McCombs School of Business
- Español ( Spanish )
Videos Concepts Unwrapped View All 36 short illustrated videos explain behavioral ethics concepts and basic ethics principles. Concepts Unwrapped: Sports Edition View All 10 short videos introduce athletes to behavioral ethics concepts. Ethics Defined (Glossary) View All 58 animated videos - 1 to 2 minutes each - define key ethics terms and concepts. Ethics in Focus View All One-of-a-kind videos highlight the ethical aspects of current and historical subjects. Giving Voice To Values View All Eight short videos present the 7 principles of values-driven leadership from Gentile's Giving Voice to Values. In It To Win View All A documentary and six short videos reveal the behavioral ethics biases in super-lobbyist Jack Abramoff's story. Scandals Illustrated View All 30 videos - one minute each - introduce newsworthy scandals with ethical insights and case studies. Video Series
Case Study UT Star Icon

Apple Suppliers & Labor Practices
Is tech company Apple, Inc. ethically obligated to oversee the questionable working conditions of other companies further down their supply chain?

With its highly coveted line of consumer electronics, Apple has a cult following among loyal consumers. During the 2014 holiday season, 74.5 million iPhones were sold. Demand like this meant that Apple was in line to make over $52 billion in profits in 2015, the largest annual profit ever generated from a company’s operations. Despite its consistent financial performance year over year, Apple’s robust profit margin hides a more complicated set of business ethics. Similar to many products sold in the U.S., Apple does not manufacture most its goods domestically. Most of the component sourcing and factory production is done overseas in conditions that critics have argued are dangerous to workers and harmful to the environment.
For example, tin is a major component in Apple’s products and much of it is sourced in Indonesia. Although there are mines that source tin ethically, there are also many that do not. One study found workers—many of them children—working in unsafe conditions, digging tin out by hand in mines prone to landslides that could bury workers alive. About 70% of the tin used in electronic devices such as smartphones and tablets comes from these more dangerous, small-scale mines. An investigation by the BBC revealed how perilous these working conditions can be. In interviews with miners, a 12-year-old working at the bottom of a 70-foot cliff of sand said: “I worry about landslides. The earth slipping from up there to the bottom. It could happen.”
Apple defends its practices by saying it only has so much control over monitoring and regulating its component sources. The company justifies its sourcing practices by saying that it is a complex process, with tens of thousands of miners selling tin, many of them through middle-men. In a statement to the BBC, Apple said “the simplest course of action would be for Apple to unilaterally refuse any tin from Indonesian mines. That would be easy for us to do and would certainly shield us from criticism. But that would also be the lazy and cowardly path, since it would do nothing to improve the situation. We have chosen to stay engaged and attempt to drive changes on the ground.”
In an effort for greater transparency, Apple has released annual reports detailing their work with suppliers and labor practices. While more recent investigations have shown some improvements to suppliers’ working conditions, Apple continues to face criticism as consumer demand for iPhones and other products continues to grow.
Discussion Questions
1. Do you think Apple should be responsible for ethical lapses made by individuals further down its supply chain? Why or why not?
2. Should Apple continue to work with the suppliers in an effort to change practices, or should they stop working with every supplier, even the conscientious ones, to make sure no “bad apples” are getting through? Explain your reasoning.
3. Do you think consumers should be expected to take into account the ethical track record of companies when making purchases? Why or why not?
4. Can you think of other products or brands that rely on ethically questionable business practices? Do you think consumers are turned off by their track record or are they largely indifferent to it? Explain.
5. Would knowing that a product was produced under ethically questionable conditions affect your decision to purchase it? Explain with examples.
6. If you were part of a third-party regulating body, how would you deal with ethically questionable business practices of multinational corporations like Apple? Would you feel obligated to do something, or do you think the solution rests with the companies themselves? Explain your reasoning.
Related Videos

Ethical Fading
Ethical fading occurs when we are so focused on other aspects of a decision that its ethical dimensions fade from view.
Bibliography
Apple ‘failing to protect Chinese factory workers’ http://www.bbc.com/news/business-30532463
How Apple could make a $53 billion profit this year http://money.cnn.com/2015/07/17/technology/apple-earnings-2015/
Global Apple iPhone sales from 3rd quarter 2007 to 2nd quarter 2016 (in million units) http://www.statista.com/statistics/263401/global-apple-iphone-sales-since-3rd-quarter-2007/
Despite successes, labor violations still haunt Apple http://www.theverge.com/2015/2/12/8024895/apple-slave-labor-working-conditions-2015
Reports – Supplier Responsibility – Apple https://www.apple.com/supplier-responsibility/progress-report/
Stay Informed
Support our work.
Advertisement
Research and Practice of AI Ethics: A Case Study Approach Juxtaposing Academic Discourse with Organisational Reality
- Original Research/Scholarship
- Open access
- Published: 08 March 2021
- Volume 27 , article number 16 , ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Mark Ryan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4850-0111 1 ,
- Josephina Antoniou 2 ,
- Laurence Brooks 3 ,
- Tilimbe Jiya 4 ,
- Kevin Macnish 5 &
- Bernd Stahl 3
12k Accesses
20 Citations
7 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This study investigates the ethical use of Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies (BD + AI)—using an empirical approach. The paper categorises the current literature and presents a multi-case study of 'on-the-ground' ethical issues that uses qualitative tools to analyse findings from ten targeted case-studies from a range of domains. The analysis coalesces identified singular ethical issues, (from the literature), into clusters to offer a comparison with the proposed classification in the literature. The results show that despite the variety of different social domains, fields, and applications of AI, there is overlap and correlation between the organisations’ ethical concerns. This more detailed understanding of ethics in AI + BD is required to ensure that the multitude of suggested ways of addressing them can be targeted and succeed in mitigating the pertinent ethical issues that are often discussed in the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others

