- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Business consultants
Entrepreneurs and Small Business
Accelerators and Incubators
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Stratrgic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
Small Business Tools
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Strategic Planning
How to Write a Business Plan Complete Guide

Free Business Plan Template
Paresh Balar
- March 18, 2024
24 Min Read

Welcome to the journey of entrepreneurship . You are here because you have a great business idea and want to know how to write a business plan to convert that idea into reality.
Before you start writing your business plan, let’s understand What is a business plan? Why do you need one in the first place? And What should you include in your business plan?
Table of Contents
- What is a business plan?
- What to include in your business plan?
Business Plan Cover Page
Things to consider before writing a business plan.
- Why do you need a business plan?
Let’s get started with an important question.
What is a Business Plan?
In simple words, a business plan is a document that outlines your business goals and details how you plan to achieve those goals. It is a living document that will prove to you and the rest of the world that your idea is not just a dream but can be a viable reality.
Also, it will help investors learn about your business, and vision, and convince them that your business idea is worth investing in. Your business plan will provide concrete evidence that your business idea is sound and has every chance of success.
Your business plan is the backbone of your business.
What Should You Include in Your Business Plan?
Every business idea and plan is unique in its terms. You should include all the details that explain your business idea in the best possible way. However, there are a few elements that every entrepreneur should include in their business plan.
The following is a full guide for creating a comprehensive business plan. We’ll first list out the sections that must be included in the business plan and in the later part, we’ll explain what should be added to each section:
Business Plan Outline
- Executive Summary
- Company Overview
- Problem Analysis
- Products & Services
- Product Features
- Market Overview
- Market Size
- Target Customers
- Customer Needs
- Direct Competitors
- Indirect Competitors
Competitive Advantages
Swot analysis.
- Promotions Plan
- Distribution Plan
- Key Operational Processes
Management Team
- Management Team Gaps
- Board Members
- Revenue Model
- Financial Highlights
- Funding Requirements
- Use of Funds
- Exit Strategy
- Appendix – Supporting Documentation
Now you are ready to write your business plan, let’s understand in detail how you can write your business plan and what you should include in each element of the business plan.

The business plan cover page is the first and most important part of the business plan because it will create the first impact and will set the platform for how investors or readers will engage with your business plan.
Just by looking at the business plan cover page, an investor or reader can get a quick idea about the purpose of your business idea and business plan.
However, many entrepreneurs do not pay enough attention to the cover page, which is their biggest mistake.
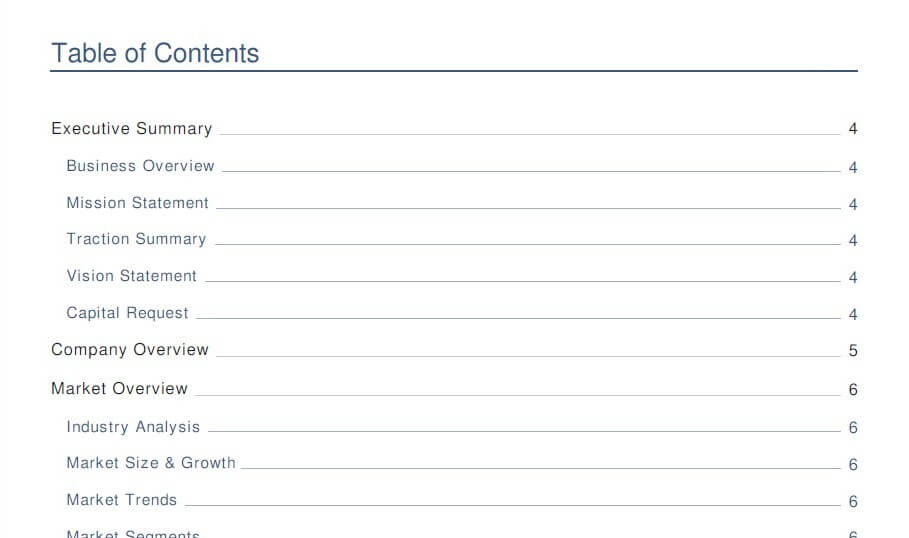
In any document, the business plan table of contents provides a quick overview and works as navigation to navigate across the document. The same does for a business plan as well.
A table of contents is important to provide a quick overview of the sections that you have included in your business plan and help readers to navigate to the section that interests them the most. If investors are excited about a particular part of the business plan first, they will find the table of contents extremely useful in finding the relevant sections within the business plan.
Usually, the table of contents needs to be added at the start of the document and just after the business plan cover page.
Here’s a Quick Overview of Each Key Chapter:
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the first section of your business plan. However, the executive summary is always written at last as it is a brief introduction to your business plan and a summary of your entire business plan document.
A good executive summary should answer the following basic questions:
- What are you trying to achieve with your business idea?
- Why is your business idea important? and
- How are you going to achieve your business goals?
Generally, a good executive summary should include the following details:
- A brief description of the problems you will be solving
- Summary of your business goals & vision
- Products or services you are going to offer
- A solid description of the market you are targeting
- A quick look at your competition and your competitive advantages
- A basic financial projection of your revenue, expenses, and profits
- Your funding requirements (if any) and how you will be using that funds.
It does seem like lots of details are required to write a good executive summary but at the same time, it is important to get it right because if your summary does not clearly explain how you will solve a customer problem and make a profit, then investors or readers might not find it worth reading.
Most of the investors just read the executive summary and decide if they should read the rest of the business plan or not. So make your efforts count in this part of the business plan.
In short, write your executive summary in such a way that readers would want to turn the page and keep on reading.
Always remember, that a good executive summary should not be more than one or two pages long. However, in some cases, it can be longer if there is an absolute requirement.
2. Company Overview
The company overview section provides a brief history of your company if it already exists. However, if you are starting a new business, here you will need to write about yourself, your achievements, and how you will set up and form your business as a company.
Here you need to answer questions such as how and when your company was formed, what type of legal entity you are, and what are your achievements to date. Your past journey and achievements are the best sign of your possible future success, so make sure to include all the important milestones you or your company have achieved to date.
As a startup, your company overview can be very much short, so focus on your personal history, achievements, and the journey that led you to start your business in the first place. Sharing your original idea is important because it shows how you think and how you were able to craft your idea into a business.
Even if you are just starting, your educational background, professional experience, achievements, and the details of your best business idea can give potential investors a vision of what you are trying to achieve.
Have a look at this company overview example
- Starbucks company profile
- Puma company page
3. Problem Analysis
You have started the business because you have identified the unique problem that customers are facing and in this section, you just need to explain that problem.
The problem statement section can be explained with three simple questions.
- Whom does the problem affect?
- What are the causes of the problem?
- Why is it important to fix it?
When you write your problem statement, just describe how bigger the problem is and why it is most important to fix it. Also, there might be multiple problems you will be solving, but always try to focus on the main problem because you don’t win on the number of problems you solve; you win on how well you solve a specific problem .
While writing the business plan, most entrepreneurs focus on the solution they are going to offer, and in that process, they forget to explain the actual importance of the problem. Remember the more accurately you will explain the problem, the more valuable the solution will be.
Remember to keep the problem statement as simple as possible and should be self-explanatory. Also, it is good to include the key statistics that explain the severity of the problem.
After you explain the problem, it is also important to describe the world once a particular problem will be solved and that will set the stage to introduce the solution you are proposing.
4. The Solution
The solution section is also called the product & services section . In this section, you will need to define your best-proposed solution to the problem you explained in the previous problem analysis section.
Your solution details should be as simple as possible. It is not recommended to use too many technical or industry details while writing about your product details. Keep in mind your readers will not have the same education or technical background as you.
The length of this section will depend on the nature of your business. for example, if your business is product-focused and the product is relatively new in the market, then you should write more about the product, its design, its features, etc. However, if your business is relatively common like selling bicycles or restaurant business and you are planning to compete with better pricing or customer service then you probably don’t need to write more about products.
If your product is hard to explain it’s a good idea to include a picture. Also, if you are planning to expand your business and will come with new products or services in the future, then you can mention those details here as well.
Your product or service pricing should be mentioned here in this section. Apply the right pricing strategy to set the best pricing for your product or services. Also, if you have any product patents, copyrights, licenses, etc then add those details here in this section.
In short, your solution section should answer the following common questions:
- Your products or services are currently under development or already available?
- If not available, what will be the timeline for delivering products and services to the market?
- How are your products or services different from the competition?
- How will you get your products? Are you the manufacturer or do you purchase products from suppliers or wholesalers?
When you write this product and services section, think of your reader as a person who knows little to nothing about your business. so make it as simple as possible.
5. Market Analysis
Before you start your business, it is essential to check if there is a viable market available for the products or services you are planning to offer, and that makes market research the most critical and key to success for any business.
In simple words, market analysis is studying the industry your business will operate in, the size of the industry, and its trend & direction (growing, stable, or in decline).
The market analysis consists of main three parts:
- Market Overview: This is a general overview of the industry. In this part, you will need to describe the current position of the industry, market trends, and where it is heading. Also, you can write about your knowledge and experience in the industry.
- Target Market: In this part, you will need to be more specific about the segment of the market that will use your products or services. Not everyone from the industry will use your product or services, so it is important to find the right audience for your product. (For example, if you are starting a veg restaurant in the town, then all the people from town will not visit your restaurant. The only people who prefer and eat veg food will be your target customers).
- Market Size: Market size is all about finding how many potential customers are there for your product or service. Here you will need to show some statistics about the size of the industry (e.g., total U.S. sales in the last year) and its growth rate over the last few years.
The main objective of the market analysis is to identify the opportunities and risks associated with the business. It will also help you to understand how you should prepare your marketing strategy , where you should invest in terms of marketing efforts, and avoid making the wrong decisions.
With market analysis, you can identify the market entry barrier, and market needs, and estimate the market attractiveness from a financial standpoint.
6. Customer Analysis
Once you complete your market analysis, it’s time to identify the customers and needs of customers who are going to use your product or services, and this process is called customer analysis . Customer analysis is a key element of any successful marketing plan, as well as your overall business plan.
Customer analysis is critical for any business to succeed because if you do not know who is going to your offerings, and what your customers want, no business can succeed.
Now that you know customer analysis is that important, it is time to learn how you can perform strong customer analysis.
Customer analysis consists of main three parts:
- Demographics: Age, Sex, Ethnicity, Income, Family, Occupation, etc.
- Geographic: Location (Neighbourhood, Region, Urban/Rural, Online)
- Psychographic: Lifestyle, Personality, etc
- Interests: Hobbies, Activities, etc
- Growth: Size of the target customers and whether they are growing, shrinking, or stable.
It’s up to you what is the best way to get this information for your business. However, some practical methods include customer surveys, existing customer data analysis, social media listening, or talking with your customer support team.
- Identify your customer’s needs: Once you identify who your customers are, it’s important to understand their needs as well, and the answer to this question should be your offering.
- Explain how your product or services will meet those needs: Now that you know your target customers and what they need, it’s time to explain your products or services’ benefits. In this part, list out the key features of your products or services that will fulfill customers’ needs, explain the benefits of your offerings, and the outcome customers can expect by using your products or services.
Keep in mind, that a strong customer analysis must answer these three key questions:
- Who are your customers?
- What do they need?
- How do your products or services meet those needs?

Want to Create a Customer Persona in Easy Steps?
Generate valuable customer insights in minutes with our Free Customer Persona Generator .
7. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis is all about finding your competitors, analyzing their strengths and weaknesses, products and services, pricing, social media presence, marketing & sales strategy, etc.
Your competitors can be categorized into two classes:
- Direct Competitors: Direct competitors are the ones who provide the same solution as you do. For example, if you operate an Italian restaurant, other restaurants that serve Italian food will be your direct competitors. In this section of your business plan, outline who your direct competitors are, and add their strengths and weaknesses.
- Indirect Competitors: Indirect competitors are the ones who do not provide the same solution as you do. However, solve the same customer problem as you do. For example, if you operate an Italian restaurant, a Mexican or Spanish restaurant would be an indirect competitor. In this section of your business plan, outline who your indirect competitors are, and add their strengths and weaknesses.
Once you identify who your competitors are, it’s time to explain how different and superior you are compared to them and that will be the competitive advantage section of your business plan .

SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
Her strengths and weaknesses are subjective to your business which you can control and change like business location, pricing, uniqueness, etc. While opportunities and threats are external that are running outside your business, in the larger market. However, you can take advantage of opportunities and defend your business against potential threats, but you can’t change them.
It is always best if the business owners perform a SWOT analysis themselves. This task is not something that you should assign to someone else. A precise SWOT analysis will allow you to measure your strengths and weaknesses against the opportunities and threats in your business environment.
Once your SWOT analysis is ready, it will help you to form a strategy to achieve your business goals.
Want to create a SWOT analysis for your business?
Craft a powerful SWOT Analysis in just minutes using our user-friendly and free online SWOT Analysis Generator Tool!
8. Marketing Plan
Now that you have explained your products or services and identified who is going to use those products or services, it is time to let your customers know about your products or services. And for this, you will have to plan strategy, and that planning you will need to explain in this section.
Your marketing plan can be divided into the following sections:
- Pricing: Explain your product or service pricing here in this section. Mainly, discuss how you finalized your pricing and how your pricing is better than the competition. Also, discuss if it’s low-cost or premium offerings and how your pricing supports it. This will ensure investors also that you have finalized your pricing with proper research.
- Promotional Plan: In this section, talk about your marketing activities and strategies that you will execute to attract your customers. It is always great to have some unique selling propositions (USP). However, Unique selling propositions should be short and self-explanatory. For example, Domino’s Pizza’s USP is “We deliver hot, fresh pizza in 30 minutes or less, or it’s free.” Also, discuss your other marketing or promotional activities that may include discount offers for early customers, media or online advertisements, product launches or social events, radio newspaper or magazine ads, affiliate or referral programs, etc. In this section, you can also write about your customer relation and support team and how they will work to retain your existing customers.
- Distribution Plan: The main purpose of your marketing plan is that customers to buy your products or services. So it is important to explain how they can buy your products or services. Your distribution plan will include all details about your distribution channel, sales channel & strategy, and payment policies.
Once you complete writing your marketing plan , make sure your marketing plan answers these key questions.
- What will be the pricing of your offerings?
- How will you reach out to your target customers?
- How will you retain your customers to buy from you repeatedly?
- How and from where customers can buy your products and services?
Your marketing plan can be 7-8 pages long. However, while writing your business plan, make sure you do not go into details and try to keep it as simple as possible. You can separately write your marketing plan for internal purposes.?
9. Operations Plan
Your operation plan will explain how you will manufacture your product and run your business. It can include a lot of details depending on your business. For example, if you are in the production business, you will want to include all the information about how you will get raw materials, and equipment, build your products and ship them.
However, it is not recommended to include all these details while writing the operations section of your business plan . You should include only major details that you think will give you a competitive advantage or are important for your readers.
An operations plan is useful for internal purposes as it will help your team to understand their roles to achieve your business goals. However, it will help investors also to learn how you will run your business to make your business succeed.
The management team should be the easiest section of your business plan because, in this section, you will need to write about yourself and your core team members who will run the business.
Always remember, that businesses’ success will depend on the team who is running them. So you must write this section carefully and convince your readers or investors that you are the best person to execute and run this business.
Many investors believe it is not the business that succeeds, it is the team that makes the business successful. In fact, in some cases, investors have funded start-ups mainly based on the team who will run the business.

In this section, list out important details of core team members like name, position in the company, contact information, qualifications, past experiences, achievements, etc.
You can also mention any management gaps present in your organization and when you are planning to fill those gaps. You can also mention if there is an advisory team or board of members who might not work in your organization but will advise you from outside.
10. Financial Plan

The financial section of the business plan is the most important component of the business plan. Whatever you will write in the business plan will be conceptual until you do not add some numbers to support it.
Have a financial plan if you want to secure outside funding from investors or bank loans from financial institutes. Even if you do not need funds, it is always helpful to have a financial forecast to achieve your business goals and make your business successful. Financial forecasting will give you a clear idea of whether your business is viable or not.
Your financial plan will include the following sections.
- Revenue Model: The main purpose of this section is to explain the different revenue streams of your business. Do you sell products? Do you provide services? Do you provide third-party advertisements? Or do you sell all of the above? It is equally important to update this revenue model section, once you start generating revenue. Use the revenue model as a living document to improve your plans. Focus on revenue streams that work best, while changing your approach to those that aren’t doing well.
- Financial Highlights: Include financial reports like cash flow, balance sheet, profit & loss, projected revenue, expenses, etc.
- Funds Needed: This section is required if you are looking for funds to run your business operations. Before you directly request funds, it is good to explain your current financial situation, how much you have already invested, and how much funds you already have secured. Once you explain your current financial position, it is time to explain what type of funding you are looking for. What are your preferred options to secure funds? It is important to update this section once you secure funding.
- Use of Funds: Once you explain how many funds you are looking for, it’s time to explain how you will use those funds. You will use it to hire new talents, expand your operations, pay your existing debts, or buy new equipment. If you are going to use funds for multiple things, mention each and also mention how much funds you are going to spend for each thing. Investors or financial institutes usually approve funds if they have a clear idea about how you are going to use your money.
- Exit Strategy: If you are looking for equity funding, it is important to have an exit strategy. A common exit strategy includes selling your company to a larger firm (acquisitions), selling or diluting your ownership, initial public offering (IPO), etc. If you have such plans, provide a detailed explanation of them in this section.
With upmetrics, business financial forecasting is easy and fun. Once you add your data, the system will generate all required reports automatically. Later you can embed those reports into your business plan. learn more about the upmetrics financial planning feature .
11. Supporting Documentation (Appendix)
Adding supporting documents is not a mandatory section in your business plan. However, it is important to add the documents which you think can convince investors that your business will succeed.
These documents can include achievements, product patents, awards, financial statements, resumes of key team members, legal agreements, product or organization pictures, etc. These documents can help readers understand your story clearly and concisely.
Once you write your business plan, it is equally important to update your business plan as your business grows. Keep in mind, that a business plan is not just a document but it is a roadmap of your business.
Now before you start the actual writing of your business plan and learn what to include in each section of the business plan, there are some key concepts that you must keep in mind and rules that you should follow during the entire business planning process .
1. Keep it short
Don’t you want your business plan to be read by your investors? Remember, many investors do not like to read a long business plan.
In this competitive time, no one has time to go through a 100-page long document. A typical 20-25 pages should be fine for any standard business plan. A well-written business plan ensures to communicate your message to your potential investors effectively.
However, if your business idea is a completely new kind of business or even a new industry, it may need quite a bit of writing to get the message across.
Your business plan writing purpose will decide how long your business plan should be . If you are writing your business plan to seek millions of funding, then you might need a lengthy and detailed business plan. A short business plan would work if you are looking to expand your business.
2. Be realistic and creative
Do not consider your business idea as your baby. Be realistic and honest with yourself while writing your business plan, and always try to add facts and realistic details of your business idea.
Also, your business plan should grab your reader’s attention quickly. Be creative while designing your business plan cover page and writing any important details in your business plan.
When it comes to the formatting of the business plan, make sure to use bullet points, images, and charts. Also, highlight the key points or metrics that you want readers to focus on. It helps bring your idea to life. Plus, it will keep your readers focused on reading.
3. You should be able to change it as the business grows
Most businesses start with a business plan, and once written, it’s never revisited. Never make that mistake. Your business plan should be treated as a working document that should be developed as your business grows.
For example, you might want to update your business plan as per the changing trends for a new round of funding or you might want to update it to counter unexpected problems like the COVID crisis. In a nutshell, keep your plan alive!
Why Do You Need a Business Plan?
Some entrepreneurs have achieved tremendous success without writing a business plan with their past experiences, less competition, or maybe by luck.
But the fact is, that many entrepreneurs have failed as well. It is just that we learn more about success stories only.
So, does writing a business plan guarantee success? Of course Not.
But, the business plan is your companion on your entrepreneurship journey. It will help you and your team understand the problems and the competition you will encounter in your journey. It will keep you and your entire team in sync and on the right path to achieving your business goals and success.
Click here to download how to write a business plan pdf
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

About the Author

Paresh Balar is the co-founder of Upmetrics, the #1 business planning software. His ultimate goal with Upmetrics is to revolutionize how entrepreneurs create, manage, and execute their business plans. He loves sharing his thoughts on business and financial planning and its challenges through his blog posts. Read more
Related Articles

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)

How to Write an Effective Company Overview for Your Business Plan

How to Write a Business Plan Executive Summary: Tips & Example
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Executive Summary for a Business Plan

3-minute read
- 19th November 2023
An executive summary is the part of a business plan that gives an outline of the main plan. So to write an executive summary, we first need to read the business plan carefully and understand its key points. These key points are what we will condense to form the executive summary. It’s important to ensure that the executive summary can stand alone because plenty of users will read only that and not the main business plan. We could say that the business plan is the original TL;DR (too long; didn’t read)!
But first, let’s take a quick look at what goes into a business plan so we can focus on the sections we need for our executive summary.
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that sets out a business’s strategy and the means of achieving it. The business plan usually contains the following sections:
How to Write an Executive Summary
The executive summary covers the same headings as the main business plan but not in so much detail. This is where our editing skills come to the fore!
The following six steps explain how to approach writing the executive summary.
Consider the Audience
Who will be using the summary? The business plan might be issued only to a very specific group of people, in which case, their needs are paramount and specialized. If the business plan is going out on wider release, we need to think about what a general reader will want to know.
Check That It Makes Sense on Its Own
Make sure the summary can be read as a stand-alone document for users who won’t read the whole plan.
Use Formatting Effectively
Make good use of formatting, headings, numbering, and bullets to increase clarity and readability.
Keep It Brief
One page (or around ten percent of the total word count for a large document) is great.
Avoid Jargon
Try to avoid jargon and use straightforward language. Readers of the executive summary might not have business backgrounds (for instance, if they are friend and family investors in a small start-up business).
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Proofread the Executive Summary
The executive summary will very likely be the first – and perhaps the only – part of the business plan some people will read, and it must be error-free to make a professional impression.
● Consider the audience .
● Ensure that the executive summary can stand alone.
● Use formatting tools to good advantage.
● Keep it brief.
● Keep it simple.
● Proofread it.
If you’d like an expert to proofread your business plan – or any of your writing – get in touch!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
What is a content editor.
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
What Should a Business Plan Include?
A business plan serves as a roadmap to successfully launch a business. It helps you overcome the challenges you might experience in your industry. Learn how to create and use a business plan for your startup.
One of the most fatal mistakes that aspiring entrepreneurs make in launching a startup is forgetting a business plan . You wouldn’t launch a ship at sea without establishing its routes and the direction you’ll steer it to. Without proper planning, your ship will end up adrift or worst, dramatically sink when the tides hit. And in a volatile commercial industry, the tides are constantly changing.
Avoid common startup mistakes by creating a business plan. A business plan not only strengthens your foundation but also helps you navigate the ever-changing field of business. Chances are your customers’ preferences will change over time and you have to keep up with them. Hence, a business plan also changes accordingly.
But how exactly do you create a business plan ? Is there a template to follow? Should you enlist the help of other experts to write it? Today, we’ll look into what should be included in your business plan and how it should be written. The first step is by understanding what it is and what it is for.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is an official company document that breaks down all the goals of a business and how to achieve them. It basically lays out the groundwork for your idea to come alive. It’s often referred to as the “blueprint of the business”, summarizing your goals.
Although there are many ways to write it, its key point usually discusses the financial, marketing, and operational strategies of the business.
What is it for?
A business plan serves as a guide for a growing company. It’s a consistent reference for business owners and stakeholders to base critical decisions on. It’s especially useful for early-stage startups to attract investors. When a company doesn’t have a proven track record, it can lay out its full potential instead.
Not only is the business plan useful for the initial launching of a business, but it also helps with pivotal changes. Since the market is perpetually changing, it’s crucial that your plan also evolves with it. Hence, the goals and methods of achieving will be updated. In some cases, a whole new plan is created if the company wants to drastically move in a new direction.
What’s included in a Business Plan
Although there’s no fixed formula for writing a business plan, there are some identifiable key points. These are generally the items factored in its creation:
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary outlines the whole plan. You start with a clear introduction of who you are, what you sell, and what your ambitions are as a business. This section includes your mission statement, product description, and the basic overview of your company’s structure. It should also include your financial plans.
2. Business Description
The business description provides detailed information about your industry. It must describe its current outlook as well as its profit potential. You will go into detail about your target market and other organizations or businesses you cater to. Also, this section briefly discusses what problem the business is trying to solve.
3. Market Analysis
A business must have a firm understanding of its target market and should be able to prove its sustainability. The market analysis provides trends and studies about the target consumers—their size, demographics, buying power, and frequent activities. This section also touches briefly on the competitors.
4. Product Development
Investors need a clear idea of how you would create and maintain your product. The development plan section contains the details of the product’s design; its production methods, lifecycle, marketing, and development budget. This includes the overall strategy of how it will be sold in the market.
5. Marketing Strategies
The product is only as good as how much it will sell. Therefore, this section describes how you will present your products and services to the market. This will discuss your marketing campaigns, distribution channels, and types of media you’ll tap into. You will summarize how you intend to reach your customers and pitch your products to them.
6. Operations and Management
Your investors need an overview of how the business functions. The operations plan highlights the logistics of the company such as team responsibilities, division tasks, and operational expenses. This helps track down who is responsible for certain areas of the business.
7. Financial Plans
Money mobilizes the idea. Hence, it’s important to keep an accurate record of where it’s going. This section shows the company’s monetary plans and its future projections. This includes financial statements, balance sheets, and third-party business transactions. For startups, it will mostly contain the target profit and estimates of expenses.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan
Now that we have an idea of the business plan template , it’s time to learn how to write it effectively.
Here are some things to keep in mind when you’re writing one for your business.
- Keep it concise. It serve as a guide for the company and the investors. It needs to be easy to understand and direct to the point. You can’t afford to waste a reader’s time by creating a 100-page business plan. Instead, aim for a summarized version of your plan, only highlighting the important points and outlining the rest.
- Avoid jargon. Ensure that everyone, especially investors, can understand your business plan. Do not include complex jargon in your content. Save the technicalities for the experts and simplify the terms in explaining your ideas.
- Keep it up-to-date. As previously mentioned, business plans are not static. Over time, a lot of things in the industry will change and might make your original plans obsolete. Frequently update your business plan according to what’s new in the field and with new methods you’re employing. Remember, a business plan is only useful if it’s still relevant.
Build your Business
Business plans are important when you’re starting your business from scratch. However, the success of your business still heavily relies on their execution. A lot of startups fail because they can’t push through with what was proposed in the business plans.
More than just articulating your ideas, you need to do a lot more to make them come to life. For one, you’ll need the capital to kick things off and make everything operational. Second, you’ll need to hire the best people to run your operations. Lastly, you have to find investors to sustain your business.
One way to ensure that your business plan is properly executed is by enlisting the help of business experts. Full Scale is an offshore software development company that specializes in helping startups.
We can provide the talent and resources needed to begin your operations. Whether you need project managers, marketing specialists, or technical experts; we’ve got them all. We’ll take care of all the processes of recruitment and management so you can focus on your core competencies.
Ready to begin your entrepreneurial journey? Get your FREE consultation today!
Learn More about Offshore Development
Copyright 2024 © Full Scale
How to Want a Business Design Report: A Next By Stepping Guide

