

PhD Admission Guide
Gain admission to your dream school, guide to phd admission.
While some students swear off further education after undergrad, some love the thrill of intellectual discovery and research. For these students, graduate school is a natural choice. Graduate degrees are separated into “professional” and “academic” categories. Professional degrees are JDs and MDs, while academic degrees are PhDs (literally “Doctorates of Philosophy” regardless of what field you actually study).
Whether or not you need to pursue a PhD depends entirely on what career you wish to have. Some require higher education, while many others do not. In this guide we’ll go over how to apply to PhD programs, what they are looking for, and how the application process works. This guide is focused on the US and Canada; Europe has a system which is simultaneously similar and very different.
What PhD Programs Look For

PhD programs want to make sure you are prepared academically for the rigors of the program, and that you have a concrete research goal in mind. PhD programs culminate with each student answering a research question they devise, contributing new knowledge to the world in the process.
Thus these programs seek to evaluate your intellectual ability, research goals, previous research experience, and how you will contribute to their program. To determine this, they ask for the following:
Letters of Recommendation
We’ll go through each of these in turn, and explain what graduate programs are looking for from each.
Your GPA in undergrad is the single most important factor in PhD admissions. If your GPA is too low your application will be dismissed out of hand. While there are no hard limits, we suggest a minimum GPA of 3.5 for serious contention, especially at top schools. If your GPA is below 3.0 then you will likely not get admitted into any PhD programs.
The reason for this is that PhD programs are a lot of work. Being intelligent is necessary, but is far from sufficient alone. Everyone in PhD programs is intelligent, and everyone is also willing to do the work. Your GPA is seen as the primary indicator of your willingness and ability to do academic work to a high standard, and your preparation for the rigors of a PhD program.
Along with your overall GPA, schools request your major GPA. This is your GPA when calculated only using courses in your major. This is usually expected to be higher than your overall GPA. Your major GPA should be over 3.5.
While taking harder courses in undergrad is a great experience, they can also harm your overall GPA. Of course, the best approach is to take very hard classes and do well in them, but this is not always possible. We recommend taking a blend of courses, so you are never overloaded, and able to give each the attention it needs to do well.
Academic Preparation
Your GPA and transcript is also used to judge your academic preparation for the program. You should have a solid grounding in the field, and have taken advanced courses as well. Taking graduate level courses in undergrad can exemplify this.
Some PhD programs also require research languages. This is more common in the social sciences and humanities, but all students will benefit from knowing other languages well enough to do research in them. You should look up language requirements when researching programs to apply to.
The Graduate Record Examinations (GRE) is a standardized test meant for students who intend to apply to graduate programs. Both MA and PhD programs ask for GRE scores. Much like the SAT or ACT in college exams, the test is meant to be a standardized measure of academic preparation and logical skill.
The test consists of six sections. The first is writing, next are two on verbal reasoning, then two on quantitative reasoning, and finally a research or experimental section, meant to test new questions. The entire test is offered on the computer, with one minute breaks after each section, and a ten minute break after the third section. While there is also a paper-based test, almost all testing is now done on a computer. Due to the pandemic, both testing centers and at-home testing are offered. The GRE is a multi-stage test, and how well you do on earlier sections determines the difficulty of later sections and questions.
The verbal sections each consist of 20 questions, to be answered over 30 minutes. The whole is scored on a scale of 130-170. The quantitative section is scored the same, and consists of two 20 question sections, each of which should be completed in 35 minutes. The writing section is scored from 0-6. For this section, you write an essay on a given issue in 30 minutes, and offer a response critiquing a provided argument for 30 minutes.
Your total score from the GRE is given from 130-170. While the exact scores you need to enter graduate school vary, higher is better. In addition, some programs only care about your verbal score, while others only care about your quantitative score. How much weight each program puts on GRE scores varies greatly.
We recommend studying for the GRE for some time before testing. You can take the GRE up to five times per year, but must wait at least 21 days between testing dates. Only scores from the past 5 years will be released or considered by graduate programs.
Curriculum Vitae
This is akin to a resume, but is dissimilar enough that the two cannot be used interchangeably. The purpose of a CV is, like a resume, to detail what you have accomplished academically and in your career. It is far more focused on academics however, and is widely used for academic careers.
We recommend finding a template for a CV online, or asking your college’s advisors for help in creating one. If you already have a resume, then you will easily be able to convert it into a CV.
What admissions officers are looking for in your activities is primarily signs of research. This should be in whatever field you intend to pursue a PhD in. Publications are also incredibly valuable. All of academia runs on publication, and getting an early start helps your career at every step.
You should try to do research while still in undergrad. What this looks like depends entirely on what field you are pursuing. While the research does not have to exactly line up with what you wish to pursue, it should teach you skills which are cross applicable. Higher level academic research has its own set of methods and language which must be learned, and students who are already familiar with the forms and structures of research have a leg up in graduate school.
Publication is not required, but is nice to see. If you have completed a master’s degree, you should have some publication history; of your thesis if nothing else. Speak with your academic advisors about getting your work published.
Each graduate school you apply to will ask for an essay. You will be able to use the same basic form for each, but will need to edit it to be about the particular program you are applying to. Most schools only require a single essay, although some programs ask for a second on diversity.
The purpose of this essay is to explain your research interests, what you have studied, your intended area of specialization, and what your focus will be on. Every PhD student is asking and trying to answer a very specific research question. This question forms the basis of their dissertation, and will be the focus of your life for several years if you are accepted.
Thus the essay is the most important part of your application. Your grades and GRE are required to see if you are academically ready for graduate school, but the essay lets readers know if you are a match for their program, and serious about your research.
Your essay should begin by stating which program you are applying to, and why. Next, go through your previous academic experience in the field, both coursework and research. You don’t have to go through every class, but cover the ones most relevant to your desired research topic.
You should discuss any prior research you have done in the field. If you completed a thesis for your undergraduate degree or a master’s program, cover that here. If you have any publication credits, cover those as well. This should relate directly to the field you are trying to enter. If you wish to pursue lab work, discuss your previous experiences; if instead you are pursuing field work, talk about your experiences there.
Next you should talk about the research you specifically wish to pursue through a PhD. You don’t need to have an exact research question worked out, but it is helpful to have some idea; you should at least know the subfield you will be focusing on. The more specific you are, the better. Having some discussion of methodology can be nice, but is not always necessary.
If there are any ongoing research projects ongoing at the school you wish to work on, cover those next. You should discuss how these projects specifically relate to your own research interests. Finally, you should talk about which professors you wish to work with. Professors take on graduate students to advise, and you ideally want one with a specialization at least tangentially related to your field of interest. The more closely related the professor’s studies are to your own, the better.
You will be able to leave much of this essay the same for each school you apply to, changing only the name of the program, the research projects, and the professors you wish to work with.
This essay should be a page and a half to two pages long, single spaced. You should go into sufficient detail for those reading it to understand the research you want to pursue. These essays are reviewed by the faculty who run the department, and they make the admissions decisions for PhD programs. There are many more applicants than there are spaces, and admissions rates are low. The more specific and detailed you are in this essay, the better the faculty will understand your research aims, and the better your chances will be.
Diversity Statements
Not all programs ask for these, but you will likely be able to reuse the same essay for those that do. The purpose of the diversity statement is to see what unique points of view and experiences you will be able to contribute to the program. PhDs are about learning, and the more viewpoints and ideas within a program, the broader the experience will be.
If you are a member of an underrepresented group, an immigrant, come from an underprivileged background, or come from an area which is generally underrepresented, we suggest discussing that in this essay. You should not write an essay about your interactions with members of these groups, or a study abroad experience.
Above all, this essay should be authentic to you and your experience. The goal is to show how your background has shaped you as a person, and how it impacts your view of the world.
As with college applications, letters of recommendation are required for PhD admissions. These tell admissions committees who you are as a student and researcher, and give their opinion on how you will perform when doing graduate level work. Academic fields are small and often insular, and the professors writing your letters will often be known by those reading them, either by reputation or in person.
Programs ask for two to four letters. These should primarily come from professors who know you and your work well. If you had a thesis advisor, they should write one of your letters. If you’ve worked doing research for some time, then a mentor or lab director can also be a good source of a letter, even if they haven’t taught you in class. Letters should not come from non-academic sources, unless you have worked professionally in that field.
While you have the option to read the letters that are written for you, you should always waive that right. If you don’t trust your writers to craft good letters for you, then you shouldn’t be asking them for letters. Asking to see letters is considered a sign of lack of trust, and is gauche. Many professors will decline to write letters if you insist on seeing them.
You should ask for letters well in advance of when they are due; we recommend at least a month or two. If you are asking non-tenured faculty for a letter, more leeway is recommended, as they have more on their plate, and are often more stressed. You may need to send a reminder as deadlines approach. You should also share a copy of your essay with letter writers, so they know exactly what subfield you intend to pursue, and can discuss this in their letters.
Finally, you should be aware of politics when asking for letters. Some professors do not like each other at all. If you are seen as the protege of a professor who others detest, this can impact your admissions chances. Always discuss which schools and programs you are applying to with your letter writers. You should also discuss your choices of writers with an advisor (for example a thesis advisor) familiar with the field. Academic politics are incredibly petty, but if you plan to pursue a PhD you need to be aware of the game, and how it is played.
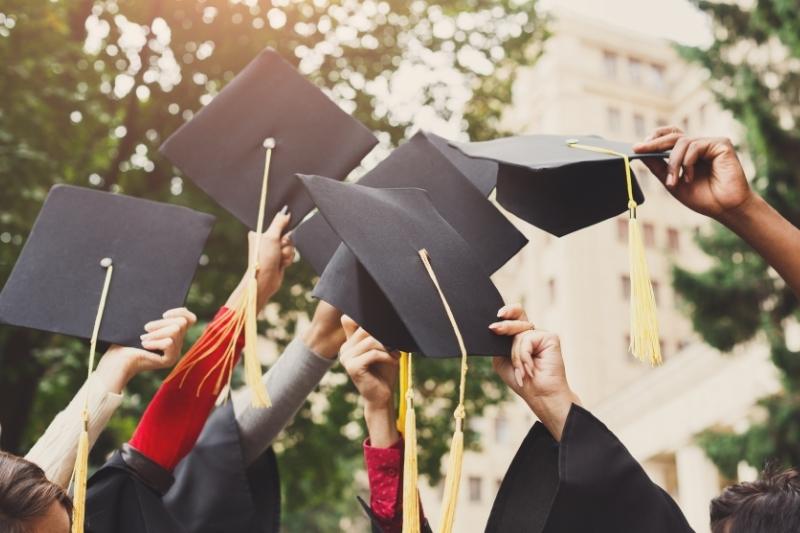

If your application passes the first review, you will be invited to do an interview. This will be with faculty in the program you are applying to. This is to further get to know you, and to understand your research objectives.
You should be able to clearly explain what you want to research, and how this program will help you do so. The people talking to you will all be familiar with the field, though not necessarily your specific subfield. They are looking for your ability to communicate and explain your view. Be prepared to answer some questions about the specifics of your goals, though it’s ok if you don’t know everything right now.
Interviews are generally in person, though due to the pandemic, virtual interviews have become more common. This is also your chance to ask any questions you have about the program you were unable to find answers to online. You can practice for this interview with an advisor or mentor; many schools have career centers which hold mock grad school interviews as well.
When and How to Apply to Grad School
There is no unified platform for PhD applications. Instead you must apply to each program individually, through the school’s website. This will mean filling out information multiple times, but they fortunately don’t ask for much. Once you have your documents in order, the rest is personal, demographic, and contact information.
You will need to pay to have your GRE scores sent to each school you apply to. Even though this is all electronic, they still charge dearly for it.
Applications are generally due in December or January, with interviews held over the next few months. Applications open in September or October. We recommend getting your applications in before the due date, though most programs don’t use rolling admissions. Each program sets their own deadlines, so you should track when each of your applications is due carefully to make sure nothing gets overlooked.
Paying for Grad School
PhD programs are for the most part fully funded. This means you will not be paying tuition, and will also get funding to live on. This funding is generally contingent on academic standing, and doing work TAing, teaching, or on ongoing research projects (or most commonly, all of the above). Many grad students also work full or part time to support themselves.
While you will not need to take on additional debt to pay for graduate school, you will not be well paid either. While the exact amount graduate students receive varies by school and program, it is generally in the range of $20-30,000 annually. This goes towards food, housing, and supplies.
While you are in a PhD program, you will not have to make payments on any government loans you took out to pay for undergrad, though they will continue to accrue interest. Making payments on them during grad school is difficult, but will greatly cut down on the amount you need to pay back later.
There are also outside scholarships available to help pay for graduate studies. While the amounts offered by these vary, most are small. They can help greatly with paying for the necessities however, and applying to them is usually worth the time investment.
Grad School Admission FAQ
Now we’ll answer some of the most common questions about applying to PhD programs.
Can older students apply?
Yes. Many professionals return to school for a PhD long out of undergrad. We suggest taking some courses at a local university in the field you plan on entering before you do this however. Academic research advances quickly, and this will familiarize you with the latest developments. Further, this will introduce you to professors who can provide you with letters of recommendation.
What are my odds of acceptance?
This depends on both your field and program. Generally, however, it is quite difficult to gain admissions to a PhD program, and admission rates hover around 10%. Only the best students get accepted, and this is even more the case at the top schools and programs.
When should I start thinking about applications?
When you choose your major, you should decide what level you want to reach within that field. Some majors lend themselves to PhDs if you want to work in that field, while others allow employment at various levels.
Where should I apply?
You should find programs with professors who are dedicated to your particular subfield. A prestigious institution which does not focus on your area is far less useful, regardless of how famous its name is. You are looking for someone who will be able to advise you, and help you perform worthwhile research. Further, professors are looking for students studying fields similar to their own when they admit graduate students.
How long are PhD programs?
Generally programs last 4-5 years, though this can vary based on field. The exact structure of the programs also varies a lot based on field and program.

Ivy Scholars is the leading educational consultant in Sugar Land, Texas, providing admissions coaching, test prep, and more to help students enroll at top tier schools.

Get In Touch
Call us now: (281) 215-5148
Houston: 4265 San Felipe St, Suite 1100, Houston, TX 77027
Get Started
Subscribe for updates, © all rights reserved.

Which program are you applying to?
Accepted Admissions Blog
Everything you need to know to get Accepted
April 10, 2024
Applying to PhD Programs: When, Where, How, and Why?
So, you are thinking you might want to pursue a PhD. That’s great! However, it can sometimes be difficult to decide whether to really go for it. Maybe you are weighing the time commitment required or the prospect of leaving a job you love. Maybe you are wondering whether you are prepared for such an undertaking or whether you’d even have a shot at getting in. When considering such an important move, it’s good to adopt a methodical approach to the decision-making process.
This article is designed to help you think through some key factors in making important decisions about graduate school. You might ask yourself the following key questions:
- When should I apply?
- Where should I apply?
- How do I get in?
- Why do I want to go?
Let’s consider these questions one at a time.
Question 1: “When should I apply?”
The right time to apply to graduate school is when your personal, academic, and professional experiences have aligned such that you know for certain you want to further your knowledge and skills in a specific field. Read on for some signs that these experiences are, in fact, aligned.
In your personal life
Think about when you were first introduced to your field of study. What made you want to keep learning about it? Is that drive to know more about your field of study still there? If the answer is yes, then you might be personally ready for graduate study. Memorable personal experiences – and the lessons you have learned from them – can also make you personally ready for graduate study.
For example, perhaps you were diagnosed with a condition and have spent the past decade managing it. The psychological strain of this experience has made you highly empathic toward patients suffering from chronic conditions. You’re now committed to studying the effectiveness of various approaches to promoting mental health among this population.
Or maybe one of your fondest childhood memories is birdwatching with your dad, who taught you all about various species and their migration patterns. This experience led you to pursue ornithology, and you still get excited about learning about birds.
Something doesn’t have to be profound to others for it to be deeply meaningful to you.
In your academic life
You’ve demonstrated – via high grades or assignments on which you went above and beyond the basic requirements – that you have a strong grasp of the technical aspects of your intended field. You’ve done more than memorize core concepts and theories; you’ve contemplated how they relate to the broader aims of the field. You’ve taken more advanced classwork, completed an independent project, or did professional work that involved innovation and research. And you now want to apply those theories and concepts in graduate school and your career.
Let’s say you majored in civil engineering. You’ve excelled in all your engineering courses, as well as in chemistry, math, and physics. In the process, you’ve learned how to apply the core principles of each field to design resilient infrastructure that does not fail in extraordinary events and is socially, economically, and environmentally sustainable.
In your professional life
Whether you’ve worked/volunteered in a relevant setting for six months or six years, you’ve learned about and contributed to the rigorous research process. Ideally, you’ve taken on multiple roles, each one more demanding than the previous one. But at every stage, you’ve taken your responsibilities seriously, because you understand that each task, no matter how seemingly trivial, must be performed diligently, lest you risk compromising the data and ultimately the findings of the entire study.
As an undergraduate research assistant, you might have begun with basic responsibilities, such as data entry and cleaning in Excel. After demonstrating that you are reliable and diligent, you were able to help conduct studies and maybe even run some of your own analyses using the data.
Then, by the time you entered your current role (the one you’re in when you apply to PhD programs), you are able to not only evaluate all the variables being assessed but also identify other variables that aren’t being measured and articulate why they should be included in future research. At this point, you’re able to generate your own research questions, formulate testable hypotheses, and even design a hypothetical study in which the findings are interesting regardless of whether your hypotheses are supported.
When you’ve identified these signs in your personal, academic, and professional experiences, you’re ready to apply.
Question 2: “Where should I apply?”
To identify the right program(s) to apply to, it is crucial to look beyond the school’s ranking or reputation . The “2024-2025 Best National University Rankings” by U.S. News & World Report should not be your primary source for one simple reason: PhD programs are very idiosyncratic. Even if you have chosen a field of study (ideally, the field in which you received your undergraduate and/or master’s degree), there are likely many research areas within that field and even more specific topics within each area. The right research area for you will depend on your previous research experience, as well as on the specific topic(s) you want to investigate.
For example, within the field of psychology , there are many areas, including clinical psychology, cognitive psychology, developmental psychology, health psychology, evolutionary psychology, personality psychology, and social psychology. Then, within, say, social psychology, there’s a vast array of specific topics, such as attitudes, aggression, decision-making, emotion, prejudice, and prosocial behavior, to name a few. As you can imagine, these topics are not mutually exclusive. In fact, combining topics can generate unique findings. Therefore, when thinking about where to apply, you might prioritize programs where the faculty are studying combinations of topics you find particularly interesting.
Another factor to consider is that programs differ as a function of the research methods they employ. Thus, when thinking about where to apply, in addition to identifying programs where the faculty are researching the specific topics you are most interested in, it’s necessary to consider whether those faculty members are using methods that you would like to apply in your future career. Do you want to master advanced statistical techniques? Do you want to work with state-of-the-art technologies? Do you want to interact with people? Do you want to observe phenomena in the “real world” or in experimental settings? It’s not only about what you’re researching; it’s also about how you’re researching it.
Once you’ve identified programs based on those considerations, it’s time to identify prospective faculty advisors within your chosen programs . After all, you’re not just applying to PhD programs; you’re applying to work with specific faculty members, and they are the ones who will be reviewing your application and deciding whether to accept you. Based on the faculty members’ professional biographies (which you can usually find on the program’s website), you’ll probably be able to identify the professors whose interests are most like your own.
But it is not enough to be confident that you want to work with a given faculty member. Next, you’ll want to familiarize yourself with that professor’s recent work by reading research papers they’ve published in the past couple years. As you’re reading, ask yourself whether this faculty member writes and thinks clearly and presents arguments and evidence in a compelling manner. You will be mentored by this person for five years (or more!), so it’s crucial that you find someone you admire and are motivated to learn from.
In sum, the steps in deciding where to apply for PhD study are as follows:
- Choose your field of study.
- Identify your preferred area(s) within that field.
- Discover the specific topics you find most fascinating.
- Consider what methods you want to employ.
- Evaluate the merits of prospective faculty advisors.
Question 3: “How do I get in?”
Once you’ve determined that you’re ready to apply, and you know where you want to apply , the focus shifts to whether you’ll be accepted. Getting into a PhD program is largely a matter of fit . The faculty members who evaluate your application want to know what insights you can offer to their current and future research studies, how your interpersonal style will contribute to their lab or research hub dynamics, and whether you are committed to extending their research in a meaningful way after you obtain your doctorate. You can convey all this crucial information in your statement of purpose.
It’s difficult to overstate the importance of your statement of purpose. You might have an exceptional CV, but if your statement of purpose is lackluster and fails to convey to your prospective faculty advisor that you are the right fit, then you are unlikely to be accepted. Conversely, you might have a modest CV, or even a weakness, such as a low GPA, but nevertheless be accepted if you convey in your statement that (1) you have taken (and will continue to take) concrete steps to become more prepared for PhD training, and (2) you possess unique skills and knowledge that are highly relevant to your prospective advisor’s research area but that might not be reflected in traditional metrics of achievement (e.g., your CV, GPA).
To write a compelling statement of purpose , you need to articulate everything relevant to Question 1: “When should I apply?” You have already reflected on how your personal, academic, and professional experiences have aligned such that you know that you are ready to apply. But it is not enough for you to know that you are ready. You need to convince your prospective advisor that you are.
This is where Accepted can help . The most valuable service we offer is essay consulting. We can teach you how to craft a narrative about your journey that is coherent, authentic, and distinctive. During each consultation, we will challenge you to think more deeply and clearly than you ever have about where you’ve been and where you’re going. You will learn how to identify and effectively convey the reasons your prospective advisor should accept you.
Question 4: “Why do I want to go?”
A PhD is an academic degree that prepares you to conduct original research, perform advanced statistical analyses, interpret empirical results, and evaluate competing theories. You will be trained to become an academic – that is, a university professor who directs a research lab and teaches students the nuances of a specific field. The skills you acquire during your doctoral training can be applied to industry, governmental, and nonprofit settings; however, doing so should not be your primary goal. Your prospective advisor will want to know that you are committed to the work of an academic. It is great if your research has important implications for those other sectors, so long as you are still committed first and foremost to the production and dissemination of knowledge in your field. The thought of conducting original research in a university setting should make you excited to get started.
Thus, the best reasons to pursue a PhD are intrinsic. After all, a PhD is a Doctor of Philosophy . You get a PhD because you are passionately drawn to the philosophy of your chosen field. You can’t help but think about it in your everyday life, because you see it everywhere. It is a lens through which life makes sense. Discovering its guiding principles, subject matter, and potential applications allows you to identify patterns in the world around you – and sometimes within yourself as well. So why should you pursue a PhD? Because you can’t not .
Vanessa Febo has ten years of experience teaching academic and professional writing at UCLA, with a special certification in teaching writing techniques. She has drawn on this expertise to guide clients to placements at top institutions, including Harvard, Stanford, and USC. Before joining Accepted, Vanessa coached UCLA students through the application process for graduate programs, major grants, fellowships, and scholarships, including the Fulbright, Stanford Knight-Hennessey, and the Ford Foundation Fellowship. Additionally, Vanessa has extensive experience successfully guiding clients through applications for a diverse range of programs, including those in business, humanities, social sciences, and STEM fields. Want Vanessa to help you get accepted? Click here to get in touch!
Related Resources
- Get Accepted to PhD Programs in the Humanities , podcast Episode 568
- How to Apply Successfully to STEM PhD Programs , podcast Episode 566
- Graduate School in Psychology: PsyD or Psy Phd, Which Is Right for You?
About Us Press Room Contact Us Podcast Accepted Blog Privacy Policy Website Terms of Use Disclaimer Client Terms of Service
Accepted 1171 S. Robertson Blvd. #140 Los Angeles CA 90035 +1 (310) 815-9553 © 2022 Accepted