Organisational responses to the ethical issues of artificial intelligence

Ethical AI governance: mapping a research ecosystem

From Principled to Applied AI Ethics in Organizations: A Scoping Review
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (BD + AI) are emerging technologies that offer great potential for business, healthcare, the public sector, and development agencies alike. The increasing impact of these two technologies and their combined potential in these sectors can be highlighted for diverse organisational aspects such as for customisation of organisational processes and for automated decision making. The combination of Big Data and AI, often in the form of machine learning applications, can better exploit the granularity of data and analyse it to offer better insights into behaviours, incidents, and risk, eventually aiming at positive organisational transformation.
Big Data offers fresh and interesting insights into structural patterns, anomalies, and decision-making in a broad range of different applications (Cuquet & Fensel, 2018 ), while AI provides predictive foresight, intelligent recommendations, and sophisticated modelling. The integration and combination of AI + BD offer phenomenal potential for correlating, predicting and prescribing recommendations in insurance, human resources (HR), agriculture, and energy, as well as many other sectors. While BD + AI provides a wide range of benefits, they also pose risks to users, including but not limited to privacy infringements, threats of unemployment, discrimination, security concerns, and increasing inequalities (O’Neil, 2016 ). Footnote 1 Adequate and timely policy needs to be implemented to prevent many of these risks occurring.
One of the main limitations preventing key decision-making for ethical BD + AI use is that there are few rigorous empirical studies carried out on the ethical implications of these technologies across multiple application domains. This renders it difficult for policymakers and developers to identify when ethical issues resulting from BD + AI use are only relevant for isolated domains and applications, or whether there are repeated/universal concerns which can be seen across different sectors. While the field lacks literature evaluating ethical issues Footnote 2 ‘on the ground’, there are even fewer multi-case evaluations.
This paper provides a cohesive multi-case study analysis across ten different application domains, including domains such as government, agriculture, insurance, and the media. It reviews ethical concerns found within these case studies to establish cross-cutting thematic issues arising from the implementation and use of BD + AI. The paper collects relevant literature and proposes a simple classification of ethical issues (short term, medium term, long term), which is then juxtaposed with the ethical concerns highlighted from the multiple-case study analysis. This multiple-case study analysis of BD + AI offers an understanding of current organisational practices.
The work described in this paper makes an important contribution to the literature, based on its empirical findings. By presenting the ethical issues across an array of application areas, the paper provides much-needed rigorous empirical insight into the social and organisational reality of ethics of AI + BD. Our empirical research brings together a collection of domains that gives a broad oversight about issues that underpin the implementation of AI. Through its empirical insights the paper provides a basis for a broader discussion of how these issues can and should be addressed.
This paper is structured in six main sections: this introduction is followed by a literature review, which allows for an integrated review of ethical issues, contrasting them with those found in the cases. This provides the basis for a categorisation or classification of ethical issues in BD + AI. The third section contains a description of the interpretivist qualitative case study methodology used in this paper. The subsequent section provides an overview of the organisations participating in the cases to contrast similarities and divisions, while also comparing the diversity of their use of BD + AI. Footnote 3 The fifth section provides a detailed analysis of the ethical issues derived from using BD + AI, as identified in the cases. The concluding section analyses the differences between theoretical and empirical work and spells out implications and further work.
Literature Review
An initial challenge that any researcher faces when investigating ethical issues of AI + BD is that, due to the popularity of the topic, there is a vast and rapidly growing literature to be considered. Ethical issues of AI + BD are covered by a number of academic venues, including some specific ones such as the AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society ( https://dl.acm.org/doi/proceedings/10.1145/3306618 ), policy initiative and many publicly and privately financed research reports (Whittlestone, Nyrup, Alexandrova, Dihal, & Cave, 2019 ). Initial attempts to provide overviews of the area have been published (Jobin, 2019 ; Mittelstadt, Allo, Taddeo, Wachter, & Floridi, 2016 ), but there is no settled view on what counts as an ethical issue and why. In this paper we aim to provide a broad overview of issues found through the case studies. This paper puts forward what are commonly perceived to be ethical issues within the literature or concerns that have ethical impacts and repercussions. We explicitly do not apply a particular philosophical framework of ethics but accept as ethical issues those issues that we encounter in the literature. This review is based on an understanding of the current state of the literature by the paper's authors. It is not a structured review and does not claim comprehensive coverage but does share some interesting insights.
To be able to undertake the analysis of ethical issues in our case studies, we sought to categorise the ethical issues found in the literature. There are potentially numerous ways of doing so and our suggestion does not claim to be authoritative. Our suggestion is to order ethical issues in terms of their temporal horizon, i.e., the amount of time it is likely to take to be able to address them. Time is a continuous variable, but we suggest that it is possible to sort the issues into three clusters: short term, medium term, and long term (see Fig. 1 ).
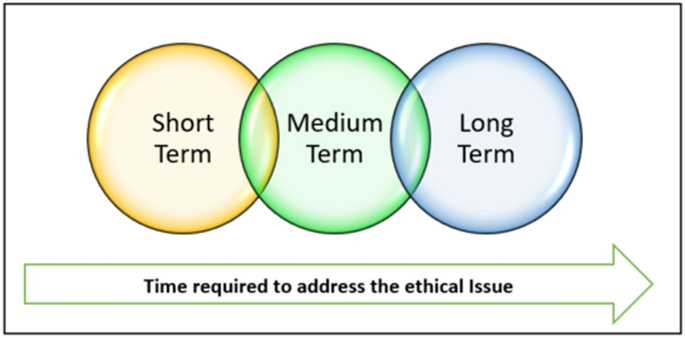
Temporal horizon for addressing ethical issues
As suggested by Baum ( 2017 ), it is best to acknowledge that there will be ethical issues and related mitigating activities that cannot exclusively fit in as short, medium or long term.
ather than seeing it as an authoritative classification, we see this as a heuristic that reflects aspects of the current discussion. One reason why this categorisation is useful is that the temporal horizon of ethical issues is a potentially useful variable, with companies often being accused of favouring short-term gains over long-term benefits. Similarly, short-term issues must be able to be addressed on the local level for short-term fixes to work.
Short-term issues
These are issues for which there is a reasonable assumption that they are capable of being addressed in the short term. We do not wish to quantify what exactly counts as short term, as any definition put forward will be contentious when analysing the boundaries and transition periods. A better definition of short term might therefore be that such issues can be expected to be successfully addressed in technical systems that are currently in operation or development. Many of the issues we discuss under the heading of short-term issues are directly linked to some of the key technologies driving the current AI debate, notably machine learning and some of its enabling techniques and approaches such as neural networks and reinforcement learning.
Many of the advantages promised by BD + AI involve the use of personal data, data which can be used to identify individuals. This includes health data; customer data; ANPR data (Automated Number Plate Recognition); bank data; and even includes data about farmers’ land, livestock, and harvests. Issues surrounding privacy and control of data are widely discussed and recognized as major ethical concerns that need to be addressed (Boyd & Crawford, 2012 ; Tene & Polonetsky, 2012 , 2013 ; Mittelstadt, Allo, Taddeo, Wachter, & Floridi, 2016 ; Jain, Gyanchandani, & Khare, 2016 ; Mai, 2016 ; Macnish, 2018 ). The concern surrounding privacy can be put down to a combination of a general level of awareness of privacy issues and the recently-introduced General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Closely aligned with privacy issues are those relating to transparency of processes dealing with data, which can often be classified as internal, external, and deliberate opaqueness (Burrell, 2016 ; Lepri, Staiano, Sangokoya, Letouzé, & Oliver, 2017 ; Mittelstadt, Allo, Taddeo, Wachter, & Floridi, 2016 ).
The Guidelines for Trustworthy AI Footnote 4 were released in 2018 by the High-Level Expert Group on Artificial Intelligence (AI HLEG Footnote 5 ), and address the need for technical robustness and safety, including accuracy, reproducibility, and reliability. Reliability is further linked to the requirements of diversity, fairness, and social impact because it addresses freedom from bias from a technical point of view. The concept of reliability, when it comes to BD + AI, refers to the capability to verify the stability or consistency of a set of results (Bush, 2012 ; Ferraggine, Doorn, & Rivera, 2009 ; Meeker and Hong, 2014 ).
If a technology is unreliable, error-prone, and unfit-for-purpose, adverse ethical issues may result from decisions made by the technology. The accuracy of recommendations made by BD + AI is a direct consequence of the degree of reliability of the technology (Barolli, Takizawa, Xhafa, & Enokido, 2019 ). Bias and discrimination in algorithms may be introduced consciously or unconsciously by those employing the BD + AI or because of algorithms reflecting pre-existing biases (Baroccas and Selbst, 2016 ). Examples of bias have been documented often reflecting “an imbalance in socio-economic or other ‘class’ categories—ie, a certain group or groups are not sampled as much as others or at all” (Panch et al., 2019 ). have the potential to affect levels of inequality and discrimination, and if biases are not corrected these systems can reproduce existing patterns of discrimination and inherit the prejudices of prior decision makers (Barocas & Selbst, 2016 , p. 674). An example of inherited prejudices is documented in the United States, where African-American citizens, more often than not, have been given longer prison sentences than Caucasians for the same crime.
Medium-term issues
Medium-term issues are not clearly linked to a particular technology but typically arise from the integration of AI techniques including machine learning into larger socio-technical systems and contexts. They are thus related to the way life in modern societies is affected by new technologies. These can be based on the specific issues listed above but have their main impact on the societal level. The use of BD + AI may allow individuals’ behaviour to be put under scrutiny and surveillance , leading to infringements on privacy, freedom, autonomy, and self-determination (Wolf, 2015 ). There is also the possibility that the increased use of algorithmic methods for societal decision-making may create a type of technocratic governance (Couldry & Powell, 2014 ; Janssen & Kuk, 2016 ), which could infringe on people’s decision-making processes (Kuriakose & Iyer, 2018 ). For example, because of the high levels of public data retrieval, BD + AI may harm people’s freedom of expression, association, and movement, through fear of surveillance and chilling effects (Latonero, 2018 ).
Corporations have a responsibility to the end-user to ensure compliance, accountability, and transparency of their BD + AI (Mittelstadt, Allo, Taddeo, Wachter, & Floridi, 2016 ). However, when the source of a problem is difficult to trace, owing to issues of opacity, it becomes challenging to identify who is responsible for the decisions made by the BD + AI. It is worth noting that a large-scale survey in Australia in 2020 indicated that 57.9% of end-users are not at all confident that most companies take adequate steps to protect user data. The significance of understanding and employing responsibility is an issue targeted in many studies (Chatfield et al., 2017 ; Fothergill et al., 2019 ; Jirotka et al., 2017 ; Pellé & Reber, 2015 ). Trust and control over BD + AI as an issue is reiterated by a recent ICO report demonstrating that most UK citizens do not trust organisations with their data (ICO, 2017 ).
Justice is a central concern in BD + AI (Johnson, 2014 , 2018 ). As a starting point, justice consists in giving each person his or her due or treating people equitably (De George, p. 101). A key concern is that benefits will be reaped by powerful individuals and organisations, while the burden falls predominantly on poorer members of society (Taylor, 2017 ). BD + AI can also reflect human intentionality, deploying patterns of power and authority (Portmess & Tower, 2015 , p. 1). The knowledge offered by BD + AI is often in the hands of a few powerful corporations (Wheeler, 2016 ). Power imbalances are heightened because companies and governments can deploy BD + AI for surveillance, privacy invasions and manipulation, through personalised marketing efforts and social control strategies (Lepri, Staiano, Sangokoya, Letouzé, & Oliver, 2017 , p. 11). They play a role in the ascent of datafication, especially when specific groups (such as corporate, academic, and state institutions) have greater unrestrained access to big datasets (van Dijck, 2014 , p. 203).
Discrimination , in BD + AI use, can occur when individuals are profiled based on their online choices and behaviour, but also their gender, ethnicity and belonging to specific groups (Calders, Kamiran, & Pechenizkiy, 2009 ; Cohen et al., 2014 ; and Danna & Gandy, 2002 ). Data-driven algorithmic decision-making may lead to discrimination that is then adopted by decision-makers and those in power (Lepri, Staiano, Sangokoya, Letouzé, & Oliver, 2017 , p. 4). Biases and discrimination can contribute to inequality . Some groups that are already disadvantaged may face worse inequalities, especially if those belonging to historically marginalised groups have less access and representation (Barocas & Selbst, 2016 , p. 685; Schradie, 2017 ). Inequality-enhancing biases can be reproduced in BD + AI, such as the use of predictive policing to target neighbourhoods of largely ethnic minorities or historically marginalised groups (O’Neil, 2016 ).
BD + AI offers great potential for increasing profit, reducing physical burdens on staff, and employing innovative sustainability practices (Badri, Boudreau-Trudel, & Souissi, 2018 ). They offer the potential to bring about improvements in innovation, science, and knowledge; allowing organisations to progress, expand, and economically benefit from their development and application (Crawford et al., 2014 ). BD + AI are being heralded as monumental for the economic growth and development of a wide diversity of industries around the world (Einav & Levin, 2014 ). The economic benefits accrued from BD + AI may be the strongest driver for their use, but BD + AI also holds the potential to cause economic harm to citizens and businesses or create other adverse ethical issues (Newman, 2013 ).
However, some in the literature view the co-development of employment and automation as somewhat naïve outlook (Zuboff, 2015 ). BD + AI companies may benefit from a ‘post-labour’ automation economy, which may have a negative impact on the labour market (Bossman, 2016 ), replacing up to 47% of all US jobs within the next 20 years (Frey & Osborne, 2017 ). The professions most at risk of affecting employment correlated with three of our case studies: farming, administration support and the insurance sector (Frey & Osborne, 2017 ).
Long-term issues
Long-term issues are those pertaining to fundamental aspects of nature of reality, society, or humanity. For example, that AI will develop capabilities far exceeding human beings (Kurzweil, 2006 ). At this point, sometimes called the ‘ singularity ’ machines achieve human intelligence, are expected to be able to improve on themselves and thereby surpass human intelligence and become superintelligent (Bostrom, 2016 ). If this were to happen, then it might have dystopian consequences for humanity as often depicted in science fiction. Also, it stands to reason that the superintelligent, or even just the normally intelligent machines may acquire a moral status.
It should be clear that these expectations are not universally shared. They refer to what is often called ‘ artificial general intelligence’ (AGI), a set of technologies that emulate human reasoning capacities more broadly. Footnote 6
Furthermore, if we may acquire new capabilities, e.g. by using technical implants to enhance human nature. The resulting being might be called a transhuman , the next step of human evolution or development. Again, it is important to underline that this is a contested idea (Livingstone, 2015 ) but one that has increasing traction in public discourse and popular science accounts (Harari, 2017 ).
We chose this distinction of three groups of issues for understanding how mitigation strategies within organisations can be contextualised. We concede that this is one reading of the literature and that many others are possible. In this account of the literature we tried to make sense of the current discourse to allow us to understand our empirical findings which are introduced in the following sections.
Case Study Methodology
Despite the impressive amount of research undertaken on ethical issues of AI + BD (e.g. Mittelstadt, Allo, Taddeo, Wachter, & Floridi, 2016 ; Zwitter, 2014 ), there are few case studies exploring such issues. This paper builds upon this research and employs an interpretivist methodology to do so, focusing on how, what, and why questions relevant to the ethical use of BD + AI (Walsham, 1995a , b ). The primary research questions for the case studies were: How do organisations perceive ethical concerns related to BD + AI and in what ways do they deal with them?
We sought to elicit insights from interviews, rather than attempting to reach an objective truth about the ethical impacts of BD + AI. The interpretivist case study approach (Stake 2003) allowed the researchers ‘to understand ‘reality’ as the blending of the various (and sometimes conflicting) perspectives which coexist in social contexts, the common threads that connect the different perspectives and the value systems that give rise to the seeming contradictions and disagreements around the topics discussed. Whether one sees this reality as static (social constructivism) or dynamic (social constructionism) was also a point of consideration, as they both belong in the same “family” approach where methodological flexibility is as important a value as rigour’ (XXX).
Through extensive brainstorming within the research team, and evaluations of relevant literature, 16 social application domains were established as topics for case study analysis. Footnote 7 The project focused on ten out of these application domains in accordance with the partners’ competencies. The case studies have covered ten domains, and each had their own unique focus, specifications, and niches, which added to the richness of the evaluations (Table 1 ).
The qualitative analysis approach adopted in this study focused on these ten standalone operational case studies that were directly related to the application domains presented in Table 1 . These individual case studies provide valuable insights (Yin, 2014 , 2015 ); however, a multiple-case study approach offers a more comprehensive analysis of ethical issues related to BD + AI use (Herriott & Firestone, 1983 ). Thus, this paper adopts a multiple-case study methodology to identify what insights can be obtained from the ten cases, identifies whether any generalisable understandings can be retrieved, and evaluates how different organisations deal with issues pertaining to BD + AI development and use. The paper does not attempt to derive universal findings from this analysis, in line with the principles of interpretive research, but further attempts to gain an in-depth understanding of the implications of selected BD + AI applications.
The data collection was guided by specific research questions identified through each case, including five desk research questions (see appendix 1); 24 interview questions (see appendix 2); and a checklist of 17 potential ethical issues, developed by the project leader Footnote 8 (see appendix 3). A thematic analysis framework was used to ‘highlight, expose, explore, and record patterns within the collected data. The themes were patterns across data sets that were important to describe several ethical issues which arise through the use of BD + AI across different types of organisations and application domains’ (XXX).
A workshop was then held after the interviews were carried out. The workshop brought together the experts in the case study team to discuss their findings. This culminated in 26 ethical issues Footnote 9 that were inductively derived from the data collected throughout the interviews (see Fig. 2 and Table 3). Footnote 10 In order to ensure consistency and rigour in the multiple-case study approach, researchers followed a standardised case study protocol (Yin, 2014 ). Footnote 11
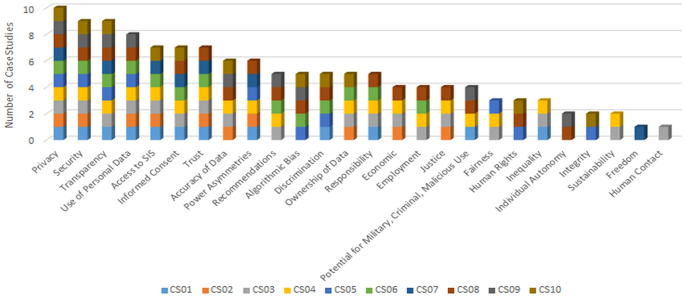
The Prevalence of Ethical Issues in the Case Studies
Thirteen different organisations were interviewed for 10 case studies, consisting of 22 interviews in total. Footnote 12 These ranged from 30 min to 1 ½ hours in-person or Skype interviews. The participants that were selected for interviews represented a very broad range of application domains and organisations that use BD + AI. The case study organisations were selected according to their relevance to the overall case study domains and considering their fit with the domains and likelihood of providing interesting insights. The interviewees were then selected according to their ability to explain their BD + AI and its role in their organisation. In addition to interviews, a document review provided supporting information about the organisation. Thus, websites and published material were used to provide background to the research.
Findings: Ten Case Studies
This section gives a brief overview of the cases, before analysing their similarities and differences. It also highlights the different types of BD + AI being used, and the types of data used by the BD + AI in the case study organisations, before conducting an ethical analysis of the cases. Table 2 presents an overview of the 10 cases to show the roles of the interviewees, the focus of the technologies being used, and the data retrieved by each organisation’s BD + AI. All interviews were conducted in English.
The types of organisations that were used in the case studies varied extensively. They included start-ups (CS10), niche software companies (CS1), national health insurers (Organisation X in CS6), national energy providers (CS7), chemical/agricultural multinational (CS3), and national (CS9) and international (CS8) telecommunications providers. The case studies also included public (CS2, Organisation 1 and 4 in CS4) and semi-public (Organisation 2 in CS4) organisations, as well as a large scientific research project (CS5).
The types of individuals interviewed also varied extensively. For example, CS6 and CS7 did not have anyone with a specific technical background, which limited the possibility of analysing issues related to the technology itself. Some case studies only had technology experts (such as CS1, CS8, and CS9), who mostly concentrated on technical issues, with much less of a focus on ethical concerns. Other case studies had a combination of both technical and policy-focused experts (i.e. CS3, CS4, and CS5). Footnote 13
Therefore, it must be made fundamentally clear that we are not proposing that all of the interviewees were authorities in the field, or that even collectively they represent a unified authority on the matter, but instead, that we are hoping to show what are the insights and perceived ethical issues of those currently working with AI on the ground view as ethical concerns. While the paper is presenting the ethical concerns found within an array of domains, we do not claim that any individual case study is representative of their entire industry, but instead, our intent was to capture a wide diversity of viewpoints, domains, and applications of AI, to encompass a broad amalgamation of concerns. We should also state that this is not a shortcoming of the study but that it is the normal approach that social science often takes.
The diversity of organisations and their application focus areas also varied. Some organisations focused more so on the Big Data component of their AI, while others more strictly on the AI programming and analytics. Even when organisations concentrated on a specific type of BD + AI, such as Big Data, its use varied immensely, including retrieval (CS1), analysis (CS2), predictive analytics (CS10), and transactional value (Organisation 2 in CS4). Some domains adopted BD + AI earlier and more emphatically than others (such as communications, healthcare, and insurance). Also, the size, investment, and type of organisation played a part in the level of BD + AI innovation (for example, the two large multinationals in CS3 and CS8 had well-developed BD + AI).
The maturity level of BD + AI was also determined by how it was integrated, and its importance, within an organisation. For instance, in organisations where BD + AI were fundamental for the success of the business (e.g. CS1 and CS10), they played a much more important role than in companies where there was less of a reliance (e.g. CS7). In some organisations, even when BD + AI was not central to success, the level of development was still quite advanced because of economic investment capabilities (e.g. CS3 and CS8).
These differences provided important questions to ask throughout this multi-case study analysis, such as: Do certain organisations respond to ethical issues relating to BD + AI in a certain way? Does the type of interviewee affect the ethical issues discussed—e.g. case studies without technical experts, those that only had technical experts, and those that had both? Does the type of BD + AI used impact the types of ethical issues discussed? What significance does the type of data retrieved have on ethical issues identified by the organisations? These inductive ethical questions provided a template for the qualitative analysis in the following section.
Ethical Issues in the Case Studies
Based on the interview data, the ethical issues identified in the case studies were grouped into six specific thematic sections to provide a more conducive, concise, and pragmatic methodology. Those six sections are: control of data, reliability of data, justice, economic issues, role of organisations, and individual freedoms. From the 26 ethical issues, privacy was the only ethical issue addressed in all 10 case studies, which was not surprising because it has received a great deal of attention recently because of the GDPR. Also, security, transparency, and algorithmic bias are regularly discussed in the literature, so we expected them to be significant issues across many of the cases. However, there were many issues that received less attention in the literature—such as access to BD + AI, trust, and power asymmetries—which were discussed frequently in the interviews. In contrast to this, there were ethical issues that were heavily discussed in the literature which received far less attention in the interviews, such as employment, autonomy, and criminal or malicious use of BD + AI (Fig. 2 ).
The ethical analysis was conducted using a combination of literature reviews and interviews carried out with stakeholders. The purpose of the interviews was to ensure that there were no obvious ethical issues faced by stakeholders in their day-to-day activities which had been missed in the academic literature. As such, the starting point was not an overarching normative theory, which might have meant that we looked for issues which fit well with the theory but ignored anything that fell outside of that theory. Instead the combined approach led to the identification of the 26 ethical issues, each labelled based on particular words or phrases used in the literature or by the interviewees. For example, the term "privacy" was used frequently and so became the label for references to and instances of privacy-relevant concerns. In this section we have clustered issues together based on similar problems faced (e.g. accuracy of data and accuracy of algorithms within the category of ‘reliability of data’).
In an attempt to highlight similar ethical issues and improve the overall analysis to better capture similar perspectives, the research team decided to use the method of clustering, a technique often used in data mining to efficiently group similar elements together. Through discussion in the research team, and bearing in mind that the purpose of the clustering process was to form clusters that would enhance understanding of the impact of these ethical issues, we arrived at the following six clusters: the control of data (covering privacy, security, and informed consent); the reliability of data (accuracy of data and accuracy of algorithms); justice (power asymmetries, justice, discrimination, and bias); economic issues (economic concerns, sustainability, and employment); the role of organisations (trust and responsibility); and human freedoms (autonomy, freedom, and human rights). Both the titles and the precise composition of each cluster of issues are the outcome of a reasoned agreement of the research team. However, it should be clear that we could have used different titles and different clustering. The point is not that each cluster forms a distinct group of ethical issues, independent from any other. Rather the ethical issues faced overlap and play into one another, but to present them in a manageable format we have opted to use this bottom-up clustering approach.
Human Freedoms
An interviewee from CS10 stated that they were concerned about human rights because they were an integral part of the company’s ethics framework. This was beneficial to their business because they were required to incorporate human rights to receive public funding by the Austrian government. The company ensured that they would not grant ‘full exclusivity on generated social unrest event data to any single party, unless the data is used to minimise the risk of suppression of unrest events, or to protect the violation of human rights’ (XXX). The company demonstrates that while BD + AI has been criticised for infringing upon human rights in the literature, they also offer the opportunity to identify and prevent human rights abuses. The company’s moral framework definitively stemmed from regulatory and funding requirements, which lends itself to the benefit of effective ethical top-down approaches, which is a divisive topic in the literature, with diverging views about whether top-down or bottom-up approaches are better options for improved AI ethics.
Trust & Responsibility
Responsibility was a concern in 5 of the case studies, confirming the importance it is given in the literature (see Sect. 3 ). Trust appeared in seven of the case studies. The cases focused on concerns found in the literature, such as BD + AI use in policy development, public distrust about automated decision-making and the integrity of corporations utilising datafication methods (van Dijck 2014 ).
Trust and control over BD + AI were an issue throughout the case studies. The organisation from the predictive intelligence case study (CS10) identified that their use of social media data raised trust issues. They converged with perspectives found in the literature that when people feel disempowered to use or be part of the BD + AI development process, they tend to lose trust in the BD + AI (Accenture, 2016 , 2017 ). In CS6, stakeholders (health insurers) trusted the decisions made by BD + AI when they were engaged and empowered to give feedback on how their data was used. Trust is enhanced when users can refuse the use of their data (CS7), which correlates with the literature. Companies discussed the benefits of establishing trustworthy relationships. For example, in CS9, they have “ been trying really hard to avoid the existence of fake [mobile phone] base stations, because [these raise] an issue with the trust that people put in their networks” (XXX).
Corporations need to determine the objective of the data analysis (CS3), what data is required for the BD + AI to work (CS2), and accountability for when it does not work as intended or causes undesirable outcomes (CS4). The issue here is whether the organisation takes direct responsibility for these outcomes, or, if informed consent has been given, can responsibility be shared with the granter of consent (CS3). The cases also raised the question of ‘responsible to whom’, the person whose data is being used or the proxy organisation who has provided data (CS6). For example, in the insurance case study, the company stated that they only had a responsibility towards the proxy organisation and not the sources of the data. All these issues are covered extensively in the literature in most application domains.
Control of Data
Concerns surrounding the control of data for privacy reasons can be put down to a general awareness of privacy issues in the press, reinforced by the recently-introduced GDPR. This was supported in the cases, where interviewees expressed the opinion that the GDPR had raised general awareness of privacy issues (CS1, CS9) or that it had lent weight to arguments concerning the importance of privacy (CS8).
The discussion of privacy ranged from stressing that it was not an issue for some interviewees, because there was no personal information in the data they used (CS4), to its being an issue for others, but one which was being dealt with (CS2 and CS8). One interviewee (CS5) expressed apprehension that privacy concerns conflicted with scientific innovation, introducing hitherto unforeseen costs. This view is not uncommon in scientific and medical innovation, where harms arising from the use of anonymised medical data are often seen as minimal and the potential benefits significant (Manson & O’Neill, 2007 ). In other cases (CS1), there was a confusion between anonymisation (data which cannot be traced back to the originating source) and pseudonymisation (where data can be traced back, albeit with difficulty) of users’ data. A common response from the cases was that providing informed consent for the use of personal data waived some of the rights to privacy of the user.
Consent may come in the form of a company contract Footnote 14 or an individual agreement. Footnote 15 In the former, the company often has the advantage of legal support prior to entering a contract and so should be fully aware of the information provided. In individual agreements, though, the individual is less likely to be legally supported, and so may be at risk of exploitation through not reading the information sufficiently (CS3), or of responding without adequate understanding (CS9). In one case (CS5), referring to anonymised data, consent was implied rather than given: the interviewee suggested that those involved in the project may have contributed data without giving clear informed consent. The interviewee also noted that some data may have been shared without the permission, or indeed knowledge, of those contributing individuals. This was acknowledged by the interviewee as a potential issue.
In one case (CS6), data was used without informed consent for fraud detection purposes. The interviewees noted that their organisation was working within the parameters of national and EU legislation, which allows for non-consensual use of data for these ends. One interviewee in this case stated that informed consent was sought for every novel use of the data they held. However, this was sought from the perceived owner of the data (an insurance company) rather than from the originating individuals. This case demonstrates how people may expect their data to be used without having a full understanding of the legal framework under which the data are collected. For example, data relating to individuals may legally be accessed for fraud detection without notifying the individual and without relying on the individual’s consent.
This use of personal data for fraud detection in CS6 also led to concerns regarding opacity. In both CS6 and CS10 there was transparency within the organisations (a shared understanding among staff as to the various uses of the data) but that did not extend to the public outside those organisations. In some cases (CS5) the internal transparency/external opacity meant that those responsible for developing BD + AI were often hard to meet. Of those who were interviewed in CS5, many did not know the providence of the data or the algorithms they were using. Equally, some organisations saw external opacity as integral to the business environment in which they were operating (CS9, CS10) for reasons of commercial advantage. The interviewee in CS9 cautioned that this approach, coupled with a lack of public education and the speed of transformation within the industry, would challenge any meaningful level of public accountability. This would render processes effectively opaque to the public, despite their being transparent to experts.
Reliability of Data
There can be multiple sources of unreliability in BD + AI. Unreliability originating from faults in the technology can lead to algorithmic bias, which can cause ethical issues such as unfairness, discrimination, and general negative social impact (CS3 and CS6). Considering algorithmic bias as a key input to data reliability, there exist two types of issues that may need to be addressed. Primarily, bias may stem from the input data, referred to as training data, if such data excludes adequate representation of the world, e.g. gender-biased datasets (CS6). Secondly, an inadequate representation of the world may be the result of lack of data, e.g. a correctly designed algorithm to learn from and predict a rare disease, may not have sufficient representative data to achieve correct predictions (CS5). In either case the input data are biased and may result in inaccurate decision-making and recommendations.
The issues of reliability of data stemming from data accuracy and/or algorithmic bias, may escalate depending on their use, as for example in predictive or risk-assessment algorithms (CS10). Consider the risks of unreliable data in employee monitoring situations (CS1), detecting pests and diseases in agriculture (CS3), in human brain research (CS5) or cybersecurity applications (CS8). Such issues are not singular in nature but closely linked to other ethical issues such as information asymmetries, trust, and discrimination. Consequently, the umbrella issue of reliability of data must be approached from different perspectives to ensure the validity of the decision-making processes of the BD + AI.
Data may over-represent some people or social groups who are likely to be already privileged or under-represent disadvantaged and vulnerable groups (CS3). Furthermore, people who are better positioned to gain access to data and have the expertise to interpret them may have an unfair advantage over people devoid of such competencies. In addition, BD + AI can work as a tool of disciplinary power, used to evaluate people’s conformity to norms representing the standards of disciplinary systems (CS5). We focus on the following aspects of justice in our case study analysis: power asymmetries, discrimination, inequality, and access.
The fact that issues of power can arise in public as well as private organisations was discussed in our case studies. The smart city case (CS4) showed that the public organisations were aware of potential problems arising from companies using public data and were trying to put legal safeguards in place to avoid such misuse. As a result of misuse, there is the potential that cities, or the companies with which they contract, may use data in harmful or discriminatory ways. Our case study on the use of BD + AI in scientific research showed that the interviewees were acutely aware of the potential of discrimination (CS10). They stated that biases in the data may not be easy to identify, and may lead to misclassification or misinterpretation of findings, which may in turn skew results. Discrimination refers to the recognition of difference, but it may also refer to unjust treatment of different categories of people based on their gender, sex, religion, race, class, or disability. BD + AI are often employed to distinguish between different cases, e.g. between normal and abnormal behaviour in cybersecurity. Determining whether such classification entails discrimination in the latter sense can be difficult, due to the nature of the data and algorithms involved.
Examples of potential inequality based on BD + AI could be seen in several case studies. The agricultural case (CS3) highlighted the power differential between farmers and companies with potential implications for inequality, but also the global inequality between farmers, linked to farming practices in different countries (CS3). Subsistence farmers in developing countries, for example, might find it more difficult to benefit from these technologies than large agro-businesses. The diverging levels of access to BD + AI entail different levels of ability to benefit from them and counteract possible disadvantages (CS3). Some companies restrict access to their data entirely, and others sell access at a fee, while others offer small datasets to university-based researchers (Boyd & Crawford, 2012 , p. 674).
Economic Issues
One economic impact of BD + AI outlined in the agriculture case study (CS3) focused on whether this technology, and their ethical implementation, were economically affordable. If BD + AI could not improve economic efficiency, they would be rejected by the end-user, whether they were more productive, sustainable, and ethical options. This is striking, as it raises a serious challenge for the AI ethics literature and industry. It establishes that no matter how well intentioned and principled AI ethics guidelines and charters are, unless their implementation can be done in an economically viable way, their implementation will be challenged and resisted by those footing the bill.
The telecommunications case study (CS9) focused on how GDPR legislation may economically impact businesses using BD + AI by creating disparities in competitiveness between EU and non-EU companies developing BD + AI. Owing to the larger data pools of the latter, their BD + AI may prove to be more effective than European-manufactured alternatives, which cannot bypass the ethical boundaries of European law in the same way (CS8). This is something that is also being addressed in the literature and is a very serious concern for the future profitability and development of AI in Europe (Wallace & Castro, 2018 ). The literature notes additional issues in this area that were not covered in the cases. There is the potential that the GDPR will increase costs of European AI companies by having to manually review algorithmic decision-making; the right to explanation could reduce AI accuracy; and the right to erasure could damage AI systems (Wallace & Castro, 2018 , p. 2).
One interviewee stated that public–private BD + AI projects should be conducted in a collaborative manner, rather than a sale-of-service (CS4). However, this harmonious partnership is often not possible. Another interviewee discussed the tension between public and private interests on their project—while the municipality tried to focus on citizen value, the ICT company focused on the project’s economic success. The interviewee stated that the project would have terminated earlier if it were the company’s decision, because it was unprofitable (CS4). This is a huge concern in the literature, whereby private interests will cloud, influence, and damage public decision-making within the city because of their sometimes-incompatible goals (citizen value vs. economic growth) (Sadowski & Pasquale, 2015 ). One interviewee said that the municipality officials were aware of the problems of corporate influence and thus are attempting to implement the approach of ‘data sovereignty’ (CS2).
During our interviews, some viewed BD + AI as complementary to human employment (CS3), collaborative with such employment (CS4), or as a replacement to employment (CS6). The interviewees from the agriculture case study (CS3) stated that their BD + AI were not sufficiently advanced to replace humans and were meant to complement the agronomist, rather than replace them. However, they did not indicate what would happen when the technology is advanced enough, and it becomes profitable to replace the agronomist. The insurance company interviewee (CS6) stated that they use BD + AI to reduce flaws in personal judgment. The literature also supports this viewpoint, where BD + AI is seen to offer the potential to evaluate cases impartially, which is beneficial to the insurance industry (Belliveau, Gray, & Wilson, 2019 ). Footnote 16 The interviewee reiterated this and also stated that BD + AI would reduce the number of people required to work on fraud cases. The interviewee stated that BD + AI are designed to replace these individuals, but did not indicate whether their jobs were secure or whether they would be retrained for different positions, highlighting a concern found in the literature about the replacement and unemployment of workers by AI (Bossman, 2016 ). In contrast to this, a municipality interviewee from CS4 stated that their chat-bots are used in a collaborative way to assist customer service agents, allowing them to concentrate on higher-level tasks, and that there are clear policies set in place to protect their jobs.
Sustainability was only explicitly discussed in two interviews (CS3 and CS4). The agriculture interviewees stated that they wanted to be the ‘first’ to incorporate sustainability metrics into agricultural BD + AI, indicating a competitive and innovative rationale for their company (CS3). Whereas the interviewee from the sustainable development case study (CS4) stated that their goal of using BD + AI was to reduce Co2 emissions and improve energy and air quality. He stated that there are often tensions between ecological and economic goals and that this tension tends to slow down the efforts of BD + AI public–private projects—an observation also supported by the literature (Keeso, 2014 ). This tension between public and private interests in BD + AI projects was a recurring issue throughout the cases, which will be the focus of the next section on the role of organisations.
Discussion and Conclusion
The motivation behind this paper is to come to a better understanding of ethical issues related to BD + AI based on a rich empirical basis across different application domains. The exploratory and interpretive approach chosen for this study means that we cannot generalise from our research to all possible examples of BD + AI, but it does allow us to generalise to theory and rich insights (Walsham, 1995a , b , 2006 ). These theoretical insights can then provide the basis for further empirical research, possibly using other methods to allow an even wider set of inputs to move beyond some of the limitations of the current study.
Organisational Practice and the Literature