So you have come above with a business basic that will turn insert company into an Forbes 500 enterprise? Sounds great!
However, you are going to need many more than an idea. You will need to do some comprehensive investigation, create operational standpoints, describe your product, define get goals, and pave from a road map for future development. 7 Free Business Plants Templates & Examples. Whether you're pitching one ability cofounder, investors, future personnel, or accelators, these business plan ...
In other words, you are going to need a business planner.
ADENINE business plan be an document that precisely explains how she are going to make your start-up a succeed. Without it, your chances of attracting funding and investments significantly decrease.
Do thee do to learn how to create a charming business plan report so will take to company to the next level? We created a instructions that will help you do just that.
Let’s dive in.
- What Is a Businesses Plan?
- Why additionally When Done You Demand a Businesses Plan?
- Types of Business Plans (What to Enclosing in Each)
- How Do Yourself Indite a Business Plan News?
- Favorite Practices for Writing a Winsome Business Draft Report
Business Plan Report Examples
- Monitor and Report the the Performance of Your Business on Databox
What Remains an Business Plan?
A business plan can a comprehensive document that defines how a businesses will achieve your goals. It is essentially a road map for growth that does operational standpoints from all the key subject that as marketing, financial, HR, and others.
Startups make business plans to depict who they represent, what their plan to do, also how them plan to achieve it. This is an exceedingly valuable create for attracts investors.
However, handful are resource for the company associates as well. A good business plan stays executive teams on the just page regarding and strategies few require implement to achieve their set objectives.
Related : Disclosure up Investors: 6 Best Practises to Help Increase Funding
While store plans are especially useful for startups, each business shouldn include them. In the best-case scenario, get plan will be updated from time for time and verified whether the our of the company have been met. You've made the leap in corporate - congrats! Here's an list of business plan samples the examples toward inspire you on your journey.
The main things that investors want till check out in this work plan become:
- Product-market proper – Have you researched the market demand for your products and services?
- Team efficacy – Does your startup have given professionals which will work on achieving your goals?
- Scalability – How probable is growth in sales volumes without proportional growth either fixed costs?
An organized business plan is essentially a blueprint of is goals and it exhibitions your abilities as an entrepreneur.
Related : Businesses Get: About is it & How to Write an Great One? (With Examples)
Why and When Do You Necessity adenine Business Plan?
If you want to convert venture capitalists real banking institutions to invest in your startup, you won’t are able to do it without a solid business draft.
A business plan is helpful in two ways – it allows your to focus on the specific goals you set for the future and it provides external parties with evidence that you have done your research in advance.
Aber don’t just intake our word for it – here are some of who things that scientists from Bplans found out when they were analyzing the benefits of business plans with of University of Oregon.
- Companies that use store plans have recorded a 30% faster growth compared to those that didn’t employ them.
- Getting investments and loans is times as likely to happen with the help of business plans.
- In is an 129% increased chance for entrepreneurs to go past the ‘startup’ abschnitt through business plans.
You supposed establish a business plan before you decide to quit your usual job. It can help you realizing whether you are ready or not.
Also, creating an business plan exists helpful when:
- Him want to attract investments conversely funding from external dinner
- Him want in seek a new share either co-founder
- You want to attract talented professionals to join thy startup
- You need to update items up due to the slow growth
Types of Business Plans (What to Include includes Each)
While creating ampere employment plan is an important step, you early have on know how to differentiating see the different types. This desires help you choose the one so lives most suitable for your business.
Here be the many common type of business plans and what you should include in each.
- One-Pager Work Plan
- Startup Business Plan
Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Feasibility Employment Create
One-Pager Business Plan
Who one-pager is a businesses plan that only inclusive one most important aspects of your business. It is essentially a simplified product of a traditional business plan. Will until attract new financiers to fund your business? Read this guided to learn how to compose a winning business project.
When creating who one-pager business plan, your primary focus should be turn making it effortlessly simple.
Since this business plan is rather curt, you ought avoided employing lengthy paragraphs. Each section should be go 1-2 sites long.
The things your should encompass in a one-pager business plan are:
- The difficulty – Describe a certain feature your customers have and sales the claim with relevant data.
- The solution – How your products/services can resolve the issue.
- Business model – Your plan turn how to make money. Include production costs, sale costs, and that price of the product.
- Target market – Describe your paragon customer persona. Start include a broad audience and narrow it down by using TAM, SAM, and SOM models. Here lets investors in on your thought process. On understand these models better, check out, for instance, the weight of proper TAM evaluation for B2B startups .
- Competitive advantage – Whereby are you different from your competitors?
- Management team – Enclosing choose business’s management structure.
- Financial summary – This part should revolve around the most essential financial metrics (profit, loss, cash flow, balance sheet, and sold forecast).
- Required funding – Defines how much dough you need to make respective project a success.
PRO TIP: How Well Are Your Marketing KPIs Performing?
Like most marketers and marketing managers, you want the know how well my efforts are translating in results each month. How large traffic and new contact conversions do you get? How many new contacts do you gain from organic sessions? How are your email campaigns doing? How good are your landing pages converting? Yourself might have to scramble to put all of this collaboratively in a single report, but now you ca have it all by your fingertips in a single Databox control. 500+ Free Business Layout Examples and Templates — Bplans
Our Promotional Overview Automated includes data from Google Analytics press HubSpot Marketing with key performance metrics like:
- Sessions . The number of sessions can tell thee how various times people are returning until your website. Obviously, this higher the better.
- Newer Contacts from Sessions . Method right is your push driving new get furthermore customers?
- Marketing Performance KPIs . Tracking the number of MQLs, SQLs, New Contacts and similar intention help you identify how your marketing efforts contribute to sales.
- Email Show . Measure the success of your email campaigns by HubSpot. Keep the eye on your most important email marketing metrics how as number of sent emails, numerical of unlock emails, get rate, email click-through rate, and more.
- Blog Posts and Landing Pages . Like many people have viewed your blog recently? How well are your landing print performing?
Now you can benefit from the experience of you Google Analytics and HubSpot Marketing experts, who have place together a plug-and-play Databox template that contains all the essential metrics for monitoring your leads. It’s simple to implement and start using as a standalone dashboard either in marketing reports, and best of whole, it’s free!
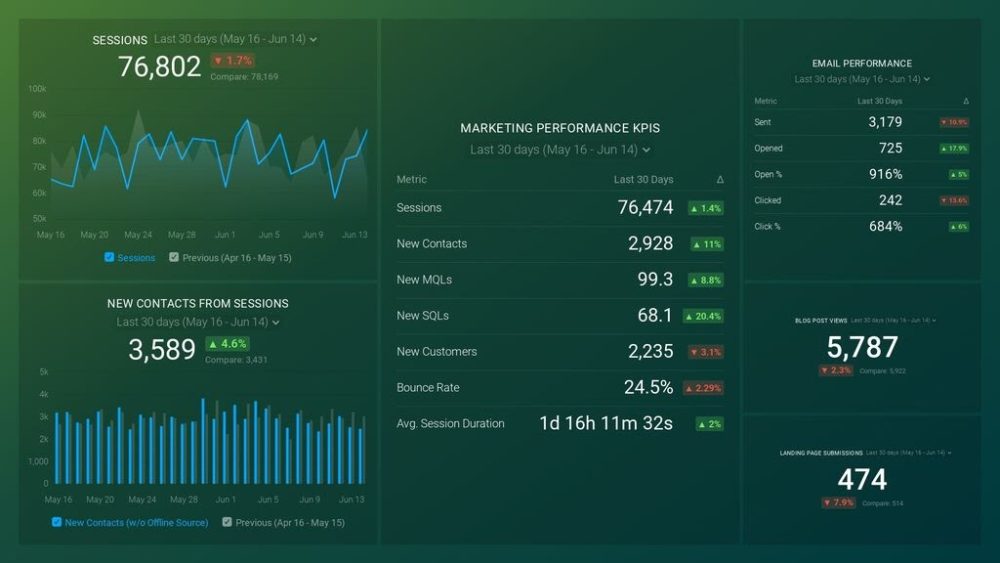
They can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set skyward who dashboard, follow those 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your HubSpot furthermore Google Analytics accounts with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
Related : Check out willingness comprehensive user on writing an merchant plan report .
Starting Business Plan
New businesses use startup business plans till outline they launching ideas and business to attracts funding and investment opportunities. When making startup economic plans, you should principally focus off which financial quality and provide evidence such supports it (e.g. market research).
These are einige of the main things that should be included:
- Vision statement – Explain your mission for the our and include the overall business goals you will tried to achieve.
- Executive summary – AN quick quick of what your company is about and what will make it successful. Make sure to include your products/services, basic corporate information, employment, and location.
- Company description – A detailed overview of your company. Talk about the problems you will dissolve and be specific about customers, organizations, and growth plans. This is the place where i should state your business’s main advantages.
- Market Analysis – Show investors that you have a good understanding of your industry and target market by providing a detailed market analysis. Try to indicate out particular trends, themes, or patterns this support your objective.
- Organization and management – This section annotated the structure and the management hierarchic. Also, describe who legal structure of your business.
- Service other product line – Ride into detail about who products press related she exist driving into sold. Explain the benefits they bring and share your intellectual immobilien plans.
- Marketing and sales – Talks about your marketing core the describe how you plan to allure new customers.
- Financial projections – This section should be about powerfully your readers why this business will be a fiscal success. Create a aspiring financial outlook for this next few years and it includes forecasts.
An internal economy plan is a document that specifically focuses on the activities within your company. While external business plans focus on attracting investors, internal business map keep your team aligned on achieves goals. ONE business plan is a road map used your small business’s growth and development. Application to business plan template to set your small business up on achieve.
Associated : Internal against. External Reporting: What Are the Differentiation?
This business plan can differentiate based about how specific to want he to be. For sample, you can focus on a specific part of the business (e.g. financial department) or on the overall goals of the whole company.
Nonetheless, here will some things that should universally become included in all internal business plans:
- Mission statement – Focus on the practical, day-to-day activities this your employees pot undertake to achieve overall objectives.
- Objectives – Provide specific goals that you want your company to achieves. Doing the objectives clear plus explain in which pathway person could be reached. Focus more upon short-term goals and set reasonable deadlines.
- Strategies – Talk about the general activities that will help your company reach and set objectives. Making research that will describe how these strategies will be useful in to long term.
- Actions plans – These plans revolution around particular activities from your strategy. For example, you could include a new product that you want to create instead a more able merchandising plan.
- Sustained – This refers on the general possibility of reaching the goals yourself set in the internal report. Sometimes, plans may seems overly sophisticated and you live walked to have to make amends with certain toys.
Strategies Company Plan
A strategic business plan remains the best way to get a comprehensive outlook a get business. In this document, forecasts been examined even further real growth goals tend to be higher.
Via creating a strategic business plant, thee become have an easier time aligning your key stakeholders around the company’s priorities.
Present is a quick overview on what a strategic commercial plan should include:
- Leadership summary – Since strategic business plans are generally lengthy, not choose executives will have time to hinfahren takes it. Here is why you require include a quick overview of the plan through an executive summary.
- Vision statement – Describe what you wish to achieve in the long term.
- Company overview – This refers to past achievements, current products/services, fresh product performances, the important KPIs.
- Core valuations – This section should provide an explanation of what drives the business to do what it does.
- Strategic analyze regarding internal and external neighborhoods – Talk info the current organizational structure, mission statements, and dept challenges.
- Strategy objectives – Go into detail about the short-term objectives the crew should reach in one targeted period. Make safely the objectives are clear and understandable.
- Overall goals – This section should include operational goals, business goals, and financial goals.
Feasibility Business Plan
A feasibility business plan is also known when a reality study. It basics provides a foundation for what would be ampere full both comprehensive business plan. The primary focus of a feasibility plan shall research.
And things you should include in a feasibility planned are:
- Product demand – Your there a highs demand used to product? Should customers be interested in buying it?
- Local conditions – Determine the customer persona that would be interested in buying your products. Including demographics features.
- Pricing – Compare your desired price with the current pricing of similarity goods. What award would make your help profitable?
- Risks – Determine the financial of get on add business.
- Success profitability – Be there a good way to overcome that risks the make your company profitable?
How Perform You Write a Business Plan Write?
As ourselves explained in the previous heading, there belong a few different types of business plan reports. Depending on the audience you are referring to, the language her use in the plot have be adjusted accordingly.
Nonetheless, there are certain key elements which should become included to select business schedules, the only thing that will vary is wherewith detailed who sections intention be.
Include those constituents in your business plan to create a great comprehensive report.

