- The Highlight

Nobody knows what the point of homework is
The homework wars are back.
by Jacob Sweet

As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework. But whether or not students could complete it at home varied. For some, schoolwork became public-library work or McDonald’s-parking-lot work.
Luis Torres, the principal of PS 55, a predominantly low-income community elementary school in the south Bronx, told me that his school secured Chromebooks for students early in the pandemic only to learn that some lived in shelters that blocked wifi for security reasons. Others, who lived in housing projects with poor internet reception, did their schoolwork in laundromats.
According to a 2021 Pew survey , 25 percent of lower-income parents said their children, at some point, were unable to complete their schoolwork because they couldn’t access a computer at home; that number for upper-income parents was 2 percent.
The issues with remote learning in March 2020 were new. But they highlighted a divide that had been there all along in another form: homework. And even long after schools have resumed in-person classes, the pandemic’s effects on homework have lingered.
Over the past three years, in response to concerns about equity, schools across the country, including in Sacramento, Los Angeles , San Diego , and Clark County, Nevada , made permanent changes to their homework policies that restricted how much homework could be given and how it could be graded after in-person learning resumed.
Three years into the pandemic, as districts and teachers reckon with Covid-era overhauls of teaching and learning, schools are still reconsidering the purpose and place of homework. Whether relaxing homework expectations helps level the playing field between students or harms them by decreasing rigor is a divisive issue without conclusive evidence on either side, echoing other debates in education like the elimination of standardized test scores from some colleges’ admissions processes.
I first began to wonder if the homework abolition movement made sense after speaking with teachers in some Massachusetts public schools, who argued that rather than help disadvantaged kids, stringent homework restrictions communicated an attitude of low expectations. One, an English teacher, said she felt the school had “just given up” on trying to get the students to do work; another argued that restrictions that prohibit teachers from assigning take-home work that doesn’t begin in class made it difficult to get through the foreign-language curriculum. Teachers in other districts have raised formal concerns about homework abolition’s ability to close gaps among students rather than widening them.
Many education experts share this view. Harris Cooper, a professor emeritus of psychology at Duke who has studied homework efficacy, likened homework abolition to “playing to the lowest common denominator.”
But as I learned after talking to a variety of stakeholders — from homework researchers to policymakers to parents of schoolchildren — whether to abolish homework probably isn’t the right question. More important is what kind of work students are sent home with and where they can complete it. Chances are, if schools think more deeply about giving constructive work, time spent on homework will come down regardless.
There’s no consensus on whether homework works
The rise of the no-homework movement during the Covid-19 pandemic tapped into long-running disagreements over homework’s impact on students. The purpose and effectiveness of homework have been disputed for well over a century. In 1901, for instance, California banned homework for students up to age 15, and limited it for older students, over concerns that it endangered children’s mental and physical health. The newest iteration of the anti-homework argument contends that the current practice punishes students who lack support and rewards those with more resources, reinforcing the “myth of meritocracy.”
But there is still no research consensus on homework’s effectiveness; no one can seem to agree on what the right metrics are. Much of the debate relies on anecdotes, intuition, or speculation.
Researchers disagree even on how much research exists on the value of homework. Kathleen Budge, the co-author of Turning High-Poverty Schools Into High-Performing Schools and a professor at Boise State, told me that homework “has been greatly researched.” Denise Pope, a Stanford lecturer and leader of the education nonprofit Challenge Success, said, “It’s not a highly researched area because of some of the methodological problems.”
Experts who are more sympathetic to take-home assignments generally support the “10-minute rule,” a framework that estimates the ideal amount of homework on any given night by multiplying the student’s grade by 10 minutes. (A ninth grader, for example, would have about 90 minutes of work a night.) Homework proponents argue that while it is difficult to design randomized control studies to test homework’s effectiveness, the vast majority of existing studies show a strong positive correlation between homework and high academic achievement for middle and high school students. Prominent critics of homework argue that these correlational studies are unreliable and point to studies that suggest a neutral or negative effect on student performance. Both agree there is little to no evidence for homework’s effectiveness at an elementary school level, though proponents often argue that it builds constructive habits for the future.
For anyone who remembers homework assignments from both good and bad teachers, this fundamental disagreement might not be surprising. Some homework is pointless and frustrating to complete. Every week during my senior year of high school, I had to analyze a poem for English and decorate it with images found on Google; my most distinct memory from that class is receiving a demoralizing 25-point deduction because I failed to present my analysis on a poster board. Other assignments really do help students learn: After making an adapted version of Chairman Mao’s Little Red Book for a ninth grade history project, I was inspired to check out from the library and read a biography of the Chinese ruler.
For homework opponents, the first example is more likely to resonate. “We’re all familiar with the negative effects of homework: stress, exhaustion, family conflict, less time for other activities, diminished interest in learning,” Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, which challenges common justifications for homework, told me in an email. “And these effects may be most pronounced among low-income students.” Kohn believes that schools should make permanent any moratoria implemented during the pandemic, arguing that there are no positives at all to outweigh homework’s downsides. Recent studies , he argues , show the benefits may not even materialize during high school.
In the Marlborough Public Schools, a suburban district 45 minutes west of Boston, school policy committee chair Katherine Hennessy described getting kids to complete their homework during remote education as “a challenge, to say the least.” Teachers found that students who spent all day on their computers didn’t want to spend more time online when the day was over. So, for a few months, the school relaxed the usual practice and teachers slashed the quantity of nightly homework.
Online learning made the preexisting divides between students more apparent, she said. Many students, even during normal circumstances, lacked resources to keep them on track and focused on completing take-home assignments. Though Marlborough Schools is more affluent than PS 55, Hennessy said many students had parents whose work schedules left them unable to provide homework help in the evenings. The experience tracked with a common divide in the country between children of different socioeconomic backgrounds.
So in October 2021, months after the homework reduction began, the Marlborough committee made a change to the district’s policy. While teachers could still give homework, the assignments had to begin as classwork. And though teachers could acknowledge homework completion in a student’s participation grade, they couldn’t count homework as its own grading category. “Rigorous learning in the classroom does not mean that that classwork must be assigned every night,” the policy stated . “Extensions of class work is not to be used to teach new content or as a form of punishment.”
Canceling homework might not do anything for the achievement gap
The critiques of homework are valid as far as they go, but at a certain point, arguments against homework can defy the commonsense idea that to retain what they’re learning, students need to practice it.
“Doesn’t a kid become a better reader if he reads more? Doesn’t a kid learn his math facts better if he practices them?” said Cathy Vatterott, an education researcher and professor emeritus at the University of Missouri-St. Louis. After decades of research, she said it’s still hard to isolate the value of homework, but that doesn’t mean it should be abandoned.
Blanket vilification of homework can also conflate the unique challenges facing disadvantaged students as compared to affluent ones, which could have different solutions. “The kids in the low-income schools are being hurt because they’re being graded, unfairly, on time they just don’t have to do this stuff,” Pope told me. “And they’re still being held accountable for turning in assignments, whether they’re meaningful or not.” On the other side, “Palo Alto kids” — students in Silicon Valley’s stereotypically pressure-cooker public schools — “are just bombarded and overloaded and trying to stay above water.”
Merely getting rid of homework doesn’t solve either problem. The United States already has the second-highest disparity among OECD (the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) nations between time spent on homework by students of high and low socioeconomic status — a difference of more than three hours, said Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University and author of No More Mindless Homework .
When she interviewed teachers in Boston-area schools that had cut homework before the pandemic, Bempechat told me, “What they saw immediately was parents who could afford it immediately enrolled their children in the Russian School of Mathematics,” a math-enrichment program whose tuition ranges from $140 to about $400 a month. Getting rid of homework “does nothing for equity; it increases the opportunity gap between wealthier and less wealthy families,” she said. “That solution troubles me because it’s no solution at all.”
A group of teachers at Wakefield High School in Arlington, Virginia, made the same point after the school district proposed an overhaul of its homework policies, including removing penalties for missing homework deadlines, allowing unlimited retakes, and prohibiting grading of homework.
“Given the emphasis on equity in today’s education systems,” they wrote in a letter to the school board, “we believe that some of the proposed changes will actually have a detrimental impact towards achieving this goal. Families that have means could still provide challenging and engaging academic experiences for their children and will continue to do so, especially if their children are not experiencing expected rigor in the classroom.” At a school where more than a third of students are low-income, the teachers argued, the policies would prompt students “to expect the least of themselves in terms of effort, results, and responsibility.”
Not all homework is created equal
Despite their opposing sides in the homework wars, most of the researchers I spoke to made a lot of the same points. Both Bempechat and Pope were quick to bring up how parents and schools confuse rigor with workload, treating the volume of assignments as a proxy for quality of learning. Bempechat, who is known for defending homework, has written extensively about how plenty of it lacks clear purpose, requires the purchasing of unnecessary supplies, and takes longer than it needs to. Likewise, when Pope instructs graduate-level classes on curriculum, she asks her students to think about the larger purpose they’re trying to achieve with homework: If they can get the job done in the classroom, there’s no point in sending home more work.
At its best, pandemic-era teaching facilitated that last approach. Honolulu-based teacher Christina Torres Cawdery told me that, early in the pandemic, she often had a cohort of kids in her classroom for four hours straight, as her school tried to avoid too much commingling. She couldn’t lecture for four hours, so she gave the students plenty of time to complete independent and project-based work. At the end of most school days, she didn’t feel the need to send them home with more to do.
A similar limited-homework philosophy worked at a public middle school in Chelsea, Massachusetts. A couple of teachers there turned as much class as possible into an opportunity for small-group practice, allowing kids to work on problems that traditionally would be assigned for homework, Jessica Flick, a math coach who leads department meetings at the school, told me. It was inspired by a philosophy pioneered by Simon Fraser University professor Peter Liljedahl, whose influential book Building Thinking Classrooms in Mathematics reframes homework as “check-your-understanding questions” rather than as compulsory work. Last year, Flick found that the two eighth grade classes whose teachers adopted this strategy performed the best on state tests, and this year, she has encouraged other teachers to implement it.
Teachers know that plenty of homework is tedious and unproductive. Jeannemarie Dawson De Quiroz, who has taught for more than 20 years in low-income Boston and Los Angeles pilot and charter schools, says that in her first years on the job she frequently assigned “drill and kill” tasks and questions that she now feels unfairly stumped students. She said designing good homework wasn’t part of her teaching programs, nor was it meaningfully discussed in professional development. With more experience, she turned as much class time as she could into practice time and limited what she sent home.
“The thing about homework that’s sticky is that not all homework is created equal,” says Jill Harrison Berg, a former teacher and the author of Uprooting Instructional Inequity . “Some homework is a genuine waste of time and requires lots of resources for no good reason. And other homework is really useful.”
Cutting homework has to be part of a larger strategy
The takeaways are clear: Schools can make cuts to homework, but those cuts should be part of a strategy to improve the quality of education for all students. If the point of homework was to provide more practice, districts should think about how students can make it up during class — or offer time during or after school for students to seek help from teachers. If it was to move the curriculum along, it’s worth considering whether strategies like Liljedahl’s can get more done in less time.
Some of the best thinking around effective assignments comes from those most critical of the current practice. Denise Pope proposes that, before assigning homework, teachers should consider whether students understand the purpose of the work and whether they can do it without help. If teachers think it’s something that can’t be done in class, they should be mindful of how much time it should take and the feedback they should provide. It’s questions like these that De Quiroz considered before reducing the volume of work she sent home.
More than a year after the new homework policy began in Marlborough, Hennessy still hears from parents who incorrectly “think homework isn’t happening” despite repeated assurances that kids still can receive work. She thinks part of the reason is that education has changed over the years. “I think what we’re trying to do is establish that homework may be an element of educating students,” she told me. “But it may not be what parents think of as what they grew up with. ... It’s going to need to adapt, per the teaching and the curriculum, and how it’s being delivered in each classroom.”
For the policy to work, faculty, parents, and students will all have to buy into a shared vision of what school ought to look like. The district is working on it — in November, it hosted and uploaded to YouTube a round-table discussion on homework between district administrators — but considering the sustained confusion, the path ahead seems difficult.
When I asked Luis Torres about whether he thought homework serves a useful part in PS 55’s curriculum, he said yes, of course it was — despite the effort and money it takes to keep the school open after hours to help them do it. “The children need the opportunity to practice,” he said. “If you don’t give them opportunities to practice what they learn, they’re going to forget.” But Torres doesn’t care if the work is done at home. The school stays open until around 6 pm on weekdays, even during breaks. Tutors through New York City’s Department of Youth and Community Development programs help kids with work after school so they don’t need to take it with them.
As schools weigh the purpose of homework in an unequal world, it’s tempting to dispose of a practice that presents real, practical problems to students across the country. But getting rid of homework is unlikely to do much good on its own. Before cutting it, it’s worth thinking about what good assignments are meant to do in the first place. It’s crucial that students from all socioeconomic backgrounds tackle complex quantitative problems and hone their reading and writing skills. It’s less important that the work comes home with them.
Jacob Sweet is a freelance writer in Somerville, Massachusetts. He is a frequent contributor to the New Yorker, among other publications.
Most Popular
“everyone is absolutely terrified”: inside a us ally’s secret war on its american critics, leaked openai documents reveal aggressive tactics toward former employees, the real reason it costs so much to go to a concert, hacks shows cancel culture is a joke, take a mental break with the newest vox crossword, today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
More in The Highlight

Social media platforms aren’t equipped to handle the negative effects of their algorithms abroad. Neither is the law.

The real science behind the billionaire pursuit of immortality

If you want to belong, find a third place

America’s prison system is turning into a de facto nursing home

The one huge obstacle standing in the way of progress on gene-editing medicine

We can make birth safer for Black mothers. Here’s how.

