An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Public Health

Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review
Ioannis manisalidis.
1 Delphis S.A., Kifisia, Greece
2 Laboratory of Hygiene and Environmental Protection, Faculty of Medicine, Democritus University of Thrace, Alexandroupolis, Greece
Elisavet Stavropoulou
3 Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois (CHUV), Service de Médicine Interne, Lausanne, Switzerland
Agathangelos Stavropoulos
4 School of Social and Political Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom
Eugenia Bezirtzoglou
One of our era's greatest scourges is air pollution, on account not only of its impact on climate change but also its impact on public and individual health due to increasing morbidity and mortality. There are many pollutants that are major factors in disease in humans. Among them, Particulate Matter (PM), particles of variable but very small diameter, penetrate the respiratory system via inhalation, causing respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, reproductive and central nervous system dysfunctions, and cancer. Despite the fact that ozone in the stratosphere plays a protective role against ultraviolet irradiation, it is harmful when in high concentration at ground level, also affecting the respiratory and cardiovascular system. Furthermore, nitrogen oxide, sulfur dioxide, Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), dioxins, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are all considered air pollutants that are harmful to humans. Carbon monoxide can even provoke direct poisoning when breathed in at high levels. Heavy metals such as lead, when absorbed into the human body, can lead to direct poisoning or chronic intoxication, depending on exposure. Diseases occurring from the aforementioned substances include principally respiratory problems such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), asthma, bronchiolitis, and also lung cancer, cardiovascular events, central nervous system dysfunctions, and cutaneous diseases. Last but not least, climate change resulting from environmental pollution affects the geographical distribution of many infectious diseases, as do natural disasters. The only way to tackle this problem is through public awareness coupled with a multidisciplinary approach by scientific experts; national and international organizations must address the emergence of this threat and propose sustainable solutions.
Approach to the Problem
The interactions between humans and their physical surroundings have been extensively studied, as multiple human activities influence the environment. The environment is a coupling of the biotic (living organisms and microorganisms) and the abiotic (hydrosphere, lithosphere, and atmosphere).
Pollution is defined as the introduction into the environment of substances harmful to humans and other living organisms. Pollutants are harmful solids, liquids, or gases produced in higher than usual concentrations that reduce the quality of our environment.
Human activities have an adverse effect on the environment by polluting the water we drink, the air we breathe, and the soil in which plants grow. Although the industrial revolution was a great success in terms of technology, society, and the provision of multiple services, it also introduced the production of huge quantities of pollutants emitted into the air that are harmful to human health. Without any doubt, the global environmental pollution is considered an international public health issue with multiple facets. Social, economic, and legislative concerns and lifestyle habits are related to this major problem. Clearly, urbanization and industrialization are reaching unprecedented and upsetting proportions worldwide in our era. Anthropogenic air pollution is one of the biggest public health hazards worldwide, given that it accounts for about 9 million deaths per year ( 1 ).
Without a doubt, all of the aforementioned are closely associated with climate change, and in the event of danger, the consequences can be severe for mankind ( 2 ). Climate changes and the effects of global planetary warming seriously affect multiple ecosystems, causing problems such as food safety issues, ice and iceberg melting, animal extinction, and damage to plants ( 3 , 4 ).
Air pollution has various health effects. The health of susceptible and sensitive individuals can be impacted even on low air pollution days. Short-term exposure to air pollutants is closely related to COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, asthma, respiratory disease, and high rates of hospitalization (a measurement of morbidity).
The long-term effects associated with air pollution are chronic asthma, pulmonary insufficiency, cardiovascular diseases, and cardiovascular mortality. According to a Swedish cohort study, diabetes seems to be induced after long-term air pollution exposure ( 5 ). Moreover, air pollution seems to have various malign health effects in early human life, such as respiratory, cardiovascular, mental, and perinatal disorders ( 3 ), leading to infant mortality or chronic disease in adult age ( 6 ).
National reports have mentioned the increased risk of morbidity and mortality ( 1 ). These studies were conducted in many places around the world and show a correlation between daily ranges of particulate matter (PM) concentration and daily mortality. Climate shifts and global planetary warming ( 3 ) could aggravate the situation. Besides, increased hospitalization (an index of morbidity) has been registered among the elderly and susceptible individuals for specific reasons. Fine and ultrafine particulate matter seems to be associated with more serious illnesses ( 6 ), as it can invade the deepest parts of the airways and more easily reach the bloodstream.
Air pollution mainly affects those living in large urban areas, where road emissions contribute the most to the degradation of air quality. There is also a danger of industrial accidents, where the spread of a toxic fog can be fatal to the populations of the surrounding areas. The dispersion of pollutants is determined by many parameters, most notably atmospheric stability and wind ( 6 ).
In developing countries ( 7 ), the problem is more serious due to overpopulation and uncontrolled urbanization along with the development of industrialization. This leads to poor air quality, especially in countries with social disparities and a lack of information on sustainable management of the environment. The use of fuels such as wood fuel or solid fuel for domestic needs due to low incomes exposes people to bad-quality, polluted air at home. It is of note that three billion people around the world are using the above sources of energy for their daily heating and cooking needs ( 8 ). In developing countries, the women of the household seem to carry the highest risk for disease development due to their longer duration exposure to the indoor air pollution ( 8 , 9 ). Due to its fast industrial development and overpopulation, China is one of the Asian countries confronting serious air pollution problems ( 10 , 11 ). The lung cancer mortality observed in China is associated with fine particles ( 12 ). As stated already, long-term exposure is associated with deleterious effects on the cardiovascular system ( 3 , 5 ). However, it is interesting to note that cardiovascular diseases have mostly been observed in developed and high-income countries rather than in the developing low-income countries exposed highly to air pollution ( 13 ). Extreme air pollution is recorded in India, where the air quality reaches hazardous levels. New Delhi is one of the more polluted cities in India. Flights in and out of New Delhi International Airport are often canceled due to the reduced visibility associated with air pollution. Pollution is occurring both in urban and rural areas in India due to the fast industrialization, urbanization, and rise in use of motorcycle transportation. Nevertheless, biomass combustion associated with heating and cooking needs and practices is a major source of household air pollution in India and in Nepal ( 14 , 15 ). There is spatial heterogeneity in India, as areas with diverse climatological conditions and population and education levels generate different indoor air qualities, with higher PM 2.5 observed in North Indian states (557–601 μg/m 3 ) compared to the Southern States (183–214 μg/m 3 ) ( 16 , 17 ). The cold climate of the North Indian areas may be the main reason for this, as longer periods at home and more heating are necessary compared to in the tropical climate of Southern India. Household air pollution in India is associated with major health effects, especially in women and young children, who stay indoors for longer periods. Chronic obstructive respiratory disease (CORD) and lung cancer are mostly observed in women, while acute lower respiratory disease is seen in young children under 5 years of age ( 18 ).
Accumulation of air pollution, especially sulfur dioxide and smoke, reaching 1,500 mg/m3, resulted in an increase in the number of deaths (4,000 deaths) in December 1952 in London and in 1963 in New York City (400 deaths) ( 19 ). An association of pollution with mortality was reported on the basis of monitoring of outdoor pollution in six US metropolitan cities ( 20 ). In every case, it seems that mortality was closely related to the levels of fine, inhalable, and sulfate particles more than with the levels of total particulate pollution, aerosol acidity, sulfur dioxide, or nitrogen dioxide ( 20 ).
Furthermore, extremely high levels of pollution are reported in Mexico City and Rio de Janeiro, followed by Milan, Ankara, Melbourne, Tokyo, and Moscow ( 19 ).
Based on the magnitude of the public health impact, it is certain that different kinds of interventions should be taken into account. Success and effectiveness in controlling air pollution, specifically at the local level, have been reported. Adequate technological means are applied considering the source and the nature of the emission as well as its impact on health and the environment. The importance of point sources and non-point sources of air pollution control is reported by Schwela and Köth-Jahr ( 21 ). Without a doubt, a detailed emission inventory must record all sources in a given area. Beyond considering the above sources and their nature, topography and meteorology should also be considered, as stated previously. Assessment of the control policies and methods is often extrapolated from the local to the regional and then to the global scale. Air pollution may be dispersed and transported from one region to another area located far away. Air pollution management means the reduction to acceptable levels or possible elimination of air pollutants whose presence in the air affects our health or the environmental ecosystem. Private and governmental entities and authorities implement actions to ensure the air quality ( 22 ). Air quality standards and guidelines were adopted for the different pollutants by the WHO and EPA as a tool for the management of air quality ( 1 , 23 ). These standards have to be compared to the emissions inventory standards by causal analysis and dispersion modeling in order to reveal the problematic areas ( 24 ). Inventories are generally based on a combination of direct measurements and emissions modeling ( 24 ).
As an example, we state here the control measures at the source through the use of catalytic converters in cars. These are devices that turn the pollutants and toxic gases produced from combustion engines into less-toxic pollutants by catalysis through redox reactions ( 25 ). In Greece, the use of private cars was restricted by tracking their license plates in order to reduce traffic congestion during rush hour ( 25 ).
Concerning industrial emissions, collectors and closed systems can keep the air pollution to the minimal standards imposed by legislation ( 26 ).
Current strategies to improve air quality require an estimation of the economic value of the benefits gained from proposed programs. These proposed programs by public authorities, and directives are issued with guidelines to be respected.
In Europe, air quality limit values AQLVs (Air Quality Limit Values) are issued for setting off planning claims ( 27 ). In the USA, the NAAQS (National Ambient Air Quality Standards) establish the national air quality limit values ( 27 ). While both standards and directives are based on different mechanisms, significant success has been achieved in the reduction of overall emissions and associated health and environmental effects ( 27 ). The European Directive identifies geographical areas of risk exposure as monitoring/assessment zones to record the emission sources and levels of air pollution ( 27 ), whereas the USA establishes global geographical air quality criteria according to the severity of their air quality problem and records all sources of the pollutants and their precursors ( 27 ).
In this vein, funds have been financing, directly or indirectly, projects related to air quality along with the technical infrastructure to maintain good air quality. These plans focus on an inventory of databases from air quality environmental planning awareness campaigns. Moreover, pollution measures of air emissions may be taken for vehicles, machines, and industries in urban areas.
Technological innovation can only be successful if it is able to meet the needs of society. In this sense, technology must reflect the decision-making practices and procedures of those involved in risk assessment and evaluation and act as a facilitator in providing information and assessments to enable decision makers to make the best decisions possible. Summarizing the aforementioned in order to design an effective air quality control strategy, several aspects must be considered: environmental factors and ambient air quality conditions, engineering factors and air pollutant characteristics, and finally, economic operating costs for technological improvement and administrative and legal costs. Considering the economic factor, competitiveness through neoliberal concepts is offering a solution to environmental problems ( 22 ).
The development of environmental governance, along with technological progress, has initiated the deployment of a dialogue. Environmental politics has created objections and points of opposition between different political parties, scientists, media, and governmental and non-governmental organizations ( 22 ). Radical environmental activism actions and movements have been created ( 22 ). The rise of the new information and communication technologies (ICTs) are many times examined as to whether and in which way they have influenced means of communication and social movements such as activism ( 28 ). Since the 1990s, the term “digital activism” has been used increasingly and in many different disciplines ( 29 ). Nowadays, multiple digital technologies can be used to produce a digital activism outcome on environmental issues. More specifically, devices with online capabilities such as computers or mobile phones are being used as a way to pursue change in political and social affairs ( 30 ).
In the present paper, we focus on the sources of environmental pollution in relation to public health and propose some solutions and interventions that may be of interest to environmental legislators and decision makers.
Sources of Exposure
It is known that the majority of environmental pollutants are emitted through large-scale human activities such as the use of industrial machinery, power-producing stations, combustion engines, and cars. Because these activities are performed at such a large scale, they are by far the major contributors to air pollution, with cars estimated to be responsible for approximately 80% of today's pollution ( 31 ). Some other human activities are also influencing our environment to a lesser extent, such as field cultivation techniques, gas stations, fuel tanks heaters, and cleaning procedures ( 32 ), as well as several natural sources, such as volcanic and soil eruptions and forest fires.
The classification of air pollutants is based mainly on the sources producing pollution. Therefore, it is worth mentioning the four main sources, following the classification system: Major sources, Area sources, Mobile sources, and Natural sources.
Major sources include the emission of pollutants from power stations, refineries, and petrochemicals, the chemical and fertilizer industries, metallurgical and other industrial plants, and, finally, municipal incineration.
Indoor area sources include domestic cleaning activities, dry cleaners, printing shops, and petrol stations.
Mobile sources include automobiles, cars, railways, airways, and other types of vehicles.
Finally, natural sources include, as stated previously, physical disasters ( 33 ) such as forest fire, volcanic erosion, dust storms, and agricultural burning.
However, many classification systems have been proposed. Another type of classification is a grouping according to the recipient of the pollution, as follows:
Air pollution is determined as the presence of pollutants in the air in large quantities for long periods. Air pollutants are dispersed particles, hydrocarbons, CO, CO 2 , NO, NO 2 , SO 3 , etc.
Water pollution is organic and inorganic charge and biological charge ( 10 ) at high levels that affect the water quality ( 34 , 35 ).
Soil pollution occurs through the release of chemicals or the disposal of wastes, such as heavy metals, hydrocarbons, and pesticides.
Air pollution can influence the quality of soil and water bodies by polluting precipitation, falling into water and soil environments ( 34 , 36 ). Notably, the chemistry of the soil can be amended due to acid precipitation by affecting plants, cultures, and water quality ( 37 ). Moreover, movement of heavy metals is favored by soil acidity, and metals are so then moving into the watery environment. It is known that heavy metals such as aluminum are noxious to wildlife and fishes. Soil quality seems to be of importance, as soils with low calcium carbonate levels are at increased jeopardy from acid rain. Over and above rain, snow and particulate matter drip into watery ' bodies ( 36 , 38 ).
Lastly, pollution is classified following type of origin:
Radioactive and nuclear pollution , releasing radioactive and nuclear pollutants into water, air, and soil during nuclear explosions and accidents, from nuclear weapons, and through handling or disposal of radioactive sewage.
Radioactive materials can contaminate surface water bodies and, being noxious to the environment, plants, animals, and humans. It is known that several radioactive substances such as radium and uranium concentrate in the bones and can cause cancers ( 38 , 39 ).
Noise pollution is produced by machines, vehicles, traffic noises, and musical installations that are harmful to our hearing.
The World Health Organization introduced the term DALYs. The DALYs for a disease or health condition is defined as the sum of the Years of Life Lost (YLL) due to premature mortality in the population and the Years Lost due to Disability (YLD) for people living with the health condition or its consequences ( 39 ). In Europe, air pollution is the main cause of disability-adjusted life years lost (DALYs), followed by noise pollution. The potential relationships of noise and air pollution with health have been studied ( 40 ). The study found that DALYs related to noise were more important than those related to air pollution, as the effects of environmental noise on cardiovascular disease were independent of air pollution ( 40 ). Environmental noise should be counted as an independent public health risk ( 40 ).
Environmental pollution occurs when changes in the physical, chemical, or biological constituents of the environment (air masses, temperature, climate, etc.) are produced.
Pollutants harm our environment either by increasing levels above normal or by introducing harmful toxic substances. Primary pollutants are directly produced from the above sources, and secondary pollutants are emitted as by-products of the primary ones. Pollutants can be biodegradable or non-biodegradable and of natural origin or anthropogenic, as stated previously. Moreover, their origin can be a unique source (point-source) or dispersed sources.
Pollutants have differences in physical and chemical properties, explaining the discrepancy in their capacity for producing toxic effects. As an example, we state here that aerosol compounds ( 41 – 43 ) have a greater toxicity than gaseous compounds due to their tiny size (solid or liquid) in the atmosphere; they have a greater penetration capacity. Gaseous compounds are eliminated more easily by our respiratory system ( 41 ). These particles are able to damage lungs and can even enter the bloodstream ( 41 ), leading to the premature deaths of millions of people yearly. Moreover, the aerosol acidity ([H+]) seems to considerably enhance the production of secondary organic aerosols (SOA), but this last aspect is not supported by other scientific teams ( 38 ).
Climate and Pollution
Air pollution and climate change are closely related. Climate is the other side of the same coin that reduces the quality of our Earth ( 44 ). Pollutants such as black carbon, methane, tropospheric ozone, and aerosols affect the amount of incoming sunlight. As a result, the temperature of the Earth is increasing, resulting in the melting of ice, icebergs, and glaciers.
In this vein, climatic changes will affect the incidence and prevalence of both residual and imported infections in Europe. Climate and weather affect the duration, timing, and intensity of outbreaks strongly and change the map of infectious diseases in the globe ( 45 ). Mosquito-transmitted parasitic or viral diseases are extremely climate-sensitive, as warming firstly shortens the pathogen incubation period and secondly shifts the geographic map of the vector. Similarly, water-warming following climate changes leads to a high incidence of waterborne infections. Recently, in Europe, eradicated diseases seem to be emerging due to the migration of population, for example, cholera, poliomyelitis, tick-borne encephalitis, and malaria ( 46 ).
The spread of epidemics is associated with natural climate disasters and storms, which seem to occur more frequently nowadays ( 47 ). Malnutrition and disequilibration of the immune system are also associated with the emerging infections affecting public health ( 48 ).
The Chikungunya virus “took the airplane” from the Indian Ocean to Europe, as outbreaks of the disease were registered in Italy ( 49 ) as well as autochthonous cases in France ( 50 ).
An increase in cryptosporidiosis in the United Kingdom and in the Czech Republic seems to have occurred following flooding ( 36 , 51 ).
As stated previously, aerosols compounds are tiny in size and considerably affect the climate. They are able to dissipate sunlight (the albedo phenomenon) by dispersing a quarter of the sun's rays back to space and have cooled the global temperature over the last 30 years ( 52 ).
Air Pollutants
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports on six major air pollutants, namely particle pollution, ground-level ozone, carbon monoxide, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and lead. Air pollution can have a disastrous effect on all components of the environment, including groundwater, soil, and air. Additionally, it poses a serious threat to living organisms. In this vein, our interest is mainly to focus on these pollutants, as they are related to more extensive and severe problems in human health and environmental impact. Acid rain, global warming, the greenhouse effect, and climate changes have an important ecological impact on air pollution ( 53 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) and Health
Studies have shown a relationship between particulate matter (PM) and adverse health effects, focusing on either short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic) PM exposure.
Particulate matter (PM) is usually formed in the atmosphere as a result of chemical reactions between the different pollutants. The penetration of particles is closely dependent on their size ( 53 ). Particulate Matter (PM) was defined as a term for particles by the United States Environmental Protection Agency ( 54 ). Particulate matter (PM) pollution includes particles with diameters of 10 micrometers (μm) or smaller, called PM 10 , and extremely fine particles with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers (μm) and smaller.
Particulate matter contains tiny liquid or solid droplets that can be inhaled and cause serious health effects ( 55 ). Particles <10 μm in diameter (PM 10 ) after inhalation can invade the lungs and even reach the bloodstream. Fine particles, PM 2.5 , pose a greater risk to health ( 6 , 56 ) ( Table 1 ).
Penetrability according to particle size.
| >11 μm | Passage into nostrils and upper respiratory tract |
| 7–11 μm | Passage into nasal cavity |
| 4.7–7 μm | Passage into larynx |
| 3.3–4.7 μm | Passage into trachea-bronchial area |
| 2.1–3.3 μm | Secondary bronchial area passage |
| 1.1–2.1 μm | Terminal bronchial area passage |
| 0.65–1.1 μm | Bronchioles penetrability |
| 0.43–0.65 μm | Alveolar penetrability |
Multiple epidemiological studies have been performed on the health effects of PM. A positive relation was shown between both short-term and long-term exposures of PM 2.5 and acute nasopharyngitis ( 56 ). In addition, long-term exposure to PM for years was found to be related to cardiovascular diseases and infant mortality.
Those studies depend on PM 2.5 monitors and are restricted in terms of study area or city area due to a lack of spatially resolved daily PM 2.5 concentration data and, in this way, are not representative of the entire population. Following a recent epidemiological study by the Department of Environmental Health at Harvard School of Public Health (Boston, MA) ( 57 ), it was reported that, as PM 2.5 concentrations vary spatially, an exposure error (Berkson error) seems to be produced, and the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects are not yet completely elucidated. The team developed a PM 2.5 exposure model based on remote sensing data for assessing short- and long-term human exposures ( 57 ). This model permits spatial resolution in short-term effects plus the assessment of long-term effects in the whole population.
Moreover, respiratory diseases and affection of the immune system are registered as long-term chronic effects ( 58 ). It is worth noting that people with asthma, pneumonia, diabetes, and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases are especially susceptible and vulnerable to the effects of PM. PM 2.5 , followed by PM 10 , are strongly associated with diverse respiratory system diseases ( 59 ), as their size permits them to pierce interior spaces ( 60 ). The particles produce toxic effects according to their chemical and physical properties. The components of PM 10 and PM 2.5 can be organic (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, dioxins, benzene, 1-3 butadiene) or inorganic (carbon, chlorides, nitrates, sulfates, metals) in nature ( 55 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) is divided into four main categories according to type and size ( 61 ) ( Table 2 ).
Types and sizes of particulate Matter (PM).
| Particulate contaminants | Smog | 0.01–1 |
| Soot | 0.01–0.8 | |
| Tobacco smoke | 0.01–1 | |
| Fly ash | 1–100 | |
| Cement Dust | 8–100 | |
| Biological Contaminants | Bacteria and bacterial spores | 0.7–10 |
| Viruses | 0.01–1 | |
| Fungi and molds | 2–12 | |
| Allergens (dogs, cats, pollen, household dust) | 0.1–100 | |
| Types of Dust | Atmospheric dust | 0.01–1 |
| Heavy dust | 100–1000 | |
| Settling dust | 1–100 | |
| Gases | Different gaseous contaminants | 0.0001–0.01 |
Gas contaminants include PM in aerial masses.
Particulate contaminants include contaminants such as smog, soot, tobacco smoke, oil smoke, fly ash, and cement dust.
Biological Contaminants are microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, mold, and bacterial spores), cat allergens, house dust and allergens, and pollen.
Types of Dust include suspended atmospheric dust, settling dust, and heavy dust.
Finally, another fact is that the half-lives of PM 10 and PM 2.5 particles in the atmosphere is extended due to their tiny dimensions; this permits their long-lasting suspension in the atmosphere and even their transfer and spread to distant destinations where people and the environment may be exposed to the same magnitude of pollution ( 53 ). They are able to change the nutrient balance in watery ecosystems, damage forests and crops, and acidify water bodies.
As stated, PM 2.5 , due to their tiny size, are causing more serious health effects. These aforementioned fine particles are the main cause of the “haze” formation in different metropolitan areas ( 12 , 13 , 61 ).
Ozone Impact in the Atmosphere
Ozone (O 3 ) is a gas formed from oxygen under high voltage electric discharge ( 62 ). It is a strong oxidant, 52% stronger than chlorine. It arises in the stratosphere, but it could also arise following chain reactions of photochemical smog in the troposphere ( 63 ).
Ozone can travel to distant areas from its initial source, moving with air masses ( 64 ). It is surprising that ozone levels over cities are low in contrast to the increased amounts occuring in urban areas, which could become harmful for cultures, forests, and vegetation ( 65 ) as it is reducing carbon assimilation ( 66 ). Ozone reduces growth and yield ( 47 , 48 ) and affects the plant microflora due to its antimicrobial capacity ( 67 , 68 ). In this regard, ozone acts upon other natural ecosystems, with microflora ( 69 , 70 ) and animal species changing their species composition ( 71 ). Ozone increases DNA damage in epidermal keratinocytes and leads to impaired cellular function ( 72 ).
Ground-level ozone (GLO) is generated through a chemical reaction between oxides of nitrogen and VOCs emitted from natural sources and/or following anthropogenic activities.
Ozone uptake usually occurs by inhalation. Ozone affects the upper layers of the skin and the tear ducts ( 73 ). A study of short-term exposure of mice to high levels of ozone showed malondialdehyde formation in the upper skin (epidermis) but also depletion in vitamins C and E. It is likely that ozone levels are not interfering with the skin barrier function and integrity to predispose to skin disease ( 74 ).
Due to the low water-solubility of ozone, inhaled ozone has the capacity to penetrate deeply into the lungs ( 75 ).
Toxic effects induced by ozone are registered in urban areas all over the world, causing biochemical, morphologic, functional, and immunological disorders ( 76 ).
The European project (APHEA2) focuses on the acute effects of ambient ozone concentrations on mortality ( 77 ). Daily ozone concentrations compared to the daily number of deaths were reported from different European cities for a 3-year period. During the warm period of the year, an observed increase in ozone concentration was associated with an increase in the daily number of deaths (0.33%), in the number of respiratory deaths (1.13%), and in the number of cardiovascular deaths (0.45%). No effect was observed during wintertime.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is produced by fossil fuel when combustion is incomplete. The symptoms of poisoning due to inhaling carbon monoxide include headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, and, finally, loss of consciousness.
The affinity of carbon monoxide to hemoglobin is much greater than that of oxygen. In this vein, serious poisoning may occur in people exposed to high levels of carbon monoxide for a long period of time. Due to the loss of oxygen as a result of the competitive binding of carbon monoxide, hypoxia, ischemia, and cardiovascular disease are observed.
Carbon monoxide affects the greenhouses gases that are tightly connected to global warming and climate. This should lead to an increase in soil and water temperatures, and extreme weather conditions or storms may occur ( 68 ).
However, in laboratory and field experiments, it has been seen to produce increased plant growth ( 78 ).
Nitrogen Oxide (NO 2 )
Nitrogen oxide is a traffic-related pollutant, as it is emitted from automobile motor engines ( 79 , 80 ). It is an irritant of the respiratory system as it penetrates deep in the lung, inducing respiratory diseases, coughing, wheezing, dyspnea, bronchospasm, and even pulmonary edema when inhaled at high levels. It seems that concentrations over 0.2 ppm produce these adverse effects in humans, while concentrations higher than 2.0 ppm affect T-lymphocytes, particularly the CD8+ cells and NK cells that produce our immune response ( 81 ).It is reported that long-term exposure to high levels of nitrogen dioxide can be responsible for chronic lung disease. Long-term exposure to NO 2 can impair the sense of smell ( 81 ).
However, systems other than respiratory ones can be involved, as symptoms such as eye, throat, and nose irritation have been registered ( 81 ).
High levels of nitrogen dioxide are deleterious to crops and vegetation, as they have been observed to reduce crop yield and plant growth efficiency. Moreover, NO 2 can reduce visibility and discolor fabrics ( 81 ).
Sulfur Dioxide (SO 2 )
Sulfur dioxide is a harmful gas that is emitted mainly from fossil fuel consumption or industrial activities. The annual standard for SO 2 is 0.03 ppm ( 82 ). It affects human, animal, and plant life. Susceptible people as those with lung disease, old people, and children, who present a higher risk of damage. The major health problems associated with sulfur dioxide emissions in industrialized areas are respiratory irritation, bronchitis, mucus production, and bronchospasm, as it is a sensory irritant and penetrates deep into the lung converted into bisulfite and interacting with sensory receptors, causing bronchoconstriction. Moreover, skin redness, damage to the eyes (lacrimation and corneal opacity) and mucous membranes, and worsening of pre-existing cardiovascular disease have been observed ( 81 ).
Environmental adverse effects, such as acidification of soil and acid rain, seem to be associated with sulfur dioxide emissions ( 83 ).
Lead is a heavy metal used in different industrial plants and emitted from some petrol motor engines, batteries, radiators, waste incinerators, and waste waters ( 84 ).
Moreover, major sources of lead pollution in the air are metals, ore, and piston-engine aircraft. Lead poisoning is a threat to public health due to its deleterious effects upon humans, animals, and the environment, especially in the developing countries.
Exposure to lead can occur through inhalation, ingestion, and dermal absorption. Trans- placental transport of lead was also reported, as lead passes through the placenta unencumbered ( 85 ). The younger the fetus is, the more harmful the toxic effects. Lead toxicity affects the fetal nervous system; edema or swelling of the brain is observed ( 86 ). Lead, when inhaled, accumulates in the blood, soft tissue, liver, lung, bones, and cardiovascular, nervous, and reproductive systems. Moreover, loss of concentration and memory, as well as muscle and joint pain, were observed in adults ( 85 , 86 ).
Children and newborns ( 87 ) are extremely susceptible even to minimal doses of lead, as it is a neurotoxicant and causes learning disabilities, impairment of memory, hyperactivity, and even mental retardation.
Elevated amounts of lead in the environment are harmful to plants and crop growth. Neurological effects are observed in vertebrates and animals in association with high lead levels ( 88 ).
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(PAHs)
The distribution of PAHs is ubiquitous in the environment, as the atmosphere is the most important means of their dispersal. They are found in coal and in tar sediments. Moreover, they are generated through incomplete combustion of organic matter as in the cases of forest fires, incineration, and engines ( 89 ). PAH compounds, such as benzopyrene, acenaphthylene, anthracene, and fluoranthene are recognized as toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic substances. They are an important risk factor for lung cancer ( 89 ).
Volatile Organic Compounds(VOCs)
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), such as toluene, benzene, ethylbenzene, and xylene ( 90 ), have been found to be associated with cancer in humans ( 91 ). The use of new products and materials has actually resulted in increased concentrations of VOCs. VOCs pollute indoor air ( 90 ) and may have adverse effects on human health ( 91 ). Short-term and long-term adverse effects on human health are observed. VOCs are responsible for indoor air smells. Short-term exposure is found to cause irritation of eyes, nose, throat, and mucosal membranes, while those of long duration exposure include toxic reactions ( 92 ). Predictable assessment of the toxic effects of complex VOC mixtures is difficult to estimate, as these pollutants can have synergic, antagonistic, or indifferent effects ( 91 , 93 ).
Dioxins originate from industrial processes but also come from natural processes, such as forest fires and volcanic eruptions. They accumulate in foods such as meat and dairy products, fish and shellfish, and especially in the fatty tissue of animals ( 94 ).
Short-period exhibition to high dioxin concentrations may result in dark spots and lesions on the skin ( 94 ). Long-term exposure to dioxins can cause developmental problems, impairment of the immune, endocrine and nervous systems, reproductive infertility, and cancer ( 94 ).
Without any doubt, fossil fuel consumption is responsible for a sizeable part of air contamination. This contamination may be anthropogenic, as in agricultural and industrial processes or transportation, while contamination from natural sources is also possible. Interestingly, it is of note that the air quality standards established through the European Air Quality Directive are somewhat looser than the WHO guidelines, which are stricter ( 95 ).
Effect of Air Pollution on Health
The most common air pollutants are ground-level ozone and Particulates Matter (PM). Air pollution is distinguished into two main types:
Outdoor pollution is the ambient air pollution.
Indoor pollution is the pollution generated by household combustion of fuels.
People exposed to high concentrations of air pollutants experience disease symptoms and states of greater and lesser seriousness. These effects are grouped into short- and long-term effects affecting health.
Susceptible populations that need to be aware of health protection measures include old people, children, and people with diabetes and predisposing heart or lung disease, especially asthma.
As extensively stated previously, according to a recent epidemiological study from Harvard School of Public Health, the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects have not been completely clarified ( 57 ) due to the different epidemiological methodologies and to the exposure errors. New models are proposed for assessing short- and long-term human exposure data more successfully ( 57 ). Thus, in the present section, we report the more common short- and long-term health effects but also general concerns for both types of effects, as these effects are often dependent on environmental conditions, dose, and individual susceptibility.
Short-term effects are temporary and range from simple discomfort, such as irritation of the eyes, nose, skin, throat, wheezing, coughing and chest tightness, and breathing difficulties, to more serious states, such as asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis, and lung and heart problems. Short-term exposure to air pollution can also cause headaches, nausea, and dizziness.
These problems can be aggravated by extended long-term exposure to the pollutants, which is harmful to the neurological, reproductive, and respiratory systems and causes cancer and even, rarely, deaths.
The long-term effects are chronic, lasting for years or the whole life and can even lead to death. Furthermore, the toxicity of several air pollutants may also induce a variety of cancers in the long term ( 96 ).
As stated already, respiratory disorders are closely associated with the inhalation of air pollutants. These pollutants will invade through the airways and will accumulate at the cells. Damage to target cells should be related to the pollutant component involved and its source and dose. Health effects are also closely dependent on country, area, season, and time. An extended exposure duration to the pollutant should incline to long-term health effects in relation also to the above factors.
Particulate Matter (PMs), dust, benzene, and O 3 cause serious damage to the respiratory system ( 97 ). Moreover, there is a supplementary risk in case of existing respiratory disease such as asthma ( 98 ). Long-term effects are more frequent in people with a predisposing disease state. When the trachea is contaminated by pollutants, voice alterations may be remarked after acute exposure. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may be induced following air pollution, increasing morbidity and mortality ( 99 ). Long-term effects from traffic, industrial air pollution, and combustion of fuels are the major factors for COPD risk ( 99 ).
Multiple cardiovascular effects have been observed after exposure to air pollutants ( 100 ). Changes occurred in blood cells after long-term exposure may affect cardiac functionality. Coronary arteriosclerosis was reported following long-term exposure to traffic emissions ( 101 ), while short-term exposure is related to hypertension, stroke, myocardial infracts, and heart insufficiency. Ventricle hypertrophy is reported to occur in humans after long-time exposure to nitrogen oxide (NO 2 ) ( 102 , 103 ).
Neurological effects have been observed in adults and children after extended-term exposure to air pollutants.
Psychological complications, autism, retinopathy, fetal growth, and low birth weight seem to be related to long-term air pollution ( 83 ). The etiologic agent of the neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's and Parkinson's) is not yet known, although it is believed that extended exposure to air pollution seems to be a factor. Specifically, pesticides and metals are cited as etiological factors, together with diet. The mechanisms in the development of neurodegenerative disease include oxidative stress, protein aggregation, inflammation, and mitochondrial impairment in neurons ( 104 ) ( Figure 1 ).

