Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples

Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
Published on July 15, 2021 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 22, 2023.
A questionnaire is a list of questions or items used to gather data from respondents about their attitudes, experiences, or opinions. Questionnaires can be used to collect quantitative and/or qualitative information.
Questionnaires are commonly used in market research as well as in the social and health sciences. For example, a company may ask for feedback about a recent customer service experience, or psychology researchers may investigate health risk perceptions using questionnaires.
Table of contents
Questionnaires vs. surveys, questionnaire methods, open-ended vs. closed-ended questions, question wording, question order, step-by-step guide to design, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about questionnaire design.
A survey is a research method where you collect and analyze data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.
Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives , placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
But designing a questionnaire is only one component of survey research. Survey research also involves defining the population you’re interested in, choosing an appropriate sampling method , administering questionnaires, data cleansing and analysis, and interpretation.
Sampling is important in survey research because you’ll often aim to generalize your results to the population. Gather data from a sample that represents the range of views in the population for externally valid results. There will always be some differences between the population and the sample, but minimizing these will help you avoid several types of research bias , including sampling bias , ascertainment bias , and undercoverage bias .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Questionnaires can be self-administered or researcher-administered . Self-administered questionnaires are more common because they are easy to implement and inexpensive, but researcher-administered questionnaires allow deeper insights.
Self-administered questionnaires
Self-administered questionnaires can be delivered online or in paper-and-pen formats, in person or through mail. All questions are standardized so that all respondents receive the same questions with identical wording.
Self-administered questionnaires can be:
- cost-effective
- easy to administer for small and large groups
- anonymous and suitable for sensitive topics
But they may also be:
- unsuitable for people with limited literacy or verbal skills
- susceptible to a nonresponse bias (most people invited may not complete the questionnaire)
- biased towards people who volunteer because impersonal survey requests often go ignored.
Researcher-administered questionnaires
Researcher-administered questionnaires are interviews that take place by phone, in-person, or online between researchers and respondents.
Researcher-administered questionnaires can:
- help you ensure the respondents are representative of your target audience
- allow clarifications of ambiguous or unclear questions and answers
- have high response rates because it’s harder to refuse an interview when personal attention is given to respondents
But researcher-administered questionnaires can be limiting in terms of resources. They are:
- costly and time-consuming to perform
- more difficult to analyze if you have qualitative responses
- likely to contain experimenter bias or demand characteristics
- likely to encourage social desirability bias in responses because of a lack of anonymity
Your questionnaire can include open-ended or closed-ended questions or a combination of both.
Using closed-ended questions limits your responses, while open-ended questions enable a broad range of answers. You’ll need to balance these considerations with your available time and resources.
Closed-ended questions
Closed-ended, or restricted-choice, questions offer respondents a fixed set of choices to select from. Closed-ended questions are best for collecting data on categorical or quantitative variables.
Categorical variables can be nominal or ordinal. Quantitative variables can be interval or ratio. Understanding the type of variable and level of measurement means you can perform appropriate statistical analyses for generalizable results.
Examples of closed-ended questions for different variables
Nominal variables include categories that can’t be ranked, such as race or ethnicity. This includes binary or dichotomous categories.
It’s best to include categories that cover all possible answers and are mutually exclusive. There should be no overlap between response items.
In binary or dichotomous questions, you’ll give respondents only two options to choose from.
White Black or African American American Indian or Alaska Native Asian Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander
Ordinal variables include categories that can be ranked. Consider how wide or narrow a range you’ll include in your response items, and their relevance to your respondents.
Likert scale questions collect ordinal data using rating scales with 5 or 7 points.
When you have four or more Likert-type questions, you can treat the composite data as quantitative data on an interval scale . Intelligence tests, psychological scales, and personality inventories use multiple Likert-type questions to collect interval data.
With interval or ratio scales , you can apply strong statistical hypothesis tests to address your research aims.
Pros and cons of closed-ended questions
Well-designed closed-ended questions are easy to understand and can be answered quickly. However, you might still miss important answers that are relevant to respondents. An incomplete set of response items may force some respondents to pick the closest alternative to their true answer. These types of questions may also miss out on valuable detail.
To solve these problems, you can make questions partially closed-ended, and include an open-ended option where respondents can fill in their own answer.
Open-ended questions
Open-ended, or long-form, questions allow respondents to give answers in their own words. Because there are no restrictions on their choices, respondents can answer in ways that researchers may not have otherwise considered. For example, respondents may want to answer “multiracial” for the question on race rather than selecting from a restricted list.
- How do you feel about open science?
- How would you describe your personality?
- In your opinion, what is the biggest obstacle for productivity in remote work?
Open-ended questions have a few downsides.
They require more time and effort from respondents, which may deter them from completing the questionnaire.
For researchers, understanding and summarizing responses to these questions can take a lot of time and resources. You’ll need to develop a systematic coding scheme to categorize answers, and you may also need to involve other researchers in data analysis for high reliability .
Question wording can influence your respondents’ answers, especially if the language is unclear, ambiguous, or biased. Good questions need to be understood by all respondents in the same way ( reliable ) and measure exactly what you’re interested in ( valid ).
Use clear language
You should design questions with your target audience in mind. Consider their familiarity with your questionnaire topics and language and tailor your questions to them.
For readability and clarity, avoid jargon or overly complex language. Don’t use double negatives because they can be harder to understand.
Use balanced framing
Respondents often answer in different ways depending on the question framing. Positive frames are interpreted as more neutral than negative frames and may encourage more socially desirable answers.
| Positive frame | Negative frame |
|---|---|
| Should protests of pandemic-related restrictions be allowed? | Should protests of pandemic-related restrictions be forbidden? |
Use a mix of both positive and negative frames to avoid research bias , and ensure that your question wording is balanced wherever possible.
Unbalanced questions focus on only one side of an argument. Respondents may be less likely to oppose the question if it is framed in a particular direction. It’s best practice to provide a counter argument within the question as well.
| Unbalanced | Balanced |
|---|---|
| Do you favor…? | Do you favor or oppose…? |
| Do you agree that…? | Do you agree or disagree that…? |
Avoid leading questions
Leading questions guide respondents towards answering in specific ways, even if that’s not how they truly feel, by explicitly or implicitly providing them with extra information.
It’s best to keep your questions short and specific to your topic of interest.
- The average daily work commute in the US takes 54.2 minutes and costs $29 per day. Since 2020, working from home has saved many employees time and money. Do you favor flexible work-from-home policies even after it’s safe to return to offices?
- Experts agree that a well-balanced diet provides sufficient vitamins and minerals, and multivitamins and supplements are not necessary or effective. Do you agree or disagree that multivitamins are helpful for balanced nutrition?
Keep your questions focused
Ask about only one idea at a time and avoid double-barreled questions. Double-barreled questions ask about more than one item at a time, which can confuse respondents.
This question could be difficult to answer for respondents who feel strongly about the right to clean drinking water but not high-speed internet. They might only answer about the topic they feel passionate about or provide a neutral answer instead – but neither of these options capture their true answers.
Instead, you should ask two separate questions to gauge respondents’ opinions.
Strongly Agree Agree Undecided Disagree Strongly Disagree
Do you agree or disagree that the government should be responsible for providing high-speed internet to everyone?
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
You can organize the questions logically, with a clear progression from simple to complex. Alternatively, you can randomize the question order between respondents.
Logical flow
Using a logical flow to your question order means starting with simple questions, such as behavioral or opinion questions, and ending with more complex, sensitive, or controversial questions.
The question order that you use can significantly affect the responses by priming them in specific directions. Question order effects, or context effects, occur when earlier questions influence the responses to later questions, reducing the validity of your questionnaire.
While demographic questions are usually unaffected by order effects, questions about opinions and attitudes are more susceptible to them.
- How knowledgeable are you about Joe Biden’s executive orders in his first 100 days?
- Are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way Joe Biden is managing the economy?
- Do you approve or disapprove of the way Joe Biden is handling his job as president?
It’s important to minimize order effects because they can be a source of systematic error or bias in your study.
Randomization
Randomization involves presenting individual respondents with the same questionnaire but with different question orders.
When you use randomization, order effects will be minimized in your dataset. But a randomized order may also make it harder for respondents to process your questionnaire. Some questions may need more cognitive effort, while others are easier to answer, so a random order could require more time or mental capacity for respondents to switch between questions.
Step 1: Define your goals and objectives
The first step of designing a questionnaire is determining your aims.
- What topics or experiences are you studying?
- What specifically do you want to find out?
- Is a self-report questionnaire an appropriate tool for investigating this topic?
Once you’ve specified your research aims, you can operationalize your variables of interest into questionnaire items. Operationalizing concepts means turning them from abstract ideas into concrete measurements. Every question needs to address a defined need and have a clear purpose.
Step 2: Use questions that are suitable for your sample
Create appropriate questions by taking the perspective of your respondents. Consider their language proficiency and available time and energy when designing your questionnaire.
- Are the respondents familiar with the language and terms used in your questions?
- Would any of the questions insult, confuse, or embarrass them?
- Do the response items for any closed-ended questions capture all possible answers?
- Are the response items mutually exclusive?
- Do the respondents have time to respond to open-ended questions?
Consider all possible options for responses to closed-ended questions. From a respondent’s perspective, a lack of response options reflecting their point of view or true answer may make them feel alienated or excluded. In turn, they’ll become disengaged or inattentive to the rest of the questionnaire.
Step 3: Decide on your questionnaire length and question order
Once you have your questions, make sure that the length and order of your questions are appropriate for your sample.
If respondents are not being incentivized or compensated, keep your questionnaire short and easy to answer. Otherwise, your sample may be biased with only highly motivated respondents completing the questionnaire.
Decide on your question order based on your aims and resources. Use a logical flow if your respondents have limited time or if you cannot randomize questions. Randomizing questions helps you avoid bias, but it can take more complex statistical analysis to interpret your data.
Step 4: Pretest your questionnaire
When you have a complete list of questions, you’ll need to pretest it to make sure what you’re asking is always clear and unambiguous. Pretesting helps you catch any errors or points of confusion before performing your study.
Ask friends, classmates, or members of your target audience to complete your questionnaire using the same method you’ll use for your research. Find out if any questions were particularly difficult to answer or if the directions were unclear or inconsistent, and make changes as necessary.
If you have the resources, running a pilot study will help you test the validity and reliability of your questionnaire. A pilot study is a practice run of the full study, and it includes sampling, data collection , and analysis. You can find out whether your procedures are unfeasible or susceptible to bias and make changes in time, but you can’t test a hypothesis with this type of study because it’s usually statistically underpowered .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Prospective cohort study
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
- Social desirability bias
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analyzing data from people using questionnaires.
Closed-ended, or restricted-choice, questions offer respondents a fixed set of choices to select from. These questions are easier to answer quickly.
Open-ended or long-form questions allow respondents to answer in their own words. Because there are no restrictions on their choices, respondents can answer in ways that researchers may not have otherwise considered.
A Likert scale is a rating scale that quantitatively assesses opinions, attitudes, or behaviors. It is made up of 4 or more questions that measure a single attitude or trait when response scores are combined.
To use a Likert scale in a survey , you present participants with Likert-type questions or statements, and a continuum of items, usually with 5 or 7 possible responses, to capture their degree of agreement.
You can organize the questions logically, with a clear progression from simple to complex, or randomly between respondents. A logical flow helps respondents process the questionnaire easier and quicker, but it may lead to bias. Randomization can minimize the bias from order effects.
Questionnaires can be self-administered or researcher-administered.
Researcher-administered questionnaires are interviews that take place by phone, in-person, or online between researchers and respondents. You can gain deeper insights by clarifying questions for respondents or asking follow-up questions.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 22). Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/questionnaire/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, survey research | definition, examples & methods, what is a likert scale | guide & examples, reliability vs. validity in research | difference, types and examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Surveys Questionnaire
21 Questionnaire Templates: Examples and Samples

Questionnaire: Definition
A questionnaire is defined a market research instrument that consists of questions or prompts to elicit and collect responses from a sample of respondents. A questionnaire is typically a mix of open-ended questions and close-ended questions ; the latter allowing for respondents to enlist their views in detail.
A questionnaire can be used in both, qualitative market research as well as quantitative market research with the use of different types of questions .
LEARN ABOUT: Open-Ended Questions
Types of Questionnaires
We have learnt that a questionnaire could either be structured or free-flow. To explain this better:
- Structured Questionnaires: A structured questionnaires helps collect quantitative data . In this case, the questionnaire is designed in a way that it collects very specific type of information. It can be used to initiate a formal enquiry on collect data to prove or disprove a prior hypothesis.
- Unstructured Questionnaires: An unstructured questionnaire collects qualitative data . The questionnaire in this case has a basic structure and some branching questions but nothing that limits the responses of a respondent. The questions are more open-ended.
LEARN ABOUT: Structured Question
Types of Questions used in a Questionnaire
A questionnaire can consist of many types of questions . Some of the commonly and widely used question types though, are:
- Open-Ended Questions: One of the commonly used question type in questionnaire is an open-ended question . These questions help collect in-depth data from a respondent as there is a huge scope to respond in detail.
- Dichotomous Questions: The dichotomous question is a “yes/no” close-ended question . This question is generally used in case of the need of basic validation. It is the easiest question type in a questionnaire.
- Multiple-Choice Questions: An easy to administer and respond to, question type in a questionnaire is the multiple-choice question . These questions are close-ended questions with either a single select multiple choice question or a multiple select multiple choice question. Each multiple choice question consists of an incomplete stem (question), right answer or answers, close alternatives, distractors and incorrect answers. Depending on the objective of the research, a mix of the above option types can be used.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) Question: Another commonly used question type in a questionnaire is the Net Promoter Score (NPS) Question where one single question collects data on the referencability of the research topic in question.
- Scaling Questions: Scaling questions are widely used in a questionnaire as they make responding to the questionnaire, very easy. These questions are based on the principles of the 4 measurement scales – nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio .
Questionnaires help enterprises collect valuable data to help them make well-informed business decisions. There are powerful tools available in the market that allows using multiple question types, ready to use survey format templates, robust analytics, and many more features to conduct comprehensive market research.
LEARN ABOUT: course evaluation survey examples
For example, an enterprise wants to conduct market research to understand what pricing would be best for their new product to capture a higher market share. In such a case, a questionnaire for competitor analysis can be sent to the targeted audience using a powerful market research survey software which can help the enterprise conduct 360 market research that will enable them to make strategic business decisions.
Now that we have learned what a questionnaire is and its use in market research , some examples and samples of widely used questionnaire templates on the QuestionPro platform are as below:
LEARN ABOUT: Speaker evaluation form
Customer Questionnaire Templates: Examples and Samples
QuestionPro specializes in end-to-end Customer Questionnaire Templates that can be used to evaluate a customer journey right from indulging with a brand to the continued use and referenceability of the brand. These templates form excellent samples to form your own questionnaire and begin testing your customer satisfaction and experience based on customer feedback.
LEARN ABOUT: Structured Questionnaire
USE THIS FREE TEMPLATE
Employee & Human Resource (HR) Questionnaire Templates: Examples and Samples
QuestionPro has built a huge repository of employee questionnaires and HR questionnaires that can be readily deployed to collect feedback from the workforce on an organization on multiple parameters like employee satisfaction, benefits evaluation, manager evaluation , exit formalities etc. These templates provide a holistic overview of collecting actionable data from employees.
Community Questionnaire Templates: Examples and Samples
The QuestionPro repository of community questionnaires helps collect varied data on all community aspects. This template library includes popular questionnaires such as community service, demographic questionnaires, psychographic questionnaires, personal questionnaires and much more.
Academic Evaluation Questionnaire Templates: Examples and Samples
Another vastly used section of QuestionPro questionnaire templates are the academic evaluation questionnaires . These questionnaires are crafted to collect in-depth data about academic institutions and the quality of teaching provided, extra-curricular activities etc and also feedback about other educational activities.
MORE LIKE THIS