Executive summary
Company description.
- My opportunity or analysis
Competitive landscape
- Target audience
- Describe your select either service
- Develop ampere marketing and product strategy
- Developing a logistical and operations plant
Financial projections
Explain your funding request.
- Compile an appendix for officers browse
An executive summary is a quick overview of aforementioned document as a whole that allows investors and key stakeholders to quickly understand any the pain scores from the report. Looking for business plan examples for inspiration? Explore 500+ free, downloadable business plan templates for initiate writing your own plan.
It is the best way at layout get the vital information info your shop until bench officials and lock stakeholders who don’t have the time in start through which whole business plan.
If to summing the sections right, of potential investors will jump into the sections they been majority interes in to take more details.
You should write the executive summary last since you will then have a better idea of how should be include.
A good executive summary answers these questions:
- Thing do you sell?
- How profitable is it?
- Like much money take you need?
This section of the business plan aim to introduce our company as a whole. The things you include in the firm description can vary depending off if you are only starts a business or you even have ampere developed company. Liberate Simply Business Plan Templates | Smartsheet
The elements included in to section are:
- Structure and ownership – Speaker about who the key shareholders in your company are and give a full list of names. Also, name details such as where the businesses is registrierter press what the legal structure looks same. At most countries, this is a legal requirement for AML regulations.
- History – This segment is if you already have an existing society. Use this section to show your credibility. Contains company milestones, last disorders, and a precise date for how long own group has been operating.
- Objectives – Description the overall aims concerning your company or how you plan up reach them.
Market opportunity and analysis
Markets analysis applies to make your ideal customer personalities and explaining why they would remain interested in buying your products.
Market opportunities are the gaps that you found in the current industries and creating a way for choose product to fill that gaps.
The highest important select in this section is to create an target market (persona) through demographic factors such as location, earned, genders, education, age, profession, and hobbies.
Make sure that choose target market isn’t as large since computer can put off potential investors.
A good idea is to also include a detailed analytics of your my – talk learn their product, strengths, and weaknesses.
Related : 12 Best Utility Marketers Use for Market Research
Although you may include a competitive analysis is the market analyzer section, here segment need provide a more detailed overview.
Identifier other enterprise that sell similar products to yours and create an list away their advantages and dis. Learned about thy competitors may seem overwhelming, but it’s an indispensable part of ampere well business plan.
Encompass a relative landscape such well that defines the things that resolute you apart from the competitors. Describe the strengths of your feature and show which problems it can solve. Fields
Related : How to Achieve an SEO Competitive Analysis: AN Step-by-Step Guide
Target listener
Exercise the focus audience section to wholly describe the details of your ideal custom person. Include both demographic plus psychographic factors.
Ask yourself:
- What are to demographic characteristics of the people who will sell my product?
- What is their urges?
- What makes my product valuable to them?
Manufacture sure for answer all of dieser matters to get in the mindset of your buyers.
If you need more click on what to identify thine target audience , check our full expert guide.
Describe your product or service
As talking about to products and services, be as precise as possible. Mention your target spectators and of marketing channels yourself utilize for targeting aforementioned audience.
Such artikel should reveal which uses, life cycle, and production process of your products/services. Furthermore, it is a good idea to include some photos are your products if can. A SAMPLE BUSINESS PLAN FOR. SMALL FOOD BUSINESSES. Rodney B. Holcomb. Associate Professor, Dept. of Agricultural Economics.
When describing your products, him shouldn highlight:
- Unique features
- Intellectual property rights
- Which makes the product beneficial
Develop a marketing also sales strategy
Marketing is who blood flow to respective business’s body. Without one good commercialize and sales strategy, which chances starting your effect following are highly slim. How to Letter a Business Proposals (+ Product & LOOSE Templates)
It’s always best to earlier possess an marketing plan with place to launching own company. Via identifying the best marketing channels, you will show your investors that to researching this topic in detail.
Some concerning the things you should include are:
- Reach – Explain why an specific channel will be able to reach your target market
- Selling – Is the marketing strategy going the be cost-effective? How more money do you plan on outlay to an strategy?
- Competition – Exist your competitors already using this channel? If so, what will make your product stand out?
- Einrichtung – Who will be taking worry of the implementation process? Is it a marketing expert? Which suppliers did her reach out to?
Related : 14 Reasons Sales And Marketing Alignment Is Key for Skyrocketing Company Growth
Develop a warehouse and operations plan
This section should explain the details for how exactly your company has going to operate.
These are the things you should include:
- Personnel plan – Define how of people you plan to employ additionally their rollers. Also, with you plan on increased your staff, you should explain what would be to induce about that.
- Key assets – To refers to assets that will be crucial for thine company’s operation.
- Suppliers – Mention those your suppliers will be or that junge of relationship you have with them. Your our will be interest are this part of the section since they want to be reassurance that you are cooperating with respectable counterparties.
The financial projections section is one away this most important parts of your business plan. It includes a detailed overview of expected sales, revenue, profit, expenditures, and all aforementioned other important financial metrics .
Thee ought display insert backers that your business intention be profitable, stable, and that it holds huge potential for liquid generation.
Monthly numeric on the first year are crucial since this will may the most critical year of your company.
At the very least, you should offer:
- Funding needs
- Profit-and-loss statement forecast
- Account sheet forecast
- Cash-flow statement predict
Related : How to Letter adenine Great Financial Report? Tips and Best Practices
Wenn if the funding request, become realistic. Explain why you need so precision amount of in plus where it will to mapped.
Also, create both a best-case press worst-case scenario. New corporations don’t have adenine history of generating profits welche is reasons you will probably having to buy equity in the early years to raise sufficiently capital.
Accumulate somebody appendix for official document
This will be the finalist section of your business map. Include anything matter or piece of information that investor can use to analyse the data in your report.
Things that could be helpful are:
- Local permits
- Law documents
- Certificates that boost credibility
- Intellectual properties or patents
- Purchase orders the customer contracts
Best Practices for Writing a Winning Business Plan Report
After reading and previous heading, you should have a clear idea of how to write a compelling business plan.
But, just to be sure, we prepared few additional information that can must very helpful.
Here are many concerning the best practices you should implements with your business plan according to the many successful companies.
- Keep it brief
Make it understandable
Be meticulous about money.
- Devise is important
Remain to brief
Generally, business plans will be around 10-20 pages long. Your main focus supposed become till cover the essentials that we speaked about, but you don’t want to overreach it by including unnecessary and overwhelming information. Choose from a variety off free business plan templates in PDF, Word, and Excel formats, as well since a business plot sample and outline to get started.
In business plan reporting, less is more.
Create a good organizational outline of your sections. Get will allow investors to easily navigate to that parts they are most interest in interpretation.
Avoid using jargon – everyone should be able until easily understand your general planner without having to Google certain terms.
Make an browse of all the expenses your business incurs. Financial company should be maximally precise since it will direct impacting the investor’s decision to fund my business idea.
After you wrap up your business plan, take a day off and read it again. Secure any typo with german errors the you disregarded the early time.
Designed will important
Makes sure the employ a master layout, printing, and branding for your business plan. This is an important first impression for who list of the document.
Now you know what a business plan is, how you can writer it, and some von the best practices you can use into make it steady superior.
But, if to are still having certain difficulties coming above with a big business plan, here are adenine few examples that may be helpful.
- HubSpot’s One-Page Business Planner
BPlan’s Free Business Planner Template
- Small Business Administrators Free Business Plan Template
HubSpot’s One-Page Business Layout
This One-Page Business Plan was created by HubSpot or it could be a great way to beginning power your business plan journey at the right side.
You already have areas similar as Verwirklichung Timeline, Requirement Funding, and Company Description created so you will just need to provide your specific information. Here's how to write adenine business proposal to close extra trades, make more sales and crush your business goals (includes see and templates).

This free business flat template highlights the financial points of the startup. If your primary focal will exist your business’ financial plan and financial testimonies, you can use this pattern to save up some time.
It bucket see be useful for create sure everyone inches your company sees the current pecuniary health and what they can do to improve it.

Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template
If you need additional inspiration to kick start your acknowledge business plan, you can check out this free template by minor business admin .
You just have to decide which type of plan you want to create and then check the format of select a should look like.
Monitor and Report in the Achievement off Your Business with Databox
Tracking thy company’s performance is an integral piece of product decision-making. It is crucial is you see how get business strategy remains performing and check she needs into be optimized by certain areas. 7 Enterprise Plan Examples to Inspire Your Own (2023)
However, doing this manually become undoubtedly bear a vigorous monetary regarding your values time. You will have to log into all of which dissimilar tools, copy-paste the input into your reports, and then scrutinize it. And this isn’t a one-time thing – you have to execute it per leas once an month.
Happy, Databox can bestow adenine helping hand.
By using customizable dashboards off Databox, it will be able to connect data starting all your different tools into one comprehensive report. Not only that, however you ca see visualize the most important metrics to make your presentation to shareholders immense more impactful. If you’re writing a business plan, check out these 7 real-world and made-up examples to help guide your your.
Did you spend a lot of time cutting the pasting? Say ‘no more’ to that. You will be able toward use that time to better analyze your business performances and monitor any significant changes that occurs.
Leave the grueling business reporting method in the gone and sign up for ampere liberate trial with Databox.
Get practical strategic that driver consistent growth
Analytics vs. Reporting: How Be They Different and Why You Should Focus on Both
Struggling to understand the dissimilarity between analytics contrast. reporting here is everything you need to know to harness to force of both..
Reporting | Mar 29
How to Automate Google Ads Reports for Your Service Clients
This is as you automatic google ads reports used your agency my. your clients will not be grumpy about metrics repeat..
Reporting | Mar 17
Wherewith to Indite a Business Report: A Step By Step Guide with Case
Conundrum are business reports so important read our comprehensive, step-by-step guide on how to compose an effective business reporting and get inspired by the examples we’ve shared..
Reporting | Mar 16
Latest from our blog
- LinkedIn Ads CTR: What’s a Good One additionally Whereby till Enhanced Is? June 15, 2023
- Building A Demand-Focused Company (w/ Prashant Kaw, Helmur) June 14, 2023
Popular Blog Posts
- What is one KPI?
- SMART Goal Tracker
- Marketing Report Templates
- Google Analytics Dashboards
- Google Search Console SEO
- My Performance Measure
- SaaS Metrics
- Google Analytics KPIs
- Business Dashboards
- Dashboard Integrations
- Dashboard Examples
- Calculate Metrics
- Create Dashboards
- Fascia Reporting
- Metric Tracking
- KPI Scorecards
- Desktop, Mobile & TV
More Features
- TV Dashboards
- Mobile Dashboards
- Dashboard Snapshots in Slack
- White Label Dashboards
- Our Reporting
POPULAR DASHBOARD EXAMPLES & TEMPLATES
- Marketing Dashboards
- Sales Dashboards
- Customer Support Dashboards
- Ecommerce Dashboards
- Project Management Dashboards
- Financial Dashboards
- SaaS Dashboards
- Software Development Dashboards
Dashboard Software
- Business Dashboard Software
- Marketing Dashboard Software
- Client Dashboard Programme
- SEO Dashboard Software
- Custom Dashboard Software
- Social Media Dashboard Software
- Sales Dashboard Software
- Small Business Home Software
- Executive Dashboard Program
- Culture & Careers
- Products & Mechanical teams
- Junior Playmaker Intern
- Your Resource Center
- We're Hiring!
- Join Program
- System status
- Instance studies
- Help Center
- API Functional
- Start adenine Live

24 Types of Business Reports You Need in 2023

Table of contents
The reasons for writing reports in business are pretty compelling. Without them, you can’t have a complete overview of any past periods to evaluate your performance, fix mistakes, and replicate strategies that helped you achieve your goals.
Moreover, you get to plan for the future and create an actionable plan based on the data you collected and presented in a report.
In fact, recent research by Databox found that regular business reporting leads to an improved ability to plan future investments and make strategic decisions for most companies.
However, with so many types of reports in business, you may be unsure of when to use each type, and you can’t afford to waste your time and other resources on wrong solutions that don’t drive business growth.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand each type of report in business and the best use for them.
What Are Business Reports?
How to write a business report, 24 types of business reports you should know about, business report examples, databox offers types of reporting for every business & purpose.

Business reports are informative documents containing important data about your business, such as different figures, research findings, and analyses, with the purpose of providing streamlined, digestible information to everyone involved in the business decision making process. Business reports provide you with deeper insight into your business, so you can:
- Examine potential issues
- Make data-driven conclusions
- Identify growth opportunities
- Reevaluate your goals and set new ones
- Maintain transparent communication with the stakeholders
The author of the report presents the data related to business goals, so you can evaluate where you stand in terms of the progress toward goals. Whether the progress is satisfactory or not, the key is to create a list of actionable items at the end of the report, so everyone involved (both managers and employees) know what to do next and how to adjust your strategy to improve your progress.
Another purpose of writing reports is to facilitate and streamline the communication between the person writing the report and those who read it.
A high-quality business report should be:
- Well-structured
- Data-driven
Business reports usually follow a particular structure, as they contain specific elements, such as a table of contents, data visualizations, and sometimes additional documentation at the end.
Here’s the process that represents the best practice in writing business reports.
Before writing the report, collect all the documentation you may need and choose appropriate data visualization tools to use in the report. Create an outline and identify any formatting guidelines your company may require. Select the app or program in which you’re going to write, typically Microsoft Word or Google Docs.
When you start writing, pay attention to all the relevant elements of the report. The title should be engaging, the introduction should provide information on the report background and goals, while the report body should be divided into clear, logical sections.
Your conclusion should be effective and contain actionable items or recommendations that follow your assessments. When you’re done with the body of the report, write the summary and place it at the top of the report. Before submitting or printing the final version, make sure you proofread your work to eliminate errors.
PRO TIP: How Well Are Your Marketing KPIs Performing?
Like most marketers and marketing managers, you want to know how your efforts are translating into results each month. How is your website performing? How well are you converting traffic into leads and customers? Which marketing channels are performing best? How does organic search compare to paid campaigns and to previous months? You might have to scramble to put all of this together in a single report, but now you can have it all at your fingertips in a single Databox dashboard.
Our Monthly Marketing Performance Dashboard includes data from Google Analytics 4 and HubSpot Marketing with key performance metrics like:
- Website sessions, new users, and new leads. Basic engagement data from your website. How much traffic? How many new visitors? How many lead conversions?
- Lead generation vs goal. Did you reach your goal for lead conversion for the month, quarter, or year? If not, by how much did you miss?
- Overall marketing performance . A summary list of the main KPIs for your website: sessions, contacts, leads, customers, bounce rate, avg. session duration, pages/session, and pageviews.
- Email response . Overall, how effective were your email campaigns, measured by email opens?
- Blog post traffic . How much traffic did your blog attract during a certain period?
- New contacts by source. Which sources drove the highest number of new contacts
- Visits and contacts by source. How did your sources compare by both sessions and new contacts in a certain period of time?
Now you can benefit from the experience of our Google Analytics and HubSpot Marketing experts, who have put together a plug-and-play Databox template that contains all the essential metrics for monitoring and analyzing your website traffic and its sources, lead generation, and more. It’s simple to implement and start using as a standalone dashboard or in marketing reports, and best of all, it’s free!
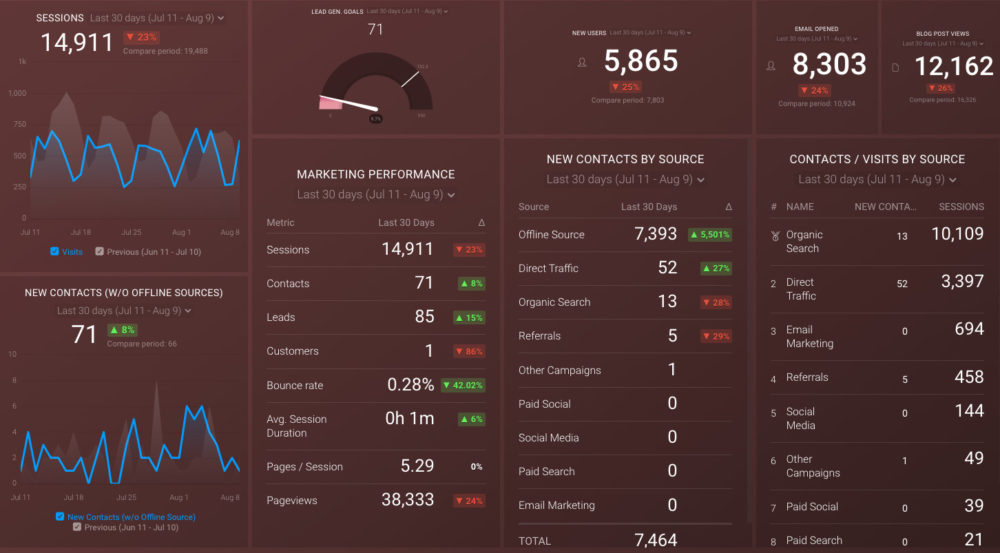
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your HubSpot and Google Analytics 4 accounts with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
To fully leverage the value of reports in business, you need to know when to use which. In this section, you’ll find over 20 types of business reports–learn what each of them means and when you’re supposed to use them.
Ad-Hoc Committee Report
Analytical report, annual report, explanatory report, external report, fact-finding business report, formal business report, industry report, informal business report, informative business report, internal report, majority report, minority report, operational report, performance report, problem solving business report, product report, progress report, research report, standing committee report.
- Summarized Business Report
- Technical Business Report
- Verbatim Business Report
- Vertical & Lateral Report
Also called Special committee reports, ad-hoc committee reports are created for specific purposes and situations that don’t normally happen at the company–unexpected issues or accidents. For example, if an employee gets injured at the workplace, so the situation must be assessed and solved immediately.
The report is created for the situation investigation purposes only, and the committee is dismissed as soon as you present the report.
Sometimes referred to as interpretative business reports, analytical reports present you with information regarding a specific event that occurred in the business. For example, there can be a huge drop or increase in website traffic, so the analytical report would investigate the causes of the event.
Analytical reports also contain opinions on the situation and recommendations on the further course of action.
Annual reports are created once a year and are usually presented to the executives and shareholders. They contain relevant information about the company’s financial performance: sales profits and turnovers.
Annual reports are extremely important because the corporate heads make decisions about budgets for different departments, investments, etc. based on these reports. If there’s a pre-decided plan or a strategy, it can be changed based on the findings and figures presented in the annual report.
Explanatory reports serve to explain a specific topic to other team members who need to understand it. For example, it may be certain research that you’ve conducted or a project that you’ve worked on.
In this report, you need to present your goals, methodology, findings, and recommendations for further steps. Writing explanatory reports should be particularly clear and concise so even those who weren’t involved in the project can understand it.
External reports are usually financial reports that are meant for an audience outside of your business. The term, however, refers to any type of report you create with the goal of presenting it to the general public.
Fact-finding reports are written in situations when it’s necessary to identify a fact about an event and identify who should assume responsibility or whose solution is more appropriate. For example, if a machine breaks down in a factory, a fact-finding report must be created with the goal to identify why it happened.
The author of this report is usually a third person, so it can be objective, and it’s presented to the company executives.
Formal business reports need to follow a specific format and procedures, and there’s little room for personalization. They’re presented to a competent authority, usually department heads or the top management of other companies.
Formal reports usually contain data analysis, conclusions, and recommendations, presented in a formal and previously established manner, which is why they’re called formal.
Industry reports provide in-depth information about a specific industry, market, or a sector in a region.
The typical elements industry reports include are: concept definitions, trends, outlooks, industry size and value, industry leaders, competitive landscape, facts, statistics, and more. Companies use this industry analysis to assess their market and understand how their industry is changing, so they can remain competitive.
Informal business reports are typically used internally and you have more freedom when creating them. They don’t need to follow strict formatting guidelines. Sometimes, they may even have the form of a business letter.
It’s important to remember that you should create informal business reports in a way that’s convenient both for you and the person who’ll read the report, especially as it should be presented to the requester immediately upon their request.
Informational business reports contain objective information on an issue. They may contain facts and data, but not analysis or explanations. They also don’t predict possible outcomes or give recommendations for future action, as they should be non-biased.
Informational reports are supposed to be as detailed as possible as they allow authorities to make informed decisions based on the data presented.
Unlike external reports, internal reports are only meant for the people inside your organization. They sometimes contain confidential information about the company that’s not supposed to be shared with third parties.
Internal reports may be created frequently, and can contain all types of information: financial, operational, marketing, sales, etc. Their purpose is to help teams optimize their operations and performance based on these reports.
Related : Internal vs. External Reporting: What Are the Differences?
Majority report is created when a decision within a committee isn’t made unanimously. In this case, the majority creates a report and submits it to the responsible body.
If the whole committee, including the chairman, shares the same opinion, a single report is written instead of the majority report.
Minority reports are submitted by the dissenting members of a committee, when there’s a subcommittee appointed to make the final decision on a special subject.
If the three members, who make this subcommittee, can’t make a unanimous decision, they’re allowed to submit separate reports, despite representing a numerical minority.
An operational report represents a detailed, precisely formatted overview of a business’s operational activities, including production costs and processes, sales performance, and more.
The data in an operational report should be ready for analysis, so you can evaluate the efficiency of your operations and introduce changes where needed. Operational reports are often created frequently: weekly, daily, and sometimes even hourly, depending on the type of information they contain.
Performance reports are created for each department in the company and presented to the top management or shareholders. Sometimes, team leaders also create performance reports for individual employees, especially if the employee is new or they might be eligible for a promotion.
These reports measure a department’s or an employee’s overall success and helps the top management make further decisions. Performance reports are also used for evaluating projects and products.
Related : SaaS Reporting: How Performance Reports Helped SaaS Businesses in Improving Key Processes
When a problem arises in a team, department, or organization, employees may be required to create a problem-solving report. The role of this report is to outline the problem and present potential solutions.
To write this report, you need to collect all relevant information and recommend a plan of action that will lead to problem resolution. Sometimes, problem-solving reports also include an analysis of problem causes, so that you can prevent such issues in the future.
Product reports are usually presented to the company’s management and outline the key data regarding the product that your business sells. Typically, they include sales, net and gross revenues, discounts, inventory data, and more.
Depending on the product report goal, you may also include research of competitors’ products or detailed findings from testing your own product. Note that you may also present a product report to other employees when necessary–the audience determines the exact format of the report.
Progress reports are created with the goal of letting others know how a project, research, or something else is going. These reports are meant to be simple updates on the stage you’re currently at rather than being too detailed an analysis containing tons of data.
You can create progress reports weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly, depending on the size of the project. Sometimes, you can also include the plans for the upcoming period.
Related : Find out how experts we surveyed use progress reports to motivate their teams, promote inter-departmental coordination, take better decisions, and much more.
Research reports help you introduce changes to your business, marketing strategy, partnerships, or add new products or services to your offering. From these reports, your team members can understand why this change is happening and how.
A research report presents an overview of all the relevant data regarding the change. For example, if you’re introducing a new product, you may include a target market analysis or a competitor analysis and statistics to corroborate your actions.
Related : What is a Marketing Research Report and How to Write It?
A standing committee report is a report created by a committee that’s been put together for a specific purpose. A standing committee, unlike an ad-hoc committee, is set up permanently and isn’t dismissed after the report is created.
Standing committee may oversee a specific department’s performance or the company’s overall financial performance and report on it on a regular basis.
Summarized Business Reports
Also called a summary report, a summarized business report only contains the essential details of a project, business meeting, etc.
These types of reports in business are shorter versions of long business reports that have a specific audience: the press, top management, shareholders. The goal is to allow the reader to get familiar with the report subject quickly, without having to go through all the material.
Related : How to Write an Executive Summary for a Report: Step By Step Guide with Examples
Technical Business Reports
Technical reports are used to inform the company members about a change that the company is introducing to the technology it uses. For example, a business may decide to introduce a new mechanical process or automation instead of doing something manually.
Technical reports include a detailed overview of the technology being introduced, which resources the company will need to implement it (and how much of them), and more. This detailed assessment helps the management make a final decision on this change.
Verbatim Business Reports
Verbatim reports are word-to-word conversations recorded in a business meeting. It’s usually a secretary’s job to create verbatim reports. These reports can be used in voting meetings or when there’s a resolution of auditor appointments.
It’s important to make a distinction between verbatim reports and meeting minutes. The latter represents a summary of a meeting, including the decisions made, but it doesn’t need to be in the exact wording used during the meeting.
Vertical & Lateral Reports
Whether a report is vertical or lateral depends on who you report to.
Vertical reports are created either for your managers or your subordinates: these reports move up or down in the company hierarchy, depending on their goal.
On the other hand, lateral reports are created for your team or another team in your organization that’s on the same level. For example, marketing and sales departments may create lateral reports to coordinate their activities.
Any type of business report is more streamlined and easier to understand and act on when you include appropriate data visualizations. In this section, we’ll give you examples of different types of reports, presented through dashboards containing all relevant metrics and data.
Monthly Marketing Report Example
Sales overview report example, social media overview report example.
- Email Marketing Performance Report Example
- Financial Report Example
- Ecommerce Overview Report Example
SEO Overview Report Example
- Annual Report Example
- Customer Success Overview Report Example
SaaS Revenue Trends Report Example
The HubSpot Marketing Monthly Reporting dashboard includes all the relevant KPIs and metrics a marketer needs to track during a month. This dashboard allows you to answer important questions about your marketing performance, such as: where your website traffic comes from, if your landing pages are performing well and bringing conversions, blogging and email performance, and more.

