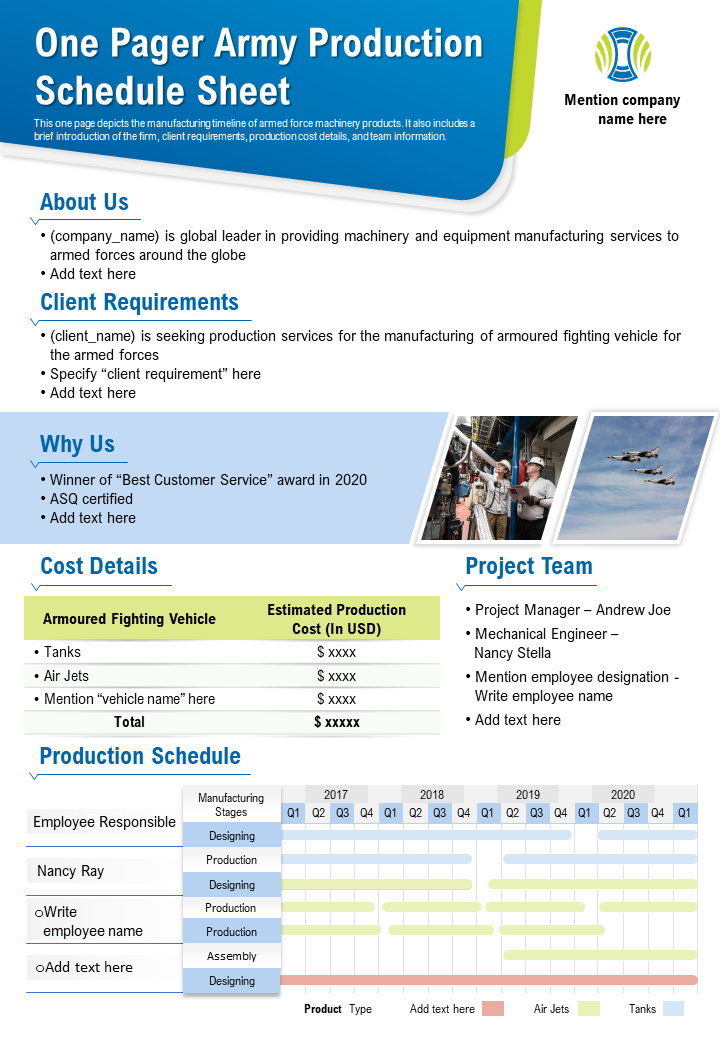
Template 6: Industry Capability Analysis Current Production Schedule Template
Deploy this PowerPoint Template to accomplish industry capacity analysis, in terms of raw material production. This PPT Template is divided into four stages: Current production by the shop, overall equipment effectiveness, production status, and asset status. Keep a check on the equipment effectiveness using a pie chart. Why wait? Grab this template immediately to ramp up production to gain market share.
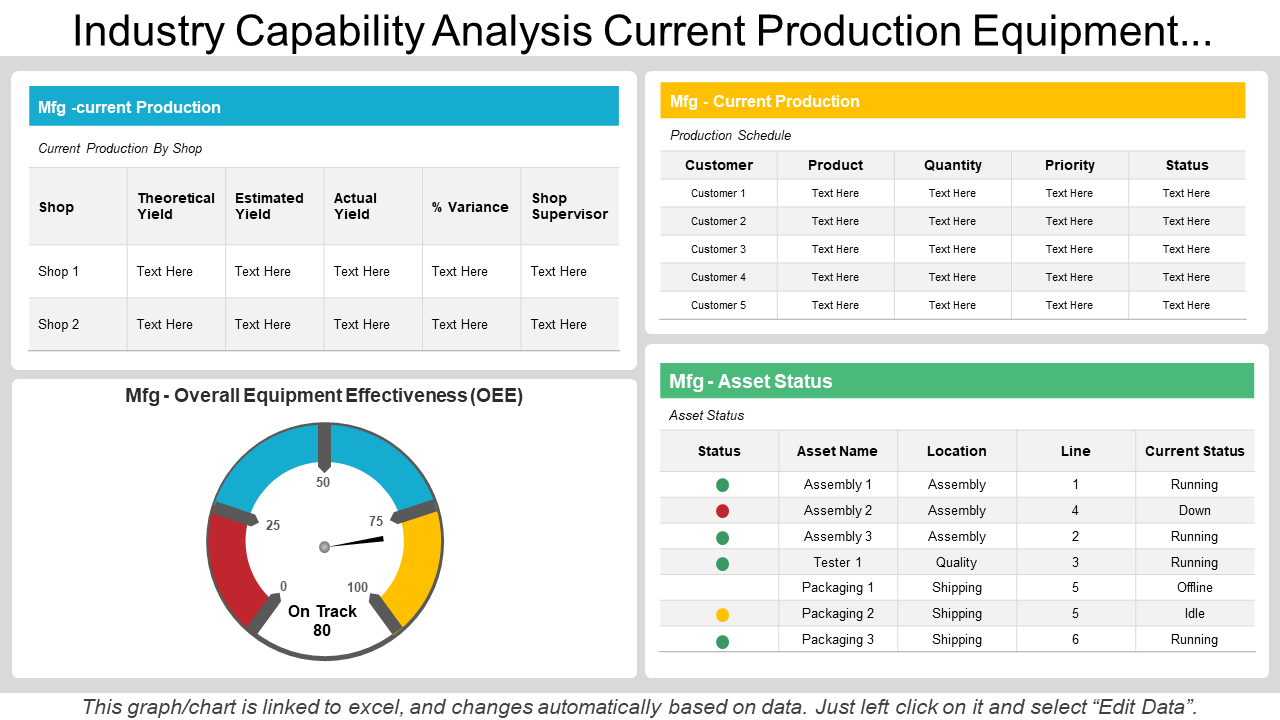
Template 7: Work Plan Schedule Analytics Advertising Design and Production Proposal
Are you looking for a way to get your work plan schedule analytics advertising design and production proposal done like clockwork? Look no further than our innovative new product! This template comes with everything you need to plan and schedule your advertising campaign, including an analytics tracker so you can measure your results. It's easy to use and edit, so you can tailor it to your specific needs.
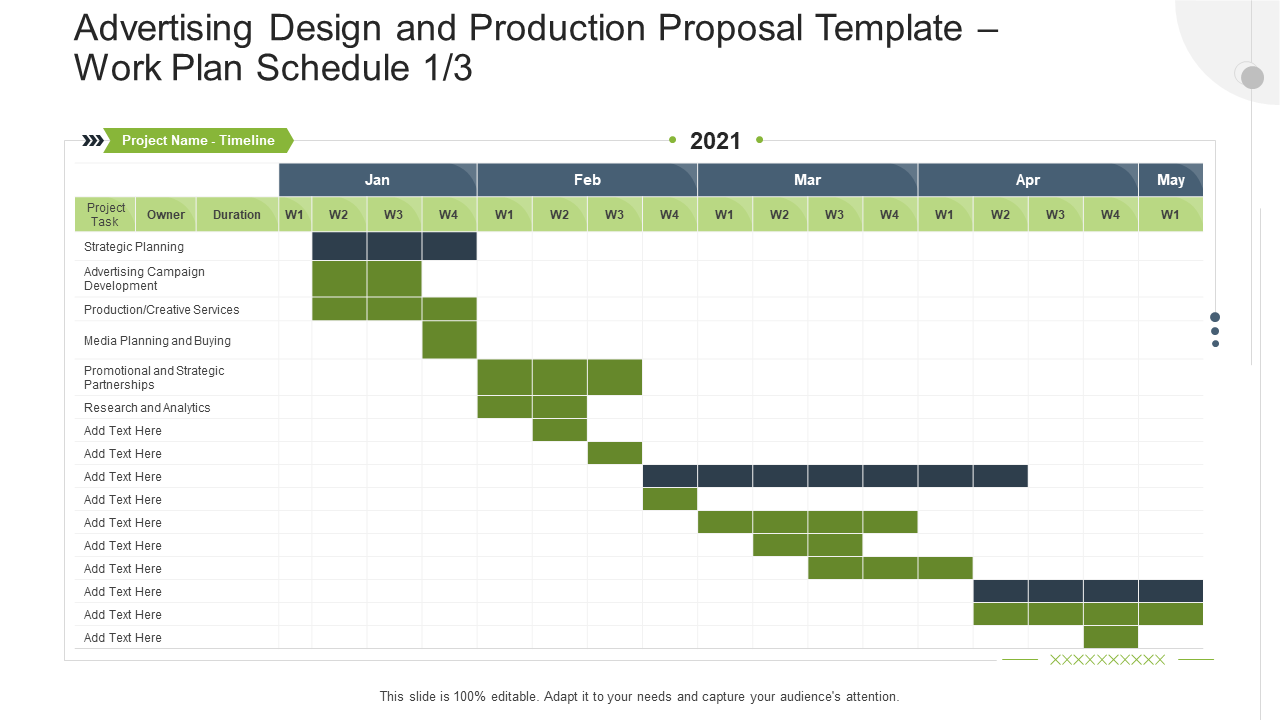
Template 8: Production Schedule Maker PowerPoint Presentation Gallery Template
Use our top-class production schedule maker PPT Template that has four stages. It helps run your manufacturing process smoothly and deliver your products on time under a cost-effective budget. From content (data and statistics, image, text) to layout (font, color, icons), personalize this PPT Template. Without any delay, get started with this template now!
Template 9: Video Production Project Proposal One-Pager PowerPoint Slides
Do you need help presenting your video production project proposal? Use our video production project proposal one-pager Template and say goodbye to all the fuss and confusion. Highlight your project goals, production process, client statement, key deliverables, video package, and much more. Simply customize the presentation template design for a more personalized look, fill in the details and impress clients.

