How Long Should a Research Paper Be? Data from 61,519 Examples
I analyzed a random sample of 61,519 full-text research papers, uploaded to PubMed Central between the years 2016 and 2021, in order to answer the questions:
What is the typical overall length of a research paper? and how long should each section be?
I used the BioC API to download the data (see the References section below).

Here’s a summary of the key findings
1- The median length of a research paper is 4,133 words (equivalent to 166 sentences or 34 paragraphs), excluding the abstract and references, with 90% of papers being between 2,023 and 8,284 words.
2- A typical article is divided in the following way:
- Introduction section: 14.6% of the total word count.
- Methods section: 29.7% of the total word count.
- Results section: 26.2% of the total word count.
- Discussion section: 29.4% of the total word count.
Notice that the Materials and methods is the longest section of a professionally written article. So always write this section in enough depth to provide the readers with the necessary details that allow them to replicate your study if they wanted to without requiring further information.
Overall length of a research paper
Let’s start by looking at the maximum word count allowed in some of the well-known journals. Note that the numbers reported in this table include the Abstract , Figure legends and References unless otherwise specified:
[1] excluding figure legends [2] excluding references
⚠ Note A review paper is either a systematic review or a meta-analysis, and an original research paper refers to either an observational or an experimental study conducted by the authors themselves.
Notice the large variability between these journals: The maximum number of words allowed ranges between 3,000 and 9,000 words.
Next, let’s look at our data.
Here’s a table that describes the length of a research paper in our sample:
90% of research papers have a word count between 2,023 and 8,284. So it will be a little weird to see a word count outside of this range.
Our data also agree that a typical review paper is a little bit longer than a typical original research paper but not by much (3,858 vs 3,708 words).
Length of each section in a research article
The median article with an IMRaD structure (i.e. contains the following sections: Introduction , Methods , Results and Discussion ) is in general characterized by a short 553 words introduction. And the methods, results and discussion sections are about twice the size of the introduction:
For more information, see:
- How Long Should a Research Title Be? Data from 104,161 Examples
- How Long Should the Abstract Be? Data 61,429 from Examples
- How Long Should the Introduction of a Research Paper Be? Data from 61,518 Examples
- How Long Should the Methods Section Be? Data from 61,514 Examples
- How Long Should the Results Section Be? Data from 61,458 Examples
- How Long Should the Discussion Section Be? Data from 61,517 Examples
- Length of a Conclusion Section: Analysis of 47,810 Examples
- Comeau DC, Wei CH, Islamaj Doğan R, and Lu Z. PMC text mining subset in BioC: about 3 million full text articles and growing, Bioinformatics , btz070, 2019.

How Long Should a Research Paper Be?

How Long Should A Research Paper Be? An Overview
In short, research paper's average length can range from 1,500 words for research proposals and case studies - all the way to 100,000 words for large dissertations.
Research, by its nature of being complex, requires a careful and thorough elucidation of facts, notions, information, and the like - which is all reflected in its most optimal length.
Thus, one of the critical points that you need to focus on when writing either a complex research paper or a less complex research paper is your objective and how you can relay the latter in a particular context. Say you are writing a book review. Since you will only need to synthesize information from other sources to solidify your claim about a certain topic, you will perhaps use paraphrasing techniques, which offer a relatively lower word count when compared to a full-blown descriptive research paper.
Even when both types of research differ in word counts, they can effectively attain their objectives, given the different contexts in which they are written and constructed.
Certainly, when asked about how long is a research paper, it surely depends on the objective or the type of research you will be using. Carrying out these objectives will warrant you to do certain paper writing tasks and techniques that are not necessarily long or short when you compare them to other research types.
At Studyfy, we care for the attainment of your research objectives. We understand that achieving such will contribute to the success of your research completion. While maintaining the ideal word count for a research paper, you are in a meaningful position to understand the various elements that can enrich your paper, even if it looks overwhelming.
How Long Should the Introduction of a Research Paper Be?
The research introduction section most likely occupies approximately 30-40% of the entire research paper.
The introduction of a regular academic paper can total 1750-2000 words depending on the research type and complexity of the research niche or topic. That is why, in writing this section, you must enrich the content of your paper while maintaining readability and coherence for the benefit of your readers.
The introduction houses the background of the study. This is the part of the paper where the entire context of the paper is established. We all know that the research context is important as it helps the readers understand why the paper is even conducted in the first place. Thus, the impression of having a well-established context can only be found in the introduction. Now that we know the gravity of creating a good introduction, let us now ask how long this section should be.
Generally speaking, the paper’s introduction is the longest among all the sections. Aside from establishing the context, the introduction must house the historical underpinnings of the study (important for case studies and ethnographic research), salient information about all the variables in the study (including their relationship with other variables), and related literature and studies that can provide insight into the novelty and peculiarities of the current research project.
To better understand the general composition of your research introduction, you may refer to the breakdown of this section below:
- Context Establishment and Introduction of Key Terms. In this subsection, you will articulate the background (historical, social, economic, psychological, etc.) of the study, including the ecosystem and the niche of your study interest. Furthermore, key terms found as variables in your study must be properly defined operationally and theoretically, if necessary. This comprises 20% of the introduction, or about 350-500 words.
- Related Literature and Studies. This is the subsection where you will criticize and integrate existing literature and studies to highlight the research gap that you intend to fill in. This comprises 25% of the introduction or about 450-600 words.
- Thesis statement. This part of the introduction can only be a paragraph or a couple of sentences, as this needs to be straightforward in relaying the identified research gap of the researchers. This comprises 5% of the introduction or about 90-100 words.
- Objectives or Research Questions. This subsection should outline the aims of the study, especially highlighting the inquiries that concern the relationship between the variables and how the research will progress to fill in the identified gaps. This comprises 5% of the introduction or about 90-100 words.
Theoretical and/or Conceptual Framework. These frameworks, when better assisted with a visual representation, guide the entire research process and provide a structure for understanding the relationship between the variables in the study. This comprises 10% of the introduction or about 180-200 words.

Elements of Good Research Writing Process– While Maintaining the Ideal Word Count!
- Clarity of Purpose . All types of writing, whether long or short, have its clarity of purpose as the heart of the text. In research, it is manifested through the inclusion of a research question or hypothesis. A good research paper does not repeat these elements without a purpose in mind. Though they can be emphasized throughout the development of the paper, the manner of doing it must be in a logical and purposeful way.
To guide you in writing process of doing so, you can ask yourself the following questions:
- Is the research question or hypothesis clearly stated?
- Does the introduction provide a clear overview of the purpose of the study?
- Does the purpose of the study repeat purposefully in the latter sections of the paper?
- Does the purpose of the study repeat logically in the latter sections of the paper?
2. Literature Review . When appending related literature and studies to your paper, the question must not revolve around whether you have supplied a lot of these pieces of information, making your article wordy and ideal. While the literature review adds a significant ‘chunk’ to your paper, with some paper formats even allotting a specific section for it, we must carefully consider what and how we can integrate them. It subsequently entails a critical analysis of a piece of literature or study and logically places it beside information that you desire to contest. As they say, a good literature review identifies knowledge gaps, highlights the author’s familiarity with the topic, and provides an overview of the research areas that show a disparity of agreement. In order to have these characteristics, you can ask yourself the following questions:
- Have I integrated relevant literature in my review?
- Have I placed it logically within a specific piece of information based on my presumption?
- Do they identify a concept or piece of information that is otherwise unknown to the field?
- Have I critically analyzed existing research to identify the research gap?
3. Logical Flow. Research will not be whole without its parts. Researchers must know how to tie everything together and ensure that each part is functional in itself and supplements with other parts. When dealing with a large body of text, the logical flow of the paper might be a considerable concern. Along with the confusion brought about by the wordiness and complexity of the topic, your readers might get lost because of incoherence and inconsistencies with the presentation of ideas, leading to them not reading your paper any further. Thus, while ensuring that you get the word count that you want, you might want to ask yourself these questions first:
- Does the introduction progress logically from the general background to the specific research question?
- Do the transition devices between sections and individual paragraphs of the body facilitate a smooth flow of ideas?
- Is there a clear hierarchy of ideas, with each paragraph contributing to the overall argument?
- Have I organized ideas in a way that makes the document easy to track?
- Have I pursued a logical sequence of presenting information?
4. Language Use and Style. Developing an academic language throughout your paper and maintaining a formal style of paper writing are all the more important in research writing process, and mind you, it can also help you increase your word count in a sustainable way! Incorporating this form of language and style into your paper entails more than just adding incoherent or overly manufactured words that may be viewed as fillers.
Strategies and known practices are said to hit multiple objectives without compromising the quality of the paper. You may expand your points by providing detailed explanations, introducing sufficient pieces of evidence that supports your claims, addressing counterargument through the presentation of related literature or studies, or clarifying complex concepts through chunking. To better understand these techniques, some of these questions might be helpful for you:
- Is the language clear and concise?
- Have I avoided unnecessary jargon or complex sentences or paragraphs?
- Have I avoided repetition or redundancy in the document?
- Have I expanded on key points by providing more detailed explanations and examples?
- Have I discussed nuances, variations, or exceptions to your results?
- Have I clarified some complex concepts or theories by chunking them into more detailed explanations?
How Long Should a Paragraph Be in a Research Paper?
For the research paper introduction section, a typical paragraph count will be 12-15, excluding the literature review section. Each subsection has 1-2 individual paragraphs. The mentioned section, on the other hand, can have paragraphs totaling 10-20. The conclusion section, on the other hand, is considered ideal if it has 5-7 paragraphs.
The paragraph count differs from one research type to another and even from one paper section to another. While it is worth deciding how long should a paragraph be in a research paper, it is more important to take note of the importance of ideas that should be included in each paragraph within a certain section. Take the review of the literature section as an example. The number of literature in the paper is said to be equal to the number of paragraphs allotted for the section. The reason lies in the uniformity of importance these pieces of literature hold, provided that they are closely associated with the research gap.
Do you feel like you need to pay for a research paper in hopes of finding a model article with the right paragraph count? Look no further, as Studyfy has its in-house research paper writing service that houses professionals and experts for your academic paper writing help. Its reasonable price– no deadline markup nor additional hidden charges– is tantamount to the expertise each writer has put into their work.
How Long Should a Conclusion Be in a Research Paper?
A concluding section, then, must only comprise 5% of the total word count of the paper, translating to approximately 400 words. This measly allocation may put you into a flimsy situation, especially if you do not know how to manage your vocabulary well and you keep on adding filler words that can sacrifice the importance of this section. Ditch the nonsense and construct your conclusion in a concise yet enriching way.
In concluding a research paper, it is important to always synthesize the big chunks of information examined in the data analysis and discussion. As worn out as the reader may look after reaching this point, the conclusion must act as a “mellow point” for them, entrusting them only with important pointers of the study. Sometimes, the conclusion part of the paper, even though less wordy than its preceding sections, may be difficult to construct, as you still need to have a basis– a scaffold– to refer to, and synthesizing, just like analyzing and evaluating data, is just as hard and laborious.
Through its superb essay writing services , plus applying top-notch quality assurance to academic papers like research articles, Studyfy can help you achieve the best for last with an effective, meaningful, and content-rich conclusion. Your readers will not think twice about using your study as a model for their own works!
How Long is a Research Paper in terms of its Various Types?
As mentioned in the first part of the article, the word count of an academic paper is dependent on the type of research you wish to conduct. While the general word count has been given, we cannot deny the fact that this threshold is only an estimation. There might be a time when you are tasked to create a research article that is different from a standard IMRAD-structured (Introduction, Methodology, Results, Analysis, Discussion) research paper. You are in for a treat, as we will provide you with a cheat sheet for the word count of several types of write-ups in the realm of research:

