
Please wait while we process your request

Abortion Argumentative Essay: Definitive Guide
Academic writing
Abortion remains a debatable issue even today, especially in countries like the USA, where a controversial ban was upheld in 13 states at the point this article was written. That’s why an essay on abortion has become one of the most popular tasks in schools, colleges, and universities. When writing this kind of essay, students learn to express their opinion, find and draw arguments and examples, and conduct research.
It’s very easy to speculate on topics like this. However, this makes it harder to find credible and peer-reviewed information on the topic that isn’t merely someone’s opinion. If you were assigned this kind of academic task, do not lose heart. In this article, we will provide you with all the tips and tricks for writing about abortion.
Where to begin?
Conversations about abortion are always emotional. Complex stories, difficult decisions, bitter moments, and terrible diagnoses make this topic hard to cover. Some young people may be shocked by this assignment, while others would be happy to express their opinion on the matter.
One way or another, this topic doesn't leave anyone indifferent. However, it shouldn’t have an effect on the way you approach the research and writing process. What should you remember when working on an argumentative essay about abortion?
- Don’t let your emotions take over. As this is an academic paper, you have to stay impartial and operate with facts. The topic is indeed sore and burning, causing thousands of scandals on the Internet, but you are writing it for school, not a Quora thread.
- Try to balance your opinions. There are always two sides to one story, even if the story is so fragile. You need to present an issue from different angles. This is what your tutors seek to teach you.
- Be tolerant and mind your language. It is very important not to hurt anybody with the choice of words in your essay. So make sure you avoid any possible rough words. It is important to respect people with polar opinions, especially when it comes to academic writing.
- Use facts, not claims. Your essay cannot be based solely on your personal ideas – your conclusions should be derived from facts. Roe v. Wade case, WHO or Mayo Clinic information, and CDC are some of the sources you can rely on.

Speaking of Outline
An argumentative essay on abortion outline is a must-have even for experienced writers. In general, each essay, irrespective of its kind or topic, has a strict outline. It may be brief or extended, but the major parts are always the same:
- Introduction. This is a relatively short paragraph that starts with a hook and presents the background information on the topic. It should end with a thesis statement telling your reader what your main goal or idea is.
- Body. This section usually consists of 2-4 paragraphs. Each one has its own structure: main argument + facts to support it + small conclusion and transition into the next paragraph.
- Conclusion. In this part, your task is to summarize all your thoughts and come to a general conclusive idea. You may have to restate some info from the body and your thesis statement and add a couple of conclusive statements without introducing new facts.
Why is it important to create an outline?
- You will structure your ideas. We bet you’ve got lots on your mind. Writing them down and seeing how one can flow logically into the other will help you create a consistent paper. Naturally, you will have to abandon some of the ideas if they don’t fit the overall narrative you’re building.
- You can get some inspiration. While creating your outline, which usually consists of some brief ideas, you can come up with many more to research. Some will add to your current ones or replace them with better options.
- You will find the most suitable sources. Argumentative essay writing requires you to use solid facts and trustworthy arguments built on them. When the topic is as controversial as abortion, these arguments should be taken from up-to-date, reliable sources. With an outline, you will see if you have enough to back up your ideas.
- You will write your text as professionals do. Most expert writers start with outlines to write the text faster and make it generally better. As you will have your ideas structured, the general flow of thoughts will be clear. And, of course, it will influence your overall grade positively.

Abortion Essay Introduction
The introduction is perhaps the most important part of the whole essay. In this relatively small part, you will have to present the issue under consideration and state your opinion on it. Here is a typical introduction outline:
- The first sentence is a hook grabbing readers' attention.
- A few sentences that go after elaborate on the hook. They give your readers some background and explain your research.
- The last sentence is a thesis statement showing the key idea you are building your text around.
Before writing an abortion essay intro, first thing first, you will need to define your position. If you are in favor of this procedure, what exactly made you think so? If you are an opponent of abortion, determine how to argue your position. In both cases, you may research the point of view in medicine, history, ethics, and other fields.
When writing an introduction, remember:
- Never repeat your title. First of all, it looks too obvious; secondly, it may be boring for your reader right from the start. Your first sentence should be a well-crafted hook. The topic of abortion worries many people, so it’s your chance to catch your audience’s attention with some facts or shocking figures.
- Do not make it too long. Your task here is to engage your audience and let them know what they are about to learn. The rest of the information will be disclosed in the main part. Nobody likes long introductions, so keep it short but informative.
- Pay due attention to the thesis statement. This is the central sentence of your introduction. A thesis statement in your abortion intro paragraph should show that you have a well-supported position and are ready to argue it. Therefore, it has to be strong and convey your idea as clearly as possible. We advise you to make several options for the thesis statement and choose the strongest one.
Hooks for an Abortion Essay
Writing a hook is a good way to catch the attention of your audience, as this is usually the first sentence in an essay. How to start an essay about abortion? You can begin with some shocking fact, question, statistics, or even a quote. However, always make sure that this piece is taken from a trusted resource.
Here are some examples of hooks you can use in your paper:
- As of July 1, 2022, 13 states banned abortion, depriving millions of women of control of their bodies.
- According to WHO, 125,000 abortions take place every day worldwide.
- Is abortion a woman’s right or a crime?
- Since 1994, more than 40 countries have liberalized their abortion laws.
- Around 48% of all abortions are unsafe, and 8% of them lead to women’s death.
- The right to an abortion is one of the reproductive and basic rights of a woman.
- Abortion is as old as the world itself – women have resorted to this method since ancient times.
- Only 60% of women in the world live in countries where pregnancy termination is allowed.
Body Paragraphs: Pros and Cons of Abortion
The body is the biggest part of your paper. Here, you have a chance to make your voice concerning the abortion issue heard. Not sure where to start? Facts about abortion pros and cons should give you a basic understanding of which direction to move in.
First things first, let’s review some brief tips for you on how to write the best essay body if you have already made up your mind.
Make a draft
It’s always a good idea to have a rough draft of your writing. Follow the outline and don’t bother with the word choice, grammar, or sentence structure much at first. You can polish it all later, as the initial draft will not likely be your final. You may see some omissions in your arguments, lack of factual basis, or repetitiveness that can be eliminated in the next versions.
Trust only reliable sources
This part of an essay includes loads of factual information, and you should be very careful with it. Otherwise, your paper may look unprofessional and cost you precious points. Never rely on sources like Wikipedia or tabloids – they lack veracity and preciseness.
Edit rigorously
It’s best to do it the next day after you finish writing so that you can spot even the smallest mistakes. Remember, this is the most important part of your paper, so it has to be flawless. You can also use editing tools like Grammarly.
Determine your weak points
Since you are writing an argumentative essay, your ideas should be backed up by strong facts so that you sound convincing. Sometimes it happens that one argument looks weaker than the other. Your task is to find it and strengthen it with more or better facts.
Add an opposing view
Sometimes, it’s not enough to present only one side of the discussion. Showing one of the common views from the opposing side might actually help you strengthen your main idea. Besides, making an attempt at refuting it with alternative facts can show your teacher or professor that you’ve researched and analyzed all viewpoints, not just the one you stand by.
If you have chosen a side but are struggling to find the arguments for or against it, we have complied abortion pro and cons list for you. You can use both sets if you are writing an abortion summary essay covering all the stances.
Why Should Abortion Be Legal
If you stick to the opinion that abortion is just a medical procedure, which should be a basic health care need for each woman, you will definitely want to write the pros of abortion essay. Here is some important information and a list of pros about abortion for you to use:
- Since the fetus is a set of cells – not an individual, it’s up to a pregnant woman to make a decision concerning her body. Only she can decide whether she wants to keep the pregnancy or have an abortion. The abortion ban is a violation of a woman’s right to have control over her own body.
- The fact that women and girls do not have access to effective contraception and safe abortion services has serious consequences for their own health and the health of their families.
- The criminalization of abortion usually leads to an increase in the number of clandestine abortions. Many years ago, fetuses were disposed of with improvised means, which included knitting needles and half-straightened metal hangers. 13% of women’s deaths are the result of unsafe abortions.
- Many women live in a difficult financial situation and cannot support their children financially. Having access to safe abortion takes this burden off their shoulders. This will also not decrease their quality of life as the birth and childcare would.
- In countries where abortion is prohibited, there is a phenomenon of abortion tourism to other countries where it can be done without obstacles. Giving access to this procedure can make the lives of women much easier.
- Women should not put their lives or health in danger because of the laws that were adopted by other people.
- Girls and women who do not have proper sex education may not understand pregnancy as a concept or determine that they are pregnant early on. Instead of educating them and giving them a choice, an abortion ban forces them to become mothers and expects them to be fit parents despite not knowing much about reproduction.
- There are women who have genetic disorders or severe mental health issues that will affect their children if they're born. Giving them an option to terminate ensures that there won't be a child with a low quality of life and that the woman will not have to suffer through pregnancy, birth, and raising a child with her condition.
- Being pro-choice is about the freedom to make decisions about your body so that women who are for termination can do it safely, and those who are against it can choose not to do it. It is an inclusive option that caters to everyone.
- Women and girls who were raped or abused by their partner, caregiver, or stranger and chose to terminate the pregnancy can now be imprisoned for longer than their abusers. This implies that the system values the life of a fetus with no or primitive brain function over the life of a living woman.
- People who lived in times when artificial termination of pregnancy was scarcely available remember clandestine abortions and how traumatic they were, not only for the physical but also for the mental health of women. Indeed, traditionally, in many countries, large families were a norm. However, the times have changed, and supervised abortion is a safe and accessible procedure these days. A ban on abortion will simply push humanity away from the achievements of the civilized world.

Types of abortion
There are 2 main types of abortions that can be performed at different pregnancy stages and for different reasons:
- Medical abortion. It is performed by taking a specially prescribed pill. It does not require any special manipulations and can even be done at home (however, after a doctor’s visit and under supervision). It is considered very safe and is usually done during the very first weeks of pregnancy.
- Surgical abortion. This is a medical operation that is done with the help of a suction tube. It then removes the fetus and any related material. Anesthesia is used for this procedure, and therefore, it can only be done in a hospital. The maximum time allowed for surgical abortion is determined in each country specifically.
Cases when abortion is needed
Center for Reproductive Rights singles out the following situations when abortion is required:
- When there is a risk to the life or physical/mental health of a pregnant woman.
- When a pregnant woman has social or economic reasons for it.
- Upon the woman's request.
- If a pregnant woman is mentally or cognitively disabled.
- In case of rape and/or incest.
- If there were congenital anomalies detected in the fetus.
Countries and their abortion laws
- Countries where abortion is legalized in any case: Australia, Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Sweden, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Hungary, the Netherlands, Norway, Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Lithuania, etc.
- Countries where abortion is completely prohibited: Angola, Venezuela, Egypt, Indonesia, Iraq, Lebanon, Nicaragua, Oman, Paraguay, Palau, Jamaica, Laos, Haiti, Honduras, Andorra, Aruba, El Salvador, Dominican Republic, Sierra Leone, Senegal, etc.
- Countries where abortion is allowed for medical reasons: Afghanistan, Israel, Argentina, Nigeria, Bangladesh, Bolivia, Ghana, Israel, Morocco, Mexico, Bahamas, Central African Republic, Ecuador, Ghana, Algeria, Monaco, Pakistan, Poland, etc.
- Countries where abortion is allowed for both medical and socioeconomic reasons: England, India, Spain, Luxembourg, Japan, Finland, Taiwan, Zambia, Iceland, Fiji, Cyprus, Barbados, Belize, etc.
Why Abortion Should Be Banned
Essays against abortions are popular in educational institutions since we all know that many people – many minds. So if you don’t want to support this procedure in your essay, here are some facts that may help you to argument why abortion is wrong:
- Abortion at an early age is especially dangerous because a young woman with an unstable hormonal system may no longer be able to have children throughout her life. Termination of pregnancy disrupts the hormonal development of the body.
- Health complications caused by abortion can occur many years after the procedure. Even if a woman feels fine in the short run, the situation may change in the future.
- Abortion clearly has a negative effect on reproductive function. Artificial dilation of the cervix during an abortion leads to weak uterus tonus, which can cause a miscarriage during the next pregnancy.
- Evidence shows that surgical termination of pregnancy significantly increases the risk of breast cancer.
- In December 1996, the session of the Council of Europe on bioethics concluded that a fetus is considered a human being on the 14th day after conception.
You are free to use each of these arguments for essays against abortions. Remember that each claim should not be supported by emotions but by facts, figures, and so on.
Health complications after abortion
One way or another, abortion is extremely stressful for a woman’s body. Apart from that, it can even lead to various health problems in the future. You can also cover them in your cons of an abortion essay:
- Continuation of pregnancy. If the dose of the drug is calculated by the doctor in the wrong way, the pregnancy will progress.
- Uterine bleeding, which requires immediate surgical intervention.
- Severe nausea or even vomiting occurs as a result of a sharp change in the hormonal background.
- Severe stomach pain. Medical abortion causes miscarriage and, as a result, strong contractions of the uterus.
- High blood pressure and allergic reactions to medicines.
- Depression or other mental problems after a difficult procedure.
Abortion Essay Conclusion
After you have finished working on the previous sections of your paper, you will have to end it with a strong conclusion. The last impression is no less important than the first one. Here is how you can make it perfect in your conclusion paragraph on abortion:
- It should be concise. The conclusion cannot be as long as your essay body and should not add anything that cannot be derived from the main section. Reiterate the key ideas, combine some of them, and end the paragraph with something for the readers to think about.
- It cannot repeat already stated information. Restate your thesis statement in completely other words and summarize your main points. Do not repeat anything word for word – rephrase and shorten the information instead.
- It should include a call to action or a cliffhanger. Writing experts believe that a rhetorical question works really great for an argumentative essay. Another good strategy is to leave your readers with some curious ideas to ponder upon.
Abortion Facts for Essay
Abortion is a topic that concerns most modern women. Thousands of books, research papers, and articles on abortion are written across the world. Even though pregnancy termination has become much safer and less stigmatized with time, it still worries millions. What can you cover in your paper so that it can really stand out among others? You may want to add some shocking abortion statistics and facts:
- 40-50 million abortions are done in the world every year (approximately 125,000 per day).
- According to UN statistics, women have 25 million unsafe abortions each year. Most of them (97%) are performed in the countries of Africa, Asia, and Latin America. 14% of them are especially unsafe because they are done by people without any medical knowledge.
- Since 2017, the United States has shown the highest abortion rate in the last 30 years.
- The biggest number of abortion procedures happen in the countries where they are officially banned. The lowest rate is demonstrated in the countries with high income and free access to contraception.
- Women in low-income regions are three times more susceptible to unplanned pregnancies than those in developed countries.
- In Argentina, more than 38,000 women face dreadful health consequences after unsafe abortions.
- The highest teen abortion rates in the world are seen in 3 countries: England, Wales, and Sweden.
- Only 31% of teenagers decide to terminate their pregnancy. However, the rate of early pregnancies is getting lower each year.
- Approximately 13 million children are born to mothers under the age of 20 each year.
- 5% of women of reproductive age live in countries where abortions are prohibited.
We hope that this abortion information was useful for you, and you can use some of these facts for your own argumentative essay. If you find some additional facts, make sure that they are not manipulative and are taken from official medical resources.

Abortion Essay Topics
Do you feel like you are lost in the abundance of information? Don’t know what topic to choose among the thousands available online? Check our short list of the best abortion argumentative essay topics:
- Why should abortion be legalized essay
- Abortion: a murder or a basic human right?
- Why we should all support abortion rights
- Is the abortion ban in the US a good initiative?
- The moral aspect of teen abortions
- Can the abortion ban solve birth control problems?
- Should all countries allow abortion?
- What consequences can abortion have in the long run?
- Is denying abortion sexist?
- Why is abortion a human right?
- Are there any ethical implications of abortion?
- Do you consider abortion a crime?
- Should women face charges for terminating a pregnancy?
Want to come up with your own? Here is how to create good titles for abortion essays:
- Write down the first associations. It can be something that swirls around in your head and comes to the surface when you think about the topic. These won’t necessarily be well-written headlines, but each word or phrase can be the first link in the chain of ideas that leads you to the best option.
- Irony and puns are not always a good idea. Especially when it comes to such difficult topics as abortion. Therefore, in your efforts to be original, remain sensitive to the issue you want to discuss.
- Never make a quote as your headline. First, a wordy quote makes the headline long. Secondly, readers do not understand whose words are given in the headline. Therefore, it may confuse them right from the start. If you have found a great quote, you can use it as your hook, but don’t forget to mention its author.
- Try to briefly summarize what is said in the essay. What is the focus of your paper? If the essence of your argumentative essay can be reduced to one sentence, it can be used as a title, paraphrased, or shortened.
- Write your title after you have finished your text. Before you just start writing, you might not yet have a catchy phrase in mind to use as a title. Don’t let it keep you from working on your essay – it might come along as you write.
Abortion Essay Example
We know that it is always easier to learn from a good example. For this reason, our writing experts have complied a detailed abortion essay outline for you. For your convenience, we have created two options with different opinions.
Topic: Why should abortion be legal?
Introduction – hook + thesis statement + short background information
Essay hook: More than 59% of women in the world do not have access to safe abortions, which leads to dreading health consequences or even death.
Thesis statement: Since banning abortions does not decrease their rates but only makes them unsafe, it is not logical to ban abortions.
Body – each paragraph should be devoted to one argument
Argument 1: Woman’s body – women’s rules. + example: basic human rights.
Argument 2: Banning abortion will only lead to more women’s death. + example: cases of Polish women.
Argument 3: Only women should decide on abortion. + example: many abortion laws are made by male politicians who lack knowledge and first-hand experience in pregnancies.
Conclusion – restated thesis statement + generalized conclusive statements + cliffhanger
Restated thesis: The abortion ban makes pregnancy terminations unsafe without decreasing the number of abortions, making it dangerous for women.
Cliffhanger: After all, who are we to decide a woman’s fate?
Topic: Why should abortion be banned?
Essay hook: Each year, over 40 million new babies are never born because their mothers decide to have an abortion.
Thesis statement: Abortions on request should be banned because we cannot decide for the baby whether it should live or die.
Argument 1: A fetus is considered a person almost as soon as it is conceived. Killing it should be regarded as murder. + example: Abortion bans in countries such as Poland, Egypt, etc.
Argument 2: Interrupting a baby’s life is morally wrong. + example: The Bible, the session of the Council of Europe on bioethics decision in 1996, etc.
Argument 3: Abortion may put the reproductive health of a woman at risk. + example: negative consequences of abortion.
Restated thesis: Women should not be allowed to have abortions without serious reason because a baby’s life is as priceless as their own.
Cliffhanger: Why is killing an adult considered a crime while killing an unborn baby is not?

Examples of Essays on Abortion
There are many great abortion essays examples on the Web. You can easily find an argumentative essay on abortion in pdf and save it as an example. Many students and scholars upload their pieces to specialized websites so that others can read them and continue the discussion in their own texts.
In a free argumentative essay on abortion, you can look at the structure of the paper, choice of the arguments, depth of research, and so on. Reading scientific papers on abortion or essays of famous activists is also a good idea. Here are the works of famous authors discussing abortion.
A Defense of Abortion by Judith Jarvis Thomson
Published in 1971, this essay by an American philosopher considers the moral permissibility of abortion. It is considered the most debated and famous essay on this topic, and it’s definitely worth reading no matter what your stance is.
Abortion and Infanticide by Michael Tooley
It was written in 1972 by an American philosopher known for his work in the field of metaphysics. In this essay, the author considers whether fetuses and infants have the same rights. Even though this work is quite complex, it presents some really interesting ideas on the matter.
Some Biological Insights into Abortion by Garret Hardin
This article by American ecologist Garret Hardin, who had focused on the issue of overpopulation during his scholarly activities, presents some insights into abortion from a scientific point of view. He also touches on non-biological issues, such as moral and economic. This essay will be of great interest to those who support the pro-choice stance.
H4 Hidden in Plain View: An Overview of Abortion in Rural Illinois and Around the Globe by Heather McIlvaine-Newsad
In this study, McIlvaine-Newsad has researched the phenomenon of abortion since prehistoric times. She also finds an obvious link between the rate of abortions and the specifics of each individual country. Overall, this scientific work published in 2014 is extremely interesting and useful for those who want to base their essay on factual information.
H4 Reproduction, Politics, and John Irving’s The Cider House Rules: Women’s Rights or “Fetal Rights”? by Helena Wahlström
In her article of 2013, Wahlström considers John Irving’s novel The Cider House Rules published in 1985 and is regarded as a revolutionary work for that time, as it acknowledges abortion mostly as a political problem. This article will be a great option for those who want to investigate the roots of the abortion debate.

FAQs On Abortion Argumentative Essay
- Is abortion immoral?
This question is impossible to answer correctly because each person independently determines their own moral framework. One group of people will say that abortion is a woman’s right because only she has power over her body and can make decisions about it. Another group will argue that the embryo is also a person and has the right to birth and life.
In general, the attitude towards abortion is determined based on the political and religious views of each person. Religious people generally believe that abortion is immoral because it is murder, while secular people see it as a normal medical procedure. For example, in the US, the ban on abortion was introduced in red states where the vast majority have conservative views, while blue liberal states do not support this law. Overall, it’s up to a person to decide whether they consider abortion immoral based on their own values and beliefs.
- Is abortion legal?
The answer to this question depends on the country in which you live. There are countries in which pregnancy termination is a common medical procedure and is performed at the woman's request. There are also states in which there must be a serious reason for abortion: medical, social, or economic. Finally, there are nations in which abortion is prohibited and criminalized. For example, in Jamaica, a woman can get life imprisonment for abortion, while in Kenya, a medical worker who volunteers to perform an abortion can be imprisoned for up to 14 years.
- Is abortion safe?
In general, modern medicine has reached such a level that abortion has become a common (albeit difficult from various points of view) medical procedure. There are several types of abortion, as well as many medical devices and means that ensure the maximum safety of the pregnancy termination. Like all other medical procedures, abortion can have various consequences and complications.
Abortions – whether safe or not - exist in all countries of the world. The thing is that more than half of them are dangerous because women have them in unsuitable conditions and without professional help. Only universal access to abortion in all parts of the world can make it absolutely safe. In such a case, it will be performed only after a thorough assessment and under the control of a medical professional who can mitigate the potential risks.
- How safe is abortion?
If we do not talk about the ethical side of the issue related to abortion, it still has some risks. In fact, any medical procedure has them to a greater or lesser extent.
The effectiveness of the safe method in a medical setting is 80-99%. An illegal abortion (for example, the one without special indications after 12 weeks) can lead to a patient’s death, and the person who performed it will be criminally liable in this case.
Doctors do not have universal advice for all pregnant women on whether it is worth making this decision or not. However, many of them still tend to believe that any contraception - even one that may have negative side effects - is better than abortion. That’s why spreading awareness on means of contraception and free access to it is vital.
Your email address will not be published / Required fields are marked *
Try it now!
Calculate your price
Number of pages:
Order an essay!

