Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Data Collection | Definition, Methods & Examples

Data Collection | Definition, Methods & Examples
Published on June 5, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 21, 2023.
Data collection is a systematic process of gathering observations or measurements. Whether you are performing research for business, governmental or academic purposes, data collection allows you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem .
While methods and aims may differ between fields, the overall process of data collection remains largely the same. Before you begin collecting data, you need to consider:
- The aim of the research
- The type of data that you will collect
- The methods and procedures you will use to collect, store, and process the data
To collect high-quality data that is relevant to your purposes, follow these four steps.
Table of contents
Step 1: define the aim of your research, step 2: choose your data collection method, step 3: plan your data collection procedures, step 4: collect the data, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about data collection.
Before you start the process of data collection, you need to identify exactly what you want to achieve. You can start by writing a problem statement : what is the practical or scientific issue that you want to address and why does it matter?
Next, formulate one or more research questions that precisely define what you want to find out. Depending on your research questions, you might need to collect quantitative or qualitative data :
- Quantitative data is expressed in numbers and graphs and is analyzed through statistical methods .
- Qualitative data is expressed in words and analyzed through interpretations and categorizations.
If your aim is to test a hypothesis , measure something precisely, or gain large-scale statistical insights, collect quantitative data. If your aim is to explore ideas, understand experiences, or gain detailed insights into a specific context, collect qualitative data. If you have several aims, you can use a mixed methods approach that collects both types of data.
- Your first aim is to assess whether there are significant differences in perceptions of managers across different departments and office locations.
- Your second aim is to gather meaningful feedback from employees to explore new ideas for how managers can improve.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Based on the data you want to collect, decide which method is best suited for your research.
- Experimental research is primarily a quantitative method.
- Interviews , focus groups , and ethnographies are qualitative methods.
- Surveys , observations, archival research and secondary data collection can be quantitative or qualitative methods.
Carefully consider what method you will use to gather data that helps you directly answer your research questions.
When you know which method(s) you are using, you need to plan exactly how you will implement them. What procedures will you follow to make accurate observations or measurements of the variables you are interested in?
For instance, if you’re conducting surveys or interviews, decide what form the questions will take; if you’re conducting an experiment, make decisions about your experimental design (e.g., determine inclusion and exclusion criteria ).
Operationalization
Sometimes your variables can be measured directly: for example, you can collect data on the average age of employees simply by asking for dates of birth. However, often you’ll be interested in collecting data on more abstract concepts or variables that can’t be directly observed.
Operationalization means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations. When planning how you will collect data, you need to translate the conceptual definition of what you want to study into the operational definition of what you will actually measure.
- You ask managers to rate their own leadership skills on 5-point scales assessing the ability to delegate, decisiveness and dependability.
- You ask their direct employees to provide anonymous feedback on the managers regarding the same topics.
You may need to develop a sampling plan to obtain data systematically. This involves defining a population , the group you want to draw conclusions about, and a sample, the group you will actually collect data from.
Your sampling method will determine how you recruit participants or obtain measurements for your study. To decide on a sampling method you will need to consider factors like the required sample size, accessibility of the sample, and timeframe of the data collection.
Standardizing procedures
If multiple researchers are involved, write a detailed manual to standardize data collection procedures in your study.
This means laying out specific step-by-step instructions so that everyone in your research team collects data in a consistent way – for example, by conducting experiments under the same conditions and using objective criteria to record and categorize observations. This helps you avoid common research biases like omitted variable bias or information bias .
This helps ensure the reliability of your data, and you can also use it to replicate the study in the future.
Creating a data management plan
Before beginning data collection, you should also decide how you will organize and store your data.
- If you are collecting data from people, you will likely need to anonymize and safeguard the data to prevent leaks of sensitive information (e.g. names or identity numbers).
- If you are collecting data via interviews or pencil-and-paper formats, you will need to perform transcriptions or data entry in systematic ways to minimize distortion.
- You can prevent loss of data by having an organization system that is routinely backed up.
Finally, you can implement your chosen methods to measure or observe the variables you are interested in.
The closed-ended questions ask participants to rate their manager’s leadership skills on scales from 1–5. The data produced is numerical and can be statistically analyzed for averages and patterns.
To ensure that high quality data is recorded in a systematic way, here are some best practices:
- Record all relevant information as and when you obtain data. For example, note down whether or how lab equipment is recalibrated during an experimental study.
- Double-check manual data entry for errors.
- If you collect quantitative data, you can assess the reliability and validity to get an indication of your data quality.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Likert scale
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Framing effect
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
When conducting research, collecting original data has significant advantages:
- You can tailor data collection to your specific research aims (e.g. understanding the needs of your consumers or user testing your website)
- You can control and standardize the process for high reliability and validity (e.g. choosing appropriate measurements and sampling methods )
However, there are also some drawbacks: data collection can be time-consuming, labor-intensive and expensive. In some cases, it’s more efficient to use secondary data that has already been collected by someone else, but the data might be less reliable.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something:
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions).
- Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
If you are doing experimental research, you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
Operationalization means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioral avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalize the variables that you want to measure.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 21). Data Collection | Definition, Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/data-collection/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, sampling methods | types, techniques & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Join thousands of product people at Insight Out Conf on April 11. Register free.
Insights hub solutions
Analyze data
Uncover deep customer insights with fast, powerful features, store insights, curate and manage insights in one searchable platform, scale research, unlock the potential of customer insights at enterprise scale.
Featured reads
Tips and tricks
Make magic with your customer data in Dovetail

Four ways Dovetail helps Product Managers master continuous product discovery
Product updates
Dovetail retro: our biggest releases from the past year
Events and videos
© Dovetail Research Pty. Ltd.
Data collection in research: Your complete guide
Last updated
31 January 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
In the late 16th century, Francis Bacon coined the phrase "knowledge is power," which implies that knowledge is a powerful force, like physical strength. In the 21st century, knowledge in the form of data is unquestionably powerful.
But data isn't something you just have - you need to collect it. This means utilizing a data collection process and turning the collected data into knowledge that you can leverage into a successful strategy for your business or organization.
Believe it or not, there's more to data collection than just conducting a Google search. In this complete guide, we shine a spotlight on data collection, outlining what it is, types of data collection methods, common challenges in data collection, data collection techniques, and the steps involved in data collection.
Analyze all your data in one place
Uncover hidden nuggets in all types of qualitative data when you analyze it in Dovetail
- What is data collection?
There are two specific data collection techniques: primary and secondary data collection. Primary data collection is the process of gathering data directly from sources. It's often considered the most reliable data collection method, as researchers can collect information directly from respondents.
Secondary data collection is data that has already been collected by someone else and is readily available. This data is usually less expensive and quicker to obtain than primary data.
- What are the different methods of data collection?
There are several data collection methods, which can be either manual or automated. Manual data collection involves collecting data manually, typically with pen and paper, while computerized data collection involves using software to collect data from online sources, such as social media, website data, transaction data, etc.
Here are the five most popular methods of data collection:
Surveys are a very popular method of data collection that organizations can use to gather information from many people. Researchers can conduct multi-mode surveys that reach respondents in different ways, including in person, by mail, over the phone, or online.
As a method of data collection, surveys have several advantages. For instance, they are relatively quick and easy to administer, you can be flexible in what you ask, and they can be tailored to collect data on various topics or from certain demographics.
However, surveys also have several disadvantages. For instance, they can be expensive to administer, and the results may not represent the population as a whole. Additionally, survey data can be challenging to interpret. It may also be subject to bias if the questions are not well-designed or if the sample of people surveyed is not representative of the population of interest.
Interviews are a common method of collecting data in social science research. You can conduct interviews in person, over the phone, or even via email or online chat.
Interviews are a great way to collect qualitative and quantitative data . Qualitative interviews are likely your best option if you need to collect detailed information about your subjects' experiences or opinions. If you need to collect more generalized data about your subjects' demographics or attitudes, then quantitative interviews may be a better option.
Interviews are relatively quick and very flexible, allowing you to ask follow-up questions and explore topics in more depth. The downside is that interviews can be time-consuming and expensive due to the amount of information to be analyzed. They are also prone to bias, as both the interviewer and the respondent may have certain expectations or preconceptions that may influence the data.
Direct observation
Observation is a direct way of collecting data. It can be structured (with a specific protocol to follow) or unstructured (simply observing without a particular plan).
Organizations and businesses use observation as a data collection method to gather information about their target market, customers, or competition. Businesses can learn about consumer behavior, preferences, and trends by observing people using their products or service.
There are two types of observation: participatory and non-participatory. In participatory observation, the researcher is actively involved in the observed activities. This type of observation is used in ethnographic research , where the researcher wants to understand a group's culture and social norms. Non-participatory observation is when researchers observe from a distance and do not interact with the people or environment they are studying.
There are several advantages to using observation as a data collection method. It can provide insights that may not be apparent through other methods, such as surveys or interviews. Researchers can also observe behavior in a natural setting, which can provide a more accurate picture of what people do and how and why they behave in a certain context.
There are some disadvantages to using observation as a method of data collection. It can be time-consuming, intrusive, and expensive to observe people for extended periods. Observations can also be tainted if the researcher is not careful to avoid personal biases or preconceptions.
Automated data collection
Business applications and websites are increasingly collecting data electronically to improve the user experience or for marketing purposes.
There are a few different ways that organizations can collect data automatically. One way is through cookies, which are small pieces of data stored on a user's computer. They track a user's browsing history and activity on a site, measuring levels of engagement with a business’s products or services, for example.
Another way organizations can collect data automatically is through web beacons. Web beacons are small images embedded on a web page to track a user's activity.
Finally, organizations can also collect data through mobile apps, which can track user location, device information, and app usage. This data can be used to improve the user experience and for marketing purposes.
Automated data collection is a valuable tool for businesses, helping improve the user experience or target marketing efforts. Businesses should aim to be transparent about how they collect and use this data.
Sourcing data through information service providers
Organizations need to be able to collect data from a variety of sources, including social media, weblogs, and sensors. The process to do this and then use the data for action needs to be efficient, targeted, and meaningful.
In the era of big data, organizations are increasingly turning to information service providers (ISPs) and other external data sources to help them collect data to make crucial decisions.
Information service providers help organizations collect data by offering personalized services that suit the specific needs of the organizations. These services can include data collection, analysis, management, and reporting. By partnering with an ISP, organizations can gain access to the newest technology and tools to help them to gather and manage data more effectively.
There are also several tools and techniques that organizations can use to collect data from external sources, such as web scraping, which collects data from websites, and data mining, which involves using algorithms to extract data from large data sets.
Organizations can also use APIs (application programming interface) to collect data from external sources. APIs allow organizations to access data stored in another system and share and integrate it into their own systems.
Finally, organizations can also use manual methods to collect data from external sources. This can involve contacting companies or individuals directly to request data, by using the right tools and methods to get the insights they need.
- What are common challenges in data collection?
There are many challenges that researchers face when collecting data. Here are five common examples:
Big data environments
Data collection can be a challenge in big data environments for several reasons. It can be located in different places, such as archives, libraries, or online. The sheer volume of data can also make it difficult to identify the most relevant data sets.
Second, the complexity of data sets can make it challenging to extract the desired information. Third, the distributed nature of big data environments can make it difficult to collect data promptly and efficiently.
Therefore it is important to have a well-designed data collection strategy to consider the specific needs of the organization and what data sets are the most relevant. Alongside this, consideration should be made regarding the tools and resources available to support data collection and protect it from unintended use.
Data bias is a common challenge in data collection. It occurs when data is collected from a sample that is not representative of the population of interest.
There are different types of data bias, but some common ones include selection bias, self-selection bias, and response bias. Selection bias can occur when the collected data does not represent the population being studied. For example, if a study only includes data from people who volunteer to participate, that data may not represent the general population.
Self-selection bias can also occur when people self-select into a study, such as by taking part only if they think they will benefit from it. Response bias happens when people respond in a way that is not honest or accurate, such as by only answering questions that make them look good.
These types of data bias present a challenge because they can lead to inaccurate results and conclusions about behaviors, perceptions, and trends. Data bias can be avoided by identifying potential sources or themes of bias and setting guidelines for eliminating them.
Lack of quality assurance processes
One of the biggest challenges in data collection is the lack of quality assurance processes. This can lead to several problems, including incorrect data, missing data, and inconsistencies between data sets.
Quality assurance is important because there are many data sources, and each source may have different levels of quality or corruption. There are also different ways of collecting data, and data quality may vary depending on the method used.
There are several ways to improve quality assurance in data collection. These include developing clear and consistent goals and guidelines for data collection, implementing quality control measures, using standardized procedures, and employing data validation techniques. By taking these steps, you can ensure that your data is of adequate quality to inform decision-making.
Limited access to data
Another challenge in data collection is limited access to data. This can be due to several reasons, including privacy concerns, the sensitive nature of the data, security concerns, or simply the fact that data is not readily available.
Legal and compliance regulations
Most countries have regulations governing how data can be collected, used, and stored. In some cases, data collected in one country may not be used in another. This means gaining a global perspective can be a challenge.
For example, if a company is required to comply with the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), it may not be able to collect data from individuals in the EU without their explicit consent. This can make it difficult to collect data from a target audience.
Legal and compliance regulations can be complex, and it's important to ensure that all data collected is done so in a way that complies with the relevant regulations.
- What are the key steps in the data collection process?
There are five steps involved in the data collection process. They are:
1. Decide what data you want to gather
Have a clear understanding of the questions you are asking, and then consider where the answers might lie and how you might obtain them. This saves time and resources by avoiding the collection of irrelevant data, and helps maintain the quality of your datasets.
2. Establish a deadline for data collection
Establishing a deadline for data collection helps you avoid collecting too much data, which can be costly and time-consuming to analyze. It also allows you to plan for data analysis and prompt interpretation. Finally, it helps you meet your research goals and objectives and allows you to move forward.
3. Select a data collection approach
The data collection approach you choose will depend on different factors, including the type of data you need, available resources, and the project timeline. For instance, if you need qualitative data, you might choose a focus group or interview methodology. If you need quantitative data , then a survey or observational study may be the most appropriate form of collection.
4. Gather information
When collecting data for your business, identify your business goals first. Once you know what you want to achieve, you can start collecting data to reach those goals. The most important thing is to ensure that the data you collect is reliable and valid. Otherwise, any decisions you make using the data could result in a negative outcome for your business.
5. Examine the information and apply your findings
As a researcher, it's important to examine the data you're collecting and analyzing before you apply your findings. This is because data can be misleading, leading to inaccurate conclusions. Ask yourself whether it is what you are expecting? Is it similar to other datasets you have looked at?
There are many scientific ways to examine data, but some common methods include:
looking at the distribution of data points
examining the relationships between variables
looking for outliers
By taking the time to examine your data and noticing any patterns, strange or otherwise, you can avoid making mistakes that could invalidate your research.
- How qualitative analysis software streamlines the data collection process
Knowledge derived from data does indeed carry power. However, if you don't convert the knowledge into action, it will remain a resource of unexploited energy and wasted potential.
Luckily, data collection tools enable organizations to streamline their data collection and analysis processes and leverage the derived knowledge to grow their businesses. For instance, qualitative analysis software can be highly advantageous in data collection by streamlining the process, making it more efficient and less time-consuming.
Secondly, qualitative analysis software provides a structure for data collection and analysis, ensuring that data is of high quality. It can also help to uncover patterns and relationships that would otherwise be difficult to discern. Moreover, you can use it to replace more expensive data collection methods, such as focus groups or surveys.
Overall, qualitative analysis software can be valuable for any researcher looking to collect and analyze data. By increasing efficiency, improving data quality, and providing greater insights, qualitative software can help to make the research process much more efficient and effective.
Learn more about qualitative research data analysis software
Get started today.
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 17 February 2024
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

A Guide to Data Collection: Methods, Process, and Tools

Whether your field is development economics, international development, the nonprofit sector, or myriad other industries, effective data collection is essential. It informs decision-making and increases your organization’s impact. However, the process of data collection can be complex and challenging. If you’re in the beginning stages of creating a data collection process, this guide is for you. It outlines tested methods, efficient procedures, and effective tools to help you improve your data collection activities and outcomes. At SurveyCTO, we’ve used our years of experience and expertise to build a robust, secure, and scalable mobile data collection platform. It’s trusted by respected institutions like The World Bank, J-PAL, Oxfam, and the Gates Foundation, and it’s changed the way many organizations collect and use data. With this guide, we want to share what we know and help you get ready to take the first step in your data collection journey.
Main takeaways from this guide
- Before starting the data collection process, define your goals and identify data sources, which can be primary (first-hand research) or secondary (existing resources).
- Your data collection method should align with your goals, resources, and the nature of the data needed. Surveys, interviews, observations, focus groups, and forms are common data collection methods.
- Sampling involves selecting a representative group from a larger population. Choosing the right sampling method to gather representative and relevant data is crucial.
- Crafting effective data collection instruments like surveys and questionnaires is key. Instruments should undergo rigorous testing for reliability and accuracy.
- Data collection is an ongoing, iterative process that demands real-time monitoring and adjustments to ensure high-quality, reliable results.
- After data collection, data should be cleaned to eliminate errors and organized for efficient analysis. The data collection journey further extends into data analysis, where patterns and useful information that can inform decision-making are discovered.
- Common challenges in data collection include data quality and consistency issues, data security concerns, and limitations with offline data collection. Employing robust data validation processes, implementing strong security protocols, and using offline-enabled data collection tools can help overcome these challenges.
- Data collection, entry, and management tools and data analysis, visualization, reporting, and workflow tools can streamline the data collection process, improve data quality, and facilitate data analysis.
What is data collection?
The traditional definition of data collection might lead us to think of gathering information through surveys, observations, or interviews. However, the modern-age definition of data collection extends beyond conducting surveys and observations. It encompasses the systematic gathering and recording of any kind of information through digital or manual methods. Data collection can be as routine as a doctor logging a patient’s information into an electronic medical record system during each clinic visit, or as specific as keeping a record of mosquito nets delivered to a rural household.
Getting started with data collection

