- Share full article


College Is All About Curiosity. And That Requires Free Speech.
True learning can only happen on campuses where academic freedom is paramount — within and outside the classroom.
Credit... Illustration by Andrew Rae
Supported by
By Stephen L. Carter
- Jan. 24, 2024
I have served happily as a professor at Yale for most of my adult life, but in my four-plus decades at the mast, I have never seen campuses roiled as they’re roiling today. On the one hand are gleeful activists on the right, taking victory laps over the tragic tumble from grace of Harvard’s president, Claudine Gay. On the other is a campus left that has spent years crafting byzantine and vague rules on hate speech that it suddenly finds turned back on its allies. For those of us who love the academy, these are unhappy times.
Listen to This Article
The controversy began with criticisms of some universities, Harvard included, for soft-pedaling their responses to the horrific Oct. 7 Hamas attack on Israel, and for then ignoring the overheated rhetoric of many pro-Palestinian protesters on campus. It has since spiraled into a full-bore battle in the never-ending culture wars.
There’s something sad but deeply American about the way that the current crisis stems not from the terror attacks but from a subsequent congressional hearing at which the presidents of Harvard, the University of Pennsylvania and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology gave such cautious responses that it was hard to understand their positions. It was all very embarrassing; and, in its way, very McCarthyist.
Still, some good may yet come of the debacle. I have in mind not, as the left might think, a fresh rallying of the angry troops; nor, as the right might think, an eager readiness for the next battle. Rather, the controversy provides us with an opportunity to engage in a serious debate about what higher education is for.
The Oct. 7 attack was hardly an auspicious moment to unfurl campus demands that the world pay attention to the context underlying the vicious assault. Measured by casualties, the Hamas attack is the third-deadliest terror incident in the half century for which we have data; measured in per capita terms, it was by far the worst, with more than 1 in every 10,000 Israelis killed. I have a fair degree of sympathy — quite a lot, actually — for many aspects of decolonial theory. I have taught, for example, the works of Frantz Fanon and Talal Asad, both of whom seek, in different ways, to offer an explanation for anti-Western violence that most observers find inexplicable. I have no sympathy whatsoever for the intentional targeting of children and the weaponization of sexual violence. Drawing a distinction between civilian and military targets might benefit the more powerful side, but the distinction is nonetheless correct.
In the wake of so traumatizing and polarizing an episode, to say nothing of its aftermath, students of different ideological persuasions will nevertheless behave like the rest of us, selecting facts from sources that share their predilections. This behavior is intellectually inside-out. A goal of higher education must be to train our students (and often ourselves) away from re-enacting endlessly the famous 1954 experiment by Albert H. Hastorf and Hadley Cantril, in which students at Dartmouth and Princeton watched a film of a penalty-ridden football game between the two schools. When questioned about what they witnessed, each side’s partisans saw mainly the fouls committed by their opponents.
In short, they found only what they were looking for.
The university classroom is the place to press students to look for more.
The classroom is said to be an outdated technology: A teacher stands up front explaining a subject as students take notes. Future-minded critics insist that the model is near its inevitable end. The Covid-19 shutdowns accelerated the drive to develop better tools for asynchronous learning. The rise of generative A.I., together with the mutually parasitic relationship between young people and their screens, suggests that the old way is nearly done.
Here I am moved to argue for the defense. These dire predictions might fall into line with what’s happening on campus, but what universities are becoming bears little relation to what the classroom should be. The difficulty stems, as my Yale Law School colleague Anthony Kronman has accurately noted, from the yielding of universities to the “vocational ideal,” the notion that what’s most important in life is work (together with the wallet), and concomitantly that the purpose of higher education is to inculcate the skills needed to excel in the labor market. In short, college as a path to a better job and a higher income.
If that’s how the mavens of higher education see their institutions, they will deservedly lose the battle over how students are taught. For if the purpose of the university classroom is simply to impart information, digital agents will soon perform the task better than experienced teachers, and colleges will find themselves unnecessary, merely duplicative of what students can get at home, cheaply and efficiently.
But this stumble toward redundancy rests upon a fatal misunderstanding of why the classroom exists. Teaching a subject is important; it is also in a sense incidental. The classroom is, first and foremost, a place to train young minds toward a yearning for knowledge and a taste for argument — to be intellectually curious — even if what they wind up discovering challenges their most cherished convictions. If the behavioral economist George Loewenstein is right that curiosity is a result of an “information gap” — a desire to know more than we do — then the most vital tasks of higher education are to help students realize that the gap always exists and to stoke their desire to bridge it.
Impediments to free speech are impediments to free thought and can only interfere with that search. That’s why academic freedom is so precious.

The lineage of academic freedom can be traced back at least to the 15th century, but historians tell us that the modern conception comes largely from the German universities of the 19th century. As the physicist and philosopher Hermann von Helmholtz put the point in 1869, scholars must be “more fearless of the consequences of the whole truth than any other people.” In a world where so many “other people” are on the lookout for wrongthink, the ability to pursue truth becomes more precious still.
A 1938 essay in Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science described academic freedom as the professor’s “special need of elbowroom in his work”; with apologies to Virginia Woolf, we might call it the need for elbowroom of one’s own. The image is one of adequate space to do your work, secure in the knowledge that nobody is looking over your shoulder to enforce ideological conformity. For the university to do its job of inculcating curiosity, academic freedom should be a near-absolute, within the classroom as well as without. College administrators who believe otherwise shouldn’t be college administrators.
In her fine book “Curiosity: A Cultural History of Early Modern Inquiry,” Barbara M. Benedict shows how this quality that we nowadays consider a virtue was in the past often regarded as a dangerous disruption of the social order. The view on campus today is often much the same, with scholarly work guided along particular ideological paths, and with those who transgress often marked down as unpersons. What the essayist and literary critic George Steiner derided half a century ago as a “nostalgia for the absolute” is these days everyday academic life.
What made the congressional hearing so sad was not merely the accusatory quality of the committee’s questions, or even the evasive quality of the presidents’ answers. It was that the presidents were being asked to interpret their own rules on campus speech — and couldn’t.
They’re not alone. Existing campus speech rules have led to all sorts of horror stories. Many are true. Because the regulations tend to be standardless — often, deciding what’s hateful based on the response of the listener, a so-called “heckler’s veto” — they give no fair warning of what’s forbidden, leading to such absurdities as stopping a student from passing out copies of the Constitution on Constitution Day; or investigating a professor for the sin of stopping to watch a “Back the Blue” rally; or rebuking an untenured lecturer who in a discussion about race showed a documentary that included graphic images of lynching, and read aloud from the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s “Letter from Birmingham Jail.” Evidently the film, like the letter, included what we’re now supposed to call the N-word. (Full disclosure: I’ve used the word often in my books — fiction and nonfiction alike — and, seemingly only yesterday, I used it in the pages of The Times.)
But even were the rules crystal clear, they’d have both students and faculty looking over their shoulders, wondering which of their ideas might bring forth not disagreement — the mother’s milk of academic life — but condemnation from their fellows and, most dreaded of all, investigation. The inculcation of fear as part of daily work on campus is very McCarthyist; more McCarthyist, even, than hauling college presidents before Congress to try to force them to place even more speech off limits. Because having to look over your shoulder is something you contend with every day.
Many investigations and rules are justified on the grounds of ensuring that students feel safe. But I’m not at all sure the college classroom should be a place of comfort. It should be a place, rather, where students regularly face the challenge of difficult questions, as their professors help prepare them for the life of the mind. The more successful the teaching, the more students will carry their taste for the give-and-take of argument out of the classroom and into the larger world.
This is why those who insist that pro-Palestinian protesters be punished for their views have matters inside-out: What campuses need is less regulation of speech, not more.
This year marks the 60th anniversary of the “free speech” movement that began among students at the University of California, Berkeley, and spread swiftly across the country. The anniversary is a reminder of a sort that students, too, are entitled to academic freedom — and I don’t just mean the freedom to protest, cherished as that right may be. What’s far more important is the freedom of students to grow into distinct thinking individuals. The student must be, in the phrasing of the German philosopher Friedrich Paulsen, “free to devote himself wholly to his task of forming himself into an independent personality.”
I agree with the philosopher Seana Valentine Shiffrin that when we search for the justifications for free speech, we tend to overlook its value in crafting our own identities, the way that a self can try on ideas like clothes, to discover which fit best. Sometimes the ideas will be beautiful; sometimes they’ll be ugly; sometimes they’ll look better on one person than another.
This process of testing ideas should be encouraged, particularly among the young. But it carries risks, not least because of what we might call influencers, who wind up dictating which ideas it’s fashionable to wear and which should be tossed out. When large majorities of college students report pressure to self-censor, this is what they’re talking about. Surveys suggest that the principal reason students keep controversial ideas to themselves is to avoid the disdain not of their professors but of their peers.
That is unfortunate, not least because it tells us how badly the educational process has failed.
The strength of my commitment to free inquiry and free speech might be traceable in part to an adolescence spent in mostly white schools, full of students and teachers alike who sought to tell me what I should think and say. I didn’t like it then; I don’t like it now. My father used to say that from the time I was a toddler, all I seemed to do was ask questions. Yet a chunk of my formative years was spent among peers who thought answers were obvious and questions were in poor taste. As it happened, the views they pressed upon me were mostly conservative; but I didn’t fight them off so that I might later subject myself to the same condescending nonsense from progressives.
I was probably attracted to academic life because I believed I had found in it the antithesis of that attitude. But then I was fortunate enough to come along at a time when campuses, still embarrassed by their feckless surrender to the McCarthyist right in the 1950s, had developed a broad and rich tolerance for uncomfortable speech.
My undergraduate education at Stanford in the 1970s was full of serious argument over controversial propositions. Little was out of bounds. In my history courses, we eagerly debated such subjects as whether slavery was more efficient than wage labor, or whether the influence of Christian missionaries on Asia and Africa and Latin America had been a net negative or net positive. When the great Carl Degler solemnly told a lecture class that slavery in Brazil had been harsher than slavery in the United States, nobody got mad, nobody circulated an outraged petition; instead, a group of Black students, myself among them, went to the lectern afterward to question, argue and learn.
Few professors tried to foist their own views on students. I thoroughly enjoyed a philosophy-of-religion seminar where the professor, an adamant atheist, took obvious glee in slapping down student arguments against the existence of God; and a political science course in which the professor was unapologetic in his view that Brown v. Board of Education was wrongly decided. Nobody boycotted him; in fact, his classes were hugely popular, even though his use of the Socratic method, for most of us our first exposure, had us trembling. Yet arguing with him over fine points of constitutional law not only improved my ability to defend my positions; it also helped establish my love of argument, of studying the evidence and listening with care.
Perhaps the high-water mark of my tiny corner of the Golden Age was my brief encounter with William Shockley, a brilliant engineer who shared the Nobel Prize in Physics as an inventor of the transistor, a device whose descendants we use every time we start our cars, fire up our laptops or pick up our phones. By the time he crossed my path, Shockley had become notorious for his avowed certainty that racial differences in I.Q. were driven principally by genetics — and for his proposal that we could increase national intelligence by paying those with low I.Q. scores not to reproduce.
Student protesters argued that Shockley shouldn’t be allowed to teach; on more than one occasion, they disrupted his classes. But I didn’t want to see him punished. I wanted to see him refuted.
As it happened, I worked at The Stanford Daily, which sponsored regular lunches at which a faculty member would be peppered with questions. During my sophomore year, The Daily invited Shockley, who much to our surprise agreed to participate. I spent weeks before his appearance haunting the campus libraries, reading every article I could find on the relationship among race, genetics and I.Q. — and learning a lot along the way about a subject into which I otherwise might never have delved. (Again, curiosity had its innings.)
On the appointed day, Shockley showed up, bringing along a tape recorder. He gave his talk (which I didn’t find impressive) and then answered questions in his polite, but firm way. After all these decades I don’t remember what I asked, except that it was long and complicated and well rehearsed, and that it was related to potential weaknesses in a particular study he kept citing; what I remember instead is the way his eyes narrowed as he listened. “That’s rather clever,” he said when I was done. I like to think that I put him off his game a bit; but, in truth, I doubt it.
That same year Shockley appeared on a campus stage, debating the issue of I.Q. and inheritance with Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza, one of the world’s great geneticists. Cavalli-Sforza made mincemeat of Shockley’s arguments — which is the way that academic disagreements should be decided. It’s a tragedy that subsequent debates at Harvard (1973) and Yale (1974) were canceled because of student protests. The more exposure Shockley got, the weaker his claims appeared.
This, I thought then and think now — this is how one lives the life of the mind! No, not everyone on campus need see things this way; but no one should interfere with those who do.
What should happen to those who do interfere? Yale suspended a dozen students from among those who, in the words of the physicist’s biographer, “jeered and booed for more than an hour until Shockley finally left the stage.” President Kingman Brewster Jr. accused them publicly of “storm trooper tactics.” Well, maybe; or maybe they were passionate about their cause and, in their passion, went too far. I quite agree that schools should punish those who disrupt the educational process, no matter how noble-sounding their reasons. Interrupting classes, making noise so that others can’t hear speakers, blocking access, taking over buildings — all of these are less acts of dissent than assertions of raw power.
The commitment to curiosity includes a commitment to understanding why those whose views are objectionable think as they do. The sharp line between propounding a position and trying to suppress dissenting voices is one that the campus should always honor.
I find something admirable in protesters who willingly suffer punishment for their actions rather than disrupting the academic enterprise and expecting (even demanding) no consequences. A student who takes an ugly position should be tolerated. A student who tries to prevent someone else’s ugly position from being heard should be suspended.
Stanford could have taken action against Shockley on other grounds, entirely consistent with academic freedom. He was accused of telling a Nigerian graduate student in a quantum-mechanics seminar that he did not belong in the class because of his race and should consider merely auditing the course. That act of singling out an individual illustrates how weakly the famous physicist understood statistics; it also constitutes a form of discrimination that a university can regulate without violating academic freedom, for Shockley was evaluating not the abilities of the student as an individual but the abilities of the student as representative of a class. But in the end Stanford took no action. (The student in question subsequently earned a physics Ph.D.)
If telling students and faculty what they must not say is bad, telling them what they must say is often worse. The success of the university, Paulsen wrote, rests upon the notion “that truth is the sole aim and not the proof of officially prescribed and quasi-officially desired or at least permitted views.” During the second Red Scare, which began after World War II, the most significant threat to this view was the loyalty oath. Faculty members across the country were asked to swear allegiance to the United States and, often, to affirm that they were not and had never been Communists. Many who refused lost their jobs — including at the nation’s wealthiest and most powerful institutions.
Nowadays, I worry that we’re repeating the same mischief, with mandated (or strongly encouraged) “diversity statements” and the like. I’m often told that because I obviously agree with the goals the statements promote, I shouldn’t make a big deal out of them. But this objection misses the point. The “what’s the big deal?” approach puts me in mind of the philosopher Sidney Hook, who in a 1953 essay in The Times argued that an academic who refused to swear to not being a member of the Communist Party was like a chef who refused to say whether he was the one who poisoned the food. Not for a moment did Hook entertain the notion that the hypothetical professor might simply believe, as a matter of principle, that it is wrong to screen the professorate for ideological conformity.
It was wrong then; it is wrong now.
Don’t mistake me. I’m not against ideology and social movements, except when they interfere with academic curiosity. On campus, at least, you should be able to support Israel in the Gaza War, yet feel free to argue that the Israelis have prosecuted the conflict too aggressively; or to support the aspirations of the Palestinians, yet be willing to condemn unequivocally Oct. 7.
This understanding points toward the proper resolution of other campus conflicts as well. Consider, for instance, the recent controversy at the University of California, Berkeley, law school over student organizations that require invited speakers to be “anti-Zionist,” an explicit ideological screen. The answer is not to argue over whether such demands violate school rules, but to emphasize the ways in which such restrictions violate the norms of curiosity and engagement that lie at the heart of higher education. Hanging out only with those they already agree with is one of the worst ways for young people to waste their years on campus.
Should the scope of campus debate be unlimited? Of course not. There will of necessity always be a palisade marking the boundary line of civilized conversation, and some opinions will always rest in the wilderness beyond freedom’s protection. Most obviously, calls for violence based on racial or other differences rest in that wilderness, and need not be tolerated in the classroom. Neither should playing Shockley’s game, judging intellectual ability according to the color of a student’s skin. But the force that exiled these topics from serious discussion was history, not top-down ordering. If we believe in the values of the academy, then the wilderness must be small, and the palisade in the far distance, scarcely visible to the unaided eye.
All of which brings us back to the tragedy of Claudine Gay. One way to look at the question she had such trouble answering was whether the universe of rational discourse — the space education properly occupies — is broad enough to accommodate demands for genocide. Of course, the only reasonable answer is no, and that is what the presidents should have said, clearly and concisely. Yet I think I know what they were worried about. On today’s campuses, the word “genocide” is tossed about frequently by activists, to describe what might better be called “sharp disagreement.” Part of the responsibility of the classroom teacher is to guide debate away from apocalyptic terminology, in the hope that students, rather than reaching for the language of horror, will seek to engage their opponents — that they’ll be more curious.
I’ve argued elsewhere that each generation should be permitted to place, at most, one issue beyond the fence. I believe it still. But that exclusion should follow, not precede, the waves of social change. Especially today, as the world teems with ferment, as every activist left or right pushes to move this issue or that outside the universe of rational discourse, the academy must be the last to yield.
Stephen L. Carter is the William Nelson Cromwell professor of law at Yale and the author of 17 books. He is working on a memoir titled “The Case for the Classroom.” He most recently wrote for the magazine about his long association with Thurgood Marshall. Andrew Rae is an illustrator, a graphic novelist and an art director known for his irreverent images of characters using a simple hand-rendered line. He is based in London.
Advertisement
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Importance of Education Speech

Speech on Importance of Education in English for Students
In one's life, education is an important concern. It is the key to a successful future and to the numerous opportunities we come across in our lives. For an individual, education has many advantages. It not only enlightens the mind but also enhances the thought process of a person. This makes it possible for students to qualify for jobs or pursue higher education. Moreover, education develops the personality, thoughts, and social skills of humans. It not only prepares an individual for various experiences and circumstances in their life but also makes them hold a unique significance in society.
It increases the knowledge of a person and provides them with confidence that is going to help them through their life. Education is important for people of all age groups. People of any age group can get education anytime and anywhere, education has no limitations if you want to have it you can get it anytime and from anywhere. When you talk about education it not only makes you a self-dependent person but it is going to cultivate such values in you that will help you to be a respected person in society.
Long Speech on Importance of Education in English
Today I am going to speak about the Importance of Education. Education plays a key role in the development of an individual. When we think of education, the first thing that strikes our minds is gaining knowledge. Education not only provides an individual with Education is a tool that provides knowledge, skill sets, techniques, and information to people, allowing them to understand their rights and duties to their family, society, and nation. It enhances vision and perspective to see the world. Not only this but it is also the most significant element in the nation's evolution. One will not explore innovative ideas without education. It implies that one can not develop the world as there is no creativity without ideas and there is no development of a nation without creativity.
There are certain ways in which you can teach the students and small children about the importance that education holds. Following are some important ways that you need to follow while teaching the students about the importance of education.
Since we all know that children tend to observe whatever is happening around them, you need to focus on being their role model, if you want them to learn something important like education.
Education can empower individuals in various ways. It helps in eradicating poverty, as it makes an individual capable of getting a job and fulfilling all the basic needs and requirements of the family. A well-educated person is not easily fooled and is less likely to be involved in social evils. It makes them less susceptible to cheating and getting involved in crime. An increase in educated people ultimately boosts the trade and commerce of a country. It provides the citizens with a deeper understanding of law and order and they are more likely to become law-abiding citizens, as they understand the importance of law and order. Education helps in fighting several societal evils; it demolishes certain sexist customs of child marriage, the Dowry system, Sati Pratha, and also encourages women to become independent.
Education empowers women to stand up for themselves and voice their opinions. A good education adds to the communication skills of a person and helps them express themselves more effectively. We are regarded as a valuable source of knowledge for our society as educated individuals. Education helps us to teach necessary morals, good manners, and wise ethics to others. As well as being good at the physical, mental and social level,besides, it promotes the feeling of living a better life. A good education is constructive, which creates our future. This allows an individual to enhance his mental, physical and spiritual level. By offering knowledge of many areas, it makes us confident individuals. It's enough to say that education matters. Studies show that those educated are more likely to live longer, live healthier lives, and help strangers more.
While children are young, investing in different types of education ensures that they have a strong foundation. Good education is intended not only to get hard work and good results but to accomplish new things for the welfare of the whole human race. Not only does education allow us to study history, science, mathematics, geography, and other subjects, but it also teaches us how to deal with life's bad situations. Therefore, education is essential for a better future. Education not only means getting bookish knowledge but it involves you having knowledge that will help you to evolve as a better human and the one who can protect society from all the evils.
Short Speech on Importance of Education in English
Today, I am here to share my views on the importance of education. Education among uneducated and poor people is still an issue in this modern, technologically advanced world that urgently needs to be addressed. People's education is a solution to all social, personal, and business issues. To live in society, proper and higher education makes us more civilized.
Besides, it is very well known that education often generates self-confidence. To have self-confidence, which leads to many positive effects and success in life, is a great blessing for us. It enables us, for instance, to handle specific tasks, to tackle the challenges of life, and to maintain positive positions. Education also directs the individual's undeveloped capabilities, attitudes, interests, impulses, and needs into desirable channels. With the aid of education, the individual can change and modify his environment according to his needs. There are two aspects to man—biological and social. Education not only maintains and transmits the social aspect of mankind but also provides you with knowledge about the biological aspects.
In addition to preserving and transmitting social elements from generation to generation, education also contributes to the enrichment of culture. Our Constitution provides for free and compulsory education, the right of minorities to set up and administer educational institutions, education for weaker sectors, secular education, education for women, primary education in the mother tongue, preservation of national heritage, education in the Union Territories, etc. These constitutional provisions are nothing but our attempt to attain the objective 'Education for All'. Having the right education will help you to be a good human and also enable you to understand how to survive in our society and tackle all the difficulties in our way easily. Whenever we talk about education we know that we are talking about the growth of an individual as a whole. Education is the basic necessity that everyone should have. It helps you to grow mentally and will enable you to be a better human being.
10 Lines on Why Education is Important in Our Life Speech
The ultimate way to gain victory over personal and social problems is education.By altering our mind and personality and improving our confidence level, it transforms us completely from outside as well as inside.
There are no constraints, people of any age group can get an education at any moment. This allows us to shape our moral conscience.
Anyone can receive education at any age, you just need to have the will to get educated and all the paths are open for you. Education is the most important weapon to improve a person's life. Not only does it provide you with information about the norms of the society but also increases the chances of employment.
Being well educated never only means earning certificates and good salaries from recognized and reputable organizational companies or organizations, but in life, it also means being a good and social person.
Education is the fundamental right of all capable of bringing any desired change and upliftment in the human mind and society.
Teachers play a very important part in providing a good level of education. The basic education that we receive is from our school. All the basic manners about the ways how to behave or protect the environment and all the other basic education that help you to be a well behaved and sophisticated individual.
Better education instills better communication among individuals. Furthermore, education helps an individual make better use of technology. This is a technical world, today everywhere you come across a number of technologies every second person is a user of technology whether it is a phone, laptop or any other technology. You only can use these technologies when you are having a better education and knowledge about these technologies.
Whatever we learn from our parents and teachers stays throughout life with us and we pass it on to our next generation.
Our goal of getting an education should be to help other people in society who are needed to get over their vulnerabilities and superstitions. We have often observed that lower sections of society are still so much into superstitions but if they are educated in the right way then only they can overcome such superstitions and can lead a better life.
By maintaining the balance between body, mind, and soul, keeps our mind calm and peaceful.
One can open his/her lock to success through the key of education.

FAQs on Importance of Education Speech
1. How does education help an individual to get employment?
Education provides an individual with information on vivid topics. It not only instils knowledge into an individual but also makes them more confident. It is an obvious fact that if you have information on all the topics that your employer is going to ask you then only you can answer them and it instills a lot of confidence in you. It is observed that an employer always looks for a confident individual who can carry forward the work in difficult situations also. So education is the basic need for employment.
2. Mention the ways in which education will help society?
Education is the most important when we want to bring some changes to our society. We know that the lower uneducated section of the society still follows a lot of superstitions, if only we can educate them with the proper information they can come over these norms and superstitions.
Education helps society by spreading knowledge, the more knowledge the society will gain, the better will be their standard of living.
3. How can you instill education in the children?
To instil education in children, you need to follow a few important tips.
You need to become a role model for the children. They tend to learn from what they observe in society.
You need to give them diverse opportunities to learn different topics then only they will be able to gain more knowledge.
They should focus more on learning rather than studying. Only studying will not be beneficial anyhow except gaining you some marks.
4. What is the importance of education in an individual's life?
Education provides a person with the knowledge and along with it, it boosts your confidence. It helps you to improve in your career and not only that it also improves your personal life. There are no limitations when we talk about education. You can get an education anywhere at any time, you just need to be willing to acquire the education. Numerous sources will be provided to you that will increase your knowledge. There is a popular saying that says that a person never stops getting educated and it is a fact.
5. How can education change the world?
Education improves the economic growth of the country. It not only increases economic growth but also increases innovation, productivity, as well as human capital. Education besides this fosters positive changes in the society by removing superstitions and many useless norms that were followed for a long time back without the knowledge behind these norms. Education also encourages political participation, environmental sustainability, along with social equality among the individuals of the society.
Search Icon
Events See all →
Hands on history.

