- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Executive summary.

It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
Company Description
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market
Market analysis.
The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
Competitive Analysis
Organization and management team.
Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
Logistics and Operations Plan
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Income Statement
Cash flow statement.
A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
| Section | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Summary | Brief overview of the business plan | Overview of EcoTech and its mission |
| Overview & Objectives | Outline of company's goals and strategies | Market leadership in sustainable technology |
| Company Description | Detailed explanation of the company and its unique selling proposition | EcoTech's history, mission, and vision |
| Target Market | Description of ideal customers and their needs | Environmentally conscious consumers and businesses |
| Market Analysis | Examination of industry trends, customer needs, and competitors | Trends in eco-friendly technology market |
| SWOT Analysis | Evaluation of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats | Strengths and weaknesses of EcoTech |
| Competitive Analysis | In-depth analysis of competitors and their strategies | Analysis of GreenTech and EarthSolutions |
| Organization & Management | Overview of the company's structure and management team | Key roles and team members at EcoTech |
| Products & Services | Description of offerings and their unique features | Energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers |
| Marketing & Sales | Outline of marketing channels and sales strategies | Digital advertising, content marketing, influencer partnerships |
| Logistics & Operations | Details about daily operations, supply chain, inventory, and quality control | Partnerships with manufacturers, quality control |
| Financial Projections | Forecast of revenue, expenses, and profit for the next 3-5 years | Projected growth in revenue and net profit |
| Income Statement | Summary of company's revenues and expenses over a specified period | Revenue, Cost of Goods Sold, Gross Profit, Net Income |
| Cash Flow Statement | Overview of cash inflows and outflows within the business | Net Cash from Operating Activities, Investing Activities, Financing Activities |
Tips on Writing a Business Plan
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
What is a Business Plan?
Why you should write a business plan.
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
| Type of Business Plan | Purpose | Key Components | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Startup Business Plan | Outlines the company's mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. | Mission Statement, Company Description, Market Analysis, Competitive Analysis, Organizational Structure, Marketing and Sales Strategy, Financial Projections. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Internal Business Plan | Serves as a management tool for guiding the company's growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. | Strategies, Milestones, Deadlines, Resource Allocation. | Internal Team Members |
| Strategic Business Plan | Outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them. | SWOT Analysis, Market Research, Competitive Analysis, Long-Term Goals. | Executives, Managers, Investors |
| Feasibility Business Plan | Assesses the viability of a business idea. | Market Demand, Competition, Financial Projections, Potential Obstacles. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Growth Business Plan | Focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. | Market Analysis, New Product/Service Offerings, Financial Projections. | Business Owners, Investors |
| Operational Business Plan | Outlines the company's day-to-day operations. | Processes, Procedures, Organizational Structure. | Managers, Employees |
| Lean Business Plan | A simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements. | Value Proposition, Customer Segments, Revenue Streams, Cost Structure. | Entrepreneurs, Startups |
| One-Page Business Plan | A concise summary of your company's key objectives, strategies, and milestones. | Key Objectives, Strategies, Milestones. | Entrepreneurs, Investors, Partners |
| Nonprofit Business Plan | Outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation for nonprofit organizations. | Mission Statement, Goals, Target Audience, Fundraising Strategies, Budget. | Nonprofit Leaders, Board Members, Donors |
| Franchise Business Plan | Focuses on the franchisor's requirements, as well as the franchisee's goals, strategies, and financial projections. | Franchise Agreement, Brand Standards, Marketing Efforts, Operational Procedures, Financial Projections. | Franchisors, Franchisees, Investors |
Using Business Plan Software
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
| Software | Key Features | User Interface | Additional Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| LivePlan | Over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking against KPIs | User-friendly, visually appealing | Allows creation of professional-looking business plans |
| Upmetrics | Customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, collaboration capabilities | Simple and intuitive | Provides a resource library for business planning |
| Bizplan | Drag-and-drop builder, modular sections, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking | Simple, visually engaging | Designed to simplify the business planning process |
| Enloop | Industry-specific templates, financial forecasting tools, automatic business plan generation, unique performance score | Robust, user-friendly | Offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget |
| Tarkenton GoSmallBiz | Guided business plan builder, customizable templates, financial projection tools | User-friendly | Offers CRM tools, legal document templates, and additional resources for small businesses |
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
Can i write a business plan by myself, is it possible to create a one-page business plan.
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
What is a business plan outline, what are the 5 most common business plan mistakes, what questions should be asked in a business plan.
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
How is business planning for a nonprofit different.
How to make a business plan
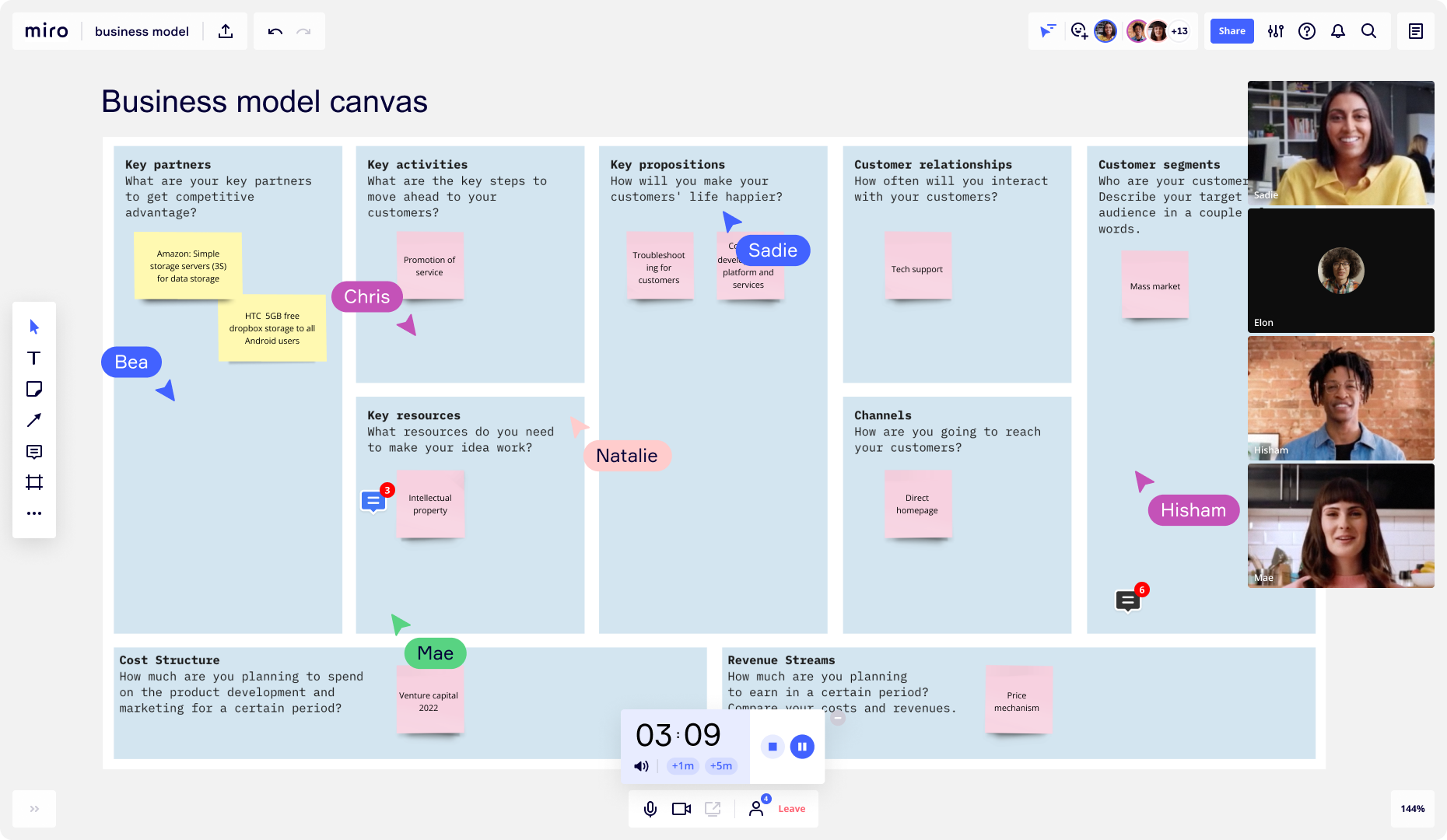
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024
If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage. It helps you develop a working business and avoid consequences that could stop you before you ever start.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
Related Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
The best way to start is by reviewing examples and downloading a business plan template. These resources will provide you with guidance and inspiration to help you write a plan.
We recommend starting with a simple one-page plan ; it streamlines the planning process and helps you organize your ideas. However, if one page doesn’t fit your needs, there are plenty of other great templates available that will put you well on your way to writing a useful business plan.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
How and Where to Write About Technology in Your Business Plan

7 Min. Read
3 Key Steps to Create a Promotional Plan

16 Min. Read
How to Write a Mission Statement + 10 Great Examples

3 Min. Read
Celebrate National Write a Business Plan Month in December
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

The 12 Key Components of a Business Plan
There are 12 components of a business plan entrepreneurs must know as they lay out how their business will work.

Entrepreneurs who create business plans are more likely to succeed than those who don’t.
Not only can a sound plan help your business access investment capital but—as the study found—it can even determine the success or failure of your venture.
Here are the critical components of a business plan to help you craft your own.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document outlining your business goals and your strategies for achieving them. It might include your company’s mission statement , details about your products or services, how you plan to bring them to market, and how much time and money you need to execute the plan.
For a thorough explanation of how to write a business plan, refer to Shopify’s guide .

12 components of a business plan
Business plans vary depending on the product or service. Some entrepreneurs choose to use diagrams and charts, while others rely on text alone. Regardless of how you go about it, good business plans tend to include the following elements:
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis
- Marketing plan
- Competitive analysis
- Organizational structure
- Products and services
- Operating plan
- Financial plan
- Funding sources
1. Executive summary
The executive summary briefly explains your business’s products or services and why it has the potential to be profitable. You may also include basic information about your company, such as its location and the number of employees.
2. Company description
The company description helps customers, lenders, and potential investors gain a deeper understanding of your product or service. It provides detailed descriptions of your supply chains and explains how your company plans to bring its products or services to market.
3. Market analysis
The market analysis section outlines your plans to reach your target audience . It usually includes an estimate of the potential demand for the product or service and a summary of market research .
The market analysis also includes information about marketing strategies, advertising ideas, or other ways of attracting customers.
Another component of this section is a detailed breakdown of target customers. Many businesses find it helpful to analyze their target market using customer segments , often with demographic data such as age or income. This way, you can customize your marketing plans to reach different groups of customers.
4. Marketing plan
The marketing plan section details how you plan to attract and retain customers. It covers the marketing mix: product, price, place, and promotion. It shows you understand your market and have clear, measurable goals to guide your marketing strategy.
For example, a fashion retail store might focus on online sales channels, competitive pricing strategies, high-quality products, and aggressive social media promotion.
5. Sales plan
This section focuses on the actions you’ll take to achieve sales targets and drive revenue. It’s different from a marketing plan because it’s more about the direct process of selling the product to your customer. It looks at the methods used from lead generation to closing the sale, as well as revenue targets.
An ecommerce sales strategy might involve optimizing your online shopping experience, using targeted digital marketing to drive traffic, and employing tactics like flash sales , personalized email marketing, or loyalty programs to boost sales.
6. Competitive analysis
It’s essential that you understand your competitors and distinguish your business. There are two main types of competitors: direct and indirect competitors.
- Direct competitors. Direct competitors offer the same or similar products and services. For example, the underwear brand Skims is a direct competitor with Spanx .
- Indirect competitors. Indirect competitors, on the other hand, offer different products and services that may satisfy the same customer needs. For example, cable television is an indirect competitor to Netflix.
A competitive analysis explains your business’s unique strengths that give it a competitive advantage over other businesses.
7. Organizational structure
The organizational structure explains your company’s legal structure and provides information about the management team. It also describes the business’s operating plan and details who is responsible for which aspects of the company.
8. Products and services
This component goes in-depth on what you’re actually selling and why it’s valuable to customers. It’ll provide a description of your products and services with all their features, benefits, and unique selling points. It may also discuss the current development stage of your products and plans for the future.
The products and services section also looks at pricing strategy , intellectual property (IP) rights, and any key supplier information. For example, in an ecommerce business plan focusing on eco-friendly home products, this section would detail the range of products, explain how they are environmentally friendly, outline sourcing and production practices, discuss pricing, and highlight any certifications or eco-labels the products have received.
9. Operating plan
Here is where you explain the day-to-day operations of the business. Your operating plan will cover aspects from production or service delivery to human and resource management. It shows readers how you plan to deliver on your promises.
For example, in a business plan for a startup selling artisanal crafts, this section would include details on how artisans are sourced, how products are cataloged and stored, the ecommerce platform used for sales, and the logistics for packaging and shipping orders worldwide.
10. Financial plan
The financial plan is one of the most critical parts of the business plan, especially for companies seeking outside funding.
A plan often includes capital expenditure budgets, forecasted income statements , and cash flow statements , which can help predict when your company will become profitable and how it expects to survive in the meantime.
If your business is already profitable, your financial plan can help with convincing investors of future growth. At the end of the financial section, you may also include a value proposition , which estimates the value of your business.
11. Funding sources
Some businesses planning to expand or to seek funds from venture capitalists may include a section devoted to their long-term growth strategy, including ways to broaden product offerings and penetrate new markets.
12. Appendix
The final component of a business plan is the appendix. Here, you may include additional documents cited in other sections or requested by readers. These might be résumés, financial statements, product pictures, patent approvals, and legal records.
Components of a business plan FAQ
What are 8 common parts of a good business plan.
Some of the most common components of a business plan are an executive summary, a company description, a marketing analysis, a competitive analysis, an organization description, a summary of growth strategies, a financial plan, and an appendix.
What is a business plan format?
A business plan format is a way of structuring a business plan. Shopify offers a free business plan template for startups that you can use to format your business plan.
What are the 5 functions of a business plan?
A business plan explains your company’s products or services, how you expect to make money, the reliability of supply chains, and factors that might affect demand.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts
The most intuitive, powerful
Shopify yet
Shopify Editions Summer ’24

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Jul 2, 2024
Jul 1, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Rosalie Murphy is a small-business writer at NerdWallet. Since 2021, she has covered business insurance, banking, credit cards and e-commerce software, and her reporting has been featured by The Associated Press, MarketWatch, Entrepreneur and many other publications. Rosalie holds a graduate certificate in Quantitative Business Management from Kent State University and is now pursuing an MBA. She is based in Chicago.

