

How to Implement Hypothesis-Driven Development
Remember back to the time when we were in high school science class. Our teachers had a framework for helping us learn – an experimental approach based on the best available evidence at hand. We were asked to make observations about the world around us, then attempt to form an explanation or hypothesis to explain what we had observed. We then tested this hypothesis by predicting an outcome based on our theory that would be achieved in a controlled experiment – if the outcome was achieved, we had proven our theory to be correct.
We could then apply this learning to inform and test other hypotheses by constructing more sophisticated experiments, and tuning, evolving or abandoning any hypothesis as we made further observations from the results we achieved.
Experimentation is the foundation of the scientific method, which is a systematic means of exploring the world around us. Although some experiments take place in laboratories, it is possible to perform an experiment anywhere, at any time, even in software development.
Practicing Hypothesis-Driven Development is thinking about the development of new ideas, products and services – even organizational change – as a series of experiments to determine whether an expected outcome will be achieved. The process is iterated upon until a desirable outcome is obtained or the idea is determined to be not viable.
We need to change our mindset to view our proposed solution to a problem statement as a hypothesis, especially in new product or service development – the market we are targeting, how a business model will work, how code will execute and even how the customer will use it.
We do not do projects anymore, only experiments. Customer discovery and Lean Startup strategies are designed to test assumptions about customers. Quality Assurance is testing system behavior against defined specifications. The experimental principle also applies in Test-Driven Development – we write the test first, then use the test to validate that our code is correct, and succeed if the code passes the test. Ultimately, product or service development is a process to test a hypothesis about system behaviour in the environment or market it is developed for.
The key outcome of an experimental approach is measurable evidence and learning.
Learning is the information we have gained from conducting the experiment. Did what we expect to occur actually happen? If not, what did and how does that inform what we should do next?
In order to learn we need use the scientific method for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, and correcting and integrating previous knowledge back into our thinking.
As the software development industry continues to mature, we now have an opportunity to leverage improved capabilities such as Continuous Design and Delivery to maximize our potential to learn quickly what works and what does not. By taking an experimental approach to information discovery, we can more rapidly test our solutions against the problems we have identified in the products or services we are attempting to build. With the goal to optimize our effectiveness of solving the right problems, over simply becoming a feature factory by continually building solutions.
The steps of the scientific method are to:
- Make observations
- Formulate a hypothesis
- Design an experiment to test the hypothesis
- State the indicators to evaluate if the experiment has succeeded
- Conduct the experiment
- Evaluate the results of the experiment
- Accept or reject the hypothesis
- If necessary, make and test a new hypothesis
Using an experimentation approach to software development
We need to challenge the concept of having fixed requirements for a product or service. Requirements are valuable when teams execute a well known or understood phase of an initiative, and can leverage well understood practices to achieve the outcome. However, when you are in an exploratory, complex and uncertain phase you need hypotheses.
Handing teams a set of business requirements reinforces an order-taking approach and mindset that is flawed.
Business does the thinking and ‘knows’ what is right. The purpose of the development team is to implement what they are told. But when operating in an area of uncertainty and complexity, all the members of the development team should be encouraged to think and share insights on the problem and potential solutions. A team simply taking orders from a business owner is not utilizing the full potential, experience and competency that a cross-functional multi-disciplined team offers.
Framing hypotheses
The traditional user story framework is focused on capturing requirements for what we want to build and for whom, to enable the user to receive a specific benefit from the system.
As A…. <role>
I Want… <goal/desire>
So That… <receive benefit>
Behaviour Driven Development (BDD) and Feature Injection aims to improve the original framework by supporting communication and collaboration between developers, tester and non-technical participants in a software project.
In Order To… <receive benefit>
As A… <role>
When viewing work as an experiment, the traditional story framework is insufficient. As in our high school science experiment, we need to define the steps we will take to achieve the desired outcome. We then need to state the specific indicators (or signals) we expect to observe that provide evidence that our hypothesis is valid. These need to be stated before conducting the test to reduce biased interpretations of the results.
If we observe signals that indicate our hypothesis is correct, we can be more confident that we are on the right path and can alter the user story framework to reflect this.
Therefore, a user story structure to support Hypothesis-Driven Development would be;
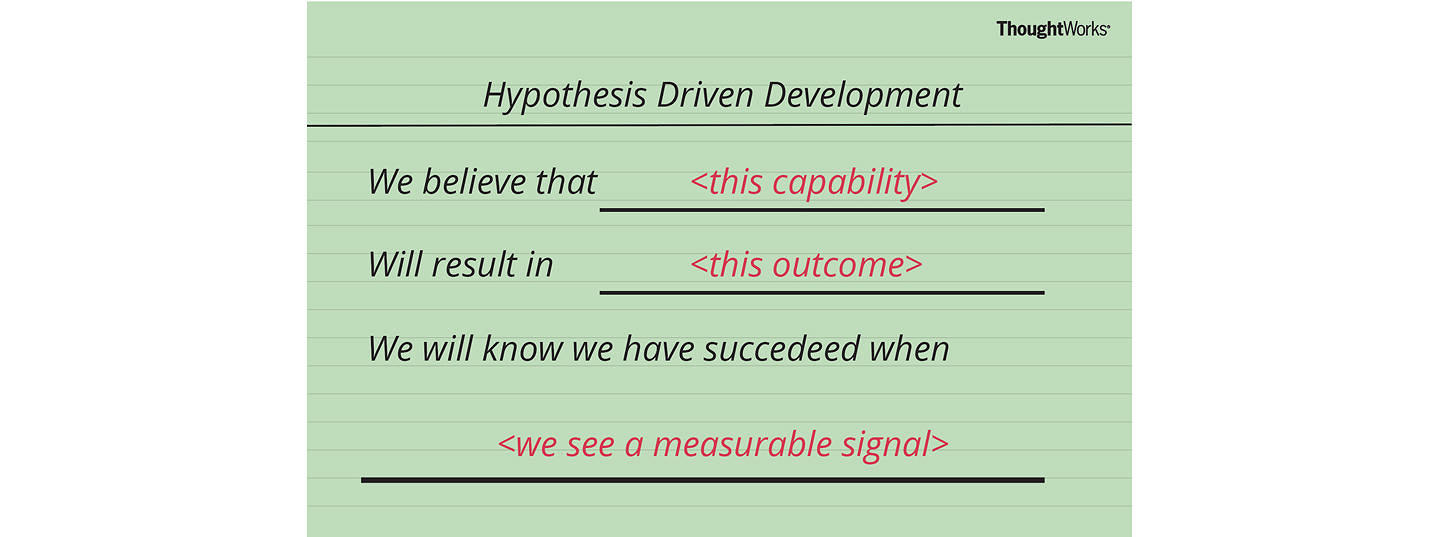
We believe < this capability >
What functionality we will develop to test our hypothesis? By defining a ‘test’ capability of the product or service that we are attempting to build, we identify the functionality and hypothesis we want to test.
Will result in < this outcome >
What is the expected outcome of our experiment? What is the specific result we expect to achieve by building the ‘test’ capability?
We will know we have succeeded when < we see a measurable signal >
What signals will indicate that the capability we have built is effective? What key metrics (qualitative or quantitative) we will measure to provide evidence that our experiment has succeeded and give us enough confidence to move to the next stage.
The threshold you use for statistically significance will depend on your understanding of the business and context you are operating within. Not every company has the user sample size of Amazon or Google to run statistically significant experiments in a short period of time. Limits and controls need to be defined by your organization to determine acceptable evidence thresholds that will allow the team to advance to the next step.
For example if you are building a rocket ship you may want your experiments to have a high threshold for statistical significance. If you are deciding between two different flows intended to help increase user sign up you may be happy to tolerate a lower significance threshold.
The final step is to clearly and visibly state any assumptions made about our hypothesis, to create a feedback loop for the team to provide further input, debate and understanding of the circumstance under which we are performing the test. Are they valid and make sense from a technical and business perspective?
Hypotheses when aligned to your MVP can provide a testing mechanism for your product or service vision. They can test the most uncertain areas of your product or service, in order to gain information and improve confidence.
Examples of Hypothesis-Driven Development user stories are;
Business story
We Believe That increasing the size of hotel images on the booking page
Will Result In improved customer engagement and conversion
We Will Know We Have Succeeded When we see a 5% increase in customers who review hotel images who then proceed to book in 48 hours.
It is imperative to have effective monitoring and evaluation tools in place when using an experimental approach to software development in order to measure the impact of our efforts and provide a feedback loop to the team. Otherwise we are essentially blind to the outcomes of our efforts.
In agile software development we define working software as the primary measure of progress.
By combining Continuous Delivery and Hypothesis-Driven Development we can now define working software and validated learning as the primary measures of progress.
Ideally we should not say we are done until we have measured the value of what is being delivered – in other words, gathered data to validate our hypothesis.
Examples of how to gather data is performing A/B Testing to test a hypothesis and measure to change in customer behaviour. Alternative testings options can be customer surveys, paper prototypes, user and/or guerrilla testing.
One example of a company we have worked with that uses Hypothesis-Driven Development is lastminute.com . The team formulated a hypothesis that customers are only willing to pay a max price for a hotel based on the time of day they book. Tom Klein, CEO and President of Sabre Holdings shared the story of how they improved conversion by 400% within a week.
Combining practices such as Hypothesis-Driven Development and Continuous Delivery accelerates experimentation and amplifies validated learning. This gives us the opportunity to accelerate the rate at which we innovate while relentlessly reducing cost, leaving our competitors in the dust. Ideally we can achieve the ideal of one piece flow: atomic changes that enable us to identify causal relationships between the changes we make to our products and services, and their impact on key metrics.
As Kent Beck said, “Test-Driven Development is a great excuse to think about the problem before you think about the solution”. Hypothesis-Driven Development is a great opportunity to test what you think the problem is, before you work on the solution.
How can you achieve faster growth?
- Work together
- Product development
- Ways of working

Have you read my two bestsellers, Unlearn and Lean Enterprise? If not, please do. If you have, please write a review!
- Read my story
- Get in touch

- Oval Copy 2 Blog
How to Implement Hypothesis-Driven Development
- Facebook__x28_alt_x29_ Copy
Remember back to the time when we were in high school science class. Our teachers had a framework for helping us learn – an experimental approach based on the best available evidence at hand. We were asked to make observations about the world around us, then attempt to form an explanation or hypothesis to explain what we had observed. We then tested this hypothesis by predicting an outcome based on our theory that would be achieved in a controlled experiment – if the outcome was achieved, we had proven our theory to be correct.
We could then apply this learning to inform and test other hypotheses by constructing more sophisticated experiments, and tuning, evolving, or abandoning any hypothesis as we made further observations from the results we achieved.
Experimentation is the foundation of the scientific method, which is a systematic means of exploring the world around us. Although some experiments take place in laboratories, it is possible to perform an experiment anywhere, at any time, even in software development.
Practicing Hypothesis-Driven Development [1] is thinking about the development of new ideas, products, and services – even organizational change – as a series of experiments to determine whether an expected outcome will be achieved. The process is iterated upon until a desirable outcome is obtained or the idea is determined to be not viable.
We need to change our mindset to view our proposed solution to a problem statement as a hypothesis, especially in new product or service development – the market we are targeting, how a business model will work, how code will execute and even how the customer will use it.
We do not do projects anymore, only experiments. Customer discovery and Lean Startup strategies are designed to test assumptions about customers. Quality Assurance is testing system behavior against defined specifications. The experimental principle also applies in Test-Driven Development – we write the test first, then use the test to validate that our code is correct, and succeed if the code passes the test. Ultimately, product or service development is a process to test a hypothesis about system behavior in the environment or market it is developed for.
The key outcome of an experimental approach is measurable evidence and learning. Learning is the information we have gained from conducting the experiment. Did what we expect to occur actually happen? If not, what did and how does that inform what we should do next?
In order to learn we need to use the scientific method for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, and correcting and integrating previous knowledge back into our thinking.
As the software development industry continues to mature, we now have an opportunity to leverage improved capabilities such as Continuous Design and Delivery to maximize our potential to learn quickly what works and what does not. By taking an experimental approach to information discovery, we can more rapidly test our solutions against the problems we have identified in the products or services we are attempting to build. With the goal to optimize our effectiveness of solving the right problems, over simply becoming a feature factory by continually building solutions.
The steps of the scientific method are to:
- Make observations
- Formulate a hypothesis
- Design an experiment to test the hypothesis
- State the indicators to evaluate if the experiment has succeeded
- Conduct the experiment
- Evaluate the results of the experiment
- Accept or reject the hypothesis
- If necessary, make and test a new hypothesis
Using an experimentation approach to software development
We need to challenge the concept of having fixed requirements for a product or service. Requirements are valuable when teams execute a well known or understood phase of an initiative and can leverage well-understood practices to achieve the outcome. However, when you are in an exploratory, complex and uncertain phase you need hypotheses. Handing teams a set of business requirements reinforces an order-taking approach and mindset that is flawed. Business does the thinking and ‘knows’ what is right. The purpose of the development team is to implement what they are told. But when operating in an area of uncertainty and complexity, all the members of the development team should be encouraged to think and share insights on the problem and potential solutions. A team simply taking orders from a business owner is not utilizing the full potential, experience and competency that a cross-functional multi-disciplined team offers.
Framing Hypotheses
The traditional user story framework is focused on capturing requirements for what we want to build and for whom, to enable the user to receive a specific benefit from the system.
As A…. <role>
I Want… <goal/desire>
So That… <receive benefit>
Behaviour Driven Development (BDD) and Feature Injection aims to improve the original framework by supporting communication and collaboration between developers, tester and non-technical participants in a software project.
In Order To… <receive benefit>
As A… <role>
When viewing work as an experiment, the traditional story framework is insufficient. As in our high school science experiment, we need to define the steps we will take to achieve the desired outcome. We then need to state the specific indicators (or signals) we expect to observe that provide evidence that our hypothesis is valid. These need to be stated before conducting the test to reduce the bias of interpretation of results.
If we observe signals that indicate our hypothesis is correct, we can be more confident that we are on the right path and can alter the user story framework to reflect this.
Therefore, a user story structure to support Hypothesis-Driven Development would be;