Impact of air pollutants on the brain.
Brain inflammation was observed in dogs living in a highly polluted area in Mexico for a long period ( 105 ). In human adults, markers of systemic inflammation (IL-6 and fibrinogen) were found to be increased as an immediate response to PNC on the IL-6 level, possibly leading to the production of acute-phase proteins ( 106 ). The progression of atherosclerosis and oxidative stress seem to be the mechanisms involved in the neurological disturbances caused by long-term air pollution. Inflammation comes secondary to the oxidative stress and seems to be involved in the impairment of developmental maturation, affecting multiple organs ( 105 , 107 ). Similarly, other factors seem to be involved in the developmental maturation, which define the vulnerability to long-term air pollution. These include birthweight, maternal smoking, genetic background and socioeconomic environment, as well as education level.
However, diet, starting from breast-feeding, is another determinant factor. Diet is the main source of antioxidants, which play a key role in our protection against air pollutants ( 108 ). Antioxidants are free radical scavengers and limit the interaction of free radicals in the brain ( 108 ). Similarly, genetic background may result in a differential susceptibility toward the oxidative stress pathway ( 60 ). For example, antioxidant supplementation with vitamins C and E appears to modulate the effect of ozone in asthmatic children homozygous for the GSTM1 null allele ( 61 ). Inflammatory cytokines released in the periphery (e.g., respiratory epithelia) upregulate the innate immune Toll-like receptor 2. Such activation and the subsequent events leading to neurodegeneration have recently been observed in lung lavage in mice exposed to ambient Los Angeles (CA, USA) particulate matter ( 61 ). In children, neurodevelopmental morbidities were observed after lead exposure. These children developed aggressive and delinquent behavior, reduced intelligence, learning difficulties, and hyperactivity ( 109 ). No level of lead exposure seems to be “safe,” and the scientific community has asked the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to reduce the current screening guideline of 10 μg/dl ( 109 ).
It is important to state that impact on the immune system, causing dysfunction and neuroinflammation ( 104 ), is related to poor air quality. Yet, increases in serum levels of immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM) and the complement component C3 are observed ( 106 ). Another issue is that antigen presentation is affected by air pollutants, as there is an upregulation of costimulatory molecules such as CD80 and CD86 on macrophages ( 110 ).
As is known, skin is our shield against ultraviolet radiation (UVR) and other pollutants, as it is the most exterior layer of our body. Traffic-related pollutants, such as PAHs, VOCs, oxides, and PM, may cause pigmented spots on our skin ( 111 ). On the one hand, as already stated, when pollutants penetrate through the skin or are inhaled, damage to the organs is observed, as some of these pollutants are mutagenic and carcinogenic, and, specifically, they affect the liver and lung. On the other hand, air pollutants (and those in the troposphere) reduce the adverse effects of ultraviolet radiation UVR in polluted urban areas ( 111 ). Air pollutants absorbed by the human skin may contribute to skin aging, psoriasis, acne, urticaria, eczema, and atopic dermatitis ( 111 ), usually caused by exposure to oxides and photochemical smoke ( 111 ). Exposure to PM and cigarette smoking act as skin-aging agents, causing spots, dyschromia, and wrinkles. Lastly, pollutants have been associated with skin cancer ( 111 ).
Higher morbidity is reported to fetuses and children when exposed to the above dangers. Impairment in fetal growth, low birth weight, and autism have been reported ( 112 ).
Another exterior organ that may be affected is the eye. Contamination usually comes from suspended pollutants and may result in asymptomatic eye outcomes, irritation ( 112 ), retinopathy, or dry eye syndrome ( 113 , 114 ).
Environmental Impact of Air Pollution
Air pollution is harming not only human health but also the environment ( 115 ) in which we live. The most important environmental effects are as follows.
Acid rain is wet (rain, fog, snow) or dry (particulates and gas) precipitation containing toxic amounts of nitric and sulfuric acids. They are able to acidify the water and soil environments, damage trees and plantations, and even damage buildings and outdoor sculptures, constructions, and statues.
Haze is produced when fine particles are dispersed in the air and reduce the transparency of the atmosphere. It is caused by gas emissions in the air coming from industrial facilities, power plants, automobiles, and trucks.
Ozone , as discussed previously, occurs both at ground level and in the upper level (stratosphere) of the Earth's atmosphere. Stratospheric ozone is protecting us from the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. In contrast, ground-level ozone is harmful to human health and is a pollutant. Unfortunately, stratospheric ozone is gradually damaged by ozone-depleting substances (i.e., chemicals, pesticides, and aerosols). If this protecting stratospheric ozone layer is thinned, then UV radiation can reach our Earth, with harmful effects for human life (skin cancer) ( 116 ) and crops ( 117 ). In plants, ozone penetrates through the stomata, inducing them to close, which blocks CO 2 transfer and induces a reduction in photosynthesis ( 118 ).
Global climate change is an important issue that concerns mankind. As is known, the “greenhouse effect” keeps the Earth's temperature stable. Unhappily, anthropogenic activities have destroyed this protecting temperature effect by producing large amounts of greenhouse gases, and global warming is mounting, with harmful effects on human health, animals, forests, wildlife, agriculture, and the water environment. A report states that global warming is adding to the health risks of poor people ( 119 ).
People living in poorly constructed buildings in warm-climate countries are at high risk for heat-related health problems as temperatures mount ( 119 ).
Wildlife is burdened by toxic pollutants coming from the air, soil, or the water ecosystem and, in this way, animals can develop health problems when exposed to high levels of pollutants. Reproductive failure and birth effects have been reported.
Eutrophication is occurring when elevated concentrations of nutrients (especially nitrogen) stimulate the blooming of aquatic algae, which can cause a disequilibration in the diversity of fish and their deaths.
Without a doubt, there is a critical concentration of pollution that an ecosystem can tolerate without being destroyed, which is associated with the ecosystem's capacity to neutralize acidity. The Canada Acid Rain Program established this load at 20 kg/ha/yr ( 120 ).
Hence, air pollution has deleterious effects on both soil and water ( 121 ). Concerning PM as an air pollutant, its impact on crop yield and food productivity has been reported. Its impact on watery bodies is associated with the survival of living organisms and fishes and their productivity potential ( 121 ).
An impairment in photosynthetic rhythm and metabolism is observed in plants exposed to the effects of ozone ( 121 ).
Sulfur and nitrogen oxides are involved in the formation of acid rain and are harmful to plants and marine organisms.
Last but not least, as mentioned above, the toxicity associated with lead and other metals is the main threat to our ecosystems (air, water, and soil) and living creatures ( 121 ).
In 2018, during the first WHO Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health, the WHO's General Director, Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, called air pollution a “silent public health emergency” and “the new tobacco” ( 122 ).
Undoubtedly, children are particularly vulnerable to air pollution, especially during their development. Air pollution has adverse effects on our lives in many different respects.
Diseases associated with air pollution have not only an important economic impact but also a societal impact due to absences from productive work and school.
Despite the difficulty of eradicating the problem of anthropogenic environmental pollution, a successful solution could be envisaged as a tight collaboration of authorities, bodies, and doctors to regularize the situation. Governments should spread sufficient information and educate people and should involve professionals in these issues so as to control the emergence of the problem successfully.
Technologies to reduce air pollution at the source must be established and should be used in all industries and power plants. The Kyoto Protocol of 1997 set as a major target the reduction of GHG emissions to below 5% by 2012 ( 123 ). This was followed by the Copenhagen summit, 2009 ( 124 ), and then the Durban summit of 2011 ( 125 ), where it was decided to keep to the same line of action. The Kyoto protocol and the subsequent ones were ratified by many countries. Among the pioneers who adopted this important protocol for the world's environmental and climate “health” was China ( 3 ). As is known, China is a fast-developing economy and its GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is expected to be very high by 2050, which is defined as the year of dissolution of the protocol for the decrease in gas emissions.
A more recent international agreement of crucial importance for climate change is the Paris Agreement of 2015, issued by the UNFCCC (United Nations Climate Change Committee). This latest agreement was ratified by a plethora of UN (United Nations) countries as well as the countries of the European Union ( 126 ). In this vein, parties should promote actions and measures to enhance numerous aspects around the subject. Boosting education, training, public awareness, and public participation are some of the relevant actions for maximizing the opportunities to achieve the targets and goals on the crucial matter of climate change and environmental pollution ( 126 ). Without any doubt, technological improvements makes our world easier and it seems difficult to reduce the harmful impact caused by gas emissions, we could limit its use by seeking reliable approaches.
Synopsizing, a global prevention policy should be designed in order to combat anthropogenic air pollution as a complement to the correct handling of the adverse health effects associated with air pollution. Sustainable development practices should be applied, together with information coming from research in order to handle the problem effectively.
At this point, international cooperation in terms of research, development, administration policy, monitoring, and politics is vital for effective pollution control. Legislation concerning air pollution must be aligned and updated, and policy makers should propose the design of a powerful tool of environmental and health protection. As a result, the main proposal of this essay is that we should focus on fostering local structures to promote experience and practice and extrapolate these to the international level through developing effective policies for sustainable management of ecosystems.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
IM is employed by the company Delphis S.A. The remaining authors declare that the present review paper was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Air pollution, explained
Pollutants in the air aren't always visible and come from many different sources.
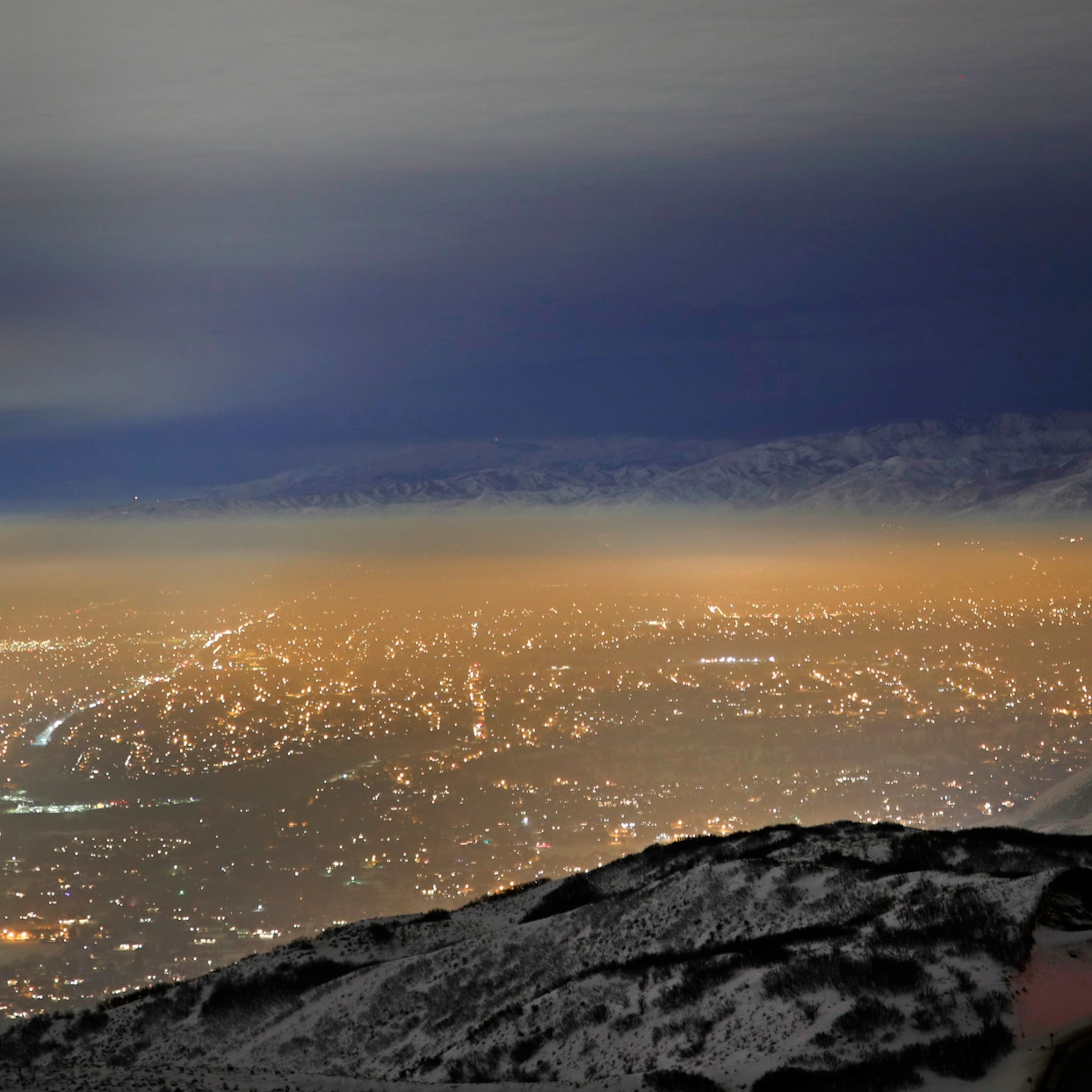
Despite decades of progress, the air quality in the United States has started to decline over the past few years, according to data provided in summer 2019 by the Environmental Protection Agency . The agency recorded 15 percent more days with unhealthy air in the country in 2018 and 2017 compared to the average from 2013 to 2016.
The reasons for the recent decline in air quality remain unclear, says the agency, but may be related to high numbers of wildfires , a warming climate, and increasing human consumption patterns driven by population growth and a strong economy. The long-term outlook also remains unclear, even as politicians debate air pollution standards.
What is air pollution?
Air pollution is a mix of particles and gases that can reach harmful concentrations both outside and indoors. Its effects can range from higher disease risks to rising temperatures. Soot, smoke, mold, pollen, methane, and carbon dioxide are a just few examples of common pollutants.
In the U.S., one measure of outdoor air pollution is the Air Quality Index, or AQI which rates air conditions across the country based on concentrations of five major pollutants: ground-level ozone, particle pollution (or particulate matter), carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen dioxide. Some of those also contribute to indoor air pollution , along with radon, cigarette smoke, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), formaldehyde, asbestos, and other substances.
A global health hazard
Poor air quality kills people. Worldwide, bad outdoor air caused an estimated 4.2 million premature deaths in 2016 , about 90 percent of them in low- and middle-income countries, according to the World Health Organization. Indoor smoke is an ongoing health threat to the 3 billion people who cook and heat their homes by burning biomass, kerosene, and coal. Air pollution has been linked to higher rates of cancer, heart disease, stroke, and respiratory diseases such as asthma. In the U.S. nearly 134 million people—over 40 percent of the population—are at risk of disease and premature death because of air pollution, according to American Lung Association estimates .

While those effects emerge from long-term exposure, air pollution can also cause short-term problems such as sneezing and coughing, eye irritation, headaches, and dizziness. Particulate matter smaller than 10 micrometers (classified as PM 10 and the even smaller PM 2.5 ) pose higher health risks because they can be breathed deeply into the lungs and may cross into the bloodstream.
Air pollutants cause less-direct health effects when they contribute to climate change . Heat waves, extreme weather, food supply disruptions, and other effects related to increased greenhouse gases can have negative impacts on human health. The U.S. Fourth National Climate Assessment released in 2018 noted, for example, that a changing climate "could expose more people in North America to ticks that carry Lyme disease and mosquitoes that transmit viruses such as West Nile, chikungunya, dengue, and Zika."
You May Also Like

What the Air Quality Index measures—and what to do when it’s code red

What is the ozone layer, and why does it matter?

Ground-level ozone is getting worse. Here's what it means for your health.
Environmental impacts.
Though many living things emit carbon dioxide when they breathe, the gas is widely considered to be a pollutant when associated with cars, planes, power plants, and other human activities that involve the burning of fossil fuels such as gasoline and natural gas. That's because carbon dioxide is the most common of the greenhouse gases, which trap heat in the atmosphere and contribute to climate change. Humans have pumped enough carbon dioxide into the atmosphere over the past 150 years to raise its levels higher than they have been for hundreds of thousands of years .
Other greenhouse gases include methane —which comes from such sources as landfills, the natural gas industry, and gas emitted by livestock —and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which were used in refrigerants and aerosol propellants until they were banned in the late 1980s because of their deteriorating effect on Earth's ozone layer.

Another pollutant associated with climate change is sulfur dioxide, a component of smog. Sulfur dioxide and closely related chemicals are known primarily as a cause of acid rain . But they also reflect light when released in the atmosphere, which keeps sunlight out and creates a cooling effect. Volcanic eruptions can spew massive amounts of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere, sometimes causing cooling that lasts for years. In fact, volcanoes used to be the main source of atmospheric sulfur dioxide; today, people are.
Airborne particles, depending on their chemical makeup, can also have direct effects separate from climate change. They can change or deplete nutrients in soil and waterways, harm forests and crops, and damage cultural icons such as monuments and statues.
What can be done?
Countries around the world are tackling various forms of air pollution. China, for example, is making strides in cleaning up smog-choked skies from years of rapid industrial expansion, partly by closing or canceling coal-fired power plants. In the U.S., California has been a leader in setting emissions standards aimed at improving air quality, especially in places like famously hazy Los Angeles. And a variety of efforts aim to bring cleaner cooking options to places where hazardous cookstoves are prevalent.
In any home, people can safeguard against indoor air pollution by increasing ventilation, testing for radon gas, using air purifiers, running kitchen and bathroom exhaust fans, and avoiding smoking. When working on home projects, look for paint and other products low in volatile organic compounds: organizations such as Green Seal , UL (GREENGUARD) , and the U.S. Green Building Council can help.
To curb global warming, a variety of measures need to be taken , such as adding more renewable energy and replacing gasoline-fueled cars with zero-emissions vehicles such as electric ones. On a larger scale, governments at all levels are making commitments to limit emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. The Paris Agreement , ratified on November 4, 2016, is one effort to combat climate change on a global scale. And the Kigali Amendment seeks to further the progress made by the Montreal Protocol , banning heat-trapping hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) in addition to CFCs.
Related Topics
- AIR POLLUTION
- ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION

The scientific case against gas stoves

Scented candles may be cozy—but are they polluting your home’s air?

What do long flights do to our bodies?

The science of 'superbolts,' the world's strongest lightning strikes

Tonga's volcanic eruption triggered a staggering 2,600 lightning flashes a minute
- Environment
- Paid Content
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Destination Guide
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Air Pollution: Everything You Need to Know
How smog, soot, greenhouse gases, and other top air pollutants are affecting the planet—and your health.

- Share this page block
What is air pollution?
What causes air pollution, effects of air pollution, air pollution in the united states, air pollution and environmental justice, controlling air pollution, how to help reduce air pollution, how to protect your health.
Air pollution refers to the release of pollutants into the air—pollutants that are detrimental to human health and the planet as a whole. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) , each year, indoor and outdoor air pollution is responsible for nearly seven million deaths around the globe. Ninety-nine percent of human beings currently breathe air that exceeds the WHO’s guideline limits for pollutants, with those living in low- and middle-income countries suffering the most. In the United States, the Clean Air Act , established in 1970, authorizes the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to safeguard public health by regulating the emissions of these harmful air pollutants.
“Most air pollution comes from energy use and production,” says John Walke , director of the Clean Air team at NRDC. Driving a car on gasoline, heating a home with oil, running a power plant on fracked gas : In each case, a fossil fuel is burned and harmful chemicals and gases are released into the air.
“We’ve made progress over the last 50 years in improving air quality in the United States, thanks to the Clean Air Act. But climate change will make it harder in the future to meet pollution standards, which are designed to protect health ,” says Walke.
Air pollution is now the world’s fourth-largest risk factor for early death. According to the 2020 State of Global Air report —which summarizes the latest scientific understanding of air pollution around the world—4.5 million deaths were linked to outdoor air pollution exposures in 2019, and another 2.2 million deaths were caused by indoor air pollution. The world’s most populous countries, China and India, continue to bear the highest burdens of disease.
“Despite improvements in reducing global average mortality rates from air pollution, this report also serves as a sobering reminder that the climate crisis threatens to worsen air pollution problems significantly,” explains Vijay Limaye , senior scientist in NRDC’s Science Office. Smog, for instance, is intensified by increased heat, forming when the weather is warmer and there’s more ultraviolet radiation. In addition, climate change increases the production of allergenic air pollutants, including mold (thanks to damp conditions caused by extreme weather and increased flooding) and pollen (due to a longer pollen season). “Climate change–fueled droughts and dry conditions are also setting the stage for dangerous wildfires,” adds Limaye. “ Wildfire smoke can linger for days and pollute the air with particulate matter hundreds of miles downwind.”
The effects of air pollution on the human body vary, depending on the type of pollutant, the length and level of exposure, and other factors, including a person’s individual health risks and the cumulative impacts of multiple pollutants or stressors.
Smog and soot
These are the two most prevalent types of air pollution. Smog (sometimes referred to as ground-level ozone) occurs when emissions from combusting fossil fuels react with sunlight. Soot—a type of particulate matter —is made up of tiny particles of chemicals, soil, smoke, dust, or allergens that are carried in the air. The sources of smog and soot are similar. “Both come from cars and trucks, factories, power plants, incinerators, engines, generally anything that combusts fossil fuels such as coal, gasoline, or natural gas,” Walke says.
Smog can irritate the eyes and throat and also damage the lungs, especially those of children, senior citizens, and people who work or exercise outdoors. It’s even worse for people who have asthma or allergies; these extra pollutants can intensify their symptoms and trigger asthma attacks. The tiniest airborne particles in soot are especially dangerous because they can penetrate the lungs and bloodstream and worsen bronchitis, lead to heart attacks, and even hasten death. In 2020, a report from Harvard’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health showed that COVID-19 mortality rates were higher in areas with more particulate matter pollution than in areas with even slightly less, showing a correlation between the virus’s deadliness and long-term exposure to air pollution.
These findings also illuminate an important environmental justice issue . Because highways and polluting facilities have historically been sited in or next to low-income neighborhoods and communities of color, the negative effects of this pollution have been disproportionately experienced by the people who live in these communities.
Hazardous air pollutants
A number of air pollutants pose severe health risks and can sometimes be fatal, even in small amounts. Almost 200 of them are regulated by law; some of the most common are mercury, lead , dioxins, and benzene. “These are also most often emitted during gas or coal combustion, incineration, or—in the case of benzene—found in gasoline,” Walke says. Benzene, classified as a carcinogen by the EPA, can cause eye, skin, and lung irritation in the short term and blood disorders in the long term. Dioxins, more typically found in food but also present in small amounts in the air, is another carcinogen that can affect the liver in the short term and harm the immune, nervous, and endocrine systems, as well as reproductive functions. Mercury attacks the central nervous system. In large amounts, lead can damage children’s brains and kidneys, and even minimal exposure can affect children’s IQ and ability to learn.
Another category of toxic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), are by-products of traffic exhaust and wildfire smoke. In large amounts, they have been linked to eye and lung irritation, blood and liver issues, and even cancer. In one study , the children of mothers exposed to PAHs during pregnancy showed slower brain-processing speeds and more pronounced symptoms of ADHD.
Greenhouse gases
While these climate pollutants don’t have the direct or immediate impacts on the human body associated with other air pollutants, like smog or hazardous chemicals, they are still harmful to our health. By trapping the earth’s heat in the atmosphere, greenhouse gases lead to warmer temperatures, which in turn lead to the hallmarks of climate change: rising sea levels, more extreme weather, heat-related deaths, and the increased transmission of infectious diseases. In 2021, carbon dioxide accounted for roughly 79 percent of the country’s total greenhouse gas emissions, and methane made up more than 11 percent. “Carbon dioxide comes from combusting fossil fuels, and methane comes from natural and industrial sources, including large amounts that are released during oil and gas drilling,” Walke says. “We emit far larger amounts of carbon dioxide, but methane is significantly more potent, so it’s also very destructive.”
Another class of greenhouse gases, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) , are thousands of times more powerful than carbon dioxide in their ability to trap heat. In October 2016, more than 140 countries signed the Kigali Agreement to reduce the use of these chemicals—which are found in air conditioners and refrigerators—and develop greener alternatives over time. (The United States officially signed onto the Kigali Agreement in 2022.)
Pollen and mold
Mold and allergens from trees, weeds, and grass are also carried in the air, are exacerbated by climate change, and can be hazardous to health. Though they aren’t regulated, they can be considered a form of air pollution. “When homes, schools, or businesses get water damage, mold can grow and produce allergenic airborne pollutants,” says Kim Knowlton, professor of environmental health sciences at Columbia University and a former NRDC scientist. “ Mold exposure can precipitate asthma attacks or an allergic response, and some molds can even produce toxins that would be dangerous for anyone to inhale.”
Pollen allergies are worsening because of climate change . “Lab and field studies are showing that pollen-producing plants—especially ragweed—grow larger and produce more pollen when you increase the amount of carbon dioxide that they grow in,” Knowlton says. “Climate change also extends the pollen production season, and some studies are beginning to suggest that ragweed pollen itself might be becoming a more potent allergen.” If so, more people will suffer runny noses, fevers, itchy eyes, and other symptoms. “And for people with allergies and asthma, pollen peaks can precipitate asthma attacks, which are far more serious and can be life-threatening.”