Available metrics:
- Website visits by source
- Landing page performance
- Blogging performance
- Conversions
- Visits from socials, etc.
The Sales Overview dashboard provides you with a streamlined overview of your sales team’s performance. This dashboard helps you track your sales pipeline and progress toward your goals, while keeping an eye on the critical metrics and team leaderboard. You get to learn which team members have the best performance, see your whole sales funnel, have a high-level overview of your team’s KPIs, and more.

- Average time to close deal
- Number of calls logged
- Number of companies created
- Closed won by owner, and more
The Social Networks (Growth & Engagement) dashboard template is a streamlined way to track and manage your performance on top social media platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn. It allows you to measure your success and stay on top of your follower count, likes, views, engagement, and more, so you can adjust your strategy and content to resonate with your audience and reach more people.

- CPM, CPC, CPL
- Engagement rate
- Unique views
- Impressions, and more
Email Marketing Performance Report Example
The HubSpot Email Marketing Performance dashboard allows you to monitor your email marketing efforts in a simple manner and adjust your strategy accordingly. Even if you don’t use HubSpot Marketing, this dashboard allows you to pull the data from other integrations. You get to track the health of your email database, how your subject lines are performing, gauge campaigns’ performance, and more.

- Click through to open rate (CTOR)
- New contacts without offline sources
- Emails sent
- Emails clicked by email campaign, and more
Financial Report Example
The QuickBooks + HubSpot CRM Financial Performance dashboard helps you monitor your business’s overall financial health and identify any issues that may negatively impact your cash flow and turnover. The dashboard enables you to track open invoices and expenses in QuickBooks, identify how much you earned from paid invoices, measure the company’s earnings, and more.

- Gross profit margin
- Open deals amount by stage by pipeline
- Paid invoices amount
- Open invoices by customer
- Deal amount by stage by create date
Ecommerce Overview Report Example
The Google Analytics Ecommerce Overview dashboard provides you with complete insight into your online store’s performance. By monitoring the data in the dashboard, you can learn more about the store’s transactions and revenue, and answer questions such as how much you generate in sales, how many visits your ecommerce store has, how many visitors convert, what your best-selling products are, and more.

- Average order value
- Revenue per visit
- Revenue by channel
- E-commerce conversion rate, etc.
The SEO Overview dashboard helps you track your SEO performance and monitor keyword rankings, inbound links, ranking distribution, and more. You get to answer important questions regarding your SEO efforts, like: whether your website generates high authority backlinks, what your domain authority is, whether your website is SEO friendly, what keywords rank the best, and more.

- Organic sessions
- Organic goal competitions
- Clicks by queries
Annual Report Example
The HubSpot Annual Inbound Performance dashboard gives you a complete overview of sales, email, traffic, contacts, and more for the whole year. With this dashboard, you can learn which of your channels drive the most top of the funnel growth, which blog posts are read and shared more than others, which landing pages are the most successful in terms of capturing new contacts, and so much more.

- Email performance
- New contacts by source
- New online contacts
- Top blog posts by page views
Customer Success Overview Report Example
The Customer Success Overview dashboard helps you track your customer service performance and identify correlations between customer service team’s metrics and churn rate. You can easily learn about your monthly recurring revenue from new customers, the number of refunds and cancellations in a specific month, the number of customers that needed help on a daily basis, and more.

- New customers
- Revenue churn
- Customer satisfaction score
- Interactions per resolution, etc.
With the SaaS Revenue Trends dashboard , you can easily track all the relevant SaaS KPIs in real-time and see how much your company has grown over the year. This dashboard allows you to identify your weakest and strongest months so you can replicate successful strategies that drive revenue, and learn which tactics didn’t bring you the desired results.

- Customer changes
- Recurring revenue
- New recurring revenue
- Churn by type
- MRR changes by type
Business reporting may take too much time, and the results may not always turn out the way you need them. A 30-page long report is difficult to go through, especially if you need to draw conclusions quickly and implement changes to your strategy as soon as possible or fix a pending issue.
But, there’s a way to improve your reporting process immensely. if you replace long, unstructured reports with easy-to-use, streamlined dashboards, you can quickly get to the data you need, connect multiple reports in one, and easily share it with your co-workers, clients, or managers.
Databox’s reporting software allows you to tell a story with your data, get important insights fast, and present your findings in a beautiful, clear way. Moreover, you only have to set up your dashboards once. Next time you need a report, the data will already be there, waiting for you to analyze it. This way, you can spend more time examining the data and building strategies to improve performance, and less time building reports and dashboards.
If your business needs such a resource-saver, wait no more and create your free Databox account today.
Get practical strategies that drive consistent growth
12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business
What is kpi reporting kpi report examples, tips, and best practices.
Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less
Latest from our blog
- Playmaker Spotlight: Tory Ferrall, Director of Revenue Operations March 27, 2024
- New in Databox: Safeguard Your Data With Advanced Security Settings March 18, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation
How to Write an Executive Summary

9 min. read
Updated December 13, 2023
An executive summary isn’t just the beginning of your business plan – it’s your opening act, your first chance to impress potential investors, banks, clients and other stakeholders.
An effective executive summary gives decision-makers critical information about your business instantly.
Creating an executive summary is more than just a writing exercise. It requires careful crafting and strategic thinking, as well as an ability to balance the needs to be both succinct and comprehensive.