We believe < this capability >
What functionality we will develop to test our hypothesis? By defining a ‘test’ capability of the product or service that we are attempting to build, we identify the functionality and hypothesis we want to test.
Will result in < this outcome >
What is the expected outcome of our experiment? What is the specific result we expect to achieve by building the ‘test’ capability?
We will have confidence to proceed when < we see a measurable signal >
What signals will indicate that the capability we have built is effective? What key metrics (qualitative or quantitative) we will measure to provide evidence that our experiment has succeeded and give us enough confidence to move to the next stage.
The threshold you use for statistical significance will depend on your understanding of the business and context you are operating within. Not every company has the user sample size of Amazon or Google to run statistically significant experiments in a short period of time. Limits and controls need to be defined by your organization to determine acceptable evidence thresholds that will allow the team to advance to the next step.
For example, if you are building a rocket ship you may want your experiments to have a high threshold for statistical significance. If you are deciding between two different flows intended to help increase user sign up you may be happy to tolerate a lower significance threshold.
The final step is to clearly and visibly state any assumptions made about our hypothesis, to create a feedback loop for the team to provide further input, debate, and understanding of the circumstance under which we are performing the test. Are they valid and make sense from a technical and business perspective?
Hypotheses, when aligned to your MVP, can provide a testing mechanism for your product or service vision. They can test the most uncertain areas of your product or service, in order to gain information and improve confidence.
Examples of Hypothesis-Driven Development user stories are;
Business story.
We Believe That increasing the size of hotel images on the booking page Will Result In improved customer engagement and conversion We Will Have Confidence To Proceed When we see a 5% increase in customers who review hotel images who then proceed to book in 48 hours.
It is imperative to have effective monitoring and evaluation tools in place when using an experimental approach to software development in order to measure the impact of our efforts and provide a feedback loop to the team. Otherwise, we are essentially blind to the outcomes of our efforts.
In agile software development, we define working software as the primary measure of progress. By combining Continuous Delivery and Hypothesis-Driven Development we can now define working software and validated learning as the primary measures of progress.
Ideally, we should not say we are done until we have measured the value of what is being delivered – in other words, gathered data to validate our hypothesis.
Examples of how to gather data is performing A/B Testing to test a hypothesis and measure to change in customer behavior. Alternative testings options can be customer surveys, paper prototypes, user and/or guerilla testing.
One example of a company we have worked with that uses Hypothesis-Driven Development is lastminute.com . The team formulated a hypothesis that customers are only willing to pay a max price for a hotel based on the time of day they book. Tom Klein, CEO and President of Sabre Holdings shared the story of how they improved conversion by 400% within a week.
Combining practices such as Hypothesis-Driven Development and Continuous Delivery accelerates experimentation and amplifies validated learning. This gives us the opportunity to accelerate the rate at which we innovate while relentlessly reducing costs, leaving our competitors in the dust. Ideally, we can achieve the ideal of one-piece flow: atomic changes that enable us to identify causal relationships between the changes we make to our products and services, and their impact on key metrics.
As Kent Beck said, “Test-Driven Development is a great excuse to think about the problem before you think about the solution”. Hypothesis-Driven Development is a great opportunity to test what you think the problem is before you work on the solution.
We also run a workshop to help teams implement Hypothesis-Driven Development . Get in touch to run it at your company.
[1] Hypothesis-Driven Development By Jeffrey L. Taylor
More strategy insights
Creating new markets, how to build a venture studio with ben yoskovitz, founding partner at highline beta, how high performance organizations innovate at scale, read my newsletter.
Insights in every edition. News you can use. No spam, ever. Read the latest edition
We've just sent you your first email. Go check it out!
- Explore Insights
- Nobody Studios
- LinkedIn Learning: High Performance Organizations
The 6 Steps that We Use for Hypothesis-Driven Development

One of the greatest fears of product managers is to create an app that flopped because it's based on untested assumptions. After successfully launching more than 20 products, we're convinced that we've found the right approach for hypothesis-driven development.
In this guide, I'll show you how we validated the hypotheses to ensure that the apps met the users' expectations and needs.
What is hypothesis-driven development?
Hypothesis-driven development is a prototype methodology that allows product designers to develop, test, and rebuild a product until it’s acceptable by the users. It is an iterative measure that explores assumptions defined during the project and attempts to validate it with users’ feedbacks.
What you have assumed during the initial stage of development may not be valid for the users. Even if they are backed by historical data, user behaviors can be affected by specific audiences and other factors. Hypothesis-driven development removes these uncertainties as the project progresses.

Why we use hypothesis-driven development
For us, the hypothesis-driven approach provides a structured way to consolidate ideas and build hypotheses based on objective criteria. It’s also less costly to test the prototype before production.
Using this approach has reliably allowed us to identify what, how, and in which order should the testing be done. It gives us a deep understanding of how we prioritise the features, how it’s connected to the business goals and desired user outcomes.
We’re also able to track and compare the desired and real outcomes of developing the features.
The process of Prototype Development that we use
Our success in building apps that are well-accepted by users is based on the Lean UX definition of hypothesis. We believe that the business outcome will be achieved if the user’s outcome is fulfilled for the particular feature.
Here’s the process flow:
How Might We technique → Dot voting (based on estimated/assumptive impact) → converting into a hypothesis → define testing methodology (research method + success/fail criteria) → impact effort scale for prioritizing → test, learn, repeat.
Once the hypothesis is proven right, the feature is escalated into the development track for UI design and development.

Step 1: List Down Questions And Assumptions
Whether it’s the initial stage of the project or after the launch, there are always uncertainties or ideas to further improve the existing product. In order to move forward, you’ll need to turn the ideas into structured hypotheses where they can be tested prior to production.
To start with, jot the ideas or assumptions down on paper or a sticky note.
Then, you’ll want to widen the scope of the questions and assumptions into possible solutions. The How Might We (HMW) technique is handy in rephrasing the statements into questions that facilitate brainstorming.
For example, if you have a social media app with a low number of users, asking, “How might we increase the number of users for the app?” makes brainstorming easier.
Step 2: Dot Vote to Prioritize Questions and Assumptions
Once you’ve got a list of questions, it’s time to decide which are potentially more impactful for the product. The Dot Vote method, where team members are given dots to place on the questions, helps prioritize the questions and assumptions.
Our team uses this method when we’re faced with many ideas and need to eliminate some of them. We started by grouping similar ideas and use 3-5 dots to vote. At the end of the process, we’ll have the preliminary data on the possible impact and our team’s interest in developing certain features.
This method allows us to prioritize the statements derived from the HMW technique and we’re only converting the top ones.
Step 3: Develop Hypotheses from Questions
The questions lead to a brainstorming session where the answers become hypotheses for the product. The hypothesis is meant to create a framework that allows the questions and solutions to be defined clearly for validation.
Our team followed a specific format in forming hypotheses. We structured the statement as follow:
We believe we will achieve [ business outcome],
If [ the persona],
Solve their need in [ user outcome] using [feature].
Here’s a hypothesis we’ve created:
We believe we will achieve DAU=100 if Mike (our proto persona) solve their need in recording and sharing videos instantaneously using our camera and cloud storage .

Step 4: Test the Hypothesis with an Experiment
It’s crucial to validate each of the assumptions made on the product features. Based on the hypotheses, experiments in the form of interviews, surveys, usability testing, and so forth are created to determine if the assumptions are aligned with reality.
Each of the methods provides some level of confidence. Therefore, you don’t want to be 100% reliant on a particular method as it’s based on a sample of users.
It’s important to choose a research method that allows validation to be done with minimal effort. Even though hypotheses validation provides a degree of confidence, not all assumptions can be tested and there could be a margin of error in data obtained as the test is conducted on a sample of people.
The experiments are designed in such a way that feedback can be compared with the predicted outcome. Only validated hypotheses are brought forward for development.
Testing all the hypotheses can be tedious. To be more efficient, you can use the impact effort scale. This method allows you to focus on hypotheses that are potentially high value and easy to validate.
You can also work on hypotheses that deliver high impact but require high effort. Ignore those that require high impact but low impact and keep hypotheses with low impact and effort into the backlog.
At Uptech, we assign each hypothesis with clear testing criteria. We rank the hypothesis with a binary ‘task success’ and subjective ‘effort on task’ where the latter is scored from 1 to 10.
While we’re conducting the test, we also collect qualitative data such as the users' feedback. We have a habit of segregation the feedback into pros, cons and neutral with color-coded stickers. (red - cons, green -pros, blue- neutral).
The best practice is to test each hypothesis at least on 5 users.
Step 5 Learn, Build (and Repeat)
The hypothesis-driven approach is not a single-ended process. Often, you’ll find that some of the hypotheses are proven to be false. Rather than be disheartened, you should use the data gathered to finetune the hypothesis and design a better experiment in the next phase.
Treat the entire cycle as a learning process where you’ll better understand the product and the customers.
We’ve found the process helpful when developing an MVP for Carbon Club, an environmental startup in the UK. The app allows users to donate to charity based on the carbon-footprint produced.
In order to calculate the carbon footprint, we’re weighing the options of
- Connecting the app to the users’ bank account to monitor the carbon footprint based on purchases made.
- Allowing users to take quizzes on their lifestyles.
Upon validation, we’ve found that all of the users opted for the second option as they are concerned about linking an unknown app to their banking account.
The result makes us shelves the first assumption we’ve made during pre-Sprint research. It also saves our client $50,000, and a few months of work as connecting the app to the bank account requires a huge effort.
.png)
Step 6: Implement Product and Maintain
Once you’ve got the confidence that the remaining hypotheses are validated, it’s time to develop the product. However, testing must be continued even after the product is launched.
You should be on your toes as customers’ demands, market trends, local economics, and other conditions may require some features to evolve.