Fill out the order form

Make a secure payment
Receive your order by email
Essay paper writing
How to Write a Killer Essay on Gun Control
What is this all about? The topic of gun control has always been a subject of heated debates. However, this issue became a burning one in the 20th century, with the new gun laws released. The two…
9th Jul 2020

Classification Essay Topics
At a certain educational stage, students of high schools and colleges face the necessity to make a classification essay. Such assignments are often given to learners by teachers to check a…
6th Sep 2018

Criminal Justice Research Paper Topics
The criminal justice field is as old as society itself. Unfortunately, there are people who prefer not abiding by rules in every country. The judicial system is a factor that deters them from…
26th Mar 2019
Get your project done perfectly
Professional writing service
Reset password
We’ve sent you an email containing a link that will allow you to reset your password for the next 24 hours.
Please check your spam folder if the email doesn’t appear within a few minutes.
Find anything you save across the site in your account
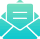
How the Right to Legal Abortion Changed the Arc of All Women’s Lives
By Katha Pollitt

I’ve never had an abortion. In this, I am like most American women. A frequently quoted statistic from a recent study by the Guttmacher Institute, which reports that one in four women will have an abortion before the age of forty-five, may strike you as high, but it means that a large majority of women never need to end a pregnancy. (Indeed, the abortion rate has been declining for decades, although it’s disputed how much of that decrease is due to better birth control, and wider use of it, and how much to restrictions that have made abortions much harder to get.) Now that the Supreme Court seems likely to overturn Roe v. Wade sometime in the next few years—Alabama has passed a near-total ban on abortion, and Ohio, Georgia, Kentucky, Mississippi, and Missouri have passed “heartbeat” bills that, in effect, ban abortion later than six weeks of pregnancy, and any of these laws, or similar ones, could prove the catalyst—I wonder if women who have never needed to undergo the procedure, and perhaps believe that they never will, realize the many ways that the legal right to abortion has undergirded their lives.
Legal abortion means that the law recognizes a woman as a person. It says that she belongs to herself. Most obviously, it means that a woman has a safe recourse if she becomes pregnant as a result of being raped. (Believe it or not, in some states, the law allows a rapist to sue for custody or visitation rights.) It means that doctors no longer need to deny treatment to pregnant women with certain serious conditions—cancer, heart disease, kidney disease—until after they’ve given birth, by which time their health may have deteriorated irretrievably. And it means that non-Catholic hospitals can treat a woman promptly if she is having a miscarriage. (If she goes to a Catholic hospital, she may have to wait until the embryo or fetus dies. In one hospital, in Ireland, such a delay led to the death of a woman named Savita Halappanavar, who contracted septicemia. Her case spurred a movement to repeal that country’s constitutional amendment banning abortion.)
The legalization of abortion, though, has had broader and more subtle effects than limiting damage in these grave but relatively uncommon scenarios. The revolutionary advances made in the social status of American women during the nineteen-seventies are generally attributed to the availability of oral contraception, which came on the market in 1960. But, according to a 2017 study by the economist Caitlin Knowles Myers, “The Power of Abortion Policy: Re-Examining the Effects of Young Women’s Access to Reproductive Control,” published in the Journal of Political Economy , the effects of the Pill were offset by the fact that more teens and women were having sex, and so birth-control failure affected more people. Complicating the conventional wisdom that oral contraception made sex risk-free for all, the Pill was also not easy for many women to get. Restrictive laws in some states barred it for unmarried women and for women under the age of twenty-one. The Roe decision, in 1973, afforded thousands upon thousands of teen-agers a chance to avoid early marriage and motherhood. Myers writes, “Policies governing access to the pill had little if any effect on the average probabilities of marrying and giving birth at a young age. In contrast, policy environments in which abortion was legal and readily accessible by young women are estimated to have caused a 34 percent reduction in first births, a 19 percent reduction in first marriages, and a 63 percent reduction in ‘shotgun marriages’ prior to age 19.”
Access to legal abortion, whether as a backup to birth control or not, meant that women, like men, could have a sexual life without risking their future. A woman could plan her life without having to consider that it could be derailed by a single sperm. She could dream bigger dreams. Under the old rules, inculcated from girlhood, if a woman got pregnant at a young age, she married her boyfriend; and, expecting early marriage and kids, she wouldn’t have invested too heavily in her education in any case, and she would have chosen work that she could drop in and out of as family demands required.
In 1970, the average age of first-time American mothers was younger than twenty-two. Today, more women postpone marriage until they are ready for it. (Early marriages are notoriously unstable, so, if you’re glad that the divorce rate is down, you can, in part, thank Roe.) Women can also postpone childbearing until they are prepared for it, which takes some serious doing in a country that lacks paid parental leave and affordable childcare, and where discrimination against pregnant women and mothers is still widespread. For all the hand-wringing about lower birth rates, most women— eighty-six per cent of them —still become mothers. They just do it later, and have fewer children.
Most women don’t enter fields that require years of graduate-school education, but all women have benefitted from having larger numbers of women in those fields. It was female lawyers, for example, who brought cases that opened up good blue-collar jobs to women. Without more women obtaining law degrees, would men still be shaping all our legislation? Without the large numbers of women who have entered the medical professions, would psychiatrists still be telling women that they suffered from penis envy and were masochistic by nature? Would women still routinely undergo unnecessary hysterectomies? Without increased numbers of women in academia, and without the new field of women’s studies, would children still be taught, as I was, that, a hundred years ago this month, Woodrow Wilson “gave” women the vote? There has been a revolution in every field, and the women in those fields have led it.
It is frequently pointed out that the states passing abortion restrictions and bans are states where women’s status remains particularly low. Take Alabama. According to one study , by almost every index—pay, workforce participation, percentage of single mothers living in poverty, mortality due to conditions such as heart disease and stroke—the state scores among the worst for women. Children don’t fare much better: according to U.S. News rankings , Alabama is the worst state for education. It also has one of the nation’s highest rates of infant mortality (only half the counties have even one ob-gyn), and it has refused to expand Medicaid, either through the Affordable Care Act or on its own. Only four women sit in Alabama’s thirty-five-member State Senate, and none of them voted for the ban. Maybe that’s why an amendment to the bill proposed by State Senator Linda Coleman-Madison was voted down. It would have provided prenatal care and medical care for a woman and child in cases where the new law prevents the woman from obtaining an abortion. Interestingly, the law allows in-vitro fertilization, a procedure that often results in the discarding of fertilized eggs. As Clyde Chambliss, the bill’s chief sponsor in the state senate, put it, “The egg in the lab doesn’t apply. It’s not in a woman. She’s not pregnant.” In other words, life only begins at conception if there’s a woman’s body to control.
Indifference to women and children isn’t an oversight. This is why calls for better sex education and wider access to birth control are non-starters, even though they have helped lower the rate of unwanted pregnancies, which is the cause of abortion. The point isn’t to prevent unwanted pregnancy. (States with strong anti-abortion laws have some of the highest rates of teen pregnancy in the country; Alabama is among them.) The point is to roll back modernity for women.
So, if women who have never had an abortion, and don’t expect to, think that the new restrictions and bans won’t affect them, they are wrong. The new laws will fall most heavily on poor women, disproportionately on women of color, who have the highest abortion rates and will be hard-pressed to travel to distant clinics.
But without legal, accessible abortion, the assumptions that have shaped all women’s lives in the past few decades—including that they, not a torn condom or a missed pill or a rapist, will decide what happens to their bodies and their futures—will change. Women and their daughters will have a harder time, and there will be plenty of people who will say that they were foolish to think that it could be otherwise.
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
By Jia Tolentino

By Isaac Chotiner

By Jonathan Blitzer
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Key facts about the abortion debate in America
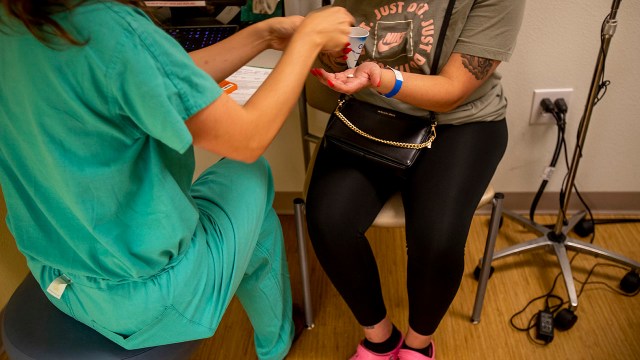
The U.S. Supreme Court’s June 2022 ruling to overturn Roe v. Wade – the decision that had guaranteed a constitutional right to an abortion for nearly 50 years – has shifted the legal battle over abortion to the states, with some prohibiting the procedure and others moving to safeguard it.
As the nation’s post-Roe chapter begins, here are key facts about Americans’ views on abortion, based on two Pew Research Center polls: one conducted from June 25-July 4 , just after this year’s high court ruling, and one conducted in March , before an earlier leaked draft of the opinion became public.
This analysis primarily draws from two Pew Research Center surveys, one surveying 10,441 U.S. adults conducted March 7-13, 2022, and another surveying 6,174 U.S. adults conducted June 27-July 4, 2022. Here are the questions used for the March survey , along with responses, and the questions used for the survey from June and July , along with responses.
Everyone who took part in these surveys is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
A majority of the U.S. public disapproves of the Supreme Court’s decision to overturn Roe. About six-in-ten adults (57%) disapprove of the court’s decision that the U.S. Constitution does not guarantee a right to abortion and that abortion laws can be set by states, including 43% who strongly disapprove, according to the summer survey. About four-in-ten (41%) approve, including 25% who strongly approve.
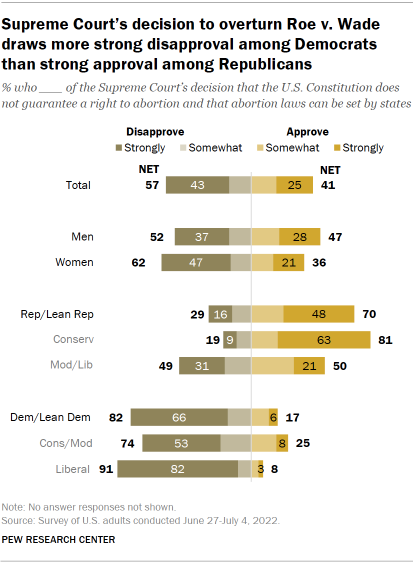
About eight-in-ten Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (82%) disapprove of the court’s decision, including nearly two-thirds (66%) who strongly disapprove. Most Republicans and GOP leaners (70%) approve , including 48% who strongly approve.
Most women (62%) disapprove of the decision to end the federal right to an abortion. More than twice as many women strongly disapprove of the court’s decision (47%) as strongly approve of it (21%). Opinion among men is more divided: 52% disapprove (37% strongly), while 47% approve (28% strongly).
About six-in-ten Americans (62%) say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, according to the summer survey – little changed since the March survey conducted just before the ruling. That includes 29% of Americans who say it should be legal in all cases and 33% who say it should be legal in most cases. About a third of U.S. adults (36%) say abortion should be illegal in all (8%) or most (28%) cases.
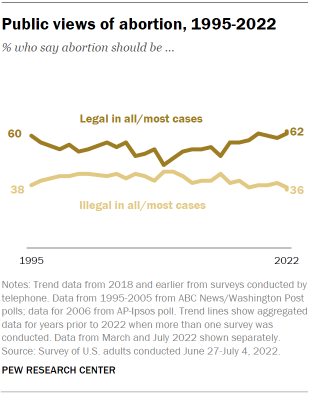
Generally, Americans’ views of whether abortion should be legal remained relatively unchanged in the past few years , though support fluctuated somewhat in previous decades.
Relatively few Americans take an absolutist view on the legality of abortion – either supporting or opposing it at all times, regardless of circumstances. The March survey found that support or opposition to abortion varies substantially depending on such circumstances as when an abortion takes place during a pregnancy, whether the pregnancy is life-threatening or whether a baby would have severe health problems.
While Republicans’ and Democrats’ views on the legality of abortion have long differed, the 46 percentage point partisan gap today is considerably larger than it was in the recent past, according to the survey conducted after the court’s ruling. The wider gap has been largely driven by Democrats: Today, 84% of Democrats say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, up from 72% in 2016 and 63% in 2007. Republicans’ views have shown far less change over time: Currently, 38% of Republicans say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, nearly identical to the 39% who said this in 2007.
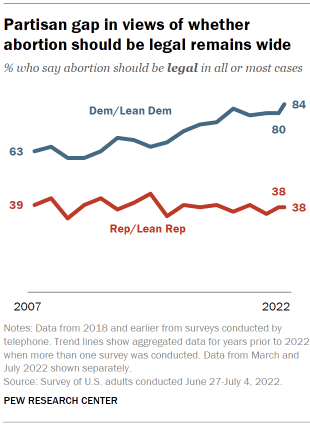
However, the partisan divisions over whether abortion should generally be legal tell only part of the story. According to the March survey, sizable shares of Democrats favor restrictions on abortion under certain circumstances, while majorities of Republicans favor abortion being legal in some situations , such as in cases of rape or when the pregnancy is life-threatening.
There are wide religious divides in views of whether abortion should be legal , the summer survey found. An overwhelming share of religiously unaffiliated adults (83%) say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, as do six-in-ten Catholics. Protestants are divided in their views: 48% say it should be legal in all or most cases, while 50% say it should be illegal in all or most cases. Majorities of Black Protestants (71%) and White non-evangelical Protestants (61%) take the position that abortion should be legal in all or most cases, while about three-quarters of White evangelicals (73%) say it should be illegal in all (20%) or most cases (53%).
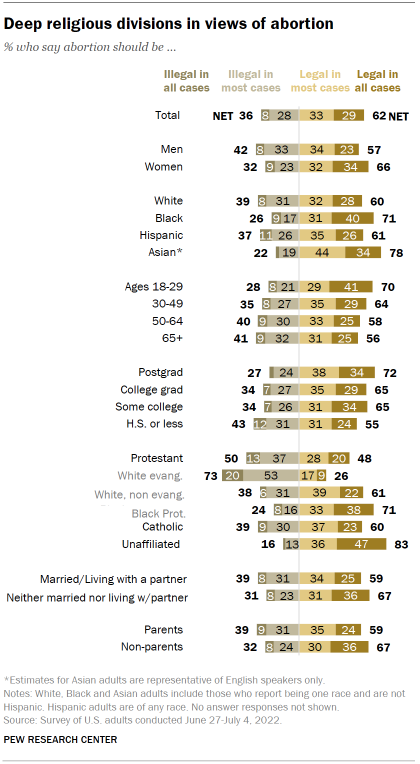
In the March survey, 72% of White evangelicals said that the statement “human life begins at conception, so a fetus is a person with rights” reflected their views extremely or very well . That’s much greater than the share of White non-evangelical Protestants (32%), Black Protestants (38%) and Catholics (44%) who said the same. Overall, 38% of Americans said that statement matched their views extremely or very well.
Catholics, meanwhile, are divided along religious and political lines in their attitudes about abortion, according to the same survey. Catholics who attend Mass regularly are among the country’s strongest opponents of abortion being legal, and they are also more likely than those who attend less frequently to believe that life begins at conception and that a fetus has rights. Catholic Republicans, meanwhile, are far more conservative on a range of abortion questions than are Catholic Democrats.
Women (66%) are more likely than men (57%) to say abortion should be legal in most or all cases, according to the survey conducted after the court’s ruling.
More than half of U.S. adults – including 60% of women and 51% of men – said in March that women should have a greater say than men in setting abortion policy . Just 3% of U.S. adults said men should have more influence over abortion policy than women, with the remainder (39%) saying women and men should have equal say.
The March survey also found that by some measures, women report being closer to the abortion issue than men . For example, women were more likely than men to say they had given “a lot” of thought to issues around abortion prior to taking the survey (40% vs. 30%). They were also considerably more likely than men to say they personally knew someone (such as a close friend, family member or themselves) who had had an abortion (66% vs. 51%) – a gender gap that was evident across age groups, political parties and religious groups.
Relatively few Americans view the morality of abortion in stark terms , the March survey found. Overall, just 7% of all U.S. adults say having an abortion is morally acceptable in all cases, and 13% say it is morally wrong in all cases. A third say that having an abortion is morally wrong in most cases, while about a quarter (24%) say it is morally acceptable in most cases. An additional 21% do not consider having an abortion a moral issue.
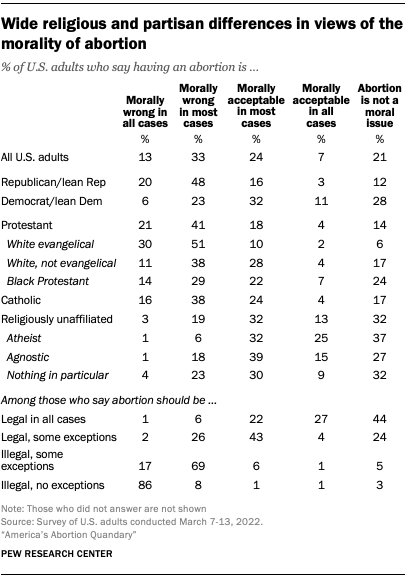
Among Republicans, most (68%) say that having an abortion is morally wrong either in most (48%) or all cases (20%). Only about three-in-ten Democrats (29%) hold a similar view. Instead, about four-in-ten Democrats say having an abortion is morally acceptable in most (32%) or all (11%) cases, while an additional 28% say it is not a moral issue.
White evangelical Protestants overwhelmingly say having an abortion is morally wrong in most (51%) or all cases (30%). A slim majority of Catholics (53%) also view having an abortion as morally wrong, but many also say it is morally acceptable in most (24%) or all cases (4%), or that it is not a moral issue (17%). Among religiously unaffiliated Americans, about three-quarters see having an abortion as morally acceptable (45%) or not a moral issue (32%).
- Religion & Abortion

Carrie Blazina is a former digital producer at Pew Research Center .
Cultural Issues and the 2024 Election
Support for legal abortion is widespread in many places, especially in europe, public opinion on abortion, americans overwhelmingly say access to ivf is a good thing, broad public support for legal abortion persists 2 years after dobbs, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