Before starting your data collection process, you must clearly understand what you aim to achieve and how you’ll get there. Below are some actionable steps to help you get started.
1. Define your goals
Defining your goals is a crucial first step. Engage relevant stakeholders and team members in an iterative and collaborative process to establish clear goals. It’s important that projects start with the identification of key questions and desired outcomes to ensure you focus your efforts on gathering the right information.
Start by understanding the purpose of your project– what problem are you trying to solve, or what change do you want to bring about? Think about your project’s potential outcomes and obstacles and try to anticipate what kind of data would be useful in these scenarios. Consider who will be using the data you collect and what data would be the most valuable to them. Think about the long-term effects of your project and how you will measure these over time. Lastly, leverage any historical data from previous projects to help you refine key questions that may have been overlooked previously.
Once questions and outcomes are established, your data collection goals may still vary based on the context of your work. To demonstrate, let’s use the example of an international organization working on a healthcare project in a remote area.
- If you’re a researcher , your goal will revolve around collecting primary data to answer specific questions. This could involve designing a survey or conducting interviews to collect first-hand data on patient improvement, disease or illness prevalence, and behavior changes (such as an increase in patients seeking healthcare).
- If you’re part of the monitoring and evaluation ( M&E) team , your goal will revolve around measuring the success of your healthcare project. This could involve collecting primary data through surveys or observations and developing a dashboard to display real-time metrics like the number of patients treated, percentage of reduction in incidences of disease,, and average patient wait times. Your focus would be using this data to implement any needed program changes and ensure your project meets its objectives.
- If you’re part of a field team , your goal will center around the efficient and accurate execution of project plans. You might be responsible for using data collection tools to capture pertinent information in different settings, such as in interviews takendirectly from the sample community or over the phone. The data you collect and manage will directly influence the operational efficiency of the project and assist in achieving the project’s overarching objectives.
2. Identify your data sources
The crucial next step in your research process is determining your data source. Essentially, there are two main data types to choose from: primary and secondary.
- Primary data is the information you collect directly from first-hand engagements. It’s gathered specifically for your research and tailored to your research question. Primary data collection methods can range from surveys and interviews to focus groups and observations. Because you design the data collection process, primary data can offer precise, context-specific information directly related to your research objectives. For example, suppose you are investigating the impact of a new education policy. In that case, primary data might be collected through surveys distributed to teachers or interviews with school administrators dealing directly with the policy’s implementation.
- Secondary data, on the other hand, is derived from resources that already exist. This can include information gathered for other research projects, administrative records, historical documents, statistical databases, and more. While not originally collected for your specific study, secondary data can offer valuable insights and background information that complement your primary data. For instance, continuing with the education policy example, secondary data might involve academic articles about similar policies, government reports on education or previous survey data about teachers’ opinions on educational reforms.
While both types of data have their strengths, this guide will predominantly focus on primary data and the methods to collect it. Primary data is often emphasized in research because it provides fresh, first-hand insights that directly address your research questions. Primary data also allows for more control over the data collection process, ensuring data is relevant, accurate, and up-to-date.
However, secondary data can offer critical context, allow for longitudinal analysis, save time and resources, and provide a comparative framework for interpreting your primary data. It can be a crucial backdrop against which your primary data can be understood and analyzed. While we focus on primary data collection methods in this guide, we encourage you not to overlook the value of incorporating secondary data into your research design where appropriate.
3. Choose your data collection method
When choosing your data collection method, there are many options at your disposal. Data collection is not limited to methods like surveys and interviews. In fact, many of the processes in our daily lives serve the goal of collecting data, from intake forms to automated endpoints, such as payment terminals and mass transit card readers. Let us dive into some common types of data collection methods:
Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are tools for gathering information about a group of individuals, typically by asking them predefined questions. They can be used to collect quantitative and qualitative data and be administered in various ways, including online, over the phone, in person (offline), or by mail.
- Advantages : They allow researchers to reach many participants quickly and cost-effectively, making them ideal for large-scale studies. The structured format of questions makes analysis easier.
- Disadvantages : They may not capture complex or nuanced information as participants are limited to predefined response choices. Also, there can be issues with response bias, where participants might provide socially desirable answers rather than honest ones.
Interviews involve a one-on-one conversation between the researcher and the participant. The interviewer asks open-ended questions to gain detailed information about the participant’s thoughts, feelings, experiences, and behaviors.
- Advantages : They allow for an in-depth understanding of the topic at hand. The researcher can adapt the questioning in real time based on the participant’s responses, allowing for more flexibility.
- Disadvantages : They can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, as they require trained interviewers and a significant amount of time for both conducting and analyzing responses. They may also introduce interviewer bias if not conducted carefully, due to how an interviewer presents questions and perceives the respondent, and how the respondent perceives the interviewer.
Observations
Observations involve directly observing and recording behavior or other phenomena as they occur in their natural settings.
- Advantages : Observations can provide valuable contextual information, as researchers can study behavior in the environment where it naturally occurs, reducing the risk of artificiality associated with laboratory settings or self-reported measures.
- Disadvantages : Observational studies may suffer from observer bias, where the observer’s expectations or biases could influence their interpretation of the data. Also, some behaviors might be altered if subjects are aware they are being observed.
Focus Groups
Focus groups are guided discussions among selected individuals to gain information about their views and experiences.
- Advantages : Focus groups allow for interaction among participants, which can generate a diverse range of opinions and ideas. They are good for exploring new topics where there is little pre-existing knowledge.
- Disadvantages : Dominant voices in the group can sway the discussion, potentially silencing less assertive participants. They also require skilled facilitators to moderate the discussion effectively.
Forms are standardized documents with blank fields for collecting data in a systematic manner. They are often used in fields like Customer Relationship Management (CRM) or Electronic Medical Records (EMR) data entry. Surveys may also be referred to as forms.
- Advantages : Forms are versatile, easy to use, and efficient for data collection. They can streamline workflows by standardizing the data entry process.
- Disadvantages : They may not provide in-depth insights as the responses are typically structured and limited. There is also potential for errors in data entry, especially when done manually.
Selecting the right data collection method should be an intentional process, taking into consideration the unique requirements of your project. The method selected should align with your goals, available resources, and the nature of the data you need to collect.
If you aim to collect quantitative data, surveys, questionnaires, and forms can be excellent tools, particularly for large-scale studies. These methods are suited to providing structured responses that can be analyzed statistically, delivering solid numerical data.
However, if you’re looking to uncover a deeper understanding of a subject, qualitative data might be more suitable. In such cases, interviews, observations, and focus groups can provide richer, more nuanced insights. These methods allow you to explore experiences, opinions, and behaviors deeply. Some surveys can also include open-ended questions that provide qualitative data.
The cost of data collection is also an important consideration. If you have budget constraints, in-depth, in-person conversations with every member of your target population may not be practical. In such cases, distributing questionnaires or forms can be a cost-saving approach.
Additional considerations include language barriers and connectivity issues. If your respondents speak different languages, consider translation services or multilingual data collection tools . If your target population resides in areas with limited connectivity and your method will be to collect data using mobile devices, ensure your tool provides offline data collection , which will allow you to carry out your data collection plan without internet connectivity.
4. Determine your sampling method
Now that you’ve established your data collection goals and how you’ll collect your data, the next step is deciding whom to collect your data from. Sampling involves carefully selecting a representative group from a larger population. Choosing the right sampling method is crucial for gathering representative and relevant data that aligns with your data collection goal.
Consider the following guidelines to choose the appropriate sampling method for your research goal and data collection method:
- Understand Your Target Population: Start by conducting thorough research of your target population. Understand who they are, their characteristics, and subgroups within the population.
- Anticipate and Minimize Biases: Anticipate and address potential biases within the target population to help minimize their impact on the data. For example, will your sampling method accurately reflect all ages, gender, cultures, etc., of your target population? Are there barriers to participation for any subgroups? Your sampling method should allow you to capture the most accurate representation of your target population.
- Maintain Cost-Effective Practices: Consider the cost implications of your chosen sampling methods. Some sampling methods will require more resources, time, and effort. Your chosen sampling method should balance the cost factors with the ability to collect your data effectively and accurately.
- Consider Your Project’s Objectives: Tailor the sampling method to meet your specific objectives and constraints, such as M&E teams requiring real-time impact data and researchers needing representative samples for statistical analysis.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can make informed choices when selecting a sampling method, maximizing the quality and relevance of your data collection efforts.
5. Identify and train collectors
Not every data collection use case requires data collectors, but training individuals responsible for data collection becomes crucial in scenarios involving field presence.
The SurveyCTO platform supports both self-response survey modes and surveys that require a human field worker to do in-person interviews. Whether you’re hiring and training data collectors, utilizing an existing team, or training existing field staff, we offer comprehensive guidance and the right tools to ensure effective data collection practices.
Here are some common training approaches for data collectors:
- In-Class Training: Comprehensive sessions covering protocols, survey instruments, and best practices empower data collectors with skills and knowledge.
- Tests and Assessments: Assessments evaluate collectors’ understanding and competence, highlighting areas where additional support is needed.
- Mock Interviews: Simulated interviews refine collectors’ techniques and communication skills.
- Pre-Recorded Training Sessions: Accessible reinforcement and self-paced learning to refresh and stay updated.
Training data collectors is vital for successful data collection techniques. Your training should focus on proper instrument usage and effective interaction with respondents, including communication skills, cultural literacy, and ethical considerations.
Remember, training is an ongoing process. Knowledge gaps and issues may arise in the field, necessitating further training.
Moving Ahead: Iterative Steps in Data Collection

Once you’ve established the preliminary elements of your data collection process, you’re ready to start your data collection journey. In this section, we’ll delve into the specifics of designing and testing your instruments, collecting data, and organizing data while embracing the iterative nature of the data collection process, which requires diligent monitoring and making adjustments when needed.
6. Design and test your instruments
Designing effective data collection instruments like surveys and questionnaires is key. It’s crucial to prioritize respondent consent and privacy to ensure the integrity of your research. Thoughtful design and careful testing of survey questions are essential for optimizing research insights. Other critical considerations are:
- Clear and Unbiased Question Wording: Craft unambiguous, neutral questions free from bias to gather accurate and meaningful data. For example, instead of asking, “Shouldn’t we invest more into renewable energy that will combat the effects of climate change?” ask your question in a neutral way that allows the respondent to voice their thoughts. For example: “What are your thoughts on investing more in renewable energy?”
- Logical Ordering and Appropriate Response Format: Arrange questions logically and choose response formats (such as multiple-choice, Likert scale, or open-ended) that suit the nature of the data you aim to collect.
- Coverage of Relevant Topics: Ensure that your instrument covers all topics pertinent to your data collection goals while respecting cultural and social sensitivities. Make sure your instrument avoids assumptions, stereotypes, and languages or topics that could be considered offensive or taboo in certain contexts. The goal is to avoid marginalizing or offending respondents based on their social or cultural background.
- Collect Only Necessary Data: Design survey instruments that focus solely on gathering the data required for your research objectives, avoiding unnecessary information.
- Language(s) of the Respondent Population: Tailor your instruments to accommodate the languages your target respondents speak, offering translated versions if needed. Similarly, take into account accessibility for respondents who can’t read by offering alternative formats like images in place of text.
- Desired Length of Time for Completion: Respect respondents’ time by designing instruments that can be completed within a reasonable timeframe, balancing thoroughness with engagement. Having a general timeframe for the amount of time needed to complete a response will also help you weed out bad responses. For example, a response that was rushed and completed outside of your response timeframe could indicate a response that needs to be excluded.
- Collecting and Documenting Respondents’ Consent and Privacy: Ensure a robust consent process, transparent data usage communication, and privacy protection throughout data collection.
Perform Cognitive Interviewing
Cognitive interviewing is a method used to refine survey instruments and improve the accuracy of survey responses by evaluating how respondents understand, process, and respond to the instrument’s questions. In practice, cognitive interviewing involves an interview with the respondent, asking them to verbalize their thoughts as they interact with the instrument. By actively probing and observing their responses, you can identify and address ambiguities, ensuring accurate data collection.
Thoughtful question wording, well-organized response options, and logical sequencing enhance comprehension, minimize biases, and ensure accurate data collection. Iterative testing and refinement based on respondent feedback improve the validity, reliability, and actionability of insights obtained.
Put Your Instrument to the Test
Through rigorous testing, you can uncover flaws, ensure reliability, maximize accuracy, and validate your instrument’s performance. This can be achieved by:
- Conducting pilot testing to enhance the reliability and effectiveness of data collection. Administer the instrument, identify difficulties, gather feedback, and assess performance in real-world conditions.
- Making revisions based on pilot testing to enhance clarity, accuracy, usability, and participant satisfaction. Refine questions, instructions, and format for effective data collection.
- Continuously iterating and refining your instrument based on feedback and real-world testing. This ensures reliable, accurate, and audience-aligned methods of data collection. Additionally, this ensures your instrument adapts to changes, incorporates insights, and maintains ongoing effectiveness.
7. Collect your data
Now that you have your well-designed survey, interview questions, observation plan, or form, it’s time to implement it and gather the needed data. Data collection is not a one-and-done deal; it’s an ongoing process that demands attention to detail. Imagine spending weeks collecting data, only to discover later that a significant portion is unusable due to incomplete responses, improper collection methods, or falsified responses. To avoid such setbacks, adopt an iterative approach.
Leverage data collection tools with real-time monitoring to proactively identify outliers and issues. Take immediate action by fine-tuning your instruments, optimizing the data collection process, addressing concerns like additional training, or reevaluating personnel responsible for inaccurate data (for example, a field worker who sits in a coffee shop entering fake responses rather than doing the work of knocking on doors).
SurveyCTO’s Data Explorer was specifically designed to fulfill this requirement, empowering you to monitor incoming data, gain valuable insights, and know where changes may be needed. Embracing this iterative approach ensures ongoing improvement in data collection, resulting in more reliable and precise results.
8. Clean and organize your data
After data collection, the next step is to clean and organize the data to ensure its integrity and usability.
- Data Cleaning: This stage involves sifting through your data to identify and rectify any errors, inconsistencies, or missing values. It’s essential to maintain the accuracy of your data and ensure that it’s reliable for further analysis. Data cleaning can uncover duplicates, outliers, and gaps that could skew your results if left unchecked. With real-time data monitoring , this continuous cleaning process keeps your data precise and current throughout the data collection period. Similarly, review and corrections workflows allow you to monitor the quality of your incoming data.
- Organizing Your Data: Post-cleaning, it’s time to organize your data for efficient analysis and interpretation. Labeling your data using appropriate codes or categorizations can simplify navigation and streamline the extraction of insights. When you use a survey or form, labeling your data is often not necessary because you can design the instrument to collect in the right categories or return the right codes. An organized dataset is easier to manage, analyze, and interpret, ensuring that your collection efforts are not wasted but lead to valuable, actionable insights.
Remember, each stage of the data collection process, from design to cleaning, is iterative and interconnected. By diligently cleaning and organizing your data, you are setting the stage for robust, meaningful analysis that can inform your data-driven decisions and actions.
What happens after data collection?

The data collection journey takes us next into data analysis, where you’ll uncover patterns, empowering informed decision-making for researchers, evaluation teams, and field personnel.
Process and Analyze Your Data
Explore data through statistical and qualitative techniques to discover patterns, correlations, and insights during this pivotal stage. It’s about extracting the essence of your data and translating numbers into knowledge. Whether applying descriptive statistics, conducting regression analysis, or using thematic coding for qualitative data, this process drives decision-making and charts the path toward actionable outcomes.
Interpret and Report Your Results
Interpreting and reporting your data brings meaning and context to the numbers. Translating raw data into digestible insights for informed decision-making and effective stakeholder communication is critical.
The approach to interpretation and reporting varies depending on the perspective and role:
- Researchers often lean heavily on statistical methods to identify trends, extract meaningful conclusions, and share their findings in academic circles, contributing to their knowledge pool.
- M&E teams typically produce comprehensive reports, shedding light on the effectiveness and impact of programs. These reports guide internal and sometimes external stakeholders, supporting informed decisions and driving program improvements.
Field teams provide a first-hand perspective. Since they are often the first to see the results of the practical implementation of data, field teams are instrumental in providing immediate feedback loops on project initiatives. Field teams do the work that provides context to help research and M&E teams understand external factors like the local environment, cultural nuances, and logistical challenges that impact data results.
Safely store and handle data
Throughout the data collection process, and after it has been collected, it is vital to follow best practices for storing and handling data to ensure the integrity of your research. While the specifics of how to best store and handle data will depend on your project, here are some important guidelines to keep in mind:
- Use cloud storage to hold your data if possible, since this is safer than storing data on hard drives and keeps it more accessible,
- Periodically back up and purge old data from your system, since it’s safer to not retain data longer than necessary,
- If you use mobile devices to collect and store data, use options for private, internal apps-specific storage if and when possible,
- Restrict access to stored data to only those who need to work with that data.
Further considerations for data safety are discussed below in the section on data security .
Remember to uphold ethical standards in interpreting and reporting your data, regardless of your role. Clear communication, respectful handling of sensitive information, and adhering to confidentiality and privacy rights are all essential to fostering trust, promoting transparency, and bolstering your work’s credibility.
Common Data Collection Challenges

Data collection is vital to data-driven initiatives, but it comes with challenges. Addressing common challenges such as poor data quality, privacy concerns, inadequate sample sizes, and bias is essential to ensure the collected data is reliable, trustworthy, and secure.
In this section, we’ll explore three major challenges: data quality and consistency issues, data security concerns, and limitations with offline data collection , along with strategies to overcome them.
Data Quality and Consistency
Data quality and consistency refer to data accuracy and reliability throughout the collection and analysis process.
Challenges such as incomplete or missing data, data entry errors, measurement errors, and data coding/categorization errors can impact the integrity and usefulness of the data.
To navigate these complexities and maintain high standards, consistency, and integrity in the dataset:
- Implement robust data validation processes,
- Ensure proper training for data entry personnel,
- Employ automated data validation techniques, and
- Conduct regular data quality audits.
Data security
Data security encompasses safeguarding data through ensuring data privacy and confidentiality, securing storage and backup, and controlling data sharing and access.
Challenges include the risk of potential breaches, unauthorized access, and the need to comply with data protection regulations.
To address these setbacks and maintain privacy, trust, and confidence during the data collection process:
- Use encryption and authentication methods,
- Implement robust security protocols,
- Update security measures regularly,
- Provide employee training on data security, and
- Adopt secure cloud storage solutions.
Offline Data Collection
Offline data collection refers to the process of gathering data using modes like mobile device-based computer-assisted personal interviewing (CAPI) when t here is an inconsistent or unreliable internet connection, and the data collection tool being used for CAPI has the functionality to work offline.
Challenges associated with offline data collection include synchronization issues, difficulty transferring data, and compatibility problems between devices, and data collection tools.
To overcome these challenges and enable efficient and reliable offline data collection processes, employ the following strategies:
- Leverage offline-enabled data collection apps or tools that enable you to survey respondents even when there’s no internet connection, and upload data to a central repository at a later time.
- Your data collection plan should include times for periodic data synchronization when connectivity is available,
- Use offline, device-based storage for seamless data transfer and compatibility, and
- Provide clear instructions to field personnel on handling offline data collection scenarios.
Utilizing Technology in Data Collection