The first point worth stating is that there is a high level of consistency both among the case studies and between cases and literature. Many of the ethical issues identified cut across the cases and are interpreted in similar ways by different stakeholders. The frequency distribution of ethical issues indicates that very few, if any, issues are relevant to all cases but many, such as privacy, have a high level of prevalence. Despite appearing in all case studies, privacy was not seen as overly problematic and could be dealt with in the context of current regulatory principles (GDPR). Most of the issues that we found in the literature (see Sect. 2 ) were also present in the case studies. In addition to privacy and data protection, this included accuracy, reliability, economic and power imbalances, justice, employment, discrimination and bias, autonomy and human rights and freedoms.
Beyond the general confirmation of the relevance of topics discussed in the literature, though, the case studies provide some further interesting insights. From the perspective of an individual case some societal factors are taken for granted and outside of the control of individual actors. For example, intellectual property regimes have significant and well-recognised consequences for justice, as demonstrated in the literature. However, there is often little that individuals or organisations can do about them. Even in cases where individuals may be able to make a difference and the problem is clear, it is not always obvious how to do this. Some well-publicised discrimination cases may be easy to recognise, for example where an HR system discriminates against women or where a facial recognition system discriminates against black people. But in many cases, it may be exceedingly difficult to recognise discrimination where it is not clear how a person is discriminated against. If, for example, an image-based medical diagnostic system leads to disadvantages for people with genetic profiles, this may not be easy to identify.
With regards to the classification of the literature suggested in Sect. 2 along the temporal dimension, we can see that the attention of the case study respondents seems to be correlated to the temporal horizon of the issues. The issues we see as short-term figures most prominently, whereas the medium-term issues, while still relevant and recognisable, appear to be less pronounced. The long-term questions are least visible in the cases. This is not very surprising, as the short-term issues are those that are at least potentially capable of being addressed relatively quickly and thus must be accessible on the local level. Organisations deploying or using AI therefore are likely to have a responsibility to address these issues and our case studies have shown that they are aware of this and putting measures in place. This is clearly true for data protection or security issues. The medium-term issues that are less likely to find local resolutions still figure prominently, even though an individual organisation has less influence on how they can be addressed. Examples of this would be questions of unemployment, justice, or fairness. There was little reference to what we call long-term issues, which can partly be explained by the fact that the type of AI user organisations we investigated have very limited influence on how they are perceived and how they may be addressed.
Interpretative Differences on Ethical Issues
Despite general agreement on the terminology used to describe ethical issues, there are often important differences in interpretation and understanding. In the first ethics theme, control of data, the perceptions of privacy ranged from ‘not an issue’ to an issue that was being dealt with. Some of this arose from the question of informed consent and the GDPR. However, a reliance on legislation, such as GDPR, without full knowledge of the intricacies of its details (i.e. that informed consent is only one of several legal bases of lawful data processing), may give rise to a false sense of security over people’s perceived privacy. This was also linked to the issue of transparency (of processes dealing with data), which may be external to the organisation (do people outside understand how an organisation holds and processes their data), or internal (how well does the organisation understand the algorithms developed internally) and sometimes involve deliberate opacity (used in specific contexts where it is perceived as necessary, such as in monitoring political unrest and its possible consequences). Therefore, a clearer and more nuanced understanding of privacy and other ethical terms raised here might well be useful, albeit tricky to derive in a public setting (for an example of complications in defining privacy, see Macnish, 2018 ).
Some issues from the literature were not mentioned in the cases, such as warfare. This can easily be explained by our choice of case studies, none of which drew on work done in this area. It indicates that even a set of 10 case studies falls short of covering all issues.
A further empirical insight is in the category we called ‘role of organisations’, which covers trust and responsibility. Trust is a key term in the discussion of the ethics of AI, prominently highlighted by the focus on trustworthy AI by the EU’s High-Level Expert Group, among others. We put this into the ‘role of organisations’ category because our interaction with the case study respondents suggested that they felt it was part of the role of their organisations to foster trust and establish responsibilities. But we are open to the suggestion that these are concepts on a slightly different level that may provide the link between specific issues in applications and broader societal debate.
Next Steps: Addressing the Ethics of AI and Big Data
This paper is predominantly descriptive, and it aims to provide a theoretically sound and empirically rich account of ethical concerns in AI + BD. While we hope that it proves to be insightful it is only a first step in the broader journey towards addressing and resolving these issues. The categorisation suggested here gives an initial indication of which type of actor may be called upon to address which type of issue. The distinction between micro-, meso- and macro perspectives suggested by Haenlein and Kaplan ( 2019 ) resonates to some degree with our categorisation of issues.
This points to the question what can be done to address these ethical issues and by whom should it be done? We have not touched on this question in the theoretical or empirical part of the paper, but the question of mitigation is the motivating force behind much of the AI + BD ethics research. The purpose of understanding these ethical questions is to find ways of addressing them.
This calls for a more detailed investigation of the ethical nature of the issues described here. As indicated earlier, we did not begin with a specific ethical theoretical framework imposed onto the case studies, but did have some derived ethics concepts which we explored within the context of the cases and allowed others to emerge over the course of the interviews. One issue is the philosophical question whether the different ethical issues discussed here are of a similar or comparable nature and what characterises them as ethical issues. This is not only a philosophical question but also a practical one for policymakers and decision makers. We have alluded to the idea that privacy and data protection are ethical issues, but they also have strong legal implications and can also be human rights issues. It would therefore be beneficial to undertake a further analysis to investigate which of these ethical issues are already regulated and to what degree current regulation covers BD + AI, and how this varies across the various EU nations and beyond.
Another step could be to expand an investigation like the one presented here to cover the ethics of AI + BD debate with a focus on suggested resolutions and policies. This could be achieved by adopting the categorisation and structure presented here and extending it to the currently discussed option for addressing the ethical issues. These include individual and collective activities ranging from technical measures to measure bias in data or individual professional guidance to standardisation, legislation, the creation of a specific regulator and many more. It will be important to understand how these measures are conceptualised as well as which ones are already used to which effect. Any such future work, however, will need to be based on a sound understanding of the issues themselves, which this paper contributes to. The key contribution of the paper, namely the presentation of empirical findings from 10 case studies show in more detail how ethical issues play out in practice. While this work can and should be expanded by including an even broader variety of cases and could be supplemented by other empirical research methods, it marks an important step in the development of our understanding of these ethical issues. This should form a part of the broader societal debate about what these new technologies can and should be used for and how we can ensure that their consequences are beneficial for individuals and society.
Throughout the paper, XXX will be used to anonymise relevant text that may identify the authors, either through the project and/or publications resulting from the individual case studies. All case studies have been published individually. Several the XXX references in the findings refer to these individual publications which provide more detail on the cases than can be provided in this cross-case analysis.
The ethical issues that we discussed throughout the case studies refers to issues broadly construed as ethical issues, or issues that have ethical significance. While some issues may not be directly obvious how they are ethical issues, they may give rise to significant harm relevant to ethics. For example, accuracy of data may not explicitly be an ethical issue, if inaccurate data is used in algorithms, it may lead to discrimination, unfair bias, or harms to individuals.
Such as chat-bots, natural language processing AI, IoT data retrieval, predictive risk analysis, cybersecurity machine-learning, and large dataset exchanges.
https://ec.europa.eu/futurium/en/ai-alliance-consultation/guidelines/1 .
https://ec.europa.eu/digital-single-market/en/high-level-expert-group-artificial-intelligence .
The type of AI currently in vogue, as outlined earlier, is based on machine learning, typically employing artificial neural networks for big data analysis. This is typically seen as ‘narrow AI’ and it is not clear whether there is a way from narrow to general AI, even if one were to accept that achieving general AI is fundamentally possible.
The 16 social domains were: Banking and securities; Healthcare; Insurance; Retail and wholesale trade; Science; Education; Energy and utilities; Manufacturing and natural resources; Agriculture; Communications, media and entertainment; Transportation; Employee monitoring and administration; Government; Law enforcement and justice; Sustainable development; and Defence and national security.
This increased to 26 ethical issues following a group brainstorming session at the case study workshop.
The nine additional ethical issues from the initial 17 drafted by the project leader were: human rights, transparency, responsibility, ownership of data, algorithmic bias, integrity, human rights, human contact, and accuracy of data.
The additional ethical issues were access to BD + AI, accuracy of data, accuracy of recommendations, algorithmic bias, economic, human contact, human rights, integrity, ownership of data, responsibility, and transparency. Two of the initial ethical concerns were removed (inclusion of stakeholders and environmental impact). The issues raised concerning inclusion of stakeholders were deemed to be sufficiently included in access to BD + AI, and those relating to environmental impact were felt to be sufficiently covered by sustainability.
The three appendices attached in this paper comprise much of this case study protocol.
CS4 evaluated four organisations, but one of these organisations was also part of CS2 – Organisation 1. CS6 analysed two insurance organisations.
Starting out, we aimed to have both policy/ethics-focused experts within the organisation and individuals that could also speak with us about the technical aspects of the organisation’s BD + AI. However, this was often not possible, due to availability, organisations’ inability to free up resources (e.g. employee’s time) for interviews, or lack of designated experts in those areas.
For example, in CS1, CS6, and CS8.
For example, in CS2, CS3, CS4, CS5, CS6, and CS9.
As is discussed elsewhere in this paper, algorithms also hold the possibility of reinforcing our prejudices and biases or creating new ones entirely.
Accenture. (2016). Building digital trust: The role of data ethics in the digital age. Retrieved December 1, 2020 from https://www.accenture.com/t20160613T024441__w__/us-en/_acnmedia/PDF-22/Accenture-Data-Ethics-POV-WEB.pdf .
Accenture. (2017). Embracing artificial intelligence. Enabling strong and inclusive AI driven growth. Retrieved December 1, 2020 from https://www.accenture.com/t20170614T130615Z__w__/us-en/_acnmedia/Accenture/next-gen-5/event-g20-yea-summit/pdfs/Accenture-Intelligent-Economy.pdf .
Antoniou, J., & Andreou, A. (2019). Case study: The Internet of Things and Ethics. The Orbit Journal, 2 (2), 67.
Google Scholar
Badri, A., Boudreau-Trudel, B., & Souissi, A. S. (2018). Occupational health and safety in the industry 4.0 era: A cause for major concern? Safety Science, 109, 403–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2018.06.012
Article Google Scholar
Barolli, L., Takizawa, M., Xhafa, F., & Enokido, T. (ed.) (2019). Web, artificial intelligence and network applications. In Proceedings of the workshops of the 33rd international conference on advanced information networking and applications , Springer.
Barocas, S., & Selbst, A. D. (2016). Big data’s disparate impact. California Law Review, 104 (671), 671–732. https://doi.org/10.15779/Z38BG31
Baum, S. D. (2017). Reconciliation between factions focused on near-term and long-term artificial intelligence. AI Society, 2018 (33), 565–572.
Belliveau, K. M., Gray, L. E., & Wilson, R. J. (2019). Busting the Black Box: Big Data Employment and Privacy | IADC LAW. https://www.iadclaw.org/publications-news/defensecounseljournal/busting-the-black-box-big-data-employment-and-privacy/ . Accessed 10 May 2019.
Bossman, J. (2016). Top 9 ethical issues in artificial intelligence. World Economic Forum . https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/10/top-10-ethical-issues-in-artificial-intelligence/ . Accessed 10 May 2019.
Bostrom, N. (2016). Superintelligence: Paths . OUP Oxford.
Boyd, D., & Crawford, K. (2012). Critical questions for big data. Information, Communication and Society, 15 (5), 662–679. https://doi.org/10.1080/1369118X.2012.678878
Burrell, J. (2016). How the machine ‘thinks’: Understanding opacity in machine learning algorithms. Big Data and Society, 3 (1), 2053951715622512.
Bush, T., (2012). Authenticity in Research: Reliability, Validity and Triangulation. Chapter 6 in edited “Research Methods in Educational Leadership and Management”, SAGE Publications.
Calders, T., Kamiran, F., & Pechenizkiy, M. (2009). Building classifiers with independency constraints. In IEEE international conference data mining workshops , ICDMW’09, Miami, USA.
Chatfield, K., Iatridis, K., Stahl, B. C., & Paspallis, N. (2017). Innovating responsibly in ICT for ageing: Drivers, obstacles and implementation. Sustainability, 9 (6), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9060971 .
Cohen, I. G., Amarasingham, R., Shah, A., et al. (2014). The legal and ethical concerns that arise from using complex predictive analytics in health care. Health Affairs, 33 (7), 1139–1147.
Couldry, N., & Powell, A. (2014). Big Data from the bottom up. Big Data and Society, 1 (2), 205395171453927. https://doi.org/10.1177/2053951714539277
Crawford, K., Gray, M. L., & Miltner, K. (2014). Big data| critiquing big data: Politics, ethics, epistemology | special section introduction. International Journal of Communication, 8, 10.
Cuquet, M., & Fensel, A. (2018). The societal impact of big data: A research roadmap for Europe. Technology in Society, 54, 74–86.
Danna, A., & Gandy, O. H., Jr. (2002). All that glitters is not gold: Digging beneath the surface of data mining. Journal of Business Ethics, 40 (4), 373–438.
European Convention for the Protection of HUman Rights and Fundamental Freedoms, pmbl., Nov. 4, 1950, 213 UNTS 221.
Herriott, E. R., & Firestone, W. (1983). Multisite qualitative policy research: Optimizing description and generalizability. Educational Researcher, 12, 14–19. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X012002014
Einav, L., & Levin, J. (2014). Economics in the age of big data. Science, 346 (6210), 1243089. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1243089
Ferraggine, V. E., Doorn, J. H., & Rivera, L. C. (2009). Handbook of research on innovations in database technologies and applications: Current and future trends (pp. 1–1124). IGI Global.
Fothergill, B. T., Knight, W., Stahl, B. C., & Ulnicane, I. (2019). Responsible data governance of neuroscience big data. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 13 . https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2019.00028
Frey, C. B., & Osborne, M. A. (2017). The future of employment: How susceptible are jobs to computerisation? Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 114, 254–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2016.08.019
Haenlein, M., & Kaplan, A. (2019). A brief history of artificial intelligence: On the past, present, and future of artificial intelligence. California Management Review, 61 (4), 5–14.
Harari, Y. N. (2017). Homo deus: A brief history of tomorrow (1st ed.). Vintage.
Book Google Scholar
ICO. (2017). Big data, artificial intelligence, machine learning and data protection. Retrieved December 1, 2020 from Information Commissioner’s Office website: https://iconewsblog.wordpress.com/2017/03/03/ai-machine-learning-and-personal-data/ .
Ioannidis, J. P. (2013). Informed consent, big data, and the oxymoron of research that is not research. The American Journal of Bioethics., 2, 15.
Jain, P., Gyanchandani, M., & Khare, N. (2016). Big data privacy: A technological perspective and review. Journal of Big Data, 3 (1), 25.
Janssen, M., & Kuk, G. (2016). The challenges and limits of big data algorithms in technocratic governance. Government Information Quarterly, 33 (3), 371–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2016.08.011
Jirotka, M., Grimpe, B., Stahl, B., Hartswood, M., & Eden, G. (2017). Responsible research and innovation in the digital age. Communications of the ACM, 60 (5), 62–68. https://doi.org/10.1145/3064940
Jiya, T. (2019). Ethical Implications Of Predictive Risk Intelligence. ORBIT Journal, 2 (2), 51.
Jiya, T. (2019). Ethical reflections of human brain research and smart information systems. The ORBIT Journal, 2 (2), 1–24.
Jobin, A., Ienca, M., & Vayena, E. (2019). The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nature Machine Intelligence, 1 (9), 389–399. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-019-0088-2
Johnson, J. A. (2014). From open data to information justice. Ethics and Information Technology, 4 (16), 263–274.
Johnson, J. A. (2018). Open data, big data, and just data. In J. A. Johnson (Ed.), Toward information justice (pp. 23–49). Berlin: Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Kancevičienė, N. (2019). Insurance, smart information systems and ethics: a case study. The ORBIT Journal, 2 (2), 1–27.
Keeso, A. (2014). Big data and environmental sustainability: A conversation starter . https://www.google.com/search?rlz=1C1CHBF_nlNL796NL796&ei=YF3VXN3qCMLCwAKp4qjYBQ&q=Keeso+Big+Data+and+Environmental+Sustainability%3A+A+Conversation+Starter&oq=Keeso+Big+Data+and+Environmental+Sustainability%3A+A+Conversation+Starter&gs_l=psy-ab.3...15460.16163..16528...0.0..0.76.371.6......0....1..gws-wiz.......0i71j35i304i39j0i13i30.M_8nNbaL2E8 . Accessed 10 May 2019.
Kuriakose, F., & Iyer, D. (2018). Human Rights in the Big Data World (SSRN Scholarly Paper No. ID 3246969). Rochester, NY: Social Science Research Network. https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=3246969 . Accessed 13 May 2019.
Kurzweil, R. (2006). The singularity is near . Gerald Duckworth & Co Ltd.
Latonero, M. (2018). Big data analytics and human rights. New Technologies for Human Rights Law and Practice. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781316838952.007
Lepri, B., Staiano, J., Sangokoya, D., Letouzé, E., & Oliver, N. (2017). The tyranny of data? the bright and dark sides of data-driven decision-making for social good. In Transparent data mining for big and small data (pp. 3–24). Springer.
Livingstone, D. (2015). Transhumanism: The history of a dangerous idea . CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform.
Macnish, K. (2018). Government surveillance and why defining privacy matters in a post-snowden world. Journal of Applied Philosophy, 35 (2), 417–432.
Macnish, K., & Inguanzo, A. (2019). Case study-customer relation management, smart information systems and ethics. The ORBIT Journal, 2 (2), 1–24.
Macnish, K., Inguanzo, A. F., & Kirichenko, A. (2019). Smart information systems in cybersecurity. ORBIT Journal, 2 (2), 15.
Mai, J. E. (2016). Big data privacy: The datafication of personal information. The Information Society, 32 (3), 192–199.
Manson, N. C., & O’Neill, O. (2007). Rethinking informed consent in bioethics . Cambridge University Press.
Mittelstadt, B. D., Allo, P., Taddeo, M., Wachter, S., & Floridi, L. (2016). The ethics of algorithms: Mapping the debate. Big Data and Society, 3 (2), 2053951716679679.
Meeker, Q. W., & , Hong, Y. . (2014). Reliability Meets big data: Opportunities and challenges. Quality Engineering, 26 (1), 102–116.
Newman, N. (2013). The costs of lost privacy: Consumer harm and rising economic inequality in the age of google (SSRN Scholarly Paper No. ID 2310146). Rochester: Social Science Research Network. https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=2310146 . Accessed 10 May 2019.
O’Neil, C. (2016). Weapons of math destruction: How big data increases inequality and threatens democracy . Crown Publishers.
Panch, T., Mattie, H., & Atun, R. (2019). Artificial intelligence and algorithmic bias: implications for health systems. Journal of global health, 9 (2).
Pellé, S., & Reber, B. (2015). Responsible innovation in the light of moral responsibility. Journal on Chain and Network Science, 15 (2), 107–117. https://doi.org/10.3920/JCNS2014.x017
Portmess, L., & Tower, S. (2015). Data barns, ambient intelligence and cloud computing: The tacit epistemology and linguistic representation of Big Data. Ethics and Information Technology, 17 (1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10676-014-9357-2
Ryan, M. (2019). Ethics of public use of AI and big data. ORBIT Journal, 2 (2), 15.
Ryan, M. (2019). Ethics of using AI and big data in agriculture: The case of a large agriculture multinational. The ORBIT Journal, 2 (2), 1–27.
Ryan, M., & Gregory, A. (2019). Ethics of using smart city AI and big data: The case of four large European cities. The ORBIT Journal, 2 (2), 1–36.
Sadowski, J., & Pasquale, F. A. (2015). The spectrum of control: A social theory of the smart city. First Monday, 20 (7), 16.
Schradie, J. (2017). Big data is too small: Research implications of class inequality for online data collection. In D. June & P. Andrea (Eds.), Media and class: TV, film and digital culture . Abingdon: Taylor and Francis.
Taylor, L. (2017). ‘What is data justice? The case for connecting digital rights and freedoms globally’ In Big data and society (pp. 1–14). https://doi.org/10.1177/2053951717736335 .
Tene, O., & Polonetsky, J. (2012). Big data for all: Privacy and user control in the age of analytics. The Northwestern Journal of Technology and Intellectual Property, 11, 10.
Tene, O., & Polonetsky, J. (2013). A theory of creepy: technology, privacy and shifting social norms. Yale JL and Technology, 16, 59.
Van Dijck, J., & Poell, T. (2013). Understanding social media logic. Media and Communication, 1 (1), 2–14.
Voinea, C., & Uszkai, R. (n.d.). An assessement of algorithmic accountability methods .
Walsham, G. (1995). Interpretive case studies in IS research: nature and method. European Journal of Information Systems, 4 (2), 74–81.
Wallace, N., & Castro, D. (2018) The Impact of the EU’s New Data Protection Regulation on AI, Centre for Data Innovation .
Walsham, G. (1995). Interpretive case-studies in IS research-nature and method. European Journal of Information Systems, 4 (2), 74–81.
Walsham, G. (2006). Doing interpretive research. European Journal of Information Systems, 15 (3), 320–330.
Wheeler, G. (2016). Machine epistemology and big data. In L. McIntyre & A. Rosenburg (Eds.), Routledge Companion to Philosophy of Social Science . Routledge.
Whittlestone, J., Nyrup, R., Alexandrova, A., Dihal, K., & Cave, S. (2019). Ethical and societal implications of algorithms, data, and artificial intelligence: A roadmap for research. https://www.nuffieldfoundation.org/sites/default/files/files/Ethical-and-Societal-Implications-of-Data-and-AI-report-Nuffield-Foundat.pdf .
Wolf, B. (2015). Burkhardt Wolf: Big data, small freedom? / Radical Philosophy. Radical Philosophy . https://www.radicalphilosophy.com/commentary/big-data-small-freedom . Accessed 13 May 2019.
Yin, R. K. (2014). Case study research: Design and methods (5th ed.). SAGE.
Yin, R. K. (2015). Qualitative research from start to finish . Guilford Publications.
Zwitter, A. (2014). Big data ethics. Big Data and Society, 1 (2), 51.
Zuboff, S. (2015). Big other: Surveillance capitalism and the prospects of an information civilization (April 4, 2015). Journal of Information Technology, 2015 (30), 75–89. https://doi.org/10.1057/jit.2015.5
Download references
Acknowledgements
This SHERPA Project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Framework Programme for Research and Innovation under the Specific Grant Agreement No. 786641. The author(s) acknowledge the contribution of the consortium to the development and design of the case study approach.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Wageningen Economic Research, Wageningen University and Research, Wageningen, The Netherlands
UCLan Cyprus, Larnaka, Cyprus
Josephina Antoniou
De Montford University, Leicester, UK
Laurence Brooks & Bernd Stahl
Northampton University, Northampton, UK
Tilimbe Jiya
The University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands
Kevin Macnish
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mark Ryan .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1: Desk Research Questions
Number Research Question.
In which sector is the organisation located (e.g. industry, government, NGO, etc.)?
What is the name of the organisation?
What is the geographic scope of the organisation?
What is the name of the interviewee?
What is the interviewee’s role within the organisation?
Appendix 2: Interview Research Questions
No Research Question.
What involvement has the interviewee had with BD + AI within the organisation?
What type of BD + AI is the organisation using? (e.g. IBM Watson, Google Deepmind)
What is the field of application of the BD + AI (e.g. administration, healthcare, retail)
Does the BD + AI work as intended or are there problems with its operation?
What are the innovative elements introduced by the BD + AI (e.g. what has the technology enabled within the organisation?)
What is the level of maturity of the BD + AI ? (i.e. has the technology been used for long at the organisation? Is it a recent development or an established approach?)
How does the BD + AI interact with other technologies within the organisation?
What are the parameters/inputs used to inform the BD + AI ? (e.g. which sorts of data are input, how is the data understood within the algorithm?). Does the BD + AI collect and/or use data which identifies or can be used to identify a living person (personal data)?. Does the BD + AI collect personal data without the consent of the person to whom those data relate?
What are the principles informing the algorithm used in the BD + AI (e.g. does the algorithm assume that people walk in similar ways, does it assume that loitering involves not moving outside a particular radius in a particular time frame?). Does the BD + AI classify people into groups? If so, how are these groups determined? Does the BD + AI identify abnormal behaviour? If so, what is abnormal behaviour to the BD + AI ?
Are there policies in place governing the use of the BD + AI ?
How transparent is the technology to administrators within the organisation, to users within the organisation?
Who are the stakeholders in the organisation?
What has been the impact of the BD + AI on stakeholders?
How transparent is the technology to people outside the organisation?
Are those stakeholders engaged with the BD + AI ? (e.g. are those affected aware of the BD + AI, do they have any say in its operation?). If so, what is the nature of this engagement? (focus groups, feedback, etc.)
In what way are stakeholders impacted by the BD + AI ? (e.g. what is the societal impact: are there issues of inequality, fairness, safety, filter bubbles, etc.?)
What are the costs of using the BD + AI to stakeholders? (e.g. potential loss of privacy, loss of potential to sell information, potential loss of reputation)
What is the expected longevity of this impact? (e.g. is this expected to be temporary or long-term?)
Are those stakeholders engaged with the BD + AI ? (e.g. are those affected aware of the BD + AI, do they have any say in its operation?)
If so, what is the nature of this engagement? (focus groups, feedback, etc.)
Appendix 3: Checklist of Ethical Issues
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ryan, M., Antoniou, J., Brooks, L. et al. Research and Practice of AI Ethics: A Case Study Approach Juxtaposing Academic Discourse with Organisational Reality. Sci Eng Ethics 27 , 16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11948-021-00293-x
Download citation
Received : 26 August 2019
Accepted : 10 February 2021
Published : 08 March 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11948-021-00293-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Smart information systems
- Big data analytics
- Artificial intelligence ethics
- Multiple-case study analysis
- Philosophy of technology
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Site Search
- How to Search
- Advisory Group
- Editorial Board
- OEC Fellows
- History and Funding
- Using OEC Materials
- Collections
- Research Ethics Resources
- Ethics Projects
- Communities of Practice
- Get Involved
- Submit Content
- Open Access Membership
- Become a Partner
Using Case Studies in Teaching Research Ethics
An essay exploring how to effectively use case studies to teach research ethics.
It is widely believed that discussing case studies is the most effective method of teaching the responsible conduct of research (Kovac 1996; Macrina and Munro 1995), probably because discussing case studies is an effective way to get students involved in the issues. (I use the word “student” to cover all those who study, including faculty members and other professionals.)
Case studies are stories, 1 and narrative – the telling of stories – is a fundamental human tool for organizing, understanding, and explaining experience. Alasdair MacIntyre offers an amusing example of how one might make sense of a nonsensical event by embedding it into a story.
I am standing waiting for a bus and the young man standing next to me suddenly says, ‘The name of the common wild duck is Histrionicus histrionicus histrionicus.’ There is no problem as to the meaning of the sentence he uttered; the problem is, how to answer the question, what was he doing in uttering it? Suppose he just uttered such sentences at random intervals; this would be one possible form of madness. We would render his act of utterance intelligible if one of the following turned out to be true: He has mistaken me for someone who yesterday had approached him in the library and asked: ‘Do you by any chance know the Latin name of the common wild duck?’ Or he has just come from a session with his psychotherapist who has urged him to break down his shyness by talking to strangers. ‘But what shall I say?’ ‘Oh, anything at all.’ Or he is a Soviet spy waiting at a prearranged rendez-vous and uttering the ill-chosen code sentence which will identify him to his contact. In each case the act of utterance becomes intelligible by finding its place in a narrative. [MacIntyre 1981:195-196, italics in original] 2
Just as unintelligible actions invite us to put them into a story, stories invite us to interpret them. Stories imply causality, intention, and meaning; in the forms of parables, fables, and allegories, stories are favored vehicles for moral and religious instruction worldwide.
An in-depth discussion of a case is the closest approximation to actually confronting an ethical problem that can easily be set up in a classroom. Experience is the best teacher, but we can’t predict whether or when our students will face an actual ethical conflict in research, and we would not want to wish such an experience on them. Although a good case discussion is not the same as dealing with a real ethical problem, it can be an approximation of such an experience, just as watching a film about the decline and death of an aged friend can be a highly affecting approximation of the actual experience. Watching the film The Dresser can bring a person to real tears; discussing a case can bring a student to genuine ethical development.
The value of case study discussion can be illustrated with an anecdote. In the first year of the Teaching Research Ethics Workshop, we might have spent a bit too much time talking about using case studies and how to lead case study discussions. By Wednesday (the workshop began on a Sunday that year), one participant complained, saying something like, “Aren’t you going to talk about anything but cases? I’ve used them and students get bored with them.”
We spent less time on case studies thereafter, but I mention the incident because of an evaluation we did in the third year of the workshop. We hired an external evaluator to talk to past workshop participants about its impact on them. I asked our evaluator to talk to several specific participants, including the one who had complained about case studies. To my complete surprise, the report showed that this participant “identified mastery of the case study approach as having had the greatest direct impact” on his teaching. The other past participants interviewed made similar comments.
Like all teaching techniques, case study discussion can be done well or poorly, and I hope to provide some guidance to help you avoid the worst pitfalls. I will assume that you already know how to lead a discussion and limit my comments to considerations pertaining directly to using case studies in research ethics. My comments are rooted in what has worked for me with the assumption that most of it will work for you, too – but probably not all of it. Teaching is an art, and success depends a great deal on the skills and personality of the teacher.
Much of what follows might sound dogmatic, but that should be taken as a stylistic quirk. I could add all the hedges and exceptions of which I can think, but that would only muddy things. Use your own judgment and take the advice for what it’s worth. Also note that this is general advice; some cases are designed to be used in a particular way (see Bebeau et al. 1995).
Preparing to lead a case study discussion is much the same as preparing to teach anything – figure out what you want to accomplish, how much time you can spend on it, and the like.
In the classroom, start by laying out ground rules. In many settings this step does not have to be overt – if it is a group you have been meeting with already, and you have established a tone of respect and openness, there’s no need to go over this again. If the group has not established this kind of rapport, then it is important to make it clear that everyone’s opinion will be heard – and challenged – respectfully.
You might also want to offer your students some strategies and tactics before plunging into the discussion.
Strategies cover the broad direction for the discussion. For example, you can tell your students that you want them to:
- Decide which of two positions to defend – “Should Peterson copy the notes? Why or why not?”
- Solve a problem – “What should Peterson do?”
- Take a role – “What would you do if you were Peterson?” • Think about how the problem could have been avoided – “What went wrong here?”
Clearly these are not mutually exclusive, and there are probably other strategies you could use.
It is often also helpful to suggest some tactics . Sometimes students see a case study (or ethics) as an inchoate mass – or as too well integrated to analyze. It can be useful to give them some specific things to dig out of the case.
For example, in Moral Reasoning in Scientific Research: Cases for Teaching and Assessment , which I developed along with Mickey Bebeau, Karen Muskavitch, and several other colleagues (Bebeau et al. 1995), we suggest that students try to identify (a) the ethical issues and points of conflict, (b) the interested parties, (c) the likely consequences of the proposed course of action, and (d) the moral obligations of the protagonist.
Lucinda Peach (included in Penslar 1995) offers a different approach, suggesting the value of paying attention to six factors: facts; interpretations of the facts; consequences; obligations; rights; and virtues (or character). I have found it particularly helpful to point out the distinction between the facts presented in the case and the interpretations of facts that are sometimes made unconsciously.
When the time comes to start the actual discussion, I always distribute a copy of the case study to all students, and I often also display it using an overhead projector. If a case is at all complex or subtle, or has more than one or two characters, it is very difficult to take part in the discussion without having the case on hand for reference.
I usually ask one or more students to volunteer to read the case aloud . If there are several characters in the case, I often take the part of narrator and ask students to read the parts of the characters. Reading the case aloud ensures that everyone finishes at the same time; asking students to take part gets their voices heard early.
Then I give students a chance to ask any questions of factual clarification they might have. The answers might already be in the case, but they aren’t always. I don’t always answer all of these questions at this point, saying instead, “Let’s make sure we get to that when we discuss the case.” For example, if a student were to ask: “What kind of student is Peterson? Is she any good?” I would want to wait until the discussion period, when I would respond by asking, “What difference does it make?” (Not to imply that it doesn’t make a difference, but to see why the students think it does.)
I often then give students a few minutes to write some thoughts – perhaps to answer the strategic question, or identify the tactical elements I had already outlined. I usually don’t collect the papers; 3 the object here is to give students a chance to collect their thoughts and make a commitment, however tentative, to a few of them. Ideas that remain only half-formed in the mind often fly away when the discussion begins, but the written ideas are there for the students’ reference.
If the group isn’t too large, I find it very useful to go around the room and ask every student to make one short response to the case. When the strategy is to defend a position, I first ask them each to answer the first question – “Should Peterson copy the notes?” – yes or no. I tally their answers on the board. Then I go around again and ask each student to offer one reason for their answer. (If the responses are unbalanced – say 10 yes and 2 no – I give the students who said “no” the chance to state their case first.) In larger groups, I get a random sample of responses.
Then I plunge into the discussion, trying to be as quiet as I can and to get the students to talk as much as possible. My part is to keep things orderly, to clarify points in the case (including relevant rules and regulations), and to gently direct the discussion toward profitable paths. I usually write main points on the board.
Finally, the case should be brought to some kind of closure . Sometimes this means describing what I take to be the areas of agreement and disagreement and the relative weight of each (“Almost everyone agrees on X, but we’re still pretty divided on Y”). Sometimes it even includes a pronouncement: “It would be wrong for Peterson to copy the notes.” But I would generally qualify the pronouncement by describing some of Peterson’s other options.
Case study discussion can work even if you use it only once, but the more often a group discusses cases, the better. Using case studies is not the only technique for teaching responsible science, but it is, I think, one of the best.
Works Cited
Barnbaum, Deborah R., and Michael Byron. 2001. Research Ethics: Text and Readings . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Bebeau, Muriel J., et al. 1995. Moral Reasoning in Scientific Research : Cases for Teaching and Assessment. Bloomington, IN.: Poynter Center. http://poynter.indiana.edu/mr-main.shtml
Elliott, Deni, and Judy E. Stern, eds. 1997. Research Ethics: A Reader . Hanover, CT: University Press of New England.
Harris, Charles E. Jr., Michael S. Pritchard, and Michael J. Rabins. 1995. Engineering Ethics: Concepts and Cases . Belmont: Wadsworth Publishing Company.
King, Nancy M. P., Gail E. Henderson, and Jane Stein, eds. 1999. Beyond Regulations: Ethics in Human Subjects Research . Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina Press.
Kovac, Jeffrey. 1996. “Scientific ethics in chemical education.” Journal of Chemical Education 73(10): 926-928.
MacIntyre, Alasdair. 1981. After Virtue: A Study in Moral Theory . Notre Dame: University of Notre Dame Press.
Macrina, Francis L. 2000. Scientific Integrity: An Introductory Text with Cases . 2nd ed. Washington, DC: ASM Press.
Macrina, Francis L. and Cindy L. Munro. 1995. “The case-study approach to teaching scientific integrity in nursing and the biomedical sciences.” Journal of Professional Nursing 11(1): 40- 44.
Orlans, F. Barbara, et al. 1998. The Human Use of Animals: Case Studies in Ethical Choice . New York: Oxford University Press. Penslar, Robin Levin. 1995. Research Ethics: Cases and Materials. Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
Seebauer, Edmund G., and Robert L. Barry. 2001. Fundamentals of Ethics for Scientists and Engineers . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Schrag, Brian, ed. 1997-2002. Research Ethics: Cases and Commentaries . Six volumes. Bloomington, IN: Association for Practical and Professional Ethics.
Appendix: Types of case studies
I don’t know of any thorough typology of case studies, but it is clear that case studies take many forms. Here are some of the forms that I have come across. The list is not intended to be exhaustive, and the descriptive names are my own – they should not be construed as definitive or in common use.
Illustrative cases are perhaps the most common form. They are included in textbooks written specifically for instruction in the responsible conduct of research and are generally found at the end of each chapter to illustrate the chapter’s major points. For examples, see Barnbaum and Byron 2001; Elliott and Stern 1997; Harris, Pritchard, and Rabins 1995; Macrina 2000; and Seebauer and Barry 2001.
Historical case studies start with a particular controversy, event, or series of related events. Good examples can be found in The Human Use of Animals (Orlans et al. 1998). The first case, “Baboon-human liver transplants: The Pittsburgh case,” describes an operation performed in 1992 at the University of Pittsburgh to replace a dying man’s defective liver with a healthy liver from a baboon. The case itself is presented in two pages, followed by about a page of historical context. The bulk of the chapter, about eight pages, consists of commentary on the ethical issues raised by the case. (See also King et.al 1999.) Historical cases are good because they are real, not made up, and students cannot dismiss them by saying, “That would never happen.” On the other hand, though, some students will view historical cases as settled and over with; the very fact that they have been written up can seem to imply that the issues raised have all be solved.
Historical synopses are shorter, often focusing on a well-known event. Fundamentals of Ethics for Scientists and Engineers (Seebauer and Barry 2001), for example, includes sixteen “real-life cases,” generally one or two pages long with a few questions for discussion. The first three cases are titled “Destruction of the Spaceship Challenger,” “Toxic Waste at Love Canal,” and “Dow Corning Corp. and Breast Implants.”
Journalistic case studies are historical case studies written by journalists for mass consumption. A recent example, “The Stuttering Doctor’s ‘Monster Study’,” can be found in the New York Times Magazine (Reynolds 2003). It is the story of Wendell Johnson’s research in the late 1930’s that involved inducing stuttering in orphans. Journalistic accounts generally are written in a more literary, less academic style – they are often more passionate and viscerally engaging than case studies prepared by philosophers and ethicists.
Cases with commentary present the case study first and then follow it with one or more commentaries. The six-volume series Research Ethics: Cases and Commentaries (Schrag 1996- 2002) presents a short case (about two-four pages) followed by a commentary by the case’s author and a second commentary by another expert. (See also King et.al 1999.)
Dramatic cases are formatted like a script, which allows the characters’ voices to carry most of the story. I find them very good for conveying subtleties.
Trigger tapes are short videos intended to trigger discussion. Among the best available are the five videos in the series “Integrity in Scientific Research” (see http://www.aaas.org/spp/video/ ).
Finally, a series of casuistic cases presents several very short, related cases, each one in some way a variation or elaboration of one or more of the previous cases in the series. The first one or two cases are generally straightforward, presenting, for example, a clear-cut case of cheating and a clear-cut case of acceptable sharing of information. Later cases are less straightforward, pushing the boundaries that make the earlier cases clear-cut. Excellent examples can be found in Penslar 1995 (see, e.g., Chapters 5 and 6). This book also includes examples of many of the other kinds of case studies described here.
- 1 Some of the many forms case studies can take are described in the Appendix.
- 2 The young man is mistaken, by the way. Ducks belong to the family Anatidae, not Histrionicus.
- 3 I do collect the papers when I use Moral Reasoning in Scientific Research; it’s part of the method outlined in the booklet.
Portions of this paper are adapted from a presentation at the Planning Workshop for a Guide for Teaching Responsible Science, sponsored by the National Academy of Sciences, the National Science Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health, February 1997.
Copyright 2003, 2007, Kenneth D. Pimple, Ph.D. All rights reserved.
Permission is hereby granted to reproduce and distribute copies of this work for nonprofit educational purposes, provided that copies are distributed at or below cost, and that the author, source, and copyright notice are included on each copy. This permission is in addition to rights of reproduction granted under Sections 107, 108, and other provisions of the U.S. Copyright Act.
Also available at the TeachRCR.us site.
Related Resources
Submit Content to the OEC Donate