How to get a PhD?
Interested in obtaining a phd learn more about the steps to earn a phd, careers with phd, list of colleges offering programs and more..
Updated by TCM Staff on 15th April 2021
How to get a PhD: Steps and Requirements Explained
15th April 2021
College Monk — How to Get a PhD
A PhD is a postgraduate doctoral degree awarded to those students who produce an original thesis and make a significant research contribution to their respective field.
PhDs are available for those in a variety of different fields, and it’s often considered the highest and most well-respected degree available. Earning a PhD truly establishes someone as an expert in their field and indicates the deepest level of knowledge on a particular subject.
What is a PhD?
PhD — technically short for Doctor of Philosophy — is a type of doctoral degree, often considered the highest-level degree one can earn.
A PhD is a type of research degree that requires students to do an extensive amount of research and produce an original work, known as a dissertation.
People often use their PhD as a launchpad to pursue a career in academia. But, it’s also a popular option for those pursuing a career in STEM.
Those with PhDs make up a fairly exclusive club. Data from the US Census Bureau shows that fewer than 5% of the population holds a doctorate. And it’s not surprising, considering it often takes up to eight years to achieve this coveted title and requires writing an original dissertation the length of a book.
A PhD is actually just one type of doctoral degree. PhDs are research-focused. The other type of doctorate is application-focused (also known as an applied doctorate).
Source: https://strathsltresearchers.wordpress.com
PhD admission requirements
Not just anyone can earn a PhD. Given how well-respected the title is, it takes a lot of work and very specific criteria to enter a doctoral program.
The most basic requirement that all PhD candidates must have is a bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution. You won’t be accepted without this. You also usually need a high GPA.
Another requirement is a statement of purpose. In this statement, doctoral candidates will describe why they’re seeking a PhD, what they’ve done so far to prepare themselves, and what goals they plan to accomplish later.
Finally, PhD applicants will need several letters of recommendation.
If you’re considering pursuing a PhD, it’s critical that you work to build relationships with professors and mentors who might recommend you. There’s a lot of competition, especially for the top PhD programs, and excellent recommendations will help you to stand out.
Keep in mind that the requirements might vary somewhat from one school to the next, so it’s important to do your research and decide ahead of time where you’ll apply.
Steps to obtain a PhD
Earning a PhD is no easy feat. It takes most students years to do so. Let’s look into the steps someone must take to get a PhD.
Step 1: Complete an undergraduate degree
Before you can take the next step toward your PhD, you’ll first have to receive a bachelor’s degree through an undergraduate program at a reputable university.
This education will provide the foundation for your more advanced coursework later. It’s important that you maintain a high GPA throughout your undergraduate years.
Step 2: Complete a master's program
Once you complete your bachelor’s degree, the next natural step is to pursue a master’s degree.
Graduate school requires that a student take the Graduate Record Examinations (GRE) or the Graduate Management Admissions Test (GMAT). A master’s degree typically takes about two years to achieve, and will be in a particular field of study.
While not technically required for a PhD, most people earn a master’s degree before earning their PhD.
Step 3: Apply for a PhD program
Once you complete your graduate program, it’s time to apply for your PhD program.
There are many doctoral programs to choose from, so it’s important that you research and find the best fit for your field of study.
During the application process, you’ll have to submit the following:
- A completed application
- Undergraduate and graduate transcripts
- Your GMAT or GRE scores
- Letters of recommendation
- A statement of purpose
Step 4: Complete your coursework
When you begin your PhD program, you’ll start by taking your coursework.
As is usually the case with undergraduate and graduate programs, you’ll likely have some required courses and some electives. Usually, students will prepare their own plan of study for the courses they’ll take over the next couple of years.
Step 5: Prepare a research proposal
A research proposal is a document that outlines what, exactly, a PhD student will focus on during their research.
A research proposal should include the major question or questions someone plans to answer with their dissertation, and how exactly they plan to arrive at that answer.
Even though the proposal won’t be a part of your final thesis, it plays a vital role in shaping your PhD.
Step 6: Complete a literature review
The literature review is the first thing you’ll do before starting your project report.
In this review, you’ll conduct an in-depth study of all the research in your field. During this phase, a doctoral student should critically assess the existing literature on their topic and find gaps they may be able to fill with their research.
Step 7: Research and collect results
Once a student has completed their literature review, they’ll do more first-hand research and perform experiments to help answer the questions they’re exploring for their dissertation.
Step 8: Produce a thesis and write a dissertation

Source: https://www.wikihow.com
Once you’ve completed your research and gathered sufficient results, it’s time to write your final thesis and dissertation.
Though the two terms are often used interchangeably, your thesis is the argument or conclusion you’ve arrived at, while your dissertation is where you demonstrate your thesis.
Your dissertation is the culmination of all the research you’ve done. Dissertations are original work and often focus on a newly developed theory. A dissertation is roughly the length of a book, and can often take years to produce.
Step 9: Viva Voce
Viva voce is a Latin phrase that means “with living voice” or “by word of mouth.” It’s also the final — and one of the most important — steps in the process of earning a PhD.
Unlike other degrees, where you take a final exam, a PhD candidate must defend their thesis before a panel of appointment examiners. It’s common for the examiners to ask many questions, and this process can often take several hours.
Once you successfully complete your viva voce, you’ll be awarded your doctorate and can add that coveted “Dr.” to your title.
Online colleges offering PhD programs
Many students choose to pursue a PhD through an online doctoral program for the flexibility and convenience it brings.
Here are a few popular online PhD programs:
What can you do with a PhD?
A PhD is the highest-degree that someone can earn. But after all those years of work, what exactly can you do with your degree?
One of the most common career paths for someone with a PhD is academia. Those with a doctorate degree often go on to teach at universities or spend their careers performing research, not all that different from what they did to earn the degree in the first place.
But academia isn’t the only option for PhD recipients, nor is it the most lucrative.
PhD students often study STEM fields — science, technology, engineering, and math. Those industries are thriving today more than ever, making it a great field for those holding a doctorate.

Source: https://www.jax.org
Some of the highest-paying PhD fields include:
- Information assurance
- Computer science
- Biochemistry and molecular biology
- Organic chemistry
Though academia and STEM may be the most common paths for PhD participants, they’re hardly the only ones. There are many options available to someone with a PhD. Other non-STEM fields include clinical psychology, market research, business development, linguistics, and intelligence.
A doctorate is the highest level of degree someone can achieve. There’s no doubt that it takes a considerable amount of work, and it takes most people years to achieve this recognition.
It’s important to understand these trade-offs before you get started. But once you earn your PhD, you will hold one of the most highly-respected titles in the academic field and have a lot of doors open to you.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. 1) How long does a PhD take?
A. According to CBS news on an average, an American Student takes 8.2 years to complete their Ph.D. This can change according to various courses and in various countries.
2. 2) What qualifications do I need?
A. In US Bachelors degree holders can also apply for Ph.D. For applying in a PhD program one should have completed 16 years of formal education. Qualification in the entrance test is also necessary.
3. 3) Can I take PhD as a part-time?
A. Yes, part-time PhD is possible, and it has a more flexible schedule with classes and degree completion. In some programs, a minimum one-year residency is required. But, part-time PhD will take more time, and managing a part-time PhD will be more challenging.
4. 4) What is M.Phil?
A. A M.Phil qualification is less advanced than that of a PhD. In this, the students are expected to master a content area and it can be mastered in two years. Moreover, the PhD dissertation takes more time than an M.Phil dissertation.
5. 5) What are Financial Aid options available for me?
A. For Ph.D. there are a lot of financial aid opportunities available in the form of Scholarship and loans. Eg: National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program.
- Graduate School
In Pursuit of a PhD: How to Get a PhD
Featured Expert: Dr. Benita Kapuku, PhD

Interested in how to get a PhD? Pursuing a doctorate degree is an exciting step in your educational journey, but learning how to get into grad school , how to apply to PhD programs and what to expect once you’re accepted can be intimidating, and you’ll have many questions. In this blog, we aim to answer all your questions about how to get a PhD, from whether a PhD is the right choice for you, how to choose and apply to a program, what your PhD timeline will look like and what resources out there can help you achieve your goal.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Listen to the blog!
Article Contents 11 min read
How to get a phd: decide if a phd is right for you.
Before we jump into the nuts and bolts of exactly how to get a PhD, you first need to ask yourself “ why do you want to do a PhD ?” and be sure that it’s the right path for you. If you’re still in the early stages of researching what it takes to get a PhD and whether you have the time, drive and commitment to go on this journey, first ask yourself this question. For those of you who are already sure of your course and need a step-by-step guide of how to get a PhD, feel free to skip to the next section on how to apply and what your PhD program options are!
If you’re still wondering whether a PhD is the right program for you, here’s a few reasons why you might choose to pursue a PhD:
- You have a Master’s degree and you’re interested in furthering your education
- Your chosen career path requires a PhD or advanced degree
- You’ve completed a Master’s degree but a PhD will allow you to find new job opportunities, increase your salary potential or expand your network
- You’re interested in a research or educational role in your field, or in how to find a job in academia
- You’re interested in changing careers or your field of interest
Note that if you’re an undergrad or haven’t completed a master’s program, the question of whether you should pursue a master’s or PhD program depends on your goals. For example, if you want to change your career field, you’ll most likely need to complete a Master’s degree first before applying to a PhD. But it is possible to get a PhD without a Master’s degree in some circumstances if you’re interested in jumping straight to a PhD program.
Would you like us to help you with your grad school applications? ","buttonText":"Free Strategy Call","buttonColor":"#ffffff","bannerUnderText":null,"trustpilot":false}" :url=""https:\/\/bemoacademicconsulting.com\/contact-schedule-free-strategy-call"" code="banner1" background-color="#000066" button-color="#ffffff" banner-image> Also note the differences between doctoral degrees. No matter which path you choose, you will be considered an expert in your field, but the type of work you’ll be qualified for will depend on your program and career goals. There are two general “types” of doctorate degrees: the PhD and the professional doctorate. PhD
A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy degree, is an umbrella term for a research-focused program that invites you to contribute meaningful advancements and new knowledge to your chosen field. Individuals usually pursue a PhD to become researchers, professors, consultants and sometimes even enter industry jobs after a PhD . These types of programs cover a wide range of careers, from psychology to public health, from economics to the arts.
Professional Doctorate Degree
A professional doctorate degree prepares you for professional jobs in important industries. For instance, if you want to know how to get into law school or how to get into medical school , you would actually graduate with a JD or MD, both a type of doctorate degree. Professional doctorate degrees also include a Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD), advanced Nursing degrees (DN) and even Doctor of Business Administration (DBA), to give you a few examples.
For those of you pursuing a PhD in your field, you may be drawn to a research or teaching role and want to get a tenure track position at a university, or maybe you want to transition from academia to industry once you’ve completed your studies.
Whatever your career goals are, you should think carefully about whether a PhD is either necessary or a worthy goal for you. Earning a PhD is a huge commitment not only of your time and money, but of your passions and efforts. If your answer is yes, a PhD is right for you, the next step is to figure out how to get a PhD.
First, we’ll look at how to find the right PhD program for you and how to apply to PhD programs.
Deciding between a Master’s or a PhD? We can help!
How to Get a PhD: Find and Apply to PhD Programs
How do you find PhD programs? The same way you likely searched for the best undergraduate or master’s program. University websites typically have a separate section or even a separate website for graduate admissions, and you can find information on what PhD and advanced programs they offer. You can easily search for the options in your field—or the field you’re interested in switching to—and find everything from the most competitive PhD programs to the easiest PhD programs to get into .
You can also find dual degree programs which combine a master’s and a PhD, like MD-PhD programs for those of you who want to become medical researchers. There are tons of options out there, so it’s worth checking out different universities and the many types of programs to see what the right fit for you might be.
If you’re thinking about how long it takes to get a PhD and you want to speed things up a bit, there are a few different kinds of PhD programs out there:
- Full-time PhD programs (typically 4-7 years)
- Part-time PhD programs (6-8 years)
- Direct entry PhD programs (4-5 years)
- Online and Accelerated PhD programs (1-3 years)
The right kind of PhD program may depend on a variety of factors, including your schedule, personal and professional commitments, budget and desired career path. For example, an online program is usually much faster and you can do a PhD without a dissertation , but it’s available only for a few disciplines. You can’t complete say, a PhD in Engineering in such a short time period. Direct entry PhD programs might appeal to you so you can skip the master’s degree, but they are also naturally more competitive and have more rigorous admission requirements.
Once you’ve found and chosen a PhD program or created a list of programs you want to apply to, the next step in how to get a PhD is to tackle the application. As you can imagine, the grad school application is an involved process. Fortunately the admission requirements for a PhD are similar to other graduate school programs and undergraduate programs.
Here’s the shortlist of what you’ll need for your application to a PhD:
- Transcripts from your Master’s program or Bachelor’s program
- GRE test scores
- Research proposal
- PhD motivation letter
- Graduate school statement of purpose
- CV for graduate school or research resume , depending on the program
- Letters of recommendation
- PhD interview
This is the general list of requirements for a PhD program, but some may have additional requirements, such as asking you to submit a research interest statement along with your research proposal, or to take one of the GRE subject tests. Always double check what the admission requirements are when applying, since they can vary between programs.
Here’s a brief overview of how you can meet all of the PhD admission requirements listed above:
One of the best ways to prepare for this step is to use mock PhD interviews, where you can rehearse your responses to common questions, master your nerves and practice being confident and at ease in the interview room. ","label":"PhD interview","title":"PhD interview"}]" code="tab1" template="BlogArticle">
Funding for Your PhD
A crucial part of how to get a PhD is finding funding for your degree. Unlike a bachelor’s degree or a master’s, funding a doctorate degree is a little more complicated and a little harder to do. Some PhD programs are fully funded, meaning as a PhD student, your research, student fees and expenses are covered while you’re completing your program. Other programs are partially funded or self-funded, meaning you as the PhD student have to find the money to complete your degree. Most PhD programs offer research assistantships or teaching assistantships that help you pay for your education in exchange for participation in research or teaching responsibilities at the university.
This is also where PhD scholarships, grants, bursaries and other forms of funding come in. As a PhD student, you may also be eligible to apply for financial aid at some programs. It’s up to you to figure out how you will fund your doctorate degree and your research. Fortunately, this is a common requirement for PhD students and there are many options out there, from PhD loans to scholarships to assistantships and studentships to government funding.
If you like, you can also apply exclusively to fully funded PhD programs, but this might limit your choices. Some students also work during their PhD in a part-time program, but of course it’s better not to rely only on your earnings to fund your degree.
Once you’ve submitted your application or been accepted to a PhD program, what next? Here’s a look at the PhD application timeline and curriculum you can expect, from the first meeting with your program supervisor to your graduation and beyond.
1. Initial Meeting with Your Academic Advisor
One of the first things you’ll do as a PhD student is meet with your academic advisor or supervisor. This is the university faculty member who will act as your mentor and guide throughout your PhD program. You may have a faculty member assigned to you or you may be able to choose your own advisor. Choose your advisor carefully, since they’ll be a significant resource for you in the years to come!
2. Research Proposal
Writing your research proposal is usually part of the application stage of getting a PhD, but it is essentially the first step in this journey. Once you’ve chosen a topic, you’ll write a research proposal to submit to a PhD admissions committee. It’s basically your offer of what you’ll be researching during your time as a PhD student and what you plan to contribute to the program and the field of interest. It’s important that your proposal is unique and presents fresh ideas or will bring new knowledge to your field of study. If the topic you want to research has been done before and isn’t “new”, your proposal may be rejected, and you’ll be denied admission.
Some programs may ask you to submit your research proposal later in the program or submit an updated version of your research proposal once you’ve completed required coursework or your literature review. Be ready to answer research proposal questions from your advisor and make any necessary changes. From there, your PhD committee or academic advisor will need to approve your proposal and give you the green light to start conducting research.
3. Coursework, Electives and Exams
For the first year or two of a PhD program, you’ll be completing the preliminary work of your thesis or dissertation. You may also use this time to complete required advanced coursework in your degree or take electives that interest you.
Once you’ve completed the coursework required for your PhD, you’ll take a written examination (sometimes called the ‘preliminary’ or comprehensive exam ). This exam will determine whether you’ve successfully completed the coursework requirements and have the necessary skills to continue your PhD program. Once you’ve passed it, you’ll be able to move on to the next phase of your program, which is conducting your own research and preparing to submit your thesis.
4. Extracurriculars
During your time as a PhD student, you’ll be expected to participate in a number of activities and extracurriculars, in addition to your coursework and independent research.
Teaching Responsibilities
Many PhDs will have teaching responsibilities, including hosting undergraduate seminars or acting as a teaching assistant providing feedback and grading assignments. If you’re a PhD in a science department, you might work as a lab supervisor for undergraduate students. PhDs might take on these roles as part of their program or they may fulfill them through an assistantship program.
Attending Academic Conferences
PhD students also attend academic conferences and events in their field, which allows them to expand their professional network, socialize with their colleagues and discover the latest innovations and developments in their field. You may have the chance to present during these events, which is not only an excellent addition to your resume but another way to network, improve your presentation skills and introduce your own work to your peers.
Grad Student Publishing
PhD students publish during their program to increase their academic profile and gain some experience with the academic publishing and peer review process. It’s not always a stated requirement to graduate, but publishing is a vital part of academic, as demonstrated by the saying “publish or perish” in academic circles. Whether or not you’ve published during your time as a PhD student will also certainly come up during postdoc interview questions , and you’ll be expected to talk about your experiences.
5. Research and Data Collection
Around the third year, you’ll go through the process of getting your research proposal approved and start conducting your own original research. As you work, you’ll take detailed notes and begin drafting your thesis. This is where the research-intensive work of a PhD is centered. You’ll also be doing a great deal of reading in your proposed area of research for the literature review. The review gives you a solid understanding of your research area and background information that will inform your original research.
6. Writing Your Thesis
Your research will take place over several semesters, and as you work, you’ll start working on your thesis or doctoral dissertation. This period of research and writing will also include regular reviews with your advisor or PhD committee to update them on your progress and working on other projects. For instance, you may be expected to publish as a graduate student in academic journals or continue with extracurricular work in your department.
7. Thesis Submission and Thesis Defense
The final step of completing your PhD is submitting your thesis for edits and knowing how to prepare for thesis defense . Your advisor will be helping you with these steps, but you’ll also need to get ready for the formal, oral defense of your thesis in front of your PhD committee. They will ask you common thesis defense questions and you’ll need to take them through the entirety of your research project from start to finish. The committee will then ask you questions and make a decision on whether to approve your research or make suggestions for changes.
Once you’ve completed your defense and you’re approved, congratulations! You’re on your way to the last step of getting your PhD.
8. Graduation!
The last step of your PhD journey is graduation! Once your thesis is approved, you can apply for graduation and attend the formal ceremony if you choose to receive your degree.
From here, you’ll look at how to find a job after grad school , start preparing for job interviews and enter the workforce.
No matter which field you’re in, getting accepted to a PhD program is extremely competitive. The level of competition of course will vary by university, discipline and the type of program, but any way you look at it, getting into grad school is not super easy.
Once you’ve been accepted to a program, you’re in for many years of hard work as you complete your studies and conduct your research. This educational journey will be well worth it for you in the end, but there’s no denying it’s a tough process to go through alone. Of course, you’ll have an academic advisor supporting your throughout your PhD, but there are more resources that can help you on every step of this journey, which we’ll cover briefly next.
Of course, your university will have many student support services you can take advantage of, from career counseling to writing workshops to student family support and financial aid. When you\u2019re searching for a PhD program, take a look at the student support services available to you. "}]">
The journey to get a PhD is a long and complex road, but it can be well worth all the time, effort and hard work for those individuals who want to advance their education, pursue a specialized career or deepen their knowledge of their field. To learn how to get a PhD, start with choosing the right program for you and navigating the PhD application process. From there, it’s all about learning what to expect from your PhD program and the steps you’ll need to take to graduate. Explore the options open to you, find out what resources are out there to help you succeed, and plan out your pursuit of a PhD from start to finish.
To get a PhD, you’ll first need to research PhD programs in your field, check the admission requirements and decide which one is the right fit for you. From there, you’ll need to submit a PhD application, write your research proposal and attend PhD interviews. Once you’re accepted, you’ll meet with your PhD supervisor or academic advisor and get started on completing your program. This includes taking any required coursework, conducting your own research and compiling data, participating in extracurriculars, writing your thesis or dissertation, studying for exams and preparing for your thesis defense.
The admission requirements for a PhD are similar to the requirements for any graduate program. They usually include your transcripts and GRE scores, a grad school statement of purpose, a PhD motivation letter, letters of recommendation, a resume or research interest statement, and an interview. You’ll also need to submit a research proposal.
The general timeline for how to get a PhD is to start by deciding whether a doctorate degree is right for you, research potential programs, start applying, attend interviews, meet with your academic advisor and start diving into your research and coursework. After you’ve completed your program, it’s time to think about how to find a postdoc position and what you want to do with your new degree.
It usually takes between 4 and 7 years to complete a PhD, though there are some programs which are shorter and some that may take up to 8 years.
Yes, there are ways to complete a PhD without a master’s degree, including direct entry PhD programs. Note that these types of programs tend to be more competitive than average, and may have additional requirements.
Getting into a PhD program is quite competitive, depending on the university, the field of study and the type of program. However, you can increase your chances of getting into a PhD program by being well prepared, doing your research and creating an excellent application package.
It’s never too late to further your education. Some students may go straight from their bachelor’s to their master’s and on to a PhD, or some might even skip the master’s altogether. But there are plenty of PhD students who choose to go back to school after working in their field for many years, and there is no age limit on when you can go back and earn your PhD.
Applying to a PhD is a huge step and an important personal choice. Whether you pursue a master’s or a PhD might depend on what your career goals are, whether you have the drive, money and time to complete a PhD, and what you hope to accomplish with a doctorate degree.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
How To Get a PhD [2024 Guide – Campus & Online]
Are you wondering how to get a PhD? Although it requires dedication and focus to complete, the process of earning your doctorate can be broken down into a few simple steps.

