

The Difference between an Essay and a Letter
While your grandmother would probably be happy and proud to read your latest essay, she'd more than likely prefer that you just write her a nice letter. The reason is that the audience and point of a letter are usually more personal. If you really want to impress her with how smart you are, you can also send her a letter using the formal structure.

Structure in letter-writing can be quite specific. For a traditional formal letter, an address is printed at the top of the page, a greeting or salutation to the intended recipient or group of recipients begins the writing portion, the body can be made up of single or multiple paragraphs, and a signature by the writer is expected at the end.
The structure of a traditional essay is also specific, but quite different from a letter. Essays begin with a headline, include a thesis statement, have multiple paragraphs with topic sentences that relate back to and further explain the thesis of the essay, and a concluding paragraph that sums up the body's points come at the end.
Who are You Talking To?
Essays and formal letters usually have different audiences. Letters are written with a recipient or group of recipients in mind and are not required to make sense to anyone but those recipients. For instance, if you write a letter to your grandmother asking for details on the family reunion, you probably won't have to explain the history of your family reunions. She's been to all of them, so she already knows Aunt Marge will be bringing the potato salad and that no one will want to eat it.
An essay should make a point clear to anyone who reads it. An idea must be presented in the form of a thesis statement and then must be fully explained to an intended audience that a writer assumes has no background information on the subject. That audience can be anyone, there is rarely anything too personal in the communication between a writer and an essay reader.
What's Your Point?
Like an essay, some letters are written with the intention to inform its readers. However, many letters are written with no other purpose than communication. This is why the tone of a letter is generally far less formal than an essay and rarely requires that the writer provide backup arguments or sources.
Sending a surprise letter to a family member or friend makes you a good communicator. Sending an essay to anyone who didn't ask for one just makes you look like a show-off.
How Academic Writing Differs from Other Forms of Writing
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
Have you ever wondered how academic writing stacks up against different styles of writing? If you have, then you're in good company, as many curious minds have pondered that same distinction. Let's get to it!
Formal Language versus Informal Language
Academic writing should use formal language that minimizes the use of contractions and colloquialisms and avoids slang terminology whenever possible. Casual language should only be used for emphasis.
Further, academic writing generally does not employ first person pronouns like "I" or "we," but different styles of writing do offer varying degrees of flexibility when it comes to the use of language, with a diverse range of informal elements sanctioned among different styles of writing.
Check out the image below to further explore the differences between textspeak, informal language, and formal language!
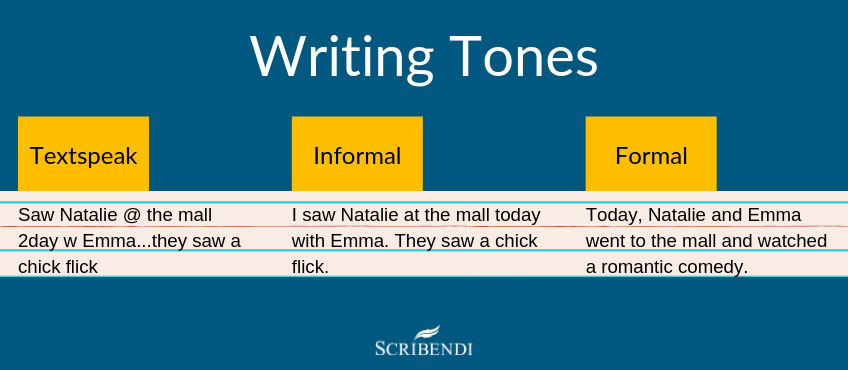
Structure and Form
Style guides like the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA) and the Chicago Manual of Style are quintessential resources for scholars engaging in academic writing, with different style guides used for different fields of academia. These style guides standardize how references should be presented and how a document should be formatted, considering things like the margins, headings, typeface, and a myriad of other elements; some guides even prescribe the kind of language to be used for various circumstances encountered most frequently within the field.
All forms of academic writing will employ a structure that should allow the information presented to flow logically from one section to the next, regardless of the segments or formatting details used according to different styles of writing. For example, a scientific research article will typically include sections for the abstract, introduction, methods, analysis, results, and conclusions, whereas a paper written for the humanities will use a drastically different framework that can vary between artistic disciplines.
Different styles of writing contain various essential structural elements. This means that some styles, such as creative writing, grant significantly more freedom to the author than other styles, such as the style used for writing engineering documents.
The tone used to communicate ideas will significantly affect how readers interpret those ideas. It's vital that different styles of writing adopt different tones appropriate for the respective target audiences.
It's especially crucial within academic writing to eliminate all personal biases, both explicit and implicit. Academic writing must display objectivity. It's often best that academic writing avoids rhetorical tactics, like sweeping generalizations and emotional arguments, as this will ensure the highest degree of objectivity expected from academic writing.
At its core, academic writing should be clear, succinct, and objective; the exact criteria for these qualities differ among different styles of writing, but without these elements, the credibility of academic writing is often shaky.
The tone, language, and formality of academic writing will all depend on the target audience . As such, the target audience is a crucial consideration for effective academic writing.
In an academic setting, your audience could comprise researchers, professors, and/or experts in the field, but a casual piece might target your family and friends. The way we speak to figures of authority is very different from how we speak to siblings or friends, and communicating with these different groups when writing is no different; the word choices used in academic writing should suit the audience just as much as a person's vocabulary and gestures might shift for face-to-face communication according to these different groups.
For example, when the public is the intended audience for a piece of academic writing, it's probably a good idea to use simple language to explain any tricky terms used in the document. You might even consider substituting the academic jargon for another phrase more easily understood by the masses. This is true for all different styles of writing. The audience needs to understand what has been written!
If you're uncertain whether a particular term might be appropriate for your audience, try consulting a friend who is unfamiliar with the topic. This should clearly indicate how easy it might be for the average person to understand the concept.
The following piece of advice applies to all different styles of writing: leave time to edit! Regardless of the document, your work should be entirely free from errors. Proofreading for things like grammatical mistakes and punctuation errors and editing for elements such as the word choices and sentence structures will ensure that the writing is cohesive and clear. Further revision will ensure that unsightly grammatical errors and embarrassing typos never appear before the unforgiving public eye.
Have a peek at the image below to review the key aspects of academic writing (you can even download the image for reference). Once these elements have been nailed, you will have officially become a master of academic writing.
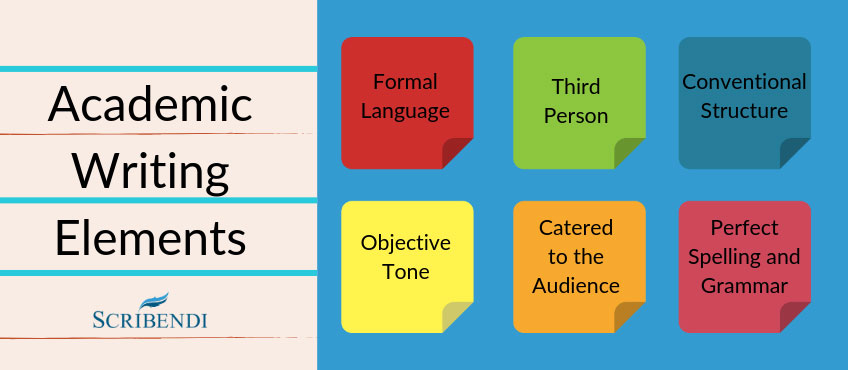
Image source: AboutImages/elements.envato.com
Make Sure Your Academic Writing Follows Conventions
Hire an expert academic editor , or get a free sample, about the author.

Scribendi’s in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing turn into a great one after the editing process. Scribendi’s in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained nearly 20 degrees collectively. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Five Habits to Avoid in Your Academic Writing

How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation

The Ultimate Journal Article Submission Checklist
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).


Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, understanding the 4 writing styles: how to identify and use them.
General Education

A piece’s writing style can help you figure out what kind of writing it is, what its purpose is, and how the author’s voice is unique. With so many different types of writing, you may think it’s difficult to figure out the specific writing style of a piece or you'll need to search through a long list of writing styles.
However, there are actually just four main types of writing styles, and together they cover practically all the writing you see, from textbooks to novels, to billboards and more. Whether you’re studying writing styles for class or trying to develop your own writing style and looking for information, we’ve got you covered.
In this guide, we explain the four styles of writing, provide examples for each one, go over the one thing you need to know to identify writing style, and give tips to help you develop your own unique style of writing.
The 4 Types of Writing
There are four main different styles of writing. We discuss each of them below, list where you’re likely to see them, and include an example so you can see for yourself what each of the writing styles looks like.
Writers who use the narrative style are telling a story with a plot and characters. It’s the most common writing style for fiction, although nonfiction can also be narrative writing as long as its focus is on characters, what they do, and what happens to them.
Common Places You’d See Narrative Writing
- Biography or autobiography
- Short stories
- Journals or diaries
“We had luncheon in the dining-room, darkened too against the heat, and drank down nervous gayety with the cold ale. ‘What’ll we do with ourselves this afternoon?’ cried Daisy, ‘and the day after that, and the next thirty years?’ ‘Don’t be morbid,’ Jordan said. ‘Life starts all over again when it gets crisp in the fall.’ ‘But it’s so hot,’ insisted Daisy, on the verge of tears, ‘and everything’s so confused. Let’s all go to town!’ - The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald
You can quickly tell that this passage from the novel The Great Gatsby is an example of narrative writing because it has the two key traits: characters and a plot. The group is discussing eating and drinking while trying to decide what to do for the rest of the day.
As in this example, narrative writing often has extended dialogue scenes since the dialogue is used to move the plot along and give readers greater insight into the characters.
Writers use the expository style when they are trying to explain a concept. Expository writing is fact-based and doesn’t include the author’s opinions or background. It’s basically giving facts from the writer to the reader.
Common Places You’d See Expository Writing
- Newspaper articles
- Academic journals
- Business memos
- Manuals for electronics
- How-to books and articles
“The 1995/1996 reintroduction of gray wolves (Canis lupus) into Yellowstone National Park after a 70 year absence has allowed for studies of tri-trophic cascades involving wolves, elk (Cervus elaphus), and plant species such as aspen (Populus tremuloides), cottonwoods (Populus spp.), and willows (Salix spp.). To investigate the status of this cascade, in September of 2010 we repeated an earlier survey of aspen and measured browsing and heights of young aspen in 97 stands along four streams in the Lamar River catchment of the park’s northern winter range. We found that browsing on the five tallest young aspen in each stand decreased from 100% of all measured leaders in 1998 to means of <25% in the uplands and <20% in riparian areas by 2010. Correspondingly, aspen recruitment (i.e., growth of seedlings/sprouts above the browse level of ungulates) increased as browsing decreased over time in these same stands.” -”Trophic cascades in Yellowstone: The first 15 years after wolf reintroduction” by William J. Ripple and Robert L. Beschta
This abstract from an academic journal article is clearly expository because it only focuses on facts. The authors aren’t giving their opinion of wolves of Yellowstone, they’re not telling a story about the wolves, and the only descriptions are number of trees, streams, etc. so readers can understand the study better.
Because expository writing is focused on facts, without any unnecessary details or stories, the writing can sometimes feel dense and dry to read.
Descriptive
Descriptive writing is, as you may guess, when the author describes something. The writer could be describing a place, person, or an object, but descriptive writing will always include lots of details so the reader can get a clear and complete idea of what is being written about.
Common Places You’d See Descriptive Writing
- Fiction passages that describe something
“In a hole in the ground there lived a hobbit. Not a nasty, dirty, wet hole, filled with the ends of worms and an oozy smell, nor yet a dry, bare sandy hole with nothing in it to sit down on or eat: it was a hobbit hole and that means comfort. It had a perfectly round door like a porthole, painted green, with a shiny yellow brass knob in the exact middle. The door opened on to a tube-shaped hall like a tunnel: a very comfortable tunnel without smoke, with panelled walls, and floors tiled and carpeted...” - The Hobbit by J.R.R. Tolkien
This is the opening passage of the novel The Hobbit . While The Hobbit is primarily an example of narrative writing, since it explores the adventures of the hobbit and his companions, this scene is definitely descriptive. There is no plot or action going on in this passage; the point is to explain to readers exactly what the hobbit’s home looks like so they can get a clear picture of it while they read. There are lots of details, including the color of the door and exactly where the doorknob is placed.
You won’t often find long pieces of writing that are purely descriptive writing, since they’d be pretty boring to read (nothing would happen in them), instead many pieces of writing, including The Hobbit , will primarily be one of the other writing styles with some descriptive writing passages scattered throughout.
When you’re trying to persuade the reader to think a certain way or do a certain thing, you’ll use persuasive writing to try to convince them. Your end goal could be to get the reader to purchase something you’re selling, give you a job, give an acquaintance of yours a job, or simply agree with your opinion on a topic.
Common Places You’d See Persuasive Writing
- Advertisements
- Cover letters
- Opinion articles/letters to the editor
- Letters of recommendation
- Reviews of books/movies/restaurants etc.
- Letter to a politician
“What General Weygand called the Battle of France is over. I expect that the battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilization. Upon it depends our own British life, and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink by the lights of perverted science. Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves, that if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, ‘This was their finest hour.’ - “This was their finest hour” by Winston Churchill
In this excerpt from his famous “Their finest hour” speech, Prime Minister Winston Churchill is clearing trying to convince his audience to see his viewpoint, and he lays out the actions he thinks they should take. In this case, Churchill is speaking to the House of Commons (knowing many other British people would also hear the speech), and he’s trying to prepare the British for the coming war and convince them how important it is to fight.
He emphasizes how important the fight will be (“Upon this battle depends the survival of the Christian civilization.” and clearly spells out what he thinks his audience should do (“Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties…”).

Common Writing Styles to Know
Each of the four main types of writing styles has multiple subsets of styles within it. Here are nine of the most common and important types of writing you’ll see.
Narrative Writing
Character voice.
Character voice is a common writing style in novels. Instead of having an unknown narrator, the audience knows who is telling the story. This first-person narrator can help the reader relate more both to the narrator and the storyline since knowing who is telling a story can help the reader feel more connected to it. Sometimes the narrator is completely truthful in telling what happens, while other times they are an unreliable narrator and will mislead or outright lie to readers to make themselves look better.
To Kill a Mockingbird (Scout is the narrator) and The Hunger Games (Katniss is the narrator) are two examples of this writing style.
Stream-of-Consciousness
This writing style attempts to emulate the thought process of the character. Instead of only writing about what the character says or does, stream-of-consciousness will include all or most of the characters thoughts, even if they jump from one topic to another randomly or include incomplete thoughts.
For example, rather than writing “I decided to take a walk to the ice cream shop,” an author using the stream-of-consciousness writing style could write, “It’s pretty hot out, and I feel like I should eat something, but I’m not really that hungry. I wonder if we have leftovers of the burgers Mom made last night? Is Mom staying late at work tonight? I can’t remember if she said. Ice cream would be a good choice, and not too filling. I can’t drive there though because my car is still in for repairs. Why is the repair shop taking so long? I should have listened when David said to check for reviews online before choosing a place. I should text David later to see how he is. He’ll think I’m mad at him if I don’t. I guess I’ll just have to walk to the shop.”
James Joyce and William Faulkner are two of the most well-known writers to have regularly used the stream-of-consciousness writing style.
Epistolary writing uses a series of documents, such as letters, diary entries, newspaper articles, or even text messages to tell a story. They don’t have a narrator, there’s just whoever purportedly gathered the documents together. This writing style can provide different points of view because a different person can be the author of each document.
Well-known examples of epistolary writing include the novels Dracula (written as a series of letters, newspaper articles, and diary entries) and Frankenstein (written as a series of letters).
Expository Writing
You’ll find this style in textbooks or academic journal articles. It’ll focus on teaching a topic or discussing an experiment, be heavy on facts, and include any sources it cited to get the information. Academic writing often assumes some previous knowledge of the topic and is more focused on providing information than being entertaining, which can make it difficult to read and understand at times.
Business writing refers to the writing done in a workplace. It can include reports, memos, and press releases. Business writing typically has a formal tone and standard formatting rules. Because employees are presumably very busy at work, business writing is very concise and to the point, without any additional flourishes intended to make the writing more interesting.
You’ll see this writing style most commonly in newspaper articles. It focuses on giving the facts in a concise, clear, and easy-to-understand way. Journalists often try to balance covering all the key facts, keeping their articles brief, and making the audience interested in the story.
This writing style is used to give information to people in a specific field, such as an explanation of a new computer programming system to people who work in software, a description of how to install pipes within a house for plumbers, or a guide to new gene modifications for microbiologists.
Technical writing is highly specialized for a certain occupational field. It assumes a high level of knowledge on the topic, and it focuses on sharing large amounts of information with the reader. If you’re not in that field, technical writing can be nearly impossible to understand because of the jargon and references to topics and facts you likely don’t know.