Template 10: Plan of Action for Media Digitalization Production Schedule One-Pager
Looking to develop a production plan for your next idea or project but don’t know where to start? Set a benchmark with our action plan for media digitalization production schedule PPT Template. This one-pager Template offers high-quality visuals and focuses on the scene, location, date, time, cost, equipment, etc. Say no to delays and download this one-pager PPT Template to revitalize you project.
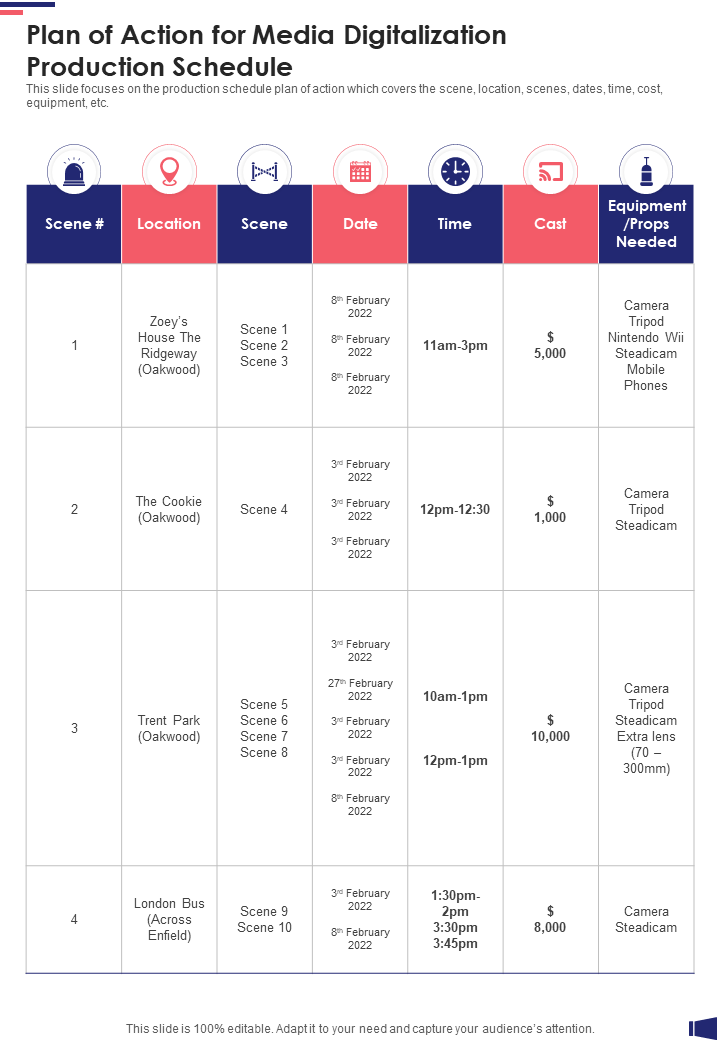
Production Schedule: A Blueprint!
A production schedule is a framework for allocating resources and listing the products that will be manufactured on a timescale. Though, it is a tricky process, SlideTeam offers the Top 10 Production Schedule Templates which will help you create a production schedule in a jiffy. You are just a click away from downloading these actionable slides. Get these Templates now!
PS: Now you have a handy production schedule template by your side, do you want to lay the groundwork for a successful video production business? Peruse our well-designed blog templates and invest your time in creating a comprehensive video production proposal.
FAQs on Production Schedule
What do you mean by production scheduling.
Production scheduling is a versatile document for planning, forecasting, and meeting demands. It is deployed in a manufacturing company to manage and control the execution of the production process. Generally, it describes how to use the manufacturing unit’s resources to satisfy a production plan, or how machines should be used by the company to manufacture products within a time frame. It is essentially the timetable that governs a business’s functioning. Over time, boundaries have blurred between production and services, hence, a production schedule has come to refer to specific business activities as well.
What are the main components of production scheduling?
If you want to formalize your production scheduling process, follow these six components:
- Planning: First, prepare your demand plan. There are two types of planning offered- static or dynamic, to collect and analyze available resources, budgets, timelines, and staff availability.
- Routing: The next step is to identify the place from where you will procure youe raw materials, and how to deliver these to the manufacturing team. Mainly, it focuses on the most cost-effective route.
- Scheduling: After routing, develop a schedule to define how you will meet all requirements, say, contingency plans. During this process, you can create a master schedule, manufacturing schedule, etc.
- Dispatching: It issues orders and instructions on how goods and people will move around from one place to another throughout the production schedule process.
- Execution: This is the final and most important step of the entire production schedule process. Here, you put your plan into action.
- Maintenance: Keep your schedule up-to-date because demand may keep fluctuating throughout the production process.
Production scheduling is a very important process for a manufacturing unit. It So, it should includes the following elements:
1. The most important factor is the product inventory, which lists all the manufactured products.
2. Later on, a variation sub-list (size, color, type) should be included.
3. Don't forget to mention the demand and delivery dates of the products.
4. Lastly, production quantities, say, the number of units you will produce each week are a must.
What to include in your production scheduling?
Production scheduling is a very important process for a manufacturing unit. It includes the following elements:
- The most important factor is the product inventory, which lists all manufactured products.
- Later on, a variation sub-list (size, color, type) should be included.
- Don’t forget to mention the demand and delivery dates of the products.
- Lastly, production quantities , say, the number of units you will produce each week are a must.
How to optimize your production scheduling?
To optimize your production scheduling, here are some strategies that you can implement:
- Improve the prediction accuracy of your market expectation. For this, you have to estimate accurate insights into the production, inventory, and selling of goods.
- Another important step is to standardize your production scheduling. It starts with process mapping to create an alignment between demand expectations and capacity utilization.
- To create solid production plans, use any tweaks and adjustments, say, digital twins, to visualize the efficiency of expected results.
- If you don’t want any delay in the production process, integrate your supply chains. You can integrate IT ecosystems with the supplier’s ecosystems, so that data can be shared in time.
- Get transparency in transport times, parts availability, etc and adjust your production schedules to keep things moving without worrying about unexpected events.
Download the free Production Schedule Templates PDF .
Related posts:
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
- 99% of the Pitches Fail! Find Out What Makes Any Startup a Success
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

How to Prepare Best Film Production Company Profile?

Top 10 Video Production Proposal Templates with Samples and Examples

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

Get started
- Project management
- CRM and Sales
- Work management
- Product development life cycle
- Comparisons
- Construction management
- monday.com updates
The easiest way to master production scheduling
Product production scheduling isn’t typically on the forefront of our minds when we walk into our favorite store, but a lot has gone on behind the scenes by the time we try on a pair of pants. Before the denim hit the shelves, a manufacturer raced to keep up with a production schedule to ensure the materials were received, processed, and shipped on time—and that’s only if everything went smoothly.
In fact, 60% of supply chain managers believe that the process could be more efficient and effective and half of them think technology will help them carry out that goal. In this article, we’re going deep into product production scheduling, how it’s changing, technology’s critical role in the supply chain, and how to use it to master production scheduling in 2023.
First up, let’s dust off our dictionary and define the term.
What is production scheduling?
Product production scheduling is the process of assigning different raw materials, resources or processes to different products. It’s meant to make your production process as efficient and cost-effective as possible when it comes to materials and people — all while delivering products on time.
Production scheduling is essential to the entire supply chain. In fact, it’s responsible for some of the most important key performance indicators (KPIs) in the supply chain as a whole.
Here are a few common production scheduling KPIs:
- Daily performance
- Cost reduction
- Production service rate
- Inventory turn
- Production time
- Order management
With the above KPIs in mind, we’ll need to come up with a reasonable timeframe and map out how we’ll reach our goals.
But first, we need to clarify an industry-related term you might have come across already; production planning. While the two are similar, there’s a key difference here.
What is production planning?
Production planning determines what and how much needs to be done, while scheduling decides who will perform the operations and when. Like with production scheduling, it allocates resources employees, materials, and production capacity, to serve different customers.
Production planning is the step before scheduling, and though both are essential to the process, we’ll use the remaining time to focus on production scheduling, starting with creating the schedule.
For example, if you are working on producing a video, you would start with a production calendar to schedule the process.
What are the stages of production scheduling?
The production schedule is adjusted based on the availability of resources and staff, as well as the number of orders to fill.
Basically, you want to balance your customers’ needs with the materials you have available.
The production schedule is created and executed in 5 steps:
- Planning – You can do two types of planning — static or dynamic. Static assumes nothing will change throughout the production process and dynamic assumes anything could change. Both include collecting and analyzing available resources, budgets, timelines and staff availability.
- Routing – Routing is the path from raw material to the finished product. Ideally, production routing identifies the most cost-effective and efficient steps for product manufacturing.
- Master schedule: master production scheduling includes people, routing steps, resources, etc.
- Operations or Manufacturing schedule : this includes the routing steps only.
- Retail operations scheduling : Specifically for retail, this includes the routing steps for products, which are slightly different as they’re manufactured to sit on a shelf or in an e-commerce queue as opposed to being sent straight to the customer.
4. Dispatching – This is the process of moving the goods and people around — issuing orders and instructions for products and parts to move from place to place throughout the entire production scheduling process.
5. Execution – This is where you get it all done, it’s the process of executing your production schedule.
As we’ve seen above, a successful schedule requires several elements and it can sometimes feel overwhelming to know where to start. We won’t leave you high and dry; check out our favorite strategy for managing production scheduling.
How do you optimize production scheduling?
There are a lot of strategies out there for optimizing the production scheduling process, but we think there’s one that trumps all others: agile scheduling.
Here’s how to build an agile production schedule:
- Build a dynamic schedule – You need to be able to adjust in real-time when something goes wrong, that means redistributing resources, contacting reinforcements, and understanding worker capacity.
- Control what is actually work-in-progress (WIP) – If everything is WIP, then nothing is a priority. Reserve the WIP label for those jobs that require completion right now.
- Prioritize based on on-time delivery as opposed to scheduling due dates – Your production schedule might prioritize a due date for an order tomorrow. But in reality, the due date that’s five days from now needs attention today or the order won’t make it on time. A dynamic schedule allows you to prioritize the latter.
Building a dynamic schedule and workflow can’t be done without the right planning and scheduling software.
While most tools lock you into a single due date, others provide the dynamic support that an operations team needs to effectively run a production schedule at maximum efficiency. Before we go any further, let’s answer the million dollar question.
What is production scheduling software?
Production scheduling software is, well, software that allows you to build and manage your production schedule.
It’s meant to make your production process more agile, and allow you to continuously update priorities, your schedule, and keep an eye on inventory plans to make adjustments where they’re needed.
Often referred to as advanced planning and scheduling (APS) software, the best of the bunch can integrate with your enterprise resource planning (ERP) or manufacturing resource planning (MRP) software so that data automatically updates across all tools.
monday.com is a modern, full work operating system (Work OS) that allows you to easily track and manage your production schedule (as well as integrate with your ERP system or MRP system). Our Work OS offers a variety of views —from dashboards to Gantt Charts— as well as apps for iOS and Android so you cant the full picture and alter your schedule as needed on the go.
Here’s a quick visual of how one company uses monday.com to track production using our production tracking template . Each production has its own status, person assigned, a clear description of each stage of the process, and relevant dates. And it’s all displayed on a view that’s easy to understand at a glance.