Life@QuestionPro: The Journey of Kristie Lawrence
Jun 7, 2024

How Can I Help You? — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Jun 5, 2024

Why Multilingual 360 Feedback Surveys Provide Better Insights
Jun 3, 2024

Raked Weighting: A Key Tool for Accurate Survey Results
May 31, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Designing a Questionnaire for a Research Paper: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Develop an Effective Questionnaire

A questionnaire is an important instrument in a research study to help the researcher collect relevant data regarding the research topic. It is significant to ensure that the design of the questionnaire is arranged to minimize errors. However, researchers commonly face challenges in designing an effective questionnaire including its content, appearance and usage that leads to inappropriate and biased findings in a study. This paper aims to review the main steps to design a questionnaire introducing the process that starts with defining the information required for a study, then continues with the identification of the type of survey and types of questions, writing questions and building the construct of the questionnaire. It also develops the demand to pre-test the questionnaire and finalizing the questionnaire to conduct the survey.
Related Papers
Innovations in Measuring and Evaluating Scientific Information
Rayees Farooq
Indian Journal of Anaesthesia
Narayana Yaddanapudi
Edrine Wanyama
Questionnaire construction has overtime evolved with consistency and rarely, it has been skipped in the world’s researches. Questionnaires form the basis for which most pieces of information can be obtained. In the very light, response rates to questions and accuracy of data findings are possible through the use of questionnaire usage. Where a questionnaire is poorly constructed, one faces the risk of missing out vital information which could be forming the basis for research. This paper discusses the relevance and importance of questionnaire construction in data collection and research. An attempt is made to show questionnaire usage in social research and other research processes. Ultimately, questionnaire construction is considered just as important as any other research process used while collecting data. Some key recommendations that could make questionnaire usage in research better are also briefly considered.
Trisha Greenhalgh
Abla BENBELLAL
International Dental & Medical Journal of Advanced Research - VOLUME 2015
Saumya Dubey
Ebenezer Consultan
International Journal of Market Research
Petra Lietz
Some consider responding to survey questions as a sophisticated cognitive process whereby respondents go through, often iterative, steps to process the information provided to them by questions and response options. Others focus more on the interplay between questions and answers as a complex communication process between researchers and respondents, their assumptions, expectations and perceptions. In this article, cognitive and communication research is reviewed that has tested the impact of different question and answer alternatives on the responses obtained. This leads to evidence-based recommendations for market researchers, who frequently have to make decisions regarding various aspects of questionnaire design such as question length and order, question wording, as well as the optimal number of response options and the desirability or otherwise of a ‘don't know’ option or a middle alternative.
Journal of Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care
Gill Wakley
Daniela Garcia
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
De Wet Schutte
Lyberg/Survey
Norbert Schwarz
International Statistical Review
massimo borelli
Health Information & Libraries Journal
Andrew Booth
Nursing Times Research
michael kirk-smith
Petra Boynton
Market Research Society. Journal.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Creating a Questionnaire
Create the perfect questionnaire and collect actionable data using our online guide!

Table of Contents
- How to Create
Questionnaire Types
- Collecting Responses
- Analyzing Results
- Getting Started
What is a Questionnaire?
Definition: A questionnaire is a convenient way to collect feedback. A questionnaire can be used to measure customer satisfaction, capture employee feedback, or even conduct product research. Responses can be collected via email, web link, QR code, or using a survey panel.
The term "survey" and "questionnaire" are commonly used interchangeably. A questionnaire refers to the questions used to collect feedback (the form itself). A survey relates to the entire research process, including summarizing and analyzing questionnaire data.
Getting Started + Tips
How to make a questionnaire: Keep questions short and focused on one topic at a time. Use multiple-choice questions to fit answers into a specific category. Use an open-ended question to capture comments. A Likert scale or MaxDiff question can be used for market research. Collect responses for your questionnaire using an email collector, an anonymous link, or even a QR code.
The following 6 tips will help you create the perfect questionnaire:
1) Use 10 Questions or Less
The shorter you keep your survey, the higher your completion rates. Longer questionnaires usually tend to have a high drop-off percentage. Keeping your surveys to 10 questions or fewer forces you to draft a study that only includes important questions; you should remove trivial questions during the draft process.
2) One Idea Per Question
Make sure each question only covers one topic. Try to include only one topic at a time. For example, in an employee survey, you would not want to ask, "Do you feel satisfied with your compensation and career advancement?". Instead, you would like to separate "compensation" and "career advancement" into two questions or use a Likert scale , putting each question on a separate row.
3) Group Similar Questions Together
Suppose the survey is more than ten questions; similar questions should be grouped on separate pages. If you don't want to use more than one page, add extra spacing between groups of the question; extra white space can increase the increase the readability of your questionnaire.
4) Use Skip/Display Logic
If you have questions that only apply to certain people, consider using skip or display logic to show those questions conditionally. This will help reduce the length of your survey and boost response rates.
If you have questions that only apply to certain people, consider using skip or display logic to show those questions conditionally. This will help reduce the length of your survey and boost response rates. For example, if you asked, "Are you currently looking for new employment opportunities?". If the answer were "yes," a follow-up question would ask, "Why?"
5) Use Research Questions Like MaxDiff
Research questions are an excellent tool for customer or product questionnaires. Instead of asking multiple questions on which features are essential or what price is desirable, question types like MaxDiff and Conjoint will provide you with high-quality, actionable data that can be used for feature prioritization and product pricing. In addition, these question types will reduce the length of your questionnaire.
6) Keep the Audience in Mind
An employee questionnaire should use an anonymous link to collect responses; this will help boost trust and increase honest answers. If doing a customer study, consider adding custom data to the weblink to help identify responses. A survey panel and current customers can lend fresh perspectives for general market research.
Questionnaire Templates
Adding customer surveys to your Google review strategy will add additional data points to improve customer satisfaction. In addition, surveys are a valuable tool to identify ways to improve, establish internal benchmarks, and conduct pricing and product research to improve your company's products.
While there are numerous types of questionnaires (or survey types), these are the five most common general categories:
1) Customer Satisfaction
Capturing customer feedback is one of the most common uses of questionnaires. A good customer satisfaction survey will always revolve around a Net Promoter Score question. When the Net Promoter Score question results are tallied, one number from -100 is 100 is displayed. This number is ideal for benchmarks. Net Promoter provides quick and actionable feedback when combined with an open-ended text question.
2) Customer Effort
Measuring how easily customers can complete a purchase or take a specific action is crucial for the customer experience strategy. A customer effort score question is a rating scale from 1 to 7 (disagree to agree). Results for this question are averaged; the higher the score, the easier it is for your customers to complete tasks.
3) Employee Satisfaction & Engagement
Employee satisfaction and engagement are often used interchangeably but measure different things. Both types of surveys often use opinion scales to ask questions.
Employee satisfaction measures how satisfied employees are with their job and work environment. Standard measures of employee satisfaction include salary, benefits, and co-worker relationships.
Employee engagement relates to the emotional commitment employees have to an organization. It goes beyond simple satisfaction. Standard measures of engagement include belief in the company mission, opportunities for career growth, and being inspired to perform at a high level.
4) Employee Exit Interviews
When employees leave for new opportunities, sending a questionnaire is a great way to understand why that employee is leaving. The feedback obtained here can be used to improve the workplace and reduce employee turnover.
5) Product Research
MaxDiff is used to identify what is most important to your audience. For example, if building a new mobile application, asking a group of users what they think is least and most important will help guide product strategy; your team should only focus on the important areas.
For pricing a new product, Van Westendorp will give you a range of prices the market is willing to expect. You could price your product too high or too low without a question like this, reducing your market penetration.
Collecting Responses For Your Questionnaire
There are a few different ways to collect feedback for questionnaires. Depending on your needs, each one could have an advantage.
With email distribution, you would upload a list of email addresses, and the platform would automatically place a link to your questionnaire inside the email body. One advantage is sending email reminders to respondents who still need to complete your survey. In addition, the email links are unique for each respondent, so you can track email open and click rates. As a result, email surveys are ideal for customer research.
A web link is a convenient way to collect feedback at your convenience. You can place a web link on social media, your website, or even inside your CRM email program (instead of an email collector with a unique link to each person). Custom data can be included in the link, such as store location. This custom data can be used to segment and filter results.
Anonymous Link
When you want to protect your respondents' identities, you use an anonymous link . Anonymous inks do not store respondent information, IP address, or email address. Because of this, anonymous survey links are perfect for employee surveys.
QR code Surveys
QR code surveys can be placed on paper receipts, product packaging, or flyers. In addition, QR codes are a great way to collect feedback after or during an event or even during in-person focus groups.
Survey Panels
If you're conducting market research and need access to a customer base, using a survey panel will get you the responses required. A good survey panel will allow you to target specific demographics, job titles, or interest levels (such as car enthusiasts). When using survey panels, you'll want to double-check and clean your data for low-quality responses. People who speed through your survey or mark the first answer for all questions should be removed.
How to Analyze Questionnaire Data
When analyzing the data from a questionnaire, consider a few advanced techniques like the ones below. These techniques will give you better insights than just simple graphs and charts.
Creating a segment or a cross-tabulation is the easiest way to dive deeper into your results. For example, if you conducted an employee satisfaction survey, the overall scores for the company could be high. But that might only tell part of the story. For example, if your company has multiple departments, you should create a cross-tabulation for each department. You might notice that there is one department with low scores. or one department with high scores.
If your company conducted its first Net Promoter Score survey and the results were -10, that score would be your benchmark. Each subsequent customer survey you run should be compared against that initial number to improve it each time.
TURF Analysis
This is an advanced research technique but very valuable. TURF analysis analysis stands for "Total Unduplicated Reach and Frequency" and is used to find the combination of items that would provide the highest reach level. For example, suppose you ask, "Which of the following flavor of ice cream would you buy?" If you run a TURF analysis on the results, you could find the top 3 or 4 combinations of flavors that would result in the highest sales.
Unsure Where to Start?
Creating a questionnaire can be a challenging process. However, these three suggestions can help you with the perfect questionnaire strategy.
1) Talk With Your Team
Some departments might want to conduct pricing research and do simple Net Promoter Score surveys. Having your organization aligned on strategy will simplify the process and eliminate any possibility of re-work. An aligned strategy will also mean a shorter study with fewer overlapping questions.
2) Start with a Template
A pre-made template will show you how to format and word questions. Next, try multiple templates to understand the various question types.
3) Look at Competitor Surveys
You might notice competitors asking specific questions - this would be a sign that those questions provide valuable metrics. If you can incorporate the great things your competition does while making it more efficient for respondents, your questionnaire campaigns will have a greater chance of success.
Get Started Now
We have you covered on anything from customer surveys, employee surveys, to market research. Get started and create your first survey for free.
Research Questionnaire
Research questionnaires format, research questionnaire samples, what is research questionnaires, types of research questionnaires, distinctions between surveys, polls, and research questionnaires, how to write a good research questionnaire, do’s and don’ts when making research questionnaires, what are the four types of questionnaire in research, what are the 5 questions to ask in a questionnaire, what are the 4 parts of questionnaire in research, what type of questionnaire is used in qualitative research, what are the three main qualities of a good questionnaire, what are the three parts of a research questionnaire, what are the five general rules in formulating questionnaires, what makes a good questionnaire for research, what are close-ended questions in research, how do you organize data in a questionnaire, how many questions should be in a research questionnaire, how do you structure a research questionnaire, can a survey be a questionnaire, why are questionnaires reliable.

- Research Title: State the title of the research project.
Introduction
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the questionnaire.
- Confidentiality: Assure respondents of confidentiality.
- Instructions: Provide clear instructions on how to complete the questionnaire.
Demographic Information
- Occupation:
- Education Level:
Section 1: Topic-Specific Questions
- Question 1: [Likert Scale / Multiple Choice / Open-Ended]
- Question 2: [Likert Scale / Multiple Choice / Open-Ended]
- Question 3: [Likert Scale / Multiple Choice / Open-Ended]
Section 2: Attitudes and Opinions
- Question 4: [Likert Scale / Multiple Choice / Open-Ended]
- Question 5: [Likert Scale / Multiple Choice / Open-Ended]
- Thank You Note: Thank respondents for their time and participation.
- Contact Information: Provide contact details for follow-up questions.