Birth control is good, actually

You really should say something if you hate your friend's partner

3 theories for America’s anti-immigrant shift

What the Biden administration is doing about ludicrously expensive concert tickets

The Supreme Court's new voting rights decision is a love letter to gerrymandering
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
share this!
August 16, 2021
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Researchers develop organic photoredox catalysts with enhanced stability and recyclability

Theory and experiment combine to shine a new light on proton spin
2 hours ago

On repeat: Biologists observe recurring evolutionary changes, over time, in stick insects
New findings on fertility: Sperm can adapt to sexually transmitted microbes
3 hours ago
Observing mammalian cells with superfast soft X-rays

New study challenges conventional wisdom that Americans are 'pocketbook voters'
Carbon dioxide, the main culprit of global warming, reborn as an antioxidant substance
4 hours ago
New study offers a cleaner path for controlling water, transforming greenhouse gases

Heavy water: How melting ice sheets and pumped groundwater can lower local sea levels—and boost them elsewhere
5 hours ago

Unveiling a novel AAK1 inhibitor: How chemical proteomics unlock therapeutic potential
Relevant physicsforums posts, physics education is 60 years out of date.
May 16, 2024
Is "College Algebra" really just high school "Algebra II"?
May 14, 2024
Plagiarism & ChatGPT: Is Cheating with AI the New Normal?
May 13, 2024
Physics Instructor Minimum Education to Teach Community College
May 11, 2024
Studying "Useful" vs. "Useless" Stuff in School
Apr 30, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Apr 29, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

First-generation medical students face unique challenges and need more targeted support, say researchers

Investigation reveals varied impact of preschool programs on long-term school success
May 2, 2024

Training of brain processes makes reading more efficient
Apr 18, 2024

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
Apr 17, 2024

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Homework Gap Could Be Back in Full Force If Lawmakers Don’t Act, Education Groups Say

- Share article
Millions of students who were unable to participate in virtual learning because of poor home internet connectivity when the pandemic struck a year and a half ago were handed a temporary lifeline, thanks in large part to federal COVID relief funds, which helped cover devices and broadband access for students in need.
But that money will likely run out after this school year, potentially leaving students in the lurch. Fifty-seven education organizations—including the American Federation of Teachers and the National Education Association—asked congressional leaders in an Oct. 7 letter to provide $4 billion in additional relief in an ambitious budget bill that lawmakers are scrambling to find agreement on.
The legislation—whose price-tag could be in the trillions of dollars—may also encompass many of the Biden administration’s priorities , including expanding universal free pre-kindergarten and offering students two years of community college for free.
The so-called “homework gap” —which disproportionately impacts poor students, students of color, and those living in rural areas—has been a persistent problem since long before the pandemic struck in March 2020. In fact, as many as 16 million students and 400,000 educators lacked sufficient connectivity to participate in online learning since COVID-19 began, according to an Oct. 7 letter the groups sent to congressional leaders.
But when kids were completely unable to attend school because they didn’t have access to virtual learning, the federal government allowed districts and schools to use a portion of the more than $180 billion in federal COVID relief funding to purchase devices and hotspots that could be used to help connect teachers and students at home, among a broad range of other purposes.
Congress also provided an additional $7.1 billion for an Emergency Connectivity Fund, which flows through the E-Rate program, long used to connect schools and libraries. So far, districts have applied for about 70 percent of those funds, or a total of $5.1 billion. The money has been used to pay for 9.1 million connected devices and 5.4 million broadband connections, the letter says.
But when those dollars stop flowing in June of next year, it’s an open question where money will be coming from to continue kids’ and educators’ home connections.
“Schools and libraries will have to come up with some way to pay for it themselves, which they haven’t budgeted for,” said Jon Bernstein, president of the Bernstein Strategy Group, which represents the American Federation of School Administrators and co-chairs the Homework Gap Big Tent Coalition.
Local and state governments may be able to help pay for the extension out of leftover COVID relief dollars or other funds. But if that doesn’t happen, “kids will lose access again,” Bernstein said.
That means, the letter said, that “students could find their online courses interrupted, their research projects and homework assignments impossible to complete, and their relationships with educators and peers shut down.”
Sign Up for EdWeek Tech Leader
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

Why I Think All Schools Should Abolish Homework

H ow long is your child’s workweek? Thirty hours? Forty? Would it surprise you to learn that some elementary school kids have workweeks comparable to adults’ schedules? For most children, mandatory homework assignments push their workweek far beyond the school day and deep into what any other laborers would consider overtime. Even without sports or music or other school-sponsored extracurriculars, the daily homework slog keeps many students on the clock as long as lawyers, teachers, medical residents, truck drivers and other overworked adults. Is it any wonder that,deprived of the labor protections that we provide adults, our kids are suffering an epidemic of disengagement, anxiety and depression ?
With my youngest child just months away from finishing high school, I’m remembering all the needless misery and missed opportunities all three of my kids suffered because of their endless assignments. When my daughters were in middle school, I would urge them into bed before midnight and then find them clandestinely studying under the covers with a flashlight. We cut back on their activities but still found ourselves stuck in a system on overdrive, returning home from hectic days at 6 p.m. only to face hours more of homework. Now, even as a senior with a moderate course load, my son, Zak, has spent many weekends studying, finding little time for the exercise and fresh air essential to his well-being. Week after week, and without any extracurriculars, Zak logs a lot more than the 40 hours adults traditionally work each week — and with no recognition from his “bosses” that it’s too much. I can’t count the number of shared evenings, weekend outings and dinners that our family has missed and will never get back.
How much after-school time should our schools really own?
In the midst of the madness last fall, Zak said to me, “I feel like I’m working towards my death. The constant demands on my time since 5th grade are just going to continue through graduation, into college, and then into my job. It’s like I’m on an endless treadmill with no time for living.”
My spirit crumbled along with his.
Like Zak, many people are now questioning the point of putting so much demand on children and teens that they become thinly stretched and overworked. Studies have long shown that there is no academic benefit to high school homework that consumes more than a modest number of hours each week. In a study of high schoolers conducted by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), researchers concluded that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance.”
In elementary school, where we often assign overtime even to the youngest children, studies have shown there’s no academic benefit to any amount of homework at all.
Our unquestioned acceptance of homework also flies in the face of all we know about human health, brain function and learning. Brain scientists know that rest and exercise are essential to good health and real learning . Even top adult professionals in specialized fields take care to limit their work to concentrated periods of focus. A landmark study of how humans develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work only about four hours per day .
Yet we continue to overwork our children, depriving them of the chance to cultivate health and learn deeply, burdening them with an imbalance of sedentary, academic tasks. American high school students , in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found.
It’s time for an uprising.
Already, small rebellions are starting. High schools in Ridgewood, N.J. , and Fairfax County, Va., among others, have banned homework over school breaks. The entire second grade at Taylor Elementary School in Arlington, Va., abolished homework this academic year. Burton Valley Elementary School in Lafayette, Calif., has eliminated homework in grades K through 4. Henry West Laboratory School , a public K-8 school in Coral Gables, Fla., eliminated mandatory, graded homework for optional assignments. One Lexington, Mass., elementary school is piloting a homework-free year, replacing it with reading for pleasure.
More from TIME
Across the Atlantic, students in Spain launched a national strike against excessive assignments in November. And a second-grade teacher in Texas, made headlines this fall when she quit sending home extra work , instead urging families to “spend your evenings doing things that are proven to correlate with student success. Eat dinner as a family, read together, play outside and get your child to bed early.”
It is time that we call loudly for a clear and simple change: a workweek limit for children, counting time on the clock before and after the final bell. Why should schools extend their authority far beyond the boundaries of campus, dictating activities in our homes in the hours that belong to families? An all-out ban on after-school assignments would be optimal. Short of that, we can at least sensibly agree on a cap limiting kids to a 40-hour workweek — and fewer hours for younger children.
Resistance even to this reasonable limit will be rife. Mike Miller, an English teacher at Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology in Alexandria, Va., found this out firsthand when he spearheaded a homework committee to rethink the usual approach. He had read the education research and found a forgotten policy on the county books limiting homework to two hours a night, total, including all classes. “I thought it would be a slam dunk” to put the two-hour cap firmly in place, Miller said.
But immediately, people started balking. “There was a lot of fear in the community,” Miller said. “It’s like jumping off a high dive with your kids’ future. If we reduce homework to two hours or less, is my kid really going to be okay?” In the end, the committee only agreed to a homework ban over school breaks.
Miller’s response is a great model for us all. He decided to limit assignments in his own class to 20 minutes a night (the most allowed for a student with six classes to hit the two-hour max). His students didn’t suddenly fail. Their test scores remained stable. And they started using their more breathable schedule to do more creative, thoughtful work.
That’s the way we will get to a sane work schedule for kids: by simultaneously pursuing changes big and small. Even as we collaboratively press for policy changes at the district or individual school level, all teachers can act now, as individuals, to ease the strain on overworked kids.
As parents and students, we can also organize to make homework the exception rather than the rule. We can insist that every family, teacher and student be allowed to opt out of assignments without penalty to make room for important activities, and we can seek changes that shift practice exercises and assignments into the actual school day.
We’ll know our work is done only when Zak and every other child can clock out, eat dinner, sleep well and stay healthy — the very things needed to engage and learn deeply. That’s the basic standard the law applies to working adults. Let’s do the same for our kids.
Vicki Abeles is the author of the bestseller Beyond Measure: Rescuing an Overscheduled, Overtested, Underestimated Generation, and director and producer of the documentaries “ Race to Nowhere ” and “ Beyond Measure. ”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Javier Milei’s Radical Plan to Transform Argentina
- The New Face of Doctor Who
- How Private Donors Shape Birth-Control Choices
- What Happens if Trump Is Convicted ? Your Questions, Answered
- The Deadly Digital Frontiers at the Border
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- The 31 Most Anticipated Movies of Summer 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
Memorial Day sales blowout: Save up to 65% off Stanley, Baublebar, Cuisinart and more
- TODAY Plaza
- Share this —

- Watch Full Episodes
- Read With Jenna
- Inspirational
- Relationships
- TODAY Table
- Newsletters
- Start TODAY
- Shop TODAY Awards
- Citi Concert Series
- Listen All Day
Follow today
More Brands
- On The Show
The end of homework? Why some schools are banning homework
Fed up with the tension over homework, some schools are opting out altogether.
No-homework policies are popping up all over, including schools in the U.S., where the shift to the Common Core curriculum is prompting educators to rethink how students spend their time.
“Homework really is a black hole,” said Etta Kralovec, an associate professor of teacher education at the University of Arizona South and co-author of “The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning.”
“I think teachers are going to be increasingly interested in having total control over student learning during the class day and not relying on homework as any kind of activity that’s going to support student learning.”
College de Saint-Ambroise, an elementary school in Quebec, is the latest school to ban homework, announcing this week that it would try the new policy for a year. The decision came after officials found that it was “becoming more and more difficult” for children to devote time to all the assignments they were bringing home, Marie-Ève Desrosiers, a spokeswoman with the Jonquière School Board, told the CBC .
Kralovec called the ban on homework a movement, though she estimated just a small handful of schools in the U.S. have such policies.
Gaithersburg Elementary School in Rockville, Maryland, is one of them, eliminating the traditional concept of homework in 2012. The policy is still in place and working fine, Principal Stephanie Brant told TODAY Parents. The school simply asks that students read 30 minutes each night.
“We felt like with the shift to the Common Core curriculum, and our knowledge of how our students need to think differently… we wanted their time to be spent in meaningful ways,” Brant said.
“We’re constantly asking parents for feedback… and everyone’s really happy with it so far. But it’s really a culture shift.”

It was a decision that was best for her community, Brant said, adding that she often gets phone calls from other principals inquiring how it’s working out.
The VanDamme Academy, a private K-8 school in Aliso Viejo, California, has a similar policy , calling homework “largely pointless.”
The Buffalo Academy of Scholars, a private school in Buffalo, New York, touts that it has called “a truce in the homework battle” and promises that families can “enjoy stress-free, homework-free evenings and more quality time together at home.”
Some schools have taken yet another approach. At Ridgewood High School in Norridge, Illinois, teachers do assign homework but it doesn’t count towards a student’s final grade.
Many schools in the U.S. have toyed with the idea of opting out of homework, but end up changing nothing because it is such a contentious issue among parents, Kralovec noted.
“There’s a huge philosophical divide between parents who want their kids to be very scheduled, very driven, and very ambitiously focused at school -- those parents want their kids to do homework,” she said.
“And then there are the parents who want a more child-centered life with their kids, who want their kids to be able to explore different aspects of themselves, who think their kids should have free time.”
So what’s the right amount of time to spend on homework?
National PTA spokeswoman Heidi May pointed to the organization’s “ 10 minute rule ,” which recommends kids spend about 10 minutes on homework per night for every year they’re in school. That would mean 10 minutes for a first-grader and an hour for a child in the sixth grade.
But many parents say their kids must spend much longer on their assignments. Last year, a New York dad tried to do his eight-grader’s homework for a week and it took him at least three hours on most nights.
More than 80 percent of respondents in a TODAY.com poll complained kids have too much homework. For homework critics like Kralovec, who said research shows homework has little value at the elementary and middle school level, the issue is simple.
“Kids are at school 7 or 8 hours a day, that’s a full working day and why should they have to take work home?” she asked.
Follow A. Pawlowski on Google+ and Twitter .
Homework could have an impact on kids’ health. Should schools ban it?
Professor of Education, Penn State
Disclosure statement
Gerald K. LeTendre has received funding from the National Science Foundation and the Spencer Foundation.
Penn State provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation US.
View all partners

Reformers in the Progressive Era (from the 1890s to 1920s) depicted homework as a “sin” that deprived children of their playtime . Many critics voice similar concerns today.
Yet there are many parents who feel that from early on, children need to do homework if they are to succeed in an increasingly competitive academic culture. School administrators and policy makers have also weighed in, proposing various policies on homework .
So, does homework help or hinder kids?
For the last 10 years, my colleagues and I have been investigating international patterns in homework using databases like the Trends in Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) . If we step back from the heated debates about homework and look at how homework is used around the world, we find the highest homework loads are associated with countries that have lower incomes and higher social inequality.

Does homework result in academic success?
Let’s first look at the global trends on homework.
Undoubtedly, homework is a global phenomenon ; students from all 59 countries that participated in the 2007 Trends in Math and Science Study (TIMSS) reported getting homework. Worldwide, only less than 7% of fourth graders said they did no homework.
TIMSS is one of the few data sets that allow us to compare many nations on how much homework is given (and done). And the data show extreme variation.
For example, in some nations, like Algeria, Kuwait and Morocco, more than one in five fourth graders reported high levels of homework. In Japan, less than 3% of students indicated they did more than four hours of homework on a normal school night.
TIMSS data can also help to dispel some common stereotypes. For instance, in East Asia, Hong Kong, Taiwan and Japan – countries that had the top rankings on TIMSS average math achievement – reported rates of heavy homework that were below the international mean.
In the Netherlands, nearly one out of five fourth graders reported doing no homework on an average school night, even though Dutch fourth graders put their country in the top 10 in terms of average math scores in 2007.
Going by TIMSS data, the US is neither “ A Nation at Rest” as some have claimed, nor a nation straining under excessive homework load . Fourth and eighth grade US students fall in the middle of the 59 countries in the TIMSS data set, although only 12% of US fourth graders reported high math homework loads compared to an international average of 21%.
So, is homework related to high academic success?
At a national level, the answer is clearly no. Worldwide, homework is not associated with high national levels of academic achievement .
But, the TIMSS can’t be used to determine if homework is actually helping or hurting academic performance overall , it can help us see how much homework students are doing, and what conditions are associated with higher national levels of homework.
We have typically found that the highest homework loads are associated with countries that have lower incomes and higher levels of social inequality – not hallmarks that most countries would want to emulate.
Impact of homework on kids
TIMSS data also show us how even elementary school kids are being burdened with large amounts of homework.
Almost 10% of fourth graders worldwide (one in 10 children) reported spending multiple hours on homework each night. Globally, one in five fourth graders report 30 minutes or more of homework in math three to four times a week.
These reports of large homework loads should worry parents, teachers and policymakers alike.
Empirical studies have linked excessive homework to sleep disruption , indicating a negative relationship between the amount of homework, perceived stress and physical health.