Earning your PhD is a way to become involved in a specific academic community while strengthening your research, writing, and presentation skills.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Professionals who earn their doctoral degree often go on to accept leadership roles in a variety of fields, including academia, education, and healthcare.
How to Get a PhD

Earning a PhD does not have to be a complex process, though it can be a long one. Regardless of the topic you choose to focus on, the journey toward your doctorate will likely begin with earning a bachelors degree and end with a public defense of your doctoral dissertation.
1. Earn an Undergraduate Degree
The road to a PhD begins with earning an undergraduate degree from an accredited school. Bachelor’s degrees generally take about 4 years to complete if you follow a traditional academic schedule.
If you are considering applying for higher degree programs after graduation, it is beneficial to maintain a high grade point average over the course of your undergraduate career. If you aren’t sure whether you’d like to pursue further education, there are generally plenty of career opportunities available for students with a bachelor’s-level education.
2. Obtain a Master’s Program

The next step in your journey will be to obtain a master’s degree from an accredited institution. During your master’s degree program, you will select an area of study on which to focus more. Over the course of your studies, you can develop expertise in your discipline through a combination of theoretical analysis and fieldwork.
Because there are fewer credits required to complete a master’s degree than a bachelor’s degree, a graduate program will typically take 2 years to complete with full-time study. Some schools offer accelerated programs, offering the possibility to finish your degree sooner.
The focus of your master’s degree program will likely inform your professional career or your doctoral field of study. So, it is beneficial to consider the areas you are passionate about and to conduct extensive research into your schools of interest prior to applying.
3. Apply for a PhD Program

After earning your master’s degree, you may be qualified to apply for a doctoral program. One factor that becomes important is the master’s degree GPA needed for a PhD program admission. Admissions requirements will vary from program to program.
Another one of the most important parts of the application process is determining what you will study during your time as a doctoral candidate. Because it may take up to 5 years to complete your PhD, it is essential that you pursue something you are passionate about.
After you decide what you’d like to study, you can begin to research programs and schools to see if they fit your needs. As you conduct your search, you may want to pay close attention to the professors who work in your field of study. You will need someone to advise you, and it can be helpful to have an understanding of the resources available to you before you apply.
4. Complete the Requisite Coursework

If you are admitted to a doctoral program, your first few semesters will be spent completing the required coursework. The courses that you’ll complete will be dependent on your field of study and the specific program you attend.
For example, a student pursuing their PhD in Comparative Studies might take classes on approaches to comparative cultural comparative studies as well as contemporary political problems. Their classes could also cover topics in narrative, culture, and representation.
Taking classes at the start of your program can help you decide on a topic for your final dissertation and may equip you with relevant research skills and tools.
5. Submit a Research Proposal

Once you complete your initial courses, you will be asked to submit a research proposal. A research proposal outlines what topic you are going to focus your research on and what your approach will consist of.
Why is this important? Not only does it give professors a clear understanding of your research, your method, and your thinking, but it also helps you get organized. As you work through your dissertation, you can refer back to what you planned in your proposal to keep you on track.
6. Research and Collect Data

Conducting research and collecting data is a critical component of your PhD. Working toward and completing your dissertation not only allows you to become an expert in your field but also provides the opportunity for you to have a voice in the academic community.
In order to ensure that the information you present is valid, it is necessary to use extensive research to back up your findings.
7. Perform a Literature Review
Once you have chosen a specific research topic, you may be required to perform a literature review. During this review, you will analyze books and papers that are related to your field of study in order to determine any strengths, weaknesses, or gaps. You may also compare different literature and take note of recurring themes.
This review process helps you develop a broader understanding of what research already exists in your field related to your topic of interest. It also helps highlight any gaps that your thesis may be able to fill and identifies prominent authors and works to which you can refer while completing your dissertation.
8. Write and Produce a Thesis and Dissertation
One of the final tasks of your Ph.D. program will be to write and produce a thesis and a dissertation. Your thesis is the question or argument to which all your research will work to answer or prove.
Your dissertation is the collection and presentation of your findings, which should be a comprehensive response to your thesis statement. Dissertations can run in length from 100 pages to 300 pages on average. They often require a significant amount of preparation and effort, along with several months or years of hard work.
9. Defend Dissertation and Public Research

As your final step in your PhD journey, you may be asked to defend your thesis. While this may sound intimidating, it is simply the opportunity for you to present your research and answer questions posed by the thesis committee.
In some cases, this portion of the process is largely symbolic because your dissertation will have already been assessed. Depending on your specific program, this process can take anywhere from 25 minutes to over an hour.
PhD Admissions Requirements

Specific PhD admissions requirements will vary between programs, but most schools typically require the following items:
- GRE or GMAT scores (only some schools require them)
- Statement of purpose
- Undergraduate and graduate degree transcripts
- Letters of recommendation
It’s strategic to research the specific admissions requirements for your schools of interest prior to applying. In addition to these items, some programs may ask for an application fee as well as a resume as proof of experience in your field of interest.
Accreditation

Accreditation is an external and internal review process of an educational program. This process signals to applicants, students, and employers that a program is legitimate.
By choosing to participate in the accreditation process, schools are ensuring that the education they offer is up to current standards. This means that you will most likely be taught by qualified staff members and receive appropriate educational materials.
It is beneficial to check for regional accreditation. This information is often posted on a school’s website, but you can also verify a prospective school’s status by looking through the US Department of Education’s list of accredited institutions.
Is Financial Aid Available?

The most common form of financial aid available to qualifying students is provided by government loans. To determine the amount of federal assistance you qualify for, you can fill out the FAFSA, or the Free Application for Federal Student Aid . This form takes into account details about your personal life and income to ensure a fair decision based on your circumstances.
In addition to federal aid, you can also apply for state aid, a process which will vary by state. You can also check for available scholarships at your schools of interests. There are often unique opportunities to apply for financial help at each school.
What Is a PhD?
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is considered to be among the highest academic degrees you can achieve. A PhD program is centered around developing an original thesis and conducting the accompanying research.
Your final product is often a written dissertation, in which you showcase your research and present your findings. If you are interested in a career in academia or research, then a PhD may be a good fit for you.
Should I Get a PhD?
The question of whether you should obtain a PhD is one that will be determined by your personal career goals and aspirations. As you make your decision, it might be helpful to consider these factors:
- Time and money . Do you have the time and finances needed to complete a PhD?
- Dedication and focus . Will you be able to stay passionate and motivated about one topic while you work through your doctoral program?
- Career goals . How will earning your PhD help propel you toward your professional goals?
Since every doctoral program is unique, you can search for schools that offer the programs that most align with your goals.
Do You Need a Masters to Get a PhD?

No, you do not always need a masters degree in order to earn a PhD, depending on the school and program. While the traditional path to getting a doctorate consists of earning your undergraduate and masters degrees before applying to a PhD program, there are some exceptions.
For schools that allow you to pursue a PhD directly after earning your undergrad degree, you will likely apply as a Master of Philosophy student. After that, you can have the opportunity to submit a thesis proposal for review. If it is accepted, you may be able to continue your research as a PhD candidate.
How Many Credits for a Doctorate Degree?
The amount of credits needed to complete your doctorate will be determined by a number of factors. These include your specific school requirements, the type of degree you earn, your chosen area of study, and the requirements of your state.

Typically, a PhD program will consist of 60 to 120 credits. Your credits will likely be split between electives, major courses, research core courses, and dissertation requirements. Some fields, such as psychology, may require more time and credits to complete.
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD?
The length of a PhD program varies widely. Most take between 3 to 5 years to complete due to the dissertation requirement.
There are some doctoral programs that require less than 60 credits and do not include a final dissertation. These types of programs can be finished more quickly if you are enrolled full-time. Professional doctorates are more likely to follow this abbreviated structure and are generally intended for students who already have their masters in a specific field.
How Hard Is It to Get a PhD?

Determining how difficult it is to earn a PhD will depend on what you consider to be the biggest roadblocks. As you research your schools of interest, it’s beneficial to check eligibility criteria and admissions requirements. This may be an area of difficulty if you lack the transcripts, finances, or test scores needed to apply.
Alternatively, the admissions process may seem simple, but you might find the prospect of researching one subject over the course of many years a difficult one. It’s strategic to conduct extensive research and consider your career goals as you make your decision.
If Someone Has a PhD, Are They a Doctor?
If someone has a PhD, they are considered a doctor in the academic sense, but they are not a medical doctor (MD).
A doctoral degree is the highest academic degree you can earn. In this case, the term “doctor” simply refers to one’s formal academic standing. Unlike a licensed medical doctor, someone with a PhD is not qualified to perform and provide medical services.
What’s the Difference Between a Professional Doctorate vs. PhD Degree?
A professional doctorate is typically pursued by those who hold a master’s degree in a specific field. A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is usually taken on by those interested in conducting extensive research into a topic.
The right degree for you will largely be determined by your career aspirations. Most professionals who pursue a PhD are interested in the field of research or academia.
What’s the Difference Between an MPhil vs. PhD?
An MPhil, or a Master of Philosophy, is a degree that can be taken in place of a PhD or as part of an existing PhD program.
You might consider pursuing an MPhil if you are short on time but would like to conduct research into a certain topic.
Is a PhD Worth It?

Yes, a PhD is worth it for many students. If you are eager to contribute to the existing research around a particular topic, then this degree may be a good fit for you. The Bureau of Labor Statistics lists positive job outlooks for a variety of PhD-level occupations.
For instance, 12% job growth is projected for postsecondary teachers over the next ten years, which is much faster than average. Top executives and management positions are also expected to have positive job outlooks.
Additionally, the research you conduct and the dissertation you create will become part of the larger academic conversation around your area of study. This could be a beneficial way to establish yourself in academia.
Getting Your PhD Degree Online

Getting a a degree from one of the best online PhD programs is a lucrative choice for many students. If you are interested in becoming a leader within academia or contributing significant research to a specific subject area, then this may be a fitting path for you.
Positive job outlooks, higher earning potential, and a multitude of career opportunities also make this degree desirable to many. A number of professionals who earn their PhD go on to pursue leadership roles in education, healthcare, and law.
If you are ready to begin your PhD journey, are are looking for the highest paying doctorate degrees , you can start by researching potential programs from accredited universities today.

- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

- Mission and History
- Moody Foundation Gift
- Administrative Handbook
- Director of Graduate Studies Handbook
- Special Announcement
- Dean's Office
- Graduate Council
- Graduate Student Advisory Board
- Degrees Offered
- Admissions Contacts
- Graduate Admissions Guide
- Application Deadlines
- Graduate School Resources
- International Applicants
- Dedman College: GRE Requirement for 2024 Applications
- Forms and Policies
- Graduate Fellowships and Awards
- Graduate Writing Center
- Career Development
- Graduate Student Organizations
- Student Services
- Graduate Student Teaching Awards
- Events Calendar
- Orientation
- Professional Development
- Three Minute Thesis
- Student Life
- Meet our Ph.D. Fellows
- Ph.D. Health Insurance
- Graduate Student Travel Grant
- Dedman Graduate Student Assembly
- Postdoctoral Affairs
- Postdoctoral Community & Resources
- Hiring Process
- Global, Online & Continuing Education
- Our Programs
- Online Program Development
- Faculty and Curriculum Committees
- About Global, Online and Continuing Education
Southern Methodist University
How to get a phd:, a guide to choosing and applying to ph.d. programs.

Here at SMU, we know that the decision to pursue a Ph.D. in any field can be difficult — it’s a significant investment of your time and resources, with several unknowns along the way. When students are just starting their search, here are some common questions we have received:
- How do you prepare a strong application?
- How do you select a program that fits your area of interest?
- Will you get in?
- What are the years in a Ph.D. program actually like?
In this resource, we offer you the insider information you need to choose a program, apply successfully, and thrive during your years of graduate study. You’ll get answers to common questions, tips for putting together your application, and testimonies from students who made it through the application process and are now pursuing a Ph.D.
Common Reasons for Getting a Ph.D.
Do you find yourself wondering, what would motivate someone to earn a Ph.D.? Only about two percent of adults over 25 hold a doctoral degree, according to a 2018 study by the U.S. Census Bureau . But what drives this group of elite learners?
A 2019 survey of more than 6,000 Ph.D. students asked a wide array of questions on topics ranging from life in a Ph.D. program to students’ satisfaction with their program. Here’s what Ph.D. students liked the most about their doctoral program:
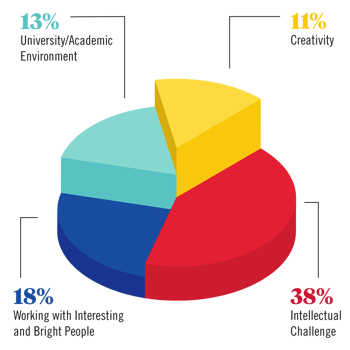
Additionally, although earning a Ph.D. is a large commitment of time and energy, 75% of respondents reported being happy with their decision to pursue a Ph.D. saying they were somewhat satisfied or very satisfied with their decision.

When you start exploring earning a Ph.D., you may encounter some setbacks and deterrence. However, if you have a genuine love for the subject and wish to become a thought leader in your area of expertise, don’t let this discourage you.
Perhaps you’re thinking that a Ph.D. in a STEM field makes sense, but don’t see how to justify your degree in Anthropology or History? In the STEM academic track, the return on investment (ROI) of a graduate degree may seem more clear than in the humanities.
Never fear. Love of the subject, not monetary gain, is what truly motivates students to journey through graduate school. A Ph.D. in any field is a feat in research, critical thought, and dedication, and these skills are extremely valuable even in disciplines with less obvious market value.
Download our Guide to Choosing and Applying to a Ph.D. Program
Access this guide at any point to make references and keep this important information at your fingertips.

We'll email you a PDF of the eBook for your reference as you apply to graduate school.
Access Insider Information!
How to pick the right ph.d. program.
So, you know what you want to study, but now you’re faced with the task of finding the right school. It can be easy to become overwhelmed by all of the options. The process of selecting which Ph.D. program is the right fit doesn’t have to be difficult or stressful, you just need an organized plan to help you sort through the factors you need to be looking for.
Not sure what you should be looking for? We can help you with that! In this short video, we walk you through each step of selecting the right Ph.D. program — making it simple and straightforward.
You’ve Decided to Go for It! Take the First Steps to Getting A Ph.D.
Ready to take the leap and begin your Ph.D. career? We’re here to help you take the first steps. To determine what program could be right for you, it’s best to begin your research early, and to consider the following things when analyzing and comparing Ph.D. programs:
Is there a professor at the school with your same interests?
What sort of funding do they offer?
Do the school’s graduates have careers that you would like to have?
Do you have geographic restraints?
Ph.d. faqs: choosing a doctoral program that’s right for you, do you need a master’s to get a ph.d..
Not always, it depends on your program. Some programs will allow you to move straight from an undergraduate degree into a doctoral program that includes graduate coursework. Other programs will require a master’s degree before beginning a Ph.D.

Read more: Here are 4 ways to get a head start on graduate school while pursuing your bachelor’s!
How many years does it take to get a Ph.D.?
It generally takes five to seven years to complete a Ph.D. program, but make sure to contact your program to learn about the specifics. For more information and an overview of the Ph.D. timeline, check out our article: The Ph.D. Timeline – What Can You Expect From Your Program?
How many doctoral programs should I apply to?
While it is tempting to apply to several Ph.D. programs to enhance your chances of being accepted, this is one example where “quality over quantity” holds particularly true. Ph.D. programs generally accept students based on how closely their research interests align with the work of their professors.
Rather than applying to a dozen programs, pick 4-6 that are truly great matches for your interests and spend the time necessary to make your application stand out as one of the best.
How to pick a Ph.D. program?
We wrote a resource that covers this exact question!
Read — Comparing Admission Offers and Selecting Your School — to learn how to pick the Ph.D. program that is right for you!
- Research proposal often determined in conjunction with departmental research
- Typically higher stipends
- Conducting experiments and then analyzing the resulting data
- Research proposal is self-directed
- Often lower stipends, but more likely to obtain a job in academia
- Analysis of texts and concepts to expound upon in your dissertation
Get to Know the Moody School of Graduate and Advanced Studies
Access this guide to d iscover world-changing research, competitive funding, & professional and community engagement at SMU.

Learn More About the $100 Million Gift from the Moody Foundation
Applying to ph.d. programs: what do ph.d. programs look for.
When starting the application process, you should review the program’s application requirements and contact the school to ask any of your remaining questions. Starting with this step will help you stay focused as you gather the assets you need and will keep you from wasting time on things that are not required.
Applicant questions usually fall into one of two categories: questions about the substance of the program (e.g. Is there an opportunity to do research as a first-year?), and questions about the logistics of the application (e.g. What is the school code for sending you my GRE scores?).
Don’t hesitate to contact faculty directly to ask questions pertaining to the substance of the program. They love talking with prospective students about what they do, and they will be able to provide much more detail than the admissions office. On the other hand, admissions or graduate office staff should be able to give you prompt guidance on logistical questions pertaining to your application (faculty are not as familiar with these topics).
Personal Statement
A student with a clear research direction can write a very compelling personal statement. You don’t need to have your exact dissertation topic worked out yet, but it’s important to have a good sense of the following:
- Your general area of interest;
- The faculty in the department you’d want to work with;
- The resources at the university that would help with your work.
Hitting these points in your personal statements tells the faculty not only that you are prepared for the work, but that this particular university is a good home for you. An applicant can be impressive, but if the faculty don’t see you as a good fit for the school’s program, they won’t be inclined to admit you.

Transcripts
When you order copies of your undergraduate and graduate school transcripts, as well as any test scores you may need, leave plenty of time to meet the deadline so that these documents do not hold up your application. Frequently, schools will accept unofficial transcripts for the initial application, but a final, official transcript will be necessary if you are accepted and decide to attend.
Letters of Recommendation
The hallmark of a Ph.D. program is that it is research-based. Success at the undergraduate level is an important factor, but a better indication of success is research experience. The strongest letter of recommendation is from a professor who knows you not just as a student in their classroom, but as a researcher. Choose someone who can speak to your work in the lab or the archive, making a contribution to the discipline rather than simply absorbing content from a lecture.

Advancing the Field: Stories and Resources for Graduate Students
Advancing the Field is a weekly blog that offers prospective graduate students insight and advice as they consider the challenges and exciting possibilities that come with getting a graduate degree.
Ready to Read More? Subscribe to Our Blog!
How to apply for a ph.d. program: the ph.d. application checklist.
In addition to the items in the section above, make sure to check off this list (or edit it to include your specific requirements).
Be sure to check your department's website for additional requirements, such as minimum test score requirements and writing sample prompts. Not all departments will ask for additional items, but for those that do, make sure you're prepared in advance.

Get Application Advice

Statement of Purpose FAQs

Should You Earn a Master's or Ph.D.?

How to Ace the TOEFL/IELTS
.png?width=1300&name=Letter%20of%20Recommendation%20(typically%203%20required).png)
Get Our Tips for Your Best Recommendations

How to Craft a Clear CV/Resume
After all these elements of your application are submitted and reviewed by the department, they may request an interview with the candidates who are moving forward. To help you with your grad school interview, we’ve created a resource with advice from admissions professionals to help you prepare.
Applications for Ph.D. programs are often reviewed on a rolling basis, but some do have hard deadlines. It’s hard to say exactly when you will hear back, as it depends on the individual department, but generally, you should not expect a response before February of your expected enrollment year.
As your offers of admission begin to roll in, we’ve compiled some advice for helping you select the best one! Read — Comparing Admission Offers and Selecting Your School .

Apply To Graduate School with Confidence
SMU's Graduate School is proud to offer doctoral and master’s degrees in a wide variety of fields. This resource is designed to give you an overview of the admissions requirements and processes for our Master’s and Doctoral programs.

- Understanding How to Finance Your Ph.D. Program
Here’s some sage advice: when it comes to funding your Ph.D. program, it should be funded by the university as a tuition scholarship and a stipend. If you are not offered any funding, it may be an indication that you are not a good fit for that program.
Your stipend offer depends on the university, but the general range for a Ph.D. stipend is $15,000-$35,000.
SMU currently has 55 Moody School funded Ph.D. students and offers a wide range of fellowships, stipends, grants , and health insurance to financially support students in our doctoral programs. SMU offers the following fellowships:

In some cases, the stipend is contingent upon the student holding a research or teaching assistantship.
RESEARCH ASSISTANSHIPS

TEACHING ASSISTANTSHIPS
Typically teaching assistantships are arranged through the university. This arrangement helps graduate students get experience in the classroom and helps institutions balance out the cost of graduate student stipends.
Fellowships beyond your university are also good opportunities for additional financial support during your years of graduate work. Check out fellowship listings like this one dedicated for women across disciplines or this list of STEM-related fellowships .
How a Ph.D. Will Benefit Your Finances?
Although the price tag of a Ph.D. can look steep, the reality is that the vast majority of doctoral students receive full, or significant, funding for their program. This means that you’ll spend 5-7 years earning your degree, but will likely graduate without additional tuition debt, ready to step into your career field as a trained expert.
But what do the numbers say? Here’s the real story on the financial impact of pursuing a Ph.D. according to research conducted by the Bureau of Labor Statistics . The truth is, people who have earned a doctoral degree are looking at a significant increase in overall lifetime earnings.
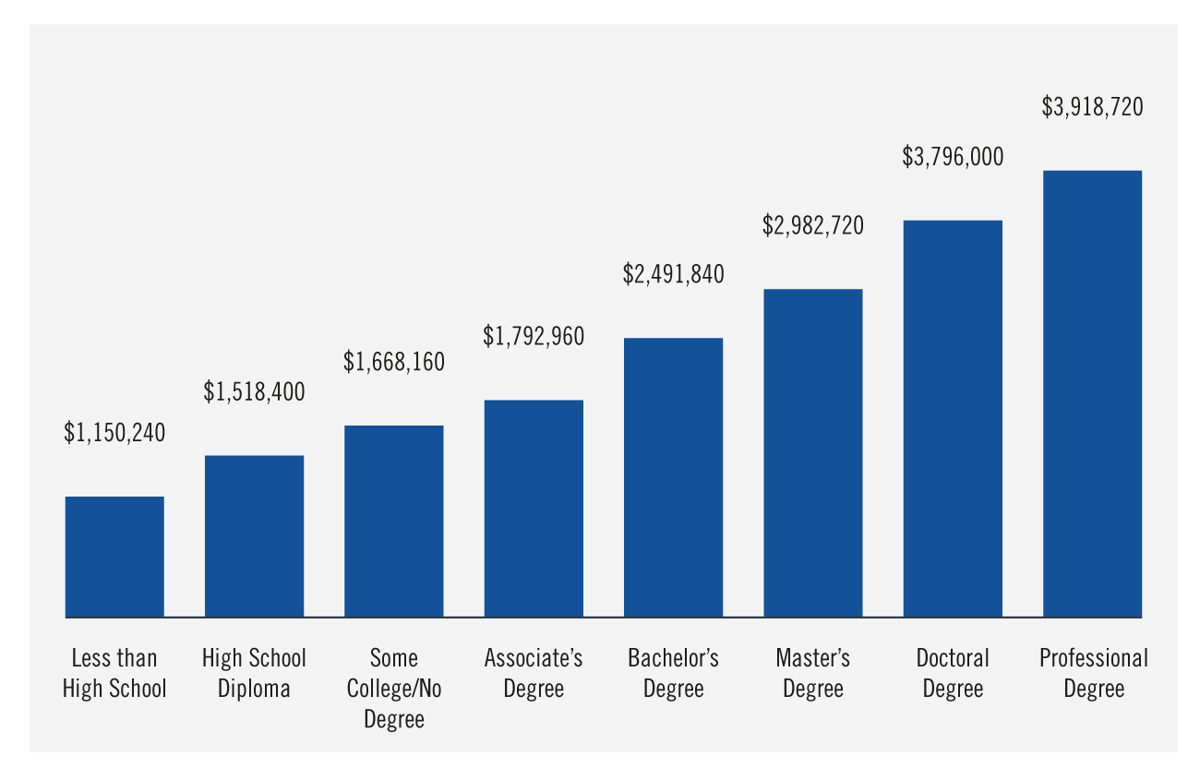
Competitive Funding and the Student Experience
Tune in for a panel discussion with current Ph.D. Fellows about the competitive graduate fellowships and funding opportunities available and the graduate student experience at SMU.
View the Recorded Webinar
- Advice from Current Ph.D. Students

Amila Nanayakkara
I am Amila Nanayakkara from Sri Lanka. I did my undergrad in University of Colombo. After that I [worked] as a research assistant for 2 years at the Industrial Technology Institute in Sri Lanka.
Now I am in my 5 th year pf my Ph.D. program, studying biology. To be specific, we study multi-drug resistant cancers and how to reverse the drug resistance.
Yes, [I did encounter some doubts during my decision process] especially about the future, or what should I do after the Ph.D. It takes 5-6 years [to complete] which is like the best part of your life. I had my doubts [about] investing this much time on the Ph.D.
But I [realized] that there are other options rather than being an academic after [getting] a Ph.D. Also, I was pretty sure that I wanted to do research, wanted to do new things always. I hated routine work. I had a short time job in a bank and I realized that I do not like office work at all [so the Ph.D. became very appealing].
I liked the research [happening at] SMU. I liked to work in cancer biology specifically, and I knew Dr. Vogel and Dr. Wise’s lab [would be] a place I would like to work. Also I think the PI (Principal Investigator, the lead researcher for a grant project) plays a huge part in your lab [experience]. So I wanted to join a lab where you are given freedom and not micromanaged. When I talked to Pia Vogel and Wise I realized this is the best place for me. The whole Biology department seemed like a very friendly place too. Also, I really liked the environment of SMU as a whole as well.
Ph.D. is like a marriage. You have to think a lot before you make the decision and you can not get out just because you do not like it in the middle.
I think you have to select a program, a lab you really love. You have to love what you do. Because this path to Ph.D. can be very difficult. I remember that I did not get any results [in the lab] during first 2 years. But I still loved what I did , so it kept me motivated.
You have to read a lot, I mean a lot! Also you have to come up with your own ideas as well. Do not always only rely on the path your supervisor shows.
You have to make several mini projects while focusing on one big project. So if you hit a road block, you still have [to keep moving on] other [parts of the project]. It can be a tough journey, but you can make it happen.
- Communication, teaching and presentation skills.
- How to interact with people/students.
- Mentorship skills.
- Problem solving ability.