Our takeaways for hypothesis-driven development
If there’s anything that you could pick from our experience, it’s these 5 points.
1. Should every idea go straight into the backlog? No, unless they are validated with substantial evidence.
2. While it’s hard to define business outcomes with specific metrics and desired values, you should do it anyway. Try to be as specific as possible, and avoid general terms. Give your best effort and adjust as you receive new data.
3. Get all product teams involved as the best ideas are born from collaboration.
4. Start with a plan consists of 2 main parameters, i.e., criteria of success and research methods. Besides qualitative insights, you need to set objective criteria to determine if a test is successful. Use the Test Card to validate the assumptions strategically.
5. The methodology that we’ve recommended in this article works not only for products. We’ve applied it at the end of 2019 for setting the strategic goals of the company and end up with robust results, engaged and aligned team.
You'll have a better idea of which features would lead to a successful product with hypothesis-driven development. Rather than vague assumptions, the consolidated data from users will provide a clear direction for your development team.
As for the hypotheses that don't make the cut, improvise, re-test, and leverage for future upgrades.
Keep failing with product launches? I'll be happy to point you in the right direction. Drop me a message here.
Tell us about your idea. We will reach you out.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Developing a Hypothesis
Rajiv S. Jhangiani; I-Chant A. Chiang; Carrie Cuttler; and Dana C. Leighton
Learning Objectives
- Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis.
- Discover how theories are used to generate hypotheses and how the results of studies can be used to further inform theories.
- Understand the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Theories and Hypotheses
Before describing how to develop a hypothesis, it is important to distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis. A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition (1965) [1] . He proposed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
A hypothesis , on the other hand, is a specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. It is an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts. Hypotheses are often specific predictions about what will happen in a particular study. They are developed by considering existing evidence and using reasoning to infer what will happen in the specific context of interest. Hypotheses are often but not always derived from theories. So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies of data. So if our research question is really original then we may need to collect some data and make some observations before we can develop a broader theory.
Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relationship. “ If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster, and a branching runway more slowly, when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in this chapter and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this question is an interesting one on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991) [2] . Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged themselves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.
Theory Testing
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). Researchers begin with a set of phenomena and either construct a theory to explain or interpret them or choose an existing theory to work with. They then make a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researchers then conduct an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, they reevaluate the theory in light of the new results and revise it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researchers can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure 2.3 shows, this approach meshes nicely with the model of scientific research in psychology presented earlier in the textbook—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research.
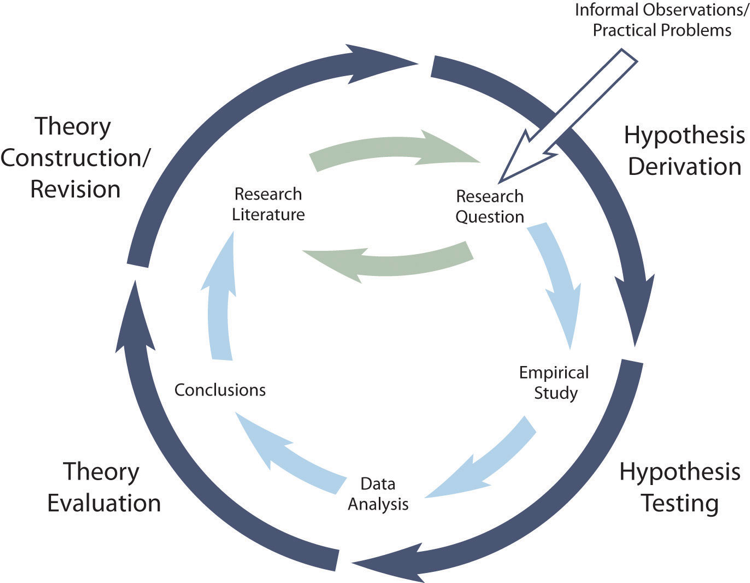
As an example, let us consider Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This theory predicts social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969) [3] . The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cockroach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cockroaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory. (Zajonc also showed that drive theory existed in humans [Zajonc & Sales, 1966] [4] in many other studies afterward).
Incorporating Theory into Your Research
When you write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
To use theories in your research will not only give you guidance in coming up with experiment ideas and possible projects, but it lends legitimacy to your work. Psychologists have been interested in a variety of human behaviors and have developed many theories along the way. Using established theories will help you break new ground as a researcher, not limit you from developing your own ideas.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable . We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you’ll recall Popper’s falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical. As described above, hypotheses are more than just a random guess. Hypotheses should be informed by previous theories or observations and logical reasoning. Typically, we begin with a broad and general theory and use deductive reasoning to generate a more specific hypothesis to test based on that theory. Occasionally, however, when there is no theory to inform our hypothesis, we use inductive reasoning which involves using specific observations or research findings to form a more general hypothesis. Finally, the hypothesis should be positive. That is, the hypothesis should make a positive statement about the existence of a relationship or effect, rather than a statement that a relationship or effect does not exist. As scientists, we don’t set out to show that relationships do not exist or that effects do not occur so our hypotheses should not be worded in a way to suggest that an effect or relationship does not exist. The nature of science is to assume that something does not exist and then seek to find evidence to prove this wrong, to show that it really does exist. That may seem backward to you but that is the nature of the scientific method. The underlying reason for this is beyond the scope of this chapter but it has to do with statistical theory.
- Zajonc, R. B. (1965). Social facilitation. Science, 149 , 269–274 ↵
- Schwarz, N., Bless, H., Strack, F., Klumpp, G., Rittenauer-Schatka, H., & Simons, A. (1991). Ease of retrieval as information: Another look at the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61 , 195–202. ↵
- Zajonc, R. B., Heingartner, A., & Herman, E. M. (1969). Social enhancement and impairment of performance in the cockroach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 13 , 83–92. ↵
- Zajonc, R.B. & Sales, S.M. (1966). Social facilitation of dominant and subordinate responses. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 2 , 160-168. ↵
A coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena.
A specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate.
A cyclical process of theory development, starting with an observed phenomenon, then developing or using a theory to make a specific prediction of what should happen if that theory is correct, testing that prediction, refining the theory in light of the findings, and using that refined theory to develop new hypotheses, and so on.
The ability to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and the possibility to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false.
Developing a Hypothesis Copyright © by Rajiv S. Jhangiani; I-Chant A. Chiang; Carrie Cuttler; and Dana C. Leighton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
2.4 Developing a Hypothesis
Learning objectives.
- Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis.
- Discover how theories are used to generate hypotheses and how the results of studies can be used to further inform theories.
- Understand the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Theories and Hypotheses
Before describing how to develop a hypothesis it is imporant to distinguish betwee a theory and a hypothesis. A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition. He proposed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
A hypothesis , on the other hand, is a specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. It is an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts. Hypotheses are often specific predictions about what will happen in a particular study. They are developed by considering existing evidence and using reasoning to infer what will happen in the specific context of interest. Hypotheses are often but not always derived from theories. So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies of data. So if our research question is really original then we may need to collect some data and make some observation before we can develop a broader theory.
Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relationship. “ If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster, and a branching runway more slowly, when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in this chapter and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this question is an interesting one on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991) [1] . Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged themselves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.
Theory Testing
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). A researcher begins with a set of phenomena and either constructs a theory to explain or interpret them or chooses an existing theory to work with. He or she then makes a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researcher then conducts an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, he or she reevaluates the theory in light of the new results and revises it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researcher can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure 2.2 shows, this approach meshes nicely with the model of scientific research in psychology presented earlier in the textbook—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research.

Figure 2.2 Hypothetico-Deductive Method Combined With the General Model of Scientific Research in Psychology Together they form a model of theoretically motivated research.
As an example, let us consider Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This theory predicts social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969) [2] . The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cockroach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cockroaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory. (Zajonc also showed that drive theory existed in humans (Zajonc & Sales, 1966) [3] in many other studies afterward).
Incorporating Theory into Your Research
When you write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
To use theories in your research will not only give you guidance in coming up with experiment ideas and possible projects, but it lends legitimacy to your work. Psychologists have been interested in a variety of human behaviors and have developed many theories along the way. Using established theories will help you break new ground as a researcher, not limit you from developing your own ideas.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable . We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you’ll recall Popper’s falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical. As described above, hypotheses are more than just a random guess. Hypotheses should be informed by previous theories or observations and logical reasoning. Typically, we begin with a broad and general theory and use deductive reasoning to generate a more specific hypothesis to test based on that theory. Occasionally, however, when there is no theory to inform our hypothesis, we use inductive reasoning which involves using specific observations or research findings to form a more general hypothesis. Finally, the hypothesis should be positive. That is, the hypothesis should make a positive statement about the existence of a relationship or effect, rather than a statement that a relationship or effect does not exist. As scientists, we don’t set out to show that relationships do not exist or that effects do not occur so our hypotheses should not be worded in a way to suggest that an effect or relationship does not exist. The nature of science is to assume that something does not exist and then seek to find evidence to prove this wrong, to show that really it does exist. That may seem backward to you but that is the nature of the scientific method. The underlying reason for this is beyond the scope of this chapter but it has to do with statistical theory.
Key Takeaways
- A theory is broad in nature and explains larger bodies of data. A hypothesis is more specific and makes a prediction about the outcome of a particular study.
- Working with theories is not “icing on the cake.” It is a basic ingredient of psychological research.
- Like other scientists, psychologists use the hypothetico-deductive method. They construct theories to explain or interpret phenomena (or work with existing theories), derive hypotheses from their theories, test the hypotheses, and then reevaluate the theories in light of the new results.
- Practice: Find a recent empirical research report in a professional journal. Read the introduction and highlight in different colors descriptions of theories and hypotheses.
- Schwarz, N., Bless, H., Strack, F., Klumpp, G., Rittenauer-Schatka, H., & Simons, A. (1991). Ease of retrieval as information: Another look at the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61 , 195–202. ↵
- Zajonc, R. B., Heingartner, A., & Herman, E. M. (1969). Social enhancement and impairment of performance in the cockroach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 13 , 83–92. ↵
- Zajonc, R.B. & Sales, S.M. (1966). Social facilitation of dominant and subordinate responses. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 2 , 160-168. ↵

Share This Book
- Increase Font Size

How to Develop a Good Research Hypothesis
The story of a research study begins by asking a question. Researchers all around the globe are asking curious questions and formulating research hypothesis. However, whether the research study provides an effective conclusion depends on how well one develops a good research hypothesis. Research hypothesis examples could help researchers get an idea as to how to write a good research hypothesis.
This blog will help you understand what is a research hypothesis, its characteristics and, how to formulate a research hypothesis
Table of Contents
What is Hypothesis?
Hypothesis is an assumption or an idea proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested. It is a precise, testable statement of what the researchers predict will be outcome of the study. Hypothesis usually involves proposing a relationship between two variables: the independent variable (what the researchers change) and the dependent variable (what the research measures).
What is a Research Hypothesis?
Research hypothesis is a statement that introduces a research question and proposes an expected result. It is an integral part of the scientific method that forms the basis of scientific experiments. Therefore, you need to be careful and thorough when building your research hypothesis. A minor flaw in the construction of your hypothesis could have an adverse effect on your experiment. In research, there is a convention that the hypothesis is written in two forms, the null hypothesis, and the alternative hypothesis (called the experimental hypothesis when the method of investigation is an experiment).
Characteristics of a Good Research Hypothesis
As the hypothesis is specific, there is a testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. You may consider drawing hypothesis from previously published research based on the theory.
A good research hypothesis involves more effort than just a guess. In particular, your hypothesis may begin with a question that could be further explored through background research.
To help you formulate a promising research hypothesis, you should ask yourself the following questions:
- Is the language clear and focused?
- What is the relationship between your hypothesis and your research topic?
- Is your hypothesis testable? If yes, then how?
- What are the possible explanations that you might want to explore?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate your variables without hampering the ethical standards?
- Does your research predict the relationship and outcome?
- Is your research simple and concise (avoids wordiness)?
- Is it clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers’ knowledge
- Is your research observable and testable results?
- Is it relevant and specific to the research question or problem?