What constitutes excessive amounts of homework varies by age, and may also be affected by cultural or family expectations. Young adolescents in middle school, or teenagers in high school, can study for longer duration than elementary school children.
But for elementary school students, even 30 minutes of homework a night, if combined with other sources of academic stress, can have a negative impact . Researchers in China have linked homework of two or more hours per night with sleep disruption .
Even though some cultures may normalize long periods of studying for elementary age children, there is no evidence to support that this level of homework has clear academic benefits . Also, when parents and children conflict over homework, and strong negative emotions are created, homework can actually have a negative association with academic achievement.
Should there be “no homework” policies?
Administrators and policymakers have not been reluctant to wade into the debates on homework and to formulate policies . France’s president, Francois Hollande, even proposed that homework be banned because it may have inegaliatarian effects.
However, “zero-tolerance” homework policies for schools, or nations, are likely to create as many problems as they solve because of the wide variation of homework effects. Contrary to what Hollande said, research suggests that homework is not a likely source of social class differences in academic achievement .
Homework, in fact, is an important component of education for students in the middle and upper grades of schooling.
Policymakers and researchers should look more closely at the connection between poverty, inequality and higher levels of homework. Rather than seeing homework as a “solution,” policymakers should question what facets of their educational system might impel students, teachers and parents to increase homework loads.
At the classroom level, in setting homework, teachers need to communicate with their peers and with parents to assure that the homework assigned overall for a grade is not burdensome, and that it is indeed having a positive effect.
Perhaps, teachers can opt for a more individualized approach to homework. If teachers are careful in selecting their assignments – weighing the student’s age, family situation and need for skill development – then homework can be tailored in ways that improve the chance of maximum positive impact for any given student.
I strongly suspect that when teachers face conditions such as pressure to meet arbitrary achievement goals, lack of planning time or little autonomy over curriculum, homework becomes an easy option to make up what could not be covered in class.
Whatever the reason, the fact is a significant percentage of elementary school children around the world are struggling with large homework loads. That alone could have long-term negative consequences for their academic success.
- Trends in Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS)
- Elementary school
- Academic success

Research Fellow

Senior Research Fellow - Women's Health Services

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health
Watch CBS News
Are schools across the country going too far by banning homework?
December 14, 2018 / 1:37 PM EST / CBS News
Are schools across the country going too far by banning homework? According to child and adolescent family therapist Darby Fox, yes.
"It's like an ultimate reaction. There is a point to homework and the right amount really is age appropriate," Fox said Friday on "CBS This Morning."
Elementary school students have an average of around 4.5 hours of homework a week, while high schoolers get an average of about 7.5 hours, according to the Wall Street Journal and Department of Education. The National Institute of Mental Health says more than 30 percent of teenagers experience some kind of anxiety, and homework is a major contributing factor.
"I think the current thing about getting rid of homework is about anxiety and trying reduce that. It should be about learning. We should be able to hit a medium," Fox said.
"Very young kids really – sometimes they like the idea that they have something industrious to do at home, and there's no harm in that. But they need time to just play and explore and become kind of curious," Fox added. "As we get older, fourth grade, you can have 45 minutes, an hour – up in through high school, 2.5 hours is appropriate, 3 hours. But schools have really taken it way too far."
She blamed the "race to get amazing resumes, the best test scores."
"But that has escalated almost directly with mental health problems, anxiety, depression," Fox said.
While parents might see sports or socializing as an important part of students' lives, Fox pointed out that's still a scheduled activity.
"What I'd really love to see is more time for kids to have nothing to do, unstructured time so that they have to figure it out on their own. And that's the most important thing they should be exploring," Fox said.
If your child is overwhelmed, Fox advised parents to let schools and teachers know.
"If there's not an appropriate response, follow it to the next level. Is it the principal or whoever is the next in command. Usually that might issue – that might alarm us that there's some kind of learning disability or processing problem if it's really overwhelming or the teachers are just simply giving too much work," she said.
More from CBS News

Bodies of three more Israeli hostages recovered from Gaza

Lenny Kravitz opens up about his insecurities

Lenny Kravitz talks new album, NYC roots and more

Trump says he believes Nikki Haley is going to be "on our team in some form"
- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters
Should homework be banned?
Social media has sparked into life about whether children should be given homework - should students be freed from this daily chore? Dr Gerald Letendre, a professor of education at Pennsylvania State University, investigates.
We’ve all done it: pretended to leave an essay at home, or stayed up until 2am to finish a piece of coursework we’ve been ignoring for weeks. Homework, for some people, is seen as a chore that’s ‘wrecking kids’ or ‘killing parents’, while others think it is an essential part of a well-rounded education. The problem is far from new: public debates about homework have been raging since at least the early-1900s, and recently spilled over into a Twitter feud between Gary Lineker and Piers Morgan.
Ironically, the conversation surrounding homework often ignores the scientific ‘homework’ that researchers have carried out. Many detailed studies have been conducted, and can guide parents, teachers and administrators to make sensible decisions about how much work should be completed by students outside of the classroom.
So why does homework stir up such strong emotions? One reason is that, by its very nature, it is an intrusion of schoolwork into family life. I carried out a study in 2005, and found that the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school, from nursery right up to the end of compulsory education, has greatly increased over the last century . This means that more of a child’s time is taken up with education, so family time is reduced. This increases pressure on the boundary between the family and the school.
Plus, the amount of homework that students receive appears to be increasing, especially in the early years when parents are keen for their children to play with friends and spend time with the family.
Finally, success in school has become increasingly important to success in life. Parents can use homework to promote, or exercise control over, their child’s academic trajectory, and hopefully ensure their future educational success. But this often leaves parents conflicted – they want their children to be successful in school, but they don’t want them to be stressed or upset because of an unmanageable workload.

However, the issue isn’t simply down to the opinions of parents, children and their teachers – governments also like to get involved. In the autumn of 2012, French president François Hollande hit world headlines after making a comment about banning homework, ostensibly because it promoted inequality. The Chinese government has also toyed with a ban, because of concerns about excessive academic pressure being put on children.
The problem is, some politicians and national administrators regard regulatory policy in education as a solution for a wide array of social, economic and political issues, perhaps without considering the consequences for students and parents.
Does homework work?
Homework seems to generally have a positive effect for high school students, according to an extensive range of empirical literature. For example, Duke University’s Prof Harris Cooper carried out a meta-analysis using data from US schools, covering a period from 1987 to 2003. He found that homework offered a general beneficial impact on test scores and improvements in attitude, with a greater effect seen in older students. But dig deeper into the issue and a complex set of factors quickly emerges, related to how much homework students do, and exactly how they feel about it.
In 2009, Prof Ulrich Trautwein and his team at the University of Tübingen found that in order to establish whether homework is having any effect, researchers must take into account the differences both between and within classes . For example, a teacher may assign a good deal of homework to a lower-level class, producing an association between more homework and lower levels of achievement. Yet, within the same class, individual students may vary significantly in how much homework improves their baseline performance. Plus, there is the fact that some students are simply more efficient at completing their homework than others, and it becomes quite difficult to pinpoint just what type of homework, and how much of it, will affect overall academic performance.
Over the last century, the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school has greatly increased
Gender is also a major factor. For example, a study of US high school students carried out by Prof Gary Natriello in the 1980s revealed that girls devote more time to homework than boys, while a follow-up study found that US girls tend to spend more time on mathematics homework than boys. Another study, this time of African-American students in the US, found that eighth grade (ages 13-14) girls were more likely to successfully manage both their tasks and emotions around schoolwork, and were more likely to finish homework.
So why do girls seem to respond more positively to homework? One possible answer proposed by Eunsook Hong of the University of Nevada in 2011 is that teachers tend to rate girls’ habits and attitudes towards work more favourably than boys’. This perception could potentially set up a positive feedback loop between teacher expectations and the children’s capacity for academic work based on gender, resulting in girls outperforming boys. All of this makes it particularly difficult to determine the extent to which homework is helping, though it is clear that simply increasing the time spent on assignments does not directly correspond to a universal increase in learning.
Can homework cause damage?
The lack of empirical data supporting homework in the early years of education, along with an emerging trend to assign more work to this age range, appears to be fuelling parental concerns about potential negative effects. But, aside from anecdotes of increased tension in the household, is there any evidence of this? Can doing too much homework actually damage children?
Evidence suggests extreme amounts of homework can indeed have serious effects on students’ health and well-being. A Chinese study carried out in 2010 found a link between excessive homework and sleep disruption: children who had less homework had better routines and more stable sleep schedules. A Canadian study carried out in 2015 by Isabelle Michaud found that high levels of homework were associated with a greater risk of obesity among boys, if they were already feeling stressed about school in general.
For useful revision guides and video clips to assist with learning, visit BBC Bitesize . This is a free online study resource for UK students from early years up to GCSEs and Scottish Highers.
It is also worth noting that too much homework can create negative effects that may undermine any positives. These negative consequences may not only affect the child, but also could also pile on the stress for the whole family, according to a recent study by Robert Pressman of the New England Centre for Pediatric Psychology. Parents were particularly affected when their perception of their own capacity to assist their children decreased.
What then, is the tipping point, and when does homework simply become too much for parents and children? Guidelines typically suggest that children in the first grade (six years old) should have no more that 10 minutes per night, and that this amount should increase by 10 minutes per school year. However, cultural norms may greatly affect what constitutes too much.
A study of children aged between 8 and 10 in Quebec defined high levels of homework as more than 30 minutes a night, but a study in China of children aged 5 to 11 deemed that two or more hours per night was excessive. It is therefore difficult to create a clear standard for what constitutes as too much homework, because cultural differences, school-related stress, and negative emotions within the family all appear to interact with how homework affects children.
Should we stop setting homework?
In my opinion, even though there are potential risks of negative effects, homework should not be banned. Small amounts, assigned with specific learning goals in mind and with proper parental support, can help to improve students’ performance. While some studies have generally found little evidence that homework has a positive effect on young children overall, a 2008 study by Norwegian researcher Marte Rønning found that even some very young children do receive some benefit. So simply banning homework would mean that any particularly gifted or motivated pupils would not be able to benefit from increased study. However, at the earliest ages, very little homework should be assigned. The decisions about how much and what type are best left to teachers and parents.
As a parent, it is important to clarify what goals your child’s teacher has for homework assignments. Teachers can assign work for different reasons – as an academic drill to foster better study habits, and unfortunately, as a punishment. The goals for each assignment should be made clear, and should encourage positive engagement with academic routines.

Parents should inform the teachers of how long the homework is taking, as teachers often incorrectly estimate the amount of time needed to complete an assignment, and how it is affecting household routines. For young children, positive teacher support and feedback is critical in establishing a student’s positive perception of homework and other academic routines. Teachers and parents need to be vigilant and ensure that homework routines do not start to generate patterns of negative interaction that erode students’ motivation.
Likewise, any positive effects of homework are dependent on several complex interactive factors, including the child’s personal motivation, the type of assignment, parental support and teacher goals. Creating an overarching policy to address every single situation is not realistic, and so homework policies tend to be fixated on the time the homework takes to complete. But rather than focusing on this, everyone would be better off if schools worked on fostering stronger communication between parents, teachers and students, allowing them to respond more sensitively to the child’s emotional and academic needs.
- Five brilliant science books for kids
- Will e-learning replace teachers?
Follow Science Focus on Twitter , Facebook , Instagram and Flipboard
Share this article

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Enter Today's Teacher Appreciation Giveaway!
Should We Ban Homework?
The cons of homework are starting to outweigh the pros.

Recent research shows that teenagers have doubled the amount of time they spend on homework since the 1990s. This is in spite of other, well-documented research that calls the efficacy of homework into question, albeit in the younger grades. Why are students spending so much time on homework if the impact is zero (for younger kids) or moderate (for older ones)? Should we ban homework? These are the questions teachers, parents, and lawmakers are asking.
Bans proposed and implemented in the U.S. and abroad
The struggle of whether or not to assign homework is not a new one. In 2017, a Florida superintendent banned homework for elementary schools in the entire district, with one very important exception: reading at home. The United States isn’t the only country to question the benefits of homework. Last August, the Philippines proposed a bill to ban homework completely, citing the need for rest, relaxation, and time with family. Another bill there proposed no weekend homework, with teachers running the risk of fines or two years in prison. (Yikes!) While a prison sentence may seem extreme, there are real reasons to reconsider homework.
Refocus on mental health and educate the “whole child”
Prioritizing mental health is at the forefront of the homework ban movement. Leaders say they want to give students time to develop other hobbies, relationships, and balance in their lives.
This month two Utah elementary schools gained national recognition for officially banning homework. The results are significant, with psychologist referrals for anxiety decreasing by 50 percent. Many schools are looking for ways to refocus on wellness, and homework can be a real cause of stress.
[contextly_auto_sidebar]
Research supports a ban for elementary schools
Supporters of a homework ban often cite research from John Hattie, who concluded that elementary school homework has no effect on academic progress. In a podcast he said, “Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?'”
In the upper grades, Hattie’s research shows that homework has to be purposeful, not busy work. And the reality is, most teachers don’t receive training on how to assign homework that is meaningful and relevant to students.
Parents push back, too
In October this Washington Post article made waves in parenting and education communities when it introduced the idea that, even if homework is assigned, it doesn’t have to be completed for the student to pass the class. The writer explains how her family doesn’t believe in homework, and doesn’t participate. In response, other parents started “opting out” of homework, citing research that homework in elementary school doesn’t further intelligence or academic success.
Of course, homework has its defenders, especially in the upper grades
“I think some homework is a good idea,” says Darla E. in our WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook. “Ideally, it forces the parents to take some responsibility for their child’s education. It also reinforces what students learn and instills good study habits for later in life.”
Jennifer M. agrees. “If we are trying to make students college-ready, they need the skill of doing homework.”
And the research does support some homework in middle and high school, as long as it is clearly tied to learning and not overwhelming.
We’d love to hear your thoughts—do you think schools should ban homework? Come and share in our WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, why you should stop assigning reading homework.

