Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples

Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
Published on 15 May 2022 by Tegan George .
The table of contents is where you list the chapters and major sections of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, alongside their page numbers. A clear and well-formatted table of contents is essential, as it demonstrates to your reader that a quality paper will follow.
The table of contents (TOC) should be placed between the abstract and the introduction. The maximum length should be two pages. Depending on the nature of your thesis, dissertation, or paper, there are a few formatting options you can choose from.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What to include in your table of contents, what not to include in your table of contents, creating a table of contents in microsoft word, table of contents examples, updating a table of contents in microsoft word, other lists in your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, frequently asked questions about the table of contents.
Depending on the length of your document, you can choose between a single-level, subdivided, or multi-level table of contents.
- A single-level table of contents only includes ‘level 1’ headings, or chapters. This is the simplest option, but it may be too broad for a long document like a dissertation.
- A subdivided table of contents includes chapters as well as ‘level 2’ headings, or sections. These show your reader what each chapter contains.
- A multi-level table of contents also further divides sections into ‘level 3’ headings. This option can get messy quickly, so proceed with caution. Remember your table of contents should not be longer than 2 pages. A multi-level table is often a good choice for a shorter document like a research paper.
Examples of level 1 headings are Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology, and Bibliography. Subsections of each of these would be level 2 headings, further describing the contents of each chapter or large section. Any further subsections would be level 3.
In these introductory sections, less is often more. As you decide which sections to include, narrow it down to only the most essential.
Including appendices and tables
You should include all appendices in your table of contents. Whether or not you include tables and figures depends largely on how many there are in your document.
If there are more than three figures and tables, you might consider listing them on a separate page. Otherwise, you can include each one in the table of contents.
- Theses and dissertations often have a separate list of figures and tables.
- Research papers generally don’t have a separate list of figures and tables.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
All level 1 and level 2 headings should be included in your table of contents, with level 3 headings used very sparingly.
The following things should never be included in a table of contents:
- Your acknowledgements page
- Your abstract
- The table of contents itself
The acknowledgements and abstract always precede the table of contents, so there’s no need to include them. This goes for any sections that precede the table of contents.
To automatically insert a table of contents in Microsoft Word, be sure to first apply the correct heading styles throughout the document, as shown below.
- Choose which headings are heading 1 and which are heading 2 (or 3!
- For example, if all level 1 headings should be Times New Roman, 12-point font, and bold, add this formatting to the first level 1 heading.
- Highlight the level 1 heading.
- Right-click the style that says ‘Heading 1’.
- Select ‘Update Heading 1 to Match Selection’.
- Allocate the formatting for each heading throughout your document by highlighting the heading in question and clicking the style you wish to apply.
Once that’s all set, follow these steps:
- Add a title to your table of contents. Be sure to check if your citation style or university has guidelines for this.
- Place your cursor where you would like your table of contents to go.
- In the ‘References’ section at the top, locate the Table of Contents group.
- Here, you can select which levels of headings you would like to include. You can also make manual adjustments to each level by clicking the Modify button.
- When you are ready to insert the table of contents, click ‘OK’ and it will be automatically generated, as shown below.
The key features of a table of contents are:
- Clear headings and subheadings
- Corresponding page numbers
Check with your educational institution to see if they have any specific formatting or design requirements.
Write yourself a reminder to update your table of contents as one of your final tasks before submitting your dissertation or paper. It’s normal for your text to shift a bit as you input your final edits, and it’s crucial that your page numbers correspond correctly.
It’s easy to update your page numbers automatically in Microsoft Word. Simply right-click the table of contents and select ‘Update Field’. You can choose either to update page numbers only or to update all information in your table of contents.
In addition to a table of contents, you might also want to include a list of figures and tables, a list of abbreviations and a glossary in your thesis or dissertation. You can use the following guides to do so:
- List of figures and tables
- List of abbreviations
It is less common to include these lists in a research paper.
All level 1 and 2 headings should be included in your table of contents . That means the titles of your chapters and the main sections within them.
The contents should also include all appendices and the lists of tables and figures, if applicable, as well as your reference list .
Do not include the acknowledgements or abstract in the table of contents.
To automatically insert a table of contents in Microsoft Word, follow these steps:
- Apply heading styles throughout the document.
- In the references section in the ribbon, locate the Table of Contents group.
- Click the arrow next to the Table of Contents icon and select Custom Table of Contents.
- Select which levels of headings you would like to include in the table of contents.
Make sure to update your table of contents if you move text or change headings. To update, simply right click and select Update Field.
The table of contents in a thesis or dissertation always goes between your abstract and your introduction.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, May 15). Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/contents-page/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation title page, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples.

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Thesis / dissertation formatting manual (2024).
- Filing Fees and Student Status
- Submission Process Overview
- Electronic Thesis Submission
- Paper Thesis Submission
- Formatting Overview
- Fonts/Typeface
- Pagination, Margins, Spacing
- Paper Thesis Formatting
- Preliminary Pages Overview
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
Table of Contents
- List of Figures (etc.)
- Acknowledgements
- Text and References Overview
- Figures and Illustrations
- Using Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Using Copyrighted Materials by Another Author
- Open Access and Embargoes
- Copyright and Creative Commons
- Ordering Print (Bound) Copies
- Tutorials and Assistance
- FAQ This link opens in a new window
The Table of Contents should follow these guidelines:
- All sections of the manuscript are listed in the Table of Contents except the Title Page, the Copyright Page, the Dedication Page, and the Table of Contents.
- You may list subsections within chapters
- Creative works are not exempt from the requirement to include a Table of Contents
Table of Contents Example
Here is an example of a Table of Contents page from the Template. Please note that your table of contents may be longer than one page.

- << Previous: Dedication Page
- Next: List of Figures (etc.) >>
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 2:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/gradmanual
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
Thesis and Dissertation Guide
- « Thesis & Dissertation Resources
- The Graduate School Home
- Introduction
Copyright Page
Dedication, acknowledgements, preface (optional), table of contents.
- List of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
List of Abbreviations
List of symbols.
- Non-Traditional Formats
- Font Type and Size
- Spacing and Indentation
- Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
- Formatting Previously Published Work
- Internet Distribution
- Open Access
- Registering Copyright
- Using Copyrighted Materials
- Use of Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Submission Steps
- Submission Checklist
- Sample Pages

I. Order and Components
Please see the sample thesis or dissertation pages throughout and at the end of this document for illustrations. The following order is required for components of your thesis or dissertation:
- Dedication, Acknowledgements, and Preface (each optional)
- Table of Contents, with page numbers
- List of Tables, List of Figures, or List of Illustrations, with titles and page numbers (if applicable)
- List of Abbreviations (if applicable)
- List of Symbols (if applicable)
- Introduction, if any
- Main body, with consistent subheadings as appropriate
- Appendices (if applicable)
- Endnotes (if applicable)
- References (see section on References for options)
Many of the components following the title and copyright pages have required headings and formatting guidelines, which are described in the following sections.
Please consult the Sample Pages to compare your document to the requirements. A Checklist is provided to assist you in ensuring your thesis or dissertation meets all formatting guidelines.
The title page of a thesis or dissertation must include the following information:

- The title of the thesis or dissertation in all capital letters and centered 2″ below the top of the page.
- Your name, centered 1″ below the title. Do not include titles, degrees, or identifiers. The name you use here does not need to exactly match the name on your university records, but we recommend considering how you will want your name to appear in professional publications in the future.
Notes on this statement:
- When indicating your degree in the second bracketed space, use the full degree name (i.e., Doctor of Philosophy, not Ph.D. or PHD; Master of Public Health, not M.P.H. or MPH; Master of Social Work, not M.S.W. or MSW).
- List your department, school, or curriculum rather than your subject area or specialty discipline in the third bracketed space. You may include your subject area or specialty discipline in parentheses (i.e., Department of Romance Languages (French); School of Pharmacy (Molecular Pharmaceutics); School of Education (School Psychology); or similar official area).
- If you wish to include both your department and school names, list the school at the end of the statement (i.e., Department of Pharmacology in the School of Medicine).
- A dissertation submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Department of Public Policy.
- A thesis submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in the School of Dentistry (Endodontics).
- A thesis submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in the Department of Nutrition in the Gillings School of Global Public Health.
- A dissertation submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the School of Education (Cultural Studies and Literacies).
- The words “Chapel Hill” must be centered 1″ below the statement.
- One single-spaced line below that, center the year in which your committee approves the completed thesis or dissertation. This need not be the year you graduate.
- Approximately 2/3 of the way across the page on the right-hand side of the page, 1″ below the year, include the phrase “Approved by:” (with colon) followed by each faculty member's name on subsequent double-spaced lines. Do not include titles such as Professor, Doctor, Dr., PhD, or any identifiers such as “chair” or “advisor” before or after any names. Line up the first letter of each name on the left under the “A” in the “Approved by:” line. If a name is too long to fit on one line, move this entire section of text slightly to the left so that formatting can be maintained.
- No signatures, signature lines, or page numbers should be included on the title page.
Include a copyright page with the following information single-spaced and centered 2″ above the bottom of the page:

© Year Author's Full Name (as it appears on the title page) ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
This page immediately follows the title page. It should be numbered with the lower case Roman numeral ii centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Inclusion of this page offers you, as the author, additional protection against copyright infringement as it eliminates any question of authorship and copyright ownership. You do not need to file for copyright in order to include this statement in your thesis or dissertation. However, filing for copyright can offer other protections.
See Section IV for more information on copyrighting your thesis or dissertation.
Include an abstract page following these guidelines:

- Include the heading “ABSTRACT” in all capital letters, and center it 2″ below the top of the page.
- One double-spaced line below “ABSTRACT”, center your name, followed by a colon and the title of the thesis or dissertation. Use as many lines as necessary. Be sure that your name and the title exactly match the name and title used on the Title page.
- One single-spaced line below the title, center the phrase “(Under the direction of [advisor's name])”. Include the phrase in parentheses. Include the first and last name(s) of your advisor or formal co-advisors. Do not include the name of other committee members. Use the advisor's name only; do not include any professional titles such as PhD, Professor, or Dr. or any identifiers such as “chair” or “advisor”.
- Skip one double-spaced line and begin the abstract. The text of your abstract must be double-spaced and aligned with the document's left margin with the exception of indenting new paragraphs. Do not center or right-justify the abstract.
- Abstracts cannot exceed 150 words for a thesis or 350 words for a dissertation.
- Number the abstract page with the lower case Roman numeral iii (and iv, if more than one page) centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Please write and proofread your abstract carefully. When possible, avoid including symbols or foreign words in your abstract, as they cannot be indexed or searched. Avoid mathematical formulas, diagrams, and other illustrative materials in the abstract. Offer a brief description of your thesis or dissertation and a concise summary of its conclusions. Be sure to describe the subject and focus of your work with clear details and avoid including lengthy explanations or opinions.
Your title and abstract will be used by search engines to help potential audiences locate your work, so clarity will help to draw the attention of your targeted readers.
You have an option to include a dedication, acknowledgements, or preface. If you choose to include any or all of these elements, give each its own page(s).

A dedication is a message from the author prefixed to a work in tribute to a person, group, or cause. Most dedications are short statements of tribute beginning with “To…” such as “To my family”.
Acknowledgements are the author's statement of gratitude to and recognition of the people and institutions that helped the author's research and writing.
A preface is a statement of the author's reasons for undertaking the work and other personal comments that are not directly germane to the materials presented in other sections of the thesis or dissertation. These reasons tend to be of a personal nature.
Any of the pages must be prepared following these guidelines:
- Do not place a heading on the dedication page.
- The text of short dedications must be centered and begin 2″ from the top of the page.
- Headings are required for the “ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS” and “PREFACE” pages. Headings must be in all capital letters and centered 2″ below the top of the page.
- The text of the acknowledgements and preface pages must begin one double-spaced line below the heading, be double-spaced, and be aligned with the document's left margin with the exception of indenting new paragraphs.
- Subsequent pages of text return to the 1″ top margin.
- The page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals (starting with the page number after the abstract) centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Include a table of contents following these guidelines:

- Include the heading “TABLE OF CONTENTS” in all capital letters, and center it 2″ below the top of the page.
- Include one double-spaced line between the heading and the first entry.
- The table of contents should not contain listings for the pages that precede it, but it must list all parts of the thesis or dissertation that follow it.
- If relevant, be sure to list all appendices and a references section in your table of contents. Include page numbers for these items but do not assign separate chapter numbers.
- Entries must align with the document's left margin or be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- Major subheadings within chapters must be included in the table of contents. The subheading(s) should be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- If an entry takes up more than one line, break up the entry about three-fourths of the way across the page and place the rest of the text on a second line, single-spacing the two lines.
- Include one double-spaced line between each entry.
- Page numbers listed in the table of contents must be located just inside the right page margin with leaders (lines of periods) filling out the space between the end of the entry and the page number. The last digit of each number must line up on the right margin.
- Information included in the table of contents must match the headings, major subheadings, and numbering used in the body of the thesis or dissertation.
- The Table of Contents page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Lists of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
If applicable, include a list of tables, list of figures, and/or list of illustrations following these guidelines:

- Include the heading(s) in all capital letters, centered 1″ below the top of the page.
- Each entry must include a number, title, and page number.
- Assign each table, figure, or illustration in your thesis or dissertation an Arabic numeral. You may number consecutively throughout the entire work (e.g., Figure 1, Figure 2, etc.), or you may assign a two-part Arabic numeral with the first number designating the chapter in which it appears, separated by a period, followed by a second number to indicate its consecutive placement in the chapter (e.g., Table 3.2 is the second table in Chapter Three).
- Numerals and titles must align with the document's left margin or be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- Page numbers must be located just inside the right page margin with leaders (lines of periods) filling out the space between the end of the entry and the page number. The last digit of each number must line up on the right margin.
- Numbers, titles, and page numbers must each match the corresponding numbers, titles, and page numbers appearing in the thesis or dissertation.
- All Lists of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
If you use abbreviations extensively in your thesis or dissertation, you must include a list of abbreviations and their corresponding definitions following these guidelines:

- Include the heading “LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS” in all capital letters, and center it 1″ below the top of the page.
- Arrange your abbreviations alphabetically.
- Abbreviations must align with the document's left margin or be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- If an entry takes up more than one line, single-space between the two lines.
- The List of Abbreviations page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
If you use symbols in your thesis or dissertation, you may combine them with your abbreviations, titling the section “LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS AND SYMBOLS”, or you may set up a separate list of symbols and their definitions by following the formatting instructions above for abbreviations. The heading you choose must be in all capital letters and centered 1″ below the top of the page.
Previous: Introduction
Next: Format
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
How to create a table of contents for a dissertation (apa), published by steve tippins on june 20, 2022 june 20, 2022.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 05:06 am
APA Dissertation Table of Contents Format Guidelines
- The table of contents should be double spaced with one-inch margins on all sides.
- It should be written in the same font and size as the rest of your dissertation.
- At the top of the page, write Table of Contents , centered and in bold.
- Although in the body of the paper you can use up to five levels of headings, up to three levels are usually provided in the Table of Contents. Including lower-level headings is optional.
- Indent each subheading five spaces.
- Write all text in title case. In title case, the first letter of major words is capitalized.
- Provide the page number where the main headings and subheadings begin, and provide dotted lines between the heading and the page number.
- Page numbers for the Dedication, Acknowledgements, and Preface should be in lower case Roman Numbers (i, v, x, l, c, d and m.). The page numbers for the rest of the text should be in Arabic numerals (1,2, 3, 4, etc.).
How to Create an APA Table of Contents Using Microsoft Word
Step 1. Instead of manually trying to write and format the table of contents, you can create a generated one using Microsoft Word. To do this, first go to the Home tab. This is where you will choose the styles for the table of contents.
Step 2. The top-level headings will be your chapter titles, so on the right side of the tab, apply the Heading 1 style.
Step 3. The second-level headings will be your subheadings, so apply the Heading 2 style. This will place your subheadings underneath your main headings.
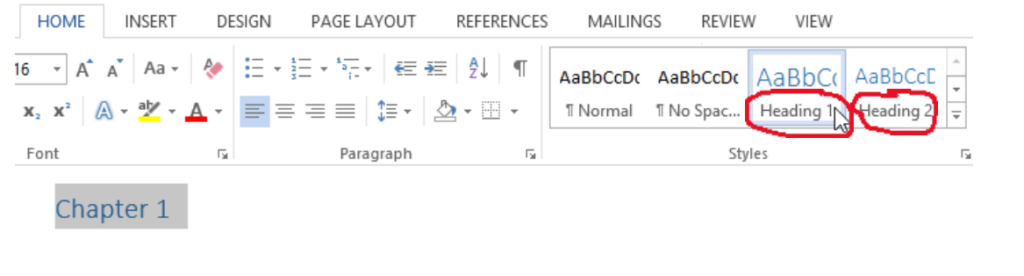
Step 4. You will now produce page links to your document. In the top ribbon, click on the References tab and select Table of Contents .
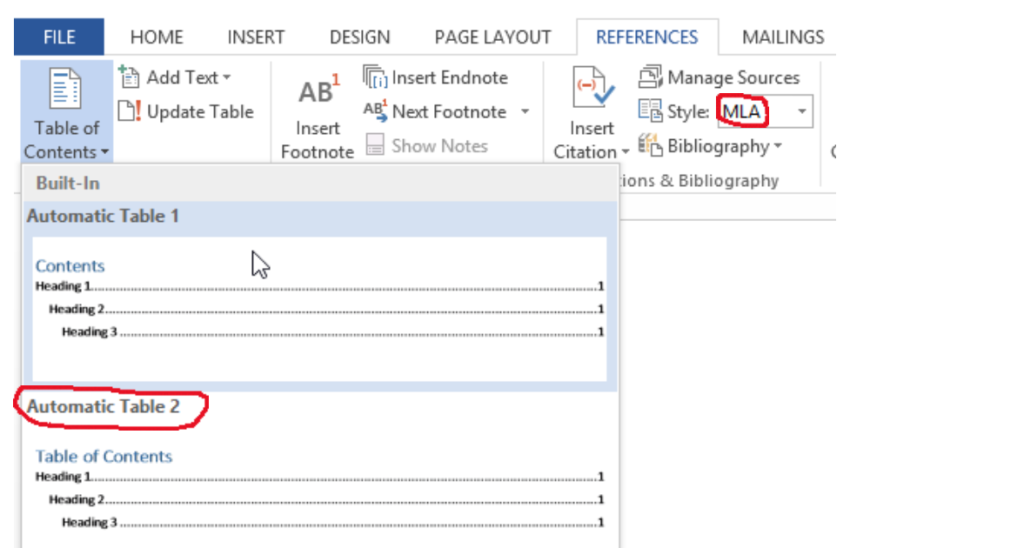
Step 5. If the style does not indicate APA, such as the one below, use the drop down arrow to select APA.
Step 6. Next, choose the number of levels that you want. In this case, you want to be able to have up to three levels, so choose Automatic Table 2 , which has the appropriate heading for a dissertation.
Step 7. Click ok , and you are all set. Microsoft word will automatically generate your dissertation’s table of contents as you write it.
List of Tables and Figures
Your list of tables and figures will be written at the end of the list of information in the body of your paper. You will create these lists the same way that you created the main table of contents.
However, the headings will be different.
Instead of the heading “Table of Contents,” the headings will be “List of Tables” and “List of Figures.” (An example is provided in the table of contents example below.)
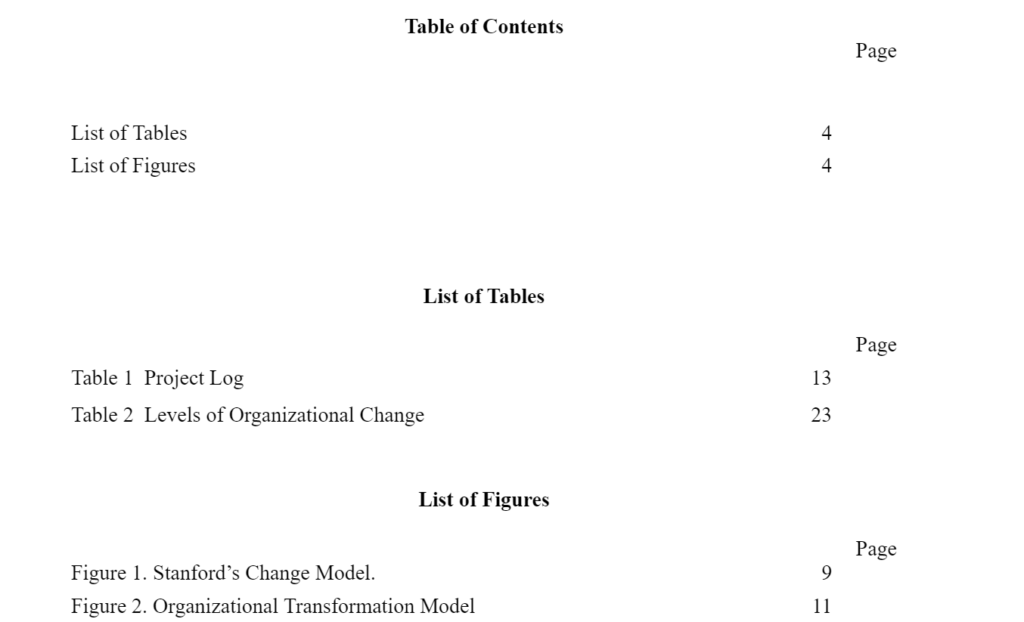
Example of Table of Contents
In the example below, there are three level headings. The list of tables and figures are provided at the bottom of the other contents. The sections in your table of contents may be different depending on your college’s requirements.
Updating the Table of Contents
As you continue working on your dissertation, you will need to update the page numbers because they may change.

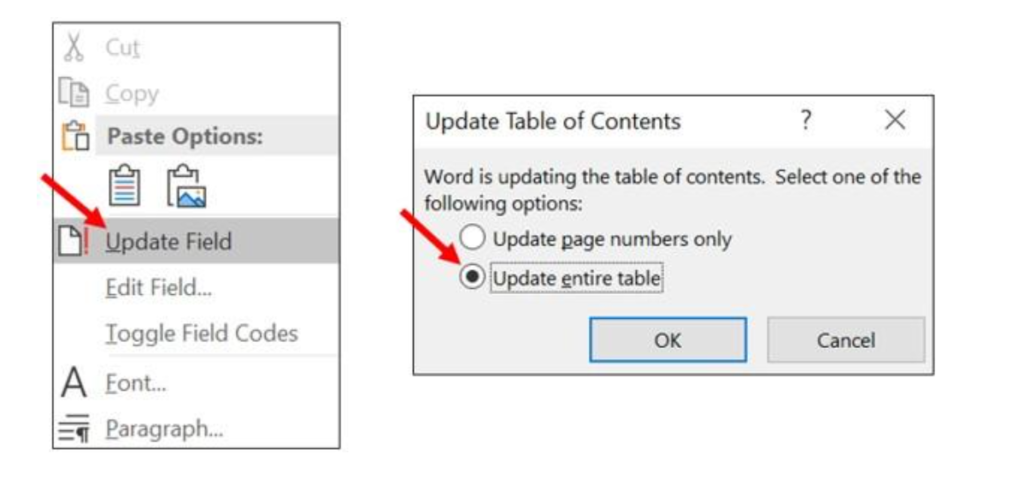
To update the page numbers, right-click on the table of contents in your document and select the Update field . Then, the Update Table of Contents box will appear.
You can choose to Update page numbers only or all the information in the table of contents by clicking on Update entire table .
Note: For more information, refer to the APA Manual 7 th edition , sections 2.2-2.27.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
Dissertation memes.
Sometimes you can’t dissertate anymore and you just need to meme. Don’t worry, I’ve got you. Here are some of my favorite dissertation memes that I’ve seen lately. My Favorite Dissertation Memes For when you Read more…

Surviving Post Dissertation Stress Disorder
The process of earning a doctorate can be long and stressful – and for some people, it can even be traumatic. This may be hard for those who haven’t been through a doctoral program to Read more…

PhD by Publication
PhD by publication, also known as “PhD by portfolio” or “PhD by published works,” is a relatively new route to completing your dissertation requirements for your doctoral degree. In the traditional dissertation route, you have Read more…
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Structure the Table of Contents for a Research Paper