10:00 a.m. - 2:30 p.m.
Penn Museum, 3260 South St.
268th Commencement

Franklin Field
Vahe Sarkissian

World Cafe Live, 3025 Walnut St.
Wawa Welcome America Day
10:00 a.m. - 5:00 p.m.
Campus & Community
The importance of free speech on college campuses
Running penn’s committee on open expression has given sigal ben-porath an up-close look at free speech on campus—and even inspired her to write a book on the topic..
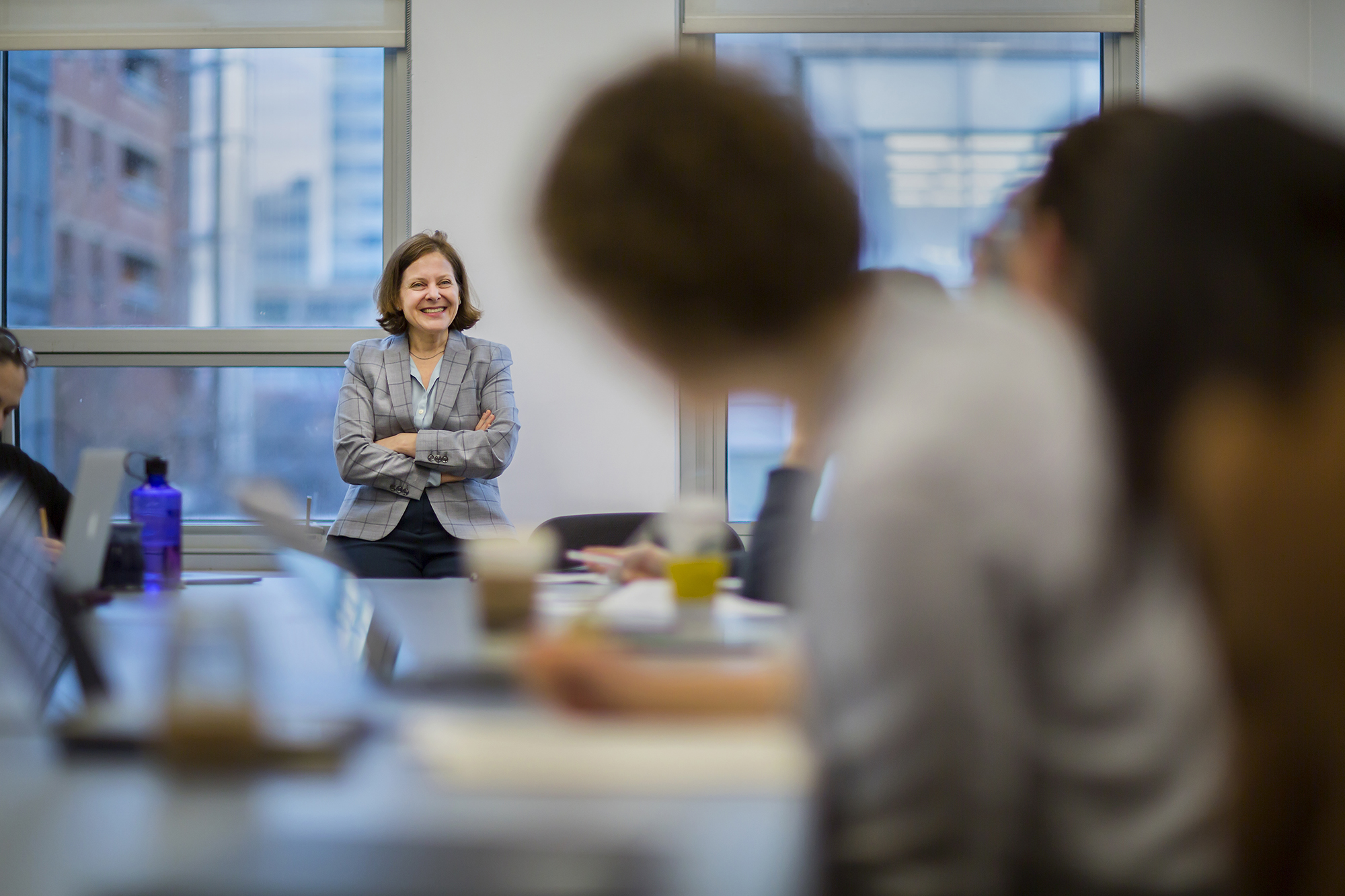

Sigal Ben-Porath , a professor at the Graduate School of Education , has been chair of Penn ’s Committee on Open Expression since the 2015-16 academic year, a position that has given her an up-close and personal view of the complications and challenges surrounding free speech, especially in the current, hyper-partisan environment.
Consisting of faculty, staff, and students , the Committee follows Penn’s longstanding Guidelines on Open Expression , which were developed in the 1960s and updated a number of times in subsequent years. Members of the Committee are tasked with upholding the Guidelines and mediating related concerns that are brought before them.
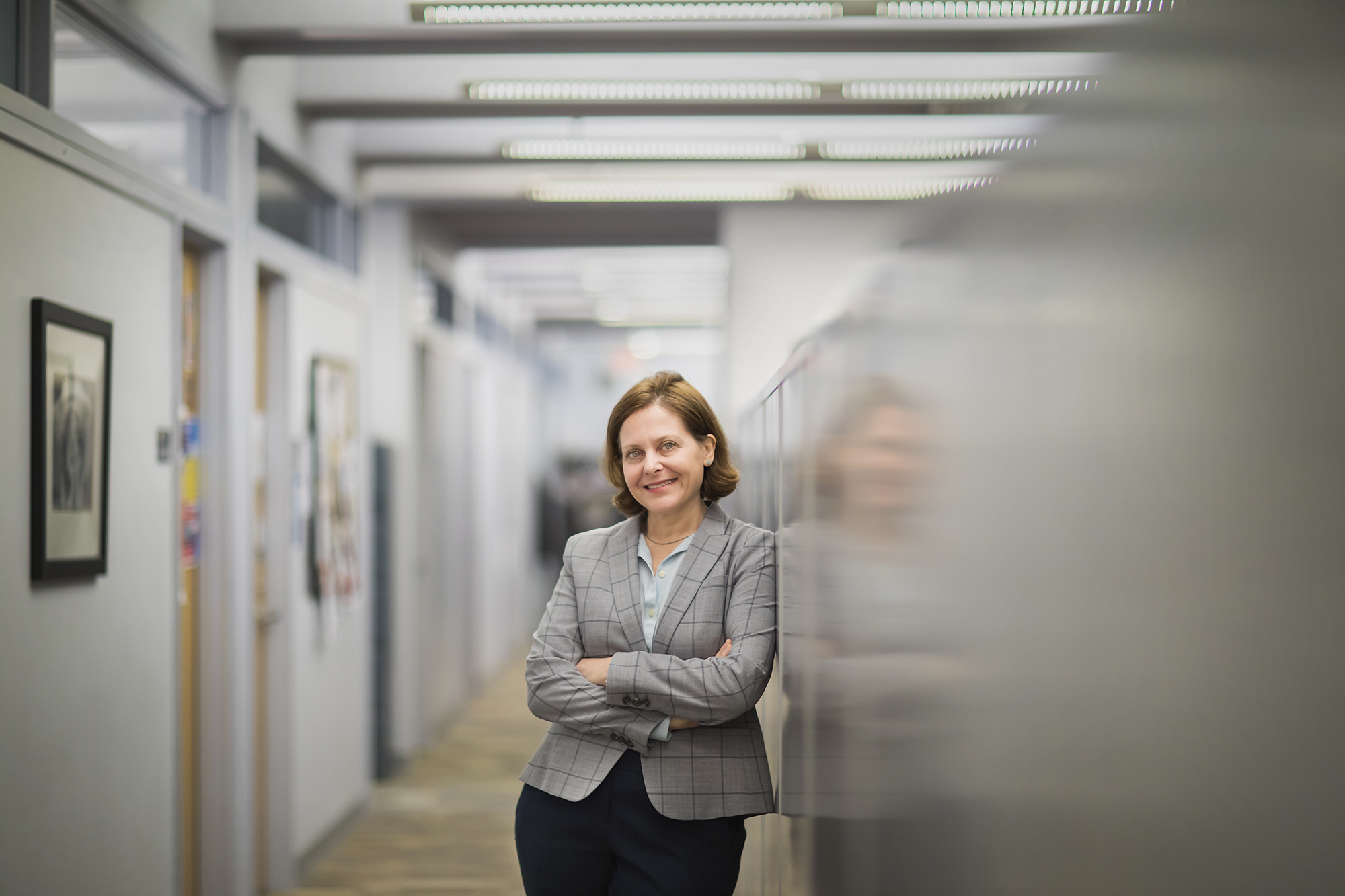

Since the 2015-16 academic year, Sigal Ben-Porath has been chair of Penn’s Committee on Open Expression.
Devotion to an open-minded atmosphere on college campuses has been embraced, by and large, by students and faculty for generations, says Ben-Porath, who both believe freedom of expression is imperative for constructive learning and research. Nonetheless, she says students with diverging ideological leanings differ on how free freedom of speech actually is. Certain students believe the right is nearly absolute; others seek to limit debate or the expression of views on topics they believe fall outside the bounds of reasonable discussion.
Ben-Porath’s work on the Open Expression committee moved her to write the book “Free Speech on Campus.” Published last year by the University of Pennsylvania Press , the manuscript examines the current state of the arguments about free speech on college campuses, using real-world examples to explore the contexts in which conflicts and tensions erupt.
In response to her book, Ben-Porath has been invited to give talks about free speech at a variety of higher education institutions, including community colleges, Ivy League universities, and public institutions, some of whom have set up committees to draft or update guidelines on open expression.

“Free Speech on Campus” was published last year by the University of Pennsylvania Press.
“I think a lot of places are just now waking up to the concern that even if you’re a small place, even if you don’t necessarily see yourself as that visible or your students as necessarily organized in this way, it’s still your problem as well,” she says. “Even if you’re not interested in free speech, free speech is interested in you.”
Administrative awakenings in relation to free speech on college campuses are the result of student activism, and also the fact that universities are a primary target in the current culture wars, Ben-Porath says. University leaders have trepidations about how the higher education sector is perceived. She says where a person stands on the issue of free speech on college campuses is now a marker for a general ideological stance that partisans can use to signal their overall position, similar to how people used to speak about marriage equality.
The most vocal critics accuse universities of being too elitist, lacking ideological diversity, and prioritizing progressive and liberal views.
Commentators and critics point to instances in which conservative speakers have been heckled or prevented from speaking as proof that students at so-called “liberal” universities are too fragile for ideological debate, fail to understand democratic commitments, and are attempting to stifle free speech.
Surveys have shown a more limited support for free speech or First Amendment protections on college campuses, but Ben-Porath says students attempting to limit speech support free speech, but object to free speech being used to harm, denigrate, or devalue another human being.
“This is not being a snowflake, this is being an activist,” she says. “What they are expressing is not oversensitivity that they can’t handle the truth. They are expressing a commitment to the values that we are teaching them and we are not always practicing, like equal dignity to all persons. That doesn’t show fragility, in my view. It actually shows a commitment to democratic values, and we need to listen to that.”
Even if you’re not interested in free speech, free speech is interested in you.
Sigal Ben-Porath, a professor in the Graduate School of Education
Ben-Porath does not support speech codes or the shutting down of speakers—even those who speak hate. Universities as an institution should not invite such speakers, but if a student or a student group is interested in inviting the person to campus, she does not think the school should intervene.
Aside from individuals calling for violence, Ben-Porath says there are very few people who should be prevented from speaking.
“From where I stand, it’s going to be a pretty small marginal group of people, and I won’t expand it, even when there are people who I see and a lot of people see as quite hateful,” she says. “I don’t necessarily want to prevent them from coming to campus because I think that they are, sadly, a part of our current political debate. I regret that, but I would like to support my students in engaging with that.”
Student activists have a large toolkit for responding to speakers they disagree with if they look historically and in present practice, Ben-Porath says. And these tools are much more effective than shutting speakers down. She says students can use humor, as has been done when responding to the anti-gay preachers on Locust Walk. To protest the preachers’ hateful signs, students created their own humorous signs and collected donations for the Attic, an LGBT youth center, while the preachers spoke.
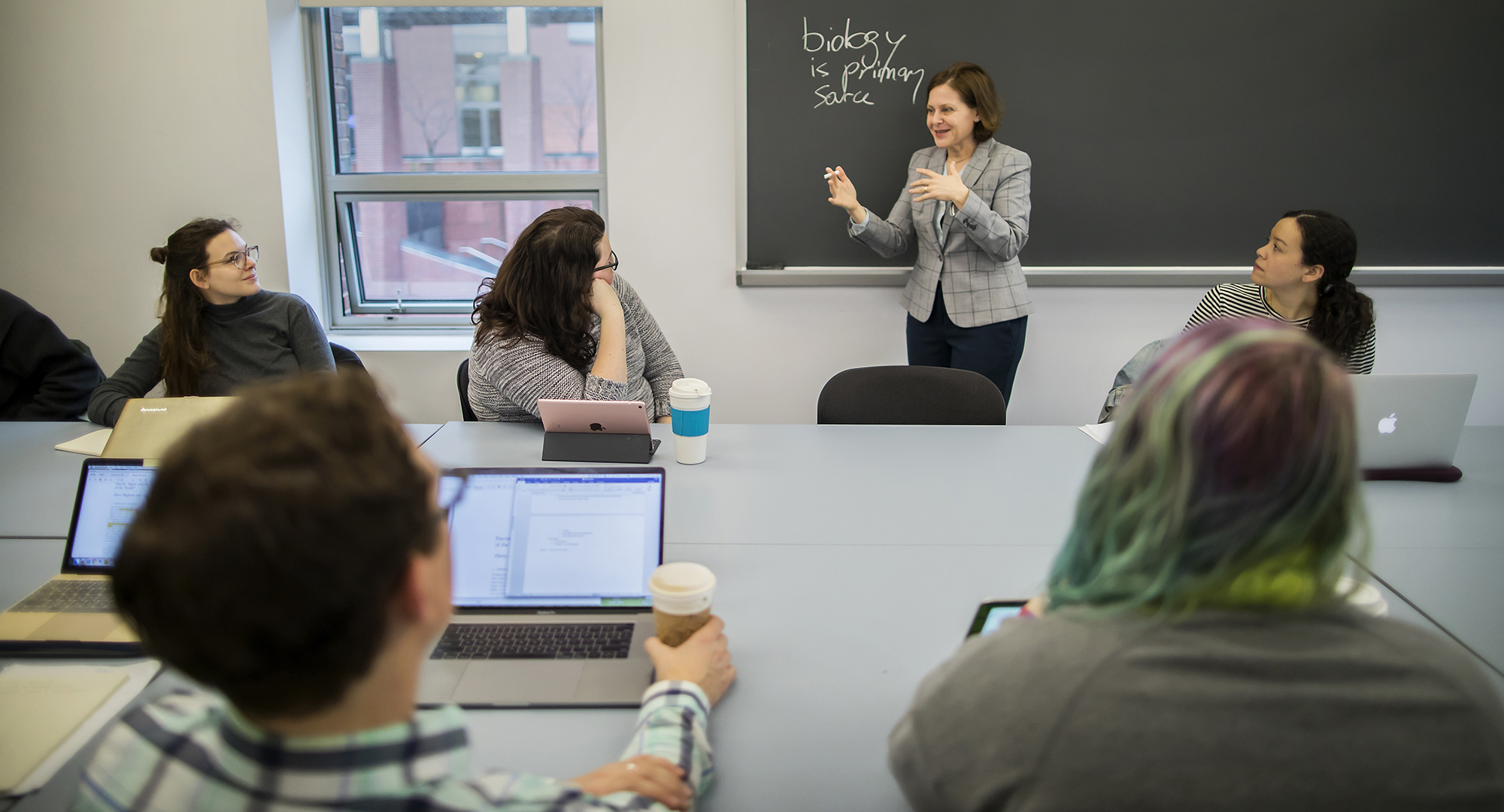

“The Black Graduate and Professional Student Assembly here on campus staged an excellent protest earlier this fall in response to a speaker speaking against the Black Lives Matter movement,” Ben-Porath says. “Excellent in the sense that it was nonviolent, but a very effective protest.” The students dressed in similar fashion, brought signs expressing their opposition, asked the speaker hard questions, and protested outside the venue.
“They engaged with the content and rejected it effectively,” she says. “They engaged with the actual invitation by their presence, by their visible appearance with their clothes and their signs. I thought that was great because they were able to express their opposition, and to express their valid perspective in opposition to her views way more effectively than if they shouted her down.”
Photo: Ben-Porath’s research focuses on citizenship education, normative aspects of educational and social policy, and the social and educational effects of war.
Class of 2025 relishes time together at Hey Day

Arts, Humanities, & Social Sciences
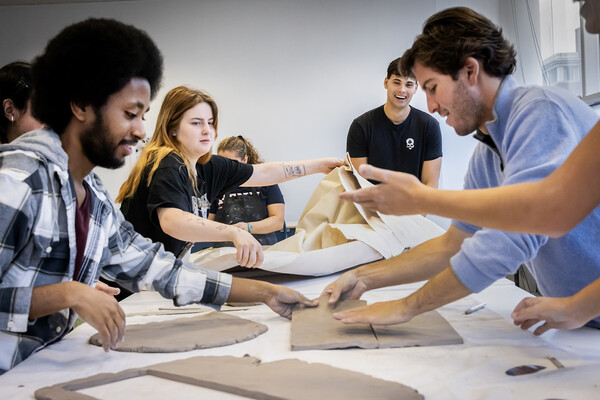
Picturing artistic pursuits
Hundreds of undergraduates take classes in the fine arts each semester, among them painting and drawing, ceramics and sculpture, printmaking and animation, photography and videography. The courses, through the School of Arts & Sciences and the Stuart Weitzman School of Design, give students the opportunity to immerse themselves in an art form in a collaborative way.
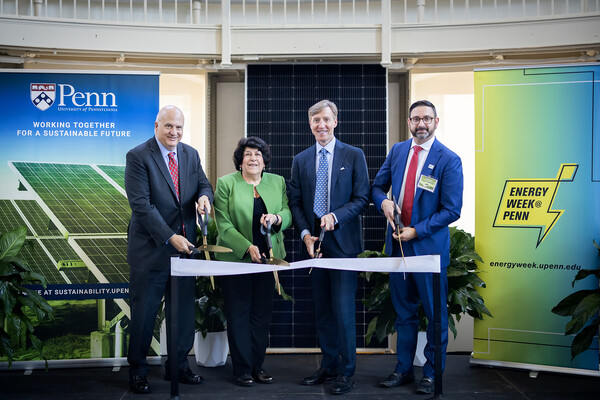

Penn celebrates operation and benefits of largest solar power project in Pennsylvania
Solar production has begun at the Great Cove I and II facilities in central Pennsylvania, the equivalent of powering 70% of the electricity demand from Penn’s academic campus and health system in the Philadelphia area.
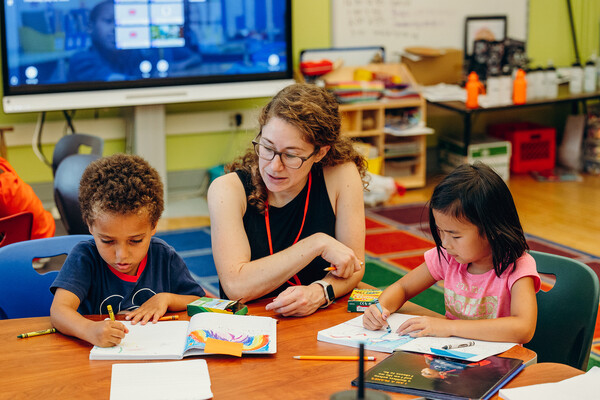

Education, Business, & Law
Investing in future teachers and educational leaders
The Empowerment Through Education Scholarship Program at Penn’s Graduate School of Education is helping to prepare and retain teachers and educational leaders.
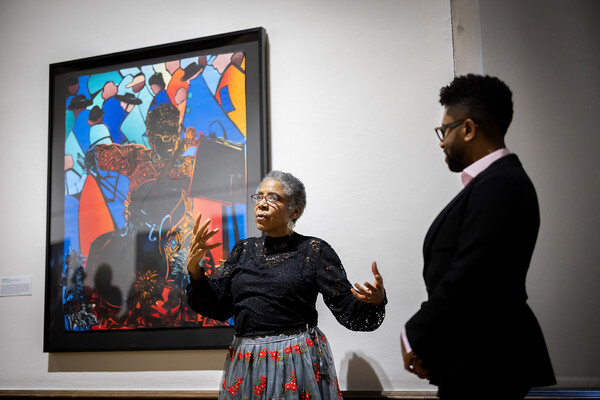

‘The Illuminated Body’ fuses color, light, and sound
A new Arthur Ross Gallery exhibition of work by artist Barbara Earl Thomas features cut-paper portraits reminiscent of stained glass and an immersive installation constructed with intricately cut material lit from behind.
Speeches > James D. Gordon III > The Joy of Education and Lifelong Learning
The Joy of Education and Lifelong Learning
James d. gordon iii.
March 15, 2013
I am happy to be here with you today. I remember when I was a university student. Like some of you, I had trouble deciding what my major should be. First I thought about majoring in economics. That way, if I couldn’t get a job after I graduated, at least I would understand why.
Then I thought I might major in physical education. I went down to the gym to lift weights, but the laughter made it difficult to concentrate.
I sampled some classes, but I didn’t always do very well. For example, I took a photography class. I just about went crazy trying to take a close-up of the horizon. The teacher in that class gave me an F minus. He said that giving me an F would be unfair to the people who failed normally.
I studied chemistry, but I thought that there were only four elements on the periodic table: earth, air, fire, and water. I thought that fire had three electrons in the outer shell.
I thought about studying math. It has been reported that 60 percent of Americans cannot do basic math. Sixty percent! That’s nearly half! But we shouldn’t laugh—and most of you didn’t, and I appreciate that.
Seek Learning
Seriously, I would like to speak about the joy of education and lifelong learning. Life is a test, and life is also a school. The Lord has invited us to seek learning. He said, “Seek ye diligently and teach one another words of wisdom; yea, seek ye out of the best books words of wisdom; seek learning, even by study and also by faith.” 2 He commanded early Church leaders to “study and learn, and become acquainted with all good books, and with languages, tongues, and people.” 3
Three reasons why we should learn are to develop personally, to increase our ability to serve others, and to be prepared in all things. Brigham Young said, “Our education should be such as to improve our minds and fit us for increased usefulness; to make us of greater service to the human family.” 4
President Thomas S. Monson taught:
Your talents will expand as you study and learn. You will be able to better assist your families in their learning, and you will have peace of mind in knowing that you have prepared yourself for the eventualities that you may encounter in life. 5
Learning helps us to be prepared in all things. The Lord said:
Teach ye diligently and my grace shall attend you, that you may be instructed more perfectly in theory, in principle, in doctrine, in the law of the gospel, in all things that pertain unto the kingdom of God, that are expedient for you to understand;
Of things both in heaven and in the earth, and under the earth; things which have been, things which are, things which must shortly come to pass; things which are at home, things which are abroad; the wars and the perplexities of the nations, and the judgments which are on the land; and a knowledge also of countries and of kingdoms—
That ye may be prepared in all things when I shall send you again to magnify the calling whereunto I have called you, and the mission with which I have commissioned you. 6
Being prepared in all things includes being prepared for the world of work so that you can provide for yourself and your family.
It is a great privilege to study at Brigham Young University. You have the opportunity to learn in an environment that is consistent with the principles of the gospel. Being a student here is a position of trust. As you know, the Church pays for much of your education. You have the responsibility to study hard, to obey the Honor Code, and to prepare for future service. Hopefully throughout your life you will look back on your time here with fondness and cherish the memories.
On Pursuing a BYU Education
I would like to offer some advice as you pursue your education here. I hope that I don’t sound like Polonius giving advice to Laertes in Shakespeare’s play Hamlet— especially when I remember what happened to Polonius. I am not referring to the fact that he was killed behind the arras, but rather to the fact that over the centuries he has been portrayed by literally thousands of bad actors.
First, do your best in school. You might recall a story about a person who was asked to build a house. He decided to cut corners, use cheap materials, and do a poor job. When he was done, the owner handed him the key and said, “I’d like to give you this house as a gift.”
Attending the university is like that. You can work hard and do a good job, or you can cut cor-ners and do a poor job. Be fair with yourself by giving your best effort. I encourage you to work diligently, to learn a lot, and to prepare well for the future.
Second, do things to enrich your education, such as having a mentored-learning experience with a faculty member, publishing an article, doing an internship, working in BYUSA, or participating in a student club. Perhaps you can be a teaching assistant or a research assistant or participate in a performing group. BYU offers so many opportunities to develop and grow. When you look back on your education here, these extra activities will have special meaning.
You might participate in intramural sports. Personally, I’m not very athletic. I tell my students that I played football in high school. They had a play designed especially for me. It was called “Pencilneck Right.” You know how BYU uses the run to set up the pass? Well, Pencilneck Right was used to set up the injury timeout.
When I was in high school I was in the chess club. I tell my students that I had a rook on my letterman jacket. Do you know what it says when you walk around campus with a rook on your letterman jacket? “Don’t mess with me, pal. Checkmate!”
Third, give service. It is important to fulfill Church callings and to perform other service. Y-Serve, the Center for Service and Learning, located in the Wilkinson Student Center, offers many opportunities to serve in the community. Service is important for its own sake, and it helps you to keep a broader perspective and to stay balanced.
Fourth, make friends. Even though your classmates are not as good-looking—and not as humble—as you are, they are bright, good, and interesting people. The friendships you make here can last throughout your whole life and can be a particularly sweet aspect of your university experience. Take time to make friends.
When I was in high school I didn’t have many friends. Once I told my dad that the other kids were giving me a hard time about my religion. My father sat down next to me, and, in his fatherly way, he said, “Son, it doesn’t matter what race you are or what religion you are. There will always be people who don’t like you—because you’re irritating.”
Fifth, attend devotional and forum addresses and other events, such as academic presentations, concerts, plays, and art exhibits. These are wonderful opportunities.
Sixth, enjoy your university education. It’s exciting, fascinating, challenging, and fun. The secret to happiness is not to look forward to some future time when all your problems will be solved. The secret is to be happy today.
The Joy and Sweetness of Lifelong Learning
There is joy in learning. In some Hebrew schools a special ceremony occurs on the first day of class. The teacher places a drop of honey on the cover of a book and gives the book to the student, who licks the honey off. The symbolic message is that learning is sweet.
Learning can also be challenging. Sometimes the learning curve is steep. When we are acquiring new knowledge or skills, we may feel uncertain, and we may make mistakes. However, being stretched means that we are growing. If we ask Heavenly Father in prayer, He will increase our ability to learn and help us to overcome our challenges.
Hopefully your university education will provide a foundation for lifelong learning. As The Aims of a BYU Education describes:
BYU should inspire students to keep alive their curiosity and prepare them to continue learning throughout their lives. BYU should produce careful readers, prayerful thinkers, and active participants in solving family, professional, religious, and social problems. . . . Thus a BYU diploma is a beginning, not an end, pointing the way to a habit of constant learning. In an era of rapid changes in technology and information, the knowledge and skills learned this year may require renewal the next. Therefore, a BYU degree should educate students in how to learn, teach them that there is much still to learn, and implant in them a love of learning “by study and also by faith.” 7
The most important area of lifelong learning is spiritual learning. We seek answers through prayer. We read the scriptures regularly so that they become part of our lives. Reading the scriptures reminds us of the Lord’s commandments, the covenants that we have made to keep them, and the blessings of the gospel. Studying the scriptures also invites the Holy Ghost, who guides our decisions and helps us to learn. Elder Russell M. Nelson said: “Faith is nurtured through knowledge of God. It comes from prayer and feasting upon the words of Christ through diligent study of the scriptures.” 8
Regardless of one’s opportunities for formal education, a person can engage in lifelong learning. My grandfather was Jim Gordon. His parents were Scottish immigrants. He was only able to finish the eighth grade before he went to work. He drove a delivery wagon in San Francisco when he was a young man.
Automobiles replaced horse-drawn wagons. Later my grandfather became a mechanic. He brought books about diesel engines home from work, and he read them. Eventually he became the supervisor over all the diesel equipment for a substantial company. Although his opportunity for formal education was limited, he kept learning on his own. His most important learning experiences occurred when, later in life, he decided to enter the waters of baptism and to receive the blessings of the temple.
When my grandfather was young, he drove a horse-drawn wagon. However, his world changed. During his lifetime he flew in passenger planes, and astronauts landed on the moon. Your world will change too. Many of the changes will be positive and exciting; others may present challenges. Will you be prepared to meet the challenges that will arise during your lifetime?
We need to continue to learn throughout our lives. President Gordon B. Hinckley told graduating BYU students:
We live in a world where knowledge is developing at an ever-accelerating rate. Drink deeply from this ever-springing well of wisdom and human experience. If you should stop now, you will only stunt your intellectual and spiritual growth. Keep everlastingly at it. Read. Read. Read. Read the word of God in sacred books of scripture. Read from the great literature of the ages. Read what is being said in our day and time and what will be said in the future. 9
Personally, I love to read. I tell my students that my first job was as a proofreader in an M&M factory. You have your own patterns for reading. One thing that helps me is that my wife, Nadine, and I belong to a book group with some friends. During the school year we meet almost monthly. We take turns: a couple chooses a book, hosts the book group in their home, leads the discussion, and serves refreshments afterward. We have read books about a wide variety of subjects. I had never even heard of many of these books before, but I have enjoyed reading them very much.
In addition, I have always enjoyed words. When I was a boy and I would encounter a word I didn’t know, sometimes I would ask my father what it meant. He would reply, “Look it up.” My father usually knew the answer, but he wanted me to learn how to look words up. So I would open the dictionary that sat on the bookshelf in our living room and look the word up.
Later I wanted to learn more words. One summer my friend John Tanner (who later became a BYU English professor) and I worked as groundskeepers at the Oakland California Temple. On some days we would each write five words and their definitions on an index card and put the card in our shirt pocket. Then we would share the words and use them in sentences during the day. My favorite word from that summer was halcyon. It means calm, peaceful, tranquil, or golden. As we pulled weeds and performed other physical labor on the beautiful temple grounds, we would exclaim, “Oh, those halcyon days of youth!” Now, as I look back, I see that they really were halcyon days.
In our busy lives, how can we make time to continue learning? I believe in consistent, incremental progress—small steps over time. For example, one doesn’t learn to play the piano in a single day. One must practice daily for several years. After many small increments, one can eventually play hymns, popular songs, or classical music. Lifelong learning is like that. We need to schedule some time each day to study the scriptures. We can also regularly read a little in other books. We learn “line upon line” and “precept upon precept.” 10
Elder Dallin H. Oaks and Sister Kristen M. Oaks wrote:
There are few things more fulfilling and fun than learning something new. Great happiness, satisfaction, and financial rewards come from this. An education is not limited to formal study. Lifelong learning can increase our ability to appreciate and relish the workings and beauty of the world around us. This kind of learning goes well beyond books and a selective use of new technology, such as the Internet. It includes artistic endeavors. It also includes experiences with people and places: conversations with friends, visits to museums and concerts, and opportunities for service. We should expand ourselves and enjoy the journey. 11
Two Stumbling Blocks of Learning
There are two issues connected with learning about which we must be careful. First, learning can lead to pride. In 2 Nephi Jacob wrote:
O that cunning plan of the evil one! O the vainness, and the frailties, and the foolishness of men! When they are learned they think they are wise, and they hearken not unto the counsel of God, for they set it aside, supposing they know of themselves, wherefore, their wisdom is foolishness and it profiteth them not. And they shall perish.
But to be learned is good if they hearken unto the counsels of God. 12
President Ezra Taft Benson taught:
Pride is the universal sin, the great vice. . . .
The antidote for pride is humility—meekness, submissiveness. (See Alma 7:23.) It is the broken heart and contrite spirit. 13
Humility opens our hearts and minds to learning. By contrast, thinking that we already know everything impedes our learning. King Benjamin taught that a person needs to become “as a child, submissive, meek, humble, patient, full of love, willing to submit to all things which the Lord seeth fit to inflict upon him, even as a child doth submit to his father.” 14
Second, we should expect that at times apparent conflicts may arise between secular learning and gospel principles. “[T]he gospel encompasses all truth.” 15 At the groundbreaking of the BYU Eyring Science Center in 1948, President George Albert Smith said:
I want to say that The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints accepts all that is true in the world from whatever source it may come, with the knowledge that it originated with the greatest of all scientists, our Father in Heaven. . . .
And so I congratulate the students of this great institution [BYU] to think that you have all the advantages that the people of the world have, plus the advantages of faith in God, a belief in the power of our Heavenly Father, and His inspiration. 16
The Aims of a BYU Education states:
Students need not ignore difficult and important questions. Rather, they should frame their questions in prayerful, faithful ways, leading them to answers that equip them to give “a reason of the hope that is in” them (1 Peter 3:15) and to articulate honestly and thoughtfully their commitments to Christ and to His Church. 17
When human knowledge and the gospel appear to conflict, we should remember that human knowledge is limited. Eternal truth is not limited, but our understanding of it is incomplete. After this life, if we are worthy, we will understand all truth. Meanwhile, we seek answers to faithful questions. We study, ponder, pray, and have patience. We exercise faith in God. He blesses us with greater knowledge, understanding, and peace in our lives.
We should be humble about what we know and what we do not know. An angel appeared to Nephi. Nephi wrote:
And he said unto me: Knowest thou the condescension of God?
And I said unto him: I know that he loveth his children; nevertheless, I do not know the meaning of all things. 18
We do not know the meaning of all things, but we do know that God loves His children.
God’s wisdom supersedes human knowledge. Elder Oaks wrote:
We are commanded to seek learning by study, the way of reason, and by faith, the way that relies on revelation. Both are pleasing to God. He uses both ways to reveal light and knowledge to his children. But when it comes to a knowledge of God and the principles of his gospel, we must give primacy to revelation because that is the Lord’s way. 19
We should also remember to put the gospel, not our academic discipline, first in our lives. Jesus said, “But seek ye first the kingdom of God and his righteousness, and all these things shall be added unto you.” 20
The Strength in Learning
This is a wonderful time to be on the earth. There are so many opportunities for lifelong learning. If we do our best and seek Heavenly Father’s help, He will strengthen us beyond our natural abilities and help us to learn. That learning will enable us to develop personally, will increase our ability to serve others, and will help us to be prepared in all things.
I testify that the gospel is true. Heavenly Father lives and loves us, and Jesus Christ is the Son of God, the Savior of the world. In the name of Jesus Christ, amen.
1. Marion B. and Rulon A. Earl Professor of Law, J. Reuben Clark Law School, Brigham Young University. Apologies and thanks to Johnny Carson, Jay Leno, Steven Wright, and others.
2. D&C 88:118.
3. D&C 90:15.
4. JD 14:83.
5. Thomas S. Monson, “Three Goals to Guide You,” Ensign, November 2007, 119.
6. D&C 88:78–80.
7. The Mission of Brigham Young University and The Aims of a BYU Education (Provo: BYU, 1996), 12.
8. Russell M. Nelson, “With God Nothing Shall Be Impossible,” Ensign, May 1988, 34.
9. Gordon B. Hinckley, “A Three-Point Challenge,” BYU commencement address, 27 April 1995; excerpt in TGBH, 171.
10. D&C 98:12; 2 Nephi 28:30.
11. Dallin H. Oaks and Kristen M. Oaks, “Learning and Latter-day Saints,” Ensign, April 2009, 27.
12. 2 Nephi 9:28–29.
13. Ezra Taft Benson, “Beware of Pride,” Ensign, May 1989, 6.
14. Mosiah 3:19.
15. Elder Cecil O. Samuelson Jr. on Elder Neal A. Maxwell’s views, quoted in Bruce C. Hafen, A Disciple’s Life: The Biography of Neal A. Maxwell (Salt Lake City: Deseret Book, 2002), 167; see also Henry Eyring, quoted in Henry J. Eyring, Mormon Scientist: The Life and Faith of Henry Eyring (Salt Lake City: Deseret Book, 2007), 60.
16. George Albert Smith, “Address at Ground Breaking Ceremonies for the Physical Science Building at Brigham Young University,” 11 May 1948, 2, 4; this quotation is posted on the fifth floor of the BYU Harold B. Lee Library.
17. The Aims, 4.
18. 1 Nephi 11:16–17.
19. Dallin H. Oaks, The Lord’s Way (Salt Lake City: Deseret Book, 1991), 72.
20. 3 Nephi 13:33.
© Brigham Young University. All rights reserved.