This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Award No. 2055332. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.

Princeton Dialogues on AI and Ethics
Princeton University
Case Studies
Princeton Dialogues on AI and Ethics Case Studies
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) systems and their deployment in society gives rise to ethical dilemmas and hard questions. By situating ethical considerations in terms of real-world scenarios, case studies facilitate in-depth and multi-faceted explorations of complex philosophical questions about what is right, good and feasible. Case studies provide a useful jumping-off point for considering the various moral and practical trade-offs inherent in the study of practical ethics.
Case Study PDFs : The Princeton Dialogues on AI and Ethics has released six long-format case studies exploring issues at the intersection of AI, ethics and society. Three additional case studies are scheduled for release in spring 2019.
Methodology : The Princeton Dialogues on AI and Ethics case studies are unique in their adherence to five guiding principles: 1) empirical foundations, 2) broad accessibility, 3) interactiveness, 4) multiple viewpoints and 5) depth over brevity.

- Crisis Data: An Ethics Case Study
- Markkula Center for Applied Ethics
- Focus Areas
- Internet Ethics
- Internet Ethics Resources

Crisis Data
An ai ethics case study.
Ethical questions about data collection, data-sharing, access, use, and privacy.

"Depression please cut to the chase." by darcyadelaide is marked with CC BY 2.0.
" Depression please cut to the chase. " by darcyadelaide is marked with CC BY 2.0 .
In January 2022, Politico published an article about a nonprofit called Crisis Text Line , which offers support via text messages for people who are going through mental health crises. For years, the nonprofit had been collecting a database of messages exchanged, and used the data to triage the incoming calls for help and to train its volunteers to better manage their difficult conversations with people in great distress. In a 2020 report , the nonprofit (which first launched in 2013) stated that “[b]y implementing data science tools and machine learning from day one, [it had] created the largest mental health dataset in the world.” A report section titled “Data Philosophy” added, “we share data to support smarter research, policy, and community organizing. Unlike other large-scale data sets on mental health and crisis, our data has incredible volume, velocity, and variety.”
As Politico reported, in 2018 the nonprofit also launched a for-profit spinoff called Loris.ai, which planned to use Crisis Text Line data (which it said was anonymized) to gain insights that would then be incorporated into customer-support software products. The plan was for a portion of the profits from that software to then be shared with the Crisis Text Line.
The Politico article sparked a great deal of criticism of that data-sharing agreement. Some critics were concerned that the data might still be traceable back to individuals who could then be stigmatized or otherwise harmed by being “outed” as dealing with severe mental health issues. Others argued that even anonymized data should not be used in ways that the people who texted in would not have anticipated—in other words, for purposes distinct from helping them directly. When the organization responded that its data-sharing agreement was disclosed to users (whose first text is answered by an automated reply that reads “By texting further with us, you agree to our Terms” and links to a 50-page agreement), critics questioned whether the mere act of users following through, under such circumstances, could be deemed to be “actual meaningful, emotional, fully understood consent.”
Some of the Crisis Text Line volunteers were greatly concerned by the secondary use of the data collected by the nonprofit, and raised those concerns both internally and externally . Once a petition was organized, demanding an end to the data sharing agreement, other volunteers expressed shock that they had not even been aware of the for-profit effort.
A few days after the Politico article was published, Crisis Text Line announced that it was ending the data-sharing agreement with Loris.ai. In a subsequent personal blog post responding to the controversy , researcher danah boyd, who had been a founding board member of CTL and had served as its board chair for some time, explained her thinking and her actions regarding the controversial arrangement. “Since my peers are asking for this to be a case study in tech ethics, I am going into significant detail,” she wrote.
Part of it highlights one of the questions that arose early on in the development of the organization: “could we construct our training so that all counselors got to learn from the knowledge developed by those who came before them? This would mean using texter data for a purpose that went beyond the care and support of that individual.” boyd writes,
Yes, the Terms of Service allowed this, but this is not just a legal question; it’s an ethical question. Given the trade-offs, I made a judgment call early on that not only was using texter data to strengthen training of counselors without their explicit consent ethical, but that to not do this would be unethical. Our mission is clear: help people in crisis. To do this, we need to help our counselors better serve texters. We needed to help counselors learn and grow and develop skills with which they can help others.
The post continues, discussing additional challenges related to scaling access to the service, triage of incoming texts, the need for funding, and the desire to facilitate important research. After noting that she struggled with the question of sharing data with the for-profit entity, boyd states that she ultimately did vote in favor of it. She adds, “Knowing what I know now, I would not have.”
The blog post ends with a call for input: “I also have some honest questions,” boyd writes, “for all of you who are frustrated, angry, disappointed, or simply unsure about us.” Among those questions: “What is the best way to balance the implicit consent of users in crisis with other potentially beneficial uses of data which they likely will not have intentionally consented to but which can help them or others?” She also asks, “Is there any structure in which lessons learned from a non-profit service provider can be transferred to a for-profit entity? Also, how might this work with partner organizations, foundations, government agencies, sponsors, or subsidiaries, and are the answers different?”
Discussion questions
Before answering these questions, please review the Markkula Center for Applied Ethics’ Framework for Ethical Decision-Making , which details the ethical lenses discussed below.
- Who are the stakeholders involved in this case?
- Consider the case through the lenses of rights, justice, utilitarianism, the common good, virtue, and care ethics; what aspects of the ethical landscape do they highlight?
- What would you say in answer to the questions posed by danah boyd, quoted above?

Register and Join Us on May 2nd!
On the multifaceted ethical issues presented by brain implants and AI, and efforts to address them.

Irina Raicu, director, internet ethics, quoted by Scientific American.

Irina Raicu, director, internet ethics, quoted by Lifewire.

- SOCIETY OF PROFESSIONAL JOURNALISTS
Home > Ethics > Ethics Case Studies
Ethics Ethics Case Studies
The SPJ Code of Ethics is voluntarily embraced by thousands of journalists, regardless of place or platform, and is widely used in newsrooms and classrooms as a guide for ethical behavior. The code is intended not as a set of "rules" but as a resource for ethical decision-making. It is not — nor can it be under the First Amendment — legally enforceable. For an expanded explanation, please follow this link .