It’s no secret we love monday.com as a solution that can manage any kind of work and that applies to production scheduling. We break down some of our favorite reasons to use monday.com.
Why you should use monday.com as your production scheduling software
monday.com isn’t just an APS. It’s a full work operating system, which means you can not only integrate production scheduling with the full supply chain — that’s a no brainer — you can also integrate with the rest of your organization’s departments across the board.
We have solutions to connect you with marketing, sales, finance, HR, and any other department that needs to know the production schedule.
We’ll start with the supply chain though, since that’s most relevant here.
Our supply orders template is a great foundation for operations teams to build an APS that works for their needs.
Anyone can adapt the rows to represent each product type or organize the information into further groups if necessary. From there, use different columns to keep track of important metrics like last order date, priority level, quantity, price, formula and current production status.
monday.com also allows for the ability to assign an owner to a specific product line or project, so that you’re never confused when it comes to who to contact for what.
Here’s an example of how retailer Mad Hatter adapted our supply order template to manage their entire order history and production of their various hat types:

They used rows to organize different groups of orders by hat type and expanded some of the columns to include information like profit, profit margin, and when each hat type was last ordered.
By collecting this information, they can view the data in different dashboards to get a more visual picture of where they stand with inventory.
Here’s how one dashboard tracks the number of hats in inventory against time to order:

You can probably track a lot of these items in a typical APS system as well, but our Work OS is built on a foundation of features that streamline your processes and cut out any unnecessary communications.
For starters, you can automate communications and notifications between team members so that when a process is complete, the correct person is immediately notified and there’s never a lag in the supply chain.
Below is a visual example of how you might automate an email send for a new lead, but you could also automate notifications between team members, when an action is completed, and much more:
And like we mentioned before, we integrate with most tools out there, so that you can stay connected with the rest of the organization and use monday.com to collect and analyze data all in one place.
For example, we integrate with tools like Shopify, WooCommerce, Salesforce, Zendesk and so much more.
And as you’ve seen in some of these examples, our beautiful user interface (UI) is colorful, and easily managed with a drag and drop interface that makes making altering the production schedule incredibly easy.
Don’t get lost in production scheduling complexities
We know that production scheduling is subject to a lot of moving parts — the ordering, tracking and movement of materials to fuel the manufacturing process is incredibly complex.
If one of those moving parts goes awry, the whole supply chain could be knocked off kilter, which is why you shouldn’t be relying on an old, clunky APS to run your operations.
If you’re interested in a tool that goes way beyond a typical APS, that’s easy to use, powerful, and can optimize your production scheduling without a hitch, check out monday.com.
Send this article to someone who’d like it.

Production Schedule

There are a number of important factors or elements that contribute to the progress of a business. One of it is the production. While production plays an essential role in a company’s success, it still has to be considered that most business fail to be optimally productive, which results in lower profit, or worse, bankruptcy. This is because the entire process of production is not properly managed. A schedule example , when properly and carefully planned, can provide the solution to this dilemma.
Production Schedule Template Example
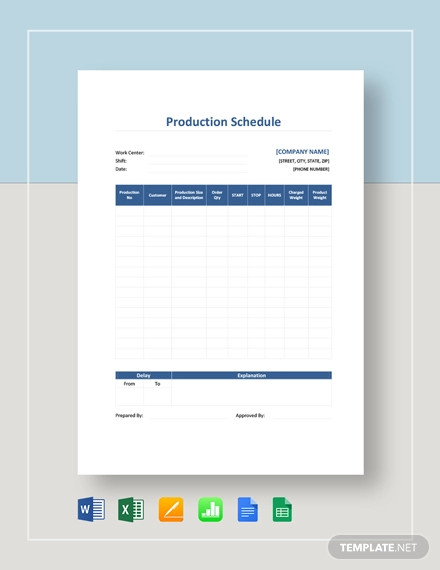
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
Size: US, A4
Event Production Schedule Template

- Editable PDF
Production Schedule Template

Size: A4, US
Work Production Schedule
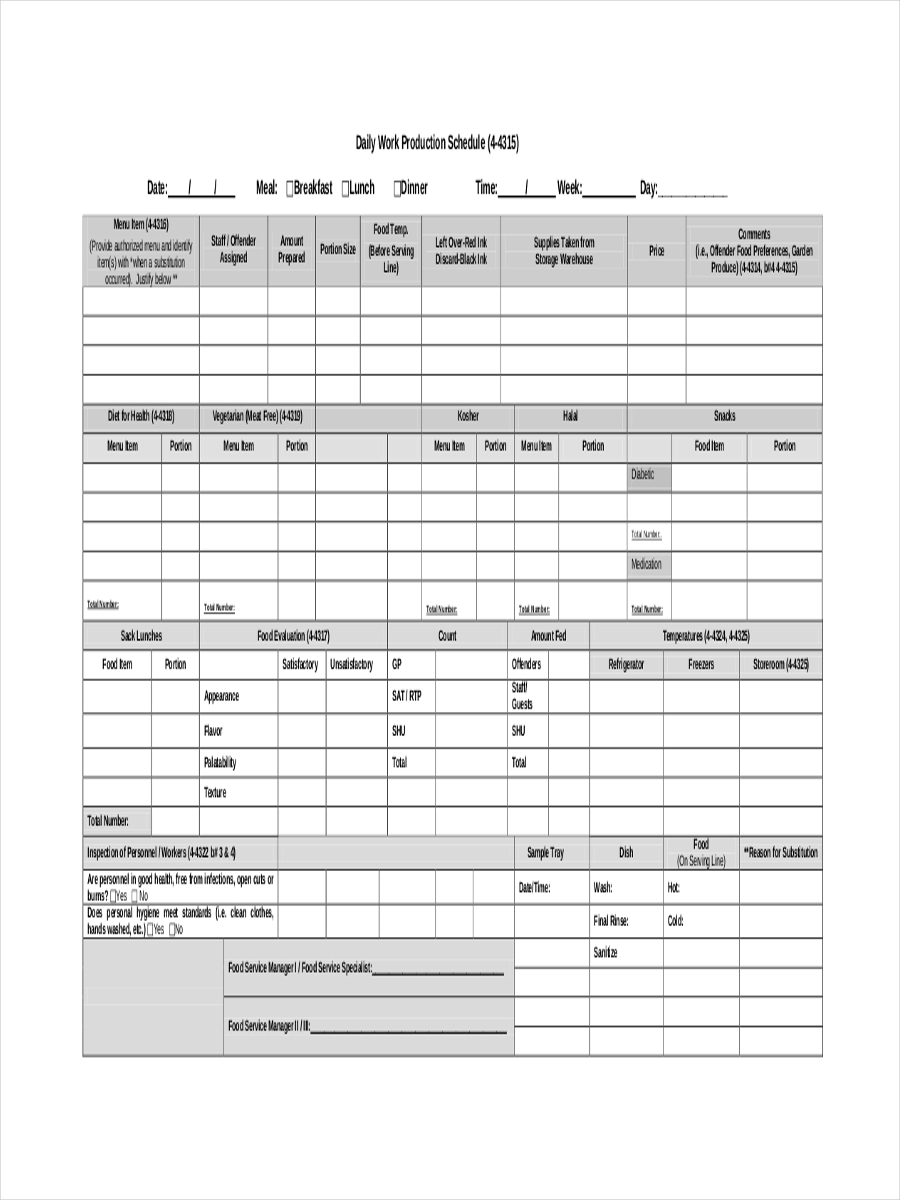
Size: 50 KB
Schedule for Film Production