The questions listed above can be used as a checklist to make sure your hypothesis is based on a solid foundation. Furthermore, it can help you identify weaknesses in your hypothesis and revise it if necessary.
Source: Educational Hub
How to formulate a research hypothesis.
A testable hypothesis is not a simple statement. It is rather an intricate statement that needs to offer a clear introduction to a scientific experiment, its intentions, and the possible outcomes. However, there are some important things to consider when building a compelling hypothesis.
1. State the problem that you are trying to solve.
Make sure that the hypothesis clearly defines the topic and the focus of the experiment.
2. Try to write the hypothesis as an if-then statement.
Follow this template: If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.
3. Define the variables
Independent variables are the ones that are manipulated, controlled, or changed. Independent variables are isolated from other factors of the study.
Dependent variables , as the name suggests are dependent on other factors of the study. They are influenced by the change in independent variable.
4. Scrutinize the hypothesis
Evaluate assumptions, predictions, and evidence rigorously to refine your understanding.
Types of Research Hypothesis
The types of research hypothesis are stated below:
1. Simple Hypothesis
It predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable.
2. Complex Hypothesis
It predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables.
3. Directional Hypothesis
It specifies the expected direction to be followed to determine the relationship between variables and is derived from theory. Furthermore, it implies the researcher’s intellectual commitment to a particular outcome.
4. Non-directional Hypothesis
It does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables. The non-directional hypothesis is used when there is no theory involved or when findings contradict previous research.
5. Associative and Causal Hypothesis
The associative hypothesis defines interdependency between variables. A change in one variable results in the change of the other variable. On the other hand, the causal hypothesis proposes an effect on the dependent due to manipulation of the independent variable.
6. Null Hypothesis
Null hypothesis states a negative statement to support the researcher’s findings that there is no relationship between two variables. There will be no changes in the dependent variable due the manipulation of the independent variable. Furthermore, it states results are due to chance and are not significant in terms of supporting the idea being investigated.
7. Alternative Hypothesis
It states that there is a relationship between the two variables of the study and that the results are significant to the research topic. An experimental hypothesis predicts what changes will take place in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated. Also, it states that the results are not due to chance and that they are significant in terms of supporting the theory being investigated.
Research Hypothesis Examples of Independent and Dependent Variables
Research Hypothesis Example 1 The greater number of coal plants in a region (independent variable) increases water pollution (dependent variable). If you change the independent variable (building more coal factories), it will change the dependent variable (amount of water pollution).
Research Hypothesis Example 2 What is the effect of diet or regular soda (independent variable) on blood sugar levels (dependent variable)? If you change the independent variable (the type of soda you consume), it will change the dependent variable (blood sugar levels)
You should not ignore the importance of the above steps. The validity of your experiment and its results rely on a robust testable hypothesis. Developing a strong testable hypothesis has few advantages, it compels us to think intensely and specifically about the outcomes of a study. Consequently, it enables us to understand the implication of the question and the different variables involved in the study. Furthermore, it helps us to make precise predictions based on prior research. Hence, forming a hypothesis would be of great value to the research. Here are some good examples of testable hypotheses.
More importantly, you need to build a robust testable research hypothesis for your scientific experiments. A testable hypothesis is a hypothesis that can be proved or disproved as a result of experimentation.
Importance of a Testable Hypothesis
To devise and perform an experiment using scientific method, you need to make sure that your hypothesis is testable. To be considered testable, some essential criteria must be met:
- There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is true.
- There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is false.
- The results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.
Without these criteria, the hypothesis and the results will be vague. As a result, the experiment will not prove or disprove anything significant.
What are your experiences with building hypotheses for scientific experiments? What challenges did you face? How did you overcome these challenges? Please share your thoughts with us in the comments section.
Frequently Asked Questions
The steps to write a research hypothesis are: 1. Stating the problem: Ensure that the hypothesis defines the research problem 2. Writing a hypothesis as an 'if-then' statement: Include the action and the expected outcome of your study by following a ‘if-then’ structure. 3. Defining the variables: Define the variables as Dependent or Independent based on their dependency to other factors. 4. Scrutinizing the hypothesis: Identify the type of your hypothesis
Hypothesis testing is a statistical tool which is used to make inferences about a population data to draw conclusions for a particular hypothesis.
Hypothesis in statistics is a formal statement about the nature of a population within a structured framework of a statistical model. It is used to test an existing hypothesis by studying a population.
Research hypothesis is a statement that introduces a research question and proposes an expected result. It forms the basis of scientific experiments.
The different types of hypothesis in research are: • Null hypothesis: Null hypothesis is a negative statement to support the researcher’s findings that there is no relationship between two variables. • Alternate hypothesis: Alternate hypothesis predicts the relationship between the two variables of the study. • Directional hypothesis: Directional hypothesis specifies the expected direction to be followed to determine the relationship between variables. • Non-directional hypothesis: Non-directional hypothesis does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables. • Simple hypothesis: Simple hypothesis predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable. • Complex hypothesis: Complex hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. • Associative and casual hypothesis: Associative and casual hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. • Empirical hypothesis: Empirical hypothesis can be tested via experiments and observation. • Statistical hypothesis: A statistical hypothesis utilizes statistical models to draw conclusions about broader populations.
Wow! You really simplified your explanation that even dummies would find it easy to comprehend. Thank you so much.
Thanks a lot for your valuable guidance.
I enjoy reading the post. Hypotheses are actually an intrinsic part in a study. It bridges the research question and the methodology of the study.
Useful piece!
This is awesome.Wow.
It very interesting to read the topic, can you guide me any specific example of hypothesis process establish throw the Demand and supply of the specific product in market
Nicely explained
It is really a useful for me Kindly give some examples of hypothesis
It was a well explained content ,can you please give me an example with the null and alternative hypothesis illustrated
clear and concise. thanks.
So Good so Amazing
Good to learn
Thanks a lot for explaining to my level of understanding
Explained well and in simple terms. Quick read! Thank you
It awesome. It has really positioned me in my research project
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Industry News
COPE Forum Discussion Highlights Challenges and Urges Clarity in Institutional Authorship Standards
The COPE forum discussion held in December 2023 initiated with a fundamental question — is…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.36(50); 2021 Dec 27

Formulating Hypotheses for Different Study Designs
Durga prasanna misra.
1 Department of Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India.
Armen Yuri Gasparyan
2 Departments of Rheumatology and Research and Development, Dudley Group NHS Foundation Trust (Teaching Trust of the University of Birmingham, UK), Russells Hall Hospital, Dudley, UK.
Olena Zimba
3 Department of Internal Medicine #2, Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, Lviv, Ukraine.
Marlen Yessirkepov
4 Department of Biology and Biochemistry, South Kazakhstan Medical Academy, Shymkent, Kazakhstan.
Vikas Agarwal
George d. kitas.
5 Centre for Epidemiology versus Arthritis, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK.
Generating a testable working hypothesis is the first step towards conducting original research. Such research may prove or disprove the proposed hypothesis. Case reports, case series, online surveys and other observational studies, clinical trials, and narrative reviews help to generate hypotheses. Observational and interventional studies help to test hypotheses. A good hypothesis is usually based on previous evidence-based reports. Hypotheses without evidence-based justification and a priori ideas are not received favourably by the scientific community. Original research to test a hypothesis should be carefully planned to ensure appropriate methodology and adequate statistical power. While hypotheses can challenge conventional thinking and may be controversial, they should not be destructive. A hypothesis should be tested by ethically sound experiments with meaningful ethical and clinical implications. The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic has brought into sharp focus numerous hypotheses, some of which were proven (e.g. effectiveness of corticosteroids in those with hypoxia) while others were disproven (e.g. ineffectiveness of hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin).
Graphical Abstract

DEFINING WORKING AND STANDALONE SCIENTIFIC HYPOTHESES
Science is the systematized description of natural truths and facts. Routine observations of existing life phenomena lead to the creative thinking and generation of ideas about mechanisms of such phenomena and related human interventions. Such ideas presented in a structured format can be viewed as hypotheses. After generating a hypothesis, it is necessary to test it to prove its validity. Thus, hypothesis can be defined as a proposed mechanism of a naturally occurring event or a proposed outcome of an intervention. 1 , 2
Hypothesis testing requires choosing the most appropriate methodology and adequately powering statistically the study to be able to “prove” or “disprove” it within predetermined and widely accepted levels of certainty. This entails sample size calculation that often takes into account previously published observations and pilot studies. 2 , 3 In the era of digitization, hypothesis generation and testing may benefit from the availability of numerous platforms for data dissemination, social networking, and expert validation. Related expert evaluations may reveal strengths and limitations of proposed ideas at early stages of post-publication promotion, preventing the implementation of unsupported controversial points. 4
Thus, hypothesis generation is an important initial step in the research workflow, reflecting accumulating evidence and experts' stance. In this article, we overview the genesis and importance of scientific hypotheses and their relevance in the era of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
DO WE NEED HYPOTHESES FOR ALL STUDY DESIGNS?
Broadly, research can be categorized as primary or secondary. In the context of medicine, primary research may include real-life observations of disease presentations and outcomes. Single case descriptions, which often lead to new ideas and hypotheses, serve as important starting points or justifications for case series and cohort studies. The importance of case descriptions is particularly evident in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic when unique, educational case reports have heralded a new era in clinical medicine. 5
Case series serve similar purpose to single case reports, but are based on a slightly larger quantum of information. Observational studies, including online surveys, describe the existing phenomena at a larger scale, often involving various control groups. Observational studies include variable-scale epidemiological investigations at different time points. Interventional studies detail the results of therapeutic interventions.
Secondary research is based on already published literature and does not directly involve human or animal subjects. Review articles are generated by secondary research. These could be systematic reviews which follow methods akin to primary research but with the unit of study being published papers rather than humans or animals. Systematic reviews have a rigid structure with a mandatory search strategy encompassing multiple databases, systematic screening of search results against pre-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria, critical appraisal of study quality and an optional component of collating results across studies quantitatively to derive summary estimates (meta-analysis). 6 Narrative reviews, on the other hand, have a more flexible structure. Systematic literature searches to minimise bias in selection of articles are highly recommended but not mandatory. 7 Narrative reviews are influenced by the authors' viewpoint who may preferentially analyse selected sets of articles. 8
In relation to primary research, case studies and case series are generally not driven by a working hypothesis. Rather, they serve as a basis to generate a hypothesis. Observational or interventional studies should have a hypothesis for choosing research design and sample size. The results of observational and interventional studies further lead to the generation of new hypotheses, testing of which forms the basis of future studies. Review articles, on the other hand, may not be hypothesis-driven, but form fertile ground to generate future hypotheses for evaluation. Fig. 1 summarizes which type of studies are hypothesis-driven and which lead on to hypothesis generation.

STANDARDS OF WORKING AND SCIENTIFIC HYPOTHESES
A review of the published literature did not enable the identification of clearly defined standards for working and scientific hypotheses. It is essential to distinguish influential versus not influential hypotheses, evidence-based hypotheses versus a priori statements and ideas, ethical versus unethical, or potentially harmful ideas. The following points are proposed for consideration while generating working and scientific hypotheses. 1 , 2 Table 1 summarizes these points.
Evidence-based data
A scientific hypothesis should have a sound basis on previously published literature as well as the scientist's observations. Randomly generated (a priori) hypotheses are unlikely to be proven. A thorough literature search should form the basis of a hypothesis based on published evidence. 7
Unless a scientific hypothesis can be tested, it can neither be proven nor be disproven. Therefore, a scientific hypothesis should be amenable to testing with the available technologies and the present understanding of science.
Supported by pilot studies
If a hypothesis is based purely on a novel observation by the scientist in question, it should be grounded on some preliminary studies to support it. For example, if a drug that targets a specific cell population is hypothesized to be useful in a particular disease setting, then there must be some preliminary evidence that the specific cell population plays a role in driving that disease process.
Testable by ethical studies
The hypothesis should be testable by experiments that are ethically acceptable. 9 For example, a hypothesis that parachutes reduce mortality from falls from an airplane cannot be tested using a randomized controlled trial. 10 This is because it is obvious that all those jumping from a flying plane without a parachute would likely die. Similarly, the hypothesis that smoking tobacco causes lung cancer cannot be tested by a clinical trial that makes people take up smoking (since there is considerable evidence for the health hazards associated with smoking). Instead, long-term observational studies comparing outcomes in those who smoke and those who do not, as was performed in the landmark epidemiological case control study by Doll and Hill, 11 are more ethical and practical.
Balance between scientific temper and controversy
Novel findings, including novel hypotheses, particularly those that challenge established norms, are bound to face resistance for their wider acceptance. Such resistance is inevitable until the time such findings are proven with appropriate scientific rigor. However, hypotheses that generate controversy are generally unwelcome. For example, at the time the pandemic of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and AIDS was taking foot, there were numerous deniers that refused to believe that HIV caused AIDS. 12 , 13 Similarly, at a time when climate change is causing catastrophic changes to weather patterns worldwide, denial that climate change is occurring and consequent attempts to block climate change are certainly unwelcome. 14 The denialism and misinformation during the COVID-19 pandemic, including unfortunate examples of vaccine hesitancy, are more recent examples of controversial hypotheses not backed by science. 15 , 16 An example of a controversial hypothesis that was a revolutionary scientific breakthrough was the hypothesis put forth by Warren and Marshall that Helicobacter pylori causes peptic ulcers. Initially, the hypothesis that a microorganism could cause gastritis and gastric ulcers faced immense resistance. When the scientists that proposed the hypothesis themselves ingested H. pylori to induce gastritis in themselves, only then could they convince the wider world about their hypothesis. Such was the impact of the hypothesis was that Barry Marshall and Robin Warren were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2005 for this discovery. 17 , 18
DISTINGUISHING THE MOST INFLUENTIAL HYPOTHESES
Influential hypotheses are those that have stood the test of time. An archetype of an influential hypothesis is that proposed by Edward Jenner in the eighteenth century that cowpox infection protects against smallpox. While this observation had been reported for nearly a century before this time, it had not been suitably tested and publicised until Jenner conducted his experiments on a young boy by demonstrating protection against smallpox after inoculation with cowpox. 19 These experiments were the basis for widespread smallpox immunization strategies worldwide in the 20th century which resulted in the elimination of smallpox as a human disease today. 20
Other influential hypotheses are those which have been read and cited widely. An example of this is the hygiene hypothesis proposing an inverse relationship between infections in early life and allergies or autoimmunity in adulthood. An analysis reported that this hypothesis had been cited more than 3,000 times on Scopus. 1
LESSONS LEARNED FROM HYPOTHESES AMIDST THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC
The COVID-19 pandemic devastated the world like no other in recent memory. During this period, various hypotheses emerged, understandably so considering the public health emergency situation with innumerable deaths and suffering for humanity. Within weeks of the first reports of COVID-19, aberrant immune system activation was identified as a key driver of organ dysfunction and mortality in this disease. 21 Consequently, numerous drugs that suppress the immune system or abrogate the activation of the immune system were hypothesized to have a role in COVID-19. 22 One of the earliest drugs hypothesized to have a benefit was hydroxychloroquine. Hydroxychloroquine was proposed to interfere with Toll-like receptor activation and consequently ameliorate the aberrant immune system activation leading to pathology in COVID-19. 22 The drug was also hypothesized to have a prophylactic role in preventing infection or disease severity in COVID-19. It was also touted as a wonder drug for the disease by many prominent international figures. However, later studies which were well-designed randomized controlled trials failed to demonstrate any benefit of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19. 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 Subsequently, azithromycin 27 , 28 and ivermectin 29 were hypothesized as potential therapies for COVID-19, but were not supported by evidence from randomized controlled trials. The role of vitamin D in preventing disease severity was also proposed, but has not been proven definitively until now. 30 , 31 On the other hand, randomized controlled trials identified the evidence supporting dexamethasone 32 and interleukin-6 pathway blockade with tocilizumab as effective therapies for COVID-19 in specific situations such as at the onset of hypoxia. 33 , 34 Clues towards the apparent effectiveness of various drugs against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in vitro but their ineffectiveness in vivo have recently been identified. Many of these drugs are weak, lipophilic bases and some others induce phospholipidosis which results in apparent in vitro effectiveness due to non-specific off-target effects that are not replicated inside living systems. 35 , 36
Another hypothesis proposed was the association of the routine policy of vaccination with Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) with lower deaths due to COVID-19. This hypothesis emerged in the middle of 2020 when COVID-19 was still taking foot in many parts of the world. 37 , 38 Subsequently, many countries which had lower deaths at that time point went on to have higher numbers of mortality, comparable to other areas of the world. Furthermore, the hypothesis that BCG vaccination reduced COVID-19 mortality was a classic example of ecological fallacy. Associations between population level events (ecological studies; in this case, BCG vaccination and COVID-19 mortality) cannot be directly extrapolated to the individual level. Furthermore, such associations cannot per se be attributed as causal in nature, and can only serve to generate hypotheses that need to be tested at the individual level. 39