- Volume 70 Masthead
- Volume 69 Masthead
- Volume 68 Masthead
- Volume 67 Masthead
- Volume 66 Masthead
- Volume 65 Masthead
- Volume 64 Masthead
- Volume 63 Masthead
- Volume 62 Masthead
- Volume 61 Masthead
- Volume 60 Masthead
- Volume 59 Masthead
- Volume 58 Masthead
- Volume 57 Masthead
- Volume 56 Masthead
- Volume 55 Masthead
- Volume 54 Masthead
- Volume 53 Masthead
- Volume 52 Masthead
- Volume 51 Masthead
- Volume 50 Masthead
- Sponsorship
- Subscriptions
- Print Archive
- Forthcoming: 2021-2022
- Special Issue: Law Meets World Vol. 68
- Symposia Topics
Equality Arguments for Abortion Rights
Introduction.
Roe v. Wade grounds constitutional protections for women’s decision whether to end a pregnancy in the Due Process Clauses. 1 But in the four decades since Roe , the U.S. Supreme Court has come to recognize the abortion right as an equality right as well as a liberty right. In this Essay, we describe some distinctive features of equality arguments for abortion rights. We then show how, over time, the Court and individual Justices have begun to employ equality arguments in analyzing the constitutionality of abortion restrictions. These arguments first appear inside of substantive due process case law, and then as claims on the Equal Protection Clause. Finally, we explain why there may be independent political significance in grounding abortion rights in equality values.
Before proceeding, we offer two important caveats. First, in this brief Essay we discuss equality arguments that Supreme Court justices have recognized—not arguments that social movement activists made in the years before Roe , that academics made in their wake, or that ordinary Americans might have made then or might make now. Second, we address, separately, arguments based on the Due Process Clauses and the Equal Protection Clause. In most respects but one, 2 however, we emphasize that a constitutional interpreter’s attention to the social organization of reproduction could play a more important role in determining the permissibility of various abortion-restrictive regulations than the particular constitutional clause on which an argument is based.
I. Equality Arguments for Abortion Rights
Equality arguments are also concerned about the gendered impact of abortion restrictions. Sex equality arguments observe that abortion restrictions deprive women of control over the timing of motherhood and so predictably exacerbate the inequalities in educational, economic, and political life engendered by childbearing and childrearing. Sex equality arguments ask whether, in protecting unborn life, the state has taken steps to ameliorate the effects of compelled motherhood on women, or whether the state has proceeded with indifference to the impact of its actions on women. 5 Liberty arguments focus less on these gendered biases and burdens on women.
To be clear, equality arguments do not suppose that restrictions on abortion are only about women. Rather, equality arguments are premised on the view that restrictions on abortion may be about both women and the unborn— both and . Instead of assuming that restrictions on abortion are entirely benign or entirely invidious, equality analysis entertains the possibility that gender stereotypes may shape how the state pursues otherwise benign ends. The state may protect unborn life in ways it would not, but for stereotypical assumptions about women’s sexual or maternal roles.
For example, the state’s bona fide interest in protecting potential life does not suffice to explain the traditional form of criminal abortion statutes in America. Such statutes impose the entire burden of coerced childbirth on pregnant women and provide little or no material support for new mothers. In this way, abortion restrictions reflect views about how it is “natural” and appropriate for a woman to respond to a pregnancy. If abortion restrictions were not premised on these views, legislatures that sought to coerce childbirth in the name of protecting life would bend over backwards to provide material support for the women who are required to bear—too often alone—the awesome physical, emotional, and financial costs of pregnancy, childbirth, and childrearing. 6 Only by viewing pregnancy and motherhood as a part of the natural order can a legislature dismiss these costs as modest in size and private in nature. Nothing about a desire to protect fetal life compels or commends this state of affairs. When abortion restrictions reflect or enforce traditional sex-role stereotypes, equality arguments insist that such restrictions are suspect and may violate the U.S. Constitution.
II. Equality Arguments in Legal Doctrine
While Roe locates the abortion right in the Due Process Clauses, the Supreme Court has since come to conceive of it as an equality right as well as a liberty right. The Court’s case law now recognizes equality arguments for the abortion right based on the Due Process Clauses. Additionally, a growing number of justices have asserted equality arguments for the abortion right independently based on the Equal Protection Clause.
A. Equality Arguments for Abortion Rights and the Due Process Clauses
The Court has also invoked equality concerns to make sense of the Due Process Clauses in the area of abortion rights. The opinion of the Court in Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey 11 is shaped to a substantial degree by equality values. At the very moment in Casey when the Court reaffirms constitutional protection for abortion rights, the Court explains that a pregnant woman’s “suffering is too intimate and personal for the State to insist, without more, upon its own vision of the woman’s role, however dominant that vision has been in the course of our history and our culture.” 12 This emphasis on the role autonomy of the pregnant woman reflects the influence of the equal protection sex discrimination cases, which prohibit the government from enforcing stereotypical roles on women. Likewise, in the stare decisis passages of Casey , the Court emphasizes, as a reason to reaffirm Roe , that “[t]he ability of women to participate equally in the economic and social life of the Nation has been facilitated by their ability to control their reproductive lives.” 13 Here, as elsewhere in Casey , the Court is interpreting the Due Process Clause and drawing on equality values in order to make sense of the substance of the right.
The equality reasoning threading through Casey is not mere surplusage. Equality values help to identify the kinds of restrictions on abortion that are unconstitutional under Casey ’s undue burden test. As the joint opinion applies the test, abortion restrictions that deny women’s equality impose an undue burden on women’s fundamental right to decide whether to become a mother. Thus, the Casey Court upheld a twenty-four-hour waiting period, but struck down a spousal notification provision that was eerily reminiscent of the common law’s enforcement of a hierarchical relationship between husband and wife. Just as the law of coverture gave husbands absolute dominion over their wives, so “[a] State may not give to a man the kind of dominion over his wife that parents exercise over their children.” 14 An equality-informed understanding of Casey ’s undue burden test prohibits government from coercing, manipulating, misleading, or stereotyping pregnant women.
B. Equality Arguments for Abortion Rights and the Equal Protection Clause
In Carhart , Justice Ginsburg invoked equal protection cases—including Virginia —to counter woman-protective arguments for restricting access to abortion, which appear in the majority opinion. Woman-protective arguments are premised on certain judgments about women’s nature and decisional competence. 22 But the equal protection precedents that Justice Ginsburg cited are responsive both to woman-protective and to fetal-protective anti-abortion arguments. As Justice Blackmun’s Casey opinion illustrates, equality arguments are concerned that gender assumptions shape abortion restrictions, even when genuine concern about fetal life is present.
C. What About Geduldig ?
Equality arguments complement liberty arguments, and are likely to travel together. There is therefore little reason to reach the abstract question of whether, if Roe and Casey were overruled, courts applying existing equal protection doctrine would accord constitutional protection to decisions concerning abortion .
Proponents of equality arguments have long regarded the state’s regulation of pregnant women as suspect—as potentially involving problems of sex-role stereotyping. But in one of its early equal protection sex discrimination decisions, the Court reasoned about the regulation of pregnancy in ways not necessarily consistent with this view. In Geduldig , the Court upheld a California law that provided workers comprehensive disability insurance for all temporarily disabling conditions that might prevent them from working, except pregnancy. According to the conventional reading of Geduldig , the Court held categorically that the regulation of pregnancy is never sex based, so that such regulation warrants very deferential scrutiny from the courts.
The conventional wisdom about Geduldig , however, is incorrect. The Geduldig Court did not hold that governmental regulation of pregnancy never qualifies as a sex classification. Rather, the Geduldig Court held that governmental regulation of pregnancy does not always qualify as a sex classification. 24 The Court acknowledged that “distinctions involving pregnancy” might inflict “an invidious discrimination against the members of one sex or the other.” 25 This reference to invidiousness by the Geduldig Court is best understood in the same way that Wendy Williams’s brief in Geduldig used the term “invidious”—namely, as referring to traditional sex-role stereotypes. 26 Particularly in light of the Court’s recognition in Nevada Department of Human Resources v. Hibbs 27 that pregnant women are routinely subject to sex-role stereotyping, 28 Geduldig should be read to say what it actually says, not what most commentators and courts have assumed it to say.
Geduldig was decided at the dawn of the Court’s sex discrimination case law and at the dawn of the Court’s modern substantive due process jurisprudence. The risk of traditional sex-role stereotyping and stereotyping around pregnancy was developed more fully in later cases, including in twenty-five years of litigation over the Pregnancy Discrimination Act. 29 This explains why, when Hibbs was decided in 2003, the Court could reason about pregnancy in ways that the Geduldig Court contemplated in theory but could not register in fact.
III. The Political Authority of the Equal Protection Clause
We have thus far considered the distinctive concerns and grounds of equality arguments, which enable them to complement liberty arguments for abortion rights. We close by considering some distinctive forms of political authority that equality arguments confer.
Some critics pejoratively refer to certain of the Court’s Due Process decisions as recognizing “unenumerated” constitutional rights. Although there are two Due Process Clauses in the Constitution, these interpreters regard decisions like Roe , Casey , and Lawrence , which recognize substantive rather than procedural due process rights, as lacking a basis in the text of the Constitution, hence as recognizing “unenumerated rights.”
The pejorative “unenumerated rights” is often deployed against Roe and Lawrence in an ad hoc manner, without clarification of whether the critic of unenumerated rights is prepared to abandon all bodies of law that have similar roots or structure. For example, those who use the objection from unenumerated rights to attack Roe and Lawrence generally assume that the First Amendment limits state governments; but of course, incorporation of the Bill of Rights against the states is also a feature of the Court’s substantive due process doctrine. 30 Other “unenumerated rights” to which most critics of Roe and Lawrence are committed include the applicability of equal protection principles to the conduct of the federal government. 31 And this view cannot readily distinguish other “unenumerated” rights of unquestioned authority, such as the rights to travel (or not), 32 marry (or not), 33 procreate (or not), 34 and use contraceptives (or not). 35 At their Supreme Court confirmation hearings, Chief Justice Roberts and Justice Alito learned from the experience of Judge Robert Bork by swearing allegiance to Griswold .
But even if the pejorative term “unenumerated” is deployed selectively and inconsistently, it has frequently been deployed in such a way as to affect popular perceptions of Roe ’s authority. Accordingly, in light of criticism of the abortion right as “unenumerated,” it is worth asking whether grounding the right in the Equal Protection Clause, as well as the Due Process Clauses, can enhance the political authority of the right.
Adding claims on the Equal Protection Clause to the due process basis for abortion rights can strengthen the case for those rights in constitutional politics as well as constitutional law. The Equal Protection Clause is a widely venerated constitutional text to which Americans across the political spectrum have long laid claim. And crucially, once the Supreme Court recognizes that people have a right to engage in certain conduct by virtue of equal citizenship, Americans do not count stripping them of this right as an increase in constitutional legitimacy. We cannot think of a precedent for this dynamic. And so: If the Court were to recognize the abortion right as an equality right, a future Court might be less likely to take this right away.
This understanding has increasingly come to shape constitutional law. We have documented the Supreme Court’s equality-informed understanding of the Due Process Clause in Lawrence and Casey . We have also identified the growing number of justices who view the Equal Protection Clause as an independent source of authority for abortion rights. We view this reading of the substantive due process and equal protection cases as contributing to a synthetic understanding of the constitutional basis of the abortion right—as grounded in both liberty and equality values. For a variety of reasons this Essay has explored, the synthetic reading leaves abortions right on stronger legal and political footing than a liberty analysis alone.
- Roe v. Wade, 410 U.S. 113 (1973). ↩
- See infra Part III on the political authority of the Equal Protection Clause. ↩
- For examples of work in the equality tradition that emerged in the years before Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey , 505 U.S. 833 (1992), see Laurence H. Tribe, American Constitutional Law § 15-10, at 1353–59 (2d ed. 1990); Ruth Bader Ginsburg, Some Thoughts on Autonomy and Equality in Relation to Roe v. Wade, 63 N.C. L. Rev. 375 (1985); Sylvia A. Law, Rethinking Sex and the Constitution , 132 U. Pa. L. Rev. 955 (1984); Catharine A. MacKinnon, Reflections on Sex Equality Under Law , 100 Yale L.J. 1281 (1991); Reva Siegel, Reasoning From the Body: A Historical Perspective on Abortion Regulation and Questions of Equal Protection , 44 Stan. L. Rev. 261 (1992) [hereinafter Siegel, Reasoning From the Body ]; and Cass R. Sunstein, Neutrality in Constitutional Law (With Special Reference to Pornography, Abortion, and Surrogacy) , 92 Colum. L. Rev. 1 (1992). For more recent sex equality work, see, for example, What Roe v. Wade Should Have Said: The Nation’s Top Legal Experts Rewrite America’s Most Controversial Decision (Jack M. Balkin ed., 2005) (sex equality opinions by Jack Balkin, Reva Siegel, and Robin West); and Reva B. Siegel, Sex Equality Arguments for Reproductive Rights: Their Critical Basis and Evolving Constitutional Expression , 56 Emory L.J. 815, 833–34 (2007) [hereinafter Siegel, Sex Equality Arguments for Reproductive Rights ] (surveying equality arguments after Casey ). ↩
- See, e.g. , Siegel, Sex Equality Arguments for Reproductive Rights , supra note 3, at 817–22. ↩
- See id. at 819. ↩
- See generally Siegel, Reasoning From the Body , supra note 3. ↩
- 539 U.S. 558 (2003). ↩
- Id. at 578. ↩
- Id. at 575. ↩
- Thus the Court wrote that the very “continuance” of Bowers v. Hardwick , 478 U.S. 186 (1986), “as precedent demeans the lives of homosexual persons.” Lawrence , 539 U.S. at 575. ↩
- 505 U.S. 833 (1992). ↩
- Id. at 852. ↩
- Id. at 856. ↩
- Id. at 898. ↩
- Id. at 928 (Blackmun, J., concurring in part, concurring in the judgment in part, and dissenting in part). ↩
- Id. ↩
- 550 U.S. 124 (2007). ↩
- Id. at 172 (Ginsburg, J., dissenting). For an argument that “equal citizenship stature” is central to Justice Ginsburg’s constitutional vision, see generally Neil S. Siegel, “Equal Citizenship Stature”: Justice Ginsburg’s Constitutional Vision , 43 New Eng. L. Rev. 799 (2009). ↩
- 518 U.S. 515 (1996). ↩
- Id. at 534. ↩
- See generally Neil S. Siegel, The Virtue of Judicial Statesmanship , 86 Tex. L. Rev. 959, 1014–30 (2008); Reva B. Siegel, Dignity and the Politics of Protection: Abortion Restrictions Under Casey / Carhart, 117 Yale L.J. 1694 (2008). ↩
- 417 U.S. 484 (1974). ↩
- See Neil S. Siegel & Reva B. Siegel, Pregnancy and Sex Role Stereotyping: From Struck to Carhart, 70 Ohio St. L.J. 1095, 1111–13 (2009); Reva B. Siegel, You’ve Come a Long Way, Baby: Rehnquist’s New Approach to Pregnancy Discrimination in Hibbs, 58 Stan. L. Rev. 1871, 1891–97 (2006). ↩
- Geduldig , 417 U.S. at 496–97 n.20. ↩
- See Brief for Appellees at 38, Geduldig , 417 U.S. 484 (No. 73-640), 1974 WL 185752, at *38 (“The issue for courts is not whether pregnancy is, in the abstract, sui generis, but whether the legal treatment of pregnancy in various contexts is justified or invidious. The ‘gross, stereotypical distinctions between the sexes’ . . . are at the root of many laws and regulations relating to pregnancy.” (quoting Frontiero v. Richardson, 411 U.S. 677, 685 (1973))). ↩
- 538 U.S. 721 (2003). ↩
- Id. at 731 (majority opinion of Rehnquist, C.J.) (asserting that differential workplace leave policies for fathers and mothers “were not attributable to any differential physical needs of men and women, but rather to the pervasive sex-role stereotype that caring for family members is women’s work”); id. at 736 (quoting Congress’s finding that the “prevailing ideology about women’s roles has . . . justified discrimination against women when they are mothers or mothers-to-be” (citation omitted) (internal quotation marks omitted)). ↩
- Pregnancy Discrimination Act of 1978, 42 U.S.C. § 2000e(k) (2006) (“The terms ‘because of sex’ or ‘on the basis of sex’ include, but are not limited to, because of or on the basis of pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions; and women affected by pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions shall be treated the same for all employment-related purposes . . . .”). Concerns about sex-role stereotyping played a significant part in Congress’s decision to amend Title VII . See, e.g. , H.R. Rep. No. 95-948, at 3 (1978) (“[T]he assumption that women will become [pregnant] and leave the labor force leads to the view of women as marginal workers, and is at the root of the discriminatory practices which keep women in low-paying and dead-end jobs.”). ↩
- See, e.g. , McDonald v. City of Chicago, 130 S. Ct. 3020, 3050 (2010) (Scalia, J., concurring) (“Despite my misgivings about Substantive Due Process as an original matter, I have acquiesced in the Court’s incorporation of certain guarantees in the Bill of Rights ‘because it is both long established and narrowly limited.’” This case does not require me to reconsider that view, since straightforward application of settled doctrine suffices to decide it.” (quoting Albright v. Oliver, 510 U.S. 266, 275 (1994))). ↩
- See Bolling v. Sharpe, 347 U.S. 497 (1954) (holding that de jure school segregation in Washington, D.C. violates the equal protection component of the Due Process Clause of the Fifth Amendment); see also, e.g. , Adarand Constructors, Inc. v. Pena, 515 U.S. 200, 240 (1995) (Thomas, J., concurring in part and concurring in the judgment) (“These programs not only raise grave constitutional questions, they also undermine the moral basis of the equal protection principle. Purchased at the price of immeasurable human suffering, the equal protection principle reflects our Nation’s understanding that such classifications ultimately have a destructive impact on the individual and our society.” (emphasis added)). ↩
- See Shapiro v. Thompson, 394 U.S. 618 (1969) (right to travel as a fundamental right). ↩
- See Zablocki v. Redhail, 434 U.S. 374 (1978) (right to marry as a fundamental right); Loving v. Virginia, 388 U.S. 1 (1967) (same). ↩
- See Skinner v. Oklahoma, 316 U.S. 535 (1942) (right to procreate as a fundamental right). ↩
- See Eisenstadt v. Baird, 405 U.S. 438 (1972) (right to contraception for all individuals as a fundamental right); Griswold v. Connecticut, 381 U.S. 479 (1965) (right to contraception for married couples as a fundamental right). ↩
- Gonzales v. Carhart, 550 U.S. 124, 172 (2007) (Ginsburg, J., dissenting). ↩
Share this:
About the author.
Neil S. Siegel is Professor of Law and Political Science, Co-Director, Program in Public Law, Duke Law School. Reva B. Siegel is Nicholas deB. Katzenbach Professor of Law, Yale University.
Bringing Visibility to AAPI Reproductive Care After Dobbs
Abstract Dobbs’ impact on growing AAPI communities is underexamined in legal scholarship. This Essay begins to fill that gap, seeking to bring together an overdue focus on the socio-legal experiences of AAPI communities with examination of the...
Can CRT Save DEI?: Workplace Diversity, Equity & Inclusion in the Shadow of Anti-Affirmative Action
Abstract Just four years after the nation’s summer of 2020 protests—sparked by the murder of George Floyd—culminated in a racial reckoning in which many organizations across the country instituted racial equity measures and policies, legislators...
Algorithms in Judges’ Hands: Incarceration and Inequity in Broward County, Florida
Abstract Judicial and carceral systems increasingly use criminal risk assessment algorithms to make decisions that affect individual freedoms. While the accuracy, fairness, and legality of these algorithms have come under scrutiny, their tangible...
Can AI Standards Have Politics?
Abstract How to govern a technology like artificial intelligence (AI)? When it comes to designing and deploying fair, ethical, and safe AI systems, standards are a tempting answer. By establishing the best way of doing something, standards might...
Abortion Law
Human rights devolution: integrating international law into state abortion governance, introduction.
Court Reform
Dobbs and Democracy
- Melissa Murray
- Katherine Shaw
Precedent, Reliance, and Dobbs
- Nina Varsava
Fifth Amendment Rights as Abortion Rights
- Madalyn K. Wasilczuk
The Labor and Delivery of Reproductive Justice for Workers: The Post- Dobbs Workforce
Chapter Four
Disobedience, Medicine, and the Rule of Law
- Mary Ziegler
Medical Disobedience
Complicit bias and the supreme court.
- Michele Goodwin
PAK v. Attorney General
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
As the Supreme Court considers Roe v. Wade, a look at how abortion became legal

Nina Totenberg

The future of abortion, always a contentious issue, is up at the Supreme Court on Dec. 1. Arguments are planned challenging Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey , the court's major decisions over the last half-century that guarantee a woman's right to an abortion nationwide. J. Scott Applewhite/AP hide caption
The future of abortion, always a contentious issue, is up at the Supreme Court on Dec. 1. Arguments are planned challenging Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey , the court's major decisions over the last half-century that guarantee a woman's right to an abortion nationwide.
For nearly a half-century, abortion has been a constitutional right in the United States. But this week, the U.S. Supreme Court hears arguments in a Mississippi case that directly challenges Roe v. Wade and subsequent decisions.
Those rulings consistently declared that a woman has a constitutional right to terminate a pregnancy in the first two trimesters of pregnancy when a fetus is unable to survive outside the womb. But with that abortion right now in doubt, it's worth looking back at its history.
Abortion did not become illegal in most states until the mid to late 1800s. But by the 1960s, abortion, like childbirth, had become a safe procedure when performed by a doctor, and women were entering the workforce in ever larger numbers.
Still, being pregnant out of wedlock was seen as scandalous, and women increasingly sought out abortions, even though they were illegal. What's more, to be pregnant often meant that women's educations were stunted, as were their chances for getting a good job. Because of these phenomena, illegal abortion began to skyrocket and became a public health problem. Estimates of numbers each year ranged from 200,000 to over a million, a range that was so wide precisely because illegal procedures often went undocumented.
At the time, young women could see the perils for themselves. Anyone who lived in a college dormitory back then might well have seen one or more women carried out of the dorm hemorrhaging from a botched illegal abortion.
George Frampton clerked for Justice Harry Blackmun the year that his boss authored Roe v. Wade , and he remembers that until Roe , "those abortions had to be obtained undercover if you had a sympathetic doctor" and you were "wealthy enough." But most abortions were illegal and mainly took place "in backrooms by abortion quacks" using "crude tools" and "no hygiene."
By the early to mid-1960s, Frampton notes, thousands of women in large cities were arriving at hospitals, bleeding and often maimed.
One woman, in an interview with NPR, recalled "the excruciatingly painful [illegal] procedure," describing it as "the equivalent of having a hot poker stuck up your uterus and scraping the walls." She remembered that the attendant had to "hold her down on the table."
The result, says Frampton, was that by the mid-1960s, a reform movement had begun, aimed at decriminalizing abortion and treating it more like other medical procedures. Driving the reform movement were doctors, who were concerned about the effect that illegal abortions were having on women's health. Soon, the American Law Institute — a highly respected group of lawyers, judges and scholars — published a model abortion reform law supported by major medical groups, including the American Medical Association.
Many states then began to loosen their abortion restrictions. Four states legalized abortion, and a dozen or so adopted some form of the model law, which permitted abortion in cases of rape, incest and fetal abnormality, as well as to save the life or health of the mother.
By the early 1970s, when nearly half the states had adopted reform laws, there was a small backlash. Still, as Frampton observes, "it wasn't a big political or ideological issue at all."
In fact, the justices in 1973 were mainly establishment conservatives. Six were Republican appointees, including the court's only Catholic. And five were generally conservative, as defined at the time, including four appointed by President Richard Nixon. Ultimately, the court voted 7-to-2 that abortion is a private matter to be decided by a woman during the first two trimesters of her pregnancy.
That framework has remained in place ever since, with the court repeatedly upholding that standard. In 1992, it reiterated the framework yet again, though it said that states could enact some limited restrictions — for example, a 24-hour waiting period — as long as the restrictions didn't impose an "undue burden" on a woman's right to abortion.
Frampton says that the court established the viability framework because of the medical consensus that a fetus could not survive outside the womb until the last trimester. He explains that "the justices thought that this was going to dispose of the constitutional issues about abortion forever."
Although many had thought that fetal viability might change substantially, that has not happened. But in the years that followed, the backlash to the court's abortion decisions grew louder and louder, until the Republican Party, which had earlier supported Roe , officially abandoned it in 1984.
Looking at the politicization of the Supreme Court nomination and confirmation process in recent years, one can't help but wonder whether Roe played a part in that polarization. What does Frampton think?
"I'm afraid," he concedes, "that analysis is absolutely spot on. I think they [the justices] saw it as a very important landmark constitutional decision but had no idea that it would become so politicized and so much a subject of turmoil."
Just why is abortion such a controversial issue in the United States but not in so many other countries where abortion is now legal? Florida State University law professor Mary Ziegler, author of Abortion and the Law in America , points out that in many countries, the abortion question has been resolved through democratic means — in some countries by national referendum, in others by parliamentary votes and, in some, by the courts. In most of those countries, however, abortions, with some exceptions, must be performed earlier, by week 12, 15 or 18.
But — and it is a big but — in most of those countries, unlike in the U.S., national health insurance guarantees easy access to abortions.
Lastly, Ziegler observes, "there are a lot of people in the United States who have a stake in our polarized politics. ... It's a way to raise money. It's a way to get people out to the polls."
And it's striking, she adds, how little our politics resemble what most people say they want. Public opinion polls consistently show that large majorities of Americans support the right to abortion in all or most cases. A poll conducted last May by the Pew Research Center found 6 in 10 Americans say that abortion should be legal in all or most cases. And a Washington Post -ABC poll conducted last month found that Americans by a roughly 2-to-1 margin say the Supreme Court should uphold its landmark Roe v. Wade decision.
But an NPR poll conducted in 2019 shows just how complex — and even contradictory — opinions are about abortion. The poll found that 77% of Americans support Roe . But that figure dropped to 34% in the second trimester. Other polls had significantly higher support for second trimester abortions. A Reuters poll pegged the figure at 47% in 2021. And an Associated Press poll found that 49% of poll respondents supported legal abortion for anyone who wants one "for any reason," while 50% believed that this should not be the case. And 86% said they would support abortion at any time during a pregnancy to protect the life or health of the woman.
All this would seem to suggest that there is overwhelming support for abortion rights earlier in pregnancy, but less support later in pregnancy, and overwhelming support for abortions at any time to protect the life or, importantly, the health of the mother. That, however, is not where the abortion debate is in the 25 or so states that have enacted very strict anti-abortion laws, including outright bans, in hopes that the Supreme Court will overturn Roe .