More than one in three U.S. residents—120 million people—live in counties with unhealthy levels of air pollution, according to the 2023 State of the Air report by the American Lung Association (ALA). Since the annual report was first published, in 2000, its findings have shown how the Clean Air Act has been able to reduce harmful emissions from transportation, power plants, and manufacturing.
Recent findings, however, reflect how climate change–fueled wildfires and extreme heat are adding to the challenges of protecting public health. The latest report—which focuses on ozone, year-round particle pollution, and short-term particle pollution—also finds that people of color are 61 percent more likely than white people to live in a county with a failing grade in at least one of those categories, and three times more likely to live in a county that fails in all three.
In rankings for each of the three pollution categories covered by the ALA report, California cities occupy the top three slots (i.e., were highest in pollution), despite progress that the Golden State has made in reducing air pollution emissions in the past half century. At the other end of the spectrum, these cities consistently rank among the country’s best for air quality: Burlington, Vermont; Honolulu; and Wilmington, North Carolina.
No one wants to live next door to an incinerator, oil refinery, port, toxic waste dump, or other polluting site. Yet millions of people around the world do, and this puts them at a much higher risk for respiratory disease, cardiovascular disease, neurological damage, cancer, and death. In the United States, people of color are 1.5 times more likely than whites to live in areas with poor air quality, according to the ALA.
Historically, racist zoning policies and discriminatory lending practices known as redlining have combined to keep polluting industries and car-choked highways away from white neighborhoods and have turned communities of color—especially low-income and working-class communities of color—into sacrifice zones, where residents are forced to breathe dirty air and suffer the many health problems associated with it. In addition to the increased health risks that come from living in such places, the polluted air can economically harm residents in the form of missed workdays and higher medical costs.
Environmental racism isn't limited to cities and industrial areas. Outdoor laborers, including the estimated three million migrant and seasonal farmworkers in the United States, are among the most vulnerable to air pollution—and they’re also among the least equipped, politically, to pressure employers and lawmakers to affirm their right to breathe clean air.
Recently, cumulative impact mapping , which uses data on environmental conditions and demographics, has been able to show how some communities are overburdened with layers of issues, like high levels of poverty, unemployment, and pollution. Tools like the Environmental Justice Screening Method and the EPA’s EJScreen provide evidence of what many environmental justice communities have been explaining for decades: that we need land use and public health reforms to ensure that vulnerable areas are not overburdened and that the people who need resources the most are receiving them.
In the United States, the Clean Air Act has been a crucial tool for reducing air pollution since its passage in 1970, although fossil fuel interests aided by industry-friendly lawmakers have frequently attempted to weaken its many protections. Ensuring that this bedrock environmental law remains intact and properly enforced will always be key to maintaining and improving our air quality.
But the best, most effective way to control air pollution is to speed up our transition to cleaner fuels and industrial processes. By switching over to renewable energy sources (such as wind and solar power), maximizing fuel efficiency in our vehicles, and replacing more and more of our gasoline-powered cars and trucks with electric versions, we'll be limiting air pollution at its source while also curbing the global warming that heightens so many of its worst health impacts.
And what about the economic costs of controlling air pollution? According to a report on the Clean Air Act commissioned by NRDC, the annual benefits of cleaner air are up to 32 times greater than the cost of clean air regulations. Those benefits include up to 370,000 avoided premature deaths, 189,000 fewer hospital admissions for cardiac and respiratory illnesses, and net economic benefits of up to $3.8 trillion for the U.S. economy every year.
“The less gasoline we burn, the better we’re doing to reduce air pollution and the harmful effects of climate change,” Walke explains. “Make good choices about transportation. When you can, ride a bike, walk, or take public transportation. For driving, choose a car that gets better miles per gallon of gas or buy an electric car .” You can also investigate your power provider options—you may be able to request that your electricity be supplied by wind or solar. Buying your food locally cuts down on the fossil fuels burned in trucking or flying food in from across the world. And most important: “Support leaders who push for clean air and water and responsible steps on climate change,” Walke says.
- “When you see in the news or hear on the weather report that pollution levels are high, it may be useful to limit the time when children go outside or you go for a jog,” Walke says. Generally, ozone levels tend to be lower in the morning.
- If you exercise outside, stay as far as you can from heavily trafficked roads. Then shower and wash your clothes to remove fine particles.
- The air may look clear, but that doesn’t mean it’s pollution free. Utilize tools like the EPA’s air pollution monitor, AirNow , to get the latest conditions. If the air quality is bad, stay inside with the windows closed.
- If you live or work in an area that’s prone to wildfires, stay away from the harmful smoke as much as you’re able. Consider keeping a small stock of masks to wear when conditions are poor. The most ideal masks for smoke particles will be labelled “NIOSH” (which stands for National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) and have either “N95” or “P100” printed on it.
- If you’re using an air conditioner while outdoor pollution conditions are bad, use the recirculating setting to limit the amount of polluted air that gets inside.
This story was originally published on November 1, 2016, and has been updated with new information and links.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
Related Stories

The Particulars of PM 2.5
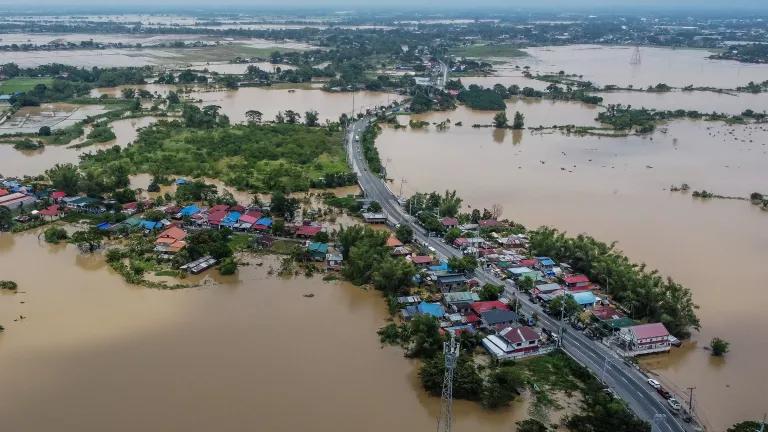

What Are the Effects of Climate Change?
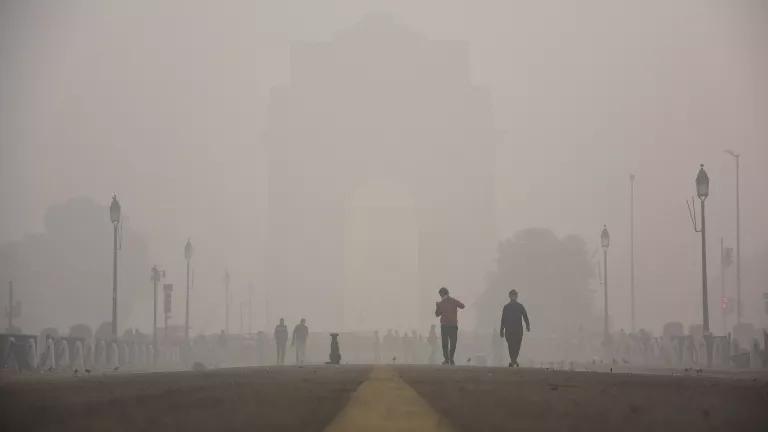

Fossil Fuel Air Pollution Kills One in Five People
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.
What Is Air Pollution? Definition, Types, and Environmental Impact
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/russell-mclendon-bw-d70f143a7ef34ebebf837d66c621dd07.jpg)
- University of Georgia
- Planet Earth
- Climate Crisis
- Recycling & Waste
- Natural Disasters
- Transportation
Air Pollution Definition
How to reduce air pollution.
Air pollution occurs when certain gases, droplets, or particles mix with ambient air, rendering the air harmful to living things. There are many different kinds of air pollution, produced from many sources and resulting in many different problems for people, other animals, plants, and the environment.
Ambient air pollution accounts for an estimated 4.2 million annual deaths globally , according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Air pollutants also lead to environmental problems ranging from acid rain and poor visibility to ozone depletion and global climate change.
Pollutants that can become suspended in air include gases, particulates, and organic molecules. They end up in the air in a variety of ways, including human activities such as burning fossil fuels as well as natural sources like dust, wildfires, and volcanoes.
Both natural and human-induced air pollution can be dangerous, although the latter tends to be more widespread and continuous, like the ongoing combustion of fossil fuels for energy.
In some cases, the distinction is blurring between natural and human-induced air pollution. That’s partly due to carbon dioxide, a natural and vital gas in Earth’s atmosphere that’s also being emitted in unnaturally large amounts by human activities, namely the burning of fossil fuels, resulting in a global greenhouse effect.
That greenhouse effect is now amplifying some natural phenomena like wildfires, resulting in even more air pollution. In addition, people often start wildfires in more direct ways, such as intentionally burning forests for farmland or accidentally sparking dry brush, all of which also create air pollution.
Natural Air Pollution
Aside from wildfires, common natural causes of air pollution include volcanoes, dust storms, methane gas from cattle and other ruminants, and radon gas from underground radium deposits. These tend to be limited to certain locations and time periods, although some can be widespread or chronic.
Ash and sulfur from volcanoes can travel around the planet, for example, and the methane from cattle can be a significant contributor to Earth’s growing greenhouse effect. Radon gas can also become trapped and accumulate in basements and cellars as it seeps up from the ground, posing a long-term health risk to humans.
Human-Induced Air Pollution
Thorsten Nilson / Getty Images
Perhaps the most notorious human-induced source of air pollution is the combustion of fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, and natural gas), which can take many forms and can produce a variety of pollutants. This includes the visible plumes rising from smokestacks at factories and power plants, but also many invisible gases and particulates emanating from countless vehicles, facilities, and other sources all around us.
Types of Air Pollution
Some air pollutants are directly dangerous, while others cause trouble in less obvious ways. Noxious gases like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulfur dioxide (SO2) are among the former group, along with particulate matter (PM) like sulfates, nitrates, carbon, or mineral dust.
A specific type of very small particulate matter (PM 2.5), which is 30 times thinner than the width of a human hair, poses especially grave concerns. There are also polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), a group of organic compounds produced by combustion as well as by some industrial processes. And a broad group of air pollutants known as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are emitted by sources ranging from paints and permanent markers to petroleum fuels.
Other air pollutants are dangerous not necessarily because they harm us when we inhale them, but because of how they interact with other aspects of the environment. Perhaps the most salient example in modern times is carbon dioxide (CO2), the primary greenhouse gas fueling global climate change.
Although carbon dioxide occurs naturally in the air and is vital for life, it’s also a greenhouse gas that traps solar heat in Earth’s atmosphere, and it’s released when people burn fossil fuels for energy. CO2 levels in Earth’s atmosphere are now higher than ever before in human history, and may be at their highest levels since the Pliocene Epoch .
Sources of Air Pollution
There are several ways to classify air pollution beyond natural vs. man-made. There is point-source air pollution, for example, which comes from a single identifiable source, like a factory, farm, or power plant. Nonpoint-source pollution, on the other hand, comes from a more dispersed array of sources that are more difficult to trace individually, like the tailpipes of cars on a highway or charcoal cookstoves spread throughout a community.
Coal Burning
Coal-fired power plants have long been a major source of many types of air pollution. Burning coal to generate electricity is notorious for releasing carbon dioxide, accounting for an estimated 30% of global CO2 emissions.
Coal combustion can also release SO2, NOx, particulates, and heavy metals like mercury, and while some power plants now use special equipment to control some of those emissions, coal remains a leading source of air pollution around the world.
Natural Gas
Natural gas has become a popular substitute for coal in the electricity-generation sector in recent years, largely due to its reputation as a cleaner-burning fossil fuel. It does release less CO2 than coal, although while coal releases about 200 pounds of CO2 per million British thermal units (MMBtu), an equivalent amount of natural gas still releases about 117 pounds of CO2.
Natural gas is mostly methane, itself a potent greenhouse gas, and it’s responsible for methane that escapes into the atmosphere not just when natural gas is burned for energy, but also the “fugitive” methane that escapes during extraction and transportation.
Petroleum Fuels
Petroleum fuels are another source of air pollution, whether they’re burned at industrial facilities or, more commonly, to propel cars, trucks, and other vehicles.
This nonpoint-source pollution from burning gasoline and other petroleum fuels is a major source of air pollution in many cities around the world, releasing a blend of airborne contaminants including carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, VOCs, PAHs, and particulate matter. It plays a key role in the formation of smog, and also adds a substantial amount of CO2 into the atmosphere.
Overall, transportation accounts for 29% of U.S. CO2 emissions and 14% of global CO2 emissions . About 90% of all fuel used for transportation is petroleum-based, mainly gasoline and diesel.
Smog is created by chemical reactions in which nitrogen oxides mix with VOCs in the presence of sunlight to form ozone. Ozone is beneficial high in the atmosphere, where it forms the planet’s protective ozone layer , but it can be dangerous to human health at ground level.
Unlike some types of air pollution, smog is visible; while its exact composition and appearance vary, it often appears as a brownish or orange haze, which often forms in urban areas on sunny days.
While we often think of air pollution as an outdoor problem, many people unwittingly inhale harmful indoor air pollution , too. This often comes from VOCs, which waft up from products such as paint, lacquer, solvents, building materials, and various household cleaners and other chemicals.
Older buildings may contain other kinds of potentially air-polluting building materials, such as those made with asbestos. Some indoor air pollution even comes from naturally occurring sources—in the form of mildew and black mold, for example, or radon gas seeping up from the ground and accumulating in basements, cellars, and other lower levels of buildings.
Effects of Air Pollution
Air pollution can affect humans, other animals, plants, and the broader environment in many ways.
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide emissions may not be directly dangerous to humans, but they represent some of this century’s most important air pollution due to CO2’s influence on climate.
CO2 is known as a greenhouse gas because it traps solar heat within Earth’s atmosphere, fueling the global climate crisis we face today, which entails widespread threats to humans and wildlife.
Concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere are now well above 400 parts per million (ppm), a level unseen since long before our species existed, and international efforts to rein in growing CO2 emissions have made little progress for decades. Methane is a more potent greenhouse gas, but CO2 lingers longer in the atmosphere, potentially trapping heat for centuries.
Particulate Matter
Particulate matter is a broad category of air pollution, including all sorts of tiny solids and liquids suspended in the air, often as a result of combustion. It could come from wildfires, power plants, or vehicle traffic, and those tiny particulates can cause big problems when they’re inhaled, especially the very smallest ones.
Particles less than 10 micrometers wide pose the most risk, according to the EPA , because they’re small enough to become embedded deep in the lungs, and might even reach the bloodstream.
Aside from its potential effects on humans and other animals, particulate matter also leads to broader environmental effects depending on its location. It can affect cloud formation and provide reaction centers for other air pollutants in the upper atmosphere, while reducing visibility and influencing weather in the lower atmosphere.
Particulates often contribute to hazy, low-visibility conditions in urban areas, but because they can be carried long distances by wind, they also hinder views in some wilderness areas, including national parks.
Nitrogen Oxides
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and other nitrogen oxides (NOx) can irritate airways in the human respiratory system, according to the EPA, and aggravate respiratory diseases like asthma. NOx can also react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form nitrate particulates , which may pose additional dangers.
NOx has been known to help generate nitric acid in the atmosphere, too, which ultimately falls as acid rain . After reaching the surface, acidic runoff eventually washes into waterways or wetlands, reducing pH levels and leaching aluminum from soil along the way, potentially harming fish, insects, and other wildlife. Because it contains nitrogen, this runoff can also contribute to the nutrient pollution behind aquatic dead zones.
Acid rain and acid fog also harm some trees and other plants, both by damaging foliage and by removing nutrients from the soil.
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide can similarly irritate airways and make breathing difficult, according to the EPA. SO2 and SOx can react with other compounds in the air to form particulates, thus reducing visibility and potentially posing the various dangers associated with PM pollution.
SO2 and other sulfur oxides can also contribute to the formation of sulfuric acid in the air, and thus acid rain.
Heavy Metals
Heavy metals like mercury and lead can be emitted by burning fossil fuels, often falling to the surface relatively close to their source, although they and other air pollutants may travel farther if they’re emitted from taller smokestacks.
Once airborne mercury descends, it commonly washes into waterways and bioaccumulates in animal tissue as it moves up the food web . That’s why large, predatory fish like tuna and swordfish tend to have higher levels of mercury than smaller fish like sardines and anchovies.
Mercury, lead, cadmium, and some other toxic metals can have serious health effects in humans and other animals.
Volatile Organic Compounds
VOCs include a variety of air pollutants both outdoors and indoors. One example is benzene , a sweet-smelling chemical that can be emitted from many different sources, including tobacco smoke, industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, fuel fumes, wildfires, and volcanic eruptions.
CFCs and HCFCs
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are not toxic to humans, but like CO2, they still pose significant environmental threats. That’s because they contribute to the depletion of Earth’s natural ozone layer —while ground-level ozone is itself an air pollutant, ozone in the upper atmosphere protects us from excess solar radiation.
Once widely used as refrigerants, aerosols, and solvents, CFCs have been largely phased out under the Montreal Protocol , often heralded as a rare success story in pollution control.
Use Less Electricity
Because so much air pollution comes from power plants, one of the simplest ways for anyone to help reduce air pollution is to use less electricity, thus reducing the demand for energy from those power plants.
Governments and large corporations have a far greater ability to make an impact with changes like that compared with most individual people, but every little bit helps.
Transportation is another major contributor to air pollution, including CO2 emissions as well as the particulates and ozone that plague many urban and rural areas.
Fewer vehicles on roads generally means less air pollution, so it’s often in the interest of human and ecological health to adopt public policies that incentivize and support working remotely as well as cleaner modes of travel, from walking and cycling to driving electric vehicles, carpooling, and using public transit.
When you do drive a gasoline-powered vehicle, avoid idling any more than necessary, since this creates additional air pollution without the benefit of propulsion. Keep gasoline engines well-tuned and car tires properly inflated. Consider buying an electric or low-emission vehicle.
Avoid Burning Material
Try to limit the amount of wood or other biomass you burn, whether in a burn pile, fire pit, or fireplace.
Mulch or compost yard waste instead of burning it. Never burn plastic.
Plant More Trees
Aside from taking steps to limit air pollution, you could also help mitigate its effects by planting trees, which sequester CO2 and also filter some other air pollutants with their leaves. Along with cleaner air, you’ll also get to enjoy the many other benefits trees can bring .
Larry West is an award-winning environmental journalist and writer. He won the Edward J. Meeman Award for Environmental Reporting.
- What Does 'Unhealthy Air Quality for Sensitive Groups' Mean?
- How Much Air Pollution Comes From Cars?
- 6 Common Air Pollutants
- Are Fireworks Bad for the Environment?
- What Is Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)?
- What Is Climate Sensitivity? Definition and Examples
- How Do Volcanoes Contribute to Climate Change?
- What Is Biogas? Is It Sustainable?
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Pros and Cons
- What Is Clean Coal Technology? Overview, History, Carbon Emissions
- The Causes and Effects of Smog
- The Harmful Effects of Acid Rain
- What Is Coal Ash and How Dangerous Is It?
- Carbon Dioxide: The No. 1 Greenhouse Gas
- Greenhouse Gas Effect on the Economy and You
- PM2.5 From Fossil Fuels Killing Way More People Than Previously Thought

Air Pollution
Our overview of indoor and outdoor air pollution.
By: Hannah Ritchie and Max Roser
This article was first published in October 2017 and last revised in February 2024.
Air pollution is one of the world's largest health and environmental problems. It develops in two contexts: indoor (household) air pollution and outdoor air pollution.
In this topic page, we look at the aggregate picture of air pollution – both indoor and outdoor. We also have dedicated topic pages that look in more depth at these subjects:
Indoor Air Pollution
Look in detail at the data and research on the health impacts of Indoor Air Pollution, attributed deaths, and its causes across the world
Outdoor Air Pollution
Look in detail at the data and research on exposure to Outdoor Air Pollution, its health impacts, and attributed deaths across the world
Look in detail at the data and research on energy consumption, its impacts around the world today, and how this has changed over time
See all interactive charts on Air Pollution ↓
Other research and writing on air pollution on Our World in Data:
- Air pollution: does it get worse before it gets better?
- Data Review: How many people die from air pollution?
- Energy poverty and indoor air pollution: a problem as old as humanity that we can end within our lifetime
- How many people do not have access to clean fuels for cooking?
- What are the safest and cleanest sources of energy?
- What the history of London’s air pollution can tell us about the future of today’s growing megacities
- When will countries phase out coal power?
Air pollution is one of the world's leading risk factors for death
Air pollution is responsible for millions of deaths each year.
Air pollution – the combination of outdoor and indoor particulate matter and ozone – is a risk factor for many of the leading causes of death, including heart disease, stroke, lower respiratory infections, lung cancer, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), in its Global Burden of Disease study, provides estimates of the number of deaths attributed to the range of risk factors for disease. 1
In the visualization, we see the number of deaths per year attributed to each risk factor. This chart shows the global total but can be explored for any country or region using the "change country" toggle.
Air pollution is one of the leading risk factors for death. In low-income countries, it is often very near the top of the list (or is the leading risk factor).
Air pollution contributes to one in ten deaths globally
In recent years, air pollution has contributed to one in ten deaths globally. 2
In the map shown here, we see the share of deaths attributed to air pollution across the world.
Air pollution is one of the leading risk factors for disease burden
Air pollution is one of the leading risk factors for death. But its impacts go even further; it is also one of the main contributors to the global disease burden.
Global disease burden takes into account not only years of life lost to early death but also the number of years lived in poor health.
In the visualization, we see risk factors ranked in order of DALYs – disability-adjusted life years – the metric used to assess disease burden. Again, air pollution is near the top of the list, making it one of the leading risk factors for poor health across the world.
Air pollution not only takes years from people's lives but also has a large effect on the quality of life while they're still living.
Who is most affected by air pollution?
Death rates from air pollution are highest in low-to-middle-income countries.
Air pollution is a health and environmental issue across all countries of the world but with large differences in severity.
In the interactive map, we show death rates from air pollution across the world, measured as the number of deaths per 100,000 people in a given country or region.
The burden of air pollution tends to be greater across both low and middle-income countries for two reasons: indoor pollution rates tend to be high in low-income countries due to a reliance on solid fuels for cooking, and outdoor air pollution tends to increase as countries industrialize and shift from low to middle incomes.
A map of the number of deaths from air pollution by country can be found here .
How are death rates from air pollution changing?
Death rates from air pollution are falling – mainly due to improvements in indoor pollution.
In the visualization, we show global death rates from air pollution over time – shown as the total air pollution – in addition to the individual contributions from outdoor and indoor pollution.
Globally, we see that in recent decades, the death rates from total air pollution have declined: since 1990, death rates have nearly halved. But, as we see from the breakdown, this decline has been primarily driven by improvements in indoor air pollution.
Death rates from indoor air pollution have seen an impressive decline, while improvements in outdoor pollution have been much more modest.
You can explore this data for any country or region using the "change country" toggle on the interactive chart.
Interactive charts on air pollution
Murray, C. J., Aravkin, A. Y., Zheng, P., Abbafati, C., Abbas, K. M., Abbasi-Kangevari, M., ... & Borzouei, S. (2020). Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 . The Lancet , 396 (10258), 1223-1249.
Here, we use the term 'contributes,' meaning it was one of the attributed risk factors for a given disease or cause of death. There can be multiple risk factors for a given disease that can amplify one another. This means that in some cases, air pollution was not the only risk factor but one of several.
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this topic page, please also cite the underlying data sources. This topic page can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
REVIEW article
Environmental and health impacts of air pollution: a review.

- 1 Delphis S.A., Kifisia, Greece
- 2 Laboratory of Hygiene and Environmental Protection, Faculty of Medicine, Democritus University of Thrace, Alexandroupolis, Greece
- 3 Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois (CHUV), Service de Médicine Interne, Lausanne, Switzerland
- 4 School of Social and Political Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom
One of our era's greatest scourges is air pollution, on account not only of its impact on climate change but also its impact on public and individual health due to increasing morbidity and mortality. There are many pollutants that are major factors in disease in humans. Among them, Particulate Matter (PM), particles of variable but very small diameter, penetrate the respiratory system via inhalation, causing respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, reproductive and central nervous system dysfunctions, and cancer. Despite the fact that ozone in the stratosphere plays a protective role against ultraviolet irradiation, it is harmful when in high concentration at ground level, also affecting the respiratory and cardiovascular system. Furthermore, nitrogen oxide, sulfur dioxide, Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), dioxins, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are all considered air pollutants that are harmful to humans. Carbon monoxide can even provoke direct poisoning when breathed in at high levels. Heavy metals such as lead, when absorbed into the human body, can lead to direct poisoning or chronic intoxication, depending on exposure. Diseases occurring from the aforementioned substances include principally respiratory problems such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), asthma, bronchiolitis, and also lung cancer, cardiovascular events, central nervous system dysfunctions, and cutaneous diseases. Last but not least, climate change resulting from environmental pollution affects the geographical distribution of many infectious diseases, as do natural disasters. The only way to tackle this problem is through public awareness coupled with a multidisciplinary approach by scientific experts; national and international organizations must address the emergence of this threat and propose sustainable solutions.
Approach to the Problem
The interactions between humans and their physical surroundings have been extensively studied, as multiple human activities influence the environment. The environment is a coupling of the biotic (living organisms and microorganisms) and the abiotic (hydrosphere, lithosphere, and atmosphere).
Pollution is defined as the introduction into the environment of substances harmful to humans and other living organisms. Pollutants are harmful solids, liquids, or gases produced in higher than usual concentrations that reduce the quality of our environment.
Human activities have an adverse effect on the environment by polluting the water we drink, the air we breathe, and the soil in which plants grow. Although the industrial revolution was a great success in terms of technology, society, and the provision of multiple services, it also introduced the production of huge quantities of pollutants emitted into the air that are harmful to human health. Without any doubt, the global environmental pollution is considered an international public health issue with multiple facets. Social, economic, and legislative concerns and lifestyle habits are related to this major problem. Clearly, urbanization and industrialization are reaching unprecedented and upsetting proportions worldwide in our era. Anthropogenic air pollution is one of the biggest public health hazards worldwide, given that it accounts for about 9 million deaths per year ( 1 ).
Without a doubt, all of the aforementioned are closely associated with climate change, and in the event of danger, the consequences can be severe for mankind ( 2 ). Climate changes and the effects of global planetary warming seriously affect multiple ecosystems, causing problems such as food safety issues, ice and iceberg melting, animal extinction, and damage to plants ( 3 , 4 ).
Air pollution has various health effects. The health of susceptible and sensitive individuals can be impacted even on low air pollution days. Short-term exposure to air pollutants is closely related to COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, asthma, respiratory disease, and high rates of hospitalization (a measurement of morbidity).
The long-term effects associated with air pollution are chronic asthma, pulmonary insufficiency, cardiovascular diseases, and cardiovascular mortality. According to a Swedish cohort study, diabetes seems to be induced after long-term air pollution exposure ( 5 ). Moreover, air pollution seems to have various malign health effects in early human life, such as respiratory, cardiovascular, mental, and perinatal disorders ( 3 ), leading to infant mortality or chronic disease in adult age ( 6 ).
National reports have mentioned the increased risk of morbidity and mortality ( 1 ). These studies were conducted in many places around the world and show a correlation between daily ranges of particulate matter (PM) concentration and daily mortality. Climate shifts and global planetary warming ( 3 ) could aggravate the situation. Besides, increased hospitalization (an index of morbidity) has been registered among the elderly and susceptible individuals for specific reasons. Fine and ultrafine particulate matter seems to be associated with more serious illnesses ( 6 ), as it can invade the deepest parts of the airways and more easily reach the bloodstream.
Air pollution mainly affects those living in large urban areas, where road emissions contribute the most to the degradation of air quality. There is also a danger of industrial accidents, where the spread of a toxic fog can be fatal to the populations of the surrounding areas. The dispersion of pollutants is determined by many parameters, most notably atmospheric stability and wind ( 6 ).
In developing countries ( 7 ), the problem is more serious due to overpopulation and uncontrolled urbanization along with the development of industrialization. This leads to poor air quality, especially in countries with social disparities and a lack of information on sustainable management of the environment. The use of fuels such as wood fuel or solid fuel for domestic needs due to low incomes exposes people to bad-quality, polluted air at home. It is of note that three billion people around the world are using the above sources of energy for their daily heating and cooking needs ( 8 ). In developing countries, the women of the household seem to carry the highest risk for disease development due to their longer duration exposure to the indoor air pollution ( 8 , 9 ). Due to its fast industrial development and overpopulation, China is one of the Asian countries confronting serious air pollution problems ( 10 , 11 ). The lung cancer mortality observed in China is associated with fine particles ( 12 ). As stated already, long-term exposure is associated with deleterious effects on the cardiovascular system ( 3 , 5 ). However, it is interesting to note that cardiovascular diseases have mostly been observed in developed and high-income countries rather than in the developing low-income countries exposed highly to air pollution ( 13 ). Extreme air pollution is recorded in India, where the air quality reaches hazardous levels. New Delhi is one of the more polluted cities in India. Flights in and out of New Delhi International Airport are often canceled due to the reduced visibility associated with air pollution. Pollution is occurring both in urban and rural areas in India due to the fast industrialization, urbanization, and rise in use of motorcycle transportation. Nevertheless, biomass combustion associated with heating and cooking needs and practices is a major source of household air pollution in India and in Nepal ( 14 , 15 ). There is spatial heterogeneity in India, as areas with diverse climatological conditions and population and education levels generate different indoor air qualities, with higher PM 2.5 observed in North Indian states (557–601 μg/m 3 ) compared to the Southern States (183–214 μg/m 3 ) ( 16 , 17 ). The cold climate of the North Indian areas may be the main reason for this, as longer periods at home and more heating are necessary compared to in the tropical climate of Southern India. Household air pollution in India is associated with major health effects, especially in women and young children, who stay indoors for longer periods. Chronic obstructive respiratory disease (CORD) and lung cancer are mostly observed in women, while acute lower respiratory disease is seen in young children under 5 years of age ( 18 ).
Accumulation of air pollution, especially sulfur dioxide and smoke, reaching 1,500 mg/m3, resulted in an increase in the number of deaths (4,000 deaths) in December 1952 in London and in 1963 in New York City (400 deaths) ( 19 ). An association of pollution with mortality was reported on the basis of monitoring of outdoor pollution in six US metropolitan cities ( 20 ). In every case, it seems that mortality was closely related to the levels of fine, inhalable, and sulfate particles more than with the levels of total particulate pollution, aerosol acidity, sulfur dioxide, or nitrogen dioxide ( 20 ).
Furthermore, extremely high levels of pollution are reported in Mexico City and Rio de Janeiro, followed by Milan, Ankara, Melbourne, Tokyo, and Moscow ( 19 ).
Based on the magnitude of the public health impact, it is certain that different kinds of interventions should be taken into account. Success and effectiveness in controlling air pollution, specifically at the local level, have been reported. Adequate technological means are applied considering the source and the nature of the emission as well as its impact on health and the environment. The importance of point sources and non-point sources of air pollution control is reported by Schwela and Köth-Jahr ( 21 ). Without a doubt, a detailed emission inventory must record all sources in a given area. Beyond considering the above sources and their nature, topography and meteorology should also be considered, as stated previously. Assessment of the control policies and methods is often extrapolated from the local to the regional and then to the global scale. Air pollution may be dispersed and transported from one region to another area located far away. Air pollution management means the reduction to acceptable levels or possible elimination of air pollutants whose presence in the air affects our health or the environmental ecosystem. Private and governmental entities and authorities implement actions to ensure the air quality ( 22 ). Air quality standards and guidelines were adopted for the different pollutants by the WHO and EPA as a tool for the management of air quality ( 1 , 23 ). These standards have to be compared to the emissions inventory standards by causal analysis and dispersion modeling in order to reveal the problematic areas ( 24 ). Inventories are generally based on a combination of direct measurements and emissions modeling ( 24 ).
As an example, we state here the control measures at the source through the use of catalytic converters in cars. These are devices that turn the pollutants and toxic gases produced from combustion engines into less-toxic pollutants by catalysis through redox reactions ( 25 ). In Greece, the use of private cars was restricted by tracking their license plates in order to reduce traffic congestion during rush hour ( 25 ).
Concerning industrial emissions, collectors and closed systems can keep the air pollution to the minimal standards imposed by legislation ( 26 ).
Current strategies to improve air quality require an estimation of the economic value of the benefits gained from proposed programs. These proposed programs by public authorities, and directives are issued with guidelines to be respected.
In Europe, air quality limit values AQLVs (Air Quality Limit Values) are issued for setting off planning claims ( 27 ). In the USA, the NAAQS (National Ambient Air Quality Standards) establish the national air quality limit values ( 27 ). While both standards and directives are based on different mechanisms, significant success has been achieved in the reduction of overall emissions and associated health and environmental effects ( 27 ). The European Directive identifies geographical areas of risk exposure as monitoring/assessment zones to record the emission sources and levels of air pollution ( 27 ), whereas the USA establishes global geographical air quality criteria according to the severity of their air quality problem and records all sources of the pollutants and their precursors ( 27 ).
In this vein, funds have been financing, directly or indirectly, projects related to air quality along with the technical infrastructure to maintain good air quality. These plans focus on an inventory of databases from air quality environmental planning awareness campaigns. Moreover, pollution measures of air emissions may be taken for vehicles, machines, and industries in urban areas.
Technological innovation can only be successful if it is able to meet the needs of society. In this sense, technology must reflect the decision-making practices and procedures of those involved in risk assessment and evaluation and act as a facilitator in providing information and assessments to enable decision makers to make the best decisions possible. Summarizing the aforementioned in order to design an effective air quality control strategy, several aspects must be considered: environmental factors and ambient air quality conditions, engineering factors and air pollutant characteristics, and finally, economic operating costs for technological improvement and administrative and legal costs. Considering the economic factor, competitiveness through neoliberal concepts is offering a solution to environmental problems ( 22 ).
The development of environmental governance, along with technological progress, has initiated the deployment of a dialogue. Environmental politics has created objections and points of opposition between different political parties, scientists, media, and governmental and non-governmental organizations ( 22 ). Radical environmental activism actions and movements have been created ( 22 ). The rise of the new information and communication technologies (ICTs) are many times examined as to whether and in which way they have influenced means of communication and social movements such as activism ( 28 ). Since the 1990s, the term “digital activism” has been used increasingly and in many different disciplines ( 29 ). Nowadays, multiple digital technologies can be used to produce a digital activism outcome on environmental issues. More specifically, devices with online capabilities such as computers or mobile phones are being used as a way to pursue change in political and social affairs ( 30 ).
In the present paper, we focus on the sources of environmental pollution in relation to public health and propose some solutions and interventions that may be of interest to environmental legislators and decision makers.
Sources of Exposure
It is known that the majority of environmental pollutants are emitted through large-scale human activities such as the use of industrial machinery, power-producing stations, combustion engines, and cars. Because these activities are performed at such a large scale, they are by far the major contributors to air pollution, with cars estimated to be responsible for approximately 80% of today's pollution ( 31 ). Some other human activities are also influencing our environment to a lesser extent, such as field cultivation techniques, gas stations, fuel tanks heaters, and cleaning procedures ( 32 ), as well as several natural sources, such as volcanic and soil eruptions and forest fires.
The classification of air pollutants is based mainly on the sources producing pollution. Therefore, it is worth mentioning the four main sources, following the classification system: Major sources, Area sources, Mobile sources, and Natural sources.
Major sources include the emission of pollutants from power stations, refineries, and petrochemicals, the chemical and fertilizer industries, metallurgical and other industrial plants, and, finally, municipal incineration.
Indoor area sources include domestic cleaning activities, dry cleaners, printing shops, and petrol stations.
Mobile sources include automobiles, cars, railways, airways, and other types of vehicles.
Finally, natural sources include, as stated previously, physical disasters ( 33 ) such as forest fire, volcanic erosion, dust storms, and agricultural burning.
However, many classification systems have been proposed. Another type of classification is a grouping according to the recipient of the pollution, as follows:
Air pollution is determined as the presence of pollutants in the air in large quantities for long periods. Air pollutants are dispersed particles, hydrocarbons, CO, CO 2 , NO, NO 2 , SO 3 , etc.
Water pollution is organic and inorganic charge and biological charge ( 10 ) at high levels that affect the water quality ( 34 , 35 ).
Soil pollution occurs through the release of chemicals or the disposal of wastes, such as heavy metals, hydrocarbons, and pesticides.
Air pollution can influence the quality of soil and water bodies by polluting precipitation, falling into water and soil environments ( 34 , 36 ). Notably, the chemistry of the soil can be amended due to acid precipitation by affecting plants, cultures, and water quality ( 37 ). Moreover, movement of heavy metals is favored by soil acidity, and metals are so then moving into the watery environment. It is known that heavy metals such as aluminum are noxious to wildlife and fishes. Soil quality seems to be of importance, as soils with low calcium carbonate levels are at increased jeopardy from acid rain. Over and above rain, snow and particulate matter drip into watery ' bodies ( 36 , 38 ).
Lastly, pollution is classified following type of origin:
Radioactive and nuclear pollution , releasing radioactive and nuclear pollutants into water, air, and soil during nuclear explosions and accidents, from nuclear weapons, and through handling or disposal of radioactive sewage.
Radioactive materials can contaminate surface water bodies and, being noxious to the environment, plants, animals, and humans. It is known that several radioactive substances such as radium and uranium concentrate in the bones and can cause cancers ( 38 , 39 ).
Noise pollution is produced by machines, vehicles, traffic noises, and musical installations that are harmful to our hearing.
The World Health Organization introduced the term DALYs. The DALYs for a disease or health condition is defined as the sum of the Years of Life Lost (YLL) due to premature mortality in the population and the Years Lost due to Disability (YLD) for people living with the health condition or its consequences ( 39 ). In Europe, air pollution is the main cause of disability-adjusted life years lost (DALYs), followed by noise pollution. The potential relationships of noise and air pollution with health have been studied ( 40 ). The study found that DALYs related to noise were more important than those related to air pollution, as the effects of environmental noise on cardiovascular disease were independent of air pollution ( 40 ). Environmental noise should be counted as an independent public health risk ( 40 ).
Environmental pollution occurs when changes in the physical, chemical, or biological constituents of the environment (air masses, temperature, climate, etc.) are produced.
Pollutants harm our environment either by increasing levels above normal or by introducing harmful toxic substances. Primary pollutants are directly produced from the above sources, and secondary pollutants are emitted as by-products of the primary ones. Pollutants can be biodegradable or non-biodegradable and of natural origin or anthropogenic, as stated previously. Moreover, their origin can be a unique source (point-source) or dispersed sources.
Pollutants have differences in physical and chemical properties, explaining the discrepancy in their capacity for producing toxic effects. As an example, we state here that aerosol compounds ( 41 – 43 ) have a greater toxicity than gaseous compounds due to their tiny size (solid or liquid) in the atmosphere; they have a greater penetration capacity. Gaseous compounds are eliminated more easily by our respiratory system ( 41 ). These particles are able to damage lungs and can even enter the bloodstream ( 41 ), leading to the premature deaths of millions of people yearly. Moreover, the aerosol acidity ([H+]) seems to considerably enhance the production of secondary organic aerosols (SOA), but this last aspect is not supported by other scientific teams ( 38 ).
Climate and Pollution
Air pollution and climate change are closely related. Climate is the other side of the same coin that reduces the quality of our Earth ( 44 ). Pollutants such as black carbon, methane, tropospheric ozone, and aerosols affect the amount of incoming sunlight. As a result, the temperature of the Earth is increasing, resulting in the melting of ice, icebergs, and glaciers.
In this vein, climatic changes will affect the incidence and prevalence of both residual and imported infections in Europe. Climate and weather affect the duration, timing, and intensity of outbreaks strongly and change the map of infectious diseases in the globe ( 45 ). Mosquito-transmitted parasitic or viral diseases are extremely climate-sensitive, as warming firstly shortens the pathogen incubation period and secondly shifts the geographic map of the vector. Similarly, water-warming following climate changes leads to a high incidence of waterborne infections. Recently, in Europe, eradicated diseases seem to be emerging due to the migration of population, for example, cholera, poliomyelitis, tick-borne encephalitis, and malaria ( 46 ).
The spread of epidemics is associated with natural climate disasters and storms, which seem to occur more frequently nowadays ( 47 ). Malnutrition and disequilibration of the immune system are also associated with the emerging infections affecting public health ( 48 ).
The Chikungunya virus “took the airplane” from the Indian Ocean to Europe, as outbreaks of the disease were registered in Italy ( 49 ) as well as autochthonous cases in France ( 50 ).
An increase in cryptosporidiosis in the United Kingdom and in the Czech Republic seems to have occurred following flooding ( 36 , 51 ).
As stated previously, aerosols compounds are tiny in size and considerably affect the climate. They are able to dissipate sunlight (the albedo phenomenon) by dispersing a quarter of the sun's rays back to space and have cooled the global temperature over the last 30 years ( 52 ).
Air Pollutants
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports on six major air pollutants, namely particle pollution, ground-level ozone, carbon monoxide, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and lead. Air pollution can have a disastrous effect on all components of the environment, including groundwater, soil, and air. Additionally, it poses a serious threat to living organisms. In this vein, our interest is mainly to focus on these pollutants, as they are related to more extensive and severe problems in human health and environmental impact. Acid rain, global warming, the greenhouse effect, and climate changes have an important ecological impact on air pollution ( 53 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) and Health
Studies have shown a relationship between particulate matter (PM) and adverse health effects, focusing on either short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic) PM exposure.
Particulate matter (PM) is usually formed in the atmosphere as a result of chemical reactions between the different pollutants. The penetration of particles is closely dependent on their size ( 53 ). Particulate Matter (PM) was defined as a term for particles by the United States Environmental Protection Agency ( 54 ). Particulate matter (PM) pollution includes particles with diameters of 10 micrometers (μm) or smaller, called PM 10 , and extremely fine particles with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers (μm) and smaller.
Particulate matter contains tiny liquid or solid droplets that can be inhaled and cause serious health effects ( 55 ). Particles <10 μm in diameter (PM 10 ) after inhalation can invade the lungs and even reach the bloodstream. Fine particles, PM 2.5 , pose a greater risk to health ( 6 , 56 ) ( Table 1 ).