Descriptive Writing
Poetry is one of the most challenging styles of writing to define since it can come in many forms. In general, poems use rhythmic language and careful word choice to express an idea. A poem can be an example of descriptive writing or narrative writing, depending on whether it’s describing something or telling a story. Poetry doesn’t need to rhyme, and it often won’t follow standard grammatical or structural rules. Line breaks can, and often do, occur in the middle of sentences.
Persuasive Writing
Copywriting.
Copywriting is writing that is done for advertising or marketing purposes. It’s attempting to get the reader to buy whatever the writer is trying to sell. Examples of copywriting include catalogs, billboards, ads in newspapers or magazines, and social media ads.
In an attempt to get the reader to spend their money, copywriters may use techniques such as descriptive language (“This vanilla was harvested from the lush and exotic island of Madagascar"), exciting language (Stop what you’re doing and learn about this new product that will transform your life!”) and exaggeration (“This is the best cup of coffee you will ever taste!”).
Opinion
People write opinion pieces for the purpose of stating their beliefs on a certain topic and to try to get readers to agree with them. You can see opinion pieces in newspaper opinion sections, certain blog posts, and some social media posts. The quality of opinion writing can vary widely. Some papers or sites will only publish opinion pieces if all the facts in them can be backed up by evidence, but other opinion pieces, especially those that are self-published online, don't go through any fact-checking process and can include inaccuracies and misinformation.
What If You’re Unsure of a Work’s Writing Style?
If you’re reading a piece of writing and are unsure of its main writing style, how can you figure which style it is? The best method is to think about what the purpose or main idea of the writing is. Each of the four main writing styles has a specific purpose:
- Descriptive: to describe things
- Expository: to give facts
- Narrative: to tell a story
- Persuasive: to convince the reader of something
Here’s an example of a passage with a somewhat ambiguous writing style:
It can be tricky to determine the writing style of many poems since poetry is so varied and can fit many styles. For this poem, you might at first think it has a narrative writing style, since it begins with a narrator mentioning a walk he took after church. Character + plot = narrative writing style, right?
Before you decide, you need to read the entire passage. Once you do, it’ll become clear that there really isn’t much narrative. There’s a narrator, and he’s taking a walk to get a birch from another man, but that’s about all we have for character development and plot. We don’t know anything about the narrator or his friend’s personality, what’s going to happen next, what his motivations are, etc.
The poem doesn’t devote any space to that, instead, the majority of the lines are spent describing the scene. The narrator mentions the heat, scent of sap, the sound of frogs, what the ground is like, etc. It’s clear that, since the majority of the piece is dedicated to describing the scene, this is an example of descriptive writing.

How Can You Develop Your Own Writing Style?
A distinctive writing style is one of the hallmarks of a good writer, but how can you develop your own? Below are four tips to follow.
Read Many Different Styles of Writing
If you don’t read lots of different kinds of writing, you won’t be able to write in those styles, so before you try to get your own writing style, read different writing styles than what you’re used to. This doesn’t mean that, if you mostly read novels, you suddenly need to shift to reading computer manuals. Instead, you can try to read novels that use unreliable narrators, stream-of-consciousness writing, etc.
The more you read, the more writing styles you’ll be exposed to, and the easier it’ll be able to combine some of those into your own writing style.
Consider Combining Multiple Types of Writing Styles
There’s no rule that you can only use one style for a piece of writing. In fact, many longer works will include multiple styles. A novel may be primarily narrative, but it can also contain highly descriptive passages as well as expository parts when the author wants the readers to understand a new concept.
However, make sure you don’t jump around too much. A paper or book that goes from dense academic text to impassioned plea for a cause to a story about your childhood and back again will confuse readers and make it difficult for them to understand the point you’re trying to make.
Find a Balance Between Comfort and Boundary-Pushing
You should write in a style that feels natural to you, since that will be what comes most easily and what feels most authentic to the reader. An academic who never ventures outside the city trying to write a book from the perspective of a weathered, unschooled cowboy may end up with writing that seems fake and forced.
A great way to change up your writing and see where it can be improved is to rewrite certain parts in a new writing style. If you’ve been writing a novel with narrative voice, change a few scenes to stream-of-consciousness, then think about how it felt to be using that style and if you think it improved your writing or gave you any new ideas. If you’re worried that some writing you did is dull and lacking depth, add in a few passages that are purely descriptive and see if they help bring the writing to life.
You don’t always need to do this, and you don’t need to keep the new additions in what you wrote, but trying new things will help you get a better idea of what you want your own style to be like.
The best way to develop your own writing style is to expose yourself to numerous types of writing, both through reading and writing. As you come into contact with more writing styles and try them out for yourself, you’ll naturally begin to develop a writing style that you feel comfortable with.
Summary: The 4 Different Styles of Writing
There are four main writing styles, and each has a different purpose:
If you’re struggling to figure out the writing style of a piece, ask yourself what its purpose is and why the author wants you to read it.
To develop your own writing style, you should:
- Read widely
- Consider mixing styles
- Balance writing what you know and trying new things
What's Next?
Literary devices are also an important part of understanding writing styles. Learn the 24 literary devices you must know by reading our guide on literary devices.
Writing a research paper for school but not sure what to write about? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.
Are you reading The Great Gatsby for class or even just for fun? Then you'll definitely want to check out our expert guides on the biggest themes in this classic book, from love and relationships to money and materialism .

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

Reports and essays: key differences

Know what to expect
Explore the main differences between reports and essays and how to write for your assignments
You'll complete assignments with different requirements throughout your degree, so it's important to understand what you need to do for each of them. Here we explore the key differences between reports and essays.
This page describes general features of academic reports and essays. Depending on your subject you may use all of these features, a selection of them, or you may have additional requirements.
There is no single right way to write a report or essay, but they are different assignments. At a glance:
- Reports depend heavily on your subject and the type of report.
- Essays usually have specific content and a planned structure with a focus on sense and flow. You subject might need different types of information in your introduction – some disciplines include a short background and context here, while others begin their discussion, discuss their resources or briefly signpost the topic.
Differences between reports and essays
This table compares reports and essays and provides an outline of the standard structure for each. Your assignment will also depend on your discipline, the purpose of your work, and your audience – so you should check what you need to do in your course and module handbooks, instructions from your lecturer, and your subject conventions.
Table adapted from Cottrell, 2003, p. 209.
The structure of reports
Most reports use an IMRaD structure: Introduction, Methods, Results and Discussion.
Below are some common sections that also appear in reports. Some sections include alternative headings.
1. Table of contents
Your contents shows the number of each report section, its title, page number and any sub-sections. Sub-section numbers and details start under the section title, not the margin or the number.
2. Abstract or Executive summary
This brief summary of the report is usually the last thing you write.
3. Introduction
Your introduction describes the purpose of the report, explains why it necessary or useful, and sets out its precise aims and objectives.
4. Literature review
This describes current research and thinking about the problem or research question, and is often incorporated into the introduction.
5. Methods or Methodology
This describes and justifies the methods or processes used to collect your data.
6. Results or Findings
This section presents the results (or processed data) from the research and may consist of mainly tables, charts and or diagrams.
7. Discussion, or Analysis, or Interpretation
This section analyses the results and evaluates the research carried out.
8. Conclusion
The conclusion summarises the report and usually revisits the aims and objectives.
9. Recommendations
In this section the writer uses the results and conclusions from the report to make practical suggestions about a problem or issue. This may not be required.
10. Appendices
You can include raw data or materials that your report refers to in the appendix, if you need to. The data is often presented as charts, diagrams and tables. Each item should be numbered : for example, write Table 1 and its title; Table 2 and its title, and so on as needed.
Structure of essays
Introduction.
Your essay introduction contextualises and gives background information about the topic or questions being discussed, and sets out what the essay is going to cover.
Your essay body is divided into paragraphs. These paragraphs help make a continuous, flowing text.
The conclusion summarises the main points made in the essay. Avoid introducing new information in your conclusion.
Bibliography or Reference list
This is a list of the resources you've used in your essay. This is usually presented alphabetically by authors’ surname.
Reference for the Table of Distinctions above:
Cottrell, S. (2003). The Study Skills Handbook (2nd ed.). Basingstoke: Palgrave.
Download our report and essay differences revision sheet
Download this page as a PDF for your report and essay revision notes.

Key features of academic reports

Basic essay structure

Writing clear sentences
Find an undergraduate or postgraduate degree course that suits you at Portsmouth.

Guidance and support
Find out about the guidance and support you'll get if you need a helping hand with academic life – or life in general – when you study with us at Portsmouth.

Informal Vs. Formal Writing: What’s The Difference?
- What Is Formal Writing?
- What Is Informal Writing?
- Formal Vs. Informal Writing
- Formal Example
- Informal Example
As a writer, you’re faced with a lot of choices related to your writing: how long should your essay be ? Who should be addressed in a cover letter ? What is a thesis statement ? But there’s one question that also applies to every composition: how do you distinguish writing that’s informal vs. formal?
That’s right. Whether a piece is informal or formal will influence everything down to the smallest comma and period. But what, exactly, is the difference between formal and informal writing? When do you use one over the other? Are they really that different? If you are wondering the answers to those questions, then read on as we explore the many different features between formal and informal writing.
What is formal writing ?
First, you should know that it is the intended readers that will determine if a writer should use formal writing or informal writing . Generally, formal writing is defined as writing targeted toward an audience that a person doesn’t personally know. Typically, formal writing is used when a person wants their writing to be viewed as professional, polite, authoritative, or some combination thereof. For this reason, formal writing is often used in professional settings. For example, formal writing is often the form of writing used in research and academic papers, corporate memos and emails, press releases, and job applications.
What is informal writing ?
Informal writing is the inverse of formal writing . In a manner of speaking, informal writing is the T-shirt-and-jeans counterpart to formal writing’s dress coat and pants. In general, informal writing is defined as writing targeted toward an audience that the writer knows personally or with whom the writer wants to establish a friendly tone. Informal writing may include inside jokes, slang, abbreviations, and local colloquialisms .
As you might expect, informal writing is common in casual settings such as social media and in texting between friends. However, you will often see informal writing used in other situations, such as in literature or in lighthearted feature stories in newspapers and magazines.
Formal vs. informal writing
There are many differences between formal and informal writing. We will cover a large number of them here, but this list won’t be exhaustive. Still, you should have a good idea how formal and informal writing differ after looking at these different features.
Grammar, spelling, and punctuation
In almost all cases, formal writing adheres to the proper rules of grammar, spelling, and punctuation . Informal writing, on the other hand, may not. A person may not intentionally break the rules of grammar in informal writing, but they know that a reader is unlikely to care about errors or nonstandard sentence structure.
- Formal writing: The writing was clear but had several mistakes; you should revise and redraft the article.
- Informal writing: The writing was clear, but had alot of mistakes… u should revise and redraft the article.
Formal writing doesn’t always have to follow stuffy, antiquated rules. Check out 5 formulaic writing rules you can explore breaking.