April Simpson
I am originally from Chattanooga, Tenn. In 2009, I earned a Bachelor of Arts in Religious Studies (with minors in Math and World Languages) at Gardner-Webb University. I also completed two master’s degrees at Gardner-Webb between 2010 and 2014: Master of Arts in Religious Studies (concentration in Biblical Studies) and Master of Divinity. From the start of my master’s program, I knew I planned to pursue a Ph.D.
I am now in my third year at SMU. I am a student in the Graduate Program in Religious Studies (Dedman College), and my field of study is New Testament. I have completed all my coursework as well as my comprehensive field exams, and I am in the process of writing my dissertation proposal this fall; I expect to be admitted into candidacy sometime in the next few months.
There were three major factors that could have inhibited my pursuit of the Ph.D.: highly selective admissions processes, cost, and rigor of the Ph.D..
I knew long before I applied that elite programs are highly selective due to funding limitations and high standards. At times I wondered whether I would be able to stand out enough to be selected. My response was to do my part—to work as hard as I could reasonably work—to make myself a desirable candidate for admission. I maintained an excellent GPA, prepared intensely for the GRE, gained teaching experience, involved myself in the Society of Biblical Literature (an important professional organization in my field), and sought out references who could speak to my academic and professional abilities and work ethic. I decided that, while the application and selection process was not totally within my control (you cannot make them pick you), I would foster my own drive to work hard and excel in an attempt to accomplish what was in my own control.
Another factor was cost. I knew that, without tuition funding and stipendiary support, I would not be able to afford pursuit of the Ph.D., nor is it advised in my field to take out loans at this level. Fortunately, most elite programs are fully funded, including a stipend that helps cover living expenses (and unfortunately, this means those programs have even more competitive admission, as I already noted). I decided to apply only to fully funded, widely respected programs so that, if admitted, I would be able to afford a Ph.D. program. And, again, I worked hard to make myself the best applicant I could be.
Finally, I knew that the Ph.D. is a rigorous degree. At times I worried that I would not be cut out for this level of work. Interestingly, these worries tend to manifest themselves not only among aspiring students but also among current Ph.D. students, something we refer to as “imposter syndrome.” At any rate, I listened to and trusted faculty mentors who told me I was, indeed, able to complete a Ph.D.; I listened to my own inner voice that told me to keep at it and to give it my best. And, again, I worked hard.
I did a great deal of selection before ever applying to Ph.D. programs, so that I only applied to programs I was fairly confident I would be willing to attend. Despite some overlap in the application process, each program application is different in some way, and it takes time and resources to apply to schools. As I prepared to apply, I looked for well-respected/highly rated schools that had the following qualities (this list is not ranked): (1) full funding, (2) faculty and program structure that would support my research/career interests and goals, (3) generally, an environment of collaboration rather than of antagonistic competition, (4) high academic standards, (5) a professional atmosphere, (6) a clear commitment to the success of students enrolled in the program, and (7) an interest in professional development not only in terms of research and general professionalism but also—and importantly—in terms of teaching.
When I visited SMU, I was very impressed with the faculty (both their achievements and their willingness to work with me and support my work), the Graduate Program in Religious Studies students (including other newly admitted students), the facilities (including SMU’s beautiful campus and especially Bridwell Library), and the funding. I could envision myself as part of the community here. It became even clearer to me that enrolling in the Graduate Program in Religious Studies (Ph.D.) at SMU was such a great opportunity, one that I could not pass up. Although this meant that my husband and I would be moving far away from family and friends and that we would be adjusting to life in a new city, we embraced this opportunity.
One piece of counsel I received early on was to maintain a realistic attitude about the admissions process, specifically how competitive it is. This means taking seriously the task of being a competitive applicant. Just as importantly, it means not being overly critical of oneself when rejection inevitably comes (from one school or another). This process requires the development of thick skin and reflective self-confidence.
Another key piece of advice I received was to be genuine about my interests and preparation. There is always a degree to which school and applicant alike try to determine best fit, and of course as applicants we want to be competitive and appealing to multiple schools; however, misrepresenting one’s interests does not benefit the applicant or the student in the long run.
I would encourage prospective students to seek out their strongest faculty supporters and cheerleaders as references; to consider each aspect of the application process to be an opportunity to highlight a strength or compliment an area that may not stand out as much; to ask questions about the culture and collegiality of the schools in which they are interested; to be professional but also to be themselves; and to be aware that, while having a sense of one’s research direction and career path is valuable even during the application process, there is also value in remaining open to how one’s interests or specific career aspirations might change in the course of a program.
I have had several opportunities to develop my teaching skills, not only through opportunities to teach courses, to teach individual class sessions, and to lead workshops, but also through various seminars and trainings that are aimed at developing pedagogical skills in both a face-to-face and online format.
Other skills I have developed include general professional development, understanding and engaging religious studies and theology colleagues across disciplinary lines, reading and writing against deadlines, identifying and dissecting arguments more clearly, identifying and engaging various methodologies employed across the humanities, book editing, and website editing.
Through my service on the GPRS Graduate Student Organization and the GPRS Faculty Steering Committee (as a student member), I have developed an increased understanding of the administrative matters that relate to university programs in general and the GPRS in particular. Serving in such an administrative fashion as a member on a committee or otherwise is a transferable skill that I anticipate being valuable to me throughout my professional academic career.
I’ll put it this way. If I could go back and give my pre-Ph.D. self a pep talk about what was coming, I’d say the following: (1) You are more prepared than you know. (2) You will learn so much so fast, so there is no need to worry about feeling out of practice or as if you don’t know how to be a Ph.D. student (and this is only natural—you’ve never been a Ph.D. student before!). (3) It is perfectly fine that you still have questions about how you’ll focus your research; these things take time (and it turns out you are on the right track with your ideas anyhow). (4) You’re going to grow and change a lot during this process, and you’ll have good and bad days. It is worth it. (5) Self-care and relationship-care matter.
Discover Life in Dallas
Get to know the city of Dallas through our guide and learn what it is like to live, work, eat, study, and relax here while completing your graduate degree at SMU.
![how to get in a phd program [SMU] Dallas Guide eBook_iPad mock-up](https://grad.smu.edu/hs-fs/hubfs/Dallas-Guide/%5BSMU%5D%20Dallas%20Guide%20eBook_iPad%20mock-up.png?width=300&name=%5BSMU%5D%20Dallas%20Guide%20eBook_iPad%20mock-up.png)
We'll email you a PDF of the eBook, so you can save it for your reference as you apply to graduate school.
Get the Graduate Student's Guide to Living in Dallas
How many years to get a ph.d. our advice for thriving every step of the way.
You’ve applied, been accepted, and decided to attend your Ph.D. program. In the flurry of excitement around your decision, the reality of what the next 5-7 years will look like may have eluded you. What does life as a Ph.D. student really look like? And how long does it take to get a Ph.D.?
Your time in your Ph.D. program is both exciting and challenging and, depending on your school and program, the next 5-7 years will look a little different for everyone. Here’s what you can generally expect in your Ph.D. program:
In the first year, your department should offer you guidance about what classes to take and requirements to fulfill. It’s tempting to jump right into research, but make sure you pace yourself and take advantage of networking opportunities , such as program and college events, graduate associations, and additional lectures. Each of these will expose you to the field and help you to make meaningful connections that will serve you throughout your doctoral program.
Read more: 4 Tactics to Help You Build a Professional Network While Getting Your Ph.D.
Much the same as year one, your focus will be attending seminars and honing in your dissertation topic. Continue to network and get to know your professors. Usually, sometime in the second or third year you will take your qualifying exams and be admitted to candidacy, formally moving into the dissertation research and writing phase.
In the beginning of Year 2, (if you have not already done so) you’ll want to begin reaching out to faculty mentors and building relationships with them. As you progress through your Ph.D. your faculty mentor, or dissertation advisor, will become one of your most important connections.
Read more: 3 Tips for Graduate Students to Consider When Choosing a Faculty Mentor
Read more: 5 Common Myths About Ph.D. Programs — Setting the Record Straight
Typically, course requirements for your Ph.D. will be completed after the first two years, but this can vary depending on the discipline and program. Keep in mind that some programs have average durations far longer than five years. For example, anthropologists usually do fieldwork for their Ph.D. degrees, which extends the program by several years compared to STEM programs.
Read More: The Ph.D. Timeline – What Can You Expect From Your Program?
The Final Step: Writing Your Dissertation
The most general statement that can be made about writing your dissertation would describe the process as: do research, propose a prospectus, and then write about it! Writing is a skill perfected by regular practice, so be sure you are consciously honing this skill during your years of coursework and seeking out feedback about how you could improve.
Read more: Get a sense of what it takes to complete your Ph.D. Here are 5 tips for writing your Ph.D. dissertation
However, the particulars vary a lot by discipline. In some cases, you will research and write as you go (more often in the humanities); whereas in the sciences, you’ll generally perform research over many years and compile your findings in a dissertation over one to two semesters. In some cases, you are publishing articles throughout your 5 years, and those articles can provide the basis or rough outline for a dissertation.
As you think about your dissertation, it might seem overwhelming to imagine finding something new or interesting enough to write about it and be deemed an expert. Often your first years in a Ph.D. program, taking coursework and working more directly under faculty, will help you find your research niche that will then become your dissertation. A good Ph.D. program will help you grow and develop as you prepare to work independently as a scholar.
In almost all cases, dissertation research and writing are self-driven. After you are admitted to candidacy, it is up to YOU to decide what you need to do, when you are going to do it, and what your final product will be. This is where a good advisor, who can provide guidance and help you implement a system to stay on track, is crucial. In addition to having good research, one of the biggest keys to success in writing your dissertation is to be organized.

- Ph.D. Programs at SMU: A Look at Your Options Across the Disciplines
SMU is a distinguished center for global research with a liberal arts tradition, and our graduate programs are known for their rigor and commitment to research. Here at the Moody School of Graduate and Advanced Studies, we are proud to offer 32 Ph.D. programs that are the backbone of the high caliber research taking place at the University.

Learn more about some of the Ph.D. programs offered at SMU

A Complete Guide to Studying Statistical Science
Data is not the same as knowledge. Without context to understand what types of data are valuable, what makes data reliable, and what the data signify, data are useless.

Discovering Your Planet: A Complete Guide to Earning A Ph.D. In Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences address the complex interactions among the physical and biological components of our planet. Earth Scientists set out to address the most pressing environmental issues of our day and to offer immediate and long-term research-based solutions for geohazards, resources, and climate issues.

Exploring the Universe: A Guide to Studying Physics at Southern Methodist University
Physics is the study of space, time, energy, and matter. Physicists try to ask and answer, in a verifiable and reproducible way, the deepest questions about the origin, nature, and fate of the universe.

Download our Guide to Choosing and Applying to Ph.D. Programs
Access this guide at any point to make references and keep this important information at your fingertips.
Receive this resource as an eBook now!
- Want to Learn More?
If your interest is piqued and you’d like to learn more about choosing, applying for, and thriving in a Ph.D. program, you can explore the following resources below. You can also reach out to the Moody School of Graduate and Advanced Studies — we would be happy to assist you.

Request More Information
Are you curious about what the next step towards grad school should be? Want to learn more about SMU’s 32 Ph.D. programs?
Send us your information, we will be in touch!
Jump to section.
- Should You Get a Ph.D.? Exploring the Reasons to Get a Terminal Degree
- You’ve Decided to Go for It! Getting Started on Your Ph.D. Journey
- Putting Together an Strong Ph.D. Application
- Looking Ahead: SMU’s Advice for the Ph.D. Years


- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
How to Choose a PhD Program
Successfully completing a doctoral program requires commitment and perseverance. the most important step in this process is to consider whether academic life is right for you and what kind of doctoral program — from discipline to environment — will be the best fit for your goals and preferences., we asked our current students and faculty, “what is key to making this decision” following are some questions they suggested you ask yourself, and answer, in order to select the appropriate program..
First, a basic description of a doctoral program:
As a doctoral student, you will spend the first two years of your program exploring areas of interest through coursework. In the two to three years that follow, you will select and pursue your own research topic, one which will make an original contribution to the existing body of knowledge in your field. Your original research culminates in an extensive written document known as the doctoral dissertation.
General Questions
If you are considering your career options, answering these questions will help you clarify your goals and ambitions — and determine if a doctoral program is the right decision for you.
- Am I the type of person who is suited for a career in academia? Am I independently motivated to answer questions that I find interesting?
- Do I want to spend the rest of my career doing research, as well as reading and talking about it?
- Do I have a strong enough academic background in order to apply and be accepted by the program?
- Is now the time for me to pursue a PhD?
- What are my goals after completing the PhD?
Program Questions
If you know you want to pursue a doctoral degree, answers to these questions will help you select the right program for you.
- How many faculty are working with students?
- How many faculty members are doing research in areas related to my own interests?
- What opportunities are there to work with a variety of faculty and to be exposed to different approaches in research (modeling, work with data, experiment design)?
- Am I technically prepared to learn to do research in this field?
- Most PhD students change their vision of research and many change their intended concentration area after joining the program and being exposed to a variety of research styles. Does my program of choice offer flexibility needed to do so?
- Is there financial support for students to attend academic conferences to present their own research?
- What opportunities are there for students to participate in colloquia, both as an attendee and as a presenter?
- What is the department’s placement record? What types of jobs do graduates take and where?
- Finally, how well do graduates of the program perform in the long term (contributing to the field through publication, practice of management and earning tenure)?
Hear From Our Doctoral Community
From undergrad to phd, why i chose academic research instead of consulting.
Andrea Contigiani
How Wharton Makes It Easy to Be Successful
- Harvard Business School →
- Doctoral Programs →
PhD Programs
- Accounting & Management
- Business Economics
- Health Policy (Management)
- Organizational Behavior
- Technology & Operations Management
Students in our PhD programs are encouraged from day one to think of this experience as their first job in business academia—a training ground for a challenging and rewarding career generating rigorous, relevant research that influences practice.
Our doctoral students work with faculty and access resources throughout HBS and Harvard University. The PhD program curriculum requires coursework at HBS and other Harvard discipline departments, and with HBS and Harvard faculty on advisory committees. Faculty throughout Harvard guide the programs through their participation on advisory committees.
How do I know which program is right for me?
There are many paths, but we are one HBS. Our PhD students draw on diverse personal and professional backgrounds to pursue an ever-expanding range of research topics. Explore more here about each program’s requirements & curriculum, read student profiles for each discipline as well as student research , and placement information.
The PhD in Business Administration grounds students in the disciplinary theories and research methods that form the foundation of an academic career. Jointly administered by HBS and GSAS, the program has five areas of study: Accounting and Management , Management , Marketing , Strategy , and Technology and Operations Management . All areas of study involve roughly two years of coursework culminating in a field exam. The remaining years of the program are spent conducting independent research, working on co-authored publications, and writing the dissertation. Students join these programs from a wide range of backgrounds, from consulting to engineering. Many applicants possess liberal arts degrees, as there is not a requirement to possess a business degree before joining the program
The PhD in Business Economics provides students the opportunity to study in both Harvard’s world-class Economics Department and Harvard Business School. Throughout the program, coursework includes exploration of microeconomic theory, macroeconomic theory, probability and statistics, and econometrics. While some students join the Business Economics program directly from undergraduate or masters programs, others have worked in economic consulting firms or as research assistants at universities or intergovernmental organizations.
The PhD program in Health Policy (Management) is rooted in data-driven research on the managerial, operational, and strategic issues facing a wide range of organizations. Coursework includes the study of microeconomic theory, management, research methods, and statistics. The backgrounds of students in this program are quite varied, with some coming from public health or the healthcare industry, while others arrive at the program with a background in disciplinary research
The PhD program in Organizational Behavior offers two tracks: either a micro or macro approach. In the micro track, students focus on the study of interpersonal relationships within organizations and the effects that groups have on individuals. Students in the macro track use sociological methods to examine organizations, groups, and markets as a whole, including topics such as the influence of individuals on organizational change, or the relationship between social missions and financial objectives. Jointly administered by HBS and GSAS, the program includes core disciplinary training in sociology or psychology, as well as additional coursework in organizational behavior.
Accounting & Management
Business economics , health policy (management) , management , marketing , organizational behavior , strategy , technology & operations management .
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Degrees
- Doctoral Studies
How to Get a PhD
Last Updated: January 10, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Carrie Adkins, PhD . Carrie Adkins is the cofounder of NursingClio, an open access, peer-reviewed, collaborative blog that connects historical scholarship to current issues in gender and medicine. She completed her PhD in American History at the University of Oregon in 2013. While completing her PhD, she earned numerous competitive research grants, teaching fellowships, and writing awards. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 687,581 times.
A PhD, short for Doctor of Philosophy, may help you secure a position as a college or university professor, a researcher in a government or industrial laboratory, a consultant, or an independent practitioner. [1] X Research source If you have the curiosity to explore a subject in depth and the tenacity to do so for many years, applying for a graduate PhD program may be an excellent step in reaching your full potential. By learning the steps necessary to complete your prerequisite education, apply to graduate schools, and complete the work, you'll be well on your way.
Completing Prerequisite Education

- Generally, it's recommended that students interested in pursuing advanced degrees should develop a wide skill-base during their undergrad. In other words, while you may ultimately be interested in studying Zoology, an undergrad degree in basic Biology might provide you with a diverse base that you'll be able to narrow in your future studies.
- Many universities offer majors designed to funnel you into an advanced degree. Pre-law majors and Pre-med majors are two notable examples of this. Talk to your academic advisor about your interest in pursuing a PhD after you graduate, if you've yet to select a major.

- A good way to develop a relationship with a professor is to take multiple classes with her and join her lab, or research team. Go to office hours, introduce yourself, and express your interest in advanced degree work. Most professors are more than happy to work with a talented student who shows a sincere interest in their work.
- It's also a good idea to forge relationships with graduate students at your school. Speak to graduate students and faculty about their experiences at the school, even if you plan on going elsewhere for your advanced degree. Many will be happy to let you know about the advantages and disadvantages of studying for and obtaining a Ph.D. It can be a great way to get insider information and get ahead of the game.

- Work-study programs in your field of interest can also be extremely attractive of graduate applications. If you're studying English, try to secure employment in the Writing Lab, rather than the cafeteria to give yourself an edge and valuable experience.

- National and regional conferences, such as the National Conference on Undergraduate Research (NCUR), allow dedicated undergrads the opportunity to rub elbows with experts and contribute to the discussion.

- Look for programs with a good reputation, but give more weight to the faculty and the research interests of the other graduate students at prospective schools. What you're looking for in an advanced degree program is camaraderie and common ground, not an arbitrary ranking on some "prestigious" list.
- The applications are expensive--sometimes $50 or $80 dollars each--so you won't be able to apply to all programs. Try to select a range of programs to apply to: choose a few big dream schools with great facilities and prestigious faculty and lots of competition to see if you can't get in. Apply to smaller programs that you'd also be happy attending. Apply to as many as you can afford to give yourself the best chance.
- For some fields, a master's degree will be a more appropriate subsidiary or even terminal degree. At worst, a master's degree can be an excellent primer for the graduate school life, especially if teaching assistantships or fellowships are available.
Applying to Graduate Programs

- While most Master's programs only require the general test, which is like an advanced version of the SAT, some Ph.D programs will require that you take the subject test, which is given in several sections, including biology, literature, and other fields. It's a much more difficult test than the general--the reading list for the Subject test in lit is several hundred authors from a variety of periods. Make sure you take the correct test for the program to which you're applying. [5] X Research source
- Schedule your test early in the application season, to give yourself enough time to retake it, if necessary. The test can be somewhat expensive, more than $100, so start studying now with a good-quality commercial study guide.
- When you arrive for the test, you can arrange to have your scores sent directly to the graduate programs you'll be applying to. This has the advantage of cutting out an extra step in your application process, but also ensures that the school will see your scores, good or bad. If you're worried about your score, arrange to have them sent to you instead.

- It's important to ask for these letters as early as possible, preferably at least 3 months before you need to submit your applications. Professors will be inundated with letter-writing requests at the last minute, increasing the possibility of them writing a poor evaluation. Don't be one of those students.
Carrie Adkins, PhD
" Ask well in advance, and supply any materials that might help them ," adds Carrie Adkins, PhD in History. "Professors can only write so many thorough, detailed letters of recommendation, so if you help them out by asking a month or two before the deadline and providing them with your CV and statement of purpose, you’ll be more likely to get their best efforts ."

- If you're planning on applying to lots of schools, it can be a time-saver to write a "form" version of your letter, allowing space to customize the letter for more specific programs. It's very important to tailor each statement of purpose to the particular program to which you're applying. This demonstrates your seriousness and interest in the school. Each letter should read as if you're only interested in studying at that school.

- a completed application form
- Undergraduate and graduate transcripts
- A curriculum vitae (CV) or resume
- Recent GRE scores
- Statement of Purpose
- TOEFL or IELTS scores (for international students)
- 2-3 Letters of Recommendation

- Applying for financial aid will often involve supplementary application materials, like a teaching statement, research statement, or other short writing prompts. Research the specific requirements at each university for specific instructions when applying for financial aid.
- If full funding isn't an option, consider applying for need-based scholarships. Often, these are available to minority applicants or students in financial straits. Likewise, the application fee can often be waived. Contact individual departments when you're applying to check about need-based application waivers.
Completing Your Degree

- Choose people who you can work with, and who share a common research interest, as well as people you get along with personally. Personal differences often pop up during these kinds of working relationships, making it important to avoid them in the beginning.
- Your proposed academic advisor/research supervisor should ideally be named in your statement of purpose, with the reasons you want to work with that person. Those reasons should show that you know something about that person's background and why he or she would make an effective advisor.

- The names and signatures of your committee members , the program director, and the student. You'll also need your student ID number and other personal information.
- A brief statement of your academic and research goals . This will typically be a super-condensed version of your research question or thesis statement, probably no more than 50-100 words.
- A list of the required courses you'll take over the next two years, listing course number, title, department, and instructor, as well as the semester you intend to take the course. Most programs require around 12 hours of required coursework for an advanced degree.
- A list of the elective courses you'll take , with corresponding course numbers, titles, departments, and instructors, as well as the semester you intend to take the course. Most programs require somewhere between 20 and 30 elective hours for an advanced degree.
- Dissertation hours . When you've passed your preliminary examinations, your coursework will change to independent research and dissertation work, but you'll still be registered for a course with a course number and a particular number of credit hours, with your major professor or thesis chair as the instructor. This information will also need to be included on the plan of study form.