Embracing technology throughout your data collection process can help you overcome many challenges described in the previous section. Data collection tools can streamline your data collection, improve the quality and security of your data, and facilitate the analysis of your data. Let’s look at two broad categories of tools that are essential for data collection:
Data Collection, Entry, & Management Tools
These tools help with data collection, input, and organization. They can range from digital survey platforms to comprehensive database systems, allowing you to gather, enter, and manage your data effectively. They can significantly simplify the data collection process, minimize human error, and offer practical ways to organize and manage large volumes of data. Some of these tools are:
- Microsoft Office
- Google Docs
- SurveyMonkey
- Google Forms
Data Analysis, Visualization, Reporting, & Workflow Tools
These tools assist in processing and interpreting the collected data. They provide a way to visualize data in a user-friendly format, making it easier to identify trends and patterns. These tools can also generate comprehensive reports to share your findings with stakeholders and help manage your workflow efficiently. By automating complex tasks, they can help ensure accuracy and save time. Tools for these purposes include:
- Google sheets
Data collection tools like SurveyCTO often have integrations to help users seamlessly transition from data collection to data analysis, visualization, reporting, and managing workflows.
Master Your Data Collection Process With SurveyCTO
As we bring this guide to a close, you now possess a wealth of knowledge to develop your data collection process. From understanding the significance of setting clear goals to the crucial process of selecting your data collection methods and addressing common challenges, you are equipped to handle the intricate details of this dynamic process.
Remember, you’re not venturing into this complex process alone. At SurveyCTO, we offer not just a tool but an entire support system committed to your success. Beyond troubleshooting support, our success team serves as research advisors and expert partners, ready to provide guidance at every stage of your data collection journey.
With SurveyCTO , you can design flexible surveys in Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, collect data online and offline with above-industry-standard security, monitor your data in real time, and effortlessly export it for further analysis in any tool of your choice. You also get access to our Data Explorer, which allows you to visualize incoming data at both individual survey and aggregate levels instantly.
In the iterative data collection process, our users tell us that SurveyCTO stands out with its capacity to establish review and correction workflows. It enables you to monitor incoming data and configure automated quality checks to flag error-prone submissions.
Finally, data security is of paramount importance to us. We ensure best-in-class security measures like SOC 2 compliance, end-to-end encryption, single sign-on (SSO), GDPR-compliant setups, customizable user roles, and self-hosting options to keep your data safe.
As you embark on your data collection journey, you can count on SurveyCTO’s experience and expertise to be by your side every step of the way. Our team would be excited and honored to be a part of your research project, offering you the tools and processes to gain informative insights and make effective decisions. Partner with us today and revolutionize the way you collect data.
Better data, better decision making, better world.

INTEGRATIONS
Scientific Research and Methodology : An introduction to quantitative research and statistics
10 collecting data.
So far, you have learnt to ask a RQ and design the study. In this chapter , you will learn how to:
- record the important steps in data collection.
- describe study protocols.
- ask survey questions.

10.1 Protocols
If the RQ is well-constructed, terms are clearly defined, and the study is well designed and explained, then the process for collecting the data should be easy to describe. Data collection is often time-consuming, tedious and expensive, so collecting the data correctly first time is important.
Before collecting the data, a plan should be established and documented that explains exactly how the data will be obtained, which will include operational definitions (Sect. 2.11 ). This plan is called a protocol .
Definition 10.1 (Protocol) A protocol is a procedure documenting the details of the design and implementation of studies, and for data collection.
Unforeseen complications are not unusual, so often a pilot study (or a practice run ) is conducted before the real data collection, to identify problems with the study design or data collection, or ways to improve the study design or data collection. The pilot study may suggest changes to the protocol. (Pilot studies may also be useful for determining the size of the sample; see Sect. 30.4 .)
Definition 10.2 (Pilot study) A pilot study is a small test run of the study protocol used to check that the protocol is appropriate and practical, and to identify (and hence fix) possible problems with the study design or protocol.
A pilot study allows the researcher to:
- determine the feasibility of the data collection protocol.
- identify unforeseen challenges.
- obtain data to determine appropriate sample sizes (Sect. 30 ).
- potentially save time and money.
The data can be collected once the protocol has been finalised. Protocols ensure studies are repeatable (Sect. 4.4 ) so others can confirm or compare results, and others can understand exactly what was done, and how. Protocols should indicate how design aspects (such as blinding the individuals, random allocation of treatments, etc.) will happen. The final protocol , without pedantic detail, should be reported. Diagrams can be useful to support explanations. All studies should have a well-established protocol for describing how the study was done.
A protocol usually has at least three components that describe:
- How individuals are chosen from the population (i.e., external validity); and
- How information is collected from the individuals (i.e., internal validity); and
- The analyses, and what software (and version) was used.
Example 10.1 (Protocol) To increase the nutritional value of cookies, researchers made cookies using pureed green peas in place of margarine ( Romanchik-Cerpovicz, Jeffords, and Onyenwoke 2018 ) . The researchers wanted to assess the acceptance of these cookies to college students.
The protocol discussed how the individuals were chosen (p. 4):
...through advertisement across campus from students attending a university in the southeastern United States.
This voluntary sample comprised \(80.6\) % women, a higher percentage of women than in the general population, or the college population. (Other extraneous variables were also recorded.)
Exclusion criteria were also applied, excluding people "with an allergy or sensitivity to an ingredient used in the preparation of the cookies" (p. 5). The researchers also described how the data was obtained from the individuals (p. 5):
During the testing session, panelists were seated at individual tables. Each cookie was presented one at a time on a disposable white plate. Samples were previously coded and randomized. The presentation order for all samples was \(25\) %, \(0\) %, \(50\) %, \(100\) % and \(75\) % substitution of fat with puree of canned green peas. To maintain standard procedures for sensory analysis [...], panelists cleansed their palates between cookie samples with distilled water ( \(25^\circ\) C) [...] characteristics of color, smell, moistness, flavor, aftertaste, and overall acceptability, for each sample of cookies [was recorded]...
Thus, internal validity was managed using random allocation, blinding individuals, and washouts. Details are also given of how the cookies were prepared, and how objective measurements (such as moisture content) were determined.
The analyses and software used were also given.
Consider this partial protocol, which shows honesty in describing a protocol:
Fresh cow dung was obtained from free-ranging, grass fed, and antibiotic-free Milking Shorthorn cows ( Bos taurus ) in the Tilden Regional Park in Berkeley, CA. Resting cows were approached with caution and startled by loud shouting, whereupon the cows rapidly stood up, defecated, and moved away from the source of the annoyance. Dung was collected in ZipLoc bags ( \(1\) gallon), snap-frozen and stored at \(-80\) C. --- Hare et al. ( 2008 ) , p. 10
10.2 Collecting data using questionnaires
10.2.1 writing questions.
Collecting data using questionnaires is common for both observational and experimental studies. Questionnaires are very difficult to do well: question wording is crucial, and surprisingly difficult to get right ( Fink 1995 ) . Pilot testing questionnaires is crucial!
Definition 10.3 (Questionnaire) A questionnaire is a set of questions for respondents to answer.
A questionnaire is a set of question to obtain information from individuals. A survey is an entire methodology, that includes gathering data using a questionnaire, finding a sample, and other components.
Questions in a questionnaire may be open-ended (respondents can write their own answers) or closed (respondents select from a small number of possible answers, as in multiple-choice questions). Open and closed questions both have advantages and disadvantages. Answers to open questions more easily lend themselves to qualitative analysis.
This section briefly discusses writing questions (Sect. 10.2 ).
Example 10.2 (Open and closed questions) German students were asked a series of questions about microplastics ( Raab and Bogner 2021 ) , including:
- Name sources of microplastics in the household.
- In which ecosystems are microplastics in Germany? Tick the answer (multiple ticks are possible). Options : (a) sea; (b) rivers; (c) lakes; (d) groundwater.
- Assess the potential danger posed by microplastics. Options : (a) very dangerous; (b) dangerous; (c) hardly dangerous; (d) not dangerous.
The first question is an open : respondents could provide their own answers. The second question is closed , where multiple options can be selected. The third question is closed , where only one option can be selected
When framing questionnaire questions, remember:
- Avoid leading questions , which may lead respondents to answer a certain way. Question wording is the usual reason for leading questions.
- Avoid ambiguity : avoid unfamiliar terms and unclear questions.
- Avoid asking the uninformed : avoid asking respondents about issues they don't know about. Many people will give a response even if they do not understand (such responses are worthless). For example, people may give directions to places that do not even exist ( Collett and O’Shea 1976 ) .
- Avoid complex and double-barrelled questions , which can be hard to understand.
- Avoid problems with ethics : avoid questions about people breaking laws, or revealing confidential or private information. In special cases and with justification, ethics committees may allow such questions.
- Ensure clarity in question wording.
- Ensure options are mutually exhaustive , so that answers fit into only one category.
- Ensure options are exhaustive , so that the categories cover all options.
Example 10.3 (Poor question wording) Consider a questionnaire asking these questions:
- Because bottles from bottled water create enormous amounts of non-biodegradable landfill and hence threaten native wildlife, do you support banning bottled water?
- Do you drink more water now?
- Are you more concerned about Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus or Neisseria pharyngis in bottled water?
- Do you drink water in plastic and glass bottles?
- Do you have a water tank installed illegally, without permission?
- Do you avoid purchasing water in plastic bottles unless it is carbonated, unless the bottles are plastic but not necessarily if the lid is recyclable?
Question 1 is leading because the expected response is obvious.
Question 2 is ambiguous : it is unclear what 'more water now' is being compared to.
Question 3 is unlikely to be answerable, as most people will be uninformed . Nonetheless, many people will still give an opinion. This data will be effectively useless, but the researcher may not realise this.
Question 4 is double-barrelled , and would be better asked as two separate questions (one asking about plastic bottles, and one about glass bottles).
Question 5 is unlikely to be given ethical approval or to obtain truthful answers, as respondents are unlikely to admit to breaking rules.
Question 6 is unclear , since knowing what a yes or no answer means is confusing.
Example 10.4 (Question wording) Question wording can be important ( Jardina 2018 ) .
In the 2014 General Social Survey ( https://gss.norc.org ), when white Americans were asked for their opinion of the amount America spends on welfare , \(58\) % of respondents answered 'Too much'.
However, when white Americans were asked for their opinion of the amount America spends on assistance to the poor , only \(16\) % of respondents answered 'Too much'.
Example 10.5 (Leading question) Consider this question:
Do you like this new orthotic?
This question is leading , since liking is the only option presented. Better would be:
Do you like or dislike this new orthotic?
Example 10.6 (Mutually exclusive options) In a study to determine the time doctors spent on patients (from Chan et al. ( 2008 ) ), doctors were given the options:
- \(0\) -- \(5\) mins;
- \(5\) -- \(10\) mins; or
- more than \(10\) mins.
This is a poor question, because a respondent does not know which option to select for an answer of ' \(5\) minutes'. The options are not mutually exclusive .
The following (humourous) video shows how questions can be manipulated by those not wanting to be ethical:
10.2.2 Challenges using questionnaires
Using questionnaires presents myriad challenges.
- Non-response bias (Sect. 5.10 ): Non-response bias is common with questionnaires, as they are often used with voluntary-response samples. The people who do not respond to the survey may be different than those who do respond.
- Response bias (Sect. 5.10 ): People do not always answer truthfully; for example, what people say may not correspond with what people do (Sect. 9.4 ). Sometimes this is unintentional (e.g., poor questions wording), due to embarrassment or because questions are controversial. Sometimes, respondents repeatedly provide the same answer when a series of multichoice questions are presented (perhaps due to boredom).
- Recall bias : People may not be able to accurately recall past events clearly, or recall when they happened.
- Question order : The order of the questions can influence the responses.
- Interpretation : Phrases and words such as "Sometimes" and "Somewhat disagree" may means different things to different people.
Many of these can be managed with careful questionnaire design, but discussing the methods are beyond the scope of this book.
10.3 Chapter summary
Having a detailed procedure for collecting the data (the protocol ) is important. Using a pilot study to trial the protocol an often reveal unexpected changes necessary for a good protocol. Creating good questionnaires questions is difficult, but important.
10.4 Quick review questions
What is the biggest problem with this question: 'Do you have bromodosis?'
What is the biggest problem with this question: 'Do you spend too much time connected to the internet?'
What is the biggest problem with this question: 'Do you eat fruits and vegetables?'
Which of these are reasons for producing a well-defined protocol?
- It allows the researchers to make the study externally valid. TRUE FALSE
- It ensures that others know exactly what was done. TRUE FALSE
- It ensures that the study is repeatable for others. TRUE FALSE
Which of the following questionnaire questions likely to be leading questions?
- Do you, or do you not, believe that permeable pavements are a viable alternative to traditional pavements? TRUE FALSE
- Do you support a ban on bottled water? TRUE FALSE
- Do you believe that double-gloving by paramedics reduces the risk of infection, increases the risk of infection, or makes no difference to the risk of infection? TRUE FALSE
- Should Ireland ban breakfast cereals with unhealthy sugar levels? TRUE FALSE
10.5 Exercises
Selected answers are available in App. E .
Exercise 10.1 What is the problem with this question?
What is your age? (Select one option) Under \(18\) Over \(18\)
Exercise 10.2 What is the problem with this question?
How many children do you have? (Select one option) None 1 or 2 2 or 3 More than 4
Exercise 10.3 Which of these questionnaire questions is better? Why?
- Should concerned cat owners vaccinate their pets?
- Should domestic cats be required to be vaccinated or not?
- Do you agree that pet-owners should have their cats vaccinated?
Exercise 10.4 Which of these questionnaire questions is better? Why?
- Do you own an environmentally-friendly electric vehicle?
- Do you own an electric vehicle?
- Do you own or do you not own an electric vehicle?
Exercise 10.5 In a study of sunscreen use ( Falk and Anderson 2013 ) , participants were asked questions, including these:
- How often do you sun bathe with the intention to tan during the summer in Sweden? (Possible answers: never, seldom, sometimes, often, always).
- How long do you usually stay in the sun between \(11\) am and \(3\) pm, during a typical day-off in the summer (June--August)? (Possible answers: \(<30\) min, \(30\) min-- \(1\) h, \(1\) -- \(2\) h, \(2\) -- \(3\) h, \(>3\) h).
Critique these questions. What biases may be present?
Exercise 10.6 In a study of children's knowledge of their natural environment ( Morón-Monge, Hamed, and Morón Monge 2021 ) , primary school children (from Andalusia, Spain) were asked three questions:
- No, I don’t like parks.
- No, I don’t usually visit it.
- Yes, once per week.
- Yes, more than once a week
- Two to three times
- More than three times
- Write a story
- Draw a picture
Which questions are open and which are closed ? Critique the questions.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Data Collection Methods | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Data Collection Methods | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on 4 May 2022 by Pritha Bhandari .
Data collection is a systematic process of gathering observations or measurements. Whether you are performing research for business, governmental, or academic purposes, data collection allows you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem .
While methods and aims may differ between fields, the overall process of data collection remains largely the same. Before you begin collecting data, you need to consider:
- The aim of the research
- The type of data that you will collect
- The methods and procedures you will use to collect, store, and process the data
To collect high-quality data that is relevant to your purposes, follow these four steps.
Table of contents
Step 1: define the aim of your research, step 2: choose your data collection method, step 3: plan your data collection procedures, step 4: collect the data, frequently asked questions about data collection.
Before you start the process of data collection, you need to identify exactly what you want to achieve. You can start by writing a problem statement : what is the practical or scientific issue that you want to address, and why does it matter?
Next, formulate one or more research questions that precisely define what you want to find out. Depending on your research questions, you might need to collect quantitative or qualitative data :
- Quantitative data is expressed in numbers and graphs and is analysed through statistical methods .
- Qualitative data is expressed in words and analysed through interpretations and categorisations.
If your aim is to test a hypothesis , measure something precisely, or gain large-scale statistical insights, collect quantitative data. If your aim is to explore ideas, understand experiences, or gain detailed insights into a specific context, collect qualitative data.
If you have several aims, you can use a mixed methods approach that collects both types of data.
- Your first aim is to assess whether there are significant differences in perceptions of managers across different departments and office locations.
- Your second aim is to gather meaningful feedback from employees to explore new ideas for how managers can improve.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Based on the data you want to collect, decide which method is best suited for your research.
- Experimental research is primarily a quantitative method.
- Interviews , focus groups , and ethnographies are qualitative methods.
- Surveys , observations, archival research, and secondary data collection can be quantitative or qualitative methods.
Carefully consider what method you will use to gather data that helps you directly answer your research questions.
When you know which method(s) you are using, you need to plan exactly how you will implement them. What procedures will you follow to make accurate observations or measurements of the variables you are interested in?
For instance, if you’re conducting surveys or interviews, decide what form the questions will take; if you’re conducting an experiment, make decisions about your experimental design .
Operationalisation
Sometimes your variables can be measured directly: for example, you can collect data on the average age of employees simply by asking for dates of birth. However, often you’ll be interested in collecting data on more abstract concepts or variables that can’t be directly observed.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations. When planning how you will collect data, you need to translate the conceptual definition of what you want to study into the operational definition of what you will actually measure.
- You ask managers to rate their own leadership skills on 5-point scales assessing the ability to delegate, decisiveness, and dependability.
- You ask their direct employees to provide anonymous feedback on the managers regarding the same topics.
You may need to develop a sampling plan to obtain data systematically. This involves defining a population , the group you want to draw conclusions about, and a sample, the group you will actually collect data from.
Your sampling method will determine how you recruit participants or obtain measurements for your study. To decide on a sampling method you will need to consider factors like the required sample size, accessibility of the sample, and time frame of the data collection.
Standardising procedures
If multiple researchers are involved, write a detailed manual to standardise data collection procedures in your study.
This means laying out specific step-by-step instructions so that everyone in your research team collects data in a consistent way – for example, by conducting experiments under the same conditions and using objective criteria to record and categorise observations.
This helps ensure the reliability of your data, and you can also use it to replicate the study in the future.
Creating a data management plan
Before beginning data collection, you should also decide how you will organise and store your data.
- If you are collecting data from people, you will likely need to anonymise and safeguard the data to prevent leaks of sensitive information (e.g. names or identity numbers).
- If you are collecting data via interviews or pencil-and-paper formats, you will need to perform transcriptions or data entry in systematic ways to minimise distortion.
- You can prevent loss of data by having an organisation system that is routinely backed up.
Finally, you can implement your chosen methods to measure or observe the variables you are interested in.
The closed-ended questions ask participants to rate their manager’s leadership skills on scales from 1 to 5. The data produced is numerical and can be statistically analysed for averages and patterns.
To ensure that high-quality data is recorded in a systematic way, here are some best practices:
- Record all relevant information as and when you obtain data. For example, note down whether or how lab equipment is recalibrated during an experimental study.
- Double-check manual data entry for errors.
- If you collect quantitative data, you can assess the reliability and validity to get an indication of your data quality.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
When conducting research, collecting original data has significant advantages:
- You can tailor data collection to your specific research aims (e.g., understanding the needs of your consumers or user testing your website).
- You can control and standardise the process for high reliability and validity (e.g., choosing appropriate measurements and sampling methods ).
However, there are also some drawbacks: data collection can be time-consuming, labour-intensive, and expensive. In some cases, it’s more efficient to use secondary data that has already been collected by someone else, but the data might be less reliable.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something:
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions).
- Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
If you are doing experimental research , you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, May 04). Data Collection Methods | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 20 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/data-collection-guide/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods, triangulation in research | guide, types, examples, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Methodology
Definition:
Research Methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to conduct research, investigate problems, and gather data and information for a specific purpose. It involves the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect , analyze , and interpret data to answer research questions or solve research problems . Moreover, They are philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process.
Structure of Research Methodology
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section:
I. Introduction
- Provide an overview of the research problem and the need for a research methodology section
- Outline the main research questions and objectives
II. Research Design
- Explain the research design chosen and why it is appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Discuss any alternative research designs considered and why they were not chosen
- Describe the research setting and participants (if applicable)
III. Data Collection Methods
- Describe the methods used to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations)
- Explain how the data collection methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or instruments used for data collection
IV. Data Analysis Methods
- Describe the methods used to analyze the data (e.g., statistical analysis, content analysis )
- Explain how the data analysis methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or software used for data analysis
V. Ethical Considerations
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise from the research and how they were addressed
- Explain how informed consent was obtained (if applicable)
- Detail any measures taken to ensure confidentiality and anonymity
VI. Limitations
- Identify any potential limitations of the research methodology and how they may impact the results and conclusions
VII. Conclusion
- Summarize the key aspects of the research methodology section
- Explain how the research methodology addresses the research question(s) and objectives
Research Methodology Types
Types of Research Methodology are as follows:
Quantitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data using statistical methods. This type of research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Qualitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Mixed-Methods Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research. This approach can be particularly useful for studies that aim to explore complex phenomena and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Case Study Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves in-depth examination of a single case or a small number of cases. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and anthropology to gain a detailed understanding of a particular individual or group.
Action Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves a collaborative process between researchers and practitioners to identify and solve real-world problems. Action research is often used in education, healthcare, and social work.
Experimental Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the manipulation of one or more independent variables to observe their effects on a dependent variable. Experimental research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.