Abortion is an issue that has ethical, moral, and religious considerations for many people, making it a topic that impacts all of society. Read the overview below to gain a balanced understanding of the issue and explore the previews of opinion articles that showcase many perspectives on reproductive rights.
Access Through your Library >>
Topic Home | Social Issues | Literature | Lifelong Learning & DIY | World History
Abortion topic overview.
"Abortion" Opposing Viewpoints Online Collection , Gale, 2024.
Abortion is a medical or surgical procedure to deliberately end a pregnancy. In 1973 the US Supreme Court decision in Roe v. Wade ruled that the Constitution protects the right to an abortion prior to the viability of a fetus. Until the 2022 ruling in Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization, Roe v. Wade allowed a person living in any US state to exercise the right to an abortion at their own discretion through the end of the first trimester, around the twelfth week of pregnancy. States were allowed some power to regulate abortion access during the second and third trimesters. The Dobbs ruling, however, ended the federal protections for abortion rights and returned to the states the authority to determine abortion law.
In the decades between Roe and Dobbs , activists and policy makers in many states sought to change legal protections for reproductive rights. In 2020 lawmakers in twelve states tried to use the COVID-19 pandemic as justification to temporarily ban abortion as a "nonessential service." In 2021 several states introduced new restrictions on abortion, implementing over one hundred new abortion restrictions. Though the public has consistently indicated opposition to bans on abortion, several state legislatures passed bans in anticipation of the conservative Supreme Court majority overturning the nearly fifty-year-old Roe decision. Since the decision, new abortion laws have been passed across the country, some restricting and some easing access to abortion.
Main Ideas
- Abortion refers to a procedure to terminate a pregnancy. The term is typically applied to a planned medical or surgical procedure.
- People who support legal access to abortion typically identify as pro-choice , while those who support bans and heavy restrictions identify as pro-life .
- Medical abortions can take place during the first trimester of a pregnancy. In these procedures, the patient takes a combination of drugs to induce an abortion.
- In 1973 the US Supreme Court ruled in Roe v. Wade that state laws banning abortion during the first trimester of pregnancy were unconstitutional. Reproductive rights advocates challenged subsequent restrictions placed on abortion in federal court.
- Passed in 1976, the Hyde Amendment forbids the use of federal funds for abortions except under cases of rape, incest, or in which continuing the pregnancy would threaten the woman's health.
- In 2022 the US Supreme Court ruled in Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization that the US Constitution did not guarantee the right to abortion. The decision overturned the court's previous ruling in Roe v. Wade .
- After the Dobbs ruling, many states passed or implemented abortion bans or restrictions, despite continuing US public support for legal abortion. Bans have increased travel to obtain abortions to states where it remains legal and resulted in increased maternal and infant deaths in states where abortion was banned.
SUPPORT FOR AND OPPOSITION TO ABORTION
Opponents of abortion, who generally refer to themselves as pro-life , typically object to the practice for religious or ethical reasons, contending that the procedure amounts to the killing of what they consider to be a human life. Supporters of abortion rights, who typically identify as pro-choice , consider it an issue of human rights, asserting that individuals should be able to make medical decisions about their own bodies and lives. Both movements encompass a range of opinions on the subject. Some pro-life activists may condone abortions in cases of rape or incest, while others argue that all abortion is murder. Within the pro-choice movement, some activists contend that no restrictions should be placed on abortion, while others support laws requiring a waiting period before abortions can be performed or that minors obtain permission from their parents.
The majority of Americans oppose banning abortion altogether, with just 13 percent of respondents to a May 2022 Gallup poll indicating a belief that abortion should be illegal under all circumstances. However, the public has remained divided on the extent to which the government should be allowed to impose restrictions. A 2023 Pew Research Center poll found that 64 percent of US adults believed abortion should be legal in all or most cases, compared to 34 percent who said it should be prohibited in all or most cases. Poll results also showed a partisan divide on abortion that has widened over time, with almost 90 percent of Democrats believing abortion should be legal in all or most cases in 2022 compared to 21 percent of Republicans. According to an April 2023 report from the Pew Research Center, 54 percent of Americans said it would be very or somewhat easy to get an abortion in their area, compared to 65 percent in 2019. A further 34 percent of respondents told Pew it should be easier to have an abortion in their area, up from 26 percent in 2019.
After Roe was overturned, protest marches and demonstrations erupted across the United States and lasted for days, with some commentators noting the wide discrepancy between popular support for Roe and the court's rejection of it. While abortion has long been considered a feminist or women's rights issue, the protests highlighted its effects on all Americans regardless of gender. The Dobbs ruling removed precedents related to the right to privacy and the right to bodily autonomy, neither of which is specifically stated in the Constitution. However, these assumed rights have been foundational to rulings decriminalizing interracial marriage, contraception, nonprocreative sex, and same-sex marriage.
Surgical and Medical Abortions
Most abortions take place within the first trimester of pregnancy. The two types of abortion are surgical and medication . The most commonly performed surgical abortion procedure is suction abortion , also referred to as vacuum aspiration , which involves removing tissue from the uterus through a thin tube. The procedure is less invasive than surgeries at later stages of pregnancy, which require labor to be induced. First-trimester surgical abortions performed by trained medical professionals are among the safest and simplest forms of surgery. Data from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) suggests that many fewer women die from legal abortions than from childbirth or many other common procedures, leading many medical experts to conclude that abortion is safer than giving birth in the United States.
Abortions achieved with drugs instead of surgery are called medication abortions and are considered safe and effective until between nine and eleven weeks after the last menstrual period. The most commonly used drugs for medication abortions in the United States are mifepristone and misoprostol, taken in sequence as prescribed by a health care provider. Patients first take mifepristone (previously called RU-486), which blocks the body's natural production of progesterone, an essential pregnancy hormone. The patient takes the second pill, misoprostol, two days later. This drug causes the uterus to contract and expel the embryo. Medication abortions are different from emergency contraception, a type of birth control pill used after unprotected sexual intercourse that prevents pregnancy.
The number of medication abortions surpassed the number of surgical abortions for the first time in 2020, accounting for an estimated 54 percent of all abortions that year, according to the Guttmacher Institute. In April 2021, due in part to COVID-19's impact on providing and accessing health care services, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) lifted a ban on dispensing abortion medication through the mail. The decision enabled patients to access abortion without risking COVID exposure and allowed abortion providers that operate online to mail pills to more states. The FDA made this change permanent in December 2021.
Roe V. Wade
Abortions were commonly performed in the United States at the time of its founding and were not restricted by law until Connecticut passed the first anti-abortion law in 1821. Until the Roe v. Wade ruling in 1973 there was no federal standard for abortion laws, which were left to the discretion of state legislatures. By 1967 forty-nine states and the District of Columbia had classified abortion as a felony crime in most cases. That same year, however, Colorado passed a law that allowed women to seek voluntary abortions. Several states followed Colorado in liberalizing their abortion laws. By 1973 laws prohibiting abortions had been repealed in four states and loosened in fourteen. In states where abortions were prohibited by law, women who wished to terminate their pregnancies sought out illegal abortions provided by health care workers who risked jeopardizing their careers or by individuals without the proper skills or tools to perform the procedure safely.
In Roe v. Wade , the Supreme Court ruled that restrictive abortion laws are unconstitutional and violate a woman's right to privacy, as implied by the due process clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. The court's decision also determined that an embryo or unviable fetus is not a person in the legal sense. The ruling established that the decision to terminate a pregnancy during the first trimester was the sole decision of the pregnant person and their physician but permitted state governments to regulate abortion during the second trimester. States could ban abortion after the fetus had reached viability, except in cases where the pregnant person's health is endangered. Viability refers to a fetus's ability to survive outside of the womb. The point at which viability is achieved during a pregnancy remains a topic of debate, though it is usually accepted as near the end of the second trimester, at around twenty-four weeks.
In Doe v. Bolton , a companion case to Roe v. Wade decided on the same day, the Supreme Court reaffirmed its decision in Roe v. Wade by prohibiting laws that require admission to a hospital, approval by a hospital abortion committee, a second and third medical opinion, or legal residence in a state before an abortion can be performed. The decision also extended the definition of what posed a health threat to the pregnant person when performing a post-viability abortion by allowing a health care provider to consider such factors as the woman's age and emotional and psychological health. These two court decisions contributed to a notable decrease in mortality rates among pregnant women.
After Roe , the Supreme Court heard several cases that challenged the ruling. In Planned Parenthood v. Danforth (1976), the court ruled against several restrictions imposed by Missouri's abortion laws, thus expanding access to abortion. One year later, however, the court ruled in Maher v. Roe that state governments could choose to deny public funds for an abortion, granting the government additional control over reproductive health care. The Maher v. Roe decision took advantage of the Hyde Amendment, legislation passed by Congress in 1976 that excluded abortion from the list of medical services provided and covered through Medicaid, the federal and state government program that subsidizes medical costs for patients with limited financial means.
CAMPAIGN TO OVERTURN ROE V. WADE
Responding first to a trend in the states toward liberalizing abortion laws and later to the court's decision in Roe v. Wade , activists founded several organizations in the late 1960s and 1970s, giving rise to a network of fervent pro-life groups. On the one-year anniversary of the Roe decision, approximately twenty thousand activists in Washington, DC, participated in the first March for Life, which became an annual event for anti-abortion activists. Activists also commonly hold public demonstrations outside abortion clinics, brandishing signs with disturbing images of fetuses and shouting condemnations toward people entering the buildings. In 1994 the Freedom of Access to Clinic Entrances (FACE) Act made blocking the entrances of places providing abortion counseling or services a federal offense punishable by fines and imprisonment.
Some anti-abortion activists have taken more extreme, surreptitious, or violent measures. Members of groups such as Project Veritas, for instance, have posed as patients and secretly filmed abortion providers, using the footage to create misinformation campaigns alleging unethical and criminal behavior. Anti-abortion groups also operate crisis pregnancy centers (CPCs), nonprofit organizations that seek to deter women from terminating unintended pregnancies. CPCs have been accused of using misleading and deceptive advertising and purposefully providing inaccurate information to stop individuals from accessing abortion services. Members of militant pro-life organizations such as Operation Rescue have committed acts of domestic terrorism, including the bombing of clinics and waging of aggressive harassment campaigns. Several doctors who provided abortions have been murdered by pro-life activists.
Meanwhile, in states where pro-life conservatives hold power, legislatures passed laws that placed additional regulations on abortion providers and had the effect of making abortion services more difficult to obtain. Some of these laws included provisions that required the examination rooms in which the procedure would be performed to be a certain size. Other laws required abortion providers and facilities to be affiliated with a hospital or located within a certain distance from a hospital. Pro-choice groups refer to these laws as Targeted Regulation (or Restriction) for Abortion Providers (TRAP) laws. The Supreme Court ruled against TRAP bills from Texas and Louisiana in Whole Woman's Health v. Hellerstedt (2016) and June Medical Services, LLC v. Russo (2020), determining that such requirements did not produce sufficient medical benefit to justify the imposition placed on women seeking abortions.
Many anti-abortion activists celebrated the election of President Donald Trump in 2016, as he had committed during his campaign to nominating pro-life judges. Anticipating a conservative majority in the Supreme Court, lawmakers in several states began advancing more restrictive anti-abortion legislation, including many laws intended to prohibit abortions before the end of the first trimester. For example, some states passed legislation outlawing abortion after a "fetal heartbeat" is detected. Reproductive health doctors consider this terminology misleading, as they describe the noise heard as the electrical activity of the ultrasound machine rather than a heartbeat produced by a functioning heart. Texas' "fetal heartbeat" law prohibited abortions after six weeks and relied on private citizens for enforcement by allowing anyone in any state to file a civil suit against any person who helps someone get an abortion in Texas. Out of fear of possible litigation, most providers in the state had ceased operations months before the Supreme Court issued its ruling in Dobbs .
In the courts, pro-life attorneys brought challenges to Roe in the hopes the Supreme Court would eventually strike it down, while pro-life activists built an organized pipeline of judicial nominees. In 1982 a group of conservatives and libertarians founded the Federalist Society as a professional network that would support and promote judges who shared a similar legal vision, including the overturning of Roe v. Wade . The Trump administration nominated several Federalist Society members as federal judges, including Supreme Court justices Neil Gorsuch, Brett Kavanaugh, and Amy Coney Barrett. As of 2023, six of the nine Supreme Court justices were members of the Federalist Society.
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS
- What factors do you think prevented federal lawmakers from adding a constitutional amendment or passing a federal law establishing a national standard regarding abortion rights?
- Under what circumstances, if any, do you think state governments should restrict a person's access to abortion services? Explain your answer.
- How has the Supreme Court's 2022 overturning of abortion rights affected abortion access in the country? What do you consider to be the most significant effect of those changes?
ABORTION RIGHTS POST- ROE
The Dobbs ruling, which denied that the Constitution ever recognized or implied a right to abortion in the US Constitution, has had a significant impact on abortion access throughout the country. In the late 2010s, in anticipation of a conservative majority on the court, lawmakers in some states began passing legislation to safeguard the right to legal and safe abortions in the event Roe v. Wade was overturned. In 2019, for example, New York passed the Reproductive Health Act, which removed several restrictions, decriminalized abortion, and limited government interference with the decisions of women and their health care providers. Before Roe 's overturning, ten states—Alaska, Arizona, California, Florida, Kansas, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Montana, New Jersey, and New Mexico—had state constitutions protecting abortion rights. As of October 2023, twenty-two states had expanded or protected access to abortion, though the governments of some of these states were challenging those protections.
Before the Dobbs ruling, thirteen US states had passed trigger laws that would outlaw abortion in all or most cases, but not all went into effect immediately after the decision. Some triggered the beginning of a process to ban abortion, while others triggered the ban going into effect. Some laws were blocked from taking effect while lawsuits against them moved through the courts. In some states nearly all abortions became illegal, with some not allowing exceptions in instances of rape and incest or when continuing the pregnancy could be fatal.
President Joe Biden issued an executive order aimed at protecting reproductive rights in July 2022, following the Dobbs ruling. The order directed federal agencies, including the FDA and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), to develop plans to protect patient privacy, safety, and security, as well as ensure access to comprehensive and reliable medical information and medical services, including abortion and contraception. Additionally, the order created a reproductive health care task force. Despite the sweeping intentions of the executive order, the Biden administration's ability to affect abortion rights remains limited without congressional action.
Since Dobbs , states have passed new laws either protecting or restricting abortion. State legislatures introduced 563 abortion restriction provisions, fifty of which were signed into law, and 369 abortion protection provisions, seventy-seven of which were passed. Six states also held ballot initiatives in which voters chose to protect abortion rights, reflecting the 64 percent majority of Americans who reported supporting abortion rights. As of October 2023, the Guttmacher Institute categorized six US states as "very protective" of abortion rights, with Oregon's laws identified as "most protective." An additional nine states, plus Washington, DC, had policies that protected the right to abortion but imposed some restrictions. Eight states were characterized as "restrictive" and three as "very restrictive." Fifteen states—Alabama, Arkansas, Idaho, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, North Dakota, Oklahoma, South Carolina, South Dakota, Texas, Tennessee, and West Virginia—had the "most restrictive" abortion policies, a significant increase from the five states with the designation in 2022.
One major point of contention between states is the ability of people to travel in order to access abortion. As of June 2023, twenty-five million people who can become pregnant had less access to legal abortion in their state than they did before the ruling, resulting in significant numbers of people traveling across state borders for the procedure. In response, so-called shield laws , which protect abortion patents and providers from prosecution in states where abortion is illegal, have been passed in fourteen states since Dobbs , bringing the total to fifteen states. In September 2023, lawmakers in Texas began passing measures restricting access to roadways for people on their way to an abortion appointment. In response to a federal rule allowing military personnel stationed in states where access to abortion is restricted to travel to states where abortion is legal, Senator Tommy Tuberville (R–AL) blocked the Senate from voting on military promotions, leaving several crucial high-level posts vacant for months. As of October 2023, despite pressure to relent from both sides of the aisle, Tuberville's blockade continued.
With the FDA allowing delivery of pills for medication abortion through the mail, pro-choice lawmakers and reproductive rights activists hoped that expanding access to medication abortion through telemedicine would mitigate some of the travel burden. However, in states where abortion is restricted, anti-abortion lawmakers began to explore ways of preventing the use of medication abortion. Despite a lack of medical or scientific evidence, several states passed legislation requiring doctors to inform patients that medical abortions can be interrupted or "reversed" by replacing the second pill with a dose of progesterone. Conservative states and legal groups have also pursued overturning the FDA's approval of mifepristone, one of the two drugs used in medication abortions. In April 2023 the Supreme Court ruled that mifepristone could continue to be prescribed while lawsuits continued.
In the year following Dobbs , the US maternal death rate, already the highest among industrialized countries, rose in states where abortion access was illegal or highly restricted. According to a January 2023 report by the Gender Equity Policy Institute, pregnant people in states where abortion is banned were up to three times more likely to die during pregnancy or labor or soon after than pregnant people in less restrictive states. Of these deaths, one in seven occurred in Texas. Babies were 30 percent likelier to die during their first month of life in states with abortion bans, and teen birth rates were twice as high in abortion restriction states.
The number of abortions performed in the United States increased after the Dobbs decision, according to the Guttmacher Institute, which found about 511,000 abortions performed between January and June 2023, compared to 465,000 in the same period of 2020. Less restrictive states bordering more restrictive states experienced most of the increase, with Illinois providers reporting a 69 percent increase and New Mexico reporting a 220 percent increase. States with total bans or six-week bans had an estimated 114,590 fewer abortions performed within their borders, according to the research group WeCount. Experts have raised concerns that the country's remaining abortion clinics are experiencing unsustainable demand for the procedure.
More Articles
Parental involvement laws can impose harmful burdens on pregnant minors.
"They talked about making sure they did really well in school from now on, so that their abortions weren't in vain."
Francie Diep is a staff writer at Pacific Standard . In the following viewpoint, Diep argues that parental involvement laws for minors seeking abortions can be detrimental to young women's physical and mental health. Discussing a study of minors who sought a judge's approval, a process commonly referred to as judicial bypass, in lieu of obtaining parental consent, the author reveals wide variation among experiences with the process. Diep notes that judicial bypass frequently delays a minor's abortion by several weeks. Citing the experiences of study participants, the author characterizes securing judicial bypass as a humiliating experience and provides several examples of a judge or a minor's guardian ad litem demonstrating anti-abortion bias. Despite these negative experiences, the author maintains, many of the minors subjected to parental involvement laws support such restrictions on minors seeking abortions.
Parental Consent Laws Protect Teens
“According to a national study conducted by researchers associated with Guttmacher, disappointment is the most common response of parents who learn that their teen daughter is pregnant, and almost no parent responds with violence.”
Teresa S. Collett is a professor of law at the University of St. Thomas School of Law in Minneapolis.
In the following viewpoint, Collett contends that parental consent laws are constitutional and in the best interest of girls seeking abortion. Citing the likelihood that adult men are most often the fathers of school-age pregnancies, parental involvement ensures that cases of coercion and statutory rape do not go unreported. Additionally, parents are in the best position to provide health information and care for their daughters during a time of acute vulnerability and need.
Late-Term Abortions Are Cruel, Common, and Unjustified
"In one recording taken on May 2, an unidentified woman is able to schedule an abortion at 30 weeks of pregnancy, even after she says there's nothing wrong with the fetus."
Bradford Richardson is a reporter at the Washington Times .
In the following viewpoint, Richardson argues that abortion providers in New Mexico, Louisiana, and Texas frequently terminate pregnancies during the third trimester (twenty-eight to forty weeks) and employ methods that cause the fetus undue harm. Defending comments made by Donald Trump during the 2016 presidential debates, the author disputes assertions made by reproductive rights groups and media outlets that late-term abortions are performed only in special circumstances and that the procedure referred to as partial-birth abortion is not considered legitimate among US medical experts. The author commends the efforts of anti-abortion activists and organizations like the Center for Medical Progress, which made covert recordings of abortion providers, for drawing attention to medical practices employed at reproductive health clinics.
Overregulation Forces Women To Have Late-Term Abortions
"Animal advocates, as well as many scientists, are increasingly questioning the scientific validity and reliability of animal experimentation."
“[A]dding hurdles that force women to obtain an abortion later in pregnancy—or to seek out options on their own, such as online medications of unknown quality—is bad for women’s health.”
Daniel Grossman is a professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of Advancing New Standards in Reproductive Health (ANSIRH) at the Bixby Center for Global Reproductive Health.
In the following viewpoint, Grossman argues that restrictions on abortion access contribute to women delaying abortions. He explains how abortions that take place earlier in a pregnancy tend to be safer for the woman’s health than abortions performed later. He argues that women already encounter significant obstacles to obtaining the procedure without additional regulations. He contends that several restrictions prevent patients from choosing medical abortions, which are significantly less invasive than surgical abortions and could be administered by more health care providers than specific state laws allow.
Looking for information on other topics?
Access Through Your Library >>
There’s a Better Way to Debate Abortion
Caution and epistemic humility can guide our approach.
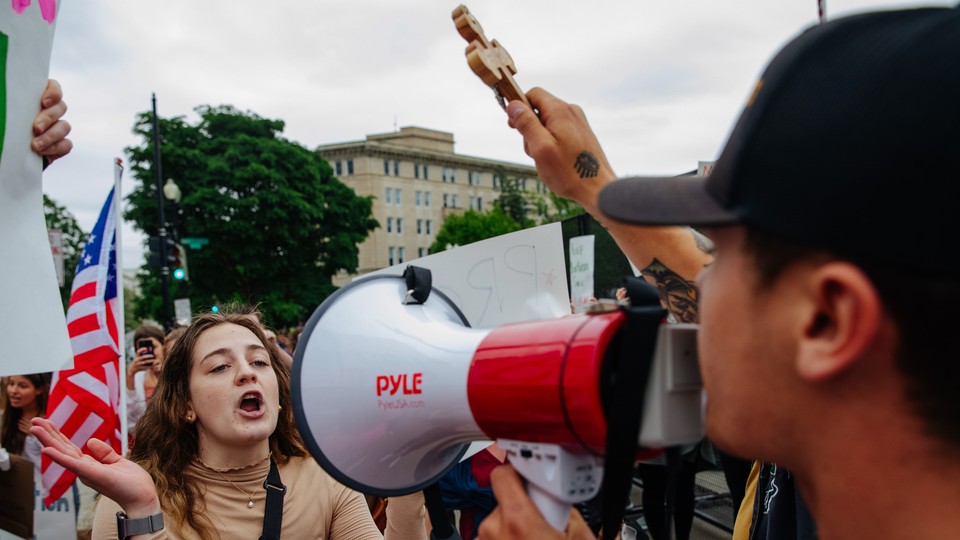

If Justice Samuel Alito’s draft majority opinion in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization becomes law, we will enter a post– Roe v. Wade world in which the laws governing abortion will be legislatively decided in 50 states.
In the short term, at least, the abortion debate will become even more inflamed than it has been. Overturning Roe , after all, would be a profound change not just in the law but in many people’s lives, shattering the assumption of millions of Americans that they have a constitutional right to an abortion.
This doesn’t mean Roe was correct. For the reasons Alito lays out, I believe that Roe was a terribly misguided decision, and that a wiser course would have been for the issue of abortion to have been given a democratic outlet, allowing even the losers “the satisfaction of a fair hearing and an honest fight,” in the words of the late Justice Antonin Scalia. Instead, for nearly half a century, Roe has been the law of the land. But even those who would welcome its undoing should acknowledge that its reversal could convulse the nation.
From the December 2019 issue: The dishonesty of the abortion debate
If we are going to debate abortion in every state, given how fractured and angry America is today, we need caution and epistemic humility to guide our approach.
We can start by acknowledging the inescapable ambiguities in this staggeringly complicated moral question. No matter one’s position on abortion, each of us should recognize that those who hold views different from our own have some valid points, and that the positions we embrace raise complicated issues. That realization alone should lead us to engage in this debate with a little more tolerance and a bit less certitude.
Many of those on the pro-life side exhibit a gap between the rhetoric they employ and the conclusions they actually seem to draw. In the 1990s, I had an exchange, via fax, with a pro-life thinker. During our dialogue, I pressed him on what he believed, morally speaking , should be the legal penalty for a woman who has an abortion and a doctor who performs one.
My point was a simple one: If he believed, as he claimed, that an abortion even moments after conception is the killing of an innocent child—that the fetus, from the instant of conception, is a human being deserving of all the moral and political rights granted to your neighbor next door—then the act ought to be treated, if not as murder, at least as manslaughter. Surely, given what my interlocutor considered to be the gravity of the offense, fining the doctor and taking no action against the mother would be morally incongruent. He was understandably uncomfortable with this line of questioning, unwilling to go to the places his premises led. When it comes to abortion, few people are.
Humane pro-life advocates respond that while an abortion is the taking of a human life, the woman having the abortion has been misled by our degraded culture into denying the humanity of the child. She is a victim of misinformation; she can’t be held accountable for what she doesn’t know. I’m not unsympathetic to this argument, but I think it ultimately falls short. In other contexts, insisting that people who committed atrocities because they truly believed the people against whom they were committing atrocities were less than human should be let off the hook doesn’t carry the day. I’m struggling to understand why it would in this context.
There are other complicating matters. For example, about half of all fertilized eggs are aborted spontaneously —that is, result in miscarriage—usually before the woman knows she is pregnant. Focus on the Family, an influential Christian ministry, is emphatic : “Human life begins at fertilization.” Does this mean that when a fertilized egg is spontaneously aborted, it is comparable—biologically, morally, ethically, or in any other way—to when a 2-year-old child dies? If not, why not? There’s also the matter of those who are pro-life and contend that abortion is the killing of an innocent human being but allow for exceptions in the case of rape or incest. That is an understandable impulse but I don’t think it’s a logically sustainable one.
The pro-choice side, for its part, seldom focuses on late-term abortions. Let’s grant that late-term abortions are very rare. But the question remains: Is there any point during gestation when pro-choice advocates would say “slow down” or “stop”—and if so, on what grounds? Or do they believe, in principle, that aborting a child up to the point of delivery is a defensible and justifiable act; that an abortion procedure is, ethically speaking, the same as removing an appendix? If not, are those who are pro-choice willing to say, as do most Americans, that the procedure gets more ethically problematic the further along in a pregnancy?
Read: When a right becomes a privilege
Plenty of people who consider themselves pro-choice have over the years put on their refrigerator door sonograms of the baby they are expecting. That tells us something. So does biology. The human embryo is a human organism, with the genetic makeup of a human being. “The argument, in which thoughtful people differ, is about the moral significance and hence the proper legal status of life in its early stages,” as the columnist George Will put it.
These are not “gotcha questions”; they are ones I have struggled with for as long as I’ve thought through where I stand on abortion, and I’ve tried to remain open to corrections in my thinking. I’m not comfortable with those who are unwilling to grant any concessions to the other side or acknowledge difficulties inherent in their own position. But I’m not comfortable with my own position, either—thinking about abortion taking place on a continuum, and troubled by abortions, particularly later in pregnancy, as the child develops.
The question I can’t answer is where the moral inflection point is, when the fetus starts to have claims of its own, including the right to life. Does it depend on fetal development? If so, what aspect of fetal development? Brain waves? Feeling pain? Dreaming? The development of the spine? Viability outside the womb? Something else? Any line I might draw seems to me entirely arbitrary and capricious.
Because of that, I consider myself pro-life, but with caveats. My inability to identify a clear demarcation point—when a fetus becomes a person—argues for erring on the side of protecting the unborn. But it’s a prudential judgment, hardly a certain one.
At the same time, even if one believes that the moral needle ought to lean in the direction of protecting the unborn from abortion, that doesn’t mean one should be indifferent to the enormous burden on the woman who is carrying the child and seeks an abortion, including women who discover that their unborn child has severe birth defects. Nor does it mean that all of us who are disturbed by abortion believe it is the equivalent of killing a child after birth. In this respect, my view is similar to that of some Jewish authorities , who hold that until delivery, a fetus is considered a part of the mother’s body, although it does possess certain characteristics of a person and has value. But an early-term abortion is not equivalent to killing a young child. (Many of those who hold this position base their views in part on Exodus 21, in which a miscarriage that results from men fighting and pushing a pregnant woman is punished by a fine, but the person responsible for the miscarriage is not tried for murder.)
“There is not the slightest recognition on either side that abortion might be at the limits of our empirical and moral knowledge,” the columnist Charles Krauthammer wrote in 1985. “The problem starts with an awesome mystery: the transformation of two soulless cells into a living human being. That leads to an insoluble empirical question: How and exactly when does that occur? On that, in turn, hangs the moral issue: What are the claims of the entity undergoing that transformation?”
That strikes me as right; with abortion, we’re dealing with an awesome mystery and insoluble empirical questions. Which means that rather than hurling invective at one another and caricaturing those with whom we disagree, we should try to understand their views, acknowledge our limitations, and even show a touch of grace and empathy. In this nation, riven and pulsating with hate, that’s not the direction the debate is most likely to take. But that doesn’t excuse us from trying.
- Our Writers
- How to Order
- Assignment Writing Service
- Report Writing Service
- Buy Coursework
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service
- All Essay Services
- Buy Research Paper
- Buy Term Paper
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Case study
- Buy Presentation
- Buy Personal statement
Persuasive Essay Guide
Persuasive Essay About Abortion
Crafting a Convincing Persuasive Essay About Abortion
-9248.jpg&w=640&q=75)
People also read
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing an Effective Persuasive Essay
200+ Persuasive Essay Topics to Help You Out
Learn How to Create a Persuasive Essay Outline
30+ Persuasive Essay Examples To Get You Started
Read Excellent Examples of Persuasive Essay About Gun Control
How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid19 | Examples & Tips
Learn to Write Persuasive Essay About Business With Examples and Tips
Check Out 12 Persuasive Essay About Online Education Examples
Persuasive Essay About Smoking - Making a Powerful Argument with Examples
Are you about to write a persuasive essay on abortion but wondering how to begin?
Writing an effective persuasive essay on the topic of abortion can be a difficult task for many students.
It is important to understand both sides of the issue and form an argument based on facts and logical reasoning. This requires research and understanding, which takes time and effort.
In this blog, we will provide you with some easy steps to craft a persuasive essay about abortion that is compelling and convincing. Moreover, we have included some example essays and interesting facts to read and get inspired by.
So let's start!
- 1. How To Write a Persuasive Essay About Abortion?
- 2. Persuasive Essay About Abortion Examples
- 3. Examples of Argumentative Essay About Abortion
- 4. Abortion Persuasive Essay Topics
- 5. Facts About Abortion You Need to Know
How To Write a Persuasive Essay About Abortion?
Abortion is a controversial topic, with people having differing points of view and opinions on the matter. There are those who oppose abortion, while some people endorse pro-choice arguments.
It is also an emotionally charged subject, so you need to be extra careful when crafting your persuasive essay .
Before you start writing your persuasive essay, you need to understand the following steps.
Step 1: Choose Your Position
The first step to writing a persuasive essay on abortion is to decide your position. Do you support the practice or are you against it? You need to make sure that you have a clear opinion before you begin writing.
Once you have decided, research and find evidence that supports your position. This will help strengthen your argument.
Check out the video below to get more insights into this topic:
Step 2: Choose Your Audience
The next step is to decide who your audience will be. Will you write for pro-life or pro-choice individuals? Or both?
Knowing who you are writing for will guide your writing and help you include the most relevant facts and information.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Step 3: Define Your Argument
Now that you have chosen your position and audience, it is time to craft your argument.
Start by defining what you believe and why, making sure to use evidence to support your claims. You also need to consider the opposing arguments and come up with counter arguments. This helps make your essay more balanced and convincing.
Step 4: Format Your Essay
Once you have the argument ready, it is time to craft your persuasive essay. Follow a standard format for the essay, with an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
Make sure that each paragraph is organized and flows smoothly. Use clear and concise language, getting straight to the point.
Step 5: Proofread and Edit
The last step in writing your persuasive essay is to make sure that you proofread and edit it carefully. Look for spelling, grammar, punctuation, or factual errors and correct them. This will help make your essay more professional and convincing.
These are the steps you need to follow when writing a persuasive essay on abortion. It is a good idea to read some examples before you start so you can know how they should be written.
Continue reading to find helpful examples.
Persuasive Essay About Abortion Examples
To help you get started, here are some example persuasive essays on abortion that may be useful for your own paper.
Short Persuasive Essay About Abortion
Persuasive Essay About No To Abortion
What Is Abortion? - Essay Example
Persuasive Speech on Abortion
Legal Abortion Persuasive Essay
Persuasive Essay About Abortion in the Philippines
Persuasive Essay about legalizing abortion
You can also read m ore persuasive essay examples to imp rove your persuasive skills.
Examples of Argumentative Essay About Abortion
An argumentative essay is a type of essay that presents both sides of an argument. These essays rely heavily on logic and evidence.
Here are some examples of argumentative essay with introduction, body and conclusion that you can use as a reference in writing your own argumentative essay.
Abortion Persuasive Essay Introduction
Argumentative Essay About Abortion Conclusion
Argumentative Essay About Abortion Pdf
Argumentative Essay About Abortion in the Philippines
Argumentative Essay About Abortion - Introduction
Abortion Persuasive Essay Topics
If you are looking for some topics to write your persuasive essay on abortion, here are some examples:
- Should abortion be legal in the United States?
- Is it ethical to perform abortions, considering its pros and cons?
- What should be done to reduce the number of unwanted pregnancies that lead to abortions?
- Is there a connection between abortion and psychological trauma?
- What are the ethical implications of abortion on demand?
- How has the debate over abortion changed over time?
- Should there be legal restrictions on late-term abortions?
- Does gender play a role in how people view abortion rights?
- Is it possible to reduce poverty and unwanted pregnancies through better sex education?
- How is the anti-abortion point of view affected by religious beliefs and values?
These are just some of the potential topics that you can use for your persuasive essay on abortion. Think carefully about the topic you want to write about and make sure it is something that interests you.
Check out m ore persuasive essay topics that will help you explore other things that you can write about!
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Facts About Abortion You Need to Know
Here are some facts about abortion that will help you formulate better arguments.
- According to the Guttmacher Institute , 1 in 4 pregnancies end in abortion.
- The majority of abortions are performed in the first trimester.
- Abortion is one of the safest medical procedures, with less than a 0.5% risk of major complications.
- In the United States, 14 states have laws that restrict or ban most forms of abortion after 20 weeks gestation.
- Seven out of 198 nations allow elective abortions after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- In places where abortion is illegal, more women die during childbirth and due to complications resulting from pregnancy.
- A majority of pregnant women who opt for abortions do so for financial and social reasons.
- According to estimates, 56 million abortions occur annually.
In conclusion, these are some of the examples, steps, and topics that you can use to write a persuasive essay. Make sure to do your research thoroughly and back up your arguments with evidence. This will make your essay more professional and convincing.
Need the services of a persuasive essay writing service ? We've got your back!
MyPerfectWords.com that provides help to students in the form of professionally written essays. Our persuasive essay writer can craft quality persuasive essays on any topic, including abortion.
So, just ask our experts ' do my essay ' and get professional help.