Size: 149 KB
Master Production Schedule
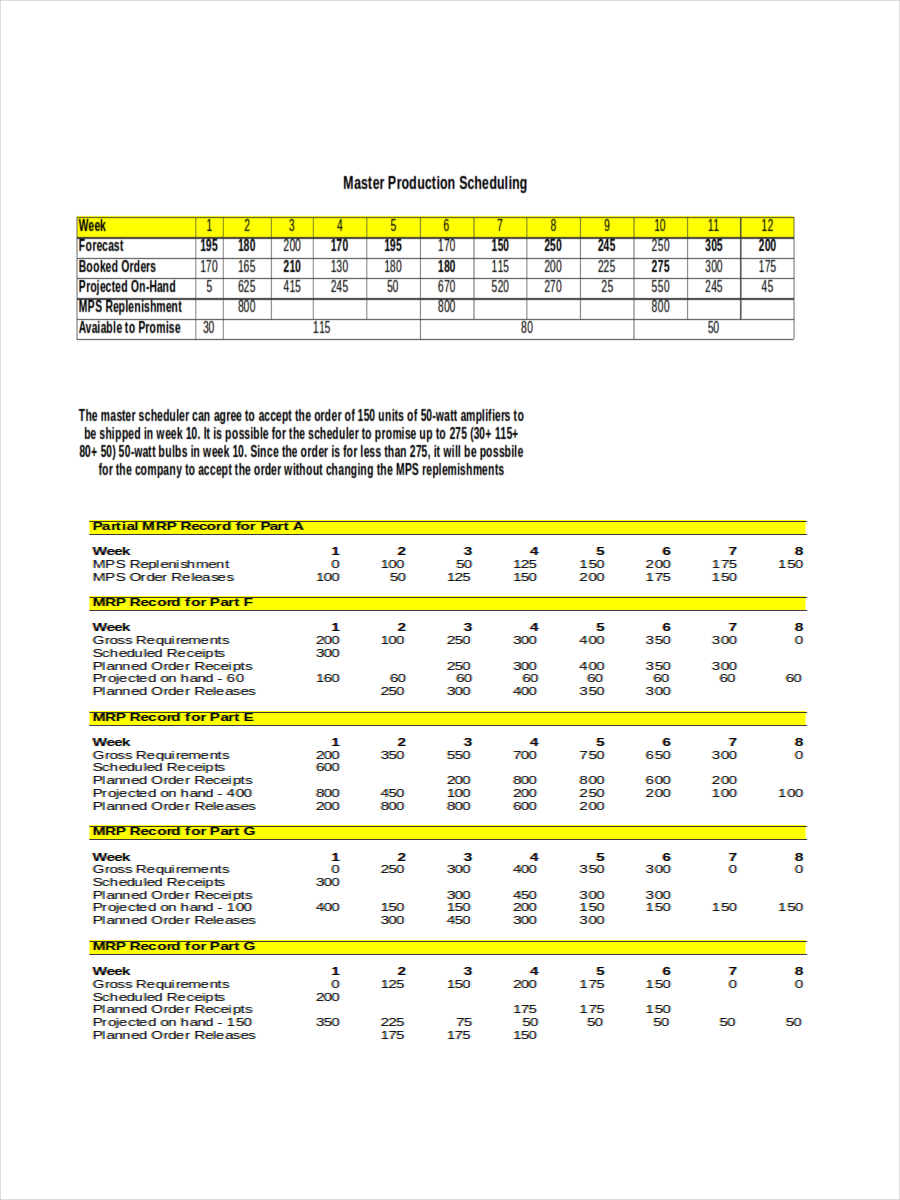
Sample Production Schedule
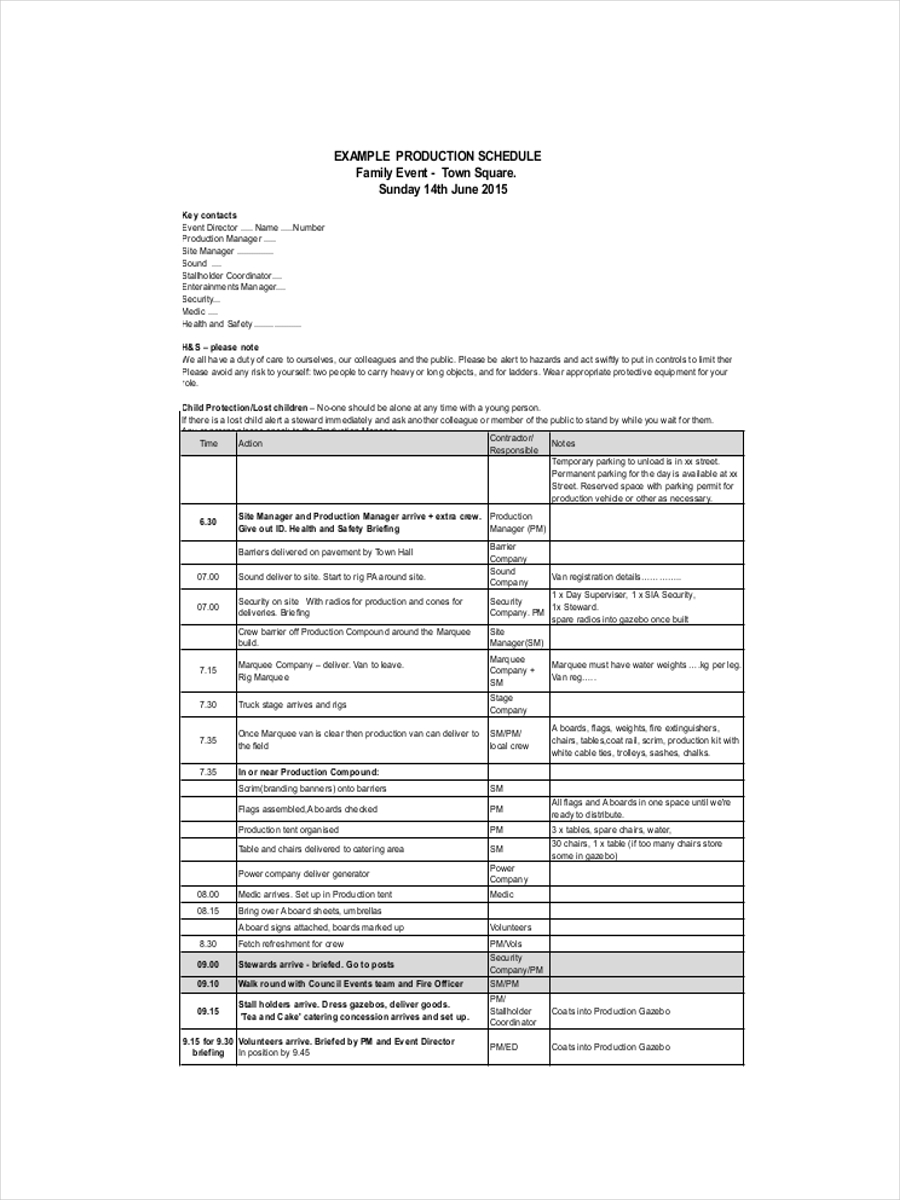
Size: 92 KB
What Is a Production Schedule?
A production schedule is a document that contains a detailed information relating to the formulation and generation of goods or materials with reference to its proper timeline. It can also be defined as a plan of how the production budget for a project will be spent over a determined timeline, through each phase of production.
Production schedules are often used in connection with employee schedules . These two work hand in hand to properly facilitate the entire course of action. In addition to that, the former can also be applied in many businesses such as manufacturing, agriculture, and filming industry.
How to Make a Production Schedule
A good production schedule sample can both accommodate the needs of its subjects and provide good results. And in order to make one, you need to consider a lot of elements.
- Create an objective. This is the same discipline that you need to apply just like when you create a training schedule . Creating an objective allows you to think out of the box and look at production in a different perspective.
- Consider your resources. Once you have established your smart goal , think of the supporting components like the materials and other resources needed for the production.
- Set a reasonable timeline. It is important that you think practical when setting the timeline. It makes your target attainable.
Schedule for Event Production

Size: 207 KB
Pre Production Schedule

Size: 31 KB
Schedule for Video Production

Size: 88 KB
Free Production Schedule
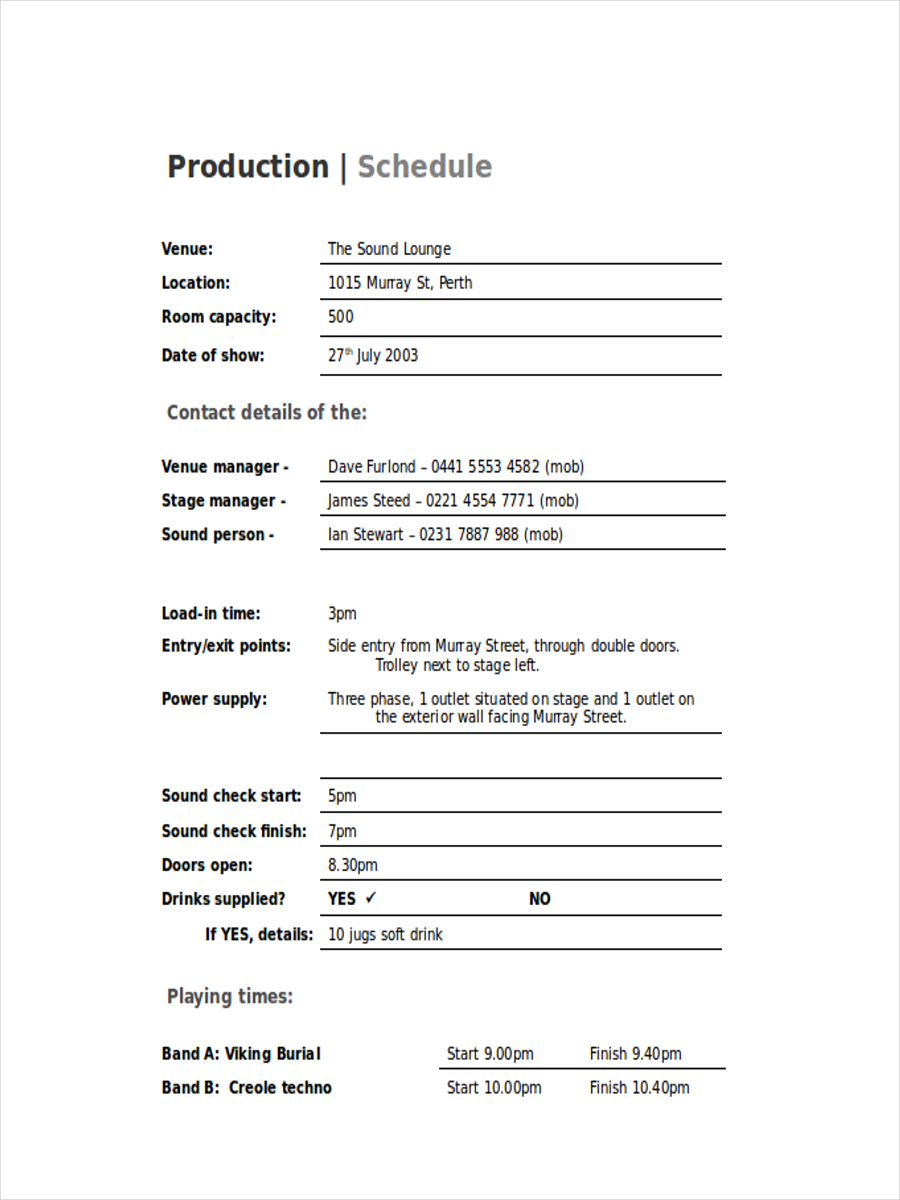
Size: 11 KB
How to Improve Production Scheduling
Making a production schedule is not an easy task. You need multidisciplinary skills and a clear understanding of the objective. In order to improve your production scheduling competence you need to be able to address the hidden needs in the production. This allows you to create a flexible schedule examples in PDF .
In addition to that, you need to think out of the box. Think extraordinary. Just because somebody says everything is okay doesn’t mean you have to settle in. Always think one step ahead. You can always come up with solutions to any problems that might arise in the process.
Why Do You Need a Production Schedule?
You need a production schedule in excel simply because nothing can be accomplished by way of impulsive and random action. Everything has to be planned, especially in the field of production. You cannot always come up with abrupt solutions and think that they will work instantaneously.
Schedules are designed to help you plan ahead of time. They allow you to set a series of activities, give them appropriate timescales, and work out any backup strategies in case the first one fails. A production schedule helps you create parameters and step-by-step activities essential to attain your target and make you reach your goal.
Any of the above examples should give you further insight.
Schedule Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a personalized class schedule to keep track of your school subjects and homework due dates.
Design a weekly planner for students to organize school assignments and exam preparation efficiently.
- Learn center
- Project management
What is production scheduling, and why is it important?
Georgina Guthrie
September 17, 2021
Remember the great toilet paper panic of 2020 ? Hundreds of thousands of people rushed out and stockpiled what became, for a few months, one of America’s most sought-after commodities.
There’s absolutely no way manufacturers could’ve predicted this once-in-a-lifetime combination of events, and the result was… we ran out.
We’re so used to going to the store and seeing the stuff we need in abundance because, over time, manufacturers have gotten very good at getting the right materials in, manufacturing on time, anticipating demand, and shipping it off to the store. When you do see empty shelves, it’s usually because someone has struggled with procuring materials, work orders — or there’s been a natural disaster or pandemic.
It’s nearly impossible to predict an event like COVID-19, but for everything else, there’s production scheduling. It’s a handy process that helps your business meet customer demand more efficiently. Read on to find out more!
What is production scheduling?
A production schedule lists every single product that’ll be manufactured, including where and when they’ll be made.
It includes every detail, from raw materials to logistics. It also incorporates various processes designed to make production run smoothly while helping managers spot potential issues — like bottlenecks — and stop them before they explode into something bigger. For this reason, it’s a flexible, changeable document that you’ll need to update and check regularly.
As well as helping managers plan ahead, the production schedule works as a line of communication between production and sales teams. Sales inform the manufacturing team about the levels of demand. Manufacturers then tell sales when the product is ready.
What is a production schedule used for?
The production schedule is a versatile and important document for planning, forecasting, predicting, and meeting demand. It helps keep your operations working on time and under budget, which helps you keep your commitment to your customers. Let’s get into its main functions in a little more detail.
Planning : Predicting demand and matching that to labor, materials, and equipment capacity
Scheduling : Assigning workers and detailing contingency plans for when unexpected delays happen
Stockout prevention : Planning to maintain output, even if materials are delayed, or a swell in orders increases demand
Improved efficiency : Spotting bottlenecks and looking for areas of improvement. This results in improved lead times and smoother demand flows
Improved communication : With one master document detailing every element of the production workflow, communication is standard across the entire business
How to create a production scheduling process
Your production schedule is a big, evolving thing — and without a formalized process in place, it could end up getting a bit unruly. Here are five key steps to follow.
- Planning : Begin with your demand plan. How much raw material will you need, and when? There are two types of planning you can do here: static and dynamic. Static assumes nothing will change, whereas dynamic assumes everything could change. Both involve collecting information about resources, timelines, and team availability.
- Routing : Identify where your raw materials will come from and how they’ll be delivered to your production or manufacturing team, with a focus on the most cost-effective route.
- Scheduling : Develop a schedule that sets out how you’ll meet requirements — including contingency plans . – Create a master schedule that encompasses the entire process, from start to finish – Set up a manufacturing schedule that covers raw material routing – Plan a retail schedule that covers how products move from manufacturing to the shelf or eCommerce store
- Communicating : Share the production schedule to everyone involved and make sure it’s understood
- Dispatching : Plot the process of items and people moving around — including when and where throughout the entire process
- Execution : This is the process of putting your plan into action
- Maintenance : Keep your schedule updated regularly as demand changes
What to include in your production scheduling
Your production schedule will include these elements:
- A product inventory that lists all of the products you make
- A variation sublist (size, color, type)
- Demand and delivery dates
- Production quantities (the number of units you’ll produce each week)
The benefits of using a production schedule
Your production scheduling will help with demand planning, supply, and the changing needs of your customers. It should help you better anticipate the ebb and flow of work, not to mention give you a framework to use when things don’t go quite as planned.
Here’s a summary of what your production schedule does:
- It gives you an inventory of your entire stock, so you always know what you have and where you need to replenish items
- It helps HR know in advance how many staff you’ll need at any given time
- It’ll help you navigate risks and prevent issues from bringing production to a standstill
- It helps you avoid stockouts because you know how much raw material you have, how long production will take, and how much you’ll need
How to optimize your production schedule
Your production schedule will be a big document that you will regularly update. Not only that, but multiple people will need to be told about that change as soon as it happens. Here are some tips on how best to manage that:
Create a dynamic schedule
Flexibility is the name of the game, so make sure you create your schedule on something that’s easy to edit in real-time. Project management software is the gold standard here.
Prioritize tasks according to delivery dates:
Your schedule might prioritize an order that’s due in two days’ time, but if you know there’s an order due in 10 days, and it won’t make its deadline if you don’t see to it now, then focus on that first. Having a dynamic schedule makes it easier to reprioritize those orders.
Use project management tools
With a project management tool, you can create your schedule using a Gantt chart . This is essentially a virtual diagram that helps you schedule tasks and resources across a timeline. As the project evolves, individuals can enter their data, and the chart automatically updates in real-time — meaning everyone’s on the same page at once. If there are delays in raw materials or staff are off, the team can edit it, and the new data turned into an updated schedule with recalculated times, costs, and other metrics. No more manual adjustments, no more update emails — just the entire team working like a well-oiled machine.
Final thoughts
Production scheduling is a big job with a cocktail of people and tasks all happening at once. Then there’s the largely unpredictable nature of supply and demand, the movement of materials, and the complex manufacturing process — all of which can send your carefully constructed plan out the window.
If one of those things goes off-track, then the whole lot could grind to a halt. This is why dynamic production schedules are so important.
If you’re looking for a tool that offers so much more than a typical APS, that automatically updates schedules and recalculates resources, that can send out notifications and operate in real-time, then Backlog — our own project management software — may just be what you’re looking for. Give it a try today.

