Social Norms Essay


Social Norms
Norms, traditions, and customs The norms reflect the conditions, experiences and the social relation between individuals and groups. Norms reflect also the customs and the rules of the society. The norms could be applied to the society as a whole or on a specific group in the society. The norms include the traditions, beliefs, and traits. Norms are guided the peaceful interactions in a varies situation ( Elegy, 2018). Egyptian people are considerd “friend in heart” which is mean that they love people
Introduction Social norms are powerful to the point that they influence the actions of all who are members of society. Social norms are so ingrained in most people that to not follow such untold rules of behavior, likely creates serious tension for oneself. Social norms appear to be unique to sentient life meaning something about intelligence helps in their formation and propagation. It is obvious that some level of greater intelligence is needed in the formation of social norms. There are many theories
Breaking Social Norms
Social Norms dictate what is acceptable in society and in some ways help society to productive and orderly. Norms are a set of protocol that we have all learned and follow and laws that we are held to because we participate in society. Many times social norms keep the average citizen to themselves and within their own sphere unless an emergency arrives where or a situation when spontaneous must occur. When individuals within the society break the social norms and step outside the standards that everyone
Social Norms In Sociology
To start, I will discuss what social norms are. Societal norms are both unwritten informal rules that are accepted by people and written formal rules that are strictly enforced laws, of how people should carry themselves (Keirns, et al., 2016). Social norms are part of the socialization process. The socialization process is the way people “learn the norms and beliefs of our society” to fit in (Keirns, et al., 2016, n.p.). Some examples of social norms are looking into the eyes of the person you are
Violation Of Social Norms
At a very early age, children learn about social norms to help them become proper citizens in society. Examples of some social norms that students learn are: “do not yell in the library,” “do not speak unless spoken to,” “do not talk to strangers,” and “close the door when you use the restroom.” As you grow older, these rules become unspoken because everyone knows how to act like a proper individual in society. The textbook definition of a social norm is something that is a rule of behavior that
The norms of a culture are the rules that govern behavior. Norms define what behavior is required, accepted, or prohibited in particular circumstances and provide cues regarding how we should act—what people “ought to do” in their daily routine. Because there are cultural norms in society ideas about how we should behave, dress, think, etc. We generally have to meet the expectations of others that we will conform to these norms. Break a norm in public and judge the reactions of others. Norm: Not
Social Norm Analysis
that a norm is an expectation that we set of “right” behavior within any setting (49). A norm violation can vary in many situations from affecting a person’s hearing, sight, smell, taste, personal space or just making an individual uncomfortable. Presenting a different type of behavior that is “enforced because they are thought essential to core values or the wellbeing of a group” (51) may be a different view of defining a norm violation. Putting it to the test I went out to observe two norms and
Social Norm Experiment
In our society, there are many social norms we are expected to abide by. These unwritten rules and standards of behavior often go unnoticed, leaving society to take them for granted. We only become truly aware of the norms of society when they are actually violated. When a violation occurs, those who continue to conform may respond with positive or negative sanctions, such as humor, alarm, irritation, fear, or a wide variety of emotions. Our society also relies on language as its major bases for
Violate Social Norm
Social norm are rules of behaviour that are considered acceptable by groups or society. So violating a norm will be unacceptable by groups or people that you are with. The norm that I choose to violate was chewing my food with my mouth closed around people I know. I choose to violate this norm because as we get older and start gaining common knowledge we will learn and know to chew with our mouth closed as a sign of good manners. To violate this norm I asked a couple of friends to go out and eat
In order to break a social norm, one must understand what a norm is. According to The Real World: An Introduction to Sociology, norms are guidelines and rules that are acceptable within a certain culture or society. These rules and behaviors generally come from the society's values (Ferris and Stein, 79). In simple terms, norms are things that people follow in order to fit and belong within a society. If someone likes to make extremely racist remarks and the society in which they live in does not
Popular Topics
- Social Phenomenon Essay
- Social Policy Essay
- Social Problems Essay
- Social Psychology Essay
- Social Relationships Essay
- Social Responsibility Essay
- Social Security Essay
- Social Stigma Essay
- Social Stratification Essay
- Social Theory Essay

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Social Norms
Social norms, the informal rules that govern behavior in groups and societies, have been extensively studied in the social sciences. Anthropologists have described how social norms function in different cultures (Geertz 1973), sociologists have focused on their social functions and how they motivate people to act (Durkheim 1895 [1982], 1950 [1957]; Parsons 1937; Parsons & Shils 1951; James Coleman 1990; Hechter & Opp 2001), and economists have explored how adherence to norms influences market behavior (Akerlof 1976; Young 1998a). More recently, also legal scholars have touted social norms as efficient alternatives to legal rules, as they may internalize negative externalities and provide signaling mechanisms at little or no cost (Ellickson 1991; Posner 2000).
With a few exceptions, the social science literature conceives of norms as exogenous variables. Since norms are mainly seen as constraining behavior, some of the key differences between moral, social, and legal norms—as well as differences between norms and conventions—have been blurred. Much attention has instead been paid to the conditions under which norms will be obeyed. Because of that, the issue of sanctions has been paramount in the social science literature. Moreover, since social norms are seen as central to the production of social order or social coordination, research on norms has been focused on the functions they perform. Yet even if a norm may fulfill important social functions (such as welfare maximization or the elimination of externalities), it cannot be explained solely on the basis of the functions it performs. The simplistic functionalist perspective has been rejected on several accounts; in fact, even though a given norm can be conceived as a means to achieve some goal, this is usually not the reason why it emerged in the first place (Elster 1989a, 1989b). Moreover, although a particular norm may persist (as opposed to emerge) because of some positive social function it fulfills, there are many others that are inefficient and even widely unpopular.
Philosophers have taken a different approach to norms. In the literature on norms and conventions, both social constructs are seen as the endogenous product of individuals’ interactions (Lewis 1969; Ullmann-Margalit 1977; Vandershraaf 1995; Bicchieri 2006). Norms are represented as equilibria of games of strategy, and as such they are supported by a cluster of self-fulfilling expectations. Beliefs, expectations, group knowledge and common knowledge have thus become central concepts in the development of a philosophical view of social norms. Paying attention to the role played by expectations in supporting social norms has helped differentiate between social norms, conventions, and descriptive norms: an important distinction often overlooked in the social science accounts, but crucial when we need to diagnose the nature of a pattern of behavior in order to intervene on it.
1. General Issues
2. early theories: socialization, 3. early theories: social identity, 4. early theories: cost-benefit models, 5. game-theoretic accounts, 6. experimental evidence, 7. evolutionary models, 8. conclusion, other internet resources, related entries.
Social norms, like many other social phenomena, are the unplanned result of individuals’ interaction. It has been argued that social norms ought to be understood as a kind of grammar of social interactions. Like a grammar, a system of norms specifies what is acceptable and what is not in a society or group. And, analogously to a grammar, it is not the product of human design. This view suggests that a study of the conditions under which norms come into being—as opposed to one stressing the functions fulfilled by social norms—is important to understand the differences between social norms and other types of injunction (such as hypothetical imperatives, moral codes, or legal rules).
Another important issue often blurred in the literature on norms is the relationship between normative beliefs and behavior. Some authors identify norms with observable, recurrent patterns of behavior. Others only focus on normative beliefs and expectations. Such accounts find it difficult to explain the complexity and heterogeneity of norm-driven behaviors, as they offer an explanation of conformity that is at best partial.
Some popular accounts of why social norms exist are the following. Norms are efficient means to achieve social welfare (Arrow 1971; Akerlof 1976), prevent market failures (Jules Coleman 1989), or cut social costs (Thibaut & Kelley 1959; Homans 1961); norms are either Nash equilibria of coordination games or cooperative equilibria of prisoner’s dilemma-type games (Lewis 1969; Ullmann-Margalit 1977), and as such they solve collective action problems.
Akerlof’s (1976) analysis of the norms that regulate land systems is a good example of the tenet that “norms are efficient means to achieve social welfare”. Since the worker is much poorer and less liquid than the landlord, it would be more natural for the landlord rather than the tenant to bear the risk of crop failure. This would be the case if the landlord kept all the crops, and paid the worker a wage (i.e., the case of a “wage system”). Since the wage would not directly depend on the worker’s effort, this system leaves no incentive to the worker for any effort beyond the minimum necessary. In sharecropping, on the contrary, the worker is paid both for the effort and the time he puts in: a more efficient arrangement in that it increases production.
Thibaut and Kelley’s (1959) view of norms as substitutes for informal influence has a similar functionalist flavor. As an example, they consider a repeated battle of the sexes game. In this game, some bargaining is necessary for each party to obtain, at least occasionally, the preferred outcome. The parties can engage in a costly sequence of threats and promises, but it seems better to agree beforehand on a rule of behavior, such as alternating between the respectively preferred outcomes. Rules emerge because they reduce the costs involved in face-to-face personal influence.
Likewise, Ullman-Margalit (1977) uses game theory to show that norms solve collective action problems, such as prisoner’s dilemma-type situations; in her own words, “… a norm solving the problem inherent in a situation of this type is generated by it” (1977: 22). In a collective action problem, self-centered rational choices produce a Pareto-inefficient outcome. Pareto-efficiency is restored by means of norms backed by sanctions. James Coleman (1990), too, believes that norms emerge in situations in which there are externalities, that is, in all those cases in which an activity produces negative (positive) effects on other parties, without this being reflected in direct compensation; thus the producer of the externality pays no cost for (reaps no benefit from) the unintended effect of their activity. A norm solves the problem by regulating the externality-producing activity, introducing a system of sanctions (rewards).
Also Brennan, Eriksson, Goodin, and Southwood (2013) argue that norms have a function. Norms function to hold us accountable to each other for adherence to the principles that they cover. This may or may not create effective coordination over any given principle, but they place us in positions where we may praise and blame people for their behaviors and attitudes. This function of accountability, they argue, can help create another role for norms, which is imbuing practices with social meaning. This social meaning arises from the expectations that we can place on each other for compliance, and the fact that those behaviors can come to represent shared values, and even a sense of shared identity. This functional role of norms separates it from bare social practices or even common sets of desires, as those non-normative behaviors don’t carry with them the social accountability that is inherent in norms. The distinctive feature of the Brennan et al. account of norms is the centrality of accountability: this feature is what distinguishes norms from other social practices.
All of the above are examples of a functionalist explanation of norms. Functionalist accounts are sometimes criticized for offering a post hoc justification for the existence of norms (i.e., the mere presence of a norm does not justify inferring that that norm exists to accomplish some social function). Indeed, a purely functionalist view may not account for the fact that many social norms are harmful or inefficient (e.g., discriminatory norms against women and minorities), or are so rigid as to prevent the fine-tuning that would be necessary to accommodate new cases. There, one would expect increasing social pressure to abandon such norms.
According to some authors, we can explain the emergence of norms without any reference to the functions they eventually come to perform. Since the norms that are most interesting to study are those that emerge naturally from individuals’ interactions (Schelling 1978), an important theoretical task is to analyze the conditions under which such norms come into being. Because norms often provide a solution to the problem of maintaining social order—and social order requires cooperation—many studies on the emergence and dynamics of norms have focused on cooperation. Norms of honesty, loyalty, reciprocity and promise-keeping are indeed important to the smooth functioning of social groups. One hypothesis is that such cooperative norms emerge in close-knit groups where people have ongoing interactions with each other (Hardin 1982). Evolutionary game theory provides a useful framework for investigating this hypothesis, since repeated games serve as a simple approximation of life in a close-knit group (Axelrod 1984, 1986; Skyrms 1996; Gintis 2000). In repeated encounters people have an opportunity to learn from each other’s behavior, and to secure a pattern of reciprocity that minimizes the likelihood of misperception. In this regard, it has been argued that the cooperative norms likely to develop in close-knit groups are simple ones (Alexander 2000, 2005, 2007); in fact, delayed and disproportionate punishment, as well as belated rewards, are often difficult to understand and hence ineffective. Although norms originate in small, close-knit groups, they often spread well beyond the narrow boundaries of the original group. The challenge thus becomes one of explaining the dynamics of the norm propagation from small groups to large populations.
If norms can thrive and spread, they can also die out. A poorly understood phenomenon is the sudden and unexpected change of well-established patterns of behavior. For example, smoking in public without asking for permission has become unacceptable, and only a few years ago nobody would have worried about using gender-laden language. One would expect inefficient norms (such as discriminatory norms against women and minorities) to disappear more rapidly and with greater frequency than more efficient norms. However, Bicchieri (2016) points out that inefficiency is not a sufficient condition for a norm’s demise. This can be seen by the study of crime and corruption: corruption results in huge social costs, but such costs—even when they take a society to the brink of collapse—are not enough to generate an overhaul of the system. Muldoon (2018a, 2018b, 2020) has argued that social norms are a challenging form of social regulation precisely because there is no simple way to intentionally modify a social norm, as one can with a law or institutional rule. Social norms can even shape one's understanding of how much agency one has (Muldoon 2017).
An influential view of norms considers them as clusters of self-fulfilling expectations (Schelling 1960), in that some expectations often result in behavior that reinforces them. A related view emphasizes the importance of conditional preferences in supporting social norms (Sugden 2000). In particular, according to Bicchieri’s (2006) account, preferences for conformity to social norms are conditional on “empirical expectations” (i.e., first-order beliefs that a certain behavior will be followed) as well as “normative expectations” (i.e., second-order beliefs that a certain behavior ought to be followed). Thus, norm compliance results from the joint presence of a conditional preference for conformity and the belief that other people will conform as well as approve of conformity.
Note that characterizing norms simply as clusters of expectations might be misleading; similarly, a norm cannot simply be identified with a recurrent behavioral pattern either. If we were to adopt a purely behavioral account of norms there would be no way to distinguish shared rules of fairness from, say, the collective morning habit of tooth brushing. After all, such a practice does not depend on whether one expects others to do the same; however, one would not even try to ask for a salary proportionate to one’s education, if one expected compensation to merely follow a seniority rule. In fact, there are behavioral patterns that can only be explained by the existence of norms, even if the behavior prescribed by the norm in question is currently unobserved. For example, in a study of the Ik people, Turnbull (1972) reported that starved hunters-gatherers tried hard to avoid situations where their compliance with norms of reciprocity was expected. Thus they would go out of their way not to be in the position of gift-taker, and hunted alone so that they would not be forced to share their prey with anyone else. Much of the Ik’s behavior could be explained as a way of eluding existing reciprocity norms.
There are many other instances of discrepancies between expectations and behavior . For example, it is remarkable to observe how often people expect others to act selfishly, even when they are prepared to act altruistically themselves (Miller & Ratner 1996). Studies have shown that people’s willingness to give blood is not altered by monetary incentives, but typically those very people who are willing to donate blood for free expect others to donate blood only in the presence of monetary rewards. Similarly, all the interviewed landlords answered positively to a question about whether they would rent an apartment to an unmarried couple; however, they estimated that only 50% of other landlords would accept unmarried couples as tenants (Dawes 1972). Such cases of pluralistic ignorance are rather common; what is puzzling is that people may expect a given norm to be upheld in the face of personal evidence to the contrary (Bicchieri & Fukui 1999). Furthermore, there is evidence suggesting that people who donate blood, tip on a foreign trip, give money to beggars or return a lost wallet often attempt to downplay their altruistic behavior (by supplying selfish motives that seemingly align their actions with a norm of self-interest; Wuthnow 1991, 77).
In a nutshell, norms refer to actions over which people have control, and are supported by shared expectations about what should or should not be done in different types of social situations. However, norms cannot be identified just with observable behavior, nor can they merely be equated with normative beliefs.
The varying degrees of correlation between normative beliefs and actions are an important factor researchers can use to differentiate among various types of norms. Such a correlation is also a key element to consider when critically assessing competing theories of norms: we begin by surveying the socialized actor theory, the social identity theory, and some early rational choice (cost-benefit) models of conformity.
In the theory of the socialized actor (Parsons 1951), individual action is intended as a choice among alternatives. Human action is understood within a utilitarian framework as instrumentally oriented and utility maximizing. Although a utilitarian setting does not necessarily imply a view of human motives as essentially egoistic, this is the preferred interpretation of utilitarianism adopted by Talcott Parsons and much contemporary sociology. In this context, it becomes crucial to explain through which mechanisms social order and stability are attained in a society that would otherwise be in a permanent Hobbesian state of nature. In short, order and stability are essentially socially derived phenomena, brought about by a common value system —the “cement” of society. The common values of a society are embodied in norms that, when conformed to, guarantee the orderly functioning and reproduction of the social system. In the Parsonian framework norms are exogenous: how such a common value system is created and how it may change are issues left unexplored. The most important question is rather how norms get to be followed, and what prompts rational egoists to abide by them. The answer given by the theory of the socialized actor is that people voluntarily adhere to the shared value system, because it is introjected to form a constitutive element of the personality itself (Parsons 1951).
In Parsons’ own words, a norm is
a verbal description of a concrete course of action, … , regarded as desirable, combined with an injunction to make certain future actions conform to this course. (1937: 75)
Norms play a crucial role in individual choice since—by shaping individual needs and preferences—they serve as criteria for selecting among alternatives. Such criteria are shared by a given community and embody a common value system. People may choose what they prefer, but what they prefer in turn conforms to social expectations: norms influence behavior because, through a process of socialization that starts in infancy, they become part of one’s motives for action. Conformity to standing norms is a stable, acquired disposition that is independent of the consequences of conforming. Such lasting dispositions are formed by long-term interactions with significant others (e.g., one’s parents): through repeated socialization, individuals come to learn and internalize the common values embodied in the norms. Internalization is conceived as the process by which people develop a psychological need or motive to conform to a set of shared norms. When norms are internalized norm-abiding behavior will be perceived as good or appropriate, and people will typically feel guilt or shame at the prospect of behaving in a deviant way. If internalization is successful external sanctions will play no role in eliciting conformity and, since individuals are motivated to conform, it follows that normative beliefs and actions will be consistent.
Although Parsons’ analysis of social systems starts with a theory of individual action, he views social actors as behaving according to roles that define their identities and actions (through socialization and internalization). The goal of individual action is to maximize satisfaction. The potential conflict between individual desires and collective goals is resolved by characterizing the common value system as one that precedes and constrains the social actor. The price of this solution is the disappearance of the individual actor as the basic unit of analysis. Insofar as individuals are role-bearers, in Parsons’ theory it is social entities that act: entities that are completely detached from the individual actions that created them. This consideration forms the basis for most of the criticisms raised against the theory of the socialized actor (Wrong 1961); such criticisms are typically somewhat abstract as they are cast in the framework of the holism/individualism controversy.
On the other hand, one may easily verify whether empirical predictions drawn from the socialized actor theory are supported by experimental evidence. For instance, the following predictions can be derived from the theory and easily put to test. (a) Norms will change very slowly and only through intensive social interaction. (b) Normative beliefs are positively correlated to actions; whenever such beliefs change, behavior will follow. (c) If a norm is successfully internalized, expectations of others’ conformity will have no effect on an individual’s choice to conform.