Survey Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection of data from a sample of individuals using questionnaires or interviews. Survey research is often used to study attitudes, opinions, and behaviors.
Grounded Theory Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the development of theories based on the data collected during the research process. Grounded theory is often used in sociology and anthropology to generate theories about social phenomena.
Research Methodology Example
An Example of Research Methodology could be the following:
Research Methodology for Investigating the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Reducing Symptoms of Depression in Adults
Introduction:
The aim of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. To achieve this objective, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach.
Research Design:
The study will follow a pre-test and post-test design with two groups: an experimental group receiving CBT and a control group receiving no intervention. The study will also include a qualitative component, in which semi-structured interviews will be conducted with a subset of participants to explore their experiences of receiving CBT.
Participants:
Participants will be recruited from community mental health clinics in the local area. The sample will consist of 100 adults aged 18-65 years old who meet the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder. Participants will be randomly assigned to either the experimental group or the control group.
Intervention :
The experimental group will receive 12 weekly sessions of CBT, each lasting 60 minutes. The intervention will be delivered by licensed mental health professionals who have been trained in CBT. The control group will receive no intervention during the study period.
Data Collection:
Quantitative data will be collected through the use of standardized measures such as the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7). Data will be collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at a 3-month follow-up. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a subset of participants from the experimental group. The interviews will be conducted at the end of the intervention period, and will explore participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-tests, and mixed-model analyses of variance (ANOVA) to assess the effectiveness of the intervention. Qualitative data will be analyzed using thematic analysis to identify common themes and patterns in participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Ethical Considerations:
This study will comply with ethical guidelines for research involving human subjects. Participants will provide informed consent before participating in the study, and their privacy and confidentiality will be protected throughout the study. Any adverse events or reactions will be reported and managed appropriately.
Data Management:
All data collected will be kept confidential and stored securely using password-protected databases. Identifying information will be removed from qualitative data transcripts to ensure participants’ anonymity.
Limitations:
One potential limitation of this study is that it only focuses on one type of psychotherapy, CBT, and may not generalize to other types of therapy or interventions. Another limitation is that the study will only include participants from community mental health clinics, which may not be representative of the general population.
Conclusion:
This research aims to investigate the effectiveness of CBT in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. By using a randomized controlled trial and a mixed-methods approach, the study will provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the relationship between CBT and depression. The results of this study will have important implications for the development of effective treatments for depression in clinical settings.
How to Write Research Methodology
Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It’s an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are the steps to write a research methodology:
- Start by explaining your research question: Begin the methodology section by restating your research question and explaining why it’s important. This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods.
- Describe your research design: Explain the overall approach you used to conduct research. This could be a qualitative or quantitative research design, experimental or non-experimental, case study or survey, etc. Discuss the advantages and limitations of the chosen design.
- Discuss your sample: Describe the participants or subjects you included in your study. Include details such as their demographics, sampling method, sample size, and any exclusion criteria used.
- Describe your data collection methods : Explain how you collected data from your participants. This could include surveys, interviews, observations, questionnaires, or experiments. Include details on how you obtained informed consent, how you administered the tools, and how you minimized the risk of bias.
- Explain your data analysis techniques: Describe the methods you used to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, content analysis, thematic analysis, or discourse analysis. Explain how you dealt with missing data, outliers, and any other issues that arose during the analysis.
- Discuss the validity and reliability of your research : Explain how you ensured the validity and reliability of your study. This could include measures such as triangulation, member checking, peer review, or inter-coder reliability.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your research: Discuss any limitations of your study, including any potential threats to validity or generalizability. This helps readers understand the scope of your findings and how they might apply to other contexts.
- Provide a summary: End the methodology section by summarizing the methods and techniques you used to conduct your research. This provides a clear overview of your research methodology and helps readers understand the process you followed to arrive at your findings.
When to Write Research Methodology
Research methodology is typically written after the research proposal has been approved and before the actual research is conducted. It should be written prior to data collection and analysis, as it provides a clear roadmap for the research project.
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
The methodology should be written in a clear and concise manner, and it should be based on established research practices and standards. It is important to provide enough detail so that the reader can understand how the research was conducted and evaluate the validity of the results.
Applications of Research Methodology
Here are some of the applications of research methodology:
- To identify the research problem: Research methodology is used to identify the research problem, which is the first step in conducting any research.
- To design the research: Research methodology helps in designing the research by selecting the appropriate research method, research design, and sampling technique.
- To collect data: Research methodology provides a systematic approach to collect data from primary and secondary sources.
- To analyze data: Research methodology helps in analyzing the collected data using various statistical and non-statistical techniques.
- To test hypotheses: Research methodology provides a framework for testing hypotheses and drawing conclusions based on the analysis of data.
- To generalize findings: Research methodology helps in generalizing the findings of the research to the target population.
- To develop theories : Research methodology is used to develop new theories and modify existing theories based on the findings of the research.
- To evaluate programs and policies : Research methodology is used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies by collecting data and analyzing it.
- To improve decision-making: Research methodology helps in making informed decisions by providing reliable and valid data.
Purpose of Research Methodology
Research methodology serves several important purposes, including:
- To guide the research process: Research methodology provides a systematic framework for conducting research. It helps researchers to plan their research, define their research questions, and select appropriate methods and techniques for collecting and analyzing data.
- To ensure research quality: Research methodology helps researchers to ensure that their research is rigorous, reliable, and valid. It provides guidelines for minimizing bias and error in data collection and analysis, and for ensuring that research findings are accurate and trustworthy.
- To replicate research: Research methodology provides a clear and detailed account of the research process, making it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings.
- To advance knowledge: Research methodology enables researchers to generate new knowledge and to contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. It provides a means for testing hypotheses, exploring new ideas, and discovering new insights.
- To inform decision-making: Research methodology provides evidence-based information that can inform policy and decision-making in a variety of fields, including medicine, public health, education, and business.
Advantages of Research Methodology
Research methodology has several advantages that make it a valuable tool for conducting research in various fields. Here are some of the key advantages of research methodology:
- Systematic and structured approach : Research methodology provides a systematic and structured approach to conducting research, which ensures that the research is conducted in a rigorous and comprehensive manner.
- Objectivity : Research methodology aims to ensure objectivity in the research process, which means that the research findings are based on evidence and not influenced by personal bias or subjective opinions.
- Replicability : Research methodology ensures that research can be replicated by other researchers, which is essential for validating research findings and ensuring their accuracy.
- Reliability : Research methodology aims to ensure that the research findings are reliable, which means that they are consistent and can be depended upon.
- Validity : Research methodology ensures that the research findings are valid, which means that they accurately reflect the research question or hypothesis being tested.
- Efficiency : Research methodology provides a structured and efficient way of conducting research, which helps to save time and resources.
- Flexibility : Research methodology allows researchers to choose the most appropriate research methods and techniques based on the research question, data availability, and other relevant factors.
- Scope for innovation: Research methodology provides scope for innovation and creativity in designing research studies and developing new research techniques.
Research Methodology Vs Research Methods
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Thesis Outline – Example, Template and Writing...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...
- 7 Data Collection Methods & Tools For Research

- Data Collection
The underlying need for Data collection is to capture quality evidence that seeks to answer all the questions that have been posed. Through data collection businesses or management can deduce quality information that is a prerequisite for making informed decisions.
To improve the quality of information, it is expedient that data is collected so that you can draw inferences and make informed decisions on what is considered factual.
At the end of this article, you would understand why picking the best data collection method is necessary for achieving your set objective.
Sign up on Formplus Builder to create your preferred online surveys or questionnaire for data collection. You don’t need to be tech-savvy! Start creating quality questionnaires with Formplus.
What is Data Collection?
Data collection is a methodical process of gathering and analyzing specific information to proffer solutions to relevant questions and evaluate the results. It focuses on finding out all there is to a particular subject matter. Data is collected to be further subjected to hypothesis testing which seeks to explain a phenomenon.
Hypothesis testing eliminates assumptions while making a proposition from the basis of reason.

For collectors of data, there is a range of outcomes for which the data is collected. But the key purpose for which data is collected is to put a researcher in a vantage position to make predictions about future probabilities and trends.
The core forms in which data can be collected are primary and secondary data. While the former is collected by a researcher through first-hand sources, the latter is collected by an individual other than the user.
Types of Data Collection
Before broaching the subject of the various types of data collection. It is pertinent to note that data collection in itself falls under two broad categories; Primary data collection and secondary data collection.
Primary Data Collection
Primary data collection by definition is the gathering of raw data collected at the source. It is a process of collecting the original data collected by a researcher for a specific research purpose. It could be further analyzed into two segments; qualitative research and quantitative data collection methods.
- Qualitative Research Method
The qualitative research methods of data collection do not involve the collection of data that involves numbers or a need to be deduced through a mathematical calculation, rather it is based on the non-quantifiable elements like the feeling or emotion of the researcher. An example of such a method is an open-ended questionnaire.

- Quantitative Method
Quantitative methods are presented in numbers and require a mathematical calculation to deduce. An example would be the use of a questionnaire with close-ended questions to arrive at figures to be calculated Mathematically. Also, methods of correlation and regression, mean, mode and median.