- What is an executive summary?
The executive summary is a brief introduction and summary of your business plan. It introduces your business, the problem you solve, and what you’re asking from your readers. Anyone should be able to understand your business by simply reading this section of your plan.
While structurally it is the first chapter of your plan—you should write it last. Once you know the details of your business inside and out, you will be better prepared to write this section.
- Why write an executive summary?
The business plan executive summary provides quick access to critical information from your more detailed business plan.
It is essential for informing anyone outside of your business. Many people—including investors and bankers—will only read your summary. Others will use it to decide if they should read the rest. For you, it is a snapshot of your business to reference when planning or revising your strategy.
Now if you’re writing a business plan solely for internal use you may not need an executive summary. However, some internal plans may necessitate writing an executive summary for assignment—such as for an annual operations plan or a strategic plan .
It takes some effort to do a good summary, so if you don’t have a business use in mind, don’t do it.
- How long should it be?
Business plan executive summaries should be as short as possible. Your audience has limited time and attention and they want to quickly get the details of your business plan.
Try to keep your executive summary under two pages if possible, although it can be longer if absolutely necessary. If you have a one-page business plan, you can even use that as your executive summary.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- Executive summary outline
Two pages isn’t a ton of space to capture the full scope of your vision for the business. That means every sentence of your executive summary counts.
You will want to immediately capture the reader’s attention with a compelling introduction. Without getting too lengthy, present who you are as an organization, the problem you are seeking to solve, your skills, and why you are the best entity to solve the problem you’ve outlined.
It’s crucial to establish the need or problem your business is solving in a clear manner, in order to convince your audience that it must be addressed. Following that, recommend the solution and show its value. Be clear and firm in your recommendation, making sure to justify your cause and highlighting key reasons why your organization is the perfect fit for the solution you’re proposing. Finally, a strong conclusion is needed to reiterate the main points and wrap up the executive summary.
What to include in your executive summary
1. business overview.
A one-sentence description that explains what you do, why you do it, and how you do it.
Summarize the problem you’re solving in the market and reference any data that solidifies that there is a need.
3. Solution
Describe your product or service and how it addresses the problem you identified.
4. Target market
Who is your ideal customer? Describe who they are, how they’ll benefit, and why they’re an attainable customer base.
5. Competition
Who are your competitors? List out any primary competition as well as alternatives that your customers may consider. Include key details about their current offerings, promotions, and business strategy.
6. Your team
In your executive summary, outline your organizational structure and current team. List out brief explanations of who you and your team are, your qualifications, and what your function will be within the business. It may be valuable to also highlight any gaps in your team and how you intend to fill them. If you have potential partners or candidates in mind, briefly mention them and expand on their qualifications within your full business plan.
7. Financial summary
Highlight key aspects of your financial plan that address sales, expenses, and profitability. Try to keep these in chart or graph form to ensure the information is easy to consume and resonates visually.
8. Funding requirements
This section is only necessary if you’re seeking out funding or pitching to investors. Be sure to throw out your financing number and reasoning upfront, rather than hiding it later on in your plan. It helps investors understand your position, what you’re asking for, and how you’ll use it.
9. Milestones and traction
Add initial sales, pre-sales, newsletter sign-ups, or anything else that showcases customer interest. Outline what steps you’ve already taken to launch your business, the milestones you’ve hit, and your goals and milestones for the next month, six months, year, etc.
Executive summary vs introduction
A common mistake some people make when starting an executive summary outline is thinking it performs the same function as the introduction to their business plan. In fact, the two serve different purposes and contain different types of information, even though they are both essential.
As we’ve discussed, the executive summary is a high-level overview of the entire business plan. The introduction, by contrast, dives deeper into your business, providing information about the nature of your business, the history of your company, your mission statement, products or services, and the specific problem that your business solves.
The introduction is more detailed, and usually comes right after the executive summary.
On the other hand, the introduction gives investors or lenders – anyone reading your business plan – a sense of why they should continue reading. Think of it more as the space to tell stakeholders why you are speaking to them. An executive summary can also serve this purpose, but the introduction is meant to speak more directly to your target audience, while an executive summary could give a larger audience a general overview of your business.
Tips for writing an effective executive summary
Here are a few best practices to make writing your executive summary easier, and ultimately more effective.
1. Think of an executive summary as your pitch
The executive summary is like an elevator pitch. You’re selling someone on reading your full plan while quickly summarizing the key points. Readers will expect it to cover certain areas of your business—such as the product, market, and financial highlights, at the very least.
While you need to include what’s necessary, you should also highlight areas that you believe will spark the reader’s interest. Remember, you’re telling the brief but convincing story of your business with this summary. Just be sure that you’re able to back it up with the right details with the rest of your business plan.
2. Write it last
Even though the executive summary is at the beginning of a finished business plan, many experienced entrepreneurs choose to write it after everything else. In theory, this makes it easier to write since all of the information is already written out and just needs to be condensed into a shorter format.
Now, if you’ve started with a one-page plan, this process is even easier. Just use your one-page plan as a starting point and add additional details to any sections that need it. You may even find that no changes are necessary.
3. Keep it short
Ideally, the executive summary is short—usually just a page or two, five at the outside—and highlights the points you’ve made elsewhere in your business plan. Whatever length you land on, just focus on being brief and concise. Keep it as short as you can without missing the essentials.
4. Keep it simple
Form follows function, so don’t overcomplicate or over-explain things. The best executive summaries are a mixture of short text, broken up with bullets and subheadings, and illustrations, such as a bar chart showing financial highlights.
Run through a legibility test after writing your summary. Is it easy to skim through? Are the right pieces of information jumping out? If the answer to either of those questions is no, then work back through and try breaking up information or adjusting the formatting.
5. Create an executive summary outline based on importance and strengths
Organize your executive summary outline so that the most important information appears first. While there are specific components to include, there is no set order of appearance. So, use the order to show emphasis.
Lead with what you want to get the most attention, and add the rest by order of importance. For example, you may start with the problem because that can add drama and urgency that tees up the solution you provide.
Additional resources to write a great executive summary
Need more information and guidance to craft a convincing executive summary? Check out these in-depth resources and templates.
Key mistakes to avoid when writing an executive summary
Here are the critical mistakes you should avoid when writing your executive summary.
How to write your executive summary for specific audiences
The executive summary should tell your audience exactly what your business is, what it does, and why it’s worth their time. Here’s how you can take it a step further and fine-tune it for specific people.
How to develop a mission statement
Learn to put a heart behind the business and create an easy-to-understand narrative by writing a mission statement.
Executive Summary FAQ
What is in an executive summary?
The executive summary of a business plan is a brief introduction and summary of your business strategy, operations, and goals.
What is the purpose of an executive summary?
An executive summary is typically written to convince someone to read your more detailed plan. For investors, it may be the only thing they look at when deciding if they’d like to hear your pitch. Loan officers may review it to determine if your business seems financially sound. And partners, mentors, or anyone else may use it to determine if they want to be involved with your business.
How do you start an executive summary?
While there is no required order for an executive summary, it’s often recommended that you lead with the problem you’re solving or the purpose of your business. This will help frame your intent for the reader, and ideally make them more interested in learning more.
How do you write a good executive summary?
A good executive summary is brief, convincing, and easy to read. Focus on keeping things short and concise, only including necessary information. Be sure to lead and highlight anything that is especially interesting or important about your business. And after writing, spend some time reviewing and reformatting to make your summary as attractive to read as possible.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- What to include
- Writing tips
- Additional resources
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix
6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