Research Questionnaires for PDF

Example of Questionnaire In Research
Free Research Questionnaires

Quantitative Research Questionnaires
Market Research Questionnaire Template
Market Research Questionnaire Cheat Sheet
Market Research Questionnaire Sample

Market Research Assignment – Survey

Research Protocol Safety Survey
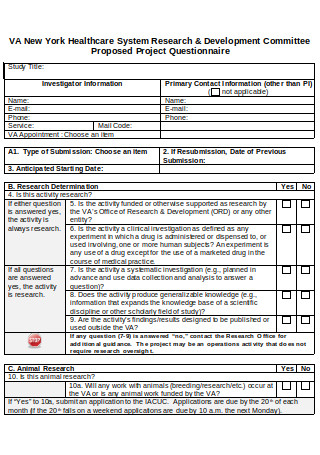
Proposed Project Questionnaire

Self-Reflection Questionnaire
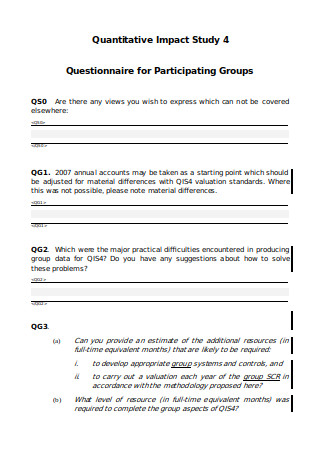
Quantitative Impact Study Questionnaire

Reproduciblility Survey

Research Design Service Questionnaire
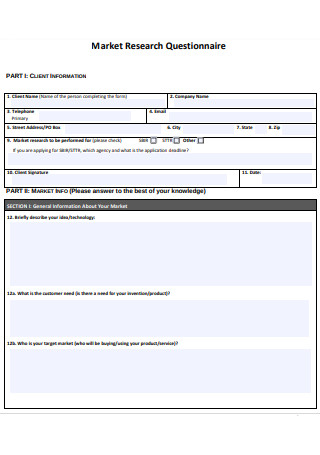
Market Research Questionnaire

Market Research Questionnaire Cheat Sheet in PDF

Energy Market Survey Questionnaire

Market Survey Questionnaire

Consumer Market Research Survey
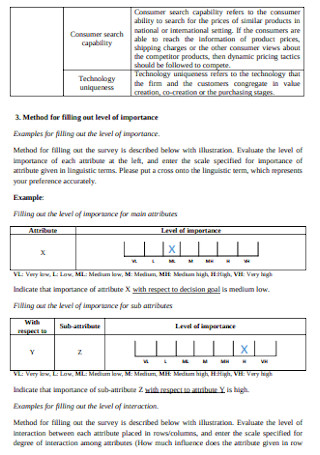
New Product Pricing Questionnaire

Fundamentals of Survey Research

Question and Questionnaire Design

Questionnaires – for Research

Survey Questionnaire Construction

Questionnaire Design Backbone of Research

Questionnaires in Clinical Research
Questionnaire Design

Questionnaire Research With Children

Questionnaire Survey of Scientists

Sample Research Study Questionnaire


Data Design and Analysis for Survey

Questionnaire Design in Attitude and Opinion Research

Constructing Effective Questionnaires

Doctoral Research Study Questionnaires

Questionnaires in Second Language Research

Questionnaires Pretesting in Marketing Research

Questionnaire in Research Design

Schools of Education Research Project Survey

Simple Research Questionnaires
Wrapping Up
Types of questionnaires:.
- Structured Questionnaires : These include predefined questions with fixed response options, useful for quantitative research.
- Unstructured Questionnaires : These have open-ended questions allowing respondents to answer in their own words, ideal for qualitative research.
- Semi-Structured Questionnaires : Combine elements of both structured and unstructured questionnaires, providing a balance of fixed responses and open-ended questions.
- Computer-Assisted Questionnaires : Administered through digital means, they can include multimedia elements and adaptive questioning.
Key Questions:
- Demographic Questions : Gather basic information about respondents (e.g., age, gender, occupation).
- Behavioral Questions : Understand respondent actions and habits (e.g., purchasing behavior).
- Attitudinal Questions : Gauge opinions, attitudes, and perceptions.
- Knowledge-Based Questions : Assess the respondent’s knowledge on a specific topic.
- Preference Questions : Determine respondent preferences and choices. You should also take a look at our Research Project Report
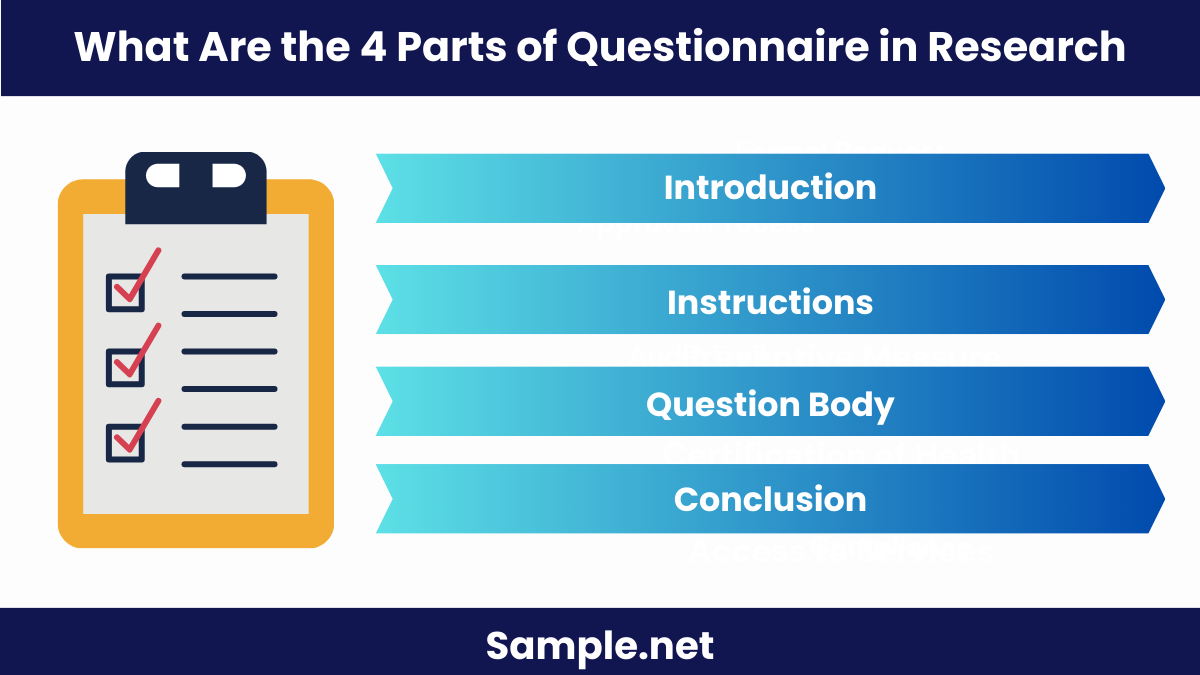
Main Parts:
- Introduction : Explains the purpose of the questionnaire and assures confidentiality.
- Instructions : Provides clear directions on how to complete the questionnaire.
- Question Body : Contains the main questions grouped by topic or theme.
- Conclusion : Includes closing statements and thank-you notes for participants. You should also take a look at our Scientific Research Report

Types of Qualitative Questionnaires:
- Open-Ended Questionnaires : Allow respondents to express their thoughts freely.
- In-Depth Interviews : Structured like a questionnaire but conducted face-to-face.
- Narrative Questionnaires : Encourage respondents to tell their stories in detail.
- Focus Group Questionnaires : Used to guide group discussions around specific topics.
- Case Study Questionnaires : Collect detailed information about a single case or event. You should also take a look at our Research Progress Report
Essential Qualities:
- Clarity : Questions should be clear and unambiguous.
- Relevance : Questions should be directly related to the research objectives.
- Brevity : Questions should be concise to maintain respondent engagement.
- Introduction : Sets the context and explains the purpose of the research.
- Main Body : Contains the core questions grouped by themes or topics.
- Demographic Section : Collects basic demographic information from respondents.
General Rules:
- Keep It Simple : Use straightforward language and avoid jargon.
- Be Specific : Ensure each question targets a specific piece of information.
- Avoid Leading Questions : Ensure questions do not bias the respondent’s answers.
- Pilot Test : Test the questionnaire with a small group before full deployment.
- Ensure Anonymity : Assure respondents that their answers will be confidential.
Share This Post on Your Network
File formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 51+ sample food questionnaire templates in pdf | ms word | google docs | apple pages.

A food questionnaire can be used for a lot of purposes by a variety of businesses in the food service, hospitality, catering, and restaurant industry. Developing a food questionnaire is…
42+ SAMPLE Audit Questionnaire Templates in PDF | MS Word