James D. Gordon III1 was assistant to the president for planning and assessment and a professor of law at BYU when this devotional address was given on 26 March 2013.
Related Speeches
Paul and Alma and Harold B. Lee: What Prophets and Common Sense Can Teach Us About Learning From Our Mistakes
Language Learning: A Truly Educational Experience

Rochester News
- Science & Technology
- Society & Culture
- Campus Life
- University News
Why free speech—and especially disagreement—matters on college campuses

- Facebook Share on Facebook
- X/Twitter Share on Twitter
- LinkedIn Share on LinkedIn
A Rochester political scientist explains why the ‘clash of ideas’ resulting from free speech is necessary for a well-functioning university.
In September, the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression released a survey of undergraduates on college campuses across the United States in an effort to gauge the state of free speech and expression in American higher education. Recruiting students from the College Pulse American College Student Panel, the organization sought to measure how comfortable students were in discussing controversial topics in various campus settings; how tolerant they were of campus speakers whose views were offensive to liberals; how tolerant they were of campus speakers whose views were offensive to conservatives; and how well or how poorly their institutions’ administration did in supporting a culture of free expression.
About David Primo
An expert on campaign finance laws, the federal debt, corporate social responsibility, and budget rules, David Primo is the author or coauthor of several books, including Rules and Restraint: Government Spending and the Design of Institutions (University of Chicago Press, 2007) and Campaign Finance and American Democracy: What the Public Really Thinks and Why It Matters (University of Chicago Press, 2020).
Among those polled were 250 University of Rochester students. Twenty-seven percent of the Rochester cohort said that they hesitate “fairly often” or “very often” to express an opinion out of fear of their professors’ or classmates’ reaction. The situation is not unique to Rochester; it exists on many US college campuses and follows a national trend, the survey found.
David Primo , the Ani and Mark Gabrellian Professor and a professor of political science and of business administration at the University of Rochester, has made promoting free speech and expression a pedagogical priority—bringing guests from across the political spectrum to his classes and teaching an undergraduate course devoted to the topic, Disagreement in a Democratic Society . Primo also directs the Politics and Markets Project, an initiative he created in 2014 to encourage robust but civil discussions about contentious policy issues.
During a recent campus event, Primo urged universities to remain steadfast in their historical role as places of discussion and dissent. The “clash of ideas is the foundation for a college education. Without that you can’t have a well-functioning university,” he said. “Ideas that shape the world often emerge from college campuses.”
Fortunately, in the United States free speech is legally enshrined in the First Amendment to the US Constitution, and many private universities (which are not bound by the First Amendment in the same way as public universities are) have explicit commitments to support free speech and free inquiry on their campuses. “In other words, students have the right to speak freely, debate speech, and also protest against speech they don’t agree with,” Primo explained. “Of course, some universities do a better job than others of living up to these ideals.”
Even at universities that uphold the principles of free expression, problems arise, according to Primo, when faculty and students become unwilling to express their own ideas or challenge each other’s. Primo argues the fear of being professionally or socially ostracized is often on the minds of those with unorthodox or unpopular perspectives.
So, what happens when students think they can’t speak freely—to professors, administration, staff, or each other?
“A fear of speaking out means that important ideas may not be heard, important discoveries may not be made, and the boundaries of knowledge may not be pushed,” Primo said. “That kind of self-censorship can also extend to faculty members and influence the kind of research projects they pursue, or feel they ought to pursue. The acceptable range of ideas narrows more than it should.”
Read on for more highlights from Primo’s remarks.

1. Heeding John Stuart Mill on the importance of ‘the heretics’
“You may say there are some people who just shouldn’t be able to speak—those crazy people on the left and those crazy people on the right. The 19th-century English philosopher John Stuart Mill had a name for these people—he’d call them the heretics, which was particularly appropriate given when he was writing, but I would argue is still appropriate now.”
Primo outlined three guiding principles on disagreement, distilled from Mill’s 1859 treatise, On Liberty :
- We should care about disagreement. We should interact with those we disagree with because we could be wrong. Otherwise we are assuming we’re infallible.
- You might understand your views on a contentious issue at a deeper level if you talk to someone who disagrees with you. It pushes you to understand your own ideas and positions better, and to learn to understand theirs.
- Society is going to make progress through error. That’s the hallmark of science: we have to be open to error and have ideas clash so that we can take the best parts of these ideas and move forward with knowledge generation.
2. On ‘affective polarization,’ or when politics became your identity
“When people’s political convictions become their identity—the blue team versus the red team—that’s what we political scientists call ‘affective polarization.’ Practically speaking, that means if I know that you’re a Democrat, I generally know much more about you than I would’ve known 30 years ago. Same if I know you’re a Republican. As a result, we’ve seen a rise in this idea that we don’t like somebody because they support the other party. In other words, it’s not just that we disagree with people on the other side; it’s that we actively dislike them as people because of their ideology or party affiliation.
“College students today are practicing affective polarization. In an NBC News poll a couple of months ago, nearly half of all college students said they wouldn’t room with somebody of a different political party. We ought to be figuring out exactly why that is—and how we can fix it.”
3. Responding to disinformation on social media
“There are serious issues with false information’s being transmitted on social media, but that’s something that we have to manage rather than regulate. Because if governments start limiting what can be said on social media, and if governments start regulating how social media companies moderate what’s allowed on their platforms, it becomes a slippery slope. Where then do you draw the line?
“When I think about restrictions on speech, I think about whether I would want those restrictions to exist when somebody I disagree with fundamentally is in a position of power. Because then they’re the ones who are going to control whether or not I can speak.”
4. Avoiding the ‘noise’ of MSNBC and Fox News
“Students need to cut through the noise and yelling on channels like MSNBC and Fox News and instead focus on having rigorous, courteous, civil debates. They should be shown why it’s important to care about the fact that we, as a society, are currently not disagreeing effectively.
“In class we have vigorous and valuable discussions, which signals to me that there’s a lot of support for the idea of open disagreement on college campuses. That’s why I am worried about the 27 percent of students who feel they can’t speak out. But I’m also heartened by the fact that we still have a tremendous number of students who are deeply engaged, who are willing to explore ideas. So, if we can help support them within the University then, that’s going to help because students are the ones who’ll be going out into society; they’re the ones who are going to be making the decisions and running the show in a few years. That’s why it’s vitally important they learn those skills here.”
5. Encouraging free speech among students—and supporting one another
“Students need to be supportive of each other as they explore ideas. On the first day of my seminar courses, I work with the students to set class norms and talk about the terms of debate in our class. One of the things we agreed upon this semester was that you can discuss outside of class what was said in class but not attribute specific ideas to specific people. I want students to be free to explore ideas without worrying that in two hours’ time what they just said in class would appear somewhere on social media. We want to have a truly safe space for the discussion of ideas without this fear. Of course, I can’t police whether students live up to these ideals. But I think the fact that students supported this ground rule shows that you can create this foundation to build up agreement to disagree on college campuses.
“When the heretics get to speak, I am reassured that we are protecting the right for all of us to express ourselves freely.”

A Rochester expert sheds light on the underrecognized challenges faced by college students recovering from trauma, and answers questions on the real meaning of trigger warnings.

On college campuses, where safe spaces and free inquiry often coexist, do trigger warnings protect students or hinder free speech? This episode of the University’s Quadcast podcast takes on the growing debate.

Three Rochester professors discuss the nature of America’s political and social divide and offer ideas on how higher education might help bridge the widening gap.
More in Society & Culture

Knight Foundation
- Communities
- Learning and Impact
- Philadelphia
- Community Foundations Program
- Press Releases
- Arts and Technology
- Diverse Asset Managers
- Elections and Voting
- Freedom of Expression
- Knight Research Network
- Local Journalism
- Public Spaces
- Smart Cities
- Technology and Democracy
- Trust in News
- Board of Trustees
- Internship Program
- Financial Information

College Student Views on Free Expression and Campus Speech 2022
Full reports, a look at key trends in student speech views since 2016 .
College campuses have long been places where the limits of free expression are debated and tested. In recent years, this dialogue has grown more fraught as some schools have sought to create a more protective speech environment for students. Moreover, key events shaping the past two years, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, the racial justice movement and the 2020 election, have only added deeper dimensions to the dialogue around free speech playing out on campus and in society at large.
The “Knight-Ipsos College Student Views on Free Expression and Campus Speech” report is the fourth in a series of Knight Foundation reports measuring college student attitudes toward speech and the First Amendment since 2016. For this report, Knight Foundation commissioned Ipsos to conduct a survey with a nationally representative sample of over 1,000 college students ages 18-24 enrolled in all types of higher education institutions, along with 4,000 American adults, offering insight into how college students’ views on free speech compare with those of the general public. In addition to the past Knight-Gallup campus speech surveys (2016, 2017, 2019), Knight has studied free speech views among high school students since 2004. Trends in college student attitudes are included throughout this report.
For findings on how the adult population views free speech and expression, please see “Free Expression in America Post -2020,” published earlier in January 2022.
This Knight Foundation-Ipsos report offers nuanced insight into how college students perceive campus speech and First Amendment protections today, including how views are evolving within different factions of the student body. This survey reinforces that students are not a monolithic group when it comes to speech, finding that partisanship, race, and ethnicity drive meaningful differences in how college students view speech. Understanding where different groups stand is vitally important for higher education leaders as they seek to foster free expression on college campuses and create a campus environment that is diverse, equitable, and inclusive.
The findings described in this report cover many, but not all, of the rich insights possible from this complex dataset. We invite the public and researchers to explore this publicly available resource in further detail.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- Students view speech rights as important, yet less secure than in years past: Students continue to believe First Amendment rights and concepts of free speech are important to democracy. However, the percentage of students saying speech rights are secure has fallen every year since this question was first asked in 2016. This includes a 12-point decrease from 2019 as an increasing number of students—particularly Republicans—say they believe speech rights are threatened.
- Students of color believe their speech is less protected: While a majority of college students express confidence that the First Amendment protects “people like them,” Black students in particular feel much less protected, with a sharp decline from 2019 to 2021.
- Students believe exposure to a wide spectrum of speech at college is important: Most students continue to say colleges should allow students to be exposed to all types of speech, including political speech that is offensive or biased, rather than prohibiting speech they may find offensive.
- Students favor college policies that limit racist speech, but support for other speech interventions remains low: Most students favor colleges instituting policies that restrict the use of racial slurs on campus, suggesting that, for them, this particular category of speech does not merit mandated exposure on campus. Just 1 in 4 students favor schools disinviting controversial speakers, down from more than 2 in 5 in 2019. Similarly, the number of students who support colleges providing safe spaces or speech codes has fallen over the past two years.
- Students say the campus climate stifles free expression, yet speech on campus is making nearly 1 in 5 feel unsafe: More students now say the climate at school prevents some from saying things others might find offensive, and fewer feel comfortable disagreeing in class. Yet slightly more now report feeling unsafe because of comments made on campus than in 2019. This is particularly true for female students and students of color.
A selection of key trends among students over the years. Full findings are in the body of the report.
KEY POPULATIONS
Experience with and attitudes toward speech vary widely among different student groups. The greatest differences exist among race and partisanship, and less so by gender or other demographic groupings. The following is a brief summary of the major findings and how opinion has changed over time, including the degree to which students have a formed opinion at all.
Democratic students
A majority of Democratic students believe that freedom of speech is secure in America today, a view that has held constant since 2019. When it comes to free expression broadly on campus, just over half of Democratic students favor schools fostering an environment in which all forms of speech are allowed, a view that’s softened since the last time Knight asked these questions two years ago.
Democrats are most likely to favor colleges implementing restrictions on certain forms of speech on campus, particularly around speech that is offensive to minority groups, something that was also true in prior Knight-Gallup research. Both now and in 2019, a large majority of Democratic students believe that colleges should be able to restrict the use of racial slurs on campus. When it comes to other speech policies, 3 in 4 support the creation of safe spaces on campus, close to half support the creation of speech codes that could limit offensive or biased speech, and 2 in 5 favor schools disinviting potentially controversial speakers. These views are consistent with previous surveys.
A majority of Democrats feel that their campus climate prevents people from saying what they believe for fear of offending others, although they are less likely to feel this way than Republicans and independents. Compared with two years ago, Democratic students now feel less comfortable voicing disagreements in class.
Independent students
Independent students express growing concerns about the fundamental security of free speech in America today while indicating their wariness of colleges limiting speech on campus. Just under half of all independents feel that free speech is secure today, down from 3 in 4 who felt this way in 2016. At the same time, a strong majority (8 in 10) believe that they are protected under the First Amendment. This puts them on about equal footing with Democrats, but slightly behind Republicans.
A majority believe that colleges should allow students to be exposed to all forms of speech. Opinion is split among the remaining minority with equal numbers (around 1 in 5 each) either believing that colleges should foster a protective environment or having no opinion on the matter. Much like two years ago, few support colleges disinviting controversial speakers or instituting speech codes.
A majority feel that their campus climate limits free expression, a view that has remained the same since 2019.
Independents were more likely than other groups of students to respond with the newly prompted “No opinion” option this year, indicating that many of them do not have strong views on these issues at all.
Republican students
Republican students are increasingly likely to feel that freedom of speech is under threat—just over a quarter believe it is secure today, down from two-thirds in 2016. More now also believe that their school’s climate stifles free expression.
A strong majority (7 in 10, down from 90% in 2019) say it is more important for colleges to allow students to be exposed to all types of speech, even if they find it offensive or biased, than to prohibit offensive or biased speech. A majority (56%)—albeit a smaller share than either Democratic or independent students—believe that colleges should be allowed to prohibit the use of racial slurs on campus. Moreover, for Republican students, this represents a more than 20-point drop from 2019 in the percentage who feel that colleges should restrict the use of racial slurs on campus.
Republicans are more divided around whether safe spaces should be allowed on campus—half favor this—but come down firmly against schools disinviting controversial speakers, something that was also true two years ago. A slim majority oppose schools instituting speech codes that could restrict offensive or biased speech. Unlike their Democratic counterparts, there has been no change over time in their already low level of comfort voicing disagreements with professors or other students; less than half remain comfortable.
White students
White students tend to favor allowing all types of speech on campus, over protecting students by prohibiting certain speech. They are least likely to report having felt unsafe or uncomfortable on campus because of comments about their identity, as compared with Black and Hispanic students. This has not changed substantially since 2019.
Overall, half of white college students believe that freedom of speech is under threat in America today. Yet a large majority feel that the First Amendment protects them, a view that has held steady since 2019.
When it comes to free expression on college campuses, white students are more likely than their Black or Hispanic counterparts to agree that schools should favor exposing students to all forms of speech, rather than protecting them from speech they may find offensive or biased. This was also true two years ago. They are slightly more likely than Black or Hispanic students to believe that the campus environment stifles free expression.
Black students
Fewer Black students express confidence that the First Amendment protects people like them. At the same time, a growing number of Black students favor a more protective campus environment.
The share of Black students who feel the First Amendment protects them a great deal has fallen by 20 percentage points over the past two years. Black students also express less confidence than the broader Black adult population about how effectively the First Amendment protects either them or the average American.
When it comes to campus free speech, the number of Black students who favor a campus environment that protects students by prohibiting speech that they might find offensive or biased has grown from 28% in 2019 to 36% in 2021. Both in 2019 and 2021, a majority of Black students feel that colleges should restrict the use of offensive racial slurs on campus.
Black students are more likely than white or Hispanic students to say that they have been made to feel uncomfortable due to statements that others have made in their presence about their identity or political beliefs, both in daily life and on campus. This has remained constant since 2019.
Hispanic students
Hispanic students’ views of campus speech, and personal experiences, fall somewhere between the differing views of Black and white students.
A strong majority of Hispanic students believe that the First Amendment protects people like them, something that was also true two years ago. The number of Hispanic students saying this is nearly equal to the number of white students. Similarly, Hispanic students align closely with white students on perceptions that free speech is under threat; half agree.
However, with regard to colleges restricting offensive racial slurs, Hispanic students fall closer to Black students, with 7 in 10 supporting such an action.
Hispanic students (along with independents) are among the most likely to say they have no opinion about whether colleges should foster a more protective speech environment or allow all types of speech on campus. A plurality oppose disinviting controversial speakers, but they are split around instituting speech codes. Like white students, close to 6 in 10 favor the creation of safe spaces on campus, less than the share of Black students who do.
Male and female students
For the most part, male and female students are aligned in their attitudes and experiences of free speech, with a few key differences. Overall, a majority of both male and female students say that free speech rights are important to American democracy, although fewer feel this way than in 2019. Now, female students are more likely than male students to say that free speech rights are extremely important, a change from 2019 when more men said free speech rights were extremely important.
Nearly 1 in 5 male and female students alike report having felt unsafe due to comments on campus, whereas larger gender differences were observed in prior years. A more meaningful difference appears when male and female students are asked if they have felt uncomfortable on campus. Female students remain significantly more likely to have felt uncomfortable due to speech on campus, as they did in 2019.
Download full report:

Related Resources

Knight Free Expression Research Series

Free Expression in America Post-2020
A Knight-Ipsos study from the Knight Free Expression Research Series A Landmark Survey of Americans’ Views on Speech Rights
Post-2020, college students see speech as less secure, and students of color feel less protected
An uproar over a climate scientist’s canceled lecture at MIT. A furor over a Charles Murray talk at Middlebury College. An ongoing controversy concerning racist remarks by a University of Pennsylvania law professor. In recent years, headline-grabbing events like these have sparked an energetic debate about how higher education should treat speech in the 21st […]
Knight-Ipsos poll: College students covet free speech rights, but view them as increasingly fragile
A new study from the Knight Free Expression (KFX) Research Series shows that most college students in America strongly value free speech […]
In the News

Do Students Self-Censor? Here’s What the Data Tell Us
Most Iowa college students feel free to share opinions in class
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

‘I haven’t really had a proper weekend in a long time’