Some of the above statements are not supported by empirical evidence from social psychology. For example, it has been shown that there may not be a relation between people’s normative beliefs (or attitudes) and what people in fact do. In this respect, it should be noted that experimental psychologists have generally focused on “attitudes”, that is, “evaluative feelings of pro or con, favorable or unfavorable, with regard to particular objects” (where the objects may be “concrete representations of things or actions, or abstract concepts”; Insko & Schopler 1967: 361–362). As such, the concept of attitude is quite broad: it includes normative beliefs, as well as personal opinions and preferences. That said, a series of field experiments has provided evidence contrary to the assumption that attitudes and behaviors are closely related. LaPiere (1934) famously reported a sharp divergence between the widespread anti-Chinese attitudes in the United States and the tolerant behavior he witnessed. Other studies have pointed to inconsistencies between an individual’s stated normative beliefs and her actions (Wicker 1969): several reasons may account for such a discrepancy. For example, studies of racial prejudice indicate that normative beliefs are more likely to determine behavior in long-lasting relationships, and least likely to determine behavior in the transient situations typical of experimental studies (Harding et al. 1954 [1969]; Gaertner & Dovidio 1986). Warner and DeFleur (1969) reported that the main variable affecting discriminatory behavior is one’s belief about what society (e.g., most other people) says one should do, as opposed to what one personally thinks one should do.
In brief, the social psychology literature provides mixed evidence in support of the claim that an individual’s normative beliefs and attitudes influence her actions. Such studies, however, do not carefully discriminate among various types of normative beliefs. In particular, one should distinguish between “personal normative beliefs” (i.e., beliefs that a certain behavior ought to be followed) and “normative expectations” (i.e., what one believes others believe ought to be done, that is, a second-order belief): it then becomes apparent that oftentimes only such second-order beliefs affect behavior.
The above constitutes an important criticism of the socialized actor theory. According to Parsons, once a norm is internalized, members of society are motivated to conform by an internal sanctioning system; therefore, one should observe a high correlation among all orders of normative beliefs and behavior. However, experimental evidence does not support such a view (see also: Fishbein 1967; Cialdini et al. 1991). Another indication that the socialized actor theory lacks generality is the observation that norms can change rather quickly, and that new norms often emerge in a short period of time among complete strangers (Mackie 1996). Long-term or close interactions do not seem to be necessary for someone to acquire a given normative disposition, as is testified by the relative ease with which individuals learn new norms when they change status or group (e.g., from single to married, from student to faculty, etc.). Moreover, studies of emergent social and political groups have shown that new norms may form rather rapidly, and that the demise of old patterns of behavior is often abrupt (Robinson 1932; Klassen et al. 1989; Prentice & Miller 1993; Matza 1964). Given the aforementioned limitations, Parsons’ theory might perhaps be taken as an explanation of a particular conception of moral norms (in the sense of internalized, unconditional imperatives), but it cannot be viewed as a general theory of social norms.
It has been argued that behavior is often closely embedded in a network of personal relations, and that a theory of norms should not leave the specific social context out of consideration (Granovetter 1985). Critics of the socialized actor theory have called for an alternative conception of norms that may account for the often weak relation between beliefs and behavior (Deutscher 1973). This alternative approach takes social relations to be crucial in explaining social action, and considers social identity as a key motivating factor. (A strong support for this view among anthropologists is to be found in the work of Cancian 1975.)
Since the notion of social identity is inextricably linked to that of group behavior, it is important to clarify the relation between these concepts. By “social identity” we refer, in Tajfel’s own words, to
that part of an individual’s self-concept which derives from his knowledge of his membership of a social group (or groups) together with the value and emotional significance attached to that membership. (Tajfel 1981: 255)
Note that a crucial feature of social identity is that one’s identification with the group is in some sense a conscious choice: one may accidentally belong to a group, but we can meaningfully talk of social identification only when being a group-member becomes (at least in part) constitutive of who one is. According to Tajfel’s theory, when we categorize ourselves as belonging to a particular group, the perception and definition of the self—as well as our motives—change. That is, we start perceiving ourselves and our fellow group-members along impersonal, “typical” dimensions that characterize the group to which we belong. Such dimensions include specific roles and the beliefs (or actions) that accompany them.
Turner et al.’s (1987) “self-categorization theory” provides a more specific characterization of self-perception, or self-definition, as a system of cognitive self-schemata that filter and process information. Such schemata result in a representation of the social situation that guides the choice of appropriate action. This system has at least two major components, i.e., social and personal identity. Social identity refers to self-descriptions related to group memberships. Personal identity refers to self-descriptions such as individual character traits, abilities, and tastes. Although personal and social identities are mutually exclusive levels of self-definition, this distinction must be taken as an approximation (in that there are many interconnections between social and personal identities). It is, however, important to recognize that we often perceive ourselves primarily in terms of our relevant group memberships rather than as differentiated, unique individuals. So—depending on the situation—personal or group identity will become salient (Brewer 1991).
For example, when one makes interpersonal comparisons between oneself and other group-members, personal identity will become salient; instead, group identity will become salient in situations in which one’s group is compared to another group. Within a group, all those factors that lead members to categorize themselves as different (or endowed with special characteristics and traits) will enhance personal identity. If a group has to solve a common task, but each member is to be rewarded according to her contribution, personal abilities are highlighted and individuals will perceive themselves as unique and different from the rest of the group. Conversely, if all group-members are to equally share the reward for a jointly performed task, group identification will be enhanced. When the difference between self and fellow group-members is accentuated, we are likely to observe selfish motives and self-favoritism against other group-members. When instead group identification is enhanced, in-group favoritism against out-group members will be activated, as well as behavior contrary to self-interest.
According to Turner, social identity is basically a cognitive mechanism whose adaptive function is to make “group behavior” possible. Whenever social identification becomes salient, a cognitive mechanism of categorization is activated in such a way to produce perceptual and behavioral changes. Such categorization is called a stereotype, the prototypical description of what members of a given category are (or are believed to be). It is a cluster of physical, mental and psychological characteristics attributed to a “typical” member of a given group. Stereotyping, like any other categorization process, activates scripts or schemata, and what we call group behavior is nothing but scripted behavior. For example, the category “Asian student” is associated with a cluster of behaviors, personality traits, and values: we often think of Asian students as respectful, diligent, disciplined, and especially good with technical subjects. When thinking of an Asian student solely in terms of group membership, we attribute her the stereotypical characteristics associated with her group, so she becomes interchangeable with other group-members. When we perceive people in terms of stereotypes, we depersonalize them and see them as “typical” members of their group. The same process is at work when we perceive ourselves as group-members: self-stereotyping is a cognitive shift from “perceiving oneself as unique” to “perceiving oneself in terms of the attributes that characterize the group”. It is this cognitive shift that mediates group behavior.
Group behavior (as opposed to individual behavior) is characterized by features such as a perceived similarity between group-members, cohesiveness, a tendency to cooperate to achieve common goals, shared attitudes or beliefs, and conformity to group norms. Once an individual self-categorizes as member of a group, she will perceive herself as “depersonalized” and similar to other group-members in the relevant stereotypical dimensions. Insofar as group-members perceive their interests and goals as identical—because such interests and goals are stereotypical attributes of the group—self-stereotyping will induce a group-member to embrace such interests and goals as her own. It is thus predicted that pro-social behavior will be enhanced by group membership, and diluted when people act in an individualistic mode (Brewer 1979).
The groups with which we happen to identify ourselves may be very large (as in the case in which one self-defines as Muslim or French), or as small as a friends’ group. Some general group identities may not involve specific norms, but there are many cases in which group identification and social norms are inextricably connected. In that case group-members believe that certain patterns of behavior are unique to them, and use their distinctive norms to define group membership. Many close-knit groups (such as the Amish or the Hasidic Jews) enforce norms of separation proscribing marriage with outsiders, as well as specific dress codes and a host of other prescriptive and proscriptive norms. There, once an individual perceives herself as a group-member, she will adhere to the group prototype and behave in accordance with it. Hogg and Turner (1987) have called the process through which individuals come to conform to group norms “referent informational influence”.
Group-specific norms have (among other things) the twofold function of minimizing perceived differences among group-members and maximizing differences between the group and outsiders. Once formed, such norms become stable cognitive representations of appropriate behavior as a group-member. Social identity is built around group characteristics and behavioral standards, and hence any perceived lack of conformity to group norms is seen as a threat to the legitimacy of the group. Self-categorization accentuates the similarities between one’s behavior and that prescribed by the group norm, thus causing conformity as well as the disposition to control and punish transgressors. In the social identity framework, group norms are obeyed because one identifies with the group, and conformity is mediated by self-categorization as an in-group member. A telling historical example of the relationship between norms and group membership was the division of England into the two parties of the Roundheads and Cavaliers. Charles Mackay reports that
in those days every species of vice and iniquity was thought by the Puritans to lurk in the long curly tresses of the monarchists, while the latter imagined that their opponents were as destitute of wit, of wisdom, and of virtue, as they were of hair. A man’s locks were a symbol of his creed, both in politics and religion. The more abundant the hair, the more scant the faith; and the balder the head, the more sincere the piety. (Mackay 1841: 351)
It should be noted that in this framework social norms are defined by collective—as opposed to personal—beliefs about appropriate behaviors (Homans 1950, 1961). To a certain extent, this characterization of social norms is closer to recent accounts than it is to Parsons’ socialized actor theory. On the other hand, a distinct feature of the social identity framework is that people’s motivation to conform comes from their desire to validate their identity as group-members. In short, there are several empirical predictions one can draw from such a framework. Given the theory’s emphasis on identity as a motivating factor, conformity to a norm is not assumed to depend on an individual’s internalization of that norm; in fact, a change in social status or group membership will bring about a change in the norms relevant to the new status/group. Thus a new norm can be quickly adopted without much interaction, and beliefs about identity validation may change very rapidly under the pressure of external circumstances. In this case, not just norm compliance, but norms themselves are potentially unstable.
The experimental literature on social dilemmas has utilized the “priming of group identity” as a mechanism for promoting cooperative behavior (Dawes 1980; Brewer & Schneider 1990). The typical hypothesis is that a pre-play, face-to-face communication stage may induce identification with the group, and thus promote cooperative behavior among group-members. In effect, rates of cooperation have been shown to be generally higher in social dilemma experiments preceded by a pre-play communication stage (Dawes 1991). However, it has been argued that face-to-face communication may actually help group-members gather relevant information about one another: such information may therefore induce subjects to trust each other’s promises and act cooperatively, regardless of any group identification. In this respect, it has been shown that communication per se does not foster cooperation, unless subjects are allowed to talk about relevant topics (Bicchieri & Lev-On 2007). This provides support for the view that communication does not enhance cohesion but rather focuses subjects on relevant rules of behavior, which do not necessarily depend on group identification.
Cooperative outcomes can thus be explained without resorting to the concept of social identity. A social identity explanation appears to be more appropriate in the context of a relatively stable environment, where individuals have had time to make emotional investments (or at least can expect repeated future interactions within the same group). In artificial lab settings, where there are no expectations of future interactions, the concept of social identity seems less persuasive as an explanation of the observed rates of cooperation. On the other hand, we note that social identity does appear to play a role in experimental settings in which participants are divided into separate groups. (In that case, it has been shown that participants categorize the situation as “we versus them”, activating in-group loyalty and trust, and an equal degree of mistrust toward the out-group; Kramer & Brewer 1984; Bornstein & Ben-Yossef 1994.)
Even with stable environments and repeated interactions, however, a theory of norm compliance in terms of social identity cannot avoid the difficulty of making predictions when one is simultaneously committed to different identities. We may concurrently be workers, parents, spouses, friends, club members, and party affiliates, to name but a few of the possible identities we embrace. For each of them there are rules that define what is appropriate, acceptable, or good behavior. In the social identity framework, however, it is not clear what happens when one is committed to different identities that may involve conflicting behaviors.
Finally, there is ample evidence that people’s perceptions may change very rapidly. Since in this framework norms are defined as shared perceptions about group beliefs, one would expect that—whenever all members of a group happen to believe that others have changed their beliefs about core membership rules—the very norms that define membership will change. The study of fashion, fads and speculative bubbles clearly shows that there are some domains in which rapid (and possibly disruptive) changes of collective expectations may occur; it is, however, much less clear what sort of norms are more likely to be subject to rapid changes (think of dress codes rather than codes of honor). The social identity view does not offer a theoretical framework for differentiating these cases: although some norms are indeed related to group membership, and thus compliance may be explained through identity-validation mechanisms, there appear to be limits to the social identity explanation.
Early rational choice models of conformity maintained that, since norms are upheld by sanctions, compliance is merely a payoff-maximizing strategy (Rommetveit 1955; Thibaut & Kelley 1959): when others’ approval and disapproval act as external sanctions, we have a “cost-benefit model” of compliance (Axelrod 1986; James Coleman 1990). Rule-complying strategies are rationally chosen in order to avoid negative sanctions or to attract positive sanctions. This class of rational choice models defines norms behaviorally, equating them with patterns of behavior (while disregarding expectations or values). Such approach relies heavily on sanctions as a motivating factor. According to Axelrod (1986), for example, if we observe individuals to follow a regular pattern of behavior and to be punished if they act otherwise, then we have a norm. Similarly, Coleman (1990) argues that a norm coincides with a set of sanctions that act to direct a given behavior.
However, it has been shown that not all social norms involve sanctions (Diamond 1935; Hoebel 1954). Moreover, sanctioning works generally well in small groups and in the context of repeated interactions, where the identity of participants is known and monitoring is relatively easy. Still, even in such cases there may be a so-called second-order public goods problem. That is, imposing negative sanctions on transgressors is in everybody’s interest, but the individual who observes a transgression faces a dilemma: she is to decide whether or not to punish the transgressor, where punishing typically involves costs; besides, there is no guarantee that other individuals will also impose a penalty on transgressors when faced with the same dilemma. An answer to this problem has been to assume that there exist “meta-norms” that tell people to punish transgressors of lower-level norms (Axelrod 1986). This solution, however, only shifts the problem one level up: upholding the meta-norm itself requires the existence of a higher-level sanctioning system.
Another problem with sanctions is the following: a sanction, to be effective, must be recognized as such. Coleman and Axelrod typically take the repeated prisoner’s dilemma game as an example of the working of sanctions. However, in a repeated prisoner’s dilemma the same action (“C” or “D”) must serve as both the sanctioning action and the target action. By simply looking at behavior, it is unclear whether the action is a function of a sanction or a sanction itself. It thus becomes difficult to determine the presence of a norm, or to assess its effect on choice as distinct from the individual strategies of players.
A further consideration weakens the credibility of the view that norms are upheld only because of external sanctions. Often we keep conforming to a norm even in situations of complete anonymity, where the probability of being caught transgressing is almost zero. In this case fear of sanctions cannot be a motivating force. As a consequence, it is often argued that cases of “spontaneous” compliance are the result of internalization (Scott 1971): people who have developed an internal sanctioning system feel guilt and shame at behaving in a deviant way. Yet, we have seen that the Parsonian view of internalization and socialization is inadequate, as it leads to predictions about compliance that often run counter to empirical evidence.
In particular, James Coleman (1990) has argued in favor of reducing internalization to rational choice, insofar as it is in the interest of a group to get another group to internalize certain norms. In this case internalization would still be the result of some form of socialization. This theory faces some of the same objections raised against Parsons’ theory: norms that are passed on from parents to children, for example, should be extremely resistant to change; hence, one should expect a high degree of correlation between such norms and behavior, especially in those cases where norms prescribe specific kinds of actions. However, studies of normative beliefs about honesty—which one typically acquires during childhood—show that such beliefs are often uncorrelated with behavior (Freeman & Ataöv 1960).
Bicchieri (1990, 1997) has presented a third, alternative view about internalization. This view of internalization is cognitive, and is grounded on the assumption that social norms develop in small, close-knit groups where ongoing interactions are the rule. Once an individual has learned to behave in a way consistent with the group’s interests, she will tend to persist in the learned behavior unless it becomes clear that—on average—the cost of upholding the norm significantly outweighs the benefits. Small groups can typically monitor their members’ behavior and successfully employ retaliation whenever free-riding is observed. In such groups an individual will learn, maybe at some personal cost, to cooperate; she will then uphold the cooperative norm as a “default rule” in any new encounter, unless it becomes evident that the cost of conformity has become excessive. The idea that norms may be “sluggish” is in line with well-known results from cognitive psychology showing that, once a norm has emerged in a group, it will tend to guide the behavior of its members even when they face a new situation (or are isolated from the original group; Sherif 1936).
Empirical evidence shows that norm-abiding behavior is not, as the early rational choice models would have it, a matter of cost/benefit calculation. Upholding a norm that has led one to fare reasonably well in the past is a way of economizing on the effort one would have to exert to devise a strategy when facing a new situation . This kind of “bounded rationality” approach explains why people tend to obey norms that sometimes put them at a disadvantage, as is the case with norms of honesty. This does not mean, however, that external sanctions never play a role in compliance: for example, in the initial development of a norm sanctions may indeed play an important role. Yet, once a norm is established, there are several mechanisms that may account for conformity.
Finally, the view that one conforms only because of the threat of negative sanctions does not distinguish norm-abiding behavior from an obsession or an entrenched habit; nor does that view distinguish social norms from hypothetical imperatives enforced by sanctions (such as the rule that prohibits naked sunbathing on public beaches). In these cases avoidance of the sanctions associated with transgressions constitutes a decisive reason to conform, independently of what others do. In fact, in the traditional rational choice perspective, the only expectations that matter are those about the sanctions that follow compliance or non-compliance. In those frameworks, beliefs about how other people will act—as opposed to what they expect us to do—are not a relevant explanatory variable: however, this leads to predictions about norm compliance that often run counter to empirical evidence.
The traditional rational choice model of compliance depicts the individual as facing a decision problem in isolation: if there are sanctions for non-compliance, the individual will calculate the benefit of transgression against the cost of norm compliance, and eventually choose so as to maximize her expected utility. Individuals, however, seldom choose in isolation: they know the outcome of their choice will depend on the actions and beliefs of other individuals. Game theory provides a formal framework for modeling strategic interactions.
Thomas Schelling (1960), David Lewis (1969), Edna Ullmann-Margalit (1977), Robert Sugden (1986) and, more recently, Peyton Young (1993), Cristina Bicchieri (1993), and Peter Vanderschraaf (1995) have proposed a game-theoretic account according to which a norm is broadly defined as an equilibrium of a strategic interaction. In particular, a Nash equilibrium is a combination of strategies (one for each individual), such that each individual’s strategy is a best reply to the others’ strategies. Since it is an equilibrium, a norm is supported by self-fulfilling expectations in the sense that players’ beliefs are consistent, and thus the actions that follow from players’ beliefs will validate those very beliefs. Characterizing social norms as equilibria has the advantage of emphasizing the role that expectations play in upholding norms. On the other hand, this interpretation of social norms does not prima facie explain why people prefer to conform if they expect others to conform.
Take for example conventions such as putting the fork to the left of the plate, adopting a dress code, or using a particular sign language. In all these cases, my choice to follow a certain rule is conditional upon expecting most other people to follow it. Once my expectation is met, I have every reason to adopt the rule in question. In fact, if I do not use the sign language everybody else uses, I will not be able to communicate. It is in my immediate interest to follow the convention, since my main goal is to coordinate with other people. In the case of conventions, there is a continuity between the individual’s self-interest and the interests of the community that supports the convention. This is the reason why David Lewis models conventions as equilibria of coordination games . Such games have multiple equilibria, but once one of them has been established, players will have every incentive to keep playing it (as any deviation will be costly).