Never skip creating a master schedule for your project

A simple guide to project scheduling (and 3 project scheduling techniques to know)
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Learn with Nulab to bring your best ideas to life
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Get your free
Production Schedule Template
Get your Production Schedule Template for Excel or open it in ProjectManager, the best way to manage your projects online.
Getting goods to customers involves a lot of coordination. There are demands to meet and raw materials to procure. And of course, you need to create a manufacturing schedule to deliver the commodity on time and meet customer needs. Use our free production schedule template for Excel to get those pieces together, and keep your manufacturing process running smoothly.
But, if you want to make an even better production schedule than Excel can offer, open ProjectManager’s free production schedule template. It lets you build a dynamic production schedule that can be managed online with an interactive Gantt chart, spreadsheet or kanban board. Track progress, create dependencies, find the critical path, attach files and more. Get started for free with ProjectManager and build a better production schedule.
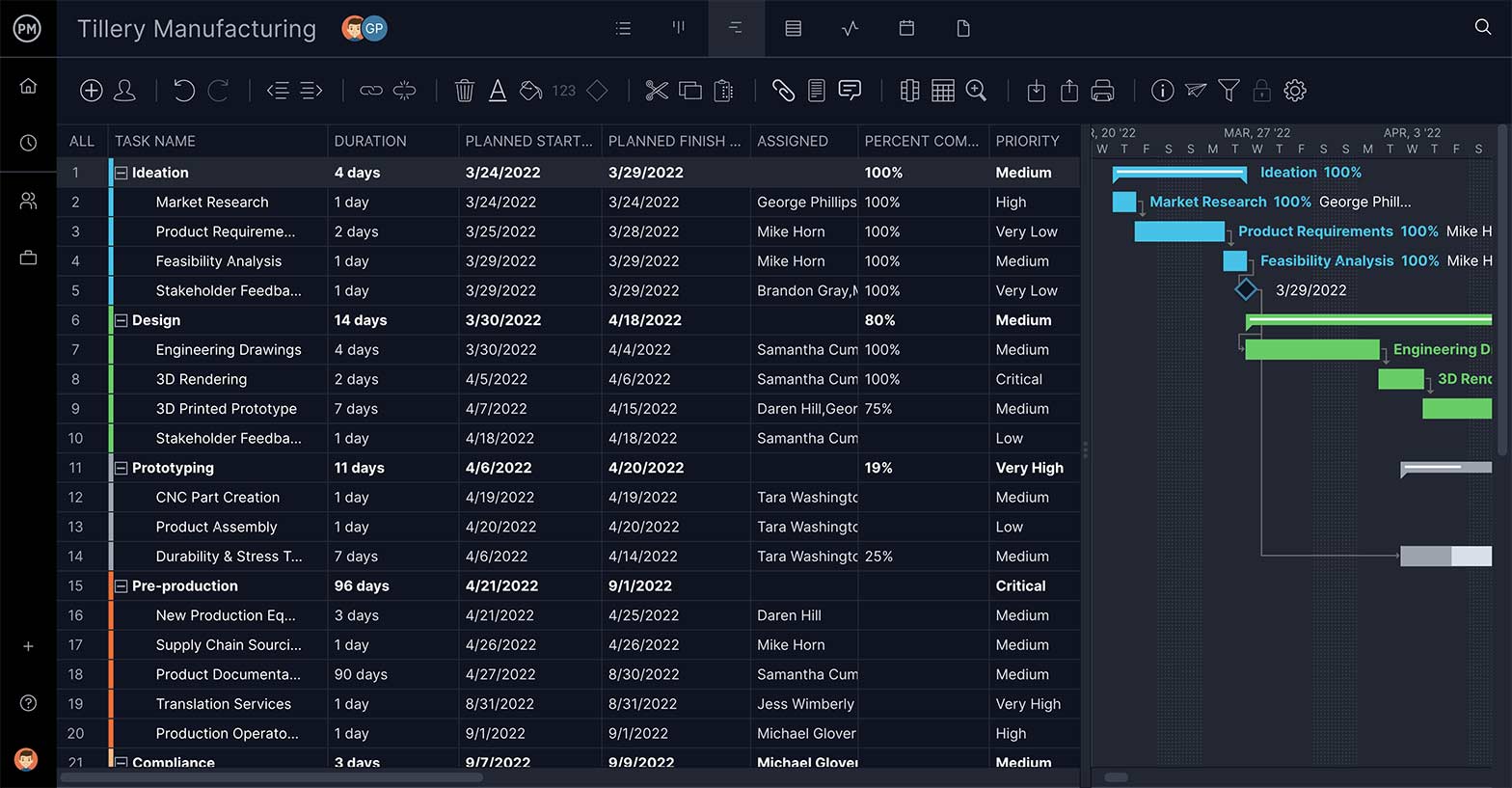
What Is a Production Schedule?
A production schedule is a plan to balance supply and demand in the production of a commodity. It tracks the production of a product over a period of time, and is a fundamental piece of any manufacturing business.
Like any schedule, a production schedule is built to be flexible. It responds to fluctuations in demand and sets up inventory to avoid stockouts. Using our free production schedule template for excel will help you improve efficiency and control costs.
Everything about the manufacturing process is covered in this template. It helps you determine what needs to be produced, how much of it you need to make and when it needs to happen.
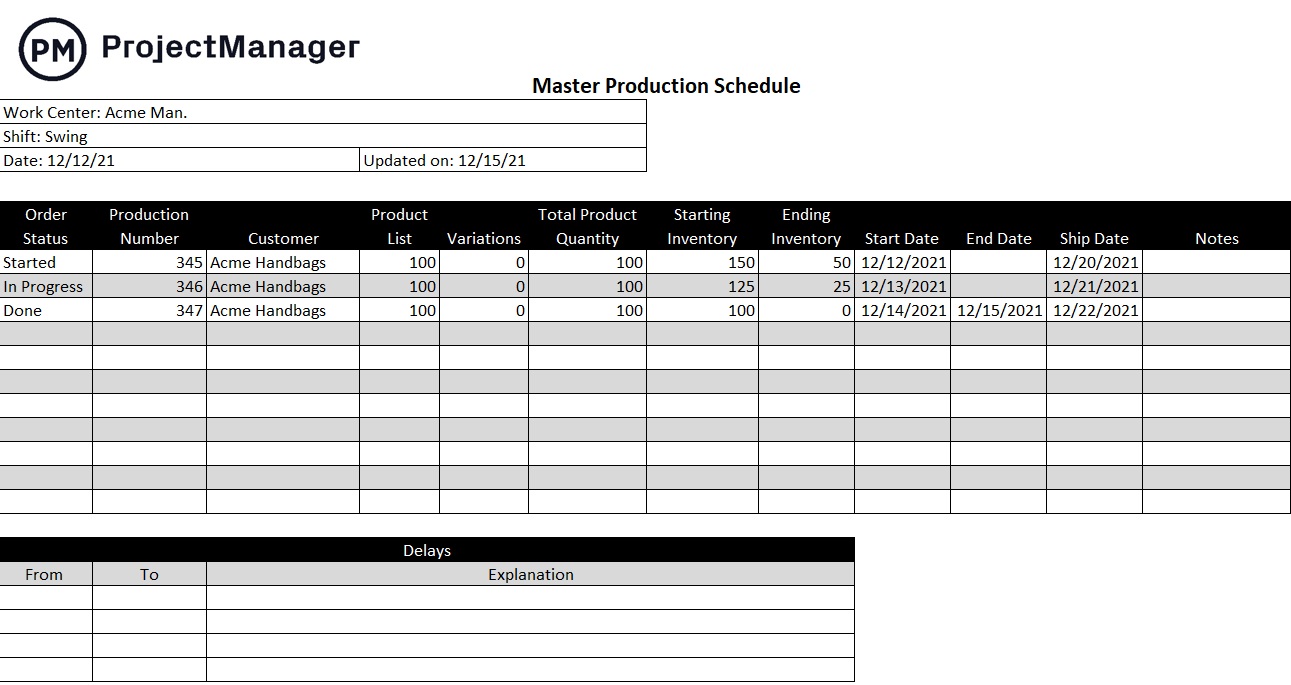
Why You Need a Production Schedule Template
The production schedule is part of your supply chain management . Not only does it manage your resources, but it helps your sales team work with production to plan a schedule that delivers the goods to customers as needed.
Using the production schedule template will help you estimate an accurate and realistic production plan, one that can be revisited and revised as needed. It helps to manage your inventory and stock movements. It also allows you to track your targets , manage deliveries and allocate resources, which includes both raw materials and personnel.
When to Use a Production Schedule Template
Use the production schedule template during production planning. This is when you start to estimate the number of raw materials, people, workstations, processes and supplies you’ll need to get the work done.
The next step is to determine the route of the raw materials through the production to the finished product. This will help you know where you are in the production cycle. This way you can accurately map the route from one workstation to the next.
This is when the production schedule comes in. It’s a way to manage these processes to match your deadline and budget. Then you can execute orders without having to make wild guesses. During the execution phase, you have most of the work laid out and just have to respond to supporting issues.
If you find yourself constantly updating and revising this template and other Excel sheets, it might be time to upgrade to project management software. Project management software automates much of that process and adds resource management tools to help you produce more efficiently. Workload charts with real-time resource availability keep your team productive. ProjectManager also has kanban boards that show you exactly where you are in the production cycle, so you can add resources to match your capacity. Try it for yourself with a free 30-day trial.
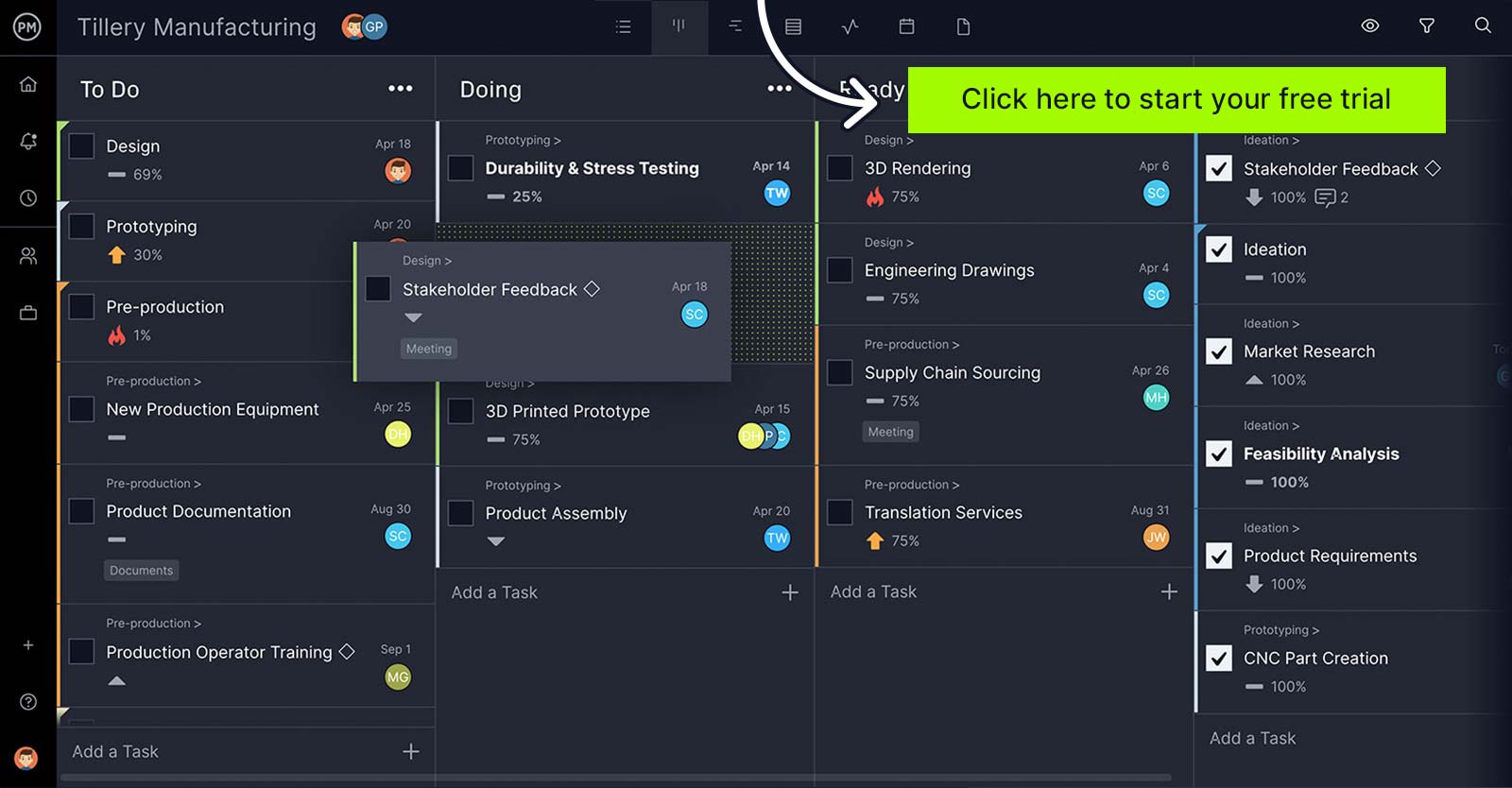
Who Should Use a Production Schedule Template?
Depending on your business, there can be one or more people who use the production schedule template. A production planning manager oversees the production of a business. This person is more likely to manage the plan itself, though the schedule is part of that plan.
There are also production schedulers who are tasked with making the schedule on the required timeline. They are sometimes called a master scheduler. They look at historic data and inventory to make accurate and effective schedules.
Whether you have a production planning manager or a production scheduler, the person who uses the production schedule template needs to stay in close communication with suppliers, sales representatives and other stakeholders to make sure they are calculating current numbers and meeting current demand.
How to Use ProjectManager’s Production Schedule Template
Our free production schedule template for Excel has all the information you need to add mapped out for you. Just put in how much and when, then you can organize your manufacturing to meet deadlines.
Company Info