Read Also: 15 Reasons to Choose Quantitative over Qualitative Research
Secondary Data Collection
Secondary data collection, on the other hand, is referred to as the gathering of second-hand data collected by an individual who is not the original user. It is the process of collecting data that is already existing, be it already published books, journals, and/or online portals. In terms of ease, it is much less expensive and easier to collect.
Your choice between Primary data collection and secondary data collection depends on the nature, scope, and area of your research as well as its aims and objectives.
Importance of Data Collection
There are a bunch of underlying reasons for collecting data, especially for a researcher. Walking you through them, here are a few reasons;
- Integrity of the Research
A key reason for collecting data, be it through quantitative or qualitative methods is to ensure that the integrity of the research question is indeed maintained.
- Reduce the likelihood of errors
The correct use of appropriate data collection of methods reduces the likelihood of errors consistent with the results.
- Decision Making
To minimize the risk of errors in decision-making, it is important that accurate data is collected so that the researcher doesn’t make uninformed decisions.
- Save Cost and Time
Data collection saves the researcher time and funds that would otherwise be misspent without a deeper understanding of the topic or subject matter.
- To support a need for a new idea, change, and/or innovation
To prove the need for a change in the norm or the introduction of new information that will be widely accepted, it is important to collect data as evidence to support these claims.
What is a Data Collection Tool?
Data collection tools refer to the devices/instruments used to collect data, such as a paper questionnaire or computer-assisted interviewing system. Case Studies, Checklists, Interviews, Observation sometimes, and Surveys or Questionnaires are all tools used to collect data.
It is important to decide on the tools for data collection because research is carried out in different ways and for different purposes. The objective behind data collection is to capture quality evidence that allows analysis to lead to the formulation of convincing and credible answers to the posed questions.
The objective behind data collection is to capture quality evidence that allows analysis to lead to the formulation of convincing and credible answers to the questions that have been posed – Click to Tweet
The Formplus online data collection tool is perfect for gathering primary data, i.e. raw data collected from the source. You can easily get data with at least three data collection methods with our online and offline data-gathering tool. I.e Online Questionnaires , Focus Groups, and Reporting.
In our previous articles, we’ve explained why quantitative research methods are more effective than qualitative methods . However, with the Formplus data collection tool, you can gather all types of primary data for academic, opinion or product research.
Top Data Collection Methods and Tools for Academic, Opinion, or Product Research
The following are the top 7 data collection methods for Academic, Opinion-based, or product research. Also discussed in detail are the nature, pros, and cons of each one. At the end of this segment, you will be best informed about which method best suits your research.
An interview is a face-to-face conversation between two individuals with the sole purpose of collecting relevant information to satisfy a research purpose. Interviews are of different types namely; Structured, Semi-structured , and unstructured with each having a slight variation from the other.
Use this interview consent form template to let an interviewee give you consent to use data gotten from your interviews for investigative research purposes.
- Structured Interviews – Simply put, it is a verbally administered questionnaire. In terms of depth, it is surface level and is usually completed within a short period. For speed and efficiency, it is highly recommendable, but it lacks depth.
- Semi-structured Interviews – In this method, there subsist several key questions which cover the scope of the areas to be explored. It allows a little more leeway for the researcher to explore the subject matter.
- Unstructured Interviews – It is an in-depth interview that allows the researcher to collect a wide range of information with a purpose. An advantage of this method is the freedom it gives a researcher to combine structure with flexibility even though it is more time-consuming.
- In-depth information
- Freedom of flexibility
- Accurate data.
- Time-consuming
- Expensive to collect.
What are The Best Data Collection Tools for Interviews?
For collecting data through interviews, here are a few tools you can use to easily collect data.
- Audio Recorder
An audio recorder is used for recording sound on disc, tape, or film. Audio information can meet the needs of a wide range of people, as well as provide alternatives to print data collection tools.
- Digital Camera
An advantage of a digital camera is that it can be used for transmitting those images to a monitor screen when the need arises.
A camcorder is used for collecting data through interviews. It provides a combination of both an audio recorder and a video camera. The data provided is qualitative in nature and allows the respondents to answer questions asked exhaustively. If you need to collect sensitive information during an interview, a camcorder might not work for you as you would need to maintain your subject’s privacy.
Want to conduct an interview for qualitative data research or a special report? Use this online interview consent form template to allow the interviewee to give their consent before you use the interview data for research or report. With premium features like e-signature, upload fields, form security, etc., Formplus Builder is the perfect tool to create your preferred online consent forms without coding experience.
- QUESTIONNAIRES
This is the process of collecting data through an instrument consisting of a series of questions and prompts to receive a response from the individuals it is administered to. Questionnaires are designed to collect data from a group.
For clarity, it is important to note that a questionnaire isn’t a survey, rather it forms a part of it. A survey is a process of data gathering involving a variety of data collection methods, including a questionnaire.
On a questionnaire, there are three kinds of questions used. They are; fixed-alternative, scale, and open-ended. With each of the questions tailored to the nature and scope of the research.
- Can be administered in large numbers and is cost-effective.
- It can be used to compare and contrast previous research to measure change.
- Easy to visualize and analyze.
- Questionnaires offer actionable data.
- Respondent identity is protected.
- Questionnaires can cover all areas of a topic.
- Relatively inexpensive.
- Answers may be dishonest or the respondents lose interest midway.
- Questionnaires can’t produce qualitative data.
- Questions might be left unanswered.
- Respondents may have a hidden agenda.
- Not all questions can be analyzed easily.
What are the Best Data Collection Tools for Questionnaires?
- Formplus Online Questionnaire
Formplus lets you create powerful forms to help you collect the information you need. Formplus helps you create the online forms that you like. The Formplus online questionnaire form template to get actionable trends and measurable responses. Conduct research, optimize knowledge of your brand or just get to know an audience with this form template. The form template is fast, free and fully customizable.
- Paper Questionnaire
A paper questionnaire is a data collection tool consisting of a series of questions and/or prompts for the purpose of gathering information from respondents. Mostly designed for statistical analysis of the responses, they can also be used as a form of data collection.
By definition, data reporting is the process of gathering and submitting data to be further subjected to analysis. The key aspect of data reporting is reporting accurate data because inaccurate data reporting leads to uninformed decision-making.
- Informed decision-making.
- Easily accessible.
- Self-reported answers may be exaggerated.
- The results may be affected by bias.
- Respondents may be too shy to give out all the details.
- Inaccurate reports will lead to uninformed decisions.
What are the Best Data Collection Tools for Reporting?
Reporting tools enable you to extract and present data in charts, tables, and other visualizations so users can find useful information. You could source data for reporting from Non-Governmental Organizations (NGO) reports, newspapers, website articles, and hospital records.
- NGO Reports
Contained in NGO report is an in-depth and comprehensive report on the activities carried out by the NGO, covering areas such as business and human rights. The information contained in these reports is research-specific and forms an acceptable academic base for collecting data. NGOs often focus on development projects which are organized to promote particular causes.
Newspaper data are relatively easy to collect and are sometimes the only continuously available source of event data. Even though there is a problem of bias in newspaper data, it is still a valid tool in collecting data for Reporting.
- Website Articles
Gathering and using data contained in website articles is also another tool for data collection. Collecting data from web articles is a quicker and less expensive data collection Two major disadvantages of using this data reporting method are biases inherent in the data collection process and possible security/confidentiality concerns.
- Hospital Care records
Health care involves a diverse set of public and private data collection systems, including health surveys, administrative enrollment and billing records, and medical records, used by various entities, including hospitals, CHCs, physicians, and health plans. The data provided is clear, unbiased and accurate, but must be obtained under legal means as medical data is kept with the strictest regulations.
- EXISTING DATA
This is the introduction of new investigative questions in addition to/other than the ones originally used when the data was initially gathered. It involves adding measurement to a study or research. An example would be sourcing data from an archive.
- Accuracy is very high.
- Easily accessible information.
- Problems with evaluation.
- Difficulty in understanding.
What are the Best Data Collection Tools for Existing Data?
The concept of Existing data means that data is collected from existing sources to investigate research questions other than those for which the data were originally gathered. Tools to collect existing data include:
- Research Journals – Unlike newspapers and magazines, research journals are intended for an academic or technical audience, not general readers. A journal is a scholarly publication containing articles written by researchers, professors, and other experts.
- Surveys – A survey is a data collection tool for gathering information from a sample population, with the intention of generalizing the results to a larger population. Surveys have a variety of purposes and can be carried out in many ways depending on the objectives to be achieved.
- OBSERVATION
This is a data collection method by which information on a phenomenon is gathered through observation. The nature of the observation could be accomplished either as a complete observer, an observer as a participant, a participant as an observer, or as a complete participant. This method is a key base for formulating a hypothesis.
- Easy to administer.
- There subsists a greater accuracy with results.
- It is a universally accepted practice.
- It diffuses the situation of the unwillingness of respondents to administer a report.
- It is appropriate for certain situations.
- Some phenomena aren’t open to observation.
- It cannot be relied upon.
- Bias may arise.
- It is expensive to administer.
- Its validity cannot be predicted accurately.
What are the Best Data Collection Tools for Observation?
Observation involves the active acquisition of information from a primary source. Observation can also involve the perception and recording of data via the use of scientific instruments. The best tools for Observation are:
- Checklists – state-specific criteria, that allow users to gather information and make judgments about what they should know in relation to the outcomes. They offer systematic ways of collecting data about specific behaviors, knowledge, and skills.
- Direct observation – This is an observational study method of collecting evaluative information. The evaluator watches the subject in his or her usual environment without altering that environment.
FOCUS GROUPS
The opposite of quantitative research which involves numerical-based data, this data collection method focuses more on qualitative research. It falls under the primary category of data based on the feelings and opinions of the respondents. This research involves asking open-ended questions to a group of individuals usually ranging from 6-10 people, to provide feedback.
- Information obtained is usually very detailed.
- Cost-effective when compared to one-on-one interviews.
- It reflects speed and efficiency in the supply of results.
- Lacking depth in covering the nitty-gritty of a subject matter.
- Bias might still be evident.
- Requires interviewer training
- The researcher has very little control over the outcome.
- A few vocal voices can drown out the rest.
- Difficulty in assembling an all-inclusive group.
What are the Best Data Collection Tools for Focus Groups?
A focus group is a data collection method that is tightly facilitated and structured around a set of questions. The purpose of the meeting is to extract from the participants’ detailed responses to these questions. The best tools for tackling Focus groups are:
- Two-Way – One group watches another group answer the questions posed by the moderator. After listening to what the other group has to offer, the group that listens is able to facilitate more discussion and could potentially draw different conclusions .
- Dueling-Moderator – There are two moderators who play the devil’s advocate. The main positive of the dueling-moderator focus group is to facilitate new ideas by introducing new ways of thinking and varying viewpoints.
- COMBINATION RESEARCH
This method of data collection encompasses the use of innovative methods to enhance participation in both individuals and groups. Also under the primary category, it is a combination of Interviews and Focus Groups while collecting qualitative data . This method is key when addressing sensitive subjects.
- Encourage participants to give responses.
- It stimulates a deeper connection between participants.
- The relative anonymity of respondents increases participation.
- It improves the richness of the data collected.
- It costs the most out of all the top 7.
- It’s the most time-consuming.
What are the Best Data Collection Tools for Combination Research?
The Combination Research method involves two or more data collection methods, for instance, interviews as well as questionnaires or a combination of semi-structured telephone interviews and focus groups. The best tools for combination research are:
- Online Survey – The two tools combined here are online interviews and the use of questionnaires. This is a questionnaire that the target audience can complete over the Internet. It is timely, effective, and efficient. Especially since the data to be collected is quantitative in nature.
- Dual-Moderator – The two tools combined here are focus groups and structured questionnaires. The structured questionnaires give a direction as to where the research is headed while two moderators take charge of the proceedings. Whilst one ensures the focus group session progresses smoothly, the other makes sure that the topics in question are all covered. Dual-moderator focus groups typically result in a more productive session and essentially lead to an optimum collection of data.
Why Formplus is the Best Data Collection Tool
- Vast Options for Form Customization
With Formplus, you can create your unique survey form. With options to change themes, font color, font, font type, layout, width, and more, you can create an attractive survey form. The builder also gives you as many features as possible to choose from and you do not need to be a graphic designer to create a form.
- Extensive Analytics
Form Analytics, a feature in formplus helps you view the number of respondents, unique visits, total visits, abandonment rate, and average time spent before submission. This tool eliminates the need for a manual calculation of the received data and/or responses as well as the conversion rate for your poll.
- Embed Survey Form on Your Website
Copy the link to your form and embed it as an iframe which will automatically load as your website loads, or as a popup that opens once the respondent clicks on the link. Embed the link on your Twitter page to give instant access to your followers.
.png?resize=845%2C418&ssl=1)
- Geolocation Support
The geolocation feature on Formplus lets you ascertain where individual responses are coming. It utilises Google Maps to pinpoint the longitude and latitude of the respondent, to the nearest accuracy, along with the responses.
- Multi-Select feature
This feature helps to conserve horizontal space as it allows you to put multiple options in one field. This translates to including more information on the survey form.
Read Also: 10 Reasons to Use Formplus for Online Data Collection
How to Use Formplus to collect online data in 7 simple steps.
- Register or sign up on Formplus builder : Start creating your preferred questionnaire or survey by signing up with either your Google, Facebook, or Email account.

Formplus gives you a free plan with basic features you can use to collect online data. Pricing plans with vast features starts at $20 monthly, with reasonable discounts for Education and Non-Profit Organizations.
2. Input your survey title and use the form builder choice options to start creating your surveys.
Use the choice option fields like single select, multiple select, checkbox, radio, and image choices to create your preferred multi-choice surveys online.

3. Do you want customers to rate any of your products or services delivery?
Use the rating to allow survey respondents rate your products or services. This is an ideal quantitative research method of collecting data.

4. Beautify your online questionnaire with Formplus Customisation features.

- Change the theme color
- Add your brand’s logo and image to the forms
- Change the form width and layout
- Edit the submission button if you want
- Change text font color and sizes
- Do you have already made custom CSS to beautify your questionnaire? If yes, just copy and paste it to the CSS option.
5. Edit your survey questionnaire settings for your specific needs
Choose where you choose to store your files and responses. Select a submission deadline, choose a timezone, limit respondents’ responses, enable Captcha to prevent spam, and collect location data of customers.

Set an introductory message to respondents before they begin the survey, toggle the “start button” post final submission message or redirect respondents to another page when they submit their questionnaires.
Change the Email Notifications inventory and initiate an autoresponder message to all your survey questionnaire respondents. You can also transfer your forms to other users who can become form administrators.
6. Share links to your survey questionnaire page with customers.
There’s an option to copy and share the link as “Popup” or “Embed code” The data collection tool automatically creates a QR Code for Survey Questionnaire which you can download and share as appropriate.

Congratulations if you’ve made it to this stage. You can start sharing the link to your survey questionnaire with your customers.
7. View your Responses to the Survey Questionnaire
Toggle with the presentation of your summary from the options. Whether as a single, table or cards.

8. Allow Formplus Analytics to interpret your Survey Questionnaire Data

With online form builder analytics, a business can determine;
- The number of times the survey questionnaire was filled
- The number of customers reached
- Abandonment Rate: The rate at which customers exit the form without submitting it.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of customers who completed the online form
- Average time spent per visit
- Location of customers/respondents.
- The type of device used by the customer to complete the survey questionnaire.
7 Tips to Create The Best Surveys For Data Collections
- Define the goal of your survey – Once the goal of your survey is outlined, it will aid in deciding which questions are the top priority. A clear attainable goal would, for example, mirror a clear reason as to why something is happening. e.g. “The goal of this survey is to understand why Employees are leaving an establishment.”
- Use close-ended clearly defined questions – Avoid open-ended questions and ensure you’re not suggesting your preferred answer to the respondent. If possible offer a range of answers with choice options and ratings.
- Survey outlook should be attractive and Inviting – An attractive-looking survey encourages a higher number of recipients to respond to the survey. Check out Formplus Builder for colorful options to integrate into your survey design. You could use images and videos to keep participants glued to their screens.
- Assure Respondents about the safety of their data – You want your respondents to be assured whilst disclosing details of their personal information to you. It’s your duty to inform the respondents that the data they provide is confidential and only collected for the purpose of research.
- Ensure your survey can be completed in record time – Ideally, in a typical survey, users should be able to respond in 100 seconds. It is pertinent to note that they, the respondents, are doing you a favor. Don’t stress them. Be brief and get straight to the point.
- Do a trial survey – Preview your survey before sending out your surveys to the intended respondents. Make a trial version which you’ll send to a few individuals. Based on their responses, you can draw inferences and decide whether or not your survey is ready for the big time.
- Attach a reward upon completion for users – Give your respondents something to look forward to at the end of the survey. Think of it as a penny for their troubles. It could well be the encouragement they need to not abandon the survey midway.
Try out Formplus today . You can start making your own surveys with the Formplus online survey builder. By applying these tips, you will definitely get the most out of your online surveys.
Top Survey Templates For Data Collection
- Customer Satisfaction Survey Template
On the template, you can collect data to measure customer satisfaction over key areas like the commodity purchase and the level of service they received. It also gives insight as to which products the customer enjoyed, how often they buy such a product, and whether or not the customer is likely to recommend the product to a friend or acquaintance.
- Demographic Survey Template
With this template, you would be able to measure, with accuracy, the ratio of male to female, age range, and the number of unemployed persons in a particular country as well as obtain their personal details such as names and addresses.
Respondents are also able to state their religious and political views about the country under review.
- Feedback Form Template
Contained in the template for the online feedback form is the details of a product and/or service used. Identifying this product or service and documenting how long the customer has used them.
The overall satisfaction is measured as well as the delivery of the services. The likelihood that the customer also recommends said product is also measured.
- Online Questionnaire Template
The online questionnaire template houses the respondent’s data as well as educational qualifications to collect information to be used for academic research.
Respondents can also provide their gender, race, and field of study as well as present living conditions as prerequisite data for the research study.
- Student Data Sheet Form Template
The template is a data sheet containing all the relevant information of a student. The student’s name, home address, guardian’s name, record of attendance as well as performance in school is well represented on this template. This is a perfect data collection method to deploy for a school or an education organization.
Also included is a record for interaction with others as well as a space for a short comment on the overall performance and attitude of the student.
- Interview Consent Form Template
This online interview consent form template allows the interviewee to sign off their consent to use the interview data for research or report to journalists. With premium features like short text fields, upload, e-signature, etc., Formplus Builder is the perfect tool to create your preferred online consent forms without coding experience.
What is the Best Data Collection Method for Qualitative Data?
Answer: Combination Research
The best data collection method for a researcher for gathering qualitative data which generally is data relying on the feelings, opinions, and beliefs of the respondents would be Combination Research.
The reason why combination research is the best fit is that it encompasses the attributes of Interviews and Focus Groups. It is also useful when gathering data that is sensitive in nature. It can be described as an all-purpose quantitative data collection method.
Above all, combination research improves the richness of data collected when compared with other data collection methods for qualitative data.

What is the Best Data Collection Method for Quantitative Research Data?
Ans: Questionnaire
The best data collection method a researcher can employ in gathering quantitative data which takes into consideration data that can be represented in numbers and figures that can be deduced mathematically is the Questionnaire.
These can be administered to a large number of respondents while saving costs. For quantitative data that may be bulky or voluminous in nature, the use of a Questionnaire makes such data easy to visualize and analyze.
Another key advantage of the Questionnaire is that it can be used to compare and contrast previous research work done to measure changes.
Technology-Enabled Data Collection Methods
There are so many diverse methods available now in the world because technology has revolutionized the way data is being collected. It has provided efficient and innovative methods that anyone, especially researchers and organizations. Below are some technology-enabled data collection methods:
- Online Surveys: Online surveys have gained popularity due to their ease of use and wide reach. You can distribute them through email, social media, or embed them on websites. Online surveys allow you to quickly complete data collection, automated data capture, and real-time analysis. Online surveys also offer features like skip logic, validation checks, and multimedia integration.
- Mobile Surveys: With the widespread use of smartphones, mobile surveys’ popularity is also on the rise. Mobile surveys leverage the capabilities of mobile devices, and this allows respondents to participate at their convenience. This includes multimedia elements, location-based information, and real-time feedback. Mobile surveys are the best for capturing in-the-moment experiences or opinions.
- Social Media Listening: Social media platforms are a good source of unstructured data that you can analyze to gain insights into customer sentiment and trends. Social media listening involves monitoring and analyzing social media conversations, mentions, and hashtags to understand public opinion, identify emerging topics, and assess brand reputation.
- Wearable Devices and Sensors: You can embed wearable devices, such as fitness trackers or smartwatches, and sensors in everyday objects to capture continuous data on various physiological and environmental variables. This data can provide you with insights into health behaviors, activity patterns, sleep quality, and environmental conditions, among others.
- Big Data Analytics: Big data analytics leverages large volumes of structured and unstructured data from various sources, such as transaction records, social media, and internet browsing. Advanced analytics techniques, like machine learning and natural language processing, can extract meaningful insights and patterns from this data, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions.
Read Also: How Technology is Revolutionizing Data Collection
Faulty Data Collection Practices – Common Mistakes & Sources of Error
While technology-enabled data collection methods offer numerous advantages, there are some pitfalls and sources of error that you should be aware of. Here are some common mistakes and sources of error in data collection:
- Population Specification Error: Population specification error occurs when the target population is not clearly defined or misidentified. This error leads to a mismatch between the research objectives and the actual population being studied, resulting in biased or inaccurate findings.
- Sample Frame Error: Sample frame error occurs when the sampling frame, the list or source from which the sample is drawn, does not adequately represent the target population. This error can introduce selection bias and affect the generalizability of the findings.
- Selection Error: Selection error occurs when the process of selecting participants or units for the study introduces bias. It can happen due to nonrandom sampling methods, inadequate sampling techniques, or self-selection bias. Selection error compromises the representativeness of the sample and affects the validity of the results.
- Nonresponse Error: Nonresponse error occurs when selected participants choose not to participate or fail to respond to the data collection effort. Nonresponse bias can result in an unrepresentative sample if those who choose not to respond differ systematically from those who do respond. Efforts should be made to mitigate nonresponse and encourage participation to minimize this error.
- Measurement Error: Measurement error arises from inaccuracies or inconsistencies in the measurement process. It can happen due to poorly designed survey instruments, ambiguous questions, respondent bias, or errors in data entry or coding. Measurement errors can lead to distorted or unreliable data, affecting the validity and reliability of the findings.
In order to mitigate these errors and ensure high-quality data collection, you should carefully plan your data collection procedures, and validate measurement tools. You should also use appropriate sampling techniques, employ randomization where possible, and minimize nonresponse through effective communication and incentives. Ensure you conduct regular checks and implement validation processes, and data cleaning procedures to identify and rectify errors during data analysis.
Best Practices for Data Collection
- Clearly Define Objectives: Clearly define the research objectives and questions to guide the data collection process. This helps ensure that the collected data aligns with the research goals and provides relevant insights.
- Plan Ahead: Develop a detailed data collection plan that includes the timeline, resources needed, and specific procedures to follow. This helps maintain consistency and efficiency throughout the data collection process.
- Choose the Right Method: Select data collection methods that are appropriate for the research objectives and target population. Consider factors such as feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to capture the required data accurately.
- Pilot Test : Before full-scale data collection, conduct a pilot test to identify any issues with the data collection instruments or procedures. This allows for refinement and improvement before data collection with the actual sample.
- Train Data Collectors: If data collection involves human interaction, ensure that data collectors are properly trained on the data collection protocols, instruments, and ethical considerations. Consistent training helps minimize errors and maintain data quality.
- Maintain Consistency: Follow standardized procedures throughout the data collection process to ensure consistency across data collectors and time. This includes using consistent measurement scales, instructions, and data recording methods.
- Minimize Bias: Be aware of potential sources of bias in data collection and take steps to minimize their impact. Use randomization techniques, employ diverse data collectors, and implement strategies to mitigate response biases.
- Ensure Data Quality: Implement quality control measures to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of the collected data. Conduct regular checks for data entry errors, inconsistencies, and missing values.
- Maintain Data Confidentiality: Protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants’ data by implementing appropriate security measures. Ensure compliance with data protection regulations and obtain informed consent from participants.
- Document the Process: Keep detailed documentation of the data collection process, including any deviations from the original plan, challenges encountered, and decisions made. This documentation facilitates transparency, replicability, and future analysis.
FAQs about Data Collection
- What are secondary sources of data collection? Secondary sources of data collection are defined as the data that has been previously gathered and is available for your use as a researcher. These sources can include published research papers, government reports, statistical databases, and other existing datasets.
- What are the primary sources of data collection? Primary sources of data collection involve collecting data directly from the original source also known as the firsthand sources. You can do this through surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, or other direct interactions with individuals or subjects of study.
- How many types of data are there? There are two main types of data: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative data is non-numeric and it includes information in the form of words, images, or descriptions. Quantitative data, on the other hand, is numeric and you can measure and analyze it statistically.
Sign up on Formplus Builder to create your preferred online surveys or questionnaire for data collection. You don’t need to be tech-savvy!