Take instead a norm of cooperation. In this case, the expectation that almost everyone abides by it may not be sufficient to induce compliance. If everyone is expected to cooperate one may be tempted, if unmonitored, to behave in the opposite way. The point is that conforming to social norms , as opposed to conventions, is almost never in the immediate interest of the individual. Often there is a discontinuity between the individual’s self-interest and the interests of the community that supports the social norm.
The typical game in which following a norm would provide a better solution (than the one attained by self-centered agents) is a mixed-motive game such as the prisoner’s dilemma or the trust game. In such games the unique Nash equilibrium represents a suboptimal outcome. It should be stressed that—whereas a convention is one among several equilibria of a coordination game—a social norm can never be an equilibrium of a mixed-motive game. However, Bicchieri (2006) has argued that when a norm exists it transforms the original mixed-motive game into a coordination one. As an example, consider the following prisoner’s dilemma game ( Figure 1 ), where the payoffs are B=Best, S=Second, T=Third, and W=Worst. Clearly the only Nash equilibrium is to defect (D), in which case both players get (T,T), a suboptimal outcome. Suppose, however, that society has developed a norm of cooperation; that is, whenever a social dilemma occurs, it is commonly understood that the parties should privilege a cooperative attitude. Should, however, does not imply “will”, therefore the new game generated by the existence of the cooperative norm has two equilibria: either both players defect or both cooperate.
Note that, in the new coordination game (which was created by the existence of the cooperative norm), the payoffs are quite different from those of the original prisoner’s dilemma. Thus there are two equilibria: if both players follow the cooperative norm they will play an optimal equilibrium and get (B,B), whereas if they both choose to defect they will get the suboptimal outcome (S,S). Players’ payoffs in the new coordination game differ from the original payoffs because their preferences and beliefs will reflect the existence of the norm. More specifically, if a player knows that a cooperative norm exists and has the right kind of expectations, then she will have a preference to conform to the norm in a situation in which she can choose to cooperate or to defect. In the new game generated by the norm’s existence, choosing to defect when others cooperate is not a good choice anymore (T,W). To understand why, let us look more closely to the preferences and expectations that underlie the conditional choice to conform to a social norm.
Bicchieri (2006) defines the expectations that underlie norm compliance, as follows:
Note that universal compliance is not usually needed for a norm to exist. However, how much deviance is socially tolerable will depend on the norm in question. Group norms and well-entrenched social norms will typically be followed by almost all members of a group or population, whereas greater deviance is usually accepted when norms are new or they are not deemed to be socially important. Furthermore, as it is usually unclear how many people follow a norm, different individuals may have different beliefs about the size of the group of followers, and may also have different thresholds for what “sufficiently large” means. What matters to conformity is that an individual believes that her threshold has been reached or surpassed. For a critical assessment of the above definition of norm-driven preferences, see Hausman (2008).
Brennan et al. (2013) also argue that norms of all kinds share in an essential structure. Norms are clusters of normative attitudes in a group, combined with the knowledge that such a cluster of attitudes exists. On their account, “A normative principle P is a norm within a group G if and only if:
- A significant proportion of the members of G have P -corresponding normative attitudes; and
- A significant proportion of the members of G know that a significant proportion of the members of G have P -corresponding attitudes” (Brennan et al. 2013: 29)
On this account, a “ P -corresponding normative attitude” is understood to be a judgment, emotional state, expectation, or other properly first personal normative belief that supports the principle P (e.g., Alice thinking most people should P would count as a normative attitude). Condition (i) is meant to reflect genuine first personal normative commitments, attitudes or beliefs. Condition (ii) is meant to capture those cases where individuals know that a large part of their group also shares in those attitudes. Putting conditions (i) and (ii) together offers a picture that the authors argue allows for explanatory work to be done on a social-level normative concept while remaining grounded in individual-level attitudes.
Consider again the new coordination game of Figure 1 : for players to obey the norm, and thus choose C, it must be the case that each expects the other to follow it. In the original prisoner’s dilemma, empirical beliefs would not be sufficient to induce cooperative behavior. When a norm exists, however, players also believe that others believe they should obey the norm, and may even punish them if they do not. The combined force of empirical and normative expectations makes norm conformity a compelling choice, be it because punishment may follow or just because one recognizes the legitimacy of others’ expectations (Sugden 2000).
It is important to understand that conformity to a social norm is always conditional on the expectations of what the relevant other/s will do. We prefer to comply with the norm as we have certain expectations. To make this point clear, think of the player who is facing a typical one-shot prisoner’s dilemma with an unknown opponent. Suppose the player knows a norm of cooperation exists and is generally followed, but she is uncertain as to whether the opponent is a norm-follower. In this case the player is facing the following situation ( Figure 2 ).
With probability p , the opponent is a norm-following type, and with probability \(1 - p\) she is not. According to Bicchieri, conditional preferences imply that having a reason to be fair, reciprocate or cooperate in a given situation does not entail having any general motive or disposition to be fair, reciprocate or cooperate as such. Having conditional preferences means that one may follow a norm in the presence of the relevant expectations, but disregard it in its absence. Whether a norm is followed at a given time depends on the actual proportion of followers, on the expectations of conditional followers about such proportion, and on the combination of individual thresholds.
As an example, consider a community that abides by strict norms of honesty. A person who, upon entering the community, systematically violates these norms will certainly be met with hostility, if not utterly excluded from the group. But suppose that a large group of thieves makes its way into this community. In due time, people would cease to expect honesty on the part of others, and would find no reason to be honest themselves in a world overtaken by crime. In this case, probably norms of honesty would cease to exist, as the strength of a norm lies in its being followed by many of the members of the relevant group (which in turn reinforces people’s expectations of conformity).
What we have discussed is a “rational reconstruction” of what a social norm is. Such a reconstruction is meant to capture some essential features of norm-driven behavior; also, this analysis helps us distinguish social norms from other constructs such as conventions or personal norms. A limit of this account, however, is that it does not indicate how such equilibria are attained or, in other terms, how expectations become self-fulfilling.
While neoclassical economics and game theory traditionally conceived of institutions as exogenous constraints, research in political economy has generated new insights into the study of endogenous institutions . Specifically, endogenous norms have been shown to restrict the individual’s action set and drive preferences over action profiles (Bowles 1998; Ostrom 2000). As a result, the “standard” economic framework positing exogenous (and in particular self-centered) preferences has come under scrutiny. Widely documented deviations from the predictions of models with self-centered agents have informed alternative accounts of individual choice (for one of the first models of “interdependent preferences”, see Stigler & Becker 1977).
Some alternative accounts have helped reconcile insights about norm-driven behavior with instrumental rationality (Elster 1989b). Moreover, they have contributed to informing the design of laboratory experiments on non-standard preferences (for a survey of early experiments, see Ledyard 1995; more recent experiments are reviewed by Fehr & Schmidt 2006 and Kagel & Roth 2016). In turn, experimental findings have inspired the formulation of a wide range of models aiming to rationalize the behavior observed in the lab (Camerer 2003; Dhami 2016).
It has been argued that the upholding of social norms could simply be modeled as the optimization of a utility function that includes the others’ welfare as an argument. For instance, consider some of the early “social preference” theories, such as Bolton and Ockenfels’ (2000) or Fehr and Schmidt’s (1999) models of inequity aversion. These frameworks can explain a good wealth of evidence on preferences for equitable income distributions; they cannot however account for conditional preferences like those reflecting principles of reciprocity (e.g., I will keep the common bathroom clean, if I believe my roommates do the same). As noted above, the approach to social norms taken by philosophically-inclined scholars has emphasized the importance of conditional preferences in supporting social norms. In this connection, we note that some of the social preference theories do account for motivations conditional on empirical beliefs, whereby a player upholds a principle of “fair” behavior if she believes her co-players will uphold it too (Rabin 1993; Dufwenberg & Kirchsteiger 2004; Falk & Fischbacher 2006; Charness & Rabin 2002). These theories presuppose that players are hardwired with a notion of fair or kind behavior, as exogenously defined by the theorist. Since they implicitly assume that all players have internalized a unique—exogenous—normative standpoint (as reflected in some notion of fairness or kindness), these theories do not explicitly model normative expectations. Hence, players’ preferences are assumed to be conditional solely on their empirical beliefs; that is, preferences are conditional on whether others will behave fairly (according to an exogenous principle) or not.
That said, we stress that social preferences should not be conflated with social norms. Social preferences capture stable dispositions toward an exogenously defined principle of conduct (Binmore 2010). By contrast, social norms are better studied as group-specific solutions to strategic problems (Sugden 1986; Bicchieri 1993; Young 1998b). Such solutions are brought about by a particular class of preferences (“norm-driven preferences”), conditional on the relevant set of empirical beliefs and normative expectations. In fact, we stress that “what constitutes fair or appropriate behavior” often varies with cultural or situational factors (Henrich et al. 2001; Cappelen et al. 2007; Ellingsen et al. 2012). Accounting for endogenous expectations is therefore key to a full understanding of social norms.
Relatedly, Guala (2016) offers a game-theoretic account of institutions, arguing that institutions are sets of rules in equilibrium. Guala’s view incorporates insights from two competing accounts of institutions: institutions-as-rules (perhaps best rendered by North 1990), and institutions-as-equilibria. From the first account, he captures the idea that institutions create rules that help to guide our behaviors and reduce uncertainty. With rules in place, we more or less know what to do, even in new situations. From the second, he captures the idea that institutions are solutions to coordination problems that arise from our normal interactions. The institutions give us reasons to follow them. The function of the rules, then, is to point to actions that promote coordination and cooperation. Because of the equilibrium nature of the rules, each individual has an incentive to choose those actions, provided others do too. Guala relies on a correlated equilibrium concept to unite the rules and equilibria accounts. On this picture, an institution is simply a correlated equilibrium in a game, where other correlated equilibria would have been possible.
Thrasher (2018) offers a comparative-functional analysis of norms that broadly aligns with the Bicchieri (2006) framework to help understand the durability of “bad norms.” Abbink et al. (2017) use public goods-like experiments to show how peer punishment can hold inefficient norms in place. This general framework can be helpful to understand why duels and honor killings can become stable (e.g. Thrasher and Handfield 2018, Handfield and Thrasher 2019). This work explores the signaling function of socially costly norms.
An alternative class of models explains norm compliance in terms of social image or self-image concerns (e.g., Andreoni and Bernheim 2009; Bénabou and Tirole 2006, 2011). These models assume that one tries to signal (to others or to one’s future self) that one has good “personal traits”, with such type-specific traits being imperfectly observed. More precisely, Bénabou and Tirole (2006) model the individual’s utility from contributing to a public good as a function of (i) material payoffs, (ii) intrinsic rewards from behaving altruistically, and (iii) reputational returns; in particular, the authors assume that reputational returns depend on the observers’ posterior expectations of the individual’s type. Bénabou and Tirole then consider (a refinement of) signaling equilibria, thereby allowing for multiple solutions to occur as a result of the interplay of individual motivations and of the level of observability of the actions. While models with reputational concerns do not explicitly define normative expectations, they generally posit that players care about their reputation under the assumption that acting altruistically is good or appropriate. Looking ahead, there is still work to do to fully formalize the interplay of (endogenous) normative expectations and empirical beliefs within a general model that is applicable to any game setting. Such a model should probably build on the “psychological game theory” framework (for discussion, see Battigalli and Dufwenberg 2022, p. 857; see also Bicchieri and Sontuoso 2015).
In what follows we focus on lab experiments that identify social norms by explicitly measuring both empirical and normative expectations.
Xiao and Bicchieri (2010) designed an experiment to investigate the impact on trust games of two potentially applicable—but conflicting—principles of conduct, namely, equality and reciprocity . Note that the former can be broadly defined as a rule that recommends minimizing payoff differences, whereas the latter recommends taking a similar action as others (regardless of payoff considerations). The experimental design involved two trust game variants: in the first one, players started with equal endowments; in the second one, the investor was endowed with twice the money that the trustee was given. In both cases, the investor could choose to transfer a preset amount of money to the trustee or keep it all. Upon receiving the money, the trustee could in turn keep it or else transfer back some of it to the investor: in the equal endowment condition (“baseline treatment”), both equality and reciprocity dictate that the trustee transfer some money back to the investor; by contrast, in the unequal endowment condition (“asymmetry treatment”), equality and reciprocity dictate different actions as the trustee could guarantee payoff equality only by making a zero back-transfer. Xiao and Bicchieri elicited subjects’ first- and second-order empirical beliefs (“how much do you think other participants in your role will transfer to their counterpart?”; “what does your counterpart think you will do?”) and normative expectations (“how much do you think your counterpart believes you should transfer to her?”). The experimental results show that a majority of trustees returned a positive amount whenever reciprocity would reduce payoff inequality (in the baseline treatment); by contrast, a majority of trustees did not reciprocate the investors’ transfer when doing so would increase payoff inequality (in the asymmetry treatment). Moreover, investors correctly believed that less money would be returned in the asymmetry treatment than in the baseline treatment, and most trustees correctly estimated investors’ beliefs in both treatments. However, in the asymmetry treatment empirical beliefs and normative expectations conflicted: this highlights that, when there is ambiguity as to which principle of conduct is in place, each subject will support the rule of behavior that favors her most.
Reuben and Riedl (2013) examine the enforcement of norms of contribution to public goods in homogeneous and heterogeneous groups, such as groups whose members vary in their endowment, contribution capacity, or marginal benefits. In particular, Reuben and Riedl are interested in the normative appeal of two potentially applicable rules: the efficiency rule (prescribing maximal contributions by all) and the class of relative contribution rules (prescribing a contribution that is “fair” relative to the contributions of others; e.g., equality and equity rules). Reuben and Riedl’s results show that, in the absence of punishment, no positive contribution norm emerged and all groups converged toward free-riding. By contrast, with punishment, contributions were consistent with the prescriptions of the efficiency rule in a significant subset of groups (irrespective of the type of group heterogeneity); in other groups, contributions were consistent with relative contribution rules. These results suggest that even in heterogeneous groups individuals can successfully enforce a contribution norm. Most notably, survey data involving third parties confirmed well-defined yet conflicting normative views about the aforementioned contribution rules; in other words, both efficiency and relative contribution rules are normatively appealing, and are indeed potential candidates for emerging contribution norms in different groups.
Bicchieri and Chavez (2010) designed an experiment to investigate norm compliance in ultimatum games. Specifically, their experiment involved a variant of the ultimatum game whereby the proposer could choose one of the following three options: ($5, $5) , ($8, $2) , or Coin (in which case one of the other two allocations would be selected at random). This design allows for two plausible notions of fairness: as an equal outcome ($5, $5) or as a fair procedure (Coin). The experimenters elicited subjects’ normative expectations about the actions they thought would be considered fair by most participants: proposers and responders showed a remarkable degree of agreement in their notions of fairness, as most subjects believed that a majority of participants deemed both ($5, $5) and Coin to be appropriate. Further, the experimenters had subjects play three instances of the above ultimatum game under different information conditions. In the “full information” condition, all participants knew that the Coin option was available, and that responders would know if their respective proposer had chosen Coin. In the “private information” condition, responders did not know that Coin was available to proposers, and proposers were aware of responders’ ignorance. In the “limited information” condition, participants knew that the Coin option was available, but responders would not be able to distinguish whether their respective proposer had implemented one of the two allocations directly or had chosen Coin instead. The experimental results show that when normative expectations supporting the Coin option were either absent (in the private condition) or could be defied without consequence (in the limited condition), the frequency of choice of ($5, $5) and ($8, $2), respectively, were considerably higher than those of Coin. Moreover, the frequency of Coin choices was highest in the public information condition, where such option was common knowledge and its outcome transparent: this shows that there proposers followed the rule of behavior that favored them most, and that such a rule was effectively a social norm. On the other hand, substantial norm evasion characterized proposers’ behavior in the limited information condition, where ($8, $2) was the most frequent choice.
In a subsequent study, Chavez and Bicchieri (2013) measured empirical and normative expectations (as well as behavior) of third parties who were given the opportunity to add to or deduct from the payoffs of subjects who had participated in an ultimatum game. Third parties tended to reward subjects involved in equal allocations and to compensate victims of unfair allocations (rather than punish unfair behavior); on the other hand, third parties were willing to punish when compensation was not an available option. The experimental results further show that third parties shared a notion of fairness (as indicated by their normative expectations), and that such notion was sensitive to contextual differences.
Krupka and Weber (2013) introduced an interesting procedure for identifying social norms by means of pre-play coordination games. In brief, using alternative (between-subjects) variants of the dictator game, Krupka and Weber had participants assess the extent to which different actions were collectively perceived as socially appropriate: subjects providing these ratings effectively faced a coordination game, as they were incentivized to match the modal response given by others in the same situation (such a pre-play coordination game was intended to verify the presence of shared normative expectations). Krupka and Weber went on to use these elicited assessments to predict other subjects’ compliance with the relevant social norm in each dictator game variant (for another application of the same elicitation procedure, see Gächter et al. 2013).
Similarly, Schram and Charness’ (2015) proposed a procedure for inducing a shared understanding of the relevant rule of behavior, in the lab. In short, Schram and Charness had participants in dictator games receive advice from a group of third parties. The information received simply revealed what a group of uninvolved subjects thought dictators ought to do : as such, the information received generated an exogenous variation in the dictators’ normative expectations. Schram and Charness’ results show that choices are indeed affected by this information.
Bicchieri and Xiao (2009) designed an experiment to investigate what happens when empirical and normative expectations conflict. To that end, participants in a dictator game were exposed to different pieces of information. Specifically, two groups of dictators were given some “descriptive information”; that is, they were told what other subjects had done in another session (i.e., one group was told that previous participants had made for the most part a generous offer, while the other group was told that most participants had made a selfish offer). Further, another two groups of dictators were given some “normative information”; that is, they were told what previous subjects said ought to be done (i.e., one group was told that most previous participants thought that one should make a generous offer, while the other group was told that most participants thought that one should make a selfish offer). Other groups were given both descriptive and normative information. The experimental results show that—whenever such information did not conflict—both descriptive and normative messages had a significant influence on dictators’ own expectations and subsequent choices. When messages conflicted in that one indicated generosity and the other indicated selfishness, only the descriptive information affected dictators’ behavior. This suggests that if people recognize that others are breaching the norm, then they will no longer feel compelled to follow the relevant rule of behavior themselves.
To conclude, the studies surveyed here provide evidence of the role played by expectations in affecting behavior in a variety of social dilemmas. In this regard, we note that in contrast to the vast literature on empirical beliefs, the number of lab studies that directly measure normative expectations is relatively limited: more research is clearly needed to investigate the interplay of empirical and normative information about applicable rules of behavior.
Thus far we have examined accounts of social norms that take for granted that a particular norm exists in a population. However, for a full account of social norms, we must answer two questions related to the dynamics of norms. First, we must ask how a norm can emerge. Norms require a set of corresponding beliefs and expectations to support them, and so there must be an account of how these arise. Second, we must investigate the conditions under which a norm is stable under some competitive pressure from other norms. Sometimes, multiple candidate norms vie for dominance in a population. Even if one norm has come to dominate the population, new norms can try to “invade” the existing norm’s population of adherents.
Let us now turn to the question of norm emergence. Here we can see three classes of models: first, a purely biological approach, second, a more cognitive approach, and third, a structured interactions approach. The most famous of the biological approaches to norms seek to explain cooperative behavior. The simplest models are kin selection models (Hamilton 1964). These models seek to explain altruistic tendencies in animals by claiming that, as selection acts on genes, those genes have an incentive to promote the reproductive success of other identical sets of genes found in other animals. This mode of explanation can provide an account of why we see cooperative behaviors within families, but being gene-centered, cannot explain cooperative behavior toward strangers (as strangers should not be sufficiently genetically related to merit altruistic behavior).