Research Proposal
Specific Purpose/s: A preliminary outline that contains the research question, minimal literature review, methodology, and significance of the research undertaking.
"Word Count Range: 1500-3000 words"
Review Article
Specific Purpose/s: Review bodies of literature about an overarching topic or niche, analyze a particular section, synthesize according to certain themes, and identify knowledge gaps from the findings.
"Word Count Range: 5000-10,000 words"
Meta-Analysis
Specific Purpose/s: Involves the use of statistical analyses of multiple studies to provide a quantitative synthesis of the evidence.
"Word Count Range: 5000-15,000 words"
Specific Purpose/s: Presents an in-depth and intrusive analysis of a specific case, one which aims to illustrate a broader concept or novel phenomenon.
"Word Count Range: 1500-5000 words"
Conference Paper
Specific Purpose/s: Presents a brief introduction, salient research findings, and implications connected to a given theme by a conference or colloquium.
"Word Count Range: 2000-5000 words"
Dissertation
Specific Purpose/s: Regarded as a terminal scholarly requirement for doctorate students, this is an in-depth discussion of an otherwise original research finding, often written in chapters. It contributes significantly to the body of knowledge of a particular study of interest.
"Word Count Range: 50,000-100,000 words (depending on the institution)"
Are you contemplating buying research papers of different types? Studyfy got your back! Its roster of writers and editing experts leaves no space for errors, ensuring that both quality and quantity– that’s right: content and word count are not compromised. The variety of expertise within ensures that all research and scholarly works are delivered to your liking. Pay less– no hidden charges and markups while you enjoy the best quality of writing with Studyfy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long is the introduction in a research paper.
AThe introduction takes up about 30-40% of the entire paper since the context and research background should be specified and further discussed. For a general academic paper with 4000 words, the introduction must be approximately 1500 words. You can do the math for the rest!
How long is a research paper, considering that there are many of them?
There is no one-size-fits-all guideline in determining the word count of a plethora of research papers in the world. Although there is an accepted word count range for each research type (as presented in the previous section), there are several factors that should likewise be considered in determining the word count: specific guidelines set by the institution you are working with, the complexity of the topic, audience, and depth of analysis.
Do I have to include all of the prescribed subsections of the introduction to increase the word count?
While the prescribed subsections have significant functions in the research paper introduction, some of them are not required to be included. The decisions depend on the type of research you wish to conduct and the external guidelines that you might need to follow. Some disciplines, such as social sciences, require a research article to have a theoretical framework, whereas others do not. Some research papers follow the standard IMRAD paper format that infuses the literature review section into the introduction, while the Germanic Thesis paper format, for example, regards the former as a separate section.
How do I increase my word count without compromising the quality of my research paper?
The dilemma of choosing quality over quantity has long been debunked: you do not have to choose in the first place. All you need is a set of writing strategies and techniques that will target those two birds using one stone. You may provide more detail to some ambiguous or novel terms. You can add additional works of literature to some concepts that promote abstraction. You may include examples or empirical pieces of evidence to create a more concrete representation of a concept or theory. Lastly, you may use subheadings to efficiently allocate word count for your chosen discussion topics.
Why is it important to track the word count of a research paper?
There are various reasons why we need to do it. Some institutions that publish scholarly journals follow certain guidelines in word count as one of the primary requirements. A specified limit enables researchers to allocate the number of words to several sections of their writing efficiently. Most institutions also use paper length as a predictor of publication cost. The longer the word count is, the costlier the publication will be. Lastly, reading engagement is affected by word count, as readers tend to shy away from reading an article that is long, boring, and insubstantial.
Can a writing service help me achieve my goals of writing within the right word count range?
Certainly! Studyfy offers several academic services, including writing services and research papers for sale . Understanding your various writing needs, writers can cater to the needed style, word count, formatting, and any other aspects so that you can have the best quality write-up without having to fear extra charges and big markups.
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications. If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms, including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies, or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data, conducting interviews, or doing field research.
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research. Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research. Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
alwaysresearching.com
never stop your research process
What is the normal research paper length.
Research papers are popular for frightening students due to the many hours and hard effort needed. Fortunately, there are several ways to assist you through them. One of them is by understanding the basics, like how to conduct research and the standard length of a research paper.
You’ll discover that if you know the research paper length and how much research you’ll have to do, they’re not that unpleasant to undertake.
In this article, you’ll find the general guidelines for the length of an academic research paper. We’ll also look at the research paper paragraph length and how many pages you can fit your research into.
How many words should a research paper be?
First, let’s begin with the average word count of the research.
How many words are sufficient? A thousand? Or a lot more? To be clear, there’s no general answer specific to all fields. Factors like topics chosen, fields of study, and instructions from an academic professional come into play.
However, a research paper can be between 4000 to 6000 words on average. In some fields, that may get up to 8000 or even more.
How long is a research paper in high school?
How many pages is a research paper in high school? Research papers are often called term papers, and most high school instructors expect their pupils to produce 3 to 5 pages of them.
They are usually given during a semester and sometimes may be up to 5 and 7 pages long if they are final papers.
How long is a short research paper?
A short research paper can be between 2000 to 3000 words long. These are often seen in high school research papers mentioned above. In fewer cases, they can be for college studies.
How long is a research paper: length guide
The length of a research paper varies depending on the stage of education, course of study, and departmental guidelines. In addition, of course, the volume of relevant findings and the length of your conclusion and discussion can also play a part. But these are often personal factors.
However, academic pieces like essays are usually shorter than research papers or theses.
Your research paper assignment will often come with straightforward guidelines on the pages or word count range it is expected to fall within.
For instance, you could be given a paper that should fall between 4500–5000 words or 20–25 pages. If you’re not given a specific range or limit, don’t forget to confirm with your instructor.
A research paper is often divided into:
- Introduction : 15% of the final word count.
- Methods : 35% of the final word count.
- Analysis and Results : 30% of the final word count.
- Discussion : 20% of the final word count.
To answer the question, “how long is a typical research paper?” We intend to look at them through various lenses. The ideal length of a research paper should be up to 8000 words. That means without the references and abstract sections, and you should have over 150 sentences and 30 paragraphs.
Although there are no hard and fast rules for choosing the length of individual paragraphs in a research paper, the most common length is between 90 and 130 words. Any paragraph under 90 words is judged insufficient to support an argument, whereas any paragraph above 130 words is seen as over-inflated.
It is also worth noting that the length of the written piece dictates the paragraph lengths. Therefore, when the document is brief, the paragraphs should be similar and vice versa.
On the other hand, a paragraph should include more than four sentences. This is because some topics in specific fields may require lengthier paragraphs to add facts and statistics to your work. And because every section should concentrate on a single concept, the length of a paragraph should be dictated by its supporting ideas.
For example, if an explanation demands detailed evidence in the form of statistics, illustrations, quotations, examples, and definitions, it would naturally be longer.
However, very brief paragraphs also exist in papers of roughly 2,000 words. These can be frequent and large papers of over 10,000 words. The type of paper and course of study often cause these drastic changes.
The average length of a research paper will always differ because of dissimilar types, structures, topics, and instructions. When giving precise specifications for your research paper length, tailor your research to meet its requirements. Remember to avoid adding irrelevant ideas just to beef up your writing. Stick to concise and rich ideas.

You Might Also Like

Best Way to Organize Research and Write a Perfect Paper
Guide on how to write results and discussion in a research paper, term paper help guide for your perfect piece, leave a reply cancel.
Jerz's Literacy Weblog (est. 1999)
Short research papers: how to write academic essays.
Jerz > Writing > Academic > Research Papers [ Title | Thesis | Blueprint | Quoting | Citing | MLA Format ]
This document focuses on the kind of short, narrowly-focused research papers that might be the final project in a freshman writing class or 200-level literature survey course.
In high school, you probably wrote a lot of personal essays (where your goal was to demonstrate you were engaged) and a lot of info-dump paragraphs (where your goal was to demonstrate you could remember and organize information your teacher told you to learn).
How is a college research essay different from the writing you did in high school?
This short video covers the same topic in a different way; I think the video and handout work together fairly well.
The assignment description your professor has already given you is your best source for understanding your specific writing task, but in general, a college research paper asks you to use evidence to defend some non-obvious, nuanced point about a complex topic.
Some professors may simply want you to explain a situation or describe a process; however, a more challenging task asks you to take a stand, demonstrating you can use credible sources to defend your original ideas.