The first part of the template is where you identify the work center and the shift. There’s a place to date the template and then another where you can add the date it was revised.
Order Status
This is where you indicate the status of the order. You can customize this column to mirror your nomenclature. We have set the template with options of started, in progress, done and more.
Production Number
Next is where you indicate the production number for internal tracking. What follows is the name of the customer for whom you’re making the product to sell. The product list is simply the quantity of items you’re going to manufacture.
Variations refers to any differences in the product. For example, if you’re manufacturing lunchboxes, this would indicate different colors or designs. Then you add up the product list and variations to come up with the total product quantity.
Starting Inventory
The starting inventory is how much inventory you have at the beginning of the manufacturing job. The ending inventory is what you’re left with. This will help you gauge your inventory to make sure you always have enough of what you need in stock.
Manufacturing Dates
Next is the start date for the manufacturing, followed by the end date, which gives you a timeframe by which the work must be completed. When it is done, there’s a place for the ship date, which can be seen as the hard deadline by which time your product must leave the manufacturing floor.
There’s a place for notes to fill in any gaps that aren’t part of the overall production schedule template. Under that is a place to capture any delays in manufacturing, listing the from-to dates and adding an explanation for the delay.
How to Schedule Production in ProjectManager
The free production schedule template is a great start to managing your manufacturing schedule, but if you want to plan better, organize resources, set dependencies and more, you’ll want to use a project management software tool like ProjectManager to simplify your scheduling. Use our online Gantt charts to get all your tasks identified, described and laid out over a timeline, with start and finish dates. Now you can see your entire manufacturing schedule in one place. There are likely dependent tasks that can cause a bottleneck in your manufacturing. With the Gantt chart it’s easy to link these tasks together by simply dragging one to another so they don’t slip through the cracks and cause delays.
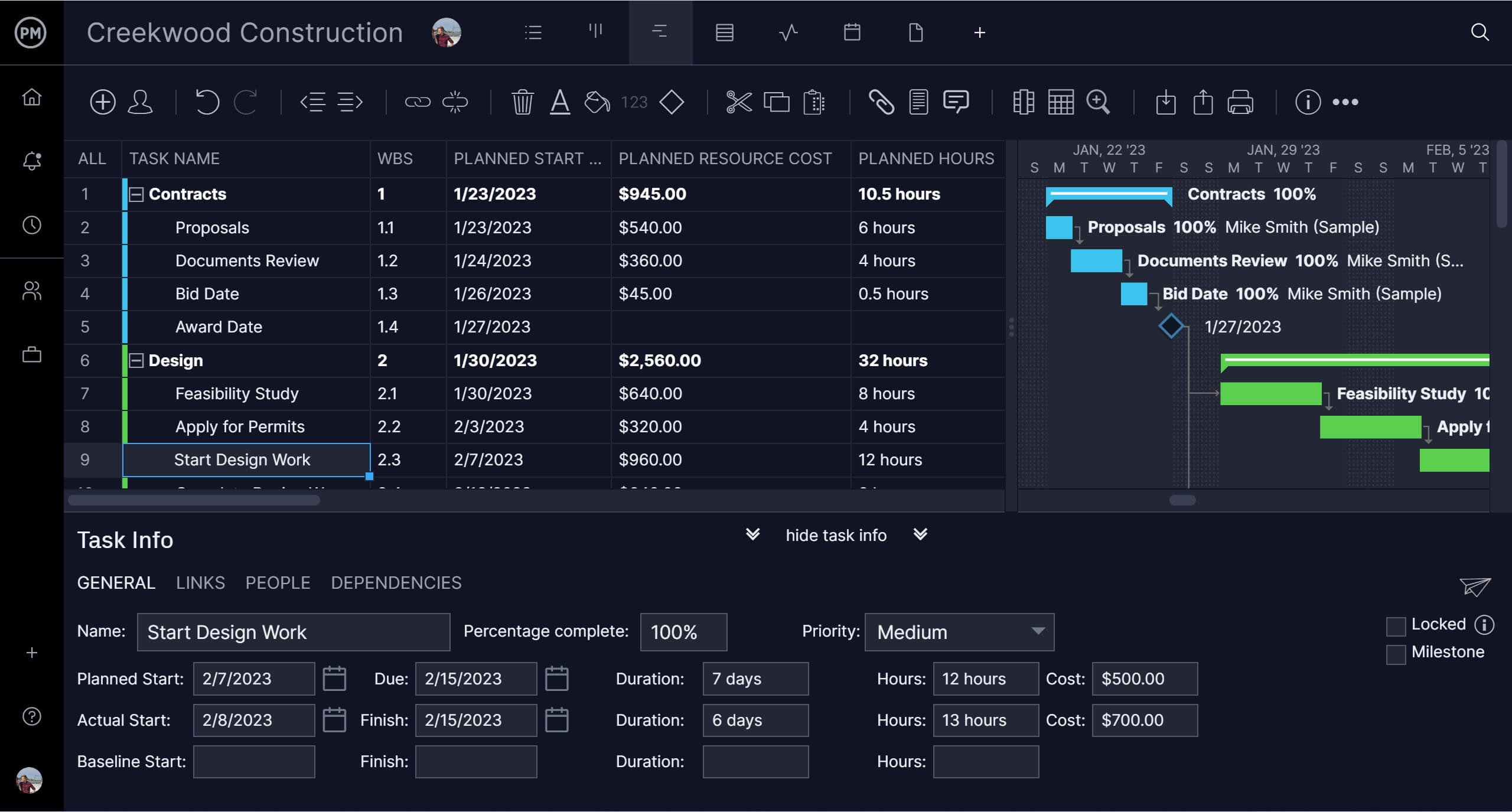
Resource Tracking
Because our software is online you can monitor your manufacturing in real-time and reallocate resources quickly to stay on track. There’s even a workload chart to balance your team’s tasks so they work more efficiently. All resource costs are managed, which gives you more control over the supplies and raw materials you need to make your product.
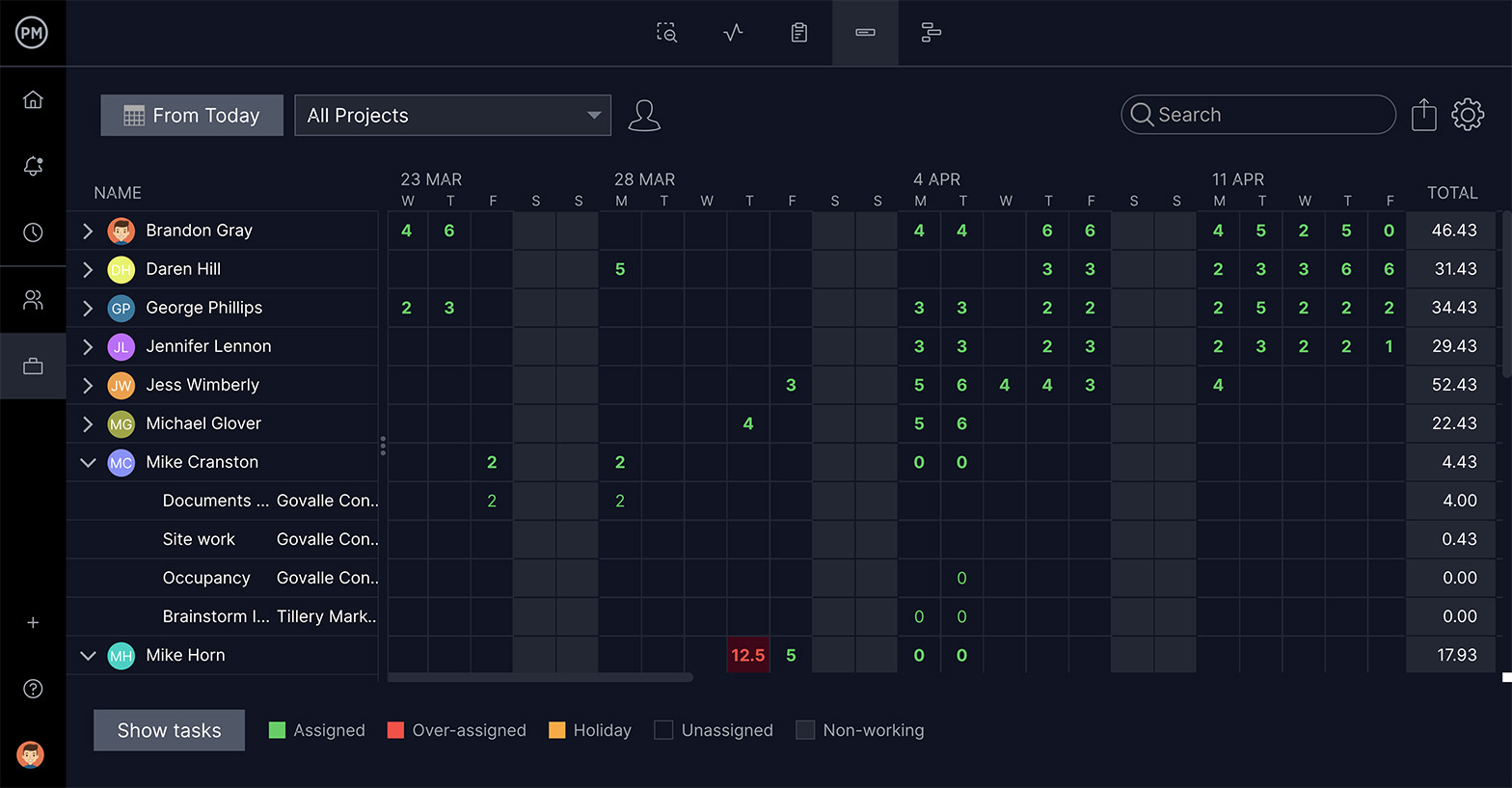
What Other Templates Can Help With Scheduling?
Our free production schedule template is one of dozens of free project management templates on our site that can help you better plan and schedule your work.
Gantt Chart Template
While not as dynamic as our online Gantt chart, the free Gantt chart template is still very helpful when making your schedule. It gives you a visual tool to organize your schedule by showing you start and end dates and setting milestones to break up your production into more manageable bits.
Work Schedule Template
Our free work schedule template will help you organize your workforce by letting you list all your employees, where they’re located, the times they’re working and what they’re responsible for doing over their shift. It can manage the traditional weekday, but also shift work for those manufacturers that are running their machinery all week long, 24 hours a day.
Project Plan Template
The free project plan template is used to organize all the activities of your manufacturing production. That includes tasks and resources. It breaks the work into phases, activities into a schedule with tasks and durations, dependencies and more.
Related Production Scheduling Content
We publish blogs, videos and guides that explain all the different aspects of production management. Here are a few of the ones that focus on production scheduling and other similar topics:
- Best Production Scheduling Software Rankings
- Production Scheduling Basics
- How to Create a Master Production Schedule (MPS)
- Production Management: A Quick Guide
- Production Planning in Manufacturing: Best Practices
ProjectManager is a cloud-based tool that helps you organize work, teams and gives you real-time data to help you make better decisions. It is used by tens of thousands of teams across many industries to help them plan, schedule, monitor, track and report on the progress and performance of their work. See what it can do to help you stay on schedule by taking this free 30-day trial today.
Start your free 30-day trial
Deliver faster, collaborate better, innovate more effectively — without the high prices and months-long implementation and extensive training required by other products.
- Encyclopedia of Management
- Production Planning and Scheduling
PRODUCTION PLANNING AND SCHEDULING