Ryan Lane is an editor on NerdWallet’s small-business team. He joined NerdWallet in 2019 as a student loans writer, serving as an authority on that topic after spending more than a decade at student loan guarantor American Student Assistance. In that role, Ryan co-authored the Student Loan Ranger blog in partnership with U.S. News & World Report, as well as wrote and edited content about education financing and financial literacy for multiple online properties, e-courses and more. Ryan also previously oversaw the production of life science journals as a managing editor for publisher Cell Press. Ryan is located in Rochester, New York.

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.

- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
The Essential Guide to Writing a Business Plan Here's the no-nonsense guide on how to write a business plan that will help you map success for your startup.
By Carolyn Sun
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
President Dwight D. Eisenhower once said, "In preparing for battle I have always found that plans are useless, but planning is indispensable." If you're starting a business, you should have a business plan regardless of whether you're bootstrapping it or looking for outside funding.
The best sorts of business plans tell a clear story of what the company plans to do and how it will do it. Given the high failure rate of startups in their first year, a business plan is also an ideal opportunity to safely test out the feasibility of a business and spot flaws, set aside unrealistic projections and identify and analyze the competition.
A business plan doesn't need to be complicated, but for it to serve its purpose and set you up for success, it must be clear to whomever is reading your plan that you have a realistic handle on the why and how your business will be a success.
To get you moving in the right direction, here's a guide on how to write a business plan.
Overall tips
There's a lot of advice in the infosphere about how to write a business plan, but there's no single correct way. Your approach depends on your industry, who is reading your plan and what the plan is intended for. Are you trying to get funding? Sara Sutton Fell, founder of FlexJobs , a job site for flexible telecommuting jobs, says her business plan was an initiator for more in-depth conversation with potential investors. "A plan does help to see if investors and entrepreneurs are on the same page with general expectations for the business," she says.
A business plan serves many purposes, but there is universal consensus on the following when it comes to your business plan:
Have several versions tailored for specific audiences: "One of the mistakes that inexperienced business owners make is not understanding who they're writing the plan for," says David Ciccarelli, a small business owner who got consultation from his local Small Business Association (SBA) when he was starting his company Voices.com , which connects employers with voiceover talent.
Your plan is a living document: Tim Berry, the founder of a business planning software company Palo Alto Software , took his company from zero to $5 million in sales in its first three years. To do so requires frequent review and close tracking, says Berry, who met with his management team every month to review the plan versus what actually happened -- and then to revise. "There is no virtue to sticking to a plan if it's not useful and responsive to what actually happens," he cautions.
Be realistic about financial estimates and projections: "When you present a plan to bankers and financiers, or even to your employees, people will get way more excited about what's real rather than some huge thing that's never going to happen," says Ciccarelli. So present an achievable sales forecasts based on bottom-upwards information (i.e. how many units per month get sold in how many stores) and stop over projecting profits.
Writing your business plan is about the process and having a blueprint: Your business plan "reflects your ideas, intuitions, instincts and insights about your business and its future," according to Write Your Business Plan (Entrepreneur, 2015). The plan serves as a safe way to test these out before you commit to a course of action. And once you get your business going, the plan also serves as a reference point. "I still print the document," says Ciccarelli. "You're capturing it in time. If you're changing it all the time, you kind of don't remember where you were last year."
Back up any claims: Follow up your projections and assertions with statistics, facts or quotes from a knowledgeable source to lend your plan credibility.
Presentation counts: Reading any long, text-heavy document is hard on the eyes, so format with this in mind. Consider formatting your text pages into two-columns and break up long passages with charts or graphs. Arial, Verdana or Times New Roman are standard industry fonts.
Writing your business plan isn't busy work or a luxury; it's a vital part of the process of starting a business and arms you with information you need to know. So, let's get into what information goes into your business plan.
Related: Bu siness Plans: A Step-by-Step Guide
What goes into a business plan?
A typical business plan is 15 to 25 pages. Its length depends on a variety of factors, such as whether your business is introducing a new product or belongs to a new industry (which requires explanation to the reader), or if you're pitching to bankers, who generally expect to see a traditional written business plan and financials.
"Most equity investors prefer either an executive summary or pitch deck for first contact, but will often request a more detailed plan later in the due diligence process. Potential customers don't need all the details of your internal operation. Your management team needs access to everything," says Akira Hirai, managing director of business plan consulting service Cayenne Consulting .
Most business plans include these seven sections:
1. Executive summary : The executive summary follows the title page and explains the fundamentals of your business. It should provide a short and clear synopsis of your business plan that describes your business concept, financial features and requirements (i.e. cash flow and sales projections plus capital needed), your company's current business position (i.e. its legal form of operation, when the company was formed, principals and key personnel) and any major achievements in the company that are relevant to its success, including patents, prototypes or results from test marketing.
2. Business description : This section typically begins with a brief description of your industry and its outlook. Get into the various markets within the industry, including any new products that will benefit or hurt your business. For those seeking funding, reinforce your data with reliable sources and footnote when possible. Also provide a description of your business operation's structure (i.e. wholesale, retail or service-oriented), who you will sell to, how you will distribute your products/services, the products/services itself (what gives you the competitive edge), your business's legal structure, your principals and what they bring to the organization.
Here are some worksheets from Write Your Business Plan that will help determine your unique selling proposition and analyze your industry.
Click to Enlarge+

3. Market strategies: Here is where you define your target market and how you plan to reach them. Market analysis requires research and familiarity with the market so that the target market can be defined and the company can be positioned (i.e. are you a premium product or a price-competitive product?) in order to garner its market share. Analyze your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends and sales/growth potential. This section also talks about distribution plans and promotion strategy and tactics that will allow you to fulfill your plans.
Here is a worksheet from Write Your Business Plan that will guide you toward identifying your target market.

4. Competitive analysis: The purpose of the competitive analysis is to determine the strengths and weaknesses of the competitors within your market, strategies that will provide you with a distinct advantage, the barriers that can be developed in order to prevent competition from entering your market, and any weaknesses that can be exploited within the product development cycle. Show why your business will be a success over others.
5. Design and development plan: You will only need this section if you have a product in development, such as an app. The purpose of this section is to provide investors with a description of the product's design, chart its development within the context of production and marketing and show a development budget that will enable the company to reach its goals.
6. Operations and management plan: This section describes how the business functions on a daily basis, its location, equipment, people, processes and surrounding environment. If you have a product that needs to be manufactured, explain the how and where; also, describe your work facility, the personnel, the legal environment (such as licensing, permits, special regulations, etc.), key suppliers and inventory. This section will also highlight the logistics of the organization such as the various responsibilities of the management team and the tasks assigned to each division within the company.
7. Financial factors: Financial data is always at the back of a business plan -- yet it's extremely important. The financial data can include your personal financial statement, startup expenses and capital, your projected cash flow statement and 12-month profit-and-loss statement. PaloAlto's Berry stresses that if you're going after investors, you'll need to show a cash flow statement and a break-even analysis -- or the breakdown to see where your business breaks even.
The best way to prepare for running a business is to have all the components of the plan ready. So if you are are showing a prospective lender your business plan on 10 PowerPoint slides and get asked about something that isn't in the presentation, you can speak knowledgeably and follow up with a more fleshed out plan -- and quickly.
Some business owners hire business plan writing services. Cayenne Consulting's Hirai says that his clients generally fall into one of two categories: those intimidated by the process and those who could write the plan themselves but would prefer to spend their time on other priorities.
If you find yourself intimidated or stuck, you can always write the parts of plan yourself that you understand and hire a consultant or researcher to help with parts that you find confusing.
Or if you're a startup watching every dollar, then tap the free services of the federal Small Business Association (SBA). Every state has a district office . Through the SBA, you can get business plan assistance through its various resource partners, which includes Women's Business Centers , Small Business Development Centers and Service Corps of Retired Executives .
Allow this business plan template for Business Plan for a Startup Business to guide you:
Different types of business plans
Generally, business plans can be divided into four categories :
Working plan: This plan is what you will use to operate your business and is not meant to be admired. This version of your plan is an internal document and will be long on detail, short on presentation. Here, you can omit descriptions that you need not explain to yourself or your team.
Mini plan: The reader may request a mini plan, or a condensed version of your business plan (1-10 pages), which includes most of the same components as in a longer traditional plan -- minus the details and explanation. This includes the business concept, financing needs, marketing plan, financial statements (especially cash flow), income project and balance sheet. This shorter plan is not meant to be a substitute for a full-length plan, but serves as an option to present to potential partners or investors.
Presentation plan: Whether you're using a pitch deck or a written business plan, the information in your presentation plan will be, more or less, the same as in your working plan but worded differently and styled for the eyes of an outsider. The reader of your presentation plan will be someone who is unfamiliar with your business, such as investor or venture capitalist, so lose any jargon or shorthand from your working plan, which only makes sense to you. Also, keep in mind that investors will want to see due diligence on your competition threats and risks as well as financial projections. In addition, looks count, so use the color printer, a nice cover and bindings and the fancy paper stock. Or else, if you're presenting your business plan as a PowerPoint presentation, you can use this business plan presentation template .
What-if plan: This is a contingency plan -- in case your worst case scenario happens, such as market share loss, heavy price competition or defection of a key member of your team. You want to think about what to do in the face of an of these, and if you're trying to get outside funds, having a contingency plan shows that you've considered what to do if things don't go according to plan. You don't necessarily need this, but if you are getting outside funding, then it can strengthen your credibility showing that you have thought about these what-if possibilities. Even if you're not going to get outside funding, shouldn't you be thinking of the what ifs?
If four plans seem like a mountain of work, don't panic. Select two to start off -- a working plan and a mini plan, which will be an abbreviated version of your working plan.
Take several months to write your business plan. Consider it a journey, not a sprint.
Related: The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Business Plan
Carolyn Sun is a freelance writer for Entrepreneur.com. Find out more on Twitter and Facebook .
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Lock The Average American Can't Afford a House in 99% of the U.S. — Here's a State-By-State Breakdown of the Mortgage Rates That Tip the Scale
- Richard Branson Shares His Extremely Active Morning Routine : 'I've Got to Look After Myself'
- Lock This Flexible, AI-Powered Side Hustle Lets a Dad of Four Make $32 an Hour , Plus Tips: 'You Can Make a Substantial Amount of Money'
- Tennis Champion Coco Gauff Reveals the Daily Habits That Help Her Win On and Off the Court — Plus a 'No Brainer' Business Move
- Lock 3 Essential Skills I Learned By Growing My Business From the Ground Up
- 50 Cent Once Sued Taco Bell for $4 Million. Here's How the Fast-Food Giant Got on the Rapper's Bad Side .
Most Popular Red Arrow
One of america's oldest companies just laid off 600 workers as it shifts focus to production in mexico.
Over 600 John Deere employees in Iowa and Illinois were laid off effective August 30.
Here's How Much Investing $10,000 in Nvidia When It Went Public Would Be Worth Now
Nvidia was founded in 1993 and went public in January 1999, first trading at $12 per share.
How to Text Customers Without Getting Sued — Your SMS Marketing Compliance Guide
SMS marketing is a growing channel, but you've got to stay compliant with regulations. Here's what to know and do.
I Created 2 Habits That Significantly Improved My Daily Life — Here's How You Can Do the Same
Good habits are a powerful way to live your best life. Here's how I created new habits to enable me to start my day off right.
Apple iPhone 7 Users May Be Owed a Slice of a $35 Million Settlement — Here's How to Claim Your Share
Previous (and current, no judgment) iPhone 7 users may be entitled to up to $349. The deadline to file a claim has been extended to July 3.
This is What is Missing From Your Customer Experience Playbook
One-size-fits-all customer experience playbooks don't exist — and for good reason. Every business has distinct customers with distinct feelings, needs and preferences.
Successfully copied link
Business Plan Example and Template
Learn how to create a business plan
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing .

A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all the important business plan elements. Typically, it should present whatever information an investor or financial institution expects to see before providing financing to a business.
Contents of a Business Plan
A business plan should be structured in a way that it contains all the important information that investors are looking for. Here are the main sections of a business plan:

1. Title Page
The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date, and the company logo.
2. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most important section because it is the first section that investors and bankers see when they open the business plan. It provides a summary of the entire business plan. It should be written last to ensure that you don’t leave any details out. It must be short and to the point, and it should capture the reader’s attention. The executive summary should not exceed two pages.
3. Industry Overview
The industry overview section provides information about the specific industry that the business operates in. Some of the information provided in this section includes major competitors, industry trends, and estimated revenues. It also shows the company’s position in the industry and how it will compete in the market against other major players.
4. Market Analysis and Competition
The market analysis section details the target market for the company’s product offerings. This section confirms that the company understands the market and that it has already analyzed the existing market to determine that there is adequate demand to support its proposed business model.
Market analysis includes information about the target market’s demographics , geographical location, consumer behavior, and market needs. The company can present numbers and sources to give an overview of the target market size.
A business can choose to consolidate the market analysis and competition analysis into one section or present them as two separate sections.
5. Sales and Marketing Plan
The sales and marketing plan details how the company plans to sell its products to the target market. It attempts to present the business’s unique selling proposition and the channels it will use to sell its goods and services. It details the company’s advertising and promotion activities, pricing strategy, sales and distribution methods, and after-sales support.
6. Management Plan
The management plan provides an outline of the company’s legal structure, its management team, and internal and external human resource requirements. It should list the number of employees that will be needed and the remuneration to be paid to each of the employees.
Any external professionals, such as lawyers, valuers, architects, and consultants, that the company will need should also be included. If the company intends to use the business plan to source funding from investors, it should list the members of the executive team, as well as the members of the advisory board.
7. Operating Plan
The operating plan provides an overview of the company’s physical requirements, such as office space, machinery, labor, supplies, and inventory . For a business that requires custom warehouses and specialized equipment, the operating plan will be more detailed, as compared to, say, a home-based consulting business. If the business plan is for a manufacturing company, it will include information on raw material requirements and the supply chain.
8. Financial Plan
The financial plan is an important section that will often determine whether the business will obtain required financing from financial institutions, investors, or venture capitalists. It should demonstrate that the proposed business is viable and will return enough revenues to be able to meet its financial obligations. Some of the information contained in the financial plan includes a projected income statement , balance sheet, and cash flow.
9. Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits part is the last section of a business plan. It includes any additional information that banks and investors may be interested in or that adds credibility to the business. Some of the information that may be included in the appendices section includes office/building plans, detailed market research , products/services offering information, marketing brochures, and credit histories of the promoters.
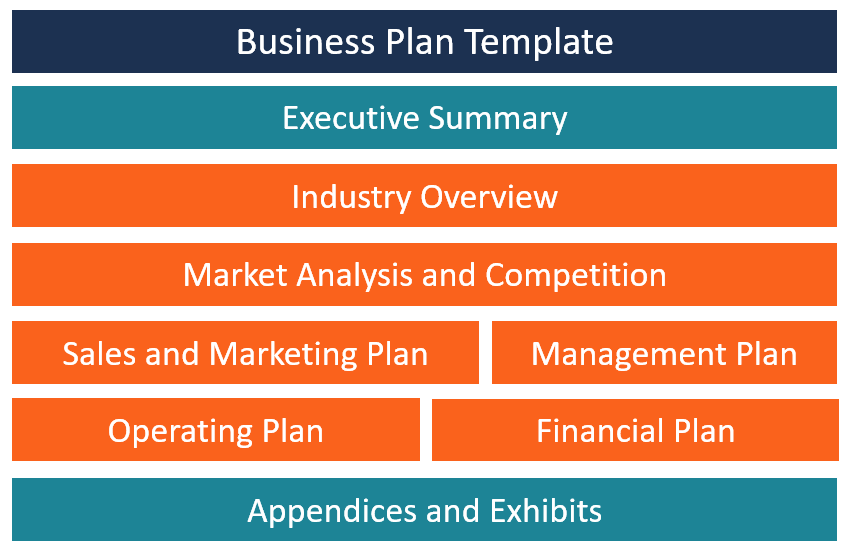
Business Plan Template
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan:
Section 1: Executive Summary
- Present the company’s mission.
- Describe the company’s product and/or service offerings.
- Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
- Summarize the industry competition and how the company will capture a share of the available market.
- Give a summary of the operational plan, such as inventory, office and labor, and equipment requirements.
Section 2: Industry Overview
- Describe the company’s position in the industry.
- Describe the existing competition and the major players in the industry.
- Provide information about the industry that the business will operate in, estimated revenues, industry trends, government influences, as well as the demographics of the target market.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
- Define your target market, their needs, and their geographical location.
- Describe the size of the market, the units of the company’s products that potential customers may buy, and the market changes that may occur due to overall economic changes.
- Give an overview of the estimated sales volume vis-à-vis what competitors sell.
- Give a plan on how the company plans to combat the existing competition to gain and retain market share.
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
- Describe the products that the company will offer for sale and its unique selling proposition.
- List the different advertising platforms that the business will use to get its message to customers.
- Describe how the business plans to price its products in a way that allows it to make a profit.
- Give details on how the company’s products will be distributed to the target market and the shipping method.
Section 5: Management Plan
- Describe the organizational structure of the company.
- List the owners of the company and their ownership percentages.
- List the key executives, their roles, and remuneration.
- List any internal and external professionals that the company plans to hire, and how they will be compensated.
- Include a list of the members of the advisory board, if available.
Section 6: Operating Plan
- Describe the location of the business, including office and warehouse requirements.
- Describe the labor requirement of the company. Outline the number of staff that the company needs, their roles, skills training needed, and employee tenures (full-time or part-time).
- Describe the manufacturing process, and the time it will take to produce one unit of a product.
- Describe the equipment and machinery requirements, and if the company will lease or purchase equipment and machinery, and the related costs that the company estimates it will incur.
- Provide a list of raw material requirements, how they will be sourced, and the main suppliers that will supply the required inputs.
Section 7: Financial Plan
- Describe the financial projections of the company, by including the projected income statement, projected cash flow statement, and the balance sheet projection.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
- Quotes of building and machinery leases
- Proposed office and warehouse plan
- Market research and a summary of the target market
- Credit information of the owners
- List of product and/or services
Related Readings
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Business Plans. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful:
- Corporate Structure
- Three Financial Statements
- Business Model Canvas Examples
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in

- Case Studies
- Flexible Products

- Expert Insights
- Research Studies

- Creativity and Culture
- Management and Leadership
- Business Solutions
- Member Spotlight
- Employee Spotlight
How to write a business plan in seven simple steps
When written effectively, a business plan can help raise capital, inform decisions, and draw new talent.

Companies of all sizes have one thing in common: They all began as small businesses. Starting small is the corner for those just getting off the ground. Learn about how to make that first hire, deal with all things administrative, and set yourself up for success.
Writing a business plan is often the first step in transforming your business from an idea into something tangible . As you write, your thoughts begin to solidify into strategy, and a path forward starts to emerge. But a business plan is not only the realm of startups; established companies can also benefit from revisiting and rewriting theirs. In any case, the formal documentation can provide the clarity needed to motivate staff , woo investors, or inform future decisions.
No matter your industry or the size of your team, the task of writing a business plan—a document filled with so much detail and documentation—can feel daunting. Don’t let that stop you, however; there are easy steps to getting started.
What is a business plan and why does it matter?
A business plan is a formal document outlining the goals, direction, finances, team, and future planning of your business. It can be geared toward investors, in a bid to raise capital, or used as an internal document to align teams and provide direction. It typically includes extensive market research, competitor analysis, financial documentation, and an overview of your business and marketing strategy. When written effectively, a business plan can help prescribe action and keep business owners on track to meeting business goals.
Who needs a business plan?
A business plan can be particularly helpful during a company’s initial growth and serve as a guiding force amid the uncertainty, distractions, and at-times rapid developments involved in starting a business . For enterprise companies, a business plan should be a living, breathing document that guides decision-making and facilitates intentional growth.
“You should have a game plan for every major commitment you’ll have, from early-stage founder agreements to onboarding legal professionals,” says Colin Keogh, CEO of the Rapid Foundation—a company that brings technology and training to communities in need—and a WeWork Labs mentor in the UK . “You can’t go out on funding rounds or take part in accelerators without any planning.”
How to make a business plan and seven components every plan needs
While there is no set format for writing a business plan, there are several elements that are typically included. Here’s what’s important to consider when writing your business plan.
1. Executive summary
No longer than half a page, the executive summary should briefly introduce your business and describe the purpose of the business plan. Are you writing the plan to attract capital? If so, specify how much money you hope to raise, and how you’re going to repay the loan. If you’re writing the plan to align your team and provide direction, explain at a high level what you hope to achieve with this alignment, as well as the size and state of your existing team.
The executive summary should explain what your business does, and provide an introductory overview of your financial health and major achievements to date.
2. Company description
To properly introduce your company, it’s important to also describe the wider industry. What is the financial worth of your market? Are there market trends that will affect the success of your company? What is the state of the industry and its future potential? Use data to support your claims and be sure to include the full gamut of information—both positive and negative—to provide investors and your employees a complete and accurate portrayal of your company’s milieu.
Go on to describe your company and what it provides your customers. Are you a sole proprietor , LLC, partnership, or corporation? Are you an established company or a budding startup? What does your leadership team look like and how many employees do you have? This section should provide both historical and future context around your business, including its founding story, mission statement , and vision for the future.
It’s essential to showcase your point of difference in your company description, as well as any advantages you may have in terms of expert talent or leading technology. This is typically one of the first pieces of the plan to be written.
3. Market analysis and opportunity
Research is key in completing a business plan and, ideally, more time should be spent on research and analysis than writing the plan itself. Understanding the size, growth, history, future potential, and current risks inherent to the wider market is essential for the success of your business, and these considerations should be described here.
In addition to this, it’s important to include research into the target demographic of your product or service. This might be in the form of fictional customer personas, or a broader overview of the income, location, age, gender, and buying habits of your existing and potential customers.
Though the research should be objective, the analysis in this section is a good place to reiterate your point of difference and the ways you plan to capture the market and surpass your competition.
4. Competitive analysis
Beyond explaining the elements that differentiate you from your competition, it’s important to provide an in-depth analysis of your competitors themselves.
This research should delve into the operations, financials, history, leadership, and distribution channels of your direct and indirect competitors. It should explore the value propositions of these competitors, and explain the ways you can compete with, or exploit, their strengths and weaknesses.
5. Execution plan: operations, development, management
This segment provides details around how you’re going to do the work necessary to fulfill this plan. It should include information about your organizational structure and the everyday operations of your team, contractors, and physical and digital assets.
Consider including your company’s organizational chart, as well as more in-depth information on the leadership team: Who are they? What are their backgrounds? What do they bring to the table? Potentially include the résumés of key people on your team.
For startups, your execution plan should include how long it will take to begin operations, and then how much longer to reach profitability. For established companies, it’s a good idea to outline how long it will take to execute your plan, and the ways in which you will change existing operations.
If applicable, it’s also beneficial to include your strategy for hiring new team members and scaling into different markets.
6. Marketing plan
It’s essential to have a comprehensive marketing plan in place as you scale operations or kick off a new strategy—and this should be shared with your stakeholders and employees. This segment of your business plan should show how you’re going to promote your business, attract customers, and retain existing clients.
Include brand messaging, marketing assets, and the timeline and budget for engaging consumers across different channels. Potentially include a marketing SWOT analysis into your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Evaluate the way your competitors market themselves, and how your target audience responds—or doesn’t respond—to these messages.