Frequently Asked Questions
What should i talk about in an essay about abortion.
When writing an essay about abortion, it is important to cover all the aspects of the subject. This includes discussing both sides of the argument, providing facts and evidence to support your claims, and exploring potential solutions.
What is a good argument for abortion?
A good argument for abortion could be that it is a woman’s choice to choose whether or not to have an abortion. It is also important to consider the potential risks of carrying a pregnancy to term.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Rom J Morphol Embryol
- v.61(1); Jan-Mar 2020

A research on abortion: ethics, legislation and socio-medical outcomes. Case study: Romania
Andreea mihaela niţă.
1 Faculty of Social Sciences, University of Craiova, Romania
Cristina Ilie Goga
This article presents a research study on abortion from a theoretical and empirical point of view. The theoretical part is based on the method of social documents analysis, and presents a complex perspective on abortion, highlighting items of medical, ethical, moral, religious, social, economic and legal elements. The empirical part presents the results of a sociological survey, based on the opinion survey method through the application of the enquiry technique, conducted in Romania, on a sample of 1260 women. The purpose of the survey is to identify Romanians perception on the decision to voluntary interrupt pregnancy, and to determine the core reasons in carrying out an abortion.
The analysis of abortion by means of medical and social documents
Abortion means a pregnancy interruption “before the fetus is viable” [ 1 ] or “before the fetus is able to live independently in the extrauterine environment, usually before the 20 th week of pregnancy” [ 2 ]. “Clinical miscarriage is both a common and distressing complication of early pregnancy with many etiological factors like genetic factors, immune factors, infection factors but also psychological factors” [ 3 ]. Induced abortion is a practice found in all countries, but the decision to interrupt the pregnancy involves a multitude of aspects of medical, ethical, moral, religious, social, economic, and legal order.
In a more simplistic manner, Winston Nagan has classified opinions which have as central element “abortion”, in two major categories: the opinion that the priority element is represented by fetus and his entitlement to life and the second opinion, which focuses around women’s rights [ 4 ].
From the medical point of view, since ancient times there have been four moments, generally accepted, which determine the embryo’s life: ( i ) conception; ( ii ) period of formation; ( iii ) detection moment of fetal movement; ( iv ) time of birth [ 5 ]. Contemporary medicine found the following moments in the evolution of intrauterine fetal: “ 1 . At 18 days of pregnancy, the fetal heartbeat can be perceived and it starts running the circulatory system; 2 . At 5 weeks, they become more clear: the nose, cheeks and fingers of the fetus; 3 . At 6 weeks, they start to function: the nervous system, stomach, kidneys and liver of the fetus, and its skeleton is clearly distinguished; 4 . At 7 weeks (50 days), brain waves are felt. The fetus has all the internal and external organs definitively outlined. 5 . At 10 weeks (70 days), the unborn child has all the features clearly defined as a child after birth (9 months); 6 . At 12 weeks (92 days, 3 months), the fetus has all organs definitely shaped, managing to move, lacking only the breath” [ 6 ]. Even if most of the laws that allow abortion consider the period up to 12 weeks acceptable for such an intervention, according to the above-mentioned steps, there can be defined different moments, which can represent the beginning of life. Nowadays, “abortion is one of the most common gynecological experiences and perhaps the majority of women will undergo an abortion in their lifetimes” [ 7 ]. “Safe abortions carry few health risks, but « every year, close to 20 million women risk their lives and health by undergoing unsafe abortions » and 25% will face a complication with permanent consequences” [ 8 , 9 ].
From the ethical point of view, most of the times, the interruption of pregnancy is on the border between woman’s right over her own body and the child’s (fetus) entitlement to life. Judith Jarvis Thomson supported the supremacy of woman’s right over her own body as a premise of freedom, arguing that we cannot force a person to bear in her womb and give birth to an unwanted child, if for different circumstances, she does not want to do this [ 10 ]. To support his position, the author uses an imaginary experiment, that of a violinist to which we are connected for nine months, in order to save his life. However, Thomson debates the problem of the differentiation between the fetus and the human being, by carrying out a debate on the timing which makes this difference (period of conception, 10 weeks of pregnancy, etc.) and highlighting that for people who support abortion, the fetus is not an alive human being [ 10 ].
Carol Gilligan noted that women undergo a true “moral dilemma”, a “moral conflict” with regards to voluntary interruption of pregnancy, such a decision often takes into account the human relationships, the possibility of not hurting the others, the responsibility towards others [ 11 ]. Gilligan applied qualitative interviews to a number of 29 women from different social classes, which were put in a position to decide whether or not to commit abortion. The interview focused on the woman’s choice, on alternative options, on individuals and existing conflicts. The conclusion was that the central moral issue was the conflict between the self (the pregnant woman) and others who may be hurt as a result of the potential pregnancy [ 12 ].
From the religious point of view, abortion is unacceptable for all religions and a small number of abortions can be seen in deeply religious societies and families. Christianity considers the beginning of human life from conception, and abortion is considered to be a form of homicide [ 13 ]. For Christians, “at the same time, abortion is giving up their faith”, riot and murder, which means that by an abortion we attack Jesus Christ himself and God [ 14 ]. Islam does not approve abortion, relying on the sacral life belief as specified in Chapter 6, Verse 151 of the Koran: “Do not kill a soul which Allah has made sacred (inviolable)” [ 15 ]. Buddhism considers abortion as a negative act, but nevertheless supports for medical reasons [ 16 ]. Judaism disapproves abortion, Tanah considering it to be a mortal sin. Hinduism considers abortion as a crime and also the greatest sin [ 17 ].
From the socio-economic point of view, the decision to carry out an abortion is many times determined by the relations within the social, family or financial frame. Moreover, studies have been conducted, which have linked the legalization of abortions and the decrease of the crime rate: “legalized abortion may lead to reduced crime either through reductions in cohort sizes or through lower per capita offending rates for affected cohorts” [ 18 ].
Legal regulation on abortion establishes conditions of the abortion in every state. In Europe and America, only in the XVIIth century abortion was incriminated and was considered an insignificant misdemeanor or a felony, depending on when was happening. Due to the large number of illegal abortions and deaths, two centuries later, many states have changed legislation within the meaning of legalizing voluntary interruption of pregnancy [ 6 ]. In contemporary society, international organizations like the United Nations or the European Union consider sexual and reproductive rights as fundamental rights [ 19 , 20 ], and promotes the acceptance of abortion as part of those rights. However, not all states have developed permissive legislation in the field of voluntary interruption of pregnancy.
Currently, at national level were established four categories of legislation on pregnancy interruption area:
( i ) Prohibitive legislations , ones that do not allow abortion, most often outlining exceptions in abortion in cases where the pregnant woman’s life is endangered. In some countries, there is a prohibition of abortion in all circumstances, however, resorting to an abortion in the case of an imminent threat to the mother’s life. Same regulation is also found in some countries where abortion is allowed in cases like rape, incest, fetal problems, etc. In this category are 66 states, with 25.5% of world population [ 21 ].
( ii ) Restrictive legislation that allow abortion in cases of health preservation . Loosely, the term “health” should be interpreted according to the World Health Organization (WHO) definition as: “health is a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity” [ 22 ]. This type of legislation is adopted in 59 states populated by 13.8% of the world population [ 21 ].
( iii ) Legislation allowing abortion on a socio-economic motivation . This category includes items such as the woman’s age or ability to care for a child, fetal problems, cases of rape or incest, etc. In this category are 13 countries, where we have 21.3% of the world population [ 21 ].
( iv ) Legislation which do not impose restrictions on abortion . In the case of this legislation, abortion is permitted for any reason up to 12 weeks of pregnancy, with some exceptions (Romania – 14 weeks, Slovenia – 10 weeks, Sweden – 18 weeks), the interruption of pregnancy after this period has some restrictions. This type of legislation is adopted in 61 countries with 39.5% of the world population [21].
The Centre for Reproductive Rights has carried out from 1998 a map of the world’s states, based on the legislation typology of each country (Figure (Figure1 1 ).