Sentence length
Generally speaking, formal writing often uses long, complex sentences that are connected using transitions. Informal writing often includes shorter sentences that may abruptly move from topic to topic.
- Formal writing: Surprise inspections will be performed on a regular basis as determined by the acting supervisor, who has the authority to request them as needed. Furthermore, employees should be prepared to submit their work for review in a timely fashion.
- Informal writing: I love my new sweater! Thank you!! Where do you want to meet for lunch?
Vocabulary and tone
Typically, formal writing has a serious tone and uses a sophisticated vocabulary that often includes large, complex words. Additionally, formal writing often uses technical terms that match the topic being discussed. For example, a medical text using formal writing will often use the term tibia rather than shinbone or a similar term. Informal writing will often instead have a lighter tone that uses simpler, commonly used words.
- Formal writing: The research team expeditiously and meticulously analyzed the findings in order to identify the origin of the Staphylococcus infection.
- Informal writing: We were out back chopping down some trees when Mom called.
Third person vs. first person/second person
In general, formal writing is usually written from the third person . Formal writing typically avoids using first- or second-person pronouns such as I, me, we, us, and you . By contrast, informal writing often uses first-, second-, and third-person perspectives while making frequent use of personal pronouns. Because of this difference, formal writing is also more likely to use the passive voice in order to avoid using a first- or second-person perspective.
- Formal writing: The data were gathered by using sorting algorithms.
- Informal writing: I used sorting algorithms to gather the data.
Make Your Writing Shine!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Word choice
In general, formal writing will most likely avoid using many of the words or phrases that our dictionary has tagged as being informal. This includes terms such as wanna , gotta , gonna , ‘nuff , kerfuffle, cept, ’Merica, thingamajig , and many other examples of informal language. Relatedly, phrasal verbs are also often typically not used in formal writing . Formal writing will also typically avoid using slang, euphemisms , colloquialisms, expletives, vulgarities, nonstandard abbreviations, jargon , and online acronyms.
- Formal writing: Gregory wanted to remove the items from the box, but it was sealed tightly. Being unable to find scissors, he admitted defeat and ate a sandwich.
- Informal writing: Greg was dying to get the stuff outta the box, but the box was like it ain’t happening bro lol. He couldn’t find the damn scissors, so he said the hell with it and bounced to go scarf a hoagie.
Interjections
Typically, interjections are not used in formal writing . Going further, exclamation points usually don’t appear very often in formal writing. Both interjections and exclamation points are used in informal writing.
- Formal writing: The mixture violently erupted, catching bystanders unaware.
- Informal writing: The stuff exploded! Wow!
Contractions
Typically, contractions are avoided in formal writing , and the words are instead spelled out. In informal writing, contractions are commonly used.
Examples:
- Formal writing: The team would have purchased extra materials, but the store was not open.
- Informal writing: The team would’ve purchased extra materials, but the store wasn’t open.
Objectivity
In general, formal writing is usually written objectively . In most cases, writers attempt to avoid stating subjective thoughts or presenting personal opinions in the main text of formal writing. When presenting arguments in formal writing, writers often calmly present their side backed by supporting evidence and trustworthy sources . Informal writing can include (strongly worded) personal opinions, emotional appeals, and inflammatory language presented without evidence or supporting facts.
- Formal writing: As the evidence clearly shows, the director severely miscalculated production costs when initially presenting the film’s budget.
- Informal writing: The incompetent buffoon who claims to be a professional director blew the budget so badly that the studio should fire him as soon as possible.
Formal writing often entails referencing or researching what others have written. Check out these tips to avoid plagiarism.
Example of formal writing
The following excerpt shows an example of formal writing that was used in a statement released by American president Joe Biden:
Love is love, and Americans should have the right to marry the person they love. Today’s bipartisan vote brings the United States one step closer to protecting that right in law. The Respect for Marriage Act will ensure that LGBTQI+ couples and interracial couples are respected and protected equally under federal law, and provide more certainty to these families since the Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs . I want to thank the Members of Congress whose leadership has sent a strong message that Republicans and Democrats can work together to secure the fundamental right of Americans to marry the person they love. I urge Congress to quickly send this bill to my desk where I will promptly sign it into law.
Example of informal writing
The following example of informal writing is a review of the movie Fight Club by a user of the aggregator website Metacritic:
Best movie of all time. Period. Seen it more than 28 times. Its a bible of what we have to learn. I say you are not your clothes. You are not the brands u wear, even when u think they re part of ur personality. Comb your hair. I ll tell everyone here the end of the movie, but that its not what this movie is about. First rule of fight club is… you do not talk about fight club. And if u havent seen this film then you are a hollow shell. Become human again and start by watching this lesson.
Explore the resources we've created for you to help up your writing game, all in one place.