Party like it’s 2020

Study of Psychedelics in Society and Culture announces funding recipients
Stephanie Mitchell/Harvard Staff Photographer
Break down walls. Vanquish villains. Stand up and speak out. Facts and truth matter.
6 past harvard commencement speakers offer inspiring messages of justice, courage, resilience, empathy.
Harvard graduates this week will hear from two high-profile leaders, New Zealand Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern and U.S. Attorney General Merrick Garland, Thursday and Sunday. Ahead of the ceremonies, we look back at Commencement addresses from recent years.
“My philosophy is very simple. When you see something that’s not right, not fair, not just, stand up, say something, and speak out.”
U.S. Rep. John Lewis
2018 The Civil Rights icon delivers a powerful message on the importance of truth, justice, and equality at a time when those values have come under assault.
Thank you so much for those kind words of introduction. I must tell you that I’m delighted, very pleased and really happy to be here. You look good! The weather is good, rain stayed away. I’m happy. It’s good to see each and every one of you. Fellows of Harvard University, members of the Board of Overseers, members of the alumni board, distinguished deans, guests, faculty and all of the students, all of the wonderful graduates, and madam president, thank you. Thank you for your leadership, thank you for getting in good trouble! Necessary trouble. To lead this great University.
I want to take just a moment to honor the tenure of a great leader, who, through her courage and vision, worked to lead this historic university to even higher heights. Madam president, thank you for being a friend, but more importantly, thank you for using your office to move Harvard toward a more all-inclusive institution. Somewhere along the way, you realized that the brilliant mind is not confined to one discipline or one way of thinking.
In fact, true genius sees connections and relationships across barriers, to build a new understanding of the world around us. Creating one Harvard is much like the work I dedicated my life to. Ever since as a young girl you wrote a letter to President Eisenhower as a little girl, you have been responding to the cry for human dignity that rings out in our world. You used your vision and your talent, you used the great resources of this university to respond to that call, and I thank you. Thank you for your contribution to human unity in our world.
Today I say to each and every one of you who graduated from this University, you must lead. You’re never too young to lead, you’re never too old to lead! We need your leadership now more than ever before. We need it! We must save our country! We must save it! We must save our democracy. There are forces in America today and around the world trying to take us to some other place. Our foremothers and forefathers brought us to this place. Maybe our foremothers and our forefathers all came to this great land in different ships but as the late great A. Philip Randolph said “we are all in the same boat now” and we must look out for each other and care for each other. You’re never too young or too old to lead! To speak up! Speak out! And get in good trouble, necessary trouble. You cannot afford to stand on the sidelines.
Another generation of young people and people not so young are inspired to get in the way. Students from Harvard, Dr. Cole, who I have been knowing for many years came to Mississippi, came to the South and gave everything you had. During the 63 young men that I knew, Andrew Goodman, Michael Schwermer, and James Chaney gave their very lives while they were helping people to register to vote. The vote is precious. It’s almost sacred. It is the most powerful, nonviolent instrument or tool we have in a democratic society and we must use t if we fail to use it, we will lose it.
So during this election year, I urge you, I plead with you to do what you can to save and rescue America. To do what you can to save the planet! Save this spaceship we call earth and leave it a little cleaner, a little greener, and a little more peaceful. For generations yet unborn. We have a mission and a mandate to go out there, play a role and play it so well as Dr. King would say, that no one else can play it any better. Some of you have heard me say from time to time that I grew up in rural Alabama on a farm, picking cotton, gathering peanuts, gathering corn. Sometimes I would be out there working and my mother would say, “boy, you’re falling behind! You need to catch up.” And I would say “this is hard work.” And she said “hard work never killed anybody.” And I said “well it’s about to kill me!” We need to work hard! There is work to be done. These smart graduates will lead us. High school students lead us, and guys, I say to you, if you’re not mindful, the women are going to lead us! It is my belief, it is my feeling as a traveler of America that the women and young. People, high school students, elementary school students and College students will lead us as part of a nonviolent revolution. We will create an America that is better, a little more humane and no one, but no one can deny us of that.
I just want to say one or two words to the graduates. Take a deep breath and take it all in. But tomorrow, I hope you roll up your sleeves, because the world is waiting for talented men and women to lead it to a better place. During the 60s, people literally put their bodies on the line! Many came from this University, came from Cambridge, from Boston, throughout the state and throughout America. Just think a few short years ago that Black people and white people couldn’t be seated together on a Greyhound business or trailway bus, leaving Washington, D.C., to travel through Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi. We were on our way to New Orleans to test a decision of the United States Supreme Court. We were beaten, arrested, and more than 400 of us were jailed. My seatmate was a young white gentleman from Connecticut. We arrived in a small town in South Carolina. We were beaten, left bloody. But many years later, and this was May 1961, same year that Barack Obama was born, but many years later, one of the guys that beat us came to my office in Washington. He got information from a local reporter. He was in his 70s, his son came with him in his 40s. He said, “Mr. Lewis, I’m one of the people that beat you. Beat your seatmate. I’ve been a member of the Klan.” He said “will you forgive me? I want to apologize. Will you accept my apology? Will you forgive me?” His son started crying, he started crying and I said, “I forgive you. I accept your apology.” They hugged me, I hugged them back, and I cried with them. It is the power of the way of peace, the power of love, it is the power of the philosophy and discipline of nonviolence. We need to create a society where we can be reconciled and lay down the burden of hath for hate is too heavy of a burden to bear.
Fifty years ago the man that I admired, the man that was like a brother, Martin Luther King Jr., was taken from us. When we heard that Dr. King had been assassinated I was in Indianapolis, Indiana, campaigning with Bobby Kennedy. I cried. Stopped crying and I said to myself “we still have bobby.” Two months later Bobby Kennedy was gone. And I cried some more. Today we’ve got to get rid of our are tears and not be down. And not get lost in the sea of despair. We’ve got to be hopeful and keep the faith and turn the ship around. We can do it and we must do it!
Here at Harvard you’ve been well trained. You must lead. You must get out there and as Dr. King would say, be a headlight, not a taillight! It’s your time, it’s your calling. During the 60s I got arrested a few times, 40 times! And since I’ve been in Congress another five times! And I’m probably going to get arrested again! My philosophy is very simple, when you see something that is not right, not fair, not just, stand up! Say something! Speak up and speak out!
When I was growing up as a young boy in rural Alabama, 50 miles from Montgomery, I had an aunt by the name of Seneva and my aunt lived in a shotgun house. Here at Harvard you never seen a shotgun house, you don’t even know what I’m talking about. One way in, one way out. What is a shotgun house? Old house, dirt yard. Sometimes my aunt Seneva would go out on the weekend, Friday or Saturday, and take a brush broom made from dogwood branches and sweep the yard very clean. One Saturday afternoon few of my brothers and sisters, cousins, about 15 of us young children were playing in her dirt yard. And an unbelievable storm came up. The wind started blowing, the thunder started rolling and the lightning started flashing and she told us to come in. We went in. The wind continued to blow, the thunder continued to roll, the lightning continued to flash, and the rain continued to beat on this old tin roof of the shotgun house. And we cried and cried. And in one corner of the old house appeared to be lifting up. And my aunt walked over to that side to hold the house down with her body. When the other corner appeared to be lifting she had us walk to that corner, we were children walking with the wind, but we never, ever left the house! I say to each of you, each and every one of us, the wind may blow, the thunder may roll, the lightning may flash, and the rain may beat down on an old house. Call it a house of Harvard, call it a house of Cambridge, call it a house of Boston, call it the house of Washington, or Alabama or Georgia, we all live in the same house. We all must hold our little house down. So I say to you: Walk with the wind. Let the spirit of history be your guide.
Thank you very much.
“Rock bottom became the solid foundation on which I rebuilt my life.”
J.K. Rowling
2008 Drawing from her own life story, the “Harry Potter” author urges graduates not to fear failure but to learn from it and emphasized the power of empathy and imagination.
Read the speech.
“If we break down the walls that hem us in, if we step out into the open and have the courage to embrace new beginnings, everything is possible.”
Angela Merkel
2019 Like the Berlin Wall, “anything that seems set in stone or inalterable can indeed change,” Germany’s first woman chancellor said.
Herman Hesse wrote, “In all beginnings dwells a magic force for guarding us and helping us to live.” These words by Herman Hesse inspired me when I completed my physics degree at the age of 24. That was back in 1978. The world was divided into east and west, and it was in the grips of the Cold War. I grew up in East Germany, in the GDR, the part of my country which was not free at that time, in a dictatorship. People were oppressed and under state surveillance. Political dissidents were persecuted. The East German government was afraid that the people would flee to freedom. And that’s why it built the Berlin Wall, a wall made of concrete and steel. Anyone caught trying to overcome it was arrested or shot dead. This wall, which cut Berlin in half, divided a people and it divided families. My family was also divided.My first job after college was as a physicist at the Academy of Sciences in East Berlin. I lived near the Berlin Wall. I walked towards it every day on my way home from my institute. Behind it lay West Berlin, freedom. And every day, when I was very close to the wall, I had to turn away at the last minute in order to head towards my apartment. Every day, I had to turn away from freedom at the last minute. I don’t know how often I thought that I just couldn’t take it anymore. It was so frustrating.
Now, I was not a dissident. I didn’t run up and bang against the wall. Nor, however, did I deny its existence, for I didn’t want to lie to myself. The Berlin Wall limited my opportunities. It quite literally stood in my way. However, there was one thing which this wall couldn’t do during all those years. It couldn’t impose limits on my inner thoughts. My personality, my imagination, my dreams and desires, prohibitions or coercion couldn’t limit any of that. Then came 1989. A common desire for freedom unleashed incredible forces throughout Europe. In Poland, in Hungary, in Czechoslovakia, as well as in East Germany, hundreds of thousands of people dared to take to the streets. The people demonstrated and brought down the wall. Something which many people, including myself, would not have believed possible became reality. Where there was once only a dark wall, a door suddenly opened. For me, too, the moment had come to walk through that door. I no longer had to turn away from freedom at the last minute. I was able to cross this border and venture out into the great wide open.
During these months, 30 years ago, I experienced firsthand that nothing has to stay the way it is. This experience, dear graduates, is the first thought I want to share with you today for your future. Anything that seems to be set in stone or inalterable can, indeed, change. In matters both large and small, it holds true that every change begins in the mind. My parents’ generation discovered this in a most painful way. My father and mother were born in 1926 and 1928.
When they weren’t as old as most of you here today, the betrayal of all civilized well values that was the Shoah and World War II had just ended. My country, Germany, had brought unimaginable suffering on Europe and the world. The victors and the defeated could easily have remained irreconcilable for many years, but instead, Europe overcame centuries old conflicts. A peaceful order based on common values rather than suppose at national strength emerged. Despite all the discussions and temporary setbacks, I firmly believe that we Europeans have United for the better. And the relationship between Germans and Americans, too, demonstrates how former wartime enemies can become friends.
It was George Marshall who gave a crucial contribution to this for the plan he announced at the commencement ceremonies in 1947 in this very place. The transatlantic partnership based on values, such as democracy and human rights, has given us an era of peace and prosperity of benefit to all sides, which has lasted for more than 70 years now. And today, it will not be long now before the politicians of my generation are no longer the subject of the exercising leadership program, and at most will be dealt with in leadership in history. Harvard class of 2019, your generation will be faced with the challenges of the 21st century in the coming decades. You are among those who will lead us into the future.
Protectionism and trade conflicts, jeopardize free international trade, and thus the very foundations of our prosperity. The digital transformation affects all facets of our lives, wars and terrorism lead to displacement and forced migration, climate change poses a threat to our planet’s natural resources, it and the resulting crises are caused by humans. Therefore, we can and must do everything humanly possible to truly master this challenge to humankind. It’s still possible. However, each and every one of us must play our part. And I say this with a measure of self criticism, get better. I will therefore do everything in my power to ensure that Germany, my country, will achieve climate neutrality by 2050. Changes for the better are possible if we tackle them together. If we were to go it alone, we could not achieve much. The second thought I want to share with you is therefore, more than ever our way of thinking and our actions have to be multilateral rather than unilateral, global rather than national, outward looking rather than isolationists. In short, we have to work together rather than alone.
You, dear graduates, will have quite different opportunities to do this in future than my generation did. After all, your smartphone probably has considerably more processing power than the copy of an IBM mainframe computer manufactured in the Soviet Union, which I was allowed to use for my dissertation in East Germany in 1986.
Today we use artificial intelligence, for example, to search through millions of images for symptoms of diseases.In order, among other things, to better diagnose cancer. In future, empathetic robots could help doctors and nurses to focus on the individual needs of patients. We cannot predict today which applications will be possible. However, the opportunities it brings are truly breathtaking.
Class of 2019, how we use these opportunities will be largely up to you as graduates. You are the ones who will be involved in deciding how our approach to how we work, communicate, get about, indeed, our entire way of life will develop. As federal chancellor, I often have to ask myself, “Am I doing the right thing?” “Am I doing something? Because it isn’t right? Or simply because it is possible.” That is something you two need to keep asking yourselves. And that is the third thought I wish to share with you today.
Are we laying down the rules for technology or is technology dictating how we interact? Do we prioritize people as individuals with their human dignity and all their many facets? Or do we see in them merely consumers, data sources, objects of surveyance. These are difficult questions.
I have learned that we can find good answers even to difficult questions if we always try to view the world through the eyes of others. If we respect other people’s history, traditions, religion, and identity. If we hold fast to our inalienable values and act in accordance with them. And if we don’t always act on our first impulses, even when there is pressure to make a snap decision.
But instead take a moment to stop. Be still. Think. Pause. Granted, that certainly takes courage. Above all it calls for truthfulness in our attitude towards others. And perhaps most importantly, it calls for us to be honest with ourselves.
What better place to begin to do so than here, in this place, where so many young people from all over the world come to learn, research, and discuss the issues of our time under the maxim of truth. That requires us not to describe lies as truth and truth as lies. It requires us not to accept shortcomings as our normality. Yet what, dear graduates, could stop you? What could stop us from doing that?
Once again, the answer is walls.
Walls in people’s minds. Walls of ignorance and narrow-mindedness. They exist between family members, as well as between groups within the society, between people of different skin colors, nations, and religions. I would like us to break down these walls. Walls that keep preventing us from envisioning the world in which, together, we want to live.
Whether we manage to do that is up to us. That’s why my full thought for you, dear graduates, to consider is this. Nothing can be taken for granted. Our individual liberties are not givens. Democracy is not something we can take for granted. Neither is peace and neither is prosperity.
But if we break down… If we break down the walls that hem us in, if we step out into the open and have the courage to embrace new beginnings, everything is possible. Walls can collapse. Dictatorships can disappear. We can halt global warming. We can eradicate starvation. We can eliminate diseases. We can give people, especially girls, access to education. We can fight the causes of displacement and forced migration. We can do all of that. Let’s not start by asking what isn’t possible, or focusing on what has always been that way. Let’s start by asking what is possible and looking for things that have never been done like that before. This is exactly what I said to the Bundestag, the German Parliament, in 2005 in my first policy statement as newly elected Chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany and the first woman to hold this office. I want to use precisely these words to share with you my fifth thought. Let us surprise ourselves by showing what is possible. Let us surprise ourselves by showing what we are capable of. In my own life, it was the fall of the Berlin Wall that allowed me almost 30 years ago to step out into the open. At that point, I left my work as a scientist behind me and entered politics. That was an exciting and magical time, just as your lives will be exciting and magical.
I also experienced moments of doubt and worry, for at that time, we all knew what lay behind us, but not what might lie ahead. Perhaps that reflects a little how you, too, are feeling today, amidst all the joy of this occasion.
The six thought I also want to share with you is this. The moment when you step out into the open is also a moment of risk-taking. Letting go of the old is part of a new beginning. There is no beginning without an end, no day without night, no life without death. Our whole life consists of the difference, the space between beginning and ending.
It is what lies in between that we call life and experience. I believe at time and time again, we need to be prepared to keep bringing things to an end in order to feel the magic of new beginnings and to make the most of opportunities. That was what I learned as a student, and it is what I now in politics. Who knows what life will bring after my time as a politician? That, too, is completely open. Only one thing is clear. It will again be something different and something new.
That’s why I want to leave this wish with you. Tear down walls of ignorance and narrow mindedness for nothing has to stay as it is.
It’s six things. Take joint action in the interest of the moderate lateral global world. Keep asking yourselves, “Am I doing something because it is right, or simply because it’s possible?” Don’t forget that freedom is never something that can be taken for granted. Surprise yourself with what is possible. Remember that openness always involves risks. Letting go of the old is part of the new beginning. Above all, nothing can be taken for granted. Everything is possible. Thank you.
“In a two-hour movie, you get a handful of character-defining moments, but in real life, you face them every day. Life is one strong, long string of character-defining moments.”
Steven Spielberg
2016 Don’t shy away from the world’s pain, the filmmaker urged grads. Instead, examine it, challenge it and, while you’re at it, find “a villain to vanquish.”
Thank you, thank you, President Faust, and Paul Choi, thank you so much.
It’s an honor and a thrill to address this group of distinguished alumni and supportive friends and kvelling parents. We’ve all gathered to share in the joy of this day, so please join me in congratulating Harvard’s Class of 2016.
I can remember my own college graduation, which is easy, since it was only 14 years ago. How many of you took 37 years to graduate? Because, like most of you, I began college in my teens, but sophomore year, I was offered my dream job at Universal Studios, so I dropped out. I told my parents if my movie career didn’t go well, I’d re-enroll. It went all right.But eventually, I returned for one big reason. Most people go to college for an education, and some go for their parents, but I went for my kids. I’m the father of seven, and I kept insisting on the importance of going to college, but I hadn’t walked the walk. So, in my fifties, I re-enrolled at Cal State — Long Beach, and I earned my degree.I just have to add: It helped that they gave me course credit in paleontology for the work I did on Jurassic Park. That’s three units for Jurassic Park, thank you. Well I left college because I knew exactly what I wanted to do, and some of you know, too — but some of you don’t. Or maybe you thought you knew but are now questioning that choice. Maybe you’re sitting there trying to figure out how to tell your parents that you want to be a doctor and not a comedy writer.
Well, what you choose to do next is what we call in the movies the “character-defining moment.” Now, these are moments you’re very familiar with, like in the last “Star Wars: The Force Awakens,” when Rey realizes the force is with her. Or Indiana Jones choosing mission over fear by jumping over a pile of snakes. Now in a two-hour movie, you get a handful of character-defining moments, but in real life, you face them every day. Life is one strong, long string of character-defining moments. And I was lucky that at 18 I knew what I exactly wanted to do. But I didn’t know who I was. How could I? And how could any of us? Because for the first 25 years of our lives, we are trained to listen to voices that are not our own. Parents and professors fill our heads with wisdom and information, and then employers and mentors take their place and explain how this world really works. And usually these voices of authority make sense, but sometimes, doubt starts to creep into our heads and into our hearts. And even when we think, “that’s not quite how I see the world,” it’s kind of easier to just to nod in agreement and go along, and for a while, I let that going along define my character. Because I was repressing my own point of view, because like in that Nilsson song, “Everybody was talkin’ at me, so I couldn’t hear the echoes of my mind.” And at first, the internal voice I needed to listen to was hardly audible, and it was hardly noticeable — kind of like me in high school.
But then I started paying more attention, and my intuition kicked in. And I want to be clear that your intuition is different from your conscience. They work in tandem, but here’s the distinction: Your conscience shouts, “here’s what you should do,” while your intuition whispers, “here’s what you could do.” Listen to that voice that tells you what you could do. Nothing will define your character more than that. Because once I turned to my intuition, and I tuned into it, certain projects began to pull me into them, and others, I turned away from. And up until the 1980s, my movies were mostly, I guess what you could call “escapist.” And I don’t dismiss any of these movies — not even 1941. Not even that one. And many of these early films reflected the values that I cared deeply about, and I still do. But I was in a celluloid bubble, because I’d cut my education short, my worldview was limited to what I could dream up in my head, not what the world could teach me.
But then I directed “The Color Purple.” And this one film opened my eyes to experiences that I never could have imagined, and yet were all too real. This story was filled with deep pain and deeper truths, like when Shug Avery says, “Everything wants to be loved.” My gut, which was my intuition, told me that more people needed to meet these characters and experience these truths. And while making that film, I realized that a movie could also be a mission. I hope all of you find that sense of mission. Don’t turn away from what’s painful. Examine it. Challenge it. My job is to create a world that lasts two hours. Your job is to create a world that lasts forever. You are the future innovators, motivators, leaders and caretakers. And the way you create a better future is by studying the past.
“Jurassic Park” writer Michael Crichton, who graduated from both this college and this medical school, liked to quote a favorite professor of his who said that if you didn’t know history, you didn’t know anything. You were a leaf that didn’t know it was part of a tree. So history majors: Good choice, you’re in great shape…Not in the job market, but culturally. The rest of us have to make a little effort. Social media that we’re inundated and swarmed with is about the here and now. But I’ve been fighting and fighting inside my own family to get all my kids to look behind them, to look at what already has happened. Because to understand who they are is to understand who we were, and who their grandparents were, and then, what this country was like when they emigrated here. We are a nation of immigrants at least for now.
So to me, this means we all have to tell our own stories. We have so many stories to tell. Talk to your parents and your grandparents, if you can, and ask them about their stories. And I promise you, like I have promised my kids, you will not be bored. And that’s why I so often make movies based on real-life events. I look to history not to be didactic, cause that’s just a bonus, but I look because the past is filled with the greatest stories that have ever been told. Heroes and villains are not literary constructs, but they’re at the heart of all history.
And again, this is why it’s so important to listen to your internal whisper. It’s the same one that compelled Abraham Lincoln and Oskar Schindler to make the correct moral choices. In your defining moments, do not let your morals be swayed by convenience or expediency. Sticking to your character requires a lot of courage. And to be courageous, you’re going to need a lot of support.And if you’re lucky, you have parents like mine. I consider my mom my lucky charm. And when I was 12 years old, my father handed me a movie camera, the tool that allowed me to make sense of this world. And I am so grateful to him for that. And I am grateful that he’s here at Harvard, sitting right down there. My dad is 99 years old, which means he’s only one year younger than Widener Library. But unlike Widener, he’s had zero cosmetic work. And dad, there’s a lady behind you, also 99, and I’ll introduce you after this is over, okay? But look, if your family’s not always available, there’s backup. Near the end of “It’s a Wonderful Life” — you remember that movie, “It’s a Wonderful Life”? Clarence the Angel inscribes a book with this: “No man is a failure who has friends.” And I hope you hang on to the friendships you’ve made here at Harvard. And among your friends, I hope you find someone you want to share your life with.
I imagine some of you in this yard may be a tad cynical, but I want to be unapologetically sentimental. I spoke about the importance of intuition and how there’s no greater voice to follow. That is, until you meet the love of your life. And this is what happened when I met and married Kate, and that became the greatest character-defining moment of my life.Love, support, courage, intuition. All of these things are in your hero’s quiver, but still, a hero needs one more thing: A hero needs a villain to vanquish. And you’re all in luck. This world is full of monsters. And there’s racism, homophobia, ethnic hatred, class hatred, there’s political hatred, and there’s religious hatred.As a kid, I was bullied — for being Jewish. This was upsetting, but compared to what my parents and grandparents had faced, it felt tame. Because we truly believed that anti-Semitism was fading. And we were wrong. Over the last two years, nearly 20,000 Jews have left Europe to find higher ground. And earlier this year, I was at the Israeli embassy when President Obama stated the sad truth. He said: “We must confront the reality that around the world, anti-Semitism is on the rise. We cannot deny it.”
My own desire to confront that reality compelled me to start, in 1994, the Shoah Foundation. And since then, we’ve spoken to over 53,000 Holocaust survivors and witnesses in 63 countries and taken all their video testimonies. And we’re now gathering testimonies from genocides in Rwanda, Cambodia, Armenia and Nanking. Because we must never forget that the inconceivable doesn’t happen — it happens frequently. Atrocities are happening right now. And so we wonder not just, “When will this hatred end?” but, “How did it begin?”
Now, I don’t have to tell a crowd of Red Sox fans that we are wired for tribalism. But beyond rooting for the home team, tribalism has a much darker side. Instinctively and maybe even genetically, we divide the world into “us” and “them.” So the burning question must be: How do all of us together find the “we?” How do we do that? There’s still so much work to be done, and sometimes I feel the work hasn’t even begun. And it’s not just anti-Semitism that’s surging — Islamophobia’s on the rise, too. Because there’s no difference between anyone who is discriminated against, whether it’s the Muslims, or the Jews, or minorities on the border states, or the LGBT community — it is all big one hate.
And to me, and, I think, to all of you, the only answer to more hate is more humanity. We gotta repair — we have to replace fear with curiosity. “Us” and “them” — we’ll find the “we” by connecting with each other. And by believing that we’re members of the same tribe. And by feeling empathy for every soul — even Yalies.
My son graduated from Yale, thank you …
But make sure this empathy isn’t just something that you feel. Make it something you act upon. That means vote. Peaceably protest. Speak up for those who can’t and speak up for those who may be shouting but aren’t being hard. Let your conscience shout as loud as it wants if you’re using it in the service of others.
And as an example of action in service of others, you need to look no further than this Hollywood-worthy backdrop of Memorial Church. Its south wall bears the names of Harvard alumni — like President Faust has already mentioned — students and faculty members, who gave their lives in World War II. All told, 697 souls, who once tread the ground where stand now, were lost. And at a service in this church in late 1945, Harvard President James Conant — which President Faust also mentioned — honored the brave and called upon the community to “reflect the radiance of their deeds.”
Seventy years later, this message still holds true. Because their sacrifice is not a debt that can be repaid in a single generation. It must be repaid with every generation. Just as we must never forget the atrocities, we must never forget those who fought for freedom. So as you leave this college and head out into the world, continue please to ‘reflect the radiance of their deeds,’ or as Captain Miller in Saving Private Ryan would say, “Earn this.”
And please stay connected. Please never lose eye contact. This may not be a lesson you want to hear from a person who creates media, but we are spending more time looking down at our devices than we are looking in each other’s eyes. So, forgive me, but let’s start right now. Everyone here, please find someone’s eyes to look into. Students, and alumni and you too, President Faust, all of you, turn to someone you don’t know or don’t know very well. They may be standing behind you, or a couple of rows ahead. Just let your eyes meet. That’s it. That emotion you’re feeling is our shared humanity mixed in with a little social discomfort.
But, if you remember nothing else from today, I hope you remember this moment of human connection. And I hope you all had a lot of that over the past four years. Because today you start down the path of becoming the generation on which the next generation stands. And I’ve imagined many possible futures in my films, but you will determine the actual future. And I hope that it’s filled with justice and peace.
And finally, I wish you all a true, Hollywood-style happy ending. I hope you outrun the T. rex, catch the criminal and for your parents’ sake, maybe every now and then, just like E.T.: Go home. Thank you.
“Facts and truth are matters of life and death. Misinformation, disinformation, delusions, and deceit can kill.”
Martin Baron
2020 “Imperfect though [it] may be” an independent press is key to ensuring that facts are presented and truth defended in society,” the Washington Post executive editor said.
Good morning from my home. Like you, I wish we were together on campus.There is so much now we can no longer take for granted. The air we breathe is first among them. So, those of us who are healthy have ample reason to be grateful. I am also grateful to Harvard and to President Bacow for inviting me to be with you. To the Harvard Class of 2020, congratulations. And congratulations to the parents, professors, mentors and friends who helped you along the way. Joining you for graduation is a high honor.
For me, this is an opportunity – an opportunity to speak about subjects that I believe are of real urgency. Especially now during a worldwide health emergency.
I would like to discuss with you the need for a commitment to facts and to truth. Only a few months ago, I would have settled for emphasizing that our democracy depends on facts and truth. And it surely does. But now, as we can plainly see, it is more elemental than that.
Facts and truth are matters of life and death. Misinformation, disinformation, delusions and deceit can kill. Here is what can move us forward: Science and medicine. Study and knowledge. Expertise and reason. In other words, fact and truth. I want to tell you why free expression by all of us and an independent press, imperfect though we may be, is essential to getting at the truth. And why we must hold government to account. And hold other powerful interests to account as well.When I began thinking about these remarks, I expected, of course, to be on Harvard’s campus. And I thought: Not a bad place to talk about a free press. Not a bad place to talk about our often-testy relationship with official power.
It was in Boston, after all, where the first newspaper of the American colonies was founded. Its first edition was published September 25th, 1690. The very next day, the governor and council of Massachusetts shut it down. So, the press of this country has long known what it means to face a government that aims to silence it. Fortunately, there has been progress. With the First Amendment, James Madison championed the right of “freely examining public characters and measures.”
But it took a very long time before we as a nation fully absorbed what Madison was talking about. We took many ominous turns. We had the Alien and Sedition acts under John Adams, the Sedition and Espionage Acts under Woodrow Wilson, the McCarthy era. It was not always clear where we as a nation would end up.
Finally, witnessing the authoritarianism of Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan, we began to secure a free press in this country. The Supreme Court would forcefully emphasize the press’ role in guaranteeing a democracy. Justice Hugo Black said it well decades later: “The press was protected so that it could bare the secrets of government and inform the people.” Not only the secrets of government, I would add. Our duty to inform the public does not stop there. Not by a long shot.
That was evident during my years as a journalist in Boston. Amid today’s crisis, it seems like another era. And I guess it is. But I want to tell you about it — because I think it remains instructive about what a strong, independent press must do.
I started as editor of the Boston Globe in the summer of 2001. One day prior to my start date, a Globe columnist wrote about a shocking case. A priest had been accused of abusing as many as 80 kids. A lawsuit alleged that the cardinal in Boston at the time knew about the serial abuse, didn’t do anything about it — and repeatedly reassigned this priest from parish to parish, warning no one, over decades. The Archdiocese called the accusations baseless and reckless. The Globe columnist wrote that the truth might never be known. Internal documents that might reveal it had been sealed by a judge. On my first day of work, we asked the question: How do we get at the truth? Because the public deserved to know.
That question led us to challenge the judge’s secrecy order. And our journalists launched an investigation of their own. In early 2002, we published what we had learned through reporting and by prevailing in court. We published the truth: The cardinal did know about the abuse by this priest. Yet he kept him in ministry, thus enabling further abuse. Dozens of clergy in the diocese had committed similar offenses. The cardinal had covered it all up.
And a bigger truth would emerge: Covering up such abuse had been practice and policy in the Church for decades. Only now the powerful were being held to account.
Late in 2002, after hundreds of stories on this subject, I received a letter from a Father Thomas P. Doyle. Father Doyle had struggled for years – in vain — to get the Church to confront the very issue we were writing about. He expressed deep gratitude for our work. “It is momentous,” he wrote, “and its good effects will reverberate for decades.” Father Doyle did not see journalists as the enemy. He saw us an ally when one was sorely needed. So did abuse survivors. I kept Father Doyle’s letter on my desk — a daily reminder of what journalists must do when we see evidence of wrongdoing.
Harvard’s commencement speaker two years ago, civil rights pioneer John Lewis, once said this: “When you see something that is not right, not fair, not just, you have to speak up. You have to say something; you have to do something.” We as journalists have the capacity – along with the constitutional right — to say and do something. We also have the obligation. And we must have the will. So must you. Every one of you has a stake in this idea of free expression. You want to be free to express your views. You should be free to hear the views of others, the same or different. You want to be free to watch any movie. To read any book. To listen to any lyrics. You should be free to say what you know is true without threat of government reprisal.And you should acknowledge this if you value these freedoms that come with democracy: Democracy cannot exist without a free and independent press. It never has.
Leaders who crave more power for themselves always move quickly to crush an independent press. Next, they destroy free expression itself. Sadly, much of the world is on that worrisome path. And efforts in this country to demonize, delegitimize and dehumanize the press give license to other governments to do the same – and to do far worse.
By the end of last year, a near-record 250 journalists worldwide were sitting in prison. Thirty of them faced accusations of “false news,” a charge virtually unheard-of only seven years earlier.
Turkey has been trading places with China as No. 1 on the list of countries that jail the most journalists. The Turkish government has shut down more than 100 media outlets and charged many journalists as terrorists. Independent media have been largely extinguished. China, of course, imposes some of the world’s tightest censorship on what its citizens can see and hear.
In Hungary, the prime minister has waged war on independent media. Harvard Nieman fellow Andras Petho, who runs an investigative reporting center there, notes that the prime minister’s business allies are “taking over hundreds of outlets and turning them into propaganda machines.”
Like other heads of state, Hungary’s prime minister has exploited the pandemic to grab more power, suppress inconvenient facts, and escalate pressure on news outlets. A new law threatens up to five-year jail terms against those accused of spreading supposedly false information. Independent news outlets have questioned how the crisis was managed. And the fear now is that such accountability journalism will lead to harassment and arrests, as it has in other countries.
In the Philippines, the courageous Maria Ressa, who founded the country’s largest online-only news site, has been battling government harassment for years on other fronts. She now faces prosecution on bogus charges of violating foreign ownership laws. By the end of last year, she had posted bail eight times. Her real violation? She brought scrutiny to the president. In Myanmar, two Reuters journalists — Wa Lone and Kyaw Soe Oo – were imprisoned for more than 500 days for investigating the killing of 10 Rohingya Muslim men and boys. Finally, a year ago, they were released. In 2018, an opinion writer for The Washington Post, Jamal Khashoggi, walked into Saudi Arabia’s consulate in Istanbul to get documents he needed to marry. He was murdered there at the hands of a team sent by highest-level Saudi officials. His offense? He had sharply criticized the Saudi government. In Mexico, murderous vengeance against journalists is common. Last year, at least five were killed, more than in any other country. I think also of the risks that American journalists have taken to inform the public. Among them are colleagues I can never forget.
One is Elizabeth Neuffer. Seventeen years ago this month, I stood before her friends at the Boston Globe to report that she had died covering the war in Iraq. Elizabeth was 46, an experienced foreign correspondent, a mentor to others; vivacious and brave. Her Iraqi driver was traveling at high speed because of the risk of abductions. He lost control. Elizabeth died instantly; her translator, too. Elizabeth had a record of fearlessness in investigating war crimes and human rights abuses. Her goal: Reveal the world as it is — because someone might then make things better.
Another colleague was Anthony Shadid. In 2002, I visited Anthony, then a reporter for the Globe, after he was shot and wounded in Ramallah. Lying in a hospital in Jerusalem, it was clear that he had narrowly escaped being paralyzed. Anthony recovered and went on to report from Iraq, where he won two Pulitzer Prizes for The Washington Post. From Egypt, where he was harassed by police. From Libya, where he and three New York Times colleagues were detained by pro-government militias and physically abused. He died in 2012, at age 43, while reporting in Syria, apparently of an asthma attack. Anthony told the stories of ordinary people. Without him, their voices would have gone unheard.
And now I think constantly of reporters, photographers and videographers who risk their own well-being to be with heroic frontline health workers — frontline workers of every sort – to share their stories. Anthony, Elizabeth and my present-day colleagues sought to be eyewitnesses. To see the facts for themselves. To discover the truth and tell it. As a profession, we maintain there is such a thing as fact, there is such a thing as truth.
At Harvard, where the school’s motto is “Veritas,” presumably you do, too. Truth, we know, is not a matter of who wields power or who speaks loudest. It has nothing to do with who benefits or what is most popular. And ever since the Enlightenment, modern society has rejected the idea that truth derives from any single authority on Earth.
To determine what is factual and true, we rely on certain building blocks. Start with education. Then there is expertise. And experience. And, above all, we rely on evidence. We see that acutely now when people’s health can be jeopardized by false claims, wishful thinking and invented realities. The public’s safety requires the honest truth. Yet education, expertise, experience and evidence are being devalued, dismissed and denied. The goal is clear: to undermine the very idea of objective fact, all in pursuit of political gain. Along with that is a systematic effort to disqualify traditional independent arbiters of fact. The press tops the list of targets. But others populate the list, too: courts, historians, even scientists and medical professionals – subject-matter experts of every type.
And so today the government’s leading scientists find their motives questioned, their qualifications mocked — despite a lifetime of dedication and achievement that has made us all safer. In any democracy, we want vigorous debate about our challenges and the correct policies. But what becomes of democracy if we cannot agree on a common set of facts, if we can’t agree on what even constitutes a fact? Are we headed for extreme tribalism, believing only what our ideological soulmates say? Or do we become so cynical that we think everyone always lies for selfish reasons? Or so nihilistic that we conclude no one can ever really know what is true or false; so, no use trying to find out? Regardless, we risk entering dangerous territory. Hannah Arendt, in 1951, wrote of this in her first major work, “The Origins of Totalitarianism.” There, she observed “the possibility that gigantic lies and monstrous falsehoods can eventually be established as unquestioned facts … that the difference between truth and falsehood may cease to be objective and may become a mere matter of power and cleverness, of pressure and infinite repetition.”
One hundred years ago – in 1920 – a renowned journalist and leading thinker, Walter Lippmann, harbored similar worries. Lippmann, once a writer for the Harvard Crimson, warned of a society where people “cease to respond to truths, and respond simply to opinions … what somebody asserts, not what actually is.” Lippmann wrote those words because of concerns about the press itself. He saw our defects and hoped we might fix them, thus improving how information got to the public.
Ours is a profession that still has many flaws. We make mistakes of fact, and we make mistakes of judgment. We are at times overly impressed with what we know when much remains for us to learn. In making mistakes, we are like people in every other profession. And we, too, must be held accountable. What frequently gets lost, though, is the contribution of a free and independent press to our communities and our country — and to the truth.
I think back to the aftermath of Hurricane Andrew in 1992 when the Miami Herald showed how lax zoning, inspection and building codes had contributed to the massive destruction. Homes and lives are safer today as a result. In 2016, the Charleston Gazette-Mail in West Virginia exposed how opioids had flooded the state’s depressed communities, contributing to the highest death rates in the country. In 2005, after Hurricane Katrina, Louisiana’s newspapers were indispensable sources of reliable information for residents. The Washington Post in 2007 revealed the shameful neglect and mistreatment of wounded veterans at Walter Reed Hospital. Corrective action was immediate. The Associated Press in 2015 documented a slave trade behind our seafood supply. Two thousand slaves were freed as a result. The New York Times and The New Yorker in 2017 exposed sexual predators in elite boardrooms. A movement of accountability for abuses against women took root. The New York Times in 1971 was the first to publish the Pentagon Papers, revealing a pattern of official deceit in a war that killed more than 58,000 Americans and countless others. The Washington Post broke open the Watergate scandal in 1972. That led ultimately to the president’s resignation.Those news organizations searched for the truth and told it, undeterred by pushback or pressure or vilification.Facing the truth can cause extreme discomfort. But history shows that we as a nation become better for that reckoning. It is in the spirit of the preamble to our Constitution: “to form a more perfect union.” Toward that end, it is an act of patriotism.
W.E.B. Du Bois, the great scholar and African American activist — and the first African American to graduate with a PhD from Harvard – cautioned against the falsification of events in relating our nation’s history. In 1935, distressed at how deceitfully America’s Reconstruction period was being taught, Du Bois assailed the propaganda of the era. “Nations reel and stagger on their way,” he wrote. “They make hideous mistakes; they commit frightful wrongs; they do great and beautiful things. And shall we not best guide humanity by telling the truth about all this, so far as the truth be ascertainable?”
At this university, you answer that question with your motto — “Veritas.” You seek the truth — with scholarship, teaching and dialogue – knowing that it really matters.My profession shares with you that mission — the always arduous, often tortuous and yet essential pursuit of truth. It is the demand that democracy makes upon us. It is the work we must do. We will keep at it. You should, too. None of us should ever stop.
Thank you for listening. Thank you for honoring me. Good luck to you all. And please, stay well.
“While the legacy of enslavement, racism, discrimination, and exclusion still influences so much of contemporary attitudes, we must never conclude that it is too late to overcome such a legacy. For it is never too late to do justice.”
Ruth J. Simmons
2021 The president of Prairie View A&M University and former president of Brown University and Smith College exhorted graduates to fight inequality and foster diversity and inclusion.
Share this article
Good day and congratulations to the Harvard University Class of 2021.
It is a singular honor to be invited to address you on this important milestone occasion. To all completing their studies today, I offer my best wishes as you undertake the next exciting phase of your lives. That you have succeeded so well during such a time as this is commendable and augurs well for the years to come when the world will rely greatly on your knowledge, your discernment, and your empathy for those less fortunate than you.
When first approached about delivering this Commencement address, I was, frankly, taken aback. I did not immediately feel up to the task. Recalling occasions when I sat in Tercentenary Theatre looking across the expanse of graduates to the steps of Widener Library, I could not picture myself confidently delivering remarks from a dais where so many more eminent figures had stood and, indeed, made history. Growing up on a constant Jim Crow diet that offered assertions of my inferiority, I’m always that same little Black girl trying to believe in and demonstrate her worthiness. Further, I thought about the challenge of what I might impart in such a pivotal national moment when social gains seem more like losses, when clarity gives way so easily to confusion, and when much heralded progress recedes like a trompe l’oeil that was never real.
I extend greetings from the faculty, administration and students of our 145 year old institution, Prairie View A&M University. And, though I have not been anointed to do so, I also bring greetings from the collection of Historically Black and Minority Serving institutions that have the weight and privilege of advancing access, equity and opportunity for so many communities across the world. Our university, like many others HBCUs, was founded at the end of Reconstruction when Blacks were thought to be unable to perform the highest level academic study. I speak to you, in fact, from the Prairie View campus whose 1500 acres were once the site of the Alta Vista Plantation. That plantation, before being sold to the State of Texas, was the site where 400 human beings were held in slavery. Thus, our very steps as they daily tread upon vestiges of the suffering of our ancestors, call to us constantly to do our duty as full citizens. Painful as such memories are, they are a powerful force that calls us to action when challenges arise.
During the 145 years following our 1876 founding, it would take many years for most universities in our nation to grant access to Blacks. So, universities like Prairie View, designed with limited resources, served the state and nation by admitting students to whom full access to the fruits of liberty was intentionally blocked. We are therefore proud of our legacy of endurance and even prouder of the fact that we converted an assertion of the inferiority of African Americans into a triumph of human capacity. Like other HBCUs, we made a place to empower rather than disparage, to open minds rather than imprison them, to create pathways to promise rather than to stifle opportunity.
Such is the task of every true university. Those of you graduating today can well attest to that. When you first arrived at Harvard as undergraduate or post-graduate students, you most likely could not have imagined the many ways that your ability would be tested, your insights sharpened and expanded, and your prospects in life improved by studying at the University. I certainly didn’t expect such results when I arrived at Harvard and yet I know now that it is likely primarily because I studied at Harvard that I have had the deeply rich and satisfying career that I’ve enjoyed for so many years.
A product of a segregated upbringing in Houston and undergraduate study at an HBCU, I am ashamed to say that in my youth, I secretly bought into the prevailing racial assumptions of the day: that someone like me would be ill-prepared to benefit from and contribute to study at a university of Harvard’s stature. I expected to be flatfooted if not oafish in the company of well-heeled and urbane students who had the advantage of the best education and a wealth of experiences. While not outwardly immobilized by fear of failing the biggest test of my life, I was inwardly terrified that I would fail to measure up. Uncertainty and malaise governed my early days at the university.
Harvard was, you see, a place steeped in other peoples’ traditions—traditions that I could not easily access. My reaction was very much akin to the French expression denoting window shopping: “lécher les vitrines.” Those of us who are outsiders are often as mere observers looking through windows, salivating and wondering how we might ever be able to attain a sense of inclusion, acceptance and respect. Just as when, as a child, I was banned from white establishments, I identified as the outsider looking enviously at others who not only had full access to Harvard’s history and traditions but who also could so easily see themselves reflected in them. Few things that I could see at Harvard at the time represented me. Perhaps it is the memory of that feeling that moved me to remain in university life to make that experience easier for others who felt excluded.
The need to make universities more aware of how first generation and underserved communities reacted to the stultified tradition in many universities shaped my conviction about the importance of individuals feeling fully embraced and respected as learners, erasing vestiges of disparagement that inevitably accrue in an unequal society. Having been profiled and racially isolated and having carried within me for so many years the weight of that sentence, I understood that to change our country, we had to insist that everyone’s humanity, everyone’s traditions and history, everyone’s identity contributes to our learning about the world we must live in together. I came to believe what Harvard expressed in its admission philosophy: that such human differences, intentionally engaged in the educational context, are as much a resource to our intellectual growth as the magnificent tomes that we build libraries to protect and the state of the art equipment proudly arrayed in our laboratories. The encounter with difference rocks!
I believe that each of us has a solemn duty to learn about and embrace that difference. That undertaking takes not a month or a year but a lifetime of concerted action to ensure that we are equipped to play a role in caring for and improving the world we inhabit together. This responsibility should encourage us to commit to our individual as well as professional role in advancing access, equality and mutual respect.
Thus, I believe that the task of a great university is not merely to test the mettle and stamina of brilliant minds but to guide them toward enlightenment, enabling thereby the most fruitful and holistic use of their students’ intelligence and humanity. That enlightenment suggests the need for improving upon students’ self-knowledge but it also means helping them judge others fairly, using the full measure of their empathy and intelligence to do so. In an environment rich in differences of background, experience and perspectives, learning is turbo charged and intensified by the juxtaposition of these differences. Those open minded enough to benefit fully from the power of this learning opportunity are bound for leadership in this time of confusion and division. The Harvard model intentionally and successfully provides to students a head start in understanding how to mediate difference in an ever more complex reality in which some exploit those differences for corrupt purposes.
Today, irrational hatred of targeted groups is seemingly on the rise, stoked by opportunists seeking advantage for themselves and their profits. What stands between such malefactors and the destruction of our common purpose are people like you who, having experienced learning through difference, courageously stand up for the rights of those who are targeted. Your Harvard education, if you were paying close attention here, should have encouraged you to commit willingly to playing such a role. If you follow through on this commitment, in addition to anything else you accomplish in life, you will be saving lives, stanching the flow of hatred and the dissolution of our national bond. You will be serving the mighty cause of justice. If we are to thrive on this orb that we share, our schools and universities must contribute deliberately to increasing our understanding of the ways to interact meaningfully with others.
Harvard is, in some ways, the most powerful university bully pulpit in the nation. It did not achieve that status merely through its age and wealth; it attained that status principally through the efforts of its faculty and graduates’ scholarly and professional output. Through its gates have come generations of scholars with immense intelligence and passionate purpose to whom fate bequeathed the laurels of success. But it is important that universities model in their own values and actions the high purpose that they hope to see in the actions of their scholars.
In that vein, Harvard has a special responsibility as both a prod and steward of the national conscience. It could sit on the hill and congratulate itself on its prowess but it could also use its immense stature to address the widening gaps in how different groups experience freedom and justice. I spoke earlier about the heroic work of HBCUs and minority serving institutions that keep our country open and advancing the cause of equality and access. Yet, many of them have been starved for much of their history by the legacy of underfunding and isolation from the mainstream of higher education.
I call on universities like Harvard to acknowledge the limitations imposed on these institutions over the past decades. While universities like Harvard had the wind at their back, flourishing from endowments, strong enrollments, constant curricular expansion, massive infrastructure improvements, and significant endowment growth, HBCUs often had gale force winds impeding their development. Our nation is finally coming to terms with the consequences of the underfunding of HBCUs but we are far from where we need to be if we are to be assured continued progress in the fight for equal educational benefits.
I ask the university that did so much for me to add to its luster by embracing the opportunity to stand alongside these historic and other minority serving institutions to build stronger partnerships, advocate for greater funding, and elevate the fight for parity and justice to the level it deserves. Let us not complain in a hundred years that those historically excluded from access and opportunity continue to ask how much longer it will take to gain the respect, inclusion and support that their service to the nation deserves.
Many minority serving institutions accept students from impoverished underserved communities where educational preparation often lacks the pre-requisites needed for certain careers. Children in those communities may experience the same or a worse fate than I and my peers did during the pre-Civil Rights era. Consigned to underfunded schools and alienating curricula, they must wonder as I did what will befall them in life. ublic schools saved me and they have the burden still of saving millions of children across this land. In so very many cases, these institutions are the only hope for many children and their families. Support for public education in this moment is as important as it was in the early days of the country when Horace Mann first called for universal education. For Mann, it was a matter of what our young country would need; it still is today as Mann’s emphasis on civic virtue continues to ring true.
Further, in such a moment, universities and all of you must play a leadership role in reversing the designation of the teaching profession as less intellectually worthy, less glamorous, and less important than the high-flying careers of financiers and technologists. Attention to and investment in K-12 teacher preparation and curricular content remains one of the most important ways for universities and the average citizen to contribute to the civic good.
None of us is exempt from responsibility for the future we give our children. Harvard has its role and so do all of you. I have come to ask you who graduate today what you are prepared to do to acknowledge and address the historic biases and inequities that so many continue to experience. Will your actions point us in a more uplifting direction? For, just as we recount the moral bankruptcy of those who cruelly enslaved others, we also tell the story of those who were equally guilty because they refused to challenge the practice of slavery. In the future, the history of these times will reveal both what we do and what we fail to do to address the unjust treatment of marginalized groups. Among all that you will have learned at Harvard, I hope that the consciousness of your responsibility in the struggle for equality remains with you. While the legacy of enslavement, racism, discrimination and exclusion still influences so much of contemporary attitudes, we must never conclude that it is too late to overcome such a legacy. For it is never too late to do justice.
Today, I call on all of you to declare that you will not give sanction to discriminatory actions that hold some groups back to the advantage of others. I call on you to be a force for inclusion by not choosing enclaves of wealth, privilege and tribalism such that you abandon the lessons you learned from your Harvard experience of diversity. I call on you to do your part to ensure that generations to come will no longer be standing on the outside fighting for fairness, respect and inclusion.
Today, after decades in the academy, my path has taken me back to a place where students are waging the same battles that were so hard fought when I was a teenager: safe passage in the face of bigotry, the right to vote, and equal access to educational and professional opportunities. Sandra Bland, a Prairie View alumna, was stopped for a minor traffic offense at the entrance to our campus. Jailed for this offense, she was found deceased in her cell three days later. Must every generation add more tragic evidence of the racial hatred that has troubled the world? Our work is not done as long as there are young people growing up with the thought that they matter less than others. As long as they have fewer and narrower educational opportunities. As long as they must fear for their safety every moment of every day of their lives. As long as their full participation in society is circumscribed by policies that willfully chip away at or block their rights.
Just as I ask Harvard to use its voice on behalf of minority institutions that have been unfairly treated across time, I ask you to add your voice to the cause of justice wherever you go. Help the children of need wherever they are: in underfunded public schools, in neighborhoods bereft of resources, in search of a way to belong. If they do not hear your voices advocating for them and their worth, what must they conclude about their place in the world?
If you take up the cause of these children, you are taking up the greatest cause—that of justice. Today, you earn your laurels as a scholar. Taking up the cause of justice, you will earn your laurels as a human being.
Congratulations, once again, and God speed.
You might like
Longtime supporter of grads Kathy Hanley caps 13-year quest with a Commencement of her own