- Choose a Narrow Topic
- Use Sources Appropriately
Avoid Distractions
Outside the classroom, if I want to “research” which phone I should buy, I would start with Google.
I would watch some YouTube unboxing videos, and I might ask my friends on social media. I’d assume somebody already has written about or knows about the latest phones, and the goal of my “research” is to find what the people I trust think is the correct answer.
An entomologist might do “research” by going into the forest, and catching and observing hundreds or thousands of butterflies. If she had begun and ended her research by Googling for “butterflies of Pennsylvania” she would never have seen, with her own eyes, that unusual specimen that leads her to conclude she has discovered a new species.
Her goal as a field researcher is not to find the “correct answer” that someone else has already published. Instead, her goal is to add something new to the store of human knowledge — something that hasn’t been written down yet.
As an undergraduate with a few short months or weeks to write a research paper, you won’t be expected to discover a new species of butterfly, or convince everyone on the planet to accept what 99.9% of scientists say about vaccines or climate change, or to adopt your personal views on abortion, vaping, or tattoos.
But your professor will probably want you to read essays published by credentialed experts who are presenting their results to other experts, often in excruciating detail that most of us non-experts will probably find boring.
Your instructor probably won’t give the results of a random Google search the same weight as peer-reviewed scholarly articles from academic journals. (See “ Academic Journals: What Are They? “)
The best databases are not free, but your student ID will get you access to your school’s collection of databases, so you should never have to pay to access any source. (Your friendly school librarian will help you find out exactly how to access the databases at your school.)
1. Plan to Revise
Even a very short paper is the result of a process.
- You start with one idea, you test it, and you hit on something better.
- You might end up somewhere unexpected. If so, that’s good — it means you learned something.
- If you’re only just starting your paper, and it’s due tomorrow, you have already robbed yourself of your most valuable resource — time.
Showcase your best insights at the beginning of your paper (rather than saving them for the end).
You won’t know what your best ideas are until you’ve written a full draft. Part of revision involves identifying strong ideas and making them more prominent, identifying filler and other weak material, and pruning it away to leave more room to develop your best ideas.
- It’s normal, in a your very first “discovery draft,” to hit on a really good idea about two-thirds of the way through your paper.
- But a polished academic paper is not a mystery novel. (A busy reader will not have the patience to hunt for clues.)
- A thesis statement that includes a clear reasoning blueprint (see “ Blueprinting: Planning Your Essay “) will help your reader identify and follow your ideas.
Before you submit your draft, make sure the title, the introduction, and the conclusion match . (I am amazed at how many students overlook this simple step.)
2. Choose a Narrow Topic
A short undergraduate research paper is not the proper occasion for you to tackle huge issues, such as, “Was Hamlet Shakespeare’s Best Tragedy?” or “Women’s Struggle for Equality” or “How to Eliminate Racism.” You won’t be graded down simply because you don’t have all the answers right away. The trick is to zoom in on one tiny little part of the argument .
Short Research Paper: Sample Topics
How would you improve each of these paper topics? (My responses are at the bottom of the page.)
- Environmentalism in America
- Immigration Trends in Wisconsin’s Chippewa Valley
- Drinking and Driving
- Local TV News
- 10 Ways that Advertisers Lie to the Public
- Athletes on College Campuses
3. Use Sources Appropriately
Unless you were asked to write an opinion paper or a reflection statement, your professor probably expects you to draw a topic from the assigned readings (if any).
- Some students frequently get this backwards — they write the paper first, then “look for quotes” from sources that agree with the opinions they’ve already committed to. (That’s not really doing research to learn anything new — that’s just looking for confirmation of what you already believe.)
- Start with the readings, but don’t pad your paper with summary .
- Many students try doing most of their research using Google. Depending on your topic, the Internet may simply not have good sources available.
- Go ahead and surf as you try to narrow your topic, but remember: you still need to cite whatever you find. (See: “ Researching Academic Papers .”)
When learning about the place of women in Victorian society, Sally is shocked to discover women couldn’t vote or own property. She begins her paper by listing these and other restrictions, and adds personal commentary such as:
Women can be just as strong and capable as men are. Why do men think they have the right to make all the laws and keep all the money, when women stay in the kitchen? People should be judged by what they contribute to society, not by the kind of chromosomes they carry.
After reaching the required number of pages, she tacks on a conclusion about how women are still fighting for their rights today, and submits her paper.
- during the Victorian period, female authors were being published and read like never before
- the public praised Queen Victoria (a woman!) for making England a world empire
- some women actually fought against the new feminists because they distrusted their motives
- many wealthy women in England were downright nasty to their poorer sisters, especially the Irish.
- Sally’s paper focused mainly on her general impression that sexism is unfair (something that she already believed before she started taking the course), but Sally has not engaged with the controversies or surprising details (such as, for instance, the fact that for the first time male writers were writing with female readers in mind; or that upperclass women contributed to the degradation of lower-class women).
On the advice of her professor, Sally revises her paper as follows:
Sally’s focused revision (right) makes specific reference to a particular source , and uses a quote to introduce a point. Sally still injects her own opinion, but she is offering specific comments on complex issues, not bumper-sticker slogans and sweeping generalizations, such as those given on the left.
Documenting Evidence
Back up your claims by quoting reputable sources . If you write”Recent research shows that…” or “Many scholars believe that…”, you are making a claim. You will have to back it up with authoritative evidence. This means that the body of your paper must include references to the specific page numbers where you got your outside information. (If your document is an online source that does not provide page numbers, ask your instructor what you should do. There might be a section title or paragraph number that you could cite, or you might print out the article and count the pages in your printout.)
Avoid using words like “always” or “never,” since all it takes is a single example to the contrary to disprove your claim. Likewise, be careful with words of causation and proof. For example, consider the claim that television causes violence in kids. The evidence might be that kids who commit crimes typically watch more television than kids who don’t. But… maybe the reason kids watch more television is that they’ve dropped out of school, and are unsupervised at home. An unsupervised kid might watch more television, and also commit more crimes — but that doesn’t mean that the television is the cause of those crimes.
You don’t need to cite common facts or observations, such as “a circle has 360 degrees” or “8-tracks and vinyl records are out of date,” but you would need to cite claims such as “circles have religious and philosophical significance in many cultures” or “the sales of 8-track tapes never approached those of vinyl records.”
Don’t waste words referring directly to “quotes” and “sources.”
If you use words like “in the book My Big Boring Academic Study , by Professor H. Pompous Windbag III, it says” or “the following quote by a government study shows that…” you are wasting words that would be better spent developing your ideas.
In the book Gramophone, Film, Typewriter , by Fredrich A. Kittler, it talks about writing and gender, and says on page 186, “an omnipresent metaphor equated women with the white sheet of nature or virginity onto which a very male stylus could inscribe the glory of its authorship.” As you can see from this quote, all this would change when women started working as professional typists.
The “it talks about” and “As you can see from this quote” are weak attempts to engage with the ideas presented by Kittler. “In the book… it talks” is wordy and nonsensical (books don’t talk).
MLA style encourages you to expend fewer words introducing your sources , and more words developing your own ideas. MLA style involves just the author’s last name, a space ( not a comma), and then the page number. Leave the author’s full name and the the title of the source for the Works Cited list at the end of your paper. Using about the same space as the original, see how MLA style helps an author devote more words to developing the idea more fully:
Before the invention of the typewriter, “an omnipresent metaphor” among professional writers concerned “a very male stylus” writing upon the passive, feminized “white sheet of nature or virginity” (Kittler 186). By contrast, the word “typewriter” referred to the machine as well as the female typist who used it (183).
See “ Quotations: Integrating them in MLA-Style Papers. ”
Stay On Topic
It’s fairly normal to sit and stare at the computer screen for a while until you come up with a title, then pick your way through your topic, offering an extremely broad introduction (see glittering generalities , below)..
- You might also type in a few long quotations that you like.
- After writing generalities and just poking and prodding for page or two, you will eventually hit on a fairly good idea .
- You will pursue it for a paragraph or two, perhaps throwing in another quotation.
- By then, you’ll realize that you’ve got almost three pages written, so you will tack on a hasty conclusion.
Hooray, you’ve finished your paper! Well, not quite…
- At the very least, you ought to rewrite your title and introduction to match your conclusion , so it looks like the place you ended up was where you were intending to go all along. You probably won’t get an A, because you’re still submitting two pages of fluff; but you will get credit for recognizing whatever you actually did accomplish.
- To get an A, you should delete all that fluff, use the “good idea” that you stumbled across as your new starting point , and keep going. Even “good writers” have to work — beefing up their best ideas and shaving away the rest, in order to build a whole paper that serves the good idea, rather than tacking the good idea on at the end and calling it a day.
See: Sally Slacker Writes a Paper , and Sally’s Professor Responds
Avoid Glittering Generalities
Key: Research Paper Topics
15 thoughts on “ Short Research Papers: How to Write Academic Essays ”
Hi, I was searching for some information on how to write quality academic paper when I came across your awesome article on Short Research Papers: How to Writer Academic Essays ( https://jerz.setonhill.edu/writing/academic1/short-research-papers/ ) Great stuff!!! I especially like the way you recommend sticking to the 4 basics of writing academic essays. Very few students have mastered how to avoid distractions and focus on a single topic. Many students think that the broad, sweeping statements could give them better grades but they are wrong.
However, I came across a few links that didn’t seem to be working for you. Want me to forward you the short list I jotted down? Cheers Elias
I see some broken links in the comments, but otherwise I’m not sure what you mean.
I found the part about not using my personal opinion or generalities to be very helpful. I am currently writing a 2 page paper and was having a hard time keeping it short. Now I know why. Thanks. Stick to the facts.
This seem to be old but very relevant. Most of what you have stated are things my professor has stated during class trying to prepare us to write a short thesis reading this information verses hearing it was very helpful. You have done an awesome job! I just hope I can take this and apply it to my papers!
Great Post! Thank u!
Thank you for all your effort and help. You´ve taught me a number of things, especially on what college professors´ look for in assigning students short research papers. I am bookmarking your page, and using it as a reference.
Thank you kindly. YOU´VE HELPED A LOST STUDENT FIND HER WAY!
I appreaciate all the help your web site has given to me. I have referred to it many times. I think there may be a typo under the headline of AVOID GLITTERING GENERALITIES: “Throughout the ages, mankind has found many uses for salt. Ancient tribes used it preserve meat;” This is in no way a slight – I thought you might want to know. Please forgive me if I am incorrect. Thank you again – you rock!
You are right — I’ll fix it the next time I’m at my desktop. Thank you!
i would like to say thank you for your detailed information even though it takes time to read as well as we’ve got learnings out from it . even though it’s holiday next week our teacher assigned us to make a short research paper in accordance of our selected topic ! I’m hoping that we can make it cause if we can’t make it, right away, for sure we will get a grade’s that can drop our jaws ! :) ♥ tnx ! keep it up ! ♪♪
Sorry I have not done this for years
Hello I am the mother of a high school student that needs help doing a paper proposal for her senior project. Her topic is Photography. To be honest I have done this for years and I am trying to help, but i am completely lost. What can you recommend since she told me a little late and the paper is due tomorrow 11/11/11.
This page is designed for college students, but I am sure your daughter’s teacher has assigned readings that will guide your daughter through her homework.
Any paper that your daughter writes herself, even if it is late, will be a valuable learning experience — showing her the value of managing her time better for the next time, and preparing her for the day when she will have to tackle grown-up problems on her own.
I am having a hard time with my government essay. I am 55 taking a college course for the first time, and I barely passed high school. Last year I took this course wrote the essay, and did many things wrong. It was all in the typing. I had good story line, excellent site words, and good points of arguments. It wasn’t right on paper. My format is off. Where can I find and print a format. also I need to learn site words.
Most teachers will provide a model to follow. If it’s not already part of the assignment instructions, you could ask your prof. Better yet, bring a near-complete draft to your prof’s office hours, a few days before the due date, and ask for feedback. Your school probably has a writing center or tutoring center, too.
I would like to thank you for such detailed information. I am not a native speaker and I am doing a research paper;so, as you may think, it is really a hard job for me. A friend of mine who saw my draft of Lit. Rev asked me what type of citation format i was using, MLA or APA and I was puzzeled; then I decided to check the net and came across to this! It is being such a help Elsa
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How Long Should A Research Paper Be?