You Might Also Like

Dear Parents: Please Stop Asking Teachers To Give Your Kids Homework
If your kid's teacher isn't assigning homework, it's for a good reason. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter

Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners

Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce
15 Should Homework Be Banned Pros and Cons
Homework was a staple of the public and private schooling experience for many of us growing up. There were long nights spent on book reports, science projects, and all of those repetitive math sheets. In many ways, it felt like an inevitable part of the educational experience. Unless you could power through all of your assignments during your free time in class, then there was going to be time spent at home working on specific subjects.
More schools are looking at the idea of banning homework from the modern educational experience. Instead of sending work home with students each night, they are finding alternative ways to ensure that each student can understand the curriculum without involving the uncertainty of parental involvement.
Although banning homework might seem like an unorthodox process, there are legitimate advantages to consider with this effort. There are some disadvantages which some families may encounter as well.
These are the updated lists of the pros and cons of banning homework to review.
List of the Pros of Banning Homework
1. Giving homework to students does not always improve their academic outcomes. The reality of homework for the modern student is that we do not know if it is helpful to have extra work assigned to them outside of the classroom. Every study that has looked at the subject has had design flaws which causes the data collected to be questionable at best. Although there is some information to suggest that students in seventh grade and higher can benefit from limited homework, banning it for students younger than that seems to be beneficial for their learning experience.
2. Banning homework can reduce burnout issues with students. Teachers are seeing homework stress occur in the classroom more frequently today than ever before. Almost half of all high school teachers in North America have seen this issue with their students at some point during the year. About 25% of grade school teachers say that they have seen the same thing.
When students are dealing with the impact of homework on their lives, it can have a tremendously adverse impact. One of the most cited reasons for students dropping out of school is that they cannot complete their homework on time.
3. Banning homework would increase the amount of family time available to students. Homework creates a significant disruption to family relationships. Over half of all parents in North America say that they have had a significant argument with their children over homework in the past month. 1/3 of families say that homework is their primary source of struggle in the home. Not only does it reduce the amount of time that everyone has to spend together, it reduces the chances that parents have to teach their own skills and belief systems to their kids.
4. It reduces the negative impact of homework on the health of a student. Many students suffer academically when they cannot finish a homework assignment on time. Although assumptions are often made about the time management skills of the individual when this outcome occurs, the reasons why it happens is usually more complex. It may be too difficult, too boring, or there may not be enough time in the day to complete the work.
When students experience failure in this area, it can lead to severe mental health issues. Some perceive themselves as a scholarly failure, which translates to an inability to live life successfully. It can disrupt a desire to learn. There is even an increased risk of suicide for some youth because of this issue. Banning it would reduce these risks immediately.
5. Eliminating homework would allow for an established sleep cycle. The average high school student requires between 8-10 hours of sleep to function at their best the next day. Grade-school students may require an extra hour or two beyond that figure. When teachers assign homework, then it increases the risk for each individual that they will not receive the amount that they require each night.
When children do not get enough sleep, a significant rest deficit occurs which can impact their ability to pay attention in school. It can cause unintended weight gain. There may even be issues with emotional control. Banning homework would help to reduce these risks as well.
6. It increases the amount of socialization time that students receive. People who are only spending time in school and then going home to do more work are at a higher risk of experiencing loneliness and isolation. When these emotions are present, then a student is more likely to feel “down and out” mentally and physically. They lack meaningful connections with other people. These feelings are the health equivalent of smoking 15 cigarettes per day. If students are spending time on homework, then they are not spending time connecting with their family and friends.
7. It reduces the repetition that students face in the modern learning process. Most of the tasks that homework requires of students is repetitive and uninteresting. Kids love to resolve challenges on tasks that they are passionate about at that moment in their lives. Forcing them to complete the same problems repetitively as a way to “learn” core concepts can create issues with knowledge retention later in life. When you add in the fact that most lessons sent for homework must be done by themselves, banning homework will reduce the repetition that students face, allowing for a better overall outcome.
8. Home environments can be chaotic. Although some students can do homework in a quiet room without distractions, that is not the case for most kids. There are numerous events that happen at home which can pull a child’s attention away from the work that their teacher wants them to do. It isn’t just the Internet, video games, and television which are problematic either. Household chores, family issues, employment, and athletic requirements can make it a challenge to get the assigned work finished on time.
List of the Cons of Banning Homework
1. Homework allows parents to be involved with the educational process. Parents need to know what their children are learning in school. Even if they ask their children about what they are learning, the answers tend to be in generalities instead of specifics. By sending home work from the classroom, it allows parents to see and experience the work that their kids are doing when they are in school during the day. Then moms and dads can get involved with the learning process to reinforce the core concepts that were discovered by their children each day.
2. It can help parents and teachers identify learning disabilities. Many children develop a self-defense mechanism which allows them to appear like any other kid that is in their classroom. This process allows them to hide learning disabilities which may be hindering their educational progress. The presence of homework makes it possible for parents and teachers to identify this issue because kids can’t hide their struggles when they must work 1-on-1 with their parents on specific subjects. Banning homework would eliminate 50% of the opportunities to identify potential issues immediately.
3. Homework allows teachers to observe how their students understand the material. Teachers often use homework as a way to gauge how well a student is understanding the materials they are learning. Although some might point out that assignments and exams in the classroom can do the same thing, testing often requires preparation at home. It creates more anxiety and stress sometimes then even homework does. That is why banning it can be problematic for some students. Some students experience more pressure than they would during this assessment process when quizzes and tests are the only measurement of their success.
4. It teaches students how to manage their time wisely. As people grow older, they realize that time is a finite commodity. We must manage it wisely to maximize our productivity. Homework assignments are a way to encourage the development of this skill at an early age. The trick is to keep the amount of time required for the work down to a manageable level. As a general rule, students should spend about 10 minutes each school day doing homework, organizing their schedule around this need. If there are scheduling conflicts, then this process offers families a chance to create priorities.
5. Homework encourages students to be accountable for their role. Teachers are present in the classroom to offer access to information and skill-building opportunities that can improve the quality of life for each student. Administrators work to find a curriculum that will benefit the most people in an efficient way. Parents work hard to ensure their kids make it to school on time, follow healthy routines, and communicate with their school district to ensure the most effective learning opportunities possible. None of that matters if the student is not invested in the work in the first place. Homework assignments not only teach children how to work independently, but they also show them how to take responsibility for their part of the overall educational process.
6. It helps to teach important life lessons. Homework is an essential tool in the development of life lessons, such as communicating with others or comprehending something they have just read. It teaches kids how to think, solve problems, and even build an understanding for the issues that occur in our society right now. Many of the issues that lead to the idea to ban homework occur because someone in the life of a student communicated to them that this work was a waste of time. There are times in life when people need to do things that they don’t like or want to do. Homework helps a student begin to find the coping skills needed to be successful in that situation.
7. Homework allows for further research into class materials. Most classrooms offer less than 1 hour of instruction per subject during the day. For many students, that is not enough time to obtain a firm grasp on the materials being taught. Having homework assignments allows a student to perform more research, using their at-home tools to take a deeper look into the materials that would otherwise be impossible if homework was banned. That process can lead to a more significant understanding of the concepts involved, reducing anxiety levels because they have a complete grasp on the materials.
The pros and cons of banning homework is a decision that ultimately lies with each school district. Parents always have the option to pursue homeschooling or online learning if they disagree with the decisions that are made in this area. Whether you’re for more homework or want to see less of it, we can all agree on the fact that the absence of any reliable data about its usefulness makes it a challenge to know for certain which option is the best one to choose in this debate.
Homework in America
- 2014 Brown Center Report on American Education
Subscribe to the Brown Center on Education Policy Newsletter
Tom loveless tom loveless former brookings expert @tomloveless99.
March 18, 2014
- 18 min read
Part II of the 2014 Brown Center Report on American Education