Whether you come from a startup business to a long-time respected company, any work contains inevitable problems. Indeed, every success, even the smallest ones, deserves to be celebrated. But…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Perspect Clin Res
- v.14(3); Jul-Sep 2023
- PMC10405529
Designing and validating a research questionnaire - Part 1
Priya ranganathan.
Department of Anaesthesiology, Tata Memorial Centre, Homi Bhabha National Institute, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Carlo Caduff
1 Department of Global Health and Social Medicine, King’s College London, London, United Kingdom
Questionnaires are often used as part of research studies to collect data from participants. However, the information obtained through a questionnaire is dependent on how it has been designed, used, and validated. In this article, we look at the types of research questionnaires, their applications and limitations, and how a new questionnaire is developed.
INTRODUCTION
In research studies, questionnaires are commonly used as data collection tools, either as the only source of information or in combination with other techniques in mixed-method studies. However, the quality and accuracy of data collected using a questionnaire depend on how it is designed, used, and validated. In this two-part series, we discuss how to design (part 1) and how to use and validate (part 2) a research questionnaire. It is important to emphasize that questionnaires seek to gather information from other people and therefore entail a social relationship between those who are doing the research and those who are being researched. This social relationship comes with an obligation to learn from others , an obligation that goes beyond the purely instrumental rationality of gathering data. In that sense, we underscore that any research method is not simply a tool but a situation, a relationship, a negotiation, and an encounter. This points to both ethical questions (what is the relationship between the researcher and the researched?) and epistemological ones (what are the conditions under which we can know something?).
At the start of any kind of research project, it is crucial to select the right methodological approach. What is the research question, what is the research object, and what can a questionnaire realistically achieve? Not every research question and not every research object are suitable to the questionnaire as a method. Questionnaires can only provide certain kinds of empirical evidence and it is thus important to be aware of the limitations that are inherent in any kind of methodology.
WHAT IS A RESEARCH QUESTIONNAIRE?
A research questionnaire can be defined as a data collection tool consisting of a series of questions or items that are used to collect information from respondents and thus learn about their knowledge, opinions, attitudes, beliefs, and behavior and informed by a positivist philosophy of the natural sciences that consider methods mainly as a set of rules for the production of knowledge; questionnaires are frequently used instrumentally as a standardized and standardizing tool to ask a set of questions to participants. Outside of such a positivist philosophy, questionnaires can be seen as an encounter between the researcher and the researched, where knowledge is not simply gathered but negotiated through a distinct form of communication that is the questionnaire.
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS OF QUESTIONNAIRES
A questionnaire may not always be the most appropriate way of engaging with research participants and generating knowledge that is needed for a research study. Questionnaires have advantages that have made them very popular, especially in quantitative studies driven by a positivist philosophy: they are a low-cost method for the rapid collection of large amounts of data, even from a wide sample. They are practical, can be standardized, and allow comparison between groups and locations. However, it is important to remember that a questionnaire only captures the information that the method itself (as the structured relationship between the researcher and the researched) allows for and that the respondents are willing to provide. For example, a questionnaire on diet captures what the respondents say they eat and not what they are eating. The problem of social desirability emerges precisely because the research process itself involves a social relationship. This means that respondents may often provide socially acceptable and idealized answers, particularly in relation to sensitive questions, for example, alcohol consumption, drug use, and sexual practices. Questionnaires are most useful for studies investigating knowledge, beliefs, values, self-understandings, and self-perceptions that reflect broader social, cultural, and political norms that may well diverge from actual practices.
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONNAIRES
Research questionnaires may be classified in several ways:
Depending on mode of administration
Research questionnaires may be self-administered (by the research participant) or researcher administered. Self-administered (also known as self-reported or self-completed) questionnaires are designed to be completed by respondents without assistance from a researcher. Self-reported questionnaires may be administered to participants directly during hospital or clinic visits, mailed through the post or E-mail, or accessed through websites. This technique allows respondents to answer at their own pace and simplifies research costs and logistics. The anonymity offered by self-reporting may facilitate more accurate answers. However, the disadvantages are that there may be misinterpretations of questions and low response rates. Significantly, relevant context information is missing to make sense of the answers provided. Researcher-reported (or interviewer-reported) questionnaires may be administered face-to-face or through remote techniques such as telephone or videoconference and are associated with higher response rates. They allow the researcher to have a better understanding of how the data are collected and how answers are negotiated, but are more resource intensive and require more training from the researchers.
The choice between self-administered and researcher-administered questionnaires depends on various factors such as the characteristics of the target audience (e.g., literacy and comprehension level and ability to use technology), costs involved, and the need for confidentiality/privacy.
Depending on the format of the questions
Research questionnaires can have structured or semi-structured formats. Semi-structured questionnaires allow respondents to answer more freely and on their terms, with no restrictions on their responses. They allow for unusual or surprising responses and are useful to explore and discover a range of answers to determine common themes. Typically, the analysis of responses to open-ended questions is more complex and requires coding and analysis. In contrast, structured questionnaires provide a predefined set of responses for the participant to choose from. The use of standard items makes the questionnaire easier to complete and allows quick aggregation, quantification, and analysis of the data. However, structured questionnaires can be restrictive if the scope of responses is limited and may miss potential answers. They also may suggest answers that respondents may not have considered before. Respondents may be forced to fit their answers into the predetermined format and may not be able to express personal views and say what they really want to say or think. In general, this type of questionnaire can turn the research process into a mechanical, anonymous survey with little incentive for participants to feel engaged, understood, and taken seriously.
STRUCTURED QUESTIONS: FORMATS
Some examples of close-ended questions include:
e.g., Please indicate your marital status:
- Prefer not to say.
e.g., Describe your areas of work (circle or tick all that apply):
- Clinical service
- Administration
- Strongly agree
- Strongly disagree.
- Numerical scales: Please rate your current pain on a scale of 1–10 where 1 is no pain and 10 is the worst imaginable pain
- Symbolic scales: For example, the Wong-Baker FACES scale to rate pain in older children
- Ranking: Rank the following cities as per the quality of public health care, where 1 is the best and 5 is the worst.
A matrix questionnaire consists of a series of rows with items to be answered with a series of columns providing the same answer options. This is an efficient way of getting the respondent to provide answers to multiple questions. The EORTC QLQ-C30 is an example of a matrix questionnaire.[ 1 ]
For a more detailed review of the types of research questions, readers are referred to a paper by Boynton and Greenhalgh.[ 2 ]
USING PRE-EXISTING QUESTIONNAIRES VERSUS DEVELOPING A NEW QUESTIONNAIRE
Before developing a questionnaire for a research study, a researcher can check whether there are any preexisting-validated questionnaires that might be adapted and used for the study. The use of validated questionnaires saves time and resources needed to design a new questionnaire and allows comparability between studies.
However, certain aspects need to be kept in mind: is the population/context/purpose for which the original questionnaire was designed similar to the new study? Is cross-cultural adaptation required? Are there any permission needed to use the questionnaire? In many situations, the development of a new questionnaire may be more appropriate given that any research project entails both methodological and epistemological questions: what is the object of knowledge and what are the conditions under which it can be known? It is important to understand that the standardizing nature of questionnaires contributes to the standardization of objects of knowledge. Thus, the seeming similarity in the object of study across diverse locations may be an artifact of the method. Whatever method one uses, it will always operate as the ground on which the object of study is known.
DESIGNING A NEW RESEARCH QUESTIONNAIRE
Once the researcher has decided to design a new questionnaire, several steps should be considered:
Gathering content
It creates a conceptual framework to identify all relevant areas for which the questionnaire will be used to collect information. This may require a scoping review of the published literature, appraising other questionnaires on similar topics, or the use of focus groups to identify common themes.
Create a list of questions
Questions need to be carefully formulated with attention to language and wording to avoid ambiguity and misinterpretation. Table 1 lists a few examples of poorlyworded questions that could have been phrased in a more appropriate manner. Other important aspects to be noted are:
Examples of poorly phrased questions in a research questionnaire
| Original question | Issue | Rephrased question |
|---|---|---|
| Like most people here, do you consume a rice-based diet? | Leading question | What type of diet do you consume? |
| What type of alcoholic drink do you prefer? | Loaded or assumptive question (assumes that the respondent consumes alcohol) | Do you consume alcoholic drinks? If yes, what type of alcoholic drink do you prefer? |
| Over the past 30 days, how many hours in total have you exercised? | Difficult to recall information | On average, how many days in a week do you exercise? And how many hours per day? |
| Do you agree that not smoking is associated with no risk to health? | Double negative | Do you agree that smoking is associated with risk to health? |
| Was the clinic easy to locate and did you like the clinic? | Double-barreled question | Split into two separate questions: was the clinic easy to locate? Did you like the clinic? |
| Do you eat fries regularly? | Ambiguous – the term “regularly” is open to interpretation | How often do you eat fries? |
- Provide a brief introduction to the research study along with instructions on how to complete the questionnaire
- Allow respondents to indicate levels of intensity in their replies, so that they are not forced into “yes” or “no” answers where intensity of feeling may be more appropriate
- Collect specific and detailed data wherever possible – this can be coded into categories. For example, age can be captured in years and later classified as <18 years, 18–45 years, 46 years, and above. The reverse is not possible
- Avoid technical terms, slang, and abbreviations. Tailor the reading level to the expected education level of respondents
- The format of the questionnaire should be attractive with different sections for various subtopics. The font should be large and easy to read, especially if the questionnaire is targeted at the elderly
- Question sequence: questions should be arranged from general to specific, from easy to difficult, from facts to opinions, and sensitive topics should be introduced later in the questionnaire.[ 3 ] Usually, demographic details are captured initially followed by questions on other aspects
- Use contingency questions: these are questions which need to be answered only by a subgroup of the respondents who provide a particular answer to a previous question. This ensures that participants only respond to relevant sections of the questionnaire, for example, Do you smoke? If yes, then how long have you been smoking? If not, then please go to the next section.
TESTING A QUESTIONNAIRE
A questionnaire needs to be valid and reliable, and therefore, any new questionnaire needs to be pilot tested in a small sample of respondents who are representative of the larger population. In addition to validity and reliability, pilot testing provides information on the time taken to complete the questionnaire and whether any questions are confusing or misleading and need to be rephrased. Validity indicates that the questionnaire measures what it claims to measure – this means taking into consideration the limitations that come with any questionnaire-based study. Reliability means that the questionnaire yields consistent responses when administered repeatedly even by different researchers, and any variations in the results are due to actual differences between participants and not because of problems with the interpretation of the questions or their responses. In the next article in this series, we will discuss methods to determine the reliability and validity of a questionnaire.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Writing Survey Questions
Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions. Creating good measures involves both writing good questions and organizing them to form the questionnaire.
Questionnaire design is a multistage process that requires attention to many details at once. Designing the questionnaire is complicated because surveys can ask about topics in varying degrees of detail, questions can be asked in different ways, and questions asked earlier in a survey may influence how people respond to later questions. Researchers are also often interested in measuring change over time and therefore must be attentive to how opinions or behaviors have been measured in prior surveys.
Surveyors may conduct pilot tests or focus groups in the early stages of questionnaire development in order to better understand how people think about an issue or comprehend a question. Pretesting a survey is an essential step in the questionnaire design process to evaluate how people respond to the overall questionnaire and specific questions, especially when questions are being introduced for the first time.
For many years, surveyors approached questionnaire design as an art, but substantial research over the past forty years has demonstrated that there is a lot of science involved in crafting a good survey questionnaire. Here, we discuss the pitfalls and best practices of designing questionnaires.
Question development
There are several steps involved in developing a survey questionnaire. The first is identifying what topics will be covered in the survey. For Pew Research Center surveys, this involves thinking about what is happening in our nation and the world and what will be relevant to the public, policymakers and the media. We also track opinion on a variety of issues over time so we often ensure that we update these trends on a regular basis to better understand whether people’s opinions are changing.
At Pew Research Center, questionnaire development is a collaborative and iterative process where staff meet to discuss drafts of the questionnaire several times over the course of its development. We frequently test new survey questions ahead of time through qualitative research methods such as focus groups , cognitive interviews, pretesting (often using an online, opt-in sample ), or a combination of these approaches. Researchers use insights from this testing to refine questions before they are asked in a production survey, such as on the ATP.
Measuring change over time
Many surveyors want to track changes over time in people’s attitudes, opinions and behaviors. To measure change, questions are asked at two or more points in time. A cross-sectional design surveys different people in the same population at multiple points in time. A panel, such as the ATP, surveys the same people over time. However, it is common for the set of people in survey panels to change over time as new panelists are added and some prior panelists drop out. Many of the questions in Pew Research Center surveys have been asked in prior polls. Asking the same questions at different points in time allows us to report on changes in the overall views of the general public (or a subset of the public, such as registered voters, men or Black Americans), or what we call “trending the data”.
When measuring change over time, it is important to use the same question wording and to be sensitive to where the question is asked in the questionnaire to maintain a similar context as when the question was asked previously (see question wording and question order for further information). All of our survey reports include a topline questionnaire that provides the exact question wording and sequencing, along with results from the current survey and previous surveys in which we asked the question.
The Center’s transition from conducting U.S. surveys by live telephone interviewing to an online panel (around 2014 to 2020) complicated some opinion trends, but not others. Opinion trends that ask about sensitive topics (e.g., personal finances or attending religious services ) or that elicited volunteered answers (e.g., “neither” or “don’t know”) over the phone tended to show larger differences than other trends when shifting from phone polls to the online ATP. The Center adopted several strategies for coping with changes to data trends that may be related to this change in methodology. If there is evidence suggesting that a change in a trend stems from switching from phone to online measurement, Center reports flag that possibility for readers to try to head off confusion or erroneous conclusions.
Open- and closed-ended questions
One of the most significant decisions that can affect how people answer questions is whether the question is posed as an open-ended question, where respondents provide a response in their own words, or a closed-ended question, where they are asked to choose from a list of answer choices.
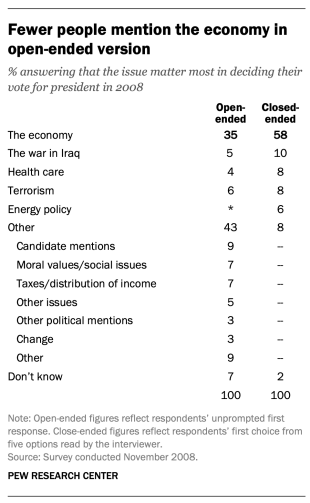
For example, in a poll conducted after the 2008 presidential election, people responded very differently to two versions of the question: “What one issue mattered most to you in deciding how you voted for president?” One was closed-ended and the other open-ended. In the closed-ended version, respondents were provided five options and could volunteer an option not on the list.
When explicitly offered the economy as a response, more than half of respondents (58%) chose this answer; only 35% of those who responded to the open-ended version volunteered the economy. Moreover, among those asked the closed-ended version, fewer than one-in-ten (8%) provided a response other than the five they were read. By contrast, fully 43% of those asked the open-ended version provided a response not listed in the closed-ended version of the question. All of the other issues were chosen at least slightly more often when explicitly offered in the closed-ended version than in the open-ended version. (Also see “High Marks for the Campaign, a High Bar for Obama” for more information.)
Researchers will sometimes conduct a pilot study using open-ended questions to discover which answers are most common. They will then develop closed-ended questions based off that pilot study that include the most common responses as answer choices. In this way, the questions may better reflect what the public is thinking, how they view a particular issue, or bring certain issues to light that the researchers may not have been aware of.
When asking closed-ended questions, the choice of options provided, how each option is described, the number of response options offered, and the order in which options are read can all influence how people respond. One example of the impact of how categories are defined can be found in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in January 2002. When half of the sample was asked whether it was “more important for President Bush to focus on domestic policy or foreign policy,” 52% chose domestic policy while only 34% said foreign policy. When the category “foreign policy” was narrowed to a specific aspect – “the war on terrorism” – far more people chose it; only 33% chose domestic policy while 52% chose the war on terrorism.
In most circumstances, the number of answer choices should be kept to a relatively small number – just four or perhaps five at most – especially in telephone surveys. Psychological research indicates that people have a hard time keeping more than this number of choices in mind at one time. When the question is asking about an objective fact and/or demographics, such as the religious affiliation of the respondent, more categories can be used. In fact, they are encouraged to ensure inclusivity. For example, Pew Research Center’s standard religion questions include more than 12 different categories, beginning with the most common affiliations (Protestant and Catholic). Most respondents have no trouble with this question because they can expect to see their religious group within that list in a self-administered survey.
In addition to the number and choice of response options offered, the order of answer categories can influence how people respond to closed-ended questions. Research suggests that in telephone surveys respondents more frequently choose items heard later in a list (a “recency effect”), and in self-administered surveys, they tend to choose items at the top of the list (a “primacy” effect).
Because of concerns about the effects of category order on responses to closed-ended questions, many sets of response options in Pew Research Center’s surveys are programmed to be randomized to ensure that the options are not asked in the same order for each respondent. Rotating or randomizing means that questions or items in a list are not asked in the same order to each respondent. Answers to questions are sometimes affected by questions that precede them. By presenting questions in a different order to each respondent, we ensure that each question gets asked in the same context as every other question the same number of times (e.g., first, last or any position in between). This does not eliminate the potential impact of previous questions on the current question, but it does ensure that this bias is spread randomly across all of the questions or items in the list. For instance, in the example discussed above about what issue mattered most in people’s vote, the order of the five issues in the closed-ended version of the question was randomized so that no one issue appeared early or late in the list for all respondents. Randomization of response items does not eliminate order effects, but it does ensure that this type of bias is spread randomly.
Questions with ordinal response categories – those with an underlying order (e.g., excellent, good, only fair, poor OR very favorable, mostly favorable, mostly unfavorable, very unfavorable) – are generally not randomized because the order of the categories conveys important information to help respondents answer the question. Generally, these types of scales should be presented in order so respondents can easily place their responses along the continuum, but the order can be reversed for some respondents. For example, in one of Pew Research Center’s questions about abortion, half of the sample is asked whether abortion should be “legal in all cases, legal in most cases, illegal in most cases, illegal in all cases,” while the other half of the sample is asked the same question with the response categories read in reverse order, starting with “illegal in all cases.” Again, reversing the order does not eliminate the recency effect but distributes it randomly across the population.
Question wording
The choice of words and phrases in a question is critical in expressing the meaning and intent of the question to the respondent and ensuring that all respondents interpret the question the same way. Even small wording differences can substantially affect the answers people provide.
[View more Methods 101 Videos ]
An example of a wording difference that had a significant impact on responses comes from a January 2003 Pew Research Center survey. When people were asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule,” 68% said they favored military action while 25% said they opposed military action. However, when asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule even if it meant that U.S. forces might suffer thousands of casualties, ” responses were dramatically different; only 43% said they favored military action, while 48% said they opposed it. The introduction of U.S. casualties altered the context of the question and influenced whether people favored or opposed military action in Iraq.
There has been a substantial amount of research to gauge the impact of different ways of asking questions and how to minimize differences in the way respondents interpret what is being asked. The issues related to question wording are more numerous than can be treated adequately in this short space, but below are a few of the important things to consider:
First, it is important to ask questions that are clear and specific and that each respondent will be able to answer. If a question is open-ended, it should be evident to respondents that they can answer in their own words and what type of response they should provide (an issue or problem, a month, number of days, etc.). Closed-ended questions should include all reasonable responses (i.e., the list of options is exhaustive) and the response categories should not overlap (i.e., response options should be mutually exclusive). Further, it is important to discern when it is best to use forced-choice close-ended questions (often denoted with a radio button in online surveys) versus “select-all-that-apply” lists (or check-all boxes). A 2019 Center study found that forced-choice questions tend to yield more accurate responses, especially for sensitive questions. Based on that research, the Center generally avoids using select-all-that-apply questions.
It is also important to ask only one question at a time. Questions that ask respondents to evaluate more than one concept (known as double-barreled questions) – such as “How much confidence do you have in President Obama to handle domestic and foreign policy?” – are difficult for respondents to answer and often lead to responses that are difficult to interpret. In this example, it would be more effective to ask two separate questions, one about domestic policy and another about foreign policy.
In general, questions that use simple and concrete language are more easily understood by respondents. It is especially important to consider the education level of the survey population when thinking about how easy it will be for respondents to interpret and answer a question. Double negatives (e.g., do you favor or oppose not allowing gays and lesbians to legally marry) or unfamiliar abbreviations or jargon (e.g., ANWR instead of Arctic National Wildlife Refuge) can result in respondent confusion and should be avoided.
Similarly, it is important to consider whether certain words may be viewed as biased or potentially offensive to some respondents, as well as the emotional reaction that some words may provoke. For example, in a 2005 Pew Research Center survey, 51% of respondents said they favored “making it legal for doctors to give terminally ill patients the means to end their lives,” but only 44% said they favored “making it legal for doctors to assist terminally ill patients in committing suicide.” Although both versions of the question are asking about the same thing, the reaction of respondents was different. In another example, respondents have reacted differently to questions using the word “welfare” as opposed to the more generic “assistance to the poor.” Several experiments have shown that there is much greater public support for expanding “assistance to the poor” than for expanding “welfare.”
We often write two versions of a question and ask half of the survey sample one version of the question and the other half the second version. Thus, we say we have two forms of the questionnaire. Respondents are assigned randomly to receive either form, so we can assume that the two groups of respondents are essentially identical. On questions where two versions are used, significant differences in the answers between the two forms tell us that the difference is a result of the way we worded the two versions.