Ways To Say
Synonym of the day
IELTS Preparation with Liz: Free IELTS Tips and Lessons, 2024
- Test Information FAQ
- Band Scores
- IELTS Candidate Success Tips
- Computer IELTS: Pros & Cons
- How to Prepare
- Useful Links & Resources
- Recommended Books
- Writing Task 1
- Writing Task 2
- Speaking Part 1 Topics
- Speaking Part 2 Topics
- Speaking Part 3 Topics
- 100 Essay Questions
- On The Day Tips
- Top Results
- Advanced IELTS
IELTS General Training & Academic Writing Differences Explained
Learn about IELTS GT (General Training) exam content and writing tasks. Learn how the IELTS GT writing is different from the academic writing test. Useful links are provided for GT students below.
Understanding GT IELTS
- The GT listening test is the same as the academic test. Everyone takes the same listening test with the same scoring. You can use my free listening lessons and tips for your preparation. Click here: Free Listening Tips & Lessons
- The GT speaking test is the same for everyone. There is one speaking test only with the same scoring. You can use my free speaking lessons and tips for your preparation. Click here: Speaking Tips & Model Answers
- The GT reading test is slightly different. The question types are 100% the same as the academic test, but the passages have a different content and layout. You can use my free reading lessons and tips for your preparation, but make sure you do full authentic GT reading tests at home. See this page for more GT reading information: GT Reading Tips. Click here to use my Free Reading Lessons for All Candidates
- To understand GT writing (both task 1 and task 2), see all the tips and information listed below.
This page will explain both writing task 1 differences and writing task 2 differences.
IELTS GT Differences for Writing Task 1
General training students will need to write a letter for writing task 1 but academic students will need to write a report.
- GT Writing Task 1 = Letters: Formal, informal and semi-formal
- Academic Writing Task 1 = Report: table, pie chart, bar chart, line graph etc.
This means writing task 1 is completely different for GT candidates. GT candidates do NOT get charts, they are given letters only. See the information below:
General Training Writing Task 1 Letter
Use the following 10 tips and links to ensure you understand GT letters properly
- Candidates are required to write a letter which can be formal, semi-formal or informal.
- A list of points is given for the letter as well as the aim. It is your task to make sure your letter covers all points with a clear aim.
- Pay attention to opening lines, closing statements, paragraphs etc.
- You also need to pay attention to style and tone depending on whether the letter is formal or informal.
- Get to know the scoring for task 1 – see below. Remember, task 1 is worth only 33% of your writing marks.
- You must write over 150 words. But it is recommend not to write over 200 words.
- It is recommended to take no more than 20 minutes for this task. It is up to you to manage the one hour given for the whole writing test.
- GT students are NOT asked to write a report on a chart or graph.
- Sample Practice Letters for GT Students
- MUST READ: Essential Tips for IELTS GT Letters
Academic Task 1 Report
- Students must analyse a chart, graph, table, map or diagram.
- Students must highlight key features and present data or information.
- Students must write over 150 words.
- It is recommended to take no more than 20 minutes for this.
- IELTS Sample Academic Charts
IELTS Writing Task 1 Scoring
There are four marking criteria for IELTS writing task 1.
Only one criterion is different for GT students.
- Task Achievement General Training : This refers to using the appropriate tone and also purpose. It also relates to the word count.
- Task Achievement Academic : This is about presenting key features, having an overview and accurate information. This also relates to the word count.
- Coherence and Cohesion : This is the same for both GT and Academic. It is based on organisation of information, paragraphing and linking devices.
- Lexical Resource (Vocabulary): This is marked using the same band scores for both GT and Academic. This is about using appropriate language, using collocations and the number of errors made.
- Grammar : This is also marked using the same band scores for both GT and Academic. This is about using a range of grammar structures and tenses, punctuation and the number of errors made.
Each criterion is 25% of your total marks for writing task 1. The scoring is the same as the Academic Writing Task 1 test and used the same Band Score Descriptors, which you can find on IELTS.org. However, there is slight differences in aims with Task Achievement and that is shows in the descriptors.
IELTS GT Differences for Writing Task 2
There are only minimal differences between IELTS general training writing task 2 and the academic task 2. GT candidates can use all my free writing task 2 lessons to prepare. Click here: Free Writing Task 2 Tips & Model Essays. You can also benefit from my advanced lessons and e-books which you can find in my online store: Liz’s Store
Below is a list of the minor differences and similarities between the essays.
1. Essay Question Difficulty
One difference is that the essay question for the General Training writing task 2 is often easier. It is written in a way that makes the issues clearly and easier to understand. Here’s a sample of a GT essay question and an academic essay question.
GT Essay Question Sample
Some students travel abroad for one year before starting university. What are the advantages and disadvantages of doing this?
Academic Essay Question Sample
Some people think that space exploration is a waste of money and the funds should be relocated to other more needed areas. To what extent do you agree?
* Please note that it is still possible to get the education essay question in the academic test.
2. Topics for Essays
Another slight difference is that the topic giving for the IELTS general training essay question is a more common topic, such as family, society, TV, schools, communication etc. However, in the academic test, there is a wider range including space exploration. Even so, it is best for GT candidates to prepare all topics because the topic of space exploration could come in the speaking test.
3. Essay types for General Training
The types of essays are the same for both general training and academic IELTS papers. You could get an opinion essay, a discussion essay, an advantage disadvantage essay, a solution essay or a direct question essay. At the bottom of the 100 IELTS essay questions page , you will find some practice essays for each type. And on the writing task 2 page , you will find model essays for each type. All this is suitable for both GT and academic students.
4. Marking & Scoring
The marking criteria and band scores are the same for both GT and academic students in writing 2. Here is a link to learn about the band scores for writing task 2 from band 5 to 8 . There is only one scoring for GT Writing Task 2 and Academic Writing Task 2 with no differences at all.
5. IELTS GT Essay Writing Techniques
Another similarity is the technique for essay writing. It is the same for both GT and academic essays. Students for both the GT test and academic test will study from the same methods, tips and advice for IELTS essay writing.
This means all writing task 2 lessons on this blog are suitable for both GT and academic IELTS students. See here: I ELTS Writing Task 2 Tips, Model Essays and Free Video Lessons
6. Essay Length and Timing
The length of the GT essay is over 250 words which is the same as the academic essay. Likewise, 40 minutes is the recommended length of time for both types of essays.
Using the Official Writing Answer Sheet
Students taking the general training or academic writing test, must select the right box to tick on the official writing answer sheet in the test. Please watch this lesson about filling in the official IELTS writing answer sheet. It explains about selecting the right box for either general training or academic writing.
Recommended IELTS Tips
IELTS GT Writing Task 1 Letter: Essential Tips
IELTS Writing Task 2 Lessons, Tips & Model Essays
………..
Free Subscribe to Receive New Posts from Liz by Email
Type your email…
Hi Liz, I hope so hard that you feel better and start making videos again. I couldn’t understand better than your videos. Your videos are old, and I want to know if I write my exam this year:2023, it remain valid? I tried watching other channels, but this is where I get what is needed to become better. But I am not sure if the exam pattern still is the same for computer-based exams, and I can use your videos in 2023 as well. Lots of best wishes to you, and thank you so very much.
If my videos weren’t valid, I won’t allow them to be up. If you check this page, you’ll see any updates to the test as well as useful tips and information: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-help-faq/
Hi Liz, Thanks for your lesions, ideas and videos. Those are very helpful. First of all when I decided to write IELTS exam my mind was blank. I couldn’t figure out from where to start. Then I found you from the internet. I recently bought one of your E-Book. That looks helpful. All your tips, Videos, lesions are helpful. I am going to write my exam very soon. Thanks for being so much concerned about this field and helping candidates who are writing this exams.
I’m glad my materials have been helpful. Good luck in your test 🙂
I wanted to convey thanks from the bottom of my heart for this blog. I have decent fluency in English and used only your site to learn about IELTS, no practice tests, no other source as I had limited time and still managed to score band 8.5. This would not have been possible without this site. God bless you and wish you good health. World is a better place because of people like you.
My sincerest gratitude, Pragati.
That’s a brilliant score!! Very well done to you 🙂 Thanks for sharing your result with me and with everyone else as well 🙂
Hello Liz, Thank you for providing in-depth understanding on all the topics. You are amazing and your material is really helpful. I scored Band 8 (LRWS – 8.5, 8.5, 7.5 7.5), in my first attempt and the credit goes to you. Sincerely Shubhangi
Excellent news! Very well done 🙂
Hello Liz, Hope you are doing well, I want to know which is preferred in essay writing in academic( formal or informal), please let me know Thank you so much your time. Shubham
Writing Task 2 for both GT and Academic is formal in style.
Recently cleared my IELTS GT exam. Scored 8.5 in all sections except Writing in which I scored 7. So I’m a little confused about the outcome. I even double-checked my answers. Only thing that comes to mind is that I might have overshot my word count. But does that lead to points deduction? And accordingly, should I get my scores rechecked? Please advise.
When you say you wrote a lot, it really depends how much. If your writing task 2 essay reached about 350 words, that is really too much. Mainly because it means your essay will most likely be less focused and sentences less relevant. IELTS essays are aimed to be between 170-190 words (more or less) which makes each sentence 100% essential to the essay with no extra padding. If you have written a well focused essay, with clear signposting, good linking, relevant ideas which are well connected to the task and you aimed for accuracy in your language rather than to impress, then it is worth considering a remark. Lots of luck with whatever you decide. Let me know how it goes if you do choose a remark.
Hello Liz, I follow your website for a good time now and thank you for all the resources you put up for free, it’s really interesting and useful. I am preparing for ielts general training and I read above that almost all sections are same except the writing task 1 where you have to write a letter in GT and a report in GA and the writing tast 2 the question essay is easier than the one in GA. My question is should I give my opinion in the essay for GT.
The GT essay writing techniques are 100% the same as for Academic writing task 2. All my lessons for task 2 are for everyone. Go to this page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2/ and you’ll find all my free tips and lessons – there’s a link which will explain about when to give your opinion.
I am from New Zealand and here I am on visitor visa , I am thinking to give GT ielts test.
I just wanted to ask I am neither working or nor studying so when a examiner ask me a question are you working or studying then what should I reply.
As with all speaking questions, just be honest and answer directly: I don’t work or study at the moment. I’m here on a visitor visa.” There are no trick questions.
Dear Liz, Your info on ielts is helping me alot. I have a query in my mind i wish to ask you. can we write bullet points on question paper during listening module ? is it allowed to write points to remember on question paper ?
You can write all over the question paper in any way you wish. No one will see it. The question paper is destroyed after the test has finished.
I am planning on taking GT of IELTS and I am in USA. I would like to know if I have an option for Computer based test?
Each test center is different and offers different options. Just contact a number of test centers and ask if they do CD IELTS (computer delivered).
Recently I got stuck with a question, I am not able to understand what the statement is talking about.
Question: As well as making money, many people believe that businesses also have responsibilities to society. To what extent do you agree or disagree?
I m not able to understand this question, as well as what to do if I don’t understand questions properly?
Do you think its an academic or general type question?
Thanks Tony
This is a common question in IELTS writing and you can find ideas for that topic in my e-book “Ideas for IELTS Essay Topics”. Part of your preparation is to prepare ideas for topics. If you don’t understand the topic in the writing test, you will get low marks for your ideas (Task Response = 25% of your marks. This is typically from the Academic test, but similar topics can come in the GT test. You can see my e-book and Advanced Writing Task 2 lessons here: https://elizabethferguson.podia.com/
I purchased your tutorials for writing part 2. Now I’m much clear about the approach to be followed. Is there any other courses where you give feedback to students writings?
Sorry I don’t offer that service at the moment. Glad the advanced lessons were useful 🙂
Hi Elizabeth, I want to ask you about computer-based writing task. 1. I heard that the software they’re using for writing task underlines the misspelled words and grammatically incorrect sentences. Is this correct? 2. Does cutting affect our score if we’re attempting it on paper? 3. If someone prepared reading and listening on paper and writing on computer, what should they do? Thank you in anticipation.
1. There is NO language advantage to taking the test on a computer. The computer is not set up to help you with spelling or grammar. 2. Deleting words is fine – just make sure new words are easy to read. 3. The computer based test means you take listening, reading and writing on the computer.
Hi Liz, Based on this topic essay: Prevention is better than cure. Researching and treating diseases is too costly so it would be better to take preventive measures. to what extent do you agree?
Can my introduction and thesis be the following? – Although some people think investing in research and development to find a permanent cure for diseases is the right path to pursue, many prioritize and believe that prevention is better than cure. In my opinion, I disagree and strongly align to treating diseases that is far more superior than taking preventive measures. This essay will explain the reasons by taking an example of tobacco.
Can I write this: This essay will explain the reasons by taking an example of tobacco – is this the correct way of framing?
Does the intro + thesis make sense?
Thanks for your help G
Just a couple of points – 1. Don’t be so wordy. Control the length of your sentences and don’t use unnecessary words: “many prioritize and believe that prevention is better than cure.” = “many prioritize prevention.” 2. Don’t try to use impressive vocab in your thesis statement – get the meaning clear instead: “In my opinion, I disagree and strongly align to treating diseases that is far more superior than taking preventive measures. ” = “However, I disagree and believe that funding treatment is much more important than focusing on prevention.” 3. Keep on topic – this is about funding – it is about where money goes and how it is used. 4. Examples are not for the whole essay – this essay question is not about tobacco – don’t change the essay question. An example is a small point inside a body paragraph 5. You do not need “This essay will explain the reasons…” – that sentence is not actually required in IELTS I hope these tips help.
Hello liz, Thank you very much for all your tips. i am worried about GT task 2 . please can you help clarify my doubts about this? based on my teachers advice, if a question is asked about to what extend do you agree or disagree ? there are two ways to tackle this, first either you choose i totally agree or disagree (hence it becomes a one sided) and give only reasons for such, or you take words like i somewhat agree or disagree making it two sided .here you have to explain why you agree and what you disagree or agree about. but am confuse please can you help clarify me if this the right approach to such essay type?
Those approaches are all possible. You can agree. You can disagree. You can partially agree which means you present a specific view point which agrees in some part but disagrees in others – this means your view is specifically quantified and explained.
Hello madam! Is it true if general and academic exam on same day it makes academic exam easy ??
It makes no difference at all.
Thank you so much madam
Hello liz, I find your website very useful. Can you please let me know how sentence structure affects the band score. I got 7 in writing task and I need point five more. Although I write complex sentences in my essays, someone told me that the structure I use is quite simple and should be more complex. Can you suggest something
Grammar counts for only 25% of your marks. All mistakes will lower your score. Band 5 = frequent errors, Band 6 = some errors Band 7 = few errors. So, your aim is not just to create complex sentences, it is to avoid errors. If you make more errors using complex sentences, you should avoid using them. Aim for accuracy at all times.
Hi Liz, thanks for being a source of help as far as IELTS is concerned. I am not doing well in the writing task. Each time I try to attempt a question, I get stucked on the way. I do not really know how to put the words together even when I have ideas of what is requested of me in the question.
Your English is fine. This means the problem could be: 1. you are not familiar with the essay layout and content. 2. you need to develop more details with your ideas for topics 3. you need to approach this more naturally and just write your ideas clearly avoiding informal language. See my FREE Lessons – writing task 2 page.
Speak Your Mind Cancel reply
Notify me of new posts by email.
Advanced IELTS Lessons & E-books