Models of “reciprocal altruism” (Trivers 1971, 1985), on the other hand, tell us that cooperative behavior has no chance of evolving in random pairings, but will evolve in a social framework in which individuals can benefit from building reputations for being nice guys. Reciprocal altruism, however, does not require an evolutionary argument; a simple model of learning in ongoing close-knit groups will do, and has the further advantage of explaining why certain types of cooperative behavior are more likely to emerge than others. All that matters in these models is that agents can properly identify other agents, such that they can maintain a record of their past behavior. This allows for the possibility of reputations: people who have the reputation of being cooperative will be treated cooperatively, and those who have a reputation of being unfair will be treated unfairly.
A variation on the idea of reciprocal altruism can be seen in Axelrod (1986). Axelrod presents a “norms game” in which agents probabilistically choose to comply with the norm, or deviate from it, and then other agents can probabilistically choose to punish any deviations at some cost to them. Agents can choose over time to be more or less “bold”, which determines the rate at which they attempt defections, and they can likewise choose to be more or less “vengeful”, which determines how often they punish. Axelrod noted that if the game is left like this, we find that the stable state is constant defection and no punishment. However, if we introduce a meta-norm—one that punishes people who fail to punish defectors—then we arrive at a stable norm in which there is no boldness, but very high levels of vengefulness. It is under these conditions that we find a norm emerge and remain stable. Axelrod’s model aims to illustrate that norms require meta-norms. That is, failure to retaliate against a defection must be seen as equivalent to a defection itself. What Axelrod does not analyze is whether there is some cost to being vigilant. Namely, watching both defectors and non-punishers may have a cost that, though nominal, might encourage some to abandon vigilance once there has been no punishment for some time.
Bicchieri, Duffy and Tolle (2004) present an alternative model of norm emergence to explain how a norm of impersonal trust/reciprocity can emerge and survive in a heterogeneous population. This model does not rely on a meta-norm of punishment; instead, it is purely driven by repeated interactions of conditional strategies. In their model, agents play anywhere from 1 to 30 rounds of a trust game for 1,000 iterations, relying on the 4 unconditional strategies, and the 16 conditional strategies that are standard for the trust game. After each round, agents update their strategies based on the replicator dynamic. As the number of rounds grows, a norm of impersonal trust/reciprocity emerges in the population. Most interestingly, however, the norm is not associated with a single strategy, but it is supported by several strategies behaving in similar ways. This model suggests that Trivers’ basic model works well in normal social contexts, but we can further enrich the story by allowing a social norm to supervene on several behavioral strategies.
Muldoon et al. (2012) explore a simpler approach to norm emergence that relies on individual reasoners weighing their individual interests against their social sensitivity. This is done across a number of model variants based on a simple standing ovation. A striking finding of their “symmetric” model is that norm emergence is fairly rare, but can also be distinguished from merely common behaviors. A more cognitively demanding approach was taken by Muldoon, Lisciandra and Hartmann (2012), in which bayesian reasoners can learn to “discover” norms that were not present, and have no particular value. This can happen when agents think there might be a social rule, and then over-interpret social evidence. These models combine to suggest that we should expect many arbitrary norms, rather than a functionalist argument for the presence of norms.
The third prominent model of norm emergence comes from Brian Skyrms (1996, 2004) and Jason Alexander (2007). In this approach, two different features are emphasized: relatively simple cognitive processes and structured interactions. Both have explored a variety of games (such as the prisoner’s dilemma, the stag hunt, divide the dollar, and the ultimatum game) as exemplars of situations that offer the possibility of the emergence of a moral norm. Though Skyrms occasionally uses the replicator dynamic, both tend to emphasize simpler mechanisms in an agent-based learning context. In particular, learning rules like “imitate the best” or best response are used, as they are much less cognitively demanding. Alexander justifies the use of these simpler rules on the grounds that, rather than fully rational agents, we are cognitively limited beings who rely on fairly simple heuristics for our decision-making. Rules like imitation are extremely simple to follow. Best response requires a bit more cognitive sophistication, but is still simpler than a fully Bayesian model with unlimited memory and computational power. These simpler learning rules provide the same function as the replicator dynamic: in between rounds of play, agents rely on their learning rule to decide what strategy to employ. Note that both Skyrms and Alexander tend to treat norms as single strategies.
The largest contribution of this strain of modeling comes not from the assumption of boundedly rational agents, but rather the careful investigation of the effects of particular social structures on the equilibrium outcomes of various games. Much of the previous literature on evolutionary games has focused on the assumptions of infinite populations of agents playing games against randomly-assigned partners. Skyrms and Alexander both rightly emphasize the importance of structured interaction. As it is difficult to uncover and represent real-world network structures, both tend to rely on examining different classes of networks that have different properties, and from there investigate the robustness of particular norms against these alternative network structures. Alexander (2007) in particular has done a very careful study of the different classical network structures, where he examines lattices, small world networks, bounded degree networks, and dynamic networks for each game and learning rule he considers. A final feature of Skyrms and Alexander’s work is a refinement on this structural approach: they separate out two different kinds of networks. First, there is the interaction network, which represents the set of agents that any given agent can actively play a game with. Second is the update network , which is the set of agents that an agent can “see” when applying her learning rule. The interaction network is thus one’s immediate community, whereas the update network is all that the agent can see. To see why this is useful, we can imagine a case not too different from how we live, in which there is a fairly limited set of other people we may interact with, but thanks to a plethora of media options, we can see much more widely how others might act. This kind of situation can only be represented by clearly separating the two networks.
Thus, what makes the theory of norm emergence of Skyrms and Alexander so interesting is its enriching the set of idealizations that one must make in building a model. The addition of structured interaction and structured updates to a model of norm emergence can help make clear how certain kinds of norms tend to emerge in certain kinds of situation and not others, which is difficult or impossible to capture in random interaction models.
Now that we have examined norm emergence, we must examine what happens when a population is exposed to more than one social norm. In this instance, social norms must compete with each other for adherents. This lends itself to investigations about the competitive dynamics of norms over long time horizons. In particular, we can investigate the features of norms and of their environments, such as the populations themselves, which help facilitate one norm becoming dominant over others, or becoming prone to elimination by its competitors. An evolutionary model provides a description of the conditions under which social norms may spread. One may think of several environments to start with. A population can be represented as entirely homogeneous, in the sense that everybody is adopting the same type of behavior, or heterogeneous to various degrees. In the former case, it is important to know whether the commonly adopted behavior is stable against mutations. The relevant concept here is that of an evolutionarily stable strategy (ESS; Maynard Smith & Price 1973; Taylor & Jonker 1978): when a population of individuals adopts such a strategy, it cannot be successfully invaded by isolated mutants, since the mutants will be at a disadvantage with respect to reproductive success. An evolutionarily stable strategy is a refinement of the Nash equilibrium in game theory. Unlike standard Nash equilibria, evolutionarily stable strategies must either be strict equilibria , or have an advantage when playing against mutant strategies. Since strict equilibria are always superior to any unilateral deviations, and the second condition requires that the ESS have an advantage in playing against mutants, the strategy will remain resistant to any mutant invasion. This is a difficult criterion to meet, however. For example, a classic Tit-For-Tat strategy in the prisoner’s dilemma is not an ESS. Many strategies perform equally well against it, including the very simple “Always Cooperate” strategy, let alone Tit-For-Two-Tats, and any number of variations. Tit-For-Tat is merely an evolutionarily neutral strategy relative to these others. If we only consider strategies that are defection-oriented, then Tit-For-Tat is an ESS, since it will do better against itself, and no worse than defection strategies when paired with them.
A more interesting case, and one relevant to a study of the reproduction of norms of cooperation, is that of a population in which several competing strategies are present at any given time. What we want to know is whether the strategy frequencies that exist at a time are stable, or if there is a tendency for one strategy to become dominant over time. If we continue to rely on the ESS solution concept, we see a classic example in the hawk-dove game. If we assume that there is no uncorrelated asymmetry between the players, then the mixed Nash equilibrium is the ESS. If we further assume that there is no structure to how agents interact with each other, this can be interpreted in two ways: either each player randomizes her strategy in each round of play, or we have a stable polymorphism in the population, in which the proportion of each strategy in the population corresponds to the frequency with which each strategy would be played in a randomizing approach. So, in those cases where we can assume that players randomly encounter each other, whenever there is a mixed solution ESS we can expect to find polymorphic populations.
If we wish to avoid the interpretive challenge of a mixed solution ESS, there is an alternative analytic solution concept that we can employ: the evolutionarily stable state. An evolutionarily stable state is a distribution of (one or more) strategies that is robust against perturbations, whether they are exogenous shocks or mutant invasions, provided the perturbations are not overly large. Evolutionarily stable states are solutions to a replicator dynamic. Since evolutionarily stable states are naturally able to describe polymorphic or monomorphic populations, there is no difficulty with introducing population-oriented interpretations of mixed strategies. This is particularly important when random matching does not occur, as under those conditions, the mixed strategy can no longer be thought of as a description of population polymorphism.
Now that we have seen the prominent approaches to both norm emergence and norm stability, we can turn to some general interpretive considerations of evolutionary models. An evolutionary approach is based on the principle that strategies with higher current payoffs will be retained, while strategies that lead to failure will be abandoned. The success of a strategy is measured by its relative frequency in the population at any given time. This is most easily seen in a game theoretic framework. A game is repeated a finite number of times with randomly selected opponents. After each round of the game, the actual payoffs and strategies of the players become public knowledge; on the basis of this information, each player adjusts her strategy for the next round. The payoff to an individual player depends on her choice as well as on the choices of the other players in the game, and players are rational in the sense that they are payoff-maximizers. In an evolutionary model, however, players learn and adapt in a non-Bayesian way, that is, they do not condition on past experience using Bayes’ Rule. In this sense, they are not typical rational learners (Nachbar 1990; Binmore & Samuelson 1992).
In an evolutionary approach behavior is adaptive, so that a strategy that did work well in the past is retained, and one that fared poorly will be changed. This can be interpreted in two ways: either the evolution of strategies is the consequence of adaptation by individual agents, or the evolution of strategies is understood as the differential reproduction of agents based on their success rates in their interactions. The former interpretation assumes short timescales for interactions: many iterations of the game over time thus represent no more than a few decades in time in total. The latter interpretation assumes rather longer timescales: each instance of strategy adjustment represents a new generation of agents coming into the population, with the old generation dying simultaneously. Let us consider the ramifications of each interpretation in turn.
In the first interpretation, we have agents who employ learning rules that are less than fully rational, as defined by what a Bayesian agent would have, both in terms of computational ability and memory. As such, these rules tend to be classified as adaptive strategies: they are reacting to a more limited set of data, with lower cognitive resources than what a fully rational learner would possess. However, there are many different adaptive mechanisms we may attribute to the players. One realistic adaptive mechanism is learning by trial and error; another plausible mechanism is imitation: those who do best are observed by others who subsequently emulate their behavior (Hardin 1982). Reinforcement learning is another class of adaptive behavior, in which agents tweak their probabilities of choosing one strategy over another based on the payoffs they just received.
In the second interpretation, agents themselves do not learn, but rather the strategies grow or shrink in the population according to the reproductive advantages that they bestow upon the agents that adhere to them. This interpretation requires very long timescales, as it requires many generations of agents before equilibrium is reached. The typical dynamics that are considered in such circumstances come from biology. A standard approach is something like the replicator dynamic. Norms grow or shrink in proportion to both how many agents adhere to them at a given time, and their relative payoffs. More successful strategies gain adherents at the expense of less-successful ones. This evolutionary process assumes a constant-sized (or infinite) population over time. This interpretation of an evolutionary dynamic, which requires long timescales, raises the question of whether norms themselves evolve slowly. Norms can rapidly collapse in a very short amount of time. This phenomenon could not be represented within a model whose interpretation is generational in nature. It remains an open question, however, as to whether such timescales can be appropriate for examining the emergence of certain kinds of norms. While it is known that many norms can quickly come into being, it is not clear if this is true of all norms.
Another challenge in using evolutionary models to study social norms is that there is a potential problem of representation. In evolutionary models, there is no rigorous way to represent innovation or novelty. Whether we look at an agent-based simulation approach, or a straightforward game-theoretic approach, the strategy set open to the players, as well as their payoffs, must be defined in advance. But many social norms rely on innovations, whether they are technological or social. Wearing mini-skirts was not an option until they were invented. Marxist attitudes were largely not possible until Marx. The age at which one gets married and how many children one has are highly linked to availability of and education about birth control technologies. While much of the study of norms has focused on more generic concepts such as fairness, trust, or cooperation, the full breadth of social norms covers many of these more specific norms that require some account of social innovation.
This representational challenge has broad implications. Even when we can analytically identify evolutionarily stable states in a particular game, which is suggestive of norms that will be converged upon, we now have a problem of claiming that this norm has prospects for long-term stability. Events like the publication of the Kinsey report can dramatically shift seemingly stable norms quite rapidly. As the underlying game changes in the representation, our previous results no longer apply. In the face of this representational problem, we can either attempt to develop some metric of the robustness of a given norm in the space of similar games, or more carefully scope the claims that we can make about the social norms that we study with this methodology.
Although some questions of interpretation and challenges of representation exist, an important advantage of the evolutionary approach is that it does not require sophisticated strategic reasoning in circumstances, such as large-group interactions, in which it would be unrealistic to assume it. People are very unlikely to engage in full Bayesian calculations in making decisions about norm adherence. Agents often rely on cognitive shortcuts to determine when norms ought to be in effect given a certain context, and whether or not they should adhere to them. Evolutionary models that employ adaptive learning strategies capture these kinds of cognitive constraints, and allow the theorist to explore how these constraints influence the emergence and stability of norms.
The study of social norms can help us understand a wide variety of seemingly puzzling behaviors. According to some accounts, a social norm results from conditional preferences for conforming to a relevant behavioral rule. Such preferences are conditional on two different kinds of beliefs: empirical and normative expectations.
This and other accounts of social norms still leave much to be investigated. Explaining how normative expectations come to exist remains an open question. Another open question to consider is how one could intervene to change socially harmful norms. While there have been initial investigations into these questions (Bicchieri 2016, Muldoon 2018a, 2018b), there is much more work to be done. One frontier in this area is in deploying behavioral tools such as nudging for fostering norm changes (Bicchieri 2022, 2023).
Finally, we stress that different contextual factors (such as the framing and characteristics of the strategic problem, the role one is assigned, the social category with which one identifies, as well as historical and chance events) often come to be associated with different notions of “appropriate behavior”. Accounting for endogenous expectations is therefore key to a full understanding of norm-driven behavior. More research—both theoretical and experimental—is needed to further illuminate the impact of expectations on strategic decisions.
- Abbink, K., Gangadharan, L., Handfield, T., et al., 2017, Peer punishment promotes enforcement of bad social norms. Nat Commun 8(609). doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00731-0
- Akerlof, George A., 1976, “The Economics of Caste and of the Rat Race and Other Woeful Tales”, Quarterly Journal of Economics , 90(4): 599–617. doi:10.2307/1885324
- Alexander, Jason McKenzie, 2000, “Evolutionary Explanations of Distributive Justice”, Philosophy of Science , 67(3): 490–516. doi:10.1086/392792
- –––, 2005, “The Evolutionary Foundations of Human Altruism”, Analyse & Kritik , 27(1): 106–113. [ Alexander 2005 available online ]
- –––, 2007, The Structural Evolution of Morality , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511550997
- Andreoni, James and B. Douglas Bernheim, 2009, “Social Image and The 50–50 Norm: A Theoretical and Experimental Analysis of Audience Effects”, Econometrica , 77(5): 1607–1636. doi:10.3982/ECTA7384
- Arrow, Kenneth J., 1971, “A Utilitarian Approach to the Concept of Equality in Public Expenditure”, Quarterly Journal of Economics , 85(3): 409–15. doi:10.2307/1885930
- Axelrod, Robert, 1984, The Evolution of Cooperation , New York: Basic Books.
- –––, 1986, “An Evolutionary Approach to Norms”, American Political Science Review , 80(4): 1095–1111. doi:10.1017/S0003055400185016
- Battigalli, Pierpaolo & Dufwenberg, Martin, 2009, “Dynamic Psychological Games”, Journal of Economic Theory , 144(1): 1–35. doi:10.1016/j.jet.2008.01.004
- –––, 2022, “Belief-Dependent Motivations and Psychological Game Theory”, Journal of Economic Literature , 60(3): 833–882. doi:10.1257/jel.20201378
- Bénabou, Roland and Jean Tirole, 2006, “Incentives and Prosocial Behavior”, American Economic Review , 96(5): 1652–1678. doi:10.1257/aer.96.5.1652
- –––, 2011, “Identity, Morals, and Taboos: Beliefs as Assets”, Quarterly Journal of Economics , 126(2): 805–855. doi:10.1093/qje/qjr002
- Bicchieri, Cristina, 1990, “Norms of Cooperation”, Ethics , 100(4): 838–861. doi:10.1086/293237
- –––, 1993, Rationality and Coordination , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Second Edition, 1996.
- –––, 1997, “Learning to Cooperate”, in Cristina Bicchieri, Richard C. Jeffrey, and Brian Skyrms, The Dynamics of Norms , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 2002, “Covenants Without Swords: Group Identity, Norms, and Communication in Social Dilemmas”, Rationality and Society , 14(2): 192–228. doi:10.1177/1043463102014002003
- –––, 2006, The Grammar of Society: The Nature and Dynamics of Social Norms , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511616037
- –––, 2016, Norms in the Wild: How to Diagnose, Measure, and Change Social Norms , New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780190622046.001.0001
- –––, 2022, “Norm Nudging: How to Measure What We Want to Implement” in Behavioral Science in the Wild (pp. 82–107). University of Toronto Press.
- –––, 2023, “Norm nudging and twisting preferences”, Behavioural Public Policy , 1–10.
- Bicchieri, Cristina and Alex Chavez, 2010, “Behaving as Expected: Public Information and Fairness Norms”, Journal of Behavioral Decision Making , 23(2): 161–178. doi:10.1002/bdm.648
- Bicchieri, Cristina, John Duffy, and Gil Tolle, 2004, “Trust Among Strangers”, Philosophy of Science , 71(3): 286–319. doi:10.1086/381411
- Bicchieri, Cristina and Yoshitaka Fukui, 1999, “The Great Illusion: Ignorance, Informational Cascades and the Persistence of Unpopular Norms”, Business Ethics Quarterly , 9(1): 127–155. doi:10.2307/3857639
- Bicchieri, Cristina and Azi Lev-On, 2007, “Computer-Mediated Communication and Cooperation in Social Dilemmas: An Experimental Analysis”, Politics, Philosophy and Economics , 6(2): 139–168. doi:10.1177/1470594X07077267
- Bicchieri, Cristina and Alessandro Sontuoso, 2015, “I Cannot Cheat on You After We Talk”, in The Prisoner’s Dilemma , Martin Peterson (ed.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 101–114. doi:10.1017/CBO9781107360174.007
- –––, 2020, “Game-Theoretic Accounts of Social Norms”, in M. Capra, R. Croson, T. Rosenblatt, and M. Rigdon (eds.), The Handbook of Experimental Game Theory , Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing. doi:10.4337/9781785363337.00017
- Bicchieri, Cristina and Erte Xiao, 2009, “Do the Right Thing: But Only If Others Do So”, Journal of Behavioral Decision Making , 22(2): 191–208. doi:10.1002/bdm.621
- Bicchieri, Cristina and Jiji Zhang, 2012, “An Embarrassment of Riches: Modeling Social Preferences in Ultimatum Games”, in Philosophy of Economics , ( Handbook of the Philosophy of Science , Volume 13), Uskali Mäki (ed.), Amsterdam: Elsevier.