IS TRADITIONAL PEER REVIEW EFFICIENT FOR EVALUATION OF WORKING AND SCIENTIFIC HYPOTHESES?
Traditionally, publication after peer review has been considered the gold standard before any new idea finds acceptability amongst the scientific community. Getting a work (including a working or scientific hypothesis) reviewed by experts in the field before experiments are conducted to prove or disprove it helps to refine the idea further as well as improve the experiments planned to test the hypothesis. 40 A route towards this has been the emergence of journals dedicated to publishing hypotheses such as the Central Asian Journal of Medical Hypotheses and Ethics. 41 Another means of publishing hypotheses is through registered research protocols detailing the background, hypothesis, and methodology of a particular study. If such protocols are published after peer review, then the journal commits to publishing the completed study irrespective of whether the study hypothesis is proven or disproven. 42 In the post-pandemic world, online research methods such as online surveys powered via social media channels such as Twitter and Instagram might serve as critical tools to generate as well as to preliminarily test the appropriateness of hypotheses for further evaluation. 43 , 44
Some radical hypotheses might be difficult to publish after traditional peer review. These hypotheses might only be acceptable by the scientific community after they are tested in research studies. Preprints might be a way to disseminate such controversial and ground-breaking hypotheses. 45 However, scientists might prefer to keep their hypotheses confidential for the fear of plagiarism of ideas, avoiding online posting and publishing until they have tested the hypotheses.
SUGGESTIONS ON GENERATING AND PUBLISHING HYPOTHESES
Publication of hypotheses is important, however, a balance is required between scientific temper and controversy. Journal editors and reviewers might keep in mind these specific points, summarized in Table 2 and detailed hereafter, while judging the merit of hypotheses for publication. Keeping in mind the ethical principle of primum non nocere, a hypothesis should be published only if it is testable in a manner that is ethically appropriate. 46 Such hypotheses should be grounded in reality and lend themselves to further testing to either prove or disprove them. It must be considered that subsequent experiments to prove or disprove a hypothesis have an equal chance of failing or succeeding, akin to tossing a coin. A pre-conceived belief that a hypothesis is unlikely to be proven correct should not form the basis of rejection of such a hypothesis for publication. In this context, hypotheses generated after a thorough literature search to identify knowledge gaps or based on concrete clinical observations on a considerable number of patients (as opposed to random observations on a few patients) are more likely to be acceptable for publication by peer-reviewed journals. Also, hypotheses should be considered for publication or rejection based on their implications for science at large rather than whether the subsequent experiments to test them end up with results in favour of or against the original hypothesis.
Hypotheses form an important part of the scientific literature. The COVID-19 pandemic has reiterated the importance and relevance of hypotheses for dealing with public health emergencies and highlighted the need for evidence-based and ethical hypotheses. A good hypothesis is testable in a relevant study design, backed by preliminary evidence, and has positive ethical and clinical implications. General medical journals might consider publishing hypotheses as a specific article type to enable more rapid advancement of science.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Data curation: Gasparyan AY, Misra DP, Zimba O, Yessirkepov M, Agarwal V, Kitas GD.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes .
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more variables . An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls. A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Step 1: ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2: Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalise more complex constructs.
Step 3: Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
Step 4: Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
Step 6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, May 06). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/hypothesis-writing/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, operationalisation | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

Developing Theories & Hypotheses
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 40843
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
2.5: Developing a Hypothesis
Learning objectives.
- Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis.
- Discover how theories are used to generate hypotheses and how the results of studies can be used to further inform theories.
- Understand the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Theories and Hypotheses
Before describing how to develop a hypothesis, it is important to distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis. A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition (1965) [1] . He proposed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
A hypothesis , on the other hand, is a specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. It is an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts. Hypotheses are often specific predictions about what will happen in a particular study. They are developed by considering existing evidence and using reasoning to infer what will happen in the specific context of interest. Hypotheses are often but not always derived from theories. So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies of data. So if our research question is really original then we may need to collect some data and make some observations before we can develop a broader theory.
Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relationship. “ If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster, and a branching runway more slowly, when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in this chapter and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this question is an interesting one on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991) [2] . Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged themselves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.
Theory Testing
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). Researchers begin with a set of phenomena and either construct a theory to explain or interpret them or choose an existing theory to work with. They then make a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researchers then conduct an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, they reevaluate the theory in light of the new results and revise it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researchers can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows, this approach meshes nicely with the model of scientific research in psychology presented earlier in the textbook—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research.
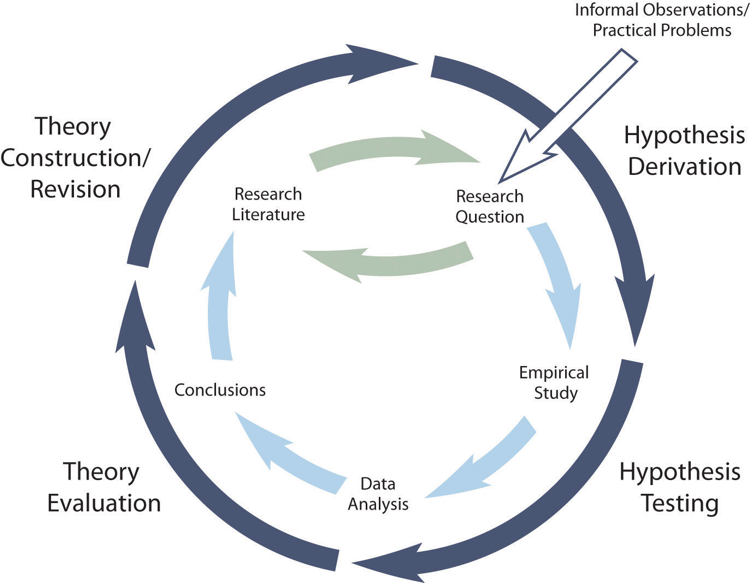
As an example, let us consider Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This theory predicts social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969) [3] . The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cockroach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cockroaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory. (Zajonc also showed that drive theory existed in humans [Zajonc & Sales, 1966] [4] in many other studies afterward).
Incorporating Theory into Your Research
When you write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
To use theories in your research will not only give you guidance in coming up with experiment ideas and possible projects, but it lends legitimacy to your work. Psychologists have been interested in a variety of human behaviors and have developed many theories along the way. Using established theories will help you break new ground as a researcher, not limit you from developing your own ideas.
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable . We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you’ll recall Popper’s falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical. As described above, hypotheses are more than just a random guess. Hypotheses should be informed by previous theories or observations and logical reasoning. Typically, we begin with a broad and general theory and use deductive reasoning to generate a more specific hypothesis to test based on that theory. Occasionally, however, when there is no theory to inform our hypothesis, we use inductive reasoning which involves using specific observations or research findings to form a more general hypothesis. Finally, the hypothesis should be positive. That is, the hypothesis should make a positive statement about the existence of a relationship or effect, rather than a statement that a relationship or effect does not exist. As scientists, we don’t set out to show that relationships do not exist or that effects do not occur so our hypotheses should not be worded in a way to suggest that an effect or relationship does not exist. The nature of science is to assume that something does not exist and then seek to find evidence to prove this wrong, to show that it really does exist. That may seem backward to you but that is the nature of the scientific method. The underlying reason for this is beyond the scope of this chapter but it has to do with statistical theory.
- Zajonc, R. B. (1965). Social facilitation. Science, 149 , 269–274 ↵
- Schwarz, N., Bless, H., Strack, F., Klumpp, G., Rittenauer-Schatka, H., & Simons, A. (1991). Ease of retrieval as information: Another look at the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61 , 195–202. ↵
- Zajonc, R. B., Heingartner, A., & Herman, E. M. (1969). Social enhancement and impairment of performance in the cockroach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 13 , 83–92. ↵
- Zajonc, R.B. & Sales, S.M. (1966). Social facilitation of dominant and subordinate responses. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 2 , 160-168. ↵

- What is Strategy?
- Business Models
- Developing a Strategy
- Strategic Planning
- Competitive Advantage
- Growth Strategy
- Market Strategy
- Customer Strategy
- Geographic Strategy
- Product Strategy
- Service Strategy
- Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Strategy
- Sales Strategy
- Marketing Strategy
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Organizational Strategy
- HR Strategy – Organizational Design
- HR Strategy – Employee Journey & Culture
- Process Strategy
- Procurement Strategy
- Cost and Capital Strategy
- Business Value
- Market Analysis
- Problem Solving Skills
- Strategic Options
- Business Analytics
- Strategic Decision Making
- Process Improvement
- Project Planning
- Team Leadership
- Personal Development
- Leadership Maturity Model
- Leadership Team Strategy
- The Leadership Team
- Leadership Mindset
- Communication & Collaboration
- Problem Solving
- Decision Making
- People Leadership
- Strategic Execution
- Executive Coaching
- Strategy Coaching
- Business Transformation
- Strategy Workshops
- Leadership Strategy Survey
- Leadership Training
- Who’s Joe?
“A fact is a simple statement that everyone believes. It is innocent, unless found guilty. A hypothesis is a novel suggestion that no one wants to believe. It is guilty until found effective.”
– Edward Teller, Nuclear Physicist
During my first brainstorming meeting on my first project at McKinsey, this very serious partner, who had a PhD in Physics, looked at me and said, “So, Joe, what are your main hypotheses.” I looked back at him, perplexed, and said, “Ummm, my what?” I was used to people simply asking, “what are your best ideas, opinions, thoughts, etc.” Over time, I began to understand the importance of hypotheses and how it plays an important role in McKinsey’s problem solving of separating ideas and opinions from facts.
What is a Hypothesis?
“Hypothesis” is probably one of the top 5 words used by McKinsey consultants. And, being hypothesis-driven was required to have any success at McKinsey. A hypothesis is an idea or theory, often based on limited data, which is typically the beginning of a thread of further investigation to prove, disprove or improve the hypothesis through facts and empirical data.
The first step in being hypothesis-driven is to focus on the highest potential ideas and theories of how to solve a problem or realize an opportunity.
Let’s go over an example of being hypothesis-driven.
Let’s say you own a website, and you brainstorm ten ideas to improve web traffic, but you don’t have the budget to execute all ten ideas. The first step in being hypothesis-driven is to prioritize the ten ideas based on how much impact you hypothesize they will create.