Homework! The topic, no, just the word itself, sparks controversy. It has for a long time. In 1900, Edward Bok, editor of the Ladies Home Journal , published an impassioned article, “A National Crime at the Feet of Parents,” accusing homework of destroying American youth. Drawing on the theories of his fellow educational progressive, psychologist G. Stanley Hall (who has since been largely discredited), Bok argued that study at home interfered with children’s natural inclination towards play and free movement, threatened children’s physical and mental health, and usurped the right of parents to decide activities in the home.
The Journal was an influential magazine, especially with parents. An anti-homework campaign burst forth that grew into a national crusade. [i] School districts across the land passed restrictions on homework, culminating in a 1901 statewide prohibition of homework in California for any student under the age of 15. The crusade would remain powerful through 1913, before a world war and other concerns bumped it from the spotlight. Nevertheless, anti-homework sentiment would remain a touchstone of progressive education throughout the twentieth century. As a political force, it would lie dormant for years before bubbling up to mobilize proponents of free play and “the whole child.” Advocates would, if educators did not comply, seek to impose homework restrictions through policy making.
Our own century dawned during a surge of anti-homework sentiment. From 1998 to 2003, Newsweek , TIME , and People , all major national publications at the time, ran cover stories on the evils of homework. TIME ’s 1999 story had the most provocative title, “The Homework Ate My Family: Kids Are Dazed, Parents Are Stressed, Why Piling On Is Hurting Students.” People ’s 2003 article offered a call to arms: “Overbooked: Four Hours of Homework for a Third Grader? Exhausted Kids (and Parents) Fight Back.” Feature stories about students laboring under an onerous homework burden ran in newspapers from coast to coast. Photos of angst ridden children became a journalistic staple.
The 2003 Brown Center Report on American Education included a study investigating the homework controversy. Examining the most reliable empirical evidence at the time, the study concluded that the dramatic claims about homework were unfounded. An overwhelming majority of students, at least two-thirds, depending on age, had an hour or less of homework each night. Surprisingly, even the homework burden of college-bound high school seniors was discovered to be rather light, less than an hour per night or six hours per week. Public opinion polls also contradicted the prevailing story. Parents were not up in arms about homework. Most said their children’s homework load was about right. Parents wanting more homework out-numbered those who wanted less.
Now homework is in the news again. Several popular anti-homework books fill store shelves (whether virtual or brick and mortar). [ii] The documentary Race to Nowhere depicts homework as one aspect of an overwrought, pressure-cooker school system that constantly pushes students to perform and destroys their love of learning. The film’s website claims over 6,000 screenings in more than 30 countries. In 2011, the New York Times ran a front page article about the homework restrictions adopted by schools in Galloway, NJ, describing “a wave of districts across the nation trying to remake homework amid concerns that high stakes testing and competition for college have fueled a nightly grind that is stressing out children and depriving them of play and rest, yet doing little to raise achievement, especially in elementary grades.” In the article, Vicki Abeles, the director of Race to Nowhere , invokes the indictment of homework lodged a century ago, declaring, “The presence of homework is negatively affecting the health of our young people and the quality of family time.” [iii]
A petition for the National PTA to adopt “healthy homework guidelines” on change.org currently has 19,000 signatures. In September 2013, Atlantic featured an article, “My Daughter’s Homework is Killing Me,” by a Manhattan writer who joined his middle school daughter in doing her homework for a week. Most nights the homework took more than three hours to complete.
The Current Study
A decade has passed since the last Brown Center Report study of homework, and it’s time for an update. How much homework do American students have today? Has the homework burden increased, gone down, or remained about the same? What do parents think about the homework load?
A word on why such a study is important. It’s not because the popular press is creating a fiction. The press accounts are built on the testimony of real students and real parents, people who are very unhappy with the amount of homework coming home from school. These unhappy people are real—but they also may be atypical. Their experiences, as dramatic as they are, may not represent the common experience of American households with school-age children. In the analysis below, data are analyzed from surveys that are methodologically designed to produce reliable information about the experiences of all Americans. Some of the surveys have existed long enough to illustrate meaningful trends. The question is whether strong empirical evidence confirms the anecdotes about overworked kids and outraged parents.
Data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) provide a good look at trends in homework for nearly the past three decades. Table 2-1 displays NAEP data from 1984-2012. The data are from the long-term trend NAEP assessment’s student questionnaire, a survey of homework practices featuring both consistently-worded questions and stable response categories. The question asks: “How much time did you spend on homework yesterday?” Responses are shown for NAEP’s three age groups: 9, 13, and 17. [iv]
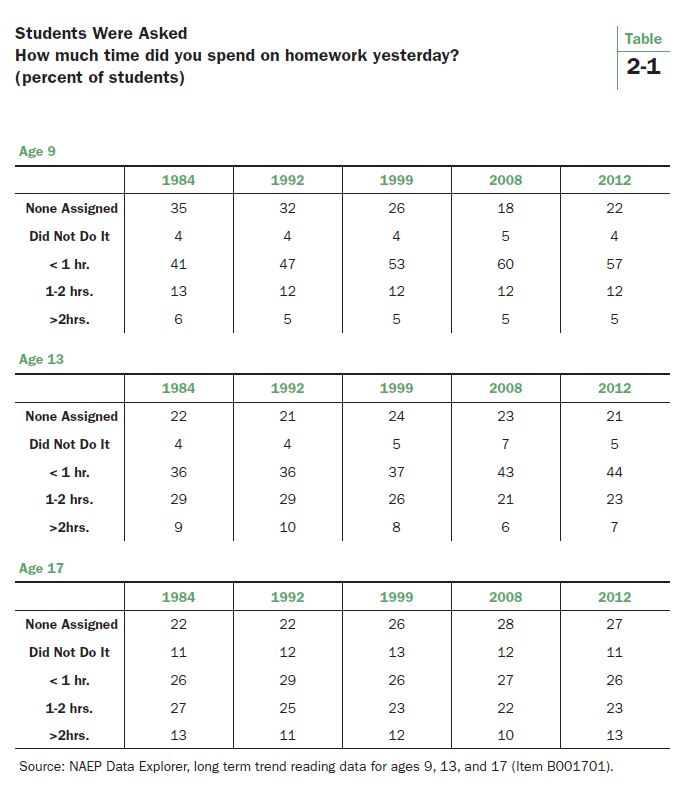
Today’s youngest students seem to have more homework than in the past. The first three rows of data for age 9 reveal a shift away from students having no homework, declining from 35% in 1984 to 22% in 2012. A slight uptick occurred from the low of 18% in 2008, however, so the trend may be abating. The decline of the “no homework” group is matched by growth in the percentage of students with less than an hour’s worth, from 41% in 1984 to 57% in 2012. The share of students with one to two hours of homework changed very little over the entire 28 years, comprising 12% of students in 2012. The group with the heaviest load, more than two hours of homework, registered at 5% in 2012. It was 6% in 1984.
The amount of homework for 13-year-olds appears to have lightened slightly. Students with one to two hours of homework declined from 29% to 23%. The next category down (in terms of homework load), students with less than an hour, increased from 36% to 44%. One can see, by combining the bottom two rows, that students with an hour or more of homework declined steadily from 1984 to 2008 (falling from 38% to 27%) and then ticked up to 30% in 2012. The proportion of students with the heaviest load, more than two hours, slipped from 9% in 1984 to 7% in 2012 and ranged between 7-10% for the entire period.
For 17-year-olds, the homework burden has not varied much. The percentage of students with no homework has increased from 22% to 27%. Most of that gain occurred in the 1990s. Also note that the percentage of 17-year-olds who had homework but did not do it was 11% in 2012, the highest for the three NAEP age groups. Adding that number in with the students who didn’t have homework in the first place means that more than one-third of seventeen year olds (38%) did no homework on the night in question in 2012. That compares with 33% in 1984. The segment of the 17-year-old population with more than two hours of homework, from which legitimate complaints of being overworked might arise, has been stuck in the 10%-13% range.
The NAEP data point to four main conclusions:
- With one exception, the homework load has remained remarkably stable since 1984.
- The exception is nine-year-olds. They have experienced an increase in homework, primarily because many students who once did not have any now have some. The percentage of nine-year-olds with no homework fell by 13 percentage points, and the percentage with less than an hour grew by 16 percentage points.
- Of the three age groups, 17-year-olds have the most bifurcated distribution of the homework burden. They have the largest percentage of kids with no homework (especially when the homework shirkers are added in) and the largest percentage with more than two hours.
- NAEP data do not support the idea that a large and growing number of students have an onerous amount of homework. For all three age groups, only a small percentage of students report more than two hours of homework. For 1984-2012, the size of the two hours or more groups ranged from 5-6% for age 9, 6-10% for age 13, and 10-13% for age 17.
Note that the item asks students how much time they spent on homework “yesterday.” That phrasing has the benefit of immediacy, asking for an estimate of precise, recent behavior rather than an estimate of general behavior for an extended, unspecified period. But misleading responses could be generated if teachers lighten the homework of NAEP participants on the night before the NAEP test is given. That’s possible. [v] Such skewing would not affect trends if it stayed about the same over time and in the same direction (teachers assigning less homework than usual on the day before NAEP). Put another way, it would affect estimates of the amount of homework at any single point in time but not changes in the amount of homework between two points in time.
A check for possible skewing is to compare the responses above with those to another homework question on the NAEP questionnaire from 1986-2004 but no longer in use. [vi] It asked students, “How much time do you usually spend on homework each day?” Most of the response categories have different boundaries from the “last night” question, making the data incomparable. But the categories asking about no homework are comparable. Responses indicating no homework on the “usual” question in 2004 were: 2% for age 9-year-olds, 5% for 13 year olds, and 12% for 17-year-olds. These figures are much less than the ones reported in Table 2-1 above. The “yesterday” data appear to overstate the proportion of students typically receiving no homework.
The story is different for the “heavy homework load” response categories. The “usual” question reported similar percentages as the “yesterday” question. The categories representing the most amount of homework were “more than one hour” for age 9 and “more than two hours” for ages 13 and 17. In 2004, 12% of 9-year-olds said they had more than one hour of daily homework, while 8% of 13-year-olds and 12% of 17-year-olds said they had more than two hours. For all three age groups, those figures declined from1986 to 2004. The decline for age 17 was quite large, falling from 17% in 1986 to 12% in 2004.
The bottom line: regardless of how the question is posed, NAEP data do not support the view that the homework burden is growing, nor do they support the belief that the proportion of students with a lot of homework has increased in recent years. The proportion of students with no homework is probably under-reported on the long-term trend NAEP. But the upper bound of students with more than two hours of daily homework appears to be about 15%–and that is for students in their final years of high school.
College Freshmen Look Back
There is another good source of information on high school students’ homework over several decades. The Higher Education Research Institute at UCLA conducts an annual survey of college freshmen that began in 1966. In 1986, the survey started asking a series of questions regarding how students spent time in the final year of high school. Figure 2-1 shows the 2012 percentages for the dominant activities. More than half of college freshmen say they spent at least six hours per week socializing with friends (66.2%) and exercising/sports (53.0%). About 40% devoted that much weekly time to paid employment.
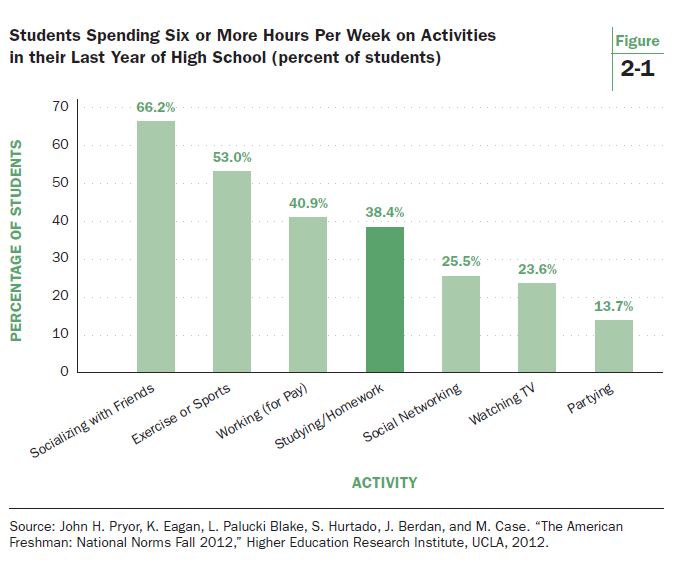
Homework comes in fourth pace. Only 38.4% of students said they spent at least six hours per week studying or doing homework. When these students were high school seniors, it was not an activity central to their out of school lives. That is quite surprising. Think about it. The survey is confined to the nation’s best students, those attending college. Gone are high school dropouts. Also not included are students who go into the military or attain full time employment immediately after high school. And yet only a little more than one-third of the sampled students, devoted more than six hours per week to homework and studying when they were on the verge of attending college.
Another notable finding from the UCLA survey is how the statistic is trending (see Figure 2-2). In 1986, 49.5% reported spending six or more hours per week studying and doing homework. By 2002, the proportion had dropped to 33.4%. In 2012, as noted in Figure 2-1, the statistic had bounced off the historical lows to reach 38.4%. It is slowly rising but still sits sharply below where it was in 1987.
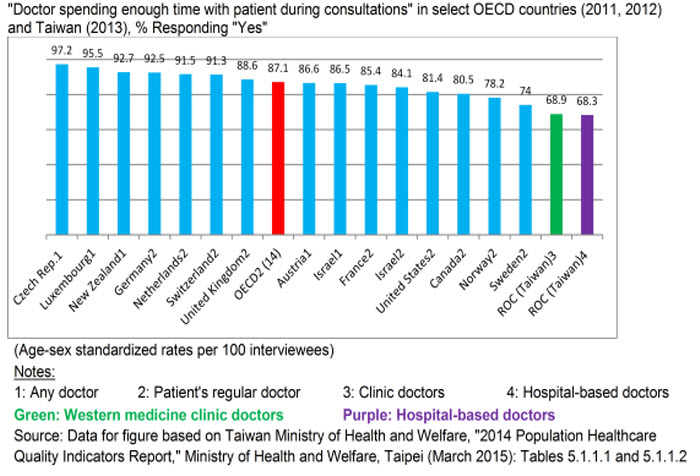
What Do Parents Think?
Met Life has published an annual survey of teachers since 1984. In 1987 and 2007, the survey included questions focusing on homework and expanded to sample both parents and students on the topic. Data are broken out for secondary and elementary parents and for students in grades 3-6 and grades 7-12 (the latter not being an exact match with secondary parents because of K-8 schools).
Table 2-2 shows estimates of homework from the 2007 survey. Respondents were asked to estimate the amount of homework on a typical school day (Monday-Friday). The median estimate of each group of respondents is shaded. As displayed in the first column, the median estimate for parents of an elementary student is that their child devotes about 30 minutes to homework on the typical weekday. Slightly more than half (52%) estimate 30 minutes or less; 48% estimate 45 minutes or more. Students in grades 3-6 (third column) give a median estimate that is a bit higher than their parents’ (45 minutes), with almost two-thirds (63%) saying 45 minutes or less is the typical weekday homework load.
One hour of homework is the median estimate for both secondary parents and students in grade 7-12, with 55% of parents reporting an hour or less and about two-thirds (67%) of students reporting the same. As for the prevalence of the heaviest homework loads, 11% of secondary parents say their children spend more than two hours on weekday homework, and 12% is the corresponding figure for students in grades 7-12.
The Met Life surveys in 1987 and 2007 asked parents to evaluate the amount and quality of homework. Table 2-3 displays the results. There was little change over the two decades separating the two surveys. More than 60% of parents rate the amount of homework as good or excellent, and about two-thirds give such high ratings to the quality of the homework their children are receiving. The proportion giving poor ratings to either the quantity or quality of homework did not exceed 10% on either survey.
Parental dissatisfaction with homework comes in two forms: those who feel schools give too much homework and those who feel schools do not give enough. The current wave of journalism about unhappy parents is dominated by those who feel schools give too much homework. How big is this group? Not very big (see Figure 2-3). On the Met Life survey, 60% of parents felt schools were giving the right amount of homework, 25% wanted more homework, and only 15% wanted less.
National surveys on homework are infrequent, but the 2006-2007 period had more than one. A poll conducted by Public Agenda in 2006 reported similar numbers as the Met Life survey: 68% of parents describing the homework load as “about right,” 20% saying there is “too little homework,” and 11% saying there is “too much homework.” A 2006 AP-AOL poll found the highest percentage of parents reporting too much homework, 19%. But even in that poll, they were outnumbered by parents believing there is too little homework (23%), and a clear majority (57%) described the load as “about right.” A 2010 local survey of Chicago parents conducted by the Chicago Tribune reported figures similar to those reported above: approximately two-thirds of parents saying their children’s homework load is “about right,” 21% saying it’s not enough, and 12% responding that the homework load is too much.
Summary and Discussion
In recent years, the press has been filled with reports of kids over-burdened with homework and parents rebelling against their children’s oppressive workload. The data assembled above call into question whether that portrait is accurate for the typical American family. Homework typically takes an hour per night. The homework burden of students rarely exceeds two hours a night. The upper limit of students with two or more hours per night is about 15% nationally—and that is for juniors or seniors in high school. For younger children, the upper boundary is about 10% who have such a heavy load. Polls show that parents who want less homework range from 10%-20%, and that they are outnumbered—in every national poll on the homework question—by parents who want more homework, not less. The majority of parents describe their children’s homework burden as about right.
So what’s going on? Where are the homework horror stories coming from?
The Met Life survey of parents is able to give a few hints, mainly because of several questions that extend beyond homework to other aspects of schooling. The belief that homework is burdensome is more likely held by parents with a larger set of complaints and concerns. They are alienated from their child’s school. About two in five parents (19%) don’t believe homework is important. Compared to other parents, these parents are more likely to say too much homework is assigned (39% vs. 9%), that what is assigned is just busywork (57% vs. 36%), and that homework gets in the way of their family spending time together (51% vs. 15%). They are less likely to rate the quality of homework as excellent (3% vs. 23%) or to rate the availability and responsiveness of teachers as excellent (18% vs. 38%). [vii]
They can also convince themselves that their numbers are larger than they really are. Karl Taro Greenfeld, the author of the Atlantic article mentioned above, seems to fit that description. “Every parent I know in New York City comments on how much homework their children have,” Mr. Greenfeld writes. As for those parents who do not share this view? “There is always a clique of parents who are happy with the amount of homework. In fact, they would prefer more . I tend not to get along with that type of parent.” [viii]
Mr. Greenfeld’s daughter attends a selective exam school in Manhattan, known for its rigorous expectations and, yes, heavy homework load. He had also complained about homework in his daughter’s previous school in Brentwood, CA. That school was a charter school. After Mr. Greenfeld emailed several parents expressing his complaints about homework in that school, the school’s vice-principal accused Mr. Greenfeld of cyberbullying. The lesson here is that even schools of choice are not immune from complaints about homework.
The homework horror stories need to be read in a proper perspective. They seem to originate from the very personal discontents of a small group of parents. They do not reflect the experience of the average family with a school-age child. That does not diminish these stories’ power to command the attention of school officials or even the public at large. But it also suggests a limited role for policy making in settling such disputes. Policy is a blunt instrument. Educators, parents, and kids are in the best position to resolve complaints about homework on a case by case basis. Complaints about homework have existed for more than a century, and they show no signs of going away.
Part II Notes:
[i]Brian Gill and Steven Schlossman, “A Sin Against Childhood: Progressive Education and the Crusade to Abolish Homework, 1897-1941,” American Journal of Education , vol. 105, no. 1 (Nov., 1996), 27-66. Also see Brian P. Gill and Steven L. Schlossman, “Villain or Savior? The American Discourse on Homework, 1850-2003,” Theory into Practice , 43, 3 (Summer 2004), pp. 174-181.
[ii] Bennett, Sara, and Nancy Kalish. The Case Against Homework: How Homework Is Hurting Our Children and What We Can Do About It (New York: Crown, 2006). Buell, John. Closing the Book on Homework: Enhancing Public Education and Freeing Family Time . (Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 2004). Kohn, Alfie. The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing (Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press, 2006). Kralovec, Etta, and John Buell. The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning (Boston: Beacon Press, 2000).
[iii] Hu, Winnie, “ New Recruit in Homework Revolt: The Principal ,” New York Times , June 15, 2011, page a1.
[iv] Data for other years are available on the NAEP Data Explorer. For Table 1, the starting point of 1984 was chosen because it is the first year all three ages were asked the homework question. The two most recent dates (2012 and 2008) were chosen to show recent changes, and the two years in the 1990s to show developments during that decade.
[v] NAEP’s sampling design lessens the probability of skewing the homework figure. Students are randomly drawn from a school population, meaning that an entire class is not tested. Teachers would have to either single out NAEP students for special homework treatment or change their established homework routine for the whole class just to shelter NAEP participants from homework. Sampling designs that draw entact classrooms for testing (such as TIMSS) would be more vulnerable to this effect. Moreover, students in middle and high school usually have several different teachers during the day, meaning that prior knowledge of a particular student’s participation in NAEP would probably be limited to one or two teachers.
[vi] NAEP Question B003801 for 9 year olds and B003901 for 13- and 17-year olds.
[vii] Met Life, Met Life Survey of the American Teacher: The Homework Experience , November 13, 2007, pp. 21-22.
[viii] Greenfeld, Karl Taro, “ My Daughter’s Homework Is Killing Me ,” The Atlantic , September 18, 2013.
Education Policy K-12 Education
Governance Studies
Brown Center on Education Policy
Annelies Goger, Katherine Caves, Hollis Salway
May 16, 2024
Sofoklis Goulas, Isabelle Pula
Melissa Kay Diliberti, Elizabeth D. Steiner, Ashley Woo
Should Kids Get Homework?
Homework gives elementary students a way to practice concepts, but too much can be harmful, experts say.