The analysis of states according to the legislation regarding abortion. Source: Centre for Reproductive Rights. The World’s Abortion Laws, 2018 [ 23 ]
An unplanned pregnancy, socio-economic context or various medical problems [ 24 ], lead many times to the decision of interrupting pregnancy, regardless the legislative restrictions. In the study “Unsafe abortion: global and regional estimates of the incidence of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2008” issued in 2011 by the WHO , it was determined that within the states with restrictive legislation on abortion, we may also encounter a large number of illegal abortions. The illegal abortions may also be resulting in an increased risk of woman’s health and life considering that most of the times inappropriate techniques are being used, the hygienic conditions are precarious and the medical treatments are incorrectly administered [ 25 ]. Although abortions done according to medical guidelines carry very low risk of complications, 1–3 unsafe abortions contribute substantially to maternal morbidity and death worldwide [ 26 ].
WHO has estimated for the year 2008, the fact that worldwide women between the ages of 15 and 44 years carried out 21.6 million “unsafe” abortions, which involved a high degree of risk and were distributed as follows: 0.4 million in the developed regions and a number of 21.2 million in the states in course of development [ 25 ].
Case study: Romania
Legal perspective on abortion
In Romania, abortion was brought under regulation by the first Criminal Code of the United Principalities, from 1864.
The Criminal Code from 1864, provided the abortion infringement in Article 246, on which was regulated as follows: “Any person, who, using means such as food, drinks, pills or any other means, which will consciously help a pregnant woman to commit abortion, will be punished to a minimum reclusion (three years).
The woman who by herself shall use the means of abortion, or would accept to use means of abortion which were shown or given to her for this purpose, will be punished with imprisonment from six months to two years, if the result would be an abortion. In a situation where abortion was carried out on an illegitimate baby by his mother, the punishment will be imprisonment from six months to one year.
Doctors, surgeons, health officers, pharmacists (apothecary) and midwives who will indicate, will give or will facilitate these means, shall be punished with reclusion of at least four years, if the abortion took place. If abortion will cause the death of the mother, the punishment will be much austere of four years” (Art. 246) [ 27 ].
The Criminal Code from 1864, reissued in 1912, amended in part the Article 246 for the purposes of eliminating the abortion of an illegitimate baby case. Furthermore, it was no longer specified the minimum of four years of reclusion, in case of abortion carried out with the help of the medical staff, leaving the punishment to the discretion of the Court (Art. 246) [ 28 ].
The Criminal Code from 1936 regulated abortion in the Articles 482–485. Abortion was defined as an interruption of the normal course of pregnancy, being punished as follows:
“ 1 . When the crime is committed without the consent of the pregnant woman, the punishment was reformatory imprisonment from 2 to 5 years. If it caused the pregnant woman any health injury or a serious infirmity, the punishment was reformatory imprisonment from 3 to 6 years, and if it has caused her death, reformatory imprisonment from 7 to 10 years;
2 . When the crime was committed by the unmarried pregnant woman by herself, or when she agreed that someone else should provoke the abortion, the punishment is reformatory imprisonment from 3 to 6 months, and if the woman is married, the punishment is reformatory imprisonment from 6 months to one year. Same penalty applies also to the person who commits the crime with the woman’s consent. If abortion was committed for the purpose of obtaining a benefit, the punishment increases with another 2 years of reformatory imprisonment.
If it caused the pregnant woman any health injuries or a severe disablement, the punishment will be reformatory imprisonment from one to 3 years, and if it has caused her death, the punishment is reformatory imprisonment from 3 to 5 years” (Art. 482) [ 29 ].
The criminal legislation from 1936 specifies that it is not considered as an abortion the interruption from the normal course of pregnancy, if it was carried out by a doctor “when woman’s life was in imminent danger or when the pregnancy aggravates a woman’s disease, putting her life in danger, which could not be removed by other means and it is obvious that the intervention wasn’t performed with another purpose than that of saving the woman’s life” and “when one of the parents has reached a permanent alienation and it is certain that the child will bear serious mental flaws” (Art. 484, Par. 1 and Par. 2) [ 29 ].
In the event of an imminent danger, the doctor was obliged to notify prosecutor’s office in writing, within 48 hours after the intervention, on the performance of the abortion. “In the other cases, the doctor was able to intervene only with the authorization of the prosecutor’s office, given on the basis of a medical certificate from hospital or a notice given as a result of a consultation between the doctor who will intervene and at least a professor doctor in the disease which caused the intervention. General’s Office Prosecutor, in all cases provided by this Article, shall be obliged to maintain the confidentiality of all communications or authorizations, up to the intercession of any possible complaints” (Art. 484) [ 29 ].
The legislation of 1936 provided a reformatory injunction from one to three years for the abortions committed by doctors, sanitary agents, pharmacists, apothecary or midwives (Art. 485) [ 29 ].
Abortion on demand has been legalized for the first time in Romania in the year 1957 by the Decree No. 463, under the condition that it had to be carried out in a hospital and to be carried out in the first quarter of the pregnancy [ 30 ]. In the year 1966, demographic policy of Romania has dramatically changed by introducing the Decree No. 770 from September 29 th , which prohibited abortion. Thus, the voluntary interruption of pregnancy became a crime, with certain exceptions, namely: endangering the mother’s life, physical or mental serious disability; serious or heritable illness, mother’s age over 45 years, if the pregnancy was a result of rape or incest or if the woman gave birth to at least four children who were still in her care (Art. 2) [ 31 ].
In the Criminal Code from 1968, the abortion crime was governed by Articles 185–188.
The Article 185, “the illegal induced abortion”, stipulated that “the interruption of pregnancy by any means, outside the conditions permitted by law, with the consent of the pregnant woman will be punished with imprisonment from one to 3 years”. The act referred to above, without the prior consent from the pregnant woman, was punished with prison from two to five years. If the abortion carried out with the consent of the pregnant woman caused any serious body injury, the punishment was imprisonment from two to five years, and when it caused the death of the woman, the prison sentence was from five to 10 years. When abortion was carried out without the prior consent of the woman, if it caused her a serious physical injury, the punishment was imprisonment from three to six years, and if it caused the woman’s death, the punishment was imprisonment from seven to 12 years (Art. 185) [ 32 ].
“When abortion was carried out in order to obtain a material benefit, the maximum punishment was increased by two years, and if the abortion was made by a doctor, in addition to the prison punishment could also be applied the prohibition to no longer practice the profession of doctor”.
Article 186, “abortion caused by the woman”, stipulated that “the interruption of the pregnancy course, committed by the pregnant woman, was punished with imprisonment from 6 months to 2 years”, quoting the fact that by the same punishment was also sanctioned “the pregnant woman’s act to consent in interrupting the pregnancy course made out by another person” (Art. 186) [ 26 ].
The Regulations of the Criminal Code in 1968, also provided the crime of “ownership of tools or materials that can cause abortion”, the conditions of this holding being met when these types of instruments were held outside the hospital’s specialized institutions, the infringement shall be punished with imprisonment from three months to one year (Art. 187) [ 32 ].
Furthermore, the doctors who performed an abortion in the event of extreme urgency, without prior legal authorization and if they did not announce the competent authority within the legal deadline, they were punished by imprisonment from one month to three months (Art. 188) [ 32 ].
In the year 1985, it has been issued the Decree No. 411 of December 26 th , by which the conditions imposed by the Decree No. 770 of 1966 have been hardened, meaning that it has increased the number of children, that a woman could have in order to request an abortion, from four to five children [ 33 ].
The Articles 185–188 of the Criminal Code and the Decree No. 770/1966 on the interruption of the pregnancy course have been abrogated by Decree-Law No. 1 from December 26 th , 1989, which was published in the Official Gazette No. 4 of December 27 th , 1989 (Par. 8 and Par. 12) [ 34 ].
The Criminal Code from 1968, reissued in 1997, maintained Article 185 about “the illegal induced abortion”, but drastically modified. Thus, in this case of the Criminal Code, we identify abortion as “the interruption of pregnancy course, by any means, committed in any of the following circumstances: ( a ) outside medical institutions or authorized medical practices for this purpose; ( b ) by a person who does not have the capacity of specialized doctor; ( c ) if age pregnancy has exceeded 14 weeks”, the punishment laid down was the imprisonment from 6 months to 3 years” (Art. 185, Par. 1) [ 35 ]. For the abortion committed without the prior consent of the pregnant woman, the punishment consisted in strict prison conditions from two to seven years and with the prohibition of certain rights (Art. 185, Par. 2) [ 35 ].
For the situation of causing serious physical injury to the pregnant woman, the punishment was strict prison from three to 10 years and the removal of certain rights, and if it had as a result the death of the pregnant woman, the punishment was strict prison from five to 15 years and the prohibition of certain rights (Art. 185, Par. 3) [ 35 ].
The attempt was punished for the crimes specified in the various cases of abortion.
Consideration should also be given in the Criminal Code reissued in 1997 for not punishing the interruption of the pregnancy course carried out by the doctor, if this interruption “was necessary to save the life, health or the physical integrity of the pregnant woman from a grave and imminent danger and that it could not be removed otherwise; in the case of a over fourteen weeks pregnancy, when the interruption of the pregnancy course should take place from therapeutic reasons” and even in a situation of a woman’s lack of consent, when it has not been given the opportunity to express her will, and abortion “was imposed by therapeutic reasons” (Art. 185, Par. 4) [ 35 ].
Criminal Code from 2004 covers abortion in Article 190, defined in the same way as in the prior Criminal Code, with the difference that it affects the limits of the punishment. So, in the event of pregnancy interruption, in accordance with the conditions specified in Paragraph 1, “the penalty provided was prison time from 6 months to one year or days-fine” (Art. 190, Par. 1) [ 36 ].
Nowadays, in Romania, abortion is governed by the criminal law of 2009, which entered into force in 2014, by the section called “aggression against an unborn child”. It should be specified that current criminal law does not punish the woman responsible for carrying out abortion, but only the person who is involved in carrying out the abortion. There is no punishment for the pregnant woman who injures her fetus during pregnancy.
In Article 201, we can find the details on the pregnancy interruption infringement. Thus, the pregnancy interruption can be performed in one of the following circumstances: “outside of medical institutions or medical practices authorized for this purpose; by a person who does not have the capacity of specialist doctor in Obstetrics and Gynecology and the right of free medical practice in this specialty; if gestational age has exceeded 14 weeks”, the punishment is the imprisonment for six months to three years, or fine and the prohibition to exercise certain rights (Art. 201, Par. 1) [ 37 ].
Article 201, Paragraph 2 specifies that “the interruption of the pregnancy committed under any circumstances, without the prior consent of the pregnant woman, can be punished with imprisonment from 2 to 7 years and with the prohibition to exercise some rights” (Art. 201, Par. 1) [ 37 ].
If by facts referred to above (Art. 201, Par. 1 and Par. 2) [ 37 ] “it has caused the pregnant woman’s physical injury, the punishment is the imprisonment from 3 to 10 years and the prohibition to exercise some rights, and if it has had as a result the pregnant woman’s death, the punishment is the imprisonment from 6 to 12 years and the prohibition to exercise some rights” (Art. 201, Par. 3) [ 37 ]. When the facts have been committed by a doctor, “in addition to the imprisonment punishment, it will also be applied the prohibition to exercise the profession of doctor (Art. 201, Par. 4) [ 37 ].
Criminal legislation specifies that “the interruption of pregnancy does not constitute an infringement with the purpose of a treatment carried out by a specialist doctor in Obstetrics and Gynecology, until the pregnancy age of twenty-four weeks is reached, or the subsequent pregnancy interruption, for the purpose of treatment, is in the interests of the mother or the fetus” (Art. 201, Par. 6) [ 37 ]. However, it can all be found in the phrases “therapeutic purposes” and “the interest of the mother and of the unborn child”, which predisposes the text of law to an interpretation, finally the doctors are the only ones in the position to decide what should be done in such cases, assuming direct responsibility [ 38 ].
Article 202 of the Criminal Code defines the crime of harming an unborn child, pointing out the punishments for the various types of injuries that can occur during pregnancy or in the childbirth period and which can be caused by the mother or by the persons who assist the birth, with the specification that the mother who harms her fetus during pregnancy is not punished and does not constitute an infringement if the injury has been committed during pregnancy or during childbirth period if the facts have been “committed by a doctor or by an authorized person to assist the birth or to follow the pregnancy, if they have been committed in the course of the medical act, complying with the specific provisions of his profession and have been made in the interest of the pregnant woman or fetus, as a result of the exercise of an inherent risk in the medical act” (Art. 202, Par. 6) [ 37 ].
The fact situation in Romania
During the period 1948–1955, called “the small baby boom” [ 39 ], Romania registered an average fertility rate of 3.23 children for a woman. Between 1955 and 1962, the fertility rate has been less than three children for a woman, and in 1962, fertility has reached an average of two children for a woman. This phenomenon occurred because of the Decree No. 463/1957 on liberalization of abortion. After the liberalization from 1957, the abortion rate has increased from 220 abortions per 100 born-alive children in the year 1960, to 400 abortions per 100 born-alive children, in the year 1965 [ 40 ].
The application of provisions of Decrees No. 770 of 1966 and No. 411 of 1985 has led to an increase of the birth rate in the first three years (an average of 3.7 children in 1967, and 3.6 children in 1968), followed by a regression until 1989, when it was recorded an average of 2.2 children, but also a maternal death rate caused by illegal abortions, raising up to 85 deaths of 100 000 births in the year of 1965, and 170 deaths in 1983. It was estimated that more than 80% of maternal deaths between 1980–1989 was caused by legal constraints [ 30 ].
After the Romanian Revolution in December 1989 and after the communism fall, with the abrogation of Articles 185–188 of the Criminal Code and of the Decree No. 770/1966, by the Decree of Law No. 1 of December 26 th , 1989, abortion has become legal in Romania and so, in the following years, it has reached the highest rate of abortion in Europe. Subsequently, the number of abortion has dropped gradually, with increasing use of birth control [ 41 ].
Statistical data issued by the Ministry of Health and by the National Institute of Statistics (INS) in Romania show corresponding figures to a legally carried out abortion. The abortion number is much higher, if it would take into account the number of illegal abortion, especially those carried out before 1989, and those carried out in private clinics, after the year 1990. Summing the declared abortions in the period 1958–2014, it is to be noted the number of them, 22 037 747 exceeds the current Romanian population. A detailed statistical research of abortion rate, in terms of years we have exposed in Table Table1 1 .
The number of abortions declared in Romania in the period 1958–2016
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1958 | 112 100 | 1970 | 292 410 | 1982 | 468 041 | 1994 | 530 191 | 2006 | 150 246 |
| 1959 | 578 000 | 1971 | 330 000 | 1983 | – | 1995 | 502 840 | 2007 | 137 226 |
| 1960 | 774 000 | 1972 | 381 000 | 1984 | 303 123 | 1996 | 456 221 | 2008 | 137 226 |
| 1961 | 865 000 | 1973 | 376 000 | 1985 | 302 838 | 1997 | 347 126 | 2009 | 115 457 |
| 1962 | 967 000 | 1974 | 335 000 | 1986 | 183 959 | 1998 | 271 496 | 2010 | 101 915 |
| 1963 | 1 037 000 | 1975 | 359 417 | 1987 | 182 442 | 1999 | 259 888 | 2011 | 101 915 |
| 1964 | 1 100 000 | 1976 | 383 000 | 1988 | 185 416 | 2000 | 257 865 | 2012 | 88 135 |
| 1965 | 1 115 000 | 1977 | 379 000 | 1989 | 193 084 | 2001 | 254 855 | 2013 | 86 432 |
| 1966 | 973 000 | 1978 | 394 000 | 1990 | 992 265 | 2002 | 247 608 | 2014 | 78 371 |
| 1967 | 206 000 | 1979 | 404 000 | 1991 | 866 934 | 2003 | 224 807 | 2015 | 70 447 |
| 1968 | 220 000 | 1980 | 413 093 | 1992 | 691 863 | 2004 | 191 038 | 2016 | 63 085 |
| 1969 | 258 000 | 1981 | – | 1993 | 585 761 | 2005 | 163 459 |
|
|
Source: Pro Vita Association (Bucharest, Romania), National Institute of Statistics (INS – Romania), EUROSTAT [ 42 , 43 , 44 ]
Data issued by the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF) in June 2016, for the period 1989–2014, in matters of reproductive behavior, indicates a fertility rate for Romania with a continuous decrease, in proportion to the decrease of the number of births, but also a lower number of abortion rate reported to 100 deliveries (Table (Table2 2 ).
Reproductive behavior in Romania in 1989–2014
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Total fertility rate (births per woman) | 2.2 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.36 | 1.40 | 1.44 |
| Live births (1000s) | 369.5 | 314.7 | 275.3 | 260.4 | 250.0 | 246.7 | 236.6 | 231.3 | 236.9 | 237.3 | 234.6 | 234.5 | 220.4 | 210.5 | 212.5 | 216.3 | 221.0 | 219.5 | 214.7 | 221.9 | 222.4 | 212.2 | 196.2 | 201.1 | 182.3 | 183.7 |
| Abortion rate (legally induced abortions per 100 live births) | – | 315.3 | 314.9 | 265.7 | 234.3 | 214.9 | 212.5 | 197.2 | 146.5 | 114.4 | 110.8 | 110.0 | 115.6 | 117.6 | 105.8 | 88.3 | 73.9 | 68.5 | 63.9 | 57.6 | 52.2 | 48.0 | 52.7 | 43.7 | 47.2 | 42.7 |
Source: United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF), Transformative Monitoring for Enhanced Equity (TransMonEE) Data. Country profiles: Romania, 1989–2015 [ 45 ].
By analyzing data issued for the period 1990–2015 by the International Organization of Health , UNICEF , United Nations Fund for Population Activity (UNFPA), The World Bank and the United Nations Population Division, it is noticed that maternal mortality rate has currently dropped as compared with 1990 (Table (Table3 3 ).
Maternal mortality estimation in Romania in 1990–2015
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2015 | 31 [22–44] | 56 | 179 | 1.1 |
| 2010 | 30 [26–35] | 61 | 202 | 1.2 |
| 2005 | 33 [28–38] | 71 | 217 | 1.1 |
| 2000 | 51 [44–58] | 110 | 222 | 1.5 |
| 1995 | 77 [66–88] | 180 | 241 | 2.1 |
| 1990 | 124 [108–141] | 390 | 318 | 5.2 |
Source: World Health Organization (WHO), Global Health Observatory Data. Maternal mortality country profiles: Romania, 2015 [ 46 ].
Opinion survey: women’s opinion on abortion
Argument for choosing the research theme
Although the problematic on abortion in Romania has been extensively investigated and debated, it has not been carried out in an ample sociological study, covering Romanian women’s perception on abortion. We have assumed making a study at national level, in order to identify the opinion on abortion, on the motivation to carry out an abortion, and to identify the correlation between religious convictions and the attitude toward abortion.
Examining the literature field of study
In the conceptual register of the research, we have highlighted items, such as the specialized literature, legislation, statistical documents.
Formulation of hypotheses and objectives
The first hypothesis was that Romanian women accept abortion, having an open attitude towards this act. Thus, the first objective of the research was to identify Romanian women’s attitude towards abortion.
The second hypothesis, from which we started, was that high religious beliefs generate a lower tolerance towards abortion. Thus, the second objective of our research has been to identify the correlation between the religious beliefs and the attitude towards abortion.
The third hypothesis of the survey was that, the main motivation in carrying out an abortion is the fact that a woman does not want a baby, and the main motivation for keeping the pregnancy is that the person wants a baby. In this context, the third objective of the research was to identify main motivation in carrying out an abortion and in maintaining a pregnancy.
Another hypothesis was that modern Romanian legislation on the abortion is considered fair. Based on this hypothesis, we have assumed the fourth objective, which is to identify the degree of satisfaction towards the current regulatory provisions governing the abortion.
Research methodology
The research method is that of a sociological survey by the application of the questionnaire technique. We used the sampling by age and residence looking at representative numbers of population from more developed as well as underdeveloped areas.
Determination of the sample to be studied
Because abortion is a typical women’s experience, we have chosen to make the quantitative research only among women. We have constructed the sample by selecting a number of 1260 women between the ages of 15 and 44 years (the most frequently encountered age among women who give birth to a child). We also used the quota sampling techniques, taking into account the following variables: age group and the residence (urban/rural), so that the persons included in the sample could retain characteristic of the general population.
By the sample of 1260 women, we have made a percentage of investigation of 0.03% of the total population.
The Questionnaires number applied was distributed as follows (Table (Table4 4 ).
The sampling rates based on the age, and the region of residence
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Women in North-West | Urban | 37 898 | 58 839 | 50 527 | 54 944 | 53 962 | 60 321 | 316 491 |
| Rural | 36 033 | 37 667 | 36 515 | 41 837 | 43 597 | 42 877 | 238 526 | |
| Sample in North-West | Urban | 11 | 18 | 15 | 17 | 16 | 18 | 95 |
| Rural | 11 | 11 | 11 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 72 | |
| Women in the Center | Urban | 32 661 | 46 697 | 46 713 | 54 031 | 52 590 | 59 084 | 291 776 |
| Rural | 29 052 | 31 767 | 29 562 | 34 402 | 35 334 | 35 502 | 195 619 | |
| Sample in the Center | Urban | 10 | 14 | 14 | 16 | 16 | 18 | 88 |
| Rural | 9 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 59 | |
| Women in North-East | Urban | 38 243 | 50 228 | 45 924 | 51 818 | 49 959 | 63 157 | 299 329 |
| Rural | 63 466 | 51 814 | 47 524 | 60 495 | 67 009 | 65 717 | 356 025 | |
| Sample in North-East | Urban | 11 | 15 | 14 | 16 | 15 | 19 | 90 |
| Rural | 19 | 16 | 14 | 18 | 20 | 20 | 107 | |
| Women in South-East | Urban | 31 556 | 40 879 | 43 317 | 53 461 | 53 756 | 67 135 | 290 104 |
| Rural | 34 494 | 32 446 | 29 987 | 37 828 | 41 068 | 42 836 | 218 659 | |
| Sample in South-East | Urban | 10 | 12 | 13 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 87 |
| Rural | 10 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 65 | |
| Women in South Muntenia | Urban | 30 480 | 38 066 | 40 049 | 47 820 | 49 272 | 64 739 | 270 426 |
| Rural | 52 771 | 55 286 | 49 106 | 60 496 | 67 660 | 74 401 | 359 720 | |
| Sample in South Muntenia | Urban | 9 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 15 | 19 | 80 |
| Rural | 16 | 17 | 15 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 108 | |
| Women in Bucharest–Ilfov | Urban | 41 314 | 83 927 | 90 607 | 102 972 | 86 833 | 98 630 | 504 283 |
| Rural | 5385 | 7448 | 7952 | 9997 | 9400 | 10 096 | 50 278 | |
| Sample in Bucharest–Ilfov | Urban | 12 | 25 | 27 | 31 | 26 | 30 | 151 |
| Rural | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 15 | |
| Women in South-West Oltenia | Urban | 26 342 | 31 155 | 33 493 | 39 064 | 39 615 | 50 516 | 220 185 |
| Rural | 31 223 | 29 355 | 26 191 | 32 946 | 36 832 | 40 351 | 196 898 | |
| Sample in South-West Oltenia | Urban | 8 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 12 | 15 | 66 |
| Rural | 9 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 59 | |
| Women in West | Urban | 30 258 | 45 687 | 39 583 | 44 808 | 44 834 | 54 155 | 259 325 |
| Rural | 19 205 | 20 761 | 19 351 | 22 788 | 24 333 | 26 792 | 133 230 | |
| Sample in West | Urban | 9 | 14 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | 78 |
| Rural | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 40 | |
| Total women | 540 381 | 662 022 | 636 401 | 749 707 | 756 054 | 856 309 | 4 200 874 | |
| Total sample | 162 | 198 | 191 | 225 | 227 | 257 | 1260 | |
Source: Sample built, based on the population data issued by the National Institute of Statistics (INS – Romania) based on population census conducted in 2011 [ 47 ].
Data collection
Data collection was carried out by questionnaires administered by 32 field operators between May 1 st –May 31 st , 2018.
The analysis of the research results
In the next section, we will present the main results of the quantitative research carried out at national level.
Almost three-quarters of women included in the sample agree with carrying out an abortion in certain circumstances (70%) and only 24% have chosen to support the answer “ No, never ”. In modern contemporary society, abortion is the first solution of women for which a pregnancy is not desired. Even if advanced medical techniques are a lot safer, an abortion still carries a health risk. However, 6% of respondents agree with carrying out abortion regardless of circumstances (Table (Table5 5 ).
Opinion on the possibility of carrying out an abortion
|
| |
|
|
|
| Yes, under certain circumstances | 70% |
| No, never | 24% |
| Yes, regardless the situation | 6% |
| Total | 100% |
Although abortions carried out after 14 weeks are illegal, except for medical reasons, more than half of the surveyed women stated they would agree with abortion in certain circumstances. At the opposite pole, 31% have mentioned they would never agree on abortions after 14 weeks. Five percent were totally accepting the idea of abortion made to a pregnancy that has exceeded 14 weeks (Table (Table6 6 ).
Opinion on the possibility of carrying out an abortion after the period of 14 weeks of pregnancy
|
| |
|
|
|
| Yes, under certain circumstances | 64% |
| No, never | 31% |
| Yes, regardless the situation | 5% |
| Total | 100% |
For 53% of respondents, abortion is considered a crime as well as the right of a women. On the other hand, 28% of the women considered abortion as a crime and 16% associate abortion with a woman’s right (Table (Table7 7 ).
Opinion on abortion: at the border between crime and a woman’s right
|
| |
|
|
|
| A crime and a woman’s right | 53% |
| A crime | 28% |
| A woman’s right | 16% |
| I don’t know | 2% |
| I don’t answer | 1% |
| Total | 100% |
Opinions on what women abort at the time of the voluntary pregnancy interruption are split in two: 59% consider that it depends on the time of the abortion, and more specifically on the pregnancy development stage, 24% consider that regardless of the period in which it is carried out, women abort a child, and 14% have opted a fetus (Table (Table8 8 ).
Abortion of a child vs. abortion of a fetus
|
| |
|
|
|
| Both, depending on the moment when the abortion takes place | 59% |
| A child | 24% |
| A fetus | 14% |
| I don’t answer | 3% |
| Total | 100% |
Among respondents who consider that women abort a child or a fetus related to the time of abortion, 37.5% have considered that the difference between a baby and a fetus appears after 14 weeks of pregnancy (the period legally accepted for abortion). Thirty-three percent of them have mentioned that the distinction should be performed at the first few heartbeats; 18.1% think it is about when the child has all the features definitively outlined and can move by himself; 2.8% consider that the difference appears when the first encephalopathy traces are being felt and the child has formed all internal and external organs. A percentage of 1.7% of respondents consider that this difference occurs at the beginning of the central nervous system, and 1.4% when the unborn child has all the features that we can clearly see to a newborn child (Table (Table9 9 ).
The opinion on the moment that makes the difference between a fetus and a child
|
| |
|
|
|
| Over 14 weeks (the period legally accepted for abortion) | 37.5% |
| From the very first heart beat (18 days) | 33.3% |
| When the child has all organs contoured and can move by himself (12 weeks) | 18.1% |
| When the first encephalon traces are being felt and the child has formed all internal and external organs (seven weeks) | 2.8% |
| At the beginning of the central nervous system, liver, kidneys, stomach (six weeks) | 1.7% |
| When the unborn child has all the characteristics that we can clearly observe to a child after birth | 1.4% |
| When you can clearly distinguish his features (nose, cheeks, eyes) (five weeks) | 1.2% |
| Other | 1% |
| I don’t know | 3% |
| Total | 100% |
We noticed that highly religious people make a clear association between abortion and crime. They also consider that at the time of pregnancy interruption it is aborted a child and not a fetus. However, unexpectedly, we noticed that 27% of the women, who declare themselves to be very religious, have also stated that they see abortion as a crime but also as a woman’s right. Thirty-one percent of the women, who also claimed profound religious beliefs, consider that abortion may be associated with the abortion of a child but also of a fetus, this depending on the time of abortion (Tables (Tables10 10 and and11 11 ).
The correlation between the level of religious beliefs and the perspective on abortion seen as a crime or a right
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| A woman’s right | A crime | Both depending on the moment when it took place | Not know | No | |||
| Are you a religious person? | A very religious and practicant person | 1% | 11% | 12% | – | – | 24% |
| A very religious but non practicant person | 4% | 7% | 15% | – | 1% | 27% | |
| A relatively religious and practicant person | 5% | 6% | 13% | – | – | 24% | |
| Relatively religious but non practicant person | 6% | 4% | 13% | 2% | – | 25% | |
| Total | 16% | 28% | 53% | 2% | 1% | 100% | |
The correlation between the level of religious beliefs and the perspective on abortion procedure conducted on a fetus or a child
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
| ||||
| A fetus | A child | Both depending on the time of abortion | Not know | |||
| Are you a religious person? | A very religious and practicant person | 2% | 8% | 14% | – | 24% |
| A very religious but non practicant person | 3% | 7% | 17% | – | 27% | |
| A relatively religious and practicant person | 4% | 5% | 16% | 3% | 28% | |
| Relatively religious but non practicant person | 5% | 4% | 12% | 3% | 24% | |
| Total | 14% | 24% | 59% | 6% | 100% | |
More than half of the respondents have opted for the main reason for abortion the appearance of medical problems to the child. Baby’s health represents the main concern of future mothers, and of each parent, and the birth of a child with serious health issues, is a factor which frightens any future parent, being many times, at least theoretically, one good reason for opting for abortion. At the opposite side, 12% of respondents would not choose abortion under any circumstances. Other reasons for which women would opt for an abortion are: if the woman would have a medical problem (22%) or would not want the child (10%) (Table (Table12 12 ).
Potential reasons for carrying out an abortion
|
| |
|
|
|
| If the child would have a medical problem (genetic or developmental abnormalities of fetus) | 55% |
| If I would have a medical problem | 22% |
| In any of these situations, I would abort | 12% |
| If the child would not be desired | 10% |
| I don’t know | 1% |
| Total | 100% |
Most of the women want to give birth to a child, 56% of the respondents, representing also the reason that would determine them to keep the child. Morality (26%), faith (10%) or legal restrictions (4%), are the three other reasons for which women would not interrupt a pregnancy. Only 2% of the respondents have mentioned other reasons such as health or age.
A percentage of 23% of the surveyed people said that they have done an abortion so far, and 77% did not opted for a surgical intervention either because there was no need, or because they have kept the pregnancy (Table (Table13 13 ).
Rate of abortion among women in the sample
|
| |
|
|
|
| No | 77% |
| Yes | 23% |
| Total | 100% |
Most respondents, 87% specified that they have carried out an abortion during the first 14 weeks – legally accepted limit for abortion: 43.6% have made abortion in the first four weeks, 39.1% between weeks 4–8, and 4.3% between weeks 8–14. It should be noted that 8.7% could not appreciate the pregnancy period in which they carried out abortion, by opting to answer with the option “ I don’t know ”, and a percentage of 4.3% refused to answer to this question.
Performing an abortion is based on many reasons, but the fact that the women have not wanted a child is the main reason mentioned by 47.8% of people surveyed, who have done minimum an abortion so far. Among the reasons for the interruption of pregnancy, it is also included: women with medical problems (13.3%), not the right time to be a mother (10.7%), age motivation (8.7%), due to medical problems of the child (4.3%), the lack of money (4.3%), family pressure (4.3%), partner/spouse did not wanted. A percentage of 3.3% of women had different reasons for abortion, as follows: age difference too large between children, career, marital status, etc. Asked later whether they regretted the abortion, a rate of 69.6% of women who said they had at least one abortion regret it (34.8% opted for “ Yes ”, and 34.8% said “ Yes, partially ”). 26.1% of surveyed women do not regret the choice to interrupted the pregnancy, and 4.3% chose to not answer this question. We noted that, for women who have already experienced abortion, the causes were more diverse than the grounds on which the previous question was asked: “What are the reasons that determined you to have an abortion?” (Table (Table14 14 ).
The reasons that led the women in the sample to have an abortion
|
| |
|
|
|
| I did not desired the child | 47.8% |
| Because of my medical problems | 13.3% |
| It was not the right time | 10.7% |
| I was too young | 8.7% |
| Because the child had health problems (genetic or developmental abnormalities of fetus) | 4.3% |
| Because I did not have financial resources (I couldn’t afford raising a child) | 4.3% |
| Because of the pressure of my family | 4.3% |
| The partner/husband did not wanted | 4.3% |
| Other reasons | 3.3% |
| Total | 100% |
The majority of the respondents (37.5%) considered that “nervous depression” is the main consequence of abortion, followed by “insomnia and nightmares” (24.6%), “disorders in alimentation” and “affective disorders” (each for 7.7% of respondents), “deterioration of interpersonal relationships” and “the feeling of guilt”(for 6.3% of the respondents), “sexual disorders” and “panic attacks” (for 6.3% of the respondents) (Table (Table15 15 ).
Opinion on the consequences of abortion
|
| |
|
|
|
| Nervous depression | 37.5% |
| Insomnia and nightmares | 24.6% |
| Disorders in alimentation | 7.7% |
| Affective disorders | 7.7% |
| Deterioration of interpersonal relationships | 6.3% |
| The feeling of guilt | 6.3% |
| Sexual disorders | 3.3% |
| Panic attacks | 3.3% |
| Other reasons | 3.3% |
| Total | 100% |
Over half of the respondents believe that abortion should be legal in certain circumstances, as currently provided by law, 39% say it should be always legal, and only 6% opted for the illegal option (Table (Table16 16 ).
Opinion on the legal regulation of abortion
|
| |
|
|
|
| Legal in certain terms | 53% |
| Always legal | 39% |
| Illegal | 6% |
| I don’t know | 2% |
| Total | 100% |
Although the current legislation does not punish pregnant women who interrupt pregnancy or intentionally injured their fetus, survey results indicate that 61% of women surveyed believe that the national law should punish the woman and only 28% agree with the current legislation (Table (Table17 17 ).
Opinion on the possibility of punishing the woman who interrupts the course of pregnancy or injures the fetus
|
| |
|
|
|
| Yes | 61% |
| No | 28% |
| I don’t know | 7% |
| I don’t answer | 4% |
| Total | 100% |
For the majority of the respondents (40.6%), the penalty provided by the current legislation, the imprisonment between six months and three years or a fine and deprivation of certain rights for the illegal abortion is considered fair, for a percentage of 39.6% the punishment is too small for 9.5% of the respondents is too high. Imprisonment between two and seven years and deprivation of certain rights for an abortion performed without the consent of the pregnant woman is considered too small for 65% of interviewees. Fourteen percent of them think it is fair and only 19% of respondents consider that Romanian legislation is too severe with people who commit such an act considering the punishment as too much. The imprisonment from three to 10 years and deprivation of certain rights for the facts described above, if an injury was caused to the woman, is considered to be too small for more than half of those included in the survey, 64% and almost 22% for nearly a quarter of them. Only 9% of the respondents mentioned that this legislative measure is too severe for such actions (Table (Table18 18 ).
Opinion on the regulation of abortion of the Romanian Criminal Code (Art. 201)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Reasonable | 40.6% | 14% | 22% |
| Too small | 39.6% | 65% | 64% |
| Too big | 9.5% | 19% | 9% |
| I don’t know | 6.6% | 2% | 3% |
| I don’t answer | 3.7% | – | 2% |
| Total | 100% | 100% | 100% |
Conclusions
After analyzing the results of the sociological research regarding abortion undertaken at national level, we see that 76% of the Romanian women accept abortion, indicating that the majority accepts only certain circumstances (a certain period after conception, for medical reasons, etc.). A percentage of 64% of the respondents indicated that they accept the idea of abortion after 14 weeks of pregnancy (for solid reasons or regardless the reason). This study shows that over 50% of Romanian women see abortion as a right of women but also a woman’s crime and believe that in the moment of interruption of a pregnancy, a fetus is aborted. Mostly, the association of abortion with crime and with the idea that a child is aborted is frequently found within very religious people. The main motivation for Romanian women in taking the decision not to perform an abortion is that they would want the child, and the main reason to perform an abortion is the child’s medical problems. However, it is noted that, in real situations, in which women have already done at least one abortion, most women resort to abortion because they did not want the child towards the hypothetical situation in which women felt that the main reason of abortion is a medical problem. Regarding the satisfaction with the current national legislation of the abortion, the situation is rather surprising. A significant percentage (61%) of respondents felt as necessary to punish the woman who performs an illegal abortion, although the legislation does not provide a punishment. On the other hand, satisfaction level to the penalties provided by law for various violations of the legal conditions for conducting abortion is low, on average only 25.5% of respondents are being satisfied with these, the majority (average 56.2%) considering the penalties as unsatisfactory. Understood as a social phenomenon, intensified by human vulnerabilities, of which the most obvious is accepting the comfort [ 48 ], abortion today is no longer, in Romanian society, from a legal or religious perspective, a problem. Perceptions on the legislative sanction, moral and religious will perpetual vary depending on beliefs, environment, education, etc. The only and the biggest social problem of Romania is truly represented by the steadily falling birth rate.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
The Supreme Court overturned Roe vs. Wade in 2022. Here’s the state of abortion rights in the U.S.
- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
Judges, state lawmakers and voters are deciding the future of abortion in the U.S. two years after the Supreme Court jolted the legal status quo with a ruling that overturned Roe vs. Wade.
The June 24, 2022, ruling in Dobbs vs. Jackson Women’s Health Organization sparked legislative action, protest and lawsuits — placing the issue at the center of politics across the country.
Abortion is now banned at all stages of pregnancy, with limited exceptions, in 14 Republican-controlled states.
In three other states, it’s barred after about the first six weeks, which is before many know they are pregnant. Most Democratic-led states have taken actions to protect abortion rights, becoming sanctuaries for out-of-state patients seeking care.
That’s changed the landscape of abortion access, making it more of a logistical and financial ordeal for many in conservative states. But it has not reduced the overall number of procedures done each month across the U.S.
Here’s what to know about the state of abortion rights in the U.S. now.
Limited abortion access prompts more out-of-state travel
Bans in Republican-led states have prompted many people seeking abortions to travel to get care.
That translates into higher costs for gas or plane tickets, hotels and meals; more logistics to figure out, including child care; and more days off work.
A new study by the Guttmacher Institute, which advocates for abortion access, found that out of just over a million abortions provided in clinics, hospitals and doctors’ offices, more than 161,000 — or 16% — were for people who crossed state lines to get them.
More than two-thirds of abortions done in Kansas and New Mexico were for out-of-staters, particularly Texans.
Since Florida’s six-week abortion ban took effect in May, many people had to travel farther than before, because throughout the Southeast, most states have bans.
Low-income patients and those lacking legal permission to be in the country are more likely to be unable to travel. There can be lasting costs for those who do.