The second step in being hypothesis-driven is to apply the scientific method to your hypotheses by creating the fact base to prove or disprove your hypothesis, which then allows you to turn your hypothesis into fact and knowledge. Running with our example, you could prove or disprove your hypothesis on the ideas you think will drive the most impact by executing:
1. An analysis of previous research and the performance of the different ideas 2. A survey where customers rank order the ideas 3. An actual test of the ten ideas to create a fact base on click-through rates and cost
While there are many other ways to validate the hypothesis on your prioritization , I find most people do not take this critical step in validating a hypothesis. Instead, they apply bad logic to many important decisions . An idea pops into their head, and then somehow it just becomes a fact.
One of my favorite lousy logic moments was a CEO who stated,
“I’ve never heard our customers talk about price, so the price doesn’t matter with our products , and I’ve decided we’re going to raise prices.”
Luckily, his management team was able to do a survey to dig deeper into the hypothesis that customers weren’t price-sensitive. Well, of course, they were and through the survey, they built a fantastic fact base that proved and disproved many other important hypotheses.

Why is being hypothesis-driven so important?
Imagine if medicine never actually used the scientific method. We would probably still be living in a world of lobotomies and bleeding people. Many organizations are still stuck in the dark ages, having built a house of cards on opinions disguised as facts, because they don’t prove or disprove their hypotheses. Decisions made on top of decisions, made on top of opinions, steer organizations clear of reality and the facts necessary to objectively evolve their strategic understanding and knowledge. I’ve seen too many leadership teams led solely by gut and opinion. The problem with intuition and gut is if you don’t ever prove or disprove if your gut is right or wrong, you’re never going to improve your intuition. There is a reason why being hypothesis-driven is the cornerstone of problem solving at McKinsey and every other top strategy consulting firm.
How do you become hypothesis-driven?
Most people are idea-driven, and constantly have hypotheses on how the world works and what they or their organization should do to improve. Though, there is often a fatal flaw in that many people turn their hypotheses into false facts, without actually finding or creating the facts to prove or disprove their hypotheses. These people aren’t hypothesis-driven; they are gut-driven.
The conversation typically goes something like “doing this discount promotion will increase our profits” or “our customers need to have this feature” or “morale is in the toilet because we don’t pay well, so we need to increase pay.” These should all be hypotheses that need the appropriate fact base, but instead, they become false facts, often leading to unintended results and consequences. In each of these cases, to become hypothesis-driven necessitates a different framing.
• Instead of “doing this discount promotion will increase our profits,” a hypothesis-driven approach is to ask “what are the best marketing ideas to increase our profits?” and then conduct a marketing experiment to see which ideas increase profits the most.
• Instead of “our customers need to have this feature,” ask the question, “what features would our customers value most?” And, then conduct a simple survey having customers rank order the features based on value to them.
• Instead of “morale is in the toilet because we don’t pay well, so we need to increase pay,” conduct a survey asking, “what is the level of morale?” what are potential issues affecting morale?” and what are the best ideas to improve morale?”
Beyond, watching out for just following your gut, here are some of the other best practices in being hypothesis-driven:
Listen to Your Intuition
Your mind has taken the collision of your experiences and everything you’ve learned over the years to create your intuition, which are those ideas that pop into your head and those hunches that come from your gut. Your intuition is your wellspring of hypotheses. So listen to your intuition, build hypotheses from it, and then prove or disprove those hypotheses, which will, in turn, improve your intuition. Intuition without feedback will over time typically evolve into poor intuition, which leads to poor judgment, thinking, and decisions.
Constantly Be Curious
I’m always curious about cause and effect. At Sports Authority, I had a hypothesis that customers that received service and assistance as they shopped, were worth more than customers who didn’t receive assistance from an associate. We figured out how to prove or disprove this hypothesis by tying surveys to transactional data of customers, and we found the hypothesis was true, which led us to a broad initiative around improving service. The key is you have to be always curious about what you think does or will drive value, create hypotheses and then prove or disprove those hypotheses.
Validate Hypotheses
You need to validate and prove or disprove hypotheses. Don’t just chalk up an idea as fact. In most cases, you’re going to have to create a fact base utilizing logic, observation, testing (see the section on Experimentation ), surveys, and analysis.
Be a Learning Organization
The foundation of learning organizations is the testing of and learning from hypotheses. I remember my first strategy internship at Mercer Management Consulting when I spent a good part of the summer combing through the results, findings, and insights of thousands of experiments that a banking client had conducted. It was fascinating to see the vastness and depth of their collective knowledge base. And, in today’s world of knowledge portals, it is so easy to disseminate, learn from, and build upon the knowledge created by companies.
NEXT SECTION: DISAGGREGATION
DOWNLOAD STRATEGY PRESENTATION TEMPLATES
THE $150 VALUE PACK - 600 SLIDES 168-PAGE COMPENDIUM OF STRATEGY FRAMEWORKS & TEMPLATES 186-PAGE HR & ORG STRATEGY PRESENTATION 100-PAGE SALES PLAN PRESENTATION 121-PAGE STRATEGIC PLAN & COMPANY OVERVIEW PRESENTATION 114-PAGE MARKET & COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS PRESENTATION 18-PAGE BUSINESS MODEL TEMPLATE
JOE NEWSUM COACHING

EXECUTIVE COACHING STRATEGY COACHING ELEVATE360 BUSINESS TRANSFORMATION STRATEGY WORKSHOPS LEADERSHIP STRATEGY SURVEY & WORKSHOP STRATEGY & LEADERSHIP TRAINING
THE LEADERSHIP MATURITY MODEL
Explore other types of strategy.
BIG PICTURE WHAT IS STRATEGY? BUSINESS MODEL COMP. ADVANTAGE GROWTH
TARGETS MARKET CUSTOMER GEOGRAPHIC
VALUE PROPOSITION PRODUCT SERVICE PRICING
GO TO MARKET DISTRIBUTION SALES MARKETING
ORGANIZATIONAL ORG DESIGN HR & CULTURE PROCESS PARTNER
EXPLORE THE TOP 100 STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP COMPETENCIES
TYPES OF VALUE MARKET ANALYSIS PROBLEM SOLVING
OPTION CREATION ANALYTICS DECISION MAKING PROCESS TOOLS
PLANNING & PROJECTS PEOPLE LEADERSHIP PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT
Chapter 6 - Hypothesis Development
Chapter 6 overview.
This chapter discusses the third step of the SGAM, highlighted below in gold, Hypothesis Development.
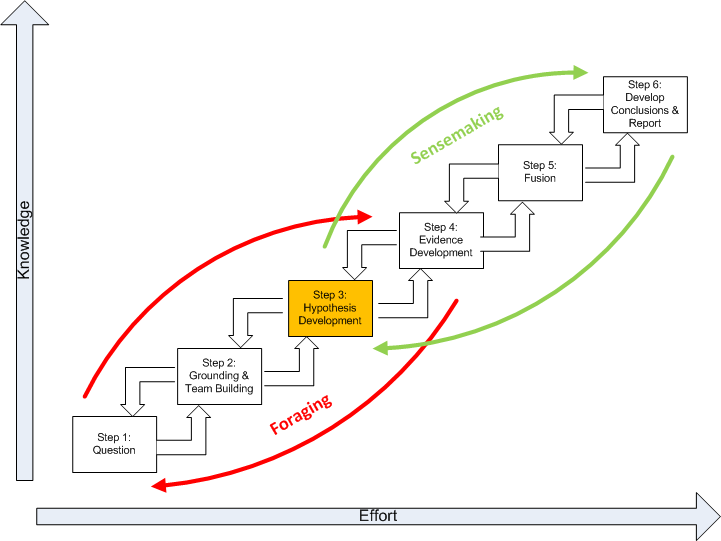
A hypothesis is often defined as an educated guess because it is informed by what you already know about a topic. This step in the process is to identify all hypotheses that merit detailed examination, keeping in mind that there is a distinction between the hypothesis generation and hypothesis evaluation .
If the analysis does not begin with the correct hypothesis, it is unlikely to get the correct answer. Psychological research into how people go about generating hypotheses shows that people are actually rather poor at thinking of all the possibilities. Therefore, at the hypothesis generation stage, it is wise to bring together a group of analysts with different backgrounds and perspectives for a brainstorming session. Brainstorming in a group stimulates the imagination and usually brings out possibilities that individual members of the group had not thought of. Experience shows that initial discussion in the group elicits every possibility, no matter how remote, before judging likelihood or feasibility. Only when all the possibilities are on the table, is the focus on judging them and selecting the hypotheses to be examined in greater detail in subsequent analysis.
When screening out the seemingly improbable hypotheses, it is necessary to distinguish hypotheses that appear to be disproved (i.e., improbable) from those that are simply unproven. For an unproven hypothesis, there is no evidence that it is correct. For a disproved hypothesis, there is positive evidence that it is wrong. Early rejection of unproven, but not disproved, hypotheses biases the analysis, because one does not then look for the evidence that might support them. Unproven hypotheses should be kept alive until they can be disproved. One example of a hypothesis that often falls into this unproven but not disproved category is the hypothesis that an opponent is trying to deceive us. You may reject the possibility of denial and deception because you see no evidence of it, but rejection is not justified under these circumstances. If deception is planned well and properly implemented, one should not expect to find evidence of it readily at hand. The possibility should not be rejected until it is disproved, or, at least, until after a systematic search for evidence has been made, and none has been found.
There is no "correct" number of hypotheses to be considered. The number depends upon the nature of the analytical problem and how advanced you are in the analysis of it. As a general rule, the greater your level of uncertainty, or the greater the impact of your conclusion, the more alternatives you may wish to consider. More than seven hypotheses may be unmanageable; if there are this many alternatives, it may be advisable to group several of them together for your initial cut at the analysis.
Developing Multiple Hypotheses
Developing good hypotheses requires divergent thinking to ensure that all hypotheses are considered. It also requires convergent thinking to ensure that redundant and irrational hypotheses are eliminated. A hypothesis is stated as an "if … then" statement. There are two important qualities about a hypothesis expressed as an "if … then" statement. These are:
- Is the hypothesis testable; in other words, could evidence be found to test the validity of the statement?
- Is the hypothesis falsifiable; in other words, could evidence reveal that such an idea is not true?
Hypothesis development is ultimately experience-based. In this experienced-based reasoning, new knowledge is compared to previous knowledge. New knowledge is added to this internal knowledge base. Before long, an analyst has developed an internal set of spatial rules. These rules are then used to develop possible hypotheses.
Looking Forward
Developing hypotheses and evidence is the beginning of the sensemaking and Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) process. ACH is a general purpose intelligence analysis methodology developed by Richards Heuer while he was an analyst at the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). ACH draws on the scientific method, cognitive psychology, and decision analysis. ACH became widely available when the CIA published Heuer’s The Psychology of Intelligence Analysis . The ACH methodology can help the geospatial analyst overcome cognitive biases common to analysis in national security, law enforcement, and competitive intelligence. ACH forces analysts to disprove hypotheses rather than jump to conclusions and permit biases and mindsets to determine the outcome. ACH is a very logical step-by-step process that has been incorporated into our Structured Geospatial Analytical Method. A complete discussion of ACH is found in Chapter 8 of Heuer’s book.
General Approaches to Problem Solving Utilizing Hypotheses
Science follows at least three general methods of problem solving using hypotheses. These can be called the:
- method of the ruling theory
- method of the working hypothesis
- method of multiple working hypotheses
The first two are the most popular but they can lead to overlooking relevant perspectives, data, and encourage biases. It has been suggested that multiple hypotheses offers a more effective way of overcoming this problem.
Ruling Theories and Working Hypotheses
Our desire to reach an explanation commonly leads us to a tentative interpretation that is based on a single case. The explanation can blind us to other possibilities that we ignored at first glance. This premature explanation can become a ruling theory, and our research becomes focused on proving that ruling theory. The result is a bias to evidence that disproves the ruling theory or supports an alternate explanation. Only if the original hypothesis was by chance correct does our analysis lead to any meaningful intelligence work. The working hypothesis is supposed to be a hypothesis to be tested, not in order to prove the hypothesis, but as a stimulus for study and fact-finding. Nonetheless, the single working hypothesis can become a ruling theory, and the desire to prove the working hypothesis, despite evidence to the contrary, can become as strong as the desire to prove the ruling theory.
Multiple Hypotheses
The method of multiple working hypotheses involves the development, prior to our search for evidence, of several hypotheses that might explain what are attempting to explain. Many of these hypotheses should be contradictory, so that many will prove to be improbable. However, the development of multiple hypotheses prior to the intelligence analysis lets us avoid the trap of the ruling hypothesis and thus makes it more likely that our intelligence work will lead to meaningful results. We open-mindedly envision all the possible explanations of the events, including the possibility that none of the hypotheses are plausible and the possibility that more research and hypothesis development is needed. The method of multiple working hypotheses has several other beneficial effects on intelligence analysis. Human actions are often the result of several factors, not just one, and multiple hypotheses make it more likely that we will see the interaction of the several factors. The beginning with multiple hypotheses also promotes much greater thoroughness than analysis directed toward one hypothesis, leading to analytic lines that we might otherwise overlook, and thus to evidence and insights that might never have been considered. Thirdly, the method makes us much more likely to see the imperfections in our understanding and thus to avoid the pitfall of accepting weak or flawed evidence for one hypothesis when another provides a more possible explanation.
Drawbacks of Multiple Hypotheses
Multiple hypotheses have drawbacks. One is that it is difficult to express multiple hypotheses simultaneously, and therefore there is a natural tendency to favor one. Another problem is developing a large number of hypotheses that can be tested. A third possible problem is that of the indecision that arises as an analyst balances the evidence for various hypotheses, which is likely preferable to the premature rush to a false conclusion.
Actions That Help the Analyst Develop Hypotheses
Action 1: Brainstorming . Begin with a brainstorming session with your knowledge team to identify a set of alternative hypotheses. Focus on the hypotheses that are:
- logically consistent with the theories and data uncovered in your grounding;
- address the quality and relationships of spaces.
State the hypotheses stated in an "if ... then" format, for example:
- If the DC Shooter is a terrorist, then the geospatial pattern of events would be similar to other terrorist acts.
- If the DC Shooter is a serial killer, then the geospatial pattern of events would be similar to other serial killers.
Action 2: Review the hypotheses for testability , i.e., can evidence be could found to test the validity of the statement.
Action 3: Check the hypotheses for falsifiability , i.e., could evidence reveal that such an idea is not true.
Action 4: Combine redundant hypotheses.
Action 5:Consider the elimination of improbable and unproven hypotheses.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Deductive Approach (Deductive Reasoning)
A deductive approach is concerned with “developing a hypothesis (or hypotheses) based on existing theory, and then designing a research strategy to test the hypothesis” [1]
It has been stated that “deductive means reasoning from the particular to the general. If a causal relationship or link seems to be implied by a particular theory or case example, it might be true in many cases. A deductive design might test to see if this relationship or link did obtain on more general circumstances” [2] .
Deductive approach can be explained by the means of hypotheses, which can be derived from the propositions of the theory. In other words, deductive approach is concerned with deducting conclusions from premises or propositions.
Deduction begins with an expected pattern “that is tested against observations, whereas induction begins with observations and seeks to find a pattern within them” [3] .
Advantages of Deductive Approach
Deductive approach offers the following advantages:
- Possibility to explain causal relationships between concepts and variables
- Possibility to measure concepts quantitatively
- Possibility to generalize research findings to a certain extent
Alternative to deductive approach is inductive approach. The table below guides the choice of specific approach depending on circumstances:
Choice between deductive and inductive approaches
Deductive research approach explores a known theory or phenomenon and tests if that theory is valid in given circumstances. It has been noted that “the deductive approach follows the path of logic most closely. The reasoning starts with a theory and leads to a new hypothesis. This hypothesis is put to the test by confronting it with observations that either lead to a confirmation or a rejection of the hypothesis” [4] .
Moreover, deductive reasoning can be explained as “reasoning from the general to the particular” [5] , whereas inductive reasoning is the opposite. In other words, deductive approach involves formulation of hypotheses and their subjection to testing during the research process, while inductive studies do not deal with hypotheses in any ways.
Application of Deductive Approach (Deductive Reasoning) in Business Research
In studies with deductive approach, the researcher formulates a set of hypotheses at the start of the research. Then, relevant research methods are chosen and applied to test the hypotheses to prove them right or wrong.
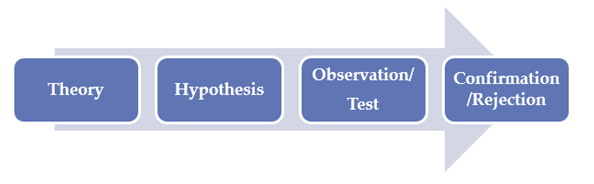
Generally, studies using deductive approach follow the following stages:
- Deducing hypothesis from theory.
- Formulating hypothesis in operational terms and proposing relationships between two specific variables
- Testing hypothesis with the application of relevant method(s). These are quantitative methods such as regression and correlation analysis, mean, mode and median and others.
- Examining the outcome of the test, and thus confirming or rejecting the theory. When analysing the outcome of tests, it is important to compare research findings with the literature review findings.
- Modifying theory in instances when hypothesis is not confirmed.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance contains discussions of theory and application of research approaches. The e-book also explains all stages of the research process starting from the selection of the research area to writing personal reflection. Important elements of dissertations such as research philosophy , research design , methods of data collection , data analysis and sampling are explained in this e-book in simple words.
John Dudovskiy