- Binmore, Ken, 2010, “Social Norms or Social Preferences?”, Mind & Society , 9(2): 139–157. doi:10.1007/s11299-010-0073-2
- Binmore, Kenneth G. and Larry Samuelson, 1992, “Evolutionary Stability in Repeated Games Played by Finite Automata”, Journal of Economic Theory , 57(2): 278–305. doI:10.1016/0022-0531(92)90037-I
- Bolton, Gary E. and Axel Ockenfels, 2000, “ERC: A Theory of Equity, Reciprocity, and Competition”, American Economic Review , 90(1): 166–193. doi:10.1257/aer.90.1.166
- Bornstein, Gary and Meyrav Ben-Yossef, 1994, “Cooperation in Intergroup and Single-Group Social Dilemmas”, Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 30(1): 52–67. doi:10.1006/jesp.1994.1003
- Bowles, Samuel, 1998, “Endogenous Preferences: The Cultural Consequences of Markets and Other Economic Institutions”, Journal of Economic Literature , 36(1): 75–111.
- Brennan, Geoffrey, Lina Eriksson, Robert E. Goodin, and Nicholas Southwood, 2013, Explaining Norms , New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199654680.001.0001
- Brewer, Marilynn B., 1979, “In-group Bias in the Minimal Intergroup Situation: A Cognitive-Motivational Analysis”, Psychological Bulletin , 86(2): 307–324. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.86.2.307
- –––, 1991, “The Social Self: On Being the Same and Different at the Same Time”, Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 17(5): 475–482. doi:10.1177/0146167291175001
- Brewer, Marilynn B. and Sherry K. Schneider, 1990, “Social Identity and Social Dilemmas: A Double-Edged Sword”, in Dominic Abrams and Michael A. Hogg (eds.), Social Identity Theory: Constructive and Critical Advances , Wheatsheaf, NY: Harvester.
- Camerer, Colin F., 2003, Behavioral Game Theory. Experiments in Strategic Interaction , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Cancian, Francesca M, 1975, What are Norms? A Study of Beliefs and Action in a Maya Community , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Cappelen, Alexander W., Astri Drange Hole, Erik Ø Sørensen and Bertil Tungodden, 2007, “The Pluralism of Fairness Ideals: An Experimental Approach”, American Economic Review , 97(3): 818–827. doi:10.1257/aer.97.3.818
- Charness, Gary and Matthew Rabin, 2002, “Understanding Social Preferences with Simple Tests”, Quarterly Journal of Economics , 117(3): 817–869. doi:10.1162/003355302760193904
- Chavez, Alex K. and Cristina Bicchieri, 2013, “Third-Party Sanctioning and Compensation Behavior: Findings from the Ultimatum Game”, Journal of Economic Psychology , 39: 268–277. doi:10.1016/j.joep.2013.09.004
- Cialdini, Robert B. and Noah J. Goldstein, 2004, “Social Influence: Compliance and Conformity”, Annual Review of Psychology , 55: 591–621. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.55.090902.142015
- Cialdini, Robert B., Carl A. Kallgren, and Raymond R. Reno, 1991, “A Focus Theory of Normative Conduct”, in Advances in Experimental Social Psychology , volume 24, Mark P. Zanna (ed.), New York: Academic Press, pp. 201–234. doi:10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60330-5
- Coleman, James S., 1990, Foundations of Social Theory , Cambridge, MA: Belknap.
- Coleman, Jules L., 1989, “Afterword: Rational Choice Approach to Legal Rules”, Chicago-Kent Law Review , 65(1): 177–191. [ Jules Coleman 1989 available online ]
- Dawes, Robyn M., 1972, Fundamentals of Attitude Measurement , New York: Wiley.
- –––, 1980, “Social Dilemmas”, Annual Review of Psychology , 31: 169–193. doi:10.1146/annurev.ps.31.020180.001125
- –––, 1991, “Social Dilemmas, Economic Self-Interest, and Evolutionary Theory”, in Donald R. Brown and J.E. Keith Smith (eds.), Recent Research in Psychology: Frontiers of Mathematical Psychology: Essays in Honor of Clyde Coombs , New York: Springer-Verlag. doi:10.1007/978-1-4612-3088-5_2
- Deutscher, Irwin, 1973, “What”, in his What We Say/What We Do: Sentiments & Acts , Glenview, IL: Scott Foresman.
- Dhami, Sanjit S., 2016, The Foundations of Behavioral Economic Analysis , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Diamond, A.S., 1935, Primitive Law , London: Watts.
- Dufwenberg, Martin and Georg Kirchsteiger, 2004, “A Theory of Sequential Reciprocity”, Games and Economic Behavior , 47(2): 268–298. doi:10.1016/j.geb.2003.06.003
- Durkheim, Émile, 1895 [1982], Les Règles de la méthode sociologique , Paris. Translated as The Rules of Sociological Method , W. D. Hall (trans.), Glencoe, IL: The Free Press.
- –––, 1950 [1957], Leçons de Sociologie: Physique des Moeurs et du Droit , Istanbul: Cituri Biraderlet Basimevi. Translated as Professional Ethics and Civic Morals , Cornelia Brookfield (trans.), Glencoe, IL: The Free Press.
- Ellickson, Robert C., 1991, Order Without Law: How Neighbors Settle Disputes , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Ellingsen, Tore, Magnus Johannesson, Johanna Mollerstrom, and Sara Munkhammar, 2012, “Social Framing Effects: Preferences or Beliefs?”, Games and Economic Behavior , 76(1): 117–130. doi:10.1016/j.geb.2012.05.007
- Elster, Jon, 1989a, The Cement of Society: A Study of Social Order , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511624995
- –––, 1989b, “Social Norms and Economic Theory” Journal of Economic Perspectives , 3(4): 99–117. doi:10.1257/jep.3.4.99
- Falk, Armin and Urs Fischbacher, 2006, “A Theory of Reciprocity”, Games and Economic Behavior , 54(2): 293–315. doi:10.1016/j.geb.2005.03.001
- Fehr, Ernst and Klaus M. Schmidt, 1999, “A Theory of Fairness, Competition, and Cooperation”, Quarterly Journal of Economics , 114(3): 817–868. doi:10.1162/003355399556151
- –––, 2006, “The Economics of Fairness, Reciprocity and Altruism—Experimental Evidence and New Theories”, in Serge-Christophe Kolm and Jean Mercier Ythier (eds.), Handbook of The Economics of Giving, Altruism and Reciprocity (Volume 1), Amsterdam: North-Holland/Elsevier, pp. 615–691. doi:10.1016/S1574-0714(06)01008-6
- Fishbein, Martin E., 1967, “A Consideration of Beliefs and Their Role in Attitude Measurement”, in Readings in Attitude Theory and Measurement , Martin E. Fishbein (ed.), New York: Wiley.
- Freeman, Linton C. and Türröz Ataöv, 1960, “Invalidity of Indirect and Direct Measures of Attitude Toward Cheating”, Journal of Personality , 28(4): 443–447. doi:10.1111/j.1467-6494.1960.tb01631.x
- Gächter, Simon, Daniele Nosenzo, and Martin Sefton, 2013, “Peer Effects in Pro-Social Behavior: Social Norms or Social Preferences?”, Journal of The European Economic Association , 11(3): 548–573. doi:10.1111/jeea.12015
- Gaertner, Samuel L. and John F. Dovidio, 1986, “The Aversive Form of Racism”, in John F. Dovidio and Samuel L. Gaertner (eds.), Prejudice, Discrimination, and Racism: Theory and Research , Orlando, FL: Academic Press, pp. 61–89.
- Geanakoplos, John, David Pearce, and Ennio Stacchetti, 1989, “Psychological Games and Sequential Rationality”, Games and Economic Behavior , 1(1): 60–79. doi:10.1016/0899-8256(89)90005-5
- Geertz, Clifford, 1973, “Thick Description: Toward an Interpretive Theory of Culture”, in The Interpretation of Cultures: Selected Essays , New York: Basic Books, pp. 3–30.
- Gintis, Herbert, 2000, Game Theory Evolving , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Granovetter, Mark, 1985, “Economic Action and Social Structure: the Problem of Embeddedness”, American Journal of Sociology , 91(3): 481–510. doi:10.1086/228311
- Guala, Francesco, 2016, Understanding Institutions: The Science and Philosophy of Living Together , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Hamilton W.D., 1964, “The Genetical Evolution of Social Behaviour I and II”, Journal of Theoretical Biology , 7: 1–16 and 17–52. doi:10.1016/0022-5193(64)90038-4 and 10.1016/0022-5193(64)90039-6
- Handfield, T., & Thrasher, J., 2019, “Two of a kind: Are norms of honor a species of morality?” Biol Philos , 34, 39. doi.org/10.1007/s10539-019-9693-z
- Hardin, Russell, 1982, Collective Action , New York: Resources for the Future.
- Harding, John, Harold Proshansky, Bernard Kutner, and Isidor Chein, 1954 [1969], “Prejudice and Ethnic Relations”, in Gardner Lindzey (ed.), Handbook of Social Psychology , volume 2, Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, pp. 1021–1061. Reprinted in Gardner Lindzey and Elliot Aronson (eds.), Handbook of Social Psychology , second edition, volume 5, Reading, MA: Addison Wesley, 1969, pp. 1–76.
- Hausman, Daniel M., 2008, “Fairness and Social Norms” Philosophy of Science , 75(5): 850–860. doi:10.1086/594529
- Hechter, Michael and Karl-Dieter Opp, 2001, Social Norms , New York: Russel Sage Foundation.
- Henrich, Joseph and Robert Boyd, 2001, “Why People Punish Defectors: Weak Conformist Transmission Can Stabilize Costly Enforcement of Norms in Cooperative Dilemmas”, Journal of Theoretical Biology , 208(1): 79–89. doi:10.1006/jtbi.2000.2202
- Henrich, Joseph, Robert Boyd, Samuel Bowles, Colin Camerer, Ernst Fehr, Herbert Gintis, and Richard McElreath, 2001, “In Search of Homo Economicus: Behavioral Experiments in 15 Small-Scale Societies”, American Economic Review , 91(2): 73–78. doi:10.1257/aer.91.2.73
- Hirshmann, Albert O., 1982, Shifting Involvements: Private Interest and Public Action , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Hoebel, Adamson E., 1954, The Law of Primitive Man , Cambridge, MA: Atheneum.
- Hogg, Michael A. and John C. Turner, 1987, “Social Identity and Conformity: A Theory of Referent Informational Influence”, in William Doise and Serge Moscovici (eds.), Current Issues in European Social Psychology , Volume 2, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 139–182.
- Homans, George Caspar, 1950, The Human Group , New York: Harcourt, Brace & Company.
- –––, 1961, Social Behavior , New York: Harcourt Brace and World.
- Insko, Chester A. and John Schopler, 1967, “Triadic Consistency: A Statement of Affective-Cognitive-Conative Consistency”, Psychological Review , 74(5): 361–376. doi:10.1037/h0020278
- Kagel, John H. and Alvin E. Roth, 2016, Handbook of Experimental Economics , Volume 2, Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Klassen, Albert D., Colin J. Williams, and Eugene E. Levitt, 1989, Sex and Morality in the U.S.: An Empirical Enquiry Under the Auspices of the Kinsey Institute , Middletown, CT: Wesleyan University Press.
- Kramer, Roderick M. and Marilynn B. Brewer, 1984, “Effects of Group Identity on Resource Use in a Simulated Commons Dilemma”, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 46(5): 1044–1057. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.46.5.1044
- Krupka, Erin L. and Roberto A. Weber, 2013, “Identifying Social Norms Using Coordination Games: Why Does Dictator Game Sharing Vary?”, Journal of The European Economic Association , 11(3): 495–524. doi:10.1111/jeea.12006
- LaPiere, Richard T., 1934, “Attitudes vs. Actions”, Social Forces , 13(2): 230–237. doi:10.2307/2570339
- Ledyard, John, 1995, “Public Goods Experiments”, in John H. Kagel and Alvin E. Roth (eds.), The Handbook of Experimental Economics , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Lewis, David, 1969, Convention: A Philosophical Study , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. doi:10.1002/9780470693711
- –––, 1975, “Languages and Language”, in Language, Mind, and Knowledge , ( Minnesota Studies in the Philosophy of Science , 6), Keith Gunderson (ed.), Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, pp. 3–35. [ Lewis 1975 available online ]
- López-Pérez, Raúl, 2008, “Aversion to Norm-Breaking: A Model”, Games and Economic Behavior , 64(1): 237–267. doi:10.1016/j.geb.2007.10.009
- Mackay, Charles, 1841, Extraordinary Popular Delusions and the Madness of Crowds , N. Stone (ed.), Hertfordshire: Wordsworth, 1995.
- Mackie, G., 1996, “Ending Footbinding and Infibulation: A Convention Account”, American Sociological Review , 61(6): 999–1017. doi:10.2307/2096305
- Matza, David, 1964, Delinquency and Drift , New York: Wiley.
- Maynard Smith, J. and G. R. Price, 1973, “The Logic of Animal Conflict”, Nature , 246(5427): 15–18. doi:10.1038/246015a0
- Miller, Dale T. and Rebecca K. Ratner, 1996, “The Power of the Myth of Self-Interest”, in Leo Montada and Melvin J. Lerner (eds.), Current Societal Concerns About Justice , New York: Plenum Press. doi:10.1007/978-1-4757-9927-9_3
- Muldoon, Ryan, 2017, “Perspectives, Norms and Agency”, Social Philosophy and Policy, 34(1): 260–276. doi:10.1017/S0265052517000127
- –––, 2018a, “Understanding Norms and Changing Them”, Social Philosophy and Policy, 35(1): 128–148. doi:10.1017/S0265052518000092
- –––, 2018b, “Norms, Nudges, and Autonomy”, In: Boonin, D. (eds) The Palgrave Handbook of Philosophy and Public Policy . Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-93907-0_18
- –––, 2020, “Social Norms and Social Order”, in: Chartier and Van Schoelandt (eds) The Routledge Handbook of Anarchy and Anarchist Thought . Routledge.
- Muldoon, R., Lisciandra, C., Bicchieri, C., Hartmann, S., & Sprenger, J., 2014, “On the emergence of descriptive norms”, Politics, Philosophy & Economics , 13(1): 3–22. doi:10.1177/1470594X12447791
- Muldoon, R., Lisciandra, C. & Hartmann, S., 2014, “Why are there descriptive norms? Because we looked for them”, Synthese 191, 4409–4429. doi:10.1007/s11229-014-0534-y
- Nachbar, J.H., 1990, “‘Evolutionary’ Selection Dynamics in Games: Convergence and Limit Properties”, International Journal of Game Theory , 19(1): 59–89. doi:10.1007/BF01753708
- North, Douglass C., 1990, “A Transaction Cost Theory of Politics” Journal of Theoretical Politics , 2(4): 355–367. doi:10.1177/0951692890002004001
- O’Gorman, Hubert J., 1975, “Pluralistic Ignorance and White Estimates of White Support for Racial Segregation”, Public Opinion Quarterly , 39(3): 313–330. doi:10.1086/268231
- Olson, Mancur, 1965 [1971], The Logic of Collective Action: Public Goods and the Theory of Groups , revised edition, Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Ostrom, Elinor, 2000, “Collective Action and The Evolution of Social Norms”, Journal of Economic Perspectives , 14(3): 137–158. doi:10.1257/jep.14.3.137
- Pagel, Elaine, 2003, Beyond Belief: The Secret Gospel of Thomas , New York: Vintage Books.
- Parsons, Talcott, 1951, The Social System , New York: Routledge.
- –––, 1937 [1968], The Structure of Social Action. A Study in Social Theory with Special Reference to a Group of Recent European Writers , New York, London: Free Press.
- Parsons, Talcott and Edward A. Shils, 1951, Towards a General Theory of Action , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Posner, Eric A., 2000, Law and Social Norms , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Prentice, Deborah A. and Dale T. Miller, 1993, “Pluralistic Ignorance and Alcohol Use on Campus: Some Consequences of Misperceiving the Social Norm”, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 64(2): 243–56. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.64.2.243
- Rabin, Matthew, 1993, “Incorporating Fairness into Game Theory and Economics”, American Economic Review , 83(5): 1281–1302.
- Reuben, Ernesto and Arno Riedl, 2013, “Enforcement of Contribution Norms in Public Good Games with Heterogeneous Populations”, Games and Economic Behavior , 77(1): 122–137. doi:10.1016/j.geb.2012.10.001
- Robinson, Claude E., 1932, Straw Votes: A Study of Political Prediction , New York: Columbia University Press.
- Rommetveit, Ragnar, 1955, Social Norms and Roles: Explorations in the Psychology of Enduring Social Pressures with Empirical Contributions from Inquiries into Religious Attitudes and Sex Roles of Adolescents from Some Districts in Western Norway , Oslo: Akedemisk Forlag.
- Schelling, Thomas C., 1960, The Strategy of Conflict , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- –––, 1978, Micromotives and Macrobehavior , New York: Norton.
- Schram, Arthur and Gary Charness, 2015, “Inducing Social Norms in Laboratory Allocation Choices”, Management Science , 61(7): 1531–1546. doi:10.1287/mnsc.2014.2073
- Scott, John Finley, 1971, Internalization of Norms: A Sociological Theory of Moral Commitment , Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Sherif, Muzafer, 1936, The Psychology of Social Norms , New York: Harper.
- Skyrms, Brian, 1996, Evolution of the Social Contract , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511806308
- –––, 2004, The Stag Hunt and the Evolution of Social Structure , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139165228
- Stigler, George J. and Gary S. Becker, 1977, “De Gustibus Non Est Disputandum”, American Economic Review , 67(2): 76–90.
- Sugden, Robert, 1986 [2004], The Economics of Rights, Co-operation and Welfare , second edition, Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan, 2004.
- –––, 2000, “The Motivating Power of Expectations”, in Julian Nida-Rümelin and Wolfgang Spohn (eds.), Practical Rationality, Rules, and Structure , Dordrecht: Kluwer. doi:10.1007/978-94-015-9616-9_7
- Tajfel, Henri, 1973, “The Roots of Prejudice: Cognitive Aspects”, in Psychology and Race , Peter Watson (ed.), Chicago: Aldine.
- –––, 1981, Human Groups and Social Categories: Studies in Social Psychology , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Taylor, Peter D. and Leo B. Jonker, 1978, “Evolutionary Stable Strategies and Game Dynamics”, Mathematical Biosciences , 40(1–2): 145–156. doi:10.1016/0025-5564(78)90077-9
- Thibaut, John W. and Harold H. Kelley, 1959, The Social Psychology of Groups , New York: Wiley.