You must have known what research looks like. It has a particular structure that should be followed at any cost since it is the criteria for writing a research paper . Several questions come into the mind of students such as how to write a research paper, how long should a research paper be, etc.
That’s why we have brought a series of research writing and addressing different questions related to it. This blog aims to answer queries about the duration your research should ideally take, including insights on how to write an 8-page paper effectively. Although it depends upon the guidelines given by your teacher, there is also a standard length of research writing. Let’s dive in and learn everything about the ideal word count of any research.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper is an essay that is based on your investigational work you have completed or will complete on just one or many specific topics of a specific discipline. Research or investigation essays are lengthy depending on the scope and extensive nature of the topic.
It’s just an analysis of the topic from your own perspective. A student or a reader present facts and their theories in front of the audience to inform them about the specific subject matter. If you dont know how long is a research paper, here we will take you on a deeper tour to help you understand these essays thoroughly.
What is the Standard Length of a Research Paper?
Discussing the standard length of a paper, it’s important to note that it varies depending on the specific instructions given to each student and the structural requirements related to their chosen finance research topics . It is never a fixed one for all types of papers yet, there are some conditions and possibilities because of which the word count varies.
Research that has a thesis statement only requires 2 to 3 arguments to be proved and will be summed up in 500 to 700 words. After providing the introduction and a little background on the research, you can directly shift to mentioning the arguments and claims so you may prove the statement and complete the research.
Some research requires detailed analysis and interpretation of the findings. This kind of paper has several stages such as introduction, background, thesis statement, objective, research questions, literature review, research methodology, data collection, discussion, findings, conclusion, and bibliography. Such research easily crosses 5000 words because it is important to discuss everything about the topic.
So it entirely depends upon the structure you are following to write the research. It could be as long as just 500 words, or 5000 words, and even more. It all varies therefore you must be prepared for writing a paper no matter how long it should be.
How long is introduction in research paper?
Many students wonder how long should an introduction be in a research paper? The simple answer to this query is as short as possible that justify the requirements and employ all the methods that are necessary for coveying your message.
Typically, a standard length of introductory paragraph is 300-500 words. If your topic needs more than the standard word count than always ask for suggestion from your professor on first priority. We hope now you know how long should an introduction be for a research paper.
Why Considering Length of a Research Paper is Important
Identifying the length of research is important because of so many reasons. You might have never realized the significance of considering how long a paper should be, so here we go with some of the vital reasons.
1. Going Extra May Ruin Your Research
You cannot write more than is required in research. If you are doing so then you are automatically ignoring the quality measures of writing a paper. If you are writing more than words than is required then there are chances you are going to submit a poor quality research work.
2. Sticking to the Guidelines is Important
When your guidelines have mentioned 1000 words maximum and you are submitting research of 2000 words, you already know what wrong you have done. If you are not sticking to the guidelines it will result in deduction of marks, fall in grades, and repetition of the class course.
3. Having a Balance is Good
It is necessary to keep a balance between the word count of all the headings. Without this much-needed balance, you might end up submitting a poor paper that has a longer introduction, and a shorter explanation of the findings. That’s why attaining a balance is important in your research word count.
4. Delivering Quality Research is the Criteria
When you are delivering quality content, you will be appreciated no matter what. If you consider the length of your research, you are one step forward in delivering quality research work to your teacher.
How Long Should a Research Paper Be?
This question is valid and one of the frequently asked questions by the students of high school and college. It is also important to know before you start working on your paper. Don’t forget to read the instructions provided by your teacher, however, we have more suggestions for you regarding the length of the research.
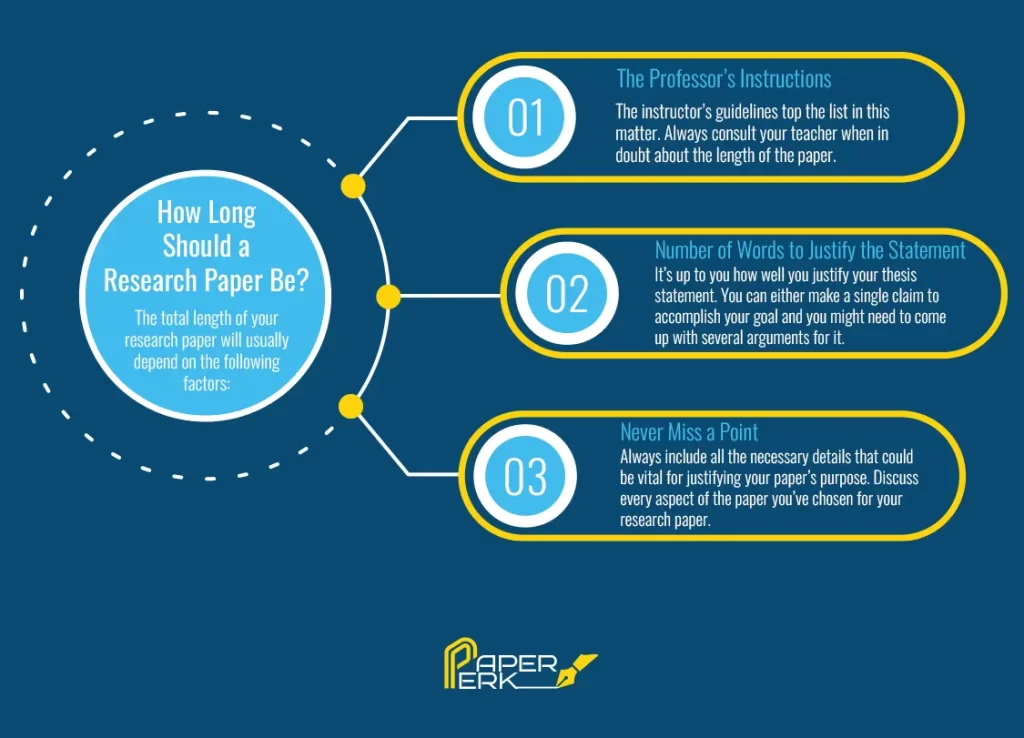
1. It All Depends On Your Teacher First
Your teacher indeed decides what should be the ideal length of your research. They have given some guidelines to you and you need to follow them. The teachers always know the best and they will suggest to you how long your essay should be.
Some teachers have kept a certain word limit for the paper while others provide you complete freedom to write as long as you want. It is necessary to figure out what’s best for your research. In high schools, a standard length of any research is a maximum of 7 to 8 pages while the minimum should be 5 pages.
2. Check How Much Length is Required to Justify Your Statement
Sometimes it is based on the thesis for research paper . From the part of the abstract to the conclusion, there must be a balance between the word count of every heading. It is your responsibility as a writer to track the word count when you are trying to justify your thesis by giving several arguments and claims.
If you have decided how many arguments it will take to prove your thesis, then you have already finalized the length of your research. All you have to do is prepare everything in advance and see if you are proving your point within 5 or 8 pages.
3. It Shouldn’t Miss Any Point
A researcher must be discussing all the standard details that could justify the purpose of writing the paper. It must have all the headings properly discussed. Since all the points must be 100% clear in the research, deciding on a word limit in the very beginning could be a little hard.
But it is not impossible to identify by making an outline and checking how many pages will be covered in writing about a certain topic. All you have to do is take care that no point is missing in the research. Cutting the research short and trying to discuss facts to the exact point won’t help unless you are entirely explaining every aspect as required.
How Long a Research Paper Should be in Words?
You have learned something about the ideal length of research. When it comes to the word count, the criterion is a bit different. For example, if you need a Ph.D. research paper help , you must know the word count, typically between 70,000 to 80,000 words. As you suggest a specific word count for every heading, it is easier to guess how many words are required to summarize every title.
1. Assign Word Count To Each Heading
It is easier to assign a specific word count to every heading and then see what’s the total word length of the paper. For instance, you have to decide how many words will be used to cover your introduction section. A literature review is a second longer part after the discussion in every research so it is necessary to make an outline in advance and see what is the ideal length of every heading.
By giving a suggested word count to each heading you will make a clear pathway to follow during the complete research. It will be automatically easier for you to see how many words will be written to explain everything in your research thoroughly.
There are several sections in research that require certain word counts. Let’s see what word count is usually subjected to every heading.
An abstract for a research paper is the first main part that summarizes the research from the beginning to the conclusion. It contains the thesis, methodology, findings, and conclusion. So to explain the complete research in a few sentences, roughly 100 to 200 words will be required. So you may keep in mind the word count for an abstract is a maximum of 200 words.
● Introduction
An introduction is also a major part of the research and it is easily covered within 300 words maximum. Nothing else is required to explain terminologies or theories in this section. However, there are many opinion on this topic and each have different answers. That’s the prime reason students spend day and night on google looking for answers on their questions such as how long should introduction be for research paper. In short, 300 to 500 words are more than enough to state your thoughts in an into section and persuade your readers.
● Literature Review
The literature review is the second-longest section in any research. It contains a reference to the past research done in a similar field by other researchers. Every research must have 5 to 8 or even more past papers discussed in it. Therefore the ideal word count for this section is 500 to 1000 words.
● Methodology
The methodology section also has subcategories in which you have to explain the method of research, data collection, population, research implications, research Instrument, etc. It will take around 300 to 400 words and 100 words extra if you are discussing a theoretical framework too.
● Discussion and Interpretation
This is the longest part of any research since you have to explain all the findings and tell your readers how successfully you have managed to prove your thesis. This part is as long as 500 to 1000 or even 1500 words depending upon the results and the explanation required.
● Conclusion
A conclusion is a not so lengthy part of the paper. It is usually done within only 100 or 150 words maximum. It is that simple and thus it doesn’t need so many words to finish the argument and put a full stop.
2. Form a Paper Outline
Forming a paper outline in advance will also help you in understanding how many words you may need to cover every heading. This is one of the best ideas for assigning a particular word count to every heading of the paper.
As you’ll create a paper outline, you will get an instant idea of how many words you have to write in total to complete the research. Following this strategy will surely help you won’t be puzzled later during the writing process.
3. Ask Your Instructor
It is always a good idea to ask your teacher or instructor before following any word count technique. They have assigned you a paper so they can provide you with a better guideline to write your paper. It is the easiest method of identifying the word count of your research as it’s something recommended by an expert. Your job will become much easier and simpler by just seeking advice from your teacher.
How Long a Research Paper Should be for Middle School?
A middle school student is just starting with the research work and they are at the initial stages of learning how to conduct research. To understand how long a paper should be for middle school, you need to do some work.
1. Seek Expert Help
It is always better to seek help from an expert to decide the word limit of your essay when you’re a high school student. It could be your teacher or any senior student who will help you and guide how many pages you should write for your research. It is suggested to write 4 to 5 pages when you are a middle school student in writing a paper.
2. Do Research
It is always important to do some research and find out what’s best for your paper. Google is always open to helping students in learning new things without any limit. You can open the Google search engine, write down your query in the search bar and click on it.
Next, you will have everything to read and understand how a paper for middle school will work. By doing so you will automatically get an in-depth idea of crafting research for the initial level project.
After analyzing everything you can easily guess what should be the length of any research written by a middle school student. In pages, it is suggested to write 3 to 5 pages, but in words, it is recommended to write 400 to 500 words only. You can also hire a professional paper writing service to aid you in the process.
As it’s a new thing for the students to perform, they might get nervous easily. That’s why starting slow and taking baby steps towards learning research writing will help a lot.
How long Should a Research Paper be for High School?
High school is a different stage than middle school. You are mature, better at studies, and even more creative than before. This stage comes with its challenges and one of them is writing the research. If you are a new high school student we bet you don’t know much about paper writing at this level.
When a high school student writes a research paper, it’s usually written within 500 to 1000 words. It could be more than this word count or just 5 to 6 pages. The teacher’s instructions do matter a lot in this aspect and without them, you can’t understand the criteria of research writing. It takes a lot of research, consultation, and creativity to write a paper that stands out. The competition is even tougher in high schools so you know how tough it can get to write a research paper fast .
Your research will decide if you are going to pass the school or not. Many students stay stuck in a class because they are incapable of submitting a brilliant research paper. Most of the time it’s because they don’t know the standard guidelines for writing a paper.
They usually end up ignoring the pattern, writing incorrect information, or exceeding or limiting the length assigned for the research. So it’s better to keep in mind what is the better approach for research writing and how a high school student can learn to write it.
How Long Should a Research Paper be for College?
Have you ever thought about how long your research should be when you have finally reached college? It is the final stage of your education and writing research in this phase will require a lot of preparation. In college, you have to write the longest research papers because it is the standard of a paper written by a college student.
So how exactly long should research be for college? It starts with roughly 3000 words and goes up to 15000 words. 15000 words is a lot but students who are working on their thesis need a lot of details to justify and complete their research. Without doing this they are not getting passed at any cost so now you know why it is so important.
Different sections of the paper require their particular word count. It is sometimes difficult to identify but your teachers will always be there to guide you. Sometimes students are given the entire freedom to keep their essay length on their own. It helps them understand how easily they can prove their thesis either in a few or a lot of pages.
For newcomers in college unsure about the ideal length for research papers, utilizing Google is a great option to delve deeper into the nuances of research writing. It’s particularly helpful in exploring various guidelines related to history research topics . A lot of content is already published on the web which teaches the students almost everything they need.
We hope you know how long is a research paper, no matter if you are writing one for your middle school, high school, or college. All of them have different requirements and basic criteria that should be followed. We also hope this blog has helped you learn everything about deciding the word count or overall length of your research.
Our comment section is always open for your discussion and feedback. If you want to get in touch with us or discuss the topic more, just leave a comment in the given box. We would love to hear from our readers and see what they have in their minds after reading our blog.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples


Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts
An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes:
- an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to read the full paper;
- an abstract prepares readers to follow the detailed information, analyses, and arguments in your full paper;
- and, later, an abstract helps readers remember key points from your paper.
It’s also worth remembering that search engines and bibliographic databases use abstracts, as well as the title, to identify key terms for indexing your published paper. So what you include in your abstract and in your title are crucial for helping other researchers find your paper or article.
If you are writing an abstract for a course paper, your professor may give you specific guidelines for what to include and how to organize your abstract. Similarly, academic journals often have specific requirements for abstracts. So in addition to following the advice on this page, you should be sure to look for and follow any guidelines from the course or journal you’re writing for.
The Contents of an Abstract
Abstracts contain most of the following kinds of information in brief form. The body of your paper will, of course, develop and explain these ideas much more fully. As you will see in the samples below, the proportion of your abstract that you devote to each kind of information—and the sequence of that information—will vary, depending on the nature and genre of the paper that you are summarizing in your abstract. And in some cases, some of this information is implied, rather than stated explicitly. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , which is widely used in the social sciences, gives specific guidelines for what to include in the abstract for different kinds of papers—for empirical studies, literature reviews or meta-analyses, theoretical papers, methodological papers, and case studies.
Here are the typical kinds of information found in most abstracts:
- the context or background information for your research; the general topic under study; the specific topic of your research
- the central questions or statement of the problem your research addresses
- what’s already known about this question, what previous research has done or shown
- the main reason(s) , the exigency, the rationale , the goals for your research—Why is it important to address these questions? Are you, for example, examining a new topic? Why is that topic worth examining? Are you filling a gap in previous research? Applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data? Resolving a dispute within the literature in your field? . . .
- your research and/or analytical methods
- your main findings , results , or arguments
- the significance or implications of your findings or arguments.
Your abstract should be intelligible on its own, without a reader’s having to read your entire paper. And in an abstract, you usually do not cite references—most of your abstract will describe what you have studied in your research and what you have found and what you argue in your paper. In the body of your paper, you will cite the specific literature that informs your research.
When to Write Your Abstract
Although you might be tempted to write your abstract first because it will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s a good idea to wait to write your abstract until after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
What follows are some sample abstracts in published papers or articles, all written by faculty at UW-Madison who come from a variety of disciplines. We have annotated these samples to help you see the work that these authors are doing within their abstracts.
Choosing Verb Tenses within Your Abstract
The social science sample (Sample 1) below uses the present tense to describe general facts and interpretations that have been and are currently true, including the prevailing explanation for the social phenomenon under study. That abstract also uses the present tense to describe the methods, the findings, the arguments, and the implications of the findings from their new research study. The authors use the past tense to describe previous research.
The humanities sample (Sample 2) below uses the past tense to describe completed events in the past (the texts created in the pulp fiction industry in the 1970s and 80s) and uses the present tense to describe what is happening in those texts, to explain the significance or meaning of those texts, and to describe the arguments presented in the article.
The science samples (Samples 3 and 4) below use the past tense to describe what previous research studies have done and the research the authors have conducted, the methods they have followed, and what they have found. In their rationale or justification for their research (what remains to be done), they use the present tense. They also use the present tense to introduce their study (in Sample 3, “Here we report . . .”) and to explain the significance of their study (In Sample 3, This reprogramming . . . “provides a scalable cell source for. . .”).
Sample Abstract 1
From the social sciences.
Reporting new findings about the reasons for increasing economic homogamy among spouses
Gonalons-Pons, Pilar, and Christine R. Schwartz. “Trends in Economic Homogamy: Changes in Assortative Mating or the Division of Labor in Marriage?” Demography , vol. 54, no. 3, 2017, pp. 985-1005.
![how long is a short research paper “The growing economic resemblance of spouses has contributed to rising inequality by increasing the number of couples in which there are two high- or two low-earning partners. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the topic under study (the “economic resemblance of spouses”). This sentence also implies the question underlying this research study: what are the various causes—and the interrelationships among them—for this trend?] The dominant explanation for this trend is increased assortative mating. Previous research has primarily relied on cross-sectional data and thus has been unable to disentangle changes in assortative mating from changes in the division of spouses’ paid labor—a potentially key mechanism given the dramatic rise in wives’ labor supply. [Annotation for the previous two sentences: These next two sentences explain what previous research has demonstrated. By pointing out the limitations in the methods that were used in previous studies, they also provide a rationale for new research.] We use data from the Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) to decompose the increase in the correlation between spouses’ earnings and its contribution to inequality between 1970 and 2013 into parts due to (a) changes in assortative mating, and (b) changes in the division of paid labor. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The data, research and analytical methods used in this new study.] Contrary to what has often been assumed, the rise of economic homogamy and its contribution to inequality is largely attributable to changes in the division of paid labor rather than changes in sorting on earnings or earnings potential. Our findings indicate that the rise of economic homogamy cannot be explained by hypotheses centered on meeting and matching opportunities, and they show where in this process inequality is generated and where it is not.” (p. 985) [Annotation for the previous two sentences: The major findings from and implications and significance of this study.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-1.png)
Sample Abstract 2
From the humanities.
Analyzing underground pulp fiction publications in Tanzania, this article makes an argument about the cultural significance of those publications
Emily Callaci. “Street Textuality: Socialism, Masculinity, and Urban Belonging in Tanzania’s Pulp Fiction Publishing Industry, 1975-1985.” Comparative Studies in Society and History , vol. 59, no. 1, 2017, pp. 183-210.
![how long is a short research paper “From the mid-1970s through the mid-1980s, a network of young urban migrant men created an underground pulp fiction publishing industry in the city of Dar es Salaam. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the context for this research and announces the topic under study.] As texts that were produced in the underground economy of a city whose trajectory was increasingly charted outside of formalized planning and investment, these novellas reveal more than their narrative content alone. These texts were active components in the urban social worlds of the young men who produced them. They reveal a mode of urbanism otherwise obscured by narratives of decolonization, in which urban belonging was constituted less by national citizenship than by the construction of social networks, economic connections, and the crafting of reputations. This article argues that pulp fiction novellas of socialist era Dar es Salaam are artifacts of emergent forms of male sociability and mobility. In printing fictional stories about urban life on pilfered paper and ink, and distributing their texts through informal channels, these writers not only described urban communities, reputations, and networks, but also actually created them.” (p. 210) [Annotation for the previous sentences: The remaining sentences in this abstract interweave other essential information for an abstract for this article. The implied research questions: What do these texts mean? What is their historical and cultural significance, produced at this time, in this location, by these authors? The argument and the significance of this analysis in microcosm: these texts “reveal a mode or urbanism otherwise obscured . . .”; and “This article argues that pulp fiction novellas. . . .” This section also implies what previous historical research has obscured. And through the details in its argumentative claims, this section of the abstract implies the kinds of methods the author has used to interpret the novellas and the concepts under study (e.g., male sociability and mobility, urban communities, reputations, network. . . ).]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-2.png)
Sample Abstract/Summary 3
From the sciences.
Reporting a new method for reprogramming adult mouse fibroblasts into induced cardiac progenitor cells
Lalit, Pratik A., Max R. Salick, Daryl O. Nelson, Jayne M. Squirrell, Christina M. Shafer, Neel G. Patel, Imaan Saeed, Eric G. Schmuck, Yogananda S. Markandeya, Rachel Wong, Martin R. Lea, Kevin W. Eliceiri, Timothy A. Hacker, Wendy C. Crone, Michael Kyba, Daniel J. Garry, Ron Stewart, James A. Thomson, Karen M. Downs, Gary E. Lyons, and Timothy J. Kamp. “Lineage Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Proliferative Induced Cardiac Progenitor Cells by Defined Factors.” Cell Stem Cell , vol. 18, 2016, pp. 354-367.
![how long is a short research paper “Several studies have reported reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes; however, reprogramming into proliferative induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPCs) remains to be accomplished. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence announces the topic under study, summarizes what’s already known or been accomplished in previous research, and signals the rationale and goals are for the new research and the problem that the new research solves: How can researchers reprogram fibroblasts into iCPCs?] Here we report that a combination of 11 or 5 cardiac factors along with canonical Wnt and JAK/STAT signaling reprogrammed adult mouse cardiac, lung, and tail tip fibroblasts into iCPCs. The iCPCs were cardiac mesoderm-restricted progenitors that could be expanded extensively while maintaining multipo-tency to differentiate into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells in vitro. Moreover, iCPCs injected into the cardiac crescent of mouse embryos differentiated into cardiomyocytes. iCPCs transplanted into the post-myocardial infarction mouse heart improved survival and differentiated into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells. [Annotation for the previous four sentences: The methods the researchers developed to achieve their goal and a description of the results.] Lineage reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs provides a scalable cell source for drug discovery, disease modeling, and cardiac regenerative therapy.” (p. 354) [Annotation for the previous sentence: The significance or implications—for drug discovery, disease modeling, and therapy—of this reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-3.png)
Sample Abstract 4, a Structured Abstract
Reporting results about the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis, from a rigorously controlled study
Note: This journal requires authors to organize their abstract into four specific sections, with strict word limits. Because the headings for this structured abstract are self-explanatory, we have chosen not to add annotations to this sample abstract.
Wald, Ellen R., David Nash, and Jens Eickhoff. “Effectiveness of Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Potassium in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis in Children.” Pediatrics , vol. 124, no. 1, 2009, pp. 9-15.
“OBJECTIVE: The role of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis (ABS) in children is controversial. The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of high-dose amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate in the treatment of children diagnosed with ABS.
METHODS : This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Children 1 to 10 years of age with a clinical presentation compatible with ABS were eligible for participation. Patients were stratified according to age (<6 or ≥6 years) and clinical severity and randomly assigned to receive either amoxicillin (90 mg/kg) with potassium clavulanate (6.4 mg/kg) or placebo. A symptom survey was performed on days 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, and 30. Patients were examined on day 14. Children’s conditions were rated as cured, improved, or failed according to scoring rules.
RESULTS: Two thousand one hundred thirty-five children with respiratory complaints were screened for enrollment; 139 (6.5%) had ABS. Fifty-eight patients were enrolled, and 56 were randomly assigned. The mean age was 6630 months. Fifty (89%) patients presented with persistent symptoms, and 6 (11%) presented with nonpersistent symptoms. In 24 (43%) children, the illness was classified as mild, whereas in the remaining 32 (57%) children it was severe. Of the 28 children who received the antibiotic, 14 (50%) were cured, 4 (14%) were improved, 4(14%) experienced treatment failure, and 6 (21%) withdrew. Of the 28children who received placebo, 4 (14%) were cured, 5 (18%) improved, and 19 (68%) experienced treatment failure. Children receiving the antibiotic were more likely to be cured (50% vs 14%) and less likely to have treatment failure (14% vs 68%) than children receiving the placebo.
CONCLUSIONS : ABS is a common complication of viral upper respiratory infections. Amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate results in significantly more cures and fewer failures than placebo, according to parental report of time to resolution.” (9)
Some Excellent Advice about Writing Abstracts for Basic Science Research Papers, by Professor Adriano Aguzzi from the Institute of Neuropathology at the University of Zurich:

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)

The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation.
The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the reader. A study will only be accepted for publishing if you can ascertain that the available literature cannot answer your research question. So it is important to ensure that you have read important studies on that particular topic, especially those within the last five to ten years, and that they are properly referenced in this section. 1 What should be included in the research paper introduction is decided by what you want to tell readers about the reason behind the research and how you plan to fill the knowledge gap. The best research paper introduction provides a systemic review of existing work and demonstrates additional work that needs to be done. It needs to be brief, captivating, and well-referenced; a well-drafted research paper introduction will help the researcher win half the battle.
The introduction for a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your research topic
- Capture reader interest
- Summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Define your specific research problem and problem statement
- Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper. Some research paper introduction examples are only half a page while others are a few pages long. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper; its length depends on the size of your paper as a whole.
- Break through writer’s block. Write your research paper introduction with Paperpal Copilot
Table of Contents
What is the introduction for a research paper, why is the introduction important in a research paper, craft a compelling introduction section with paperpal. try now, 1. introduce the research topic:, 2. determine a research niche:, 3. place your research within the research niche:, craft accurate research paper introductions with paperpal. start writing now, frequently asked questions on research paper introduction, key points to remember.
The introduction in a research paper is placed at the beginning to guide the reader from a broad subject area to the specific topic that your research addresses. They present the following information to the reader
- Scope: The topic covered in the research paper
- Context: Background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in that particular area of research and the industry problem that can be targeted
The research paper introduction conveys a lot of information and can be considered an essential roadmap for the rest of your paper. A good introduction for a research paper is important for the following reasons:
- It stimulates your reader’s interest: A good introduction section can make your readers want to read your paper by capturing their interest. It informs the reader what they are going to learn and helps determine if the topic is of interest to them.
- It helps the reader understand the research background: Without a clear introduction, your readers may feel confused and even struggle when reading your paper. A good research paper introduction will prepare them for the in-depth research to come. It provides you the opportunity to engage with the readers and demonstrate your knowledge and authority on the specific topic.
- It explains why your research paper is worth reading: Your introduction can convey a lot of information to your readers. It introduces the topic, why the topic is important, and how you plan to proceed with your research.
- It helps guide the reader through the rest of the paper: The research paper introduction gives the reader a sense of the nature of the information that will support your arguments and the general organization of the paragraphs that will follow. It offers an overview of what to expect when reading the main body of your paper.
What are the parts of introduction in the research?
A good research paper introduction section should comprise three main elements: 2
- What is known: This sets the stage for your research. It informs the readers of what is known on the subject.
- What is lacking: This is aimed at justifying the reason for carrying out your research. This could involve investigating a new concept or method or building upon previous research.
- What you aim to do: This part briefly states the objectives of your research and its major contributions. Your detailed hypothesis will also form a part of this section.
How to write a research paper introduction?
The first step in writing the research paper introduction is to inform the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening statement. The second step involves establishing the kinds of research that have been done and ending with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to address. Finally, the research paper introduction clarifies how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses. If your research involved testing hypotheses, these should be stated along with your research question. The hypothesis should be presented in the past tense since it will have been tested by the time you are writing the research paper introduction.
The following key points, with examples, can guide you when writing the research paper introduction section:
- Highlight the importance of the research field or topic
- Describe the background of the topic
- Present an overview of current research on the topic
Example: The inclusion of experiential and competency-based learning has benefitted electronics engineering education. Industry partnerships provide an excellent alternative for students wanting to engage in solving real-world challenges. Industry-academia participation has grown in recent years due to the need for skilled engineers with practical training and specialized expertise. However, from the educational perspective, many activities are needed to incorporate sustainable development goals into the university curricula and consolidate learning innovation in universities.
- Reveal a gap in existing research or oppose an existing assumption
- Formulate the research question
Example: There have been plausible efforts to integrate educational activities in higher education electronics engineering programs. However, very few studies have considered using educational research methods for performance evaluation of competency-based higher engineering education, with a focus on technical and or transversal skills. To remedy the current need for evaluating competencies in STEM fields and providing sustainable development goals in engineering education, in this study, a comparison was drawn between study groups without and with industry partners.
- State the purpose of your study
- Highlight the key characteristics of your study
- Describe important results
- Highlight the novelty of the study.
- Offer a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
Example: The study evaluates the main competency needed in the applied electronics course, which is a fundamental core subject for many electronics engineering undergraduate programs. We compared two groups, without and with an industrial partner, that offered real-world projects to solve during the semester. This comparison can help determine significant differences in both groups in terms of developing subject competency and achieving sustainable development goals.
Write a Research Paper Introduction in Minutes with Paperpal
Paperpal Copilot is a generative AI-powered academic writing assistant. It’s trained on millions of published scholarly articles and over 20 years of STM experience. Paperpal Copilot helps authors write better and faster with:
- Real-time writing suggestions
- In-depth checks for language and grammar correction
- Paraphrasing to add variety, ensure academic tone, and trim text to meet journal limits
With Paperpal Copilot, create a research paper introduction effortlessly. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through how Paperpal transforms your initial ideas into a polished and publication-ready introduction.

How to use Paperpal to write the Introduction section
Step 1: Sign up on Paperpal and click on the Copilot feature, under this choose Outlines > Research Article > Introduction
Step 2: Add your unstructured notes or initial draft, whether in English or another language, to Paperpal, which is to be used as the base for your content.
Step 3: Fill in the specifics, such as your field of study, brief description or details you want to include, which will help the AI generate the outline for your Introduction.
Step 4: Use this outline and sentence suggestions to develop your content, adding citations where needed and modifying it to align with your specific research focus.
Step 5: Turn to Paperpal’s granular language checks to refine your content, tailor it to reflect your personal writing style, and ensure it effectively conveys your message.
You can use the same process to develop each section of your article, and finally your research paper in half the time and without any of the stress.
The purpose of the research paper introduction is to introduce the reader to the problem definition, justify the need for the study, and describe the main theme of the study. The aim is to gain the reader’s attention by providing them with necessary background information and establishing the main purpose and direction of the research.
The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs. Generally, it is one of the shorter sections of the paper as the reader is assumed to have at least a reasonable knowledge about the topic. 2 For example, for a study evaluating the role of building design in ensuring fire safety, there is no need to discuss definitions and nature of fire in the introduction; you could start by commenting upon the existing practices for fire safety and how your study will add to the existing knowledge and practice.
When deciding what to include in the research paper introduction, the rest of the paper should also be considered. The aim is to introduce the reader smoothly to the topic and facilitate an easy read without much dependency on external sources. 3 Below is a list of elements you can include to prepare a research paper introduction outline and follow it when you are writing the research paper introduction. Topic introduction: This can include key definitions and a brief history of the topic. Research context and background: Offer the readers some general information and then narrow it down to specific aspects. Details of the research you conducted: A brief literature review can be included to support your arguments or line of thought. Rationale for the study: This establishes the relevance of your study and establishes its importance. Importance of your research: The main contributions are highlighted to help establish the novelty of your study Research hypothesis: Introduce your research question and propose an expected outcome. Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper
Cite only works that are most relevant to your topic; as a general rule, you can include one to three. Note that readers want to see evidence of original thinking. So it is better to avoid using too many references as it does not leave much room for your personal standpoint to shine through. Citations in your research paper introduction support the key points, and the number of citations depend on the subject matter and the point discussed. If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review articles rather than the individual articles summarized in the review. A good point to remember when citing research papers in the introduction section is to include at least one-third of the references in the introduction.
The literature review plays a significant role in the research paper introduction section. A good literature review accomplishes the following: Introduces the topic – Establishes the study’s significance – Provides an overview of the relevant literature – Provides context for the study using literature – Identifies knowledge gaps However, remember to avoid making the following mistakes when writing a research paper introduction: Do not use studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research Avoid direct quoting Do not allow literature review to be the focus of this section. Instead, the literature review should only aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
Remember the following key points for writing a good research paper introduction: 4
- Avoid stuffing too much general information: Avoid including what an average reader would know and include only that information related to the problem being addressed in the research paper introduction. For example, when describing a comparative study of non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization, information related to the traditional methods and differences between traditional and non-traditional methods would not be relevant. In this case, the introduction for the research paper should begin with the state-of-the-art non-traditional methods and methods to evaluate the efficiency of newly developed algorithms.
- Avoid packing too many references: Cite only the required works in your research paper introduction. The other works can be included in the discussion section to strengthen your findings.
- Avoid extensive criticism of previous studies: Avoid being overly critical of earlier studies while setting the rationale for your study. A better place for this would be the Discussion section, where you can highlight the advantages of your method.
- Avoid describing conclusions of the study: When writing a research paper introduction remember not to include the findings of your study. The aim is to let the readers know what question is being answered. The actual answer should only be given in the Results and Discussion section.
To summarize, the research paper introduction section should be brief yet informative. It should convince the reader the need to conduct the study and motivate him to read further. If you’re feeling stuck or unsure, choose trusted AI academic writing assistants like Paperpal to effortlessly craft your research paper introduction and other sections of your research article.
1. Jawaid, S. A., & Jawaid, M. (2019). How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, 13(Suppl 1), S18.
2. Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: Looks matter!. Indian pediatrics, 53, 235-241.
3. Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific Manuscript1. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165-167.
4. Bavdekar, S. B. (2015). Writing introduction: Laying the foundations of a research paper. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 63(7), 44-6.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
Practice vs. Practise: Learn the Difference
Academic paraphrasing: why paperpal’s rewrite should be your first choice , you may also like, ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how....
How Long Should a Research Paper Be? A Short Read.
Table of contents.
Have you ever wondered, “how long should a research paper be?” As most people would. The length of a research paper can vary depending on numerous factors. Let’s dive into the heart of academic writing and unravel the mystery.
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper is an in-depth exploration of a specific topic based on original research. It requires a structured approach and is different from a term paper or a review article. With its foundation on a strong thesis statement, a research paper defends or challenges a particular standpoint using evidence from research.
Determining the Length of Each Part
- Title Page : Usually a single page, containing the research topic, your name, and other relevant details.
- Research Paper Introduction : About 10% of the total word count, introducing your research question and setting the stage.
- Literature Review : Varies widely but is essential to summarize existing research related to your topic.
- Methods Section : Explains your research methodology, generally 10-15% of the length of the paper.
- Results Section : Presents your findings. Its length can vary based on the complexity of the data.
- Discussion Section : Often combined with results, it interprets and explores the significance of your findings.
- References Section : Lists all in-text citations and other sources. Its length is contingent on the number of sources used.
Normal Length of a Research Paper
While the length can vary based on academic level and subject, most high school assignments range from 5-20 pages, whereas longer papers are common in higher academia. Always refer to the specific guidelines provided by instructors or journal article submissions.
Page Numbering and Paper Components
Research papers must be structured. The total number of pages depends on factors like spacing, font size, and word choice. APA and MLA are common citation styles that have distinct formatting requirements.
Why are Research Papers So Lengthy?
Research papers require an exhaustive exploration of a topic. From the literature review to the discussion section, each component has a purpose. Papers are long to ensure all main points, supporting evidence, and methodologies are thoroughly covered.
Top Tools for Research Paper Writing
- Cost : Varies based on subscription.
- Description : Perfect for those who appreciate an auditory approach to revising and proofreading, Speechify converts your research paper into speech. Ideal for getting a fresh perspective and catching filler words or awkward phrasings.
- Top 5 Features : Text-to-speech conversion, adjustable voice and speed settings, offline access, multi-device synchronization, PDF compatibility.
- Cost : Free basic version; Premium starts at $11.66/month.
- Description : Grammarly is a writer’s best friend, ensuring flawless English and optimal word choice. It proofreads your research paper, provides in-depth suggestions, and even checks for plagiarism.
- Top 5 Features : Advanced grammar check, plagiarism detector, tone suggestions, word choice recommendations, and clarity and engagement scores.
- Cost : Free.
- Description : An essential tool for academic writing, Zotero simplifies the citation process, helping users collect, organize, and cite their sources. It supports multiple citation styles, including APA, MLA, and more.
- Top 5 Features : Source organization, automatic in-text citations, bibliography and references section creation, integration with word processors, and online syncing.
- Cost : Starts at $249.95 (students get discounts).
- Description : Tailored for longer papers and academic research, EndNote provides tools to search, organize, and share research. It’s particularly useful for creating a paper outline, managing references for journal articles, and maintaining a coherent thesis statement.
- Top 5 Features : Extensive reference library, manuscript matcher, PDF annotations, collaboration tools, and Microsoft Word integration.
- Cost : Free basic version; Premium at $7.99/month.
- Description : Ideal for the brainstorm phase of the writing process, Evernote lets you capture notes, articles, and images on any device, helping to keep your original research and main points organized.
- Top 5 Features : Note-taking, web clipper, templates, search handwriting feature, and document scanning.
- Description : A blend of a social network and a reference manager, Mendeley helps academics and students collaborate, share findings, and keep track of the latest research articles in the humanities and other fields.
- Top 5 Features : Annotated PDFs, academic social network, reference manager, citation plugin, and job and conference recommendations.
- Cost : $49 for standard license.
- Description : Perfect for drafting, Scrivener aids in the paper writing journey, allowing for easy reorganization, tracking changes, and breaking the research paper into manageable sections like the methods section, results and discussion, and research paper introduction.
- Top 5 Features : Corkboard outlining, full-screen writing mode, document snapshots, compiling and exporting, and customizable templates.
- Cost : Pricing varies based on institution’s agreement.
- Description : A staple in academia, Turnitin ensures the authenticity of your academic paper. It checks for similarity against a massive database, ensuring your work is plagiarism-free and based on in-depth original research.
- Top 5 Features : Plagiarism checking, grading tools, peer review assignments, feedback studio, and paper database.
- Cost : Free basic plan; Personal plan at $4.99/month.
- Description : Visual thinkers will appreciate MindMeister. Before even embarking on your first draft, this tool allows you to create mind maps to visualize and structure your research topic, ensuring no main points or supporting evidence are missed.
- Top 5 Features : Mind mapping, task management, presentation mode, customizable designs, and real-time collaboration.
Each tool brings a unique touch to the research paper journey, from the first brainstorm to the final proofread. Ensure your paper stands out in terms of content, structure, and authenticity with these powerful aids.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Research papers will depend on the field and academic level. However, dissertations and theses from Ph.D. candidates can extend to several hundred pages.
- The number varies depending on the academic level and subject but generally ranges from 5 pages in high school to upwards of 30 pages in higher academia.
- It depends on the research topic, depth, and prior knowledge. Weeks to months is common.
- A thorough 15-page research paper can take several weeks, factoring in research, drafting, revising, and proofreading.
- Approximately a month or more, depending on the depth and complexity of the topic.
- It depends on the assignment guidelines and academic level. Always adhere to provided specifications.
- Previous How to Get a Research Paper Done Fast
- Next Text to Video AI: Understanding How Video Can be Created from Text