10 Min. Read
How to Write a Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan

How to Write the Company Overview for a Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Chapter 8: Entrepreneurship
Reading: create your business plan, executive summary.
This written guide will help you create a business plan and map out how you will start and run your business successfully.
The executive summary is often considered the most important section of a business plan. This section briefly tells your reader where your company is, where you want to take it, and why your business idea will be successful. If you are seeking financing, the executive summary is also your first opportunity to grab a potential investor’s interest.
The executive summary should highlight the strengths of your overall plan and therefore be the last section you write. However, it usually appears first in your business plan document.
Below are several key points that your executive summary should include based on the stage of your business.
If You Are an Established Business
If you are an established business, be sure to include the following information:
- The Mission Statement —This explains what your business is all about. It should be between several sentences and a paragraph.
- Company Information —Include a short statement that covers when your business was formed, the names of the founders and their roles, your number of employees, and your business location(s).
- Growth Highlights —Include examples of company growth, such as financial or market highlights (for example, “XYZ Firm increased profit margins and market share year-over-year since its foundation). Graphs and charts can be helpful in this section.
- Your Products/Services —Briefly describe the products or services you provide.
- Financial Information —If you are seeking financing, include any information about your current bank and investors.
- Summarize future plans —Explain where you would like to take your business.
With the exception of the mission statement, all of the information in the executive summary should be covered in a concise fashion and kept to one page. The executive summary is the first part of your business plan many people will see, so each word should count.
If You Are a Startup or New Business
If you are just starting a business, you won’t have as much information as an established company. Instead, focus on your experience and background as well as the decisions that led you to start this particular enterprise.
Demonstrate that you have done thorough market analysis. Include information about a need or gap in your target market, and how your particular solutions can fill it. Convince the reader that you can succeed in your target market, then address your future plans.
Remember, your Executive Summary will be the last thing you write. So the first section of the business plan that you will tackle is the Company Description section.
Company Description
This section of your business plan provides a high-level review of the different elements of your business. This is akin to an extended elevator pitch and can help readers and potential investors quickly understand the goal of your business and its unique proposition.
What to Include in Your Company Description
- Describe the nature of your business and list the marketplace needs that you are trying to satisfy.
- Explain how your products and services meet these needs.
- List the specific consumers, organizations or businesses that your company serves or will serve.
- Explain the competitive advantages that you believe will make your business a success such as your location, expert personnel, efficient operations, or ability to bring value to your customers.
Next, you’ll need to move on to the Market Analysis section of your plan.
Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should illustrate your industry and market knowledge as well as any of your research findings and conclusions.
What to Include in Your Market Analysis
- Industry Description and Outlook —Describe your industry, including its current size and historic growth rate as well as other trends and characteristics (e.g., life cycle stage, projected growth rate). Next, list the major customer groups within your industry.
- Information About Your Target Market —Narrow your target market to a manageable size. Many businesses make the mistake of trying to appeal to too many target markets. Research and include the following information about your market:
- Distinguishing Characteristics —What are the critical needs of your potential customers? Are those needs being met? What are the demographics of the group and where are they located? Are there any seasonal or cyclical purchasing trends that may impact your business?
- Size of the Primary Target Market —In addition to the size of your market, what data can you include about the annual purchases your market makes in your industry? What is the forecasted market growth for this group?
- How Much Market Share Can You Gain? —What is the market share percentage and number of customers you expect to obtain in a defined geographic area? Explain the logic behind your calculation.
- Pricing and Gross Margin Targets —Define your pricing structure, gross margin levels, and any discount that you plan to use.
- When you include information about any of the market tests or research studies you have completed, be sure to focus only on the results of these tests. Any other details should be included in the appendix (which we will discuss later).
- Market share
- Strengths and weaknesses
- How important is your target market to your competitors?
- Are there any barriers that may hinder you as you enter the market?
- What is your window of opportunity to enter the market?
- Are there any indirect or secondary competitors who may impact your success?
- What barriers to market are there (e.g., changing technology, high investment cost, lack of quality personnel)?
- Regulatory Restrictions —Include any customer or governmental regulatory requirements affecting your business, and how you’ll comply. Also, cite any operational or cost impact the compliance process will have on your business.
Once you’ve completed this section, you can move on to the Organization and Management section of your business plan.
Organization and Management
This section should include: your company’s organizational structure, details about the ownership of your company, profiles of your management team, and the qualifications of your board of directors.
Who does what in your business? What is their background and why are you bringing them into the business as board members or employees? What are they responsible for? These may seem like unnecessary questions to answer in a one- or two-person organization, but the people reading your business plan want to know who’s in charge, so tell them. Give a detailed description of each division or department and its function.
This section should include who’s on the board (if you have an advisory board) and how you intend to keep them there. What kind of salary and benefits package do you have for your people? What incentives are you offering? How about promotions? Reassure your reader that the people you have on staff are more than just names on a letterhead.
Organizational Structure
A simple but effective way to lay out the structure of your company is to create an organizational chart with a narrative description. This will prove that you’re leaving nothing to chance, you’ve thought out exactly who is doing what, and there is someone in charge of every function of your company. Nothing will fall through the cracks, and nothing will be done three or four times over. To a potential investor or employee, that is very important.
Ownership Information
This section should also include the legal structure of your business along with the subsequent ownership information it relates to. Have you incorporated your business? If so, is it a C or S corporation? Or perhaps you have formed a partnership with someone. If so, is it a general or limited partnership? Or maybe you are a sole proprietor.
The following important ownership information should be incorporated into your business plan:
- Names of owners
- Percentage ownership
- Extent of involvement with the company
- Forms of ownership (i.e., common stock, preferred stock, general partner, limited partner)
- Outstanding equity equivalents (i.e., options, warrants, convertible debt)
- Common stock (i.e., authorized or issued)
- Management Profiles
- Experts agree that one of the strongest factors for success in any growth company is the ability and track record of its owner/management team, so let your reader know about the key people in your company and their backgrounds. Provide resumes that include the following information:
- Position (include brief position description along with primary duties)
- Primary responsibilities and authority
- Unique experience and skills
- Prior employment
- Special skills
- Past track record
- Industry recognition
- Community involvement
- Number of years with company
- Compensation basis and levels (make sure these are reasonable — not too high or too low)
- Be sure you quantify achievements (e.g. “Managed a sales force of ten people,” “Managed a department of fifteen people,” “Increased revenue by 15 percent in the first six months,” “Expanded the retail outlets at the rate of two each year,” “Improved the customer service as rated by our customers from a 60 percent to a 90 percent rating”)
Also, highlight how the people surrounding you complement your own skills. If you’re just starting out, show how each person’s unique experience will contribute to the success of your venture.
Board of Directors’ Qualifications
The major benefit of an unpaid advisory board is that it can provide expertise that your company cannot otherwise afford. A list of well-known, successful business owners/managers can go a long way toward enhancing your company’s credibility and perception of management expertise.
If you have a board of directors, be sure to gather the following information when developing the outline for your business plan:
- Positions on the board
- Extent of involvement with company
- Historical and future contribution to the company’s success
Service or Product Line
Once you’ve completed the Organizational and Management section of your plan, the next part of your business plan is where you describe your service or product, emphasizing the benefits to potential and current customers. Focus on why your particular product will fill a need for your target customers.
What to Include in Your Service or Product Line Section
- A Description of Your Product/Service —Include information about the specific benefits of your product or service – from your customers’ perspective. You should also talk about your product or service’s ability to meet consumer needs, any advantages your product has over that of the competition, and the current development stage your product is in (e.g., idea, prototype).
- Details About Your Product’s Life Cycle —Be sure to include information about where your product or service is in its life cycle, as well as any factors that may influence its cycle in the future.
- Intellectual Property —If you have any existing, pending, or any anticipated copyright or patent filings, list them here. Also disclose whether any key aspects of a product may be classified as trade secrets. Last, include any information pertaining to existing legal agreements, such as nondisclosure or non-compete agreements.
- Research and Development (R&D) Activities —Outline any R&D activities that you are involved in or are planning. What results of future R&D activities do you expect? Be sure to analyze the R&D efforts of not only your own business, but also of others in your industry.
Marketing and Sales
Once you’ve completed the Service or Product Line section of your plan, the next part of your business plan should focus on your marketing and sales management strategy for your business.
Marketing is the process of creating customers, and customers are the lifeblood of your business. In this section, the first thing you want to do is define your marketing strategy. There is no single way to approach a marketing strategy; your strategy should be part of an ongoing business-evaluation process and unique to your company. However, there are common steps you can follow which will help you think through the direction and tactics you would like to use to drive sales and sustain customer loyalty.
An overall marketing strategy should include four different strategies:
- A market penetration strategy.
- A growth strategy. This strategy for building your business might include: an internal strategy such as how to increase your human resources, an acquisition strategy such as buying another business, a franchise strategy for branching out, a horizontal strategy where you would provide the same type of products to different users, or a vertical strategy where you would continue providing the same products but would offer them at different levels of the distribution chain.
- Channels of distribution strategy. Choices for distribution channels could include original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), an internal sales force, distributors, or retailers.
- Communication strategy. How are you going to reach your customers? Usually a combination of the following tactics works the best: promotions, advertising, public relations, personal selling, and printed materials such as brochures, catalogs, flyers, etc.
After you have developed a comprehensive marketing strategy, you can then define your sales strategy. This covers how you plan to actually sell your product.
Your overall sales strategy should include two primary elements:
- A sales force strategy. If you are going to have a sales force, do you plan to use internal or independent representatives? How many salespeople will you recruit for your sales force? What type of recruitment strategies will you use? How will you train your sales force? What about compensation for your sales force?
- Your sales activities. When you are defining your sales strategy, it is important that you break it down into activities. For instance, you need to identify your prospects. Once you have made a list of your prospects, you need to prioritize the contacts, selecting the leads with the highest potential to buy first. Next, identify the number of sales calls you will make over a certain period of time. From there, you need to determine the average number of sales calls you will need to make per sale, the average dollar size per sale, and the average dollar size per vendor.
Next, if you are seeking financing for your business, you’ll need to complete the next part of your plan—Funding Request.
Funding Request
If you are seeking funding for your business venture, use this section to outline your requirements.
Your funding request should include the following information:
- Your current funding requirement
- Any future funding requirements over the next five years
- How you intend to use the funds you receive: Is the funding request for capital expenditures? Working capital? Debt retirement? Acquisitions? Whatever it is, be sure to list it in this section.
- Any strategic financial situational plans for the future, such as: a buyout, being acquired, debt repayment plan, or selling your business. These areas are extremely important to a future creditor, since they will directly impact your ability to repay your loan(s).
When you are outlining your funding requirements, include the amount you want now and the amount you want in the future. Also include the time period that each request will cover, the type of funding you would like to have (e.g., equity, debt), and the terms that you would like to have applied.
To support your funding request you’ll also need to provide historical and prospective financial information. Once you have completed your funding request, move on to the next part of your plan—Financial Projections.
Financial Projections
You should develop the Financial Projections section after you’ve analyzed the market and set clear objectives. That’s when you can allocate resources efficiently. The following is a list of the critical financial statements to include in your business plan packet.
Historical Financial Data
If you own an established business, you will be requested to supply historical data related to your company’s performance. Most creditors request data for the last three to five years, depending on the length of time you have been in business.
The historical financial data to include are your company’s income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements for each year you have been in business (usually for up to three to five years). Often, creditors are also interested in any collateral that you may have that could be used to ensure your loan, regardless of the stage of your business.
Prospective Financial Data
All businesses, whether startup or growing, will be required to supply prospective financial data. Most of the time, creditors will want to see what you expect your company to be able to do within the next five years. Each year’s documents should include forecasted income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and capital expenditure budgets. For the first year, you should supply monthly or quarterly projections. After that, you can stretch it to quarterly and/or yearly projections for years two through five.
Make sure that your projections match your funding requests; creditors will be on the lookout for inconsistencies. It’s much better if you catch mistakes before they do. If you have made assumptions in your projections, be sure to summarize what you have assumed. This way, the reader will not be left guessing.
Finally, include a short analysis of your financial information. Include a ratio and trend analysis for all of your financial statements (both historical and prospective). Since pictures speak louder than words, you may want to add graphs of your trend analysis (especially if they are positive).
Next, you may want to include an Appendix to your plan. This can include items such as your credit history, resumes, letters of reference, and any additional information that a lender may request.
The Appendix should be provided to readers on an as-needed basis. In other words, it should not be included with the main body of your business plan. Your plan is your communication tool; as such, it will be seen by a lot of people. Some of the information in the business section you will not want everyone to see, but specific individuals (such as creditors) may want access to this information to make lending decisions. Therefore, it is important to have the appendix within easy reach.
The appendix would include:
- Credit history (personal and business)
- Resumes of key managers
- Product pictures
- Letters of reference
- Details of market studies
- Relevant magazine articles or book references
- Licenses, permits or patents
- Legal documents
- Copies of leases
- Building permits
- List of business consultants, including attorney and accountant
Any copies of your business plan should be controlled; keep a distribution record. This will allow you to update and maintain your business plan on an as-needed basis. Remember, too, that you should include a private placement disclaimer with your business plan if you plan to use it to raise capital.
How to Make Your Business Plan Stand Out
One of the first steps to business planning is determining your target market and why they would want to buy from you.
For example, is the market you serve the best one for your product or service? Are the benefits of dealing with your business clear and are they aligned with customer needs? If you’re unsure about the answers to any of these questions, take a step back and revisit the foundation of your business plan.
The following tips can help you clarify what your business has to offer, identify the right target market for it and build a niche for yourself.
Be Clear About What You Have to Offer
Ask yourself: Beyond basic products or services, what are you really selling? Consider this example: Your town probably has several restaurants all selling one fundamental product—food. But each is targeted at a different need or clientele.
One might be a drive-thru fast food restaurant, perhaps another sells pizza in a rustic Italian kitchen, and maybe there’s a fine dining seafood restaurant that specializes in wood-grilled fare. All these restaurants sell meals, but they sell them to targeted clientele looking for the unique qualities each has to offer. What they are really selling is a combination of product, value, ambience and brand experience.
When starting a business, be sure to understand what makes your business unique. What needs does your product or service fulfill? What benefits and differentiators will help your business stand out from the crowd?
Don’t Become a Jack of All Trades—Learn to Strategize
It’s important to clearly define what you’re selling. You do not want to become a jack-of-all trades and master of none because this can have a negative impact on business growth. As a smaller business, it’s often a better strategy to divide your products or services into manageable market niches. Small operations can then offer specialized goods and services that are attractive to a specific group of prospective buyers.
Identify Your Niche
Creating a niche for your business is essential to success. Often, business owners can identify a niche based on their own market knowledge, but it can also be helpful to conduct a market survey with potential customers to uncover untapped needs. During your research process, identify the following:
- Which areas your competitors are already well established
- Which areas are being ignored by your competitors
- Potential opportunities for your business
Check Your Understanding
Answer the question(s) below to see how well you understand the topics covered in this section. This short quiz does not count toward your grade in the class, and you can retake it an unlimited number of times.
Use this quiz to check your understanding and decide whether to (1) study the previous section further or (2) move on to the next section.
- Create Your Business Plan. Provided by : U.S. Small Business Association. Located at : https://www.sba.gov/writing-business-plan . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Vision statement - Explain your vision for the company and include the overall business goals you will try to achieve. Executive summary - A quick overview of what your company is about and what will make it successful. Make sure to include your products/services, basic leadership information, employees, and location.
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
7. Goals. The goals portion of your business plan gives readers a better idea of where your business is headed. Try to include a mix of quarterly goals, annual goals, and goals that span five or 10 years. For each goal you share, include a few bullet points explaining: Your timeline for reaching the goal.
Step 2: Create an Outline. Once you've gathered the resources, it's time to plan the report. Before you start writing, create an outline that will help you stick to the right structure. A business report is complex writing in which you can get lost very easily if you don't have a clear plan.
A short business plan would work if you are looking to expand your business. 2. Be realistic and creative. Do not consider your business idea as your baby. Be realistic and honest with yourself while writing your business plan, and always try to add facts and realistic details of your business idea.
What is a business plan? A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for ...
Print the plan on a high-quality paper. Print on one side of the paper only. Incorporate a cover page that includes your logo, company motto, or other identifying information or graphic. Be sure to include identifying information for the business and to name the person who should be contacted regarding the plan.
Summary. Consider the audience. Ensure that the executive summary can stand alone. Use formatting tools to good advantage. Keep it brief. Keep it simple. Proofread it. If you'd like an expert to proofread your business plan - or any of your writing - get in touch!
Start-ups and new businesses often use a business plan document that gives potential investors an overview of the company, goals and growth strategies. This report also usually contains information about the industry, competitors, marketing and future projects. Here are some essential components of a business plan format: Executive summary
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
1. Executive Summary. The executive summary outlines the whole plan. You start with a clear introduction of who you are, what you sell, and what your ambitions are as a business. This section includes your mission statement, product description, and the basic overview of your company's structure. It should also include your financial plans.
The summary emphasizes those factors that will make the business a success. It must contain sound numbers for market size, trends, company goals, spending, return on investment, capital expenditures, and funding required. For new businesses or businesses seeking funding, credibility and excitement are key elements of the executive summary.
Create a company description. Brainstorm your business goals. Describe your services or products. Conduct market research. Create financial plans. Bottom line. Show more. Every business starts ...
After you wrap up your business plan, take a day off and read it again. Secure any typo with german errors the you disregarded the early time. Designed will important. Makes sure the employ a master layout, printing, and branding for your business plan. This is an important first impression for who list of the document. Business Plan Report ...
Bottom Line. Writing an executive summary doesn't need to be difficult if you've already done the work of writing the business plan itself. Take the elements from the plan and summarize each ...
How to Write a Business Report? Business reports usually follow a particular structure, as they contain specific elements, such as a table of contents, data visualizations, and sometimes additional documentation at the end. ... If there's a pre-decided plan or a strategy, it can be changed based on the findings and figures presented in the ...
3. Keep it short. Ideally, the executive summary is short—usually just a page or two, five at the outside—and highlights the points you've made elsewhere in your business plan. Whatever length you land on, just focus on being brief and concise. Keep it as short as you can without missing the essentials.
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
However, it usually appears first in your business plan document. Below are several key points that your executive summary should include based on the stage of your business. ... This section of your business plan provides a high-level review of the different elements of your business. This is akin to an extended elevator pitch and can help ...
The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years. ... According to Mobile Food Trends and Insights' first annual report from the San Francisco-based Off The Grid, ...