- Thrasher, John, 2018, “Evaluating bad norms” Social Philosophy and Policy, 35(1): 196–216. doi:10.1017/S0265052518000055
- Thrasher, J., & Handfield, T., 2018, “Honor and Violence”, Hum Nat 29, 371–389. doi:10.1007/s12110-018-9324-4
- Trivers, Robert L., 1971, “The Evolution of Reciprocal Altruism”, Quarterly Review of Biology , 46(1): 35–57. doi:10.1086/406755
- –––, 1985, Social Evolution , Menlo Park, CA: Benjamin/Cummings.
- Turnbull, C. M., 1972, The Mountain People , New York: Touchstone.
- Turner, John C., Michael A. Hogg, Penelope J. Oakes, Stephen D. Reicher, and Margaret S. Wetherell, 1987, Rediscovering the Social Group: A Self-Categorization Theory , Oxford: Blackwell.
- Ullmann-Margalit, Edna, 1977, The Emergence of Norms , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Vanderschraaf, Peter, 1995, “Convention as Correlated Equilibrium”, Erkenntnis , 42(1): 65–87. doi:10.1007/BF01666812
- Warner, Lyle G. and Melvin L. DeFleur, 1969, “Attitude as An Interactional Concept: Social Constraint and Social Distance as Intervening Variables Between Attitudes and Action”, American Sociological Review , 34(2): 153–169. doi:10.2307/2092174
- Wicker, Allan W., 1969, “Attitude versus Actions: The Relationship of Verbal and Overt Behavioral Responses to Attitude Objects”, A Journal of Social Issues , 25(4): 41–78. doi:10.1111/j.1540-4560.1969.tb00619.x
- Wrong, Dennis H., 1961, “The Oversocialized Conception of Man in Modern Sociology”, American Sociological Review , 26(2): 183–193. doi:10.2307/2089854
- Wuthnow, Robert, 1991, Acts of Compassion: Caring for Others and Helping Ourselves , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Xiao, Erte and Cristina Bicchieri, 2010, “When Equality Trumps Reciprocity”, Journal of Economic Psychology , 31(3): 456–470. doi:10.1016/j.joep.2010.02.001
- Young, H. Peyton, 1993, “The Evolution of Conventions”, Econometrica , 61(1): 57–84. doi:10.2307/2951778
- –––, 1998a, “Social Norms and Economic Welfare”, European Economic Review , 42(3–5): 821–830. doi:10.1016/S0014-2921(97)00138-4
- –––, 1998b, Individual Strategy and Social Structure: An Evolutionary Theory of Institutions , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Arló-Costa, Horacio and Arthur Paul Pedersen, “ Social Norms, Rational Choice and Belief Change ”, manuscript, Carnegie Mellon Research Showcase.
- Axelrod, Robert, 1992, “ How to Promote Cooperation ”, Current Contents—Social and Behavioral Sciences , 44: 10 (November 2, 1992); this is a scan of the version that appeared in Current Contents—Arts and Humanities , 23: 16 (November 9, 1992).
- Selected Papers on Social Norms at EconPapers .
- Social Norm , entry in Wikipedia .
altruism | belief | common knowledge | convention | evolution | game theory | game theory: evolutionary | morality: and evolutionary biology | normative cognition, psychology of | social institutions
Acknowledgments
A portion of section 6 of this entry has been adapted from “Game-Theoretic Accounts of Social Norms”, by Cristina Bicchieri and Alessandro Sontuoso, in The Handbook of Experimental Game Theory , Mónica Capra, Rachel Croson, Tanya Rosenblatt, and Mary Rigdon (eds.), Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing, 2020.
Copyright © 2023 by Cristina Bicchieri < cb36 @ sas . upenn . edu > Ryan Muldoon < ryan . muldoon @ gmail . com > Alessandro Sontuoso < sontuoso @ sas . upenn . edu >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
MIT Libraries home DSpace@MIT
- DSpace@MIT Home
- MIT Libraries
- Doctoral Theses
Essays on social norms

Other Contributors
Terms of use, description, date issued, collections.
Social Roles Theory: Decoding the Symphony of Identity
This essay delves into the captivating realm of the Social Roles Theory, portraying it as a dynamic narrative that transcends academic abstraction. It explores the theory’s role in understanding the fluid interplay between individual identity and societal expectations. From the ever-shifting personas individuals assume in various social contexts to the theory’s illuminating gaze on stereotypes and power dynamics, the essay paints a vivid picture of the profound implications and applications of the Social Roles Theory. Far from theoretical confines, it portrays the theory as a guiding compass and a resonant symphony shaping the intricate dance of human existence within the grand amphitheater of society.
How it works
In the vibrant landscape of social psychology, the Social Roles Theory emerges as a captivating narrative, transcending the confines of scholarly abstraction. This theory unfurls a tapestry where individuals waltz through diverse roles, each imbued with a unique set of expectations, norms, and a profound influence on the delicate dance between personal identity and societal structures.
At its essence, the Social Roles Theory paints a dynamic tableau, where individuals don different masks in varied social contexts. These roles, whether scripted by gender norms, professional obligations, or cultural affiliations, aren’t static costumes but ever-shifting personas shaped by the zeitgeist.
The theory is a testament to the malleability of identity, acknowledging its fluidity amidst the evolving dynamics of culture and time.
Delving into the core of this theory reveals its profound implications on the construction of personal identity. Whether assuming the role of a parent, a professional, or a community member, individuals grapple with a kaleidoscope of roles that not only dictate their behavior but also mold their sense of self. The dance between personal identity and societal expectations, choreographed by the Social Roles Theory, becomes a compelling exploration of the intricate negotiations shaping our multifaceted identities.
A significant facet of the Social Roles Theory lies in its illuminating gaze upon the breeding ground of stereotypes and prejudices entrenched within societal roles. By unraveling how roles sculpt perceptions and expectations, the theory becomes a lantern guiding us through the caverns of biases rooted in gender, race, or social class. It is an instrument of introspection, inviting us to critically examine the implicit scripts that influence our attitudes and actions.
Moreover, this theory is not just a compass but a profound mirror reflecting the power dynamics woven into social structures. Whether within familial circles, professional realms, or broader communities, roles are often accompanied by unequal distributions of power. Through the lens of social roles, we discern the complex interplay of privilege, oppression, and the resilient currents of resistance that define the intricate dance of societal interactions.
In essence, the Social Roles Theory transcends its theoretical moorings; it is a symphony resonating through the corridors of human existence within the grand amphitheater of society. As individuals traverse the multifaceted roles assigned to them, this theory invites contemplation on the ever-changing hues of identity, the resonance of societal expectations, and the nuanced symphony that roles compose in shaping our perceptions and engagements.
In conclusion, the Social Roles Theory isn’t a distant theoretical construct; it is a narrative, a melody, and a profound exploration of the human journey within the kaleidoscope of societal dynamics. Far from a dry academic discourse, this theory allows us to peel back the layers of societal intricacies, inviting us to participate in the orchestration of our identities as we waltz through the ever-shifting roles that define the human experience.
Cite this page
Social Roles Theory: Decoding the Symphony of Identity. (2024, Mar 02). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/social-roles-theory-decoding-the-symphony-of-identity/
"Social Roles Theory: Decoding the Symphony of Identity." PapersOwl.com , 2 Mar 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/social-roles-theory-decoding-the-symphony-of-identity/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Social Roles Theory: Decoding the Symphony of Identity . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/social-roles-theory-decoding-the-symphony-of-identity/ [Accessed: 12 Apr. 2024]
"Social Roles Theory: Decoding the Symphony of Identity." PapersOwl.com, Mar 02, 2024. Accessed April 12, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/social-roles-theory-decoding-the-symphony-of-identity/
"Social Roles Theory: Decoding the Symphony of Identity," PapersOwl.com , 02-Mar-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/social-roles-theory-decoding-the-symphony-of-identity/. [Accessed: 12-Apr-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Social Roles Theory: Decoding the Symphony of Identity . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/social-roles-theory-decoding-the-symphony-of-identity/ [Accessed: 12-Apr-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

ESSAYS ON SOCIAL NORMS AND THE MANY SIDES OF RACISM
My dissertation is divided into five relatively freestanding yet thematically linked essays, investigating a number of ways in which social norms and the question of racism are related. In these chapters, I aim to show the vital influence of social norms on our interpersonal relationships, going beyond the futile binary between individual (moral philosophy) and state (political philosophy), thereby affirming the primacy of the social over the political. Considering social norms can help us to see how individual agents are socially and culturally mediated, shaped, and distorted. In the dissertation, I discuss the racial contract (John Rawls and Charles Mills), racism as volitional states (Jorge Garcia), racism as ideology (Tommie Shelby and Sally Haslanger), and anti-racism through social movements (Elizabeth Anderson). By engaging them, I argue that racism as a socially harmful norm should be understood in the context of broader social environments. My thesis is that racism as a socially harmful norm should be understood as a manifestation in broad social environments where the mechanisms of social norms function structurally. In conclusion, I argue for the relevance of social critique instead of a narrow moral critique of racism. In this regard, my solution is not intended as a complete solution for the termination of all forms of racism, rather as certainly a needed viable approach both morally warranted and pragmatically efficacious.
Degree Type
- Doctor of Philosophy
Campus location
- West Lafayette
Advisor/Supervisor/Committee Chair
Additional committee member 2, additional committee member 3, additional committee member 4, usage metrics.
- Philosophy not elsewhere classified

GetGoodEssay
Essay on social norms and values
As a society, we thrive on a delicate fabric woven by social norms and values. They shape our interactions, behaviors, and ultimately define who we are as individuals and as a collective. In this essay, we embark on a journey to unravel the significance of social norms and values, delving deep into their origins, impact, and the reasons behind their existence. Join me as we explore this captivating realm, blending insightful knowledge with a friendly tone.
Understanding Social Norms:
Social norms serve as the invisible guidelines that dictate our behavior in social settings. They act as unwritten rules that govern how we conduct ourselves, what is considered acceptable or appropriate, and what is frowned upon. These norms are ingrained within us from a young age through socialization, education, and cultural practices.
One key aspect of social norms is their ability to vary across different cultures and societies. What may be perceived as a norm in one community may be entirely different in another. For example, personal space boundaries, greetings, and gender roles can vary significantly from one culture to another. Such diversity enriches our global tapestry, reflecting the beauty of human existence.
The Influence of Values:
Values are deeply ingrained beliefs that guide our actions and choices. They represent our moral compass, shaping our judgments and decisions. While social norms focus on external behavior, values delve into the core of our being, reflecting our personal ideals and principles.
Values often serve as the foundation for the establishment of social norms. For instance, the value of respect underlies the norm of polite behavior, while the value of fairness reinforces the norm of treating others justly. These shared values contribute to the creation of cohesive societies, fostering understanding, and facilitating harmonious relationships.
The Evolution of Social Norms and Values:
Social norms and values are not static entities but rather dynamic constructs that evolve over time. They adapt to changes in societal structures, technological advancements, and shifting cultural paradigms. As society progresses, certain norms and values may become outdated or irrelevant, leading to their modification or abandonment.
For example, gender roles have witnessed significant transformations over the years. Traditional norms that confined women to domestic responsibilities have given way to more egalitarian ideals, promoting gender equality in various spheres of life. These shifts demonstrate the power of collective consciousness and the capacity for positive change.
The Functions of Social Norms and Values:
Social norms and values play crucial roles in maintaining social order and promoting cohesion within communities. They provide a sense of predictability and stability, enabling individuals to navigate social interactions with ease. By adhering to shared norms, we create a harmonious environment where expectations are clear and cooperation is fostered.
Moreover, social norms and values act as mechanisms for social control. They discourage deviant behavior and reinforce desired conduct through positive and negative sanctions. When individuals violate social norms, they may face social disapproval, criticism, or even legal consequences. This system of rewards and punishments helps uphold the fabric of society and safeguard the well-being of its members.
The Impact of Social Norms and Values:
The influence of social norms and values extends far beyond individual behavior. They shape societal structures, influence public policies, and impact the trajectory of cultural movements. By embracing certain values and norms, societies can work collectively towards common goals, such as social justice, environmental sustainability, and equality.
However, it is essential to critically examine social norms and values to ensure they align with ethical principles and promote inclusivity. Sometimes, long-standing norms can perpetuate harmful practices, discrimination, or inequality. By challenging these norms and advocating for change, individuals can contribute to the progress of society, making it more equitable and just.
Conclusion:
Social norms and values are the threads that weave together the tapestry of our society. They guide our behavior, shape our interactions, and determine the course of our collective journey. Understanding their significance, evolution, and impact allows us to engage with them consciously, fostering a world that cherishes diversity, respects individuality, and promotes shared values of compassion, empathy, and justice.
Let us embrace the power of social norms and values, striving to create a society that embodies the best of humanity, where every individual finds acceptance, and where collective progress thrives.
Remember, social norms and values are not mere constraints but the pillars upon which we build a better future. Together, let us shape a world that embraces inclusivity, empowers individuals, and celebrates the beauty of our shared humanity.
- Recent Posts
- Race is a social construct essay - August 24, 2023
- Hunt for the Wilder people essay - August 24, 2023
- Australia’s involvement in the vietnam war essay - August 24, 2023
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
102 Examples of Social Norms (List)
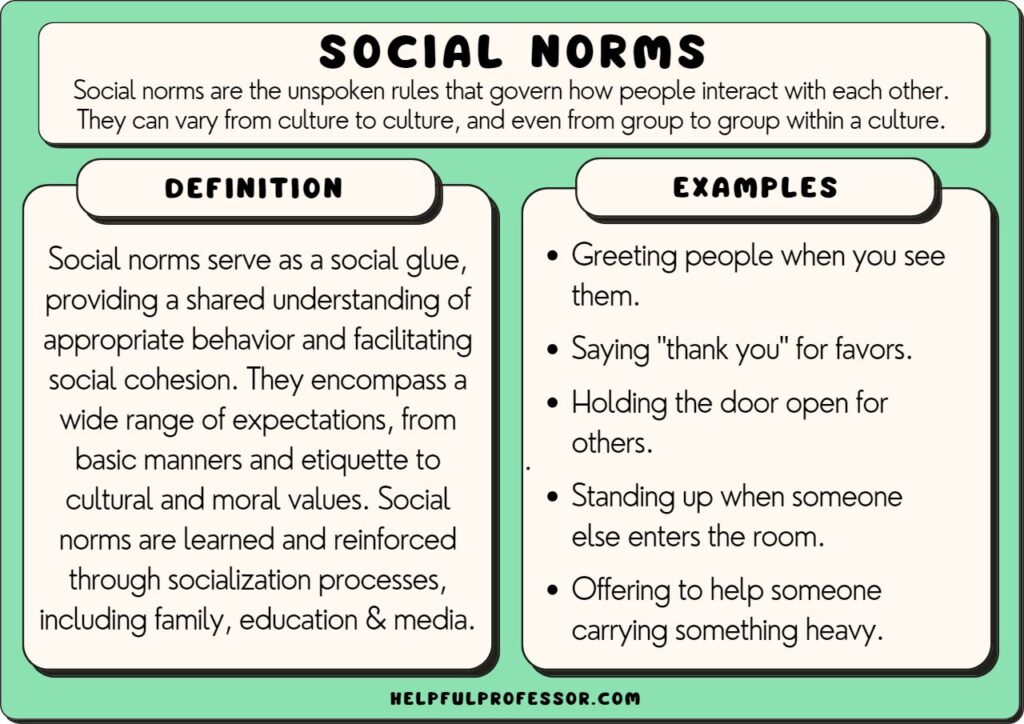
Social norms are the unspoken rules that govern how people interact with each other. They can vary from culture to culture, and even from group to group within a culture.
Some social norms are so ingrained in our psyches that we don’t even think about them; we just automatically do what is expected of us. Social norms examples include covering your mouth when you cough, waiting your turn, and speaking softly in a library.
Breaking societal norms can sometimes lead to awkward or uncomfortable situations. For example, if you’re in a library where it’s considered rude to talk on your cell phone, and you answer a call, you’ll likely get some disapproving looks from the people around you.
Understanding the social norms of the place you’re visiting is an important part of cultural etiquette to show respect for the people around you.
Examples of Social Norms
- Greeting people when you see them.
- Saying “thank you” for favors.
- Holding the door open for others.
- Standing up when someone else enters the room.
- Offering to help someone carrying something heavy.
- Speaking quietly in public places.
- Waiting in line politely.
- Respecting other people’s personal space.
- Disposing of trash properly.
- Refraining from eating smelly foods in public.
- Paying for goods or services with a smile.
- Complimenting others on their appearance or achievements.
- Asking others about their day or interests.
- Avoiding gossip and rumors.
- Volunteering to help others in need.
- Saying “I’m sorry” when you’ve made a mistake.
- Supporting others in their time of need.
- Participating in group activities.
- Respecting authority figures.
- Being on time for important engagements.
- Avoiding interrupting others when they are speaking.
- Showing interest in other people’s lives and experiences.
- Refraining from using offensive language or gestures.
- Being honest and truthful with others at all times.
- Treating others with kindness and respect, regardless of their social status or background.
- Putting the needs of others before your own.
- Participating in charitable works and activities.
- Helping others whenever possible.
- Welcoming guests into your home or place of business.
- Nodding, smiling, and looking people in the eyes to show you are listening to them.
- Following the laws and regulations of your country.
- Respecting the rights and beliefs of others.
- Cooperating with others in order to achieve common goals.
- Being tolerant and understanding of different viewpoints.
- Displaying good manners and etiquette in social interactions.
- Waiting in line for your turn.
- Taking your shoes off before walking into someone’s house.
- Putting your dog on a leash in parks and other public spaces.
- Letting the elderly or pregnant people take your seat on a bus.
Social Norms for Students
- Arrive to class on time and prepared.
- Pay attention and take notes.
- Stay quiet when other students are working.
- Raise your hand if you have a question.
- Do your homework and turn it in on time.
- Participate in class discussions.
- Respect your teachers and classmates.
- Follow the school’s rules and regulations.
- Use appropriate language and behavior.
- Ask permission to be excused if you need to go to the bathroom.
- Go to the bathroom before class begins.
- Keep your workspace clean.
- Do not plagiarize or cheat.
- Wait your turn to speak.
- Ask permission to use other people’s supplies.
- Include all your peers in your group when doing group work.
Related: Classroom Rules for Middle School
Social Norms while Dining Out
- Wait to be seated.
- Remain seated until everyone is served.
- Don’t reach across the table.
- Use your napkin.
- Don’t chew with your mouth open.
- Don’t talk with your mouth full.
- Keep elbows off the table.
- Use a fork and knife when eating.
- Drink from a glass, not from the bottle or carton.
- Request more bread or butter only if you’re going to eat it all.
- Don’t criticize the food or service.
- Thank your server when you’re finished.
- Leave a tip if you’re satisfied with the service.
Social Norms while using your Phone
- Keep your phone on silent or vibrate mode while in meetings.
- Don’t answer your phone in a public place unless it’s an emergency.
- Don’t talk on the phone while driving.
- Don’t text while driving.
- Don’t take or make calls during class.
- Don’t use your phone in a movie theater.
- Turn off your phone when you’re with someone else.
- Place your phone on airplane mode while flying.
- Do not look at someone else’s phone.
- Ensure your ringtone is inoffensive when in public or around children.
Social Norms in Libraries
- Be quiet and respect the other patrons.
- Don’t talk on your phone.
- Don’t bring food or drinks into the library.