Cliff Weitzman
Cliff Weitzman is a dyslexia advocate and the CEO and founder of Speechify, the #1 text-to-speech app in the world, totaling over 100,000 5-star reviews and ranking first place in the App Store for the News & Magazines category. In 2017, Weitzman was named to the Forbes 30 under 30 list for his work making the internet more accessible to people with learning disabilities. Cliff Weitzman has been featured in EdSurge, Inc., PC Mag, Entrepreneur, Mashable, among other leading outlets.
Recent Blogs

Is Text to Speech HSA Eligible?

Can You Use an HSA for Speech Therapy?

Surprising HSA-Eligible Items

Ultimate guide to ElevenLabs

Voice changer for Discord

How to download YouTube audio
Speechify 3.0 is the Best Text to Speech App Yet.

Voice API: Everything You Need to Know

Best text to speech generator apps

The best AI tools other than ChatGPT

Top voice over marketplaces reviewed

Speechify Studio vs. Descript

Everything to Know About Google Cloud Text to Speech API

Source of Joe Biden deepfake revealed after election interference

How to listen to scientific papers

How to add music to CapCut

What is CapCut?

VEED vs. InVideo

Speechify Studio vs. Kapwing

Voices.com vs. Voice123

Voices.com vs. Fiverr Voice Over

Fiverr voice overs vs. Speechify Voice Over Studio

Voices.com vs. Speechify Voice Over Studio

Voice123 vs. Speechify Voice Over Studio

Voice123 vs. Fiverr voice overs

HeyGen vs. Synthesia

Hour One vs. Synthesia

HeyGen vs. Hour One

Speechify makes Google’s Favorite Chrome Extensions of 2023 list

How to Add a Voice Over to Vimeo Video: A Comprehensive Guide
Speechify text to speech helps you save time
Popular blogs, the best celebrity voice generators in 2024.

YouTube Text to Speech: Elevating Your Video Content with Speechify
The 7 best alternatives to synthesia.io, everything you need to know about text to speech on tiktok.

The 10 best text-to-speech apps for Android

How to convert a PDF to speech
The top girl voice changers.

How to use Siri text to speech

Obama text to speech
Robot voice generators: the futuristic frontier of audio creation, pdf read aloud: free & paid options, alternatives to fakeyou text to speech, all about deepfake voices, tiktok voice generator.

Text to speech GoAnimate
The best celebrity text to speech voice generators, pdf audio reader, how to get text to speech indian voices, elevating your anime experience with anime voice generators, best text to speech online, top 50 movies based on books you should read, download audio, how to use text-to-speech for quandale dingle meme sounds.

Top 5 apps that read out text
The top female text to speech voices, female voice changer, sonic text to speech voice generator online, best ai voice generators – the ultimate list, voice changer.

Only available on iPhone and iPad
To access our catalog of 100,000+ audiobooks, you need to use an iOS device.
Coming to Android soon...
Join the waitlist
Enter your email and we will notify you as soon as Speechify Audiobooks is available for you.
You’ve been added to the waitlist. We will notify you as soon as Speechify Audiobooks is available for you.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Saudi J Anaesth
- v.16(1); Jan-Mar 2022
How short or long should be a questionnaire for any research? Researchers dilemma in deciding the appropriate questionnaire length
Hunny sharma.
Department of Community and Family Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India
A questionnaire plays a pivotal role in various surveys. Within the realm of biomedical research, questionnaires serve a role in epidemiological surveys and mental health surveys and to obtain information about knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) on various topics of interest. Questionnaire in border perspective can be of different types like self-administered or professionally administered and according to the mode of delivery paper-based or electronic media–based. Various studies have been conducted to assess the appropriateness of a questionnaire in a particular field and methods to translate and validate them. But very little is known regarding the appropriate length and number of questions in a questionnaire and what role it has in data quality, reliability, and response rates. Hence, this narrative review is to explore the critical issue of appropriate length and number of questions in a questionnaire while questionnaire designing.
Introduction
A questionnaire is an essential tool in epidemiological surveys and mental health surveys and to assess knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) on a particular topic of interest. In general, it is a set of predefined questions based on the aim of the research.[ 1 ]
Designing a questionnaire is an art which unfortunately is neglected by most researchers.[ 2 ] A well-designed questionnaire not only saves time for a researcher but helps to obtain relevant information most efficiently, but designing such a questionnaire is complex and time-consuming.[ 3 , 4 ]
The quality of the data obtained by a specific questionnaire depends on the length and number of questions in the questionnaire, the language, and the ease of comprehension of the questions, relevance of the population to which it is administered, and the mode of administration, i.e., the self-administered or paper method or the electronic method [ Figure 1 ].[ 5 , 6 ]

Qualities of a well-designed questionnaire
Response rate is defined as the number of people who responded to a question asked divided by the number of total potential respondents. Response rate which is a crucial factor in determining the quality and generalizability of the outcome of the survey depends indirectly on the length and number of questions in a questionnaire.[ 7 , 8 ]
Several studies have been conducted to assess the appropriateness of the questionnaire in a particular field and methods to translate and validate them. But very little is known regarding the appropriate length and number of questions in a questionnaire and what role it has in data quality and reliability. Hence, this narrative review is to explore the critical issue of appropriate length and number of questions in a questionnaire while questionnaire designing.
What is a questionnaire
Merriam Webster defines the questionnaire as “a set of questions for obtaining statistically useful or personal information from individuals,” whereas Collins defines a questionnaire as “a questionnaire is a written list of questions which are answered by a lot of people to provide information for a report or a survey.” The oxford learners’ dictionaries also give a somewhat similar definition which states that a questionnaire is “a written list of questions that are answered by several people so that information can be collected from the answers.”[ 9 , 10 , 11 ]
Thus, this provides a simpler meaning that a questionnaire in simpler terms is a collection of questions that can be used to collect information from various individuals relevant to the research aims.
Where are questionnaires generally applied?
A questionnaire, in general, can be applied to a wide variety of research which can either be quantitative or qualitative research which completely depends on how and in which a number of open-ended questions are asked.[ 12 ]
Questionnaires are generally applied when a large population has to be assessed or surveyed with relative ease where they play a crucial role in gathering information on the perspectives of individuals in the population.
There is a variety of applications of questionnaire in opinion polls, marketing surveys, and in politics, wherein the context of biomedical research questionnaires are generally used in epidemiological surveys, mental health surveys, surveys on attitudes to a health service or health service utilization, to conduction knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) studies on a particular issue or topic of interest.[ 13 , 14 ]
What are the types of questionnaire?
Questionnaires in general are of two types those which are in paper format and those which are in electronic format. The questionnaire can further be of two types i.e., self-administered or professionally administered via interview. The paper format can be administered easily both in self-administered mode or professional administered mode via direct administration when the population is relatively small as it is cumbersome to manage and store the physical questionnaire, paper format can also be administered to a larger population via postal surveys. Electronic questionnaires can be easily administered to a larger population in self-administered mode via Internet-based services like google forms, e-mails, SurveyMonkey, or Survey Junkie, etc. When administering professional-administered questionnaires professional telephonic services must be utilized to interview a larger population in a shorter duration of time.[ 15 , 16 , 17 ]
What it is required to answer individual questions in the questionnaire or the burden imparted on respondents
As mentioned by Bowling, in general, there are at least four intricated steps required in answering a particular question in a questionnaire, these steps are comprehension, recall of information asked by the question from the memory, judgment on the link between the asked question and the recall of information, and at last communication of the information to the questionnaire or evaluator [ Figure 2 ].[ 18 ]