Table 1 . Penetrability according to particle size.
Multiple epidemiological studies have been performed on the health effects of PM. A positive relation was shown between both short-term and long-term exposures of PM 2.5 and acute nasopharyngitis ( 56 ). In addition, long-term exposure to PM for years was found to be related to cardiovascular diseases and infant mortality.
Those studies depend on PM 2.5 monitors and are restricted in terms of study area or city area due to a lack of spatially resolved daily PM 2.5 concentration data and, in this way, are not representative of the entire population. Following a recent epidemiological study by the Department of Environmental Health at Harvard School of Public Health (Boston, MA) ( 57 ), it was reported that, as PM 2.5 concentrations vary spatially, an exposure error (Berkson error) seems to be produced, and the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects are not yet completely elucidated. The team developed a PM 2.5 exposure model based on remote sensing data for assessing short- and long-term human exposures ( 57 ). This model permits spatial resolution in short-term effects plus the assessment of long-term effects in the whole population.
Moreover, respiratory diseases and affection of the immune system are registered as long-term chronic effects ( 58 ). It is worth noting that people with asthma, pneumonia, diabetes, and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases are especially susceptible and vulnerable to the effects of PM. PM 2.5 , followed by PM 10 , are strongly associated with diverse respiratory system diseases ( 59 ), as their size permits them to pierce interior spaces ( 60 ). The particles produce toxic effects according to their chemical and physical properties. The components of PM 10 and PM 2.5 can be organic (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, dioxins, benzene, 1-3 butadiene) or inorganic (carbon, chlorides, nitrates, sulfates, metals) in nature ( 55 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) is divided into four main categories according to type and size ( 61 ) ( Table 2 ).
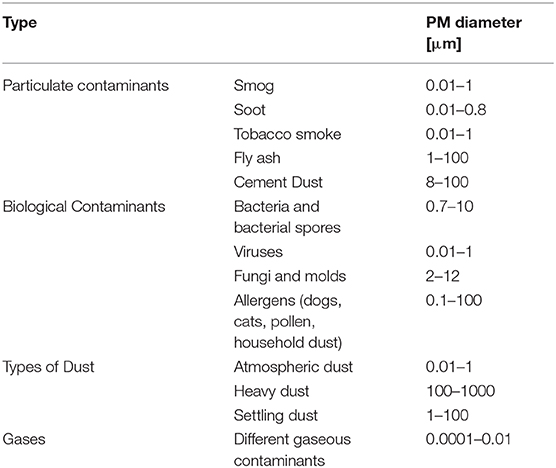
Table 2 . Types and sizes of particulate Matter (PM).
Gas contaminants include PM in aerial masses.
Particulate contaminants include contaminants such as smog, soot, tobacco smoke, oil smoke, fly ash, and cement dust.
Biological Contaminants are microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, mold, and bacterial spores), cat allergens, house dust and allergens, and pollen.
Types of Dust include suspended atmospheric dust, settling dust, and heavy dust.
Finally, another fact is that the half-lives of PM 10 and PM 2.5 particles in the atmosphere is extended due to their tiny dimensions; this permits their long-lasting suspension in the atmosphere and even their transfer and spread to distant destinations where people and the environment may be exposed to the same magnitude of pollution ( 53 ). They are able to change the nutrient balance in watery ecosystems, damage forests and crops, and acidify water bodies.
As stated, PM 2.5 , due to their tiny size, are causing more serious health effects. These aforementioned fine particles are the main cause of the “haze” formation in different metropolitan areas ( 12 , 13 , 61 ).
Ozone Impact in the Atmosphere
Ozone (O 3 ) is a gas formed from oxygen under high voltage electric discharge ( 62 ). It is a strong oxidant, 52% stronger than chlorine. It arises in the stratosphere, but it could also arise following chain reactions of photochemical smog in the troposphere ( 63 ).
Ozone can travel to distant areas from its initial source, moving with air masses ( 64 ). It is surprising that ozone levels over cities are low in contrast to the increased amounts occuring in urban areas, which could become harmful for cultures, forests, and vegetation ( 65 ) as it is reducing carbon assimilation ( 66 ). Ozone reduces growth and yield ( 47 , 48 ) and affects the plant microflora due to its antimicrobial capacity ( 67 , 68 ). In this regard, ozone acts upon other natural ecosystems, with microflora ( 69 , 70 ) and animal species changing their species composition ( 71 ). Ozone increases DNA damage in epidermal keratinocytes and leads to impaired cellular function ( 72 ).
Ground-level ozone (GLO) is generated through a chemical reaction between oxides of nitrogen and VOCs emitted from natural sources and/or following anthropogenic activities.
Ozone uptake usually occurs by inhalation. Ozone affects the upper layers of the skin and the tear ducts ( 73 ). A study of short-term exposure of mice to high levels of ozone showed malondialdehyde formation in the upper skin (epidermis) but also depletion in vitamins C and E. It is likely that ozone levels are not interfering with the skin barrier function and integrity to predispose to skin disease ( 74 ).
Due to the low water-solubility of ozone, inhaled ozone has the capacity to penetrate deeply into the lungs ( 75 ).
Toxic effects induced by ozone are registered in urban areas all over the world, causing biochemical, morphologic, functional, and immunological disorders ( 76 ).
The European project (APHEA2) focuses on the acute effects of ambient ozone concentrations on mortality ( 77 ). Daily ozone concentrations compared to the daily number of deaths were reported from different European cities for a 3-year period. During the warm period of the year, an observed increase in ozone concentration was associated with an increase in the daily number of deaths (0.33%), in the number of respiratory deaths (1.13%), and in the number of cardiovascular deaths (0.45%). No effect was observed during wintertime.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is produced by fossil fuel when combustion is incomplete. The symptoms of poisoning due to inhaling carbon monoxide include headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, and, finally, loss of consciousness.
The affinity of carbon monoxide to hemoglobin is much greater than that of oxygen. In this vein, serious poisoning may occur in people exposed to high levels of carbon monoxide for a long period of time. Due to the loss of oxygen as a result of the competitive binding of carbon monoxide, hypoxia, ischemia, and cardiovascular disease are observed.
Carbon monoxide affects the greenhouses gases that are tightly connected to global warming and climate. This should lead to an increase in soil and water temperatures, and extreme weather conditions or storms may occur ( 68 ).
However, in laboratory and field experiments, it has been seen to produce increased plant growth ( 78 ).
Nitrogen Oxide (NO 2 )
Nitrogen oxide is a traffic-related pollutant, as it is emitted from automobile motor engines ( 79 , 80 ). It is an irritant of the respiratory system as it penetrates deep in the lung, inducing respiratory diseases, coughing, wheezing, dyspnea, bronchospasm, and even pulmonary edema when inhaled at high levels. It seems that concentrations over 0.2 ppm produce these adverse effects in humans, while concentrations higher than 2.0 ppm affect T-lymphocytes, particularly the CD8+ cells and NK cells that produce our immune response ( 81 ).It is reported that long-term exposure to high levels of nitrogen dioxide can be responsible for chronic lung disease. Long-term exposure to NO 2 can impair the sense of smell ( 81 ).
However, systems other than respiratory ones can be involved, as symptoms such as eye, throat, and nose irritation have been registered ( 81 ).
High levels of nitrogen dioxide are deleterious to crops and vegetation, as they have been observed to reduce crop yield and plant growth efficiency. Moreover, NO 2 can reduce visibility and discolor fabrics ( 81 ).
Sulfur Dioxide (SO 2 )
Sulfur dioxide is a harmful gas that is emitted mainly from fossil fuel consumption or industrial activities. The annual standard for SO 2 is 0.03 ppm ( 82 ). It affects human, animal, and plant life. Susceptible people as those with lung disease, old people, and children, who present a higher risk of damage. The major health problems associated with sulfur dioxide emissions in industrialized areas are respiratory irritation, bronchitis, mucus production, and bronchospasm, as it is a sensory irritant and penetrates deep into the lung converted into bisulfite and interacting with sensory receptors, causing bronchoconstriction. Moreover, skin redness, damage to the eyes (lacrimation and corneal opacity) and mucous membranes, and worsening of pre-existing cardiovascular disease have been observed ( 81 ).
Environmental adverse effects, such as acidification of soil and acid rain, seem to be associated with sulfur dioxide emissions ( 83 ).
Lead is a heavy metal used in different industrial plants and emitted from some petrol motor engines, batteries, radiators, waste incinerators, and waste waters ( 84 ).
Moreover, major sources of lead pollution in the air are metals, ore, and piston-engine aircraft. Lead poisoning is a threat to public health due to its deleterious effects upon humans, animals, and the environment, especially in the developing countries.
Exposure to lead can occur through inhalation, ingestion, and dermal absorption. Trans- placental transport of lead was also reported, as lead passes through the placenta unencumbered ( 85 ). The younger the fetus is, the more harmful the toxic effects. Lead toxicity affects the fetal nervous system; edema or swelling of the brain is observed ( 86 ). Lead, when inhaled, accumulates in the blood, soft tissue, liver, lung, bones, and cardiovascular, nervous, and reproductive systems. Moreover, loss of concentration and memory, as well as muscle and joint pain, were observed in adults ( 85 , 86 ).
Children and newborns ( 87 ) are extremely susceptible even to minimal doses of lead, as it is a neurotoxicant and causes learning disabilities, impairment of memory, hyperactivity, and even mental retardation.
Elevated amounts of lead in the environment are harmful to plants and crop growth. Neurological effects are observed in vertebrates and animals in association with high lead levels ( 88 ).
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(PAHs)
The distribution of PAHs is ubiquitous in the environment, as the atmosphere is the most important means of their dispersal. They are found in coal and in tar sediments. Moreover, they are generated through incomplete combustion of organic matter as in the cases of forest fires, incineration, and engines ( 89 ). PAH compounds, such as benzopyrene, acenaphthylene, anthracene, and fluoranthene are recognized as toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic substances. They are an important risk factor for lung cancer ( 89 ).
Volatile Organic Compounds(VOCs)
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), such as toluene, benzene, ethylbenzene, and xylene ( 90 ), have been found to be associated with cancer in humans ( 91 ). The use of new products and materials has actually resulted in increased concentrations of VOCs. VOCs pollute indoor air ( 90 ) and may have adverse effects on human health ( 91 ). Short-term and long-term adverse effects on human health are observed. VOCs are responsible for indoor air smells. Short-term exposure is found to cause irritation of eyes, nose, throat, and mucosal membranes, while those of long duration exposure include toxic reactions ( 92 ). Predictable assessment of the toxic effects of complex VOC mixtures is difficult to estimate, as these pollutants can have synergic, antagonistic, or indifferent effects ( 91 , 93 ).
Dioxins originate from industrial processes but also come from natural processes, such as forest fires and volcanic eruptions. They accumulate in foods such as meat and dairy products, fish and shellfish, and especially in the fatty tissue of animals ( 94 ).
Short-period exhibition to high dioxin concentrations may result in dark spots and lesions on the skin ( 94 ). Long-term exposure to dioxins can cause developmental problems, impairment of the immune, endocrine and nervous systems, reproductive infertility, and cancer ( 94 ).
Without any doubt, fossil fuel consumption is responsible for a sizeable part of air contamination. This contamination may be anthropogenic, as in agricultural and industrial processes or transportation, while contamination from natural sources is also possible. Interestingly, it is of note that the air quality standards established through the European Air Quality Directive are somewhat looser than the WHO guidelines, which are stricter ( 95 ).
Effect of Air Pollution on Health
The most common air pollutants are ground-level ozone and Particulates Matter (PM). Air pollution is distinguished into two main types:
Outdoor pollution is the ambient air pollution.
Indoor pollution is the pollution generated by household combustion of fuels.
People exposed to high concentrations of air pollutants experience disease symptoms and states of greater and lesser seriousness. These effects are grouped into short- and long-term effects affecting health.
Susceptible populations that need to be aware of health protection measures include old people, children, and people with diabetes and predisposing heart or lung disease, especially asthma.
As extensively stated previously, according to a recent epidemiological study from Harvard School of Public Health, the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects have not been completely clarified ( 57 ) due to the different epidemiological methodologies and to the exposure errors. New models are proposed for assessing short- and long-term human exposure data more successfully ( 57 ). Thus, in the present section, we report the more common short- and long-term health effects but also general concerns for both types of effects, as these effects are often dependent on environmental conditions, dose, and individual susceptibility.
Short-term effects are temporary and range from simple discomfort, such as irritation of the eyes, nose, skin, throat, wheezing, coughing and chest tightness, and breathing difficulties, to more serious states, such as asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis, and lung and heart problems. Short-term exposure to air pollution can also cause headaches, nausea, and dizziness.
These problems can be aggravated by extended long-term exposure to the pollutants, which is harmful to the neurological, reproductive, and respiratory systems and causes cancer and even, rarely, deaths.
The long-term effects are chronic, lasting for years or the whole life and can even lead to death. Furthermore, the toxicity of several air pollutants may also induce a variety of cancers in the long term ( 96 ).
As stated already, respiratory disorders are closely associated with the inhalation of air pollutants. These pollutants will invade through the airways and will accumulate at the cells. Damage to target cells should be related to the pollutant component involved and its source and dose. Health effects are also closely dependent on country, area, season, and time. An extended exposure duration to the pollutant should incline to long-term health effects in relation also to the above factors.
Particulate Matter (PMs), dust, benzene, and O 3 cause serious damage to the respiratory system ( 97 ). Moreover, there is a supplementary risk in case of existing respiratory disease such as asthma ( 98 ). Long-term effects are more frequent in people with a predisposing disease state. When the trachea is contaminated by pollutants, voice alterations may be remarked after acute exposure. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may be induced following air pollution, increasing morbidity and mortality ( 99 ). Long-term effects from traffic, industrial air pollution, and combustion of fuels are the major factors for COPD risk ( 99 ).
Multiple cardiovascular effects have been observed after exposure to air pollutants ( 100 ). Changes occurred in blood cells after long-term exposure may affect cardiac functionality. Coronary arteriosclerosis was reported following long-term exposure to traffic emissions ( 101 ), while short-term exposure is related to hypertension, stroke, myocardial infracts, and heart insufficiency. Ventricle hypertrophy is reported to occur in humans after long-time exposure to nitrogen oxide (NO 2 ) ( 102 , 103 ).
Neurological effects have been observed in adults and children after extended-term exposure to air pollutants.
Psychological complications, autism, retinopathy, fetal growth, and low birth weight seem to be related to long-term air pollution ( 83 ). The etiologic agent of the neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's and Parkinson's) is not yet known, although it is believed that extended exposure to air pollution seems to be a factor. Specifically, pesticides and metals are cited as etiological factors, together with diet. The mechanisms in the development of neurodegenerative disease include oxidative stress, protein aggregation, inflammation, and mitochondrial impairment in neurons ( 104 ) ( Figure 1 ).
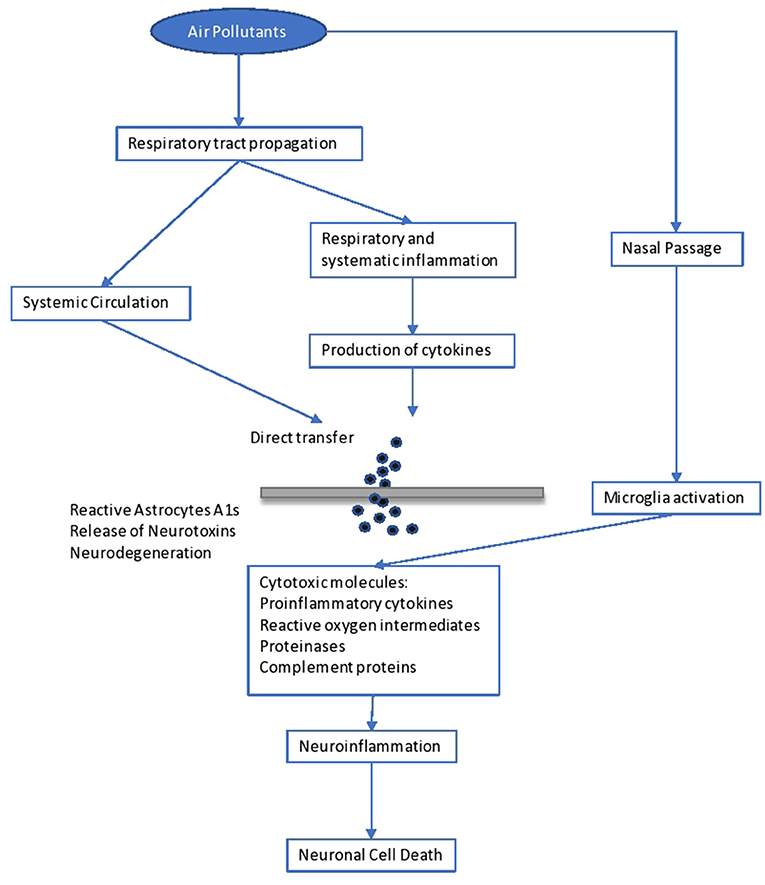
Figure 1 . Impact of air pollutants on the brain.
Brain inflammation was observed in dogs living in a highly polluted area in Mexico for a long period ( 105 ). In human adults, markers of systemic inflammation (IL-6 and fibrinogen) were found to be increased as an immediate response to PNC on the IL-6 level, possibly leading to the production of acute-phase proteins ( 106 ). The progression of atherosclerosis and oxidative stress seem to be the mechanisms involved in the neurological disturbances caused by long-term air pollution. Inflammation comes secondary to the oxidative stress and seems to be involved in the impairment of developmental maturation, affecting multiple organs ( 105 , 107 ). Similarly, other factors seem to be involved in the developmental maturation, which define the vulnerability to long-term air pollution. These include birthweight, maternal smoking, genetic background and socioeconomic environment, as well as education level.
However, diet, starting from breast-feeding, is another determinant factor. Diet is the main source of antioxidants, which play a key role in our protection against air pollutants ( 108 ). Antioxidants are free radical scavengers and limit the interaction of free radicals in the brain ( 108 ). Similarly, genetic background may result in a differential susceptibility toward the oxidative stress pathway ( 60 ). For example, antioxidant supplementation with vitamins C and E appears to modulate the effect of ozone in asthmatic children homozygous for the GSTM1 null allele ( 61 ). Inflammatory cytokines released in the periphery (e.g., respiratory epithelia) upregulate the innate immune Toll-like receptor 2. Such activation and the subsequent events leading to neurodegeneration have recently been observed in lung lavage in mice exposed to ambient Los Angeles (CA, USA) particulate matter ( 61 ). In children, neurodevelopmental morbidities were observed after lead exposure. These children developed aggressive and delinquent behavior, reduced intelligence, learning difficulties, and hyperactivity ( 109 ). No level of lead exposure seems to be “safe,” and the scientific community has asked the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to reduce the current screening guideline of 10 μg/dl ( 109 ).
It is important to state that impact on the immune system, causing dysfunction and neuroinflammation ( 104 ), is related to poor air quality. Yet, increases in serum levels of immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM) and the complement component C3 are observed ( 106 ). Another issue is that antigen presentation is affected by air pollutants, as there is an upregulation of costimulatory molecules such as CD80 and CD86 on macrophages ( 110 ).
As is known, skin is our shield against ultraviolet radiation (UVR) and other pollutants, as it is the most exterior layer of our body. Traffic-related pollutants, such as PAHs, VOCs, oxides, and PM, may cause pigmented spots on our skin ( 111 ). On the one hand, as already stated, when pollutants penetrate through the skin or are inhaled, damage to the organs is observed, as some of these pollutants are mutagenic and carcinogenic, and, specifically, they affect the liver and lung. On the other hand, air pollutants (and those in the troposphere) reduce the adverse effects of ultraviolet radiation UVR in polluted urban areas ( 111 ). Air pollutants absorbed by the human skin may contribute to skin aging, psoriasis, acne, urticaria, eczema, and atopic dermatitis ( 111 ), usually caused by exposure to oxides and photochemical smoke ( 111 ). Exposure to PM and cigarette smoking act as skin-aging agents, causing spots, dyschromia, and wrinkles. Lastly, pollutants have been associated with skin cancer ( 111 ).
Higher morbidity is reported to fetuses and children when exposed to the above dangers. Impairment in fetal growth, low birth weight, and autism have been reported ( 112 ).
Another exterior organ that may be affected is the eye. Contamination usually comes from suspended pollutants and may result in asymptomatic eye outcomes, irritation ( 112 ), retinopathy, or dry eye syndrome ( 113 , 114 ).
Environmental Impact of Air Pollution
Air pollution is harming not only human health but also the environment ( 115 ) in which we live. The most important environmental effects are as follows.
Acid rain is wet (rain, fog, snow) or dry (particulates and gas) precipitation containing toxic amounts of nitric and sulfuric acids. They are able to acidify the water and soil environments, damage trees and plantations, and even damage buildings and outdoor sculptures, constructions, and statues.
Haze is produced when fine particles are dispersed in the air and reduce the transparency of the atmosphere. It is caused by gas emissions in the air coming from industrial facilities, power plants, automobiles, and trucks.
Ozone , as discussed previously, occurs both at ground level and in the upper level (stratosphere) of the Earth's atmosphere. Stratospheric ozone is protecting us from the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. In contrast, ground-level ozone is harmful to human health and is a pollutant. Unfortunately, stratospheric ozone is gradually damaged by ozone-depleting substances (i.e., chemicals, pesticides, and aerosols). If this protecting stratospheric ozone layer is thinned, then UV radiation can reach our Earth, with harmful effects for human life (skin cancer) ( 116 ) and crops ( 117 ). In plants, ozone penetrates through the stomata, inducing them to close, which blocks CO 2 transfer and induces a reduction in photosynthesis ( 118 ).
Global climate change is an important issue that concerns mankind. As is known, the “greenhouse effect” keeps the Earth's temperature stable. Unhappily, anthropogenic activities have destroyed this protecting temperature effect by producing large amounts of greenhouse gases, and global warming is mounting, with harmful effects on human health, animals, forests, wildlife, agriculture, and the water environment. A report states that global warming is adding to the health risks of poor people ( 119 ).
People living in poorly constructed buildings in warm-climate countries are at high risk for heat-related health problems as temperatures mount ( 119 ).
Wildlife is burdened by toxic pollutants coming from the air, soil, or the water ecosystem and, in this way, animals can develop health problems when exposed to high levels of pollutants. Reproductive failure and birth effects have been reported.
Eutrophication is occurring when elevated concentrations of nutrients (especially nitrogen) stimulate the blooming of aquatic algae, which can cause a disequilibration in the diversity of fish and their deaths.
Without a doubt, there is a critical concentration of pollution that an ecosystem can tolerate without being destroyed, which is associated with the ecosystem's capacity to neutralize acidity. The Canada Acid Rain Program established this load at 20 kg/ha/yr ( 120 ).
Hence, air pollution has deleterious effects on both soil and water ( 121 ). Concerning PM as an air pollutant, its impact on crop yield and food productivity has been reported. Its impact on watery bodies is associated with the survival of living organisms and fishes and their productivity potential ( 121 ).
An impairment in photosynthetic rhythm and metabolism is observed in plants exposed to the effects of ozone ( 121 ).
Sulfur and nitrogen oxides are involved in the formation of acid rain and are harmful to plants and marine organisms.
Last but not least, as mentioned above, the toxicity associated with lead and other metals is the main threat to our ecosystems (air, water, and soil) and living creatures ( 121 ).
In 2018, during the first WHO Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health, the WHO's General Director, Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, called air pollution a “silent public health emergency” and “the new tobacco” ( 122 ).
Undoubtedly, children are particularly vulnerable to air pollution, especially during their development. Air pollution has adverse effects on our lives in many different respects.
Diseases associated with air pollution have not only an important economic impact but also a societal impact due to absences from productive work and school.
Despite the difficulty of eradicating the problem of anthropogenic environmental pollution, a successful solution could be envisaged as a tight collaboration of authorities, bodies, and doctors to regularize the situation. Governments should spread sufficient information and educate people and should involve professionals in these issues so as to control the emergence of the problem successfully.
Technologies to reduce air pollution at the source must be established and should be used in all industries and power plants. The Kyoto Protocol of 1997 set as a major target the reduction of GHG emissions to below 5% by 2012 ( 123 ). This was followed by the Copenhagen summit, 2009 ( 124 ), and then the Durban summit of 2011 ( 125 ), where it was decided to keep to the same line of action. The Kyoto protocol and the subsequent ones were ratified by many countries. Among the pioneers who adopted this important protocol for the world's environmental and climate “health” was China ( 3 ). As is known, China is a fast-developing economy and its GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is expected to be very high by 2050, which is defined as the year of dissolution of the protocol for the decrease in gas emissions.
A more recent international agreement of crucial importance for climate change is the Paris Agreement of 2015, issued by the UNFCCC (United Nations Climate Change Committee). This latest agreement was ratified by a plethora of UN (United Nations) countries as well as the countries of the European Union ( 126 ). In this vein, parties should promote actions and measures to enhance numerous aspects around the subject. Boosting education, training, public awareness, and public participation are some of the relevant actions for maximizing the opportunities to achieve the targets and goals on the crucial matter of climate change and environmental pollution ( 126 ). Without any doubt, technological improvements makes our world easier and it seems difficult to reduce the harmful impact caused by gas emissions, we could limit its use by seeking reliable approaches.
Synopsizing, a global prevention policy should be designed in order to combat anthropogenic air pollution as a complement to the correct handling of the adverse health effects associated with air pollution. Sustainable development practices should be applied, together with information coming from research in order to handle the problem effectively.
At this point, international cooperation in terms of research, development, administration policy, monitoring, and politics is vital for effective pollution control. Legislation concerning air pollution must be aligned and updated, and policy makers should propose the design of a powerful tool of environmental and health protection. As a result, the main proposal of this essay is that we should focus on fostering local structures to promote experience and practice and extrapolate these to the international level through developing effective policies for sustainable management of ecosystems.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
IM is employed by the company Delphis S.A.
The remaining authors declare that the present review paper was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
1. WHO. Air Pollution . WHO. Available online at: http://www.who.int/airpollution/en/ (accessed October 5, 2019).
Google Scholar
2. Moores FC. Climate change and air pollution: exploring the synergies and potential for mitigation in industrializing countries. Sustainability . (2009) 1:43–54. doi: 10.3390/su1010043
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
3. USGCRP (2009). Global Climate Change Impacts in the United States. In: Karl TR, Melillo JM, Peterson TC, editors. Climate Change Impacts by Sectors: Ecosystems . New York, NY: United States Global Change Research Program. Cambridge University Press.
4. Marlon JR, Bloodhart B, Ballew MT, Rolfe-Redding J, Roser-Renouf C, Leiserowitz A, et al. (2019). How hope and doubt affect climate change mobilization. Front. Commun. 4:20. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2019.00020
5. Eze IC, Schaffner E, Fischer E, Schikowski T, Adam M, Imboden M, et al. Long- term air pollution exposure and diabetes in a population-based Swiss cohort. Environ Int . (2014) 70:95–105. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2014.05.014
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
6. Kelishadi R, Poursafa P. Air pollution and non-respiratory health hazards for children. Arch Med Sci . (2010) 6:483–95. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2010.14458
7. Manucci PM, Franchini M. Health effects of ambient air pollution in developing countries. Int J Environ Res Public Health . (2017) 14:1048. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14091048
8. Burden of Disease from Ambient and Household Air Pollution . Available online: http://who.int/phe/health_topics/outdoorair/databases/en/ (accessed August 15, 2017).
9. Hashim D, Boffetta P. Occupational and environmental exposures and cancers in developing countries. Ann Glob Health . (2014) 80:393–411. doi: 10.1016/j.aogh.2014.10.002
10. Guo Y, Zeng H, Zheng R, Li S, Pereira G, Liu Q, et al. The burden of lung cancer mortality attributable to fine particles in China. Total Environ Sci . (2017) 579:1460–6. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.147
11. Hou Q, An XQ, Wang Y, Guo JP. An evaluation of resident exposure to respirable particulate matter and health economic loss in Beijing during Beijing 2008 Olympic Games. Sci Total Environ . (2010) 408:4026–32. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.12.030
12. Kan H, Chen R, Tong S. Ambient air pollution, climate change, and population health in China. Environ Int . (2012) 42:10–9. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.03.003
13. Burroughs Peña MS, Rollins A. Environmental exposures and cardiovascular disease: a challenge for health and development in low- and middle-income countries. Cardiol Clin . (2017) 35:71–86. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2016.09.001
14. Kankaria A, Nongkynrih B, Gupta S. Indoor air pollution in india: implications on health and its control. Indian J Comm Med . 39:203–7. doi: 10.4103/0970-0218.143019
15. Parajuli I, Lee H, Shrestha KR. Indoor air quality and ventilation assessment of rural mountainous households of Nepal. Int J Sust Built Env . (2016) 5:301–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsbe.2016.08.003