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- academic research
- Data collection method
- data collection techniques
- data collection tool
- data collection tools
- field data collection
- online data collection tool
- product research
- qualitative research data
- quantitative research data
- scientific research
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
Data Collection Plan: Definition + Steps to Do It
Introduction A data collection plan is a way to get specific information on your audience. You can use it to better understand what they...

Data Collection Sheet: Types + [Template Examples]
Simple guide on data collection sheet. Types, tools, and template examples.
How Technology is Revolutionizing Data Collection
As global industrialization continues to transform, it is becoming evident that there is a ubiquity of large datasets driven by the need...
User Research: Definition, Methods, Tools and Guide
In this article, you’ll learn to provide value to your target market with user research. As a bonus, we’ve added user research tools and...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Can J Hosp Pharm
- v.68(3); May-Jun 2015

Qualitative Research: Data Collection, Analysis, and Management
Introduction.
In an earlier paper, 1 we presented an introduction to using qualitative research methods in pharmacy practice. In this article, we review some principles of the collection, analysis, and management of qualitative data to help pharmacists interested in doing research in their practice to continue their learning in this area. Qualitative research can help researchers to access the thoughts and feelings of research participants, which can enable development of an understanding of the meaning that people ascribe to their experiences. Whereas quantitative research methods can be used to determine how many people undertake particular behaviours, qualitative methods can help researchers to understand how and why such behaviours take place. Within the context of pharmacy practice research, qualitative approaches have been used to examine a diverse array of topics, including the perceptions of key stakeholders regarding prescribing by pharmacists and the postgraduation employment experiences of young pharmacists (see “Further Reading” section at the end of this article).
In the previous paper, 1 we outlined 3 commonly used methodologies: ethnography 2 , grounded theory 3 , and phenomenology. 4 Briefly, ethnography involves researchers using direct observation to study participants in their “real life” environment, sometimes over extended periods. Grounded theory and its later modified versions (e.g., Strauss and Corbin 5 ) use face-to-face interviews and interactions such as focus groups to explore a particular research phenomenon and may help in clarifying a less-well-understood problem, situation, or context. Phenomenology shares some features with grounded theory (such as an exploration of participants’ behaviour) and uses similar techniques to collect data, but it focuses on understanding how human beings experience their world. It gives researchers the opportunity to put themselves in another person’s shoes and to understand the subjective experiences of participants. 6 Some researchers use qualitative methodologies but adopt a different standpoint, and an example of this appears in the work of Thurston and others, 7 discussed later in this paper.
Qualitative work requires reflection on the part of researchers, both before and during the research process, as a way of providing context and understanding for readers. When being reflexive, researchers should not try to simply ignore or avoid their own biases (as this would likely be impossible); instead, reflexivity requires researchers to reflect upon and clearly articulate their position and subjectivities (world view, perspectives, biases), so that readers can better understand the filters through which questions were asked, data were gathered and analyzed, and findings were reported. From this perspective, bias and subjectivity are not inherently negative but they are unavoidable; as a result, it is best that they be articulated up-front in a manner that is clear and coherent for readers.
THE PARTICIPANT’S VIEWPOINT
What qualitative study seeks to convey is why people have thoughts and feelings that might affect the way they behave. Such study may occur in any number of contexts, but here, we focus on pharmacy practice and the way people behave with regard to medicines use (e.g., to understand patients’ reasons for nonadherence with medication therapy or to explore physicians’ resistance to pharmacists’ clinical suggestions). As we suggested in our earlier article, 1 an important point about qualitative research is that there is no attempt to generalize the findings to a wider population. Qualitative research is used to gain insights into people’s feelings and thoughts, which may provide the basis for a future stand-alone qualitative study or may help researchers to map out survey instruments for use in a quantitative study. It is also possible to use different types of research in the same study, an approach known as “mixed methods” research, and further reading on this topic may be found at the end of this paper.
The role of the researcher in qualitative research is to attempt to access the thoughts and feelings of study participants. This is not an easy task, as it involves asking people to talk about things that may be very personal to them. Sometimes the experiences being explored are fresh in the participant’s mind, whereas on other occasions reliving past experiences may be difficult. However the data are being collected, a primary responsibility of the researcher is to safeguard participants and their data. Mechanisms for such safeguarding must be clearly articulated to participants and must be approved by a relevant research ethics review board before the research begins. Researchers and practitioners new to qualitative research should seek advice from an experienced qualitative researcher before embarking on their project.
DATA COLLECTION
Whatever philosophical standpoint the researcher is taking and whatever the data collection method (e.g., focus group, one-to-one interviews), the process will involve the generation of large amounts of data. In addition to the variety of study methodologies available, there are also different ways of making a record of what is said and done during an interview or focus group, such as taking handwritten notes or video-recording. If the researcher is audio- or video-recording data collection, then the recordings must be transcribed verbatim before data analysis can begin. As a rough guide, it can take an experienced researcher/transcriber 8 hours to transcribe one 45-minute audio-recorded interview, a process than will generate 20–30 pages of written dialogue.
Many researchers will also maintain a folder of “field notes” to complement audio-taped interviews. Field notes allow the researcher to maintain and comment upon impressions, environmental contexts, behaviours, and nonverbal cues that may not be adequately captured through the audio-recording; they are typically handwritten in a small notebook at the same time the interview takes place. Field notes can provide important context to the interpretation of audio-taped data and can help remind the researcher of situational factors that may be important during data analysis. Such notes need not be formal, but they should be maintained and secured in a similar manner to audio tapes and transcripts, as they contain sensitive information and are relevant to the research. For more information about collecting qualitative data, please see the “Further Reading” section at the end of this paper.
DATA ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT
If, as suggested earlier, doing qualitative research is about putting oneself in another person’s shoes and seeing the world from that person’s perspective, the most important part of data analysis and management is to be true to the participants. It is their voices that the researcher is trying to hear, so that they can be interpreted and reported on for others to read and learn from. To illustrate this point, consider the anonymized transcript excerpt presented in Appendix 1 , which is taken from a research interview conducted by one of the authors (J.S.). We refer to this excerpt throughout the remainder of this paper to illustrate how data can be managed, analyzed, and presented.
Interpretation of Data
Interpretation of the data will depend on the theoretical standpoint taken by researchers. For example, the title of the research report by Thurston and others, 7 “Discordant indigenous and provider frames explain challenges in improving access to arthritis care: a qualitative study using constructivist grounded theory,” indicates at least 2 theoretical standpoints. The first is the culture of the indigenous population of Canada and the place of this population in society, and the second is the social constructivist theory used in the constructivist grounded theory method. With regard to the first standpoint, it can be surmised that, to have decided to conduct the research, the researchers must have felt that there was anecdotal evidence of differences in access to arthritis care for patients from indigenous and non-indigenous backgrounds. With regard to the second standpoint, it can be surmised that the researchers used social constructivist theory because it assumes that behaviour is socially constructed; in other words, people do things because of the expectations of those in their personal world or in the wider society in which they live. (Please see the “Further Reading” section for resources providing more information about social constructivist theory and reflexivity.) Thus, these 2 standpoints (and there may have been others relevant to the research of Thurston and others 7 ) will have affected the way in which these researchers interpreted the experiences of the indigenous population participants and those providing their care. Another standpoint is feminist standpoint theory which, among other things, focuses on marginalized groups in society. Such theories are helpful to researchers, as they enable us to think about things from a different perspective. Being aware of the standpoints you are taking in your own research is one of the foundations of qualitative work. Without such awareness, it is easy to slip into interpreting other people’s narratives from your own viewpoint, rather than that of the participants.
To analyze the example in Appendix 1 , we will adopt a phenomenological approach because we want to understand how the participant experienced the illness and we want to try to see the experience from that person’s perspective. It is important for the researcher to reflect upon and articulate his or her starting point for such analysis; for example, in the example, the coder could reflect upon her own experience as a female of a majority ethnocultural group who has lived within middle class and upper middle class settings. This personal history therefore forms the filter through which the data will be examined. This filter does not diminish the quality or significance of the analysis, since every researcher has his or her own filters; however, by explicitly stating and acknowledging what these filters are, the researcher makes it easer for readers to contextualize the work.
Transcribing and Checking
For the purposes of this paper it is assumed that interviews or focus groups have been audio-recorded. As mentioned above, transcribing is an arduous process, even for the most experienced transcribers, but it must be done to convert the spoken word to the written word to facilitate analysis. For anyone new to conducting qualitative research, it is beneficial to transcribe at least one interview and one focus group. It is only by doing this that researchers realize how difficult the task is, and this realization affects their expectations when asking others to transcribe. If the research project has sufficient funding, then a professional transcriber can be hired to do the work. If this is the case, then it is a good idea to sit down with the transcriber, if possible, and talk through the research and what the participants were talking about. This background knowledge for the transcriber is especially important in research in which people are using jargon or medical terms (as in pharmacy practice). Involving your transcriber in this way makes the work both easier and more rewarding, as he or she will feel part of the team. Transcription editing software is also available, but it is expensive. For example, ELAN (more formally known as EUDICO Linguistic Annotator, developed at the Technical University of Berlin) 8 is a tool that can help keep data organized by linking media and data files (particularly valuable if, for example, video-taping of interviews is complemented by transcriptions). It can also be helpful in searching complex data sets. Products such as ELAN do not actually automatically transcribe interviews or complete analyses, and they do require some time and effort to learn; nonetheless, for some research applications, it may be a valuable to consider such software tools.
All audio recordings should be transcribed verbatim, regardless of how intelligible the transcript may be when it is read back. Lines of text should be numbered. Once the transcription is complete, the researcher should read it while listening to the recording and do the following: correct any spelling or other errors; anonymize the transcript so that the participant cannot be identified from anything that is said (e.g., names, places, significant events); insert notations for pauses, laughter, looks of discomfort; insert any punctuation, such as commas and full stops (periods) (see Appendix 1 for examples of inserted punctuation), and include any other contextual information that might have affected the participant (e.g., temperature or comfort of the room).
Dealing with the transcription of a focus group is slightly more difficult, as multiple voices are involved. One way of transcribing such data is to “tag” each voice (e.g., Voice A, Voice B). In addition, the focus group will usually have 2 facilitators, whose respective roles will help in making sense of the data. While one facilitator guides participants through the topic, the other can make notes about context and group dynamics. More information about group dynamics and focus groups can be found in resources listed in the “Further Reading” section.
Reading between the Lines
During the process outlined above, the researcher can begin to get a feel for the participant’s experience of the phenomenon in question and can start to think about things that could be pursued in subsequent interviews or focus groups (if appropriate). In this way, one participant’s narrative informs the next, and the researcher can continue to interview until nothing new is being heard or, as it says in the text books, “saturation is reached”. While continuing with the processes of coding and theming (described in the next 2 sections), it is important to consider not just what the person is saying but also what they are not saying. For example, is a lengthy pause an indication that the participant is finding the subject difficult, or is the person simply deciding what to say? The aim of the whole process from data collection to presentation is to tell the participants’ stories using exemplars from their own narratives, thus grounding the research findings in the participants’ lived experiences.
Smith 9 suggested a qualitative research method known as interpretative phenomenological analysis, which has 2 basic tenets: first, that it is rooted in phenomenology, attempting to understand the meaning that individuals ascribe to their lived experiences, and second, that the researcher must attempt to interpret this meaning in the context of the research. That the researcher has some knowledge and expertise in the subject of the research means that he or she can have considerable scope in interpreting the participant’s experiences. Larkin and others 10 discussed the importance of not just providing a description of what participants say. Rather, interpretative phenomenological analysis is about getting underneath what a person is saying to try to truly understand the world from his or her perspective.
Once all of the research interviews have been transcribed and checked, it is time to begin coding. Field notes compiled during an interview can be a useful complementary source of information to facilitate this process, as the gap in time between an interview, transcribing, and coding can result in memory bias regarding nonverbal or environmental context issues that may affect interpretation of data.
Coding refers to the identification of topics, issues, similarities, and differences that are revealed through the participants’ narratives and interpreted by the researcher. This process enables the researcher to begin to understand the world from each participant’s perspective. Coding can be done by hand on a hard copy of the transcript, by making notes in the margin or by highlighting and naming sections of text. More commonly, researchers use qualitative research software (e.g., NVivo, QSR International Pty Ltd; www.qsrinternational.com/products_nvivo.aspx ) to help manage their transcriptions. It is advised that researchers undertake a formal course in the use of such software or seek supervision from a researcher experienced in these tools.
Returning to Appendix 1 and reading from lines 8–11, a code for this section might be “diagnosis of mental health condition”, but this would just be a description of what the participant is talking about at that point. If we read a little more deeply, we can ask ourselves how the participant might have come to feel that the doctor assumed he or she was aware of the diagnosis or indeed that they had only just been told the diagnosis. There are a number of pauses in the narrative that might suggest the participant is finding it difficult to recall that experience. Later in the text, the participant says “nobody asked me any questions about my life” (line 19). This could be coded simply as “health care professionals’ consultation skills”, but that would not reflect how the participant must have felt never to be asked anything about his or her personal life, about the participant as a human being. At the end of this excerpt, the participant just trails off, recalling that no-one showed any interest, which makes for very moving reading. For practitioners in pharmacy, it might also be pertinent to explore the participant’s experience of akathisia and why this was left untreated for 20 years.
One of the questions that arises about qualitative research relates to the reliability of the interpretation and representation of the participants’ narratives. There are no statistical tests that can be used to check reliability and validity as there are in quantitative research. However, work by Lincoln and Guba 11 suggests that there are other ways to “establish confidence in the ‘truth’ of the findings” (p. 218). They call this confidence “trustworthiness” and suggest that there are 4 criteria of trustworthiness: credibility (confidence in the “truth” of the findings), transferability (showing that the findings have applicability in other contexts), dependability (showing that the findings are consistent and could be repeated), and confirmability (the extent to which the findings of a study are shaped by the respondents and not researcher bias, motivation, or interest).
One way of establishing the “credibility” of the coding is to ask another researcher to code the same transcript and then to discuss any similarities and differences in the 2 resulting sets of codes. This simple act can result in revisions to the codes and can help to clarify and confirm the research findings.
Theming refers to the drawing together of codes from one or more transcripts to present the findings of qualitative research in a coherent and meaningful way. For example, there may be examples across participants’ narratives of the way in which they were treated in hospital, such as “not being listened to” or “lack of interest in personal experiences” (see Appendix 1 ). These may be drawn together as a theme running through the narratives that could be named “the patient’s experience of hospital care”. The importance of going through this process is that at its conclusion, it will be possible to present the data from the interviews using quotations from the individual transcripts to illustrate the source of the researchers’ interpretations. Thus, when the findings are organized for presentation, each theme can become the heading of a section in the report or presentation. Underneath each theme will be the codes, examples from the transcripts, and the researcher’s own interpretation of what the themes mean. Implications for real life (e.g., the treatment of people with chronic mental health problems) should also be given.
DATA SYNTHESIS
In this final section of this paper, we describe some ways of drawing together or “synthesizing” research findings to represent, as faithfully as possible, the meaning that participants ascribe to their life experiences. This synthesis is the aim of the final stage of qualitative research. For most readers, the synthesis of data presented by the researcher is of crucial significance—this is usually where “the story” of the participants can be distilled, summarized, and told in a manner that is both respectful to those participants and meaningful to readers. There are a number of ways in which researchers can synthesize and present their findings, but any conclusions drawn by the researchers must be supported by direct quotations from the participants. In this way, it is made clear to the reader that the themes under discussion have emerged from the participants’ interviews and not the mind of the researcher. The work of Latif and others 12 gives an example of how qualitative research findings might be presented.
Planning and Writing the Report
As has been suggested above, if researchers code and theme their material appropriately, they will naturally find the headings for sections of their report. Qualitative researchers tend to report “findings” rather than “results”, as the latter term typically implies that the data have come from a quantitative source. The final presentation of the research will usually be in the form of a report or a paper and so should follow accepted academic guidelines. In particular, the article should begin with an introduction, including a literature review and rationale for the research. There should be a section on the chosen methodology and a brief discussion about why qualitative methodology was most appropriate for the study question and why one particular methodology (e.g., interpretative phenomenological analysis rather than grounded theory) was selected to guide the research. The method itself should then be described, including ethics approval, choice of participants, mode of recruitment, and method of data collection (e.g., semistructured interviews or focus groups), followed by the research findings, which will be the main body of the report or paper. The findings should be written as if a story is being told; as such, it is not necessary to have a lengthy discussion section at the end. This is because much of the discussion will take place around the participants’ quotes, such that all that is needed to close the report or paper is a summary, limitations of the research, and the implications that the research has for practice. As stated earlier, it is not the intention of qualitative research to allow the findings to be generalized, and therefore this is not, in itself, a limitation.
Planning out the way that findings are to be presented is helpful. It is useful to insert the headings of the sections (the themes) and then make a note of the codes that exemplify the thoughts and feelings of your participants. It is generally advisable to put in the quotations that you want to use for each theme, using each quotation only once. After all this is done, the telling of the story can begin as you give your voice to the experiences of the participants, writing around their quotations. Do not be afraid to draw assumptions from the participants’ narratives, as this is necessary to give an in-depth account of the phenomena in question. Discuss these assumptions, drawing on your participants’ words to support you as you move from one code to another and from one theme to the next. Finally, as appropriate, it is possible to include examples from literature or policy documents that add support for your findings. As an exercise, you may wish to code and theme the sample excerpt in Appendix 1 and tell the participant’s story in your own way. Further reading about “doing” qualitative research can be found at the end of this paper.
CONCLUSIONS
Qualitative research can help researchers to access the thoughts and feelings of research participants, which can enable development of an understanding of the meaning that people ascribe to their experiences. It can be used in pharmacy practice research to explore how patients feel about their health and their treatment. Qualitative research has been used by pharmacists to explore a variety of questions and problems (see the “Further Reading” section for examples). An understanding of these issues can help pharmacists and other health care professionals to tailor health care to match the individual needs of patients and to develop a concordant relationship. Doing qualitative research is not easy and may require a complete rethink of how research is conducted, particularly for researchers who are more familiar with quantitative approaches. There are many ways of conducting qualitative research, and this paper has covered some of the practical issues regarding data collection, analysis, and management. Further reading around the subject will be essential to truly understand this method of accessing peoples’ thoughts and feelings to enable researchers to tell participants’ stories.