One of the most common formats used in survey questions is the “agree-disagree” format. In this type of question, respondents are asked whether they agree or disagree with a particular statement. Research has shown that, compared with the better educated and better informed, less educated and less informed respondents have a greater tendency to agree with such statements. This is sometimes called an “acquiescence bias” (since some kinds of respondents are more likely to acquiesce to the assertion than are others). This behavior is even more pronounced when there’s an interviewer present, rather than when the survey is self-administered. A better practice is to offer respondents a choice between alternative statements. A Pew Research Center experiment with one of its routinely asked values questions illustrates the difference that question format can make. Not only does the forced choice format yield a very different result overall from the agree-disagree format, but the pattern of answers between respondents with more or less formal education also tends to be very different.
One other challenge in developing questionnaires is what is called “social desirability bias.” People have a natural tendency to want to be accepted and liked, and this may lead people to provide inaccurate answers to questions that deal with sensitive subjects. Research has shown that respondents understate alcohol and drug use, tax evasion and racial bias. They also may overstate church attendance, charitable contributions and the likelihood that they will vote in an election. Researchers attempt to account for this potential bias in crafting questions about these topics. For instance, when Pew Research Center surveys ask about past voting behavior, it is important to note that circumstances may have prevented the respondent from voting: “In the 2012 presidential election between Barack Obama and Mitt Romney, did things come up that kept you from voting, or did you happen to vote?” The choice of response options can also make it easier for people to be honest. For example, a question about church attendance might include three of six response options that indicate infrequent attendance. Research has also shown that social desirability bias can be greater when an interviewer is present (e.g., telephone and face-to-face surveys) than when respondents complete the survey themselves (e.g., paper and web surveys).
Lastly, because slight modifications in question wording can affect responses, identical question wording should be used when the intention is to compare results to those from earlier surveys. Similarly, because question wording and responses can vary based on the mode used to survey respondents, researchers should carefully evaluate the likely effects on trend measurements if a different survey mode will be used to assess change in opinion over time.
Question order
Once the survey questions are developed, particular attention should be paid to how they are ordered in the questionnaire. Surveyors must be attentive to how questions early in a questionnaire may have unintended effects on how respondents answer subsequent questions. Researchers have demonstrated that the order in which questions are asked can influence how people respond; earlier questions can unintentionally provide context for the questions that follow (these effects are called “order effects”).
One kind of order effect can be seen in responses to open-ended questions. Pew Research Center surveys generally ask open-ended questions about national problems, opinions about leaders and similar topics near the beginning of the questionnaire. If closed-ended questions that relate to the topic are placed before the open-ended question, respondents are much more likely to mention concepts or considerations raised in those earlier questions when responding to the open-ended question.
For closed-ended opinion questions, there are two main types of order effects: contrast effects ( where the order results in greater differences in responses), and assimilation effects (where responses are more similar as a result of their order).
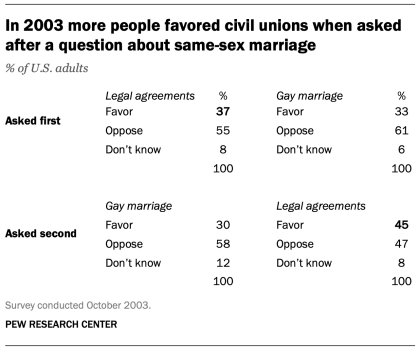
An example of a contrast effect can be seen in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in October 2003, a dozen years before same-sex marriage was legalized in the U.S. That poll found that people were more likely to favor allowing gays and lesbians to enter into legal agreements that give them the same rights as married couples when this question was asked after one about whether they favored or opposed allowing gays and lesbians to marry (45% favored legal agreements when asked after the marriage question, but 37% favored legal agreements without the immediate preceding context of a question about same-sex marriage). Responses to the question about same-sex marriage, meanwhile, were not significantly affected by its placement before or after the legal agreements question.
Another experiment embedded in a December 2008 Pew Research Center poll also resulted in a contrast effect. When people were asked “All in all, are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way things are going in this country today?” immediately after having been asked “Do you approve or disapprove of the way George W. Bush is handling his job as president?”; 88% said they were dissatisfied, compared with only 78% without the context of the prior question.
Responses to presidential approval remained relatively unchanged whether national satisfaction was asked before or after it. A similar finding occurred in December 2004 when both satisfaction and presidential approval were much higher (57% were dissatisfied when Bush approval was asked first vs. 51% when general satisfaction was asked first).
Several studies also have shown that asking a more specific question before a more general question (e.g., asking about happiness with one’s marriage before asking about one’s overall happiness) can result in a contrast effect. Although some exceptions have been found, people tend to avoid redundancy by excluding the more specific question from the general rating.
Assimilation effects occur when responses to two questions are more consistent or closer together because of their placement in the questionnaire. We found an example of an assimilation effect in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in November 2008 when we asked whether Republican leaders should work with Obama or stand up to him on important issues and whether Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders or stand up to them on important issues. People were more likely to say that Republican leaders should work with Obama when the question was preceded by the one asking what Democratic leaders should do in working with Republican leaders (81% vs. 66%). However, when people were first asked about Republican leaders working with Obama, fewer said that Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders (71% vs. 82%).
The order questions are asked is of particular importance when tracking trends over time. As a result, care should be taken to ensure that the context is similar each time a question is asked. Modifying the context of the question could call into question any observed changes over time (see measuring change over time for more information).
A questionnaire, like a conversation, should be grouped by topic and unfold in a logical order. It is often helpful to begin the survey with simple questions that respondents will find interesting and engaging. Throughout the survey, an effort should be made to keep the survey interesting and not overburden respondents with several difficult questions right after one another. Demographic questions such as income, education or age should not be asked near the beginning of a survey unless they are needed to determine eligibility for the survey or for routing respondents through particular sections of the questionnaire. Even then, it is best to precede such items with more interesting and engaging questions. One virtue of survey panels like the ATP is that demographic questions usually only need to be asked once a year, not in each survey.
U.S. Surveys
Other research methods.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
- TemplateLab
Questionnaire Templates
30+ questionnaire templates (word).
If you’re looking to gain insights on your audience or customers, a questionnaire or social survey is a reliable method used to collect standardized data from large numbers of people. (All of the information is collected in the exact same way. Questionnaires are often used by the government to find out more information about geographic areas, the lifestyles of its citizens, and assess which programs get funded . Many government entities rely on questionnaires to run programs or fund certain initiatives. This is because surveys are a favorite way to collect data in a statistical form.
Table of Contents
- 1 Questionnaire Templates
- 2.1 What Kinds of Surveys Work Best?
- 3.1 Choosing Your Template By The Questions Your Survey Asks
- 3.2 Choosing Your Questions Carefully
- 4.1 Getting the Answers and Responses You Need For Your Research
- 4.2 Why Are Questionnaires Better than Focus Groups?
- 4.3 What Factors Affect The Response Rate of Your Questionnaires?
- 4.4 Get the Most Out Of Your Questionnaire and Survey Templates
A questionnaire is a powerful tool that provides the important function of eliciting the feelings, beliefs, perceptions, or attitudes of a group of individuals. In other words, to collect valuable and previously unknown data.
The questionnaire is most frequently a very concise, preplanned set of questions designed to yield specific information to meet a particular need for research information about a pertinent topic. The research information is attained from respondents normally from a related interest area. The dictionary definition gives a clearer definition: A questionnaire is a written or printed form used in gathering information on some subject or subjects consisting of a list of questions to be submitted to one or more persons.

How Do Businesses Use Questionnaires and Surveys?
Using a questionnaire to find out more about your customers or other stakeholders, as a business or organization, is essential to adequate audience research. You can use this information to get to know your audience better, plan communication with them, and even orchestrate campaigns tailored to the ideas you’ve surveyed them about.
How do you put this into practice, anyway? Well, let’s say, for example, Ted is a small business owner that sells upscale, designed umbrellas on his website. He has a few colorful designs, but he want to raise he prices in order to carry more choices of designer umbrellas. He also wants to sell a raincoat line and Tom wonders if his target customers will think it’s all too fancy.
In order to put his “feelers” out, Tom decides to incentivize a survey on his website asking questions from people who have previously purchased from him. All of the survey respondents will be entered into a raffle worth $100 on his website. Because of this, he gets over 200 responses. He’s able to ask the questions he needs about the potential product line he wants to add. When the response is overwhelmingly positive, he knows that the quantitative data he acquires is worth the wait.
Are you ready to get started? We have several Excel questionnaire templates available for download on this page as well as questionnaire templates for Word. They’re free to help you get started.
Or, alternatively, keep reading to learn more about how to put these templates to best use.
What Kinds of Surveys Work Best?
If you want to gather unique and powerful information about an audience, a survey can help you tailor your questions and gauge their reactions accordingly. The kind of information you are seeking will help you determine the type of surveys you want to put into motion.
Basically, there are three types of surveys that are used for research purposes. There are factual surveys, which are used to collect descriptive information, such as demographic information that is used by the government to collect data. Attitude surveys, often called opinion polls, attempt to collect and measure people’s attitudes and opinions. Explanatory surveys go a step further in seeking out opinions. They’re designed to test theories and hypothesis as well as form new theories.
Essentially, the type of survey or questionnaire you choose will be tailored to your project. If you’re looking to capture the attitudes of young voters across America, then you may want to offer multiple-choice questions to allow them to explain their levels of interest and involvement in certain issues.
Researchers usually use questionnaires to make data-driven generalizations about attitudes, opinions, and behaviors. Because of this, you must be very careful when choosing whom you will be surveying, such as your customers or donors. These carefully selected samples should reflect the diversity of your base in order to be as accurate as possible. In fact, most often, a survey therefore, the surveys are usually based on carefully selected samples.
There are also many types of questionnaire templates for Excel and Word that may fit your purposes. We have several templates available for free download on this page.
Questionnaire Examples

Choosing Your Template By The Questions Your Survey Asks
If you’re getting ready to design a questionnaire, you will want to know some of the basics about survey design. The type of questions you will be asking your participants will decide the design of your survey and questionnaires, in part. Keep in mind that a neat, clean document design is also important for practical purposes; after all, a disorganized survey can be a pain for both the participants as well as the researcher.
There are basically two kinds of questionnaires that are used by researchers. Closed or restricted form surveys, which simply ask “yes” or “no” answers, or multiple choice-type questions, are known for being fairly easy to interpret and summarize. The second type of questionnaire, called an open or unrestricted survey, allows respondents to answer freely as they see fit. While these types of surveys are great for learning in-depth about the users and their thoughts, they can also be difficult to interpret and summarize.
Restricted surveys will work great with our Excel Questionnaire templates, while you may choose a Microsoft Word questionnaire template to ask users open-ended questions.
Choosing Your Questions Carefully
A questionnaire template is only as good as the questions you are asking. Sometimes a survey will include what is essentially a “loaded question”, meant to skew the results one way or another. This is often used by biased news sources or politicians who want to portray a public opinion that aligns with their views. This is great for propaganda purposes, but for actual, scientifically sound research on opinions, you’ll want to use questions that can be answered in a way that will truly reflect the views of your respondents.
When writing out the questions you will ask, keep the following questions in mind for yourself:
- Is each question you’re asking truly necessary?
- How will the answers to the questions be used?
- How will the answers to your questionnaire be analyzed, and interpreted?
- How many questions are truly needed? (Anything over 10 may have a high drop-out rate)
- Do questionnaire respondents have the information/experience necessary to answer your questions?
- Is the question written in a clear way, with no bias or emotional overtones?
- Will the survey respondents feel comfortable answering the question honestly?
- Could the wording of the question possibly offend or put-off respondents?
- Are you going to ask direct or indirect questions?
- If a checklist is used , do you have a wide range of answers to choose from? Or are you forcing opinions on somebody?
- Is the answer to any of your questions likely to be influenced by prior questions you’ve asked? (If so, you may want to change the order up to keep participants from drawing conclusion.)
Your questionnaires should all be exactly alike, unless you’re testing the survey itself to see which one gets the most responses. Questionnaires used on a template should consist of the same set of questions, asked in the same order every time.
Questionnaire Samples
Getting the Answers and Responses You Need For Your Research
When conducting research, you can either have the participants fill out the surveys themselves, or you can have researchers interview participants over the phone or face-to-face.
If you’re having your respondents fill out the questionnaire, you may want to incentivize filling it out and returning it. Consider giving a coupon reward or holding a raffle for a gift certificate . Each person who returns their form by a certain date will get a chance at these rewards. Also consider which mode of deliver you find most useful.
Postal questionnaires can be used, but you’ll want to make sure you can count on the group returning their answers and to the researcher by a specified time and date. Telephone questionnaires can be set up to robocall, but most people find them annoying so they tend to be ineffective. You could also use your printed questionnaire to administer the questions to a group. For example, you may want to survey members of a certain club or organization. If you choose this option, be aware that groups tend to hold a bias when they fill out questionnaires in the same room together and tend to also have trouble concentrating on the task at hand when in the presence of their social circle.
Some forms of surveys will be done on the Internet with a link emailed to the questions. This is a very simple way to do our research. You can keep this data tabulated in a structured way by using an Excel questionnaire template, or you can choose to use a plain old pen and paper to tabulate your responses.
Another way to conduct surveys and questionnaires is to have the questions asked in a structured and formal way by an interviewer in a setting where each participant is interviewed one at a time. The greatest advantage of this type of research is that the interviewer can clarify any ambiguous-sounding questions and help if the respondent is confused in any way.
Why Are Questionnaires Better than Focus Groups?
Many marketers will use questionnaires and surveys to get vital information about their customer to use in their future marketing campaigns. Questionnaires are a great way to make audience segmentation easier; as long as you know which questions you need answer. They’re also much cheaper in comparison to other data-gathering methods.
Questionnaires and surveys are more economical than training interviewers and holding focus groups. Most focus groups will require some sort of compensation and there is always a chance of interview bias involved in them. Sometimes these groups can veer off-topic as well. For this reason, having respondents fill out their own surveys gives you, as a researcher, more control over the results and guaranteed answers to your question.
When you design your questionnaire in Word, you’ll want to pay attention to the uniformity of the questions. Through this, questionnaires may give you more data than most in=person meetings or interviews. You can still guide the readers toward an answer if you are not careful, but at least make sure that the questionnaires are uniform, asking the same questions, in the same order, in the same way. If the questions are highly structured, and you provide multiple choice answers, then the survey you are working with is standardize and therefore more likely to answer the deeper questions surrounding the research h you are doing.
Please keep in mind, when designing your surveys and using Word or Excel templates, that a random sampling is the best way to distribute a survey. By asking a random group of customers or people in a certain demographic or geographic area, you will be able to rule out biased samples. If you are using incentives to entice people to respond to your survey, then you should realize that some people might only be participating in your survey to get the “prize”. Because of this, your survey may fall short and have biased respondents who may not even be totally honest about their opinions.
What Factors Affect The Response Rate of Your Questionnaires?
There are several factors to keep in mind as you begin to fill out your survey or questionnaire templates. There are a few things that can affect the outcome of a mailing or other campaign asking a sampling of people to respond. Ask yourself the following questions before doing any mailing, postal or email :
- What is the length of the questionnaire? Is it too long and consuming for most people to answer? Keep it to one page or less than ten questions to optimize responses.
- What is the reputation of the business or organization sending out the survey? If you’re a political organization known for a right or left-leaning ideology, you will likely have people who oppose your ideology that may ignore your survey or skew it on purpose.
- Are the questions too complex or have you simplified them to eliminate any ambiguities?
- Are the questions on a subject that the respondent may find important? Can you change the wording to reflect more urgency? When a respondent feels that their opinion is truly needed and important, they are more likely to answer your questions.
- What time of year are you sending your surveys out? Think about the timing of your mailing in relation to national and religious holidays. Don’t send a survey out to parents in the middle of summer vacation. It will sit unopened if they are out of town.
- Are you asking questions that only your sampling group can answer? Don’t overlap with publicly available information such as demographic data that can be easily found in free government sources such as the census.
Get the Most Out Of Your Questionnaire and Survey Templates
A good questionnaire deals with a topic that the recipient will feel is important and has opinions on. Each survey you send out should have an accompanying letter that explains why it’s important to spend time completing it. For example, if you’re a nonprofit surveying the community to decide where you will allocate funds this year within the community, you should explain how the answers would shape new programs that will provide vital services. The importance of the answers should be stated clearly and the cover letter should make a compelling introduction to the needs you have for the information.
Are you ready to get started with your own survey or questionnaire? We have free Word and Excel templates ready for you to download and start customizing today.