Steps involved for answering a particular question in the questionnaire
In the case of a self-administered questionnaire, there is also a need for critical reading skills which is not required in one-to-one or face-to-face interview which only requires listening and verbal skills to respond to questions in the same language in which they are being asked or interviewed.[ 18 ]
There are many other crucial factors which play an important role in deciding the utility of questionnaire in various research, one such factor is the literacy of the participants which is a major limiting factor in self-administered questionnaires. Whereas, the other factors include the respondent's age, maturity, and level of understanding and cognition, which are some of the other ways related to the comprehension of the questions.[ 19 ]
Do the length of the questionnaire matters?
Length and number of items in the questionnaire play a crucial role in questionnaire-based studies or surveys, it has a direct effect on the time taken by the respondent to complete the questionnaire, cost of the survey or study, response rate, and quality of data obtained.[ 20 ]
As evident from the study conducted by Iglesias and Torgerson in 2000, on the response rate of a mailed questionnaire, an increase in the length of the questionnaire from five pages to seven pages reduces the response rate from women aged 70 years and over but on contrary does not seems to affect the quality of response to questions.[ 21 ]
Another study conducted by Similar Koitsalu et al .[ 22 ] in 2018 reported that they were able to increase overall participation and information gathered through a long questionnaire with the help of prenotification and the use of a reminder without risking a lower response rate.
Whereas Sahlqvist, et al .[ 23 ] in 2011 reported that participants were more likely to respond to the short version of the questionnaire as compared to a long questionnaire.
Testing of ultrashort, short, and long surveys of 13, 25, and 75 questions, respectively by Kost et al .[ 24 ] in 2018, revealed that a shorter survey utilizing a short questionnaire was reliable and produce high response and completion rates than a long survey.
Bolt, on the other hand, in 2014, found a surprising find that reducing the length of a long questionnaire in a physician survey does not mean that it will necessarily improve response rate hence to improve the response rate in nonresponders’ researchers may think to utilize a drastically shortened version of the questionnaire to obtain some relevant information rather than no information.[ 25 ]
But the most interesting find comes from the web-based survey giant “Survey Monkey,” which states that there is a nonlinear relationship between the number of questions in a survey and the time spent answering each question. Which in other words can be explained as more there are questions in a survey lesser time respondent spend answering each question which is known as “speeding up” or “satisficing” through the questions. It is also observed that as the length of and the number of questions asked increased there is an increase in a nonresponse rate. This in term affects the quantity and reliability of the data gathered.[ 26 ]
What happens when respondents lose interest?
When there is a loss of interest, in the case of a long length questionnaire or extensive interviews, the bored respondents provide unconsidered and unreliable answers, or in other scenarios, it may lead to high nonresponse to questions. Where on one side a high nonresponse rate may lead to difficulty in data analysis or an unacceptable reduction in sample size, whereas on the other side, unconsidered or unreliable answers may defeat the whole purpose of the research [ Figure 3 ].[ 19 ]

Consequences of Loss of interest in research participant
Considerations while using a long questionnaire
While using a long questionnaire, a high nonresponse rate should always be expected hence appropriate measures to address the missing data should be considered such as data trimming or data imputation depending on the amount of data missing.[ 27 , 28 ]
While the loss of interest can be administering counteracted by dividing the questionnaire into sections and administering each section separating to avoid respondents’ fatigue or boredom.[ 19 ]
It is always advised that the administration of telephonic interview–based questionnaire should be kept short in general about 30 min to prevent fatigue or inattention which may adversely affect the quality of data. In the case of a very long telephonic interview, questions can be divided into sections, and each section can be administered on separate days or shifts lasting 30 min each. A long questionnaire should preferably be administered through face-to-face interviews.
Designing a questionnaire is an art and requires time and dedication, which in turn leads to the easiest way to measure the relevant information on a desired topic of interest. But many a times, this crucial step in biomedical research is ignored by researchers. With this narrative review, we were able to provide a glimpse of the importance of a good questionnaire. A good questionnaire can be of 25 to 30 questions and should be able to be administered within 30 min to keep the interest and attention of the participants intact. It is observed that as the number of questions increases there is a tendency of the participants speeding up or satisficing through the questions, which severely affect the quality, reliability, and response rates. In case a long questionnaire is essential, it should be divided into sections of 25 to 30 questions each to be delivered at a different time or day. In the case of a long questionnaire i.e., more than 30 questions, a larger amount of missing data or nonresponse rates must be anticipated and provisions should be made to address them. At last, it is always advised that shortening a relatively lengthy questionnaire significantly increases the response.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: context-aware video anomaly detection in long-term datasets.
Abstract: Video anomaly detection research is generally evaluated on short, isolated benchmark videos only a few minutes long. However, in real-world environments, security cameras observe the same scene for months or years at a time, and the notion of anomalous behavior critically depends on context, such as the time of day, day of week, or schedule of events. Here, we propose a context-aware video anomaly detection algorithm, Trinity, specifically targeted to these scenarios. Trinity is especially well-suited to crowded scenes in which individuals cannot be easily tracked, and anomalies are due to speed, direction, or absence of group motion. Trinity is a contrastive learning framework that aims to learn alignments between context, appearance, and motion, and uses alignment quality to classify videos as normal or anomalous. We evaluate our algorithm on both conventional benchmarks and a public webcam-based dataset we collected that spans more than three months of activity.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Typically, research papers run around 4,000-6,000 words, but it's common to see short papers around 2,000 words or long papers over 10,000 words. If you're writing a paper for school, the recommended length should be provided in the assignment.
1- The median length of a research paper is 4,133 words (equivalent to 166 sentences or 34 paragraphs), excluding the abstract and references, with 90% of papers being between 2,023 and 8,284 words. 2- A typical article is divided in the following way: Introduction section: 14.6% of the total word count.
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
An Overview. . In short, research paper's average length can range from 1,500 words for research proposals and case studies - all the way to 100,000 words for large dissertations. Research, by its nature of being complex, requires a careful and thorough elucidation of facts, notions, information, and the like - which is all reflected in its ...
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature. As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question.More specifically, that's called a research question, and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What's important to understand though is that you'll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources - for ...
By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers. 5. Write a thesis statement. A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction.
How long is a short research paper? A short research paper can be between 2000 to 3000 words long. These are often seen in high school research papers mentioned above. In fewer cases, they can be for college studies. How long is a research paper: length guide. The length of a research paper varies depending on the stage of education, course of ...
Key: Research Paper Topics. 1) Environmentalism in America (too general) Women's Contribution to the Modern Environmentalism in America, 1800-1950 (much better) 2) Immigration Trends in Wisconsin's Chippewa Valley. Probably okay for a research topic, since it focuses on a specific region.
Research that has a thesis statement only requires 2 to 3 arguments to be proved and will be summed up in 500 to 700 words. After providing the introduction and a little background on the research, you can directly shift to mentioning the arguments and claims so you may prove the statement and complete the research.
Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
How Long Is A Short Research Paper? Short research papers might be between 1-3 pages in length, whereas lengthier research papers can be between 5-10 pages in length. It is crucial to double-check the journal's author criteria for the precise word count and length of your work, as it has been stated previously. ...
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
Observable fact: Writing a research paper is a requirement of this course. Personal opinion: I prefer not to write research papers. A good thesis statement: Writing a research paper is relatively easy as long as the writer follows certain specific, sequential tasks. This thesis statement indicates your point of view without using expressions ...
A decimal outline is similar in format to the alphanumeric outline, but with a different numbering system: 1, 1.1, 1.2, etc. Text is written as short notes rather than full sentences. Example: 1 Body paragraph one. 1.1 First point. 1.1.1 Sub-point of first point. 1.1.2 Sub-point of first point.
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
The word count for a research paper depends on several factors, such as academic level, field of study, and specific guidelines. However, research papers commonly range from 2,500 to 10,000 words. Top 9 Tools Needed to Write Long Research Papers Speechify Text to Speech. Cost: Free to try
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes: an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to….
Introduces your topic. States your problem statement and the questions your research aims to answer. Provides context for your research. In a research proposal, an introduction can be a few paragraphs long. It should be concise, but don't feel like you need to cram all of your information into one paragraph.
Do not use a period after your title or after any heading in the paper (e.g., Works Cited). Begin your text on a new, double-spaced line after the title, indenting the first line of the paragraph half an inch from the left margin. Fig. 1. The top of the first page of a research paper.
The introduction of a research paper provides an overview of the study's purpose, scope, and significance. ... Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper. ... If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review ...
Normal Length of a Research Paper. While the length can vary based on academic level and subject, most high school assignments range from 5-20 pages, whereas longer papers are common in higher academia. Always refer to the specific guidelines provided by instructors or journal article submissions.
Testing of ultrashort, short, and long surveys of 13, 25, and 75 questions, respectively by Kost et al. in 2018, revealed that a shorter survey utilizing a short questionnaire was reliable and produce high response and completion rates than a long survey.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Research papers rely on other people's writing as a foundation to create new ideas, but you can't just use someone else's words. That's why paraphrasing is an essential writing technique for academic writing.. Paraphrasing rewrites another person's ideas, evidence, or opinions in your own words.With proper attribution, paraphrasing helps you expand on another's work and back up ...
Video anomaly detection research is generally evaluated on short, isolated benchmark videos only a few minutes long. However, in real-world environments, security cameras observe the same scene for months or years at a time, and the notion of anomalous behavior critically depends on context, such as the time of day, day of week, or schedule of events. Here, we propose a context-aware video ...
The prediction of solar radiation data is important for countries to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels. Since the development of solar energy systems relies on an accurate prediction of solar radiation data, this study is conducted to predict monthly and daily solar radiation data and contribute to the development of solar energy systems. The current study develops a long short term ...
In this paper, we consider a multiple parallel device for the steel continuous casting problem (SCC) known as one of the hardest scheduling problems. To our knowledge, this is the first work that offers a model of artificial intelligence for the SCC, in particular a recurrent neural network (RNN) with long short-term memory (LSTM) cells that ...
The results indicate that the spillover effects of short-term oil price fluctuations are mild, and the green bond market is the least affected. While the long-term oil price fluctuations have profound effects on the aforementioned three markets, the spillovers are especially enhanced by extreme events.