16. Saud T, Gautam R, Mandal TK, Gadi R, Singh DP, Sharma SK. Emission estimates of organic and elemental carbon from household biomass fuel used over the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP), India. Atmos Environ . (2012) 61:212–20. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.07.030
17. Singh DP, Gadi R, Mandal TK, Saud T, Saxena M, Sharma SK. Emissions estimates of PAH from biomass fuels used in rural sector of Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Atmos Environ . (2013) 68:120–6. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.11.042
18. Dherani M, Pope D, Mascarenhas M, Smith KR, Weber M BN. Indoor air pollution from unprocessed solid fuel use and pneumonia risk in children aged under five years: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bull World Health Organ . (2008) 86:390–4. doi: 10.2471/BLT.07.044529
19. Kassomenos P, Kelessis A, Petrakakis M, Zoumakis N, Christides T, Paschalidou AK. Air Quality assessment in a heavily-polluted urban Mediterranean environment through Air Quality indices. Ecol Indic . (2012) 18:259–68. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.11.021
20. Dockery DW, Pope CA, Xu X, Spengler JD, Ware JH, Fay ME, et al. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N Engl J Med . (1993) 329:1753–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312093292401
21. Schwela DH, Köth-Jahr I. Leitfaden für die Aufstellung von Luftreinhalteplänen [Guidelines for the Implementation of Clean Air Implementation Plans]. Landesumweltamt des Landes Nordrhein Westfalen. State Environmental Service of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia (1994).
22. Newlands M. Environmental Activism, Environmental Politics, and Representation: The Framing of the British Environmental Activist Movement . Ph.D. thesis. University of East London, United Kingdom (2015).
23. NEPIS (National Service Center for Environmental Publications) US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2017). Available online at: https://www.epa.gov/clean-air-act-overview/air-pollution-current-and-future-challenges (accessed August 15, 2017).
24. NRC (National Research Council). Available online at: https://www.nap.edu/read/10728/chapter/1,2014 (accessed September 17, 2019).
25. Bull A. Traffic Congestion: The Problem and How to Deal With It . Santiago: Nationes Unidas, Cepal (2003).
26. Spiegel J, Maystre LY. Environmental Pollution Control, Part VII - The Environment, Chapter 55, Encyclopedia of Occupational Health and Safety . Available online at: http://www.ilocis.org/documents/chpt55e.htm (accessed September 17, 2019).
27. European Community Reports. Assessment of the Effectiveness of European Air Quality Policies and Measures: Case Study 2; Comparison of the EU and US Air Quality Standards and Planning Requirements. (2004). Available online at: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/archives/cafe/activities/pdf/case_study2.pdf (accessed September 22, 2019).
28. Gibson R, Ward S. Parties in the digital age; a review. J Represent Democracy . (2009) 45:87–100. doi: 10.1080/00344890802710888
29. Kaun A, Uldam J. Digital activism: after the hype. New Media Soc. (2017) 20:2099–106. doi: 10.1177/14614448177319
30. Sivitanides M, Shah V. The era of digital activism. In: 2011 Conference for Information Systems Applied Research(CONISAR) Proceedings Wilmington North Carolina, USA . Available online at: https://www.arifyildirim.com/ilt510/marcos.sivitanides.vivek.shah.pdf (accessed September 22, 2019).
31. Möller L, Schuetzle D, Autrup H. Future research needs associated with the assessment of potential human health risks from exposure to toxic ambient air pollutants. Environ Health Perspect . (1994) 102(Suppl. 4):193–210. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102s4193
32. Jacobson MZ, Jacobson PMZ. Atmospheric Pollution: History, Science, and Regulation. Cambridge University Press (2002). p. 206. doi: 10.1256/wea.243.02
33. Stover RH. Flooding of soil for disease control. In: Mulder D, editor. Chapter 3. Developments in Agricultural and Managed Forest Ecology . Elsevier (1979). p. 19–28. Available online at: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444416926500094 doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-41692-6.50009-4 (accessed July 1, 2019).
34. Maipa V, Alamanos Y, Bezirtzoglou E. Seasonal fluctuation of bacterial indicators in coastal waters. Microb Ecol Health Dis . (2001) 13:143–6. doi: 10.1080/089106001750462687
35. Bezirtzoglou E, Dimitriou D, Panagiou A. Occurrence of Clostridium perfringens in river water by using a new procedure. Anaerobe . (1996) 2:169–73. doi: 10.1006/anae.1996.0022
36. Kjellstrom T, Lodh M, McMichael T, Ranmuthugala G, Shrestha R, Kingsland S. Air and Water Pollution: Burden and Strategies for Control. DCP, Chapter 43. 817–32 p. Available online at: https://www.dcp-3.org/sites/default/files/dcp2/DCP43.pdf (accessed September 17, 2017).
37. Pathak RK, Wang T, Ho KF, Lee SC. Characteristics of summertime PM2.5 organic and elemental carbon in four major Chinese cities: implications of high acidity for water- soluble organic carbon (WSOC). Atmos Environ . (2011) 45:318–25. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.10.021
38. Bonavigo L, Zucchetti M, Mankolli H. Water radioactive pollution and related environmental aspects. J Int Env Appl Sci . (2009) 4:357–63
39. World Health Organization (WHO). Preventing Disease Through Healthy Environments: Towards an Estimate of the Environmental Burden of Disease . 1106 p. Available online at: https://www.who.int/quantifying_ehimpacts/publications/preventingdisease.pdf (accessed September 22, 2019).
40. Stansfeld SA. Noise effects on health in the context of air pollution exposure. Int J Environ Res Public Health . (2015) 12:12735–60. doi: 10.3390/ijerph121012735
41. Ethical Unicorn. Everything You Need To Know About Aerosols & Air Pollution. (2019). Available online at: https://ethicalunicorn.com/2019/04/29/everything-you-need-to-know-about-aerosols-air-pollution/ (accessed October 4, 2019).
42. Colbeck I, Lazaridis M. Aerosols and environmental pollution. Sci Nat . (2009) 97:117–31. doi: 10.1007/s00114-009-0594-x
43. Incecik S, Gertler A, Kassomenos P. Aerosols and air quality. Sci Total Env . (2014) 355, 488–9. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.012
44. D'Amato G, Pawankar R, Vitale C, Maurizia L. Climate change and air pollution: effects on respiratory allergy. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res . (2016) 8:391–5. doi: 10.4168/aair.2016.8.5.391
45. Bezirtzoglou C, Dekas K, Charvalos E. Climate changes, environment and infection: facts, scenarios and growing awareness from the public health community within Europe. Anaerobe . (2011) 17:337–40. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2011.05.016
46. Castelli F, Sulis G. Migration and infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Infect . (2017) 23:283–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.03.012
47. Watson JT, Gayer M, Connolly MA. Epidemics after natural disasters. Emerg Infect Dis . (2007) 13:1–5. doi: 10.3201/eid1301.060779
48. Fenn B. Malnutrition in Humanitarian Emergencies . Available online at: https://www.who.int/diseasecontrol_emergencies/publications/idhe_2009_london_malnutrition_fenn.pdf . (accessed August 15, 2017).
49. Lindh E, Argentini C, Remoli ME, Fortuna C, Faggioni G, Benedetti E, et al. The Italian 2017 outbreak Chikungunya virus belongs to an emerging Aedes albopictus –adapted virus cluster introduced from the Indian subcontinent. Open Forum Infect Dis. (2019) 6:ofy321. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofy321
50. Calba C, Guerbois-Galla M, Franke F, Jeannin C, Auzet-Caillaud M, Grard G, Pigaglio L, Decoppet A, et al. Preliminary report of an autochthonous chikungunya outbreak in France, July to September 2017. Eur Surveill . (2017) 22:17-00647. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2017.22.39.17-00647
51. Menne B, Murray V. Floods in the WHO European Region: Health Effects and Their Prevention . Copenhagen: WHO; Weltgesundheits organisation, Regionalbüro für Europa (2013). Available online at: http://www.euro.who.int/data/assets/pdf_file/0020/189020/e96853.pdf (accessed 15 August 2017).
52. Schneider SH. The greenhouse effect: science and policy. Science . (1989) 243:771–81. doi: 10.1126/science.243.4892.771
53. Wilson WE, Suh HH. Fine particles and coarse particles: concentration relationships relevant to epidemiologic studies. J Air Waste Manag Assoc . (1997) 47:1238–49. doi: 10.1080/10473289.1997.10464074
54. US EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (2018). Available online at: https://www.epa.gov/pm-pollution/particulate-matter-pm-basics (accessed September 22, 2018).
55. Cheung K, Daher N, Kam W, Shafer MM, Ning Z, Schauer JJ, et al. Spatial and temporal variation of chemical composition and mass closure of ambient coarse particulate matter (PM10–2.5) in the Los Angeles area. Atmos Environ . (2011) 45:2651–62. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.02.066
56. Zhang L, Yang Y, Li Y, Qian ZM, Xiao W, Wang X, et al. Short-term and long-term effects of PM2.5 on acute nasopharyngitis in 10 communities of Guangdong, China. Sci Total Env. (2019) 688:136–42. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.470.
57. Kloog I, Ridgway B, Koutrakis P, Coull BA, Schwartz JD. Long- and short-term exposure to PM2.5 and mortality using novel exposure models, Epidemiology . (2013) 24:555–61. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e318294beaa
58. New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services. Current and Forecasted Air Quality in New Hampshire . Environmental Fact Sheet (2019). Available online at: https://www.des.nh.gov/organization/commissioner/pip/factsheets/ard/documents/ard-16.pdf (accessed September 22, 2019).
59. Kappos AD, Bruckmann P, Eikmann T, Englert N, Heinrich U, Höppe P, et al. Health effects of particles in ambient air. Int J Hyg Environ Health . (2004) 207:399–407. doi: 10.1078/1438-4639-00306
60. Boschi N (Ed.). Defining an educational framework for indoor air sciences education. In: Education and Training in Indoor Air Sciences . Luxembourg: Springer Science & Business Media (2012). 245 p.
61. Heal MR, Kumar P, Harrison RM. Particles, air quality, policy and health. Chem Soc Rev . (2012) 41:6606–30. doi: 10.1039/c2cs35076a
62. Bezirtzoglou E, Alexopoulos A. Ozone history and ecosystems: a goliath from impacts to advance industrial benefits and interests, to environmental and therapeutical strategies. In: Ozone Depletion, Chemistry and Impacts. (2009). p. 135–45.
63. Villányi V, Turk B, Franc B, Csintalan Z. Ozone Pollution and its Bioindication. In: Villányi V, editor. Air Pollution . London: Intech Open (2010). doi: 10.5772/10047
64. Massachusetts Department of Public Health. Massachusetts State Health Assessment . Boston, MA (2017). Available online at: https://www.mass.gov/files/documents/2017/11/03/2017%20MA%20SHA%20final%20compressed.pdf (accessed October 30, 2017).
65. Lorenzini G, Saitanis C. Ozone: A Novel Plant “Pathogen.” In: Sanitá di Toppi L, Pawlik-Skowrońska B, editors. Abiotic Stresses in Plant Springer Link (2003). p. 205–29. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-0255-3_8
66. Fares S, Vargas R, Detto M, Goldstein AH, Karlik J, Paoletti E, et al. Tropospheric ozone reduces carbon assimilation in trees: estimates from analysis of continuous flux measurements. Glob Change Biol . (2013) 19:2427–43. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12222
67. Harmens H, Mills G, Hayes F, Jones L, Norris D, Fuhrer J. Air Pollution and Vegetation . ICP Vegetation Annual Report 2006/2007. (2012)
68. Emberson LD, Pleijel H, Ainsworth EA, den Berg M, Ren W, Osborne S, et al. Ozone effects on crops and consideration in crop models. Eur J Agron . (2018) 100:19–34. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2018.06.002
69. Alexopoulos A, Plessas S, Ceciu S, Lazar V, Mantzourani I, Voidarou C, et al. Evaluation of ozone efficacy on the reduction of microbial population of fresh cut lettuce ( Lactuca sativa ) and green bell pepper ( Capsicum annuum ). Food Control . (2013) 30:491–6. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.09.018
70. Alexopoulos A, Plessas S, Kourkoutas Y, Stefanis C, Vavias S, Voidarou C, et al. Experimental effect of ozone upon the microbial flora of commercially produced dairy fermented products. Int J Food Microbiol . (2017) 246:5–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.01.018
71. Maggio A, Fagnano M. Ozone damages to mediterranean crops: physiological responses. Ital J Agron . (2008) 13–20. doi: 10.4081/ija.2008.13
72. McCarthy JT, Pelle E, Dong K, Brahmbhatt K, Yarosh D, Pernodet N. Effects of ozone in normal human epidermal keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol . (2013) 22:360–1. doi: 10.1111/exd.12125
73. WHO. Health Risks of Ozone From Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution . Available online at: http://www.euro.who.int/data/assets/pdf_file/0005/78647/E91843.pdf (accessed August 15, 2019).
74. Thiele JJ, Traber MG, Tsang K, Cross CE, Packer L. In vivo exposure to ozone depletes vitamins C and E and induces lipid peroxidation in epidermal layers of murine skin. Free Radic Biol Med. (1997) 23:365–91. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(96)00617-X
75. Hatch GE, Slade R, Harris LP, McDonnell WF, Devlin RB, Koren HS, et al. Ozone dose and effect in humans and rats. A comparison using oxygen- 18 labeling and bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . (1994) 150:676–83. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.3.8087337
76. Lippmann M. Health effects of ozone. A critical review. JAPCA . (1989) 39:672–95. doi: 10.1080/08940630.1989.10466554
77. Gryparis A, Forsberg B, Katsouyanni K, Analitis A, Touloumi G, Schwartz J, et al. Acute effects of ozone on mortality from the “air pollution and health: a European approach” project. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . (2004) 170:1080–7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200403-333OC
78. Soon W, Baliunas SL, Robinson AB, Robinson ZW. Environmental effects of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide. Climate Res . (1999) 13:149–64 doi: 10.1260/0958305991499694
79. Richmont-Bryant J, Owen RC, Graham S, Snyder M, McDow S, Oakes M, et al. Estimation of on-road NO2 concentrations, NO2/NOX ratios, and related roadway gradients from near-road monitoring data. Air Qual Atm Health . (2017) 10:611–25. doi: 10.1007/s11869-016-0455-7
80. Hesterberg TW, Bunn WB, McClellan RO, Hamade AK, Long CM, Valberg PA. Critical review of the human data on short-term nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) exposures: evidence for NO2 no-effect levels. Crit Rev Toxicol . (2009) 39:743–81. doi: 10.3109/10408440903294945
81. Chen T-M, Gokhale J, Shofer S, Kuschner WG. Outdoor air pollution: nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and carbon monoxide health effects. Am J Med Sci . (2007) 333:249–56. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31803b900f
82. US EPA. Table of Historical SO 2 NAAQS, Sulfur US EPA . Available online at: https://www3.epa.gov/ttn/naaqs/standards/so2/s_so2_history.html (accessed October 5, 2019).
83. WHO Regional Office of Europe (2000). Available online at: https://euro.who.int/_data/assets/pdf_file/0020/123086/AQG2ndEd_7_4Sulfuroxide.pdf
84. Pruss-Ustun A, Fewrell L, Landrigan PJ, Ayuso-Mateos JL. Lead exposure. Comparative Quantification of Health Risks . World Health Organization. p. 1495–1542. Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/cra/chapters/volume2/1495-1542.pdf?ua=1
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
85. Goyer RA. Transplacental transport of lead. Environ Health Perspect . (1990) 89:101–5. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9089101
86. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIH). Lead and Your Health . (2013). 1–4 p. Available online at: https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/materials/lead_and_your_health_508.pdf (accessed September 17, 2019).
87. Farhat A, Mohammadzadeh A, Balali-Mood M, Aghajanpoor-Pasha M, Ravanshad Y. Correlation of blood lead level in mothers and exclusively breastfed infants: a study on infants aged less than six months. Asia Pac J Med Toxicol . (2013) 2:150–2.
88. Assi MA, Hezmee MNM, Haron AW, Sabri MYM, Rajion MA. The detrimental effects of lead on human and animal health. Vet World . (2016) 9:660–71. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2016.660-671
89. Abdel-Shafy HI, Mansour MSM. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt J Pet . (2016) 25:107–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpe.2015.03.011
90. Kumar A, Singh BP, Punia M, Singh D, Kumar K, Jain VK. Assessment of indoor air concentrations of VOCs and their associated health risks in the library of Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int . (2014) 21:2240–8. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-2150-7
91. Molhave L, Clausen G, Berglund B, Ceaurriz J, Kettrup A, Lindvall T, et al. Total Volatile Organic Compounds (TVOC) in Indoor Air Quality Investigations. Indoor Air . 7:225–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0668.1997.00002.x
92. Gibb T. Indoor Air Quality May be Hazardous to Your Health . MSU Extension. Available online at: https://www.canr.msu.edu/news/indoor_air_quality_may_be_hazardous_to_your_health (accessed October 5, 2019).
93. Ebersviller S, Lichtveld K, Sexton KG, Zavala J, Lin Y-H, Jaspers I, et al. Gaseous VOCs rapidly modify particulate matter and its biological effects – Part 1: simple VOCs and model PM. Atmos Chem Phys Discuss . (2012) 12:5065–105. doi: 10.5194/acpd-12-5065-2012
94. WHO (World Health Organization). Dioxins and Their Effects on Human Health. Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dioxins-and-their-effects-on-human-health (accessed October 5, 2019).
95. EEA (European Environmental Agency). Air Quality Standards to the European Union and WHO . Available online at: https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/data-and-maps/figures/air-quality-standards-under-the
96. Nakano T, Otsuki T. [Environmental air pollutants and the risk of cancer]. (Japanese). Gan To Kagaku Ryoho . (2013) 40:1441–5.
97. Kurt OK, Zhang J, Pinkerton KE. Pulmonary health effects of air pollution. Curr Opin Pulm Med . (2016) 22:138–43. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000248
98. Guarnieri M, Balmes JR. Outdoor air pollution and asthma. Lancet . (2014) 383:1581–92. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60617-6
99. Jiang X-Q, Mei X-D, Feng D. Air pollution and chronic airway diseases: what should people know and do? J Thorac Dis . (2016) 8:E31–40.
100. Bourdrel T, Bind M-A, Béjot Y, Morel O, Argacha J-F. Cardiovascular effects of air pollution. Arch Cardiovasc Dis . (2017) 110:634–42. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2017.05.003
101. Hoffmann B, Moebus S, Möhlenkamp S, Stang A, Lehmann N, Dragano N, et al. Residential exposure to traffic is associated with coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation . (2007) 116:489–496. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.693622
102. Katholi RE, Couri DM. Left ventricular hypertrophy: major risk factor in patients with hypertension: update and practical clinical applications. Int J Hypertens . (2011) 2011:495349. doi: 10.4061/2011/495349
103. Leary PJ, Kaufman JD, Barr RG, Bluemke DA, Curl CL, Hough CL, et al. Traffic- related air pollution and the right ventricle. the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . (2014) 189:1093–100. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201312-2298OC
104. Genc S, Zadeoglulari Z, Fuss SH, Genc K. The adverse effects of air pollution on the nervous system. J Toxicol . (2012) 2012:782462. doi: 10.1155/2012/782462
105. Calderon-Garciduenas L, Azzarelli B, Acuna H, et al. Air pollution and brain damage. Toxicol Pathol. (2002) 30:373–89. doi: 10.1080/01926230252929954
106. Rückerl R, Greven S, Ljungman P, Aalto P, Antoniades C, Bellander T, et al. Air pollution and inflammation (interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, fibrinogen) in myocardial infarction survivors. Environ Health Perspect . (2007) 115:1072–80. doi: 10.1289/ehp.10021
107. Peters A, Veronesi B, Calderón-Garcidueñas L, Gehr P, Chen LC, Geiser M, et al. Translocation and potential neurological effects of fine and ultrafine particles a critical update. Part Fibre Toxicol . (2006) 3:13–8. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-3-13
108. Kelly FJ. Dietary antioxidants and environmental stress. Proc Nutr Soc . (2004) 63:579–85. doi: 10.1079/PNS2004388
109. Bellinger DC. Very low lead exposures and children's neurodevelopment. Curr Opin Pediatr . (2008) 20:172–7. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e3282f4f97b
110. Balbo P, Silvestri M, Rossi GA, Crimi E, Burastero SE. Differential role of CD80 and CD86 on alveolar macrophages in the presentation of allergen to T lymphocytes in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy J Br Soc Allergy Clin Immunol . (2001) 31:625–36. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2001.01068.x
111. Drakaki E, Dessinioti C, Antoniou C. Air pollution and the skin. Front Environ Sci Eng China . (2014) 15:2–8. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2014.00011
112. Weisskopf MG, Kioumourtzoglou M-A, Roberts AL. Air pollution and autism spectrum disorders: causal or confounded? Curr Environ Health Rep . (2015) 2:430–9. doi: 10.1007/s40572-015-0073-9
113. Mo Z, Fu Q, Lyu D, Zhang L, Qin Z, Tang Q, et al. Impacts of air pollution on dry eye disease among residents in Hangzhou, China: a case-crossover study. Environ Pollut . (2019) 246:183–9. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.109
114. Klopfer J. Effects of environmental air pollution on the eye. J Am Optom Assoc . (1989) 60:773–8.
115. Ashfaq A, Sharma P. Environmental effects of air pollution and application of engineered methods to combat the problem. J Indust Pollut Control . (2012) 29.
116. Madronich S, de Gruijl F. Skin cancer and UV radiation. Nature . (1993) 366:23–9. doi: 10.1038/366023a0
117. Teramura A. Effects of UV-B radiation on the growth and yield of crop plants. Physiol Plant . (2006) 58:415–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1983.tb04203.x
118. Singh E, Tiwari S, Agrawal M. Effects of elevated ozone on photosynthesis and stomatal conductance of two soybean varieties: a case study to assess impacts of one component of predicted global climate change. Plant Biol Stuttg Ger . (2009) 11(Suppl. 1):101–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2009.00263.x
119. Manderson L. How global Warming is Adding to the Health Risks of Poor People . The Conversation. University of the Witwatersrand. Available online at: http://theconversation.com/how-global-warming-is-adding-to-the-health-risks-of-poor-people-109520 (accessed October 5, 2019).
120. Ministers of Energy and Environment. Federal/Provincial/Territorial Ministers of Energy and Environment (Canada), editor. The Canada-Wide Acid Rain Strategy for Post-2000 . Halifax: The Ministers (1999). 11 p.
121. Zuhara S, Isaifan R. The impact of criteria air pollutants on soil and water: a review. (2018) 278–84. doi: 10.30799/jespr.133.18040205
122. WHO. First WHO Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health. (2018). Available online at: https://www.who.int/airpollution/events/conference/en/ (accessed October 6, 2019).
123. What is the Kyoto Protocol? UNFCCC . Available online at: https://unfccc.int/kyoto__protocol (accessed October 6, 2019).
124. CopenhagenClimate Change Conference (UNFCCC) . Available online at: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/conferences/past-conferences/copenhagen-climate-change-conference-december-2009/copenhagen-climate-change-conference-december-2009 (accessed October 6, 2019).
125. Durban Climate Change Conference,. UNFCCC (2011). Available online at: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/conferences/past-conferences/copenhagen-climate-change-conference-december-2009/copenhagen-climate-change-conference-december-2009 (accessed October 6, 2019).
126. Paris Climate Change Agreement,. (2016). Available online at: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement/the-paris-agreement
Keywords: air pollution, environment, health, public health, gas emission, policy
Citation: Manisalidis I, Stavropoulou E, Stavropoulos A and Bezirtzoglou E (2020) Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 8:14. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00014
Received: 17 October 2019; Accepted: 17 January 2020; Published: 20 February 2020.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2020 Manisalidis, Stavropoulou, Stavropoulos and Bezirtzoglou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ioannis Manisalidis, giannismanisal@gmail.com ; Elisavet Stavropoulou, elisabeth.stavropoulou@gmail.com
† These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Fact sheets
- Facts in pictures
- Publications
- Questions and answers
- Tools and toolkits
- HIV and AIDS
- Hypertension
- Mental disorders
- Top 10 causes of death
- All countries
- Eastern Mediterranean
- South-East Asia
- Western Pacific
- Data by country
- Country presence
- Country strengthening
- Country cooperation strategies
- News releases
Feature stories
- Press conferences
- Commentaries
- Photo library
- Afghanistan
- Cholera
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Greater Horn of Africa
- Israel and occupied Palestinian territory
- Disease Outbreak News
- Situation reports
- Weekly Epidemiological Record
- Surveillance
- Health emergency appeal
- International Health Regulations
- Independent Oversight and Advisory Committee
- Classifications
- Data collections
- Global Health Estimates
- Mortality Database
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Health Inequality Monitor
- Global Progress
- Data collection tools
- Global Health Observatory
- Insights and visualizations
- COVID excess deaths
- World Health Statistics
- Partnerships
- Committees and advisory groups
- Collaborating centres
- Technical teams
- Organizational structure
- Initiatives
- General Programme of Work
- WHO Academy
- Investment case
- WHO Foundation
- External audit
- Financial statements
- Internal audit and investigations
- Programme Budget
- Results reports
- Governing bodies
- World Health Assembly
- Executive Board
- Member States Portal
- Health topics /
Air pollution
Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere.
Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities and forest fires are common sources of air pollution. Pollutants of major public health concern include particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide. Outdoor and indoor air pollution cause respiratory and other diseases and are important sources of morbidity and mortality.
WHO data show that almost all of the global population (99%) breathe air that exceeds WHO guideline limits and contains high levels of pollutants , with low- and middle-income countries suffering from the highest exposures.
Air quality is closely linked to the earth’s climate and ecosystems globally. Many of the drivers of air pollution (i.e. combustion of fossil fuels) are also sources of greenhouse gas emissions. Policies to reduce air pollution, therefore, offer a win-win strategy for both climate and health, lowering the burden of disease attributable to air pollution, as well as contributing to the near- and long-term mitigation of climate change.
From smog hanging over cities to smoke inside the home, air pollution poses a major threat to health and climate.
Ambient (outdoor) air pollution in both cities and rural areas is causing fine particulate matter which result in strokes, heart diseases, lung cancer, acute and chronic respiratory diseases.
Additionally, around 2.4 billion people are exposed to dangerous levels of household air pollution, while using polluting open fires or simple stoves for cooking fuelled by kerosene, biomass (wood, animal dung and crop waste) and coal.
The combined effects of ambient air pollution and household air pollution is associated with 7 million premature deaths annually.
Sources of air pollution are multiple and context specific. The major outdoor pollution sources include residential energy for cooking and heating, vehicles, power generation, agriculture/waste incineration, and industry. Policies and investments that support sustainable land use, cleaner household energy and transport, energy-efficient housing, power generation, industry, and better municipal waste management can effectively reduce key sources of ambient air pollution.
WHO promotes interventions and initiatives for healthy sectoral policies (including energy, transport, housing, urban development and electrification of health-care facilities), addressing key risks to health from air pollution indoors and outdoors, and contributing to achieving health co-benefits from climate change mitigation policies.
WHO provides technical support to WHO’s Member States in the development of normative guidance, tools and provision of authoritative advice on health issues related to air pollution and its sources.
WHO monitors and reports on global trends and changes in health outcomes associated with actions taken to address air pollution at the national, regional and global levels.
WHO has also developed and implemented a strategy for raising awareness on the risk of air pollution, as well as available solutions that can be implemented to mitigate the risks of exposure to air pollution. Through digital outreach and partnerships, WHO has helped enrich the value proposition of addressing air pollution for health and environment ministries, city governments and other stakeholders from sectors with significant emissions.
- Household air pollution
- Ambient (outdoor) air pollution
- Electricity in health-care facilities
- Ambient air quality database
- Air pollution and health training toolkit for health workers
- Air quality standards
- Benefits of action to reduce household air pollution tool (BAR-HAP tool)
- Clean household energy solutions toolkit (CHEST)
- Database on electrification of health-care facilities
- Global health observatory: public health and environment
- Global health observatory: air pollution data portal
- Health impact assessment (HIA tools)
- Household energy assessment rapid tool (HEART) templates
- Household multiple emission sources (HOMES) model
- Integrating health in urban and territorial planning: the directory
- Maps and data
- National air quality standards
- Occupational Burden of Disease Application tool
- Global air pollution and health - technical advisory group
- Scientific advisory group on air pollution and health
- SDG 11.6.2 working group
- Health and the environment: addressing the health impact of air pollution (WHA68.8)
- Health and the environment: draft road map for an enhanced global response to the adverse health effects of air pollution: report by the Secretariat (WHA69.18)
- Health, environment and climate change: report by the Director-General (WHA71.10)
- Health, environment and climate change: road map for an enhanced global response to the adverse health effects of air pollution: report by the Director-General (WHA71/10 Add.1)
- Environment, climate change and health
- Air quality, energy and health
WHO to host second global conference on air pollution and health
WHO launches directory of resources for planning healthy environments
Climate change and noncommunicable diseases: connections
Monitoring air pollution levels is key to adopting and implementing WHO's Global Air Quality Guidelines
Latest publications