4-minute read
- 16th July 2023
So you’ve made it to the important step of writing the table of contents for your paper. Congratulations on making it this far! Whether you’re writing a research paper or a dissertation , the table of contents not only provides the reader with guidance on where to find the sections of your paper, but it also signals that a quality piece of research is to follow. Here, we will provide detailed instructions on how to structure the table of contents for your research paper.
Steps to Create a Table of Contents
- Insert the table of contents after the title page.
Within the structure of your research paper , you should place the table of contents after the title page but before the introduction or the beginning of the content. If your research paper includes an abstract or an acknowledgements section , place the table of contents after it.
- List all the paper’s sections and subsections in chronological order.
Depending on the complexity of your paper, this list will include chapters (first-level headings), chapter sections (second-level headings), and perhaps subsections (third-level headings). If you have a chapter outline , it will come in handy during this step. You should include the bibliography and all appendices in your table of contents. If you have more than a few charts and figures (more often the case in a dissertation than in a research paper), you should add them to a separate list of charts and figures that immediately follows the table of contents. (Check out our FAQs below for additional guidance on items that should not be in your table of contents.)
- Paginate each section.
Label each section and subsection with the page number it begins on. Be sure to do a check after you’ve made your final edits to ensure that you don’t need to update the page numbers.
- Format your table of contents.
The way you format your table of contents will depend on the style guide you use for the rest of your paper. For example, there are table of contents formatting guidelines for Turabian/Chicago and MLA styles, and although the APA recommends checking with your instructor for formatting instructions (always a good rule of thumb), you can also create a table of contents for a research paper that follows APA style .
- Add hyperlinks if you like.
Depending on the word processing software you’re using, you may also be able to hyperlink the sections of your table of contents for easier navigation through your paper. (Instructions for this feature are available for both Microsoft Word and Google Docs .)
To summarize, the following steps will help you create a clear and concise table of contents to guide readers through your research paper:
1. Insert the table of contents after the title page.
2. List all the sections and subsections in chronological order.
3. Paginate each section.
4. Format the table of contents according to your style guide.
5. Add optional hyperlinks.
If you’d like help formatting and proofreading your research paper , check out some of our services. You can even submit a sample for free . Best of luck writing your research paper table of contents!
What is a table of contents?
A table of contents is a listing of each section of a document in chronological order, accompanied by the page number where the section begins. A table of contents gives the reader an overview of the contents of a document, as well as providing guidance on where to find each section.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
What should I include in my table of contents?
If your paper contains any of the following sections, they should be included in your table of contents:
● Chapters, chapter sections, and subsections
● Introduction
● Conclusion
● Appendices
● Bibliography
Although recommendations may differ among institutions, you generally should not include the following in your table of contents:
● Title page
● Abstract
● Acknowledgements
● Forward or preface
If you have several charts, figures, or tables, consider creating a separate list for them that will immediately follow the table of contents. Also, you don’t need to include the table of contents itself in your table of contents.
Is there more than one way to format a table of contents?
Yes! In addition to following any recommendations from your instructor or institution, you should follow the stipulations of your style guide .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

- Mardigian Library
- Subject Guides
Formatting Your Thesis or Dissertation with Microsoft Word
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Copyright Page
- Dedication, Acknowledgements, & Preface
- Headings and Subheadings
- Citations and Bibliography
- Page Numbers
- Tables and Figures
- Rotated (Landscape) Pages
- Lists of Tables and Figures
- List of Abbreviations
- Some Things to Watch For
- PDF with Embedded Fonts
Table of contents
If you created your headings and subheadings with styles, and numbered your pages as demonstrated in the Page Numbers tutorial, Microsoft Word can be used to automatically generate a table of contents. Automatic generation of the table of contents has 2 advantages:
- You don't have to manually type the table of contents. Since the entries in the Table of Content must match exactly the headings, subheadings, and page numbers in the thesis, manually creating a table of contents can lead to unintended errors.
- You don't have to go back and edit the table of contents if something moves from one page to another. A couple of clicks and Word will automatically update the table of contents for you.
Below is a tutorial demonstrating how to create the table of contents.
Note: You should create the table of contents last to avoid needing to update the table of contents too often.
- << Previous: Front Matter Lists
- Next: Lists of Tables and Figures >>
- Last Updated: Mar 21, 2024 2:35 PM
- URL: https://guides.umd.umich.edu/Word_for_Theses
Call us at 313-593-5559
Chat with us
Text us: 313-486-5399
Email us your question

- 4901 Evergreen Road Dearborn, MI 48128, USA
- Phone: 313-593-5000
- Maps & Directions
- M+Google Mail
- Emergency Information
- UM-Dearborn Connect
- Wolverine Access
- How it works

How to Create the Best Table of Contents for a Dissertation
Published by Owen Ingram at August 12th, 2021 , Revised On September 20, 2023
“A table of contents is an essential part of any article, book, proceedings, essay , and paper with plenty of information. It requires providing the reader’s guidance about the position of the content.”
When preparing a dissertation , you may cram as much information into it as appropriate. The dissertation may be an extremely well-written one with a lot of valuable information to offer. Still, all that information could become perplexing if the reader cannot easily find the information.
The length of dissertations usually varies from a few pages to a few hundred pages, making it very difficult to find information that you may be after.
Instead of skimming through every page of the dissertation, there is a need for a guideline that directs the reader to the correct section of the dissertation and, more importantly, the correct page in the section.
Also read: The List of Figures and Tables in the Dissertation .
What is the Table of Contents in the Dissertation?
The table of contents is the section of a dissertation that guides each section of the dissertation paper’s contents.
Depending on the detail level in a table of contents, the most useful headings are listed to provide the reader concerning which page the said information may be found.
The table of contents is essentially a list found at the beginning of a dissertation , which contains names of the chapters, section titles and/or very brief descriptions, and page numbers indicated for each.
This allows the reader to look at the table of contents to locate the information needed from the dissertation. Having an effective table of contents is key to providing a seamless reading experience to the reader.
Here in this article, we will uncover every piece of information you need to know to write the dissertation’s abstract.
This article helps the readers on how to create the best table of contents for the dissertation. An important thing to note is that this guide discusses creating a table of contents in Microsoft Word.
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across a variety of disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!


Styles for Dissertation Table of Contents
Making an effective table of contents starts with identifying headings and designating styles to those headings.
Using heading styles to format your headings can save a lot of time by automatically converting their formatting to the defined style and serves as a tool to identify the heading and its level, used later when creating a thesis table of contents .
Each heading style already has predefined sizes, fonts, colours, spacing, etc. but can be changed as per the user’s requirements. This also helps once all headings have been created and you intend to change the style of a certain type of heading.
All that is needed to change the style of a type of heading is automatically reflected on all headings that use the style.
Below is how the styles menu looks like;