Production planning is the function of establishing an overall level of output, called the production plan. The process also includes any other activities needed to satisfy current planned levels of sales, while meeting the firm's general objectives regarding profit, productivity, lead times, and customer satisfaction, as expressed in the overall business plan. The managerial objective of production planning is to develop an integrated game plan where the operations portion is the production plan. This production plan, then, should link the firm's strategic goals to operations (the production function) as well as coordinating operations with sales objectives, resource availability, and financial budgets.
The production-planning process requires the comparison of sales requirements and production capabilities and the inclusion of budgets, pro forma financial statements, and supporting plans for materials and workforce requirements, as well as the production plan itself. A primary purpose of the production plan is to establish production rates that will achieve management's objective of satisfying customer demand. Demand satisfaction could be accomplished through the maintaining, raising, or lowering of inventories or backlogs, while keeping the workforce relatively stable. If the firm has implemented a just-in-time philosophy, the firm would utilize a chase strategy, which would mean satisfying customer demand while keeping inventories at a minimum level.
The term production planning is really too limiting since the intent is not to purely produce a plan for the operations function. Because the plan affects many firm functions, it is normally prepared with information from marketing and coordinated with the functions of manufacturing, engineering, finance, materials, and so on. Another term, sales and operations planning, has recently come into use, more accurately representing the concern with coordinating several critical activities within the firm.
Production planning establishes the basic objectives for work in each of the major functions. It should be based on the best tradeoffs for the firm as a whole, weighing sales and marketing objectives, manufacturing's cost, scheduling and inventory objectives, and the firm's financial objectives. All these must be integrated with the strategic view of where the company wants to go.
The production-planning process typically begins with an updated sales forecast covering the next 6 to 18 months. Any desired increase or decrease in inventory or backlog levels can be added or subtracted, resulting in the production plan. However, the production plan is not a forecast of demand. It is planned production, stated on an aggregate basis. An effective production-planning process will typically utilize explicit time fences for when the aggregate plan can be changed (increased or decreased). Also, there may be constraints on the degree of change (amount of increase or decrease).
The production plan also provides direct communication and consistent dialogue between the operations function and upper management, as well as between operations and the firm's other functions. As such, the production plan must necessarily be stated in terms that are meaningful to all within the firm, not just the operations executive. Some firms state the production plan as the dollar value of total input (monthly, quarterly, etc.). Other firms may break the total output down by individual factories or major product lines. Still other firms state the plan in terms of total units for each product line. The key here is that the plan be stated in some homogeneous unit, commonly understood by all, that is also consistent with that used in other plans.
PRODUCTION SCHEDULING
The production schedule is derived from the production plan; it is a plan that authorized the operations function to produce a certain quantity of an item within a specified time frame. In a large firm, the production schedule is drawn in the production planning department, whereas, within a small firm, a production schedule could originate with a lone production scheduler or even a line supervisor.
Production scheduling has three primary goals or objectives. The first involves due dates and avoiding late completion of jobs. The second goal involves throughput times; the firm wants to minimize the time a job spends in the system, from the opening of a shop order until it is closed or completed. The third goal concerns the utilization of work centers. Firms usually want to fully utilize costly equipment and personnel.
Often, there is conflict among the three objectives. Excess capacity makes for better due-date performance and reduces throughput time but wreaks havoc on utilization. Releasing extra jobs to the shop can increase the utilization rate and perhaps improve due-date performance but tends to increase throughput time.
Quite a few sequencing rules (for determining the sequence in which production orders are to be run in the production schedule) have appeared in research and in practice. Some well-known ones adapted from Vollmann, Berry, Whybark and Jacobs (2005) are presented in Operations Scheduling.
THE PRODUCTION PLANNING AND PRODUCTION SCHEDULING INTERFACE
There are fundamental differences in production planning and production scheduling. Planning models often utilize aggregate data, cover multiple stages in a medium-range time frame, in an effort to minimize total costs. Scheduling models use detailed information, usually for a single stage or facility over a short term horizon, in an effort to complete jobs in a timely manner. Despite these differences, planning and scheduling often have to be incorporated into a single framework, share information, and interact extensively with one another. They also may interact with other models such as forecasting models or facility location models.
It should be noted that a major shift in direction has occurred in recent research on scheduling methods. Much of what was discussed was developed for job shops. As a result of innovations such as computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) and just-in-time (JIT), new processes being established in today's firms are designed to capture the benefits of repetitive manufacturing and continuous flow manufacturing. Therefore, much of the new scheduling research concerns new concepts and techniques for repetitive manufacturing-type operations. In addition, many of today's firms cannot plan and schedule only within the walls of their own factory as most are an entity with an overall supply chain. Supply chain management requires the coordination and integration of operations in all stages of the chain. If successive stages in a supply belong to the same firm, then these successive stages can be incorporated into a single planning and scheduling model. If not, constant interaction and information sharing are required to optimize the overall supply chain.
SEE ALSO: Aggregate Planning ; Operations Management ; Operations Scheduling ; Product-Process Matrix ; Supply Chain Management
R. Anthony Inman
FURTHER READING:
Hurtubise, Stephanie, and Claude Olivier, and Ali Gharbi. "Planning Tools for Managing the Supply Chain." Computers & Industrial Engineering 46 (2004): 763–779.
Kreipl, Stephan, and Michael Pinedo. "Planning and Scheduling in Supply Chains: An Overview of Issues in Practice." Production and Operations Management 13, no. 1 (2004): 77–92.
Vollmann, Thomas E., William L. Berry, Clay D. Whybark, and F. Robert Jacobs. Manufacturing Planning and Control for Supply Chain Management. 5th ed. New York: Irwin McGraw-Hill, 2005.
User Contributions:
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic:.