Class of ’24 gets a do-over on high school prom that pandemic took away

Three major events, including Psychedelics Bootcamp 2024, to be hosted over summer
Epic science inside a cubic millimeter of brain
Researchers publish largest-ever dataset of neural connections
Finding right mix on campus speech policies
Legal, political scholars discuss balancing personal safety, constitutional rights, academic freedom amid roiling protests, cultural shifts
Good genes are nice, but joy is better
Harvard study, almost 80 years old, has proved that embracing community helps us live longer, and be happier
"The Purpose of Education"
Author: King, Martin Luther, Jr. (Morehouse College)
Date: January 1, 1947 to February 28, 1947
Location: Atlanta, Ga.
Genre: Published Article
Topic: Martin Luther King, Jr. - Political and Social Views
Writing in the campus newspaper, the Maroon Tiger , King argues that education has both a utilitarian and a moral function. 1 Citing the example of Georgia’s former governor Eugene Talmadge, he asserts that reasoning ability is not enough. He insists that character and moral development are necessary to give the critical intellect humane purposes. King, Sr., later recalled that his son told him, “Talmadge has a Phi Beta Kappa key, can you believe that? What did he use all that precious knowledge for? To accomplish what?” 2
As I engage in the so-called “bull sessions” around and about the school, I too often find that most college men have a misconception of the purpose of education. Most of the “brethren” think that education should equip them with the proper instruments of exploitation so that they can forever trample over the masses. Still others think that education should furnish them with noble ends rather than means to an end.
It seems to me that education has a two-fold function to perform in the life of man and in society: the one is utility and the other is culture. Education must enable a man to become more efficient, to achieve with increasing facility the ligitimate goals of his life.
Education must also train one for quick, resolute and effective thinking. To think incisively and to think for one’s self is very difficult. We are prone to let our mental life become invaded by legions of half truths, prejudices, and propaganda. At this point, I often wonder whether or not education is fulfilling its purpose. A great majority of the so-called educated people do not think logically and scientifically. Even the press, the classroom, the platform, and the pulpit in many instances do not give us objective and unbiased truths. To save man from the morass of propaganda, in my opinion, is one of the chief aims of education. Education must enable one to sift and weigh evidence, to discern the true from the false, the real from the unreal, and the facts from the fiction.
The function of education, therefore, is to teach one to think intensively and to think critically. But education which stops with efficiency may prove the greatest menace to society. The most dangerous criminal may be the man gifted with reason, but with no morals.
The late Eugene Talmadge, in my opinion, possessed one of the better minds of Georgia, or even America. Moreover, he wore the Phi Beta Kappa key. By all measuring rods, Mr. Talmadge could think critically and intensively; yet he contends that I am an inferior being. Are those the types of men we call educated?
We must remember that intelligence is not enough. Intelligence plus character—that is the goal of true education. The complete education gives one not only power of concentration, but worthy objectives upon which to concentrate. The broad education will, therefore, transmit to one not only the accumulated knowledge of the race but also the accumulated experience of social living.
If we are not careful, our colleges will produce a group of close-minded, unscientific, illogical propagandists, consumed with immoral acts. Be careful, “brethren!” Be careful, teachers!
1. In 1925, the Maroon Tiger succeeded the Athenaeum as the campus literary journal at Morehouse. In the first semester of the 1947–1948 academic year, it won a First Class Honor Rating from the Associated Collegiate Press at the University of Minnesota. The faculty adviser to the Maroon Tiger was King’s English professor, Gladstone Lewis Chandler. King’s “The Purpose of Education” was published with a companion piece, “English Majors All?” by a fellow student, William G. Pickens. Among the many prominent black academicians and journalists who served an apprenticeship on the Maroon Tiger staff were Lerone Bennett, Jr., editor of Ebony ; Brailsford R. Brazeal, dean of Morehouse College; S. W. Garlington, city editor of New York’s Amsterdam News ; Hugh Gloster, president of Morehouse College; Emory O. Jackson, editor of the Birmingham World ; Robert E. Johnson, editor of Jet ; King D. Reddick of the New York Age ; Ira De A. Reid, chair of the Sociology Department at Atlanta University; and C. A. Scott, editor and general manager of the Atlanta Daily World . See The Morehouse Alumnus , July 1948, pp. 15–16; and Edward A. Jones, A Candle in the Dark: A History of Morehouse College (Valley Forge, Pa.: Judson Press, 1967), pp. 174, 260, 289–292.
2. Martin Luther King, Sr., with Clayton Riley, Daddy King: An Autobiography (New York: William Morrow, 1980), p. 143. In an unpublished autobiographical statement, King, Sr., remembered a meeting between Governor Eugene Talmadge and a committee of blacks concerning the imposition of the death penalty on a young black man for making improper remarks to a white woman. King, Sr., reported that Talmadge “sent us away humiliated, frustrated, insulted, and without hope of redress” (“The Autobiography of Daddy King as Told to Edward A. Jones” [n.d.], p. 40; copy in CKFC). Six months before the publication of King’s article, Georgia’s race-baiting former governor Eugene Talmadge had declared in the midst of his campaign for a new term as governor that “the only issue in this race is White Supremacy.” On 12 November, the black General Missionary Baptist Convention of Georgia designated his inauguration date, 9 January 1947, as a day of prayer. Talmadge died three weeks before his inauguration. See William Anderson, The Wild Man from Sugar Creek: The Political Career of Eugene Talmadge (Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1975), pp. 226–237; Joseph L. Bernd, “White Supremacy and the Disfranchisement of Blacks in Georgia, 1946,” Georgia Historical Quarterly 66 (Winter 1982): 492–501; Clarence M. Wagner, Profiles of Black Georgia Baptists (Atlanta: Bennett Brothers, 1980), p. 104; and Benjamin E. Mays, Born to Rebel: An Autobiography (Athens: University of Georgia Press, 1987), pp. 221–223.
Source: Maroon Tiger (January-February 1947): 10.
© Copyright Information
This writer analyzed 100 graduation speeches — here are the 4 tips they all share
Share this idea.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)

Steve Jobs has been credited over the years with popularizing any number of other people’s inventions, from the personal computer to the tablet to the mobile phone. But none of these gifts may be as enduring as one of his rarely credited contributions to contemporary life — popularizing the viral commencement address.
On June 12, 2005, Jobs stood before the graduating class of Stanford University and reminded them that he had never graduated from college. “Truth be told, this is the closest I’ve ever gotten to a college graduation.” He then told three stories about his life. “That’s it. No big deal. Just three stories.”
That speech , coinciding as it did with the rise of internet virality (the first TED Talk would be posted on TED.com exactly 12 months later; the iPhone was introduced exactly 12 months after that), launched a global obsession with pithy, inspirational talks. Jobs’s speech has since been viewed more than 40 million times on YouTube.
Graduation speeches, long viewed as the burdensome interruption before diplomas were granted and mortar boards were tossed, have since become big business. Kurt Vonnegut, Ann Patchett, Carl Hiaasen, J.K. Rowling, Mary Karr, David Foster Wallace and many others have all had their commencement speeches published as books.
I’ve been fortunate to give a handful of commencement addresses over the years, and I confess to a fascination with the genre. The internet has been a boon this hobby. There are thousands of commencement speeches on the web. Can we learn anything from their messages?
I’ve spent the last few years gathering and coding hundreds of life stories, looking for patterns and takeaways that could help all of us live with more meaning, purpose and joy. I decided to put some of my coding tools to work, analyzing 100 of the most popular recent commencement speeches.
Here are the four tips they all contain:
1. Dream big
“I think it is often easier to make progress on mega-ambitious dreams. I know that sounds completely nuts. But, since no one else is crazy enough to do it, you have little competition. There are so few people this crazy that I feel like I know them all by first name. They all travel as if they are pack dogs and stick to each other like glue. The best people want to work the big challenges.” — Larry Page at University of Michigan , 2009
“We don’t beat the reaper by living longer. We beat the reaper by living well and living fully. For the reaper is always going to come for all of us. The question is: What do we do between the time we are born, and the time he shows up? Because when he shows up, it’s too late to do all the things that you’re always gonna, kinda get around to.” — Randy Pausch at Carnegie Mellon University , 2009
“Graduates, we need you. We need you to run companies and make decisions about who has access to capital. We need you to serve at the highest levels of government and determine our country’s standing in the world. We need you to work in our hospitals and in our courtrooms and in our schools. We need you to shape the future of technology. We need you because your perspective — the sum total of your intellect and your lived experience — will make our country stronger.” — Kamala Harris at Tennessee State University , 2022
2. Work hard
“Your work is going to fill a large part of your life, and the only way to be truly satisfied is to do what you believe is great work. And the only way to do great work is to love what you do. If you haven’t found it yet, keep looking. Don’t settle. As with all matters of the heart, you’ll know when you find it.” — Steve Jobs at Stanford University , 2005
“I just directed my first film. I was completely unprepared, but my own ignorance to my own limitations looked like confidence and got me into the director’s chair. Once there, I had to figure it all out, and my belief that I could handle these things, contrary to all evidence of my ability to do so was half the battle. The other half was very hard work. The experience was the deepest and most meaningful one of my career.” — Natalie Portman at Harvard University , 2015
“When you’re doing the work you’re meant to do, it feels right and every day is a bonus, regardless of what you’re getting paid … But make it your life’s work to remake the world because there is nothing more beautiful or more worthwhile than working to leave something better for humanity.” — Oprah Winfrey at Stanford University , 2008
3. Make mistakes
”Fail big. That’s right. Fail big … It’s a new world out there, and it’s a mean world out there, and you only live once. So do what you feel passionate about. Take chances, professionally. Don’t be afraid to fail. There’s an old IQ test with nine dots, and you had to draw five lines with a pencil within these nine dots without lifting the pencil, and the only way to do it was to go outside the box. So don’t be afraid to go outside the box.” — Denzel Washington at University of Pennsylvania , 2011
“The world doesn’t care how many times you fall down, as long as it’s one fewer than the number of times you get back up.” — Aaron Sorkin at Syracuse University , 2013
“My experience has been that my mistakes led to the best thing in my life. Being embarrassed when you mess up is part of the human experience of getting back up dusting yourself off and seeing who still wants to hang out with you afterward and laugh about it. That’s a gift. The times I was told no or wasn’t included wasn’t chosen, didn’t win, didn’t make the cut, looking back it really feels like those moments we’re as important if not more crucial than the moments I was told yes.” — Taylor Swift at NYU , 2022
“Work hard, be kind, and amazing things will happen.” — Conan O’Brien at Dartmouth College , 2011
“Empathy and kindness are the true signs of emotional intelligence.” — Will Ferrell at the University of Southern California , 2017
“So here’s something I know to be true, although it’s a little corny, and I don’t quite know what to do with it: What I regret most in my life are failures of kindness. Those moments when another human being was there, in front of me, suffering, and I responded … sensibly. Reservedly. Mildly. Or, to look at it from the other end of the telescope: Who, in your life, do you remember most fondly, with the most undeniable feelings of warmth? Those who were kindest to you, I bet. It’s a little facile, maybe, and certainly hard to implement, but I’d say, as a goal in life, you could do worse than: Try to be kinder.” — George Saunders at Syracuse University , 2013
So what can we learn from these themes?
Every era in American life has its own standards of what it means to be a success. Shortly after America’s founding, success was all about character. Led by Benjamin Franklin, Americans embraced virtue, industry, and frugality. In the twentieth century, success was all about personality. Led by Dale Carnegie, Americans embraced salesmanship, reinvention and charisma. Today, led by Steve Jobs, Americans are embracing meaning, authenticity and bliss. Or, as Kermit the Frog put it in a 1996 commencement speech at Southampton College , “May success and a smile always be yours … even when you’re knee-deep in the sticky muck of life.”
Dream, work, fail and smile are as good a foursome of American identity today as I know. And if those ideas don’t inspire you, you can always embrace the far more practical advice erroneously attributed to Kurt Vonnegut in a commencement speech that he never gave at MIT, but was instead delivered by Chicago Tribune columnist Mary Schmich in an imaginary speech to graduates she published in an old-fashioned newspaper, “Ladies and gentlemen of the class of ’97: Wear sunscreen.”
This post was adapted from one published on his newsletter The Nonlinear Life; go here to subscribe.
Watch his TEDxIEMadrid Talk now:
About the author
Bruce Feiler is the author of seven New York Times bestsellers, including The Secrets of Happy Families and Council of Dads, both of which became the subject of TED Talks. His latest book, Life Is in the Transitions: Mastering Change at Any Age, from which this post and TEDx Talk are adapted, describes his journey across America, collecting hundreds of life stories, exploring how we can navigate life’s growing number of transitions with more meaning, purpose and joy. To learn more, visit brucefeiler.com, follow him on Twitter (@brucefeiler), or sign up for his newsletter The Nonlinear Life.
- bruce feiler
- communication
- inspiration
- society and culture
- surprise me
TED Talk of the Day

How to make radical climate action the new normal

6 ways to give that aren't about money

A smart way to handle anxiety -- courtesy of soccer great Lionel Messi

How do top athletes get into the zone? By getting uncomfortable

6 things people do around the world to slow down

Creating a contract -- yes, a contract! -- could help you get what you want from your relationship

Could your life story use an update? Here’s how to do it

6 tips to help you be a better human now

How to have better conversations on social media (really!)

Let’s stop calling them “soft skills” -- and call them “real skills” instead

3 strategies for effective leadership, from a former astronaut

There’s a know-it-all at every job — here’s how to deal

7 things everyone should do while they're in college that can help them in the future

5 pieces of essential life advice from seniors

The two kinds of stories we tell about ourselves

What older Americans can teach us about the fight for Civil Rights
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, effective topics for a persuasive speech in college.
Got a speech class coming up in college and need to pick a solid topic for my persuasive speech. What are some college-related or high school-focused topics that'll keep my audience engaged and interested?
I'd be happy to suggest some engaging and college-related topics for your persuasive speech!
1. Mental health on college campuses: Discuss the importance of mental health support, resources, and awareness in college settings, and propose solutions for improving mental health services for students.
2. Financial aid packages and accessibility: Advocate for more transparency in financial aid offerings and argue for the need to make higher education more accessible to lower-income students.
3. Importance of internships and experiential learning: Present the benefits of internships or other experiential learning opportunities for college students in enhancing employability after graduation.
4. Reducing student loan debt: Propose methods for managing and alleviating the burden of student loan debt, such as income-based repayment plans or loan forgiveness programs.
5. The role of college athletics in academics: Debate the impact of college sports, including the allocation of funding and student-athletes' responsibilities in balancing academics and sports.
6. Open educational resources for college courses: Present the benefits of open educational resources (OER), like free, open-source textbooks, and advocate for their increased adoption by professors and universities.
7. Study abroad opportunities as a requirement: Argue for incorporating a study abroad experience as part of the graduation requirements to expose students to different cultures and perspectives.
8. Gap years before college: Discuss the advantages of taking a gap year before attending college, such as personal growth, career exploration, volunteer work, or internships.
Remember to choose a topic that you're passionate about, as it will make your speech more engaging and persuasive. Good luck with your speech class!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
How do we reinvent education? These TED Talks explore the latest thinking — from teachers, parents, kids — on how to build a better school.
Video playlists about Education

The Butterfly Effect: Talks from the TEDinArabic Summit

A love letter to science

The pursuit of curiosity and understanding

The most popular TED Talks in Hindi
Talks about education.