[1] Wilson, J. (2010) “Essentials of Business Research: A Guide to Doing Your Research Project” SAGE Publications, p.7
[2] Gulati, PM, 2009, Research Management: Fundamental and Applied Research, Global India Publications, p.42
[3] Babbie, E. R. (2010) “The Practice of Social Research” Cengage Learning, p.52
[4] Snieder, R. & Larner, K. (2009) “The Art of Being a Scientist: A Guide for Graduate Students and their Mentors”, Cambridge University Press, p.16
[5] Pelissier, R. (2008) “Business Research Made Easy” Juta & Co., p.3
New Rural Community Construction or Retention Development: A Comparative Analysis of Rural Settlement Transition Mechanism in Plain Agriculture Area of China Based on Actor Network Theory
- Published: 15 May 2024
- Volume 34 , pages 436–452, ( 2024 )
Cite this article

- Yanbo Qu 1 , 2 ,
- Xiaozhen Dong 1 , 2 ,
- Wenqiu Ma 3 &
- Weiying Zhao 1 , 2
12 Accesses
Explore all metrics
It is an important way to realize rural revitalization and sustainable development to guide rural settlement transition (RST) in an appropriate way. This paper uses actor network theory (ANT) to construct a theoretical framework for the study of RST. Taking two typical villages with different transition paths in rural areas of North China Plain as examples, this paper reveals the mechanism of RST and makes a comparative analysis. The results show that: 1) after identifying problems and obligatory passage point, key actors recruit heterogeneous actors into the actor network by entrusting them with common interests, and realize RST under the system operation. 2) Rural settlements under different transition paths have similarities in the problems to be solved, collective actions and policy factors, but there are differences in the transition process, mechanism and effect. The actor network and mechanism of RST through the path of new rural community construction are more complex and the transition effect is more thorough. In contrast, the degree of RST of retention development path is limited if there is no resource and location advantage. 3) Based on the applicable conditions of different paths, this paper designs a logical framework of ‘Situation-Structure-Behavior-Result’ to scientifically guide the identification of RST paths under the background of rural revitalization.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Re-conceptualizing the ideal homes in rural China: an actor-network theory approach
Dryland co-management in Kerman province, Iran: a dynamic analysis of social networks