Getty Images
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful.
How much homework students should get has long been a source of debate among parents and educators. In recent years, some districts have even implemented no-homework policies, as students juggle sports, music and other activities after school.
Parents of elementary school students, in particular, have argued that after-school hours should be spent with family or playing outside rather than completing assignments. And there is little research to show that homework improves academic achievement for elementary students.
But some experts say there's value in homework, even for younger students. When done well, it can help students practice core concepts and develop study habits and time management skills. The key to effective homework, they say, is keeping assignments related to classroom learning, and tailoring the amount by age: Many experts suggest no homework for kindergartners, and little to none in first and second grade.
Value of Homework
Homework provides a chance to solidify what is being taught in the classroom that day, week or unit. Practice matters, says Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University 's Wheelock College of Education & Human Development.
"There really is no other domain of human ability where anybody would say you don't need to practice," she adds. "We have children practicing piano and we have children going to sports practice several days a week after school. You name the domain of ability and practice is in there."
Homework is also the place where schools and families most frequently intersect.
"The children are bringing things from the school into the home," says Paula S. Fass, professor emerita of history at the University of California—Berkeley and the author of "The End of American Childhood." "Before the pandemic, (homework) was the only real sense that parents had to what was going on in schools."
Harris Cooper, professor emeritus of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University and author of "The Battle Over Homework," examined more than 60 research studies on homework between 1987 and 2003 and found that — when designed properly — homework can lead to greater student success. Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary.
"Every child should be doing homework, but the amount and type that they're doing should be appropriate for their developmental level," he says. "For teachers, it's a balancing act. Doing away with homework completely is not in the best interest of children and families. But overburdening families with homework is also not in the child's or a family's best interest."
Negative Homework Assignments
Not all homework for elementary students involves completing a worksheet. Assignments can be fun, says Cooper, like having students visit educational locations, keep statistics on their favorite sports teams, read for pleasure or even help their parents grocery shop. The point is to show students that activities done outside of school can relate to subjects learned in the classroom.
But assignments that are just busy work, that force students to learn new concepts at home, or that are overly time-consuming can be counterproductive, experts say.
Homework that's just busy work.
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful, experts say. Assignments that look more like busy work – projects or worksheets that don't require teacher feedback and aren't related to topics learned in the classroom – can be frustrating for students and create burdens for families.
"The mental health piece has definitely played a role here over the last couple of years during the COVID-19 pandemic, and the last thing we want to do is frustrate students with busy work or homework that makes no sense," says Dave Steckler, principal of Red Trail Elementary School in Mandan, North Dakota.
Homework on material that kids haven't learned yet.
With the pressure to cover all topics on standardized tests and limited time during the school day, some teachers assign homework that has not yet been taught in the classroom.
Not only does this create stress, but it also causes equity challenges. Some parents speak languages other than English or work several jobs, and they aren't able to help teach their children new concepts.
" It just becomes agony for both parents and the kids to get through this worksheet, and the goal becomes getting to the bottom of (the) worksheet with answers filled in without any understanding of what any of it matters for," says professor Susan R. Goldman, co-director of the Learning Sciences Research Institute at the University of Illinois—Chicago .
Homework that's overly time-consuming.
The standard homework guideline recommended by the National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association is the "10-minute rule" – 10 minutes of nightly homework per grade level. A fourth grader, for instance, would receive a total of 40 minutes of homework per night.
But this does not always happen, especially since not every student learns the same. A 2015 study published in the American Journal of Family Therapy found that primary school children actually received three times the recommended amount of homework — and that family stress increased along with the homework load.
Young children can only remain attentive for short periods, so large amounts of homework, especially lengthy projects, can negatively affect students' views on school. Some individual long-term projects – like having to build a replica city, for example – typically become an assignment for parents rather than students, Fass says.
"It's one thing to assign a project like that in which several kids are working on it together," she adds. "In (that) case, the kids do normally work on it. It's another to send it home to the families, where it becomes a burden and doesn't really accomplish very much."
Private vs. Public Schools
Do private schools assign more homework than public schools? There's little research on the issue, but experts say private school parents may be more accepting of homework, seeing it as a sign of academic rigor.
Of course, not all private schools are the same – some focus on college preparation and traditional academics, while others stress alternative approaches to education.
"I think in the academically oriented private schools, there's more support for homework from parents," says Gerald K. LeTendre, chair of educational administration at Pennsylvania State University—University Park . "I don't know if there's any research to show there's more homework, but it's less of a contentious issue."
How to Address Homework Overload
First, assess if the workload takes as long as it appears. Sometimes children may start working on a homework assignment, wander away and come back later, Cooper says.
"Parents don't see it, but they know that their child has started doing their homework four hours ago and still not done it," he adds. "They don't see that there are those four hours where their child was doing lots of other things. So the homework assignment itself actually is not four hours long. It's the way the child is approaching it."
But if homework is becoming stressful or workload is excessive, experts suggest parents first approach the teacher, followed by a school administrator.
"Many times, we can solve a lot of issues by having conversations," Steckler says, including by "sitting down, talking about the amount of homework, and what's appropriate and not appropriate."
Study Tips for High School Students

Tags: K-12 education , students , elementary school , children
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
Thanks for visiting! GoodRx is not available outside of the United States. If you are trying to access this site from the United States and believe you have received this message in error, please reach out to [email protected] and let us know.
Higher Education Isn’t the Enemy
Those who threaten academic freedom, from outside or inside campus, are threatening higher education itself—to America’s peril.

I ’ve spent more than five decades making difficult decisions in finance, government, business, and politics. Looking back, what most prepared me for the life I’ve led was the open exchange of ideas that I experienced in college and law school, supported by a society-wide understanding that universities and their faculty should be allowed to pursue areas of study as they see fit, without undue political or financial pressure. More broadly, throughout my career, I have seen firsthand the way America’s higher-education system strengthens our nation.
I cannot recall a time when the country’s colleges and universities, and the wide range of benefits they bring, have faced such numerous or serious threats. Protests over Gaza, Israel, Hamas, and anti-Semitism—and the attempt by certain elected officials and donors to capitalize on these protests and push a broader anti-higher-education agenda—have been the stuff of daily headlines for months. But the challenges facing colleges and universities have been building for years, revealed in conflicts over everything from climate change and curriculum to ideological diversity and academic governance.
But there is a threat that is being ignored, one that goes beyond any single issue or political controversy. Transfixed by images of colleges and universities in turmoil, we risk overlooking the foundational role that higher education plays in American life. With its underlying principles of free expression and academic freedom, the university system is one of the nation’s great strengths. It is not to be taken for granted. Undermining higher education would harm all Americans, weakening our country and making us less able to confront the many challenges we face.
T he most recent upheavals on American campuses—and the threat posed to the underlying principles of higher education—have been well documented.
In some cases, individuals have been silenced or suppressed, not because they were threatening anyone’s physical safety or disrupting the functioning of the university environment, but rather, it seems, because of their opinions. The University of Southern California, for example, recently canceled its valedictorian’s speech at graduation. Although administrators cited safety concerns, many on campus, including the student herself, said they believe that the true cause lay in the speaker’s pro-Palestinian, anti-Israel views . One does not have to agree with the sentiments being expressed by a speaker in order to be troubled by the idea that they would be suppressed because of their content.
Conor Friedersdorf: Columbia University’s impossible position
In other cases, it is the demonstrators themselves who have sought to force their views on others—by breaking university policies regarding shared spaces, occupying buildings, and reportedly imposing ideological litmus tests on students seeking to enter public areas of campus. Some activists have advocated violence against those with whom they disagree. Even before the unrest of recent weeks, I had heard for many years from students and professors that they felt a chilling effect on campuses that rendered true discussion—including exchanges of ideas that might make others uncomfortable—very difficult.
Even as free speech faces serious threats from inside the campus, academic freedom is under assault from outside. To an unprecedented degree, donors have involved themselves in pressure campaigns, explicitly linking financial support to views expressed on campus and the scholarship undertaken by students and faculty. At the University of Pennsylvania, one such effort pressed donors to reduce their annual contribution to $1 to protest the university’s decision to host a Palestinian literary conference. At Yale, Beverly Gage, the head of the prestigious Brady-Johnson Program in Grand Strategy, felt compelled to resign after the program came under increasing pressure from its donors. Among other things, the donors objected to an op-ed by an instructor in the program headlined “How to Protect America From the Next Donald Trump.”
It’s not just donors. Elected officials and candidates for office are also attacking academic freedom. On a Zoom call whose content was subsequently leaked, a Republican member of Congress, Jim Banks of Indiana, characterized recent hearings with the presidents of Harvard, MIT, Penn, and Columbia—along with upcoming ones with the presidents of Rutgers, UCLA, and Northwestern—as part of a strategy to “defund these universities.” In a recent campaign video, former President Trump asserted that colleges are “turning our students into Communists and terrorists and sympathizers,” and promised to retaliate by taxing, fining, and suing private universities if he wins a second term. Senator J. D. Vance of Ohio, a close ally of Trump’s, has introduced a bill that would punish schools that don’t crack down on demonstrators. The bill would tax the endowment of such schools heavily and curb their access to federal funds.
The methods of these donors and politicians—politically motivated subpoenas and hearings, social-media pressure campaigns, campaign-trail threats—may not violate the First Amendment. They do, however, seek to produce a chilling effect on free speech. The goal of these efforts is to force universities to bow to outside pressure and curtail the range of ideas they allow—not because scholars at universities believe those ideas lack merit, but because the ideas are at odds with the political views of those bringing the pressure.
A ll of this needs to be seen against a foreboding backdrop. At a time when trust in many American institutions is at an all-time low, skepticism about higher education is on the rise. Earlier this year, a noteworthy essay by Douglas Belkin in The Wall Street Journal explored “Why Americans Have Lost Faith in the Value of College.” The New York Times wondered last fall whether college might be a “risky bet.” According to Gallup, confidence in higher education has fallen dramatically—from 57 percent in 2015 to 36 percent in 2023. The attacks on free expression and academic freedom on campus are both causes and symptoms of this declining confidence.
It is ironic that, at a moment when higher education faces unprecedented assaults, more Americans than ever have a college diploma. When I graduated from college, in 1960, only 8 percent of Americans held a four-year degree. Today, that number has increased almost fivefold, to 38 percent. Even so, I suspect that many Americans don’t realize just how exceptional the country’s university system actually is. Although the United States can claim less than 5 percent of the world’s population, it is home to 65 percent of the world’s 20 highest-ranked universities (and 28 percent of the world’s top-200 universities). Americans can get a quality education at thousands of academic institutions throughout the country.
Despite the skepticism in some quarters about whether a college degree is really worth it, the financial benefits of obtaining a degree remain clear. At 25, college graduates may earn only about 27 percent more than high-school-diploma holders. However, the college wage premium doubles over the course of their lifetime, jumping to 60 percent by the time they reach age 55. Looking solely at an individual’s financial prospects, the case for attending college remains strong.
David Deming: The college backlash is going too far
But the societal benefits we gain from higher education are far greater—and that’s the larger point. Colleges and universities don’t receive tax exemptions and public funds because of the help they give to specific individuals. We invest in higher education because there’s a broad public purpose.
Our colleges and universities are seen, rightly, as centers of learning, but they are also engines of economic growth. Higher graduation rates among our young people lead to a better-educated workforce for businesses and a larger tax base for the country as a whole. Institutions of higher education spur early-stage research of all kinds, create environments for commercializing that research, provide a base for start-up and technology hubs, and serve as a mentoring incubator for new generations of entrepreneurs and business leaders. In many communities, especially smaller towns and rural areas, campuses also create jobs that would be difficult to replace.
The importance of colleges and universities to the American economy will grow in the coming decades. As the list of industries that can be automated with AI becomes longer, the liberal-arts values and critical-thinking skills taught by colleges and universities will become only more valuable. Machine learning can aid in decision making. It cannot fully replace thoughtfulness and judgment.
Colleges and universities also help the United States maintain a geopolitical edge. We continue to attract the best and brightest from around the world to study here. Although many of these students stay and strengthen the country, many more return home, bringing with them a lifelong positive association with the United States. When I served as Treasury secretary, I found it extremely advantageous that so many of my foreign counterparts had spent their formative years in the U.S. That’s just as true today. In many instances, even the leadership class in unfriendly countries aspires to send its children to study here. In a multipolar world, this kind of soft-power advantage matters more than ever.
At home, higher education helps create the kind of citizenry that is central to a democracy’s ability to function and perhaps even to survive. This impact may be hard to quantify, but that doesn’t make it any less real.
It is not just lawmakers and executives who must make difficult decisions in the face of uncertainty. All of us—from those running civil-society groups that seek to influence policy to the voters who put elected leaders in office in the first place—are called upon to make hard choices as we live our civic lives. All of us are aware that the country is not in its best condition—this is hardly news. Imagine what that condition might be if we set out to undermine the very institutions that nurture rigorous and disciplined thinking and the free exchange of ideas.
O f course , there is much about higher education that needs fixing. Precisely because colleges and universities are so valuable to society, they should do more to engage with it. Bringing down costs can help ensure that talented, qualified young people are not denied higher education for financial reasons. Being clear about the principles and policies regarding the open expression of views—even as we recognize that applying them may require judgment calls, and that it is crucial to protect student safety and maintain an environment where learning and research can be conducted—would help blunt the criticism, not always made in good faith, that universities have an ideological agenda. Communicating more effectively with the public would help more Americans understand what is truly at stake.
But the fact that universities can do more does not change a basic fact: It is harmful to society to put constraints on open discussion or to attack universities for purposes of short-term political gain. Perhaps some of those trying to discourage the open exchange of ideas at universities believe that we can maintain their quality while attacking the culture of academic independence. I disagree. Unfettered discussion and freedom of thought and expression are the foundation upon which the greatness of our higher-education system is built. You cannot undermine the former without damaging the latter. To take one recent example: After Governor Ron DeSantis reshaped Florida’s New College along ideological lines, one-third of the faculty left within a year. This included scholars not only in fields such as gender studies, which many conservatives view with distaste, but in areas such as neuroscience as well.
We can have the world’s greatest higher-education system, with all of the benefits it brings to our country, or we can have colleges and universities in which the open exchange of views is undermined by pressure campaigns from many directions. We can’t have both.
This Homework News Will Make You Do A Happy Dance!
Realizing that it's becoming close to impossible for students to devote time to the many homework assignments they're given, school officials have begun to reconsider whether homework is beneficial for students at all. With research showing that homework has limited value for students, no-homework policies are starting to pop up all over the country.
Gaithersburg Elementary School in Rockville, Maryland, banned homework in 2012 and the policy is still in place today. According to Principal Stephanie Brant, the policy has worked fine, and teachers simply ask students to read for half an hour every night. Not too bad!
Other schools have adjusted their homework policies in different ways. At Ridgewood High School in Norridge, Illinois, teachers still assign students homework but it doesn't count toward their final grade.
And while they may bug you about doing your homework, it looks like most parents are behind you on this. According to a Today.com poll, 80% of parents think their kids are assigned too much homework. You've been saying it for, like, ever— but it's nice to know parents are finally listening!
What do you think of schools banning homework? Do you think the homework sit at your school is out of control? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
The Inspiring Way One College Student Is Protesting Her School's Rape Policy
Teen Girl Forced to Wear "Shame Suit" for Violating High School Dress Code
Promposal Gone Wrong! Student Suspended For Asking Miss America To Prom
Photo Credit: Getty Images

When I'm not holed up in my room going on a completely unproductive Netflix binge or Tumblr stalking Timothée Chalomet, I'm searching for awesome celeb news stories that Seventeen readers will love!