Unlocking Indigenous knowledge: A new path for education

What happened when these 6 dictators took over

Scientists are obsessed with this lake

Why the world needs more builders — and less "us vs. them"

How could so many people support Hitler?

If you're an adult mayfly you'll probably die before the end of this video

The US has a teacher shortage — here's how to fix it

How to increase your happiness

How do gas masks actually work?

The rise and fall of the Maya Empire’s most powerful city

Does math have a major flaw?

Picture a perfect society. What does it look like?

The Nazis recruited to win the Cold War

3 strategies to address the teacher shortage crisis

How to prevent political corruption

The true story behind the legend of the 47 Rōnin
Exclusive articles about education, even gritty people get discouraged, here’s one way to make solar energy more affordable and accessible: share it with your neighbors, how to raise emotionally intelligent kids.
27 Facts on the Importance of Education (Essay or Speech)

Are you in need of ideas for an importance of education essay?
Here is a list of 27 ideas that will get you started!
These ideas come from a variety of online sources and links have been provided in case you need to provide references in your essay .
This article lists ideas on the importance of education to a person’s life (Points 1 – 16) and to society (Points 17 – 27).
Importance of Education to a Person’s Life
1. education helps people out of poverty.
Poverty is linked to low education . Families that are poor are usually less educated than families that are rich. Plus, if you are born into a low educated poor family, chances are high that you too will end up low educated and poor.
One way poverty affects education is through the direct costs. Even when school is free, the costs of uniforms, travel, and so on can be very difficult for families to cover.
To escape the poverty trap cycle , people need to gain a higher education than their parents and find upwardly mobile employment (this means: jobs that help you get from the working class into the middle class).
Here’s some facts to back up this point.
A recent report found that people with a college education are statistically less likely to be in poverty. Of people over the age of 25, only 2% of college graduates were in poverty. That compares to 13% of high school graduates over 25.
Related Article: How Can Health Influence Learning?
2. Education helps People make More Money
Jobs that require a higher education are usually more highly paid than unskilled jobs. This is because the jobs are more difficult and require a more specialized skillset. If you get an education in a skill area where there is a shortage of available workers, your wages will increase.
To underscore this point, Brookings presented findings that show:
“An individual with a college degree is nearly nine times more likely to make over $100,000 than someone with only a high school diploma and 13 times more likely to make more than $200,000 per year.”
Today, jobs that are in demand, require a high education and pay quite well include:
- Software developer (USD $101,000)
- Health care administrator (USD $98,000)
- Medical Technologist (USD $51,000)
Source: CNBC .
3. Highly Educated People have a Better chance of Getting a Job
Jobs are not that easy to come by these days – even for people with degrees. But there’s statistically a higher chance of you getting a job if you have a higher education.
The 2017 report Education Pays: The Benefits of Higher Education for Individuals and Society found that people with higher education have lower rates of unemployment.
In 2015, younger people (ages 25 – 34) with bachelor’s degrees had an unemployment rate of 2.6%. High school graduates of the same age range had an unemployment rate of 8.1 percent.
That’s a huge difference that underscores the correlation between education and employability.
>>>You Might Also Like: 21+ Ways to Make an Essay Longer
4. Highly Educated People are Statistically Healthier
Statistically, the higher your education, the healthier you are. This could potentially be due to a few factors including:
- Stable jobs with regular hours allow you to plan exercise;
- Cultural differences between working-class and middle-class people;
- More money to participate in recreational activities.
Whatever the reason, the facts stand for themselves. One of the major facts is this:
In 2014, 26% of high school graduates smoked cigarettes. In the same year, only 8% of college graduates smoked cigarettes.
Source: Education Pays: The Benefits of Higher Education for Individuals and Society

5. Highly Educated People Volunteer More
Educated people tend to do better when it comes to volunteering. The reasons for this may be very similar to the reasons for being more fit. Reasons could include:
- Stable jobs with regular hours allow time to plan regular volunteering hours;
- Highly educated people are less likely to work two jobs;
- People who are well educated have more money to travel to and from their volunteering locations.
Again, it’s a good idea to back this claim up with some facts.
In 2015, 39% of college graduates reported that they volunteered that year. Among high school graduates, it was just 16% who reported that they volunteered.
6. Education helps People make Better Decisions
We have already established that people with a higher education have more job security and more money.
The flow-on effect of this is that they can make better decisions.
When you are more certain that you have money coming in every week, you’ll be able to plan our your budget more. You’ll also have the money to make decisions about living in safer neighborhoods with more public services.
Furthermore, higher education usually teaches critical thinking skills . This means people who’ve been trained in critical thinking may have an advantage when making tough decisions. They will have the education to know how to handle complex decision-making processes.
7. Education helps People make Long-Term Decisions
Not only will highly educated people have the skillset to make tough decisions, they will also have the money to make long-term decisions.
If you have a stable job with a high income each month, you’re more likely to get a loan for a home. You also have the freedom to start investing into your retirement funds.
As you can see, the correlation between high education and high incomes has huge flow-on effects for quality of life.
8. Education can increase Social Status
An education from a respected educational institution can open lots of doors for you.
Many students from around the world flock to nations like the United Kingdom, United States and Australia to get degrees from top-ranking education nations.
Similarly, if you make it to a higher-ranking school or university such as Harvard, Yale, Cambridge, Oxford or Princeton you’ll get a lot of social status just for having attended the university.
Even at compulsory school age there are elite institutions. For example, the private school named Eton College in the UK is known for producing no less than 19 British Prime Minsters .
When you get social status from going to a good school or university, we say you have institutional or cultural capital .
This degree from a well-respected university may get you that job interview you were looking for. But, it could also get you social status amongst family, friends and – yes – potential future partners!
9. Education makes People better Conversationalists
Have you ever had a conversation with a person and they were just really interesting? They seemed to know a lot of things and be able to talk to you about anything.
Well, that person is likely very well educated.
In fact, we have some words to describe people who are well-educated in a broad range of topics. You could call them:
- A renaissance man
- A renaissance woman
There is also a type of education designed to help you become a polymath. It’s called a Liberal Education and you get it by doing a Liberal Arts Degree from a university.
10. Education helps People get Access to Important Information
In the dark ages in Europe very few people had the ability to read.
This meant that knowledge held in books was only available to very few people.
When people don’t have access to knowledge, they’re in a very vulnerable situation. They can’t educate themselves on important information and have a harder time making decisions.
Nowadays, most people in the developed world can read. This huge advance in education levels has enabled any of us to go out there and access information.
In fact, you’re doing that right now! Aren’t you glad you can read?
Educated people also have the knowledge about how to access important information. We’re taught at school about encyclopaedias and libraries. At university we’re taught about scholarly sources and how to access them .
Combine the ability to read with the skills to access information and anyone can help educate themselves on anything. You just need a basic level of education to get started!
11. Education enables People to Critically Analyze ideas
At school, you’re not just being taught facts.
You’re also being taught how to think.
This ability to think involves some pretty advanced strategies like:
- Skepticism: The reluctance to believe something until you see the facts;
- Critical Thinking : the ability to look at something from multiple perspectives;
- Analytical Thinking : the ability to investigate something deeply to find answers.
With these fantastic skills, you can go a long way! You’re less likely to be tricked into believing something that’s not true. You’ll also be able to think things through and come to reasonable, rational conclusions.
12. Education can Help People (especially Women) become Independent and Powerful
Women’s education is a major focus of the United Nations.
This is because many women who are not educated are dependent on their families or husbands to make money.
When women become educated, they can become independent . They can work in better paid jobs, move into more powerful positions in workplaces, and earn an income that’s independent of their husbands.
In the long run, this will mean that women have an equal say in the development of our world.
Furthermore, women with jobs can contribute financially to their families which can help move the whole family out of poverty and give them a better standard of living.
Read Also: Why is School Important?
13. Education reduces Unplanned Pregnancies and Sexual Diseases
Basic education on sex and relationships can dramatically reduce sexual diseases and unplanned pregnancies.
Here’s some facts:
The Borgen Project cites that completion of primary school will reduce a person’s chances of getting HIV. In fact, it reduces girls’ chances of contracting the illness 3-fold.
Educated people also have smaller families and they have them later in life. In Mali , women with a high school education have an average of 3 children. Women without a high school education have an average of 7 children.
14. Education helps us Realize our own Potential
Through education, we learn about what we like and don’t like. We learn all about things from science, math, languages and history.
After contemplating all of these different topics, we’ll be more capable of living our best life.
If you don’t get educated, you won’t open up your horizons and learn about the world. You may end up being stuck in an insular life without having experienced all the great things life has to offer.
You don’t need to go to school for this. Maybe being educated for you is just about reading books on a lot of different topics.
Either way, by educating yourself, you can realize your potential and live a more meaningful life.
15. Education can bring Enjoyment to People’s Lives
Unfortunately, it’s often overlooked that education can be pleasurable for its own sake.
I’ve talked all about how education can help people out of poverty, get them jobs, make them more powerful and less sick.
But it’s also important to remember that education can simply be enjoyable and therefore be important for helping you be happy.
Have you ever learned something really cool and just been glad you know that information now?
That’s what I mean by education being a fun activity on its own.
When people are learning just because they love learning, we say they are intrinsically motivated . This is the opposite to extrinsic motivation where people learn things so they can get a reward like a better job.
16. Education makes you more Tolerant
There is some evidence that highly educated people may be more tolerant than lowly educated people.
To take just one example, people from Latin America with a high school education are 45% more tolerant toward people with HIV than Latin Americans with only an elementary school education.
Similarly, Lorelle Espinosa argues that colleges are ideal locations for teaching tolerance. She argues:
The foundations of tolerance run deep in the college classroom, where students learn and confront new ideas, issues and experiences at times vastly different than their own.
This is, of course, if you have a good teacher who’ll teach you different people’s perspectives!
>>>You Might Also Like: How to Write a Top University Essay
Importance of Education to Society
17. education prevents diseases in society.
Health education in classrooms can make an entire society healthier and live longer.
Health care education helps people avoid risky activities and behaviors, conduct basic first aid when someone is injured, and learn when they need to see a doctor.
The Population Reference Bureau argues that education of women on matters of health is especially important because they often set the standards for household behaviors like regularly washing your hands.
Educating children on health is also very important for the future health of a society.
That’s why Save the Children spends a lot of money on health education in developing countries. Here’s what they say the benefit of education is for children’s health:
Most importantly, through education, students learn how to adapt their daily habits to improve their health, nutrition, hygiene and prevent HIV and AIDS, gaining these important skills and behaviors for life.
18. Education helps a Country’s Economy Grow
When the population of a country is more educated, the whole country gets wealthier. This surely highlights the importance of education!
Here’s some facts that might be useful for you:
Hanushek and Wobmann (2010) looked at the evidence on the links between economic growth and education. They found that good quality education systems have a strong connection to long-term economic growth in a society.
Here’s their conclusion:
Economic growth is strongly affected by the skills of workers. What people know matters.
Hassan and Rafaz (2017) looked at economic growth in Pakastan between 1990 and 2016. They argue that:
[A] 1% increase in female education, female labour force participation, education expenditure and fertility rate causes 96% increase in GDP of Pakistan
Woah! Education of women appears to be a powerful way of increasing the wealth of entire societies.
19. Education can attract High Paying Jobs of the 21 st Century
You might have heard that manufacturing and factory jobs are becoming pretty rare in developed nations.
Because the high paying jobs of the future won’t be in unskilled labor. Those jobs are disappearing and going to poorer nations.
Instead, all the good jobs of the future will require a very high education level.
Often teachers like me talk about skills for the 21 st Century . These are skills like:
- Creative thinking ;
- Critical thinking;
- Communication;
- Collaboration;
- Digital literacy
If children today aren’t educated on these important skills, they’ll have trouble finding the best jobs. And if a whole society falls behind in education, those good jobs will move overseas to where the most highly educated workers can be found.
20. Education can Prevent Wars and Conflicts
History lessons can be very powerful for helping is prevent the mistakes of the past.
If you want to avoid the mistakes of history, you have to learn about how they were made. By educating people about the events leading up to World War 1 and 2, we might be able to teach people how to avoid the same mistakes again.
Similarly, if a society is well educated on the dangers and heartbreak of wars, those wars might be prevented.
This happened during the Vietnam War when students on college campuses began protesting the war . These students worked hard to teach people all over the United States about what was really happening in Vietnam.
War journalists were also instrumental in educating the public on the terrible effects of the war. Video footage, photos and news reports sent back to the United States helped educate the population and helped boost the anti-war efforts.
21. Education is good for Democracy
Most first world nations ensure children are taught democratic citizenship .
Teaching the values of democratic societies – like the fact that we should elect our leaders – helps to keep democracy going.
If we don’t teach about how good democracy is for our freedom and prosperity, we may sleepwalk into an evil dictatorship!
Democracy is about more than voting. It’s about learning the importance of treating each other respectfully, volunteering in our community, and respecting each other’s liberty.
I think Senator Michael Bennet sums this one up well when he says in his blog post :
With education, the common man would be able to select leaders wisely and fight back against the tyrannical instincts of those in power.
22. Education leads to Medical and Technological Breakthroughs
Before we became obsessed with the link between education and money, societies still invested heavily in public universities.
Because strong higher education systems can lead to technological and medical breakthroughs.
Here’s a few things that people invented while learning and researching at universities:
- The Seat Belt: Invented at Cornell University
- Gatorade: Unvented at the University of Florida
- Ultrasound: Developed at the University of Vienna
- CAT Scans: Developed at Georgetown University
- GPS: Developed at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Polio Vaccine: Developed at the University of Pittsburgh
23. Education can lead to Entrepreneurship
The online website Talk Business argues that entrepreneurs are always in need of more education. They argue:
…at their core [Entrepreneurs] are problem solvers and spend their time investigating potential solutions.
In order to solve problems, entrepreneurs enroll themselves in courses, read books, listen to podcasts and pay for mentors. In other words, they’re huge self-educators.
The article goes on to explain that entrepreneurs often don’t seek out a formal education from a school or university. Instead, they seek out answers to their questions from people who have already solved the problems.
So, education is good for business – but don’t narrow your definition of education. Education can come in all shapes and sizes.
24. Education may be the Solution to Global Problems like Climate Change
There’s two ways education can help us get out of the problem of climate change.
Firstly, educating people about sustainability can help us to reduce our ecological footprint on this world. If we recycle more, consume less goods, and ensure we’re cleaning up after ourselves, we can do a lot to help the environment.
Secondly, educating future environmental scientists is vital for finding the solutions to our current environmental problems.
Scientists of the future might find ways to dramatically reduce carbon emissions, reduce the temperature of the globe, or come up with better ways to produce energy.
In the race against time to solve the climate crisis, education may just be the thing that saves us from ourselves.
25. Education is important for Creating a Cohesive Society
Education helps us learn how to behave appropriately.
Emile Durkheim is a major theorist who came up with this concept.
According to Durkheim, schooling is all about ‘socialization’.
By this, he means we go to school to learn about more than maths and science. School has a hidden curriculum . The hidden curriculum is all the things we learn above and beyond our textbooks.
The hidden curriculum includes:
- Learning manners;
- Learning to get along with each other;
- Learning to respect other people’s privacy;
- Learning to follow the rules for the good of society;
- and many more things besides!
So, without schools teaching us how to get along, there may be many more conflicts in our communities.
26. Education passes on Cultural Values, Heritage and Information from one Generation to the Next
How did you learn about Christmas? How about the 4 th of July? How did you learn about Native Americans?
We learn a lot of these things from school.
So, education also teaches us about our culture and who we are.
This usually takes place in history classes where we learn about the history of our nations and our world.
But we also learn cultural values from the hidden curriculum (If you haven’t read point 25, I talk about the hidden curriculum there).
For example, in western culture it’s polite to look people in the eyes and shake their hands. We also respect our elders. These are cultural values that are taught to us in everyday conversations at school.
27. Education can lead to Gender Equality
There is a lot of evidence that says education is the key to creating a more equal world.
For example, UNESCO states that women tend to be less educated than men in developing countries. However, women overall show more concern for the environment.
Why is this a problem?
Because at the moment women aren’t empowered enough (through education) to create change. More educated women means more power for women to effect change.
Here’s an example:
“Women constitute almost two-thirds of the 758 million adults who are unable to read or write a sentence – a vast pool of people we are not empowering to help us fight environmental shifts” ( UNESCO )
There is also the problem of gender stereotypes, which can be challenged through education . If we educate more people about justice and equality, gender stereotypes will diminish which will be good for gender equality.
Final Thoughts

Any importance of education speech or essay needs facts and figures backing it up. Use these 27 key points on the importance of education for your next essay!
You could also get facts from the following two sources:
- 23 Major Barriers to Education
- 11 Lifelong Effects of Lack of Education

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
1 thought on “27 Facts on the Importance of Education (Essay or Speech)”
helped me with my college work I recommend.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Speech Writing /
2-Minute Speech on Importance of Education in English for Students

- Updated on
- Apr 4, 2024

Speech on Importance of Education: Knowledge is power, and education is the ocean of knowledge. Education is a tool that can bring social change to society. A person who does not read books has no advantage over those who cannot. In every culture, education is given great importance because it has the power to enhance personal, economic, and global developments.
Here is what Mahatma Gandhi said about education, ’ By education, I mean an all-round drawing out of the best in the child and man; body, mind, and spirit. True education must correspond to the surrounding circumstances or it is not a healthy growth.’ Can you believe this century-old quote can still be of great significance? This is what we will do for you today. We will provide you with a speech on the importance of education, where we will provide samples and other details on how it can change our lives.
Quick Read: Speech on Earth Day
‘A person who never made a mistake never tried anything new.’ – Albert Einstein
Master the art of essay writing with our blog on How to Write an Essay in English .
2-Minute Speech on Importance of Education
‘Good morning my friends and teacher (s). Today, I stand before you to present my ‘Speech on importance of education’. We all want to progress and grow in our lives. Education is the only weapon that can bring peaceful and sustainable development. Every personal, professional social, and environmental issue can be solved with an educated mind.
Every society requires educated people for overall development. A society that has more education and civilized people will flourish and sustain better than those who lack education. That is why our government and educational institutions are promoting education.
In earlier times, education was given little importance, as most people were either engaged in agricultural or different manual labor jobs. With the advancement of science and technology, different sectors, like secondary, tertiary, quaternary, and quinary emerged.
Education is the key that unlocks doors of opportunity, enabling individuals to reach their full potential and contribute meaningfully to society. At a personal level, education allows us to understand the world around us. It empowers us to dream big, set goals, and work towards achieving them.
Through education, we can understand our rights and duties towards our families, society and nation. We can explore innovative ideas, as were are constantly involved in learning and growing.
Important people like big industrialists, politicians, movie actors, and even sportspersons are all educated, as they know the importance of education in life. Their contribution is essential for innovation, productivity, and economic competitiveness.
Investing in education is like investing in a future workforce. It ensures that our society remains dynamic and resilient in the face of rapid technological and global changes.
When we talk about social justice and equality, education plays a major role. Education provides equal opportunities for people from different backgrounds. Making education accessible to everyone will help in building a fair and just society, one where talent and potential are recognized.’
Also Read: 2 Minutes Adult Education Speech for School Students
10 Quotes on Importance of Education
Here are 10 quotes on the importance of education. Feel free to add these quotes to your speech or any writing topics.
- ‘Live as if you were to die tomorrow. Learn as if you were to live forever.’ – Mahatma Gandhi
- ‘The great aim of education is not knowledge but action.’ – Herbert Spencer
- ‘Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.’ – Nelson Mandela
- ‘The function of education is to teach one to think intensively and to think critically. Intelligence plus character – that is the goal of true education.’ – Martin Luther King Jr.
- ‘Education is the passport to the future, for tomorrow belongs to those who prepare for it today.’ – Malcolm X
- ‘An investment in knowledge pays the best interest.’ – Benjamin Franklin
- ‘The beautiful thing about learning is that no one can take it away from you.’ – B.B. King
- ‘Education is not the filling of a pail, but the lighting of a fire.’ – W.B. Yeats
- ‘Education is not preparation for life; education is life itself.’ – John Dewey
- ‘The more that you read, the more things you will know. The more that you learn, the more places you’ll go.’ – Dr. Seuss
Also Read: Speech on Education in English for School Students
Ans: Education is an important tool for social change. Every society requires educated people, who can help in navigating the developmental changes and lead the country to new heights. Education means knowledge and power. Every society requires educated people for overall development. A society that has more education and civilized people will flourish and sustain better than those who lack education. That is why our government and educational institutions are promoting education.
Ans: Education plays an important role in a person’s overall development and life. It can make you a responsible citizen, can offer you a better life, and make you aware of your duty towards society and country. From a personal level to social development, education has the power to change the world and counter every problem hindering developmental activities.
Ans: Literacy and education can be used interchangeably, but there is a big difference in their meaning. A person’s ability to read and write is known as literacy. Education refers to the formal and informal learning experience that a person acquires through personal experience.
Related Reads:
This was all about the speech on importance of education. We hope we were able to provide you with all the necessary information you were looking for. For more information on such interesting speech topics for your school, visit our speech writing page and follow Leverage Edu .
Shiva Tyagi
With an experience of over a year, I've developed a passion for writing blogs on wide range of topics. I am mostly inspired from topics related to social and environmental fields, where you come up with a positive outcome.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- JEE Advanced Admit Card 2024
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Admit Card
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET 2024 Exam Live
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Importance of Education Speech
Speech on the importance of education.
Education is an essential component of all human lives . Education and knowledge are not only necessary for personal development, but they are also necessary for economic development. Education develops a person's thinking and equips them with the skills to think, act, and grow in life. Education also empowers people and enables them to become more efficient in all aspects of life and work.

10 Lines Speech on Importance of Education
Education gives people the ability to think critically and form opinions on a variety of issues.
Education also allows us to learn about our history, roots, culture, and history.
Everyone in society should understand the importance and value of education in their lives.
Education is a necessary part of life, growth, and development.
Without education, a country's development and excellence are unlikely.
Education gives you the ability to learn and apply what you've learned.
Individuals' personalities are shaped by education, which plays an essential role in character development.
Youth, more than any other group in society, should have the right to an education.
A country can ensure its future development and progress by educating its youth.
Education is critical for a developing country like India.
Short Speech on Importance of Education
Every person is born with the ability to think and make decisions. Education is the means by which they learn how to put their talents to use. As a result, in order for India to develop and grow, the Indian youth must have adequate resources to learn and educate themselves. Education promotes creative and critical thinking. With proper education, India's youth can usher in a new wave of thought and practice into the country. This will help the country grow and develop further, eventually becoming one of the world's largest think tanks.
On a global scale, India accounts for approximately 37% of the total illiterate population. Closer to home, 26% of Indians lack access to education and guidance. The Central Government, in collaboration with various state governments, has developed a number of policies to educate the people of the country. All of those attempts, however, have largely been futile.
The solution to making this country thrive and progress is to make education accessible for all. Due to a lack of funds and opportunities, more than half of the people in our country do not receive an education. Only a select few are capable of obtaining a proper education and putting it to good use. Therefore, education is important. It broadens people's perspectives and helps them understand, develop, and grow.
Long Speech on Importance of Education
Education plays a crucial part in terms of a person's development. The first thing that comes to mind when we think of education is learning new things. Education is a valuable resource that provides people with information, skill sets, strategies, and knowledge so they may comprehend their responsibilities to their families, societies, and countries. It improves the perception of the world and field of vision.
In addition to this, it has been the most crucial factor in the development of the country. Without education, one cannot explore novel concepts. It means that the world would not be evolving since innovation requires ideas, and a nation would not be able to develop without creativity.
There are specific ways one can tell students and young kids about the value that education carries. You must concentrate on being their source of inspiration if you want your children to learn anything crucial like education since we all know youngsters tend to follow everything that is going on around them.
Benefits of Education
Numerous approaches exist for education to empower people. By enabling a person to obtain employment and take care of all the family's essential needs, it aids in the eradication of poverty. An educated individual has a lower chance of being duped and to participate in social injustices. As a result, they become less likely to commit fraud and other crimes. A country's trade and commerce are ultimately boosted by an increase in its educated population.
Because they comprehend the significance of law and order, the citizens have a deeper grasp of law and order, increasing their likelihood of upholding the law. Education aids in eradicating a number of social problems, including the dowry system and child marriage, and it also empowers women by promoting their independence.
Women who are educated are better able to advocate for themselves and express their thoughts. A solid education improves a person's communication abilities and allows them to express themselves more skillfully. As knowledgeable people, we are viewed as a vital resource for our society. Education enables us to pass along important morals, polite behaviour, and moral principles to others.
It also encourages the feeling that one is having a better life in addition to being beneficial on a physical, mental, and social basis. Our future is created by constructive education. As a result, an individual can improve his/her mental, physical, and spiritual state. It gives us information regarding many other domains, which boosts our self-assurance.
According to studies, those who are educated are more likely to live longer and be healthier. A solid foundation is created for the children by investing in various types of learning when they are still young, as they'd be having a good foundation. A quality education aims to achieve new things for the well being of the entire society.
Education not only allows us to learn about history, physics, arithmetic, geography, and other topics, but it also helps us in handling difficult situations in life . Education is, therefore, crucial for a brighter future. In addition to acquiring academic information, education includes acquiring knowledge that will enable you to improve as a person and become a person who can defend society against all social evils.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
Speech on Importance of Education of Students and Children
Speech on importance of education.
Education is a procedure of learning where knowledge, skills, and habits move from one generation to the other. Moreover, education is essential for the overall development of a human being. For instance, their personal, social as well as the economic development of the country. If we talk about the importance of education in our daily life, we have to admit that it improves our personal lives and helps in running the societies smoothly by protecting everyone including ourselves from the harmful and unexpected events.