- In graduate school, the course load is usually somewhat less than the undergraduate degree, because of the intensity of the coursework and other research or teaching responsibilities. A "full load" is usually considered 6 or 9 hours, though you'll be doing 20 or more hours of teaching or research in a given week. [6] X Research source
- For a PhD student, a typical coursework semester might involve three courses: a required core class and two elective courses. Typically, elective courses will still be in the department the student is studying, if not the particular program. For example, a comparative lit PhD studying Medieval literature may take a 20th century poetry course in the English department as an elective, though probably not a biology class.

- The written examination, sometimes called the "prelim," will typically be submitted to the department chair by your major professor, then administered to you toward the end of your second year of classes. When you pass the exam, you'll be considered "Post-Prelim" and may begin the process of completing your dissertation. [7] X Research source

- Start with a research question. A research question is what you'll hope to answer over the course of your dissertation research. It needs to be narrow, but with broad-reaching implications. A starting research question might be something like, "How are women represented during the silver age of American comic book publishing?" or "What are the implications of spontaneous genetic mutation during breeding in drosophila, and what effect might this have on cancer research?"

- As you complete your coursework and add complexity to the topic in which you're interested, you'll likely change and add depth to your initial research interest. That's fine. Let the research grow your understanding of the topic, and change the way you approach it. That means you're on the right track.

- In the humanities , several semesters following your coursework and preliminary examination will be devoted to completing the research involved with your interests. During this time, you'll be expected to periodically update your committee on your progress, providing them with literature reviews and outlines, depending on your arrangement. You may also be expected to publish supplementary papers periodically in academic journals.
- In the sciences , you'll spend your post-prelim semesters doing lab work, or other field work depending on your field of study. The time will be spent collecting data and performing experiments to move your research forward, to be collected in the dissertation, and probably published in peer-reviewed journals.

- Most "defenses" are cordial affairs, not debates, though you should expect to be pressed and argued with regarding your methods, your conclusions, and other aspects of your work. The best way to prepare for your defense is to know your dissertation and your research inside and out.
- At a successful defense, you'll need to present yourself and your work well both orally and in writing to earn recognition as a PhD candidate and a researcher. Practice delivering your main point quickly and your overall presentation or paper with confidence.
Funding Your Research

- In the hard sciences , money is allocated to provide different labs, projects, and individuals money on a competitive case-by-case basis. To apply, you'll typically write a detailed proposal of your research goals and submit it to the department.
- In the humanities , it's also common to seek subsequent teaching appointments in tangential fields: if your research involves the representation of women in comic books, and you've been teaching in the English department, why not pick up a special-topics course in Women's Studies?

Surviving the Process

- Don't Try to do everything at once. Because you will spend several years to earn your doctorate, it's important to slow down and do everything with the attention to detail the process deserves. You don't want to get your dissertation hung up because of a silly documentation error you rushed through.

- During the time you spend working on your doctorate, you'll face a variety of challenges. The lab's funding may be cut. You may lose grant money. Your paper may get rejected from a conference. Fail early and fail often. Create opportunities for yourself and work around the challenges.

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.findaphd.com/guides/what-is-a-phd
- ↑ https://drexel.edu/soe/resources/career-path/how-to-get-doctorate-degree/
- ↑ https://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/dec/essay.phd.html
- ↑ http://www.cs.unc.edu/~azuma/hitch4.html
- ↑ https://math.berkeley.edu/graduate/phd-program/preliminary-exam
About This Article

Before you can get a PhD, you'll need to complete your prerequisite education and take the GRE, or Graduate Record Exam. You will also need letters of recommendation from 1 or 2 distinguished professors in your field to submit with your application. Once you are admitted to graduate school, you should seek out funding opportunities, like grants or teaching positions. To earn your PhD, you will need to take courses, pass written and oral exams, conduct original research in your field, and write a dissertation. For more ways to get your PhD for free, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Sep 16, 2016
Did this article help you?

Jay Johnson
Aug 5, 2019
Valbona Braho
Mar 6, 2017
James Winchester
Jul 11, 2017
Jonah Loper
Nov 8, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Doctor of Philosophy in Education

Additional Information
- Download the Doctoral Viewbook
- Admissions & Aid
The Harvard Ph.D. in Education trains cutting-edge researchers who work across disciplines to generate knowledge and translate discoveries into transformative policy and practice.
Offered jointly by the Harvard Graduate School of Education and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the Ph.D. in Education provides you with full access to the extraordinary resources of Harvard University and prepares you to assume meaningful roles as university faculty, researchers, senior-level education leaders, and policymakers.
As a Ph.D. candidate, you will collaborate with scholars across all Harvard graduate schools on original interdisciplinary research. In the process, you will help forge new fields of inquiry that will impact the way we teach and learn. The program’s required coursework will develop your knowledge of education and your expertise in a range of quantitative and qualitative methods needed to conduct high-quality research. Guided by the goal of making a transformative impact on education research, policy, and practice, you will focus on independent research in various domains, including human development, learning and teaching, policy analysis and evaluation, institutions and society, and instructional practice.
Curriculum Information
The Ph.D. in Education requires five years of full-time study to complete. You will choose your individual coursework and design your original research in close consultation with your HGSE faculty adviser and dissertation committee. The requirements listed below include the three Ph.D. concentrations: Culture, Institutions, and Society; Education Policy and Program Evaluation; and Human Development, Learning and Teaching .
We invite you to review an example course list, which is provided in two formats — one as the full list by course number and one by broad course category . These lists are subject to modification.
Ph.D. Concentrations and Examples
Summary of Ph.D. Program
Doctoral Colloquia In year one and two you are required to attend. The colloquia convenes weekly and features presentations of work-in-progress and completed work by Harvard faculty, faculty and researchers from outside Harvard, and Harvard doctoral students. Ph.D. students present once in the colloquia over the course of their career.
Research Apprenticeship The Research Apprenticeship is designed to provide ongoing training and mentoring to develop your research skills throughout the entire program.
Teaching Fellowships The Teaching Fellowship is an opportunity to enhance students' teaching skills, promote learning consolidation, and provide opportunities to collaborate with faculty on pedagogical development.
Comprehensive Exams The Written Exam (year 2, spring) tests you on both general and concentration-specific knowledge. The Oral Exam (year 3, fall/winter) tests your command of your chosen field of study and your ability to design, develop, and implement an original research project.
Dissertation Based on your original research, the dissertation process consists of three parts: the Dissertation Proposal, the writing, and an oral defense before the members of your dissertation committee.
Culture, Institutions, and Society (CIS) Concentration
In CIS, you will examine the broader cultural, institutional, organizational, and social contexts relevant to education across the lifespan. What is the value and purpose of education? How do cultural, institutional, and social factors shape educational processes and outcomes? How effective are social movements and community action in education reform? How do we measure stratification and institutional inequality? In CIS, your work will be informed by theories and methods from sociology, history, political science, organizational behavior and management, philosophy, and anthropology. You can examine contexts as diverse as classrooms, families, neighborhoods, schools, colleges and universities, religious institutions, nonprofits, government agencies, and more.
Education Policy and Program Evaluation (EPPE) Concentration
In EPPE, you will research the design, implementation, and evaluation of education policy affecting early childhood, K–12, and postsecondary education in the U.S. and internationally. You will evaluate and assess individual programs and policies related to critical issues like access to education, teacher effectiveness, school finance, testing and accountability systems, school choice, financial aid, college enrollment and persistence, and more. Your work will be informed by theories and methods from economics, political science, public policy, and sociology, history, philosophy, and statistics. This concentration shares some themes with CIS, but your work with EPPE will focus on public policy and large-scale reforms.
Human Development, Learning and Teaching (HDLT) Concentration
In HDLT, you will work to advance the role of scientific research in education policy, reform, and practice. New discoveries in the science of learning and development — the integration of biological, cognitive, and social processes; the relationships between technology and learning; or the factors that influence individual variations in learning — are transforming the practice of teaching and learning in both formal and informal settings. Whether studying behavioral, cognitive, or social-emotional development in children or the design of learning technologies to maximize understanding, you will gain a strong background in human development, the science of learning, and sociocultural factors that explain variation in learning and developmental pathways. Your research will be informed by theories and methods from psychology, cognitive science, sociology and linguistics, philosophy, the biological sciences and mathematics, and organizational behavior.
Program Faculty
The most remarkable thing about the Ph.D. in Education is open access to faculty from all Harvard graduate and professional schools, including the Harvard Graduate School of Education, the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, the Harvard Kennedy School, the Harvard Law School, Harvard Medical School, and the Harvard School of Public Health. Learn about the full Ph.D. Faculty.

Jarvis R. Givens
Jarvis Givens studies the history of American education, African American history, and the relationship between race and power in schools.

Paul L. Harris
Paul Harris is interested in the early development of cognition, emotion, and imagination in children.

Meira Levinson
Meira Levinson is a normative political philosopher who works at the intersection of civic education, youth empowerment, racial justice, and educational ethics.

Luke W. Miratrix
Luke Miratrix is a statistician who explores how to best use modern statistical methods in applied social science contexts.

Eric Taylor
Eric Taylor studies the economics of education, with a particular interest in employer-employee interactions between schools and teachers hiring and firing decisions, job design, training, and performance evaluation.

Paola Uccelli
Paola Ucelli studies socio-cultural and individual differences in the language development of multilingual and monolingual students.

View Ph.D. Faculty
Dissertations.
The following is a complete listing of successful Ph.D. in Education dissertations to-date. Dissertations from November 2014 onward are publicly available in the Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard (DASH) , the online repository for Harvard scholarship.
- 2022 Graduate Dissertations (265 KB pdf)
- 2021 Graduate Dissertations (177 KB pdf)
- 2020 Graduate Dissertations (121 KB pdf)
- 2019 Graduate Dissertations (68.3 KB pdf)
Student Directory
An opt-in listing of current Ph.D. students with information about their interests, research, personal web pages, and contact information:
Doctor of Philosophy in Education Student Directory
Introduce Yourself
Tell us about yourself so that we can tailor our communication to best fit your interests and provide you with relevant information about our programs, events, and other opportunities to connect with us.
Program Highlights
Explore examples of the Doctor of Philosophy in Education experience and the impact its community is making on the field:


Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce

Lost in Translation
New comparative study from Ph.D. candidate Maya Alkateb-Chami finds strong correlation between low literacy outcomes for children and schools teaching in different language from home
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

Admissions & Aid
- Admissions Home
- Application Requirements
- Financing Options
- Diversity Profile

You are here
Application requirements for all doctoral programs (phd).
All of our doctoral programs are designed to develop outstanding educational researchers who have a deep understanding of the scientific, practical and policy issues they study. All require full-time study, and we promise five years of full-time financial support for every student we admit. Our doctoral programs are small, typically ranging from about 25 to 35 new students a year. The small size of our doctoral cohorts creates big educational advantages for students: the classes are almost always small, students receive individualized attention from their advisors, and they have many opportunities to develop close collegial relationships with fellow students.
It is extremely important to demonstrate in your statement of purpose that your interests converge closely with the current research of faculty who work in the program to which you are applying. Other doctoral applicants will certainly do this, and if you don't, you will forfeit an important competitive advantage to them.
If you wish to contact faculty, please read our Which Degree Which Program article, by Professor Eamonn Callan, which outlines the appropriate process for contacting faculty with whom you share research interests.
- Program website: Degrees and Programs/PhD
- Length of Program: 5 years (average length)
- Tuition: fellowship/assistantship salary and tuition guaranteed for first five years of the program (autumn, winter and spring quarters) for all students, including international students. Funding includes two summers.
Application Requirements:
Application form.
Complete and submit Stanford's graduate online application .
Application Fee
The application fee is $125 , is non-refundable, and must be received by the application deadline.
Application Fee Waivers
Stanford offers three types of application fee waivers for which GSE applicants may apply and be considered:
- GRE Fee Reduction Certificate-Based Waiver
- Diversity Program Participation-Based Waiver
- School-Based Waiver
Please visit the Stanford Graduate Diversity website for instructions, deadlines, and the fee waiver application form.
Statement of Purpose
A Statement of Purpose is required. Your statement should be typed, single-spaced and should be between one to two pages . Describe succinctly your reasons for applying to the proposed program, your preparation for this field of study, and why our program is a good fit for you, your future career plans, and other aspects of your background as well as interests which may aid the admissions committee in evaluating your aptitude and motivation for graduate study. You may indicate potential faculty mentors as part of your study and research interests. Be sure to keep a copy for your records. What's a Good Statement of Purpose?
A resume or CV is required of all applicants, depending on which document is most appropriate for your background. There is no page limit for resumes or CVs, though we typically see resumes of one page in length. Please upload your resume or CV in the online application.
Three (3) Letters of Recommendation
Applicants are required to submit three letters of recommendation . In the online application, you will be asked to identify your recommenders and their email addresses. Please notify your recommenders that they will receive an email prompt to submit their recommendation online. You can submit your request for letters of recommendation through the system without submitting the entire online application. Stanford GSE only accepts online recommendations through the application system ; Stanford GSE cannot accept mailed, emailed or faxed recommendations.
Recommendations should be written by people who have supervised you in an academic, employment, or community service setting. We very strongly recommend that at least one of these letters be from a university professor familiar with your academic work. Your recommendations should directly address your suitability for admission to a graduate program at Stanford GSE.
It is the applicant's responsibility to ensure that all three letters of recommendation are submitted through the system by the application deadline , so please work closely with your recommenders to remind them of the deadline.
College and University Transcripts
Transcripts are required from every college and university you have attended for at least one academic year as a full-time student. When submitting your online application, transcripts should be uploaded to the application as a scanned copy or PDF ; this is sufficient for the application review process. Please refrain from sending a secured PDF/transcript with a digital signature as our system cannot upload these properly. The best way to ensure we receive an upload-able document is for you to print out the secured transcript, scan it, and upload the scanned copy (not to exceed 10MB) as a PDF.
If you earned a degree at the institution from which you are submitting a transcript, please ensure that the degree conferral date and the degree conferred is clearly visible on the document. If you are currently enrolled in a degree program and will not have earned the respective degree by the time of submitting your GSE application, you should submit your most recent in-progress transcript from your institution.
Only if admitted will we contact you with instructions on sending two copies of your official transcripts to our office. We cannot accept mailed, emailed or faxed copies of your transcripts during the application process. Please note: the instructions for sending transcripts on the online application and on the general Stanford Graduate Admissions Office website differ from this Stanford GSE requirement.
Concerning course work completed in a study abroad program
If the coursework and grades are reflected on the transcript of your home institution, you do not need to submit original transcripts from the study abroad institution.
Concerning foreign institutions
If your institution provides a transcript in a language other than English, we require that you submit a translation of the transcript that is either provided by the institution or a certified translator. Translations must be literal and complete versions of the original records.
If your transcript does not include your degree conferral date and the degree conferred , please submit a scanned copy of your diploma, a conferral statement, or a conferral document in addition to your transcript . If you are currently enrolled in a degree program and will not have earned the respective degree by the time of submitting your GSE application, you should submit your most recent in-progress transcript from your institution.
Stanford University requires the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) from all applicants whose native language is not English. The GSE requires a minimum TOEFL score of 250 for the computer-based test, 600 for the paper-based test or 100 for the internet-based test in order to be considered for admission. The Test of Written English (TWE) portion of the TOEFL is not required. Applicants who have completed a four-year bachelor's degree or a two-year master's program (or its equivalent) in the U.S. or at an institution where English is the main language of instruction are not required to take the TOEFL. For more information on TOEFL requirements, please refer to the Required Exams page on the main Stanford Graduate Admissions website. You may register for the TOEFL test directly at the ETS website .
TOEFL Dates and Deadlines
PhD applicants who are required to take the TOEFL should plan to take the internet-based TOEFL test and have official TOEFL scores sent electronically to Stanford at institution code 4704 (department code does not matter) no later than November 1 . This will give your official TOEFL scores time to be sent from ETS and be received by our system in time for the December 1 deadline. PhD applicants to Knight-Hennessy Scholars should plan to take the internet-based TOEFL test no later than October 16 so your scores can be received by our system in time for the November 16 KHS GSE deadline. Please note that the TOEFL may be taken no earlier than 18 months prior to the application deadline.
Does Stanford accept tests other than TOEFL?
No. We accept only TOEFL scores; we do not accept IELTS or other test scores.
Contact Information
Admissions: [email protected]
- Financial Aid
- Current Student Info
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- Student/Faculty Portal
- Learning Hub (Brightspace)
- Continuous Professional Development

Admission requirements for the Ph.D. Program include a bachelor's degree from an accredited college or university, a strong background in the basic sciences, and prior research experience.
Prerequisites
All Ph.D. Program candidates must fulfill the following requirements for eligibility:
- A baccalaureate degree, preferably in the biological or physical sciences, must be obtained from an accredited institution
- A cumulative undergraduate GPA of 3.0 on a 4.0 scale is necessary
- Conferral of the degree is required prior to starting the program
Suggested undergraduate coursework:
- It is strongly suggested that applicants have completed one year of coursework with demonstrated competence (B average or above) in biology, chemistry, physics, and calculus
- Additional coursework in biochemistry, molecular biology, cell biology, and physiology is encouraged
- Applicants for the Biomedical Engineering and Physiology Track are encouraged to have courses in quantitative science and engineering (such as signal processing, computer science, and instrumentation)
Note that undergraduate courses are not available at Mayo Clinic Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences.
International applicants should see the International Applicant Information page.
Admissions requirements
How to apply.
Your application and all supporting documentation must be received between Sept. 1 through Dec. 4, including letters of recommendation.
The admissions application is free. There is no application fee for applying to our Ph.D. program.
Applicants can only apply to one research track of interest for each admission cycle. Applicants selected for the program may have the opportunity to do research in any Mayo Clinic research lab regardless of track choice.
When you apply to the program you need to select a location where you plan to study: Jacksonville, Florida; Phoenix/Scottsdale, Arizona; or Rochester, Minnesota. Please note if you are appointed to the program, a campus change is allowed if the research lab you ultimately select after the required lab rotations is on a different campus.
Application instructions
Complete all of the following steps to apply:
- Select - Mayo Clinic Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences
- Select - PhD
- Complete each section of the application and submit
- Upload each required item in the Supplemental Items section
- Complete the Recommendation Request section
Required application documents
The following items, including all Letters of Recommendation, must be received by the application deadline of Dec. 4 within the Supplemental Items and Documents area of the application. Incomplete applications will not be reviewed.
- Within the Supplemental Items and Documents area of the application, in the Recommendation Requests section, you will provide contact information for each letter writer. Each of your recommenders will receive an email with a link to complete a rating form and upload their letter of recommendation.
- List your prior research experience in chronological order, indicating the role you played in each project.
- Indicate which has been your most satisfying research project and why it was satisfying to you.
- Summarize your current scientific interests and career goals.
- Specifically answer the question: "Why do you want to be a biomedical scientist?"
- Your personal statement should be two to four pages if single-spaced, or three to five pages if double-spaced.
- Publications: The first two pages of each publication (which should contain the abstract and introduction sections. Be sure the name of the publication and your name are listed).
- Poster presentation award certificate information if received for any of your publications.
- International transcript requirements
- English language proficiency documents for non-native English speakers (see international applicant information ).
The most qualified applicants are invited to interview. Mayo Clinic welcomes applications from diverse learners.

"So many different kinds of opportunities"
Welcoming and inclusive
Mayo Clinic Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences is recognized as a center of excellence in training a diverse biomedical research workforce.

How Long Does it Take To Get A PhD? Doctorate Degree Timeline
Starting a PhD means you’re ready for a big academic adventure, full of tough challenges and exciting discoveries.
If you’re thinking about going for it, you’re probably wondering just how much time you’ll need to commit to this big goal.
For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you’re juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 years to complete, sometimes more.
This article breaks down what the PhD journey looks like, what can make it longer or shorter, and some tips on how to make it through.
If you’re curious about how long it’ll take to add ‘Dr.’ before your name, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive into the world of PhD timelines!
How Long Does It Take To Get A PhD?
The answer here isn’t straightforward, as it hinges on various factors, including:
- the discipline,
- the institution, and
- whether you’re a full-time or part-time student.
For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you’re juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 years to complete, sometimes more.

Distance learning PhD programs offer flexibility but similarly require a substantial time commitment, often mirroring the length of part-time studies.
The heart of a doctoral program is the dissertation, a rigorous research project that demands an in-depth exploration of your chosen field. This phase alone can take several months to years, significantly influencing the overall length of your PhD journey.
Beyond the dissertation, coursework, exams, and sometimes teaching responsibilities add layers to the doctoral experience.
The requirements for a PhD vary widely across disciplines and institutions. For instance, a doctorate in the sciences might involve extensive lab work, potentially extending the time to completion.
In contrast, a doctorate in the arts could hinge more on coursework and creative output, leading to variations in the timeline.
Does A Doctorate Degree Take Longer Than Masters?
A doctorate degree typically takes longer to complete than a master’s degree.
While a master’s program can often be completed in 1-2 years of full-time study, a doctoral program usually requires 4-6 years, depending on the:
- research complexity, and
- whether the student is enrolled full-time or part-time.
The doctoral journey is more than just additional coursework; it involves conducting original research, writing a comprehensive dissertation, and often teaching or engaging in professional development activities.
The dissertation phase, which requires students to contribute new knowledge to their field, is particularly time-consuming and can extend the duration of a PhD program significantly.
The time it takes to complete a doctorate can be influenced by your
- research topic,
- funding availability, and
- the level of support from advisors and faculty.
Master’s programs are typically more structured, with a clearer set of coursework requirements and a shorter thesis or capstone project, leading to a quicker path to graduation.

Why Does It Take So Long To Finish Doctoral Program?
Starting a doctoral program is a significant commitment, often taking longer than anticipated. If you wonder why it takes so long, here are a couple of reasons you can think about:
Extensive Coursework
Initially, you might think coursework in your PhD study is just a continuation of your previous studies.
Doctoral level courses are a different beast. They demand not just understanding but the ability to critically analyze and apply complex concepts.
Each course can feel like a mini research project, requiring more than just classroom attendance. This phase lays the foundation but is time-consuming.
The Dissertation
The heart of your doctoral journey is your dissertation. This isn’t just a long essay or an extended research paper. It’s an original contribution to your field, requiring:
- exhaustive research,
- experimentation, and
Some students find their research path straightforward, while others may hit unexpected roadblocks or need to pivot their focus, extending the time required.
Part-Time Study
Many PhD candidates choose a part-time path due to work, family, or other commitments. While this flexibility is crucial for many, it stretches the duration of the program.
What a full-time student might complete in 4-6 years, part-time students might take 7 years or more to finish.
Funding and Resources
Access to funding and resources can significantly impact the timeline. Some projects require extensive fieldwork, specialised equipment, or access to rare materials. Delays in funding or accessing necessary resources can stall progress.
If funding is an issue, consider applying for work outside of the university. You can also try your luck with the university, as a research or teaching assistant , or more.