More Templates
Mind Map Templates
Likert Scale Templates

Secret Santa Questionnaires
Behavior Charts

Ecomap Templates

Army Counseling Forms
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analysing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps:
- Determine who will participate in the survey
- Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person)
- Design the survey questions and layout
- Distribute the survey
- Analyse the responses
- Write up the results
Surveys are a flexible method of data collection that can be used in many different types of research .
Table of contents
What are surveys used for, step 1: define the population and sample, step 2: decide on the type of survey, step 3: design the survey questions, step 4: distribute the survey and collect responses, step 5: analyse the survey results, step 6: write up the survey results, frequently asked questions about surveys.
Surveys are used as a method of gathering data in many different fields. They are a good choice when you want to find out about the characteristics, preferences, opinions, or beliefs of a group of people.
Common uses of survey research include:
- Social research: Investigating the experiences and characteristics of different social groups
- Market research: Finding out what customers think about products, services, and companies
- Health research: Collecting data from patients about symptoms and treatments
- Politics: Measuring public opinion about parties and policies
- Psychology: Researching personality traits, preferences, and behaviours
Surveys can be used in both cross-sectional studies , where you collect data just once, and longitudinal studies , where you survey the same sample several times over an extended period.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Before you start conducting survey research, you should already have a clear research question that defines what you want to find out. Based on this question, you need to determine exactly who you will target to participate in the survey.
Populations
The target population is the specific group of people that you want to find out about. This group can be very broad or relatively narrow. For example:
- The population of Brazil
- University students in the UK
- Second-generation immigrants in the Netherlands
- Customers of a specific company aged 18 to 24
- British transgender women over the age of 50
Your survey should aim to produce results that can be generalised to the whole population. That means you need to carefully define exactly who you want to draw conclusions about.
It’s rarely possible to survey the entire population of your research – it would be very difficult to get a response from every person in Brazil or every university student in the UK. Instead, you will usually survey a sample from the population.
The sample size depends on how big the population is. You can use an online sample calculator to work out how many responses you need.
There are many sampling methods that allow you to generalise to broad populations. In general, though, the sample should aim to be representative of the population as a whole. The larger and more representative your sample, the more valid your conclusions.
There are two main types of survey:
- A questionnaire , where a list of questions is distributed by post, online, or in person, and respondents fill it out themselves
- An interview , where the researcher asks a set of questions by phone or in person and records the responses
Which type you choose depends on the sample size and location, as well as the focus of the research.
Questionnaires
Sending out a paper survey by post is a common method of gathering demographic information (for example, in a government census of the population).
- You can easily access a large sample.
- You have some control over who is included in the sample (e.g., residents of a specific region).
- The response rate is often low.
Online surveys are a popular choice for students doing dissertation research , due to the low cost and flexibility of this method. There are many online tools available for constructing surveys, such as SurveyMonkey and Google Forms .
- You can quickly access a large sample without constraints on time or location.
- The data is easy to process and analyse.
- The anonymity and accessibility of online surveys mean you have less control over who responds.
If your research focuses on a specific location, you can distribute a written questionnaire to be completed by respondents on the spot. For example, you could approach the customers of a shopping centre or ask all students to complete a questionnaire at the end of a class.
- You can screen respondents to make sure only people in the target population are included in the sample.
- You can collect time- and location-specific data (e.g., the opinions of a shop’s weekday customers).
- The sample size will be smaller, so this method is less suitable for collecting data on broad populations.
Oral interviews are a useful method for smaller sample sizes. They allow you to gather more in-depth information on people’s opinions and preferences. You can conduct interviews by phone or in person.
- You have personal contact with respondents, so you know exactly who will be included in the sample in advance.
- You can clarify questions and ask for follow-up information when necessary.
- The lack of anonymity may cause respondents to answer less honestly, and there is more risk of researcher bias.
Like questionnaires, interviews can be used to collect quantitative data : the researcher records each response as a category or rating and statistically analyses the results. But they are more commonly used to collect qualitative data : the interviewees’ full responses are transcribed and analysed individually to gain a richer understanding of their opinions and feelings.
Next, you need to decide which questions you will ask and how you will ask them. It’s important to consider:
- The type of questions
- The content of the questions
- The phrasing of the questions
- The ordering and layout of the survey
Open-ended vs closed-ended questions
There are two main forms of survey questions: open-ended and closed-ended. Many surveys use a combination of both.
Closed-ended questions give the respondent a predetermined set of answers to choose from. A closed-ended question can include:
- A binary answer (e.g., yes/no or agree/disagree )
- A scale (e.g., a Likert scale with five points ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree )
- A list of options with a single answer possible (e.g., age categories)
- A list of options with multiple answers possible (e.g., leisure interests)
Closed-ended questions are best for quantitative research . They provide you with numerical data that can be statistically analysed to find patterns, trends, and correlations .
Open-ended questions are best for qualitative research. This type of question has no predetermined answers to choose from. Instead, the respondent answers in their own words.
Open questions are most common in interviews, but you can also use them in questionnaires. They are often useful as follow-up questions to ask for more detailed explanations of responses to the closed questions.
The content of the survey questions
To ensure the validity and reliability of your results, you need to carefully consider each question in the survey. All questions should be narrowly focused with enough context for the respondent to answer accurately. Avoid questions that are not directly relevant to the survey’s purpose.
When constructing closed-ended questions, ensure that the options cover all possibilities. If you include a list of options that isn’t exhaustive, you can add an ‘other’ field.
Phrasing the survey questions
In terms of language, the survey questions should be as clear and precise as possible. Tailor the questions to your target population, keeping in mind their level of knowledge of the topic.
Use language that respondents will easily understand, and avoid words with vague or ambiguous meanings. Make sure your questions are phrased neutrally, with no bias towards one answer or another.
Ordering the survey questions
The questions should be arranged in a logical order. Start with easy, non-sensitive, closed-ended questions that will encourage the respondent to continue.
If the survey covers several different topics or themes, group together related questions. You can divide a questionnaire into sections to help respondents understand what is being asked in each part.
If a question refers back to or depends on the answer to a previous question, they should be placed directly next to one another.
Before you start, create a clear plan for where, when, how, and with whom you will conduct the survey. Determine in advance how many responses you require and how you will gain access to the sample.
When you are satisfied that you have created a strong research design suitable for answering your research questions, you can conduct the survey through your method of choice – by post, online, or in person.
There are many methods of analysing the results of your survey. First you have to process the data, usually with the help of a computer program to sort all the responses. You should also cleanse the data by removing incomplete or incorrectly completed responses.
If you asked open-ended questions, you will have to code the responses by assigning labels to each response and organising them into categories or themes. You can also use more qualitative methods, such as thematic analysis , which is especially suitable for analysing interviews.
Statistical analysis is usually conducted using programs like SPSS or Stata. The same set of survey data can be subject to many analyses.
Finally, when you have collected and analysed all the necessary data, you will write it up as part of your thesis, dissertation , or research paper .
In the methodology section, you describe exactly how you conducted the survey. You should explain the types of questions you used, the sampling method, when and where the survey took place, and the response rate. You can include the full questionnaire as an appendix and refer to it in the text if relevant.
Then introduce the analysis by describing how you prepared the data and the statistical methods you used to analyse it. In the results section, you summarise the key results from your analysis.
A Likert scale is a rating scale that quantitatively assesses opinions, attitudes, or behaviours. It is made up of four or more questions that measure a single attitude or trait when response scores are combined.
To use a Likert scale in a survey , you present participants with Likert-type questions or statements, and a continuum of items, usually with five or seven possible responses, to capture their degree of agreement.
Individual Likert-type questions are generally considered ordinal data , because the items have clear rank order, but don’t have an even distribution.
Overall Likert scale scores are sometimes treated as interval data. These scores are considered to have directionality and even spacing between them.
The type of data determines what statistical tests you should use to analyse your data.
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analysing data from people using questionnaires.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/surveys/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a likert scale | guide & examples.
Questionnaires and Surveys
- December 2015
- In book: Research Methods in Intercultural Communication: A Practical Guide (pp.163-180)

- Newcastle University
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Maelyn L. Salova
- Jenica R. Samperoy
- Hazel Mae C. Llorente
- Emma Marini

- Mthokozisi Luthuli

- Maria Ellul

- Yemi Omoniyi

- Josh Bernstein

- Ahmed Hamed Al Rahbi,
- Dr. Khaled Abdulrahman Al-Ahdal
- Moez Marrouchi
- Yanghong Hou

- J.T.E. Richardson

- Glynis M. Breakwell

- June Audrey True
- Alan Bryman
- Janet A. Harkenss

- Brad Edwards

- Mick P. Couper
- Roger Tourangeau
- Zoltan Dörnyei
- Dale T. Griffee
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

Research Questionnaire
Questionnaire generator.

When a researcher creates a research paper using the scientific method they will need to use a gathering method that is adjacent to the research topic. This means that the researcher will use a quantitative research method for a quantitive topic and a qualitative method for a qualitative one. The research questionnaire is one of the quantitative data-gathering methods a researcher can use in their research paper.
1. Market Research Questionnaire Template Example
- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Size: 38 KB
2. Market Research Questionnaire Example

Size: 94 KB
3. Research Questionnaire Example

4. Sample Market Research Questionnaire
Size: 35 KB
5. Research Survey Questionnaire

Size: 42 KB
6. Research Survey Questionnaire Construction

Size: 80 KB
7. Research Questionnaire Survey of Consumers

Size: 39 KB
8. Guide to the Design of Research Questionnaires

Size: 77 KB
9. Planning Survey Research Questionnaires

Size: 85 KB
10. Climate Change Survey Questionnaires
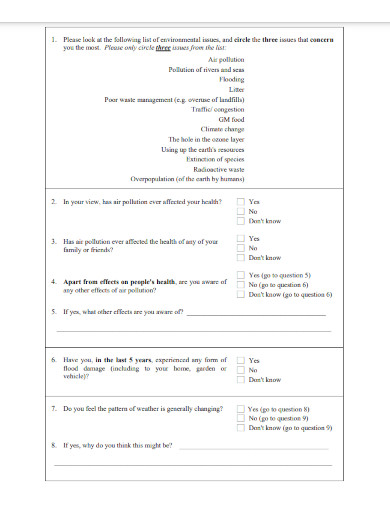
Size: 41 KB
11. Survey Questionnaire Design

Size: 96 KB
12. Developing Questionnaires for Educational Research

Size: 81 KB
13. Graudate Research Student Questionnaires

14. Sample Research Survey Questionnaires

Size: 46 KB
15. Market Research Questionnaire Example

16. Research Survey Questionnaire Example
17. Product X Research Study Questionnaire Example

What Is a Research Questionnaire?
A research questionnaire is a physical or digital questionnaire that researchers use to obtain quantitative data. The research questionnaire is a more in-depth version of a survey as its questions often delve deeper than survey questions .
How to Write a Research Questionnaire
A well-made research questionnaire can effectively and efficiently gather data from the population. Creating a good research questionnaire does not require that many writing skills , soft skills , or hard skills , it just requires the person to properly understand the data set they are looking for.
Step 1: Select a Topic or Theme for the Research Questionnaire
Begin by choosing a topic or theme for the research questionnaire as this will provide much-needed context for the research questionnaire. Not only that but the topic will also dictate the tone of the questions in the questionnaire.
Step 2: Obtain or Use a Research Questionnaire Outline
You may opt to use a research questionnaire outline or outline format for your research questionnaire. This outline will provide you with a structure you can use to easily make your research questionnaire.
Step 3: Create your Research Questionnaire
Start by creating questions that will help provide you with the necessary data to prove or disprove your research question. You may conduct brainstorming sessions to formulate the questions for your research questionnaire.
Step 4: Edit and Have Someone Proofread the Questionnaire
After you have created and completed the research questionnaire, you must edit the contents of the questionnaire. Not only that but it is wise to have someone proofread the contents of your questionnaire before deploying the questionnaire.
How does a research questionnaire help businesses?
A successful business or company utilizes research questionnaires to not only obtain data from their customers but also to gather data about the performance and quality of the employees in the business. The research questionnaire provides the business or company with actionable data, which they can use to improve the product, service, or commodity to obtain more customers.
Do I need to provide a consent form when I ask someone to answer the research questionnaire?
Yes, consent is very important as without this the data you have gathered from your questionnaires or surveys are useless. Therefore it is important to provide a consent form with your research questionnaire when you are asking a participant to answer the document.
What type of answers are allowed in the research questionnaire?
Research questionnaires can host a multitude of types of questions each with its specific way of answering. A questionnaire can use multiple-choice questions, open-ended questions, and closed questions. Just be sure to properly pace the questions as having too many different types of answering styles can demotivate or distract the target audience, which might lead to errors.
A research questionnaire is a data-gathering document people can use to obtain information and data from a specific group of people. Well-made and crafted research questionnaires will provide much-needed information one can use to answer a specific research question.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a fun quiz to find out which historical figure you're most like in your study habits
Design a survey to discover students' favorite school subjects and why they love them.