For journalism instructors and others interested in presenting ethical dilemmas for debate and discussion, SPJ has a useful resource. We've been collecting a number of case studies for use in workshops. The Ethics AdviceLine operated by the Chicago Headline Club and Loyola University also has provided a number of examples. There seems to be no shortage of ethical issues in journalism these days. Please feel free to use these examples in your classes, speeches, columns, workshops or other modes of communication.
Kobe Bryant’s Past: A Tweet Too Soon? On January 26, 2020, Kobe Bryant died at the age of 41 in a helicopter crash in the Los Angeles area. While the majority of social media praised Bryant after his death, within a few hours after the story broke, Felicia Sonmez, a reporter for The Washington Post , tweeted a link to an article from 2003 about the allegations of sexual assault against Bryant. The question: Is there a limit to truth-telling? How long (if at all) should a journalist wait after a person’s death before resurfacing sensitive information about their past?
A controversial apology After photographs of a speech and protests at Northwestern University appeared on the university's newspaper's website, some of the participants contacted the newspaper to complain. It became a “firestorm,” — first from students who felt victimized, and then, after the newspaper apologized, from journalists and others who accused the newspaper of apologizing for simply doing its job. The question: Is an apology the appropriate response? Is there something else the student journalists should have done?
Using the ‘Holocaust’ Metaphor People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals, or PETA, is a nonprofit animal rights organization known for its controversial approach to communications and public relations. In 2003, PETA launched a new campaign, named “Holocaust on Your Plate,” that compares the slaughter of animals for human use to the murder of 6 million Jews in WWII. The question: Is “Holocaust on Your Plate” ethically wrong or a truthful comparison?
Aaargh! Pirates! (and the Press) As collections of songs, studio recordings from an upcoming album or merely unreleased demos, are leaked online, these outlets cover the leak with a breaking story or a blog post. But they don’t stop there. Rolling Stone and Billboard often also will include a link within the story to listen to the songs that were leaked. The question: If Billboard and Rolling Stone are essentially pointing readers in the right direction, to the leaked music, are they not aiding in helping the Internet community find the material and consume it?
Reigning on the Parade Frank Whelan, a features writer who also wrote a history column for the Allentown, Pennsylvania, Morning Call , took part in a gay rights parade in June 2006 and stirred up a classic ethical dilemma. The situation raises any number of questions about what is and isn’t a conflict of interest. The question: What should the “consequences” be for Frank Whelan?
Controversy over a Concert Three former members of the Eagles rock band came to Denver during the 2004 election campaign to raise money for a U.S. Senate candidate, Democrat Ken Salazar. John Temple, editor and publisher of the Rocky Mountain News, advised his reporters not to go to the fundraising concerts. The question: Is it fair to ask newspaper staffers — or employees at other news media, for that matter — not to attend events that may have a political purpose? Are the rules different for different jobs at the news outlet?
Deep Throat, and His Motive The Watergate story is considered perhaps American journalism’s defining accomplishment. Two intrepid young reporters for The Washington Post , carefully verifying and expanding upon information given to them by sources they went to great lengths to protect, revealed brutally damaging information about one of the most powerful figures on Earth, the American president. The question: Is protecting a source more important than revealing all the relevant information about a news story?
When Sources Won’t Talk The SPJ Code of Ethics offers guidance on at least three aspects of this dilemma. “Test the accuracy of information from all sources and exercise care to avoid inadvertent error.” One source was not sufficient in revealing this information. The question: How could the editors maintain credibility and remain fair to both sides yet find solid sources for a news tip with inflammatory allegations?
A Suspect “Confession” John Mark Karr, 41, was arrested in mid-August in Bangkok, Thailand, at the request of Colorado and U.S. officials. During questioning, he confessed to the murder of JonBenet Ramsey. Karr was arrested after Michael Tracey, a journalism professor at the University of Colorado, alerted authorities to information he had drawn from e-mails Karr had sent him over the past four years. The question: Do you break a confidence with your source if you think it can solve a murder — or protect children half a world away?
Who’s the “Predator”? “To Catch a Predator,” the ratings-grabbing series on NBC’s Dateline, appeared to catch on with the public. But it also raised serious ethical questions for journalists. The question: If your newspaper or television station were approached by Perverted Justice to participate in a “sting” designed to identify real and potential perverts, should you go along, or say, “No thanks”? Was NBC reporting the news or creating it?
The Media’s Foul Ball The Chicago Cubs in 2003 were five outs from advancing to the World Series for the first time since 1945 when a 26-year-old fan tried to grab a foul ball, preventing outfielder Moises Alou from catching it. The hapless fan's identity was unknown. But he became recognizable through televised replays as the young baby-faced man in glasses, a Cubs baseball cap and earphones who bobbled the ball and was blamed for costing the Cubs a trip to the World Series. The question: Given the potential danger to the man, should he be identified by the media?
Publishing Drunk Drivers’ Photos When readers of The Anderson News picked up the Dec. 31, 1997, issue of the newspaper, stripped across the top of the front page was a New Year’s greeting and a warning. “HAVE A HAPPY NEW YEAR,” the banner read. “But please don’t drink and drive and risk having your picture published.” Readers were referred to the editorial page where White explained that starting in January 1998 the newspaper would publish photographs of all persons convicted of drunken driving in Anderson County. The question: Is this an appropriate policy for a newspaper?
Naming Victims of Sex Crimes On January 8, 2007, 13-year-old Ben Ownby disappeared while walking home from school in Beaufort, Missouri. A tip from a school friend led police on a frantic four-day search that ended unusually happily: the police discovered not only Ben, but another boy as well—15-year-old Shawn Hornbeck, who, four years earlier, had disappeared while riding his bike at the age of 11. Media scrutiny on Shawn’s years of captivity became intense. The question: Question: Should children who are thought to be the victims of sexual abuse ever be named in the media? What should be done about the continued use of names of kidnap victims who are later found to be sexual assault victims? Should use of their names be discontinued at that point?
A Self-Serving Leak San Francisco Chronicle reporters Mark Fainaru-Wada and Lance Williams were widely praised for their stories about sports figures involved with steroids. They turned their investigation into a very successful book, Game of Shadows . And they won the admiration of fellow journalists because they were willing to go to prison to protect the source who had leaked testimony to them from the grand jury investigating the BALCO sports-and-steroids. Their source, however, was not quite so noble. The question: Should the two reporters have continued to protect this key source even after he admitted to lying? Should they have promised confidentiality in the first place?
The Times and Jayson Blair Jayson Blair advanced quickly during his tenure at The New York Times , where he was hired as a full-time staff writer after his internship there and others at The Boston Globe and The Washington Post . Even accusations of inaccuracy and a series of corrections to his reports on Washington, D.C.-area sniper attacks did not stop Blair from moving on to national coverage of the war in Iraq. But when suspicions arose over his reports on military families, an internal review found that he was fabricating material and communicating with editors from his Brooklyn apartment — or within the Times building — rather than from outside New York. The question: How does the Times investigate problems and correct policies that allowed the Blair scandal to happen?
Cooperating with the Government It began on Jan. 18, 2005, and ended two weeks later after the longest prison standoff in recent U.S. history. The question: Should your media outlet go along with the state’s request not to release the information?
Offensive Images Caricatures of the Prophet Muhammad didn’t cause much of a stir when they were first published in September 2005. But when they were republished in early 2006, after Muslim leaders called attention to the 12 images, it set off rioting throughout the Islamic world. Embassies were burned; people were killed. After the rioting and killing started, it was difficult to ignore the cartoons. Question: Do we publish the cartoons or not?
The Sting Perverted-Justice.com is a Web site that can be very convenient for a reporter looking for a good story. But the tactic raises some ethical questions. The Web site scans Internet chat rooms looking for men who can be lured into sexually explicit conversations with invented underage correspondents. Perverted-Justice posts the men’s pictures on its Web site. Is it ethically defensible to employ such a sting tactic? Should you buy into the agenda of an advocacy group — even if it’s an agenda as worthy as this one?
A Media-Savvy Killer Since his first murder in 1974, the “BTK” killer — his own acronym, for “bind, torture, kill” — has sent the Wichita Eagle four letters and one poem. How should a newspaper, or other media outlet, handle communications from someone who says he’s guilty of multiple sensational crimes? And how much should it cooperate with law enforcement authorities?
A Congressman’s Past The (Portland) Oregonian learned that a Democratic member of the U.S. Congress, up for re-election to his fourth term, had been accused by an ex-girlfriend of a sexual assault some 28 years previously. But criminal charges never were filed, and neither the congressman, David Wu, nor his accuser wanted to discuss the case now, only weeks before the 2004 election. Question: Should The Oregonian publish this story?
Using this Process to Craft a Policy It used to be that a reporter would absolutely NEVER let a source check out a story before it appeared. But there has been growing acceptance of the idea that it’s more important to be accurate than to be independent. Do we let sources see what we’re planning to write? And if we do, when?
SPJ News SPJ-led coalition demands Texas authorities drop charges against photojournalist Carlos Sanchez Region 8 Mark of Excellence Awards 2023 winners announced Region 12 Mark of Excellence Awards 2023 winners announced
- Log In Username Enter your ACP Online username. Password Enter the password that accompanies your username. Remember me Forget your username or password ?
- Privacy Policy
- Career Connection
- Member Forums
© Copyright 2024 American College of Physicians, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 190 North Independence Mall West, Philadelphia, PA 19106-1572 800-ACP-1915 (800-227-1915) or 215-351-2600
If you are unable to login, please try clearing your cookies . We apologize for the inconvenience.
Ethics Case Studies & Education Resources
ACP ethics education resources cover a broad range of issues in clinical ethics, professionalism, teaching, research, health care delivery, and other topics. Each resource can be used as a learning activity and completed for free CME/MOC credits as indicated or used as a teaching tool.
- Ethics Case Studies for CME/MOC
- Ethics Manual Activity for CME/MOC
- Position Paper Activities for CME/MOC
Additional Ethics Case Studies
Acp ethics case study series.
Each case study draws on an ethical challenge encountered by physicians in everyday practice, teaching or research. Free CME/MOC credits are available from ACP’s Online Learning Center. Free CME/MOC credits are available for completion of case studies on Medscape as indicated (a free Medscape login is required for access and completion).
- “Why Can’t I Be There?” Ethics Regarding Restrictions on Visitation/Family Caregiver Presence CME/MOC
- Pain Management Near the End-of-Life: What Would Mom Want? CME/MOC
- Ethics, Professionalism, Physician Employment and Health Care Business Practices CME/MOC
- Show Codes, Slow Codes, Full Codes, or No Codes: What Is a Doctor to Do? CME/MOC
- When Resources Are Limited During a Public Health Catastrophe: Nondiscrimination and Ethical Allocation Guidance CME/MOC
- Patient Prejudice? The Patient Said What?... and What Comes Next CME/MOC
- Lab Results Reporting, Ethics, and the 21st Century Cures Act Rule on Information Blocking CME/MOC
- Physician Suicide Prevention: The Ethics and Role of the Physician Colleague and the Healing Community CME/MOC
- Ethics, Electronic Health Record Integrity and the Patient-Physician Relationship CME/MOC
- Ethics, Professionalism, and the Physician Social Media Influencer CME/MOC
- Professional Attire and the Patient-Physician Relationship CME/MOC
- When the Family Caregiver Is a Physician: Negotiating the Ethical Boundaries CME/MOC
- ”Doctor, Can’t You Just Phone a Prescription In?” and Other Ethical Challenges of Telemedicine Encounters CME/MOC
- Serving as an Expert Witness: Is there a Duty? CME
Ethics Manual (CME/MOC)
The ACP Ethics Manual is the core of College ethics policy. The seventh edition examines issues in medical ethics, reflecting on the ethical tenets of medicine and their application to emerging challenges while also revisiting older issues that are still very pertinent. It helps physicians be prepared to deal with ethical challenges: to identify and reaffirm the fundamentals of medical ethics—such as the patient-physician relationship—and apply principles and reasoned arguments in resolving dilemmas and in debate about ethics topics.
A 25-question quiz module on the seventh edition of the Ethics Manual is available for up to 10 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits TM and MOC Points. The activity is free for ACP members and Annals subscribers.
Annals of Internal Medicine offers the following CME/MOC activity for ACP members and Annals subscribers:
- Ethical and Professionalism Implications of Physician Employment and Health Care Business Practices (Ann Intern Med. published online 15 March 2021) CME/MOC
Additional position papers cover a broad range of health care ethics issues and can be used as a teaching tool.
- Pandemic Treatment Resource Allocation Ethics and Nondiscrimination
- Confidentiality and Privacy: Beyond HIPAA to Honey, Can We Talk?
- Secret Recordings of Office Visits by Patients
- Addressing a Colleague's Unprofessional Behavior During Sign-Out
- Patient Requests for Specific Care: 'Surely You Can Explain to My Insurer That I Need Boniva?'
- Maintaining Medical Professionalism Online: Posting of Patient Information
- Banning Harmful Health Behaviors as a Condition of Employment: Where There's Smoke There's Fired?
- Addressing a Colleague's Sexually Explicit Facebook Post
- Wellness Programs and Patient Goals of Care
- Resident Duty Hours: To Hand Over or Gloss Over?
- When an Aging Colleague Seems Impaired
- Preventive Health Screening, Ethics and the Cognitively Impaired Patient
- Stewardship of Health Care Resources: Allocating Mechanical Ventilators During Pandemic Influenza
- Copied and Pasted and Misdiagnosed (or Cloned Notes and Blind Alleys)
- Stewardship of Health Care Resources: Responding to a Patient’s Request for Antibiotics
- Who Should Get What? Mammography and the Stewardship of Health Care Resources
- Patient/Physician/Family Caregiver Relationships: When the Family Caregiver Is a Physician
- Physician Work Stoppages and Political Demonstrations -- Economic Self-Interest or Patient Advocacy? Where Is the Line?
- To Be or Not to Be: Should I Serve as an Expert Witness?
- Author! Author! Who Should Be Named in a Published Study? An Ethics Case Study
- The Difficult Patient: Should You End the Relationship? What Now? An Ethics Case Study
- Dealing with the "Disruptive" Physician Colleague
- Must You Disclose Mistakes Made by Other Physicians?
- Providing Care to Undocumented Immigrants
- Twenty-eight additional case studies are published in the book Ethical Choices: Case Studies for Medical Practice (2nd edition)
For more information on these and other educational content, please contact Lois Snyder Sulmasy, JD, at [email protected] or at 215-351-2835.
Ethics Sessions at Internal Medicine Meeting 2020
April 23 – 25, 2020, Los Angeles, CA
Sponsored by the Ethics, Professionalism & Human Rights Committee (EPHRC)
- Ethical Case Challenges: Precision Medicine and Genetics in Primary Care
- Ethics Year in Review
- Spirituality in End-of-Life Care: What is the Physician’s Role?
- Practical Palliative Care: Managing Pain at the End of Life
Ethics education sessions on different topics are offered at the annual Internal Medicine Meeting each year. Information on past Internal Medicine Meeting ethics sessions is available upon request at [email protected] .
Attending the Internal Medicine Meeting is an excellent way to fulfill your state CME relicensure requirements. The ethics sessions may fulfill specific CME content requirements of your state’s licensure renewal. Letters of participation documenting attendance are available online .
For more information on these and other educational content, please contact Lois Snyder Sulmasy, JD, at [email protected] or at 215-351-2835.
- Carbon Accounting & Carbon Neutral Strategy
- ESG, CSR, & Sustainability Reporting
- Sustainability Strategy
- ESG Regulatory Compliance
- Portfolio Management & Reporting
- AERA GHG Manager
- EPIC for Corporates
- ZENO for Financial Institutions
- ESG Academy
Ethical Business Practices: Case Studies and Lessons Learned
Introduction
Ethical business practices are a cornerstone of any successful company, influencing not only the public perception of a brand but also its long-term profitability. However, understanding what constitutes ethical behavior and how to implement it can be a complex process. This article explores some case studies that shine a light on ethical business practices, offering valuable lessons for businesses in any industry.
Case Study 1: Patagonia’s Commitment to Environmental Ethics
Patagonia, the outdoor clothing and gear company, has long set a standard for environmental responsibility. The company uses eco-friendly materials, promotes recycling of its products, and actively engages in various environmental causes.
Lessons Learned
- Transparency : Patagonia is vocal about its ethical practices and even provides information on the environmental impact of individual products.
- Consistency: Ethics are not an “add-on” for Patagonia; they are integrated into the very fabric of the company’s operations, from sourcing to production to marketing.
- Engagement: The company doesn’t just focus on its practices; it encourages consumers to get involved in the causes it supports.
Case Study 2: Salesforce and Equal Pay
Salesforce, the cloud-based software company, took a stand on the gender pay gap issue. They conducted an internal audit and found that there was indeed a significant wage disparity between male and female employees for similar roles. To address this, Salesforce spent over $6 million to balance the scales.
- Self-Audit: It’s crucial for companies to actively review their practices. What you don’t know can indeed hurt you, and ignorance is not an excuse.
- Taking Responsibility: Rather than sweeping the issue under the rug, Salesforce openly acknowledged the problem and took immediate corrective action.
- Long-Term Benefits: Fair treatment boosts employee morale and productivity, leading to long-term profitability.
Case Study 3: Starbucks and Racial Sensitivity Training
In 2018, Starbucks faced a public relations crisis when two Black men were wrongfully arrested at one of their Philadelphia stores. Instead of issuing just a public apology, Starbucks closed down 8,000 of its stores for an afternoon to conduct racial sensitivity training.
Lessons Learned
- Immediate Action : Swift and meaningful action is critical in showing commitment to ethical behavior.
- Education: Sometimes, the problem is a lack of awareness. Investing in employee education can avoid repeated instances of unethical behavior.
- Public Accountability: Starbucks made their training materials available to the public, showing a level of transparency and accountability that helped regain public trust.
Why Ethics Matter
Ethical business practices are not just morally correct; they have a direct impact on a company’s bottom line. Customers today are more informed and more sensitive to ethical considerations. They often make purchasing decisions based on a company’s ethical standing, and word-of-mouth (or the digital equivalent) travels fast.
The case studies above show that ethical business practices should be a top priority for companies of all sizes and industries. These are not isolated examples but are representative of a broader trend in consumer expectations and regulatory frameworks. The lessons gleaned from these cases—transparency, consistency, engagement, self-audit, taking responsibility, and education—are universally applicable and offer a robust roadmap for any business seeking to bolster its ethical standing.
By implementing ethical business practices sincerely and not as a marketing gimmick, companies not only stand to improve their public image but also set themselves up for long-term success, characterized by a loyal customer base and a motivated, satisfied workforce.

Monitor ESG performance in portfolios, create your own ESG frameworks, and make better informed business decisions.
In order to contact us please fill the form on the right or directly email us at the address below
3 Church Street, 25/F, Suite 21 Singapore 049483 (+65) 6692 9267
Gustav Mahlerplein 2 Amsterdam, Netherlands 1082 MA (+31) 6 4817 3634
No. 299, Tongren Road, #2604B Jing'an District, Shanghai, China 200040 (+86) 021 6229 8732
77 Dunhua South Road, 7F Section 2, Da'an District Taipei City, Taiwan 106414 (+886) 02 2706 2108
Viet Tower 1, Thai Ha, Dong Da Hanoi, Vietnam 100000 (+84) 936 075 490
Av Jorge Basadre Grohmann 607 San Isidro, Lima, Peru 15073 (+51) 951 722 377
© 2024 • Seneca Technologies Pte Ltd • All rights reserved
- ESG, CSR, & Sustainability Reporting
- ESG Data Collection and Management
- ESG Scoring and Target Setting
- ESG Report Writing (ISSB, GRI, SASB, TCFD, CSRD)
- Materiality Assessment
- ESG Ratings Analyses and Improvement
- ESG Performance Analyses and Benchmarking
- Stock Exchange Reporting
- EU Taxonomy Reporting (CSRD, SFDR, PAI)
- Portfolio Management & Reporting
- Portfolio Custom Scoring and Screening
- Portfolio Analyses and Benchmarking
- Product and Firm Level Regulatory Reporting (SFDR)
- Carbon Accounting & Carbon Neutral Strategy
- Carbon Inventory (GHG Protocol)
- Science Based Target Setting (SBTi)
- Carbon Neutral Strategy
- Privacy Policy

© 2023 • Seneca • All rights reserved
- Based Target Setting (SBTi) Carbon
Discover the latest MyICAEW app for ACA students and members, available to download now. Find out more
- Benefits of membership
Gain access to world-leading information resources, guidance and local networks.
- Visit Benefits of membership
Becoming a member
98% of the best global brands rely on ICAEW Chartered Accountants.
- Visit Becoming a member
- Pay fees and subscriptions
Your membership subscription enables ICAEW to provide support to members.
Fees and subscriptions
Member rewards.
Take advantage of the range of value added or discounted member benefits.
- Member rewards – More from your membership
- Technical and ethics support
- Support throughout your career
Information and resources for every stage of your career.
Member Insights Survey
Let us know about the issues affecting you, your business and your clients.
- Complete the survey
From software start-ups to high-flying airlines and high street banks, 98% of the best global brands rely on ICAEW Chartered Accountants. A career as an ICAEW Chartered Accountant means the opportunity to work in any organisation, in any sector, whatever your ambitions.
Everything you need to know about ICAEW annual membership fees, community and faculty subscriptions, eligibility for reduced rates and details of how you can pay.
Membership administration
Welcome to the ICAEW members area: your portal to members'-only content, offers, discounts, regulations and membership information.
- Continuing Professional Development (CPD)
Continuing Professional Development (CPD) is an integral part of being a successful ICAEW Chartered Accountant.
The ICAEW Chartered Accountant qualification, the ACA, is one of the most advanced learning and professional development programmes available. It is valued around the world in business, practice and the public sector.

ACA for employers
Train the next generation of chartered accountants in your business or organisation. Discover how your organisation can attract, train and retain the best accountancy talent, how to become authorised to offer ACA training and the support and guidance on offer if you are already providing training.
Digital learning materials via BibliU
All ACA, ICAEW CFAB and Level 4 apprenticeship learning materials are now digital only. Read our guide on how to access your learning materials on the ICAEW Bookshelf using the BibliU app or through your browser.
- Find out more
Take a look at ICAEW training films
Focusing on professional scepticism, ethics and everyday business challenges, our training films are used by firms and companies around the world to support their in-house training and business development teams.
Attract and retain the next generation of accounting and finance professionals with our world-leading accountancy qualifications. Become authorised to offer ACA training and help your business stay ahead.
CPD guidance and help
Continuing Professional Development (CPD) is an integral part of being a successful ICAEW Chartered Accountant. Find support on ICAEW's CPD requirements and access resources to help your professional development.
ICAEW flagship events
ICAEW boasts an extensive portfolio of industry-leading conferences. These flagship events offer the opportunity to hear from and interact with all the key players in the industry. Find out what's coming up.
Leadership Development Programmes
ICAEW Academy’s in-depth leadership development programmes take a holistic approach to combine insightful mentoring or coaching, to exclusive events, peer learning groups and workshops. Catering for those significant transitions in your career, these leadership development programmes are instrumental to achieving your ambitions or fulfilling your succession planning goals.
Specialist Finance Qualifications & Programmes
Whatever future path you choose, ICAEW will support the development and acceleration of your career at each stage to enhance your career.

Why a career in chartered accountancy?
If you think chartered accountants spend their lives confined to their desks, then think again. They are sitting on the boards of multinational companies, testifying in court and advising governments, as well as supporting charities and businesses from every industry all over the world.
- Why chartered accountancy?

Search for qualified ACA jobs
Matching highly skilled ICAEW members with attractive organisations seeking talented accountancy and finance professionals.