- Don’t sleep in the library.
- Don’t bring pets into the library.
- Return all books to the correct location.
- Don’t mark or damage library books.
- Make sure your cell phone is turned off.
- Return your books on time.

Social Norms in Other Countries
- In France, it is considered polite to kiss acquaintances on both cheeks when meeting them.
- In Japan, it is customary to take your shoes off when entering someone’s home.
- In India, it is considered rude to show the soles of your feet or to point your feet at someone else.
- In Italy, it is common for people to give each other a light kiss on the cheek as a gesture of hello or goodbye.
- In China, it is customary to leave some food on your plate after eating, as a sign of respect for the cook.
- In Spain, it is customary to call elders “Don” or “Doña.”
- In Iceland, it is considered polite to say “thank you” (Takk) after every meal.
- In Thailand, it is customary to remove your shoes before entering a home or temple.
- In Germany, it is customary to shake hands with everyone you meet, both men and women.
- In Argentina, it is customary for people to hug and kiss cheeks as a gesture of hello or goodbye.
Social Norms that Should be Broken
- “ Women should be polite” – Stand up for what you believe in, even if it makes you look bossy.
- “Don’t draw attention to yourself” – Embrace your uniqueness and difference so long as you’re respectful of others.
- “Don’t question your parents or your boss” – Protest bad behavior from people in authority if you know you’re morally right.
- “Mistakes are embarrassing” – It’s okay to make mistakes and be seen to fail. It means you’re making an effort and pushing your boundaries.
- “Respect your elders” – If your elders are engaging in bad behavior, stand up to them and let them know you’re taking note of what they’re doing.
Cultural vs Social Norms
Cultural norms are the customs and traditions that are passed down from one generation to the next. They’re connected to the traditions, values, and practices of a particular culture.
Societal norms, on the other hand, reflect the current social standard for appropriate behavior within a society. In modern multicultural societies, there are different groups with different cultural norms, but they must all agree on a common set of social norms for public spaces.
We also have a concept called group norms , which define how smaller groups – like workplace teams or sports teams – will operate. These might differ from group to group, and are highly dependant on the expectations and standards of the group/team leader.
Norms Change Depending on the Context
Norms are different depending on different contexts, including in different eras, and in different societies. What might be considered polite in one context could be considered rude in another.
For example, norms in the 1950s were much more gendered. Negative gender stereotypes restricted women because it was normative for women to be quiet, polite, and submissive in public. Today, women have much more equality.
Similarly, the norms and taboos in the United States will be very different from those in China. For example, Chinese businessmen are often expected to share expensive gifts during negotiations. In the United States, this could be considered bordering on bribery.
What are the Four Types of Norms?
There are four types of norms : folkways, mores, taboos, and laws.
- Folkways are social conventions that are not strictly enforced, but are generally considered to be polite or appropriate. An example of a folkway is covering your mouth when you sneeze.
- Mores are social conventions that are considered to have a moral dimension. Due to their moral dimension, they’re generally considered to be more important than folkways. Violation of mores can result in social sanctions so they often overlap with laws (mentioned below). An example of a more is not drinking and driving.
- Taboos are considered ‘negative norms’, or things that you should avoid doing. If you do them, you’ll be seen as rude. An example of a taboo is using your phone in a movie theater or spitting indoors.
- Laws are the most formal and serious type of norm. They are usually enforced by the government and can result in criminal penalties if violated. Examples of laws include not stealing from others and not assaulting others.
Conclusion: What are Social Norms?
Social norms are defined as the unspoken rules that help us to get along with others in a polite and respectful manner. It’s important to follow them so that we can maintain a positive social environment for everyone involved. Social norms examples include not spitting indoors, covering your mouth when you sneeze, and shaking hands with everyone you meet.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Reactions to Social Norm Violation Essay
We have a number of societal norms that govern day-to-day actions and reactions. Common norms involve use of he elevator. We understand that it is apparent that one should face the front, avoid distracting others by standing a side and should not look obnoxiously or stare to other users. According to Sharma and Malhotra (2007), breaking norms may cause others to respond inversely depending on the involved psychological irritation, for instance people might laugh, display fear or show apprehension and emotional irritation.
People in the society have to survey and decide on the norms. After studying my social setting, I decided to engage a common norm violation of dressing weird out in the public.
Some people will violate the norm incautiously, therefore it may seem a normal occurrence to many but the circumstances, time, and location settings determines the conclusion. My feasibility study assisted in deciding what to consider, when and where. I resolve to have a strange wear during my outing with close friends and find out their reactions and my response.
The plan was to wear bright but colour-clashing pants and shirt. A choose cloths that appeared more of private nighties than open and commonly acceptable cloths in public. The top was a bright light-green shirt while the pants were bright pink in colour. I was an easily identifiable person within a crowd from a mile. My friends and I were to go out for a movie and later for a dance until late into the night.
I organized with my friend to pick me up and I could instantly note million questions on the face but failed to enquire, probably to avoid hurting my feelings. I did feel awkward and had brought a pair of cloths with me just in case I might not be in a position to carry on until the end of the outing.
We met other friends after a couple of minutes drive. While the talks and engagements appeared usual, I noted that the five friends including my date kept staring and passing signals behind my back without saying a word to me. At the ticketing queue, I noted more stares and murmurs from other people especially those behind us. One comment was that I was probably playing a “dare game”.
At this point, I wanted to tell everyone that this was an assignment, but you do not leave the theatre when the movie is at climax, so I kept cool without discerning the stares until we got into the auditorium. The whispers were louder as I walked down the auditorium, and I was cursing why my friends could not take the back seats. I thought that since no one including my friends was raising questions, suggestions or concerns, they only ought had to accept me for what I chose.
In line with Lindsey and Beach (2002), norm is the standard value acceptable within a group such as the social norm. Some thoughts, behaviours and feelings are therefore acceptable as appropriate within a certain group while they are intolerable to another, for instance weird clothing styles or nudity. My dress code might have been acceptable if the outing was to a cultural night or hallowing party but the setting was very different.
The main problem was my inability to go on without feeling odd; I therefore had to change to a more suitable wear before the night party. I felt that breaking some social norms might hurt feelings and possibly break relationships.
No sooner had I changed than my friends got a reassurance and started commenting. One observation was a friend’s next plan to have a situation that would cancel the night dance because of my appearance. Their questioning forced my reveal that it was a school project for phycology. The reactions were laughter, mimics, and comic comparisons.
One common association of the look was to a clown. Initially I felt some insecurity over their reactions and responses. People will easily judge a person they are not close to as opposed to their close associates. I expected judgemental reactions in form of comments from everyone but this only came from strangers as opposed to the friends. The difficulties were to ignore the silent reactions of my friends. The test was a reassurance that they are great friends who are sensitive to my feelings and ready to accept me for whom I am.
Lindsey, L and Beach, S. (2002). Sociology. 3 RD Edition. New York, NY: Pearson Publishers. Print.
Sharma, A and Malhotra, D. (2007). Personality and Social Norms . New Delhi: India, Concept Publishing Company. Print.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, March 22). Reactions to Social Norm Violation. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-norm-violation-essay/
"Reactions to Social Norm Violation." IvyPanda , 22 Mar. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/social-norm-violation-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Reactions to Social Norm Violation'. 22 March.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Reactions to Social Norm Violation." March 22, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-norm-violation-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "Reactions to Social Norm Violation." March 22, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-norm-violation-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Reactions to Social Norm Violation." March 22, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-norm-violation-essay/.
- A Day’s Outing for Kindergarten Children
- Denver Buddhist Temple: Cultural Outing
- Sagging Pants' Culture in the U.S. and The Romanticization of Criminals
- Terrorism and Security Dilemma After 9/11
- Procurement to Build New Auditorium
- Cyber-Bullying Is a Crime: Discussion
- Khaki Pants Supply and Demand Factors
- Consumer Behavior in the Context of Restaurant Domino Pizza
- The Emergence of the Auditorium Theater
- Frustration and Its Consequences
- Social Phenomenon Problem
- The Negative Effects of Wealth in Society
- Accumulating Wealth for Your Retirement
- Intergenerational Social Mobility
- Social Movements and Sociology
- Homework Help
- Essay Examples
- Citation Generator
- Writing Guides
- Essay Title Generator
- Essay Topic Generator
- Essay Outline Generator
- Flashcard Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Introduction Generator
- Literature Review Generator
- Hypothesis Generator
- Social Issues
- Social Norm Essays
Social Norm Essays (Examples)
1000+ documents containing “social norm” .
Filter by Keywords:(add comma between each)
Social norm make answer question completely your.
Social Norm Make answer question completely. Your answers cohesive essays. 1. Discuss explain types social norms. What role dominant culture play establishing norms? 2. What role time place defining crime? How social norms related understanding crime? Give a crime U.S. today time considered a crime? What social contributed changing definition ? 3. Discuss and explain the various types of social norms. What role does the dominant culture play in establishing norms? A social norm in the first place refers to something that has been accepted by the society as part of their day-to-day thing/activity. It may be a belief, behavior, action or value that is appreciated by the people/community. A social norm usually varies between different age groups and social class (income bracket) within the society. There are four types of social norms. They include the folkway, custom, and fashion, more, law. All these norms have some element of evaluation of behavior and….
Aarts, H., & Dijksterhuis, A. (2003). The silence of the library: Environment, situational norm and social behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84, 18 -- 28.
Cere, D., Farrow, D., Institute for the Study of Marriage, L., & Culture. (2004). Divorcing marriage: unveiling the dangers in Canada's new social experiment: Published for the Institute for the Study of Marriage, Law and Culture by McGill-Queen's University Press.
Frank Heiland, & Shirley H. Liu. (2005). Family Structure and Wellbeing of Out-of-Wedlock Children: the Significance of the Biological Parents' Relationship. Demographic Research 15, 61 -- 104.
Hipp, J.R. (2010). A Dynamic View of Neighborhoods: The Reciprocal Relationship between Crime and Neighborhood Structural Characteristics. Social Problems, 57(2), 205-230
Social Norm Experiment Scenario 6 -- Facing
Social Norm Experiment: Scenario 6 -- Facing the rong ay in an Elevator Solomon Asch's Conformity Experiments during the 1950s demonstrated how much individual opinion and even perception of reality can be influenced by others (Gerrig & Zimbardo 2009, 577-579). In the original series of experiments, Asch tested subjects by presenting with a perceptual question that should have been very easy to identify the correct answer but within a group situation in which multiple confederates expressed confidence about the wrong answer. That experiment can be duplicated in many different settings and scenarios. The reason I selected this particular scenario is that it involves one of the more subtle types of norm violations, as opposed to others that would seem to guarantee a reaction. To my mind, Asch's principle is best demonstrated by an experimental design that excludes other provocations for a response, such as invading someone else's space (e.g. standing too close….
When we got to the Lobby, I could tell that several people who were facing the wrong way were still looking over their shoulders to see if the doors at the front opened. That suggested they had never fully abandoned their initial perceptions of where the doors were even though they conformed to the behavior they observed in others. The mirrored walls also allowed me to see that almost everybody facing the wrong way was trying to compare the back wall to the actual doors by staring at them in the mirrors. I considered these results to have confirmed Asch's original results because it was clear to me that almost everyone in the group who followed my lead was consciously aware that the behavior they were following conflicted with their perceptions of reality.
Source Cited
Gerrig, R.J. And Zimbardo, P.G. (2009). Psychology and Life. Boston: Pearson.
Violate a Social Norm
Social Norm Violations he Norm Violated: he norm was supposed to be about singing in appropriate places. I choose to sing on a public bus at about the time people were returning home (away from downtown) after work. I thought this might give me a different audience than at other times of the day. It seems reasonable that there is an expectation of the bus being an extension of privacy for some people as they go home, and thus they might not like being bothered as they travel. But as I did my project, I found that the norm wasn't that easy to isolate. here was just as likely an issue about singing badly and singing with and without the help of music technology that made the violation less clear. Was I being "punished" for singing or for singing badly even when I had a player that should have made me….
The Social Psychology: Normative values change over time and between social groups and circumstances. But what does it mean when technology gets into the act? Does it throw away the rules or change them? And does it allow for different people (those comfortable with technology) to have different social norms? If so (which I believe) this suggests that something unusual was happening on the bus. It appeared that the existence of the music player was establishing me as belonging in one group or not belonging in another (those going home from work), whose rules I was not following with or without music technology. I believe this evolution has come about because of the widespread existence of Karaoke and the flood of entertainment contests on TV that let people share their styles in very public ways. It may also be that technology and social networking is simply eliminating the idea of there being public social norms of privacy. The founder of Facebook thinks so. Others have a different take. In an older blog discussion from JOI ITO (2003) on "Which comes first, technology or social norms," the bloggers debate one person's point that technology seems to be making social norms fall behind. Others disagree, saying one cannot assume norms fall behind, but they can be baffled by what technology was doing to the norms. I think there is a willingness to allow people to use technology as a cover for what they do, but only in some ways and among some groups.
Johnson, B. (2010). Privacy no longer a social norm, says Facebook founder. The Guardian. As retrieved from http://www.guardian.co.uk/technology/2010/jan/11/facebook-privacy
JOI ITO, Which comes first, technology or social norms. (2003). As retrieved from http://joi.ito.com/weblog/2003/12/30/which-comes-fir.html
Violating Social Norm Creative
Violating Social Norm People like to keep to themselves whenever they can, especially when they are in a situation where they have the option of being to themselves, by themselves. This implicit social norm applies when one goes onto an empty bus. If there are other seats available, one goes to the empty seat; one does not go and sit next to someone who is already there sitting down. It is just an unspoken implicit norm that one knows, and one knows this affects people by their reaction when one breaks this social norm and does the unthinkable: sit next to someone on the bus when every other seat around them is empty. This is exactly what I did as a way to violate this norm. For an entire day, on different bus lines, at various times of the day, and to an array of individuals, I sat next to them….
Breaking a Social Norm --
Dining alone is unusual at a higher-end restaurant. Immediately, my jeans, sneakers and faded t-shirt drew whispered comment and stares from some diners. I was afraid I would not be admitted, but I had gone on a night when there were few diners, so I suppose the front-of-house staff though that a filled table was better than an empty table. Again, I ordered a burger, fries, and shake. When the bread basket was placed in front of me while I waited for my order to come, I ate the bread like I do at home, spreading it with butter and making a sandwich of it, rather than breaking it in half. When my shake came, I slurped the straw, just like I do at home. People nearby did give me 'a look,' I noted, I think of disapproval or surprise. Most of the restaurant was populated by older couples, all….
Ideas About Social Norms
social norms that individuals need to follow or are expected to follow at a dining table -- be it at home or in a public setting. These table etiquettes are both formal and non-formal in nature. The setting of dining often determines the etiquettes that are desired from individuals. For example, is one is dining at home, one is expected to follow lesser of the formal norms and etiquettes that are expected from the same individual while dining in public or during business meetings. The reactions that are expected from others would include a set of norms and etiquettes that start with the proper use of cutlery like the proper use of forks, knives and spoons, use of proper eating etiquettes while having food like not making funny noises while eating and waiting till all are ready to start with lunch or dinner. For example, it is expected that an….
Ted Talk Analysis on Social Norms
Is there an example that might clarify or support the authors claim?Your comment regarding the development of strict, rule-based cultures to address threatening environments from outsiders is not simply true of national or religious cultures, but even subcultures of the kind that exist online, either through sharing fan fiction, social media websites, TikTok, and other forms of spontaneous sharing. However, although the culture may be informally regulated, there can also be a great deal of gatekeeping and infighting, perhaps because certain fandoms or subcultures are so niche in terms of the scope of the community. Paradoxically on one hand, Fan cultures are examples of participatory cultures. Participatory cultures involve fans acting not only as consumers but also as producers and creators of some form of creative media but on the other hand participatory cultures can still have rigorous formal enforcement (Fandom and participatory culture, n.d., par.1).Fan participation can be mercilessly….
Vedantam, S., Lu, T., Boyle, T., Schmidt, J., & Wahba, L. (2020, April 6). Playing tight and
Loose: How rules shape our lives. NPR. https://www.npr.org/2020/04/06/828257385/playing-tight-and-loose-how-rules-shape-our-lives
Social norms Conflict and its impact on'schooling
Conflict of social norms and its effect on school environment Social norms can be defined as the rules that determine what should be done or avoided by people in their social settings and circumstances. Norms make sure that people keep promises, ranging from the lane to drive on, to sticking by the golden rule. These are tools for explaining phenomena. They are used to analyze the state of the world even as great as international diplomacy or as subtle and ordinary as traffic rules. However, the body of knowledge regarding norms is spread across disciplines and traditions of research with unclear guidelines or consensus on the way the term should be put to use. Existing research on the subject has largely majored on the effects of the norms and the content of the same. By description, social norms cut across such disciplines as sociology, game theory, economics, and legal studies so….
Violating Social Norms Essay
Social Psychological Experiment: Violating Social Norms Most Americans place a high priority on their personal space as evidenced by how far people stand apart from each other in virtually any public setting. Indeed, most Americans will unconsciously gauge just how much space is available for their personal space -- even on crowded elevators -- and when this personal space is violated, many people will experience discomfort and even alarm. While the reactions may differ, it is reasonable to posit that most Americans will react to violations of their personal space in some fashion. To gain some additional insights into this phenomenon, this paper describes a social psychological experiment in which the researcher intentionally violated a common social norm by sitting next to other people in an uncrowded movie theater where other seating was readily available in order to gauge their reactions. A more complete description of the experiment is followed by….
Social Psychology in the Case
Additionally, Sociocultural theory assumes that individuals develop self-concepts through interaction with others, and we are influenced by culture and social processes, such as social norms. Social norms dictate that girls are more sensitive and boys are less emotional, thus further explaining the gender differences in the above case study. The two predictions of how these interactions affect a child's development are: 1) if the child is treated with more love, intimacy, and talked to about feelings, the child will grow up being more sensitive to others and more open to discuss their feelings with others. If the child is taught not to respond to their feelings, or let their emotions guide them, the child will grow up to be less sensitive, more aggressive and less likely to discuss their feelings. Depending on treatment, a child may grow up to have negative qualities, such as violence or repressed anger. These interactions can….
Social Media Facebook Facebook A Vehicle
As recent events in the Middle East have clearly demonstrated, Facebook is more on the side of the politically disadvantaged and the poor as they have increasingly embraced Facebook and other social media while the governments in the region tried to ban them. Many governments such as that of China do not allow Facebook primarily because they want to avert scenarios they have seen in the Middle East. Facebook revolutions It was in the wake of 2008 when Oscar Morales, a young man in Columbia, decided that he had had enough of FARC (Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia), a Marxist group which routinely kidnaps people, keeping them as hostages for months or years, while many of the hostages die in captivity. Angry and depressed by the actions of FARC, one night he turned to Facebook which he had been using to connect with his friends and high school classmates. He used….
Works Cited
Alexanian, Janet A.. "Eyewitness Accounts and Political Claims: Transnational Responses to the 2009 Postelection Protests in Iran." Comparative Studies of South Asia, Africa and the Middle East 31.2 (2011): 425-442. Project MUSE. Web. 3 Oct. 2011. .
Burns, Alex and Ben Eltham, "Twitter free Iran: an evaluation of twitter's role in public diplomacy and information operations in Iran's 2009 election crisis," in Papandrea, Franco & Armstrong, Mark (Eds.). Record of the Communications Policy & Research Forum 2009. Sydney: Network Insight Institute. Web. 26 Nov. 2011 .