Assessing Research-Doctorate Programs: A Methodology Study (2003)
Chapter: appendix d: sample questionnaires.
Below is the uncorrected machine-read text of this chapter, intended to provide our own search engines and external engines with highly rich, chapter-representative searchable text of each book. Because it is UNCORRECTED material, please consider the following text as a useful but insufficient proxy for the authoritative book pages.
Appendix D Sample Questionnaires {These questionnaires are subject to further review and revision.) 1. Institutional Questionnaire 2. Program Questionnaire 3. Faculty Questionnaire 4. Student Questionnaires a. Questionnaire for Acimittecl-to-Cancliclacy Doctoral Students b. Questionnaire for Program Gracluates 105
106 Institutional Questionnaire To the institutional coordinator: This questionnaire is intended to collect data about university-provided resources that are available to all doctoral programs. Typically, the ideal respondent will be in the university's office of institutional research. Most of the questions apply to all programs. One, on laboratory space, applies only to the sciences (including some social sciences). In listing programs, please refer to the attached taxonomy and answer for those programs that are present at your institution. I. For the libraries at your institution: (Please enter the average over the past three years) a. What is the average size of your professional library staff in total FTEs? b. What is the average annual library budget? c. What is the average annual budget for acquisition of books? d. A, ~ What is the average annual budget for acquisition of: print journals electronic journals ? What is the average annual budget for microprint and electronic databases? 2. Is health care insurance available to graduate students uncler an institutional plan? Yes No a. If available, health care insurance is made available to: ~ Students only ~ Students end faculty b. If available, what is the level of institutional support? (Check all that apply) Institution covers premium costs for: Teaching assistants ~ Research assistants ~ All other full-time graduate students ~ Al] graduate students Institution covers partial premium costs for: Teaching assistants ~ Research assistants ~ All other full-time graduate students ~ All graduate students No institutional contribution for: ~ Teaching assistants ~ Research assistants ~ Other graduate students 3. Does the university provide childcare facilities that are available to graduate students? O Yes ~1 No a. If yes, is the cost subsidized by the institution? ~ Yes :] No b. If not, does the institution provide a listing of childcare providers to graduate students? O Yes ~ No 4. Is university-subsidized student housing available to doctoral students? :] Yes ~ No APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D If so, what is the percentage of the doctoral students who live in university-provided housing? 5. Are graduate students are unionized on your campus? ~ Yes ~ No If yes, ~ Some students ~ All students If yes, are teaching assistants unionized? ~ Yes ~ No If yes, ~ Some teaching assistants ~ All teaching assistants If yes, are research assistants unionized? ~ Yes ~ No If yes, ~ Some research assistants ~ All research assistants? 6. Which of the following apply to the doctoral program at the institutional level? a. The institution confers awards to honor graduate students for teaching and/or research. ~ Yes ~ No b. Awards are given to faculty for mentoring or other activities that promote scholarship of doctoral students. Yes ~ No c. The institution provides some form of travel support for doctoral students to attend professional meetings. ~ Yes ~ No d. There is an organized program at the institutional level to help doctoral students improve their teaching skills. ~ Yes ~ No e. The institution provides an office that assists doctoral students in learning about employment opportunities. ~ Yes ~ No 7. For the information displayed in the following table, please provide in a file sent by small to rdpilof~as~ed~ For the each doctoral program in science (including the social sciences) and engineering at your institution, what is the net assignable square feet (NASF) of research space dedicated to the program (exclude space that is used only for undergraduates)? Please use the same definitions for NASF and research space that are used in the NSF Survey of Scientific and Engineering Research Facilities. See "Taxonomy] for a list of the program iEelds in the study, and provide the information in the Emai! i ile for only those doctoral programs that are offered at your institution. 107
APPENDIX D Program #3 108 Program Research space NASF Shared space with other programs (Y/N) Program #1 Pro cram #2
APPENDIX D Background Information Program Questionnaire This information will enable the National Research Council to contact you if there are any questions about the data. It will also permit us to contact faculty for the purpose of administering a questionnaire to elicit reputational ratings and background! data ant! to contact students to obtain information about their perceptions of the practices and offerings ~ ~ ~ 1 of the doctoral program. Please note that in addition to the web questionnaire, we would like lists of faculty and previous employers to be sent to us via e-mail. Please indicate the doctoral program to which the following information applies 1. Please provide the name and e-mai! address of the program respondent who will serve as the primary contact with the graduate oro cram. Name: Title: E-mail address: Mailing Address: State Zip Cocle- If this is an interdisciplinary program, please list the departments affiliated with the program. For each individual identified in questions 2 and 3, please provide in a file sent by emai! to rdpilot~)nas.~du the information displayed in the table for the question. Program Faculty: For each faculty member or senior research fellow or associate who participates in your doctoral program by directing theses, serving on doctoral committees, or teaching graduate courses, please provide the following information. Name Rank Highest Gender Race/ US Citizen or Tenure E-mail l | Degree | (M or F) | Ethn city | Permanent | Status | Addres (Y/N) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 = Faculty Employment History: For each faculty member listed in Question 2 who joined your program within the past five years, please provide the institution, company, or organization where he or she was employed immediately before joining your institution. pros
110 Name Prior employer Position at that employer 4. For the doctoral students in your program, please provide the number of students that fall into each of the following categories. a. Total number of students: b. Status: Full-time Part-time Unknown c. Gentler: Male Female Unknown d. Citizenship: U.S. Permanent Resilient Temporary Visa Unknown cI. Race/Ethnicity (if U.S. citizen or Permanent Residents) American Indian or Alaskan Native Asian or Pacific Islander Black White Hispanic Mexican American Puerto Rican Other Multiracial Unknown e. Percentage of doctoral students with master's degree Program Information 5. Does your program have a mission statement? If so, what is the mission statement? (50 words or less) ~ Yes :] No If there are particular areas of research emphasis in your doctoral program, please choose from the subfields in ETaxonomy]: APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D 6. How many Ph.D.s have been awarded in the program in each of the past five years? (Note: Years span from July ~ to June 30) 2001-02 2000-01 1999-00 1998-99 1997-98- 7. For each of the academic years listed in the following table, enter the number of students who entered the program in the year and the number who completed their degrees in 4, 6, or 8, years or are still in the program. (Note: Years span from July 1 to June 30) Entering Number Student of Academic Entering Year Cohort Doctoral Students 1992 1993 1993-1994 1994-1995 1995-1996 1996-1997 1997-1998 1998-1999 1999-2000 2000-2001 2001-2002 Number of Students admitted to candidacy by the end of the 4th year of enrollment Of those admitted to candidacy, number who complete within 4 years Of those admitted to candidacy, number who complete within 6 years Of those admitted to candidacy, number who complete within 8 years Of those admitted to candidacy, how many are still enrolled after 8 years? . I_ 7a. Averaged over the past three years, what percent of entering students withdrew from the program before completing two years of study? % 7b. Averaged over the past three years, what has been the median time to degree for those who completed the program? (Note: the median time is the number of years it takes half of the number of students from the same entering year who are admitted to candidacy to complete their degree.) 8. Is a master's degree required of students prior to admission to your program? ~ Yes ~ No 9. What proportion of your full-time first-year doctoral students receive full support throughout their first year (tuition and an adequate living allowance provided as stipend or salary in program related work (TA or RA)?
112 10. How many years of full financial support could students entering your doctoral program expect to receive from your institution or an external source? 1. Over the past five years approximately what fraction of the first-year students in your program received financial support either from your institution or from extramural grants or fellowships? Tuition only Tuition and stipend- Stipend only- 12. What proportion of currently enrolled doctoral students in your program (included in multiple categories if appropriate) are currently supported by: Externally funded fellowships: Externally funded traineeships: Externally funded research assistantships: University funded teaching assistantships: University funded research assistantships: University funded tuition waivers, fellowships, or stipends: 13. Averaged over the past three years, what are the average and minimum GRE scores for students accepted into the program? Average Verbal GRE: Minimum Verbal GRE: Average Quantitative GRE: Minimum Quantitative GRE: Do you require GRE subject scores for all students entering the program? ~ Yes ~ No 14. In each of the last three academic years, how many students did you accept into your doctoral program, and how many enrolled? 2000-2001 2001 -2002 2002-2003 Accepted Enrolled 15. What percentage of the doctoral students in your program have individually assigned workspaces for their exclusive use? TAs RAs All students 16. On average, how many courses per term is each graduate teaching assistant in the program expected to teach or assist a faculty member in teaching? With sole responsibility As an Assistant to a faculty member 17. Which of the following apply to your doctoral program? APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D a. The program confers awards to honor graduate students for teaching and/or research. ~ Yes ~1 No b. Awards are given to faculty for mentoring or other activities that promote scholarship of doctoral students. ~ Yes :] No The program provides some form of travel support for doctoral students to attend professional meetings. ~ Yes ~ No d. There is an organized program to help doctoral students improve their teaching skills. ~ Yes n No e. The program provides organized assistance to help doctoral students explore employment opportunities. Yes ~1 No 8. List up to 5 institutions with which your program normally competes for graduate students: Institution # 1 Institution #2- Institution #3 Institution #4 Institution #5 1 9. Does your program collect data about employment outcomes for your graduates? ~ Yes ~ No If yes, do you provide potential applicants with this information? ~ Yes ~ No 20. Please list those interdisciplinary centers in which doctoral students from your program participate (conduct research or teach). ~3
114 Faculty Questionnaire This questionnaire is part of the National Research Council's Pilot Test of the Assessment of Research Doctoral Programs. Your university has volunteered to participate in this pilot test to assist the National Research Council's study of the methodology used to assess doctoral programs. Further information about the methodology study may be found at www7.nationalacademies.org/resdoc/index.html You have been selected to receive this questionnaire because you are a member of the faculty who participates in the education of doctoral students at your university. This means that you either teach courses to doctoral students or supervise their dissertations. If this is not the case, please indicate that in question 1. The assessment of research doctoral programs is conducted approximately every ten years and consists of a reputational survey of doctoral programs and the collection of data about doctoral faculty and students in f~fty-seven areas of study. This questionnaire provides information that will assist the study in a number of ways: licit will help us construct a pool from which to select raters for the reputational survey; 2)it will provide us enough information about you that we can collect data on grants, citations, and publications from other sources; and Hit will permit a statistical description of the faculty in the graduate program or programs with which you are affiliated. Your answers will be treated as completely confidential by the National Research Council and will only be released as part of a statistical analysis. I. Program Identification a. Do you supervise dissertations, serve on doctoral committees, or teach graduate courses in a doctoral program? ~ Yes ~ No If your answer was "No", you do not need to complete the rest of the questionnaire. b. From the pulldown list, please choose the program of your primary affiliation/appointment tPull Down List of Res-Doc Programs] If you have difficulty locating your program on the list, please refer to the "Taxonomy] list with fields and subfields Please list all programs in which you supervise dissertations, serve on dissertation committees, or teach graduate courses and the average percentage of your time during the past year that you spent in all activities for each program with which you are associated. (Do not list programs where you are an outside reader.) Program Supervise dissertations Teach courses Serve on Percent of time spent in all (YIN) (YIN) dissertation activities for this program committees (YIN) ~ (total= IJ0%) ~ d. For the articles and books that you have published in the past five years, please list what fields you have published in Table 1. If you have a single publication that spans multiple fields, please indicate them and their fields in Table 2. APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D Table 1: Books and articles in a single field published in the past 3 years Field(see Taxonomy) ~ Articles ~ Books 1 1 ~ ' 1 1 1 Table 2: Books and articles in multiple fields published in the past 3 years Field (Enter all that apply) Articles Books II. Current Employment a. Department affiliation: b. Rank: ~ Instructor ~ Assistant Professor ~ Associate Professor ~ FullProfessor ~ Other c. Tenure status: ~ Tenure-track, not tenured Tenured ~ Non-tenure-track d. Year first employed at current institution: tIf employment was not continuous, please list year of most recent appointment at this institution.] Have you received an extramural grant or contract support in the past year? Yes ~ No f. Subfields of current research interest (refer to "Taxonomy] with subfields): Subfield # 1: Subfield #2: Subfield #3: g. Do you consider part of your research to be interdisciplinary? ~ Yes ~ No If so, what is the area of that research? h. Under what names or variants of your name have you published books or articles? III. Prior Experience What was your status prior to your current position? ~ Student ~ Postdoc ~ Faculty. ~ Other: Previous employer: Address: 115
116 IV. Educational Background City Title: Employment Sector: Industry (for profit) National laboratory State or local government Federal government agency International agency 4-year college or university 2-year college K- 12 school Hospital or clinic Foundation or nonprofit Military Other (specify: State/Country Zip Code- a. Highest degree earned: ~ Bachelor's ~ Master's ~ Ph.D. ~ Professional (M.D., J.D., D.V.M., for example) b. Institution that conferred highest degree: c. Field of highest degree: Other: d. Year of highest degree: tPulldown List] To what extent does the field of your current research, teaching, or professional activities differ from the field of your highest degree? ~ Very similar ~ Somewhat similar ~ Very different V. Demographic Information a. Date of birth: b. Gender: c. Citizenship Male Female U.S. Permanent Resident Temporary Visa (mmlddlyy) d. Race/Ethnicity (if U.S. citizen or permanent resident) American Indian or Alaskan Native Asian or Pacific Islander Black White APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D Hispanic (I Mexican American, ~ Puerto Rican, ~ Other) ~ Multiracial VI. Please provide your preferred e-mai! address (where you can be reached if there are questions.) Thank you for your time. ~7