7. Financial history and projections
It’s essential to disclose all finances involved in running your company within your business plan. This is so your shareholders properly understand how you’re projected to perform going forward, and the progress you’ve made so far.
You should include your income statement, which outlines annual net profits or losses; a cash flow statement, which shows how much money you need to launch or scale operations; and a balance sheet that shows financial liabilities and assets.
“An income statement is the measure of your financial results for a certain period and the most accurate report of business activities during that time, [whereas a balance sheet] presents your assets, liabilities, and equity,” Amit Perry, a corporate finance expert, explained at a WeWork Labs educational session in Israel.
It’s crucial to understand the terms correctly so you know how to present your finances when you’re speaking to investors. Amit Perry, CEO and founder of Perryllion Ltd.
In addition, if you’re asking for funding, you will need to outline exactly how much money you need as well as where this money will go and how you plan to pay it back.
12 quick tips for writing a business plan
Now that you know what components are traditionally included in a business plan, it’s time to consider how you’ll actually construct the document.
Here are 12 key factors to keep in mind when writing a business plan. These overarching principles will help you write a business plan that serves its purpose (whatever that may be) and becomes an easy reference in the years ahead.
1. Don’t be long-winded
Use clear, concise language and avoid jargon. When business plans are too long-winded, they’re less likely to be used as intended and more likely to be forgotten or glazed over by stakeholders.
2. Show why you care
Let your passion for your business shine through; show employees and investors why you care (and why they should too).
3. Provide supporting documents
Don’t be afraid to have an extensive list of appendices, including the CVs of team members, built-out customer personas, product demonstrations, and examples of internal or external messaging.
4. Reference data
All information regarding the market, your competitors, and your customers should reference authoritative and relevant data points.
5. Research, research, research
The research that goes into your business plan should take you longer than the writing itself. Consider tracking your research as supporting documentation.
6. Clearly demonstrate your points of difference
At every opportunity, it’s important to drive home the way your product or service differentiates you from your competition and helps solve a problem for your target audience. Don’t shy away from reiterating these differentiating factors throughout the plan.
7. Be objective in your research
As important as it is to showcase your company and the benefits you provide your customers, it’s also important to be objective in the data and research you reference. Showcase the good and the bad when it comes to market research and your financials; you want your shareholders to know you’ve thought through every possible contingency.
8. Know the purpose of your plan
It’s important you understand the purpose of your plan before you begin researching and writing. Be clear about whether you’re writing this plan to attract investment, align teams, or provide direction.
9. Identify your audience
The same way your business plan must have a clearly defined purpose, you must have a clearly defined audience. To whom are you writing? New investors? Current employees? Potential collaborators? Existing shareholders?
Related articles
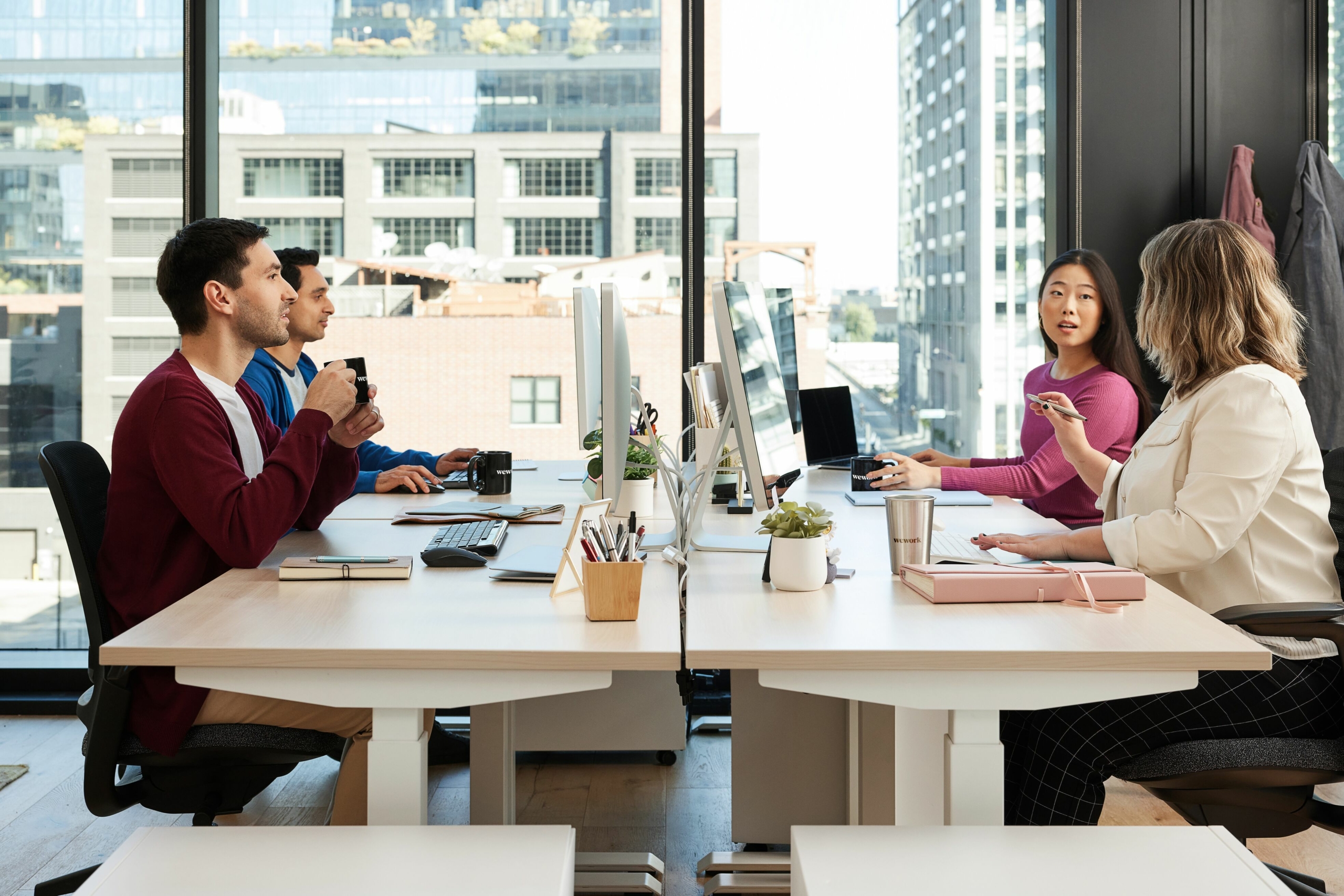

10. Avoid jargon
Avoid using industry-specific jargon, unless completely unavoidable, and try making your business plan as easy to understand as possible—for all potential stakeholders.
11. Don’t be afraid to change it
Your business plan should evolve with your company’s growth, which means your business plan document should evolve as well. Revisit and rework your business plan as needed, and remember the most important factor: having a plan in place, even if it changes.
A business plan shouldn’t just be a line on your to-do list; it should be referenced and used as intended going forward. Keep your business plan close, and use it to inform decisions and guide your team in the years ahead.
Creating a business plan is an important step in growing your company
Whether you’re just starting out or running an existing operation, writing an effective business plan can be a key predictor of future success. It can be a foundational document from which you grow and thrive . It can serve as a constant reminder to employees and clients about what you stand for, and the direction in which you’re moving. Or, it can prove to investors that your business, team, and vision are worth their investment.
No matter the size or stage of your business, WeWork can help you fulfill the objectives outlined in your business plan—and WeWork’s coworking spaces can be a hotbed for finding talent and investors, too. The benefits of coworking spaces include intentionally designed lounges, conference rooms, and private offices that foster connection and bolster creativity, while a global network of professionals allows you to expand your reach and meet new collaborators.
Using these steps to write a business plan will put you in good stead to not only create a document that fulfills a purpose but one that also helps to more clearly understand your market, competition, point of difference, and plan for the future.
For more tips on growing teams and building a business, check out all our articles on Ideas by WeWork.
Caitlin Bishop is a writer for WeWork’s Ideas by WeWork , based in New York City. Previously, she was a journalist and editor at Mamamia in Sydney, Australia, and a contributing reporter at Gotham Gazette .

Tom Hewitson, Chief AI Officer at leading AI training company General Purpose , offers tips for small businesses

Learn the differences between Class A, Class B, and Class C buildings based on their visual appeal, location, and amenities to see which of them best suits your business.

Short-term leases can offer startups and established companies some much-needed flexibility
How to Write a Business Plan: Your Step-by-Step Guide