Production Schedule
Track projects, products, promotions, sales, and other advertising timelines with this production schedule.
Sample text from Production Schedule:
People who printed this template also printed...

DISCLAIMER: The business plans, templates, and articles contained on BusinessPlanTemplate.net are not to be considered as legal advice. All content is for informational purposes, and Savetz Publishing makes no claim as to accuracy, legality or suitability. The site owner shall not be held liable for any errors, omissions or for damages of any kind.
Copyright © 2011-2024 by Savetz Publishing , Inc. Contact us . Privacy Policy .
Subscribe to the Free Printable newsletter. (No spam, ever!)
This template is easy to download and print. Each free business plan template is available in Microsoft Word (DOC) format, and many of the Business Plan Forms are available in Excel (XLS) format as well. Just choose a business plan template and download it. Open it in Word or Excel (or another program that can display the DOC or XLS format), edit it, and print your personalized business plan.
Collections of business forms are now available as convenient all-in-one downloads. There's a Start-Up collection that’s ideal for new businesses, or choose from: Budget , Theater , Restaurant , Sales , Inventory , Human Resources , Agriculture , Church , Auto , or Real Estate . Each collection is just $27.
Business Plan Forms
General Business Plans
Business Plans for Specific Industries
Business Plan Articles
Business Form Theme Packs
Newest Additions
Search All Business Plan Templates
Search all templates for:
Thank you for your suggestion.
We're always adding new printables, and would love to hear your suggestions. What are we missing?
Submit Suggestion Close
- Sustainability
- Latest News
- News Reports
- Documentaries & Shows
- TV Schedule
- CNA938 Live
- Radio Schedule
- Singapore Parliament
- Mental Health
- Interactives
- Entertainment
- Style & Beauty
- Experiences
- Remarkable Living
- Send us a news tip
- Events & Partnerships
- Business Blueprint
- Health Matters
- The Asian Traveller
Trending Topics
Follow our news, recent searches, xiaomi ceo says will introduce production capacity, delivery plan for su7 at auto show, advertisement.
FILE PHOTO: Xiaomi founder and CEO Lei Jun speaks at an event on the company's first electric vehicle, the SU7, in Beijing, China December 28, 2023. REUTERS/Florence Lo/File Photo
BEIJING : Xiaomi's CEO said the company will offer more details about its production capacity and delivery plan for the SU7 vehicle at the Beijing Auto Show, according to a Weibo post on Monday.
Lei Jun also said Xiaomi has started deliveries for the standard and MAX versions of the SU7 ahead of schedule.
Also worth reading
This browser is no longer supported.
We know it's a hassle to switch browsers but we want your experience with CNA to be fast, secure and the best it can possibly be.
To continue, upgrade to a supported browser or, for the finest experience, download the mobile app.
Upgraded but still having issues? Contact us

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A production planning template is a framework that creates a visual representation of production scheduling. The schedule establishes a production process and assigns a plan and budget, outlining the task sequence, timing, and allocation of necessary resources to create something or deliver services.
A production plan serves as a roadmap that outlines the steps, resources, and strategies required to manufacture products or deliver services efficiently. By carefully crafting a production plan within a business plan, entrepreneurs can ensure optimal utilisation of resources, timely delivery, cost efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
The following seven steps are used to design and carry out the production schedule: Planning; Static and dynamic planning are both options. Production planning can be divided into two categories: static planning and dynamic planning. ... It is a time in the future (often a business year) during which production-supporting departments arrange ...
These stages provide a structured framework for organizations to plan, schedule, and control their production processes effectively. Let's explore each stage in detail. 1. Demand forecasting and capacity planning. The first production planning and scheduling stage involves demand forecasting and capacity planning.
How to Make a Production Plan. When you set out to create a production plan, make sure to follow these steps to make it as robust as possible. 1. Estimate/Forecast Product Demand. Understanding product demand planning is the best way to decide which product planning method is the best choice for your operation.
A master production schedule (MPS) details what, when and how many products a manufacturer will produce. It links the demand as determined by sales to the capacity a company has to make the product. It helps create a realistic plan that avoids having to overstock warehouses but maintains on-time delivery.
Production scheduling helps you anticipate demand, stock resources, manage labor, and prioritize on-time production in order to avoid these crucial business objectives. In this guide, you'll learn the importance of production scheduling, the steps for creating a schedule, and optimization practices to help keep your company on track.
The first step in production planning and scheduling is to analyze demand and capacity. This includes forecasting demand, evaluating available resources, determining lead time, and identifying constraints. A demand forecast helps you to estimate the production volumes needed to fulfill customer orders. Evaluating available resources such as raw ...
Here are some actionable tips and production scheduling best practices to help you along. 1. Stay flexible. Plans often change, so a production schedule needs to be dynamic. When you create your production schedule, allow flexibility for changes to dates, tasks, and resources.
A production plan defines the production targets, required resources and overall schedule, together with all the steps involved in production and their dependencies. A well-designed production plan helps companies deliver products on time, reduce costs and respond to problems. Technology has made it easier for small and midsize companies in ...
In the production world, it's important to understand the difference between a production plan and a production schedule. Both are essential to delivering work (and they work in tandem). Production planning. This is like the big-picture planning phase for your entire project. It's where you figure out what needs to happen from start to finish ...
A production schedule is a detailed plan that outlines the specific activities and timeline for producing goods or services. It is a crucial component of production management, helping businesses efficiently allocate resources and meet production targets. In simple terms, a production schedule is like a to-do list for a business to make things.
The right combination of production scheduling methods simplifies the production process, increases customer satisfaction, and drives success. 1. Capacity planning. This method involves evaluating the capacity of key resources, such as labor, machinery, and facilities, and aligning it with the expected demand.
A master production schedule (MPS) is the overall plan to assess the production of your finished goods, detailing what you need to produce, how much you need to produce, and when you need to produce it. In short, it contains any relevant information related to production, including time frames, such as your manufacturing lead time.
Some of the most common strategies are level production, make-to-stock, and assemble-to-order. (There's also the chase strategy, but we don't recommend it.) Level production: you keep your production output fixed over time. It's the easiest to manage logistically but can quickly lead to over or underproduction.
But, in business operations, planning and scheduling aren't two peas in a pod. Planning deals with choosing the right procedures to furnish the goals of the project, scheduling assigns time, tasks, resources, and machinery to the objectives of your marketing plan. ... Template 2: Market Activity Schedule Plan for Production Promotion PPT Slides.
The production schedule is adjusted based on the availability of resources and staff, as well as the number of orders to fill. Basically, you want to balance your customers' needs with the materials you have available. The production schedule is created and executed in 5 steps: Planning - You can do two types of planning — static or ...
Master production schedule: A master schedule is a plan for manufacturing a product within a specific time frame. It includes elements such as personnel, budget, routing processes and resources. Manufacturing schedule: This type of schedule is a plan for production that only includes the steps required to turn raw materials into a finished product.
A production schedule is a document that contains a detailed information relating to the formulation and generation of goods or materials with reference to its proper timeline. It can also be defined as a plan of how the production budget for a project will be spent over a determined timeline, through each phase of production.
The production schedule is a versatile and important document for planning, forecasting, predicting, and meeting demand. It helps keep your operations working on time and under budget, which helps you keep your commitment to your customers. Let's get into its main functions in a little more detail. Planning: Predicting demand and matching ...
ProjectManager's production schedule template is free to use and more powerful than Excel. Try it now What Is a Production Schedule? A production schedule is a plan to balance supply and demand in the production of a commodity. It tracks the production of a product over a period of time, and is a fundamental piece of any manufacturing business.. Like any schedule, a production schedule is ...
The production schedule is derived from the production plan; it is a plan that authorized the operations function to produce a certain quantity of an item within a specified time frame. In a large firm, the production schedule is drawn in the production planning department, whereas, within a small firm, a production schedule could originate ...
Track projects, products, promotions, sales, and other advertising timelines with this production schedule. Download Free Version (DOC format) Download Free Version (PDF format) My safe download promise. Downloads are subject to this site's term of use. Downloaded > 1,000 times.
BEIJING : Xiaomi's CEO said the company will offer more details about its production capacity and delivery plan for the SU7 vehicle at the Beijing Auto Show, according to a Weibo post on Monday ...