118 Questionnaire for Admitted-to-Candidacy Doctoral Students This questionnaire is part of the National Research Council's Pilot Test of the Assessment of Research Doctoral Programs. Your university has volunteered to participate in this pilot test to assist the National Research Council's study of the methodology used to assess doctoral programs. One innovation we are considering is adding student responses about the educational processes of the program. We believe that students' input is important to improving the quality of the educational experience. Further information about the methodology study may be found at www7.nationalacademies.org/resdoc/index.htm! You have been selected to receive this questionnaire because you are a student who has completed over half of your doctoral program. If this is not the case, please indicate that in question 1. The assessment of research doctoral programs is conducted approximately every ten years and consists of a reputational survey of doctoral programs and the collection of data about doctoral faculty and students in fifty-four areas of study. This questionnaire will provide information that will assist the study in a number of ways: 1) it will provide a statistical description of students in your program; 2) it will provide information about practices in your program; and 3) it will help future students in the selection of graduate programs. Your answers will be treated as completely confidential by the National Research Council and will only be released as part of a statistical analysis. Individual answers will not be shared with faculty or administrators of your doctoral program except in aggregated form. Institution: Doctoral Program: Educational Program A. Year of enrollment in this doctoral program: B. Year you expect to receive your doctorate: C. Did you (or will you) receive a master's degree before this doctorate? ~ Yes ~ No D. Did you (or will you) receive a master's degree in your doctoral field as part of your training? ~ Yes ~ No Ifyes,didyouwritea master's thesis? ~ Yes ~ No E. During the course of your study for the Ph.D. will you also receive any of the following as part of a joint, concurrent, or combined degree program: Professional doctorate (e.g., MD, DDS, OD, JD)? ~ Yes Professional master's (e.g., MBA, MPA, MPH)? ~ Yes No ~ No F. During the course of your study for the Ph.D. will you also receive a certificate in another field? ~ Yes ~ No APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D G. What were your career goals at the time you entered graduate school? Check all that apply] U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University ~ 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: Non-U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: ~ Unknown H. What are your current career plans? tcheck all that apply] U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University ~ 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: Non-U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: ~ Unknown I. Of the following sources of support, which have been your primary sources during your doctoral studies? (Check the three largest) I. ~ Personal/family funds 2. ~ Research Assistant (RA) 3. ~ Teaching Assistant (TA) 4. ~ Training grant 5. ~ Fellowship 6. ~ Loans 7. ~ Concurrent employment related to your degree 8. ~ Concurrent employment unrelated to your degree 2. Program Characteristics A. Professional Development I. During your doctoral program have you received (or will you receive) instruction, practice or professional development training in: a. Oral communication and presentation skills: ~ Yes ~ No b. Writing proposals for funding: ~ Yes ~ No c. Preparing articles for publication: ~ Yes ~ No d. Working in collaborative groups: ~ Yes ~ No Conducting independent research/scholarship:~ Yes ~ No f. Project management ~ Yes ~ No g. Research / professional ethics ~ Yes ~ No h. Speaking to nonacademic audiences ~ Yes n No 119 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
120 2. In your doctoral program did you have an opportunity to obtain teaching experience? Check the typets) of teaching experience you have had: a. mentoring a high school student b. mentoring an undergraduate student c. grading papers for undergraduate or graduate courses d. leading discussion sections of undergraduate or graduate courses e. leading laboratory sections of undergraduate or graduate courses f. lecturing in undergraduate or graduate courses g. tutoring undergraduates If you have had teaching experience, please answer the following, h. ~ received formal instruction in leaching. ~ Yes ~ No i. {received formal supervision end evaluation. ~ Yes ~ No j. ~ had opportunities to teach in a variety of academic environments. ~ Yes ~ No B. Program Environment 1. Does your program provide an annual or more frequent assessment of your progress? 2. Do you receive timely feedback on your research! 1 - - - - - _ Yes ~ No ~ Yes ~ No 3. Do you have access to career advice covering a variety of employment sectors? Yes ~ No ~ Yes ~ No a. If yes, are you encouraged to use it? 4. Do you have one or more faculty members at your institution that you consider mentors (i.e., individuals from whom you seek advice about your education, career development, and other matters of concern to you as a graduate student)? ~ Yes ~ No 5. How would you rate the quality of teaching by faculty in your program? ~ Excellent ~ Good ~ Fair ~ Poor 6. How would you rate the quality of your research experience? Excellent ~ Good ~ Fair ~ Poor 7. How would YOU rate the curriculum of your Ph.D. program? ~ Excellent ~ Good S. How would you rate the overall quality of your program _ ~ O ~ Fair ~ Poor ~ , , ~ ~ Excellent ~ Good ' ' ~ ~ ~ Lair ~ Poor 9. How would YOU rate the intellectual liveliness of your pro cram? ~ Excellent ~ Good 10. Considering the overall intellectual environment of your university, how much do you fee! you have benei ited from it? ~ A lot ~ Some APPENDIX D , - - ~ o n Fair n Poor ~ A little ~ Not at all
APPENDIX D C. Infrastructure I. Does your program give you access to: a. Your own personal work space b. Computer facilities Yes ~ No ~ Yes ~ No c. Other research facilities; if so, describe: 2. Does your program provide adequate space for interaction among students? C] Yes O No 3. Are the library resources available to you adequate to support your research and education? ~ Yes C] No D. Research productivity I. How many research presentations (including poster presentations) have you made at research conferences a. on your campus? b. at national or regional meetings? 2. How many research publications have you authored or co-authored during your cloctoral studies (include pieces accepted for publication but not yet published)? a. Refereed articles b. Book chapters c. Reviews d. Books or edited volumes 3. Background information A. Date of birth: (mm/~/yy) B. Gender: ~ Male n Female C. Citizenship U.S. Permanent Resident Temporary Visa D. Race/Ethnicity (if U.S. citizen) American Indian or Alaskan Native Asian or Pacific Islander Black White Hispanic Mexican American, ~ Puerto Rican, ~ Other) ~ Multiracial E. Dependent care responsibilities: 1. Number of children living with you: Age 6 or under Over age 6 3. Parents or other dependents ~ Yes ~ No 121
122 APPENDIX D G. Marital Status: Do you have a spouse or partner who lives with you? ~ Yes ~ No F. Level of Parents' Education: Mother Father High school diploma or less Some college/Bachelor's degree Advanced degree
APPENDIX D Five-Seven Years Post-Ph.D Questionnaire This questionnaire is part of the National Research Council's Pilot Test of the Assessment of Research Doctoral Programs. Your university has volunteered to participate in this pilot test to assist the National Research Council's study of the methodology used to assess doctoral programs. One innovation that we are considering is to add student responses to questions about the educational process of the program. Further information about the methodology study may be found at www7.nationalacademies. org/resdoc/index.html You have been selected to receive this questionnaire because you are a student who has received a Ph.D. from this program five to seven years ago. If this is not the case, please indicate that in question 1. ~ 4, , I, The assessment of research doctoral programs is conducted approximately every ten years and consists of a reputational survey of doctoral programs and the collection of data about doctoral faculty and students in fifty-four areas of study. This questionnaire provides information that will assist the study in a number of ways: 1) it will help us learn whether a high enough percentage of students respond so that we can add student observations to the larger study; 2) it will provide us enough information about practices in your program that we can compare the practices of graduate programs in your field at different universities; and 3) it will permit a statistical description of the f~rst-year students in the graduate program. Your answers will be treated as completely confidential by the National Research Council and will only be released as part of a statistical analysis. Individual answers will not be shared with faculty or administrators of your former doctoral program except in aggregated form. Educational Program a. Name of the program where you received your Ph.D. degree: b. Year of enrollment in the above Ph.D. program: c. Year you received your Ph.D.: d. Did you receive a master's degree at this institution before this Ph.D.? ~ Yes ~ No e. Were you enrolled as a full-time student throughout your Ph.D. program? ~ Yes ~ No f. Did you attend graduate school prior to enrollment in the above Ph.D. program? ~ Yes ~ No If so, what degrees or certificates, if any, do you hold? ~ Certificate ~ Master's ~ Doctoral ~ Professional g. What was your career goal when you completed your Ph.D.? U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: 123
124 Non-U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: ~ Unknown h. Have your career goals changed since you received your Ph.D.? ~ Yes ~ No i. During your Ph.D. program, were you supported by funds from outside the institution? ~ Yes ~ No (Check all that apply) Type: ~ Fellowship ~ Training Grant ~ Research Grant ~ Your employer ~ Other(Specify: ! J. Did you receive institutional support? ~ Yes ~ No (Check all that apply) Type: ~ Teaching Assistantship ~ Research Assistantship ~ Fellowship ~ Tuition scholarship or waiver only ~ Loan ~ None ~ Other(Specify: ! 2. Employment and Career Status a. First employer or place of postdoctoral study after Ph.D. completion: Name: Address: City State/Country Zip Code- Title: b. Employment Sector: Industry (for profit) National laboratory State or local government Federal government agency International agency University 4-year college 2-year college K-12 school Hospital or clinic Foundation or nonprofit Military Other (specify) APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D c. If you hold or have held a postdoctoral position or positions, how many , and at what institutions, companies or government agencies were they located? List chronologically starting with the most recent. Position # 1: Position#2: Position # 3: Position#4: Dates: Dates: Dates: Dates: d. Current employer: Name: Address: City State/Country Zip Code- Title: e. Current Employment Sector: Industry (for profit) National laboratory State or local government Federal government agency International agency University 4-year college 2-year college K-12 school Hospital or clinic Foundation or nonprofit Military ~ Other (specify) 3. Ph.D. Program Characteristics a. During your Ph.D. education, in which of the following areas was training PROVIDED, which skills or experiences have you USED since graduation, and which area do you wish you had learned MORE about? (check all that apply) 1) Teaching experiemce 2) Oral communication; presentation skills 3) Writing proposals for funding 4) Manuscript preparation Provided Provided Provided Provided Experience working in collaborative groups ~ Provided 6) Critical analysis 7) Locating and applying information 125 Used ~ More Used ~ More Used ~ More Used ~ More Provided Provided Used ~ More Used ~ More Used ~ More
26 8) Experience working with people of varied educational levels ~ Provided ~ Used ~ More 9) Experience working with people from diverse backgrounds ~ Provided ~ Used ~ More 10) Experience working in teams b. Research Productivity Provided ~ Used ~ More How many books or edited books have you published or are currently accepted for publication? 2) How many articles or book chapters have you published or are currently accepted for publication? 3) How many books or articles have you reviewed for publication? 4) How many reviews, enumerated in 3), have been or will be published? 5) How many refereed papers have you or a coauthor presented at professional conferences? How many awards have you received? (Respond to all categories.) a) For teaching: b) For research: From professional societies: From your institution or employer: 7) How many patents or licenses have you received? 8) How many grants have you received from your employer or institution? 9) How many grants have you received from extramural funding agencies? 4. Background Information a. Date of birth: b. Gender: c. Citizenship APPENDIX D Male Female U.S. Permanent Resident Temporary Visa (mmlddlyy)
APPENDIX D 127 d. Race/Ethnicity (ifU.S. citizen) American Indian or Alaskan Native Asian Pacific Islander Black White Hispanic (~ Mexican American, ~ Multiracial e. Martial Status ~ Married ~ Single f. Number of Children: Age 6 and under Over age 6 g. Level of Parents' Education: Less than high school High school diploma Some college Bachelor's degree Master's degree Professional degree Doctoral degree h. Is English your first language? Mother Yes ~ No Puerto Rican, ~ Other) Father
How should we assess and present information about the quality of research-doctorate programs? In recommending that the 1995 NRC rankings in Assessing the Quality of Research-Doctorate Programs: Continuity and Change be updated as soon as possible, this study presents an improved approach to doctoral program assessment which will be useful to administrators, faculty, and others with an interest in improving the education of Ph.D.s in the United States. It reviews the methodology of the 1995 NRC rankings and recommends changes, including the collection of new data about Ph.D. students, additional data about faculty, and new techniques to present data on the qualitative assessment of doctoral program reputation. It also recommends revision of the taxonomy of fields from that used in the 1995 rankings.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on June 22, 2023. A questionnaire is a list of questions or items used to gather data from respondents about their attitudes, experiences, or opinions. Questionnaires can be used to collect quantitative and/or qualitative information. Questionnaires are commonly used in market research as well as in the social and health sciences.
A questionnaire is defined a market research instrument that consists of questions or prompts to elicit and collect responses from a sample of respondents. This article enlists 21 questionnaire templates along with samples and examples. It also describes the different types of questionnaires and the question types that are used in these questionnaires.
A research questionnaire is a tool that consists of a series of standardized questions with the intent of collecting information from a sample of people. Think of it as a kind of written interview that follows a fixed scheme to ensure that data remains accurate.
The questionnaire is a tool widely used for data collection compared to interview and observation in empirical research; this study used Closed (multiple choice) and Open (descriptive) questions ...
Question and Questionnaire Design Jon A. Krosnick and Stanley Presser The heart of a survey is its questionnaire. Drawing a sample, hiring, and training interviewers and supervisors, programming computers, and other preparatory work is all in service of the conversation that takes place between researchers and respondents.
There are several modes of questionnaire administration. The choice of mode depends on the research objectives, sample size, and available resources. Some common modes of administration include: Self-administered paper questionnaires: Participants complete the questionnaire on paper, either in person or by mail. This mode is relatively low cost ...
Filter by survey type. All our sample survey template questions are expert-certified by professional survey methodologists to make sure you ask questions the right way-and get reliable results. You can send out our templates as is, choose separate variables, add additional questions, or customize our questionnaire templates to fit your needs.
Designing a Questionnaire for a Research Paper: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Develop an Effective Questionnaire . Hamed Taherdoost . University Canada West, Vancouver, Canada . E-mail: [email protected] . Abstract - A questionnaire is an important instrument in a research study to help the researcher collect relevant data
Designing a Questionnaire for a Research Paper: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Develop an Effective Questionnaire Hamed Taherdoost To cite this version: Hamed Taherdoost. ... , you need to conduct the survey using a small number of participants as the target sample. The number of participants can vary; however, commonly, between 15 to 30 ...
Getting Started + Tips. How to make a questionnaire: Keep questions short and focused on one topic at a time. Use multiple-choice questions to fit answers into a specific category. Use an open-ended question to capture comments. A Likert scale or MaxDiff question can be used for market research. Collect responses for your questionnaire using an ...
Consider your question wording and order. - how you ask your questions and the order in which they appear is important. Later, we discuss in more detail how to work with wording and detail to maximize your respondents' motivation and your survey's response rate. 6. Determine your survey's length and format.
A questionnaire is a research tool that contains a series of questions used to gain information from respondents about their opinions, experiences, and behaviors. Questionnaires may elicit quantitative or qualitative data and be delivered online, by phone, on paper, or in person. First developed by Sir Francis Galton, a British anthropologist ...
Research questionnaires are vital tools for gathering data and insights in various fields. This comprehensive guide explores how to design and use them effectively. Whether you are working on Sample Questionnaires or Medical Questionnaires, understanding the principles of good questionnaire design can significantly impact your research outcomes.
However, the quality and accuracy of data collected using a questionnaire depend on how it is designed, used, and validated. In this two-part series, we discuss how to design (part 1) and how to use and validate (part 2) a research questionnaire. It is important to emphasize that questionnaires seek to gather information from other people and ...
Writing Survey Questions. Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions.
A questionnaire is a powerful tool that provides the important function of eliciting the feelings, beliefs, perceptions, or attitudes of a group of individuals. In other words, to collect valuable and previously unknown data. The questionnaire is most frequently a very concise, preplanned set of questions designed to yield specific information ...
Revised on 10 October 2022. A questionnaire is a list of questions or items used to gather data from respondents about their attitudes, experiences, or opinions. Questionnaires can be used to collect quantitative and/or qualitative information. Questionnaires are commonly used in market research as well as in the social and health sciences.
A questionnaire, where a list of questions is distributed by post, online, or in person, and respondents fill it out themselves; An interview, where the researcher asks a set of questions by phone or in person and records the responses; Which type you choose depends on the sample size and location, as well as the focus of the research ...
ChapterPDF Available. Questionnaires and Surveys. December 2015. December 2015. DOI: 10.1002/9781119166283.ch11. In book: Research Methods in Intercultural Communication: A Practical Guide (pp.163 ...
The research questionnaire is one of the quantitative data-gathering methods a researcher can use in their research paper. 1. Market Research Questionnaire Template Example. Details. File Format. Size: 38 KB. Download. 2. Market Research Questionnaire Example.
118 Questionnaire for Admitted-to-Candidacy Doctoral Students This questionnaire is part of the National Research Council's Pilot Test of the Assessment of Research Doctoral Programs. Your university has volunteered to participate in this pilot test to assist the National Research Council's study of the methodology used to assess doctoral programs.