World & Nation
Florida’s 6-week abortion ban takes effect as doctors worry women will lose access to healthcare
The ban has gone into effect, with doctors concerned women in the state will no longer have access to needed healthcare.
May 1, 2024
In Alabama, the Yellowhammer Fund, which previously helped residents pay for the procedure, has paused doing so since facing threats of litigation from the state.
Jenice Fountain, Yellowhammer’s executive director, said she recently met a woman who traveled from Alabama to neighboring Georgia for an abortion but found she couldn’t get one there because she was slightly too far into her pregnancy. The woman then went to Virginia. The journey wiped out her rent money, and she needed help to remain housed.
“We’re having people use every dime that they have to get out of state, or use every dime they have to have another child,” Fountain said.
It’s usually provided with pills rather than procedures
Nearly two-thirds of known abortions last year were provided with pills rather than procedures.
One report found that pills are prescribed via telehealth and mailed to about 6,000 people a month who live in states with abortion bans. They’re sent by medical providers in states with laws intended to protect them from prosecution for those prescriptions.
The laws in Colorado, Massachusetts, New York, Vermont and Washington specifically protect medical providers who prescribe the pills to patients in states with bans.
The growing prominence of pills, which were used in about half of all abortions just before the Dobbs ruling, is a frontier in the latest chapter of the legal fight.
The U.S. Supreme Court this month unanimously rejected an effort by abortion opponents who were seeking to overturn or roll back the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s approval of mifepristone, one of two drugs usually used together for medication abortions. The issue is likely to return.
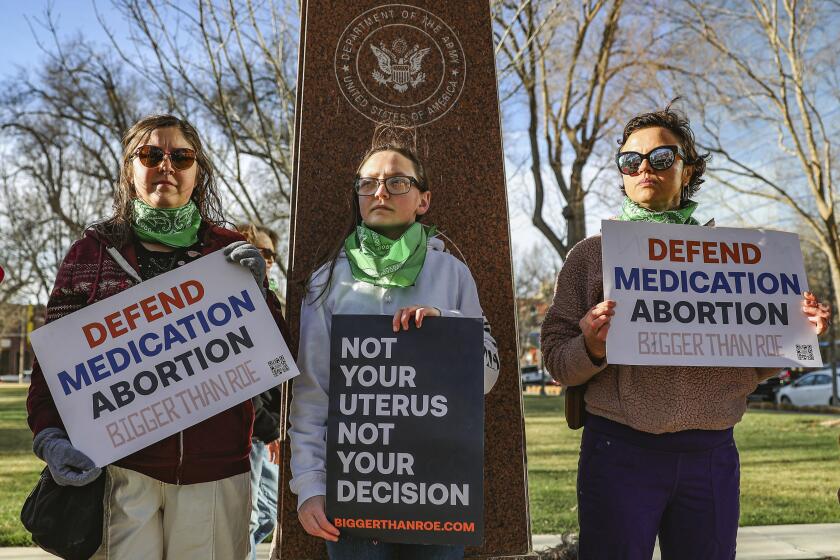

Supreme Court upholds FDA’s approval of abortion pills for early pregnancies
Supreme Court tosses out conservative Christian group’s attack on the abortion pill mifepristone, the most common method of abortion in the U.S.
June 13, 2024
Abortion is on the 2024 ballot
In this presidential election year, abortion is a key issue.
Protecting access has emerged as a key theme in the campaigns of Democrats, including President Biden in his reelection bid. Former President Trump, the presumptive Republican nominee, has said states should decide whether to restrict abortions. He also suggested states could limit contraception use but changed his tune on that.
“We recognize this could be the last Dobbs anniversary we celebrate,” Kelsey Pritchard, a spokesperson for Susan B. Anthony Pro-Life America, said in an interview. She noted that if Democrats win the presidency and regain control of both chambers of Congress, a right to abortion could be enshrined in the law.
The issue will also be put directly before voters in at least four states. Colorado, Florida, Maryland and South Dakota have ballot measures this year asking voters to approve state constitutional amendments that would protect or expand access to abortion.
A New York measure would bar discrimination against someone who has an abortion. There are attempts to put questions about abortion access on the ballots this year in Arkansas, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska and Nevada.
There’s also a push for a ballot measure in Arizona, where the state Supreme Court this year ruled that an 1864 abortion ban could be enforced. With the help of some Republicans, Democrats in the Legislature were able to repeal that law.
Generally, abortion rights expand when voters are deciding. In the seven statewide abortion policy-related votes since 2022, voters have sided with abortion-rights advocates in every case.
It’s still up to the courts — including the Supreme Court
The Dobbs ruling and its aftermath gave rise to a bevy of legal questions and lawsuits challenging nearly every ban and restriction.
Many of those questions deal with how exceptions — which factor in far more often when abortion is barred earlier in pregnancy — should apply. The issue is often raised by those who wanted to be pregnant but experienced life-threatening complications.
A group of women who had serious pregnancy complications but were denied abortions in Texas sued, claiming that the state’s ban is vague about which exceptions are allowed. The all-Republican Texas Supreme Court disagreed in a May ruling.
The U.S. Supreme Court also heard arguments in April on the federal government’s lawsuit against Idaho, which says its ban on abortions at all stages of pregnancy can extend to women in medical emergencies. The Biden administration says that violates federal law. A ruling on that case could be issued at any time.
Meanwhile, bans have been put on hold by judges in Iowa, Montana, Utah and Wyoming.
Mulvihill writes for the Associated Press.
More to Read

The newest election battlefield for abortion: State supreme courts
May 29, 2024

Abortion ban has supercharged Arizona politics. What will GOP legislators do?
April 17, 2024
Letters to the Editor: The self-defeating logic of ‘states’ rights’ abortion foes
April 16, 2024
Start your day right
Sign up for Essential California for news, features and recommendations from the L.A. Times and beyond in your inbox six days a week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Trump endorses Ten Commandments in schools, implores evangelical Christians to vote in November
June 22, 2024

Long a Republican state, Louisiana is redder than ever under new governor
June 21, 2024

Goldberg: The Supreme Court’s role in our partisan polarization has been greatly exaggerated
June 18, 2024
Judge dismisses lawsuit challenging federal rules to accommodate abortions for workers
June 15, 2024
- Historical Abortion Law Timeline: 1850 to Today
Follow the journey of abortion law in the United States — from criminalization in the late 1800s to legalization in the early 1970s — and the ongoing battles for abortion access.
1847: Formation of the American Medical Association (AMA)
In 1847, doctors banded together to form the AMA. It became the male-dominated authority on medical practices. The AMA scrutinized reproductive health care workers, like midwives and nurses, and the obstetric services they provided were phased out.
AMA members believed they should have the power to decide when an abortion could be legally performed. At the same time, the AMA was composed of physicians who lacked expertise in pregnancy and reproductive health.
- AMA members launched a full-fledged criminalization campaign against abortion and female abortion providers. State legislatures moved to ban abortion.
1880s: Criminalization and Vilification
This backlash kicked off a “century of criminalization,” which was ended by Roe v. Wade in 1973 (see below).
Laws restricting abortion access became the norm.
By 1880, all states had laws to restrict abortion — with exceptions in some states if a doctor said the abortion was needed to save the life or health of the patient, or for therapeutic reasons .
As abortion became criminalized, the stigma surrounding it grew.
1910: Abortion Bans Nationwide
By 1910 , abortion was not only restricted but outright illegal at every stage in pregnancy in every state in the country. These abortion bans had some exceptions in instances to save the patient’s life — a decision that only doctors, 95% of whom were men , had the power to make.
By this time, America had experienced several decades of increased immigration. Worried about losing their hold on the country, white men in power supported abortion bans as a way to get upper-class white women to have more children.
1930: Deaths from Illegal, Unsafe Abortions
Criminalizing abortion sent the practice underground, which resulted in a high death toll.
Unsafe, illegal abortion was the cause of death for nearly 2,700 women in 1930 — almost one out of every five (18%) of recorded maternal deaths that year, according to the Guttmacher Institute .
1955: Conference on Abortion Legalization
In response to increasingly alarming media coverage of unsafe, illegal abortions, Planned Parenthood held a first-of-its-kind conference on the issue of abortion.
The doctors who attended the national conference on abortion made the bold move to publicly call for abortion law reform.
Conference attendees said that laws should be rewritten to allow doctors greater latitude to provide abortion services, which would improve public health and access to reproductive health care for people of different economic circumstances.
1962: Thalidomide
In the late 1950s and early ’60s, thousands of pregnant women took a drug called thalidomide to ease pregnancy symptoms. The problem: It was found to cause severe birth defects.
In 1962, a pregnant TV host who ingested thalidomide could not obtain a legal abortion in the United States. The media tracked her journey to get an abortion in Sweden, and 52% of Americans supported her.
The thalidomide fallout brought greater support for abortion law reform.
1964 : Association for the Study of Abortion (ASA)
In 1964, abortion law reform activists registered their first national group: the Association for the Study of Abortion (ASA).
Planned Parenthood joined doctors and laypeople leading the ASA in advocating for abortion law reforms and for studies that would advance abortion procedure safety.
In a strategic move to incrementally increase abortion access, the ASA advocated only for " medically necessary " abortions. But members of the larger abortion law reform movement wanted a full repeal to legalize abortion for all people.
1966 : Trial of the San Francisco Nine
Nine well-respected doctors were sued in California for performing abortions on women who had been exposed to rubella, a disease known to cause birth defects.
Doctors across the country came to the defense of the San Francisco Nine, including the deans of 128 medical schools.
This resulted in one of the first abortion reform measures in the United States. California amended its prohibition on abortion to allow hospital committees to approve requests for abortion.
1969: NARAL Established
The National Association for the Repeal of Abortion Laws (NARAL) was established in Chicago at the First National Conference on Abortion Laws.
NARAL was the first national group created solely to campaign for the legalization of abortion, marking the start of direct action to repeal abortion bans.
Late 1960s and early 1970s: Abortion Reform
By the late 1960s, a nationwide effort was underway to reform abortion laws in nearly every state.
Health care providers, advocates, clergy members, and the legal community lobbied state legislatures and went to court to overturn statutes that had been in place since before the turn of the century.
Between 1967 and 1973, four states — Alaska, Hawaii, New York, and Washington — repealed their abortion bans entirely, while 13 others enacted reforms that expanded exceptions. Instead of just allowing for abortion to save the patient’s life, they now allowed it in instances where a pregnancy was dangerous for the physical or mental health of a patient, fetal abnormalities, and when the pregnancy resulted from rape or incest.
1970: Legal Abortion in New York
In 1970, New York state legalized abortion . One day after that law took effect, a Planned Parenthood health center in Syracuse became the the first Planned Parenthood health center to provide abortion services, and the first free-standing abortion center nationwide.
In the first two years after abortion was legalized in New York, two-thirds of the abortions performed in the state were on patients who had traveled from other states — most of which still outlawed abortion. At the time, other states that had legalized abortion required patients to be state residents.
1973: Roe v. Wade
In a landmark decision, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the due process clause of the 14th Amendment to the Constitution protects the right to abortion.
In particular, the Supreme Court recognized for the first time that the constitutional right to privacy “is broad enough to encompass a woman’s decision whether or not to terminate her pregnancy.”
Roe v. Wade protected the right to abortion in all 50 states, making abortion services safer and more accessible throughout the country. The decision also set a legal precedent that affected dozens of subsequent Supreme Court cases.
1976: Hyde Amendment Put Into Place
The Hyde Amendment is a discriminatory and racist policy that prevents federal dollars from being used in government insurance programs like Medicaid for abortion services (except in instances of incest, rape, or life-threatening risk to the pregnant person).
The legislation was created by Rep. Henry Hyde. “I would certainly like to prevent, if I could legally, anybody having an abortion: a rich woman, a middle class woman, or a poor woman,” he said. “Unfortunately, the only vehicle available is the [Medicaid] bill.”
Because of centuries of systemic racism and bias, Medicaid disproportionately serves Black, Latino, and LGBTQ+ communities — people who already face other barriers to care and economic opportunity.
Despite the federal law, 16 states currently include abortion in their Medicaid programs using state funds. (The remaining 34 states and the District of Columbia do not have abortion coverage in their Medicaid programs due to the Hyde Amendment).
Thanks in large part to the advocacy of reproductive justice organizations, in 2021 the Biden-Harris administration became the first administration in decades to exclude the Hyde Amendment from its presidential budget.
1984: Global Gag Rule
Former President Ronald Reagan introduced the Mexico City policy, otherwise known as the global gag rule, in 1984.
The global gag rule prevents foreign organizations that receive U.S. health aid from providing information on and referrals for abortions or advocating for abortion access.
Every president since Reagan who supports abortion access has rescinded the global gag rule, while every president since Reagan who opposes abortion access has reinstated it. That includes President Donald Trump , who not only reinstated it, but expanded the global gag rule to make it even more harmful.
1992: Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey
This landmark case reaffirmed that the Constitution protects the right to abortion.
However, Casey created an “undue burden” framework, under which laws restricting access to abortion would be judged. This framework made it more difficult to challenge laws that were less than absolute prohibitions on abortion — requiring challenges to show that a law has the purpose or effect of placing a substantial obstacle in the path of a patient seeking an abortion.
Following Casey , state politicians passed numerous medically unnecessary abortion restrictions across the country which courts have found do not impose an undue burden.
2007: Gonzales v. Carhart and Gonzales v. Planned Parenthood Federation of America
The Supreme Court upheld the first federal legislation to criminalize abortion , allowing Congress to ban certain second-trimester abortion procedures — which are sometimes the safest and best way to protect a patient’s health.
Because the legislation does not contain an exception for the patient’s health, the Supreme Court effectively overruled a key component of Roe v. Wade : that the patient’s health must be of paramount concern in laws that restrict abortion access.
2016: Whole Woman's Health v. Hellerstedt
The Supreme Court ruled that two Texas abortion restrictions were unconstitutional because they would shut down most abortion providers in the state and impose an “undue burden” on access to safe, legal abortion in Texas.
2020: June Medical Services v. Russo
On June 29, 2020 — in June Medical Services v. Russo — the Supreme Court struck down a medically unnecessary law that was nearly identical to the one it had struck down in Whole Woman’s Health . This law would have made abortion virtually inaccessible in Louisiana.
Four justices dissented, and it was the last time Ruth Bader Ginsburg had a chance to rule on abortion access before she died later that year. Ginsburg was replaced by Amy Coney Barrett — who is one of three Supreme Court justices nominated by Donald Trump.
2021: Texas Six-Week Ban
On Sept. 1, 2021, Texas implemented a dangerous law called S.B. 8. which bans abortion at approximately six weeks of pregnancy — before many people even know they’re pregnant.
The AMA denounced the Texas abortion ban, but the Supreme Court allowed it to take effect.
Where We’re Headed
This history of abortion laws and court decisions provides important context to the road ahead.
Right now, 80% of Americans want abortion to be legal.
On December 1, 2021 , the Supreme Court will hear oral arguments in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization — a case about a Mississippi ban on abortion at 15 weeks that’s a direct challenge to Roe v. Wade . The state of Mississippi not only has asked the Supreme Court to allow a pre- viability abortion ban, in violation of one of the core tenets of Roe v. Wade , but also has asked the Supreme Court to overrule Roe and Casey entirely.
The Supreme Court will issue a decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization by the end of June 2022. If Roe is overturned or its protections are dismantled, then the laws governing abortion will fall to individual state governments. Many people of reproductive age will lose access to safe, legal abortion in the United States.
No matter what happens, Planned Parenthood will continue to fight to uphold access to safe, legal abortion.
Abortion Access
- Roe v. Wade Overturned: How the Supreme Court Let Politicians Outlaw Abortion
- Federal and State Bans and Restrictions on Abortion
- Types of State Attacks on Abortion
- The State of Emergency for Women's Health
- Timeline of Attacks on Abortion: 2009–2021
The History of Abortion in America
Abortion has been legal for much of American history. Learn how.
Sign Up for Email
This website uses cookies.
Planned Parenthood cares about your data privacy. We and our third-party vendors use cookies and other tools to collect, store, monitor, and analyze information about your interaction with our site to improve performance, analyze your use of our sites and assist in our marketing efforts. You may opt out of the use of these cookies and other tools at any time by visiting Cookie Settings . By clicking “Allow All Cookies” you consent to our collection and use of such data, and our Terms of Use . For more information, see our Privacy Notice .
Cookie Settings
Planned Parenthood cares about your data privacy. We and our third-party vendors, use cookies, pixels, and other tracking technologies to collect, store, monitor, and process certain information about you when you access and use our services, read our emails, or otherwise engage with us. The information collected might relate to you, your preferences, or your device. We use that information to make the site work, analyze performance and traffic on our website, to provide a more personalized web experience, and assist in our marketing efforts. We also share information with our social media, advertising, and analytics partners. You can change your default settings according to your preference. You cannot opt-out of our Necessary Cookies as they are deployed to ensure the proper functioning of our website (such as prompting the cookie banner and remembering your settings, to log into your account, to redirect you when you log out, etc.). For more information, please see our Privacy Notice .
We use online advertising to promote our mission and help constituents find our services. Marketing pixels help us measure the success of our campaigns.
Performance
We use qualitative data, including session replay, to learn about your user experience and improve our products and services.
We use web analytics to help us understand user engagement with our website, trends, and overall reach of our products.
A state-by-state breakdown of abortion laws 2 years after Roe was overturned
A total of 14 states have ceased nearly all abortion services.
Monday marks two years since the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade , ending the constitutional right to an abortion and allowing states to decide whether to restrict access to the procedure or not.
As of Friday, 14 states have ceased nearly all abortion services and three states have enacted six-week bans, according to an ABC News tally.
At least nine states have no restrictions based on how far along a woman is in her pregnancy and many have recently added amendments enshrining the right to abortion in their state constitutions.
Here is a state-by-state breakdown or where abortion laws stand in your state, according to a review of state laws and the Guttmacher Institute , a research group that focuses on sexual and reproductive health.

Alabama has ceased nearly all abortion services, prohibiting the procedure at all stages of pregnancy unless medically necessary to protect the health or life of the woman.
Patients are required to wait 48 hours after a counseling session to receive an abortion
Patients must receive an ultrasound even if medically unnecessary and receive a medication abortion in person because state laws ban the use of telehealth.
MORE: Arizona's Supreme Court hears case on state's 1864 abortion ban
There are no laws in place restricting abortion based on gestational age in Alaska.
Abortion is banned in Arizona at 15 weeks' gestation or later. Patients are required to make two trips 24 hours apart, one for an in-person consultation and another for the procedure.
Abortion is banned in Arkansas with limited exceptions including saving the health of life of the woman.
Patients are required to wait 72 hours after an in-person counseling session to receive an abortion.
California allows abortions up until fetal viability, which is considered between 24 and 26 weeks' gestation.
Last year, voters decided to amend the state constitution to prohibit the state from denying or interfering with a woman's "reproductive freedom."

Colorado does not restrict abortion based on how far along a patient is in their pregnancy.
Connecticut
Connecticut allows abortions up until fetal viability, considered between 24 and 26 weeks' gestation.
Abortions are prohibited in Delaware after fetal viability, considered between 24 and 26 weeks' gestation.
District of Columbia
Abortion is not restricted based on how far long a woman is in their her in Washington, D.C.
In 2024, Florida enacted a six-week abortion ban . Exceptions for rape, incest and human trafficking are allowed until 15 weeks of pregnancy.
An exception is also allowed if the abortion is to "avert a serious risk of substantial and irreversible physical impairment of a major bodily function" of the woman or to her their life.

Georgia bans abortions at six weeks or later. Exceptions are allowed in cases of rape or incest up to 20 weeks of pregnancy, if a police report was filed regarding the incident.
Exceptions also include if the fetus has a condition that would likely result in death or if the pregnant woman would face harm or potentially death.
In all cases, patients are required to wait 24 hours between a counseling session, which does not have to be in person, and undergoing the abortion.
Hawaii allows abortions up until fetal viability, considered between 24 and 26 weeks' gestation.
MORE: Woman travels to New Mexico for abortion care not offered to her in Texas, joins suit
Idaho has banned nearly all abortions, with the only exceptions being to save the life of the woman.
Patients are required to wait 24 hours after a counseling session, which does not have to be in person, to obtain an abortion.
Illinois allows abortions up until fetal viability, considered between 24 and 26 weeks' gestation.
Abortion is banned in Indiana with limited exceptions including in cases of rape or incest up to 10 weeks post-fertilization and in cases of fetal anomaly up to 20 weeks post-fertilization.
Patients are required to have an in-person counseling session and then wait at least 18 hours for the abortion.
Patients are required to receive an ultrasound even if medically unnecessary and to receive a medication abortion in person because state laws ban the use of telehealth.