Academic Publishing
As part of the doctoral process, many students are encouraged or required to publish their findings.
However, the process of submitting to academic journals, undergoing peer review, and possibly revising and resubmitting, is lengthy.
This step is crucial for the academic community but adds time to the doctoral timeline. If may help to start writing and publishing work earlier to ensure you have enough time to finish.
Faculty Supervision and Mentorship
The relationship with your advisor or supervisory committee is pivotal. These mentors gatekeep your studies, as they:
- guide your research,
- provide feedback, and
- approve your progress.
Scheduling conflicts, feedback loops, and the iterative nature of research can add semesters or even years to your timeline.
Personal Growth and Professional Development
Beyond the academic requirements, doctoral students often engage in teaching, attend conferences, and network within their academic community. These activities contribute to your professional development but also extend your time in the program.
Factors That Influence The Time To Get A PhD
The time it takes to complete PhD is influenced by a multitude of factors, each significant in its own right. Let’s delve deeper into these elements to understand the intricacies of the PhD voyage.
The Scope of Research :
The ambition of your research can significantly dictate the duration of your PhD. Some projects will need more time and commitment, especially if they:
- Demand extensive fieldwork,
- elaborate experiments, or
- groundbreaking theoretical developments.
Imagine embarking on a quest that not only seeks answers but also questions the very foundations of your field. Such endeavours are thrilling but inherently time-consuming, often extending the PhD journey beyond the typical timeframe.
Program Structure and Requirements
The architecture of a PhD program—its coursework, qualifying exams, and other prerequisites—lays the groundwork for your academic expedition.
Programs with a heavy load of initial coursework aim to equip you with a broad foundation, yet this can elongate the path to your actual dissertation work.
Mode of Study
The decision between full-time and part-time study is pivotal. A full-time commitment allows you to immerse yourself in research, ideally hastening progress.
Yet, life’s obligations may necessitate a part-time route, extending the journey but offering flexibility.
Distance learning, with its inherent flexibility, caters to those balancing diverse commitments, yet this mode, too, can stretch the timeline, particularly if it lacks the immediacy and intensity of on-campus engagement.
Quality of Supervision
The symbiotic relationship with your advisor is the compass guiding your research voyage. An advisor who is both a mentor and a critic, offering timely and constructive feedback, can expedite your journey.
Less engaged supervision may leave you adrift, prolonging the process as you navigate the academic waters largely on your own.
Worse still, if you are unlucky enough, you may end up with supervisors that not only does not help you, but actively attempt to make your study life difficult. These nightmare scenarios do exist, and you should be aware of them.
Financial Stability
The financial underpinnings of your PhD endeavor are more critical than often acknowledged. Consistent funding allows you to dedicate yourself fully to your research, free from financial distractions.
Conversely, the absence of stable support might necessitate part-time employment, diluting focus and extending the timeline.
Resource Availability
Access to specialized resources—be it state-of-the-art laboratories, rare archival collections, or cutting-edge software—can be the wind in your PhD sails.
Limited or delayed access to these essential tools, however, can stall progress, turning what could be a swift journey into a prolonged odyssey.
If you found yourself in a position without the right resources to complete your PhD, consider to propose your university to allow you to work with other universities with what you need. If this is not possible, you can always transfer university, although this would mean more work.
Publishing Requirements
The adage “publish or perish” holds particularly true in the realm of PhD studies. The process of getting your research published, from initial submission to eventual acceptance, is fraught with delays and revisions. Each publication cycle can add months to your timeline,
Yet these publications are crucial stepping stones towards establishing your academic credibility. In fact, some universities want you to publish papers to graduate.
Personal Life and Circumstances
The journey towards a PhD is not undertaken in academic isolation. Life, with its unforeseen challenges and responsibilities, continues.
Personal circumstances can impact your ability to devote time and energy to your studies, necessitating pauses or a reduction in research intensity.
These issues can range from situation such as:
- such as health issues,
- family commitments, or
- significant life events

Tips To Earn Your Doctoral Degree Fast
Earning a doctoral degree is a significant academic endeavor, often perceived as a marathon rather than a sprint. However, with strategic planning and focused effort, you can navigate this journey more swiftly than you might expect.
Here are some tips to help you earn your doctoral degree faster, drawing from the experiences and strategies of successful PhD candidates.
Choose Your Program Wisely
The structure of the PhD program you choose can greatly influence how long it takes to complete your degree. Programs that allow you to start your dissertation research early, even while completing your coursework, can save you a considerable amount of time.
Some program are designed to integrate dissertation work with coursework, enabling a more seamless transition into the research phase.
Opt for Full-Time Study If Possible
While part-time PhD programs offer flexibility for working professionals, full-time study allows for a more immersive research experience.
Dedicating all your working hours to your doctoral research can expedite the process, reducing the time it takes to get your PhD significantly.
Secure Adequate Funding
Financial stability is key to focusing fully on your research without the distraction of part-time work. Look for:
- scholarships,
- grants, and
- funding opportunities from your institution.
You can also try to secure funding from external sources like the National Science Foundation.
Secure funding not only supports your financial needs but also often comes with academic resources that can accelerate your research progress.
Develop a Strong Relationship with Your Advisor
Your advisor is your guide through the PhD process. A supportive advisor can provide invaluable feedback, help you navigate academic challenges, and keep you on track.
Regular meetings and clear communication with your advisor can help you refine your research direction and avoid time-consuming pitfalls.
Focus Your Research
A well-defined research question can provide a clear path forward. The more focused your research, the less likely you are to get bogged down in unmanageable amounts of data or tangential studies.
It’s about depth rather than breadth; delving deeply into a specific area can lead to significant contributions to your field and a quicker path to completion.

Take Advantage of Existing Research and Resources
Don’t reinvent the wheel. Building on existing research and utilizing available resources can save you time. This includes:
- leveraging datasets,
- using established methodologies, and c
- ollaborating with other researchers.
Access to resources like specialized labs or archives, as provided by your institution, can also streamline the research process.
Stay Organized and Manage Your Time Effectively
Good time management is crucial. Set realistic goals, create a timeline for your research and writing, and stick to it.
Tools like Gantt charts can help you visualize your PhD timeline, including key milestones like coursework completion, comprehensive exams, and dissertation chapters.
Get Your PhD Without Taking Too Much Time – Possible
The journey to obtaining a PhD is a unique blend of personal commitment, academic rigor, and research innovation.
While the timeline can vary widely, most candidates find themselves immersed in their studies and research for anywhere from 4 to 6 years. Exceptions can happen, and you may finish earlier or later.
Key factors like your field of study, the nature of your research, and your personal life circumstances play significant roles in shaping your individual journey.
Remember, earning a PhD is more than just a race to the finish line; it’s a profound journey of learning, discovery, and personal growth. Embrace the journey, stay focused, and the day you earn the title of ‘Doctor’ will be a milestone to remember.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider
PhD Admission FAQ

General Information
When is the application due and how do i apply .
NOW CLOSED- The application is due on November 30, 2023 at 11:59 PM Pacific Time.
Apply using the application portal .
How long does it take to get a PhD in Psychology at Stanford?
The PhD program is designed to be completed in five years of full-time study. Actual time will depend on students' prior background, progress, and research requirements. The minimum residency requirement for the PhD degree is 135 units of completed coursework and research units.
What are the requirements for the PhD degree in Psychology?
Please consult the PhD Requirements page .
What are the different subfields within the graduate program in Psychology?
- Affective Science
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Neuroscience
- Social Psychology
What is the Department's teaching requirement?
PhD students must complete at least five quarters of teaching assistantship (TA) under the supervision of a faculty member. Students are required to attend a TA training workshop in their second year. In addition, students are encouraged to take advantage of department and university teacher training programs. Students for whom English is a second language are expected to acquire sufficient fluency in English. All international students must be approved by Stanford’s EFS department .
How many students apply to the Stanford Psychology PhD? How many are admitted? What are the demographics?
Stanford provides public reports with summary data about graduate programs and graduate admissions. Please consult the public dashboards published by Stanford's office of Institutional Research & Decision Support on doctoral admissions , doctoral enrollment and demographics , and doctoral completion and time-to-degree .
Is there a standalone Master of Arts program in Psychology?
The Department of Psychology does not offer a terminal Master’s degree program. Current doctoral students within the Department or in another Stanford graduate program may apply to be awarded a Master of Arts in Psychology during the course of their PhD program.
Does your department have a program in Clinical Psychology? Are you accredited by the APA?
No. Our department does not have a program in Clinical Psychology. As such, we are not accredited by the APA.
Do you have any advice about getting into grad school?
The Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences offers an online resource for prospective graduate school applicants: Guide on Getting Into Grad School . We encourage applicants to take advantage of this resource.
Financial Support
What is the annual cost of attending your program.
All students admitted to the Psychology PhD program receive five years of 12-month funding. Financial support is provided through a combination of fellowship stipend and salary, and assistantship salary and tuition allowance. Information about the cost of attendance and funding options are available from the Financial Aid Office .
What type of financial support do you offer?
All students admitted to the Psychology PhD program receive five years of 12-month funding. Financial support is provided through a combination of fellowship stipend and salary, and assistantship salary and tuition allowance. Funding is contingent upon satisfactory academic progress. Students are encouraged to pursue fellowships offered by the University and by national organizations, such as the National Science Foundation.
Stanford University also offers the Knight-Hennessy Scholars program, designed to build a multidisciplinary community of Stanford graduate students dedicated to finding creative solutions to the world's greatest challenges. The program awards up to 100 high-achieving students every year with full funding to pursue graduate education at Stanford, including the PhD in Psychology. To be considered, you must apply to Knight-Hennessy Scholars and separately apply to the Psychology Department. Note that the Knight-Hennessy Scholars program application deadline is in the spring before the autumn application cycle.
Do you offer support for the summer months?
Yes, funding is offered for 12 months a year for 5 full years, including 5 summers.
Preparing for Admission
Am i eligible to apply if my undergraduate major is not in psychology.
An undergraduate major in Psychology is not required; applicants from other backgrounds can apply and be admitted. All applicants should have sufficient foundational knowledge and research experience prior to the program to allow them to go straight into graduate-level coursework and conduct research.
My undergraduate degree was completed outside the United States. Is my degree eligible?
Please refer to the Stanford Graduate Admission Office's table of minimum level requirements for international academic credentials . These credential requirements are set by the University and nonnegotiable.
If I have prior graduate work, can it be transferred to the PhD program?
No, the Department of Psychology does not allow the transfer of unit credits from your previous program.
How competitive is admission to the PhD program?
Admission to our program is highly competitive. About 10-15 admits enter the program each year and are chosen from a pool of over 600 applicants. These students are selected on the basis of a strong academic background as demonstrated by previous coursework, research experience, and letters of recommendation. Please be assured that the Department reviews each application very carefully and makes decisions on an individual basis.
The Application Process
How do i apply.
Please visit the PhD Admissions page for instructions on how to apply to the Psychology PhD Program, graduate application requirements, and the link to the online application.
Is there an application fee? If so, can I apply for a fee waiver?
The fee to apply for graduate study at Stanford is $125, see Application Fee . Fee waivers are available for some applicants. Please visit Graduate Admissions for information on applying for an Application Fee Waiver .
Can I submit another application to a different department within the University?
You may only apply to one degree program per academic year. However, you may apply concurrently to one departmental program and to a professional school program (law, medicine, or business).
I'm interested in the joint JD/PhD in Law and Psychology - how does it work?
Students interested in the JD/Ph.D. joint degree must apply and gain entrance separately to the School of Law and the Psychology Ph.D. program. Additionally, students must secure permission from each degree program to pursue the joint degree. Interest in both degrees should be noted on the student’s admissions applications and may be considered by the admissions committee of each program. Alternatively, an enrolled student in either the Law School or the Psychology department may apply to add the other degree and undertake the joint degree program, preferably during their first year of study. Students participating in the JD/Ph.D. joint degree program are not eligible to transfer and receive credit for a masters, or other degree, towards the Psychology Ph.D.
Students interested in the MPP/Ph.D. joint degree must apply and gain entrance to the Public Policy program’s MPP degree and the Psychology Ph.D. program. Students should note their interest in both degrees on their graduate admissions applications. Additionally, students must secure permission from each degree program to pursue the joint degree
Which faculty are accepting new students this year?
All active faculty are potentially accepting new students each year. In your application, we ask you to list the top 3 faculty you are most interested in working with. Multiple readers will review your application in full regardless of who you list.
My institution does not report GPAs on a 4.0 grading scale. How should I report my GPA on the application?
Please do not convert your GPA to a 4.0 grading scale. You should enter “0.00” for the GPA and use the “Unconverted GPA” and “Unconverted GPA System” fields instead. A link to detailed instructions for reporting GPA is located near these fields on the application.
I attended multiple undergraduate institutions. In what order should I list them on the application?
The institution where you earned or expect to earn your Bachelor's degree should be listed as "Post-Secondary Institution 1." The remaining institutions don’t have to follow a particular order. List all institutions that were attended for at least one full academic year. Please note that you must submit a transcript for all courses taken towards your undergraduate degree, including those from your nonprimary institutions.
When should I submit my transcripts if my degree will still be in progress at the time of the application deadline?
The most current version of your unofficial transcript must be submitted as part of your electronic application, even if the grades from your fall term are not available. The absence of these grades will have no impact on the review of your application. If you are admitted and enrolled, we will ask you to submit your final transcript showing all grades and proof of degree conferral.
Should I submit official transcripts?
At the time of your initial application, please only submit your unofficial transcripts. Submit the unofficial transcripts as part of your electronic application, per the instructions in the application portal. A short list of applicants who move forward to the next stage of the review process will be contacted with instructions for submitting official transcripts at a later stage.
It may be helpful to understand the difference. Unofficial transcripts are transcripts issued by your college or university directly to you, the student, which you then submit to Stanford for review. Official transcripts are transcripts issued by your college or university directly to Stanford University, usually by secure electronic transfer and sometimes in hard copy in signed and sealed envelopes. The key difference is that an official transcript has never been directly handled by the applicant.
Do you have a minimum GPA score?
We do not require applicants to have a minimum GPA for consideration, and we do not release information about the average GPAs of accepted students. As a guideline, successful applicants typically earn undergraduate cumulative GPAs among the top of their class. However, please keep in mind that admission to our graduate program depends on a combination of factors, and all areas of a student’s application are weighed similarly when applications are reviewed. If our research areas meet your educational goals, we encourage you to submit an application.
May I contact the faculty directly during the application process?
Applicants are not prohibited from reaching out to faculty directly during the application cycle. However, please understand that our faculty are extremely busy, and it is quite possible that you will receive either a very short response or no response at all. This does not mean the faculty are not interested in your application. All applications will be read and reviewed in full during the formal review process. Note that per Department policy, all faculty are potentially accepting graduate students in any given cycle, so you do not need to contact faculty in advance to see if that specific mentor is accepting students for the coming year.
Can I meet with Department staff either by phone or email before I apply to discuss my application materials or ask general questions about the program?
No, the Department staff do not have meetings with or provide individualized advising for prospective applicants. Please understand that this is a matter of bandwidth and equity. We do not have the ability to offer personalized service to all interested applicants, so we do not offer them at all. By Department policy, our staff do not provide any evaluative feedback on prospective applicants' materials, so please do not contact us with CVs, academic histories, etc to request feedback or ask about odds for acceptance. For support in crafting your application, we recommend that you turn to your existing network of mentors (e.g., your letter writers) and/or the resources offered by your current or prior academic institution(s).
TOEFL and GRE
Is the general gre required is the subject gre required.
No, the Stanford Psychology PhD program does not require the general GRE or the subject GRE. We will not be collecting any information related to GRE exam scores on the application. Please do not submit GRE scores to Stanford for our program.
What is the TOEFL exam, and am I required to take it?
The TOEFL is a standardized test of English language proficiency. Per University policy, the TOEFL exam is required for international, non-native English speakers who apply to any Stanford graduate program.
The TOEFL score requirements are waived for international non-native English speakers who have received a Bachelor’s or Master’s degree from an institution in the United States or another English-speaking country. Therefore, applicants with these degrees from the U.S., Australia, Canada (except Quebec), New Zealand, Singapore, Ireland, and the United Kingdom (England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, Wales) are exempt from taking the TOEFL and do not need to submit the TOEFL waiver request form.
When should I take the TOEFL?
The TOEFL must be taken by the published application deadline.
What is the minimum TOEFL score required for admission?
Please visit the website of Stanford's Office of Graduate Admissions for more information on the University’s minimum requirements.
If my TOEFL score falls below the University’s minimum, am I still eligible to apply?
Yes, you may still apply. If your TOEFL scores fall below the University's minimum requirements and you are admitted, Stanford may require you to take an English placement exam and/or English classes.
May I submit the IELTS instead of the TOEFL to demonstrate English proficiency?
The IELTS is not accepted at Stanford University; only the TOEFL is accepted to provide proof of proficiency in English.
How do I request a TOEFL exemption or waiver?
For all questions related to TOEFL exemptions or waivers please refer to the website of Stanford’s Office of Graduate Admissions . Please note that the central office makes all final decisions regarding TOEFL waivers; the Department of Psychology is not involved in the approval of TOEFL waivers.
How do I check the status of my TOEFL scores?
Log in to your application account. It may take up to two weeks after submitting your application or sending the scores (whichever occurs later) for your official scores to show as received. Processing may be delayed or halted if the name or birthdate on the score report does not exactly match the information on your application.
Why does my TOEFL status show as “Not Applicable” even though I submitted a TOEFL score?
This may be because you listed English as your first language in the application. Please note that “first language” refers to your native language.
Is there a department code for ETS to use in order to send in my scores?
No, there are no individual department code. Use the Stanford University score recipient code 4704 to send your TOEFL scores.
Statements of Purpose
How long should my statement of purpose be.
We strongly recommend that your statement of purpose be around two pages in length.
What should I include in my statement of purpose?
Please consult the Stanford Graduate Admissions FAQ page for more information on the Statement of Purpose.
Letters of Recommendation
When are the letters of recommendation due.
The letters of recommendation have the same deadline as the rest of the application. This year, the deadline is November 30, 2023.
How many recommendations do I need, and who should I ask to be my recommenders?
Applicants need three recommendations from faculty or others qualified to evaluate your potential for graduate study. At least one evaluation and letter should be from a faculty member at the last school you attended as a full-time student (unless you have been out of school for more than five years). Substitutions for faculty recommendations may include work associates or others who can comment on your academic potential for graduate work.
My recommender will not be able to submit his/her letter by the application deadline. Will my application still be considered?
Letters of recommendation must be submitted by the application deadline. As such, we strongly encourage you to contact your recommenders directly to remind them of our deadline. If your recommender misses the deadline, please contact psych-admissions [at] stanford.edu (psych-admissions[at]stanford[dot]edu) . Depending on the circumstances, Department staff may collect the letter via email and forward it to the faculty to add to your file. That said, the program expects applicants to do everything possible to ensure that letters are submitted on time via the secure online system.
Can my recommenders submit their letters via email, fax, or postal service?
No. Recommenders must submit their letters via Stanford’s online recommender system.
My recommenders are having technical difficulties with the online letters of recommendation process. Who should they contact?
Should any of your recommenders experience technical difficulties with the online letters of recommendation process, please refer them to our application database provider's letters of recommendation help page or have them submit a Help Request Form directly to our application database provider.
Additional Materials and Updates
I realized i made a mistake on my application and/or uploaded the wrong version of my documents. what do i do.
Depending on the timing and the nature of the error, our staff may be able to correct your application. Please send an email to psych-admissions [at] stanford.edu (psych-admissions[at]stanford[dot]edu) . Include your full name, a complete description of the error, and attach the correct version of the file (if applicable). The Department reserves the right to decline to update your application after the deadline has passed. Requests will be reviewed on a case-by-case basis.
If you need to change your recommenders, please use the Activity Status Page. Note: The order of recommenders cannot be changed.
May I submit a resume/CV, list of publications, etc. as part of my application?
Applicants are permitted to upload one additional document to the online application, under the “Document Uploads” section.
Is there an interview process?
Yes, our faculty interview prospective students before making final admission decisions.
When are the interviews?
The interviews for the current admissions cycle are likely to be in February 2021. We anticipate that all interviews will take place virtually.
When can I expect to find out the decision on my application?
The Department of Psychology aims to issue all offers of admission to PhD degree applicants by the end of March.
I applied in a prior cycle and was not admitted. Can I apply again?
Applicants who applied in prior cycles and were previously not admitted are welcome to reapply if they can demonstrate significant progress made since they last applied. We encourage you to use your Statement of Purpose to explain this progress.
All documents must be resubmitted with a new application. We do not keep records from past applications.
I still have questions!
If you have questions that are not answered on this page or the Stanford Graduate Admissions FAQ page , please email psych-admissions [at] stanford.edu (psych-admissions[at]stanford[dot]edu) . If your questions are already covered on this page, your email may not receive a response.
Note that our Department staff are experts on the logistics and administration of the application, but do not answer questions related to research topics or faculty fit. Per Department policy, Department staff will not offer any evaluative feedback on application materials or applicants' academic background. Unfortunately, due to the extremely high volume of inquiries, we cannot provide individual status updates for applicants at any point in the process.
30 Fully Funded Ph.D. Programs
These fully funded Ph.D. programs are in fields like business, computer science, education and nursing.

(Getty Images) |
Many Ph.D. programs are fully funded.
Students interested in graduate research in various fields, from public health and English to computer science and engineering, have numerous options for Ph.D. programs that offer full funding. These programs typically provide waived tuition and fees and an annual stipend. Some also offer health insurance and other benefits. Gaining admittance into these small cohorts can be highly competitive, and the programs can be time-consuming . Here are 30 fully funded Ph.D. programs at U.S. colleges and universities. Keep in mind this is not a comprehensive list – there are others out there.

- Ph.D. in anthropology at the University of Chicago
Anthropology Ph.D. students at the University of Chicago can receive funding for up to eight years of study, assuming they are in good standing at the university. During that time, they will receive a full-tuition scholarship plus health insurance and a living stipend – which equated to $33,000 for the 2022-2023 school year – and can apply for external fellowships.

Ph.D. in biological sciences in public health at Harvard University (MA)
Harvard University's T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston offers a Ph.D. in biological sciences in public health that aims to provide students with expertise in disease prevention and treatment. This program includes tuition, a stipend and health insurance for five years as long as the student maintains satisfactory academic progress. International students receive the same benefits. Current research in the school's laboratories involves diseases like AIDS, cancer, diabetes, kidney disease, malaria and tuberculosis.

(Dominick Reuter) |
- Ph.D. in business at Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Students enrolled in the Sloan School of Management at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology can study a range of fields like organization studies, accounting and information technology. Those pursuing a Ph.D. will receive a full-tuition scholarship plus a monthly stipend of $4,267, capped at $51,204. They will also receive medical insurance, new laptops at the beginning of their first and fourth years of study and $4,500 over five years for conference travel expenses.

(Tommy Lavergne | Rice University)
Ph.D. in business at Rice University (TX)
At the Rice University Jones Graduate School of Business in Texas, students enjoy full financial assistance upon admission to the Ph.D. program. Aiming to prepare students to teach in fields like accounting, finance, organizational behavior and strategic management, the program provides students with a research or teaching assistantship. Students receive a tuition waiver and a $40,000 annual stipend contingent on making satisfactory academic progress and maintaining full-time student status.

Office of Strategic Communication | University of Iowa
- Ph.D. in business at the University of Iowa
The University of Iowa's Tippie College of Business offers Ph.D. degrees in fields such as accounting, economics, business analytics and marketing. The college says it provides full funding to "virtually all admitted students." This includes tuition and fees, a minimum nine-month stipend of about $20,000 with annual adjustments and comprehensive health insurance covered at 90%. Some departments offer funding for research presentations at major conferences, summer fellowships and paid time off for independent research.

Ph.D. in chemical engineering at Cornell University (NY)
According to Cornell University 's website, all students admitted to the chemical engineering Ph.D. program at the New York school receive a full tuition waiver, health insurance and a stipend. This funding can come from a teaching assistantship, research assistantship or fellowship, and full stipends are granted for nine months with the likelihood of additional aid in the summer.

Chris Taggart | Columbia University
Ph.D. in clinical psychology at Columbia University (NY)
Students enrolled in Columbia University 's Ph.D. program in clinical psychology at the Teachers College in New York receive fully funded tuition and a $25,000 stipend annually for three years. The stipend also carries into a student's fourth year. These doctoral fellows "may be expected to serve" as graduate teaching or research assistants. Students typically complete the mentor-matched program, which includes a full-year internship, in five to seven years.