So, you’ve got an idea and you want to start a business —great! Before you do anything else, like seek funding or build out a team, you'll need to know how to write a business plan. This plan will serve as the foundation of your company while also giving investors and future employees a clear idea of your purpose.
Below, Lauren Cobello, Founder and CEO of Leverage with Media PR , gives her best advice on how to make a business plan for your company.
Build your dream business with the help of a high-paying job—browse open jobs on The Muse »
What is a business plan, and when do you need one?
According to Cobello, a business plan is a document that contains the mission of the business and a brief overview of it, as well as the objectives, strategies, and financial plans of the founder. A business plan comes into play very early on in the process of starting a company—more or less before you do anything else.
“You should start a company with a business plan in mind—especially if you plan to get funding for the company,” Cobello says. “You’re going to need it.”
Whether that funding comes from a loan, an investor, or crowdsourcing, a business plan is imperative to secure the capital, says the U.S. Small Business Administration . Anyone who’s considering giving you money is going to want to review your business plan before doing so. That means before you head into any meeting, make sure you have physical copies of your business plan to share.
Different types of business plans
The four main types of business plans are:
Startup Business Plans
Internal business plans, strategic business plans, one-page business plans.
Let's break down each one:
If you're wondering how to write a business plan for a startup, Cobello has advice for you. Startup business plans are the most common type, she says, and they are a critical tool for new business ventures that want funding. A startup is defined as a company that’s in its first stages of operations, founded by an entrepreneur who has a product or service idea.
Most startups begin with very little money, so they need a strong business plan to convince family, friends, banks, and/or venture capitalists to invest in the new company.
Internal business plans “are for internal use only,” says Cobello. This kind of document is not public-facing, only company-facing, and it contains an outline of the company’s business strategy, financial goals and budgets, and performance data.
Internal business plans aren’t used to secure funding, but rather to set goals and get everyone working there tracking towards them.
As the name implies, strategic business plans are geared more towards strategy and they include an assessment of the current business landscape, notes Jérôme Côté, a Business Advisor at BDC Advisory Services .
Unlike a traditional business plan, Cobello adds, strategic plans include a SWOT analysis (which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) and an in-depth action plan for the next six to 12 months. Strategic plans are action-based and take into account the state of the company and the industry in which it exists.
Although a typical business plan falls between 15 to 30 pages, some companies opt for the much shorter One-Page Business Plan. A one-page business plan is a simplified version of the larger business plan, and it focuses on the problem your product or service is solving, the solution (your product), and your business model (how you’ll make money).
A one-page plan is hyper-direct and easy to read, making it an effective tool for businesses of all sizes, at any stage.
How to create a business plan in 7 steps
Every business plan is different, and the steps you take to complete yours will depend on what type and format you choose. That said, if you need a place to start and appreciate a roadmap, here’s what Cobello recommends:
1. Conduct your research
Before writing your business plan, you’ll want to do a thorough investigation of what’s out there. Who will be the competitors for your product or service? Who is included in the target market? What industry trends are you capitalizing on, or rebuking? You want to figure out where you sit in the market and what your company’s value propositions are. What makes you different—and better?
2. Define your purpose for the business plan
The purpose of your business plan will determine which kind of plan you choose to create. Are you trying to drum up funding, or get the company employees focused on specific goals? (For the former, you’d want a startup business plan, while an internal plan would satisfy the latter.) Also, consider your audience. An investment firm that sees hundreds of potential business plans a day may prefer to see a one-pager upfront and, if they’re interested, a longer plan later.
3. Write your company description
Every business plan needs a company description—aka a summary of the company’s purpose, what they do/offer, and what makes it unique. Company descriptions should be clear and concise, avoiding the use of jargon, Cobello says. Ideally, descriptions should be a few paragraphs at most.
4. Explain and show how the company will make money
A business plan should be centered around the company’s goals, and it should clearly explain how the company will generate revenue. To do this, Cobello recommends using actual numbers and details, as opposed to just projections.
For instance, if the company is already making money, show how much and at what cost (e.g. what was the net profit). If it hasn’t generated revenue yet, outline the plan for how it will—including what the product/service will cost to produce and how much it will cost the consumer.
5. Outline your marketing strategy
How will you promote the business? Through what channels will you be promoting it? How are you going to reach and appeal to your target market? The more specific and thorough you can be with your plans here, the better, Cobello says.
6. Explain how you’ll spend your funding
What will you do with the money you raise? What are the first steps you plan to take? As a founder, you want to instill confidence in your investors and show them that the instant you receive their money, you’ll be taking smart actions that grow the company.
7. Include supporting documents
Creating a business plan is in some ways akin to building a legal case, but for your business. “You want to tell a story, and to be as thorough as possible, while keeping your plan succinct, clear, interesting, and visually appealing,” Cobello says. “Supporting documents could include financial projects, a competitive analysis of the market you’re entering into, and even any licenses, patents, or permits you’ve secured.”
A business plan is an individualized document—it’s ultimately up to you what information to include and what story you tell. But above all, Cobello says, your business plan should have a clear focus and goal in mind, because everything else will build off this cornerstone.
“Many people don’t realize how important business plans are for the health of their company,” she says. “Set aside time to make this a priority for your business, and make sure to keep it updated as you grow.”
Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
- What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
Key Success Factors Of Business (With Examples)
- What Is A Mentor
- Mentor Traits
- Talent Management
- Performance Improvement Plan
- Performance Review Phrases
- Four Functions Of Management
- Difference Between Goals And Objectives
- How To Give Employees Feedback
- What Is An Operational Environment
- Key Success Factors
- How To Not Get Fired
- How To Be More Confident At Work
- One-On-One Meeting
- Performance Management
- Professional Development
- The Peter Principle
- Positive Feedback
- Low Hanging Fruit
- Upskill Your Employees
- Motivation Letter
Find a Job You Really Want In
Summary. The five key success factors — strategic focus, people, operations, marketing, and finance — help businesses determine their strategy for long-term success. Critical success factors, on the other hand, are the steps a company needs to complete to reach a goal.
As an organization that caters to its consumers, comprehending the needs and values of a business’s target demographic is crucial to forming a logical strategy.
Identifying and understanding the five key success factors of business is the best way to establish a foundation of knowledge about a company and its customers.
Key Takeaways
The five key success factors of business are:
Strategic focus
Companies need to implement all five key success factors in order to be successful in the long term.
Critical success factors are accomplishments businesses must have in order to meet their goals.
5 Key Success Factors of Business
What is a critical success factor, how to determine your business’s critical success factors, examples of critical success factors, factors of success in business faq.
- Sign Up For More Advice and Jobs
The key success factors are a series of five overarching aspects that ultimately determine a business’s long-term success.
The five larger groups contain ten smaller conditions, which need to be satisfied for the business to (hypothetically) thrive. In each of the world’s most profitable companies, the five success factors join together to establish a cohesive unit that’s lucrative for the long term.
The 5 Key Success Factors of business is a theory of strategic business management posed by Buck Lawrimore. The concept was derived after the analysis of over 100 popular books and 20 years.
Below is a definition for each factor:
Strategic focus. The strategic focus aspect of success means that the company’s goals, brand, and actions all move towards a targeted goal. The companies that manage to last in competitive markets are the ones whose leaders define their values and a realistic mission.
This factor is about sticking to the ultimate business objective and ensuring that every project is an effort toward this. A significant part of the strategic focus is making sure that the target chosen is constructed from the customer’s wants and needs .
Strategic Focus Key Success Factor Examples: Establishing and sharing core values that align with customers Leaders of the business are devoted to upholding the business’s core values The overall company mission is pursued through realistic goal-setting
People. The second ingredient for business success is the personnel that makes up the corporation. A company’s staff is what expands its development, which means it’s crucial to hire a team that’s qualified, dependable, and passionate about performing well.
This success factor also refers to how satisfied a business’s employees are with working there.
Just as much as employees need to strengthen the business, the business needs to provide its team with adequate opportunities for success as well. Satisfaction with working for your business builds productivity and increases employee retention rates .
People Key Success Factor Examples: Hiring the most qualified applicants based on their skills and experience The company’s employees fully understanding their job responsibilities Employees are given the chance to provide meaningful input on business decisions
Operations. The daily and long-term functioning of a company is defined as its operations. The specific operations that a business handles differ depending on the industry it exists in.
For example, the operations of a company that produces jeans likely involve sourcing materials, product creation, and generating sales. The business operations of a pediatrician ’s office would be very different.
For operations to be successful, the functions need to be recorded and have a measurable efficiency to determine if the processes need tweaking over time.
Operations Key Success Factor Examples: Processes focused on providing excellent service to the customer All operation efforts being documents and trackable over time Procedures being continually evaluated to ensure effectiveness
Marketing. Marketing acts as the branch between a company and its customers. There are many facets to good marketing, such as targeting the right audience, forming a recognizable brand, and evaluating consumer satisfaction post-purchase.
Marketing attracts new customers to your brand through media communication, supporting business growth. Without its customers, a business is quick to fall flat on its face.
Marketing Key Success Factor Examples: Defining a target marketing audience for the business Expanding the customer base through media communication and advertisements Eagerly receiving customer feedback and using it to improve
Finances. The final factor of success is often the first one that people’s mind jumps to when they consider the term, finances.
A company’s finances refer to the entirety of its assets, which include things like sums of money, properties, and materials.
In addition to maintaining the company’s financial data, it also includes their product’s financial characteristics. Pricing has a considerable impact on how customers perceive the product and how well it sells.
Finances Key Success Factor Examples: The products are appropriately priced for a profit to be made while still attracting and maintaining customers Keeping track of finances for a better understanding of company health Every employee of the company understands how their actions affect profits and finances
Critical success factors are a business management framework similar to the Five Factors, but it’s composed of the elements necessary to complete a project. It’s a checklist of qualities that enable a professional goal to be accomplished.
Unlike the Five Factors model, critical success factors do not outline the success of businesses. Rather:
They describe what needs to be done to achieve and provide a reliable system of measuring success.
A company’s critical success factors vary greatly depending on the circumstances of their industry, competitors, and what their goals are.
A business that sells alarm systems to homeowners might look at sales and the percentage of customers who left positive reviews to quantify their success.
Alternatively, a social media manager would consider their critical success factors to be the number of new customers generated monthly and website traffic.
Gather a group to manage critical success factors. Before beginning work towards establishing a business’s critical success factors, gather a team to handle the matter.
Delegating tasks ensures that nothing gets overlooked. The main participants in this group should be senior employees since they are the most experienced in the business and on the team.
Request feedback from employees . A company’s employees are its eyes and ears. As such, they usually have extremely valuable insight into what a business needs to do to succeed in long-term goals.
Develop business goals. Before evaluating the conditions needed to accomplish an objective, the business first must set its goals.
Consider what is needed to achieve these goals. This is the part where critical success factors come into play. Now that a list of achievable short and long-term goals has been set, think about what steps need to be taken to achieve them.
The elements required to reach a goal describe the company’s critical success factors when it comes to that particular project.
For example, a restaurant whose long-term goal is to improve its profits by 6% might take on the critical success factors of improving customer satisfaction and the quality of its food.
Put the plan into action. The beauty of critical success factors is that they map out a strategic plan for completing a professional goal . With an inventory of the most essential success factors settled, the only thing left to do is explain and execute the strategic plan.
To quantify the effectiveness of critical success factors over time, establish a measurement system. With a goal involving an aspect, like sales, measuring success is straightforward, but that’s not the case for every critical success factor.
Observe and evaluate as needed. A strategy based on critical success factors has been put into motion, but that doesn’t mean the job is done.
Strengthening employee satisfaction . Employees are the backbone of the company they represent. This means that boosting employee satisfaction is often a relevant critical success factor in improving other aspects like productiveness, regardless of industry.
Improving sales and profit. Since many businesses survive off of maintaining sales and profits, it makes sense that it’s a popular critical success factor. Improving these finances is implemented as a critical success factor when the long-term goal involves needing increased funding. For example, a dog groomer who wants to expand their business by buying a second location might address the success factor of improving sales to buy the new property.
Brand awareness. Customers need to know that a business exists for it to survive among its competition. A lot of companies feel this pressure and choose to focus on brand awareness as a critical success factor. Building up a name for a brand helps solidify standing in the market and assists in working towards a variety of long-term goals.
What are the five key success factors for a successful business?
The five key success factors for a successful business are:
What are success factors in business?
Success factors in business are the elements required for a business to be successful in the long term. Success factors can also be the steps a company needs to complete in order to meet a goal — these are usually called critical success factors.
University of Missouri System – Success Factors and Other Competency Models
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Sky Ariella is a professional freelance writer, originally from New York. She has been featured on websites and online magazines covering topics in career, travel, and lifestyle. She received her BA in psychology from Hunter College.
Recent Job Searches
- Registered Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Truck Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Call Center Representative Jobs Resume Location
- Customer Service Representative Jobs Resume
- Delivery Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Warehouse Worker Jobs Resume Location
- Account Executive Jobs Resume Location
- Sales Associate Jobs Resume Location
- Licensed Practical Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Company Driver Jobs Resume
Related posts

9 Common Reasons Why You Are So Indecisive
How To Get The Most Out Of A Business Conference

What Is Online Networking? (And How To Do It)

SMART Goals: Time Management Training
- Career Advice >
- Get Promoted >
- Get Started
Home >> #realtalk Blog >> Manage a business >> Writing an Effective…
Writing an Effective One-Page Business Plan: What You Need to Know (+ Free Template)
By Homebase Team

If you’ve started—or are starting—a small business, you’ve probably heard the words ‘business plan’ thrown around. That’s because a business plan is an important document with important information! Even a one-page business plan can help you address key questions early in the planning process.
That’s right—we said one page. In many cases, there’s no need for a supermassive document that takes ages to create. In this article, we walk you through what a good business plan needs—and what a business plan one-pager should contain.
Whether you’re writing your business plan for the first time or giving your existing plan a refresh, we’ve got your back. We’ve even got a free, downloadable business plan template to help you get started. Let’s get into it!
Why do you need a business plan?
A business plan is a blueprint for your business. It outlines everything your business needs, from goals to market to the steps you need to implement.
Business plans serve two main purposes:
- To help you set your business up for success. As you put together your business plan, you’ll be forced to think strategically about all your business goals and activities . Are they realistic? Is something likely to go wrong? What haven’t you thought of? The goal is for you to walk away feeling confident in the future of your business.
- To communicate the value of your business to others. It’s rare that entrepreneurs like yourself will go it 100% alone. You’ll likely work with partners, investors, or vendors to bring your small business to life. A business plan gives your collaborators confidence in you and your business and helps them support you in the best way possible.
Taking the time to create a business plan can feel like you’re wasting all-too-precious time, but it can help keep you focused and increase efficiency down the road. It’ll also help you make better business decisions off the bat so you can grow your small business quickly and wisely.
What are the 7 main points in a business plan?
Every business plan is unique, which is part of the reason writing one can feel a tad overwhelming. You can’t just copy and paste the plan from another business—instead, you need to assess your business’s idea within its niche.
Luckily, the skeleton of every plan is usually very similar. Whether you’re creating a plan for a neighborhood daycare or that cool new bar down the street , here are a few main points to put into any comprehensive business plan.
1. Executive summary
Your executive summary is an overview of your business plan.
Think about this section like a TL;DR or too long, don’t read . If someone wants to understand the gist of your business plan in just a few minutes, what information would they need to know?
| If you find yourself just sharing your executive summary with your business’s interested parties, it may be that your business plan is too long! Consider a one-page business plan as your business’s elevator pitch, or a longer executive summary. |
2. Company overview and description
In this section, you should introduce your business to the reader. By the time they finish reading this section, they should have a good idea of who you are, what you do, and what you sell—in other words, your business’s niche.
Don’t be afraid to dive into your own background and why you decided to start this business. Building a small business is personal, and your story can go a long way in giving the reader some context.
3. Market and competitive analysis
Every business needs customers. Here’s where you’ll detail who they are and the potential target market of your business, including your ideal customer.
You’ll also want to take note of potential competitors that may impact your business. These might be direct competitors, but could also be similar businesses that may compete for your customers’ time and money. For example, if you’re opening a cycling studio, you might consider any other type of fitness studio to be a competitor.
Competition isn’t a bad thing, but being aware of your competition is one way to ensure your business stands out from the crowd.
4. Business offerings
Here’s where you’ll outline what products or services your business will offer in more detail. It doesn’t have to be a complete laundry list, but it should give readers a general idea and show a certain degree of forethought and attention to details.
For example, if you’re opening a bakery , this might be a sample of your menu. Or if you’re an HVAC repair company , you might share an overview of the services you’ll offer your customers. This section might even mention the products or services you won’t offer and why, especially if it helps clarify how your business is unique.
5. Management and operational plan
From managing employees and inventory to securing equipment and a lease, there’s a lot that happens behind the scenes to keep things running smoothly. Every business plan should touch on how you’ll manage the day-to-day of your business.
This is also a great place to indicate key milestones and timelines so you know that you’re on track for a successful grand opening.
6. Sales, marketing, and PR strategy
Now that you’ve got all the research and operational plans in place , it’s time to start attracting customers and securing those sales. Even with the best products or services in town, every business can use a little marketing boost. Feel free to get creative. From social media to paid ads, there are tons of ways you can spread the word about your budding business .
7. Financial forecast and budget
No one loves to crunch financials, but when it comes to business, money talks. And a strong financial plan is key to the long-term success of your business.
This final section of your business plan should estimate the costs, revenue, and profits of your business in the short and long term. How do you plan to finance your business? What costs will you incur before opening day ? What are the ongoing costs?
Not only will this give your vendors and investors confidence in your business, but it helps you make sure that your business is profitable in the long run.
What is a one-page business plan?
A one-page business plan is essentially a condensed version of a full business plan.
It covers all the core information about your business without overwhelming the reader with details. The goal is to summarize your business plan for yourself and potential stakeholders so they can understand your business at a glance.
Depending on your business needs, this concise document may even be all you need to get your business off the ground. Or it could serve as a stepping stone to a more robust plan in the future.
Top benefits of a one-page business plan.
Bigger isn’t always better—and one-page business plans are here to prove it.
Here are some benefits and reasons why you might opt for a one-page business plan:
- To kickstart your business planning: A full business plan can be incredibly daunting. A one-page business plan gives you a place to start without feeling overwhelmed with the nitty gritty.
- To share and distribute: Sometimes potential vendors, partners, or investors want to get more information about your business before they sign on officially. Instead of leaving them with a massive document, a one-page business plan helps you share the relevant need-to-know information easily.
- To focus on the key details: If you’re early on in the business ideation process and want to make sure you have all the important information, a one-page business plan can help you easily validate your business plan.
- To save time: In the long term, you may still expect to put together a full business plan at some point. However, if you’re in a time crunch, a one-page plan can help you get the important insights without the time commitment.
- To easily edit: In an ever-changing business environment, a one-page business plan is much easier to keep updated.
Key details to include in a one-page business plan.
Above, we outlined the key components of any business plan. The key with a one-pager is to keep it brief without losing any of those important details.
Let’s look at the sections of a business plan one-pager and dig into how you can adapt them to cover all the details of your business—all on one page.
Summary and overview
Start your one-page plan by sharing the name of your business, what you do, and your main value proposition.
The problem—and your solution
In a few sentences, share the problem that your business solves and how you solve it. This clarifies why your business should exist, so it’s an important section!
Depending on your business, you may also want to share a few of your team members to help readers put a face to your business. Great examples include the executive chef for a restaurant, or the lead veterinarian for your vet clinic.
Target market
Briefly describe who you expect to be a customer and their characteristics. This could be in the form of a short “ideal customer” profile.
Competitor overview
Here, you’ll touch on potential competitors and what makes your business stand out.
Business timeline
Share the key milestones for your business. For example, pitch when you’ll start marketing your business, when you’ll hire employees , and when you expect to open.
Sales and marketing plan
Here, you’ll quickly highlight the key marketing activities that you’ll use to drive new customers to your business. Try to stick to the most interesting or high-value stuff, like a website or social media .
Financial projections
Outline your expected revenue , expenses, and profits to give the reader an idea of your financial future.
Our tips for creating a one-page business plan.
If you’ve ever written something with a limited word count, you know that sometimes keeping things concise can be easier said than done.
As you get writing your one-page business plan, here are some of our top tips so you can make the most of that one page.
- Focus on the need-to-know information.
- Avoid fluff and keep your sentences short.
- Link out to additional resources and material if more information is necessary.
- Don’t be afraid to strategically incorporate visuals to emphasize the important points.
- Feel free to up sections or have different versions of your one-page business plan based on who’s reading it.
- Get creative with formatting to keep information organized.
One-page business plan example.
If you’re skeptical that all that information can fit on one page—we have proof! Here’s an example that you can use to start thinking about your business plan.