Volunteering roles
Helping skilled and in-demand chartered accountants give back and strengthen not-for-profit sector with currently over 2,300 organisations posting a variety of volunteering roles with ICAEW.
- Search for volunteer roles
- Get ahead by volunteering
Advertise with ICAEW
From as little as £495, access to a pool of highly qualified and ambitious ACA qualified members with searchable CVs.
Early careers and training
Start your ACA training with ICAEW. Find out why a career in chartered accountancy could be for you and how to become a chartered accountant.
Qualified ACA careers
Find Accountancy and Finance Jobs
Voluntary roles
Find Voluntary roles
While you pursue the most interesting and rewarding opportunities at every stage of your career, we’re here to offer you support whatever stage you are or wherever you are in the world and in whichever sector you have chosen to work.
ACA students
"how to guides" for aca students.
- ACA student guide
- How to book an exam
- How to apply for credit for prior learning (CPL)
Exam resources
Here are some resources you will find useful while you study for the ACA qualification.
- Certificate Level
- Professional Level
- Advanced Level
Digital learning materials
All ACA learning materials are now digital only. Read our guide on how to access your learning materials on the ICAEW Bookshelf via the BibliU app, or through your browser.
- Read the guide
My online training file
Once you are registered as an ACA student, you'll be able to access your training file to log your progress throughout ACA training.
- Access your training file
- Student Insights
Fresh insights, innovative ideas and an inside look at the lives and careers of our ICAEW students and members.
- Read the latest articles
System status checks
Getting started.
Welcome to ICAEW! We have pulled together a selection of resources to help you get started with your ACA training, including our popular 'How To' series, which offers step-by-step guidance on everything from registering as an ACA student and applying for CPL, to using your online training file.
Credit for prior learning (CPL)
Credit for prior learning or CPL is our term for exemptions. High quality learning and assessment in other relevant qualifications is appropriately recognised by the award of CPL.
Apply for exams
What you need to know in order to apply for the ACA exams.
The ACA qualification has 15 modules over three levels. They are designed to complement the practical experience you will be gaining in the workplace. They will also enable you to gain in-depth knowledge across a broad range of topics in accountancy, finance and business. Here are some useful resources while you study.
- Exam results
You will receive your results for all Certificate Level exams, the day after you take the exam and usually five weeks after a Professional and Advanced Level exam session has taken place. Access your latest and archived exam results here.
Training agreement
Putting your theory work into practice is essential to complete your ACA training.
Student support and benefits
We are here to support you throughout your ACA journey. We have a range of resources and services on offer for you to unwrap, from exam resources, to student events and discount cards. Make sure you take advantage of the wealth of exclusive benefits available to you, all year round.
- Applying for membership
The ACA will open doors to limitless opportunities in all areas of accountancy, business and finance anywhere in the world. ICAEW Chartered Accountants work at the highest levels as finance directors, CEOs and partners of some of the world’s largest organisations.
ACA training FAQs
Do you have a question about the ACA training? Then look no further. Here, you can find answers to frequently asked questions relating to the ACA qualification and training. Find out more about each of the integrated components of the ACA, as well as more information on the syllabus, your training agreement, ICAEW’s rules and regulations and much more.
- Anti-money laundering
Guidance and resources to help members comply with their legal and professional responsibilities around AML.
Technical releases
ICAEW Technical Releases are a source of good practice guidance on technical and practice issues relevant to ICAEW Chartered Accountants and other finance professionals.
- ICAEW Technical Releases
- Thought leadership
ICAEW's Thought Leadership reports provide clarity and insight on the current and future challenges to the accountancy profession. Our charitable trusts also provide funding for academic research into accountancy.
- Academic research funding
Technical Advisory Services helpsheets
Practical, technical and ethical guidance highlighting the most important issues for members, whether in practice or in business.
- ICAEW Technical Advisory Services helpsheets
Bloomsbury – free for eligible firms
In partnership with Bloomsbury Professional, ICAEW have provided eligible firms with free access to Bloomsbury’s comprehensive online library of around 80 titles from leading tax and accounting subject matter experts.
- Bloomsbury Accounting and Tax Service
Country resources
Our resources by country provide access to intelligence on over 170 countries and territories including economic forecasts, guides to doing business and information on the tax climate in each jurisdiction.
Industries and sectors
Thought leadership, technical resources and professional guidance to support the professional development of members working in specific industries and sectors.
Audit and Assurance
The audit, assurance and internal audit area has information and guidance on technical and practical matters in relation to these three areas of practice. There are links to events, publications, technical help and audit representations.
The most up-to-date thought leadership, insights, technical resources and professional guidance to support ICAEW members working in and with industry with their professional development.
- Corporate Finance
Companies, advisers and investors making decisions about creating, developing and acquiring businesses – and the wide range of advisory careers that require this specialist professional expertise.
- Corporate governance
Corporate governance is the system by which companies are directed and controlled. Find out more about corporate governance principles, codes and reports, Board subcommittees, roles and responsibilities and shareholder relations. Corporate governance involves balancing the interests of a company’s many stakeholders, such as shareholders, employees, management, customers, suppliers, financiers and the community. Getting governance right is essential to build public trust in companies.
Corporate reporting
View a range of practical resources on UK GAAP, IFRS, UK regulation for company accounts and non-financial reporting. Plus find out more about the ICAEW Corporate Reporting Faculty.
Expert analysis on the latest national and international economic issues and trends, and interviews with prominent voices across the finance industry, alongside data on the state of the economy.
- Financial Services
View articles and resources on the financial services sector.
- Practice resources
For ICAEW's members in practice, this area brings together the most up-to-date thought leadership, technical resources and professional guidance to help you in your professional life.
Public Sector
Many ICAEW members work in or with the public sector to deliver public priorities and strong public finances. ICAEW acts in the public interest to support strong financial leadership and better financial management across the public sector – featuring transparency, accountability, governance and ethics – to ensure that public money is spent wisely and that public finances are sustainable.
Sustainability and climate change
Sustainability describes a world that does not live by eating into its capital, whether natural, economic or social. Members in practice, in business and private individuals all have a role to play if sustainability goals are to be met. The work being undertaken by ICAEW in this area is to change behaviour to drive sustainable outcomes.
The Tax area has information and guidance on technical and practical tax matters. There are links to events, the latest tax news and the Tax Faculty’s publications, including helpsheets, webinars and Tax representations.
Keep up-to-date with tech issues and developments, including artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, big data, and cyber security.
- Trust & Ethics
Guidance and resources on key issues, including economic crime, business law, better regulation and ethics. Read through ICAEW’s Code of Ethics and supporting information.
Communities

ICAEW Communities
Information, guidance and networking opportunities on industry sectors, professional specialisms and at various stages throughout your career. Free for ICAEW members and students.
- Discover a new community

ICAEW Faculties
The accountancy profession is facing change and uncertainty. The ICAEW Faculties can help by providing you with timely and relevant support.
- Choose to join any of the faculties
UK groups and societies
We have teams on the ground in: East of England, the Midlands, London and South East, Northern, South West, Yorkshire and Humberside, Wales and Scotland.
- Access your UK region
- Worldwide support and services
Support and services we offer our members in Africa, America, Canada, the Caribbean, Europe, Greater China, the Middle East, Oceania and South East Asia.
- Discover our services
ICAEW Faculties are 'centres of technical excellence', strongly committed to enhancing your professional development and helping you to meet your CPD requirements every year. They offer exclusive content, events and webinars, customised for your sector - which you should be able to easily record, when the time comes for the completion of your CPD declaration. Our offering isn't exclusive to Institute members. As a faculty member, the same resources are available to you to ensure you stay ahead of the competition.
Communities by industry / sector
Communities by life stage and workplace, communities by professional specialism, local groups and societies.
We aim to support you wherever in the world you work. Our regional offices and network of volunteers run events and provide access to local accounting updates in major finance centres around the globe.
- Ukraine crisis: central resource hub
Learn about the actions that ICAEW members are taking to ensure that their clients comply with sanctions imposed by different countries and jurisdictions, and read about the support available from ICAEW.
Insights pulls together the best opinion, analysis, interviews, videos and podcasts on the key issues affecting accountancy and business.
- See the latest insights
- Making COP count
This series looks at the role the accountancy profession can play in addressing the climate crisis and building a sustainable economy.
- Read more on COP28
Professional development and skills
With new requirements on ICAEW members for continuing professional development, we bring together resources to support you through the changes and look at the skills accountants need for the future.
- Visit the hub
When Chartered Accountants Save The World
Find out how chartered accountants are helping to tackle some of the most urgent social challenges within the UN Sustainable Development Goals, and explore how the profession could do even more.
- Read our major series
Insights specials
A listing of one-off Insights specials that focus on a particular subject, interviewing the key people, identifying developing trends and examining the underlying issues.
Top podcasts
Insights by topic.

ICAEW Regulation

- Regulatory News
View the latest regulatory updates and guidance and subscribe to our monthly newsletter, Regulatory & Conduct News.
- Regulatory Consultations
Strengthening trust in the profession
Our role as a world-leading improvement regulator is to strengthen trust and protect the public. We do this by enabling, evaluating and enforcing the highest standards in the profession.
Regulatory applications
Find out how you can become authorised by ICAEW as a regulated firm.
ICAEW codes and regulations
Professional conduct and complaints, statutory regulated services overseen by icaew, regulations for icaew practice members and firms, additional guidance and support, popular search results.
- Training File
- Practice Exam Software
- Ethics Cpd Course
- Routes to the ACA
- ACA students membership application
- Join as a member of another body
- How much are membership fees?
- How to pay your fees
- Receipts and invoices
- What if my circumstances have changed?
- Difficulties in making changes to your membership
- Faculty and community subscription fees
- Updating your details
- Complete annual return
- Promoting myself as an ICAEW member
- Verification of ICAEW membership
- Become a life member
- Become a fellow
- Request a new certificate
- Report the death of a member
- Membership regulations
- New members
- Career progression
- Career Breakers
- Volunteering at schools and universities
- ICAEW Member App
- Working internationally
- Self employment
Support Members Scheme
- CPD is changing
- CPD learning resources
- Your guide to CPD
- Online CPD record
- How to become a chartered accountant
- Register as a student
- Train as a member of another body
- More about the ACA and chartered accountancy
- How ACA training works
- Become a training employer
- Access the training file
- Why choose the ACA
- Training routes
- Employer support hub
- Get in touch
- Apprenticeships with ICAEW
- A-Z of CPD courses by topic
- ICAEW Business and Finance Professional (BFP)
- ICAEW Annual Conference 2024
- Audit & Assurance Conference 2024
- Restructuring & Insolvency Conference
- Virtual CPD Conference
- Virtual Healthcare Conference 2024
- All our flagship events
- Financial Talent Executive Network (F-TEN®)
- Developing Leadership in Practice (DLiP™)
- Network of Finance Leaders (NFL)
- Women in Leadership (WiL)
- Mentoring and coaching
- Partners in Learning
- Board Director's Programme e-learning
- Corporate Finance Qualification
- Diploma in Charity Accounting
- ICAEW Certificate in Insolvency
- ICAEW Data Analytics Certificate
- Financial Modeling Institute’s Advanced Financial Modeler Accreditation
- ICAEW Sustainability Certificate for Finance Professionals
- ICAEW Finance in a Digital World Programme
- All specialist qualifications
- Team training
- Start your training
- Improve your employability
- Search employers
- Find a role
- Role alerts
- Organisations
- Practice support – 11 ways ICAEW and CABA can help you
- News and advice
- ICAEW Volunteering Hub
- Support in becoming a chartered accountant
- Vacancies at ICAEW
- ICAEW boards and committees
- Exam system status
- ICAEW systems: status update
- Changes to our qualifications
- How-to guides for ACA students
- Apply for credits - Academic qualification
- Apply for credits - Professional qualification
- Credit for prior learning (CPL)/exemptions FAQs
- Applications for Professional and Advanced Level exams
- Applications for Certificate Level exams
- Tuition providers
- Latest exam results
- Archived exam results
- Getting your results
- Marks feedback service
- Exam admin check
- Training agreement: overview
- Professional development
- Ethics and professional scepticism
- Practical work experience
- Access your online training file
- How training works in your country
- Student rewards
- TOTUM PRO Card
- Student events and volunteering
- Xero cloud accounting certifications
- Student support
- Join a community
- Wellbeing support from caba
- Student mentoring programme
- Student conduct and behaviour
- Code of ethics
- Fit and proper
- Level 4 Accounting Technician Apprenticeship
- Level 7 Accountancy Professional Apprenticeship
- AAT-ACA Fast Track FAQs
- ACA rules and regulations FAQs
- ACA syllabus FAQs
- ACA training agreement FAQs
- Audit experience and the Audit Qualification FAQs
- Independent student FAQs
- Practical work experience FAQs
- Professional development FAQs
- Six-monthly reviews FAQs
- Ethics and professional scepticism FAQs
- Greater China
- Latin America
- Middle East
- North America
- Australasia
- Russia and Eurasia
- South East Asia
- Charity Community
- Construction & Real Estate
- Energy & Natural Resources Community
- Farming & Rural Business Community
- Forensic & Expert Witness
- Global Trade Community
- Healthcare Community
- Internal Audit Community
- Manufacturing Community
- Media & Leisure
- Portfolio Careers Community
- Small and Micro Business Community
- Small Practitioners Community
- Travel, Tourism & Hospitality Community
- Valuation Community
- Audit and corporate governance reform
- Audit & Assurance Faculty
- Professional judgement
- Regulation and working in audit
- Internal audit resource centre
- ICAEW acting on audit quality
- Everything business
- Latest Business news from Insights
- Strategy, risk and innovation
- Business performance management
- Financial management
- Finance transformation
- Economy and business environment
- Leadership, personal development and HR
- Webinars and publications
- Business restructuring
- The Business Finance Guide
- Capital markets and investment
- Corporate finance careers
- Corporate Finance Faculty
- Debt advisory and growth finance
- Mergers and acquisitions
- Private equity
- Start-ups, scale-ups and venture capital
- Transaction services
- Board committees and board effectiveness
- Corporate governance codes and reports
- Corporate Governance Community
- Principles of corporate governance
- Roles, duties and responsibilities of Board members
- Stewardship and stakeholder relations
- Corporate Governance thought leadership
- Corporate reporting resources
- Small and micro entity reporting
- UK Regulation for Company Accounts
- Non-financial reporting
- Improving Corporate Reporting
- Economy home
- ICAEW Business Confidence Monitor
- ICAEW Manifesto 2024
- Energy crisis
- Levelling up: rebalancing the UK’s economy
- Resilience and Renewal: Building an economy fit for the future
- Social mobility and inclusion
- Autumn Statement 2023
- Investment management
- Inspiring confidence
- Setting up in practice
- Running your practice
- Supporting your clients
- Practice technology
- TAS helpsheets
- Support for business advisers
- Join ICAEW BAS
- Public Sector hub
- Public Sector Audit and Assurance
- Public Sector Finances
- Public Sector Financial Management
- Public Sector Financial Reporting
- Public Sector Learning & Development
- Public Sector Community
- Latest public sector articles from Insights
- Climate hub
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Accountability
- Modern slavery
- Resources collection
- Sustainability Committee
- Sustainability & Climate Change community
- Sustainability and climate change home
- Tax Faculty
- Budgets and legislation
- Business tax
- Devolved taxes
- Employment taxes
- International taxes
- Making Tax Digital
- Personal tax
- Property tax
- Stamp duty land tax
- Tax administration
- Tax compliance and investigation
- UK tax rates, allowances and reliefs
- Artificial intelligence
- Blockchain and cryptoassets
- Cyber security
- Data Analytics Community
- Digital skills
- Excel community
- Finance in a Digital World
- IT management
- Technology and the profession
- Trust & Ethics home
- Better regulation
- Business Law
- UK company law
- Data protection and privacy
- Economic crime
Help with ethical problems
- ICAEW Code of Ethics
- ICAEW Trust and Ethics team.....
- Solicitors Community
- Forensic & Expert Witness Community
- Latest articles on business law, trust and ethics
- Audit and Assurance Faculty
- Corporate Reporting Faculty
- Financial Services Faculty
- Academia & Education Community
- Construction & Real Estate Community
- Entertainment, Sport & Media Community
- Retail Community
- Career Breakers Community
- Black Members Community
- Diversity & Inclusion Community
- Women in Finance Community
- Personal Financial Planning Community
- Restructuring & Insolvency Community
- Sustainability and Climate Change Community
- London and East
- South Wales
- Yorkshire and Humberside
- European public policy activities
- ICAEW Middle East
- Latest news
- Access to finance special
- Attractiveness of the profession
- Audit and Fraud
- Audit and technology
- Adopting non-financial reporting standards
- Cost of doing business
- Mental health and wellbeing
- Pensions and Personal Finance
- Public sector financial and non-financial reporting
- More specials ...
- The economics of biodiversity
- How chartered accountants can help to safeguard trust in society
- Video: The financial controller who stole £20,000 from her company
- It’s time for chartered accountants to save the world
- Video: The CFO who tried to trick the market
- Video: Could invoice fraud affect your business?
- So you want to be a leader?
- A busy new tax year, plus progress on the Economic Crime Act
- Does Britain have a farming problem?
- Budget 2024: does it change anything?
- Will accountants save the world? With ICAEW CEO Michael Izza
- Crunch time: VAT (or not) on poppadoms
- Where next for audit and governance reform?
- A taxing year ahead?
- What can we expect from 2024?
- COP28: making the business case for nature
- COP28: what does transition planning mean for accountants?
- More podcasts...
- Top charts of the week
- EU and international trade
- CEO and President's insights
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Sponsored content
- Insights index
- Charter and Bye-laws
- Archive of complaints, disciplinary and fitness processes, statutory regulations and ICAEW regulations
- Qualifications regulations
- Training and education regulations
- How to make a complaint
- Guidance on your duty to report misconduct
- Public hearings
- What to do if you receive a complaint against you
- Anti-money laundering supervision
- Working in the regulated area of audit
- Local public audit in England
- Probate services
- Designated Professional Body (Investment Business) licence
- Consumer credit
- Quality Assurance monitoring: view from the firms
- The ICAEW Practice Assurance scheme
- Licensed Practice scheme
- Professional Indemnity Insurance (PII)
- Clients' Money Regulations
- Taxation (PCRT) Regulations
- ICAEW training films
- Helpsheets and guidance by topic
- ICAEW's regulatory expertise and history
- Case studies
Practice case studies
These case studies are aimed at members and students working in public practice. They provide examples of ethical issues in the workplace and include guidance on how to resolve them.
The following case studies were developed by the UK and Ireland’s Consultative Committee of Accountancy Bodies (CCAB). They illustrate how the ethical codes of the CCAB bodies can be applied by professional accountants working in public practice. These scenarios are not intended to cover every possible circumstance, but instead to outline key principles and processes that could be considered when attempting to identify, assess and resolve ethical problems in line with the ethical codes. These case studies were published in February 2022. The CCAB welcomes comments on these cases. Please email [email protected] .
- Ethical Dilemmas Case Studies - Professional Accountants in Public Practice
The case studies are illustrative and should be read in conjunction with the guidance contained in ICAEW's Code of Ethics, in particular Part 1 and Part 3 of the Code .
You may seek advice from ICAEW's helplines, free of charge:
Ethics Advisory Service
This is a confidential free helpline, exempt from the duty to report professional misconduct within ICAEW.
Tel: +44 (0)1908 248 250 or webchat .
This is run by volunteer members of ICAEW from a wide range of backgrounds. It is a confidential, free service exempt from the duty to report misconduct within ICAEW. It provides advice and help to members in difficulties on a wide range of issues.
Tel: 0800 917 3526
Read out this code to the operator.