School & Campus Life

61 Gifts That’ll Make College 100x Better

16 “Hocus Pocus” Costumes That Are Scarily Good

TikTok's Beloved Stanley Cup is Back in Stock

AirPods Pro Are The Lowest Price Ever on Prime Day
Back-to-School Captions to Help You Win Day One

These Items Make Your Freshman Year SO Much Better

You Need These TikTok-Famous Amazon Travel Hacks

The Best Dorm Bedding for Your Cozy College Life

15 Cool Dorm Room Decor Ideas

35 Memes That Describe the Back to School Struggle
8 of the Best Dorm Mini Fridges
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
The Editorial Board
A Way Back From Campus Chaos

By The Editorial Board
The editorial board is a group of opinion journalists whose views are informed by expertise, research, debate and certain longstanding values . It is separate from the newsroom.
Protesting the world’s wrongs has been a rite of passage for generations of American youth, buoyed by our strong laws protecting free speech and free assembly. Yet the students and other demonstrators disrupting college campuses this spring are being taught the wrong lesson — for as admirable as it can be to stand up for your beliefs, there are no guarantees that doing so will be without consequence.
The highest calling of a university is to craft a culture of open inquiry, one where both free speech and academic freedom are held as ideals. Protest is part of that culture, and the issue on which so many of the current demonstrations are centered — U.S. involvement in the Israel-Hamas conflict — ought to be fiercely and regularly debated on college campuses.
The constitutional right to free speech is the protection against government interference restricting speech. Therefore, leaders at public universities, which are funded by government, have a heightened duty to respect those boundaries. Private institutions don’t have the same legal obligations, but that doesn’t relieve them of the responsibility to encourage open dialogue whenever and wherever possible on their campuses. It’s essential to the pursuit of learning.
In the real world, though, this can get messy, and nuance is required when free speech comes into tension with protecting academic freedom. The earliest universities to adopt the principle of academic freedom did so to thwart interference and influence from totalitarian states and religious zealotry. Today, the American Association of University Professors defines it as “the freedom of a teacher or researcher in higher education to investigate and discuss the issues in his or her academic field and to teach or publish findings without interference from political figures, boards of trustees, donors or other entities.”
Student codes of conduct and other guidelines are meant to relieve some of the tension between free speech and academic freedom, as well as to ensure that schools are in compliance with government regulations and laws. Every campus has them. But rules matter only when guardrails are consistently upheld. It’s in that enforcement that the leadership of too many universities has fallen short.
The point of protest is to break such rules, of course, and to disrupt daily routines so profoundly as to grab the world’s attention and sympathies. Campuses should be able to tolerate some degree of disruption, which is inherent to any protest. That makes it even more important that school administrators respond when the permissible limits for speech are violated.
During the current demonstrations, a lack of accountability has helped produce a crisis.
It has left some Jewish students feeling systematically harassed. It has deprived many students of access to parts of campus life. On campuses where in-person classes or commencement exercises were canceled, students have watched their basic expectations for a university experience evaporate. And at times, the protesters themselves have been directly endangered; the disarray and violence of the past weeks have been escalated by the continued involvement of both the police and external agitators.
Amid the protests, there has been much discussion of both antisemitism and Islamophobia and when the line is crossed into hate speech. There are profound risks to imposing overly expansive definitions of inappropriate speech, and universities were rightly chided for doing so in the past. But it should be easy to agree that no student, faculty member, administrator or university staff member on a campus should be threatened or intimidated. School policies should reflect that, and they should be enforced when necessary.
In the longer term, a lack of clarity around acceptable forms of expression and a failure to hold those who break those norms to account, has opened up the pursuit of higher learning to the whims of those motivated by hypocrisy and cynicism.
For years, right-wing Republicans, at the federal and state level, have found opportunities to crusade against academic freedom, with charges of antisemitism on campus serving as the latest vehicle. Speaker Mike Johnson of the House of Representatives used this moment of chaos as cover to begin a legislative effort to crack down on elite universities, and lawmakers in the House recently passed a proposal that would impose egregious government restrictions on free speech. The Senate should reject those efforts unequivocally.
The absence of steady and principled leadership is what opened the campus gates to such cynicism in the first place. For several years, many university leaders have failed to act as their students and faculty have shown ever greater readiness to block an expanding range of views that they deem wrong or beyond the pale. Some scholars report that this has had a chilling effect on their work, making them less willing to participate in the academy or in the wider world of public discourse. The price of pushing boundaries, particularly with more conservative ideas, has become higher and higher.
Schools ought to be teaching their students that there is as much courage in listening as there is in speaking up. It has not gone unnoticed — on campuses but also by members of Congress and by the public writ large — that many of those who are now demanding the right to protest have previously sought to curtail the speech of those whom they declared hateful.
Establishing a culture of openness and free expression is crucial to the mission of educational institutions. That includes clear guardrails on conduct and enforcement of those guardrails, regardless of the speaker or the topic. Doing so would not only help restore order on college campuses today but would also strengthen the cultural bedrock of higher education for generations to come.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
The editorial board is a group of opinion journalists whose views are informed by expertise, research, debate and certain longstanding values. It is separate from the newsroom.

Classroom cellphone rules and a ban on book bans: What school bills passed in Minnesota
W ith deficits looming, Minnesota's school districts brought their arguments for new funding to the State Capitol this year in the face of warnings not to expect much after a bountiful 2023 session.
And the final tally?
"Very modest," Scott Croonquist, executive director of the Association of Metropolitan School Districts, said this week.
Lawmakers managed to bolster funding for new literacy programs and took the first step to giving student teachers the financial support they say is needed to stick with 12 weeks of classroom training. Otherwise, it was a policy-driven year, with attention given to curbing excessive cellphone use and keeping kids in school and libraries free of book-ban politics .
"Students must be the center of our focus, and this legislation puts attention squarely on our kids," state Rep. Laurie Pryor, DFL-Minnetonka, chair of the House Education Policy Committee, said of the education policy bill approved in the session's closing days.
Here's what they did and some homework they left for later.
In an effort to keep students on task and to lessen the risks of cyberbullying, the state is requiring every school district and charter school to set cellphone use policies by March 15, 2025.
The legislation is not prescriptive, but state Rep. Sandra Feist, DFL-New Brighton, and Rep. Kristin Robbins, R-Maple Grove, made clear this year they'd like schools to be cellphone-free — and they pointed to success at a pair of middle schools where students must keep their phones locked up or out of sight.
The state's principals association will advise districts on ways to minimize the effects of cellphones on student behavior, mental health and academic achievement.
School attendance has suffered post-pandemic and lawmakers have responded by establishing a legislative work group to study chronic absenteeism in the coming months. In addition, 12 districts are being asked to come up with "promising practices" that ensure students get to class.
Minneapolis Public Schools is to take the lead and will receive $1 million of $4.7 million in state aid being dedicated to the effort. The 12 districts must conduct their first virtual meeting by Aug. 1.
The legislative work group is charged with recommending how best to tackle absenteeism and truancy, and must issue a final report by Dec. 31.
Matt Shaver, policy director with EdAllies, a group that works closely with underserved communities, said the action was a "start," but a "big deal," too, given limits on new funding this session.
A year ago, the state passed the Read Act, which tasked teachers with learning a new way to teach kids to read. But districts were left wondering about long-term funding and the time available to train personnel.
There was the question, too, of how to pay teachers for their time learning , so lawmakers this session allocated $31.4 million to districts, charter schools and cooperatives to compensate teachers as they dig into programs placing a greater emphasis on phonics.
A pair of training deadlines were extended by a year, too.
Croonquist said the Read Act funding "certainly is appreciated, but it's not going to cover all of the costs."
The state also set out to ease the financial burden on student teachers who prepare for the profession by working weeks for free. A pilot program will supply a total of $6.5 million in stipends to student teachers enrolled at eight Minnesota colleges and universities.
Denise Specht, president of Education Minnesota, commended lawmakers for finding ways to invest in current and future teachers during a tight budget year.
"Every Minnesota student deserves a great teacher who has the support and financial security they need to focus on the work," Specht said in a news release.
Another new measure prohibits book bans in schools and public libraries. The move comes at a time when books focusing on multiracial and LGBTQ themes have been removed from shelves at libraries across the U.S.
Students need access to books with "characters like themselves and their families," Specht said, praising the new policy.
Republicans said the legislation was unnecessary because book ban campaigns have been infrequent here.
A proposal to open rigorous courses to more students of color failed to advance, as did a proposed expansion of early learning scholarships to middle-income families . But the state Department of Education is receiving $7 million to establish the logistical groundwork to make the expansion happen.
Ericca Maas of the advocacy group Think Small said the move was an "important vote of confidence" in the fight to make child care more affordable to more families.
©2024 StarTribune. Visit startribune.com. Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.

US higher education is endangered
The long-held right of universities and their faculties to decide what they should teach is so precious. precious but under threat..

The following essay is adapted from remarks that Drew Gilpin Faust, former president of Harvard University, delivered at the Phi Beta Kappa ceremony at Harvard on May 21.
What is a university? We have been taking its existence and its essence for granted, even as attacks on its character and purposes have over several decades steadily, if gradually, mounted. The polarizations of race, religion, and politics that grip our country today have focused increasingly on universities. They have become a symbol for those divisions as well as the theater in which they are being acted out. But this is not just theater; it represents a threat to the foundational assumptions that have long governed higher education.
We should from the outset understand what is at stake. American universities have since at least the 1940s been preeminent in the world. Universities’ research discoveries have been central to American prosperity; their graduates have led the most important institutions of our government, society, and culture. Why are people working so hard to denigrate and destroy them?
One prong of these attacks has been directed at undermining belief in the value of college. A dramatic shift has occurred in Americans’ faith that college matters. In the 2010s, 99 percent of Republicans and 96 percent of Democrats expected their children to go to college ; now nearly half of American parents would prefer that they not. And this has occurred overwhelmingly among Republicans. College is becoming a partisan cause — with enormous potential damage both to students and the nation. College graduates still make an average of $1.2 million more than high school graduates over the course of a lifetime. They have better health and longer life expectancy and are 64 percent more likely to describe themselves as happy. Economists estimate that declining college attendance will yield $1.2 trillion lost in economic output by the end of the decade. To oppose college is to individually and collectively shoot ourselves in the foot.
Advertisement
An essential factor fueling hostility toward higher education is that college costs too much. Americans currently owe $1.7 trillion in college debt . For all our invocations of the mantra of “access and affordability,” we have not succeeded in reining in cost. But we must also recognize that this rise in price and rise in debt are in part the result of a defunding of higher education, especially in the years since the Great Recession. Public universities have transferred a growing percentage of tuition from the state to families. To offer just one example: In 1960, 78 percent of the budget of the University of Michigan at Ann Arbor came from the state. In 2023 it was13 percent. The shift in our understanding of college from a common good to a private good has left students to rely increasingly on loans to cover the tuition increases this transformation has required. Or perhaps to decide not to attend college at all.
In the case of private institutions, we might regard the tax on university endowments as another form of defunding higher education. Its passage in 2017 was acknowledged by many Republicans to be punitive , a means of expressing their objections to what they saw as universities’ liberal bias. That no tax was considered for the endowments of religious groups, museums, or other nonprofits seems telling. The debates around the endowment tax cast many of America’s finest universities as negative forces, as drains on society, not as powerful engines of its betterment. By 2017, partisan splits in views about higher education had taken firm hold.
Recently 79 percent of Republicans said that a major problem in universities was professors bringing their liberal political and social views into the classroom. Only 17 percent of Democrats agreed. Statistics about political allegiances of faculty indicate there are five Democratic professors for every Republican. But what does such a statistic mean in practice? Increasingly partisan views about higher education are likely as much cause as effect of these divides. And do we assume that connection with one political party or another necessarily implies a distortion of what is being taught?
A B.A. has neither an R or a D attached to it. The lives of Republicans and Democrats alike are improved by college attendance, just as the well-being of our society overall is advanced by the work of free and independent universities. The fear that higher levels of education may correlate with Democratic voting should not become a reason for advocating ignorance.
Universities must resist being portrayed in this partisan light by continually strengthening their dedication to the ideals of free speech and the open exploration of ideas. Just as judges are expected to transcend political leanings in their loyalty to the rule of law, so the culture of a university requires loyalty to what we might call the rule of truth. The essence of a university requires it to stand above the political fray, to uphold the value of rational argument and exchange as the pathway to finding the best ideas.
This does not mean that students and faculty cannot have their own political loyalties. But these must not marginalize other perspectives or undermine principles of academic freedom and rigor. We in higher education have been far from perfect in this regard. Frank disagreement and respectful argument are an ideal, not, alas, always a reality. And as our nation has become more polarized, and social media has made it possible to turn any interaction into an occasion of public shaming and canceling, it takes more courage to disagree with your peers or even your professors. I know that students have sometimes found it challenging to express disagreement with what seemed to be prevailing views in classrooms or in dining halls. In recent months deeply felt divisions over a raging war have made communicating across differences especially difficult. But I also know how so many students have remained committed to rational and dispassionate exchange as they have listened to one another and reached for understanding.
Much is at stake in dedicating ourselves to being good and true speakers and generous listeners. And much is at stake in how and what we teach. Academic integrity entails the obligation that faculty have to their fields of inquiry — to what I have called a rule of truth that evaluates the debates defining their disciplines. These are substantive questions of knowledge, method, and fact that are fundamentally academic, not political in nature; they require expertise and judgment about subject matter and educational goals. That is why the long-held right of universities and their faculties to decide what they should teach is so precious.
Precious but under threat.
Indiana, for example, has recently passed a law requiring faculty to teach a “variety of political or ideological frameworks.” Does that mean a biology professor must teach creationism? Or a historian must offer a portrait of our past that erases terrible injustices like slavery in service of painting an unrelievedly celebratory notion of the American experience? Or given the strictures introduced against teaching what has been demonized as critical race theory, will a historian be required to present a color-blind American history from which race is excluded altogether? To mandate what is often hailed as “viewpoint diversity” can mean presenting material that is just plain wrong. Does a politician know more about biology than a biologist? About history than a historian?
I have been arguing for the right of universities to establish their curricula and select their faculty by means of carefully established processes grounding such decisions in intellectual expertise. Such structures are designed to shield universities from political intervention, from becoming the handmaidens of a political party or agenda. Imperfectly, no doubt. But this must be our goal. We should not be permitting, and certainly not celebrating, a governor or a legislature or a member of Congress who is designing courses or degree requirements, hiring faculty, or proudly claiming responsibility for firing university presidents.
Universities must endeavor to maintain independence and distance from the partisan scrum. The value of university autonomy has been foundational to university excellence; it has made American higher education strong; it has made America strong. Universities need to imagine beyond the societies in which they find themselves — to pursue discoveries that will build a future that the present cannot yet envision; to transcend and even challenge the status quo; and to be free to criticize the powerful, whether politicians or plutocrats. Universities must have the freedom to think the unthinkable.
American higher education is endangered. Universities have rightly been reminded of the imperative to live up to their own values, to be accountable to the rule of truth that I have described. They need now more than ever to be their best selves. But they also need to defend themselves against attacks that are uninformed, undeserved, or rankly partisan, attacks fueled by political opportunism, explicitly designed to weaken and marginalize a set of institutions that are foundational to American democracy and to the well-being not just of Americans but of people around the globe.
We who have been nurtured and shaped by universities must be champions of the promise and purposes of higher education — of the rule of truth that universities stand for both within and beyond their walls.
Drew Gilpin Faust is president emerita of Harvard University and Arthur Kingsley Porter University research professor.