Modes of Education
The major types of education system are as follows:
Formal Education: Formal education is basically a practice of learning where a human learns basic, academic or some trade skills for his living. Formal education or formal learning initiates at the basic level. Further, it continues till the college or university level where people study bachelor and master courses. It comes under a certain combination of rules and regulations and it may provide a formal degree after the completion of the course. It is provided by the teachers that are highly qualified and educated and are under strict discipline as well.
Informal Education: Informal education is the type of education where people are not studying in a specific school or a college. They do not use any specific learning method or technique. When a father teaches his son how to ride a bicycle or a mother teaches her daughter how to cook food, then these learnings fall under the category of Informal Education. A person can get informal education by reading some books from any library or any educational website on the internet. However, unlike the formal education, informal education has no particular syllabus or any specific time period for learning.
Get the Huge List of 100+ Speech Topics here
Importance of Education in Our Life
Education is very important for personal development as well as for the socio-economic development of our country. Education is important for living life happily. Moreover, it empowers and motivates our mind to conceive the good thoughts and ideas and grow our knowledge day by day. Moreover, education helps us in acquiring new skills and techniques. Thus, it becomes effortless for us to do our daily life activities in the best possible ways with maximum output and excellence. Education is necessary to raise a person’s standard of living. As it gives us all the necessary goods and awareness about how we can increase our earnings with the use of our brains and knowledge.
Importance of Education in the Life of a Student
Education is one of the most important and mandatory elements in the life of a student. It helps the students to do analysis while making important decisions in life. Education is essential for a student because after being educated enough, a student will be able to select a good career option for them. So that they can succeed in life with the help of education. A good career provides the students financial freedom and support along with mental satisfaction. The Education of the students helps them in improving their communication skills. For instance, their speech, body language, and many other elements present in the communication system. Education helps the students in using the technology in a better way in this era of rapid technological development and transformation.
As we all know that education is the key element of everyone’s life today. Education has the value that helps in making people valuable and full of knowledge. Education is necessary for the growth of life for everyone. It has the same value for everyone equally. Everyone is having the right to learn. Without education, life can become so difficult and hard to survive.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Speech for Students
- Speech on India for Students and Children
- Speech on Mother for Students and Children
- Speech on Air Pollution for Students and Children
- Speech about Life for Students and Children
- Speech on Disaster Management for Students and Children
- Speech on Internet for Students and Children
- Speech on Generation Gap for Students and Children
- Speech on Indian Culture for Students and Children
- Speech on Sports for Students and Children
- Speech on Water for Students and Children
16 responses to “Speech on Water for Students and Children”
this was very helpful it saved my life i got this at the correct time very nice and helpful
This Helped Me With My Speech!!!
I can give it 100 stars for the speech it is amazing i love it.
Its amazing!!
Great !!!! It is an advanced definition and detail about Pollution. The word limit is also sufficient. It helped me a lot.
This is very good
Very helpful in my speech
Oh my god, this saved my life. You can just copy and paste it and change a few words. I would give this 4 out of 5 stars, because I had to research a few words. But my teacher didn’t know about this website, so amazing.
Tomorrow is my exam . This is Very helpfull
It’s really very helpful
yah it’s is very cool and helpful for me… a lot of 👍👍👍
Very much helpful and its well crafted and expressed. Thumb’s up!!!
wow so amazing it helped me that one of environment infact i was given a certificate
check it out travel and tourism voucher
thank you very much
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

(877) 322-NWEF | [email protected]

The Hidden Importance of Speech and Debate

Did you know that there’s a National Speech and Debate Education Day every year? The first Friday in March celebrates the positive impact of speech and debate education on students, teachers, and the country.
Sometimes pushed to the “fringe” of school activities along with theater and band, speech and debate is actually filled with hidden advantages, offering students both short-term satisfaction and long-term benefits.
James Weaver, the Director of Performing Arts for the National Federation of State High School Associations, promotes the value of speech and debate as “an education-based activity that teaches research, speaking, and problem-solving skills students will use in all facets of their lives.”
Even Congress acknowledges the importance of this educational activity, solidifying the official national day of celebration in 2018. U.S. Representative Tom Garrett weighed in on the topic , stating, “Speech and debate can be one of the most rewarding and beneficial educational activities available to students. Not only does it provide students with a chance to shine in an academic environment, but it allows for a chance to win awards for intellect.”
As you can see, speech and debate inspires appreciation in people from every walk of life—from parents and students to teachers and legislators.
But how beneficial is it, really? It’s easy to see the value for students who grow up to be public speakers or politicians, but is there value in speech and debate for future electricians, bus drivers, or structural engineers?
Let’s dive in to discover the hidden importance of speech and debate for every student, regardless of occupational interest or future aspirations!
Before any good debate, a student researches their topic. To understand and argue their point, they must have facts, statistics, and general knowledge of what they’re talking about. Research requires them to sharpen a specific skill set and be able to look at their topic with a wide lens.
Critical Thinking
Research requires a student to fully engage their critical thinking skills. They must be engaged and focused on the subject. They examine their stance from all angles before collecting the facts to support their argument.
Critical thinking skills allow them to pinpoint the strengths and weaknesses in their position and find appropriate solutions to bolster their case. This process hones their critical thinking skills in ways unique to speech and debate activities.
PubMed Central suggests that much of formal education neglects critical thinking skills. They note that “deficiencies in critical thinking skills among students may rest with the educational system itself, which often stresses memorization of voluminous amounts of material essentially unrelated to any type of application at all.”
In this light, the critical thinking opportunities available in speech and debate become even more valuable.
The National Geographic Encyclopedia asserts , “Diplomacy is the art and science of maintaining peaceful relationships between nations, groups, or individuals.” In the context of speech and debate, diplomacy provides a civil platform on which students may come together and act within a prescribed set of rules.
Diplomacy, useful in almost any situation, is a valuable asset to any functioning adult. While researching their topic, students must work to see other points of view to argue their own effectively. This practice broadens their understanding of the issue and forces a nuance of diplomacy into the equation.
An open mind learns to adapt to fluid situations—such as a live debate—allowing the student to employ effective strategies.
A Wider View of the World
Speech and debate offers students a platform to explore hot topics, form opinions, and voice their thoughts. Facilitators often choose current events and historical movements as the subject matter. Pushed to interact with complicated situations, students can open their minds and explore issues that may have escaped their notice otherwise.
Tim Alderete, a speech and debate coach at The Meadows School, notes, “Speech and debate prepares a student to engage in a democratic society. Students study a wide range of issues, which helps them become informed about society and the world around them. They learn how to engage in a civil, organized discussion that looks for solutions.”
Building an Argument
Speech and debate teaches a student how to construct logical and thoughtful arguments that support their position. Having research in hand is one thing, but building an intelligent case is a bit different. To present a winning argument, the student must arrange their research into a logical pattern and create a compelling case.
Harvard University expounds on the necessary components of a logical argument and offers strategies for building one.
Leadership and Teamwork
Ayush Midha is a 12th grader, the captain of his debate team, and the 2014-15 O’Neill Leadership Trophy winner. He expressed his appreciation for the opportunity to hone his leadership skills:
“As a captain, I have had the opportunity to foster team success and lead my teammates by example,” Ayush told Harker News Online . “Even outside of debate, these skills have allowed me to take on leadership positions and experience success.”
Speech and debate offers a chance to cultivate leadership and teamwork within the close-knit community of a debate team. Older, more experienced team members work as captains, mentoring their teammates through the year. They must create a well-oiled machine, work together, and develop viable relationships.
Communication
Students who participate in speech and debate learn how to communicate effectively—it’s sink or swim! Arguing their topic, they present points and counterpoints in a manner that allows their audience and their opponent to comprehend the case they have built.
Research and a logical argument are a great start to a compelling debate, but if the student can’t convey understandable information to others, there’s little point to the exercise. Speech and debate teaches students how to successfully exchange information, a critical skill for every functioning adult.
The Golden State Academy points out , “Speech and Debate is the art of communication.” This captures the essence of the exercise beautifully. Students grow and strive to achieve excellent communication skills to succeed in this endeavor.
Receiving Constructive Criticism
When someone works hard on a project or pours their heart into a passion, it can be difficult to accept anything less than congratulations or praise.
Unfortunately, criticism is a part of life, and it’s best to learn how to accept critiques earlier rather than later.
Speech and debate offers students a chance to demonstrate the best that they have to offer and then benefit from the (sometimes-painful) wisdom of others. When constructive criticism presents opportunities to improve, successful debaters learn to accept it with grace and poise. Speech and debate opens a new door for self-growth.
CollegeVine instructs students , “When you have the opportunity to receive direct feedback from your judges, you should take it seriously…these can be a helpful source of advice for how to adjust your performance…”
Mastering the ability to accept constructive criticism enriches the student’s life and ensures that they have the freedom to grow from each life experience.
Beyond the Exercise
Participating in speech and debate often create optimal conditions for success in the adult world. According to the National Speech and Debate Associate (NSDA) , of students who participated in speech and debate while in school,
- 90% obtain a graduate-level college degree
- 15% are top-ranking executives in their corporation
- 30% are university educators
- 10% work in government
Additionally, speech and debate’s influence on academic progress while still in school is very promising:
- 15% of speech and debate participants experience higher self-esteem
- 31% of speech and debate participants attend classes more regularly
- 36% of speech and debate participants see an increase in their reading test scores
- 87% of speech and debate participants improve their analytical skills
- 100% of speech and debate participants experience an increase in interest in their classes
- 100% of speech and debate participants are less likely to experience drug use, early pregnancy, and alcohol abuse
Statistically speaking, students who join in speech and debate have a bright future ahead of them. The skills that they acquire while practicing this academic discipline are essential to many areas of their adult life.
Forbes recognizes these qualities and admonishes future employers to be on the lookout for bright young people who have enjoyed the rigor of speech and debate: “Many business leaders are frustrated in their attempts to find Millennials (born between 1980 and 2000) who seem to have the potential to lead the company in the years ahead. I’ve got a suggestion: search for those who competed in speech and debate competition in high school (or college) and hire them….They all come dressed like business executives and they have a deep understanding of how to persuade, how to present clearly, and how to connect with an audience. It’s impressive….Be on the lookout for Millennials who have participated in speech and debate training. Hire them and put them on your leadership fast track.”
Speech and debate is a wildly profitable school subject with undeniable academic and real-world value.
Any student who wants to add to their marketable skills should consider joining their local speech and debate team. Offering students the opportunity to develop and practice their research skills, build and communicate convincing arguments, and create and nurture a team atmosphere, speech and debate is a worthy academic pursuit.
ThoughtCo. summarizes the benefits of speech and debate, both on a professional and personal level. “Knowing how to synthesize information and deliver it to an audience succinctly—even an audience of one—is a skill that benefits people throughout their lives….These ‘soft skills’ can help in most careers because debate students learn the art of persuasion….Outside of the working world, having good communication skills is useful in activities as ordinary as meeting new people or as special as making a wedding toast in front of a crowd….”
Whether a student is an old hand at speech and debate or giving it their first t ry , they will have a learning experience to remember. While most people initially struggle to perform in front of an audience and logically convey their ideas under pressure, the support and coaching that they receive with continued training will help them overcome those first hurdles.
Don’t overlook the hidden importance of speech and debate. There are some things a textbook alone can’t teach.
Leave A Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Make a difference. Run for school board.

Free course. Enroll today.
Related Posts

Resource Guide for Parents

Resource Guide for Teachers

Resource Guide for School Board Members
- DOWNLOADS AND PRINTABLES
- Upcoming Summits
- Recent Summits
- Host A Summit
- KNOW YOUR STATE
RECENT POSTS
- Resource Guide for Parents May 16, 2024
- Resource Guide for Teachers May 16, 2024
- Resource Guide for School Board Members May 16, 2024
- Collective Bargaining Is Not Related To Student Achievement May 8, 2024
- Board’s Guide to Free Speech Course Sample April 12, 2024
Mailing address: PO Box 962 Bedford, Virginia 24523 USA
Phone: (877) 322-NWEF
Email: [email protected]

© Copyright 2024 | Noah Webster Educational Foundation All Rights Reserved | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions
Biden's Upcoming Graduation Speech Roils Morehouse College, a Center of Black Politics and Culture
President Joe Biden will have his most direct engagement with college students since the start of the Israel-Hamas war when he speaks at Morehouse College's commencement
Biden's Upcoming Graduation Speech Roils Morehouse College, a Center of Black Politics and Culture

Patrick Semansky
FILE - President Joe Biden speaks in support of changing the Senate filibuster rules that have stalled voting rights legislation, at Atlanta University Center Consortium, on the grounds of Morehouse College and Clark Atlanta University, Jan. 11, 2022, in Atlanta. Biden will have his most direct engagement with college students since the start of the Israel-Hamas war when he speaks at Morehouse College's commencement. (AP Photo/Patrick Semansky, File)
ATLANTA (AP) — When he gives the commencement address at Morehouse College, President Joe Biden will have his most direct engagement with college students since the start of the Israel-Hamas war at a center of Black politics and culture.
Morehouse is located in Atlanta, the largest city in the swing state of Georgia , which Biden flipped from then-President Donald Trump four years ago. Biden's speech Sunday will come as the Democrat tries to make inroads with a key and symbolic constituency — young Black men — and repair the diverse coalition that elected him to the White House.
The announcement of the speech last month triggered peaceful protests and calls for the university administration to cancel over Biden’s handling of the war between Israel and Hamas. Some students at Morehouse and other historically Black campuses in Atlanta say they vociferously oppose Biden and the decision to have him speak, mirroring the tension Biden faces in many communities of color and with young voters nationally .
Morehouse President David Thomas said in an interview that the emotions around the speech made it all the more important that Biden speak.
“In many ways, these are the moments Morehouse was born for,” he said. “We need someplace in this country that can hold the tensions that threaten to divide us. If Morehouse can’t hold those tensions, then no place can.”
The speech comes at a critical moment for Biden in his general election rematch against Trump, a Republican. Biden is lagging in support among both Black voters and people under 30, groups that were key to his narrow 2020 victories in several battleground states, including Georgia.
Fifty-five percent of Black adults approved of the way Biden is handling his job as president, according to an AP-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research poll in March, a figure far below earlier in his presidency. Overall, 32% of 18- to 29-year-olds approved in the same poll.
“This is a global catastrophe in Gaza, and Joe Biden coming to pander for our votes is political blackface,” said Morehouse sophomore Anwar Karim, who urged Thomas and school trustees to rescind Biden’s invitation.
Recent scenes on American campuses reflect objections among many young voters about Israel’s assaults in Gaza. Biden has backed Israel since Hamas militants killed more than 1,200 Israelis and took hundreds of hostages on Oct. 7. That includes weapons shipments to the longstanding U.S. ally, even as Biden advocates for a cease-fire, criticizes Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s tactics and the death toll in Gaza surpasses 35,000 people, many of them women and children.
Many younger Black people have identified with the Palestinian cause and have at times drawn parallels between Israeli rule of the Palestinian territories and South Africa’s now-defunct apartheid system and abolished Jim Crow laws in the U.S. Israel rejects claims that its system of laws for Palestinians constitutes apartheid.
“I think that the president will do himself good if he does not duck that, especially when you think about the audience that he will be speaking to directly and to the nation,” Thomas said.
Sunday's speech will culminate a four-day span during which Biden will concentrate on reaching Black communities. On Thursday, Biden met privately with plaintiffs from the Brown v. Board of Education case that barred legal segregation of America’s public schools. The following day, Biden will address an NAACP gathering commemorating the 70th anniversary of the landmark decision.
Former U.S. Rep. Cedric Richmond, a longtime Biden ally who helped broker his speech at Morehouse, said he understood students’ concerns but emphasized that Biden has pressured Netanyahu and supports a two-state solution for the Israelis and Palestinians. Trump, meanwhile, has effectively abandoned that long-held U.S. position and said Israel should “finish the problem” in Gaza.
“That’s nowhere in the conversation,” Richmond said.
The debate over Biden's speech at Morehouse reflected a fundamental tension of historically Black colleges and universities, which are both dedicated to social justice and Black advancement and run by administrators who are committed to keeping order.
“We look like a very conservative institution” sometimes, Thomas said. “On one hand, the institution has to be the stable object where we are today in the world.”
But, he added, the university's long-term purpose is to “support our students in going out to create a better world.”
Blowback started even before Thomas publicly announced Biden was coming. Faculty sent executives a letter of concern, prompting an online town hall. Alumni gathered several hundred signatures to urge that Thomas rescind Biden’s invitation. The petition called the invitation antithetical to the pacifism Martin Luther King Jr., a Morehouse alumnus, expressed when opposing the Vietnam War.
Some students note that leaders of Morehouse and other HBCUs did not always support King and other Civil Rights activists who are venerated today. Morehouse, for instance, expelled the actor Samuel L. Jackson in 1969 after he and other students held Morehouse trustees, including King’s father, in a campus building as part of demanding curriculum changes and the appointment of more Black trustees.
Students organized two recent protests across the Atlanta University Center (AUC), a consortium of historically Black institutions in Atlanta that includes Morehouse. Chants included “Joe Biden, f— off!” and “Biden, Biden, you can’t hide. We charge you with genocide,” along with expletives directed at Thomas.
“Our institution is supporting genocide, and we turn a blind eye,” said Nyla Broddie, a student at Spelman College, which is part of the AUC. Brodie argued Biden’s Israel policy should be viewed in the broader context of U.S. foreign policy and domestic police violence against Black Americans.
Thomas said he “feels very positive about graduation” and that “not one” Morehouse senior — there are about 500 at the all-male private school — has opted out of participating. “That’s not to say that the sentiments about what’s going on in Gaza don’t resonate with people in our community,” Thomas said.
Thomas met privately with students as did several trustees. The Morehouse alumni association hosted a student town hall, featuring at least one veteran of the Atlanta Student Movement, a Civil Rights-era organization.
But there was a consistent message: Uninviting the president of the United States was not an option. When students raised questions about endowment investments in Israel and U.S. defense contractors, they said they were told the relevant amounts are negligible, a few hundred thousand dollars in mutual funds.
“I think folks are excited” about Biden coming, said Democratic Georgia Sen. Raphael Warnock, the senior pastor at King’s Ebenezer Baptist Church in Atlanta. Warnock said Biden is in “a great position” to talk about student debt relief , increased federal support for HBCUs and other achievements.
HBCUs have not seen crackdowns from law enforcement like those at Columbia University in New York City and the University of California, Los Angeles. However, Morehouse and the AUC have seen peaceful demonstrations, petitions and private meetings among campus stakeholders. Xavier University, a historically Black university in Louisiana , withdrew its commencement invitation for U.N. Ambassador Linda Thomas-Greenfield , citing a desire among students “to enjoy a commencement ceremony free of disruptions.”
Whether Morehouse graduates or other students protest Biden or disrupt the ceremony remains to be seen. Student protest leaders say they are unaware of any plans to demonstrate inside during the commencement.
Thomas, Morehouse's president, promised that forms of protest at commencement that “do not disrupt ceremonies” will not result in sanctions for any students.
But he also vowed to end the program early if disruptions grow.
“We will not — on Morehouse’s campus — create a national media moment,” he said, “where our inability to manage these tensions leads to people being taken out of a Morehouse ceremony in zip ties by law enforcement.”
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press . All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Photos You Should See - May 2024

Join the Conversation
Tags: Associated Press , politics , Georgia , education
Related Articles
Best states.

America 2024

Best States Rankings
- # 2 New Hampshire
- # 3 Nebraska
- # 4 Minnesota
Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 best states in america.
Elliott Davis Jr. May 7, 2024

Why Utah Is the Best State
Elliott Davis Jr. and Julia Haines May 7, 2024

Why Florida Is No. 1 in Education
Tim Smart May 7, 2024

Nikki Haley Faces a Murky Path Forward and a Key Decision on Whether or Not to Endorse Trump
Associated Press May 20, 2024

Plan to Boost Uber and Lyft Driver Pay in Minnesota Advances in State Legislature
Associated Press May 19, 2024

Closing Arguments Set in Trial of University of Arizona Grad Student Accused of Killing a Professor

San Diego Deputy Who Pleaded Guilty to Manslaughter Now Faces Federal Charges

11 Hurt in Mass Shooting That Marked a Weekend of Gun Violence in Savannah, Georgia

Diddy Admits Beating Ex-Girlfriend Cassie, Says He's Sorry, Calls His Actions 'Inexcusable'

Pro-Palestinian Protesters Set up a New Encampment at Drexel University

- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
At Morehouse, Biden says dissent should be heard because democracy is 'still the way'

Stephen Fowler
Jeongyoon Han

President Biden speaks to graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement Sunday, May 19, 2024, in Atlanta. Alex Brandon/AP hide caption
President Biden speaks to graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement Sunday, May 19, 2024, in Atlanta.
President Joe Biden told Morehouse College's graduating class of 2024 that he's committed to serving Black voters while defending freedom and democracy in the face of "extremist forces" that he says threaten the soul of the nation.
With just six months until the general election, the speech, which was filled with religious themes of struggle and resilience, also served as a continuation of Biden's warning to his supporters of what he thinks the country would look like if Donald Trump is elected again.
"They don't see you in the future of America, but they're wrong," he said. "To me, we make history, not erase it. We know Black history is American history."

Graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement bow their heads Sunday, May 19, 2024, in Atlanta. President Biden addressed the graduating class of 2024 and warned about "extremist forces" he says threaten the soul of the nation. Alex Brandon/AP hide caption
Graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement bow their heads Sunday, May 19, 2024, in Atlanta. President Biden addressed the graduating class of 2024 and warned about "extremist forces" he says threaten the soul of the nation.
The president's commencement address at Morehouse, a historically Black school in Atlanta, also comes as polling shows potentially lower support for his reelection efforts among Black voters and young voters, and as campus protests over conflict in Gaza have disrupted graduations around the country.
Biden said he understood angst over the direction of the country, acknowledged "dissent about America's role in the world" and said that those who have different views should have their voices heard in the name of democracy.
"That's my commitment to you," he said. "To show you: democracy, democracy democracy — it's still the way."

Biden will cap off a week of outreach to Black Americans with Morehouse commencement

Biden is set for the Morehouse graduation. Students are divided
His speech is also one of many events on his recent trip aimed at speaking to Black voters, following events with plaintiffs in the historic Brown v. Board Supreme Court case, meetings with Black Greek Letter Organizations, often known as the Divine Nine, and before he headlines an NAACP dinner in Detroit, Mich.
For weeks, several college and university campuses around the country have been roiled with student protests and encampments expressing opposition against Biden and U.S. policies and involvement around conflict in Gaza.
Morehouse has seen student demonstrations, but not occupation of campus spaces or clashes with law enforcement. Outside of the ceremony, a small number of protestors gathered while the commencement itself did not see any major disruptions.
Biden will deliver the commencement address at Morehouse College
Last week, Morehouse College President David Thomas said he would rather halt proceedings than have students escorted away for protesting.
"If my choice is 20 people being arrested on national TV on the Morehouse campus, taken away in zip ties during our commencement, before we would reach that point, I would conclude the ceremony," he said on NPR's Weekend Edition .