Ethics: To Tell or Not to Tell-A Case Study
By: Lee J. Zook
Winter 2001, Vol. 8, No. 1
by Lee J. Zook, Ph.D.
Some years ago, prior to teaching in undergraduate social work, I was working with families and children in an outpatient psychiatric setting, Children' Agency. In the previous year, I had completed my MSW, having practiced social work several years with an undergraduate degree. The Director of Social Services at the Children' Agency was my supervisor. We used a team model in our work, with any particular team consisting of at least a social worker, a psychologist, and a psychiatrist. Sometimes other professionals, such as educational specialists, early childhood development specialists, and social group workers were also on the teams. I had first-rate colleagues in whom I could confide about clinical and ethical issues. Continuous learning was valued, especially as it related to clinical practice.
While I was at Children' Agency, Mary Jones (a fictitious name) applied for a job as a social worker. Four years earlier, I had seen Mary as a client while working for an emergency service at Adult Hospital, a psychiatric facility for adults.
My contact with Mary had been rather brief at Adult Hospital. She came to be admitted to the hospital as her psychiatric condition was deteriorating. Mary told me she was a social worker with an MSW and had been in and out of psychiatric hospitals for many years. I located her chart, noted that she was previously diagnosed with schizophrenia, undifferentiated type, did the basic paperwork that social workers did on admission, consulted with the admitting psychiatrist, and took her to the hospital ward. It was a rather simple, routine admission; there were no police or court documents, and she was a voluntary client. However, the situation was a bit unsettling. My feelings had to do with the fact that I was leaving my position in the near future to pursue an MSW, and here I was, a young, rather inexperienced, “untrained” social worker, admitting an older, more experienced social worker with an MSW to a psychiatric hospital. However, I went on with my business and put the event in perspective. After all, academic degrees do not preclude a person from having a mental illness.
So now, three years later, I had my MSW, and Mary came for a job interview at Children' Agency where I was employed. I had no responsibility for employment decisions. My supervisor, who was the Director of Social Services, and the psychiatrist, who was also the Executive Director, made these decisions. But I was faced with an uncomfortable dilemma-an ethical dilemma for which I did not see any clear answer.
On one hand, I was concerned about whether Mary would function as a competent professional colleague. Was her illness in remission? If so, would it remain in remission? If not, what would the impact be on clients? Would she be able to function adequately to work with clients who came to the agency? If she would not, would harm come to clients?
On the other hand, my knowledge of her illness was unquestionably confidential. Further, what right or responsibility did I have to suggest that a person who had a mental illness should not be hired? What right or responsibility did I have to divulge information about her (past) condition to anyone?
There was also the possibility that I could speak to Mary and verbalize my concerns to her. Would this be appropriate? Would Mary remember who I was? After three years, did the brief encounter we had give me the prerogative to confront her about her past or ask about her present condition?
The following discussion focuses on the NASW Code of Ethics and how it may be useful in this situation. At the time, I was not this thorough and did not think much about the Code of Ethics. I struggled in my own mind about what to do. If this were occurring now, I would first of all confer with the Code of Ethics. The first sentence of the preamble of the Code states:
The primary mission of the social work profession is to enhance human well-being and help meet the basic human needs of all people, with particular attention to the needs and empowerment of people who are vulnerable, oppressed, and living in poverty.
In this situation, one could contend that clients coming to Children' Agency were the vulnerable people referred to in the Preamble. On the other hand, one could also make a case that Mary, a person who is living with a persistent and long-term mental illness, is a vulnerable person.
As a social worker, I am particularly concerned about creating opportunity for persons with disability. And in this instance, vulnerability of a specific person could be viewed as more important than vulnerability of a general client population.
In further examination of the Code, Section 1.07 Privacy and Confidentiality, paragraph (c) is instructive.
Social workers should protect the confidentiality of all information obtained in the course of professional service, except for compelling professional reasons. The general expectation that social workers will keep information confidential does not apply when disclosure is necessary to prevent serious, foreseeable, and imminent harm to a client or other identifiable person.
This paragraph seems to suggest intervention in the situation with Mary is not appropriate. Do not break confidentiality. However, it also says that there are situations in which confidentiality is not the primary concern. Disclosure of confidential information may be made when it is crucial to “prevent serious, foreseeable, and imminent harm to a client or other identifiable person.” But could I argue that there was such serious, foreseeable and imminent harm to anyone? Would it be appropriate, with the knowledge that I had, to suggest such harm would occur? If the answer to the last question is affirmative, what does that infer about persons with a mental illness?
Other paragraphs in Section 2.09, Impairment of Colleagues, are also on point.
(a) Social workers who have direct knowledge of a social work colleague' impairment that is due to personal problems, psychosocial distress, substance abuse, or mental health difficulties and that interferes with practice effectiveness should consult with that colleague when feasible and assist the colleague in taking remedial action.
(b) Social workers who believe that a social work colleague' impairment interferes with practice effectiveness and that the colleague has not taken adequate steps to address the impairment should take action through appropriate channels established by employers, agencies, NASW, licensing and regulatory bodies, and other professional organizations.
I did have knowledge of Mary' impairment. However, to infer that her impairment would interfere with her work as a professional social worker could be seen as prejudiced toward persons with a mental illness. Did I have enough information about Mary to “consult” with Mary as paragraph (a) suggests?
Further, Section 4.02, Discrimination, states that: “Social workers should not practice, condone, facilitate, or collaborate with any form of discrimination on the basis of race, ethnicity, national origin, color, sex, sexual orientation, age, marital status, political belief, religion, or mental or physical disability.” (Italics added.) This suggests that revealing anything about Mary' condition or even confronting Mary with the situation would be discriminatory.
Finally, since Mary was a professional, didn’t she have the responsibility to make sure her “mental health difficulties” did not interfere with her professional judgment and performance as is stated in Section 4.05, Impairment, paragraph a?
(a) Social workers should not allow their own personal problems, psychosocial distress, legal problems, substance abuse, or mental health difficulties to interfere with their professional judgment and performance or to jeopardize the best interests of people for whom they have a professional responsibility.
Paragraph b. of Section 4.05, Impairment goes on to say, in part, that social workers whose “mental health difficulties interfere with their professional judgment and performance” need to seek help, make adjustments in their work situation, or quit practicing.
Doesn’t this mean that since Mary is a professional, she needs to deal with these issues? If that is the case, what is my role?
Obviously, the Code is not a clear set of rules. Rather, it gives guidance to social workers. While it is instructive, the Code does not specify what course of action is best in all instances. As stated in the Preamble, “Core values, and the principles that flow from them, must be balanced within the context and complexity of the human experience.” Professional judgment also comes into play in making ethical decisions.
In summary, there seemed to be no ideal course of action in this situation. I did not know how to predict what would happen if I talked with Mary. It is conceivable that I would have a colleague who was less than happy with my reminding her of her illness. If I did intervene by reporting to persons responsible for hiring, confidential information would be divulged. I could be identified as practicing discrimination toward persons with a mental illness. If I did not intervene, and she was hired, harm could come to clients.
There seemed to be no ideal answer and no way to avoid the situation. There may have been other options, but none seemed apparent to me at the time.
When I relate this case in class, I ask students to work in groups, make a decision, and explain to the rest of the class how they came to their conclusion. Obviously, the Code of Ethics should be a guide in such decisions. But other questions about how to make these types of decisions are also important. Is it appropriate to discuss such issues with my other colleagues? If yes, under what circumstances should such issues be discussed, formally or informally? Should a professional social worker consult with the National Association of Social Workers about such a decision? In general, should a supervisor be consulted about such decisions? In this instance, this would not have seemed appropriate, as the supervisor was also the person in charge of hiring.
In conclusion, there are times in social work practice when professionals are placed in situations, through no wrongdoing on anybody' part, in which dilemmas occur because of a conflict in values or ethical principles within the situation itself. In those situations, it is not a matter of choosing good versus evil, or choosing right versus wrong. It is a matter of choosing between the better of two goods or, possibly more often, the lesser of two evils. Making those decisions is often not pleasant. In fact, it can be quite anxiety provoking. But it is also impossible to side step the issue when doing nothing will predictably yield a certain outcome.
I would welcome a discussion about this case. What would you do? How would you decide what you would do? What besides the Code of Ethics should aid one in making this decision? These are some of the questions that we could discuss together.
National Association of Social Workers. (1999). NASW Code of Ethics. Available online at http://www.socialworkers.org/Code/ethics.htm .
Lee J. Zook, Ph.D., is Associate Professor of Social Work at Luther College in Decorah, Iowa.
Copyright © 2001 White Hat Communications. All rights reserved. From THE NEW SOCIAL WORKER , Winter 2001, Vol. 8, No. 1. For reprints of this or other articles from THE NEW SOCIAL WORKER (or for permission to reprint), contact Linda Grobman, publisher/editor, at P.O. Box 5390, Harrisburg, PA 17110-0390, or at [email protected] .
All material published on this website Copyright 1994-2023 White Hat Communications. All rights reserved. Please contact the publisher for permission to reproduce or reprint any materials on this site. Opinions expressed on this site are the opinions of the writer and do not necessarily represent the views of the publisher. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.
- Open access
- Published: 18 April 2024
Research ethics and artificial intelligence for global health: perspectives from the global forum on bioethics in research
- James Shaw 1 , 13 ,
- Joseph Ali 2 , 3 ,
- Caesar A. Atuire 4 , 5 ,
- Phaik Yeong Cheah 6 ,
- Armando Guio Español 7 ,
- Judy Wawira Gichoya 8 ,
- Adrienne Hunt 9 ,
- Daudi Jjingo 10 ,
- Katherine Littler 9 ,
- Daniela Paolotti 11 &
- Effy Vayena 12
BMC Medical Ethics volume 25 , Article number: 46 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1145 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
The ethical governance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in health care and public health continues to be an urgent issue for attention in policy, research, and practice. In this paper we report on central themes related to challenges and strategies for promoting ethics in research involving AI in global health, arising from the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research (GFBR), held in Cape Town, South Africa in November 2022.
The GFBR is an annual meeting organized by the World Health Organization and supported by the Wellcome Trust, the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) and the South African MRC. The forum aims to bring together ethicists, researchers, policymakers, research ethics committee members and other actors to engage with challenges and opportunities specifically related to research ethics. In 2022 the focus of the GFBR was “Ethics of AI in Global Health Research”. The forum consisted of 6 case study presentations, 16 governance presentations, and a series of small group and large group discussions. A total of 87 participants attended the forum from 31 countries around the world, representing disciplines of bioethics, AI, health policy, health professional practice, research funding, and bioinformatics. In this paper, we highlight central insights arising from GFBR 2022.
We describe the significance of four thematic insights arising from the forum: (1) Appropriateness of building AI, (2) Transferability of AI systems, (3) Accountability for AI decision-making and outcomes, and (4) Individual consent. We then describe eight recommendations for governance leaders to enhance the ethical governance of AI in global health research, addressing issues such as AI impact assessments, environmental values, and fair partnerships.
Conclusions
The 2022 Global Forum on Bioethics in Research illustrated several innovations in ethical governance of AI for global health research, as well as several areas in need of urgent attention internationally. This summary is intended to inform international and domestic efforts to strengthen research ethics and support the evolution of governance leadership to meet the demands of AI in global health research.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The ethical governance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in health care and public health continues to be an urgent issue for attention in policy, research, and practice [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Beyond the growing number of AI applications being implemented in health care, capabilities of AI models such as Large Language Models (LLMs) expand the potential reach and significance of AI technologies across health-related fields [ 4 , 5 ]. Discussion about effective, ethical governance of AI technologies has spanned a range of governance approaches, including government regulation, organizational decision-making, professional self-regulation, and research ethics review [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. In this paper, we report on central themes related to challenges and strategies for promoting ethics in research involving AI in global health research, arising from the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research (GFBR), held in Cape Town, South Africa in November 2022. Although applications of AI for research, health care, and public health are diverse and advancing rapidly, the insights generated at the forum remain highly relevant from a global health perspective. After summarizing important context for work in this domain, we highlight categories of ethical issues emphasized at the forum for attention from a research ethics perspective internationally. We then outline strategies proposed for research, innovation, and governance to support more ethical AI for global health.
In this paper, we adopt the definition of AI systems provided by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) as our starting point. Their definition states that an AI system is “a machine-based system that can, for a given set of human-defined objectives, make predictions, recommendations, or decisions influencing real or virtual environments. AI systems are designed to operate with varying levels of autonomy” [ 9 ]. The conceptualization of an algorithm as helping to constitute an AI system, along with hardware, other elements of software, and a particular context of use, illustrates the wide variety of ways in which AI can be applied. We have found it useful to differentiate applications of AI in research as those classified as “AI systems for discovery” and “AI systems for intervention”. An AI system for discovery is one that is intended to generate new knowledge, for example in drug discovery or public health research in which researchers are seeking potential targets for intervention, innovation, or further research. An AI system for intervention is one that directly contributes to enacting an intervention in a particular context, for example informing decision-making at the point of care or assisting with accuracy in a surgical procedure.
The mandate of the GFBR is to take a broad view of what constitutes research and its regulation in global health, with special attention to bioethics in Low- and Middle- Income Countries. AI as a group of technologies demands such a broad view. AI development for health occurs in a variety of environments, including universities and academic health sciences centers where research ethics review remains an important element of the governance of science and innovation internationally [ 10 , 11 ]. In these settings, research ethics committees (RECs; also known by different names such as Institutional Review Boards or IRBs) make decisions about the ethical appropriateness of projects proposed by researchers and other institutional members, ultimately determining whether a given project is allowed to proceed on ethical grounds [ 12 ].
However, research involving AI for health also takes place in large corporations and smaller scale start-ups, which in some jurisdictions fall outside the scope of research ethics regulation. In the domain of AI, the question of what constitutes research also becomes blurred. For example, is the development of an algorithm itself considered a part of the research process? Or only when that algorithm is tested under the formal constraints of a systematic research methodology? In this paper we take an inclusive view, in which AI development is included in the definition of research activity and within scope for our inquiry, regardless of the setting in which it takes place. This broad perspective characterizes the approach to “research ethics” we take in this paper, extending beyond the work of RECs to include the ethical analysis of the wide range of activities that constitute research as the generation of new knowledge and intervention in the world.
Ethical governance of AI in global health
The ethical governance of AI for global health has been widely discussed in recent years. The World Health Organization (WHO) released its guidelines on ethics and governance of AI for health in 2021, endorsing a set of six ethical principles and exploring the relevance of those principles through a variety of use cases. The WHO guidelines also provided an overview of AI governance, defining governance as covering “a range of steering and rule-making functions of governments and other decision-makers, including international health agencies, for the achievement of national health policy objectives conducive to universal health coverage.” (p. 81) The report usefully provided a series of recommendations related to governance of seven domains pertaining to AI for health: data, benefit sharing, the private sector, the public sector, regulation, policy observatories/model legislation, and global governance. The report acknowledges that much work is yet to be done to advance international cooperation on AI governance, especially related to prioritizing voices from Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs) in global dialogue.
One important point emphasized in the WHO report that reinforces the broader literature on global governance of AI is the distribution of responsibility across a wide range of actors in the AI ecosystem. This is especially important to highlight when focused on research for global health, which is specifically about work that transcends national borders. Alami et al. (2020) discussed the unique risks raised by AI research in global health, ranging from the unavailability of data in many LMICs required to train locally relevant AI models to the capacity of health systems to absorb new AI technologies that demand the use of resources from elsewhere in the system. These observations illustrate the need to identify the unique issues posed by AI research for global health specifically, and the strategies that can be employed by all those implicated in AI governance to promote ethically responsible use of AI in global health research.
RECs and the regulation of research involving AI
RECs represent an important element of the governance of AI for global health research, and thus warrant further commentary as background to our paper. Despite the importance of RECs, foundational questions have been raised about their capabilities to accurately understand and address ethical issues raised by studies involving AI. Rahimzadeh et al. (2023) outlined how RECs in the United States are under-prepared to align with recent federal policy requiring that RECs review data sharing and management plans with attention to the unique ethical issues raised in AI research for health [ 13 ]. Similar research in South Africa identified variability in understanding of existing regulations and ethical issues associated with health-related big data sharing and management among research ethics committee members [ 14 , 15 ]. The effort to address harms accruing to groups or communities as opposed to individuals whose data are included in AI research has also been identified as a unique challenge for RECs [ 16 , 17 ]. Doerr and Meeder (2022) suggested that current regulatory frameworks for research ethics might actually prevent RECs from adequately addressing such issues, as they are deemed out of scope of REC review [ 16 ]. Furthermore, research in the United Kingdom and Canada has suggested that researchers using AI methods for health tend to distinguish between ethical issues and social impact of their research, adopting an overly narrow view of what constitutes ethical issues in their work [ 18 ].
The challenges for RECs in adequately addressing ethical issues in AI research for health care and public health exceed a straightforward survey of ethical considerations. As Ferretti et al. (2021) contend, some capabilities of RECs adequately cover certain issues in AI-based health research, such as the common occurrence of conflicts of interest where researchers who accept funds from commercial technology providers are implicitly incentivized to produce results that align with commercial interests [ 12 ]. However, some features of REC review require reform to adequately meet ethical needs. Ferretti et al. outlined weaknesses of RECs that are longstanding and those that are novel to AI-related projects, proposing a series of directions for development that are regulatory, procedural, and complementary to REC functionality. The work required on a global scale to update the REC function in response to the demands of research involving AI is substantial.
These issues take greater urgency in the context of global health [ 19 ]. Teixeira da Silva (2022) described the global practice of “ethics dumping”, where researchers from high income countries bring ethically contentious practices to RECs in low-income countries as a strategy to gain approval and move projects forward [ 20 ]. Although not yet systematically documented in AI research for health, risk of ethics dumping in AI research is high. Evidence is already emerging of practices of “health data colonialism”, in which AI researchers and developers from large organizations in high-income countries acquire data to build algorithms in LMICs to avoid stricter regulations [ 21 ]. This specific practice is part of a larger collection of practices that characterize health data colonialism, involving the broader exploitation of data and the populations they represent primarily for commercial gain [ 21 , 22 ]. As an additional complication, AI algorithms trained on data from high-income contexts are unlikely to apply in straightforward ways to LMIC settings [ 21 , 23 ]. In the context of global health, there is widespread acknowledgement about the need to not only enhance the knowledge base of REC members about AI-based methods internationally, but to acknowledge the broader shifts required to encourage their capabilities to more fully address these and other ethical issues associated with AI research for health [ 8 ].
Although RECs are an important part of the story of the ethical governance of AI for global health research, they are not the only part. The responsibilities of supra-national entities such as the World Health Organization, national governments, organizational leaders, commercial AI technology providers, health care professionals, and other groups continue to be worked out internationally. In this context of ongoing work, examining issues that demand attention and strategies to address them remains an urgent and valuable task.
The GFBR is an annual meeting organized by the World Health Organization and supported by the Wellcome Trust, the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) and the South African MRC. The forum aims to bring together ethicists, researchers, policymakers, REC members and other actors to engage with challenges and opportunities specifically related to research ethics. Each year the GFBR meeting includes a series of case studies and keynotes presented in plenary format to an audience of approximately 100 people who have applied and been competitively selected to attend, along with small-group breakout discussions to advance thinking on related issues. The specific topic of the forum changes each year, with past topics including ethical issues in research with people living with mental health conditions (2021), genome editing (2019), and biobanking/data sharing (2018). The forum is intended to remain grounded in the practical challenges of engaging in research ethics, with special interest in low resource settings from a global health perspective. A post-meeting fellowship scheme is open to all LMIC participants, providing a unique opportunity to apply for funding to further explore and address the ethical challenges that are identified during the meeting.
In 2022, the focus of the GFBR was “Ethics of AI in Global Health Research”. The forum consisted of 6 case study presentations (both short and long form) reporting on specific initiatives related to research ethics and AI for health, and 16 governance presentations (both short and long form) reporting on actual approaches to governing AI in different country settings. A keynote presentation from Professor Effy Vayena addressed the topic of the broader context for AI ethics in a rapidly evolving field. A total of 87 participants attended the forum from 31 countries around the world, representing disciplines of bioethics, AI, health policy, health professional practice, research funding, and bioinformatics. The 2-day forum addressed a wide range of themes. The conference report provides a detailed overview of each of the specific topics addressed while a policy paper outlines the cross-cutting themes (both documents are available at the GFBR website: https://www.gfbr.global/past-meetings/16th-forum-cape-town-south-africa-29-30-november-2022/ ). As opposed to providing a detailed summary in this paper, we aim to briefly highlight central issues raised, solutions proposed, and the challenges facing the research ethics community in the years to come.
In this way, our primary aim in this paper is to present a synthesis of the challenges and opportunities raised at the GFBR meeting and in the planning process, followed by our reflections as a group of authors on their significance for governance leaders in the coming years. We acknowledge that the views represented at the meeting and in our results are a partial representation of the universe of views on this topic; however, the GFBR leadership invested a great deal of resources in convening a deeply diverse and thoughtful group of researchers and practitioners working on themes of bioethics related to AI for global health including those based in LMICs. We contend that it remains rare to convene such a strong group for an extended time and believe that many of the challenges and opportunities raised demand attention for more ethical futures of AI for health. Nonetheless, our results are primarily descriptive and are thus not explicitly grounded in a normative argument. We make effort in the Discussion section to contextualize our results by describing their significance and connecting them to broader efforts to reform global health research and practice.
Uniquely important ethical issues for AI in global health research
Presentations and group dialogue over the course of the forum raised several issues for consideration, and here we describe four overarching themes for the ethical governance of AI in global health research. Brief descriptions of each issue can be found in Table 1 . Reports referred to throughout the paper are available at the GFBR website provided above.
The first overarching thematic issue relates to the appropriateness of building AI technologies in response to health-related challenges in the first place. Case study presentations referred to initiatives where AI technologies were highly appropriate, such as in ear shape biometric identification to more accurately link electronic health care records to individual patients in Zambia (Alinani Simukanga). Although important ethical issues were raised with respect to privacy, trust, and community engagement in this initiative, the AI-based solution was appropriately matched to the challenge of accurately linking electronic records to specific patient identities. In contrast, forum participants raised questions about the appropriateness of an initiative using AI to improve the quality of handwashing practices in an acute care hospital in India (Niyoshi Shah), which led to gaming the algorithm. Overall, participants acknowledged the dangers of techno-solutionism, in which AI researchers and developers treat AI technologies as the most obvious solutions to problems that in actuality demand much more complex strategies to address [ 24 ]. However, forum participants agreed that RECs in different contexts have differing degrees of power to raise issues of the appropriateness of an AI-based intervention.
The second overarching thematic issue related to whether and how AI-based systems transfer from one national health context to another. One central issue raised by a number of case study presentations related to the challenges of validating an algorithm with data collected in a local environment. For example, one case study presentation described a project that would involve the collection of personally identifiable data for sensitive group identities, such as tribe, clan, or religion, in the jurisdictions involved (South Africa, Nigeria, Tanzania, Uganda and the US; Gakii Masunga). Doing so would enable the team to ensure that those groups were adequately represented in the dataset to ensure the resulting algorithm was not biased against specific community groups when deployed in that context. However, some members of these communities might desire to be represented in the dataset, whereas others might not, illustrating the need to balance autonomy and inclusivity. It was also widely recognized that collecting these data is an immense challenge, particularly when historically oppressive practices have led to a low-trust environment for international organizations and the technologies they produce. It is important to note that in some countries such as South Africa and Rwanda, it is illegal to collect information such as race and tribal identities, re-emphasizing the importance for cultural awareness and avoiding “one size fits all” solutions.
The third overarching thematic issue is related to understanding accountabilities for both the impacts of AI technologies and governance decision-making regarding their use. Where global health research involving AI leads to longer-term harms that might fall outside the usual scope of issues considered by a REC, who is to be held accountable, and how? This question was raised as one that requires much further attention, with law being mixed internationally regarding the mechanisms available to hold researchers, innovators, and their institutions accountable over the longer term. However, it was recognized in breakout group discussion that many jurisdictions are developing strong data protection regimes related specifically to international collaboration for research involving health data. For example, Kenya’s Data Protection Act requires that any internationally funded projects have a local principal investigator who will hold accountability for how data are shared and used [ 25 ]. The issue of research partnerships with commercial entities was raised by many participants in the context of accountability, pointing toward the urgent need for clear principles related to strategies for engagement with commercial technology companies in global health research.
The fourth and final overarching thematic issue raised here is that of consent. The issue of consent was framed by the widely shared recognition that models of individual, explicit consent might not produce a supportive environment for AI innovation that relies on the secondary uses of health-related datasets to build AI algorithms. Given this recognition, approaches such as community oversight of health data uses were suggested as a potential solution. However, the details of implementing such community oversight mechanisms require much further attention, particularly given the unique perspectives on health data in different country settings in global health research. Furthermore, some uses of health data do continue to require consent. One case study of South Africa, Nigeria, Kenya, Ethiopia and Uganda suggested that when health data are shared across borders, individual consent remains necessary when data is transferred from certain countries (Nezerith Cengiz). Broader clarity is necessary to support the ethical governance of health data uses for AI in global health research.
Recommendations for ethical governance of AI in global health research
Dialogue at the forum led to a range of suggestions for promoting ethical conduct of AI research for global health, related to the various roles of actors involved in the governance of AI research broadly defined. The strategies are written for actors we refer to as “governance leaders”, those people distributed throughout the AI for global health research ecosystem who are responsible for ensuring the ethical and socially responsible conduct of global health research involving AI (including researchers themselves). These include RECs, government regulators, health care leaders, health professionals, corporate social accountability officers, and others. Enacting these strategies would bolster the ethical governance of AI for global health more generally, enabling multiple actors to fulfill their roles related to governing research and development activities carried out across multiple organizations, including universities, academic health sciences centers, start-ups, and technology corporations. Specific suggestions are summarized in Table 2 .
First, forum participants suggested that governance leaders including RECs, should remain up to date on recent advances in the regulation of AI for health. Regulation of AI for health advances rapidly and takes on different forms in jurisdictions around the world. RECs play an important role in governance, but only a partial role; it was deemed important for RECs to acknowledge how they fit within a broader governance ecosystem in order to more effectively address the issues within their scope. Not only RECs but organizational leaders responsible for procurement, researchers, and commercial actors should all commit to efforts to remain up to date about the relevant approaches to regulating AI for health care and public health in jurisdictions internationally. In this way, governance can more adequately remain up to date with advances in regulation.
Second, forum participants suggested that governance leaders should focus on ethical governance of health data as a basis for ethical global health AI research. Health data are considered the foundation of AI development, being used to train AI algorithms for various uses [ 26 ]. By focusing on ethical governance of health data generation, sharing, and use, multiple actors will help to build an ethical foundation for AI development among global health researchers.
Third, forum participants believed that governance processes should incorporate AI impact assessments where appropriate. An AI impact assessment is the process of evaluating the potential effects, both positive and negative, of implementing an AI algorithm on individuals, society, and various stakeholders, generally over time frames specified in advance of implementation [ 27 ]. Although not all types of AI research in global health would warrant an AI impact assessment, this is especially relevant for those studies aiming to implement an AI system for intervention into health care or public health. Organizations such as RECs can use AI impact assessments to boost understanding of potential harms at the outset of a research project, encouraging researchers to more deeply consider potential harms in the development of their study.
Fourth, forum participants suggested that governance decisions should incorporate the use of environmental impact assessments, or at least the incorporation of environment values when assessing the potential impact of an AI system. An environmental impact assessment involves evaluating and anticipating the potential environmental effects of a proposed project to inform ethical decision-making that supports sustainability [ 28 ]. Although a relatively new consideration in research ethics conversations [ 29 ], the environmental impact of building technologies is a crucial consideration for the public health commitment to environmental sustainability. Governance leaders can use environmental impact assessments to boost understanding of potential environmental harms linked to AI research projects in global health over both the shorter and longer terms.
Fifth, forum participants suggested that governance leaders should require stronger transparency in the development of AI algorithms in global health research. Transparency was considered essential in the design and development of AI algorithms for global health to ensure ethical and accountable decision-making throughout the process. Furthermore, whether and how researchers have considered the unique contexts into which such algorithms may be deployed can be surfaced through stronger transparency, for example in describing what primary considerations were made at the outset of the project and which stakeholders were consulted along the way. Sharing information about data provenance and methods used in AI development will also enhance the trustworthiness of the AI-based research process.
Sixth, forum participants suggested that governance leaders can encourage or require community engagement at various points throughout an AI project. It was considered that engaging patients and communities is crucial in AI algorithm development to ensure that the technology aligns with community needs and values. However, participants acknowledged that this is not a straightforward process. Effective community engagement requires lengthy commitments to meeting with and hearing from diverse communities in a given setting, and demands a particular set of skills in communication and dialogue that are not possessed by all researchers. Encouraging AI researchers to begin this process early and build long-term partnerships with community members is a promising strategy to deepen community engagement in AI research for global health. One notable recommendation was that research funders have an opportunity to incentivize and enable community engagement with funds dedicated to these activities in AI research in global health.
Seventh, forum participants suggested that governance leaders can encourage researchers to build strong, fair partnerships between institutions and individuals across country settings. In a context of longstanding imbalances in geopolitical and economic power, fair partnerships in global health demand a priori commitments to share benefits related to advances in medical technologies, knowledge, and financial gains. Although enforcement of this point might be beyond the remit of RECs, commentary will encourage researchers to consider stronger, fairer partnerships in global health in the longer term.
Eighth, it became evident that it is necessary to explore new forms of regulatory experimentation given the complexity of regulating a technology of this nature. In addition, the health sector has a series of particularities that make it especially complicated to generate rules that have not been previously tested. Several participants highlighted the desire to promote spaces for experimentation such as regulatory sandboxes or innovation hubs in health. These spaces can have several benefits for addressing issues surrounding the regulation of AI in the health sector, such as: (i) increasing the capacities and knowledge of health authorities about this technology; (ii) identifying the major problems surrounding AI regulation in the health sector; (iii) establishing possibilities for exchange and learning with other authorities; (iv) promoting innovation and entrepreneurship in AI in health; and (vi) identifying the need to regulate AI in this sector and update other existing regulations.
Ninth and finally, forum participants believed that the capabilities of governance leaders need to evolve to better incorporate expertise related to AI in ways that make sense within a given jurisdiction. With respect to RECs, for example, it might not make sense for every REC to recruit a member with expertise in AI methods. Rather, it will make more sense in some jurisdictions to consult with members of the scientific community with expertise in AI when research protocols are submitted that demand such expertise. Furthermore, RECs and other approaches to research governance in jurisdictions around the world will need to evolve in order to adopt the suggestions outlined above, developing processes that apply specifically to the ethical governance of research using AI methods in global health.
Research involving the development and implementation of AI technologies continues to grow in global health, posing important challenges for ethical governance of AI in global health research around the world. In this paper we have summarized insights from the 2022 GFBR, focused specifically on issues in research ethics related to AI for global health research. We summarized four thematic challenges for governance related to AI in global health research and nine suggestions arising from presentations and dialogue at the forum. In this brief discussion section, we present an overarching observation about power imbalances that frames efforts to evolve the role of governance in global health research, and then outline two important opportunity areas as the field develops to meet the challenges of AI in global health research.
Dialogue about power is not unfamiliar in global health, especially given recent contributions exploring what it would mean to de-colonize global health research, funding, and practice [ 30 , 31 ]. Discussions of research ethics applied to AI research in global health contexts are deeply infused with power imbalances. The existing context of global health is one in which high-income countries primarily located in the “Global North” charitably invest in projects taking place primarily in the “Global South” while recouping knowledge, financial, and reputational benefits [ 32 ]. With respect to AI development in particular, recent examples of digital colonialism frame dialogue about global partnerships, raising attention to the role of large commercial entities and global financial capitalism in global health research [ 21 , 22 ]. Furthermore, the power of governance organizations such as RECs to intervene in the process of AI research in global health varies widely around the world, depending on the authorities assigned to them by domestic research governance policies. These observations frame the challenges outlined in our paper, highlighting the difficulties associated with making meaningful change in this field.
Despite these overarching challenges of the global health research context, there are clear strategies for progress in this domain. Firstly, AI innovation is rapidly evolving, which means approaches to the governance of AI for health are rapidly evolving too. Such rapid evolution presents an important opportunity for governance leaders to clarify their vision and influence over AI innovation in global health research, boosting the expertise, structure, and functionality required to meet the demands of research involving AI. Secondly, the research ethics community has strong international ties, linked to a global scholarly community that is committed to sharing insights and best practices around the world. This global community can be leveraged to coordinate efforts to produce advances in the capabilities and authorities of governance leaders to meaningfully govern AI research for global health given the challenges summarized in our paper.
Limitations
Our paper includes two specific limitations that we address explicitly here. First, it is still early in the lifetime of the development of applications of AI for use in global health, and as such, the global community has had limited opportunity to learn from experience. For example, there were many fewer case studies, which detail experiences with the actual implementation of an AI technology, submitted to GFBR 2022 for consideration than was expected. In contrast, there were many more governance reports submitted, which detail the processes and outputs of governance processes that anticipate the development and dissemination of AI technologies. This observation represents both a success and a challenge. It is a success that so many groups are engaging in anticipatory governance of AI technologies, exploring evidence of their likely impacts and governing technologies in novel and well-designed ways. It is a challenge that there is little experience to build upon of the successful implementation of AI technologies in ways that have limited harms while promoting innovation. Further experience with AI technologies in global health will contribute to revising and enhancing the challenges and recommendations we have outlined in our paper.
Second, global trends in the politics and economics of AI technologies are evolving rapidly. Although some nations are advancing detailed policy approaches to regulating AI more generally, including for uses in health care and public health, the impacts of corporate investments in AI and political responses related to governance remain to be seen. The excitement around large language models (LLMs) and large multimodal models (LMMs) has drawn deeper attention to the challenges of regulating AI in any general sense, opening dialogue about health sector-specific regulations. The direction of this global dialogue, strongly linked to high-profile corporate actors and multi-national governance institutions, will strongly influence the development of boundaries around what is possible for the ethical governance of AI for global health. We have written this paper at a point when these developments are proceeding rapidly, and as such, we acknowledge that our recommendations will need updating as the broader field evolves.
Ultimately, coordination and collaboration between many stakeholders in the research ethics ecosystem will be necessary to strengthen the ethical governance of AI in global health research. The 2022 GFBR illustrated several innovations in ethical governance of AI for global health research, as well as several areas in need of urgent attention internationally. This summary is intended to inform international and domestic efforts to strengthen research ethics and support the evolution of governance leadership to meet the demands of AI in global health research.
Data availability
All data and materials analyzed to produce this paper are available on the GFBR website: https://www.gfbr.global/past-meetings/16th-forum-cape-town-south-africa-29-30-november-2022/ .
Clark P, Kim J, Aphinyanaphongs Y, Marketing, Food US. Drug Administration Clearance of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Enabled Software in and as Medical devices: a systematic review. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(7):e2321792–2321792.
Article Google Scholar
Potnis KC, Ross JS, Aneja S, Gross CP, Richman IB. Artificial intelligence in breast cancer screening: evaluation of FDA device regulation and future recommendations. JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182(12):1306–12.
Siala H, Wang Y. SHIFTing artificial intelligence to be responsible in healthcare: a systematic review. Soc Sci Med. 2022;296:114782.
Yang X, Chen A, PourNejatian N, Shin HC, Smith KE, Parisien C, et al. A large language model for electronic health records. NPJ Digit Med. 2022;5(1):194.
Meskó B, Topol EJ. The imperative for regulatory oversight of large language models (or generative AI) in healthcare. NPJ Digit Med. 2023;6(1):120.
Jobin A, Ienca M, Vayena E. The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nat Mach Intell. 2019;1(9):389–99.
Minssen T, Vayena E, Cohen IG. The challenges for Regulating Medical Use of ChatGPT and other large Language models. JAMA. 2023.
Ho CWL, Malpani R. Scaling up the research ethics framework for healthcare machine learning as global health ethics and governance. Am J Bioeth. 2022;22(5):36–8.
Yeung K. Recommendation of the council on artificial intelligence (OECD). Int Leg Mater. 2020;59(1):27–34.
Maddox TM, Rumsfeld JS, Payne PR. Questions for artificial intelligence in health care. JAMA. 2019;321(1):31–2.
Dzau VJ, Balatbat CA, Ellaissi WF. Revisiting academic health sciences systems a decade later: discovery to health to population to society. Lancet. 2021;398(10318):2300–4.
Ferretti A, Ienca M, Sheehan M, Blasimme A, Dove ES, Farsides B, et al. Ethics review of big data research: what should stay and what should be reformed? BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):1–13.
Rahimzadeh V, Serpico K, Gelinas L. Institutional review boards need new skills to review data sharing and management plans. Nat Med. 2023;1–3.
Kling S, Singh S, Burgess TL, Nair G. The role of an ethics advisory committee in data science research in sub-saharan Africa. South Afr J Sci. 2023;119(5–6):1–3.
Google Scholar
Cengiz N, Kabanda SM, Esterhuizen TM, Moodley K. Exploring perspectives of research ethics committee members on the governance of big data in sub-saharan Africa. South Afr J Sci. 2023;119(5–6):1–9.
Doerr M, Meeder S. Big health data research and group harm: the scope of IRB review. Ethics Hum Res. 2022;44(4):34–8.
Ballantyne A, Stewart C. Big data and public-private partnerships in healthcare and research: the application of an ethics framework for big data in health and research. Asian Bioeth Rev. 2019;11(3):315–26.
Samuel G, Chubb J, Derrick G. Boundaries between research ethics and ethical research use in artificial intelligence health research. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2021;16(3):325–37.
Murphy K, Di Ruggiero E, Upshur R, Willison DJ, Malhotra N, Cai JC, et al. Artificial intelligence for good health: a scoping review of the ethics literature. BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):1–17.
Teixeira da Silva JA. Handling ethics dumping and neo-colonial research: from the laboratory to the academic literature. J Bioethical Inq. 2022;19(3):433–43.
Ferryman K. The dangers of data colonialism in precision public health. Glob Policy. 2021;12:90–2.
Couldry N, Mejias UA. Data colonialism: rethinking big data’s relation to the contemporary subject. Telev New Media. 2019;20(4):336–49.
Organization WH. Ethics and governance of artificial intelligence for health: WHO guidance. 2021.
Metcalf J, Moss E. Owning ethics: corporate logics, silicon valley, and the institutionalization of ethics. Soc Res Int Q. 2019;86(2):449–76.
Data Protection Act - OFFICE OF THE DATA PROTECTION COMMISSIONER KENYA [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Sep 30]. https://www.odpc.go.ke/dpa-act/ .
Sharon T, Lucivero F. Introduction to the special theme: the expansion of the health data ecosystem–rethinking data ethics and governance. Big Data & Society. Volume 6. London, England: SAGE Publications Sage UK; 2019. p. 2053951719852969.
Reisman D, Schultz J, Crawford K, Whittaker M. Algorithmic impact assessments: a practical Framework for Public Agency. AI Now. 2018.
Morgan RK. Environmental impact assessment: the state of the art. Impact Assess Proj Apprais. 2012;30(1):5–14.
Samuel G, Richie C. Reimagining research ethics to include environmental sustainability: a principled approach, including a case study of data-driven health research. J Med Ethics. 2023;49(6):428–33.
Kwete X, Tang K, Chen L, Ren R, Chen Q, Wu Z, et al. Decolonizing global health: what should be the target of this movement and where does it lead us? Glob Health Res Policy. 2022;7(1):3.
Abimbola S, Asthana S, Montenegro C, Guinto RR, Jumbam DT, Louskieter L, et al. Addressing power asymmetries in global health: imperatives in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS Med. 2021;18(4):e1003604.
Benatar S. Politics, power, poverty and global health: systems and frames. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2016;5(10):599.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the outstanding contributions of the attendees of GFBR 2022 in Cape Town, South Africa. This paper is authored by members of the GFBR 2022 Planning Committee. We would like to acknowledge additional members Tamra Lysaght, National University of Singapore, and Niresh Bhagwandin, South African Medical Research Council, for their input during the planning stages and as reviewers of the applications to attend the Forum.
This work was supported by Wellcome [222525/Z/21/Z], the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (part of UK Research and Innovation), and the South African Medical Research Council through funding to the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Physical Therapy, Temerty Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Berman Institute of Bioethics, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
Bloomberg School of Public Health, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
Department of Philosophy and Classics, University of Ghana, Legon-Accra, Ghana
Caesar A. Atuire
Centre for Tropical Medicine and Global Health, Nuffield Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
Mahidol Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Unit, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
Phaik Yeong Cheah
Berkman Klein Center, Harvard University, Bogotá, Colombia
Armando Guio Español
Department of Radiology and Informatics, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA
Judy Wawira Gichoya
Health Ethics & Governance Unit, Research for Health Department, Science Division, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Adrienne Hunt & Katherine Littler
African Center of Excellence in Bioinformatics and Data Intensive Science, Infectious Diseases Institute, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda
Daudi Jjingo
ISI Foundation, Turin, Italy
Daniela Paolotti
Department of Health Sciences and Technology, ETH Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland
Effy Vayena
Joint Centre for Bioethics, Dalla Lana School of Public Health, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JS led the writing, contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. JA contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. CA contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. PYC contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. AE contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. JWG contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. AH contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. DJ contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. KL contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. DP contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. EV contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to James Shaw .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shaw, J., Ali, J., Atuire, C.A. et al. Research ethics and artificial intelligence for global health: perspectives from the global forum on bioethics in research. BMC Med Ethics 25 , 46 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-024-01044-w
Download citation
Received : 31 October 2023
Accepted : 01 April 2024
Published : 18 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-024-01044-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Artificial intelligence
- Machine learning
- Research ethics
- Global health
BMC Medical Ethics
ISSN: 1472-6939
- General enquiries: [email protected]