Iowa bans abortion at 22 weeks' gestation or later.
Patients are required to make two trips, one for an in-person counseling session and then 24 hours later for the abortion.
Kansas allows abortions up to 22 weeks of pregnancy.
In August 2022, Kansas voters rejected a ballot measure that would have removed the right to abortion from the state constitution.
Kentucky has banned abortion with limited exceptions including to save the health or life of the pregnant woman.
Abortions are banned in Louisiana except in cases of medical emergency and to preserve the life and health of the pregnant woman.
MORE: A court has ruled Texas doctors don't need to perform emergency abortions. Here's what that means
Maine allows abortions up until fetal viability, considered between 24 and 26 weeks' gestation.
Maryland does not restrict abortion based on gestational age.
Massachusetts
Abortion is allowed in Massachusetts up to 24 weeks of pregnancy .
Abortion in Michigan is not restricted based on gestational age. However, a 24-hour waiting period is required between an in-person counseling session and an abortion.
Michigan voters said yes to a constitutional amendment that would add protections for reproductive rights in 2023.
Minnesota does not prohibit abortion based on how far along a woman is in pregnancy.
Mississippi
Mississippi is banned with limited exceptions , including to save the life of the pregnant woman. Exceptions are also allowed for rape if a formal charge has been field with law enforcement.
MORE: How Ohio vote on Issue 1 could impact abortion access in the state
Abortion is banned in Missouri with limited exceptions including medical emergencies to save the life or health of the pregnant woman.
If a provider performs an abortion, they must prove in court that the procedure met the legal exception requirements.
Patients must receive a medication abortion in person because state laws ban the use of telehealth.
Montana allows abortions up until fetal viability, considered between 24 and 26 weeks' gestation.
Nebraska has banned abortion after 12 weeks. Exceptions include rape, incest and saving the life of the pregnant woman.
Patients are required to have a counseling session and then wait at least 24 hours before receiving an abortion.
Nevada allows abortions up until 24 weeks' gestation.
New Hampshire
Abortion is banned in New Hampshire after 24 weeks of pregnancy.
New Jersey does not restrict abortion based on how long a woman has been pregnant.
MORE: Why doctors say the 'save the mother's life' exception of abortion bans is medically risky
Abortion is not prohibited based on gestational duration in New Mexico.
New York allows abortions up until fetal viability, considered between 24 and 26 weeks' gestation.
North Carolina
North Carolina bans abortions after 12 weeks. Abortions are allowed up to 20 weeks for rape or incest, up to 24 weeks for "life-limiting" fetal anomalies and for medical emergencies.
Patients are required to make two trips, one for a counseling session -- which does not have to be in person -- and then 72 hours later for the abortion.
North Dakota
Abortion is banned with limited exceptions in North Dakota including rape, incest or a medical emergency up to six weeks' gestation. Exceptions are also in place if the life or health of a pregnant woman is in danger.
Patients have to wait 24 hours after a counseling session to receive an abortion.
Patients must also receive a medication abortion in person because state laws ban the use of telehealth.
Ohio currently allows abortion up to 22 weeks' gestation.
Last year, a ballot measure passed, changing the Ohio constitution to establish "an individual right to one's own reproductive medical treatment, including but not limited to abortion." Treatment includes contraception, fertility treatments, miscarriage care and abortion care.
Patients are required to make two trips at least 24 hours apart, first for an in-person counseling session and second for the procedure.
Oklahoma has banned abortion with no exceptions except to save the life or health of the pregnant woman.
A 72-hour waiting period is required after a counseling session to receive an abortion.
MORE: 5 women sue Texas over abortion bans, saying their lives were put at risk.
Oregon does not prohibit abortion based on how far along someone is in pregnancy.
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania allows abortions up to 24 weeks of pregnancy. However, a 24-hour waiting period is required after a counseling session to receive an abortion.
Rhode Island
Rhode Island allows abortions up until fetal viability, considered between 24 and 26 weeks' gestation.
South Carolina
South Carolina has a six-week abortion ban in place. Exceptions for rape or incest are allowed through the first trimester as well as for a "fatal fetal anomaly" and to save the life or health of the pregnant woman.
Patients are required to make two trips, one for a counseling session -- which does not have to be in person -- and then 24 hours later for the abortion.
South Dakota
South Dakota has banned all abortions except to preserve the life or health of the pregnant person.
Patients are required to make two trips, one for an in-person counseling session and then 48 hours later for the abortion.
Tennessee has banned abortion except to save the life or health of the pregnant woman.
Abortions are banned in Texas except if the woman has a life-threatening condition or is at risk of "substantial impairment of a major bodily function."

Abortions are allowed in Utah up to 18 weeks' gestation.
Patients are required to make two trips, one for an in-person counseling session and then 72 hours later for the abortion.
Vermont does not restrict abortion based on gestational age.
In 2023, Vermont voters decided to amend the state's constitution to include a right to "personal reproductive autonomy," which includes abortion.
Abortion is prohibited starting in the third trimester in Virginia.
In Washington, abortion is banned at fetal viability, considered between 24 and 26 weeks' gestation.
MORE: Idaho woman shares 19-day miscarriage on TikTok, says state's abortion laws prevented her from getting care
West Virginia
West Virginia has banned nearly all abortions with limited exceptions including if the fetus is non-viable, in cases of medical emergency and to save the life of the pregnant person.
Exceptions are allowed in cases of rape and incest but only up until eight weeks' gestation and if the incident is reported to law enforcement.
Abortions are banned in Wisconsin after 22 weeks' gestation.
Patients must receive an ultrasound even if medically unnecessary and to receive a medication abortion in person because state laws ban the use of telehealth.
Wyoming allows abortions up until fetal viability, considered between 24 and 26 weeks' gestation.
Related Topics
- Abortion Battle
Trending Reader Picks

3 men drown while swimming in Gulf Coast: Police
- Jun 22, 12:35 PM

'Hawaii Five-0' actor Taylor Wily dies at 56
- Jun 21, 3:26 PM

Water emergency halts tourist arrivals at island
- Jun 22, 8:23 AM

3 injured in shooting during funeral reception
- Jun 21, 10:31 PM

Dr. Fauci discusses advising Trump during pandemic
- Jun 21, 3:32 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
Abortion rights: Tracking state lawsuits two years after Roe reversal
- Medium Text
LAWSUITS CHALLENGING BANS OUTRIGHT
ABORTION PILLS
MEDICAL EMERGENCIES
INTERSTATE TRAVEL
LEGAL, BUT RESTRICTED
Sign up here.
Reporting By Brendan Pierson in New York, Editing by Alexia Garamfalvi and Aurora Ellis
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
Brendan Pierson reports on product liability litigation and on all areas of health care law. He can be reached at [email protected].

World Chevron

Philippines not in business of instigating wars, says President Marcos
Philippine President Ferdinand Marcos Jr said on Sunday his country is not in the business of instigating wars and will always aim to settle disputes peacefully.


Princeton Legal Journal

The First Amendment and the Abortion Rights Debate
Sofia Cipriano
4 Prin.L.J.F. 12
Following Dobbs v. Jackson ’s (2022) reversal of Roe v. Wade (1973) — and the subsequent revocation of federal abortion protection — activists and scholars have begun to reconsider how to best ground abortion rights in the Constitution. In the past year, numerous Jewish rights groups have attempted to overturn state abortion bans by arguing that abortion rights are protected by various state constitutions’ free exercise clauses — and, by extension, the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. While reframing the abortion rights debate as a question of religious freedom is undoubtedly strategic, the Free Exercise Clause is not the only place to locate abortion rights: the Establishment Clause also warrants further investigation.
Roe anchored abortion rights in the right to privacy — an unenumerated right with a long history of legal recognition. In various cases spanning the past two centuries, t he Supreme Court located the right to privacy in the First, Fourth, Fifth, Ninth, and Fourteenth Amendments . Roe classified abortion as a fundamental right protected by strict scrutiny, meaning that states could only regulate abortion in the face of a “compelling government interest” and must narrowly tailor legislation to that end. As such, Roe ’s trimester framework prevented states from placing burdens on abortion access in the first few months of pregnancy. After the fetus crosses the viability line — the point at which the fetus can survive outside the womb — states could pass laws regulating abortion, as the Court found that “the potentiality of human life” constitutes a “compelling” interest. Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey (1992) later replaced strict scrutiny with the weaker “undue burden” standard, giving states greater leeway to restrict abortion access. Dobbs v. Jackson overturned both Roe and Casey , leaving abortion regulations up to individual states.
While Roe constituted an essential step forward in terms of abortion rights, weaknesses in its argumentation made it more susceptible to attacks by skeptics of substantive due process. Roe argues that the unenumerated right to abortion is implied by the unenumerated right to privacy — a chain of logic which twice removes abortion rights from the Constitution’s language. Moreover, Roe’s trimester framework was unclear and flawed from the beginning, lacking substantial scientific rationale. As medicine becomes more and more advanced, the arbitrariness of the viability line has grown increasingly apparent.
As abortion rights supporters have looked for alternative constitutional justifications for abortion rights, the First Amendment has become increasingly more visible. Certain religious groups — particularly Jewish groups — have argued that they have a right to abortion care. In Generation to Generation Inc v. Florida , a religious rights group argued that Florida’s abortion ban (HB 5) constituted a violation of the Florida State Constitution: “In Jewish law, abortion is required if necessary to protect the health, mental or physical well-being of the woman, or for many other reasons not permitted under the Act. As such, the Act prohibits Jewish women from practicing their faith free of government intrusion and thus violates their privacy rights and religious freedom.” Similar cases have arisen in Indiana and Texas. Absent constitutional protection of abortion rights, the Christian religious majorities in many states may unjustly impose their moral and ethical code on other groups, implying an unconstitutional religious hierarchy.
Cases like Generation to Generation Inc v. Florida may also trigger heightened scrutiny status in higher courts; The Religious Freedom Restoration Act (1993) places strict scrutiny on cases which “burden any aspect of religious observance or practice.”
But framing the issue as one of Free Exercise does not interact with major objections to abortion rights. Anti-abortion advocates contend that abortion is tantamount to murder. An anti-abortion advocate may argue that just as religious rituals involving human sacrifice are illegal, so abortion ought to be illegal. Anti-abortion advocates may be able to argue that abortion bans hold up against strict scrutiny since “preserving potential life” constitutes a “compelling interest.”
The question of when life begins—which is fundamentally a moral and religious question—is both essential to the abortion debate and often ignored by left-leaning activists. For select Christian advocacy groups (as well as other anti-abortion groups) who believe that life begins at conception, abortion bans are a deeply moral issue. Abortion bans which operate under the logic that abortion is murder essentially legislate a definition of when life begins, which is problematic from a First Amendment perspective; the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment prevents the government from intervening in religious debates. While numerous legal thinkers have associated the abortion debate with the First Amendment, this argument has not been fully litigated. As an amicus brief filed in Dobbs by the Freedom From Religion Foundation, Center for Inquiry, and American Atheists points out, anti-abortion rhetoric is explicitly religious: “There is hardly a secular veil to the religious intent and positions of individuals, churches, and state actors in their attempts to limit access to abortion.” Justice Stevens located a similar issue with anti-abortion rhetoric in his concurring opinion in Webster v. Reproductive Health Services (1989) , stating: “I am persuaded that the absence of any secular purpose for the legislative declarations that life begins at conception and that conception occurs at fertilization makes the relevant portion of the preamble invalid under the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment to the Federal Constitution.” Judges who justify their judicial decisions on abortion using similar rhetoric blur the line between church and state.
Framing the abortion debate around religious freedom would thus address the two main categories of arguments made by anti-abortion activists: arguments centered around issues with substantive due process and moral objections to abortion.
Conservatives may maintain, however, that legalizing abortion on the federal level is an Establishment Clause violation to begin with, since the government would essentially be imposing a federal position on abortion. Many anti-abortion advocates favor leaving abortion rights up to individual states. However, in the absence of recognized federal, constitutional protection of abortion rights, states will ban abortion. Protecting religious freedom of the individual is of the utmost importance — the United States government must actively intervene in order to uphold the line between church and state. Protecting abortion rights would allow everyone in the United States to act in accordance with their own moral and religious perspectives on abortion.
Reframing the abortion rights debate as a question of religious freedom is the most viable path forward. Anchoring abortion rights in the Establishment Clause would ensure Americans have the right to maintain their own personal and religious beliefs regarding the question of when life begins. In the short term, however, litigants could take advantage of Establishment Clauses in state constitutions. Yet, given the swing of the Court towards expanding religious freedom protections at the time of writing, Free Exercise arguments may prove better at securing citizens a right to an abortion.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Letitia James
Attorney general james announces settlement with unitedhealthcare for failing to provide coverage of birth control, unitedhealthcare to pay $1 million penalty for failing to cover birth control for new york patients, will refund those who were denied coverage and paid out-of-pocket, june 20, 2024.
NEW YORK –– New York Attorney General Letitia James secured $1 million from UnitedHealthcare of New York, Inc. (UnitedHealthcare), the country’s largest health insurer, for failing to provide coverage of birth control through its health plans. The Office of the Attorney General (OAG) received a complaint from a patient in Brooklyn who was denied coverage for their oral contraceptive by UnitedHealthcare’s Oxford health plan, in violation of New York’s Comprehensive Contraceptive Coverage Act (CCCA). The CCCA requires health insurance plans to cover FDA-approved contraceptives without copays, restrictions, or delays. In addition to paying a $1 million penalty, UnitedHealthcare will refund consumers who were denied coverage by any of its health plans and were forced to pay out-of-pocket costs to purchase their prescribed birth control. Eligible consumers will receive payment in the mail and those with potential claims will be notified and asked to submit a claim. Consumers covered by UnitedHealthcare who paid for contraception and believe they should have been covered in full may submit a claim by emailing [email protected] . UnitedHealthcare must also ensure that all its health plans are covering birth control without restrictions or delays as required by the CCCA.
“Birth control is an important medication that millions of people use every day,” said Attorney General James . “Denying health insurance coverage of birth control can cause serious health concerns for anyone who takes the medication. Reproductive health care is essential to the safety and wellbeing of New Yorkers, and it is crucial that health insurers abide by New York’s reproductive health care laws. I encourage anyone who may have had their birth control coverage denied by their health insurance company to contact my office and file a complaint. New Yorkers can rest assured that my office will always protect access to reproductive health care.”
The OAG’s Health Care Bureau opened an investigation into UnitedHealthcare after receiving a complaint from a patient that their prescription oral contraceptive was denied coverage by UnitedHealthcare’s Oxford plan. The patient's appeal was rejected, and the health plan required the patient to obtain prior authorization or step therapy, a process requiring patients to try alternative treatments. UnitedHealthcare’s denial of coverage and further delays forced the patient to go without their birth control and violated New York’s CCCA.
Health insurers that deny, restrict, or delay coverage of birth control impose unnecessary and unwarranted costs for patients, restrict equitable access to reproductive care, and force patients to skip or delay care because of financial barriers. Under New York’s CCCA, health insurance plans are required to cover FDA-approved contraceptives without copays and to remove any actions that might limit or delay access to care, including prior authorizations, step therapy, and exception processes. The CCCA also requires health insurers to cover at least one version of approved contraceptives if there are multiple therapeutically equivalent drugs.
As a result of this settlement, UnitedHealthcare will pay a $1 million penalty and ensure that all of its health plans are covering contraception without copays, restrictions, or delays as required by New York’s CCCA. Additionally, UnitedHealthcare will ensure all staff involved in the claim approvals process for contraception are trained on compliance with New York laws.
The settlement also requires UnitedHealthcare to reimburse all out-of-pocket costs paid by consumers for their birth control, plus 12 percent interest. Eligible consumers include patients who paid a copay for contraceptives that should have been covered without cost sharing under CCCA from June 1, 2020 onwards. Eligible consumers will receive payment in the mail and those with potential claims will receive notice inviting them to submit a claim. Consumers covered by UnitedHealthcare who paid for contraception and believe they should have been covered in full may submit a claim to UnitedHealthcare by emailing [email protected] . In the claim, patients should list the exact type of contraception, approximate date(s) of the claims for coverage, and the amount they believe they overpaid.
Today’s settlement is the latest action taken by Attorney General James to protect access to reproductive healthcare. In May 2024, Attorney General James announced a sweeping lawsuit against an anti-abortion group and 11 crisis pregnancy centers claiming to offer medically unfounded abortion reversal treatments , building on her previous work in shutting down abortion clinic protestors who were harassing patients trying to get care. In April 2024, Attorney General James led a coalition of 21 Attorney Generals across the country calling on Congress to expand access to IVF. Attorney General James has continued to lead fellow attorney generals across the country in protecting reproductive health, leading amicus briefs at the Supreme Court calling on the court to protect emergency abortion services and access to medication abortion , as well as leading efforts to stand up to states criminalizing those who help others access abortions.
This matter was handled by Assistant Attorney General Carol Hunt of the Health Care Bureau, under the supervision of Bureau Chief Darsana Srinivasan and Special Counsel for Reproductive Justice Galen Leigh Sherwin. The Health Care Bureau is part of the Division of Social Justice which is led by Chief Deputy Attorney General Meghan Faux and overseen by First Deputy Attorney General Jennifer Levy.
We Value Your Privacy We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized content, and analyze our traffic. By using this website you consent to our use of cookies.
Advertisement
Supported by
In Montana, Abortion Rights Groups Submit Signatures for Ballot Measure in November
The measure would affirm the right to abortion in the State Constitution. Democrats hope that it will help Senator Jon Tester in his bid for re-election.
- Share full article

By Kate Zernike
A coalition of abortion rights groups in Montana announced Friday that it had submitted enough signatures to put a measure on the November ballot that would ask voters to affirm a right to reproductive freedom in the State Constitution.
Montana would join four other states — Colorado, South Dakota, Florida and New York — with similar ballot measures this fall. The signatures must be certified by county clerks, who send them to the secretary of state, who has until Aug. 22 to set the ballot questions. Organizers said they submitted more than 117,000 signatures, well clear of the 60,039 required.
Abortion is legal in Montana until viability, or roughly 24 weeks of pregnancy, because its highest court ruled in 1999 that the state Constitution’s provisions on privacy protect a right to abortion.
Leaders of the coalition, Montanans Securing Reproductive Rights, say the explicit constitutional right to abortion will prevent the Republican-controlled Legislature or future courts from undoing the 1999 ruling.
Abortion rights groups in six other states are collecting signatures for citizen-sponsored ballot measures for November. Those include presidential battleground states like Arizona, where Democrats hope that strong support for abortion rights can lift the fortunes of President Biden.
Montana reliably votes Republican in presidential contests, but Democrats hope that turnout for the ballot measure could help Senator Jon Tester in a tough fight for re-election .
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

COMMENTS
An outline for an abortion essay: 1.Abortion Essay Introduction 2.Body Paragraphs: Pros and Cons of Abortion 3.Abortion Essay Conclusion. Topics & examples for abortion essay. Pro-Papers Order Now. ... more than 40 countries have liberalized their abortion laws. Around 48% of all abortions are unsafe, and 8% of them lead to women's death.
As the long-running debate over abortion reaches another key moment at the Supreme Court and in state legislatures across the country, a majority of U.S. adults continue to say that abortion should be legal in all or most cases.About six-in-ten Americans (61%) say abortion should be legal in "all" or "most" cases, while 37% think abortion should be illegal in all or most cases.
The Case Against Abortion. Nov. 30, 2021. Crosses representing abortions in Lindale, Tex. Tamir Kalifa for The New York Times. Share full article. 3367. By Ross Douthat. Opinion Columnist. A ...
A frequently quoted statistic from a recent study by the Guttmacher Institute, which reports that one in four women will have an abortion before the age of forty-five, may strike you as high, but ...
Oct. 13, 2022. On June 24, the Supreme Court overruled Roe v. Wade, eliminating the constitutional right to abortion after almost 50 years in a decision that will transform American life, reshape ...
Q&A: Access to Abortion is a Human Right. "Guaranteeing access to abortion is not only a public health imperative, it is a human rights imperative as well," said Macarena Sáez, women's ...
A majority of the U.S. public disapproves of the Supreme Court's decision to overturn Roe. About six-in-ten adults (57%) disapprove of the court's decision that the U.S. Constitution does not guarantee a right to abortion and that abortion laws can be set by states, including 43% who strongly disapprove, according to the summer survey.
Authoritative interpretations of international human rights law establish that denying women, girls, and other pregnant people access to abortion is a form of discrimination and jeopardizes a ...
Roe v. Wade grounds constitutional protections for women's decision whether to end a pregnancy in the Due Process Clauses. But in the forty years since Roe, the U.S. Supreme Court has come to understand the abortion right as an equality right, as well as a liberty right. In this Essay, we describe some distinctive features of equality arguments for abortion rights. We then show how, over ...
The decision to keep the child should not be left up solely to the woman. Yes, it is her body that the child grows in, however once that child is birthed it is now two people's responsibility ...
Abortion Law . Human Rights Note. Human Rights Devolution: Integrating International Law into State Abortion Governance. ... Abortion Law Blog Essay. Fifth Amendment Rights as Abortion Rights. April 11, 2023 A Black woman arrives at a hospital in South Carolina with a medical emergency. She is having labor pains, and the medical staff ask...
The future of abortion, always a contentious issue, is up at the Supreme Court on Dec. 1. Arguments are planned challenging Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey, the court's major decisions ...
See More Articles >>. Abortion is a medical or surgical procedure to deliberately end a pregnancy. In 1973 the US Supreme Court decision in Roe v. Wade ruled that the Constitution protects the right to an abortion prior to the viability of a fetus. Until the 2022 ruling in Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization, Roe v.
May 17, 2022. If Justice Samuel Alito's draft majority opinion in Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization becomes law, we will enter a post- Roe v. Wade world in which the laws ...
Abortion services are a vital component of reproductive health care. Since the Supreme Court's 2022 ruling in Dobbs v.Jackson Women's Health Organization, access to abortion services has been increasingly restricted in the United States. Jung and colleagues review current practice and evidence on medication abortion, procedural abortion, and associated reproductive health care, as well as ...
Abortion law as a political football and a weapon against women. While the overall trend globally is toward more progressive laws, some countries where the rightwing has taken power have gone backward. In Chile, from 1931 to 1989, the law allowed abortion on therapeutic grounds, described in the Penal Code as "termination of a pregnancy ...
Abstract. Dr. Caitlin Moyer discusses the implications, for women globally, of restricting access to abortion care. In late June, the landmark Roe v. Wade ruling was overturned by the United States Supreme Court, a decision, decried by human rights experts at the United Nations [ 1 ], that leaves many women and girls without the right to obtain ...
Here are some facts about abortion that will help you formulate better arguments. According to the Guttmacher Institute, 1 in 4 pregnancies end in abortion. The majority of abortions are performed in the first trimester. Abortion is one of the safest medical procedures, with less than a 0.5% risk of major complications.
The analysis of abortion by means of medical and social documents. Abortion means a pregnancy interruption "before the fetus is viable" [] or "before the fetus is able to live independently in the extrauterine environment, usually before the 20 th week of pregnancy" [].]. "Clinical miscarriage is both a common and distressing complication of early pregnancy with many etiological ...
Guest Essay. Texas Is the Future of Abortion in America. ... the Supreme Court allowed Texas Senate Bill 8 to go into effect — the most restrictive abortion law to do so in the United States ...
Abortion is a common medical or surgical intervention used to terminate pregnancy. Although a controversial and widely debated topic, approximately 73 million induced abortions occur worldwide each year, with 29% of all pregnancies and over 60% of unintended pregnancies ending in abortion. Abortions are considered safe if they are carried out using a method recommended by WHO, appropriate to ...
Judges, state lawmakers and voters are deciding the future of abortion in the U.S. two years after the Supreme Court jolted the legal status quo with a ruling that overturned Roe vs. Wade. The ...
1962: Thalidomide. In the late 1950s and early '60s, thousands of pregnant women took a drug called thalidomide to ease pregnancy symptoms. The problem: It was found to cause severe birth defects. In 1962, a pregnant TV host who ingested thalidomide could not obtain a legal abortion in the United States.
A total of 14 states have ceased nearly all abortion services. Monday marks two years since the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade, ending the constitutional right to an abortion and ...
Medication abortion, which uses the drugs mifepristone and misoprostol to induce abortion in early pregnancy, accounted for 63% of U.S. abortions last year, up from 53% in 2020, according to the ...
Sofia Cipriano Download 4 Prin.L.J.F. 12 Following Dobbs v. Jackson's (2022) reversal of Roe v. Wade (1973) — and the subsequent revocation of federal abortion protection — activists and scholars have begun to reconsider how to best ground abortion rights in the Constitution. In the past year, numerous Jewish rights groups have attempted to overturn…
NEW YORK -- New York Attorney General Letitia James secured $1 million from UnitedHealthcare of New York, Inc. (UnitedHealthcare), the country's largest health insurer, for failing to provide coverage of birth control through its health plans. The Office of the Attorney General (OAG) received a complaint from a patient in Brooklyn who was denied coverage for their oral contraceptive by ...
A coalition of abortion rights groups in Montana announced Friday that it had submitted enough signatures to put a measure on the November ballot that would ask voters to affirm a right to ...