Globe Opinion
Advertisement
Outraged by Brown’s threats of discipline over protests, some professors call for reform
- Olivia Ebertz, The Public's Radio
It’s been more than two weeks since student protesters at Brown University struck a deal with school administrators , packed up their tents, and peacefully ended a pro-Palestinian encampment that had lasted nearly a week. But some faculty members at Brown say they are unwilling to move on and forget about a series of ominous letters the school sent to at least five professors who’d visited the student-run encampment.
“You were present at the protest,” Dean of Faculty Leah Van Wey wrote in some of the letters. “Your alleged participation in this unauthorized event would be a violation of policy.”
“Should you be observed violating policies again,” continued Van Wey, “I will review the situation and consider imposing disciplinary action.”
The school’s provost later sent out an email clarifying what constituted a policy violation. Then the president of Brown, Christina Paxson, issued a retraction and apology, and invited faculty to meet with her for a “full and candid discussion.”
The Public’s Radio spoke with more than a dozen Brown University faculty members for this story, including several who were not sent the disciplinary letters. The episode, some professors say, struck them as capricious, contradictory and confusing, and they walked away from their meeting with Paxson with their concerns still largely unaddressed, they said.
“Even though the university has apologized for these transgressions, we should not minimize them,” said Gerhard Richter, a professor of German at the school. “And even though one might say that this only affected a few professors who got these threat letters from the administration. An attack on some of us, is an attack on the entire Brown faculty, because it is an attack on the very core principles of what makes us a university that is concerned with education, and openness.”
Some professors say the school’s overall response to the ongoing pro-Palestinian protests on campus and the specific reaction to professors who visited the encampment typify a university, like others around the country, that has become more autocratic and top-heavy with administrators in recent years, is losing sight of its founding principles of free speech and education, and is overly concerned with marketing the school’s academics, when it should be focused on upholding academic freedom.
“I think it’s being turned slowly but surely into a corporation that is like Apple or McDonald’s or any other corporation,” said Richter.
They say the experience underscores the need for reforms at the 260-year-old university to give faculty a greater say in how the school is governed.
‘How do you draw the line?’
Brown University’s encampment popped up on the school’s Main Green on April 24 with about 75 campers and grew to 120 within a few days. The campers were joined by dozens, sometimes hundreds, of additional protesters during the day.
Within hours of the encampment being started, the university began conducting regular “ID checks” where students, staff and faculty members who came to the encampment had their identification cards swiped and recorded by public safety officers and athletic department employees.
Administrators said they wanted to make sure everyone within the encampment was affiliated with Brown University and clock how long people were there in order to calculate how severe their punishments should be.
In his clarifying email, Provost Francis J. Doyle III said the school considered professors who taught their classes at the encampment, or were involved in organizing the protest in some way, to be in violation of school policy.

Richter and Kristina Mendicino, president of the Brown University chapter of the American Association of University Professors, AAUP, and chair of the German Department, said that trying to prevent professors from bringing classes to a protest the school hasn’t authorized is a limit on academic freedom because it restricts where professors can use their expertise.
“How do you draw the line? Is someone who is drawing upon a body of expertise, communicating with students and teaching, is that in violation of a policy when it happens to take place in the midst of what has become a student encampment?” said Mendicino.
In his email, the provost told professors that even if all students said they were willing to have class in the encampment, “it creates a risk that these students could be mistakenly identified as participants in the unauthorized activity. We have heard that some students have been made to feel very uncomfortable being asked to have class in or alongside the encampment.”
Professors also responded negatively after Provost Doyle reminded them in his clarification letter that surveillance cameras were installed on the main green. They questioned whether his letter was meant to intimidate them and raised concerns the school was unfairly surveilling them to use the footage against them. Many professors involved in the AAUP fear that these types of actions will expand if universities like Brown continue to defer to administrators and, as they claim, limit the autonomy of professors and their ability to influence school policy.
Simmering discontent among some faculty
The Brown University chapter of the American Association of University Professors has been the primary collective voice of professors speaking out against the administration’s response to pro-Palestinian activism on campus.
The AAUP is a national organization that aims to defend tenure, faculty rights, and academic freedom at around 500 campuses across the United States. At some public institutions, it also serves as a union for professors. Brown’s AAUP chapter came into existence because of a specific clash between some teachers and their school’s leaders three years ago.
The disagreement began when administrators attempted to house six different language departments under one roof along with the Comparative Literature department. According to many within the departments, this would have created a “mega-department” and hurt the ability of the individual departments to plan their own curricula and events.
The professors believe the change would have led to budget cuts, departments being pitted against each other, and limited their options for preparing students for their chosen disciplines.
“It’s largely a question of reducing resources. Because then suddenly, when graduate student recruitment comes along, there might only be a certain number of students that the mega department can take,” said Mendicino. “There’s competition among the various units to be able to just do their basic research.”
After the professors formed their chapter of the AAUP, the school abandoned the plans for forming the consolidated department.
AAUP has more recently spoken out against academic sanctions against one of its members, Naoko Shibusawa. In June of 2022, Shibusawa released a peer-reviewed article with an unflattering anecdote about a colleague at Brown University, which administrators said did not adequately shield the co-worker’s identity.
The school responded by banning Shibusawa from departmental meetings and some larger faculty meetings. Shibusawa says the initial decision to sanction her was made unilaterally by administrators. Shibusawa was given the option to appear before a grievance committee, but only after the sanctions were already issued by administrators. By that time, Shibusawa and many of her colleagues felt her appearance before the committee was too late.
“It’s really unfair not to be able to have your say in front of peers or to even be asked, ‘What happened?’ ” Shibusawa said.
There is a body made up of 10 elected professors at Brown who do have some say in the way the university addresses some issues. It’s called the Faculty Executive Committee, although it does not have nearly as much influence over academic issues as the AAUP would prefer. Recently, the committee brought forward a motion on sanctions to the full faculty body that was approved. Now, if there are future allegations against a professor, a jury of their colleagues will need to look at the allegations and hear a defense from the professor before sanctions can be instated.
The Brown AAUP also contends the school is spending its money in a way that prioritizes administrative positions, and that is contributing to what they see as an existential threat to their academic freedom. In Spring 2023, the group commissioned a report from independent analyst Howard Bunsis, who is also a professor of accounting at Eastern Michigan University.
In his report, Bunsis painted a picture of a university that’s fiscally healthy but over-funding its administration. He wrote that, between 2018 and 2022, by percentage, administrative expenditures increased more than spending for any other area. According to Bunsis, administrative costs went up 62.9% during that time period, while instruction and research costs went up only by 12.5%.
Bunsis found that senior administrators usually make at minimum two times as much as full professors, and in some cases, more than four times the amount.
Brian Clark, a spokesperson for Brown University, did not respond to questions about the Bunsis report. However, he told the Brown Daily Herald in 2023 that Bunsis “did not properly contextualize why revenues and expenses changed so dramatically.”
A renewed call for shared faculty governance
Faculty members at Brown who are raising objections about their administration say they are interested in a shared faculty governance model called an academic senate. Under a senate, faculty are responsible for what Richter calls “the educational mission of the university.”
“So anything pertaining to academics, course of study, hirings, tenure decisions,” Richter said, arguing that a senate structure would allow professors and their students to work without fear of limitations on their research and instruction.
Brown AAUP leaders say an academic senate runs counter to Brown’s committees, which are often filled with members who are not elected and are instead picked by the president. In many cases, they also include administrators and the president often has the authority to veto decisions made by these committees.
Regardless of whether or not a senate system is adopted, many professors say they would, at the very least, like to be consulted on decisions they see as having the potential to curb their academic freedom. Additionally, some would like to have a degree of oversight on matters they see as affecting their quality of life or campus culture, such as bringing in outside police forces to arrest students.
“There is a broader question of meaningful faculty consultation when it comes to major decisions,” Mendicino said. “And I think that this is a larger structural question that could be resolved.”
Clark, the spokesperson for Brown, did not directly address the claims made by AAUP members in this story. He said the university does not discuss concerns faculty have with the administration with “news media,” and that most of their concerns are “mischaracterized claims shared by an individual or small group and not aligned with larger sentiments on campus.”
This story was originally published by The Public's Radio . It was republished as part of a partnership between The Public's Radio and WBUR.
- Student protesters, administrators at Brown University reach deal to clear encampment
More from WBUR
The US is reportedly rethinking plans to ban Russian diamonds amid industry pushback
- The US is considering reducing efforts to enforce a ban on Russian diamonds, Reuters reported.
- White House officials have noted several obstacles in certifying that diamonds are not of Russian origin.
- Scarcer supply could lead diamond prices to rise, jewelers have warned.

The US is rethinking restrictions on Russian diamonds after a wave of pushback from the industry and nations heavily involved in the diamond trade, Reuters reported on Monday.
Western countries have placed stiff restrictions on Russia's diamond trade, with fresh sanctions in December banning the gems throughout the European Union. That's a step up from the initial sanctions, which previously allowed the trade of Russian diamonds that were polished in other countries.
Diamond traders now need to self-certify that the gems they sell are not of Russian origin. By September, diamond traders in the European Union will need to send diamonds through a certification system in Belgium before selling them.
Those measures have helped crimp Russia's war revenue , given that the nation is one of the largest producers of diamonds in the world. Yet the US, one of the world's largest diamond consumers, could pull back on its commitment to implement the latest restrictions, three people familiar with the matter told Reuters.
Two sources said the US had pulled back on working with the G7 to implement the diamond ban and certifying that gems were not of Russian origin. Officials are "there but not engaging" in the discussion, one person said.
A senior White House official told Reuters the US would continue to work with the G7 on the Russian diamond ban, and that it had not changed its mind on the issue, but they noted several obstacles in enforcing the latest restrictions:
"We will want to make sure that we strike the right balance between hurting Russia and making sure that everything is implementable," the official said.
The government has received pushback from firms and nations heavily involved in the diamond trade. Some African nations and Indian diamond polishers have complained about the latest restrictions, warning that the ban was faulty in its design and could raise problems in the industry. Diamond prices could also rise due to scarcer supply, they warned.
Virginia Drosos, the CEO of Signet, asked the US government to "stand against … the G7 Belgian solution," according to a letter seen by Reuters.
De Beers, one of the world's largest diamond miners, said it supported a ban on Russian diamonds but wants diamonds to be verified at the source of production, rather than in Belgium.
"The opportunities for, and likelihood, of Russian diamonds infiltrating the legitimate supply chain are in fact higher when you move further away from the source," it told Reuters.
- Main content
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Students, read the entire article, then tell us: Should we get rid of homework? Why, or why not? ... Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited ...
This concept of homework quickly spread across Europe and was brought to the United States by Horace Mann, who encountered the idea in Prussia. ... Home Journal, decried homework's negative impact on children's physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework ...
In 1901, for instance, California banned homework for students up to age 15, and limited it for older students, ... We believe it pays off for all of us, as a society and a democracy, when our ...
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night. "Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's ...
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health ...
Tollison is part of a growing movement that believes learners can thrive academically without homework. According to Alfie Kohn, author of " The Homework Myth ," there's never a good excuse ...
The so-called "homework gap" —which disproportionately impacts poor students, students of color, and those living in rural areas—has been a persistent problem since long before the ...
In the end, the committee only agreed to a homework ban over school breaks. Miller's response is a great model for us all. He decided to limit assignments in his own class to 20 minutes a night ...
Kralovec called the ban on homework a movement, though she estimated just a small handful of schools in the U.S. have such policies. Gaithersburg Elementary School in Rockville, Maryland, is one ...
TIMSS data also show us how even elementary school kids are being burdened with large amounts of homework. Almost 10% of fourth graders worldwide (one in 10 children) reported spending multiple ...
According to child and adolescent family therapist Darby Fox, yes. "It's like an ultimate reaction. There is a point to homework and the right amount really is age appropriate," Fox said Friday on ...
Homework researcher Professor John Hattie found that homework in primary schools makes no difference to learner achievement. Other activities at home can have just as much educational benefit, such as reading, or baking, or simply playing. What's more, too much homework can also have a negative effect on students' mental health.
Homework is a controversial topic in education, but what does the science say? Explore the pros and cons of homework and its impact on students' well-being in this article from BBC Science Focus Magazine.
Bans proposed and implemented in the U.S. and abroad. The struggle of whether or not to assign homework is not a new one. In 2017, a Florida superintendent banned homework for elementary schools in the entire district, with one very important exception: reading at home. The United States isn't the only country to question the benefits of ...
For as long as homework has been a part of school life in the United States, so too has the debate over its value. In 1900, a prominent magazine published an article on the evils of homework ...
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.)
Banning homework would help to reduce these risks as well. 6. It increases the amount of socialization time that students receive. People who are only spending time in school and then going home to do more work are at a higher risk of experiencing loneliness and isolation.
Down With Homework, Say U.S. School Districts More districts ban or stop grading it amid complaints of overload, but some parents and teachers aren't on board By
Responses indicating no homework on the "usual" question in 2004 were: 2% for age 9-year-olds, 5% for 13 year olds, and 12% for 17-year-olds. These figures are much less than the ones reported ...
By Kyle Spencer. April 25, 2017. Last spring, when Public School 11, a prekindergarten through fifth-grade school in Manhattan's Chelsea neighborhood, banned mandatory traditional homework ...
Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary. "Every child should be doing homework, but the ...
Yes. Generally, the link between homework and achievement scores is stronger for math compared to subjects like English and history. For middle school students especially, math homework can strengthen school performance. There is not a lot of research into the quality of homework. Most experts agree that homework should be reinforcing what kids ...
Although the United States can claim less than 5 percent of the world's population, it is home to 65 percent of the world's 20 highest-ranked universities (and 28 percent of the world's top ...
With research showing that homework has limited value for students, no-homework policies are starting to pop up all over the country. Gaithersburg Elementary School in Rockville, Maryland, banned ...
A Way Back From Campus Chaos. May 11, 2024. Philip Cheung for The New York Times. Share full article. 926. By The Editorial Board. The editorial board is a group of opinion journalists whose views ...
In addition, 12 districts are being asked to come up with "promising practices" that ensure students get to class. Minneapolis Public Schools is to take the lead and will receive $1 million of $4. ...
The polarizations of race, religion, and politics that grip our country today have focused increasingly on universities. They have become a symbol for those divisions as well as the theater in ...
Contact Us (617) 353-0909. [email protected]. 890 Commonwealth Ave. Boston, MA 02215. More ways to get in touch. About WBUR. Who We Are; Inside WBUR; Careers; WBUR Staff; Community Advisory Board;
The US is considering reducing efforts to enforce a ban on Russian diamonds, Reuters reported. White House officials have noted several obstacles in certifying that diamonds are not of Russian origin.
May 23, 2024 at 1:16 PM PDT. Listen. 1:36. TikTok is making it easier for content creators to earn money on its shopping platform, a move that could bolster opposition to a US law that will force ...