COMMENTS
More than 70 cases pair ethics concepts with real world situations. From journalism, performing arts, and scientific research to sports, law, and business, these case studies explore current and historic ethical dilemmas, their motivating biases, and their consequences. Each case includes discussion questions, related videos, and a bibliography.
A Business Ethics Case Study. The CFO of a family business faces difficult decisions about how to proceed when the COVID-19 pandemic changes the business revenue models, and one family shareholder wants a full buyout. Case studies and scenarios illustrating ethical dilemmas in business, medicine, technology, government, and education.
Case Studies. The ACM Code of Ethics and Professional Practice ("the Code") is meant to inform practice and education. It is useful as the conscience of the profession, but also for individual decision-making. As prescribed by the Preamble of the Code, computing professionals should approach the dilemma with a holistic reading of the ...
A Business Ethics Case Study. An employee at an after-school learning institution must balance a decision to accept or decline an offered gift, while considering the cultural norms of the client, upholding the best interests of all stakeholders, and following the operational rules of his employer.
We have chosen to stay engaged and attempt to drive changes on the ground.". In an effort for greater transparency, Apple has released annual reports detailing their work with suppliers and labor practices. While more recent investigations have shown some improvements to suppliers' working conditions, Apple continues to face criticism as ...
Markkula Center for Applied Ethics. Focus Areas. Leadership Ethics. Leadership Ethics Resources. Leadership Ethics Cases. Find ethical case studies on leadership ethics, including scenarios for top management on issues such as downsizing and management responsibilities. (For permission to reprint articles, submit requests to [email protected] .)
This study investigates the ethical use of Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies (BD + AI)—using an empirical approach. The paper categorises the current literature and presents a multi-case study of 'on-the-ground' ethical issues that uses qualitative tools to analyse findings from ten targeted case-studies from a range of domains. The analysis coalesces identified singular ...
An essay exploring how to effectively use case studies to teach research ethics. It is widely believed that discussing case studies is the most effective method of teaching the responsible conduct of research (Kovac 1996; Macrina and Munro 1995), probably because discussing case studies is an effective way to get students involved in the issues.
Three additional case studies are scheduled for release in spring 2019. Methodology: The Princeton Dialogues on AI and Ethics case studies are unique in their adherence to five guiding principles: 1) empirical foundations, 2) broad accessibility, 3) interactiveness, 4) multiple viewpoints and 5) depth over brevity.
An Ethics Case Study. Ethics in Technology Practice Sections Ethics in Technology Practice. Ethics in Technology Practice; What Are These Materials? Overview of Ethics in Tech Practice; Ethical Lenses; Framework for Ethical Decision Making; Ethical Toolkit; Case Studies;
Erica Kaufman West, MD. Zoonoses are infectious diseases that pass from an animal to a human and now constitute the majority of new and emerging infections. AMA J Ethics. 2024;26 (2):E103-108. doi: 10.1001/amajethics.2024.103. Case and Commentary. Feb 2024.
In January 2022, Politico published an article about a nonprofit called Crisis Text Line, which offers support via text messages for people who are going through mental health crises. For years, the nonprofit had been collecting a database of messages exchanged, and used the data to triage the incoming calls for help and to train its volunteers ...
Many reasons underlie this trend, one being the movement towards evidence-based practice. Case studies provide a methodology by which a detailed study can be conducted of a social unit, whether that unit is a person, ... Ethics case studies allow such reflection to facilitate the development of ethical decision-making skills. This volume has ...
ethics. We teach the course in a "team-teaching" format where we, the instructors, teach. collaboratively as a model for collaborative learning. We emphasize the importance of both written and spoken communication about ethical. issues and we encourage and require creative and critical thinking about ethical issues.
EthicsEthics Case Studies. Ethics Case Studies. The SPJ Code of Ethics is voluntarily embraced by thousands of journalists, regardless of place or platform, and is widely used in newsrooms and classrooms as a guide for ethical behavior. The code is intended not as a set of "rules" but as a resource for ethical decision-making.
3. A lawyer should assist in preventing the unauthorized practice of law. 4. A lawyer should preserve the confidences and secrets of a client. 5. A lawyer should exercise independent professional judgment on behalf of a client. 6. A lawyer should represent a client competently. 7. A lawyer should represent a client zealously within the bounds ...
Twenty-eight additional case studies are published in the book Ethical Choices: Case Studies for Medical Practice (2nd edition) For more information on these and other educational content, please contact Lois Snyder Sulmasy, JD, at [email protected] or at 215-351-2835. ACP medical ethics education and case study resources cover a range of ...
This article explores some case studies that shine a light on ethical business practices, offering valuable lessons for businesses in any industry. Case Study 1: Patagonia's Commitment to Environmental Ethics. Patagonia, the outdoor clothing and gear company, has long set a standard for environmental responsibility. The company uses eco ...
In our case study, 93 year old Ms. Jones is admitted to hospital with a fragility hip fracture. As a first step, we must recognize that there is actually an ethical dilemma; in this case, the dilemma is whether the patient should proceed with surgery or not, given her underlying medical conditions and potential for perioperative complications.
Ethical Case Studies for Coach Development and Practice is an essential accompaniment for coaches. Written by seasoned practitioners, this companion coaching case study book offers a more personal perspective on ethics in practice. Its simple structured layout and focus on ethical dilemmas make it an attractive course supplementary text and ...
Ethical Dilemmas Case Studies - Professional Accountants in Public Practice ; The case studies are illustrative and should be read in conjunction with the guidance contained in ICAEW's Code of Ethics, in particular Part 1 and Part 3 of the Code. Help with ethical problems. You may seek advice from ICAEW's helplines, free of charge:
Winter 2001, Vol. 8, No. 1. Ethics: To Tell or Not to Tell-A Case Study. by Lee J. Zook, Ph.D. Some years ago, prior to teaching in undergraduate social work, I was working with families and children in an outpatient psychiatric setting, Children' Agency. In the previous year, I had completed my MSW, having practiced social work several years ...
4 Ethical Dilemmas Case Studies Professional Accountants in Public Practice • Objectivity - not to compromise professional or business judgements because of bias, conflict of interest or undue influence of others. • Professional competence and due care - to: (i) Attain and maintain professional knowledge and skill at the level required to ensure that a client or employing
The forum consisted of 6 case study presentations, 16 governance presentations, and a series of small group and large group discussions. A total of 87 participants attended the forum from 31 countries around the world, representing disciplines of bioethics, AI, health policy, health professional practice, research funding, and bioinformatics.