Ph.D. in computer science at Brown University (RI)
Brown University 's Ph.D. students in computer science have access to "full financial support while completing the degree," plus the option to take classes at nearby schools without incurring additional costs, according to the school's website. In fact, doctoral students in any program at the Rhode Island university are guaranteed five years of financial support, which includes tuition remission, a stipend, health services fees and a subsidy for health insurance.

Georgetown University |
Ph.D. in computer science at Georgetown University (DC)
Georgetown University 's Ph.D. program in computer science provides scholarships and assistantships that cover full tuition at the Washington, D.C., school and include a stipend and health insurance for the first five years. Once enrolled in the program, students must complete the Apprenticeship in Teaching Program and ultimately write and defend a full research dissertation in a seminar open to the public.

Ph.D. in computer science at Washington University in St. Louis
Ph.D. students in the computer science or computer engineering program at Washington University in St. Louis receive full tuition support and health insurance. According to the university's website: "As a doctoral candidate, you will also receive a generous stipend to cover living expenses and a new, high-end Apple laptop computer. This support is guaranteed as you continue to make satisfactory progress towards your degree." Doctoral students may also qualify for one of three fellowships.

Jeff Miller | UW-Madison
- Ph.D. in counseling psychology at the University of Wisconsin—Madison
Incoming Ph.D. students at the School of Education at the University of Wisconsin—Madison are guaranteed full funding for the duration of the time that they are expected on campus, according to the university's department of counseling psychology website. Doctoral students also receive a benefits package that includes health insurance. Funding may come from financial aid, fellowships, assistantships and/or traineeships.

Emory University |
Ph.D. in economics at Emory University (GA)
Students enrolled in the economics Ph.D. program at Emory University typically receive full funding, according to the Georgia university's website. The stipend provided to students is $36,376 per year for five years, starting in fall 2023, and the full tuition scholarship is worth $70,200 per year. Funding for admitted students also includes a $4,370 annual subsidy that covers 100% of a student's cost of health insurance. First-year students have no stipend-related work requirements.

- Ph.D. in education at New York University
New York University's Steinhardt School of Culture, Education, and Human Development offers more than 30 degree programs. Many can be pursued on campus or online. Ph.D. degrees are offered in areas like developmental psychology, educational leadership and childhood education. Full-time NYU Steinhardt Ph.D. students are eligible for a funding package that includes an annual stipend – $32,000 for the 2022-2023 academic year – tuition coverage for required coursework and student health insurance for five years.

L.A. Cicero, Stanford News Service |
Ph.D. in education at Stanford University (CA)
Stanford University's Graduate School of Education allows students numerous fellowship and assistantship opportunities at the California school, along with a "five-year funding guarantee that provides tuition aid, fellowship stipend, and assistantship salary, and covers the standard cost of attendance," the program website reads. At the Graduate School of Education, doctoral students can choose from a range of academic areas like curriculum studies and teacher education, and developmental and psychological sciences.

- Ph.D. in education at the University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania Graduate School of Education provides full funding to Ph.D. students as part of a fellowship and research apprenticeship package. This funding includes a living stipend, health insurance and coverage of tuition and fees for up to four years if the student maintains full-time enrollment. Some students may also qualify for additional summer funding.

- Ph.D. in engineering at the University of Michigan—Ann Arbor
Doctoral students in engineering at the University of Michigan—Ann Arbor can choose from numerous areas of specialization under umbrella categories like aerospace engineering, biomedical engineering, macromolecular science and engineering, and robotics. All engineering doctoral students are guaranteed full funding, a monthly living stipend and health insurance. The exact amount can vary, according to the program's website, and funding comes from a range of sources, including graduate student instructor positions and fellowships.

Boston University Photography |
- Ph.D. in English at Boston University
Annually, doctoral students studying English at Boston University receive a stipend plus full tuition, fees and basic health insurance. This funding is guaranteed for at least five years, with two of those years typically free from teaching requirements. Funding can sometimes be extended up to seven years, according to the university's website, but it's not guaranteed. Students may also apply for various prizes, fellowships and short-term research and travel grants.

(Stephanie Diani) |
- Ph.D. in English at the University of California—Los Angeles
Applicants to the Ph.D. in English program at the University of California—Los Angeles are automatically considered for various funding options. A six-year funding package includes "a minimum of two years of full fellowship, four years of summer stipend support and up to four years of teaching assistantships," according to the school website. Beyond tuition, fees and health insurance are also covered.

Jeff Watts |
Ph.D. in international relations at American University (DC)
American University offers doctoral students in its international relations program who do not have external funding a renewable four-year Dean's Fellowship that is contingent on making satisfactory academic progress. The fellowship includes the cost of tuition, fees and a stipend that must be earned via a part-time role as a teaching or research assistant. Students also must "demonstrate competency in a modern foreign language" before graduating.

Jonathan Cohen | Binghamton University
- Ph.D. in management at Binghamton University—SUNY
All students admitted to the interdisciplinary management Ph.D. program at the Binghamton University—SUNY School of Management in New York receive a combination of a full-tuition scholarship and a teaching or research assistantship for each academic year, up to four years. This STEM-designated business doctoral degree prepares students for careers in academia and work in the public and private sectors, and has a student-faculty ratio of 1-to-1, according to the university's website.

Duke University Communications |
Ph.D. in materials science and engineering at Duke University (NC)
Doctoral students at Duke University in North Carolina studying materials science and engineering generally receive full tuition, a stipend and fee support for the first five years. Students also receive up to six years of health insurance if they are on the university's student medical insurance plan. The doctoral program aims to help students publish with a faculty adviser and develop research skills, with the opportunity to present research at professional conferences.

Homewood Photography | JHU
Ph.D. in nursing at Johns Hopkins University (MD)
The School of Nursing at Johns Hopkins University in Maryland provides most doctoral students with three fully funded years of study. Available financial aid includes graduate assistantships, targeted fellowships and nursing-specific funding. The university aims to "advance the theoretical foundation of nursing practice and healthcare delivery" with the degree, its website reads. "By graduation, most Hopkins nurse scholars have been awarded grants that continue their research and set them well on their way to a successful career."

- Ph.D. in nursing at the University of Virginia
All students admitted to the University of Virginia 's Ph.D. in Nursing program are eligible for four years of scholarship funding to cover tuition, insurance and fees, as well as annual stipends. To receive certain aid, students must work 10 hours per week as a graduate teaching assistant. With a heavy research focus, students can expect courses in qualitative, quantitative and historical research, and will have to submit a research proposal for peer review.

Ph.D. in nursing at Yale University (CT)
At Yale University in Connecticut, the School of Nursing offers full funding to its Ph.D. students. They receive a monthly stipend for four years in addition to paid tuition and health care. The program allows students to gain in-depth knowledge in a particular area of study. Every incoming Ph.D. student gets paired with a faculty adviser "whose area of expertise and active research most closely matches with the student’s scholarly interest," according to the school's website.

University of Minnesota |
- Ph.D. in psychology at the University of Minnesota—Twin Cities
Students admitted to the Ph.D. program to study psychology at the University of Minnesota—Twin Cities are guaranteed full funding for five years as long as they maintain satisfactory performance and degree progress. This funding includes full-time tuition, a nine-month stipend and subsidized health insurance. Funding comes from some combination of teaching assistantships, traineeships, research assistantships and fellowships. Students in the program can specialize in areas like cognitive and brain sciences, industrial-organizational psychology and social psychology.

Matt Cashore | University of Notre Dame
Ph.D. within the Romance languages and literatures department at the University of Notre Dame (IN)
University of Notre Dame doctoral students who focus on French and Francophone studies, Iberian and Latin American studies or Italian studies are guaranteed five years of funding. Funding includes a full scholarship, including tuition and fees, plus a stipend and health insurance. Anyone who completes the Ph.D. degree requirements at the Indiana university within five years will automatically receive a one-year postdoctoral fellowship via the university's 5+1 Program. Fellows will have a teaching load limited to one course per semester.

Ph.D. in social work at Bryn Mawr College (PA)
Students admitted to Bryn Mawr College 's Ph.D. program in social work receive full tuition waivers and "substantial stipends" toward living expenses. The Pennsylvania college's website says: "Consistent with our model, all Ph.D. students are funded equally, and do not compete for basic financial support during coursework." The program's cohorts typically include only three or four students each year. According to the college, it awarded the first Ph.D. degree in social work in the U.S. in 1920.

Vanderbilt University |
Ph.D. in special education at Vanderbilt University (TN)
Funding is guaranteed for all admitted doctoral students enrolled in the special education Ph.D. program at the Peabody College of Education and Human Development at Vanderbilt University in Tennessee. This includes full tuition, a "competitive" monthly stipend and health insurance for up to four years. Students may also be nominated for additional honor scholarships and fellowships. Areas of focus within the Ph.D. program include high-incidence disabilities and early childhood education.

Ph.D. in theatre and drama at Northwestern University (IL)
This interdisciplinary Ph.D. program at Northwestern University in Illinois combines coursework in humanities, social science and the visual arts. The program's students receive a five-year full-tuition scholarship plus an annual living stipend. Ph.D students enrolling at this program in fall 2022 will receive a living stipend of at least $36,960 during the 2023-2024 school year. Stipend amounts may change from year to year. Students can apply for subsidies to facilitate conference travel and summer language study.

(Photo by Sarah L. Voisin | The Washington Post via Getty Images)
- Ph.D. in women, gender and sexuality studies at University of Maryland
At the University of Maryland 's Harriet Tubman Department of Women, Gender and Sexuality Studies, Ph.D. students without a master's degree usually have five years of guaranteed funding. Those with a master's degree usually are funded four years, with awards stemming from a mix of departmental fellowships and graduate teaching assistantships. Since the program's establishment in 1999, the department has granted 36 Ph.Ds, according to UMD's website.

Learn more about paying for graduate school.
Finding a fully funded program isn't the only option to offset the costs of graduate school. See these seven strategies to pay for graduate school to learn more. Check out the latest Best Graduate Schools rankings to see the country's top business, medicine and law programs – and more. For additional grad school tips, follow U.S. News Education on Facebook , Twitter and LinkedIn .

Ph.D. programs that are fully funded
- Ph.D. in biological sciences in public health at Harvard University
- Ph.D. in business at Rice University
- Ph.D. in chemical engineering at Cornell University
- Ph.D. in clinical psychology at Columbia University
- Ph.D. in computer science at Brown University
- Ph.D. in computer science at Georgetown University
- Ph.D. in computer science at Washington University—St. Louis
- Ph.D. in economics at Emory University
- Ph.D. in education at Stanford University
- Ph.D. in international relations at American University
- Ph.D. in materials science and engineering at Duke University
- Ph.D. in nursing at Johns Hopkins University
- Ph.D. in nursing at Yale University
- Ph.D. within the romance languages and literatures department at the University of Notre Dame
- Ph.D. in social work at Bryn Mawr College
- Ph.D. in special education at Vanderbilt University
- Ph.D. in theatre and drama at Northwestern University
More From U.S. News

Grad Degree Jobs With $100K+ Salaries

3 Ways Graduate School Pays Off

Best and Worst Reasons for Grad School
You may also like, find a strong human rights law program.
Anayat Durrani April 18, 2024

Environmental Health in Medical School
Zach Grimmett April 16, 2024

How to Choose a Law Career Path
Gabriel Kuris April 15, 2024

Questions Women MBA Hopefuls Should Ask
Haley Bartel April 12, 2024

Law Schools With the Highest LSATs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 11, 2024

MBA Programs That Lead to Good Jobs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 10, 2024

B-Schools With Racial Diversity
Sarah Wood April 10, 2024

Law Schools That Are Hardest to Get Into
Sarah Wood April 9, 2024

Ask Law School Admissions Officers This
Gabriel Kuris April 9, 2024

Grad School Housing Options
Anayat Durrani April 9, 2024

- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Credit: Will Kirk / Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins graduate programs again ranked among nation's best
'u.s. news & world report' includes 38 jhu programs among the top 10 in the u.s. in its annual rankings, including no. 1 ranked programs in nursing and public health.
By Hub staff report
Johns Hopkins University has 38 graduate schools, academic programs, and specialties ranked among the top 10 in the nation, including nine with No. 1 rankings, according to the latest edition of "Best Graduate Schools" from U.S. News & World Report , published earlier today.
Two schools at Hopkins—the Bloomberg School of Public Health and the School of Nursing —earned No. 1 rankings overall, and the School of Education entered the top 10, according to U.S. News & World Report .
Portions of the publication's annual list were released today but rankings for schools of medicine and engineering were delayed and will be released at a later date.
Among the new rankings released today:
The School of Nursing's DNP program ranked No. 1 for the third year in a row. Its master's degree programs tied at No. 1, up from No. 2 last year. In gerontology, the school moved up two spots to No. 1 for primary care, and up one spot to No. 2 for acute care. In other specialty areas, the School of Nursing's doctoral programs ranked:
- Psychiatric/mental health: No. 1
- Family: No. 3 (tied)
- Leadership: No. 4 (tied)
- Nursing Anesthesia: No. 36 (tie)
Public Health
The Bloomberg School retained its longtime No. 1 overall ranking among public health programs—it has held the top spot since 1994, the year the rankings began. In specialty areas, the Bloomberg School ranked:
- Environmental Health Sciences: No. 1
- Epidemiology: No. 1
- Health Policy and Management (Public Health): No. 1
- Social and Behavioral Sciences: No. 1
- Biostatistics: No. 2
Johns Hopkins tied at No. 8 in the Education category, up from No. 13 last year. The school also tied at No. 23 in higher education administration programs.
Public Affairs
Overall, Johns Hopkins programs in public affairs tied at No. 39. In subcategories, Johns Hopkins tied at No. 6 in Health Policy and Management (Public Affairs), No. 11 in International/Global Policy and Administration, and tied at No. 35 in Public Policy Analysis.
U.S. News & World Report updates some of its rankings each year and republishes the most recent rankings in other areas. Among the republished rankings for Hopkins, which are still current:
Biological Sciences
Hopkins is tied for No. 6 overall with six top 10 specialty rankings:
- Molecular biology: No. 3 (tie)
- Cell biology: No. 4
- Neuroscience: No. 4 (tie)
- Immunology: No. 5
- Genetics, genomics, and bioinformatics: No. 6 (tie)
- Biochemistry, biophysics, and structural biology: No. 8
Biostatistics
Hopkins is ranked No. 1 (tie) for Biostatistics at the doctoral level. (Note: U.S. News & World Report also ranks biostatistics as a sub-category of public health, where Hopkins is No. 2.)
The university is tied at No. 20 in Chemistry and ranks No. 9 in the Biochemistry subcategory.
Computer Science
The university is tied for No. 24 overall and tied at No. 21 in the specialty of Artificial Intelligence.
Earth Sciences
The university is tied at No. 30 in Earth Sciences.
Johns Hopkins' program in economics is tied at No. 22.
English tied at No. 13 overall with the following specialty rankings:
- Literary criticism and theory: No. 3
- British literature: No. 10 (tie)
- American literature after 1865: No. 17
Health Care Management
The university is No. 7.
Johns Hopkins ranks No. 10 overall, with the following specialty rankings:
- African-American history: No. 3 (tie)
- Cultural history: No. 4 (tie)
- U.S. Colonial history: No. 5 (tie)
- Women's history: No. 6 (tie)
- African history: No. 7 (tie)
- European history: No. 7 (tie)
- Modern U.S. history: No. 16 (tie)
Mathematics
Johns Hopkins is tied at No. 20 in Mathematics with the following specialty rankings: + Analysis: No. 18 (tie) + Algebra: No. 23 (tie) + Applied Math: No. 25
Overall, the university is tied at No. 13 with the following specialty rankings: + Living Systems: No. 5 (tie) + Cosmology: No. 7 + Condensed Matter: No. 13 (tie)
Political science
Overall, political science is tied at No. 41. In sub-categories, Johns Hopkins ranked: + Political theory: No. 8 (tie) + International politics: No. 24 (tie)
The university's graduate program in psychology is tied at No. 12 overall and tied at No. 5 in the subcategory of behavioral neuroscience.
Overall, sociology is tied at No. 29. The sub-category of sociology of population is tied at No. 17.
Posted in University News
Tagged u.s. news and world report , university rankings
Related Content

Engineering online programs again ranked among nation's best

Hopkins No. 9 in 'U.S. News' rankings
You might also like, news network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram
- Costs, Scholarships & Aid
- Campus Life
- Faculty & Staff
- Family & Visitors
- DFW Community
- Galaxy Login
- Academic Calendar
- Human Resources
- Accessibility
Grad Programs Get High Marks in U.S. Rankings; Audiology No. 3

The University of Texas at Dallas’ Doctor of Audiology program in the School of Behavioral and Brain Sciences ranks third in the nation in the latest Best Graduate Schools rankings, released April 9 by U.S. News & World Report .
Dr. Colleen Le Prell , the Emilie and Phil Schepps Distinguished Professor of Hearing Science and department head of speech, language, and hearing , said the program provides a highly supportive learning environment.
“Our students develop clinical competencies through exposure to evidence-based patient care at the Callier Center for Communication Disorders and additional clinical placements with our valued clinical partners across the DFW metro area,” she said. “Under the leadership of program head Dr. Carol Cokely , clinical professor of speech, language, and hearing, multiple faculty and peer mentoring programs have been developed; innovative simulation technologies have been incorporated into the curriculum; interprofessional education opportunities have been identified and offered to students; and the long tradition of novel service-based learning opportunities for audiology doctoral students has been expanded.”

Angela Shoup BS’89, MS’92, PhD’94, the Ludwig A. Michael, MD Callier Center Executive Director, said that Callier is one of a few select centers in the nation that conduct treatment, graduate training and research in communication disorders. The integration of those three elements has helped propel both the audiology program and the speech-language pathology program , which ranks 21st in the U.S., into the top graduate programs in the country.
“The mission of the Callier Center — to transform the lives of individuals and families impacted by speech, language and hearing difficulties — is accomplished through provision of leading-edge clinical services, innovative research into new treatments and technologies, and training of the next generation of compassionate and skilled audiologists and speech-language pathologists,” Shoup said. “Through the UT Dallas Department of Speech, Language, and Hearing, and the Callier Center’s commitment to excellence in clinical education and training, we strive to ensure that access to necessary clinical services and advances in health care efficiency and efficacy continue in perpetuity.”
The Naveen Jindal School of Management ranks 38th among full-time graduate business schools in the nation, while its part-time Master of Business Administration program is No. 13 nationally and second among Texas universities. The business analytics program ranks No. 25 in the country.
In the School of Economic, Political and Policy Sciences , the public affairs program climbed six spots to No. 57 and is third among Texas public universities. The public and nonprofit management program ranks 24th.
In the Erik Jonsson School of Engineering and Computer Science , the computer science program is No. 64. Rankings for the engineering graduate programs will be released at a later date.
“Rankings are but one way of evaluating universities and their programs,” said Dr. Inga H. Musselman , provost, vice president for academic affairs and the Cecil H. Green Distinguished Chair of Academic Leadership. “And while we are proud that our programs are so well regarded by our peers, we are equally proud of our students and the tremendous successes they achieve after graduation. That success is a testament to our superb faculty, as well as to the dedication and drive of the students themselves.”
Each year, U.S. News & World Report ranks professional school programs in a rotating range of fields based on expert opinions about program status, as well as statistical indicators of the quality of a school’s faculty, research and students and their postgraduate outcomes.
This information comes from surveys sent to graduate program administrators and from reputation surveys sent to academicians and professionals in the disciplines.
Media Contact: Stephen Fontenot, UT Dallas, 972-883-4405, [email protected] , or the Office of Media Relations, UT Dallas, (972) 883-2155, [email protected] .
- Researchers Develop Way To Provide Asthma Attack Early Warnings
- Professor Joins National Panel; Medical Team Earns Awards
- Total Solar Eclipse Becomes Communal Comet Experience
- Investiture Ceremony To Celebrate Distinguished Professors, Donors
- Researchers Developing Technology To Improve Offshore Wind Safety
- UTD To Celebrate Solar Eclipse with Events Totally Made for Comets
- New Findings Reveal Clearer Picture of Expanding Universe
- Researchers Find More Complexity in Aging Brain’s Memory Decline
- Mechanical Engineering Student Soars with Aerospace Fellowship
- CPRIT Grants To Advance Cancer Detection, Treatment Technology
- Space Scientists’ New Sensors Shine Spotlight on Sun-Earth Studies
800 W. Campbell Road Richardson, Texas 75080-3021
972-883-2111
COPYRIGHT INFORMATION
© The University of Texas at Dallas Questions or comments about this page?
STAY CONNECTED WITH UT DALLAS
- Emergency Preparedness
- Campus Carry
- Campus Police
- Required Links
- Tobacco-Free Campus
- Texas Veterans Portal
- Work at UT Dallas
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Title IX Initiatives
- Student Achievements
- HEERF Reporting
- Counseling/Mental Health
- Hazing Prevention
- Public Course and Syllabus Information
- Privacy Policy
- Skip Navigation
- Request Family Testimony Copy
- search SEARCH
- OUR SITES --> OUR SITES USC Shoah Foundation IWitness Visual History Archive Request Permission for Use
Azrieli Research Fellowship for PhD Candidates and Early-Career Scholars, 2024-2025

The Division of Academic Programs at the USC Shoah Foundation invites applications for its inaugural Azrieli Research Fellowships for PhD candidates and early-career scholars during the spring 2025 semester.
One applicant will be chosen to pursue their original research on the Holocaust and/or historical and contemporary antisemitism using the USC Shoah Foundation’s Visual History Archive (VHA), which currently holds over 55,000 video testimonies of survivors and witnesses of the Holocaust and other genocides. The incumbents may also wish to complement their testimony-based research in the VHA with the primary and secondary source collections related to the Holocaust at USC’s Doheny Library.
The fellowship will provide $25,000 support for one semester-long research stay at the USC Shoah Foundation. Fellows must reside in Los Angeles for the duration of their award and will hold one public lecture at USC about their research. Fellows are responsible for securing their own housing, which may be available on USC’s campus, and health insurance.
Eligibility requirements: Candidates must be enrolled in an accredited PhD program or be scholars who are either untenured or in the first five years of their career. Although any person may apply, preference will be given to Canadian scholars, those at institutions located in Canada, or research related to Canada.
This fellowship i awarded on a competitive basis. Applications must be submitted no later than midnight PT on July 31, 2024. Applications will consist of the following:
- Letter of Intent
- Project proposal of approximately 1,000 words
- Curriculum vitae
- Reference letter from dissertation committee member (for graduate students) or senior colleague (for early-career scholars)
Please note: only applications that have submitted each of the required materials will be considered for these fellowships. Applicants will be notified of the outcome by August 15, 2024. Fellowship recipients may begin their tenure at the USC Shoah Foundation in January 2025.
Please direct both questions regarding the fellowship or application process and reference letters to Dr. Jennifer L. Rodgers, Director of Academic Programs to jr77905[@]usc.edu.
Like this article? Get our e-newsletter.
Sign up today!
Be the first to learn about new articles and personal stories like the one you've just read.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
10 facts about today’s college graduates