Download our free one-page business plan template.
A one-page business plan is one of the most important pages you’ll write for your business. While there’s a lot to think about, it’s worth the effort to give both you and your partners peace of mind.
The good news is that we’ve done the heavy lifting for you! If the above one-pager looks good to you, we’ve pulled it together as a download for you. All that’s left for you to customize it for your unique business, fill in the sections, and get ready to launch your business.
Download your one-page business plan template PDF
| As you think about starting your business, think about how you’re going to keep track of your team! Get your business on track with one app to manage everything from employee scheduling to team communication. |
Get your team in sync with our easy-to-use, all-in-one employee app.
One-page business plan FAQs
Why should you create a business plan.
There are several reasons you should create a business plan, such as:
- Improving your decision-making as you start and grow your business.
- Setting realistic goals and timelines.
- Attracting top-notch suppliers, investors, and even employees.
- Keeping your business profitable and your financials in order.
What types of companies need a business plan?
From brand-new small businesses to established corporations, companies of all shapes and sizes need a business plan. It’s a key part of setting your business up for success and improving your business trajectory.
Even if you already have a business plan in place, revisiting it from time to time can help you stay on track with your goals and adapt as your business changes.
Can a business plan be one page?
Yes, in many cases a business page can be one page. The trick to creating an effective one-page business plan is making sure that you’re covering the most important pieces of information.
Our top tips? Keep it as concise and organized as possible, so you can effectively communicate the value of your business to your audience.
Writing a one-page business plan is simple. You can create a business plan from scratch or use a free template like the one above to stay on track, but generally, the steps to writing a one-page business plan include:
- Start with a short executive summary and value proposition to introduce your business.
- Share the problem your business solves and your solution.
- Give an outline of top competitors and how your business compares.
- Create a timeline of key milestones.
- Outline your sales and marketing plan for attracting customers.
- Summarize your financial projections and funding plans.
Remember: This is not legal advice. If you have questions about your particular situation, please consult a lawyer, CPA, or other appropriate professional advisor or agency.
Related posts
June 26, 2024
How to Start a Construction Business in 8 Easy Steps
Being able to build something from the ground up is an incredible skill: a skill you can monetize into your…
Top 4 Strategies to Grow Your Construction Business
For those in the construction business, laying the foundation for a house can be a piece of cake. But what…
How to Start a Retail Business: A Beginner’s Guide
So, you want to start a retail business. What now? There’s the idea, the products, the space, taxes, the employees,…
How to Start a Cleaning Business in 6 Steps
So you want to start a cleaning business. You want to work for yourself, you love a good Mr. Clean…
How to Start a Coffee Business in 10 Steps
Does the thought of running your own business make you jittery with excitement? How about going to work every day…
How to Start a Catering Business in 10 Steps
There are a lot of reasons to take a love of cooking down the path of entrepreneurship with a catering…
Subscribe to our newsletter
Looking for ways to stay up to date on employment laws and small business news?
Homebase makes managing hourly work easier for over 100,000 local businesses. With free employee scheduling , time tracking , and team communication , managers and employees can spend less time on paperwork and more time on growing their business.
- Hiring & onboarding
- Team communication
- Employee happiness
- HR & compliance
- Integrations
- Food & beverage
- Beauty & wellness
- Medical & veterinary
- Home & repair
- Hospitality & leisure
- Education & caregiving
- Contact sales
- Become a Partner
- Careers – We’re hiring!
- #realtalk Blog
How to use the mortgage calculator
Why use a mortgage calculator, key factors that affect your mortgage payments, how to calculate a mortgage payment, what is amortization, how lenders decide how much house you can afford, tips for lowering your monthly payments, common mistakes to avoid.
- Reasons your payment could increase
Mortgage Calculator: Estimate Your Monthly Payments
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate mortgages to write unbiased product reviews.
Calculating Your Mortgage Payment
Before you start house hunting, you need to know much house you can afford. A mortgage calculator can help by showing you how much you'll pay each month depending on the price of the home you buy and the size of your down payment.
The free Business Insider mortgage calculator shows how much you'll pay each month based on your home price, down payment, term length, and mortgage rate . We also provide customized tips on how to save money on your mortgage.
Mortgage Calculator
- Paying a 25% higher down payment would save you $8,916.08 on interest charges
- Lowering the interest rate by 1% would save you $51,562.03
- Paying an additional $500 each month would reduce the loan length by 146 months
To see your mortgage payment with our calculator, here's what you'll need to provide:
The purchase price of the home: This is the amount you agree to pay the seller.
Down payment: How much of your own cash you'll be bringing to the transaction. A down payment on a house may be as low as 3%, or even 0%, depending on the loan type. The calculator's default is 20%, which is the amount you'll need to put down if you want to avoid paying for private mortgage insurance if you're getting a conventional loan.
Length of the loan: Your loan term, or the amount of time it takes to pay off your mortgage. The calculator uses a 30-year mortgage term as the default.
Interest rate: The amount your mortgage lender charges you for borrowing the money to purchase your home.
With these inputs, you can use the calculator to help determine how much house you can afford and what your monthly payments and overall expenses will be.
Click on "more details" to see how much you might pay in interest over the life of your loan, and how different rates and term lengths can impact that amount. You'll also get some tips on exactly how you can save on interest.
How can it help homebuyers?
You've entered numbers into the mortgage calculator. What can you do with this information?
- Determine how much house you can afford. With our mortgage calculator, you can enter how much you want to spend on a home and the amount you have for a down payment. If the monthly payment is too high for your current budget, you may decide that you need to buy a less expensive home.
- See how much more you need to save. The calculator also shows how a higher or lower down payment will affect your monthly mortgage payments. This can help you decide if you're ready to buy a house now, or if it makes more sense to wait a little longer to save more.
- Choose a term length. Input a few term lengths to figure out which one best fits your budget. With a 30-year term, your monthly payments will be lower, but you'll pay more in the long run since you're spreading payments out over a longer period of time. A 15-year mortgage will give you a higher monthly payment but cost less over the years. Play around with term lengths and think about which one best suits your goals.
- Find out how your interest rate affects payments. This can be particularly helpful if you're thinking about refinancing , or if you think you could snag a lower rate by improving your credit score before applying for a mortgage. Use the calculator to see how much of a difference a slightly lower rate could make, and if it's worth it to you.
- Learn how to save money. Once you've entered your numbers, we provide a few suggestions on how you can either lower your monthly payments or save in the long term.
This mortgage calculator shows you how much you'll pay toward your principal and interest each month, but your actual mortgage payment will likely include a couple other charges. Here's a breakdown of the different items that make up your mortgage payment.
- Principal : This is the amount you borrow to buy your home. For example, if you want to buy a $400,000 home and have $50,000 for a down payment, you'll need to borrow $350,000. Your loan principal is $350,000. You'll pay a portion of this each month, reducing your principal balance over time.
- Interest: This is what the bank charges you to borrow money.
- Taxes: Mortgage lenders typically include your property taxes in your monthly mortgage payment and hold this part of your payment in an escrow account. When the taxes come due, the lender will pay them on your behalf using the money in the escrow account.
- Insurance: As with property taxes, your homeowners insurance premium will also be included in your monthly payment and set aside in an escrow account. If you made a small down payment or you have an FHA mortgage , a small portion of your monthly payment will also go toward a mortgage insurance premium, which protects the lender.
You may see this full mortgage payment amount referred to as "PITI."
Interest rates and their impact
Mortgage rates fluctuate from day to day and even from hour to hour. The higher your rate, the more you'll pay on your mortgage, both on a monthly basis and over the life of the loan.
You can get a better rate by making a larger down payment or improving your credit score . But overall rate trends are influenced by what's going on in the economy. So a homeowner who got their mortgage several years ago may have a significantly lower rate compared to someone getting a mortgage right now.
The role of property taxes and insurance
Because your lender benefits when you pay your property taxes and homeowners insurance, it typically will include these costs in your monthly mortgage payment.
The average cost of homeowners insurance in the US is $1,428 per year, which would add $119 to your monthly payment.
You can also check out the average property taxes in your state to get an idea of how much you might pay for this cost, but keep in mind that tax rates can vary a lot from city to city. Your mortgage lender should be able to give you an estimate based on where you're planning to buy.
Prefer to do it by hand? You can calculate your monthly mortgage payment (excluding property taxes and insurance) using the following equation:
M = P [ i(1 + i)^n ] / [ (1 + i)^n – 1]
"P" is your principal .
The "i" is your monthly interest rate . This is different than the interest rate you see on your mortgage documents. The lender provides the yearly interest rate, so divide that rate by 12 for this equation. If your interest rate is 4.25%, divide 0.0425 by 12 to find your monthly rate: 0.00354166%.
To find "n," the number of months required to repay the loan , multiply the number of years by 12. If you have a 30-year mortgage, multiply 30 by 12 to get 360 months.
Once you calculate M (monthly mortgage payment), you can add in the monthly property tax and homeowners insurance payment.
Amortization refers to the process of making payments toward a debt until you've fully repaid it. With a mortgage, you'll make monthly payments that are calculated in a way that allows you to pay off your balance by the end of your term while also accounting for the interest you owe.
When you get a mortgage, you'll receive an amortization schedule for your loan. This schedule will show you how each of your monthly payments breaks down in terms of how much you're paying toward your principal vs. interest.
For example, say you have a $300,000 mortgage with a 6.5% interest rate. Your monthly payment would be $1,896. To determine how this payment breaks down each month, you'll need to multiply the loan amount by your interest rate. Then, divide that number by 12 to see how much you'll pay in interest on a monthly basis.
300,000 × 0.065 = 19,500
19,500 / 12 = 1,625
This means that on your very first mortgage payment, you'll pay $1,625 in interest. The remaining $271 will go toward reducing your principal.
To determine how your second monthly payment breaks down, simply subtract the $271 from your principal and run the calculation again with the new loan amount.
You can use a spreadsheet tool like Excel to make it easier to calculate your full amortization schedule, or you can simply use an online amortization calculator.
Lenders have a responsibility to make sure they aren't lending more than what their borrowers can afford to pay back. This is known as the ability-to-repay rule.
To determine how much you can afford to borrow, lenders will look at your income, debts, assets, employment, and credit. They want to make sure that you have the income to afford your monthly payments, and that a mortgage wouldn't push your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) to an unacceptable level.
On conventional loans , you can't have a DTI higher than 50%, and borrowers with lower ratios will typically get better rates.
But just because a lender says you can afford a certain amount doesn't mean you'll necessarily be comfortable with the monthly payment. Think about what your budget can comfortably handle when deciding your price range.
Explore different down payment options
As you play around with the calculator, you can see how different down payment amounts will ultimately impact your monthly payment. The less money you borrow, the less you'll need to pay each month.
However, the more you put down, the less money you'll have left over for things like furnishing your new home or paying for repairs and maintenance. Find the right balance that gives you a sufficient down payment but also leaves you enough cash for other costs.
The benefits of shorter term loans vs. longer term loans
The longer your loan term is, the lower your monthly payment will be.
Paying back $200,000 over the course of 30 years is going to yield a much lower monthly payment than paying that same amount back over the course of 15 years. However, you'll pay a lot more interest on the 30-year loan. This is because you'll not only be accruing interest for a longer period of time, but longer terms also come with higher interest rates.
If you can afford a higher monthly payment, a shorter term could be worth it if your goal is to save money overall. But if you want to keep your monthly payment as low as possible, it's best to go with a longer term.
Get a better rate
Rates vary among mortgage lenders, so be sure to get approved with three or four different lenders to be sure you're getting the lowest rate possible.
You can also work on getting a higher credit score and lowering your DTI to get access to lower rates.
Buy a less expensive home
You don't need to borrow the full amount a lender is willing to lend to you. For example, if your lender offers you a loan for $300,000 but you only borrow $270,000, you could potentially save around $200 per month.
Underestimating property taxes and insurance
First-time homebuyers are often surprised by how much their taxes and insurance can raise their monthly payment amount. Property taxes in particular can be fairly expensive, often adding at least a couple hundred dollars more to the payment.
It's also important to understand that these costs can change every year. If your property taxes or homeowners insurance premium increase, your payment will go up as well.
Forgetting to consider closing costs
The down payment isn't the only thing you'll need cash for at closing. Closing costs include lender fees, the cost of your appraisal, things you need to prepay like homeowners insurance, and other costs related to the mortgage and the home purchase.
In total, you'll typically pay between 3% and 6% of the loan amount in closing costs.
Reasons your monthly mortgage payment could increase
Your monthly mortgage payment amount will likely change slightly over the years, and may go up over time. Two of the most common reasons for this include:
- You have an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM): Once your ARM's fixed-rate period is over, your rate will reset periodically, and your monthly payment could go up as a result.
- Your taxes or insurance increased: Most borrowers pay their property taxes and homeowners insurance premiums into an escrow account, which the lender pays out of on your behalf when those bills are due. If your taxes or premium have increased, so will your monthly payment.
Mortgage calculator FAQs
A mortgage calculator can give you an estimate of how much you might pay each month for a mortgage based on the home price, the size of your down payment, the loan term length, and your interest rate.
Mortgage calculators can be used for many different types of mortgages, including government-backed loans or adjustable-rate mortgages. Just be sure to account for any additional costs the calculator doesn't include (like FHA mortgage insurance, for example).
Mortgage calculators are only as good as the information they're given. If you end up with a different rate than what you put into the calculator, your monthly payment will be different, too.
With current average rates, you might be able to borrow a little over $300,000 on a 30-year loan if you're looking to pay $2,000 a month for a mortgage, not including taxes or insurance. This is higher than the median monthly mortgage payment, but lower than the average monthly mortgage payment .
You might need an annual salary of $120,000 or more to qualify for a $400,000 30-year mortgage. This is just a rough estimate — the amount you'll qualify for will depend on your current debt load and your estimated taxes and insurance in addition to your income. Depending on your individual circumstances, you may need to make more or less than this to qualify.
Based on current rates, an average mortgage payment on a $300,000 house might be between $1,700 and $1,800 per month, not including taxes or insurance. But this will vary depending on the rate you can get.
A $500,000 mortgage might cost between $3,200 or $3,300 per month plus taxes and insurance. Depending on your individual mortgage rate, you may pay more or less than this.
- Mortgages and mortgage lenders
- Home equity
- The housing market
- The economy and the forces that impact mortgage rates
- Budgeting and saving
- Retirement savings
- Main content