Recent Lessons
Ielts liz personal update 2024, ielts model essay -two questions essay type, ielts bar chart of age groups 2024, ielts topic: urban planning, ielts listening transcripts: when and how to use them, 2024 ielts speaking part 1 topics.

Click Below to Learn:
- IELTS Test Information
Copyright Notice
Copyright © Elizabeth Ferguson, 2014 – 2024
All rights reserved.
Privacy Policy & Disclaimer
- Click here: Privacy Policy
- Click here: Disclaimer
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 · Prose on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in
Soft Skills
11 minute read
Business Writing vs. Academic Writing: What’s the Difference?

Kat Boogaard
Facebook Twitter LinkedIn WhatsApp Email
Regardless of particular style or format, written information has the same goal: to present information to an audience in a clear way.
So, that must mean good writing is good writing, right?
Not exactly. When you compare business writing to academic writing, for example, there are actually some significant differences that you should be aware of.
Familiarizing yourself with what separates these two distinct writing styles will help you write in a way that’s the most effective for your intended purpose and audience.
Think about it this way: You wouldn’t give a technical manual to a child and call it a children’s book. The same holds true for business and academic writing—there are key differences in style and structure.
So, what exactly makes business writing different from academic writing? Well, roll up your sleeves, because we’re diving into some of those key differentiators below.
What is business writing?
There’s a lot of writing that happens in the business world. But, if you think this means you need to be a skilled author capable of stringing together eloquent prose and flowery language, think again.
As this fact sheet from the University of Oregon explains, business writing is transactional. It describes what actions need to be taken to solve problems, achieve company goals, and so on.
From reports to emails to press releases, business writing comes in many shapes and sizes. The recipients of business writing also run the gamut—from board members to colleagues to customers to shareholders.
Because of that, there are tons of smaller details that separate business writing from academic writing. But, the overarching one you should remember is the purpose: Business writing is intended to direct action.
Want to learn even more about business writing? Check out our business writing course !
What is academic writing?
So, what about academic writing? Take a minute to think about the various writing projects—like research papers and book reports—that you needed to complete during your schooling. You’ll quickly realize that the intention of academic writing is far different from business writing.
Rather than educating and informing others, the goal of academic writing is for students to educate themselves. They write to learn as well as to showcase what they’ve learned—and often earn a grade for doing so.
Some academic writing is then utilized to inform others (like a thesis, research paper, or dissertation). However, the original purpose of that writing work was to have the author learn something through the writing process.
In most cases, students write these academic pieces for one particular audience member: their professor or instructor.
Business writing vs. academic writing: how they differ
Obviously, the purposes behind business writing and academic writing are quite different. But what about those other details that we mentioned earlier?
Let’s dig into the numerous other differences that come up when you compare business writing to academic writing.
1. Tone and style
While both styles of writing can be somewhat formal from time to time, academic writing is typically much more so and is written from a third person perspective . Students often receive a grade on their academic writing, so you can bet there isn’t slang or jargon of any type.
However, because business writing is more oriented toward action, it leans less on long sentences and a complex vocabulary and instead focuses on short and clear sentences (and frequently, bullet points)—making it seem far less rigid and formal than academic writing.
With business writing, the audience needs to be able to extrapolate the meaning of the text and the resulting action steps without needing to wade through complicated sentences and lengthy paragraphs.
Tone and style of academic writing:
Formal, with longer sentences and well-developed paragraphs. Here’s an example:
According to recent research, audiences are far more responsive to advertising messages that portray models and actors within their own demographic. With this reasoning, one can assume that organizations should employ a diverse range of actors and models to appear in their advertising campaigns to ensure that these commercial messages resonate with a large percentage of viewers.
Tone and style of business writing:
Emphasis on keeping things short, clear, and as actionable as possible. Here’s an example:
Research shows that audiences connect more with advertising messages that showcase people in their own demographic. We should explore talent firms with diverse pools of models and actors.
2. Document structure
Reflect on most of the writing you did during your education, and this common essay format will probably pop into your head: introduction, body, conclusion. That was the tried and true formula you leaned on to complete most of your academic writing.
However, business writing has far more flexibility—mostly because there are so many different types and styles of business writing.
This means that writing in a business setting offers far more wiggle room to structure the writing to the appropriate purpose and audience. It doesn’t always stick to a specific approach the way most academic writing does.
Structure of academic writing:
Introduction, body of the written work, and a conclusion.
Structure of Business Writing:
Varies greatly depending on what you’re writing. An email will be structured much differently than a performance review, for example.
3. Audience
We touched on this briefly already, but the intended audience is another major component that separates business and academic writing.
With academic writing, students write for one crucial audience member: their instructor, who will be dishing out a grade on that written assignment. Occasionally other people will review that written work, but it’s almost always someone else who works within academia.
Business writing, in contrast, can be read and reviewed by a huge array of people—from colleagues to customers to board members to shareholders to competitors to regulatory agencies.
The list goes on and on. This is partly because the aim is to keep business writing simple and straightforward. When you aren’t sure whose eyeballs will eventually land on it, it’s best to make things explicitly clear, so that all parties can comprehend it.
Audience of academic writing:
Audience of business writing:
Almost anybody!
4. Document design
This is another area where academic writing is far more rigid than business writing—mostly because the design of these written works is often dictated by the instructor. You remember the good ol’ days of 12-point Times New Roman font, double spacing, and appropriately-sized margins, right?
Again, with business writing, authors have far more flexibility to design their work in a way that’s most suitable to their purpose and intended audience.
Perhaps that’s a highly-visual business report with lots of graphs and charts to illustrate a point. Or, maybe it’s a one-page document with headings, subheadings, and bullet points to allow for easy skimming and scanning.
The design of business writing comes in many shapes and sizes, while academic writing typically falls into a standardized mold.
Design of academic writing:
Highly standardized with requirements for text style, font size, spacing, and margins.
Design of business writing:
Flexible, depending on the purpose of the document and the audience.
5. Writing process
If you’d ask me what my writing process looked like for any academic papers, I’d tell you this: It was many late nights spent bleary-eyed alone in front of my computer, with a mug of lukewarm coffee by my side.
Sound familiar? Much of the academic writing process takes place totally alone. The assignment is dished out by the professor, and the student is tasked with cranking out that document by the deadline in order to earn an individual grade.
Things don’t work that way in the business world, where writing is a far more collaborative process. When working on business writing, you’ll likely lean on the insights and expertise of numerous different people both inside and outside your organization to pull together something that makes sense.
Additionally, the process of writing an academic paper typically involved plenty of solo research. But, in a business environment, you usually tackle writing with far more existing context and background information received through meetings, previous projects, and other efforts. Most of the time, you aren’t approaching that subject totally cold.
Process for academic writing:
Research and writing is done mostly solo.
Process for Business Writing:
A collaborative effort, with plenty of groundwork already laid for the author.
6. Citations and sources
Sigh, citations. I remember cringing every time I needed to put together that detailed resources page for my academic papers. You remember the ones, right? They included everything from the authors' names, to the published date, to the volume number. The thought alone still sends a chill down my spine.
With academic writing, students are required to cite their sources using a highly standardized format—often MLA or APA style .
However, the rules for citing sources are far more lax with business writing and can often vary greatly depending on your company’s norms and regulations for quoting various sources.
Citations and sources for academic writing:
Highly standardized and regulated.
Citations and Sources for Business Writing:
Can vary based on the rules set by the individual company.
7. Legal considerations
While students who produce academic writing absolutely need to avoid plagiarism of any kind, it’s not often that their written work will be used in any sort of court cases, legal proceedings, or anything of the sort.
But, in a business setting? People should be aware that the written work they produce is likely now the property of their employer and thus could be used as evidence in this manner if the need arises—whether it’s something like a wrongful termination lawsuit or even an audit.
For that reason, ensuring accuracy is crucial whenever you’re writing, but particularly when you’re producing a document for your organization.
Legal considerations for academic writing:
Avoiding plagiarism is the top legal concern.
Legal Considerations for business writing:
Operate with the assumption that whatever you write could come back in a variety of legal matters. I won’t say it’s common, but it’s always better to play it safe!
Over to you
As we’ve highlighted here, there are plenty of differences between academic writing and business writing. In fact, this isn’t even all of them—we’ve barely scratched the surface.
You can dig into even more elements that separate these two styles with this fact sheet from the University of Oregon . It does a great job of breaking things down in an easily digestible way, and we used it as a resource for many of the differences we outlined here.
If you’re eager to learn even more about business writing in particular and how you can level up your own game at work? Make sure to check out our business writing course to dive into the nitty-gritty of how to be a top-notch writer in a business setting.
Gain the soft skills you need to succeed
Start learning for free with GoSkills courses
Loved this? Subscribe, and join 449,790 others.
Get our latest content before everyone else. Unsubscribe whenever.