Having a bachelor’s degree remains an important advantage in many sectors of the U.S. labor market. College graduates generally out-earn those who have not attended college, and they are more likely to be employed in the first place. At the same time, many Americans say they cannot afford to get a four-year degree – or that they just don’t want to.
Here are key facts about American college graduates.
This Pew Research Center analysis about U.S. college graduates relies on data from sources including the Census Bureau, the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the National Center for Education Statistics, the National Student Clearinghouse and the Federal Reserve Bank, as well as surveys conducted by the Center.
Everyone who took the Pew Research Center surveys cited is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Nearly four-in-ten Americans ages 25 and older have a bachelor’s degree, a share that has grown over the last decade. As of 2021, 37.9% of adults in this age group held a bachelor’s degree, including 14.3% who also obtained a graduate or professional degree, according to data from the Census Bureau’s Current Population Survey. That share is up 7.5 percentage points from 30.4% in 2011.
An additional 10.5% had an associate degree in 2021. About four-in-ten Americans ages 25 and older had a high school diploma with no further education (25.3%) or completed some college but didn’t have a degree (14.9%).
In a reversal, women are now more likely than men to graduate from college, according to the Current Population Survey . In 2021, 39% of women ages 25 and older had a bachelor’s degree or more education, compared with 37% of men in the same age range. The gap in college completion is even wider among adults ages 25 to 34: 46% of women in this age group have at least a bachelor’s degree, compared with 36% of men.
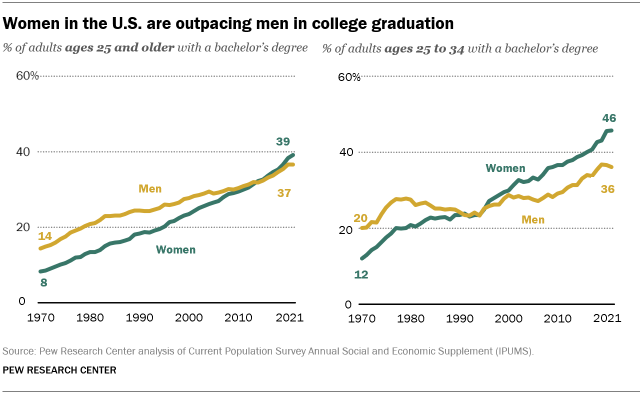
In an October 2021 Pew Research Center survey of Americans without a degree, 34% of men said a major reason why they have not received a four-year college degree is that they just didn’t want to. Only one-in-four women said the same. Men were also more likely to say a major reason they didn’t have a four-year degree is that they didn’t need more education for the job or career they wanted (26% of men said this vs. 20% of women).
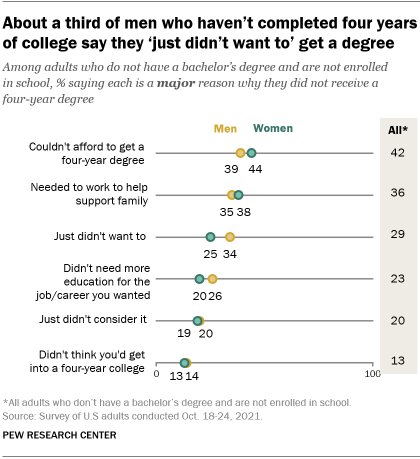
Women (44%) were more likely than men (39%) to say not being able to afford college was a major reason they don’t have a bachelor’s degree. Men and women were about equally likely to say a major impediment was needing to work to help support their family.
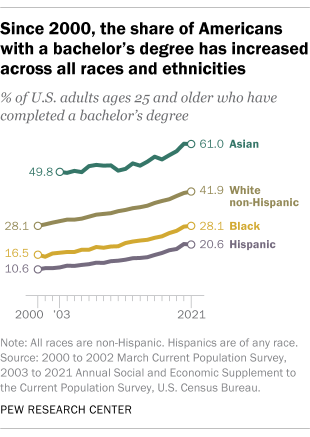
There are racial and ethnic differences in college graduation patterns, as well as in the reasons for not completing a degree. Among adults ages 25 and older, 61% of Asian Americans have a bachelor’s degree or more education, along with 42% of White adults, 28% of Black adults and 21% of Hispanic adults, according to 2021 Current Population Survey data. The share of bachelor’s degree holders in each group has increased since 2010. That year, 52% of Asian Americans had a four-year degree or more, compared with a third of White adults, 20% of Black adults and 14% of Hispanic adults.
The October 2021 Center survey found that among adults without a bachelor’s degree, Hispanic adults (52%) were more likely than those who are White (39%) or Black (41%) to say a major reason they didn’t graduate from a four-year college is that they couldn’t afford it. Hispanic and Black adults were more likely than their White counterparts to say needing to work to support their family was a major reason.
While a third of White adults said not wanting to go to school was a major reason they didn’t complete a four-year degree, smaller shares of Black (22%) and Hispanic (23%) adults said the same. White adults were also more likely to cite not needing more education for the job or career they wanted. (There weren’t enough Asian adults without a bachelor’s degree in the sample to analyze separately.)
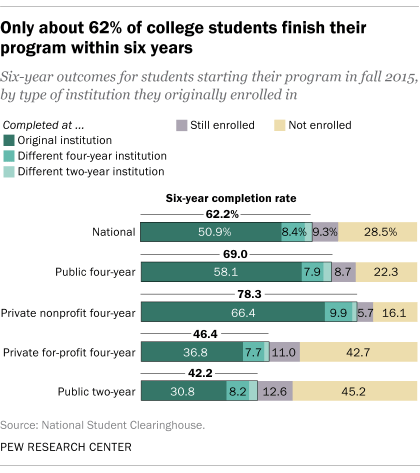
Only 62% of students who start a degree or certificate program finish their program within six years, according to the most recent data from the National Student Clearinghouse , a nonprofit verification and research organization that tracked first-time college students who enrolled in fall 2015 with the intent of pursuing a degree or certificate. The degree completion rate for this group was highest among students who started at four-year, private, nonprofit schools (78.3%), and lowest among those who started at two-year public institutions (42.2%).
Business is the most commonly held bachelor’s degree, followed by health professions. According to the National Center for Education Statistics , about a fifth (19%) of the roughly 2 million bachelor’s degrees conferred in 2019-20 were in business. Health professions and related programs were the second most-popular field, making up 12.6% of degrees conferred that year. Business has been the single most common major since 1980-81; before that, education led the way.
The least common bachelor’s degrees in 2019-20 were in military technologies and applied sciences (1,156 degrees conferred in 2019-20), library science (118), and precision production (39).
There is a growing earnings gap between young college graduates and their counterparts without degrees. In 2021, full-time workers ages 22 to 27 who held a bachelor’s degree, but no further education, made a median annual wage of $52,000, compared with $30,000 for full-time workers of the same age with a high school diploma and no degree, according to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics. This gap has widened over time. Young bachelor’s degree holders earned a median annual wage of $48,481 in 1990, compared with $35,257 for full-time workers ages 22 to 27 with a high school diploma.
The unemployment rate is lower for college graduates than for workers without a bachelor’s degree, and that gap widened as a result of the coronavirus pandemic. In February 2020, just before the COVID-19 outbreak began in the U.S., only 1.9% of college graduates ages 25 and older were unemployed, compared with 3.1% of workers who completed some college but not a four-year degree, and 3.7% of workers with only a high school diploma. By June 2020, after the pandemic hit, 6.8% of college grads, 10.8% of workers with some college, and 12.2% of high school grads were unemployed.
By March 2022, the unemployment rate had nearly returned to pre-pandemic levels for college graduates (2%) while dropping to 3% among those with some college education but no four-year degree, and 4% among those with only a high school diploma.
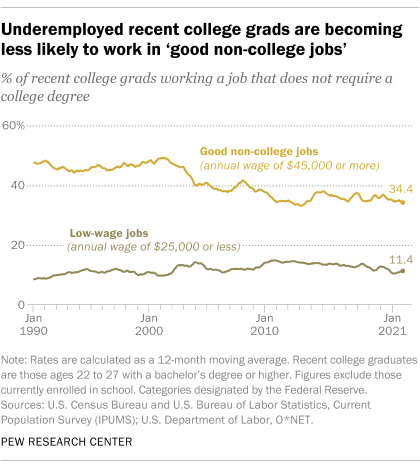
Recent college graduates are more likely than graduates overall to be underemployed – that is, working in jobs that typically do not require a college degree, according to an analysis of Census Bureau and BLS data by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York . As of December 2021, 41% of college graduates ages 22 to 27 were underemployed, compared with 34% among all college graduates. The underemployment rates for recent college grads rose in 2020 as the COVID-19 outbreak strained the job market, but have since returned to pre-pandemic levels.
As of the end of 2021, only 34% of underemployed graduates ages 22 to 27 worked what the Fed defines as “good non-college jobs” – those paying at least $45,000 a year – down from around half in the 1990s. The share of underemployed graduates ages 22 to 27 in low-wage jobs – those earning less than $25,000 annually – rose from about 9% in 1990 to 11% last year.
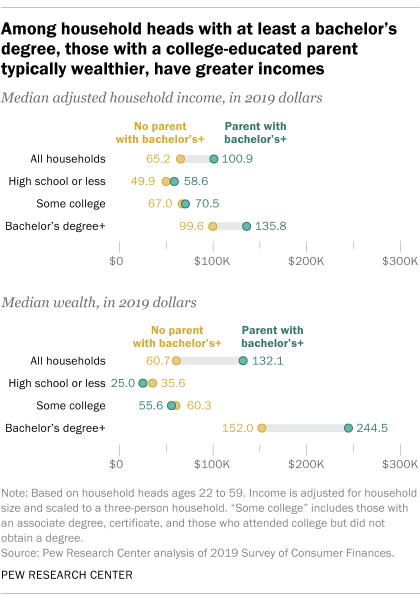
When it comes to income and wealth accumulation, first-generation college graduates lag substantially behind those with college-educated parents, according to a May 2021 Pew Research Center analysis . Households headed by a first-generation college graduate – that is, someone who has completed at least a bachelor’s degree but does not have a parent with a college degree – had a median annual income of $99,600 in 2019, compared with $135,800 for households headed by those with at least one parent who graduated from college. The median wealth of households headed by first-generation college graduates ($152,000) also trailed that of households headed by someone with a parent who graduated from college ($244,500). The higher household income of the latter facilitates saving and wealth accumulation.
The gap also reflects differences in how individuals finance their education. Second-generation college graduates tend to come from more affluent families , while first-generation college graduates are more likely to incur education debt than those with a college-educated parent.
Most Americans with college degrees see value in their experience. In the Center’s October 2021 survey , majorities of graduates said their college education was extremely or very useful when it came to helping them grow personally and intellectually (79%), opening doors to job opportunities (70%) and developing specific skills and knowledge that could be used in the workplace (65%).
Younger college graduates were less likely than older ones to see value in their college education. For example, only a third of college graduates younger than 50 said their college experience was extremely useful in helping them develop skills and knowledge that could be used in the workplace. Among college graduates ages 50 and older, 45% said this.
- Higher Education
About 1 in 4 U.S. teachers say their school went into a gun-related lockdown in the last school year
About half of americans say public k-12 education is going in the wrong direction, what public k-12 teachers want americans to know about teaching, what’s it like to be a teacher in america today, race and lgbtq issues in k-12 schools, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- Self-Service
- GoTritons Student Webmail
- Office 365 Webmail
- CollegeNET Course Evaluations
- Triton Portal
- Nuventive Improve (TracDat)
- LearningChamoru.com
- Degrees & Programs
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- Non-Degree Admissions
- UOG Online (Moodle)
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid in 3 Steps
- Types of Financial Aid
- Financial Aid Counselors
- Business Office
- Financial Aid Calculator
- Bursar Office
- Academic Calendar
- Course Catalog
- Course Schedule
- Student Forms
- Placement Tests
- Request a Transcript
- Apply Online
- College of Liberal Arts & Social Sciences
- College of Natural & Applied Sciences
- School of Business & Public Administration
- School of Education
- School of Engineering
- Margaret Perez Hattori-Uchima School of Health
- Undergraduate Degrees
- Graduate Degrees
- Professional Development & Continuing Education
- English Language Institute
- RFK Memorial Library
- Micronesian Area Research Center (MARC)
- Final Exam Schedule
- Financial Aid
- Get Involved
- Triton Athletics
- Living on Campus
- Safety & Security
- Student Organizations
- Student Government
- Student Handbook
- Graduating Students
- UOG Helpline
- Enrollment Management & Student Success
- Triton Advising Center
- RFK Library
- OIT/Computer Center
- Triton Store
- EEO/ADA & Title IX Office
- Career Development Office
- Calvo Field House
- Writing Center
- Student Achievement
- Counseling Services Resources
- Triton Career Connections
- Campus Directory
- FERPA Policy
- Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion
- Cancer Research Center
- Center for Excellence in Development Disabilities Education, Research & Service (CEDDERS)
- Center for Island Sustainability (CIS)
- Marine Laboratory
- Water and Environmental Research Institute (WERI)
- Western Pacific Tropical Research Center (WPTRC)
- Guam EPSCOR
- Pacific Islands Climate Adaptation Science Center (PI-CASC)
- Pacific Islands Cohort on Cardiometabolic Health (PICCAH)
- Research Corporation of UOG
- UOG Sea Grant
- University Libraries Digital Team
- NASA Guam Space Grant
- NASA Guam EPSCoR
- Micronesica
- Micronesian Educator
- Pacific Asia Inquiry

Download the 2015 WPTRC Impact Report
- Center for Island Sustainability
- CHamoru Language Competition
- Cooperative Extension & Outreach
- Guam Procurement Technical Assistance Center
- Guam System for Assistive Technology (GSAT)
- Isla Center for the Arts
- Isa Psychological Services Center
- Pacific Islands SBDC Network (PISBDCN)
- TADEO / COLL
- Triton Farm
- UOG Herbarium
- UOG Fine Arts
- UOG Calvo Field House
- UOG Summer Camps
- Violence Against Women Prevention Program
- 2018 Survey of Compact of Free Association (COFA)
- Endowment Foundation
- Vision 2025 - 21st Century Campus
- #MakeYourMARC - 50th Anniversary Campaign

- Board of Regents
- Office of the President
- Academic & Student Affairs
- Administration & Finance
- Research and Sponsored Programs
- Campus Leadership Directory
- Mission Statement
- The Triton Story
- Accreditation
- UOG Fact Book
- Organizational Chart
- Policies & Procedures
- Faculty Senate
- Faculty Union
- Society of Emeritus Professors & Retired Scholars
- Faculty and Experts Directory
- News & Announcements
- Events Calendar
- Marketing & Communications

You are here
Uog doctoral program set to launch in fall 2024.

The University of Guam announces that it has received approval from the Western Association of Schools and Colleges Senior College and University Commission (WSCUC) to begin offering its first ever online doctoral program — a Doctor of Education (EdD) in Instructional and Academic Leadership.
The new EdD program emphasizes development of the “scholar-practitioner” who will integrate their professional experiences with research and theory to improve educational practices within their cultural contexts and to influence change in their educational and organizational settings.
“UOG was founded as a teaching college in 1952 and has since developed tremendous capacity for teachers, counselors, and school administrators for our island and region,” said Anita Borja Enriquez, UOG President. "This new doctoral program is our commitment to advancing education, elevating the focus on research agendas relevant to our region, and addressing improvement to instructional areas and overall educational leadership."
School of Education Dean Alicia Aguon noted that the new doctorate responds to the needs of educators and school systems across the region.
“Our survey had nearly a thousand respondents including alumni, education professionals, and stakeholders throughout Micronesia, and overwhelmingly, there was a stated need for a program geared toward instructional and academic leadership,” said Aguon. “This doctoral program is groundbreaking as it has been developed with a cultural competency unique to our region.”
The School of Education will begin accepting applications to the doctoral program this summer with its first courses starting this October. UOG will release more details in the coming weeks about information sessions and the application timeline.
“This isn’t just a milestone for UOG, it’s a milestone for education across the region,” said Enriquez “I am thrilled to see the meaningful, diverse conversational and collaborative synergies unfold from our inaugural cohort.”
Overview of the Doctor of Education (EdD) in Instructional and Academic Leadership
- The EdD program is an online program with 20 required courses and a total of 60 credit hours.
- The dissertation is built in as coursework in the program of study.
- The program is expected to take four years to complete without pausing.
- The UOG Board of Regents approved the program in June 2023 and the WASC Senior College and University Commission approved the program in March 2024.
- Up to 25 students are projected for the program’s inaugural cohort.
- The program will launch in Fanuchånan (Fall) 2024.
- To express interest or for more information, email [email protected] .
Recent News

University of Guam
Unibetsedȧt Guåhan UOG Station Mangilao , Guam 96913 Contact Us
The University of Guam is a U.S. Land Grant and Sea Grant Institution accredited by the WASC Senior College and University Commission. UOG is an equal opportunity provider and employer committed to diversity, equity and inclusion through island wisdom values of inadahi yan inagofli'e: respect, compassion, and community.
BECOME A TRITON
- Student Life
- SMS Notification
- Great Expectations
- Email Login
- Course Catalogs
- Accessibility
- Fraud, Waste, and Abuse
- Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Graduate Record Examinations (GRE) is a standardized test meant for students who intend to apply to graduate programs. Both MA and PhD programs ask for GRE scores. Much like the SAT or ACT in college exams, the test is meant to be a standardized measure of academic preparation and logical skill. The test consists of six sections.
A Ph.D. is a research degree that involves the production of original knowledge and scholarship. Doctoral degrees have traditionally been regarded as training programs for academics. As such, a Ph.D. program differs from undergraduate or Master's studies. Most Ph.D. programs involve some initial coursework (specific requirements for ...
To get a sense of your chances, check out the CVs of current Ph.D. students in the programs or try to find information from professional societies. The American Psychological Association, for example, publishes the average GPA and standardized test scores of most psychology programs' incoming graduate students.
In sum, the steps in deciding where to apply for PhD study are as follows: Choose your field of study. Identify your preferred area (s) within that field. Discover the specific topics you find most fascinating. Consider what methods you want to employ. Evaluate the merits of prospective faculty advisors.
Step 1: Complete an undergraduate degree. Before you can take the next step toward your PhD, you'll first have to receive a bachelor's degree through an undergraduate program at a reputable university. This education will provide the foundation for your more advanced coursework later.
Here's a look at the PhD application timeline and curriculum you can expect, from the first meeting with your program supervisor to your graduation and beyond. 1. Initial Meeting with Your Academic Advisor. One of the first things you'll do as a PhD student is meet with your academic advisor or supervisor.
4. Ensure that you can afford the fees. Fees for international student PhD applications can be quite high, such as around $100 US dollars per application. Since you will likely need to apply to several schools in order to have a chance at a job, make sure that you can afford the fees before you start the process.
PhD costs The average cost of a PhD program in the US is $106,860, though that figure can differ based on the type of institution you attend and what you study . Reasons to get a PhD. Earning your PhD can be an immensely rewarding experience, but the degree can be a big commitment, requiring significant time, money, and work.
Regardless of the topic you choose to focus on, the journey toward your doctorate will likely begin with earning a bachelors degree and end with a public defense of your doctoral dissertation. 1. Earn an Undergraduate Degree. The road to a PhD begins with earning an undergraduate degree from an accredited school.
To apply for a PhD at an American university, you'll need to submit a list of documents which include: academic transcripts; personal statement; letters of recommendation; CV; research statements - A research statement is different from a research proposal (required if you're applying for a PhD in most other countries).
The deadline to apply for the Stanford Psychology Ph.D. program is November 30, 2024 . Applicants who are admitted to the program will matriculate in autumn 2025. In addition to the information below, please review the Graduate Admissions website prior to starting your application. The Department of Psychology does not have rolling admissions.
The hallmark of a Ph.D. program is that it is research-based. Success at the undergraduate level is an important factor, but a better indication of success is research experience. The strongest letter of recommendation is from a professor who knows you not just as a student in their classroom, but as a researcher.
Successfully completing a doctoral program requires commitment and perseverance. The most important step in this process is to consider whether academic life is right for you and what kind of doctoral program — from discipline to environment — will be the best fit for your goals and preferences. We asked our current students and faculty ...
The PhD program in Health Policy (Management) prepares students to effect powerful change rooted in data-driven research on the managerial, operational, and strategic issues facing a wide range of organizations. Coursework includes the study of microeconomics theory, management, research methods, and statistics.
A PhD program typically takes four to seven years, but a variety of factors can impact that timeline. A PhD, or doctorate degree, is the highest degree you can earn in certain disciplines, such as psychology, engineering, education, and mathematics. As a result, it often takes longer to earn than it does for a bachelor's or master's degree.
Completing Prerequisite Education. Complete an undergraduate degree in a broad field. To qualify for a PhD program, you will need a solid record of undergraduate coursework from a reputable university. [2] This degree should demonstrate your potential for both advanced coursework and independent research.
The Harvard Ph.D. in Education trains cutting-edge researchers who work across disciplines to generate knowledge and translate discoveries into transformative policy and practice. Offered jointly by the Harvard Graduate School of Education and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the Ph.D. in Education provides ...
Tips for getting into the best graduate PhD programs in the US (and Europe), with a focus on STEM. I talk about letters of recommendation, research, publicat...
All of our doctoral programs are designed to develop outstanding educational researchers who have a deep understanding of the scientific, practical and policy issues they study. All require full-time study, and we promise five years of full-time financial support for every student we admit. Our doctoral programs are small, typically ranging from about 25 to 35 new students a year.
All Ph.D. Program candidates must fulfill the following requirements for eligibility: A baccalaureate degree, preferably in the biological or physical sciences, must be obtained from an accredited institution; A cumulative undergraduate GPA of 3.0 on a 4.0 scale is necessary; Conferral of the degree is required prior to starting the program
The journey to obtaining a PhD is a unique blend of personal commitment, academic rigor, and research innovation. While the timeline can vary widely, most candidates find themselves immersed in their studies and research for anywhere from 4 to 6 years. Exceptions can happen, and you may finish earlier or later.
The program awards up to 100 high-achieving students every year with full funding to pursue graduate education at Stanford, including the PhD in Psychology. To be considered, you must apply to Knight-Hennessy Scholars and separately apply to the Psychology Department. Note that the Knight-Hennessy Scholars program application deadline is in the ...
Students enrolled in the economics Ph.D. program at Emory University typically receive full funding, according to the Georgia university's website. The stipend provided to students is $36,376 per ...
Johns Hopkins University has 38 graduate schools, academic programs, and specialties ranked among the top 10 in the nation, including nine with No. 1 rankings, according to the latest edition of "Best Graduate Schools" from U.S. News & World Report, published earlier today.. Two schools at Hopkins—the Bloomberg School of Public Health and the School of Nursing—earned No. 1 rankings overall ...
The University of Texas at Dallas' Doctor of Audiology program in the School of Behavioral and Brain Sciences ranks third in the nation in the latest Best Graduate Schools rankings, released April 9 by U.S. News & World Report. Dr. Colleen Le Prell, the Emilie and Phil Schepps Distinguished Professor of Hearing Science and department head of speech, language, and hearing, said the program ...
A Ph.D. in marketing is the most advanced degree you can earn in the field. It can help you adv. Select Region ... Graduate online tuition is the same for in-state and out-of-state students: $383 ...
Penn State saw moderate rises when it came to education and law in U.S. News & World Report's recently released 2024-2025 Best Graduate Schools rankings, although the university's overall ...
Eligibility requirements: Candidates must be enrolled in an accredited PhD program or be scholars who are either untenured or in the first five years of their career. Although any person may apply, preference will be given to Canadian scholars, those at institutions located in Canada, or research related to Canada. ...
Nearly four-in-ten Americans ages 25 and older have a bachelor's degree, a share that has grown over the last decade. As of 2021, 37.9% of adults in this age group held a bachelor's degree, including 14.3% who also obtained a graduate or professional degree, according to data from the Census Bureau's Current Population Survey.
The University of Guam announces that it has received approval from the Western Association of Schools and Colleges Senior College and University Commission (WSCUC) to begin offering its first ever online doctoral program — a Doctor of Education (EdD) in Instructional and Academic Leadership.