China, Walid. "The Facebook Revolution." New African 503 (2011): 24. MasterFILE Premier. Web. 26 Nov. 2011.
Eltahawy, Mona. "The Middle East's Generation Facebook." World Policy Journal 25.3 (2008): 69-77. Academic Search Premier. Web. 26 Nov. 2011.
Social Responsibility Henry Mintzberg 1994
There is a good case to be made for focusing on externalities and seeking to manage all of them in a social responsible manner, especially as the world becomes globalized and the key success drivers become relationships and information. orks Cited: Mintzberg, H. (1994). The rise and fall of strategic planning. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved May 16, 2010 from http://online.worcester.edu/external/evescio/Principles%20of%20Management/strategicplan.pdf Friedman, M. (1971). The social responsibility of business is to increase its profits. New York Times Magazine. Retrieved May 16, 2010 from http://www.colorado.edu/studentgroups/libertarians/issues/friedman-soc-resp-business.html De Toni, a. & Tonchia, S. (2003). Strategic planning and firms' competencies: Traditional approaches and new perspectives. International Journal of Operations and Production Management. Vol. 23 (9) 947-976. ettstein, F. (2010). For better or for worse: Corporate responsibility beyond "do no harm." Business Ethics Quarterly. Vol. 20 (2) 275-283. Peng, M., ang, D. & Yi, J. (2009). An institution-based view of international business strategy: A focus on emerging economies. Journal of International….
Works Cited:
Mintzberg, H. (1994). The rise and fall of strategic planning. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved May 16, 2010 from http://online.worcester.edu/external/evescio/Principles%20of%20Management/strategicplan.pdf
Friedman, M. (1971). The social responsibility of business is to increase its profits. New York Times Magazine. Retrieved May 16, 2010 from http://www.colorado.edu/studentgroups/libertarians/issues/friedman-soc-resp-business.html
De Toni, a. & Tonchia, S. (2003). Strategic planning and firms' competencies: Traditional approaches and new perspectives. International Journal of Operations and Production Management. Vol. 23 (9) 947-976.
Wettstein, F. (2010). For better or for worse: Corporate responsibility beyond "do no harm." Business Ethics Quarterly. Vol. 20 (2) 275-283.
Social Psychological Principles to Create
Psychological studies have confirmed 'altruistic behavior' can be elicited in people. 'Peer Pressure' could also be utilized as an effective psychological tool in reducing resource consumption and in promoting other healthy environmental practices. [Center for Naturalism] A case in point is the Chinese governments 'Grain to Green' Program that offered cash incentives to farmers to convert marginal farmlands to forests. As Alan Tessier, program director in the National Science Foundation (NSF) says, "Much of the marginal cropland in rural communities has been converted from agriculture to forests through the Grain-to-Green Program, one of the largest 'payment for ecosystem services' programs in the world," "Results of this study show that a community's social norms have substantial impacts on the sustainability of these conservation investments." [ScienceDaily] uilding this collective self-control at the community, national and international level holds the key to the success of an environmentally sustainable future. Motivated and environmentally….
Bibliography
1) Su-Houn Liu, Yu-Hsieh Sung & Hsiu-Li Liao (2006), 'Developing Sustainable Digital Opportunity: The Case of Lalashan DOWEB Model', Issues in Information Systems,
Volume VII, No. 1, 2006, retrieved Dec 30th 2009, from http://www.iacis.org/iis/2006_iis/PDFs/Liu_Sung_Liao.pdf
2) BIO, (Nov 2009) 'Agricultural Biotechnology Benefits Farmers and the environment', retrieved Dec 30th 2009, from, http://www.bio.org/foodag/positions/Benbrook_Report_PUBLIC_111709.pdf
3) John Vidal, (2009), 'Rich Nations to Offset Emissions with Birth Control', retrieved Dec 30th 2009, from http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2009/dec/03/carbon-offset-projects-climate-change
social psychology
Social psychology is the study of human behavior in social situations, showing how social pressures and sociological variables can impact psychological phenomenon such as identity, motivation, personality, or behavior. A quintessential topic in the field of social psychology is bullying. Bullying can be studied from a public health perspective, showing how the external variables such as how a school is designed and the leadership and organizational culture of the school affects risk factors implicated in bullying behaviors or victimization patterns. Alternatively, bullying can be examined from a purely psychological perspective to reveal the factors implicated in aggressive physical or verbal behaviors or alternatively, to study victim characteristics or why some bystanders refuse to step in when they observe bullying behaviors. This latter issue links in with the social psychology approach. The social psychology of bullying examines factors like why some people perpetrate bullying behaviors due to their upbringing, their sense….
Social Sciences Background- for Centuries
It was originally established in the early 19th century by Auguste Comte who tried to unify history, psychology and economics through an understanding of society as a broad paradigm. Emile Durkheim took this a bit further and focused on the way societies could maintain a sort of integrity within the modern work where past cultural trends (religion, ethnicity, etc.) were no longer the singular part of society. His view, which has become the modern view of sociology, surrounded questions of what binds individuals together as a formal group (society) and what happens to this group both collectively and for the individual. This is a broad discipline as well, and clearly an academic response to the modern age (industrialization, urbanization, secularization, etc.). The field looks at social rules, the way those rules were formed, and the way that individuals coalesce into groups, communities, institutions, and even powerful social organizations that….
American Anthropological Association. (2012, January). What is Anthropology. Retrieved from aaanet.org: http://www.aaanet.org/about/WhatisAnthropology.cfm
Backhouse, R., & Fontaine, P. (Eds.). (2010). The History of the Social Sciences Since 1945. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Bernard, H. (2011). Research Methods in Anthropology. Lanham, MD: AltaMira Press.
Fernald, L. (2008). Psychology: Six Perspectives. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Need assistance developing essay topics related to School Uniforms. Can you offer any guidance?
1. The Impact of School Uniforms on Student Behavior and Academic Performance Explore the ways in which uniforms influence student behavior, including reducing distractions, fostering a sense of equality, and promoting discipline. Examine the potential effects of uniforms on academic performance, such as improved focus, reduced tardiness, and increased attendance. 2. The Role of School Uniforms in Creating a Positive and Inclusive School Environment Discuss how uniforms can help create a level playing field for students from diverse backgrounds, reducing socioeconomic disparities and fostering a sense of belonging. Analyze the ways in which uniforms can promote a more positive school climate....
Could you help me draft an essay outline about Jane Austine
Outline for Essay on Jane Austen I. Introduction A. Jane Austen's life and background B. Overview of her literary career C. Thesis statement: Jane Austen's novels explore the complexities of human relationships and social norms in Regency England. II. The Social Landscape of Austen's Novels A. Marriage and societal expectations 1. The importance of financial security and propriety 2. The role of women in society B. The rigidity of social class 1. The contrast between the landed gentry and the middle class 2. The challenges faced by those who defy social conventions III. The Role of Love and Marriage in Austen's Works A.....
I need a spark of inspiration! Can you share some captivating essay topics related to public opinion and socialization?
Captivating Essay Topics Related to Public Opinion and Socialization I. The Role of Social Media in Shaping Public Opinion The echo chamber effect: How social media algorithms reinforce existing beliefs The spread of fake news: The role of social media in propagating misinformation Digital activism: The impact of social media on political mobilization The polarization paradox: How social media contributes to both political polarization and civic engagement II. The Influence of Mass Media on Socialization The agenda-setting theory: How mass media sets the public's priorities The cultivation theory: How television and other mass media shape our perceptions of the world The priming....
I\'ve seen the common essay topics on microeconomics concept in microeconomics analysisi. Any lesser-known but interesting ones you can recommend?
The Impact of Social Media on Consumer Behavior: This topic explores the transformative effect of social media on consumer decision-making. Analyze how platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok shape consumer preferences, influence brand loyalty, and drive purchasing patterns. Examine the role of influencers, algorithms, and target marketing in shaping consumer behavior and discuss the implications for businesses and marketers. Behavioral Economics in Healthcare: Behavioral economics integrates psychological principles into economic analysis. In healthcare, this approach can provide valuable insights into patient decision-making, adherence to treatment, and demand for healthcare services. Discuss how behavioral economics can be applied to improve healthcare outcomes, design effective....

Family and Marriage
Social Norm Make answer question completely. Your answers cohesive essays. 1. Discuss explain types social norms. What role dominant culture play establishing norms? 2. What role time place defining crime?…
Social Norm Experiment: Scenario 6 -- Facing the rong ay in an Elevator Solomon Asch's Conformity Experiments during the 1950s demonstrated how much individual opinion and even perception of reality…
Social Norm Violations he Norm Violated: he norm was supposed to be about singing in appropriate places. I choose to sing on a public bus at about the time people…
Sports - Women
Violating Social Norm People like to keep to themselves whenever they can, especially when they are in a situation where they have the option of being to themselves, by themselves.…
Agriculture
Dining alone is unusual at a higher-end restaurant. Immediately, my jeans, sneakers and faded t-shirt drew whispered comment and stares from some diners. I was afraid I would…
Research Paper
social norms that individuals need to follow or are expected to follow at a dining table -- be it at home or in a public setting. These table…
Creative Writing
Sociology - Theories
Is there an example that might clarify or support the authors claim?Your comment regarding the development of strict, rule-based cultures to address threatening environments from outsiders is not simply…
Conflict of social norms and its effect on school environment Social norms can be defined as the rules that determine what should be done or avoided by people in their…
Social Psychological Experiment: Violating Social Norms Most Americans place a high priority on their personal space as evidenced by how far people stand apart from each other in virtually any…
Additionally, Sociocultural theory assumes that individuals develop self-concepts through interaction with others, and we are influenced by culture and social processes, such as social norms. Social norms dictate…
Education - Computers
As recent events in the Middle East have clearly demonstrated, Facebook is more on the side of the politically disadvantaged and the poor as they have increasingly embraced…
Business - Management
There is a good case to be made for focusing on externalities and seeking to manage all of them in a social responsible manner, especially as the world…
Psychological studies have confirmed 'altruistic behavior' can be elicited in people. 'Peer Pressure' could also be utilized as an effective psychological tool in reducing resource consumption and in…
Social psychology is the study of human behavior in social situations, showing how social pressures and sociological variables can impact psychological phenomenon such as identity, motivation, personality, or behavior.…
Anthropology
It was originally established in the early 19th century by Auguste Comte who tried to unify history, psychology and economics through an understanding of society as a broad…
Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Social Norms — Norm Violation in Sociology
Norm Violation in Sociology
- Categories: Deviance Social Norms
About this sample

Words: 1203 |
Published: Feb 12, 2024
Words: 1203 | Pages: 3 | 7 min read
Table of contents
Social norms essay: research methodology, breaking a social norm essay: research results, discussion: the consequences of social norm violation, norm violation faq.
- What is norm violation in sociology? Norm violation in sociology refers to the intentional or unintentional breaking of social rules and norms that govern society.
- How do social norms shape society? Social norms play a significant role in shaping society by determining acceptable behavior. They provide guidelines for how individuals should act and interact with others in their community.
- Can social norms change over time? Yes, social norms are not fixed and can change over time. What was once considered typical or acceptable may now be deemed unacceptable or outdated.
- What was the focus of the norm violation experiment described in the essay? The norm violation experiment aimed to observe and analyze how individuals would respond to the violation of the social norm of using gender-segregated public restrooms. The experiment sought to determine whether people would attempt to correct the behavior or ignore it, highlighting their readiness to address norm violations.
- What were the results of the norm violation experiment? The most common reaction observed was subtle confusion without any subsequent comments. Men recognized that the woman had entered the wrong restroom but chose to either leave hurriedly or avoid entering after seeing her inside. This indicated a preference to either escape or ignore norm violations rather than confront them. Only a few individuals attempted to point out the mistake, while others simply asked her to leave. There were no signs of disrespect or physical contact, with only one instance of rude behavior.
- What were the consequences of the norm violation for the experimenter? The experimenter initially felt uncertainty and shame regarding her behavior, but as the experiment progressed, she became more accustomed to the situation. This suggests that hedonic adaptation may occur in similar circumstances, leading to a normalization of the behavior.
- What does the norm violation experiment suggest about society? The norm violation experiment suggests that people prioritize their personal space and time over addressing others' social behavior directly. This may reflect an increasing trend towards individualism and selfishness in society. However, it is important to recognize the importance of cooperation and adherence to social norms for the functioning and survival of society.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 488 words
2 pages / 1058 words
2 pages / 1005 words
3 pages / 1484 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Social Norms
Social norms are the unwritten rules that govern acceptable behavior in a society. Violating these norms can lead to social disapproval or even punishment. However, there are times when breaking social norms can be a powerful [...]
Social norms are the unwritten rules that govern behavior in a society. They dictate how individuals should act, dress, and speak in various situations. These norms are essential for maintaining order and cohesion within a [...]
Norms and social norms are powerful forces that shape our behavior and guide our social interactions. They provide a sense of order, cohesion, and predictability in society. Norms act as social guidelines, ensuring that [...]
Social norms are an integral part of society, shaping the way individuals behave and interact with one another. These norms are the unwritten rules that govern our actions, beliefs, and values, and they vary across different [...]
The norm I will be violating for this paper will be invading people’s personal space. This norm acts as a mechanism of social control because the accepted behavior in our society is to give people their personal “bubble” [...]
During the Elizabethan Era in England, spanning from 1558 to 1603, sports and recreational activities played a significant role in the daily lives of the people. These activities were more than just pastimes; they reflected the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Social norms shape the behaviors and actions of individuals to a considerable extent. They represent an unwritten policy concerning the expected human behavior. Social norms are fundamental in promoting order and control in society. These rules reflect the behavioral patterns of members of a certain group. The application of these norms can be ...
Social Norms in Society. Social norms are an integral part of society, shaping the way individuals behave and interact with one another. These norms are the unwritten rules that govern our actions, beliefs, and values, and they vary across different cultures, communities, and time periods. In this essay, we will explore the concept of social ...
Conclusion. Norms and social norms are powerful forces that shape our behavior and guide our social interactions. They provide a sense of order, cohesion, and predictability in society. Norms act as social guidelines, ensuring that individuals conform to the accepted standards of behavior.
Examples of some social norms that students learn are: "do not yell in the library," "do not speak unless spoken to," "do not talk to strangers," and "close the door when you use the restroom.". As you grow older, these rules become unspoken because everyone knows how to act like a proper individual in society.
Conclusion. In conclusion, breaking social norms can lead to a deeper understanding of human behavior and societal dynamics. Whether it involves personal space, gender roles, cultural expectations, dress codes, or authority, deviating from societal norms can lead to interesting insights into the functioning of society.While there may be consequences for breaking these norms, it can also lead ...
Social Norms in Society. Social norms are an integral part of society, shaping the way individuals behave and interact with one another. These norms are the unwritten rules that govern our actions, beliefs, and values, and they vary across different cultures, communities, and time periods. In this essay, we...
2. 3. Essays on Social Norms. by Minjae Kim. Submitted to the Sloan School of Management on April 19, 2018, in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Management. ABSTRACT. The first essay addresses why people might conform to norms that they do not endorse.
When one person violates the already established norm, various reactions observe to judge the chosen behavior. The idea of my norm violation experience lies in the intention to eat with my hands at a local restaurant and observe the reactions, addressing the concepts of the relativity of deviance and social control.
Conclusion. The study of social norms can help us understand a wide variety of seemingly puzzling behaviors. According to some accounts, a social norm results from conditional preferences for conforming to a relevant behavioral rule. ... Selected Papers on Social Norms at EconPapers. Social Norm, entry in Wikipedia. Related Entries. altruism ...
Cite this essay. Download. Our society is ruled by a massive number of social norms that we follow in our everyday lives. Social norms are these unwritten rules put into place by the society around us about what behavior, thoughts or feelings are appropriate within a given circumstance. These norms influence our actions in our everyday lives ...
e papers carry the names of the authors and should be cited accordingly. e ndings, interpretations, and conclusions expressed in this paper are entirely those of the authors. ey do not necessarily represent the views of the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/World Bank and ... Social norms affect almost every aspect of people ...
The first essay addresses why people might conform to norms that they do not endorse. One explanation is pluralistic ignorance: when everyone appears to endorse a norm, even nonendorsers will conform so as to feign their commitment to the group's values, thereby exacerbating the misperception.
Essay Example: In the vibrant landscape of social psychology, the Social Roles Theory emerges as a captivating narrative, transcending the confines of scholarly abstraction. ... In conclusion, the Social Roles Theory isn't a distant theoretical construct; it is a narrative, a melody, and a profound exploration of the human journey within the ...
It is important to stress that the American Dream assumes a long-term type of life planning directly reflected in people's actions and perceptions of society. Departing From Social Norms Can Lead to Progress. Following rules and social norms set by the community is like agreeing to the dictation of the superego.
My dissertation is divided into five relatively freestanding yet thematically linked essays, investigating a number of ways in which social norms and the question of racism are related. In these chapters, I aim to show the vital influence of social norms on our interpersonal relationships, going beyond the futile binary between individual (moral philosophy) and state (political philosophy ...
A social norm is a regulation or expectancy that dominates peoples morals, beliefs, actions, attitudes and behaviours. ... From simple essay plans, through to full dissertations, you can guarantee we have a service perfectly matched to your needs. ... In conclusion, it is evident that social norms influence behaviour and this has been supported ...
Social norms and values play crucial roles in maintaining social order and promoting cohesion within communities. They provide a sense of predictability and stability, enabling individuals to navigate social interactions with ease. By adhering to shared norms, we create a harmonious environment where expectations are clear and cooperation is ...
Examples of Social Norms. Greeting people when you see them. Saying "thank you" for favors. Holding the door open for others. Standing up when someone else enters the room. Offering to help someone carrying something heavy. Speaking quietly in public places. Waiting in line politely. Respecting other people's personal space.
In conclusion, social norms are a fundamental aspect of society that shape behavior, maintain order, and reflect cultural values and beliefs. They provide a framework for acceptable behavior and guide individuals in their interactions with others. ... Norm Violation in Sociology Essay. Social norms play a significant role in shaping society and ...
Reactions to Social Norm Violation Essay. We have a number of societal norms that govern day-to-day actions and reactions. Common norms involve use of he elevator. We understand that it is apparent that one should face the front, avoid distracting others by standing a side and should not look obnoxiously or stare to other users.
WORDS 286. Outline for Essay on Jane Austen. I. Introduction. A. Jane Austen's life and background. B. Overview of her literary career. C. Thesis statement: Jane Austen's novels explore the complexities of human relationships and social norms in Regency England. II. The Social Landscape of Austen's Novels.
Paper Type: 1300 Word Essay Examples. Conformity is a pervasive aspect of human behavior, shaping our actions, beliefs, and attitudes in alignment with prevailing social norms. This phenomenon is integral to our daily lives, influencing everything from speech and dress codes to eating habits.
Conclusion. Breaking social norms is a valuable tool for sociologists to study the underlying dynamics of society. By intentionally violating these norms, researchers can gain insights into how norms are formed, how power operates in social interactions, and how individuals exercise agency in shaping their behavior.
One example of a social norm is the separation of public restrooms for men and women. While there may be some exceptions and instances of confusion, it is generally expected that individuals will use the restroom designated for their gender. In sociology, deviant behavior is described as norm violation, where individuals intentionally or ...