To allocate a style to a heading, first select a heading and then click on one of the styles in the ‘Styles’ menu. Doing so converts the selected heading to the style that is selected in the Styles menu.
You can style a similar heading level in the same style by selecting each heading and then clicking on the style in the Style menu.
It is important to note that it greatly helps and saves time if you allocate styles systematically, i.e., you allocate the style as you write.
The styles are not limited to headings only but can be used for paragraphs and by selecting the whole paragraph and applying a style to it.
Changing Appearance of Pre-Defined Styles
To change the appearance of a style to one that suits you,
- You would need to right-click on one of the styles to open a drop-down menu.
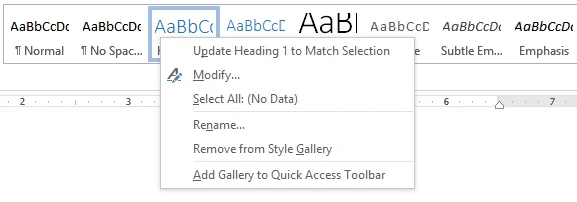
- Select ‘Modify’ from the menu. This would display a window with various formatting and appearance options. You can select the most appropriate ones and click ‘OK.’ The change that you made to the style reflects on all headings or paragraphs that use this style.
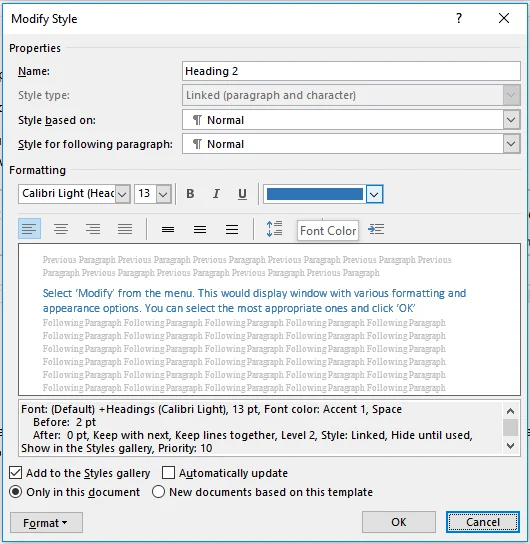
Further changes can be made to headings, but using styles is an important step for creating the table of contents for the thesis. Once this step is completed, you can continue to create a thesis table of contents.
Also Read: What is Appendix in Dissertation?
Things to Consider when Making APA Style Table of Contents
- The pages before the body of the dissertation, known as the ‘Prefatory Pages,’ should not have page numbers on them but should be numbered in the Roman Numerals instead as (i, ii, iii…).
- Table of Contents and the Abstract pages are not to contain any numbers.
- The remaining pages would carry the standard page numbers (1,2,3…).
- The section titles and page numbers in the dissertation table of contents should have dotted lines between them.
- All the Prefatory pages, Sections, Chapter Titles, Headings, Sub Headings, Reference Sections, and Appendices should be listed in the contents’ thesis table. If there are a limited number of Tables or Figures, they may be listed in the dissertation’s table contents.
- If there are many figures, tables, symbols, or abbreviations, a List of Tables, List of Figures , List of Symbols, and List of Abbreviations should be made for easy navigation. These lists, however, should not be listed in the thesis table of contents.
- The thesis/dissertation must be divided into sections even if it is not divided into chapters, with all sections being listed in the table of contents for the thesis.
Generating Dissertation Table of Contents
First, to generate the Table of Contents, start by entering a blank page after the pages you need the table of contents to follow.
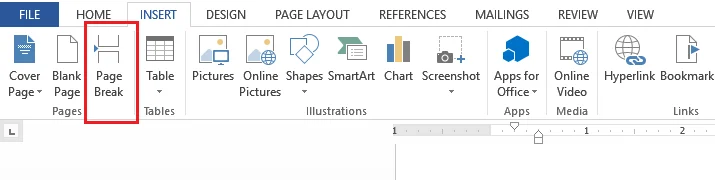
- To do so, click on the bottom of the page you want before the Table of Contents.
- Open the ‘Insert’ tab and select ‘Page Break’.
- This will create a page between the top and bottom sections of the Table of Contents area.
By the time you reach this section, you would have given each heading or sub-heading a dedicated style, distinguishing between different types of headings. Microsoft Word can automatically generate a Table of Contents, but the document, particularly the headings, needs to be formatted according to styles for this feature to work. You can assign different headings levels, different styles for Microsoft Word to recognize the level of heading.
How to Insert Table of Contents
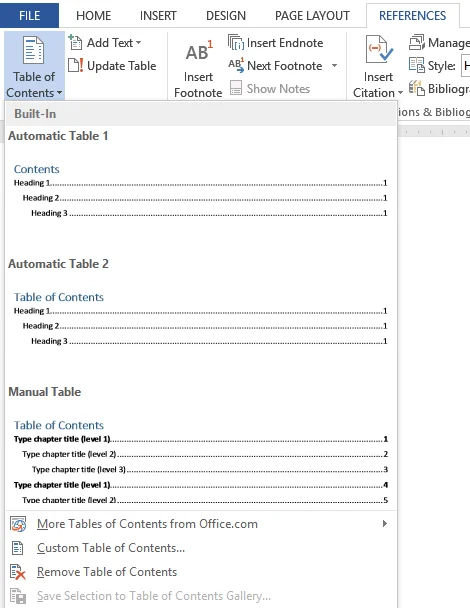
- Place the cursor where you want to place the Table of Contents on the page you added earlier.
- On the ‘References’ tab, open the Table of Contents group. This would open a list of different Table of Contents designs and a table of contents sample.
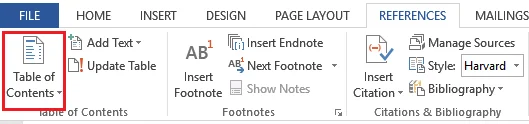
- You can select an option from the available Table of Contents or make a Custom Table of Contents. Although the available Table of Contents samples is appropriate, you may use a custom table of contents if it is more suitable to your needs. This allows you to modify different formatting options for the Table of Contents to satisfy your own
Updating the Table of Contents
As you proceed with editing your dissertation, the changes cause the page numbers and headings to vary. Often, people fail to incorporate those changes into the Table of Contents, which then effectively serves as an incorrect table and causes confusion.
It is thus important to update the changes into the table of contents as the final step once you have made all the necessary changes in the dissertation and are ready to print it.
These changes may alter the length of the thesis table of contents , which may also cause the dissertation’s formatting to be altered a little, so it is best to reformat it after updating the table of contents.
To update the table of contents,
- Select ‘Update Table’ in the References tab.
- This would open a dialogue box. Select ‘Update Entire Table’ to ensure that all changes are reflected in the contents table and not just the page numbers. This would display all changes and additions you have made to the document (Anon., 2017).
Using this guide, you should understand how to create the best table of contents for the dissertation. The use of a Table of Contents, while being important for most written work, is even more critical for dissertations, especially when the proper methodology of creating the table of contents is followed.
This includes the guidelines that must be considered to correctly format the table of contents so that it may be shaped so that it follows the norms and is effective at helping the reader navigate through the content of the dissertation.
The use of Microsoft Word’s Table of Contents generation feature has greatly helped people worldwide create, edit, and update the table of contents of their dissertations with ease.
Here in this article, we will uncover every piece of information you need to know how to write the dissertation’s abstract .
Are you in need of help with dissertation writing? At ResearchProspect, we have hundreds of Master’s and PhD qualified writers for all academic subjects, so you can get help with any aspect of your dissertation project. You can place your order for a proposal , full dissertation paper , or individual chapters .
Is it essential to add a table of content to the dissertation?
Yes, it is important to add a table of content in a dissertation .
How to make an effective table of contents for the dissertation?
Using heading styles to format your headings can save a lot of time by automatically converting their formatting to the defined style and serves as a tool to identify the heading and its level, used later when creating a thesis table of contents.
How do I update the table of contents?
You may also like.
Your dissertation introduction chapter provides detailed information on the research problem, significance of research, and research aim & objectives.
How to Structure a Dissertation or Thesis Need interesting and manageable Finance and Accounting dissertation topics? Here are the trending Media dissertation titles so you can choose one most suitable to your needs.
Finding it difficult to maintain a good relationship with your supervisor? Here are some tips on ‘How to Deal with an Unhelpful Dissertation Supervisor’.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- KU Libraries
- Subject & Course Guides
- KU Thesis and Dissertation Formatting
- Table of Contents
KU Thesis and Dissertation Formatting: Table of Contents
- Formatting Specifics
- Title and Acceptance Pages
- Fonts and Spacing
- Page Numbering
- List of Figures
- Rotating Charts or Tables
- Working with Footnotes
- Converting to PDF
- Embedding Fonts
- Completed KU Dissertations & Theses
- About: Survey of Earned Doctorates
- Copyright and ETD Release Form
- Resources for KUMC Students
- Thesis/Dissertation Filenames
- LaTeX/BibTeX Support
Office of Graduate Studies Thesis and Dissertation Formatting Guidelines
These rules are taken from the KU Office of Graduate Studies Thesis or Dissertation Formatting Guidelines. To see the full thesis or dissertation formatting requirements, visit https://graduate.ku.edu/submitting
Creating an Automated Table of Contents
Located in the Home tab, Word’s Style Gallery makes it easy to set consistent, one-click formatting for headings throughout your document. It is these style settings that Word uses to create an automatic table of contents. Using an automatic table of contents will save you the huge headache of dealing with dot leaders, spacing, and having to completely re-type your table of contents if the order of your pages changes even a little. Plus, styles are easy to use! Step-by-step how-to instructions are included below for setting heading styles and then inserting a table of contents in Word 2010, Word 2013 or Word 2011 for Mac.
- Printed Instructions (TOC Word 2010)
- Printed Instructions (TOC Word 2013)
- Printed Instructions (TOC Word 2011 for Mac)
- Printed Instructions (TOC Word 2016 Mac)
- Printed Instructions (TOC Word 2016 PC)
- Creating a Manual-Entry Table of Contents
Working with Outline Style (Numbered) Headings
Numbered headings can be very tricky and many citation styles do not require their use. If you are working with a style the does require it, however, Shauna Kelly's blog has some great help .
Subject Guide