Content Quicklinks:
✔ How to Start a Coaching Business From Scratch ✔ 8 Strategies to Build a Successful Coaching Business ✔ How Profitable is a Coaching Business? ✔ How Long Does It Take to Build a Coaching Business? Factors That Will Affect Your Timeline ✔ Is it Hard to Start a Coaching Business?
Share This Article:
How long does it take to build a coaching business from scratch.

Starting a coaching business can be a thrilling yet challenging journey. Many aspiring coaches, fueled by their passion for helping others and their newfound coaching skills, leap into the business expecting quick success. However, the reality is often more complex.
There’s no single path to building a coaching practice. Your timeline will largely depend on your expectations and circumstances.
On the other hand, being clear on those expectations and what a coaching business demands will save you time and reduce trial and error.
So, if you want to know how long it will take to build a coaching business, let’s start at the beginning.
How to Start a Coaching Business From Scratch
You simply can’t skip specific steps when building a coaching business . Here’s a checklist to help you plan this process better.
1. Reflect and Research
Identify what you’re most passionate about helping people with and what you have expertise in. Reflect on what’s unique about your skills, experiences, and interests to determine what type of coaching you are qualified to offer.
Consider what additional training and certifications you’ll need to pick up to serve your audience.
Researching the market will give you a better idea about what services you can offer and how to position them. Dig deeper into your selected coaching niches to see what strategies you want to (or don’t want to) adopt from your competitors.
2. Specialize
Choose a specific area of coaching that addresses a clear and tangible problem. For example, as a business coach, you can help executives double their revenue or help single moms build profitable online businesses from home.
[ Read: How to Find Your Coaching Niche: A Coach’s Guide ]
Narrowing down your focus helps attract clients who need your specific expertise. Define who your ideal client is and understand their needs, challenges, and goals. The more specific your niche, the easier it will be to market your services—and choose the training most relevant to your goals.
3. Get Trained
While formal certifications aren’t obligatory in coaching, it’s important to invest in your education so you can serve your clients effectively. Acquiring expertise in your niche builds credibility and enables you to address specific client needs. Credentials from organizations like the International Coach Federation (ICF) can also help you market yourself in the future.
Define your budget and time available to complete your training requirements. Coaching certification programs range from a few hundred dollars to over $10,000 and last anywhere from a few days to a year. More expensive doesn’t necessarily mean better, but comprehensive programs usually have more practical application and mentorship opportunities.
4. Develop a Business Plan
Establish your short-term and long-term goals for your coaching business. Consider the services you want to offer, such as one-on-one sessions, group coaching programs, or workshops. If you want to publish books and courses or speak on stages, include that in your plan as well.
Define how much you want to make in a year and break it down into quarterly or monthly revenue goals. List your larger potential expenses, such as hiring freelancers, working with your own coach, or spending on advertising. This will help you have clearer expectations of your cash flow .
5. Create Your Offer
Design one or more coaching packages that can meet the needs of your various clients. Structure them on various levels of your clients’ typical growth journey, each with increasing levels of support, and set clear outcomes for them. Price your packages based on the value they provide and current market rates.
[ Read: The 4 Pillars of Sold-Out Life Coaching Packages ]
To set up your packages easily, you can use Paperbell . It’s an all-in-one client management tool that lets you customize your offers and automatically generate landing pages for them. Then, those pages will be tied to your payment system, digital contract signing, and session bookings.
6. Set up Your Business
To legally establish your coaching practice , choose a business structure. As a sole proprietor, you can usually complete the paperwork in a day, while registering an LLC may take a few weeks.
Implement a solid accounting cadence or hire a professional to track your income, expenses, and taxes accurately. Consider getting life coach insurance to protect yourself from potential disputes or accidents in the future.
Consider whether you need to rent an office space for your sessions or if you want to run an online coaching business from a dedicated workspace.
7. Establish Your Brand
Building your brand as a coach starts with creating a brand identity that relates to your target audience. Create a catchy name for your business and packages and a tagline that encapsulates how you want to position yourself.
Set up a professional website that does the following:
- Communicates the benefits of your coaching services clearly
- Tells your story and credentials through your bio
- Features your client testimonials
- Any helpful resources related to your specialty
If you need a cheat sheet, download our free template pack for coaching websites and packages .
Successful coaches consider social media interactions their number one strategy for nurturing relationships with potential clients. You can use the platforms most relevant to your niche to share valuable advice and your story and connect with your audience.
8. Market Your Packages
Creating and sharing valuable content through a podcast, blog, or YouTube channel can showcase your expertise and help sell your packages. You can also build an email list to send your potential clients regular newsletters with tips, updates, and special offers.
Networking is crucial too, such as attending industry events, joining professional organizations, and connecting with other coaches and potential clients. These strategies will help you establish your reputation, attract clients, and grow your life coaching business.

8 Strategies to Build a Successful Coaching Business
Everyone’s journey is different. However, keeping these strategies in mind will help you significantly speed up your process of building a profitable coaching business.
- Get hyper-specific about your niche: Many new coaches make the mistake of offering vague, intangible results. This makes it challenging to attract and retain clients. However, the reality is that people don’t hire life coaches; they hire people who can solve their problems.
- Learn how to articulate your brand: Ditch the jargon and use everyday language that speaks to your client’s experience. Coaching skills aren’t enough to build a business; you must also get good at, or outsource, selling your practice.
- Think in packages, not sessions: Avoid offering coaching sessions without a clear goal. Instead, design packages that provide measurable outcomes to a specific problem for a defined audience.
- Leverage your experience: You can’t be good at everything. Build your coaching practice on your past professional and personal experiences that help you rise above being a generic coach.
- Build a sustainable client base: Start with a few clients, gather testimonials, and build your reputation for delivering results. Then, gradually build a sustainable client generation system with no more than one or a handful of strategies to keep it manageable.
- Invest in your education : Learning doesn’t stop with one course or training. You must continuously look for ways to improve your ability to transform your clients, businesses, and marketing strategies.
- Ask for help: Hire your coach or mentor or join a coach community for support. Don’t be afraid to seek help and guidance from those who have successfully built their coaching businesses.
- Maintain financial stability: If you have a stable job, don’t quit once your first potential client shows up. This immediately reduces the pressure of making a full-time income from coaching and allows you to focus on growth.
How Profitable is a Coaching Business?
The coaching industry is estimated to be worth $6.25 billion in 2024, generated by around 145,500 active coaches worldwide. This would mean close to $43,000 yearly in revenue for an average coach. However, estimating the profitability of coaching is not that simple.
Most coaches surveyed are certified by major organizations like the ICF. However, most of them stay under the radar. For instance, this statistic wouldn’t consider someone like Tony Robbins with a coaching empire worth $600 million .
Even if we look at the coaches who make up these numbers, it’s difficult to tell how much they make individually. Some may work full-time and only coach on the side, while others make six figures from various business activities beyond coaching, like publishing, teaching, or speaking.
Anecdotally, many successful coaches report to reach stable revenue in 1-4 years .
For example, Tim Brownson transitioned from a corporate job to coaching and took about three years to achieve sustainable income, eventually reaching over $100,000 annually through coaching, teaching, and selling products.
Karyn Greenstreet switched to coaching-consulting and mastermind groups to achieve a $100,000+ income within a year. Heather Thorkelson, on the other hand, built her business steadily over two years, generating between $50,000 and $100,000 through consistent client engagement and content creation.
As relationship coach Jill Jerabek says, there’s no set timeline to reach your ideal income as a coach. It all depends on your strategies and preferences.

How Long Does It Take to Build a Coaching Business? Factors That Will Affect Your Timeline
You can set up a landing page with your services and drive ads to it in a day. However, getting to a point where you’re profitable can take years and depends on several factors.
If you have substantial resources set aside to run campaigns and hire people to promote your business, you’ll fill up your calendar with high-ticket clients much faster. Recommendations from an extensive network can also get you more sign-ups with less effort. Getting the right mentorship can give you shortcuts but may take a larger initial investment.
Some aspiring coaches take their first clients on the side while working full-time. Their employer might even sponsor their training and certification if it’s related to their current position, usually as a manager or HR representative.
Prior experience can also make a big difference. Coming from a financial background will make you a more credible money coach, and spending time in ashrams can add to your perspective as a spiritual coach.
Last but not least, your location and personal lifestyle will affect your living costs and, in turn, impact your revenue targets. In the same way, the spending capacity of your target audience will affect how much you can charge them.
Is it Hard to Start a Coaching Business?
Starting a life coaching business isn’t easy—and it’s certainly not an overnight process. It requires dedication, time, and strategic planning.
By focusing on a specific niche, leveraging your unique skills, and continuously learning, you can transform your passion for coaching into a profitable business.
Even if the journey is challenging sometimes, persistence and the right approach will help you create a thriving practice that aligns with your values and expectations.