Appendix 1. Excerpt from a sample transcript
The participant (age late 50s) had suffered from a chronic mental health illness for 30 years. The participant had become a “revolving door patient,” someone who is frequently in and out of hospital. As the participant talked about past experiences, the researcher asked:
- What was treatment like 30 years ago?
- Umm—well it was pretty much they could do what they wanted with you because I was put into the er, the er kind of system er, I was just on
- endless section threes.
- Really…
- But what I didn’t realize until later was that if you haven’t actually posed a threat to someone or yourself they can’t really do that but I didn’t know
- that. So wh-when I first went into hospital they put me on the forensic ward ’cause they said, “We don’t think you’ll stay here we think you’ll just
- run-run away.” So they put me then onto the acute admissions ward and – er – I can remember one of the first things I recall when I got onto that
- ward was sitting down with a er a Dr XXX. He had a book this thick [gestures] and on each page it was like three questions and he went through
- all these questions and I answered all these questions. So we’re there for I don’t maybe two hours doing all that and he asked me he said “well
- when did somebody tell you then that you have schizophrenia” I said “well nobody’s told me that” so he seemed very surprised but nobody had
- actually [pause] whe-when I first went up there under police escort erm the senior kind of consultants people I’d been to where I was staying and
- ermm so er [pause] I . . . the, I can remember the very first night that I was there and given this injection in this muscle here [gestures] and just
- having dreadful side effects the next day I woke up [pause]
- . . . and I suffered that akathesia I swear to you, every minute of every day for about 20 years.
- Oh how awful.
- And that side of it just makes life impossible so the care on the wards [pause] umm I don’t know it’s kind of, it’s kind of hard to put into words
- [pause]. Because I’m not saying they were sort of like not friendly or interested but then nobody ever seemed to want to talk about your life [pause]
- nobody asked me any questions about my life. The only questions that came into was they asked me if I’d be a volunteer for these student exams
- and things and I said “yeah” so all the questions were like “oh what jobs have you done,” er about your relationships and things and er but
- nobody actually sat down and had a talk and showed some interest in you as a person you were just there basically [pause] um labelled and you
- know there was there was [pause] but umm [pause] yeah . . .
This article is the 10th in the CJHP Research Primer Series, an initiative of the CJHP Editorial Board and the CSHP Research Committee. The planned 2-year series is intended to appeal to relatively inexperienced researchers, with the goal of building research capacity among practising pharmacists. The articles, presenting simple but rigorous guidance to encourage and support novice researchers, are being solicited from authors with appropriate expertise.
Previous articles in this series:
Bond CM. The research jigsaw: how to get started. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(1):28–30.
Tully MP. Research: articulating questions, generating hypotheses, and choosing study designs. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(1):31–4.
Loewen P. Ethical issues in pharmacy practice research: an introductory guide. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2014;67(2):133–7.
Tsuyuki RT. Designing pharmacy practice research trials. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(3):226–9.
Bresee LC. An introduction to developing surveys for pharmacy practice research. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(4):286–91.
Gamble JM. An introduction to the fundamentals of cohort and case–control studies. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(5):366–72.
Austin Z, Sutton J. Qualitative research: getting started. C an J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(6):436–40.
Houle S. An introduction to the fundamentals of randomized controlled trials in pharmacy research. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014; 68(1):28–32.
Charrois TL. Systematic reviews: What do you need to know to get started? Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;68(2):144–8.
Competing interests: None declared.
Further Reading
Examples of qualitative research in pharmacy practice.
- Farrell B, Pottie K, Woodend K, Yao V, Dolovich L, Kennie N, et al. Shifts in expectations: evaluating physicians’ perceptions as pharmacists integrated into family practice. J Interprof Care. 2010; 24 (1):80–9. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gregory P, Austin Z. Postgraduation employment experiences of new pharmacists in Ontario in 2012–2013. Can Pharm J. 2014; 147 (5):290–9. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marks PZ, Jennnings B, Farrell B, Kennie-Kaulbach N, Jorgenson D, Pearson-Sharpe J, et al. “I gained a skill and a change in attitude”: a case study describing how an online continuing professional education course for pharmacists supported achievement of its transfer to practice outcomes. Can J Univ Contin Educ. 2014; 40 (2):1–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nair KM, Dolovich L, Brazil K, Raina P. It’s all about relationships: a qualitative study of health researchers’ perspectives on interdisciplinary research. BMC Health Serv Res. 2008; 8 :110. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pojskic N, MacKeigan L, Boon H, Austin Z. Initial perceptions of key stakeholders in Ontario regarding independent prescriptive authority for pharmacists. Res Soc Adm Pharm. 2014; 10 (2):341–54. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Qualitative Research in General
- Breakwell GM, Hammond S, Fife-Schaw C. Research methods in psychology. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Given LM. 100 questions (and answers) about qualitative research. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles B, Huberman AM. Qualitative data analysis. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Patton M. Qualitative research and evaluation methods. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Willig C. Introducing qualitative research in psychology. Buckingham (UK): Open University Press; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
Group Dynamics in Focus Groups
- Farnsworth J, Boon B. Analysing group dynamics within the focus group. Qual Res. 2010; 10 (5):605–24. [ Google Scholar ]
Social Constructivism
- Social constructivism. Berkeley (CA): University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley Graduate Division, Graduate Student Instruction Teaching & Resource Center; [cited 2015 June 4]. Available from: http://gsi.berkeley.edu/gsi-guide-contents/learning-theory-research/social-constructivism/ [ Google Scholar ]
Mixed Methods
- Creswell J. Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
Collecting Qualitative Data
- Arksey H, Knight P. Interviewing for social scientists: an introductory resource with examples. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- Guest G, Namey EE, Mitchel ML. Collecting qualitative data: a field manual for applied research. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
Constructivist Grounded Theory
- Charmaz K. Grounded theory: objectivist and constructivist methods. In: Denzin N, Lincoln Y, editors. Handbook of qualitative research. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2000. pp. 509–35. [ Google Scholar ]
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Data Analysis in Research: Types & Methods
Content Index
Why analyze data in research?
Types of data in research, finding patterns in the qualitative data, methods used for data analysis in qualitative research, preparing data for analysis, methods used for data analysis in quantitative research, considerations in research data analysis, what is data analysis in research.
Definition of research in data analysis: According to LeCompte and Schensul, research data analysis is a process used by researchers to reduce data to a story and interpret it to derive insights. The data analysis process helps reduce a large chunk of data into smaller fragments, which makes sense.
Three essential things occur during the data analysis process — the first is data organization . Summarization and categorization together contribute to becoming the second known method used for data reduction. It helps find patterns and themes in the data for easy identification and linking. The third and last way is data analysis – researchers do it in both top-down and bottom-up fashion.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
On the other hand, Marshall and Rossman describe data analysis as a messy, ambiguous, and time-consuming but creative and fascinating process through which a mass of collected data is brought to order, structure and meaning.
We can say that “the data analysis and data interpretation is a process representing the application of deductive and inductive logic to the research and data analysis.”
Researchers rely heavily on data as they have a story to tell or research problems to solve. It starts with a question, and data is nothing but an answer to that question. But, what if there is no question to ask? Well! It is possible to explore data even without a problem – we call it ‘Data Mining’, which often reveals some interesting patterns within the data that are worth exploring.
Irrelevant to the type of data researchers explore, their mission and audiences’ vision guide them to find the patterns to shape the story they want to tell. One of the essential things expected from researchers while analyzing data is to stay open and remain unbiased toward unexpected patterns, expressions, and results. Remember, sometimes, data analysis tells the most unforeseen yet exciting stories that were not expected when initiating data analysis. Therefore, rely on the data you have at hand and enjoy the journey of exploratory research.
Create a Free Account
Every kind of data has a rare quality of describing things after assigning a specific value to it. For analysis, you need to organize these values, processed and presented in a given context, to make it useful. Data can be in different forms; here are the primary data types.
- Qualitative data: When the data presented has words and descriptions, then we call it qualitative data . Although you can observe this data, it is subjective and harder to analyze data in research, especially for comparison. Example: Quality data represents everything describing taste, experience, texture, or an opinion that is considered quality data. This type of data is usually collected through focus groups, personal qualitative interviews , qualitative observation or using open-ended questions in surveys.
- Quantitative data: Any data expressed in numbers of numerical figures are called quantitative data . This type of data can be distinguished into categories, grouped, measured, calculated, or ranked. Example: questions such as age, rank, cost, length, weight, scores, etc. everything comes under this type of data. You can present such data in graphical format, charts, or apply statistical analysis methods to this data. The (Outcomes Measurement Systems) OMS questionnaires in surveys are a significant source of collecting numeric data.
- Categorical data: It is data presented in groups. However, an item included in the categorical data cannot belong to more than one group. Example: A person responding to a survey by telling his living style, marital status, smoking habit, or drinking habit comes under the categorical data. A chi-square test is a standard method used to analyze this data.
Learn More : Examples of Qualitative Data in Education
Data analysis in qualitative research
Data analysis and qualitative data research work a little differently from the numerical data as the quality data is made up of words, descriptions, images, objects, and sometimes symbols. Getting insight from such complicated information is a complicated process. Hence it is typically used for exploratory research and data analysis .
Although there are several ways to find patterns in the textual information, a word-based method is the most relied and widely used global technique for research and data analysis. Notably, the data analysis process in qualitative research is manual. Here the researchers usually read the available data and find repetitive or commonly used words.
For example, while studying data collected from African countries to understand the most pressing issues people face, researchers might find “food” and “hunger” are the most commonly used words and will highlight them for further analysis.
LEARN ABOUT: Level of Analysis
The keyword context is another widely used word-based technique. In this method, the researcher tries to understand the concept by analyzing the context in which the participants use a particular keyword.
For example , researchers conducting research and data analysis for studying the concept of ‘diabetes’ amongst respondents might analyze the context of when and how the respondent has used or referred to the word ‘diabetes.’
The scrutiny-based technique is also one of the highly recommended text analysis methods used to identify a quality data pattern. Compare and contrast is the widely used method under this technique to differentiate how a specific text is similar or different from each other.
For example: To find out the “importance of resident doctor in a company,” the collected data is divided into people who think it is necessary to hire a resident doctor and those who think it is unnecessary. Compare and contrast is the best method that can be used to analyze the polls having single-answer questions types .
Metaphors can be used to reduce the data pile and find patterns in it so that it becomes easier to connect data with theory.
Variable Partitioning is another technique used to split variables so that researchers can find more coherent descriptions and explanations from the enormous data.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Research Questions and Questionnaires
There are several techniques to analyze the data in qualitative research, but here are some commonly used methods,
- Content Analysis: It is widely accepted and the most frequently employed technique for data analysis in research methodology. It can be used to analyze the documented information from text, images, and sometimes from the physical items. It depends on the research questions to predict when and where to use this method.
- Narrative Analysis: This method is used to analyze content gathered from various sources such as personal interviews, field observation, and surveys . The majority of times, stories, or opinions shared by people are focused on finding answers to the research questions.
- Discourse Analysis: Similar to narrative analysis, discourse analysis is used to analyze the interactions with people. Nevertheless, this particular method considers the social context under which or within which the communication between the researcher and respondent takes place. In addition to that, discourse analysis also focuses on the lifestyle and day-to-day environment while deriving any conclusion.
- Grounded Theory: When you want to explain why a particular phenomenon happened, then using grounded theory for analyzing quality data is the best resort. Grounded theory is applied to study data about the host of similar cases occurring in different settings. When researchers are using this method, they might alter explanations or produce new ones until they arrive at some conclusion.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
Data analysis in quantitative research
The first stage in research and data analysis is to make it for the analysis so that the nominal data can be converted into something meaningful. Data preparation consists of the below phases.
Phase I: Data Validation
Data validation is done to understand if the collected data sample is per the pre-set standards, or it is a biased data sample again divided into four different stages
- Fraud: To ensure an actual human being records each response to the survey or the questionnaire
- Screening: To make sure each participant or respondent is selected or chosen in compliance with the research criteria
- Procedure: To ensure ethical standards were maintained while collecting the data sample
- Completeness: To ensure that the respondent has answered all the questions in an online survey. Else, the interviewer had asked all the questions devised in the questionnaire.
Phase II: Data Editing
More often, an extensive research data sample comes loaded with errors. Respondents sometimes fill in some fields incorrectly or sometimes skip them accidentally. Data editing is a process wherein the researchers have to confirm that the provided data is free of such errors. They need to conduct necessary checks and outlier checks to edit the raw edit and make it ready for analysis.
Phase III: Data Coding
Out of all three, this is the most critical phase of data preparation associated with grouping and assigning values to the survey responses . If a survey is completed with a 1000 sample size, the researcher will create an age bracket to distinguish the respondents based on their age. Thus, it becomes easier to analyze small data buckets rather than deal with the massive data pile.
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research
After the data is prepared for analysis, researchers are open to using different research and data analysis methods to derive meaningful insights. For sure, statistical analysis plans are the most favored to analyze numerical data. In statistical analysis, distinguishing between categorical data and numerical data is essential, as categorical data involves distinct categories or labels, while numerical data consists of measurable quantities. The method is again classified into two groups. First, ‘Descriptive Statistics’ used to describe data. Second, ‘Inferential statistics’ that helps in comparing the data .
Descriptive statistics
This method is used to describe the basic features of versatile types of data in research. It presents the data in such a meaningful way that pattern in the data starts making sense. Nevertheless, the descriptive analysis does not go beyond making conclusions. The conclusions are again based on the hypothesis researchers have formulated so far. Here are a few major types of descriptive analysis methods.
Measures of Frequency
- Count, Percent, Frequency
- It is used to denote home often a particular event occurs.
- Researchers use it when they want to showcase how often a response is given.
Measures of Central Tendency
- Mean, Median, Mode
- The method is widely used to demonstrate distribution by various points.
- Researchers use this method when they want to showcase the most commonly or averagely indicated response.
Measures of Dispersion or Variation
- Range, Variance, Standard deviation
- Here the field equals high/low points.
- Variance standard deviation = difference between the observed score and mean
- It is used to identify the spread of scores by stating intervals.
- Researchers use this method to showcase data spread out. It helps them identify the depth until which the data is spread out that it directly affects the mean.
Measures of Position
- Percentile ranks, Quartile ranks
- It relies on standardized scores helping researchers to identify the relationship between different scores.
- It is often used when researchers want to compare scores with the average count.
For quantitative research use of descriptive analysis often give absolute numbers, but the in-depth analysis is never sufficient to demonstrate the rationale behind those numbers. Nevertheless, it is necessary to think of the best method for research and data analysis suiting your survey questionnaire and what story researchers want to tell. For example, the mean is the best way to demonstrate the students’ average scores in schools. It is better to rely on the descriptive statistics when the researchers intend to keep the research or outcome limited to the provided sample without generalizing it. For example, when you want to compare average voting done in two different cities, differential statistics are enough.
Descriptive analysis is also called a ‘univariate analysis’ since it is commonly used to analyze a single variable.
Inferential statistics
Inferential statistics are used to make predictions about a larger population after research and data analysis of the representing population’s collected sample. For example, you can ask some odd 100 audiences at a movie theater if they like the movie they are watching. Researchers then use inferential statistics on the collected sample to reason that about 80-90% of people like the movie.
Here are two significant areas of inferential statistics.
- Estimating parameters: It takes statistics from the sample research data and demonstrates something about the population parameter.
- Hypothesis test: I t’s about sampling research data to answer the survey research questions. For example, researchers might be interested to understand if the new shade of lipstick recently launched is good or not, or if the multivitamin capsules help children to perform better at games.
These are sophisticated analysis methods used to showcase the relationship between different variables instead of describing a single variable. It is often used when researchers want something beyond absolute numbers to understand the relationship between variables.
Here are some of the commonly used methods for data analysis in research.
- Correlation: When researchers are not conducting experimental research or quasi-experimental research wherein the researchers are interested to understand the relationship between two or more variables, they opt for correlational research methods.
- Cross-tabulation: Also called contingency tables, cross-tabulation is used to analyze the relationship between multiple variables. Suppose provided data has age and gender categories presented in rows and columns. A two-dimensional cross-tabulation helps for seamless data analysis and research by showing the number of males and females in each age category.
- Regression analysis: For understanding the strong relationship between two variables, researchers do not look beyond the primary and commonly used regression analysis method, which is also a type of predictive analysis used. In this method, you have an essential factor called the dependent variable. You also have multiple independent variables in regression analysis. You undertake efforts to find out the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable. The values of both independent and dependent variables are assumed as being ascertained in an error-free random manner.
- Frequency tables: The statistical procedure is used for testing the degree to which two or more vary or differ in an experiment. A considerable degree of variation means research findings were significant. In many contexts, ANOVA testing and variance analysis are similar.
- Analysis of variance: The statistical procedure is used for testing the degree to which two or more vary or differ in an experiment. A considerable degree of variation means research findings were significant. In many contexts, ANOVA testing and variance analysis are similar.
- Researchers must have the necessary research skills to analyze and manipulation the data , Getting trained to demonstrate a high standard of research practice. Ideally, researchers must possess more than a basic understanding of the rationale of selecting one statistical method over the other to obtain better data insights.
- Usually, research and data analytics projects differ by scientific discipline; therefore, getting statistical advice at the beginning of analysis helps design a survey questionnaire, select data collection methods, and choose samples.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
- The primary aim of data research and analysis is to derive ultimate insights that are unbiased. Any mistake in or keeping a biased mind to collect data, selecting an analysis method, or choosing audience sample il to draw a biased inference.
- Irrelevant to the sophistication used in research data and analysis is enough to rectify the poorly defined objective outcome measurements. It does not matter if the design is at fault or intentions are not clear, but lack of clarity might mislead readers, so avoid the practice.
- The motive behind data analysis in research is to present accurate and reliable data. As far as possible, avoid statistical errors, and find a way to deal with everyday challenges like outliers, missing data, data altering, data mining , or developing graphical representation.
LEARN MORE: Descriptive Research vs Correlational Research The sheer amount of data generated daily is frightening. Especially when data analysis has taken center stage. in 2018. In last year, the total data supply amounted to 2.8 trillion gigabytes. Hence, it is clear that the enterprises willing to survive in the hypercompetitive world must possess an excellent capability to analyze complex research data, derive actionable insights, and adapt to the new market needs.
LEARN ABOUT: Average Order Value
QuestionPro is an online survey platform that empowers organizations in data analysis and research and provides them a medium to collect data by creating appealing surveys.
MORE LIKE THIS