Clean Household Energy Solutions Toolkit (CHEST)
A systematic review of the evidence has demonstrated the key role of clean household energy in improving global health, reaffirming the importance...

Health and Energy Platform of Action report 2020-2022: building connections for better health
Energy is linked to many of the sustainable development priorities, including public health, gender equality, food security, clean water, education, economic...

Compendium of WHO and other UN guidance on health and environment: version with International Classification...
In this version of the compendium, each guidance is coded using the International Classification of Health Interventions (ICHI).The compendium provides...

WHO South-East Asia Dialogue
In today’s interconnected and hyperconnected world, those in a fast-changing field such as health must keep running on the knowledge treadmill. Health...

Concept Note: Second global conference on air pollution and health
The Global conference on air pollution and health: Accelerating action for clean air, clean energy access and climate mitigation will highlight policy...

WHO Ambient Air Quality Database (Update Jan 2024)
The WHO Ambient Air Quality Database compiles data on ground measurements of annual mean concentrations of nitrogen dioxide (NO2), particulate matter of...

Frequently asked questions - directory for integrating health in urban & territorial planning
The directory is an online repository of open access resources and tools that provide information of the importance of planning and designing urban areas...


Achieving universal access and net-zero emissions by 2050
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 2030’s target for universal access to clean cooking and the overarching ambition for achieving net-zero...
Accelerating access to electricity in health-care facilities
Estimating the morbidity from air pollution and its economic costs
Identifying solutions for countries
Synthesizing evidence and knowledge on air pollution
Air pollution: The invisible health threat
Launch of WHO's Household Energy Policy Repository
What are the WHO Air quality guidelines?
Transitioning to cleaner cooking
Infographics

Household Air Pollution: Clean Cooking
Air pollution kills 13 people every minute.

SDG7 2023: Access to Clean Cooking 2

SDG7 2023: Access to Clean Cooking 1

Second global conference on air pollution and health

Clean air & energy for health webinar #5 - Clean air for public health - assessing population exposure to air pollution

Noncommunicable Diseases (NCDs) Hard Talks webinar: Toxic air is fueling NCDs - Why don't we act?

Clean air & energy for health webinar #4 - Cleaner air through better places
Second Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health
Webinar: Clean air for public health - Assessing population exposure to air pollution
Webinar: Cleaner air through better places - the Directory of resources for planning healthy environments

Related health topics
Climate change
Noncommunicable diseases
- Random article
- Teaching guide
- Privacy & cookies

by Chris Woodford . Last updated: November 22, 2022.
Photo: Air pollution is obvious when it pours from a smokestack (chimney), but it's not always so easy to spot. This is an old photo of the kind of smoke that used to come from coal-fired power plants and, apart from soot (unburned carbon particles), its pollutants include sulfur dioxide and the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide. Thanks to tougher pollution controls, modern power plants produce only a fraction as much pollution. Modern pollution made by traffic consists of gases like nitrogen dioxide and "particulates" (microscopic soot and dust fragments) that are largely invisible.
What is air pollution?
Air pollution is a gas (or a liquid or solid dispersed through ordinary air) released in a big enough quantity to harm the health of people or other animals, kill plants or stop them growing properly, damage or disrupt some other aspect of the environment (such as making buildings crumble), or cause some other kind of nuisance (reduced visibility, perhaps, or an unpleasant odor).
Natural air pollution
Photo: Forest fires are a completely natural cause of air pollution. We'll never be able to prevent them breaking out or stop the pollution they cause; our best hope is to manage forests, where we can, so fires don't spread. Ironically, that can mean deliberately burning areas of forest, as shown here, to create firebreaks. Forests are also deliberately burned to regenerate ecosystems. Photo by courtesy of US Fish and Wildlife Service .
Top-ten kinds of air pollution Photo: Flying molecules—if you could see air pollution close up, this is what it would look like. Image courtesy of US Department of Energy. Any gas could qualify as pollution if it reached a high enough concentration to do harm. Theoretically, that means there are dozens of different pollution gases. It's important to note that not all the things we think of as pollution are gases: some are aerosols (liquids or solids dispersed through gases). In practice, about ten different substances cause most concern: Sulfur dioxide : Coal, petroleum, and other fuels are often impure and contain sulfur as well as organic (carbon-based) compounds. When sulfur (spelled "sulphur" in some countries) burns with oxygen from the air, sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ) is produced. Coal-fired power plants are the world's biggest source of sulfur-dioxide air pollution, which contributes to smog, acid rain, and health problems that include lung disease. [5] Large amounts of sulfur dioxide are also produced by ships, which use dirtier diesel fuel than cars and trucks. [6] Carbon monoxide : This highly dangerous gas forms when fuels have too little oxygen to burn completely. It spews out in car exhausts and it can also build up to dangerous levels inside your home if you have a poorly maintained gas boiler , stove, or fuel-burning appliance. (Always fit a carbon monoxide detector if you burn fuels indoors.) [7] Carbon dioxide : This gas is central to everyday life and isn't normally considered a pollutant: we all produce it when we breathe out and plants such as crops and trees need to "breathe" it in to grow. However, carbon dioxide is also a greenhouse gas released by engines and power plants. Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, it's been building up in Earth's atmosphere and contributing to the problem of global warming and climate change . [8] Nitrogen oxides : Nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) and nitrogen oxide (NO) are pollutants produced as an indirect result of combustion, when nitrogen and oxygen from the air react together. Nitrogen oxide pollution comes from vehicle engines and power plants, and plays an important role in the formation of acid rain, ozone and smog. Nitrogen oxides are also "indirect greenhouse gases" (they contribute to global warming by producing ozone, which is a greenhouse gas). [9] Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) : These carbon-based (organic) chemicals evaporate easily at ordinary temperatures and pressures, so they readily become gases. That's precisely why they're used as solvents in many different household chemicals such as paints , waxes, and varnishes. Unfortunately, they're also a form of air pollution: they're believed to have long-term (chronic) effects on people's health and they play a role in the formation of ozone and smog. VOCs are also released by tobacco smoke and wildfires. [10] Particulates : There are many different kinds of particulates, from black soot in diesel exhaust to dust and organic matter from the desert. Airborne liquid droplets from farm pollution also count as particulates. Particulates of different sizes are often referred to by the letters PM followed by a number, so PM 10 means soot particles of less than 10 microns (10 millionths of a meter or 10µm in diameter, roughly 10 times thinner than a thick human hair). The smaller ("finer") the particulates, the deeper they travel into our lungs and the more dangerous they are. PM 2.5 particulates are much more dangerous (they're less than 2.5 millionths of a meter or about 40 times thinner than a typical hair). In cities, most particulates come from traffic fumes. [11] Ozone : Also called trioxygen, this is a type of oxygen gas whose molecules are made from three oxygen atoms joined together (so it has the chemical formula O 3 ), instead of just the two atoms in conventional oxygen (O 2 ). In the stratosphere (upper atmosphere), a band of ozone ("the ozone layer") protects us by screening out harmful ultraviolet radiation (high-energy blue light) beaming down from the Sun. At ground level, it's a toxic pollutant that can damage health. It forms when sunlight strikes a cocktail of other pollution and is a key ingredient of smog (see box below). [12] Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) : Once thought to be harmless, these gases were widely used in refrigerators and aerosol cans until it was discovered that they damaged Earth's ozone layer. We discuss this in more detail down below. [13] Unburned hydrocarbons : Petroleum and other fuels are made of organic compounds based on chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms. When they burn properly, they're completely converted into harmless carbon dioxide and water ; when they burn incompletely, they can release carbon monoxide or float into the air in their unburned form, contributing to smog. Lead and heavy metals : Lead and other toxic "heavy metals" can be spread into the air either as toxic compounds or as aerosols (when solids or liquids are dispersed through gases and carried through the air by them) in such things as exhaust fumes and the fly ash (contaminated waste dust) from incinerator smokestacks. [14] What are the causes of air pollution?
Photo: Even in the age of electric cars, traffic remains a major cause of air pollution. Photo by Warren Gretz courtesy of US DOE National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) (NREL photo id#46361).
Photo: Brown smog lingers over Denver, Colorado. Photo by Warren Gretz courtesy of US DOE National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) (NREL photo id#56919).
Chart: Most of the world's major cities routinely exceed World Health Organization (WHO) air pollution guidelines, though progress is being made: you can see that the 2022 figures (green) show a marked improvement on the 2016 ones (orange) in almost every case. This chart compares annual mean PM 2.5 levels in 12 representative cities around the world with the recently revised (2021) WHO guideline value of 5μg per cubic meter (dotted line). PM 2.5 particulates are those smaller than 2.5 microns and believed to be most closely linked with adverse health effects. For more about this chart and the data sources used, see note [22] .
Photo: Smokestacks billowing pollution over Moscow, Russia in 1994. Factory pollution is much less of a problem than it used to be in the world's "richer" countries—partly because a lot of their industry has been exported to nations such as China, India, and Mexico. Photo by Roger Taylor courtesy of US DOE National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) .
What effects does air pollution have?
Photo: Air pollution can cause a variety of lung diseases and other respiratory problems. This chest X ray shows a lung disease called emphysema in the patient's left lung. A variety of things can cause it, including smoking and exposure to air pollution. Photo courtesy of National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and National Institutes of Health.
" In 2016, 91% of the world population was living in places where the WHO air quality guidelines levels were not met." World Health Organization , 2018
Photo: For many years, the stonework on the Parthenon in Athens, Greece has been blackened by particulates from traffic pollution, but other sources of pollution, such as wood-burning stoves, are increasingly significant. Photo by Michael M. Reddy courtesy of U.S. Geological Survey .
How air pollution works on different scales
Indoor air pollution.
Photo: Air freshener—or air polluter?
Further reading
Acid rain—a closer look.
Photo: Acid rain can turn lakes so acidic that fish no longer survive. Picture courtesy of U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Division of Public Affairs. Why does that matter? Pure water is neither acidic nor alkaline but completely neutral (we say it has an acidity level or pH of 7.0). Ordinary rainwater is a little bit more acidic than this with about the same acidity as bananas (roughly pH 5.5), but if rain falls through sulfur dioxide pollution it can turn much more acidic (with a pH of 4.5 or lower, which is the same acidity as orange or lemon juice). When acid rain accumulates in lakes or rivers, it gradually turns the entire water more acidic. That's a real problem because fish thrive only in water that is neutral or slightly acidic (typically with a pH of 6.5–7.0). Once the acidity drops below about pH 6.0, fish soon start to die—and if the pH drops to about 4.0 or less, all the fish will be killed. Acid rain has caused major problems in lakes throughout North America and Europe. It also causes the death of forests, reduces the fertility of soil, and damages buildings by eating away stonework (the marble on the US Capitol in Washington, DC has been eroded by acid-rain, for example). One of the biggest difficulties in tackling acid rain is that it can happen over very long distances. In one notable case, sulfur dioxide air pollution produced by power plants in the UK was blamed for causing acid rain that fell on Scandinavian countries such as Norway, producing widespread damage to forests and the deaths of thousands of fish in acidified lakes. The British government refused to acknowledge the problem and that was partly why the UK became known as the "dirty man of Europe" in the 1980s and 1990s. [18] Acid rain was a particular problem in the last 30–40 years of the 20th century. Thanks to the decline in coal-fired power plants, and the sulfur dioxide they spewed out, it's less of a problem for western countries today. But it's still a big issue in places like India, where coal remains a major source of energy. Global air pollution It's hard to imagine doing anything so dramatic and serious that it would damage our entire, enormous planet—but, remarkable though it may seem, we all do things like this everyday, contributing to problems such as global warming and the damage to the ozone layer (two separate issues that are often confused). Global warming Every time you ride in a car, turn on the lights, switch on your TV , take a shower, microwave a meal, or use energy that's come from burning a fossil fuel such as oil, coal, or natural gas, you're almost certainly adding to the problem of global warming and climate change: unless it's been produced in some environmentally friendly way, the energy you're using has most likely released carbon dioxide gas into the air. While it's not an obvious pollutant, carbon dioxide has gradually built up in the atmosphere, along with other chemicals known as greenhouse gases . Together, these gases act a bit like a blanket surrounding our planet that is slowly making the mean global temperature rise, causing the climate (the long-term pattern of our weather) to change, and producing a variety of different effects on the natural world, including rising sea levels. Read more in our main article about global warming and climate change . Ozone holes
How can we solve the problem of air pollution?
Photo: Pollution solution: an electrostatic smoke precipitator helps to prevent air pollution from this smokestack at the McNeil biomass power plant in Burlington, VT. Photo by Warren Gretz courtesy of US DOE National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
What can you do to help reduce air pollution?
Photo: Buying organic food reduces the use of sprayed pesticides and other chemicals, so it helps to reduce air (as well as water) pollution.
If you liked this article...
Find out more, on this site.
- Climate change and global warming
- Environmentalism (introduction)
- Land pollution
- Organic food and farming
- Renewable energy
- Water pollution

- Breathless: Why Air Pollution Matters—and How it Affects You by Chris Woodford. Icon, 2021. My new book explores the problem in much more depth than I've been able to go into here. You can also read a bonus chapter called Angels with dirty faces: How air pollution blackens our buildings and monuments .
- The Invisible Killer: The Rising Global Threat of Air Pollution and How We Can Fight Back by Gary Fuller. Melville House, 2018.
- Reducing Pollution and Waste by Jen Green. Raintree/Capstone, 2011. A 48-page introduction for ages 9–12. The emphasis here is on getting children to think about pollution: where it comes from, who makes it, and who should solve the problem.
- Pollution Crisis by Russ Parker. Rosen, 2009. A 32-page guide for ages 8–10. It starts with a global survey of the problem; looks at air, water, and land pollution; then considers how we all need to be part of the solution.
- Earth Matters by Lynn Dicks et al. Dorling Kindersley, 2008. This isn't specifically about pollution. Instead, it explores how a range of different environmental problems are testing life to the limit in the planet's major biomes (oceans, forests, and so on). I wrote the section of this book that covers the polar regions.
- State of Global Air : One of the best sources of global air pollution data.
- American Lung Association: State of the Air Report : A good source of data about the United States.
- European Environment Agency: Air quality in Europe : A definitive overview of the situation in the European countries.
- World Health Organization (WHO) Ambient (outdoor) air pollution in cities database : A spreadsheet of pollution data for most major cities in the world (a little out of date, but a new version is expected soon).
- Our World in Data : Accessible guides to global data from Oxford University.
- The New York Times Topics: Air Pollution
- The Guardian: Pollution
- Wired: Pollution
- 'Invisible killer': fossil fuels caused 8.7m deaths globally in 2018, research finds by Oliver Milman. The Guardian, February 9, 2021. Pollution of various kinds causes something like one in five of all deaths.
- Millions of masks distributed to students in 'gas chamber' Delhi : BBC News, 1 November 2019.
- 90% of world's children are breathing toxic air, WHO study finds by Matthew Taylor. The Guardian, October 29, 2018. The air pollution affecting billions of children could continue to harm their health throughout their lives.
- Pollution May Dim Thinking Skills, Study in China Suggests by Mike Ives. The New York Times, August 29, 2018. Long-term exposure to air pollution seems to cause a decline in cognitive skills.
- Global pollution kills 9m a year and threatens 'survival of human societies' by Damian Carrington. The Guardian, October 19, 2017. Air, water, and land pollution kill millions, cost trillions, and threaten the very survival of humankind, a new study reveals.
- India's Air Pollution Rivals China's as World's Deadliest by Geeta Anand. The New York Times, February 14, 2017. High levels of pollution could be killing 1.1 million Indians each year.
- More Than 9 in 10 People Breathe Bad Air, WHO Study Says by Mike Ives. The New York Times, September 27, 2016. New WHO figures suggest the vast majority of us are compromising our health by breathing bad air.
- Study Links 6.5 Million Deaths Each Year to Air Pollution by Stanley Reed. The New York Times, June 26, 2016. Air pollution deaths are far greater than previously supposed according to a new study by the International Energy Agency.
- UK air pollution 'linked to 40,000 early deaths a year' by Michelle Roberts, BBC News, February 23, 2016. Diesel engines, cigarette smoke, and even air fresheners are among the causes of premature death from air pollution.
- This Wearable Detects Pollution to Build Air Quality Maps in Real Time by Davey Alba. Wired, November 19, 2014. A wearable pollution gadget lets people track their exposure to air pollution through a smartphone app.
- Air pollution and public health: emerging hazards and improved understanding of risk by Frank J. Kelly and Julia C. Fussell, Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2015
- Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: lines that connect by C.A. Pope and D.W. Dockery. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 2006
- Ambient and household air pollution: complex triggers of disease by Stephen A. Farmer et al, Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2014
Text copyright © Chris Woodford 2010, 2022. All rights reserved. Full copyright notice and terms of use .
Rate this page
Tell your friends, cite this page, more to explore on our website....
- Get the book
- Send feedback
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These harmful materials are called pollutants.
Biology, Ecology, Health, Earth Science, Geography
Loading ...
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment . These harmful materials are called pollutants . Pollutants can be natural, such as volcanic ash . They can also be created by human activity, such as trash or runoff produced by factories. Pollutants damage the quality of air, water, and land. Many things that are useful to people produce pollution. Cars spew pollutants from their exhaust pipes. Burning coal to create electricity pollutes the air. Industries and homes generate garbage and sewage that can pollute the land and water. Pesticides —chemical poisons used to kill weeds and insects— seep into waterways and harm wildlife . All living things—from one-celled microbes to blue whales—depend on Earth ’s supply of air and water. When these resources are polluted, all forms of life are threatened. Pollution is a global problem. Although urban areas are usually more polluted than the countryside, pollution can spread to remote places where no people live. For example, pesticides and other chemicals have been found in the Antarctic ice sheet . In the middle of the northern Pacific Ocean, a huge collection of microscopic plastic particles forms what is known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch . Air and water currents carry pollution. Ocean currents and migrating fish carry marine pollutants far and wide. Winds can pick up radioactive material accidentally released from a nuclear reactor and scatter it around the world. Smoke from a factory in one country drifts into another country. In the past, visitors to Big Bend National Park in the U.S. state of Texas could see 290 kilometers (180 miles) across the vast landscape . Now, coal-burning power plants in Texas and the neighboring state of Chihuahua, Mexico have spewed so much pollution into the air that visitors to Big Bend can sometimes see only 50 kilometers (30 miles). The three major types of pollution are air pollution , water pollution , and land pollution . Air Pollution Sometimes, air pollution is visible . A person can see dark smoke pour from the exhaust pipes of large trucks or factories, for example. More often, however, air pollution is invisible . Polluted air can be dangerous, even if the pollutants are invisible. It can make people’s eyes burn and make them have difficulty breathing. It can also increase the risk of lung cancer . Sometimes, air pollution kills quickly. In 1984, an accident at a pesticide plant in Bhopal, India, released a deadly gas into the air. At least 8,000 people died within days. Hundreds of thou sands more were permanently injured. Natural disasters can also cause air pollution to increase quickly. When volcanoes erupt , they eject volcanic ash and gases into the atmosphere . Volcanic ash can discolor the sky for months. After the eruption of the Indonesian volcano of Krakatoa in 1883, ash darkened the sky around the world. The dimmer sky caused fewer crops to be harvested as far away as Europe and North America. For years, meteorologists tracked what was known as the “equatorial smoke stream .” In fact, this smoke stream was a jet stream , a wind high in Earth’s atmosphere that Krakatoa’s air pollution made visible. Volcanic gases , such as sulfur dioxide , can kill nearby residents and make the soil infertile for years. Mount Vesuvius, a volcano in Italy, famously erupted in 79, killing hundreds of residents of the nearby towns of Pompeii and Herculaneum. Most victims of Vesuvius were not killed by lava or landslides caused by the eruption. They were choked, or asphyxiated , by deadly volcanic gases. In 1986, a toxic cloud developed over Lake Nyos, Cameroon. Lake Nyos sits in the crater of a volcano. Though the volcano did not erupt, it did eject volcanic gases into the lake. The heated gases passed through the water of the lake and collected as a cloud that descended the slopes of the volcano and into nearby valleys . As the toxic cloud moved across the landscape, it killed birds and other organisms in their natural habitat . This air pollution also killed thousands of cattle and as many as 1,700 people. Most air pollution is not natural, however. It comes from burning fossil fuels —coal, oil , and natural gas . When gasoline is burned to power cars and trucks, it produces carbon monoxide , a colorless, odorless gas. The gas is harmful in high concentrations , or amounts. City traffic produces highly concentrated carbon monoxide. Cars and factories produce other common pollutants, including nitrogen oxide , sulfur dioxide, and hydrocarbons . These chemicals react with sunlight to produce smog , a thick fog or haze of air pollution. The smog is so thick in Linfen, China, that people can seldom see the sun. Smog can be brown or grayish blue, depending on which pollutants are in it. Smog makes breathing difficult, especially for children and older adults. Some cities that suffer from extreme smog issue air pollution warnings. The government of Hong Kong, for example, will warn people not to go outside or engage in strenuous physical activity (such as running or swimming) when smog is very thick.
When air pollutants such as nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide mix with moisture, they change into acids . They then fall back to earth as acid rain . Wind often carries acid rain far from the pollution source. Pollutants produced by factories and power plants in Spain can fall as acid rain in Norway. Acid rain can kill all the trees in a forest . It can also devastate lakes, streams, and other waterways. When lakes become acidic, fish can’t survive . In Sweden, acid rain created thousands of “ dead lakes ,” where fish no longer live. Acid rain also wears away marble and other kinds of stone . It has erased the words on gravestones and damaged many historic buildings and monuments . The Taj Mahal , in Agra, India, was once gleaming white. Years of exposure to acid rain has left it pale. Governments have tried to prevent acid rain by limiting the amount of pollutants released into the air. In Europe and North America, they have had some success, but acid rain remains a major problem in the developing world , especially Asia. Greenhouse gases are another source of air pollution. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane occur naturally in the atmosphere. In fact, they are necessary for life on Earth. They absorb sunlight reflected from Earth, preventing it from escaping into space. By trapping heat in the atmosphere, they keep Earth warm enough for people to live. This is called the greenhouse effect . But human activities such as burning fossil fuels and destroying forests have increased the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This has increased the greenhouse effect, and average temperatures across the globe are rising. The decade that began in the year 2000 was the warmest on record. This increase in worldwide average temperatures, caused in part by human activity, is called global warming . Global warming is causing ice sheets and glaciers to melt. The melting ice is causing sea levels to rise at a rate of two millimeters (0.09 inches) per year. The rising seas will eventually flood low-lying coastal regions . Entire nations, such as the islands of Maldives, are threatened by this climate change . Global warming also contributes to the phenomenon of ocean acidification . Ocean acidification is the process of ocean waters absorbing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Fewer organisms can survive in warmer, less salty waters. The ocean food web is threatened as plants and animals such as coral fail to adapt to more acidic oceans. Scientists have predicted that global warming will cause an increase in severe storms . It will also cause more droughts in some regions and more flooding in others. The change in average temperatures is already shrinking some habitats, the regions where plants and animals naturally live. Polar bears hunt seals from sea ice in the Arctic. The melting ice is forcing polar bears to travel farther to find food , and their numbers are shrinking. People and governments can respond quickly and effectively to reduce air pollution. Chemicals called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are a dangerous form of air pollution that governments worked to reduce in the 1980s and 1990s. CFCs are found in gases that cool refrigerators, in foam products, and in aerosol cans . CFCs damage the ozone layer , a region in Earth’s upper atmosphere. The ozone layer protects Earth by absorbing much of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation . When people are exposed to more ultraviolet radiation, they are more likely to develop skin cancer, eye diseases, and other illnesses. In the 1980s, scientists noticed that the ozone layer over Antarctica was thinning. This is often called the “ ozone hole .” No one lives permanently in Antarctica. But Australia, the home of more than 22 million people, lies at the edge of the hole. In the 1990s, the Australian government began an effort to warn people of the dangers of too much sun. Many countries, including the United States, now severely limit the production of CFCs. Water Pollution Some polluted water looks muddy, smells bad, and has garbage floating in it. Some polluted water looks clean, but is filled with harmful chemicals you can’t see or smell. Polluted water is unsafe for drinking and swimming. Some people who drink polluted water are exposed to hazardous chemicals that may make them sick years later. Others consume bacteria and other tiny aquatic organisms that cause disease. The United Nations estimates that 4,000 children die every day from drinking dirty water. Sometimes, polluted water harms people indirectly. They get sick because the fish that live in polluted water are unsafe to eat. They have too many pollutants in their flesh. There are some natural sources of water pollution. Oil and natural gas, for example, can leak into oceans and lakes from natural underground sources. These sites are called petroleum seeps . The world’s largest petroleum seep is the Coal Oil Point Seep, off the coast of the U.S. state of California. The Coal Oil Point Seep releases so much oil that tar balls wash up on nearby beaches . Tar balls are small, sticky pieces of pollution that eventually decompose in the ocean.
Human activity also contributes to water pollution. Chemicals and oils from factories are sometimes dumped or seep into waterways. These chemicals are called runoff. Chemicals in runoff can create a toxic environment for aquatic life. Runoff can also help create a fertile environment for cyanobacteria , also called blue-green algae . Cyanobacteria reproduce rapidly, creating a harmful algal bloom (HAB) . Harmful algal blooms prevent organisms such as plants and fish from living in the ocean. They are associated with “ dead zones ” in the world’s lakes and rivers, places where little life exists below surface water. Mining and drilling can also contribute to water pollution. Acid mine drainage (AMD) is a major contributor to pollution of rivers and streams near coal mines . Acid helps miners remove coal from the surrounding rocks . The acid is washed into streams and rivers, where it reacts with rocks and sand. It releases chemical sulfur from the rocks and sand, creating a river rich in sulfuric acid . Sulfuric acid is toxic to plants, fish, and other aquatic organisms. Sulfuric acid is also toxic to people, making rivers polluted by AMD dangerous sources of water for drinking and hygiene . Oil spills are another source of water pollution. In April 2010, the Deepwater Horizon oil rig exploded in the Gulf of Mexico, causing oil to gush from the ocean floor. In the following months, hundreds of millions of gallons of oil spewed into the gulf waters. The spill produced large plumes of oil under the sea and an oil slick on the surface as large as 24,000 square kilometers (9,100 square miles). The oil slick coated wetlands in the U.S. states of Louisiana and Mississippi, killing marsh plants and aquatic organisms such as crabs and fish. Birds, such as pelicans , became coated in oil and were unable to fly or access food. More than two million animals died as a result of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Buried chemical waste can also pollute water supplies. For many years, people disposed of chemical wastes carelessly, not realizing its dangers. In the 1970s, people living in the Love Canal area in Niagara Falls, New York, suffered from extremely high rates of cancer and birth defects . It was discovered that a chemical waste dump had poisoned the area’s water. In 1978, 800 families living in Love Canal had to a bandon their homes. If not disposed of properly, radioactive waste from nuclear power plants can escape into the environment. Radioactive waste can harm living things and pollute the water. Sewage that has not been properly treated is a common source of water pollution. Many cities around the world have poor sewage systems and sewage treatment plants. Delhi, the capital of India, is home to more than 21 million people. More than half the sewage and other waste produced in the city are dumped into the Yamuna River. This pollution makes the river dangerous to use as a source of water for drinking or hygiene. It also reduces the river’s fishery , resulting in less food for the local community. A major source of water pollution is fertilizer used in agriculture . Fertilizer is material added to soil to make plants grow larger and faster. Fertilizers usually contain large amounts of the elements nitrogen and phosphorus , which help plants grow. Rainwater washes fertilizer into streams and lakes. There, the nitrogen and phosphorus cause cyanobacteria to form harmful algal blooms. Rain washes other pollutants into streams and lakes. It picks up animal waste from cattle ranches. Cars drip oil onto the street, and rain carries it into storm drains , which lead to waterways such as rivers and seas. Rain sometimes washes chemical pesticides off of plants and into streams. Pesticides can also seep into groundwater , the water beneath the surface of the Earth. Heat can pollute water. Power plants, for example, produce a huge amount of heat. Power plants are often located on rivers so they can use the water as a coolant . Cool water circulates through the plant, absorbing heat. The heated water is then returned to the river. Aquatic creatures are sensitive to changes in temperature. Some fish, for example, can only live in cold water. Warmer river temperatures prevent fish eggs from hatching. Warmer river water also contributes to harmful algal blooms. Another type of water pollution is simple garbage. The Citarum River in Indonesia, for example, has so much garbage floating in it that you cannot see the water. Floating trash makes the river difficult to fish in. Aquatic animals such as fish and turtles mistake trash, such as plastic bags, for food. Plastic bags and twine can kill many ocean creatures. Chemical pollutants in trash can also pollute the water, making it toxic for fish and people who use the river as a source of drinking water. The fish that are caught in a polluted river often have high levels of chemical toxins in their flesh. People absorb these toxins as they eat the fish. Garbage also fouls the ocean. Many plastic bottles and other pieces of trash are thrown overboard from boats. The wind blows trash out to sea. Ocean currents carry plastics and other floating trash to certain places on the globe, where it cannot escape. The largest of these areas, called the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, is in a remote part of the Pacific Ocean. According to some estimates, this garbage patch is the size of Texas. The trash is a threat to fish and seabirds, which mistake the plastic for food. Many of the plastics are covered with chemical pollutants. Land Pollution Many of the same pollutants that foul the water also harm the land. Mining sometimes leaves the soil contaminated with dangerous chemicals. Pesticides and fertilizers from agricultural fields are blown by the wind. They can harm plants, animals, and sometimes people. Some fruits and vegetables absorb the pesticides that help them grow. When people consume the fruits and vegetables, the pesticides enter their bodies. Some pesticides can cause cancer and other diseases. A pesticide called DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) was once commonly used to kill insects, especially mosquitoes. In many parts of the world, mosquitoes carry a disease called malaria , which kills a million people every year. Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Muller was awarded the Nobel Prize for his understanding of how DDT can control insects and other pests. DDT is responsible for reducing malaria in places such as Taiwan and Sri Lanka. In 1962, American biologist Rachel Carson wrote a book called Silent Spring , which discussed the dangers of DDT. She argued that it could contribute to cancer in humans. She also explained how it was destroying bird eggs, which caused the number of bald eagles, brown pelicans, and ospreys to drop. In 1972, the United States banned the use of DDT. Many other countries also banned it. But DDT didn’t disappear entirely. Today, many governments support the use of DDT because it remains the most effective way to combat malaria. Trash is another form of land pollution. Around the world, paper, cans, glass jars, plastic products, and junked cars and appliances mar the landscape. Litter makes it difficult for plants and other producers in the food web to create nutrients . Animals can die if they mistakenly eat plastic. Garbage often contains dangerous pollutants such as oils, chemicals, and ink. These pollutants can leech into the soil and harm plants, animals, and people. Inefficient garbage collection systems contribute to land pollution. Often, the garbage is picked up and brought to a dump, or landfill . Garbage is buried in landfills. Sometimes, communities produce so much garbage that their landfills are filling up. They are running out of places to dump their trash. A massive landfill near Quezon City, Philippines, was the site of a land pollution tragedy in 2000. Hundreds of people lived on the slopes of the Quezon City landfill. These people made their living from recycling and selling items found in the landfill. However, the landfill was not secure. Heavy rains caused a trash landslide, killing 218 people. Sometimes, landfills are not completely sealed off from the land around them. Pollutants from the landfill leak into the earth in which they are buried. Plants that grow in the earth may be contaminated, and the herbivores that eat the plants also become contaminated. So do the predators that consume the herbivores. This process, where a chemical builds up in each level of the food web, is called bioaccumulation . Pollutants leaked from landfills also leak into local groundwater supplies. There, the aquatic food web (from microscopic algae to fish to predators such as sharks or eagles) can suffer from bioaccumulation of toxic chemicals. Some communities do not have adequate garbage collection systems, and trash lines the side of roads. In other places, garbage washes up on beaches. Kamilo Beach, in the U.S. state of Hawai'i, is littered with plastic bags and bottles carried in by the tide . The trash is dangerous to ocean life and reduces economic activity in the area. Tourism is Hawai'i’s largest industry . Polluted beaches discourage tourists from investing in the area’s hotels, restaurants, and recreational activities. Some cities incinerate , or burn, their garbage. Incinerating trash gets rid of it, but it can release dangerous heavy metals and chemicals into the air. So while trash incinerators can help with the problem of land pollution, they sometimes add to the problem of air pollution. Reducing Pollution Around the world, people and governments are making efforts to combat pollution. Recycling, for instance, is becoming more common. In recycling, trash is processed so its useful materials can be used again. Glass, aluminum cans, and many types of plastic can be melted and reused . Paper can be broken down and turned into new paper. Recycling reduces the amount of garbage that ends up in landfills, incinerators, and waterways. Austria and Switzerland have the highest recycling rates. These nations recycle between 50 and 60 percent of their garbage. The United States recycles about 30 percent of its garbage. Governments can combat pollution by passing laws that limit the amount and types of chemicals factories and agribusinesses are allowed to use. The smoke from coal-burning power plants can be filtered. People and businesses that illegally dump pollutants into the land, water, and air can be fined for millions of dollars. Some government programs, such as the Superfund program in the United States, can force polluters to clean up the sites they polluted. International agreements can also reduce pollution. The Kyoto Protocol , a United Nations agreement to limit the emission of greenhouse gases, has been signed by 191 countries. The United States, the world’s second-largest producer of greenhouse gases, did not sign the agreement. Other countries, such as China, the world’s largest producer of greenhouse gases, have not met their goals. Still, many gains have been made. In 1969, the Cuyahoga River, in the U.S. state of Ohio, was so clogged with oil and trash that it caught on fire. The fire helped spur the Clean Water Act of 1972. This law limited what pollutants could be released into water and set standards for how clean water should be. Today, the Cuyahoga River is much cleaner. Fish have returned to regions of the river where they once could not survive. But even as some rivers are becoming cleaner, others are becoming more polluted. As countries around the world become wealthier, some forms of pollution increase. Countries with growing economies usually need more power plants, which produce more pollutants. Reducing pollution requires environmental, political, and economic leadership. Developed nations must work to reduce and recycle their materials, while developing nations must work to strengthen their economies without destroying the environment. Developed and developing countries must work together toward the common goal of protecting the environment for future use.
How Long Does It Last? Different materials decompose at different rates. How long does it take for these common types of trash to break down?
- Paper: 2-4 weeks
- Orange peel: 6 months
- Milk carton: 5 years
- Plastic bag: 15 years
- Tin can: 100 years
- Plastic bottle: 450 years
- Glass bottle: 500 years
- Styrofoam: Never
Indoor Air Pollution The air inside your house can be polluted. Air and carpet cleaners, insect sprays, and cigarettes are all sources of indoor air pollution.
Light Pollution Light pollution is the excess amount of light in the night sky. Light pollution, also called photopollution, is almost always found in urban areas. Light pollution can disrupt ecosystems by confusing the distinction between night and day. Nocturnal animals, those that are active at night, may venture out during the day, while diurnal animals, which are active during daylight hours, may remain active well into the night. Feeding and sleep patterns may be confused. Light pollution also indicates an excess use of energy. The dark-sky movement is a campaign by people to reduce light pollution. This would reduce energy use, allow ecosystems to function more normally, and allow scientists and stargazers to observe the atmosphere.
Noise Pollution Noise pollution is the constant presence of loud, disruptive noises in an area. Usually, noise pollution is caused by construction or nearby transportation facilities, such as airports. Noise pollution is unpleasant, and can be dangerous. Some songbirds, such as robins, are unable to communicate or find food in the presence of heavy noise pollution. The sound waves produced by some noise pollutants can disrupt the sonar used by marine animals to communicate or locate food.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Illustrators
Educator reviewer, last updated.
March 6, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Pollution: Samples in 100, 150 and 200 Words
- Updated on
- Apr 27, 2024