Further Reading

Are You Undercharging?
Find out in this free report.
Ever wondered exactly what other coaches are offering, and for how much? Find out if you’re charging too much or too little by benchmarking your own rates with this free report.
Subscribe to our updates for instant access:
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
- Financial Advisor
Financial Planning Basics

Updated: Jun 26, 2024, 4:51pm

No matter the size or scope of your financial goals, a financial plan can help make them a reality.
Financial planning is the process of looking at the current state of your finances and making a step-by-step plan to get it where you want it to be. That may mean devising a plan to become debt-free or figuring out how to save enough money for a down payment on a new home.
This process can include many aspects of personal finance, including investing, debt repayment, building savings, planning for retirement and even purchasing insurance.
Anyone can engage in financial planning—it’s not just for the wealthy. You can get started on making financial goals on your own, and if you choose, you can work with a financial professional to help devise the smartest plan to make those goals a reality.
Advertisement
Datalign advisory.

Access to thousands of financial advisors.
Match with a pre-screened financial advisor that is right for you.
Connect with your match for a free, no-obligation call.
5 Steps to Create a Financial Plan
A financial plan is devised of smaller goals or tasks that will help support you along your financial journey. Create a financial plan with these five steps:
1. Identify Your Financial Goals
By identifying your financial goals, you’ll have a clear idea of what you need to accomplish to make them happen. Your goals should be realistic and actionable and include a timeline of when you want to accomplish them.
Making a goal to pay off credit card debt by a certain date, for example, would be an appropriate financial goal that will set you up for success.
2. Set a Budget
Having a clear picture of your finances will make it easier to achieve any financial goals. A budget can help you understand where your money is going each month. It can also help you identify where you may be overspending, giving you opportunities to cut back and allocate that money elsewhere.
One of the easiest budgets to start with is the 50/30/20 budget . This budget plan allocates your monthly income into three buckets: mandatory expenses (50%), savings and debt repayment (20%) and discretionary spending (30%). This is just one of many types of budgeting plans out there.
A budget should be a guide to help you understand your monthly finances and devise smaller goals that will bring you closer to your long-term financial goals. You likely won’t always follow your budget down to every single penny; keeping this in mind will help you stay on track, rather than get discouraged and give up on budgeting altogether.
There are apps out there that make budgeting much easier by helping you visualize your spending and savings choices each month. Some budgeting apps even give you the option to enter your financial goals directly into their platform to help you stay on track. A fully featured budgeting app allows you to track spending, manage recurring bill payments, set savings goals and manage your monthly cash flow.
3. Build an Emergency Fund
Building an emergency fund will help make sure that a financial emergency doesn’t become a catastrophic financial event.
Experts usually recommend having six months’ worth of living expenses saved to cushion you, should the unfortunate unexpected happen, such as losing a job. But six months’ worth of money can be unattainable for those who may be struggling financially, or those living in tight financial means each month.
You can start building an emergency fund by setting a few dollars aside each paycheck. You can start with a small fund goal of $100 to $200 to establish your fund. From there, you can create other smaller goals that will add up to a larger financial cushion. Some budgeting and savings apps also give you the option of rounding up to the nearest dollar in transactions and funnel that spare change toward your savings.
4. Reduce Your Debt
Having to make debt payments each month means you’ll have less money to allocate toward your purchase goals. Plus, carrying credit card debt can be expensive; every month, you’re accruing interest on your balance, which can make it take longer to pay off.
There are a variety of debt payoff methods out there. Two of the most popular include the debt snowball and debt avalanche methods . With the snowball method, you’ll pay off your smallest balance debts first, then make your way to the ones with the higher balances. The debt avalanche, on the other hand, starts with higher interest rate debts first.
5. Invest for the Future
Although risky, investing can help grow your money, even if you’re not wealthy. You can get started with investing by enrolling in your company’s 401(k) plan or opening a low-or-no fee account through an online broker .
Keep in mind that investing always involves some risk; you could end up losing the money you invest. There are also robo-advisors that automatically recommend investments based on your goals and risk tolerance.
Looking For A Financial Advisor?
Get In Touch With A Pre-screened Financial Advisor In 3 Minutes
Via Datalign Advisory
Bottom Line
A financial plan is composed of a series of smaller goals that will help you achieve a larger financial goal, such as purchasing a home or retiring comfortably. A solid financial plan includes identifying your goals, creating a budget, building an emergency fund, paying off high interest debt and investing.
- How To Protect Your Assets
- How To Choose A Financial Advisor
- How To Build Wealth
- Are You In The Top 1%?
- Types Of Financial Advisors
- What Is A Financial Advisor?
- What Is A Financial Planner?
- What Is Fiduciary Duty?
- What Are Trust Funds?
- What Is Asset Management?
- What Is A RIA?
- What Is A CFP?
- What's My Net Worth?
- Bad Advice From Financial Advisors
- More In Financial Advisors
- Best Retirement Income Funds
- Best Roth IRA Accounts
- Best Target Date Funds For Retirement
- Top 4 Retirement Worries
- Traditional IRA Vs. Roth IRA

How To Become A Financial Advisor
What You Need to Know About Independent Financial Advisors
Financial Advisor Vs. Financial Planner: What’s The Difference?

What Is FINRA?
Fee-Only Financial Planner vs. Fee-Based: What’s the Difference?
Financial Advisors For Military Personnel: Everything You Need To Know
Jordan Tarver has spent seven years covering mortgage, personal loan and business loan content for leading financial publications such as Forbes Advisor. He blends knowledge from his bachelor's degree in business finance, his experience as a top performer in the mortgage industry and his entrepreneurial success to simplify complex financial topics. Jordan aims to make mortgages and loans understandable.

[email protected]
+44 (0)1458 253536, comparing business term deposit rates: what you need to know.

Especially nowadays, when more people are venturing into e-commerce, it’s important to have your capital. Sure, you could take out a bank loan as advised by experts to speed things up, but if you’re not in a hurry and are slowly building up your funds, then you should learn more about business term deposits.
What are business term deposits?
A business term deposit is a financial product sold by banks or other financial institutions wherein one can deposit or invest a certain amount of funds at a fixed rate of interest for a fixed term. Understanding the value financial institutions offer can be vexing, so we’ve compiled a comprehensive guide on what you need to know about business term deposits.
Key factors you need to know about business term deposit rates
Below are key factors you need to keep in mind when comparing business term deposit rates so you can make calculated decisions and effectively maximize the return on your investments.
Deposit amount. One of the factors that could influence your business term deposit rates is the amount you’re investing. It differs in every bank or financial institution, and there are cases wherein they may offer tiered interest rates that are based on the deposit amount. As a general rule, the bigger the sum, the more qualified you are for competitive rates.
Term length . Business term deposits generally work better for longer terms since they tend to offer higher interest rates compared to shorter ones. In a way, it becomes a direct reflection of your funds’ commitment to the bank for the long haul.
Financial institution. As mentioned earlier, different financial institutions and banks offer varying competitive rates, especially for longer-term deposits.
Market conditions. The most important factor that ties everything together is the overall economic conditions; this is the deciding factor that can influence business term deposit rates the most.
Strategies to effectively compare business term deposit rates
Now that you have a better understanding of the factors that affect business term deposit rates, it’s time to explore and implement strategies to assess and compare the rates effectively.
Identify your needs. Before you start your investment journey, you need to first identify what your business needs are: Do you plan on expanding your business in a matter of years? Maybe you also want to explore other ideas and bide your time. Whatever it may be, you must take into consideration the availability of your funds as well as your risk tolerance when you’re comparing rates.
Do your research. We live in an era where everything is easily accessible online, so make a list of reputable banks and financial institutions that offer competitive business term deposit rates.
Compare interest rates. Once you’ve shortlisted a few names, compare their advertised interest rate offers side by side and take note of their tiered interest rate structures.
Look into their other features. Apart from their rates, see if these banks and financial institutions offer other services that make their products more appealing. Maybe they offer flexible payment options or even automatic renewal options upon maturity with no added interest.
Review their terms and conditions. Don’t be blinded and focus on the headline rate; make sure you also read and understand the fine print, carefully reviewing their term deposit product disclosure statement to see if there are other associated fees and technicalities in their requirements.
Use online comparison tools. If you’re struggling to compare rates side by side, then you can do your research and shortlist much faster by utilizing online comparison tools. Do take note that these tools may not wholly capture the features of business term deposit rates, but they’re still helpful tools to streamline your process.
Finding the best business term deposit rate is just the tip of the iceberg; there are a couple of other considerations you should look into before choosing where to deposit, but at least this guide will get you started on your financial road. By understanding these factors that influence business term deposit rates, you can work your way around and find an institution that’s aligned with your goals and consider fostering a long-term relationship.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Featured articles
- Industry and broker news
- IT development news
- Lender and investor news
- Loans and deals completed
- People on the move
- Product news
- SMEs and economic news
- Overseas news
- Trade and export finance
Business Money magazine
Sign up to our newsletter
My Newsletter
- Present loan facilities *
- Finance currently provided by *
- Last year’s turnover *
- Business name *
- Phone number *
- Consent * I give my consent for you to retain my data for the purposes of processing and completing my request(s) * *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Agriculture and rural industries
- Contracting and building trades
- Education, training and personnel services
- Food retailing and production
- Freight, distribution and storage
- Leisure and arts
- Manufacturing and engineering
- Motor sales, repair and hire
- SME economic news
- Retail and convenience stores
- The wet trade
- training and personnel services

COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
Match every important task or function with one person in charge and accountable. Again, if you don't have that person right now, don't just ignore it. Mention in your plan that it's a known gap, when you intend to address it, and if you have anyone in mind. 5. It clearly identifies assumptions.
While your plan will be unique to your business and goals, keep these tips in mind as you write. 1. Know your audience. When you know who will be reading your plan—even if you're just writing it for yourself to clarify your ideas—you can tailor the language and level of detail to them.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and ... Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan. Not all of the plan consists of writing - there are also financial ...
4. Marketing plan. The marketing plan section details how you plan to attract and retain customers. It covers the marketing mix: product, price, place, and promotion. It shows you understand your market and have clear, measurable goals to guide your marketing strategy.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
That's where your business plan comes in. It provides investors, lenders and potential partners with an understanding of your company's structure and goals. If you want to gain the financial autonomy to run a business or become an entrepreneur, a financial advisor can help align your finances. 1. Executive Summary.
13 Key Business Plan Components. We've built a comprehensive guide to the major parts of a business plan for you. From elements like the executive summary to product descriptions, traction, and financials, we'll guide you on all of the key sections you should include in your business plan. December 14th, 2022 | By: The Startups Team | Tags ...
A typical business plan is 15 to 25 pages. Its length depends on a variety of factors, such as whether your business is introducing a new product or belongs to a new industry (which requires ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan: Section 1: Executive Summary. Present the company's mission. Describe the company's product and/or service offerings. Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
This is typically one of the first pieces of the plan to be written. 3. Market analysis and opportunity. Research is key in completing a business plan and, ideally, more time should be spent on research and analysis than writing the plan itself. Understanding the size, growth, history, future potential, and current risks inherent to the wider ...
6. Strategy and implementation plans. When it comes to starting a business, having a solid plan of attack is essential. That's why the strategy and implementation plan section of your business ...
A one-page business plan is a simplified version of the larger business plan, and it focuses on the problem your product or service is solving, the solution (your product), and your business model (how you'll make money). A one-page plan is hyper-direct and easy to read, making it an effective tool for businesses of all sizes, at any stage ...
8. Write up your financial forecast. This is one of the trickier parts of writing a business plan and requires a good understanding of business finance and accounting. If your business has been trading for a while, you'll want to start off by outlining some historical data, such as sales and gross margin.
This plan should be created in such a way that it would describe the functioning of your business in a clear manner. While creating this plan, you must highlight the logistics of your company in a ...
The 5 Key Success Factors of business is a theory of strategic business management posed by Buck Lawrimore. The concept was derived after the analysis of over 100 popular books and 20 years. ... The beauty of critical success factors is that they map out a strategic plan for completing a professional goal. With an inventory of the most ...
Even a one-page business plan can help you address key questions early in the planning process. That's right—we said one page. In many cases, there's no need for a supermassive document that takes ages to create. In this article, we walk you through what a good business plan needs—and what a business plan one-pager should contain.
Annual Revenue. Lenders will consider your annual revenue to determine whether your business can repay a loan. Many lenders set a minimum annual revenue requirement"often $100,000 to $250,000"that ...
The free Business Insider mortgage calculator shows how much you'll pay each month based on your home price, down payment, term length, and mortgage rate. We also provide customized tips on how to ...
4. Develop a Business Plan. Establish your short-term and long-term goals for your coaching business. Consider the services you want to offer, such as one-on-one sessions, group coaching programs, or workshops. If you want to publish books and courses or speak on stages, include that in your plan as well.
Financial planning is the process of looking at the current state of your finances and making a step-by-step plan to get it where you want it to be. That may mean devising a plan to become debt-fre
Below are key factors you need to keep in mind when comparing business term deposit rates so you can make calculated decisions and effectively maximize the return on your investments. Deposit amount. One of the factors that could influence your business term deposit rates is the amount you're investing.