- << Previous: Page Numbering
- Next: List of Figures >>
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024 9:48 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.ku.edu/etd
- University of Michigan Library
- Research Guides
Microsoft Word for Dissertations
- Table of Contents
- Introduction, Template, & Resources
- Formatting for All Readers
- Applying a Style
- Modifying a Style
- Setting up a Heading 1 Example
- Images, Charts, Other Objects
- Footnotes, Endnotes, & Citations
- Cross-References
- Appendix Figures & Tables
- List of Figures/Tables
- Chapter and Section Numbering
- Page Numbers
- Landscape Pages
- Combining Chapter Files
- Commenting and Reviewing
- The Two-inch Top Margin
- Troubleshooting
- Finalizing Without Styles
- Preparing Your Final Document
Automatic Table of Contents
An automatic Table of Contents relies on Styles to keep track of page numbers and section titles for you automatically. Microsoft Word can scan your document and find everything in the Heading 1 style and put that on the first level of your table of contents, put any Heading 2’s on the second level of your table of contents, and so on.
If you want an automatic table of contents you need to apply the Heading 1 style to all of your chapter titles and front matter headings (like “Dedication” and “Acknowledgements”). All section headings within your chapters should use the Heading 2 style. All sub-section headings should use Heading 3 , etc....
If you have used Heading styles in your document, creating an automatic table of contents is easy.
- Place your cursor where you want your table of contents to be.
- On the References Ribbon, in the Table of Contents Group , click on the arrow next to the Table of Contents icon, and select Custom Table of Contents .
- We suggest that you set each level (Chapters, sections, sub-sections, aka TOC 1, TOC 2, TOC 3) to be single-spaced, with 12 points of space afterwards. This makes each item in your ToC clump together if they're long enough to wrap to a second line, with the equivalent of a double space between each item, and makes the ToC easier to read and understand than if every line were double-spaced. See the video below for details.
- If you want to change which headings appear in your Table of Contents, you can do so by changing the number in the Show levels: field. Select "1" to just include the major sections (Acknowledgements, List of Figures, Chapters, etc...). Select "4" to include Chapters, sections, sub-sections, and sub-sub-sections.
- Click OK to insert your table of contents.
The table of contents is a snapshot of the headings and page numbers in your document, and does not automatically update itself as you make changes. At any time, you can update it by right-clicking on it and selecting Update field . Notice that once the table of contents is in your document, it will turn gray if you click on it. This just reminds you that it is a special field managed by Word, and is getting information from somewhere else.
Modifying the format of your Table of Contents
The video below shows how to make your Table of Contents a little easier to read by formatting the spacing between items in your Table of Contents. You may recognize the "Modify Style" window that appears, which can serve as a reminder that you can use this window to modify more than just paragraph settings. You can modify the indent distance, or font, or tab settings for your ToC, just the same as you may have modified it for Styles.

By default, the Table of Contents tool creates the ToC by pulling in Headings 1 through 3. If you'd like to modify that -- to only show H1's, or to show Headings 1 through 4 -- then go to the References tab and select Custom Table of Contents . In the window that appears, set Show Levels to "1" to only show Heading 1's in the Table of Contents, or set it to "4" to show Headings 1 through 4.
Bonus tip for updating fields like the Table of Contents
You'll quickly realize that all of the automatic Lists and Tables need to be updated occasionally to reflect any changes you've made elsewhere in the document -- they do not dynamically update by themselves. Normally, this means going to each field, right-clicking on it and selecting "Update Field".
Alternatively, to update all fields throughout your document (Figure/Table numbers & Lists, cross-references, Table of Contents, etc...), just select "Print". This will cause Word to update everything in anticipation of printing. Once the print preview window appears, just cancel.
Florida State University
FSU | The Graduate School
Main navigation Pulldown
The graduate school.
- Current Students
- Thesis, Treatise, and Dissertation
Templates & Formatting Assistance
Formatting templates.
Manuscript Clearance provides templates for both Word and LaTeX into which students can type their text directly and that are formatted according to FSU requirements. The main elements in the three templates are the same, but the layout of the Table of Contents is different. You can select a Table of Contents that lists only the main section headings (which is all The Graduate School requires) or one that also lists subheadings, either numbered or unnumbered.
Please note that these templates are created with general formatting requirements. Specific items such as chapter titles, the number of chapters you include and the content of those chapters is not dictated by The Graduate School.
Word Templates for FSU's ETDs
Latex template for fsu's etds.
This template is for use by students who prefer to use LaTeX for their manuscript. Manuscript Clearance staff are unable to assist with issues arising in LaTeX, but students are encouraged to review the User Guide and other materials in the Help section of the following website.
Click here to visit the LaTeX ETD template website.
Formatting assistance.
Manuscript Clearance also provides a number of step-by-step instructions to assist students with common formatting issues. Please review the topics in the list below for assistance.
Mon - Sat 9:00am - 12:00am
- Get a quote
Table of Contents for Thesis Proposal
The table of contents for thesis proposal on the page that is dedicated to the chapters and their respective page numbers. The headings and subheadings are also mentioned on the page. The formatting for this page should be consistent and clear.
The table of contents is added after the introduction page and before the abstract. The table of contents should be of two pages, not more than that.
If you are planning on writing your thesis, do not skip this page and read further for the format and pattern of the table of contents.
In this post, you will learn:
What should you include in the table of contents?
Appendices and tables, the do’s and don’t’s, examples of the table of contents, a checklist for the table of contents.
Now that we have covered what the table of content is, you need to know what is included within the two pages of the list. If you feel like any portion of your dissertation is troubling you, you should get dissertation writing help by all means.
The table of content is an organized list that provides basic knowledge of what your thesis contains. The names of the chapters along with subheadings are added on the left side of the page. Whereas the number of the pages is written on the right side.
The table of contents is created for the sole purpose of locating a chapter and subheading by the reader. One should check with their universities and colleges if they have a specific format for the table of content.
Let us look into the general format of a table of content. The chapters (first level) and their second-level headings should be added to this. Remember, your motive behind creating this page is to make it easy for the reader to locate your chapters.
For example: Level one heading – Chapter 2. Literature Review Level two heading -2.1 Research Gap
The table of contents must include your appendices and table of figures. If you have more than three and four figures and tables, then they deserve their chapter. But if you dint get a lot of results from research, then those tables and figures can be shared in the list of contents.
Now the question arises, what does the appendices chapter include?
- The original interviews, surveys, and questionnaires that were used to collect data for the research
- Not more than two figures and tables should be added to the table of content.
- If did not use a lot of abbreviations then you should share them in the table of content. But if you have tons of abbreviations and technical terms, then they should be listed in their chapters.
What are the Do’s and Don’t’s of the table of contents
The table of content may seem like a simple two-page table but in actuality can badly affect your thesis if not composed correctly. Due to this reason, one should be extra careful while numbering the pages and creating the different level headings.
Example of the table of contents
The page numbers assigned to the chapters in the table of contents should be the same as the number assigned at the beginning of each chapter. The example below demonstrates just that:
Checklist for the table of contents
To achieve perfection in the list of contents, you need a set of rules to follow. A starter’s checklist will guide you to do just that. Below is a checklist that will make sure your table of content is up to mark. And no matter what academic level of thesis you compose, this checklist can be used for all of them:
Collect the relevant information about the format according to your university and referencing style.
Start with the list of tables and bold the main chapters., all the titles of the chapter should be level one heading and the subheading should be level two., the numbers of the chapters and the page numbers given in the table should tally., all pages should be numbered after the chapters are written., final words:.
To create the table of contents for your thesis, use Microsoft word and customized it according to your thesis requirement. Apply the headings according to your style of preference. You can easily make the changes to the table itself at point of time with the help of the Microsoft Word table of contents.
Power Point Google Slides
It is Time to Boost Your Grades with Professional Help
Improved scores.
Get Better Grades in Every Subject
Timely Delivery
Submit Your Assignment on Time
Experienced Writers
Trust Academic Experts Based in UK
Safety is Assured
Your Privacy is Our Topmost Concern
Hire a Writer
Subject* Accounting Accounts Law Advertising Aeronautical Engineering Agency Law Agriculture Animal Management Anthropology Archaeology Architecture Art Astrophysics Biochemistry Biology Biotechnology Business Chemical Engineering Chemistry Child Care Civil Engineering Civil Litigation Law Classics Commercial Law Commercial Property Law Communications Company Law / Business Law Comparative Law Computer Engineering Computing Constitutional / Administrative Law Consumer Law Contract Law Criminal Law Criminal Litigation Criminology Crisis Management Cultural Studies Design Drama E-Commerce Econometrics Economics Education Electrical Engineering Electronic Engineering Employment Law Engineering English Language Environmental Studies Equity Law Estate Management European Law European Studies Events Management Family Law Fashion Film Studies Finance Finance Law Forensic Science General Law Genetics Geography Geology History Hospitality Housing Housing Law HRM Human Rights I.T. Immigration Law Information Systems Intellectual Property Law International Development International Law International Relations International Studies Journalism Jurisprudence Land Law / Property Law Landlord and Tenant Law Languages Law Leisure Management Linguistics Literature Management Maritime Law Marketing Materials Science Mathematics Mechanical Engineering Mechanics Media Media and Information Technology Law Medicine Mental Health Law Midwifery Military Multimedia Negligence Law Neuroscience Nursing Nutrition Operations Management Oriental Studies Pathology Pharmacology Philosophy Physical Education Physical_Sciences Physics Planning / Environmental Law Plant Science Politics Product Design Professional Conduct Law Project Management Property Psychology Public Law Quantitative Methods Religion Restitution Law Risk Management Sciences Shipping Policy Social Work Sociology Software Engineering Sports Statistics Strategic Management Succession Law Surveying Tax Law Teaching Television Theatre Theology Tort Law Tourism Trusts Law Urban Studies Veterinary Wills / Probate Law Zoology Bio-informatics Biomedical Sciences Computer Forensics Data Mining Dentistry Engineering Business Management Environmental Engineering Environmental Management Environmental Science Epidemiology Geophysics Health and Safety Management Occupational Psychology Physiotherapy Public Health Real Estate Research Methods Security Studies Shipping and Trade Finance Sports and Exercise Science Supply Chain Management Sustainable Energy Telecommunication Engineering Toxicology Public Relations Other
Paper Type* Dissertation Dissertation Topics Dissertation-Abstract Dissertation Proposal Dissertation- Analysis Chapter Dissertation- Conclusion Chapter Dissertation- Introduction Chapter Dissertation- Literature Review Chapter Dissertation- Methodology Chapter Dissertation Editing and Proof Reading Essay Admission Essay Scholarship Essay Case Study Annotated Bibliography Assignment Book Report/Review Case Analysis Course Work Information and Communication/ Computer Technology Reaction Paper Research Paper Research Proposal Statistics Project Term Paper Thesis Thesis Proposal Laboratory Report Movie Review Multiple Choice Questions Power Point Presentation Article Speech Other
Education Under Graduate Graduate Masters PhD
How to Craft Your Ideal Thesis Research Topic
.webp)
Table of contents