An attendee stands in protest with their back to President Biden as Biden speaks to graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement Sunday in Atlanta. John Bazemore/AP hide caption
An attendee stands in protest with their back to President Biden as Biden speaks to graduating students at the Morehouse College commencement Sunday in Atlanta.
Those concerns did not come to pass. Apart from the heightened security and increased media presence, Biden's speech was met with a similar response to a typical college graduation ceremony.
More than 400 graduating students walked across the stage Sunday, and during Biden's speech a handful of students, some wearing keffiyehs , turned their chairs around to face away from the president. After the ceremony, Morehouse issued a statement praising the graduating class and their intentionally muted response to Biden.
"It is fitting that a moment of organized, peaceful activism would occur on our campus while the world is watching to continue a critical conversation," the statement reads. "We are proud of the resilient class of 2024's unity in silent protest, showing their intentionality in strategy, communication, and coordination as a 414-person unit."
DeAngelo Fletcher, Morehouse College's valedictorian, closed his address to his classmates by addressing global conflict, particularly the Israel-Hamas war.
"For the first time in our lives, we've heard the global community sing one harmonious song that transcends language and culture," he said. "It is my sense as a Morehouse Man, nay – as a human being – to call for an immediate and a permanent ceasefire in the Gaza Strip."
Biden's speech at Morehouse comes with intense scrutiny as many presidential horse race polls show the president lagging with young voters, Black voters and other nonwhite groups that helped propel him to a narrow victory against Donald Trump in 2020.
Those polls — for now — signal a drop in support for Biden but not necessarily an equal shift towards Donald Trump. There are also signs that some of the displeasure with Biden is more pronounced among people who aren't as likely to vote in November.
While facing a nominal challenge in the Democratic presidential primary, Biden's best-performing areas have often come in places with a large share of Black voters. For example, in Georgia's primary contest 95% of Black voters pulled a Democratic ballot, and Biden won 95% of the overall vote.
While some students, faculty and alumni expressed opposition to Biden's selection as the commencement speaker, reaction on campus during the graduation ceremony was largely positive.
Dr. Tiffany Johnson, a 50-year-old who came to the campus green at 4:30 a.m. to see her son graduate, was also excited to see Biden.
"He is the leader of the free world, the most important job in the world, and for him to come to speak to [Morehouse] graduates, to inspire them, is phenomenal," Johnson said.
Johnson said Black voters who might not support Biden are part of a "bandwagon" that do not understand what he has done for the community, and said his speech would be an ideal opportunity to share his accomplishments.
In the speech, Biden touted a track record that he says makes key investments in Black communities, including a record $16 billion funding package towards historically Black colleges and universities, protecting voting rights, and creating economic policies that strengthens Black businesses.
- commencement address
- graduation ceremony
- morehouse college
- young voters
- Donald Trump
- black voters
The Strange Ritual of Commencement Speeches
Where everything and nothing is at stake
They appear every spring, like crocuses or robins or perhaps black flies: commencement addresses. Thousands of them, across the country and across the variety of American higher education—two-year schools, four-year schools, small colleges, universities both public and private, schools of every kind. And they will appear again, despite how unusual this spring has been. Many campuses have been roiled by protests about the war in Gaza, and some institutions will curtail graduation ceremonies. But the members of this undergraduate class, who had their high-school graduations shut down by COVID in 2020, have long looked forward to a second chance at a commencement ceremony. Over the next month or so, even in the face of disruptions or cancellations, commencement addresses will be delivered to about 4 million students earning some kind of college degree.
Most of these addresses will pass into oblivion. It is a cliché for commencement speakers to open their remarks by confessing that they remember nothing about their own graduation: They have forgotten not just what was said, but who said it. Yet even if most commencement addresses prove far from memorable, the press and public eagerly anticipate them. News stories appear throughout the winter and early spring announcing who will speak where. Then, when the speakers have spoken, journalists and commentators rush to judge which should be considered the year’s best.
A few speeches are anointed as classics to be visited or revisited for years. Admiral William McRaven’s 2014 address at the University of Texas at Austin has had more than 60 million YouTube viewers, all eager to learn the 10 takeaways from his Navy SEAL training. Thousands of Americans likely hear echoes in their head every morning of his promise that if you “make your bed,” it will change your life. More than 60 million people have also watched Steve Jobs’s Stanford University speech from 2005, which eerily anticipates his own death and urges graduates to “ follow your heart .” J. K. Rowling’s 2008 Harvard talk about failure and imagination has attracted tens of millions of viewers, as has David Foster Wallace’s 2005 Kenyon College address, “ This Is Water. ” All of these also ended up in print as well, designed to make attractive gifts. Admiral McRaven’s book became a New York Times No. 1 best seller. When Wallace died, in 2008, The Wall Street Journal republished the speech in his memory.
Read: A commencement address too honest to deliver in person
Commencement greatest hits reach well beyond these chart-toppers. Time , The New York Times , The Washington Post , Slate , Elle , and countless other outlets run articles each year on the season’s winners. “Looking for some new words of wisdom?” NPR asks on its website. The headline of its online database lists the 350 “Best Commencement Speeches, Ever” in alphabetical order (but, curiously, by first name), from Aaron Sorkin to Zubin Damania. Can all 350 really be the “best”?
The assumption behind commencement speeches seems to be that even as graduates don their black robes and mortarboards, they don’t yet know quite enough. They must await, or perhaps endure, some final instruction, absorb some last missing life lesson, before they can be safely launched into what their education has supposedly prepared them for. Almost always these days, this instructional capstone is delivered by someone outside the institution, someone expected to have insight that extends beyond a university’s walls—perhaps representing a first step in the students’ transition into the “real world.” Many colleges and universities try to attract the most famous person they can. As graduation season approaches, speaker announcements take on the hallmarks of a competition: Which institutions did President Barack Obama choose for his three or four addresses each year? Who snagged Oprah Winfrey? Or Taylor Swift?
Seeking a famous speaker may, on one level, represent an unseemly preoccupation with celebrity. But it fits the logic of the occasion. What better time to hear from someone who is regarded as, at least in some way, distinguished? Someone who has led what an institution perceives to be an inspiring and successful life? Yet even before our present moment of cancel culture and partisanship, university leaders have had to worry about selecting a speaker who might spark disruptions in a ceremony meant to be a celebration. High Point University, in North Carolina, which in 2005 welcomed Rudy Giuliani—admired in the aftermath of 9/11 as “America’s mayor”—presumably would not make that choice again today. Every spring sees its complement of speakers who are protested, heckled, or disinvited.
Speakers, in turn, are attracted by a prestigious invitation, or perhaps by the presence of a child or grandchild in the graduating class—and, at times, by the offer of a substantial honorarium. Some institutions, though a minority, pay their speakers what can be hefty sums. One agent who represents a portfolio of prominent entertainers observed that fees for graduation speakers may go as high as $500,000. “Universities are vying for customers in the form of admissions, and this can be a great way to advertise and get people on campus,” she explained . When Matthew McConaughey’s $135,000 honorarium from the University of Houston was made public by inquisitive journalists in 2015, he quickly assured critics that he had donated it to charity. The Boston Globe touched off a small scandal when it reported the same year that three state schools had paid speakers $25,000 to $35,000 each.
Serving as a commencement speaker is not all glory. Usually the honored guest must perform as the centerpiece of the lunches, dinners, and meet and greets that surround the actual ceremony. And of course there is the speech. Someone has to write it. It seems unimaginable that anyone other than David Foster Wallace could have created “This Is Water,” and Kenyon students remember seeing him surrounded by sheets of paper, inking in edits and scribbling addenda right up to the start of the ceremony. At Harvard, J. K. Rowling opened her remarks by admitting to the months of anxiety she experienced as she wrote her address. At least, she noted, her worries had resulted in her losing weight. Rowling’s speech was greeted with a two-minute standing ovation. Yet she vowed never to give a commencement address again.
Many speeches are composed by someone other than the person who utters the words. Commencement speeches are not just a cultural ritual; they are an industry. A former Obama speechwriter told me recently that the springtime atmosphere at the Washington, D.C., public-affairs and communications firm where he now works is like the high-pressure environment of an accounting firm during tax season. Some of the market comprises regular clients, but a number of customers are one-offs. A lot of speechwriters hate doing commencement speeches, he said; they find it nearly impossible to come up with something fresh and compelling. These addresses, he went on, are unlike other genres of speeches, which tend to focus on the speaker. A commencement address has to be about the graduates: It is their day. Getting the “trite ideas out”—Pursue your passions! Turn failure into opportunity!—can be the first step toward “shaking loose” an idea, an angle that is distinctive to a particular speaker, place, and moment.
In any given year, a speaker in high demand will deliver addresses at several colleges and universities. Barack Obama gave 23 graduation speeches during his presidency. In principle, these speeches should not be the same; each audience, each institution, each graduate wants to feel special. Besides, in this digital age, you are going to get caught. When word got around, in advance of his 2005 Class Day speech at Harvard, that the Meet the Press host Tim Russert sometimes recycled his remarks, students at Harvard passed around bingo cards printed with some of his favorite phrases and encouraged attendees to play.
Senator Chuck Schumer doesn’t care about being caught. He loves graduations, and shows up, sometimes unannounced—perhaps even uninvited, though none of his hosts has ever said so—at as many as eight commencement ceremonies across the state of New York every year. He delivers the same speech every time. A student complained on a Reddit thread that he had heard the speech five times in six years—at his high-school, college, and graduate-school commencements, and at his sister’s high-school and college ceremonies. “OH FUCK,” his long-suffering family finally proclaimed, “NOT AGAIN.” (Perhaps, another Reddit contributor suggested, the graduates could arrange to do a sing-along.) When John Oliver, the host of HBO’s Last Week Tonight , learned about Senator Schumer’s springtime follies, he couldn’t resist showing clips of him saying exactly the same thing year after year after year, with the same verbal sound effects and hand gestures—an “endless graduation-speech time loop.”
The peril of graduation speeches is that, however hard you struggle, you are in danger of repeating not just yourself but every person who has ever given one. Asked to generate a commencement address, ChatGPT produces a script that sounds like every speech you’ve ever heard, because it is in fact just that: a distillation of everything everyone has ever said, or at least everything that ChatGPT has found available in its training data. Graduates should practice resilience, pursue purpose, nurture relationships, embrace change, innovate, accept their responsibility to lead, and persevere as they embark on their journey into “a world of infinite possibilities.”
Read: What John F. Kennedy’s moon speech reveals 50 years later
We have all heard this speech. We’ll hear versions of it again this spring. But we hope for something better, and we’ll scour newspapers and the internet to see if it has been delivered somewhere. We ask powerful, accomplished people to stand before us and, for a moment, present a different self—to open up, become vulnerable, be reflective, let us see inside. What is a meaningful life, and how do I live one? These are questions that are customarily reserved for late nights in undergraduate dormitories, for the years before the at-once tedious and terrifying burdens of Real Life—careers, mortgages, children, aging bodies, disappointed hopes—overtake us.
Everything and nothing is at stake in a commencement address. Maybe you have already heard it eight times. Maybe there was nothing worth hearing in the first place. But perhaps you will encounter a speaker who, even in this tumultuous spring, can reach across the chasm of innocence and experience separating graduates and the person talking to them. The old endeavor to imagine themselves young and look through fresh eyes again; the young begin to imagine themselves old, as they will become all too soon.
The best commencement address is a gift—of self and of hope across generations. It is not surprising that these speeches so rarely succeed. The surprise should be when they do. Innocence can only faintly imagine experience. No generation can really explain to another what is to come. And experience can never recapture innocence, however wistful we may be for what has been lost. The beauty of commencement speeches is that they represent a moment when we try.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Biden’s upcoming graduation speech roils Morehouse College, a center of Black politics and culture
FILE - President Joe Biden speaks in support of changing the Senate filibuster rules that have stalled voting rights legislation, at Atlanta University Center Consortium, on the grounds of Morehouse College and Clark Atlanta University, Jan. 11, 2022, in Atlanta. Biden will have his most direct engagement with college students since the start of the Israel-Hamas war when he speaks at Morehouse College’s commencement. (AP Photo/Patrick Semansky, File)
President Joe Biden speaks at a memorial service to honor law enforcement officers who’ve lost their lives in the past year, during National Police Week ceremonies at the Capitol in Washington, Wednesday, May 15, 2024. (AP Photo/Susan Walsh)
A large group of faith leaders organized by the Atlanta Multifaith Coalition for Palestine address the media during a press conference at Emory on Tuesday, April 30, 2024. They’re demanding Biden not to speak at Morehouse commencement unless he calls for an immediate and permanent ceasefire in Gaza. (Miguel Martinez/Atlanta Journal-Constitution via AP)
- Copy Link copied
ATLANTA (AP) — When he gives the commencement address at Morehouse College, President Joe Biden will have his most direct engagement with college students since the start of the Israel-Hamas war at a center of Black politics and culture.
Morehouse is located in Atlanta, the largest city in the swing state of Georgia, which Biden flipped from then-President Donald Trump four years ago. Biden’s speech Sunday will come as the Democrat tries to make inroads with a key and symbolic constituency — young Black men — and repair the diverse coalition that elected him to the White House.
The announcement of the speech last month triggered peaceful protests and calls for the university administration to cancel over Biden’s handling of the war between Israel and Hamas. Some students at Morehouse and other historically Black campuses in Atlanta say they vociferously oppose Biden and the decision to have him speak, mirroring the tension Biden faces in many communities of color and with young voters nationally .
Morehouse President David Thomas said in an interview that the emotions around the speech made it all the more important that Biden speak.
“In many ways, these are the moments Morehouse was born for,” he said. “We need someplace in this country that can hold the tensions that threaten to divide us. If Morehouse can’t hold those tensions, then no place can.”
What to know about the 2024 Election
- Democracy: American democracy has overcome big stress tests since 2020. More challenges lie ahead in 2024.
- AP’s Role: The Associated Press is the most trusted source of information on election night, with a history of accuracy dating to 1848. Learn more.
- Read the latest: Follow AP’s complete coverage of this year’s election.
The speech comes at a critical moment for Biden in his general election rematch against Trump, a Republican. Biden is lagging in support among both Black voters and people under 30, groups that were key to his narrow 2020 victories in several battleground states, including Georgia.
Fifty-five percent of Black adults approved of the way Biden is handling his job as president, according to an AP-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research poll in March, a figure far below earlier in his presidency. Overall, 32% of 18- to 29-year-olds approved in the same poll.
“This is a global catastrophe in Gaza, and Joe Biden coming to pander for our votes is political blackface,” said Morehouse sophomore Anwar Karim, who urged Thomas and school trustees to rescind Biden’s invitation.
Recent scenes on American campuses reflect objections among many young voters about Israel’s assaults in Gaza. Biden has backed Israel since Hamas militants killed more than 1,200 Israelis and took hundreds of hostages on Oct. 7. That includes weapons shipments to the longstanding U.S. ally, even as Biden advocates for a cease-fire, criticizes Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s tactics and the death toll in Gaza surpasses 35,000 people, many of them women and children.
Many younger Black people have identified with the Palestinian cause and have at times drawn parallels between Israeli rule of the Palestinian territories and South Africa’s now-defunct apartheid system and abolished Jim Crow laws in the U.S. Israel rejects claims that its system of laws for Palestinians constitutes apartheid.
“I think that the president will do himself good if he does not duck that, especially when you think about the audience that he will be speaking to directly and to the nation,” Thomas said.
Sunday’s speech will culminate a four-day span during which Biden will concentrate on reaching Black communities. On Thursday, Biden met privately with plaintiffs from the Brown v. Board of Education case that barred legal segregation of America’s public schools. The following day, Biden will address an NAACP gathering commemorating the 70th anniversary of the landmark decision.
Former U.S. Rep. Cedric Richmond, a longtime Biden ally who helped broker his speech at Morehouse, said he understood students’ concerns but emphasized that Biden has pressured Netanyahu and supports a two-state solution for the Israelis and Palestinians. Trump, meanwhile, has effectively abandoned that long-held U.S. position and said Israel should “finish the problem” in Gaza.
“That’s nowhere in the conversation,” Richmond said.
The debate over Biden’s speech at Morehouse reflected a fundamental tension of historically Black colleges and universities, which are both dedicated to social justice and Black advancement and run by administrators who are committed to keeping order.
“We look like a very conservative institution” sometimes, Thomas said. “On one hand, the institution has to be the stable object where we are today in the world.”
But, he added, the university’s long-term purpose is to “support our students in going out to create a better world.”
Blowback started even before Thomas publicly announced Biden was coming. Faculty sent executives a letter of concern, prompting an online town hall. Alumni gathered several hundred signatures to urge that Thomas rescind Biden’s invitation. The petition called the invitation antithetical to the pacifism Martin Luther King Jr., a Morehouse alumnus, expressed when opposing the Vietnam War.
Some students note that leaders of Morehouse and other HBCUs did not always support King and other Civil Rights activists who are venerated today. Morehouse, for instance, expelled the actor Samuel L. Jackson in 1969 after he and other students held Morehouse trustees, including King’s father, in a campus building as part of demanding curriculum changes and the appointment of more Black trustees.
Students organized two recent protests across the Atlanta University Center (AUC), a consortium of historically Black institutions in Atlanta that includes Morehouse. Chants included “Joe Biden, f— off!” and “Biden, Biden, you can’t hide. We charge you with genocide,” along with expletives directed at Thomas.
“Our institution is supporting genocide, and we turn a blind eye,” said Nyla Broddie, a student at Spelman College, which is part of the AUC. Brodie argued Biden’s Israel policy should be viewed in the broader context of U.S. foreign policy and domestic police violence against Black Americans.
Thomas said he “feels very positive about graduation” and that “not one” Morehouse senior — there are about 500 at the all-male private school — has opted out of participating. “That’s not to say that the sentiments about what’s going on in Gaza don’t resonate with people in our community,” Thomas said.
Thomas met privately with students as did several trustees. The Morehouse alumni association hosted a student town hall, featuring at least one veteran of the Atlanta Student Movement, a Civil Rights-era organization.
But there was a consistent message: Uninviting the president of the United States was not an option. When students raised questions about endowment investments in Israel and U.S. defense contractors, they said they were told the relevant amounts are negligible, a few hundred thousand dollars in mutual funds.
“I think folks are excited” about Biden coming, said Democratic Georgia Sen. Raphael Warnock, the senior pastor at King’s Ebenezer Baptist Church in Atlanta. Warnock said Biden is in “a great position” to talk about student debt relief , increased federal support for HBCUs and other achievements.
HBCUs have not seen crackdowns from law enforcement like those at Columbia University in New York City and the University of California, Los Angeles. However, Morehouse and the AUC have seen peaceful demonstrations, petitions and private meetings among campus stakeholders. Xavier University, a historically Black university in Louisiana, withdrew its commencement invitation for U.N. Ambassador Linda Thomas-Greenfield , citing a desire among students “to enjoy a commencement ceremony free of disruptions.”
Whether Morehouse graduates or other students protest Biden or disrupt the ceremony remains to be seen. Student protest leaders say they are unaware of any plans to demonstrate inside during the commencement.
Thomas, Morehouse’s president, promised that forms of protest at commencement that “do not disrupt ceremonies” will not result in sanctions for any students.
But he also vowed to end the program early if disruptions grow.
“We will not — on Morehouse’s campus — create a national media moment,” he said, “where our inability to manage these tensions leads to people being taken out of a Morehouse ceremony in zip ties by law enforcement.”

- Nation & World
- Nation & World Politics
Biden’s upcoming graduation speech roils Morehouse College, a center of Black politics and culture
ATLANTA (AP) — When he gives the commencement address at Morehouse College, President Joe Biden will have his most direct engagement with college students since the start of the Israel-Hamas war at a center of Black politics and culture.
Morehouse is located in Atlanta, the largest city in the swing state of Georgia, which Biden flipped from then-President Donald Trump four years ago. Biden’s speech Sunday will come as the Democrat tries to make inroads with a key and symbolic constituency — young Black men — and repair the diverse coalition that elected him to the White House.
The announcement of the speech last month triggered peaceful protests and calls for the university administration to cancel over Biden’s handling of the war between Israel and Hamas. Some students at Morehouse and other historically Black campuses in Atlanta say they vociferously oppose Biden and the decision to have him speak, mirroring the tension Biden faces in many communities of color and with young voters nationally.
Morehouse President David Thomas said in an interview that the emotions around the speech made it all the more important that Biden speak.
“In many ways, these are the moments Morehouse was born for,” he said. “We need someplace in this country that can hold the tensions that threaten to divide us. If Morehouse can’t hold those tensions, then no place can.”
The speech comes at a critical moment for Biden in his general election rematch against Trump, a Republican. Biden is lagging in support among both Black voters and people under 30, groups that were key to his narrow 2020 victories in several battleground states, including Georgia.
Fifty-five percent of Black adults approved of the way Biden is handling his job as president, according to an AP-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research poll in March, a figure far below earlier in his presidency. Overall, 32% of 18- to 29-year-olds approved in the same poll.
“This is a global catastrophe in Gaza, and Joe Biden coming to pander for our votes is political blackface,” said Morehouse sophomore Anwar Karim, who urged Thomas and school trustees to rescind Biden’s invitation.
Recent scenes on American campuses reflect objections among many young voters about Israel’s assaults in Gaza. Biden has backed Israel since Hamas militants killed more than 1,200 Israelis and took hundreds of hostages on Oct. 7. That includes weapons shipments to the longstanding U.S. ally, even as Biden advocates for a cease-fire, criticizes Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s tactics and the death toll in Gaza surpasses 35,000 people, many of them women and children.
Many younger Black people have identified with the Palestinian cause and have at times drawn parallels between Israeli rule of the Palestinian territories and South Africa’s now-defunct apartheid system and abolished Jim Crow laws in the U.S. Israel rejects claims that its system of laws for Palestinians constitutes apartheid.
“I think that the president will do himself good if he does not duck that, especially when you think about the audience that he will be speaking to directly and to the nation,” Thomas said.
Sunday’s speech will culminate a four-day span during which Biden will concentrate on reaching Black communities. On Thursday, Biden met privately with plaintiffs from the Brown v. Board of Education case that barred legal segregation of America’s public schools. The following day, Biden will address an NAACP gathering commemorating the 70th anniversary of the landmark decision.
Former U.S. Rep. Cedric Richmond, a longtime Biden ally who helped broker his speech at Morehouse, said he understood students’ concerns but emphasized that Biden has pressured Netanyahu and supports a two-state solution for the Israelis and Palestinians. Trump, meanwhile, has effectively abandoned that long-held U.S. position and said Israel should “finish the problem” in Gaza.
“That’s nowhere in the conversation,” Richmond said.
The debate over Biden’s speech at Morehouse reflected a fundamental tension of historically Black colleges and universities, which are both dedicated to social justice and Black advancement and run by administrators who are committed to keeping order.
“We look like a very conservative institution” sometimes, Thomas said. “On one hand, the institution has to be the stable object where we are today in the world.”
But, he added, the university’s long-term purpose is to “support our students in going out to create a better world.”
Blowback started even before Thomas publicly announced Biden was coming. Faculty sent executives a letter of concern, prompting an online town hall. Alumni gathered several hundred signatures to urge that Thomas rescind Biden’s invitation. The petition called the invitation antithetical to the pacifism Martin Luther King Jr., a Morehouse alumnus, expressed when opposing the Vietnam War.
Some students note that leaders of Morehouse and other HBCUs did not always support King and other Civil Rights activists who are venerated today. Morehouse, for instance, expelled the actor Samuel L. Jackson in 1969 after he and other students held Morehouse trustees, including King’s father, in a campus building as part of demanding curriculum changes and the appointment of more Black trustees.
Students organized two recent protests across the Atlanta University Center (AUC), a consortium of historically Black institutions in Atlanta that includes Morehouse. Chants included “Joe Biden, f— off!” and “Biden, Biden, you can’t hide. We charge you with genocide,” along with expletives directed at Thomas.
“Our institution is supporting genocide, and we turn a blind eye,” said Nyla Broddie, a student at Spelman College, which is part of the AUC. Brodie argued Biden’s Israel policy should be viewed in the broader context of U.S. foreign policy and domestic police violence against Black Americans.
Thomas said he “feels very positive about graduation” and that “not one” Morehouse senior — there are about 500 at the all-male private school — has opted out of participating. “That’s not to say that the sentiments about what’s going on in Gaza don’t resonate with people in our community,” Thomas said.
Most Read Nation & World Stories
- Bones found in 1989 in a Wisconsin chimney identified as man who last contacted relatives in 1970
- Iran’s hard-line president still missing after likely helicopter crash in foggy, mountainous region VIEW
- Sports on TV & radio: Local listings for Seattle games and events
- She couldn’t call, so human trafficking victim texted 911 — and saved herself, officials say
- Rudy Giuliani served Arizona indictment papers for election fraud scheme at 80th birthday party
Thomas met privately with students as did several trustees. The Morehouse alumni association hosted a student town hall, featuring at least one veteran of the Atlanta Student Movement, a Civil Rights-era organization.
But there was a consistent message: Uninviting the president of the United States was not an option. When students raised questions about endowment investments in Israel and U.S. defense contractors, they said they were told the relevant amounts are negligible, a few hundred thousand dollars in mutual funds.
“I think folks are excited” about Biden coming, said Democratic Georgia Sen. Raphael Warnock, the senior pastor at King’s Ebenezer Baptist Church in Atlanta. Warnock said Biden is in “a great position” to talk about student debt relief, increased federal support for HBCUs and other achievements.
HBCUs have not seen crackdowns from law enforcement like those at Columbia University in New York City and the University of California, Los Angeles. However, Morehouse and the AUC have seen peaceful demonstrations, petitions and private meetings among campus stakeholders. Xavier University, a historically Black university in Louisiana, withdrew its commencement invitation for U.N. Ambassador Linda Thomas-Greenfield, citing a desire among students “to enjoy a commencement ceremony free of disruptions.”
Whether Morehouse graduates or other students protest Biden or disrupt the ceremony remains to be seen. Student protest leaders say they are unaware of any plans to demonstrate inside during the commencement.
Thomas, Morehouse’s president, promised that forms of protest at commencement that “do not disrupt ceremonies” will not result in sanctions for any students.
But he also vowed to end the program early if disruptions grow.
“We will not — on Morehouse’s campus — create a national media moment,” he said, “where our inability to manage these tensions leads to people being taken out of a Morehouse ceremony in zip ties by law enforcement.”
NFL | Chiefs’ Harrison Butker tells women their ‘most…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Chicago Bears
- Chicago Bulls
- Chicago Blackhawks
- Chicago Cubs
- Chicago White Sox
- Chicago Sky
- College Sports
NFL | Chiefs’ Harrison Butker tells women their ‘most important title’ should be ‘homemaker’ in commencement address

The three-time Super Bowl champion delivered the roughly 20-minute address Saturday at the Catholic private liberal arts school in Atchison, Kansas, which is located about 60 miles north of Kansas City.
Butker, who has made his conservative Catholic beliefs well known, began his address by attacking what he called “dangerous gender ideologies” in an apparent reference to Pride month, which has been celebrated in June since the Stonewall riots in 1969. He also criticized an article by The Associated Press highlighting a shift toward conservativism in some parts of the Catholic Church.
The 28-year-old Butker then took aim at Biden’s policies, including his response to COVID-19, which has killed nearly 1.2 million people in the U.S., according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“While COVID might have played a large role throughout your formative years, it is not unique,” he said. “The bad policies and poor leadership have negatively impacted major life issues. Things like abortion, IVF, surrogacy, euthanasia, as well as a growing support for the degenerate cultural values and media all stem from pervasiveness of disorder.”
Butker later addressed the women in the audience, arguing that their “most important title” should be that of “homemaker.”
“I think it is you, the women, who have had the most diabolic lies told to you,” Butker said. “Some of you may go on to lead successful careers in the world, but I would venture to guess that the majority of you are most excited about your marriage and the children you will bring into this world. I can tell you that my beautiful wife Isabelle would be the first to say her life truly started when she started living her vocation as a wife and as a mother.”
The Chiefs declined to comment on Butker’s commencement address.
The 2017 seventh-round pick out of Georgia Tech has become of the NFL’s best kickers, breaking the Chiefs’ franchise record with a 62-yard field goal in 2022. Butker helped them win their first Super Bowl in 50 years in 2020, added a second Lombardi Trophy in 2023, and he kicked the field goal that forced overtime in a Super Bowl win over San Francisco in February.
It has been an embarrassing offseason for the Chiefs, though.
Last month, voters in Jackson County, Missouri, soundly rejected a ballot initiative that would have helped pay for a downtown ballpark for the Royals and an $800 million renovation to Arrowhead Stadium, the home of the Chiefs. Many voters criticized the plan put forward by the Chiefs as catering primarily to VIPs and the wealthy.
The same week, wide receiver Rashee Rice turned himself into Dallas police on multiple charges, including aggravated assault, after he was involved in a high-speed crash that left four people with injuries. Rice has acknowledged being the driver of one of the sports cars that was going in excess of 100 mph, and video shows him leaving the scene without providing information or determining whether anyone needed medical attention.
Last week, law enforcement officials told The Dallas Morning News that Rice also was suspected of assaulting a person at a downtown nightclub; Dallas police did not name Rice as the suspect in detailing a report to The Associated Press.
Chiefs coach Andy Reid said he had spoken to the receiver and the team was letting the legal process play out.
More in NFL

NFL | Arizona Cardinals rookie Marvin Harrison Jr. sued by apparel manufacturer Fanatics for breach of contract

Sports | Kofi Hughes used football to hide from his struggles. Now he shares his experience while training a new generation of athletes.

Chicago Bears | Chicago Bears Q&A: How does Las Vegas view the over/under win total? What’s the game of the year on the schedule?

NFL | NFL distances itself from Harrison Butker after Chiefs kicker’s comments during a commencement speech
Trending nationally.

La. bill targeting free speech on college campuses advances
BATON ROUGE, La. (KALB) - A Louisiana bill seeing outcry from college officials and students aims to redefine what is considered “protected speech” for protests on college campuses.
Under current law , “expressive activities” is considered as, “any lawful verbal or written means by which individuals or groups communicate ideas to one another.” The law’s definition applies to all forms of peaceful protest, assembly and petition circulation.
Senate Bill 294 by State Senator Valarie Hodges would keep the current law’s definition and instead change the term “free expression” to “free speech and First Amendment-protected expressive activities.”
SB294 would additionally create free speech exclusions for protest groups being monetarily funded by organizations that are designated by the U.S. Dept. of State as a “foreign terrorist organization” or “foreign adversary.”
The proposed legislation would also expand the protections of college students from “ student-on-student discriminatory harassment” by granting the protections of the “protected class” to all students.
Hodges said the pro-Palestinian protests seen across the nation were not protected under free speech, calling the protests “riots.”
“We’ve seen the riots, the protests across the nation where innocent students were being terrorized, where they're blocking access to classes and taking over buildings. And this is not protected free speech, this is criminal." State Senator Valarie Hodges, (R) District 13
Central Louisiana State Representative Charles “Chuck” Owens commented on the bill during a House Education Committee hearing, saying the state is not obligated to allow a terrorist organization to support a protest group on a college campus.
“We are not obliged as a state to allow the material support of terror organizations, of criminal activities, that are funded from outside this country, who want to come in here and they want to do things on our property.” State Representative Charles “Chuck” Owens, (R) District 30
The bill saw testimonies from several state university professors and students, who argued the proposed law was “not the right answer” and could curb protestor rights to the First Amendment.
The bill unanimously passed through the House Committee on Education and has been referred to the Legislative Bureau. You can track the status of the bill here .
Click here to report a typo. Please provide the title of the article in your email.


COMMENTS
In fact, I believe college is more important than ever," she told them in her speech titled "The Case for College." Faust took on the critics of college point by point. "There is no doubt that college pays off financially," she said. "A wide range of statistics shows the economic advantage of a four-year college education."
The image is one of adequate space to do your work, secure in the knowledge that nobody is looking over your shoulder to enforce ideological conformity. For the university to do its job of ...
Speech on Importance of Education in English for Students. In one's life, education is an important concern. It is the key to a successful future and to the numerous opportunities we come across in our lives. For an individual, education has many advantages. It not only enlightens the mind but also enhances the thought process of a person.
Administrative awakenings in relation to free speech on college campuses are the result of student activism, and also the fact that universities are a primary target in the current culture wars, Ben-Porath says. University leaders have trepidations about how the higher education sector is perceived. She says where a person stands on the issue ...
He said, "Seek ye diligently and teach one another words of wisdom; yea, seek ye out of the best books words of wisdom; seek learning, even by study and also by faith." 2 He commanded early Church leaders to "study and learn, and become acquainted with all good books, and with languages, tongues, and people." 3.
Political scientist David Primo has made promoting free speech on college campuses, including at the University of Rochester, a pedagogical priority. (University of Rochester / Adrian Knaus) 1. Heeding John Stuart Mill on the importance of 'the heretics'. "You may say there are some people who just shouldn't be able to speak—those ...
The "Knight-Ipsos College Student Views on Free Expression and Campus Speech" report is the fourth in a series of Knight Foundation reports measuring college student attitudes toward speech and the First Amendment since 2016. For this report, Knight Foundation commissioned Ipsos to conduct a survey with a nationally representative sample of over 1,000 college students ages 18-24 enrolled ...
Alex Bernadotte is the founder and CEO of Beyond 12, a high-tech, high-touch nonprofit that integrates personalized coaching and intelligent technology to increase the college graduation rates of underserved students. She has more than twenty years of executive management and strategic development experience in the nonprofit and private sectors ...
6 past Harvard Commencement speakers offer inspiring messages of justice, courage, resilience, empathy. Harvard graduates this week will hear from two high-profile leaders, New Zealand Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern and U.S. Attorney General Merrick Garland, Thursday and Sunday. Ahead of the ceremonies, we look back at Commencement addresses ...
Author: King, Martin Luther, Jr. (Morehouse College) Date: January 1, 1947 to February 28, 1947 Location: Atlanta, Ga. Genre: Published Article Topic: Martin Luther King, Jr. - Political and Social Views Details. Writing in the campus newspaper, the Maroon Tiger, King argues that education has both a utilitarian and a moral function. 1 Citing the example of Georgia's former governor Eugene ...
I decided to put some of my coding tools to work, analyzing 100 of the most popular recent commencement speeches. Here are the four tips they all contain: 1. Dream big. "I think it is often easier to make progress on mega-ambitious dreams. I know that sounds completely nuts. But, since no one else is crazy enough to do it, you have little ...
The graduation rate was 50% when Johnston took over as principal. He managed to hit 100% -- with all admitted to college - in the first year. The speech reveals how he did it. But the speech ...
I'd be happy to suggest some engaging and college-related topics for your persuasive speech! 1. Mental health on college campuses: Discuss the importance of mental health support, resources, and awareness in college settings, and propose solutions for improving mental health services for students. 2. Financial aid packages and accessibility: Advocate for more transparency in financial aid ...
Video playlists about Education. 17 talks. The Butterfly Effect: Talks from the TEDinArabic Summit. In March 2023, 17 speakers from across the world gathered in Doha for the inaugural TEDinArabic Summit. From climate change and politics to sports and fashion, enjoy this sweeping selection of talks. 15 talks.
First Lady Michelle Obama speaks to sophomore class at Bell Multicultural High School in Washington, D.C. and addresses the importance of higher education an...
Importance of Education to a Person's Life. 1. Education helps people out of poverty. Poverty is linked to low education. Families that are poor are usually less educated than families that are rich. Plus, if you are born into a low educated poor family, chances are high that you too will end up low educated and poor.
February 27, 2023 by Prasanna. Importance of Education Speech: Education is an integral part of human lives. Education and knowledge are not only essential for personal development, but it is also required for the development of the economy. Education nurtures an individual's thinking and supplies them with the ability to think, act and grow ...
The Power of Speech & Debate Education. Debate is a valuable activity for students of all skill levels. Debate teaches useful skills for other academic pursuits and life more generally. Most obviously, debaters build confidence speaking in public and expressing their ideas eloquently. That comfort speaking in front of others is useful in so ...
10 Quotes on Importance of Education. Here are 10 quotes on the importance of education. Feel free to add these quotes to your speech or any writing topics. 'Live as if you were to die tomorrow. Learn as if you were to live forever.'. - Mahatma Gandhi. 'The great aim of education is not knowledge but action.'. - Herbert Spencer.
10 Lines Speech on Importance of Education. Education gives people the ability to think critically and form opinions on a variety of issues. Education also allows us to learn about our history, roots, culture, and history. Everyone in society should understand the importance and value of education in their lives.
Education is an essential aspect of human development. Education is a means of achieving a world of peace, justice, freedom, and equality for all. Thus, education is extremely necessary for all. No good life is possible without education. It indorses the intelligence of human beings, develops his skill, and enables him to be industrious.
Speech on Importance of Education. Education is a procedure of learning where knowledge, skills, and habits move from one generation to the other. Moreover, education is essential for the overall development of a human being. For instance, their personal, social as well as the economic development of the country.
Speech and debate offers students a chance to demonstrate the best that they have to offer and then benefit from the (sometimes-painful) wisdom of others. When constructive criticism presents opportunities to improve, successful debaters learn to accept it with grace and poise. Speech and debate opens a new door for self-growth.
Biden will have his most direct engagement with college students since the start of the Israel-Hamas war when he speaks at Morehouse College's commencement. (AP Photo/Patrick Semansky, File)
Facing potential headwinds with both young voters and Black voters, President Biden's Morehouse College commencement address focused on his view of the importance - and future of - democracy.
A student complained on a Reddit thread that he had heard the speech five times in six years—at his high-school, college, and graduate-school commencements, and at his sister's high-school and ...
Sunday's speech will culminate a four-day span during which Biden will concentrate on reaching Black communities. On Thursday, Biden met privately with plaintiffs from the Brown v. Board of Education case that barred legal segregation of America's public schools. The following day, Biden will address an NAACP gathering commemorating the ...
Former U.S. Rep. Cedric Richmond, a longtime Biden ally who helped broker his speech at Morehouse, said he understood students' concerns but emphasized that Biden has pressured Netanyahu and ...
Butker later addressed the women in the audience, arguing that their "most important title" should be that of "homemaker." "I think it is you, the women, who have had the most diabolic ...
SB294 would additionally create free speech exclusions for protest groups being monetarily funded by organizations that are designated by the U.S. Dept. of State as a "foreign terrorist ...