Kat is a writer specializing in career, self-development, and productivity topics. When she escapes her computer, she enjoys reading, hiking, golfing, and dishing out tips for prospective freelancers on her website.

Recommended
How to Hire the Right Candidate for the Right Job
When using the right strategies, hiring the right job candidate can be seamless and effective.

7 Essential Skills To Help Startups Meet New Challenges
Startups and SMEs face specific challenges that threaten their survival. Make sure your business' growth doesn't lead to its downfall with these 7 tips.

The Future of Sales Careers: How Training, Methods, and Software are Changing
The nature of sales has evolved due to automation, specialization, and changing consumer expectations. This guide explores how such changes are reshaping sales careers.
© 2024 GoSkills Ltd. Skills for career advancement
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Essay and Report

On the other hand, an essay can be understood as a piece of writing, on a specific topic or subject, which expresses the author’s own ideas and knowledge about the subject.
The basic difference between essay and report is that while an essay is argumentative and idea-based, reports are informative and fact-based. Now, let us move further to understand some more points of differences.
Content: Essay Vs Report
Comparison chart, definition of essay.
An essay can be understood as a comprehensive literary composition, written in a narrative style and presents a particular topic, supports an argument and highlights the writer’s view or ideology. An essay is used to check a person’s outlook and understanding on specific matters and also his/her ability to describe and argue in a way which convinces the reader or informs him/her about a specific topic.
One can make use of learned materials, along with his/her own research, to write an essay effectively. It includes both narrative and subjective thoughts. Further, an essay supports a single idea at a time, for which several components need to be covered in it so as to appear logical and chronological.
It can be a learned argument, observation of day to day life, literary criticism, political manifestos, recollections, and reflections of the writer. It starts with a question and attempts to answer or give suggestions to the problem, on the basis of the existing theories or the writer’s personal opinion and assessment.
While writing an essay, it must be kept in mind that the approach used by the writer should be positive, even if the topic of argument is negative.
Definition of Report
The report implies a well structured factual document which is created and presented after conducting an independent enquiry, research or investigation on a specific subject. It serves as a basis for problem-solving and decision making.
Reports are prepared for a definite purpose and contain relevant information in a proper format, for a particular audience. It is used to identify, observe and analyse the issues, events, findings, that occurred practically, i.e. in real life.
A report is designed with the aim of informing the reader about the event, situation or issue, in a very simple and objective manner, while enabling them to get the desired information quickly and easily. It provides recommendations for future actions. Information collected from research, or from carrying out a project work is presented in a clear and concise manner, under a set of headings and subheadings, that helps the reader to get the desired information quickly and easily.
Characteristics of an Ideal Report
- It must be clear and concise.
- It is written in easy language which the readers can understand easily.
- It has to be appropriate and accurate.
- It should be well drafted and organised, with specific sections, headings and sub-headings.
A report summary can be provided orally, however detailed reports are usually in the form of written documents. It contains – Title Page, Acknowledgement, Authorization Letter, Table of Contents, Executive Summary, Introduction, Discussion, Results, Conclusion, Recommendations and References.
Moreover, Cover letter, Copyright notice, Bibliography, Glossary and Appendices may also form part of a report.
Key Differences Between Essay and Report
The difference Between report and essay is discussed here in detail:
- An essay is a brief literary composition, which is used to describe, present, argue, and analyse the idea or topic. Conversely, a report is a formal and concise document consisting of findings from the practical research. It aims at investigating and exploring the problem under study.
- An essay is written on the basis of subjective analysis of theories and past research, by other people and own ideas, on the concerned subject. As against, a report is objective and factual, which is based on past research, as well as present data and findings.
- An essay talks about general facts and events along with the writer’s personal ideas and views, on the topic in a non-fictional manner. On the contrary, a report contains information which the reader can use to identify the facts or support in decision making or solving issues if any.
- When it comes to sections, a report usually contains different sections, with catchy headings which may attract the attention of the audience. As against, an essay does not have any section, its flow is continuous. However, it is divided into cohesive paragraphs.
- A report uses tables, charts, graphs, diagrams, statistics and many more for a clear and better presentation of the information. But, in the case of essays, they are not used.
- The conclusion in an essay is based on the writer’s personal opinion and views on the topic itself which must be optimistic, and it does not provide any recommendations for future actions. On the other hand, a report gives an independent conclusion, but it may contain the opinion of the experts or previous researchers and recommendations are included, about how the research can be improved and extended.
In a nutshell, Essays are descriptive, subjective and evaluative, whereas, a report is descriptive, objective and analytical. Essays are mainly used in an academic context, whereas reports are preferred in the field of research.
The report is used to present the researched information in a written format, to the audience. Conversely, essays are used to identify what the writer knows about the topic and how well the writer understand the question.
You Might Also Like:

Anna H. Smith says
November 26, 2020 at 3:22 pm
Thank you for explaining this so eloquently. Excellent post, I will keep this handy and refer to it often from now on, the information is so clear and so insightful, thanks for giving a clear difference. It’s a very educative article.!
Presley Dube says
November 20, 2021 at 3:43 pm
very useful to me thank you.
Leonard says
August 8, 2022 at 2:52 pm
Thanks for sharing such nice information about this topic.
Ignatius Phiri says
March 20, 2023 at 10:39 pm
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Colleges Rates and Requirements
Find the right college for you., core college requirements for competitive acceptance rates.
As you start thinking about which colleges to apply to and how to put together your college applications, don’t forget to familiarize yourself with current admissions requirements and acceptance trends. You may have seen recent headlines about college acceptance rates and how low they were for students who applied to the most selective colleges and universities. It’s important to remember that while admissions requirements for the most competitive schools didn’t change, the number of students applying to these types of institutions has gradually increased. As a result, acceptance rates of colleges, particularly elite universities, decreased. You should also keep in mind that due to the covid-19 pandemic, most institutions saw a spike in applications. This has caused acceptance rates to further decrease.
The headlines shouldn’t deter you from moving ahead with the application process. Although it might feel seem like there’s more competition than ever before, it’s important to remember two things: Acceptance rates vary among colleges, and most colleges accept two-thirds of applicants. Once you understand what college entrance requirements are and how to interpret college admission rates, you'll be better prepared to find the right school for you.
Understand These Key Requirements for College Applications.
Each college uses its own formula when evaluating applicants, and these practices vary from school to school. In addition, many colleges over the last few years have begun instituting "test optional" and "test flexible" policies for the SAT and ACT. Despite these factors, colleges still look for certain key requirements. You can learn more about admissions requirements for individual colleges in College Search .