Catherine Miller
Writing your undergraduate thesis is probably one of the most interesting parts of studying, especially because you get to choose your area of study. But as both a student and a teacher who’s helped countless students develop their research topics, I know this freedom can be just as intimidating as it is liberating.
Fortunately, there’a a step-by-step process you can follow that will help make the whole process a lot easier. In this article, I’ll show you how to choose a unique, specific thesis topic that’s true to your passions and interests, while making a contribution to your field.
.webp)
Choose a topic that you’re interested in
First things first: double-check with your teachers or supervisor if there are any constraints on your research topic. Once your parameters are clear, it’s time to identify what lights you up — after all, you’re going to be spending a lot of time thinking about it.
Within your field of study, you probably already have some topics that have grabbed your attention more than others. This can be a great place to start. Additionally, consider using the rest of your academic and extra-curricular interests as a source of ideas. At this stage, you only need a broad topic before you narrow it down to a specific question.
If you’re feeling stuck, here are some things to try:
- Look back through old course notes to remind yourself of topics you previously covered. Do any of these inspire you?
- Talk to potential supervisors about your ideas, as they can point you toward areas you might not have considered.
- Think about the things you enjoy in everyday life — whether that’s cycling, cinema, cooking, or fashion — then consider if there are any overlaps with your field of study.
- Imagine you have been asked to give a presentation or record a podcast in the next three days. What topics would you feel confident discussing?
- Watch a selection of existing lectures or explainer videos, or listen to podcasts by experts in your field. Note which topics you feel curious to explore further.
- Discuss your field of study with teachers friends and family, some with existing knowledge and some without. Which aspects do you enjoy talking about?
By doing all this, you might uncover some unusual and exciting avenues for research. For example, when writing my Master’s dissertation, I decided to combine my field of study (English teaching methodology) with one of my passions outside work (creative writing). In my undergraduate course, a friend drew on her lived experience of disability to look into the literary portrayal of disability in the ancient world.
Do your research
Once you’ve chosen your topic of interest, it’s time to dive into research. This is a really important part of this early process because it allows you to:
- See what other people have written about the topic — you don’t want to cover the same old ground as everyone else.
- Gain perspective on the big questions surrounding the topic.
- Go deeper into the parts that interest you to help you decide where to focus.
- Start building your bibliography and a bank of interesting quotations.
A great way to start is to visit your library for an introductory book. For example, the “A Very Short Introduction” series from the Oxford University Press provides overviews of a range of themes. Similar types of overviews may have the title “ A Companion to [Subject]” or “[Subject] A Student Companion”. Ask your librarian or teacher if you’re not sure where to begin.
Your introductory volume can spark ideas for further research, and the bibliography can give you some pointers about where to go next. You can also use keywords to research online via academic sites like JStor or Google Scholar. Check which subscriptions are available via your institution.
At this stage, you may not wish to read every single paper you come across in full — this could take a very long time and not everything will be relevant. Summarizing software like Wordtune could be very useful here.
Just upload a PDF or link to an online article using Wordtune, and it will produce a summary of the whole paper with a list of key points. This helps you to quickly sift through papers to grasp their central ideas and identify which ones to read in full.

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
You can also use Wordtune for semantic search. In this case, the tool focuses its summary around your chosen search term, making it even easier to get what you need from the paper.

As you go, make sure you keep organized notes of what you’ve read, including the author and publication information and the page number of any citations you want to use.
Some people are happy to do this process with pen and paper, but if you prefer a digital method, there are several software options, including Zotero , EndNote , and Mendeley . Your institution may have an existing subscription so check before you sign up.
Narrowing down your thesis research topic
Now you’ve read around the topic, it’s time to narrow down your ideas so you can craft your final question. For example, when it came to my undergraduate thesis, I knew I wanted to write about Ancient Greek religion and I was interested in the topic of goddesses. So, I:
- Did some wide reading around the topic of goddesses
- Learned that the goddess Hera was not as well researched as others and that there were some fascinating aspects I wanted to explore
- Decided (with my supervisor’s support) to focus on her temples in the Argive region of Greece

As part of this process, it can be helpful to consider the “5 Ws”: why, what, who, when, and where, as you move from the bigger picture to something more precise.
Why did you choose this research topic?
Come back to the reasons you originally chose your theme. What grabbed you? Why is this topic important to you — or to the wider world? In my example, I knew I wanted to write about goddesses because, as a woman, I was interested in how a society in which female lives were often highly controlled dealt with having powerful female deities. My research highlighted Hera as one of the most powerful goddesses, tying into my key interest.
What are some of the big questions about your topic?
During your research, you’ll probably run into the same themes time and time again. Some of the questions that arise may not have been answered yet or might benefit from a fresh look.
Equally, there may be questions that haven’t yet been asked, especially if you are approaching the topic from a modern perspective or combining research that hasn’t been considered before. This might include taking a post-colonial, feminist, or queer approach to older texts or bringing in research using new scientific methods.
In my example, I knew there were still controversies about why so many temples to the goddess Hera were built in a certain region, and was keen to explore these further.
Who is the research topic relevant to?
Considering the “who” might help you open up new avenues. Is there a particular audience you want to reach? What might they be interested in? Is this a new audience for this field? Are there people out there who might be affected by the outcome of this research — for example, people with a particular medical condition — who might be able to use your conclusions?
Which period will you focus on?
Depending on the nature of your field, you might be able to choose a timeframe, which can help narrow the topic down. For example, you might focus on historical events that took place over a handful of years, look at the impact of a work of literature at a certain point after its publication, or review scientific progress over the last five years.
With my thesis, I decided to focus on the time when the temples were built rather than considering the hundreds of years for which they have existed, which would have taken me far too long.
Where does your topic relate to?
Place can be another means of narrowing down the topic. For example, consider the impact of your topic on a particular neighborhood, city, or country, rather than trying to process a global question.
In my example, I chose to focus my research on one area of Greece, where there were lots of temples to Hera. This meant skipping other important locations, but including these would have made the thesis too wide-ranging.
Create an outline and get feedback
Once you have an idea of what you are going to write about, create an outline or summary and get feedback from your teacher(s). It’s okay if you don’t know exactly how you’re going to answer your thesis question yet, but based on your research you should have a rough plan of the key points you want to cover. So, for me, the outline was as follows:
- Context: who was the goddess Hera?
- Overview of her sanctuaries in the Argive region
- Their initial development
- Political and cultural influences
- The importance of the mythical past
In the final thesis, I took a strong view on why the goddess was so important in this region, but it took more research, writing, and discussion with my supervisor to pin down my argument.
To choose a thesis research topic, find something you’re passionate about, research widely to get the big picture, and then move to a more focused view. Bringing a fresh perspective to a popular theme, finding an underserved audience who could benefit from your research, or answering a controversial question can make your thesis stand out from the crowd.
For tips on how to start writing your thesis, don’t miss our advice on writing a great research abstract and a stellar literature review . And don’t forget that Wordtune can also support you with proofreading, making it even easier to submit a polished thesis.
How do you come up with a research topic for a thesis?
To help you find a thesis topic, speak to your professor, look through your old course notes, think about what you already enjoy in everyday life, talk about your field of study with friends and family, and research podcasts and videos to find a topic that is interesting for you. It’s a good idea to refine your topic so that it’s not too general or broad.
Do you choose your own thesis topic?
Yes, you usually choose your own thesis topic. You can get help from your professor(s), friends, and family to figure out which research topic is interesting to you.
Share This Article:

How to Craft an Engaging Elevator Pitch that Gets Results
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
.webp)
7 Common Errors in Writing + How to Fix Them (With Examples)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
UT Electronic Theses and Dissertations
Permanent URI for this community https://hdl.handle.net/2152/4
This collection contains University of Texas at Austin electronic theses and dissertations (ETDs). The collection includes ETDs primarily from 2001 to the present. Some pre-2001 theses and dissertations have been digitized and added to this collection, but those are uncommon. The library catalog is the most comprehensive list of UT Austin theses and dissertations.
Since 2010, the Office of Graduate Studies at UT Austin has required all theses and dissertations to be made publicly available in Texas ScholarWorks; however, authors are able to request an embargo of up to seven years. Embargoed ETDs will not show up in this collection. Most of the ETDs in this collection are freely accessible to all users, but some pre-2010 works require a current UT EID at point of use. Please see the FAQs for more information. If you have a question about the availability of a specific ETD, please contact [email protected].
Some items in this collection may contain offensive images or text. The University of Texas Libraries is committed to maintaining an accurate and authentic scholarly and historic record. An authentic record is essential for understanding our past and informing the present. In order to preserve the authenticity of the historical record we will not honor requests to redact content, correct errors, or otherwise remove content, except in cases where there are legal concerns (e.g. potential copyright infringement, inclusion of HIPAA/FERPA protected information or Social Security Numbers) or evidence of a clear and imminent threat to personal safety or well-being.
This policy is in keeping with the American Library Association code of ethics to resist efforts to censor library resources, and the Society of American Archivists code of ethics that states "archivists may not willfully alter, manipulate, or destroy data or records to conceal facts or distort evidence." Please see UT Libraries' Statement on Harmful Language and Content for more information.
Authors of these ETDs have retained their copyright while granting the University of Texas Libraries the non-exclusive right to reproduce and distribute their works.
Collections in this Community
- UT Electronic Theses and Dissertations 30995

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples. Published on May 15, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on July 18, 2023. The table of contents is where you list the chapters and major sections of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, alongside their page numbers.A clear and well-formatted table of contents is essential, as it demonstrates to your reader that a quality ...
The table of contents is where you list the chapters and major sections of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, alongside their page numbers. A clear and well-formatted table of contents is essential, as it demonstrates to your reader that a quality paper will follow.
Thesis / Dissertation Formatting Manual (2024) Email this link: Home; Filing Fees and Student Status; Submitting ... Here is an example of a Table of Contents page from the Template. Please note that your table of contents may be longer than one page. << Previous: Dedication Page; Next: ...
Information included in the table of contents must match the headings, major subheadings, and numbering used in the body of the thesis or dissertation. The Table of Contents page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge. Lists of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
This is where you will choose the styles for the table of contents. Step 2. The top-level headings will be your chapter titles, so on the right side of the tab, apply the Heading 1 style. Step 3. The second-level headings will be your subheadings, so apply the Heading 2 style. This will place your subheadings underneath your main headings. Step 4.
Insert the table of contents after the title page. 2. List all the sections and subsections in chronological order. 3. Paginate each section. 4. Format the table of contents according to your style guide. 5. Add optional hyperlinks.
Automatic generation of the table of contents has 2 advantages: You don't have to manually type the table of contents. Since the entries in the Table of Content must match exactly the headings, subheadings, and page numbers in the thesis, manually creating a table of contents can lead to unintended errors. You don't have to go back and edit the ...
In this detailed video tutorial, we'll walk you through the process of creating a professional Table of Contents (TOC) for your thesis or dissertation using ...
Generating Dissertation Table of Contents. First, to generate the Table of Contents, start by entering a blank page after the pages you need the table of contents to follow. To do so, click on the bottom of the page you want before the Table of Contents. Open the 'Insert' tab and select 'Page Break'.
Information for University of Kansas graduate students on required content order, page numbering, creating headings, formatting table of contents, adding captions, creating a table of figures and embedding fonts for theses and dissertations. How to create heading styles and build an automatic table of contents.
Now you need to format your headings to be included in the table of contents. Select the heading you want to include in your table of contents. Click on the "Styles" option in the top menu bar. Choose the appropriate heading style from the drop-down menu that appears. You can choose from "Heading 1," "Heading 2," "Heading 3," etc.
In Research, A Table of Contents (TOC) is a structured list of the main sections or chapters of a research paper, Thesis and Dissertation. It provides readers with an overview of the organization and structure of the document, allowing them to quickly locate specific information and navigate through the document.
An automatic Table of Contents relies on Styles to keep track of page numbers and section titles for you automatically. Microsoft Word can scan your document and find everything in the Heading 1 style and put that on the first level of your table of contents, put any Heading 2's on the second level of your table of contents, and so on.. If you want an automatic table of contents you need to ...
The table of contents should come after the title page. Appendix sections: Each appendix should have its own section with a clear and concise title that describes the contents of the appendix. Each section should be numbered with Arabic numerals (e.g., Appendix 1, Appendix 2, etc.). The sections should be listed in the table of contents.
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
A table of contents example will help you structure your own thesis, but remember to make it relevant to your discipline. Table of contents example structures can be created for different disciplines, such as social sciences, humanities and engineering. The type and length of a table of contents example will depend on the manuscript.
Formatting Templates Manuscript Clearance provides templates for both Word and LaTeX into which students can type their text directly and that are formatted according to FSU requirements. The main elements in the three templates are the same, but the layout of the Table of Contents is different. You can select a Table of Contents that lists only the main section headings (which is all The ...
The table of content is an organized list that provides basic knowledge of what your thesis contains. The names of the chapters along with subheadings are added on the left side of the page. Whereas the number of the pages is written on the right side. The table of contents is created for the sole purpose of locating a chapter and subheading by ...
A Table of Contents (TOC) is an organized list of all the parts of a document or book organized in the order in which the parts appear. The TOC usually contains the titles, chapters, figures, and major sections of a document clearly labeled by their page number. It should be added last or updated after completing the whole document or book to ...
To choose a thesis research topic, find something you're passionate about, research widely to get the big picture, and then move to a more focused view. Bringing a fresh perspective to a popular theme, finding an underserved audience who could benefit from your research, or answering a controversial question can make your thesis stand out ...
Students who are completing a dissertation, thesis, or report are invited to join the Graduate School to learn about the resources available to them to assist in scheduling their defense, formatting their documents, and submitting their documents. In one afternoon, you can learn everything you need to be successful and complete your degree in a . . .
Table of Contents. 6 Ways to Close Your Presentation With Style; Tools to Help You Create a Presentation; Key Phrases to End a Presentation; ... Visme is a robust visual content creation tool and presentation software that transforms how users create and deliver captivating presentations. With a wide range of customizable templates, an ...
This collection contains University of Texas at Austin electronic theses and dissertations (ETDs). The collection includes ETDs primarily from 2001 to the present. Some pre-2001 theses and dissertations have been digitized and added to this collection, but those are uncommon. The library catalog is the most comprehensive list of UT Austin ...