Rural restructuring in China: Theory, approaches and research prospect
Callon M, 1986. The sociology of an actor-network: the case of the electric vehicle. In: Callon M et al. (eds.). Mapping the Dynamics of Science and Technology . London: Palgrave Macmillan. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-07408-2_2
Chapter Google Scholar
Cao Yuling, You Bin, Zhang Juntao, 2022. Research on the dilemma and realization path of rural space reconstruction from the perspective of rural vitalization. Contemporary Economic Management , 44(5): 51–57. (in Chinese)
Google Scholar
Chen C, Gao J L, Chen J L, 2017. Institutional changes, land use dynamics, and the transition of rural settlements in suburban China: a case study of Huishan District in Wuxi City. Habitat International , 70: 24–33. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.09.011
Article Google Scholar
Cheng Yeqing, Wang Ting, Huang Zheng et al., 2022. Rural transformation development mechanism and rural revitalization path from the perspective of actor network: a case study of Dabian Village in the central mountainous area of Hainan Province. Economic Geography , 42(4): 34–43. (in Chinese)
Cheng Mingyang, Chen Huiling, 2023. Spatio-temporal evolution of the rural regional system and its evolution mechanism in Huang-Huai-Hai area of China. Chinese Geographical Science , 33(1): 51–68. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-022-1323-z
Coluzzi R, Bianchini L, Egidi G et al., 2022. Density matters? Settlement expansion and land degradation in peri-urban and rural districts of Italy. Environmental Impact Assessment Review , 92: 106703. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2021.106703
Da La Fuente J L M, Infante-Amate J, Travieso E, 2024. Historical changes in Mediterranean rural settlements (southern Spain, 1787–2019). Journal of Rural Studies , 106: 103217. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2024.103217
Drobnjaković M, Steinführer A, 2024. Re-thinking rurality: towards a new research approach and rural-urban spatial gradient establishment in Serbia. Applied Geography , 163: 103195. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2023.103195
Emodi N V, Haruna E U, Abdu N et al., 2022. Urban and rural household energy transition in Sub-Saharan Africa: does spatial hetero-geneity reveal the direction of the transition? Energy Policy , 168: 113118. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.113118
Gareau B J, 2012. Worlds apart: a social theoretical exploration of local networks, natural actors, and practitioners of rural development in Southern Honduras. Sustainability , 4(7): 1596–1618. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su4071596
Hoggart K, Paniagua A, 2001. What rural restructuring? Journal of Rural Studies , 17(1): 41–62. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0743-0167(00)00036-X
Kiss E, 2000. Rural restructuring in Hungary in the period of socio-economic transition. GeoJournal , 51(3): 221–233. doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017507328301
Latocha-Wites A, Kajdanek K, Sikorski D et al., 2024. Global forces and local responses-a ‘hot-spots’ model of rural revival in a pe-ripheral region in the Central-Eastern European context. Journal of Rural Studies , 106: 103212. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2024.103212
Latour B, 1987. Science in Action: How to Follow Scientists and Engineers Through Society . Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Li C X, Wu K N, 2017. Driving forces of the villages hollowing based on geographically weighted regression model: a case study of Longde County, the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Natural Hazards , 89(3): 1059–1079. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3008-y
Li Huayin, 2020. Responsive participation: an analysis of the interaction between township governments and farmers in rural reform—based on the investigation and comparison of three township reform experiments. Chinese Public Administration , (9): 128–134, 159. (in Chinese)
Li X F, Yang H, Jia J et al., 2021. Index system of sustainable rural development based on the concept of ecological livability. Environmental Impact Assessment Review , 86: 106478. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2020.106478
Li Zhigang, Yu Taofang, Wei Lihua et al., 2007. A study on the transition of ‘transitional community’ under the high-speed urbanization in China. Urban Development Studies , 14(5): 84–90. (in Chinese)
CAS Google Scholar
Liu Xuan, Wang Xiaoyi, 2013. A review on the application of actor network theory to human geography. Progress in Geography , 32(7): 1139–1147. (in Chinese)
Liu Y S, Li Y H, 2017. Revitalize the world’s countryside. Nature , 548(7667): 275–277. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/548275a
Article CAS Google Scholar
Long H L, Tu S S, Ge D Z et al., 2016. The allocation and management of critical resources in rural China under restructuring: problems and prospects. Journal of Rural Studies , 47: 392–412. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2016.03.011
Nimmo R, 2011. Actor-network theory and methodology: social research in a more-than-human world. Methodological Innovations Online , 6(3): 108–119. doi: https://doi.org/10.4256/mio.2011.010
Panzer-Krause S, 2020. The lost rural idyll? Tourists’ attitudes towards sustainability and their influence on the production of rural space at a rural tourism hotspot in Northern Ireland. Journal of Rural Studies , 80: 235–243. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2020.09.013
Qu Y B, Dong X Z, Zhan L Y et al., 2021a. Scale transition and structure-function synergy differentiation of rural residential land: a dimensionality reduction transmission process from macro to micro scale. Land , 10(6): 647. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/LAND10060647
Qu Y B, Dong X Z, Zhan L Y et al., 2022a. Achieving rural revitalization in China: a suitable framework to understand the coordination of material and social space quality of rural residential areas in the plain. Growth and Change , 53(3): 1052–1081. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/GROW.12536
Qu Y B, Jiang G H, Li Z T et al., 2019. Understanding rural land use transition and regional consolidation implications in China. Land Use Policy , 82: 742–753. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.11.014
Qu Y B, Zhao W Y, Zhao L J et al., 2022b. Research on hollow village governance based on action network: mode, mechanism and countermeasures—comparison of different patterns in plain agricultural areas of China. Land , 11(6): 792. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/land11060792
Qu Yanbo, Chai Yifan, Zhu Weiya et al., 2021b. Archetype analysis of rural homestead withdrawal patterns based on the framework of ‘diagnosis-design-outcome’. Resources Science , 43(7): 1293–1306. (in Chinese)
Stokowski P A, Kuentzel W F, Derrien M M et al., 2021. Social, cultural and spatial imaginaries in rural tourism transitions. Journal of Rural Studies , 87: 243–253. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2021.09.011
Terluin I J, 2003. Differences in economic development in rural regions of advanced countries: an overview and critical analysis of theories. Journal of Rural Studies , 19(3): 327–344. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0743-0167(02)00071-2
Tian Y S, Qian J, Wang L, 2021. Village classification in metropolitan suburbs from the perspective of urban-rural integration and improvement strategies: a case study of Wuhan, central China. Land Use Policy , 111: 105748. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105748
Tu Shuangshuang, Zheng Yuhan, Long Hualou et al., 2020. Spatio-temporal pattern of rural development and restructuring and regional path of rural vitalization in Guangxi, China. Acta Geographica Sinica , 75(2): 365–381. (in Chinese)
Tu S S, Long H L, Zhang Y N et al., 2018. Rural restructuring at village level under rapid urbanization in metropolitan suburbs of China and its implications for innovations in land use policy. Habitat International , 77: 143–152. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.12.001
Wang Xiuwei, Li Xiaojun, 2022. Characteristics and influencing factors of the key villages of rural tourism in China. Acta Geographica Sinica , 77(4): 900–917. (in Chinese)
Yang Ren, 2021. The actor-network perspective on the reconstruction process and internal mechanism of typical Taobao villages in the Pearl River Delta region. Acta Geographica Sinica , 76(12): 3076–3089. (in Chinese)
Yang Y Y, Liu Y S, Li Y R et al., 2018. Measure of urban-rural transformation in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in the new millennium: population-land-industry perspective. Land Use Policy , 79: 595–608. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.08.005
Yuan Chao, Chen Pinyu, Kong Xiang et al., 2021. Research on the interaction between actor-network theory and human geography: reconstruction, debate and reflection. Geographical Research , 40(2): 583–596. (in Chinese)
Zambon I, Colantoni A, Carlucci M et al., 2017. Land quality, sustainable development and environmental degradation in agricultural districts: a computational approach based on entropy indexes. Environmental Impact Assessment Review , 64: 37–46. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2017.01.003
Zang Y Z, Liu Y S, Yang Y Y et al., 2020. Rural decline or restructuring? Implications for sustainability transitions in rural China. Land Use Policy , 94: 104531. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104531
Zang Y Z, Yang Y Y, Liu Y S, 2021. Understanding rural system with a social-ecological framework: evaluating sustainability of rural evolution in Jiangsu province, South China. Journal of Rural Studies , 86: 171–180. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2021.05.008
Zou Mingyan, Zhou Tiejun, Pan Yin, 2019. Driving force of rural construction based on actors network theory. Planners , 35(16): 62–67. (in Chinese)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Public Administration and Policy, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Jinan, 250014, China
Yanbo Qu, Xiaozhen Dong & Weiying Zhao
Institute of Land Science and Policy, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Jinan, 250014, China
College of Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing, 100083, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
QU Yanbo: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, resources, writing-review & editing, supervision, funding acquisition; DONG Xiaozhen: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, visualization, data curation, writing-original draft, writing-review & editing, supervision; MA Wenqiu: methodology, validation, writing-review & editing, supervision, project administration; ZHAO Weiying: data curation, investigation, supervision.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Wenqiu Ma .
Ethics declarations
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of the Taishan Scholars Project Special Funds, National Natural Science Fundation of China (No. 42077434, 42001199), Youth Innovation Technology Project of Higher School in Shandong Province (No. 2019RWG016)
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Qu, Y., Dong, X., Ma, W. et al. New Rural Community Construction or Retention Development: A Comparative Analysis of Rural Settlement Transition Mechanism in Plain Agriculture Area of China Based on Actor Network Theory. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 34 , 436–452 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-024-1430-0
Download citation
Received : 23 March 2023
Accepted : 25 July 2023
Published : 15 May 2024
Issue Date : June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-024-1430-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- rural settlement transition (RST)
- actor network theory (ANT)
- transition path
- transition mechanism
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Get involved

- UNDP Mauritius Country Programme Document 2024-2028 pdf (8.1 MB)
UNDP Mauritius Country Programme Document 2024-2028
May 22, 2024.
The UNDP programme in Mauritius is be clustered around two complementary programme areas, using cross-cutting innovation, technology and digitalization to improve processes, increase efficiency and promote sustainability. The areas are: (a) socioeconomic transformation; and (b) environmental sustainability and resilience. The theory of change is underpinned by the understanding that if structural constraints that hinder investment in the public and private sectors are addressed, and underemployed women, at-risk youth and vulnerable communities, particularly in coastal regions and those affected by gender-based violence, are deliberately included in economic and alternative livelihood initiatives, and if environmental commitments for the sustainable management of natural resources, adaptation to and mitigation of climate change and disaster risk reduction are fulfilled through increased climate financing and effective implementation; then Mauritius will consolidate its path towards an inclusive and green economy aligned with the national vision.
The country programme will support innovation and experimentation for integrated solutions and inclusive digital transformation, with the support of the UNDP Global Centre for Technology, Innovation and Sustainable Development in Singapore, and exploration of innovative private financing sources through the UNDP Sustainable Finance Hub and Global Policy Network. At country level, the multi-country office aims to strengthen upstream policy advisory capacities and streamline operational capacities for improved efficiency and agility in programming. The programme will emphasize a human rights- based approach through the design, planning and implementation of development programmes at community level, with specific focus on underemployed fisherfolk in coastal communities; survivors of gender-based violence; and communities vulnerable to environmental shocks and degradation.
Regions and Countries
Related publications, publications, undp seychelles country programme document 2024-2028.
The country programme’s overarching theory of change is that if the agility of the public sector is enhanced through digital transformation; if the structural c...
Seychelles - Development Finance Assessment
The Seychelles Development Finance Assessment (DFA) was conducted on behalf of the Government of Seychelles, as part of efforts to assist the identification and...
National Employee Engagement Survey 2023
Business Mauritius launched a National Employee Engagement Survey in March 2023. This business community-wide study run in collaboration with the Human Resource...
UNDP Mauritius Annual Report 2022
In 2022, the UNDP in Mauritius collaborated across the UN system and partnered with bilateral and multilateral actors to deliver development programmes developm...
UNDP Seychelles Annual Report 2022
Over the past year, the UNDP programme in Seychelles made progress across three directions of change contributing to structural transformation, leaving no one b...
Seychelles SDG Investor Map Prospectus
The Seychelles SDG Investor Map is the product of a partnership between the Ministry of Investment, Entrepreneurship, and Industry (MIEI) and the United Nations...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Make observations. Formulate a hypothesis. Design an experiment to test the hypothesis. State the indicators to evaluate if the experiment has succeeded. Conduct the experiment. Evaluate the results of the experiment. Accept or reject the hypothesis. If necessary, make and test a new hypothesis.
Make observations. Formulate a hypothesis. Design an experiment to test the hypothesis. State the indicators to evaluate if the experiment has succeeded. Conduct the experiment. Evaluate the results of the experiment. Accept or reject the hypothesis. If necessary, make and test a new hypothesis.
How Might We technique → Dot voting (based on estimated/assumptive impact) → converting into a hypothesis → define testing methodology (research method + success/fail criteria) → impact effort scale for prioritizing → test, learn, repeat. Once the hypothesis is proven right, the feature is escalated into the development track for UI ...
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies of data. ... A cyclical process of theory development, starting with an observed phenomenon, then ...
What Is Hypothesis-Driven Development? A hypothesis-based approach allows product developers to design, test, and refactor a product until it is acceptable to consumers. This methodology involves testing and refining the product based on consumer feedback to verify the assumptions made during the ideation process.
2.4 Developing a Hypothesis. Learning Objectives. Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis. ... So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies ...
The steps to write a research hypothesis are: 1. Stating the problem: Ensure that the hypothesis defines the research problem. 2. Writing a hypothesis as an 'if-then' statement: Include the action and the expected outcome of your study by following a 'if-then' structure. 3.
Formulating Hypotheses for Different Study Designs. Generating a testable working hypothesis is the first step towards conducting original research. Such research may prove or disprove the proposed hypothesis. Case reports, case series, online surveys and other observational studies, clinical trials, and narrative reviews help to generate ...
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
Hypothesis testing example. You want to test whether there is a relationship between gender and height. Based on your knowledge of human physiology, you formulate a hypothesis that men are, on average, taller than women. To test this hypothesis, you restate it as: H 0: Men are, on average, not taller than women. H a: Men are, on average, taller ...
McKinsey consultants follow three steps in this cycle: Form a hypothesis about the problem and determine the data needed to test the hypothesis. Gather and analyze the necessary data, comparing ...
2.5: Developing a Hypothesis. Learning Objectives. Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis. ... So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger ...
3. Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
And, being hypothesis-driven was required to have any success at McKinsey. A hypothesis is an idea or theory, often based on limited data, which is typically the beginning of a thread of further investigation to prove, disprove or improve the hypothesis through facts and empirical data. The first step in being hypothesis-driven is to focus on ...
"A hypothesis is a conjectural statement of the relation between two or more variables". (Kerlinger, 1956) "Hypothesis is a formal statement that presents the expected relationship between an independent and dependent variable."(Creswell, 1994) "A research question is essentially a hypothesis asked in the form of a question."
Hypothesis development is ultimately experience-based. In this experienced-based reasoning, new knowledge is compared to previous knowledge. New knowledge is added to this internal knowledge base. Before long, an analyst has developed an internal set of spatial rules. These rules are then used to develop possible hypotheses.
Definition: Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation. Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments ...
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
Scientific hypothesis, idea that proposes an explanation for an observed phenomenon or narrow set of phenomena. ... The generation of a hypothesis frequently is described as a creative process and is based on existing scientific knowledge, intuition, ... The investigation of scientific hypotheses is an important component in the development of ...
A deductive approach is concerned with "developing a hypothesis (or hypotheses) based on existing theory, and then designing a research strategy to test the hypothesis" [1] It has been stated that "deductive means reasoning from the particular to the general. If a causal relationship or link seems to be implied by a particular theory or ...
4. Formulate your hypothesis. After collecting background information and making a prediction based on your question, plan a statement that lays out your variables, subjects and predicted outcome. Whether you write it as an "if/then" or declarative statement, your hypothesis should include the prediction to be tested.
According to the empathy-altruism hypothesis, under the function of empathy, consumers will have emotional reactions such as compassion and sympathy, thereby promoting their willingness to purchase to help farmers. Based on this, the hypothesis is proposed that the host's narrative role can trigger different degrees of empathy in consumers.
It is an important way to realize rural revitalization and sustainable development to guide rural settlement transition (RST) in an appropriate way. This paper uses actor network theory (ANT) to construct a theoretical framework for the study of RST. Taking two typical villages with different transition paths in rural areas of North China Plain as examples, this paper reveals the mechanism of ...
The UNDP programme in Mauritius is be clustered around two complementary programme areas, using cross-cutting innovation, technology and digitalization to improve processes, increase efficiency and promote sustainability. The areas are: (a) socioeconomic transformation; and (b) environmental sustainability and resilience. The theory of change is underpinned by the understanding that if ...