Standard Core Curriculum and Beyond
All colleges emphasize GPA requirements, but they focus particularly on performance in core subject areas such as mathematics, science, English, and history. Colleges look at your grades, curriculum, and the courses you take as indicators of your ability to be successful in college. To get a better understanding of which colleges might be the best fit for you, research the GPA requirements for colleges you’re interested in. Also look at the range of GPAs accepted at those institutions on the BigFuture College Search tool. Consider taking more advanced coursework such as AP courses if it fits with your career goals and if your school offers them.
Extracurriculars
Extracurriculars are where you can really stand out, especially from others with similar grades. Extra academic activities show off your personal strengths and interests to admissions officers. Ideally, they want to see students who were deeply involved in school activities outside of the classroom and held leadership positions. Learn more about how extracurriculars matter to you and colleges .
Application Essay
For colleges that require it, the application essay can be a very important part of your application and is your pitch to the university. This is your opportunity to show the school of your dreams the unique individual you are, something that may not necessarily be conveyed in your transcript. It indicates how your talents will contribute to their community. Find tips for writing your college essay here.
Standardized Test Scores
Though the trend in some U.S. colleges has been to put less emphasis on SAT scores, make no mistake: They still play an important role in the college admissions process. Test scores are still used by many colleges for course placement and merit aid. High test scores can also help you stand out and strengthen your college application. If you’re not sure if you should submit your scores, talk to your school counselor or the college’s admissions officer for guidance.
Letters of Recommendation
Although not required by all colleges, letters of recommendation can give admissions counselors insight into who you are beyond just your grades and activities. If letters are required by the institutions you’re applying to, the college will let you know who they want letters from. It’s usually a teacher or counselor. Pick someone who knows you well.
Keep on Top of College Application Deadlines.
Application deadlines can sneak up on high school seniors like a tiger in the night. It’s of utmost importance that you double-check your prospective school’s application deadlines and submit everything you need sooner rather than later. Most college application deadlines fall into the following categories:
Understand the College Application Platform.
There are two main types of college applications : The Common Application and the Coalition Application, which allow students to apply to multiple schools using a single application platform. You should check with the institutions you’re interested in applying to see which application platform they prefer.
How Do College Acceptance Rates Work?
A college’s acceptance rate is actually a ratio. It's the total number of applicants in relation to the number of students who were accepted. For example, Harvard received applications from 61,220 students in 2022─the highest-ever number of applicants to the school. Of those, only 1,214 received admission, leading to the school’s lowest-ever acceptance rate of 3.19%.
This illustrates the point earlier that college acceptance rates are on a decline as the number of applicants increases, saturating the pool with more competition than ever before.
Acceptance rates are based on the number of spots available at a college. This is a set number of applicants who can be admitted to that class of graduates, and it's not subject to change based on the volume of applicants. As you can imagine, more competitive schools, such as Ivy League colleges and universities, have fewer spots available and are thus affected more by the number of applicants.
This same logic applies to private and public colleges. Public colleges, which are characteristically larger institutions, will admit greater numbers of students, leading to higher acceptance rates. However, public colleges have also been impacted by a larger number of applicants. When you’re building your college list, it’s advisable to include a balance of reach, match, and safety schools to improve your chances of acceptance.
It's important to keep in mind that college admission rates don’t necessarily reflect the quality of education or the quality of students who apply, and you shouldn’t be discouraged from applying to schools based on these numbers.
What is the Difference Between Admission Yield and Enrollment Rate?
Admission yield is the percentage of students who accepted enrollment into a college after being granted admission. These vary significantly from school to school. For example, the University of California, Berkeley’s yield rate for 2022 was just 40% while the yield rate for Yale was a whopping 83%.
As students apply to greater numbers of colleges and have more options, yield rates decline.
Review the Latest College Acceptance Rate Stats.
Students faced competitive acceptance rates in 2022. Common Application public colleges and universities saw a 24% surge of applicants since 2019-20 and 17% for private institutions. Meanwhile, the acceptance rates continue to decline. For example, Emory University’s acceptance rate fell 8 percentage points between 2020 and 2022.
Students who are eyeing colleges with highly competitive acceptance rates must focus more than ever on the things that will set them apart: exceptional performance beyond the standard core curriculum, strong extracurricular participation, powerful application essays, letters of recommendation, and excellent standardized test scores. However, even with all of these differentiators, it’s important to remember that none of these can guarantee acceptance, especially at selective institutions. Be sure to build a balanced college list that gives you options.
Related Articles

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Difference between an Essay and a Letter. ... Structure in letter-writing can be quite specific. For a traditional formal letter, an address is printed at the top of the page, a greeting or salutation to the intended recipient or group of recipients begins the writing portion, the body can be made up of single or multiple paragraphs, and a ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
Formal Language versus Informal Language. Academic writing should use formal language that minimizes the use of contractions and colloquialisms and avoids slang terminology whenever possible. Casual language should only be used for emphasis. Further, academic writing generally does not employ first person pronouns like "I" or "we," but ...
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You'll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you'll be expected to write your essays, research papers, and dissertation in academic style. Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but ...
Descriptive: to describe things. Expository: to give facts. Narrative: to tell a story. Persuasive: to convince the reader of something. If you're struggling to figure out the writing style of a piece, ask yourself what its purpose is and why the author wants you to read it.
Harvard College Writing Center 5 Asking Analytical Questions When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a
Parts of an essay. An impactful, well-structured essay comes down to three important parts: the introduction, body, and conclusion. 1. The introduction sets the stage for your essay and is typically a paragraph long. It should grab the reader's attention and give them a clear idea of what your essay will be about.
Essays and Letter-Writing - Volume 41 Issue 2. ... Nevertheless, though both essay and letter are inchoate literary identities which have in the past taken on a variety of exteriors, there are undoubtedly points in common between them; there is even, I should like to show, sufficient evidence to argue a definite and deliberate indebtedness on ...
Essays of Michel de Montaigne. An essay is, generally, a piece of writing that gives the author's own argument, but the definition is vague, overlapping with those of a letter, a paper, an article, a pamphlet, and a short story.Essays have been sub-classified as formal and informal: formal essays are characterized by "serious purpose, dignity, logical organization, length," whereas the ...
1. Informal Letter vs. Expository Essay: a familiar letter is much more intimate in voice than an expository essay. A writer of an informal letter to a familiar audience uses "sweet style": 2nd ...
Essays don't usually include tables, charts, or diagrams. Reports usually include descriptions of the methods used. Essays don't usually refer to the methods you used to arrive at your conclusions. The discussion in a report often comments on how the report research could be improved and extended, and may evaluate the methods and processes used.
We break down some key elements of how to write for a formal and an informal audience, with examples of formal vs. informal writing along the way.
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates. In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills. Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative: you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence ...
In contrast, an essay does not have any headings, sections or bullet points, however, it is a coherent and organized form of writing. An article is always written with a definite objective, which is to inform or make the readers aware of something. Further, it is written to cater to a specific niche of audience.
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Although the writing process is different for everyone, you'll probably notice a big difference between writing the first and second drafts of a new piece.
IELTS GT Differences for Writing Task 1. General training students will need to write a letter for writing task 1 but academic students will need to write a report. GT Writing Task 1 = Letters: Formal, informal and semi-formal. Academic Writing Task 1 = Report: table, pie chart, bar chart, line graph etc. This means writing task 1 is completely ...
Let's dig into the numerous other differences that come up when you compare business writing to academic writing. 1. Tone and style. While both styles of writing can be somewhat formal from time to time, academic writing is typically much more so and is written from a third person perspective.
often require a letter of intent, personal statement, or similar essay. These may highlight your personality, interests, accomplishments, and goals, as they relate to what you want to study and why you want to attend that school to do it. Writing a personal statement for grad school could be one of your biggest opportunities.
An essay is written on the basis of subjective analysis of theories and past research, by other people and own ideas, on the concerned subject. As against, a report is objective and factual, which is based on past research, as well as present data and findings. An essay talks about general facts and events along with the writer's personal ...
Application Essay. For colleges that require it, the application essay can be a very important part of your application and is your pitch to the university. This is your opportunity to show the school of your dreams the unique individual you are, something that may not necessarily be conveyed in your transcript.
Evening Service, April 21, 2024