As the world embraced urbanization, mother nature witnessed the greener lands getting transformed into modern cities and metropolises. What followed is a trail of natural disasters signalling that something is wrong with the planet Earth. Pollution is increasingly asked under the writing section in school and college tests as well as competitive exams . This is because it is a relevant environmental issue today. This blog aims to help you with the necessary knowledge as well as tips and tricks to draft a well-written essay on pollution.
What is Pollution?
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These materials are called pollutants. They can be created by human activity like trash and natural like volcanic ash. Pollutants damage the quality of water, air and land. Pollution is a global problem. Air and water carry pollution into the ocean currents and migrating fish. Pollution is among the many things that harm our planet- once greener and healthier than it is now. Pollution is a dangerous phenomenon that is contributing to an array of health issues.
Types of Pollution
In simple terms, pollution is defined as the contamination of the physical and biological constituents in the earth’s atmosphere. It affects human life and the natural environment to a very great extent. It degrades our natural resources, from the water we drink to the air we breathe. While writing an essay on Pollution, you must mention the major four types of pollution which are as follows:
- Air Pollution : Air pollution is the contamination of air in the atmosphere when harmful or excessive quantities of substances such as smoke and harmful gases from industries, CFCs and oxides produced by automobiles, the burning of solid wastes, etc. are introduced into the environment.
- Water Pollution : This refers to the contamination of natural resources of water, due to the addition of harmful chemical, biological or physical materials, which includes industrial wastes, oil spills, domestic and farm wastes, pesticides, as well as mining and agricultural wastes, to water resource which make it unusable.
- Soil Pollution : Land/Soil Pollution occurs due to the degradation of the earth’s surface by different commercial, industrial, agricultural and domestic activities. Causes of soil pollution also include mining, deforestation, dumping of e-waste and other industrial wastes, usage of harmful chemicals such as insecticides, pesticides, etc.
- Noise Pollution : Excess noise due to sounds created by machines, loudspeakers, microphones, loud music, noise from industries, construction and civil engineering works etc. lead to noise pollution.
Causes and Health Effects of Pollution
You can include various causes and health effects in your essay on Pollution from the following table:-
| Air | Lung cancer, heart disease, asthma and respiratory problems | Lung cancer, heart diseases, asthma and respiratory problems |
| Water | Oil spills, rapid urbanisation, improper sewage system, chemical and radioactive waste dumping. | Cholera, Hepatitis A, Typhoid, Polio, Dysentery and Diarrhea |
| Noise | Man-made noises like construction, loudspeakers, etc. and natural noises like thunderstorms and animals. | Headaches, high blood pressure, loss of hearing, problems with reasoning and behavioural changes |
| Soil | Waste disposal, industrial and agricultural activities, excessive use of fertilisers and pesticides. | Loss of fertility, cancer, damage to the nervous system and kidney and liver failure |

Sample Essay on Pollution in 100 Words
Pollution is the addition of unwanted substances which are incorporated into the environment that can damage our Earth. There are mainly four types of pollution, these include water pollution, air pollution, soil pollution, and noise pollution. One should note that any form of pollution is the result of careless activity carried out by man. We, humans daily dump waste directly into water bodies which leads to water pollution.
Vehicle emissions of smoke into the atmosphere impede the ability of all living things to breathe, leading to air pollution. Our garbage is dumped into landfills directly, which results in soil pollution. Although it cannot be seen, noise pollution is a severe type of pollution that can harm our ears.
Sample Essay on Pollution in 250-300 Words
The biggest threat planet Earth is facing is pollution. Unwanted substances leave a negative impact once released into an environment. There are four types of pollution air, water, land, and noise. Pollution affects the quality of life more than any human can imagine.
Due to air pollution, even teenage kids have developed various respiratory diseases. Water pollution has led to diseases in children. The waste we humans dump on the land or chemical fertilisers which are put on the land for agricultural purposes causes land/ soil pollution.
If the soil quality deteriorates due to such practices, the soil will become infertile and no crops could be grown in future. The government has launched various schemes over the years to fight pollution but individual efforts can also play a vital role.
Start by replacing plastic bags for shopping with cloth bags, stopping littering on roads and stopping wasting water are some of the basic things to start with that can lead to big changes in the environment.
Also Read: Essay on Green Energy PDF: 150 and 250 Words
Sample Essay on Pollution in 300-350 Words
One of the most critical threats faced by our planet in the present-day scenario. Environmental pollution is a global issue affecting people around the world. It is occurring in different forms, whether by affecting the air we breathe or the water resources we utilise for several purposes.
Air pollution came into being with an increase in the level of carbon dioxide, with the increase in pollutants which are contaminating the air and causing breathing discomfort as well as skin diseases to human beings. Talking about the other aspect, there is no life without water.
The water bodies are polluting and becoming unsafe for drinking or any other use because of industrial development, rapid urbanisation and various other reasons. Due to air pollution, diseases that can occur in human beings are asthma, various skin diseases, cancer, etc. Therefore, it is the essential need of the hour to take serious steps to reduce pollution to its core.
At a personal level, we can minimise environmental pollution by taking public transport or carpools to reduce vehicular smoke, avoiding firecrackers at festivals and celebrations can also cut down on air and noise pollution, and not using fertilisers and pesticides which can cause both water and soil pollution, and switching over to organic farming. The government can also bring strict rules and regulations to lessen industrial pollution.
To sum up, any type of pollution is harmful to the environment with serious consequences like global warming, uneven climatic changes, etc. Due to our greediness and illegal human activities, the innocent lives of animals are lost. The time has come to join hands and work towards preserving and protecting the environment for the present as well as future generations.
Also Read: Essay on Environment: Examples and Tips
Short Essay on Pollution in English
Find a sample of a short essay on pollution below:

Related Reads
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay-writing page and follow Leverage Edu !
Nikita Puri
Nikita is a creative writer and editor, who is always ready to learn new skills. She has great knowledge about study abroad universities, researching and writing blogs about them. Being a perfectionist, she has a habit of keeping her tasks complete on time before the OCD hits her. When Nikita is not busy working, you can find her eating while binge-watching The office. Also, she breathes music. She has done her bachelor's from Delhi University and her master's from Jamia Millia Islamia.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
pollution is very harmful to the environment. By pollution many diseases and virus like coronavirus. So JOIN THE GREEN REVOLUTION AND STOP POLLUTION
PLANT MORE AND MORE TREES TO REDUCE POLLUTION

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Essay on Air Pollution for Students and Children
500+ words essay on air pollution.
Essay on Air Pollution – Earlier the air we breathe in use to be pure and fresh. But, due to increasing industrialization and concentration of poisonous gases in the environment the air is getting more and more toxic day by day. Also, these gases are the cause of many respiratory and other diseases . Moreover, the rapidly increasing human activities like the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation is the major cause of air pollution.

How Air Gets Polluted?
The fossil fuel , firewood, and other things that we burn produce oxides of carbons which got released into the atmosphere. Earlier there happens to be a large number of trees which can easily filter the air we breathe in. But with the increase in demand for land, the people started cutting down of trees which caused deforestation. That ultimately reduced the filtering capacity of the tree.
Moreover, during the last few decades, the numbers of fossil fuel burning vehicle increased rapidly which increased the number of pollutants in the air .
Causes Of Air Pollution
Its causes include burning of fossil fuel and firewood, smoke released from factories , volcanic eruptions, forest fires, bombardment, asteroids, CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons), carbon oxides and many more.
Besides, there are some other air pollutants like industrial waste, agricultural waste, power plants, thermal nuclear plants, etc.
Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is also the cause of air pollution because air pollution produces the gases that greenhouse involves. Besides, it increases the temperature of earth surface so much that the polar caps are melting and most of the UV rays are easily penetrating the surface of the earth.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Effects Of Air Pollution On Health

Moreover, it increases the rate of aging of lungs, decreases lungs function, damage cells in the respiratory system.
Ways To Reduce Air Pollution
Although the level of air pollution has reached a critical point. But, there are still ways by which we can reduce the number of air pollutants from the air.
Reforestation- The quality of air can be improved by planting more and more trees as they clean and filter the air.
Policy for industries- Strict policy for industries related to the filter of gases should be introduced in the countries. So, we can minimize the toxins released from factories.
Use of eco-friendly fuel- We have to adopt the usage of Eco-friendly fuels such as LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas), CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), bio-gas, and other eco-friendly fuels. So, we can reduce the amount of harmful toxic gases.
To sum it up, we can say that the air we breathe is getting more and more polluted day by day. The biggest contribution to the increase in air pollution is of fossil fuels which produce nitric and sulphuric oxides. But, humans have taken this problem seriously and are devotedly working to eradicate the problem that they have created.
Above all, many initiatives like plant trees, use of eco-friendly fuel are promoted worldwide.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [{ “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Mention five effect of air pollution on human health?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “The major risk factor related to human health are asthma, lung cancer, Alzheimer, psychological complications, and autism. Besides, there are other effects of air pollution on a person’s health.”} }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the effect of air pollution in the environment?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”:”Acid, rain, ozone depletion, greenhouse gases, smog are many other things are the cause of air pollution that affect the environment severely.”} }] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Still accepting applications for online and hybrid programs!
- Skip to content
- Skip to search
- Accessibility Policy
- Report an Accessibility Issue

- The impact of air pollution on your health
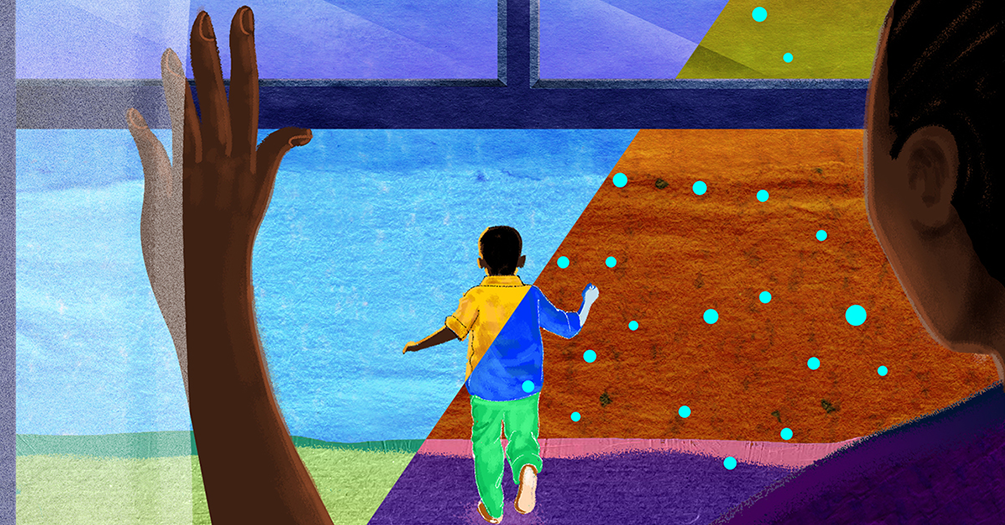

Associate Professor of Epidemiology and Global Public Health
May 31, 2024
I am fascinated with how the world around us—specifically the air we breathe—impacts our health. Growing up in the smog of Los Angeles, the haze was more than just a backdrop for my day-to-day activities; it was also an early lesson in environmental health that has become the focus of my career.
As a researcher and instructor, I use modern principles of epidemiology, environmental health, exposure science, and biostatistics to study the impacts of our environment, including air pollution, on our health.
Air pollution is important to think about because we are all obligatory breathers. We all need air to live—from the day we are born to the day we die- and our air contains contaminants that are harmful to our health. When we are experiencing high levels of pollution, like during wildfire events, we may be able to see the poor quality of our air but pollution is also present when it is invisible to us.
Exposures to air pollution, even at levels below our current regulatory standards, can have lasting effects on health. For example, in my research, I've seen how sustained exposure to dirty air can damage children's lungs and lead to plaque buildup in the arteries of adults. While this sometimes surprises people, it’s helpful to think about air pollution as being similar to smoking cigarettes. Although the exposure is much more diluted, we are still breathing in microscopic particles and gases that may originate from smoke from traffic or industry or other sources. When we inhale these pollutants, they can trigger a chain reaction in the body, similar to cigarette smoke. This may start with inflammation as a protective response but over time can lead to chronic illnesses as severe as heart disease. The smallest pollutants can pass into our bloodstream and travel to important organs in our bodies like our brains, leading to sometimes less expected outcomes like dementia. Notably, air pollution increases the risk of disease among all people but certain groups, like young children, older adults, and people with chronic diseases likely face even greater risks from these exposures.
Listen to "Breathing Easy: Navigating the Invisible Impact of Air Pollution" on Spreaker.
Even though air pollution levels have declined in the last several decades in the United States, those declines have not been the same everywhere and some neighborhoods still have high levels. Similarly, breathing in outdoor air is not the only cause of exposure. For example, children can experience high levels of exposure during their commutes to school if they ride very old diesel school buses.
Another area of my research examines the impact of school bus emissions on children’s health. Our findings present a clear message: Cleaner school buses equal healthier kids, who show up to school more and learn more. Therefore, I really must applaud the investments by the EPA and the government in helping school districts purchase newer and cleaner buses. Our findings suggest that their investments have improved the health of children, resulting in direct educational and economic benefits.
In addition to exposures from the transportation sector and other more traditional industrial sources of air pollution, we have recently seen the impact of wildfires on air quality. In some parts of the country, wildfires have emerged as a leading source of population exposure to air pollution. Our group recently demonstrated that the health impacts of these events may extend beyond the times when the air is thick with smoke and repeated exposures may increase the risk of dementia among older adults.
We found similar relationships with air pollution from agricultural activities where the application of neurotoxic pesticides are common, suggesting a compelling argument for a broader consideration of what constitutes an important pollution source for health.
We're all breathing in air pollution no matter where we live or what side of the political divide we land on, and we all experience the health impacts of those exposures.
Although we are learning that there are many health impacts of air pollution from both traditional and non-traditional sources, the silver lining is found in regulatory successes such as the National Ambient Air Quality Standards , which have significantly reduced pollution levels and contributed to the increased life expectancy of Americans.
As an eternal optimist, I often think about the many ways in which we can intervene to reduce population exposures and improve health. This will require a commitment to clean air, but the call to action is clear. Therefore, what I would love to see is that, as a society, we start to value clean air, and we approach this as a nonpartisan issue. We're all breathing in air pollution no matter where we live or what side of the political divide we land on, and we're all experiencing the health impacts of those exposures. In my dream world, our society would value clean air and protect health.
About the author

Sara Adar is an associate professor of epidemiology at the University of MichiganSchool of Public Health. Her research primarily focuses on the effects of air pollution and noise on healthy aging, with additional interestsin global health, extreme weather events, and intervention strategies to improve health.
- Listen to Adar on the Population Healthy podcast: The invisible impacts of air pollution
- READ: Sara Adar’s research informs the EPA and helps safeguard kids
- Support research and engaged learning at Michigan Public Health
- Epidemiology
- Air Quality
- Child Health
- Environmental Health
- Heart Disease
Recent Posts
- Balancing heritage and health: Significance of culturally tailored dietary recommendations for immigrant communities
- Gen Z: The emerging champions of community healthcare
- Enhancing specialty care in community health centers: A collaborative model for sustainable healthcare
What We’re Talking About
- About the Pursuit
- Adolescent Health
- Alternative Therapies
- Biostatistics
- Breastfeeding
- Chronic Disease
- Community Partnership
- Computational Epidemiology and Systems Modeling
- Disaster Relief
- Diversity Equity and Inclusion
- Engaged Learning
- Entrepreneurship
- Epidemiologic Science
- Epigenetics
- First Generation Students
- Food Policy
- Food Safety
- Global Public Health
- HMP Executive Masters
- Health Behavior and Health Education
- Health Care
- Health Care Access
- Health Care Management
- Health Care Policy
- Health Communication
- Health Disparities
- Health Informatics
- Health for Men
- Health for Women
- Hospital Administration
- Immigration
- Industrial Hygiene
- Infectious Disease
- Internships
- LGBT Health
- Maternal Health
- Mental Health
- Occupational and Environmental Epidemiology
- Pain Management
- Pharmaceuticals
- Precision Health
- Professional Development
- Reproductive Health
- Scholarships
- Sexual Health
- Social Epidemiology
- Social Media
- Student Organizations
- Urban Health
- Urban Planning
- Value-Based Care
- Water Quality
- What Is Public Health?
Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Alumni and Donors
- Community Partners and Employers
- About Public Health
- How Do I Apply?
- Departments
- Findings magazine
Student Resources
- Career Development
- Certificates
- The Heights Intranet
- Update Contact Info
- Report Website Feedback
Types of Air Pollution
Air pollution is a pressing concern among the different environmental issues that are prevalent in the world. It is the reason behind hundreds of thousands premature deaths in several countries.
The air that we breathe is contaminated with dust particles, exhaust from automobiles, chemical fumes from factories and industries, smoke and other particulate matter. These unwanted materials make their way into our airway when we respire and cause various respiratory problems like difficulty in breathing, lung inflammation, lung function decrease, asthma etc. Researchers have also linked air pollution to adverse impacts on our central nervous system.
Air pollution effects wildlife and plant life. The particulate matter can change soil chemistry and consequently bring changes in the growth of vegetation. Introduction of more gases like nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, carbon dioxide etc. also play a role in formation of harmful ozone and acid rain which effects all living organisms.
Generally, air pollution has been divided into two types.
1. Indoor pollution
It is the pollution of air caused by the introduction of materials from smoking and burning fossil fuels such as kerosene, petroleum and coal indoors. Fuels are burned indoors for cooking and cooling or heating purposes. Chemicals from cleaning products, wall paints, pesticides and air fresheners also contribute to indoor air pollution.
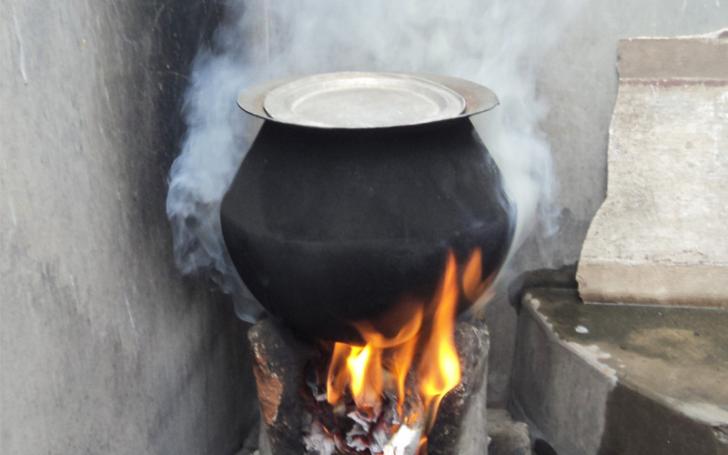

One half of the population in the world or 80% of the population in South Asia and Africa is affected by indoor air pollution from burning of coal and biomass. It is assumed that indoor air pollution is much worse than pollution outdoors.
2. Outdoor pollution
The levels of outdoor air pollution reach their peak in developing countries, most of them from Asia. The air outside is polluted mainly from vehicle exhaust and emissions from industries. Several pollutants are mixed in the air and a large portion of the world population is regularly exposed to harmful air quality.
Air pollution can also be divided into other types. According to the American Lung Association, the two major types of air pollution which harm human health are
Smog is the mixture of two components; smoke and fog. The term was introduced first in mid-20 th century in London.
Its primary component is harmful ozone found at ground level. Smog is formed as a result of complex photochemical reactions that involve nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds. Smog causing pollutants are found in sources like exhaust from vehicles, fumes from power plants and solvents.
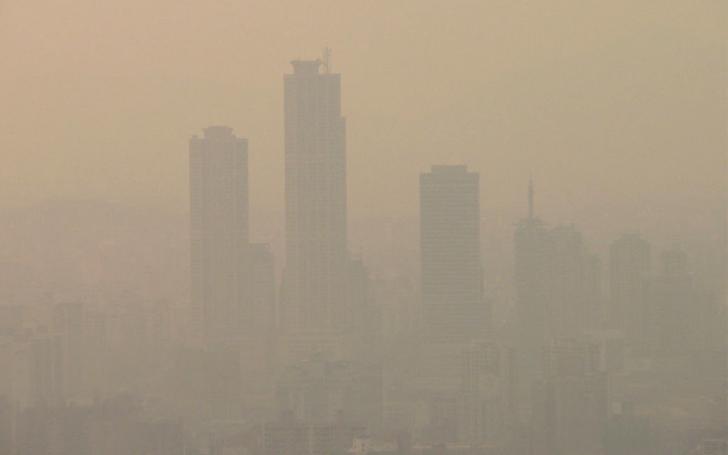

Smog can cause several health problems like breathing problems, decrease in resistance to colds and infections, irritation of eyes and throat, asthma etc.
Particle pollution
Particle pollution is also a serious issue in the world. It is widespread in cities and urban areas. This kind of pollution is caused due to the exhaust from burning diesel fuels in heavy transportation, burning of fuels in power plants and burning wood. It has been known to increase problems of heart diseases, cancer of the lungs, coughs and asthma.
Other types of air pollution are
Greenhouse effect
Greenhouse gases are responsible for the trapping of heat in the earth atmosphere which results in the warming of the planet. These gases are increased significantly because of human activities such as exhaust from vehicles and industries, agriculture and generation of electricity. Rise in greenhouse gas emissions help in the increase of global temperature.
Natural air pollution
It is the air pollution caused by natural causes. Sometimes nature is also responsible for polluting the air. Volcanic eruptions, radioactive decay and forest fires are natural causes.