Unlocking Creativity With 10 Top Idea Management Software
Mar 23, 2024

20 Best Website Optimization Tools to Improve Your Website
Mar 22, 2024

15 Best Digital Customer Experience Software of 2024

15 Best Product Experience Software of 2024
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- A/B Monadic Test
- A/B Pre-Roll Test
- Key Driver Analysis
- Multiple Implicit
- Penalty Reward
- Price Sensitivity
- Segmentation
- Single Implicit
- Category Exploration
- Competitive Landscape
- Consumer Segmentation
- Innovation & Renovation
- Product Portfolio
- Marketing Creatives
- Advertising
- Shelf Optimization
- Performance Monitoring
- Better Brand Health Tracking
- Ad Tracking
- Trend Tracking
- Satisfaction Tracking
- AI Insights
- Case Studies
quantilope is the Consumer Intelligence Platform for all end-to-end research needs
5 Methods of Data Collection for Quantitative Research

In this blog, read up on five different data collection techniques for quantitative research studies.
Quantitative research forms the basis for many business decisions. But what is quantitative data collection, why is it important, and which data collection methods are used in quantitative research?
Table of Contents:
- What is quantitative data collection?
- The importance of quantitative data collection
- Methods used for quantitative data collection
- Example of a survey showing quantitative data
- Strengths and weaknesses of quantitative data
What is quantitative data collection?
Quantitative data collection is the gathering of numeric data that puts consumer insights into a quantifiable context. It typically involves a large number of respondents - large enough to extract statistically reliable findings that can be extrapolated to a larger population.
The actual data collection process for quantitative findings is typically done using a quantitative online questionnaire that asks respondents yes/no questions, ranking scales, rating matrices, and other quantitative question types. With these results, researchers can generate data charts to summarize the quantitative findings and generate easily digestible key takeaways.
Back to Table of Contents
The importance of quantitative data collection
Quantitative data collection can confirm or deny a brand's hypothesis, guide product development, tailor marketing materials, and much more. It provides brands with reliable information to make decisions off of (i.e. 86% like lemon-lime flavor or just 12% are interested in a cinnamon-scented hand soap).
Compared to qualitative data collection, quantitative data allows for comparison between insights given higher base sizes which leads to the ability to have statistical significance. Brands can cut and analyze their dataset in a variety of ways, looking at their findings among different demographic groups, behavioral groups, and other ways of interest. It's also generally easier and quicker to collect quantitative data than it is to gather qualitative feedback, making it an important data collection tool for brands that need quick, reliable, concrete insights.
In order to make justified business decisions from quantitative data, brands need to recruit a high-quality sample that's reflective of their true target market (one that's comprised of all ages/genders rather than an isolated group). For example, a study into usage and attitudes around orange juice might include consumers who buy and/or drink orange juice at a certain frequency or who buy a variety of orange juice brands from different outlets.
Methods used for quantitative data collection
So knowing what quantitative data collection is and why it's important , how does one go about researching a large, high-quality, representative sample ?
Below are five examples of how to conduct your study through various data collection methods :
Online quantitative surveys
Online surveys are a common and effective way of collecting data from a large number of people. They tend to be made up of closed-ended questions so that responses across the sample are comparable; however, a small number of open-ended questions can be included as well (i.e. questions that require a written response rather than a selection of answers in a close-ended list). Open-ended questions are helpful to gather actual language used by respondents on a certain issue or to collect feedback on a view that might not be shown in a set list of responses).
Online surveys are quick and easy to send out, typically done so through survey panels. They can also appear in pop-ups on websites or via a link embedded in social media. From the participant’s point of view, online surveys are convenient to complete and submit, using whichever device they prefer (mobile phone, tablet, or computer). Anonymity is also viewed as a positive: online survey software ensures respondents’ identities are kept completely confidential.
To gather respondents for online surveys, researchers have several options. Probability sampling is one route, where respondents are selected using a random selection method. As such, everyone within the population has an equal chance of getting selected to participate.
There are four common types of probability sampling .
- Simple random sampling is the most straightforward approach, which involves randomly selecting individuals from the population without any specific criteria or grouping.
- Stratified random sampling divides the population into subgroups (strata) and selects a random sample from each stratum. This is useful when a population includes subgroups that you want to be sure you cover in your research.
- Cluster sampling divides the population into clusters and then randomly selects some of the clusters to sample in their entirety. This is useful when a population is geographically dispersed and it would be impossible to include everyone.
- Systematic sampling begins with a random starting point and then selects every nth member of the population after that point (i.e. every 15th respondent).
Learn how to leverage AI to help generate your online quantitative survey inputs:

While online surveys are by far the most common way to collect quantitative data in today’s modern age, there are still some harder-to-reach respondents where other mediums can be beneficial; for example, those who aren’t tech-savvy or who don’t have a stable internet connection. For these audiences, offline surveys may be needed.
Offline quantitative surveys
Offline surveys (though much rarer to come across these days) are a way of gathering respondent feedback without digital means. This could be something like postal questionnaires that are sent out to a sample population and asked to return the questionnaire by mail (like the Census) or telephone surveys where questions are asked of respondents over the phone.
Offline surveys certainly take longer to collect data than online surveys and they can become expensive if the population is difficult to reach (requiring a higher incentive). As with online surveys, anonymity is protected, assuming the mail is not intercepted or lost.
Despite the major difference in data collection to an online survey approach, offline survey data is still reported on in an aggregated, numeric fashion.
In-person interviews are another popular way of researching or polling a population. They can be thought of as a survey but in a verbal, in-person, or virtual face-to-face format. The online format of interviews is becoming more popular nowadays, as it is cheaper and logistically easier to organize than in-person face-to-face interviews, yet still allows the interviewer to see and hear from the respondent in their own words.
Though many interviews are collected for qualitative research, interviews can also be leveraged quantitatively; like a phone survey, an interviewer runs through a survey with the respondent, asking mainly closed-ended questions (yes/no, multiple choice questions, or questions with rating scales that ask how strongly the respondent agrees with statements). The advantage of structured interviews is that the interviewer can pace the survey, making sure the respondent gives enough consideration to each question. It also adds a human touch, which can be more engaging for some respondents. On the other hand, for more sensitive issues, respondents may feel more inclined to complete a survey online for a greater sense of anonymity - so it all depends on your research questions, the survey topic, and the audience you're researching.
Observations
Observation studies in quantitative research are similar in nature to a qualitative ethnographic study (in which a researcher also observes consumers in their natural habitats), yet observation studies for quant research remain focused on the numbers - how many people do an action, how much of a product consumer pick up, etc.
For quantitative observations, researchers will record the number and types of people who do a certain action - such as choosing a specific product from a grocery shelf, speaking to a company representative at an event, or how many people pass through a certain area within a given timeframe. Observation studies are generally structured, with the observer asked to note behavior using set parameters. Structured observation means that the observer has to hone in on very specific behaviors, which can be quite nuanced. This requires the observer to use his/her own judgment about what type of behavior is being exhibited (e.g. reading labels on products before selecting them; considering different items before making the final choice; making a selection based on price).
Document reviews and secondary data sources
A fifth method of data collection for quantitative research is known as secondary research : reviewing existing research to see how it can contribute to understanding a new issue in question. This is in contrast to the primary research methods above, which is research that is specially commissioned and carried out for a research project.
There are numerous secondary data sources that researchers can analyze such as public records, government research, company databases, existing reports, paid-for research publications, magazines, journals, case studies, websites, books, and more.
Aside from using secondary research alone, secondary research documents can also be used in anticipation of primary research, to understand which knowledge gaps need to be filled and to nail down the issues that might be important to explore further in a primary research study. Back to Table of Contents
Example of a survey showing quantitative data
The below study shows what quantitative data might look like in a final study dashboard, taken from quantilope's Sneaker category insights study .
The study includes a variety of usage and attitude metrics around sneaker wear, sneaker purchases, seasonality of sneakers, and more. Check out some of the data charts below showing these quantitative data findings - the first of which even cuts the quantitative data findings by demographics.
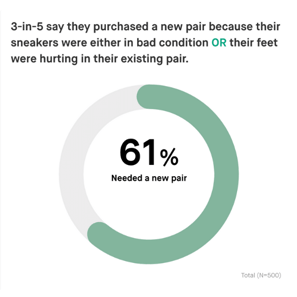
Beyond these basic usage and attitude (or, descriptive) data metrics, quantitative data also includes advanced methods - such as implicit association testing. See what these quantitative data charts look like from the same sneaker study below:
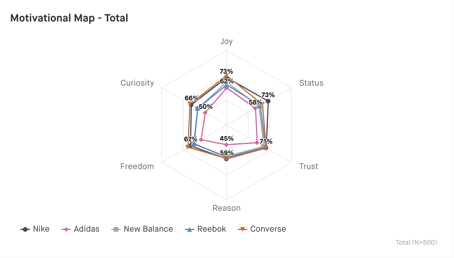
These are just a few examples of how a researcher or insights team might show their quantitative data findings. However, there are many ways to visualize quantitative data in an insights study, from bar charts, column charts, pie charts, donut charts, spider charts, and more, depending on what best suits the story your data is telling. Back to Table of Contents
Strengths and weaknesses of quantitative data collection
quantitative data is a great way to capture informative insights about your brand, product, category, or competitors. It's relatively quick, depending on your sample audience, and more affordable than other data collection methods such as qualitative focus groups. With quantitative panels, it's easy to access nearly any audience you might need - from something as general as the US population to something as specific as cannabis users . There are many ways to visualize quantitative findings, making it a customizable form of insights - whether you want to show the data in a bar chart, pie chart, etc.
For those looking for quick, affordable, actionable insights, quantitative studies are the way to go.
quantitative data collection, despite the many benefits outlined above, might also not be the right fit for your exact needs. For example, you often don't get as detailed and in-depth answers quantitatively as you would with an in-person interview, focus group, or ethnographic observation (all forms of qualitative research). When running a quantitative survey, it’s best practice to review your data for quality measures to ensure all respondents are ones you want to keep in your data set. Fortunately, there are a lot of precautions research providers can take to navigate these obstacles - such as automated data cleaners and data flags. Of course, the first step to ensuring high-quality results is to use a trusted panel provider. Back to Table of Contents
Quantitative research typically needs to undergo statistical analysis for it to be useful and actionable to any business. It is therefore crucial that the method of data collection, sample size, and sample criteria are considered in light of the research questions asked.
quantilope’s online platform is ideal for quantitative research studies. The online format means a large sample can be reached easily and quickly through connected respondent panels that effectively reach the desired target audience. Response rates are high, as respondents can take their survey from anywhere, using any device with internet access.
Surveys are easy to build with quantilope’s online survey builder. Simply choose questions to include from pre-designed survey templates or build your own questions using the platform’s drag & drop functionality (of which both options are fully customizable). Once the survey is live, findings update in real-time so that brands can get an idea of consumer attitudes long before the survey is complete. In addition to basic usage and attitude questions, quantilope’s suite of advanced research methodologies provides an AI-driven approach to many types of research questions. These range from exploring the features of products that drive purchase through a Key Driver Analysis , compiling the ideal portfolio of products using a TURF , or identifying the optimal price point for a product or service using a Price Sensitivity Meter (PSM) .
Depending on the type of data sought it might be worth considering a mixed-method approach, including both qual and quant in a single research study. Alongside quantitative online surveys, quantilope’s video research solution - inColor , offers qualitative research in the form of videoed responses to survey questions. inColor’s qualitative data analysis includes an AI-drive read on respondent sentiment, keyword trends, and facial expressions.
To find out more about how quantilope can help with any aspect of your research design and to start conducting high-quality, quantitative research, get in touch below:
Get in touch to learn more about quantitative research studies!
Related posts, quantilope's 5th consecutive year as a 'fastest growing tech company', automated survey setup: how to utilize ai-generated question inputs, quantilope & moneygram: tracking a major f1 sponsorship, quantilope & greenbook showcase: grow with mental availability.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on June 21, 2023. Data collection is a systematic process of gathering observations or measurements. Whether you are performing research for business, governmental or academic purposes, data collection allows you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem. While methods and aims may differ between ...
Additionally, a clear data collection plan will help ensure that you obtain the information you need to answer your research questions. Below are some suggestions for creating a solid data collection plan. First, it may be helpful to outline your steps. This allows you to see where your data collection procedures must begin and end.
Data collection is the process of gathering and collecting information from various sources to analyze and make informed decisions based on the data collected. This can involve various methods, such as surveys, interviews, experiments, and observation. In order for data collection to be effective, it is important to have a clear understanding ...
For instance, if you need qualitative data, you might choose a focus group or interview methodology. If you need quantitative data, then a survey or observational study may be the most appropriate form of collection. 4. Gather information. When collecting data for your business, identify your business goals first.
Now you need to plan your data collection procedures, especially if you're doing quantitative research! This video will walk you through some key steps for g...
One of the main stages in a research study is data collection that enables the researcher to find answers to research questions. Data collection is the process of collecting data aiming to gain ...
Surveys, interviews, observations, focus groups, and forms are common data collection methods. Sampling involves selecting a representative group from a larger population. Choosing the right sampling method to gather representative and relevant data is crucial. Crafting effective data collection instruments like surveys and questionnaires is key.
Definition 10.1 (Protocol) A protocol is a procedure documenting the details of the design and implementation of studies, and for data collection. Unforeseen complications are not unusual, so often a pilot study (or a practice run) is conducted before the real data collection, to identify problems with the study design or data collection, or ...
We offer best-practice recommendations for journal reviewers, editors, and authors regarding data collection and preparation. Our recommendations are applicable to research adopting different epistemological and ontological perspectives—including both quantitative and qualitative approaches—as well as research addressing micro (i.e., individuals, teams) and macro (i.e., organizations ...
If multiple researchers are involved, write a detailed manual to standardise data collection procedures in your study. This means laying out specific step-by-step instructions so that everyone in your research team collects data in a consistent way - for example, by conducting experiments under the same conditions and using objective criteria ...
Data Collection, Research Methodology, Data Collection Methods, Academic Research Paper, Data Collection Techniques. I. INTRODUCTION Different methods for gathering information regarding specific variables of the study aiming to employ them in the data analysis phase to achieve the results of the study, gain the answer of the research
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
In more details, in this part the author outlines the research strategy, the research method, the research approach, the methods of data collection, the selection of the sample, the research ...
It's time to choose your data collection methods. You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study. This video will i...
Case Studies, Checklists, Interviews, Observation sometimes, and Surveys or Questionnaires are all tools used to collect data. It is important to decide on the tools for data collection because research is carried out in different ways and for different purposes. The objective behind data collection is to capture quality evidence that allows ...
INTRODUCTION. In an earlier paper, 1 we presented an introduction to using qualitative research methods in pharmacy practice. In this article, we review some principles of the collection, analysis, and management of qualitative data to help pharmacists interested in doing research in their practice to continue their learning in this area.
Definition of research in data analysis: According to LeCompte and Schensul, research data analysis is a process used by researchers to reduce data to a story and interpret it to derive insights. The data analysis process helps reduce a large chunk of data into smaller fragments, which makes sense. Three essential things occur during the data ...
Example of writing up Data Collection Procedure 3.3 Data Collection In order to achieve the research's objectives for this study both primary and secondary data will be collected. Primary data speaks to the range of collection tools such as interviews and questionnaires that are used to gather first-hand data whereas secondary data speaks to ...
The actual data collection process for quantitative findings is typically done using a quantitative online questionnaire that asks respondents yes/no questions, ranking scales, rating matrices, and other quantitative question types. With these results, researchers can generate data charts to summarize the quantitative findings and generate ...