కాలుష్య రకాలు వ్యాసం Types of Pollution essay in Telugu
Types of Pollution essay in Telugu కాలుష్య రకాలు వ్యాసం: Even children are becoming more aware of the term pollution. Pollution is so well-known that nearly everyone recognizes that it is on the rise. Pollution is the presence of an unwelcome foreign substance in a product. We refer to pollution as the contaminating of natural resources by different pollutants. This is mostly due to human activities that cause environmental damage in more ways than one. This is why it is urgent that we address this problem immediately. This means that pollution is causing severe damage to our planet. We need to recognize its effects and take steps to reduce it. This essay will discuss the causes of pollution and ways to reduce them.
Also called as: Essay about Types of Pollution in Telugu, Kalushyam Rakalu essay in Telugu.

Pollution’s effects
Pollution has a greater impact on quality of life than anyone can imagine. Sometimes it works in ways that are difficult to see with the naked eye. It is nevertheless very present in the environment. You might not be capable of seeing the natural gases in the air but they are still present. The same goes for the pollutants that are causing pollution in the air. This is dangerous for human health. Global warming will be caused by an increase in carbon dioxide.
The water supply is also being polluted by industrial development, religious practices, and other factors that can lead to a shortage. Human life cannot be sustained without water. Land pollution can also cause soil to become toxic from the waste that is left on it. If this continues, there will be no fertile soil for our crops. It is imperative that we take serious steps to reduce the pollution.
Different types of pollution
- Air Pollution
- Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution
How can we reduce pollution?
Once you have learned the negative effects of pollution, it is important to take immediate action to prevent or reduce pollution. Public transport and carpooling are the best ways to reduce pollution. It may seem difficult, but avoiding fireworks at festivals and other celebrations can help reduce noise pollution and air pollution. We must also practice recycling. All of the plastic that isn’t used ends up in the oceans or on the land, where it pollutes the environment.
Don’t throw them away after they are used. Instead, try to reuse them as much as possible. It is important to encourage people to plant more trees that absorb harmful gases and clean the air. To maintain soil fertility, it is important that the government reduces fertilizer use. Additionally, it is important to ban industries from dumping their waste in rivers and oceans, which can cause water pollution.
All forms of pollution are dangerous and have grave consequences. Everybody must make a change, from individuals to industries. This problem requires a collective effort. We must work together now. These human activities are also threatening the lives of innocent animals. To make the earth clean, we must all stand up and speak out.
Related Posts:
- మకర సంక్రాంతి వ్యాసం Makar Sankranti essay in Telugu
- మహిళా దినోత్సవం వ్యాసం Women's Day essay in Telugu
- స్వచ్ఛ భారత్ వ్యాసం Swachh Bharat essay in Telugu
- సమాజంలో విద్యార్థుల పాత్ర వ్యాసం Role of Students in Society essay in Telugu
- ఉగాది వ్యాసం Ugadi essay in Telugu
- రహదారి భద్రత వ్యాసం Road Safety essay in Telugu
- మహాత్మా గాంధీ వ్యాసం Mahatma Gandhi essay in Telugu
- Biology Article
Air Pollution Control
Air pollution & its control, air pollution definition.
“Air Pollution is the release of pollutants such as gases, particles, biological molecules, etc. into the air that is harmful to human health and the environment.”
Air Pollution Diagram

Table of Contents
What is Air Pollution?
Types of air pollutants, primary pollutants, secondary pollutants, causes of air pollution.
Air pollution refers to any physical, chemical or biological change in the air. It is the contamination of air by harmful gases, dust and smoke which affects plants, animals and humans drastically.
There is a certain percentage of gases present in the atmosphere. An increase or decrease in the composition of these gases is harmful to survival. This imbalance in the gaseous composition has resulted in an increase in earth’s temperature, which is known as global warming.
There are two types of air pollutants:
The pollutants that directly cause air pollution are known as primary pollutants. Sulphur-dioxide emitted from factories is a primary pollutant.
The pollutants formed by the intermingling and reaction of primary pollutants are known as secondary pollutants. Smog, formed by the intermingling of smoke and fog, is a secondary pollutant.
Also Read: Water Pollution
Following are the important causes of air pollution:
Burning of Fossil Fuels
The combustion of fossil fuels emits a large amount of sulphur dioxide. Carbon monoxide released by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels also results in air pollution.
Automobiles
The gases emitted from vehicles such as jeeps, trucks, cars, buses, etc. pollute the environment. These are the major sources of greenhouse gases and also result in diseases among individuals.
Agricultural Activities
Ammonia is one of the most hazardous gases emitted during agricultural activities. The insecticides, pesticides and fertilisers emit harmful chemicals in the atmosphere and contaminate it.
Factories and Industries
Factories and industries are the main source of carbon monoxide, organic compounds, hydrocarbons and chemicals. These are released into the air, degrading its quality.
Mining Activities
In the mining process, the minerals below the earth are extracted using large pieces of equipment. The dust and chemicals released during the process not only pollute the air, but also deteriorate the health of the workers and people living in the nearby areas.
Domestic Sources
The household cleaning products and paints contain toxic chemicals that are released in the air. The smell from the newly painted walls is the smell of the chemicals present in the paints. It not only pollutes the air but also affects breathing.
Effects of Air Pollution
The hazardous effects of air pollution on the environment include:
Air pollution has resulted in several respiratory disorders and heart diseases among humans. The cases of lung cancer have increased in the last few decades. Children living near polluted areas are more prone to pneumonia and asthma. Many people die every year due to the direct or indirect effects of air pollution.
Global Warming
Due to the emission of greenhouse gases, there is an imbalance in the gaseous composition of the air. This has led to an increase in the temperature of the earth. This increase in earth’s temperature is known as global warming . This has resulted in the melting of glaciers and an increase in sea levels. Many areas are submerged underwater.
The burning of fossil fuels releases harmful gases such as nitrogen oxides and sulphur oxides in the air. The water droplets combine with these pollutants, become acidic and fall as acid rain which damages human, animal and plant life.
Ozone Layer Depletion
The release of chlorofluorocarbons, halons, and hydrochlorofluorocarbons in the atmosphere is the major cause of depletion of the ozone layer. The depleting ozone layer does not prevent the harmful ultraviolet rays coming from the sun and causes skin diseases and eye problems among individuals. Also Read: Ozone Layer Depletion
Effect on Animals
The air pollutants suspend in the water bodies and affect aquatic life. Pollution also compels the animals to leave their habitat and shift to a new place. This renders them stray and has also led to the extinction of a large number of animal species.
Following are the measures one should adopt, to control air pollution:
Avoid Using Vehicles
People should avoid using vehicles for shorter distances. Rather, they should prefer public modes of transport to travel from one place to another. This not only prevents pollution, but also conserves energy.
Energy Conservation
A large number of fossil fuels are burnt to generate electricity. Therefore, do not forget to switch off the electrical appliances when not in use. Thus, you can save the environment at the individual level. Use of energy-efficient devices such as CFLs also controls pollution to a greater level.
Use of Clean Energy Resources
The use of solar, wind and geothermal energies reduce air pollution at a larger level. Various countries, including India, have implemented the use of these resources as a step towards a cleaner environment.
Other air pollution control measures include:
- By minimising and reducing the use of fire and fire products.
- Since industrial emissions are one of the major causes of air pollution, the pollutants can be controlled or treated at the source itself to reduce its effects. For example, if the reactions of a certain raw material yield a pollutant, then the raw materials can be substituted with other less polluting materials.
- Fuel substitution is another way of controlling air pollution. In many parts of India, petrol and diesel are being replaced by CNG – Compressed Natural Gas fueled vehicles. These are mostly adopted by vehicles that aren’t fully operating with ideal emission engines.
- Although there are many practices in India, which focus on repairing the quality of air, most of them are either forgotten or not being enforced properly. There are still a lot of vehicles on roads which haven’t been tested for vehicle emissions.
- Another way of controlling air pollution caused by industries is to modify and maintain existing pieces of equipment so that the emission of pollutants is minimised.
- Sometimes controlling pollutants at the source is not possible. In that case, we can have process control equipment to control the pollution.
- A very effective way of controlling air pollution is by diluting the air pollutants.
- The last and the best way of reducing the ill effects of air pollution is tree plantation. Plants and trees reduce a large number of pollutants in the air. Ideally, planting trees in areas of high pollution levels will be extremely effective.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the major cause of air pollution, how air pollution causes global warming, what is acid rain name the gases responsible for acid rain., deforestation is a major reason for air pollution. explain..

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
| BIOLOGY Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
very well explained. I could not find so amazing information on air pollution for school hw. Epic stuff!!!
THANK U FOR THIS! THIS WAS VERY HELPFULL FOR ME!!!!!!!
😢😢😢Yes, everyone has not aware about pollution and but we do effort for reduce pollution & make our earth future bright💐💐
Right✔👉 bro😎
Thank you Byjus for such an easy lesson !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Relevant answers and easy to learn and understand Byjus helps me alot Thanks
At the time of lockdown the environment has improved but when the lockdown will end the pollution rate would increase😖😖😖😫😫😫🙁🙁🙁🙍🙍🙍
Otherwise nicely explained👍👍👍keep it up
Yaa right bro Thanks to Byjus for this
THANX FOR ALL THESE INFO.
a very informative page
There is nothing more than living in a world full of Polluted gas and we leave bad environment for our future generation. 😕 Lets keep the word a beautiful place to live for everyone.
Very useful 👌 used it for my daughter’s oral
It is very useful I understood everything
Nice presentation and explanation 👌👌👌and it’s very useful for better understanding
Thank you so much, this content was really very informative, helpful and too useful for me. Thanks to Byjus 🙏😇
Thank you soo much for this info . It was really helpful for my project
Thank you BYJUS
Thank you sooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooo much this helped me in my project
THANK YOU BYJU’S. THIS HELPED IN MY PREASENTATION👍😊👍🏻
It helped me a lot with my project, thank you so much Byjus!
It’s very good for students
Well explained!
Thank you so much.
Byjus is best
Thank you for this this was very helpful for me
Thank you soooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooo much this helped me in my project
Well explained
Thank you so much
This is very good. And this makes my project easy
Thank you so much 🙏🙏 Easily understandable language. Lots of love and respect from the “Heaven of eath”. KASHMIR 🥰🥰
Really good by byjus 👏👍👍 It really help in my projects work And I got 1 prize because of bonus
Thanks From Prabal
Thank you so much it is easy way to understan so thank you😍😍😍
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
JavaScript appears to be disabled on this computer. Please click here to see any active alerts .
Our Current Understanding of the Human Health and Environmental Risks of PFAS
What epa is doing.
Learn what EPA is doing to address PFAS.
Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Are a Group of Manufactured Chemicals
PFAS are a group of manufactured chemicals that have been used in industry and consumer products since the 1940s because of their useful properties. There are thousands of different PFAS, some of which have been more widely used and studied than others.
Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS), for example, are two of the most widely used and studied chemicals in the PFAS group. PFOA and PFOS have been replaced in the United States with other PFAS in recent years.
One common characteristic of concern of PFAS is that many break down very slowly and can build up in people, animals, and the environment over time.
PFAS Can Be Found in Many Places
PFAS can be present in our water, soil, air, and food as well as in materials found in our homes or workplaces, including:
- Drinking water – in public drinking water systems and private drinking water wells.
- Soil and water at or near waste sites - at landfills, disposal sites, and hazardous waste sites such as those that fall under the federal Superfund and Resource Conservation and Recovery Act programs.
- Fire extinguishing foam - in aqueous film-forming foams (or AFFFs) used to extinguish flammable liquid-based fires. Such foams are used in training and emergency response events at airports, shipyards, military bases, firefighting training facilities, chemical plants, and refineries.
- Manufacturing or chemical production facilities that produce or use PFAS – for example at chrome plating, electronics, and certain textile and paper manufacturers.
- Food – for example in fish caught from water contaminated by PFAS and dairy products from livestock exposed to PFAS.
- Food packaging – for example in grease-resistant paper, fast food containers/wrappers, microwave popcorn bags, pizza boxes, and candy wrappers.
- Household products and dust – for example in stain and water-repellent used on carpets, upholstery, clothing, and other fabrics; cleaning products; non-stick cookware; paints, varnishes, and sealants.
- Personal care products – for example in certain shampoo, dental floss, and cosmetics.
- Biosolids – for example fertilizer from wastewater treatment plants that is used on agricultural lands can affect ground and surface water and animals that graze on the land.
People Can Be Exposed to PFAS in a Variety of Ways
Due to their widespread production and use, as well as their ability to move and persist in the environment, surveys conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that most people in the United States have been exposed to some PFAS. Most known exposures are relatively low, but some can be high, particularly when people are exposed to a concentrated source over long periods of time. Some PFAS chemicals can accumulate in the body over time.
Current research has shown that people can be exposed to PFAS by:
- Working in occupations such as firefighting or chemicals manufacturing and processing.
- Drinking water contaminated with PFAS.
- Eating certain foods that may contain PFAS, including fish.
- Swallowing contaminated soil or dust.
- Breathing air containing PFAS.
- Using products made with PFAS or that are packaged in materials containing PFAS.
Exposure to PFAS May be Harmful to Human Health
Current scientific research suggests that exposure to certain PFAS may lead to adverse health outcomes. However, research is still ongoing to determine how different levels of exposure to different PFAS can lead to a variety of health effects. Research is also underway to better understand the health effects associated with low levels of exposure to PFAS over long periods of time, especially in children.
What We Know about Health Effects
Current peer-reviewed scientific studies have shown that exposure to certain levels of PFAS may lead to:
- Reproductive effects such as decreased fertility or increased high blood pressure in pregnant women.
- Developmental effects or delays in children, including low birth weight, accelerated puberty, bone variations, or behavioral changes.
- Increased risk of some cancers, including prostate, kidney, and testicular cancers.
- Reduced ability of the body’s immune system to fight infections, including reduced vaccine response.
- Interference with the body’s natural hormones.
- Increased cholesterol levels and/or risk of obesity.
Additional Health Effects are Difficult to Determine
Scientists at EPA, in other federal agencies, and in academia and industry are continuing to conduct and review the growing body of research about PFAS. However, health effects associated with exposure to PFAS are difficult to specify for many reasons, such as:
- There are thousands of PFAS with potentially varying effects and toxicity levels, yet most studies focus on a limited number of better known PFAS compounds.
- People can be exposed to PFAS in different ways and at different stages of their life.
- The types and uses of PFAS change over time, which makes it challenging to track and assess how exposure to these chemicals occurs and how they will affect human health.
Certain Adults and Children May Have Higher Exposure to PFAS
Some people have higher exposures to PFAS than others because of their occupations or where they live. For example:
- Industrial workers who are involved in making or processing PFAS or PFAS-containing materials, or people who live or recreate near PFAS-producing facilities, may have greater exposure to PFAS.
- Pregnant and lactating women tend to drink more water per pound of body weight than the average person and as a result they may have higher PFAS exposure compared to other people if it is present in their drinking water.
Because children are still developing, they may be more sensitive to the harmful effects of chemicals such as PFAS. They can also be exposed more than adults because:
- Children drink more water, eat more food, and breathe more air per pound of body weight than adults, which can increase their exposure to PFAS.
- Young children crawl on floors and put things in their mouths which leads to a higher risk of exposure to PFAS in carpets, household dust, toys, and cleaning products.
Breast milk from mothers with PFAS in their blood and formula made with water containing PFAS can expose infants to PFAS, and it may also be possible for children to be exposed in utero during pregnancy. Scientists continue to do research in this area. Based on current science, the benefits of breastfeeding appear to outweigh the risks for infants exposed to PFAS in breast milk . To weigh the risks and benefits of breastfeeding, mothers should contact their doctors.
Where to Go for the Latest Information on PFAS
News releases from epa about pfas.
Sign up to receive EPA’s press releases and alerts on PFAS related topics.
Federal Government Resources
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR)
- National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- United States Department of Defense (DOD)
- United States Navy
- United States Air Force, Civil Engineering Center
State Government Resources
- Association of State Drinking Water Administrators (ASDWA)
- Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council (ITRC)
- Environmental Council of the States (ECOS)
- Environmental Research Institute of the States (ERIS)
Information on How to Provide Input on Proposed Government Actions
What is a regulation.
Under federal environmental laws, EPA and other federal agencies are authorized to help put those laws into effect by creating and enforcing regulations.
Regulations are mandatory requirements that can apply to individuals, businesses, state or local governments, non-profits, and others.
Federal agencies are required to provide an opportunity for public comment when proposing a new regulation and must consider the comments in revising the proposal and issuing a final rule. In carrying out our mission to protect human health and the environment, EPA develops regulations to prevent or to clean up hazardous chemicals released into our air, land, and water, some of which relate to PFAS.
Commenting on a proposed regulation is an important opportunity to make your voice heard. It is a way for you to provide decisionmakers with key information on any or all aspects of the proposed action, including:
- Pointing out key issues in the proposed regulation that you or your community are concerned about,
- Offering additional data and scientific evidence that may not have been considered,
- Identifying factual errors, and
- Proposing alternative solutions.
EPA’s regulations will always be announced in the Federal Register and can be found at the following government websites: https://www.federalregister.gov/ , and https://www.regulations.gov/ .
For some rules, EPA holds a public hearing where you can provide comments in person or remotely. The agency always accepts comments in writing. All comments – whether in person or written – get the same level of consideration. Below are additional resources to help you comment on EPA’s proposed regulations related to PFAS.
- Learn how to get involved with EPA regulations .
- Read tips for submitting effective comments on EPA’s proposed regulations .
- Watch a webinar on “Techniques and Skills for Providing Effective Input in the EPA Rulemaking Process.”
- EPA's Current Understanding
- Increasing Our Understanding
- Action Steps to Reduce Risk
- EPA Actions to Address PFAS
- PFAS Strategic Roadmap
- Data and Tools
- State Information
- U.S. Government
- Bill of Rights and Amendments to the Constitution
- U.S. Constitution
- Supreme Court Cases
- Path to American Civil War
- Great Depression
- Reconstruction
- Franklin D. Roosevelt and the New Deal
- Vietnam War
- World War I
- World War II
- Language Quizzes
- Science Quizzes
- History Quizzes
- Facts and Stats about the Normandy Invasion
- Timeline, Facts and Stats of the Attack on Pearl Harbor
- Assault Plans, Facts and Figures At Gold, Juno, Sword Beaches During The Normandy Invasion
- Atomic Bombing of Hiroshima
- On-This-Day
- SavingEarth ›
- SpaceNext50
- Visit Britannica.com ›

INFOGRAPHICS
Discover the major kinds of pollution.

Related Infographics

Pollution can be described as a nutrient or substance that is out of place. More specifically, however, it is the addition of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or any form of energy (such as heat, sound, or radioactivity) to the environment at a rate faster than it can be dispersed, diluted, decomposed, recycled, or stored in some harmless form.
Although most of the nutrients or substances that contribute to air, land, and water pollution are limited to a single environment, air, land, and water do interact with one another.
Air pollution results when the by-product of an activity makes chemicals airborne.
Close to Earth’s surface, sulfur dioxide (SO2) interacts with the water cycle in the atmosphere to produce acid rain or other forms of acid deposition downwind.
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) in vehicle exhaust and sunlight combine to form photochemical smog.
Further aloft, carbon dioxide and methane, which are largely by-products of burning wood, oil, natural gas, and other fossil fuels, help to enhance the atmosphere’s ability to retain heat emitted from Earth’s surface, which contributes to the phenomenon known as global warming.
In the upper atmosphere, chlorofluorocarbons (that is, CFCs) and similar chemical compounds have contributed to the destruction of Earth’s ozone layer until relatively recently.
Land pollution often contributes to water pollution as nutrients and substances from polluted sites seep into the groundwater or run off into lakes and rivers before reaching the oceans.
Hydraulic fracturing, which is used to recover natural gas and oil from the ground, releases some of these hydrocarbons into the surrounding rock, which can then seep into the groundwater. With groundwater being a source of potable water for many people, groundwater contamination is a serious issue.
Pesticides, along with nitrogen and phosphorus from agricultural fertilizers, run off of croplands and into waterways, where they affect the aquatic and marine food chains. Pesticides poison insects, fish, and the animals that eat them. Nitrogenous and phosphorus fertilizers “feed” algae and other aquatic plants, which cause larger-than-normal blooms. When these plants die, they can use up most or all of the dissolved oxygen, which results in fish kills and the deaths of other animals.
Toxic materials from petroleum spills and other chemical releases can damage the surrounding soil, seep into the groundwater, and run off into waterways.
OTHER TYPES OF POLLUTION INCLUDE:
PLASTIC POLLUTION
Plastic pollution is the addition of plastic waste to the landscape and waterways. It is caused by manufactured plastics that are not properly disposed of. It is a problem because plastic does not break down easily, the chemical additives in plastic may become endocrine disruptors, plastic waste flows downstream into rivers and oceans (sea life can ingest, choke on, or become trapped in plastic waste), and plastic is a source of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), which are suspected carcinogens.
NOISE POLLUTION
Noise pollution is unwanted or excessive sound that affects health and environmental quality. It is caused by machines and engines associated with industry, as well as airports and other transportation systems. Noise is problematic because it can cause physical damage to hearing organs in humans and other animals, it produces increased stress levels, and it disrupts ecosystems by driving certain species away and altering the habits of wildlife. Noise pollution occurs primarily on land located close to industry and transportation and at sea, where it emanates from ship engines and sonar.
LIGHT POLLUTION
Light pollution is unwanted or excessive light caused by streetlights and illuminated buildings, towers, and other structures. Light pollution changes nighttime visibility of natural features, disorienting migratory animals and fostering bird collisions with lighted towers and buildings.
THERMAL POLLUTION
Thermal pollution is the addition of heat to a cool environment, and it is caused by water or air used as cooling fluids in power plants and manufacturing that becomes heated in the process. Heated cooling water from power plants may be 15 ˚C (27 ˚F) hotter than lake or stream water, which increases metabolic rates in fishes and reduces the amount of dissolved oxygen that the water may hold. In extreme cases, it can be hot enough to burn animal tissues.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Air pollution can also cause long-term damage to people's nerves, brain, kidneys, liver, and other organs. Some scientists suspect air pollutants cause birth defects. Nearly 2.5 million people die worldwide each year from the effects of outdoor or indoor air pollution. People react differently to different types of air pollution.
Lead is a heavy metal used in different industrial plants and emitted from some ... Air pollution is distinguished into two main types: Outdoor pollution is the ambient air ... the main proposal of this essay is that we should focus on fostering local structures to promote experience and practice and extrapolate these to the international level ...
Air pollution, release into the atmosphere of various gases, finely divided solids, or finely dispersed liquid aerosols at rates that exceed the natural capacity of the environment to dissipate and dilute or absorb them. High concentrations can cause undesirable health, economic, or aesthetic effects.
Air pollution is a mix of particles and gases that can reach harmful concentrations both outside and indoors. Its effects can range from higher disease risks to rising temperatures. Soot, smoke ...
A number of air pollutants pose severe health risks and can sometimes be fatal, even in small amounts. Almost 200 of them are regulated by law; some of the most common are mercury, lead, dioxins ...
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances called pollutants in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. It is also the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment either by chemical, physical, or biological agents that alters the natural features of the atmosphere.
Definition, Types, and Environmental Impact. Air pollution occurs when certain gases, droplets, or particles mix with ambient air, rendering the air harmful to living things. There are many ...
Air pollution is a health and environmental issue across all countries of the world but with large differences in severity. In the interactive map, we show death rates from air pollution across the world, measured as the number of deaths per 100,000 people in a given country or region.
Moreover, air pollution seems to have various malign health effects in early human life, such as respiratory, cardiovascular, mental, and perinatal disorders ( 3 ), leading to infant mortality or chronic disease in adult age ( 6 ). National reports have mentioned the increased risk of morbidity and mortality ( 1 ).
How air pollution affects our body. Particles with a diameter of 10 microns or less (≤ PM 10) can penetrate and lodge deep inside the lungs, causing irritation, inflammation and damaging the lining of the respiratory tract. Smaller, more health-damaging particles with a diameter of 2.5 microns or less (≤ PM 2.5 - 60 of them make up the ...
Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere. Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities and forest fires are common sources of air pollution. Pollutants of major public health concern include ...
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), air pollution is one of the world's biggest killers: outdoor (ambient) pollution causes around four million people to die prematurely each year, while indoor (household) pollution (mainly from fuel burning) kills another 3.8 million. Many of these deaths happen in less-developed or developing ...
The three major types of pollution are air pollution, water pollution, and land pollution. Air Pollution Sometimes, air pollution is visible. A person can see dark smoke pour from the exhaust pipes of large trucks or factories, for example. More often, however, air pollution is invisible. Polluted air can be dangerous, even if the pollutants ...
Effects of Pollution. Pollution affects the quality of life more than one can imagine. It works in mysterious ways, sometimes which cannot be seen by the naked eye. However, it is very much present in the environment. For instance, you might not be able to see the natural gases present in the air, but they are still there.
Sample Essay on Pollution in 250-300 Words. The biggest threat planet Earth is facing is pollution. Unwanted substances leave a negative impact once released into an environment. There are four types of pollution air, water, land, and noise. Pollution affects the quality of life more than any human can imagine.
Jerry A. Nathanson. Pollution, addition of any substance or form of energy to the environment at a rate faster than it can be dispersed or stored in a harmless form. The major kinds of pollution are usually classified by environment and include air, water, and land pollution. Learn more about the history of pollution.
Traffic-Related Air Pollution (TRAP), a mixture of gasses and particles, has most of the elements of human-made air pollution: ground-level ozone, various forms of carbon, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, volatile organic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and fine particulate matter. Ozone, an atmospheric gas, is often called smog ...
Essay on Air Pollution - Sample 1 (200 Words) Air pollution is a serious issue and a cause for major concern in today's world. A report published in 2014 by the World Health Organisation states that 4.21 million individuals died prematurely in 2012 as a result of air pollution. Air pollution existed much before humans, in the form of ...
incineration. air pollution control, the techniques employed to reduce or eliminate the emission into the atmosphere of substances that can harm the environment or human health. The control of air pollution is one of the principal areas of pollution control, along with wastewater treatment, solid-waste management, and hazardous-waste management.
Effects Of Air Pollution On Health. The air pollution has many bad effects on the health of people. It is the cause of many skins and respiratory disorder in human beings. Also, it causes heart disease too. Air pollution causes asthma, bronchitis, and many other diseases. Moreover, it increases the rate of aging of lungs, decreases lungs ...
Air pollution is important to think about because we are all obligatory breathers. We all need air to live—from the day we are born to the day we die- and our air contains contaminants that are harmful to our health. When we are experiencing high levels of pollution, like during wildfire events, we may be able to see the poor quality of our ...
Definitions and types. Various definitions of pollution exist, which may or may not recognize certain types, such as noise pollution or greenhouse gases.The United States Environmental Protection Administration defines pollution as "Any substances in water, soil, or air that degrade the natural quality of the environment, offend the senses of sight, taste, or smell, or cause a health hazard.
Generally, air pollution has been divided into two types. 1. Indoor pollution. It is the pollution of air caused by the introduction of materials from smoking and burning fossil fuels such as kerosene, petroleum and coal indoors. Fuels are burned indoors for cooking and cooling or heating purposes. Chemicals from cleaning products, wall paints ...
Tropospheric air pollution has a long and storied history (1, 2).From at least the 13th century up to the mid-20th century, documented air pollution problems were primarily associated with high concentrations of sulfur dioxide (SO 2) and soot particles.These problems are often dubbed "London Smog" because of a severe episode in that city in 1952.
Air pollution refers to the modification of the characteristics of the atmosphere induced by contaminants [1]. Sources of air pollution are, for example, any kind of combustion, vehicles, and ...
Published on: October 9, 2022 by Admin. Types of Pollution essay in Telugu కాలుష్య రకాలు వ్యాసం: Even children are becoming more aware of the term pollution. Pollution is so well-known that nearly everyone recognizes that it is on the rise. Pollution is the presence of an unwelcome foreign substance in a product.
Air pollution refers to any physical, chemical or biological change in the air. It is the contamination of air by harmful gases, dust and smoke which affects plants, animals and humans drastically. There is a certain percentage of gases present in the atmosphere. An increase or decrease in the composition of these gases is harmful to survival.
Children drink more water, eat more food, and breathe more air per pound of body weight than adults, which can increase their exposure to PFAS. Young children crawl on floors and put things in their mouths which leads to a higher risk of exposure to PFAS in carpets, household dust, toys, and cleaning products.
The Journal of Cleaner Production is an international, transdisciplinary journal focusing on Cleaner Production, Environmental, and Sustainability research and practice. Through our published articles, we aim at helping societies become more sustainable. 'Cleaner Production' is a concept that aims at preventing the production of waste, while increasing efficiencies in the uses of energy, water ...
Although most of the nutrients or substances that contribute to air, land, and water pollution are limited to a single environment, air, land, and water do interact with one another. Air pollution results when the by-product of an activity makes chemicals airborne. Close to Earth's surface, sulfur dioxide (SO2) interacts with the water cycle ...