
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

How to write a speech that your audience remembers
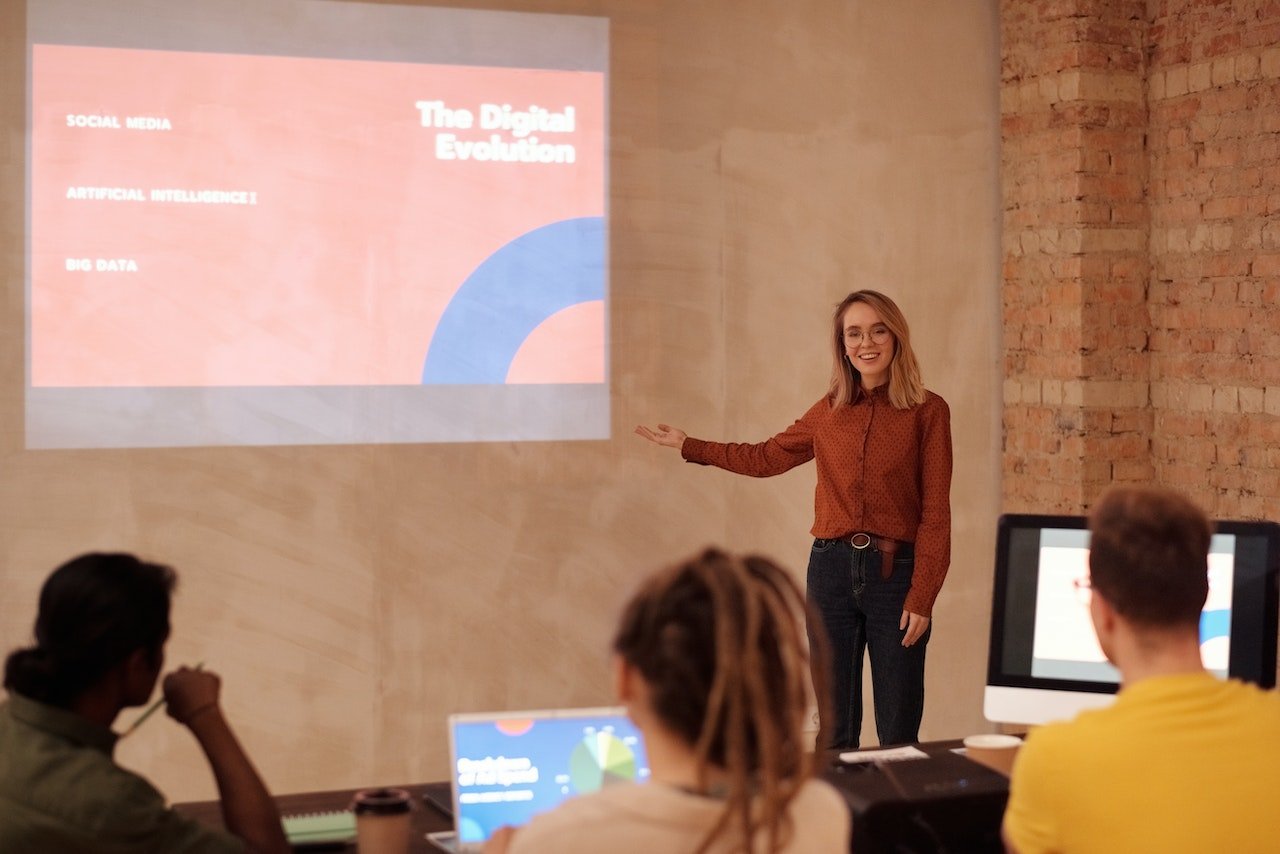

Whether in a work meeting or at an investor panel, you might give a speech at some point. And no matter how excited you are about the opportunity, the experience can be nerve-wracking .
But feeling butterflies doesn’t mean you can’t give a great speech. With the proper preparation and a clear outline, apprehensive public speakers and natural wordsmiths alike can write and present a compelling message. Here’s how to write a good speech you’ll be proud to deliver.
What is good speech writing?
Good speech writing is the art of crafting words and ideas into a compelling, coherent, and memorable message that resonates with the audience. Here are some key elements of great speech writing:
- It begins with clearly understanding the speech's purpose and the audience it seeks to engage.
- A well-written speech clearly conveys its central message, ensuring that the audience understands and retains the key points.
- It is structured thoughtfully, with a captivating opening, a well-organized body, and a conclusion that reinforces the main message.
- Good speech writing embraces the power of engaging content, weaving in stories, examples, and relatable anecdotes to connect with the audience on both intellectual and emotional levels.
Ultimately, it is the combination of these elements, along with the authenticity and delivery of the speaker , that transforms words on a page into a powerful and impactful spoken narrative.
What makes a good speech?
A great speech includes several key qualities, but three fundamental elements make a speech truly effective:
Clarity and purpose
Remembering the audience, cohesive structure.
While other important factors make a speech a home run, these three elements are essential for writing an effective speech.
The main elements of a good speech
The main elements of a speech typically include:
- Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your speech and grabs the audience's attention. It should include a hook or attention-grabbing opening, introduce the topic, and provide an overview of what will be covered.
- Opening/captivating statement: This is a strong statement that immediately engages the audience and creates curiosity about the speech topics.
- Thesis statement/central idea: The thesis statement or central idea is a concise statement that summarizes the main point or argument of your speech. It serves as a roadmap for the audience to understand what your speech is about.
- Body: The body of the speech is where you elaborate on your main points or arguments. Each point is typically supported by evidence, examples, statistics, or anecdotes. The body should be organized logically and coherently, with smooth transitions between the main points.
- Supporting evidence: This includes facts, data, research findings, expert opinions, or personal stories that support and strengthen your main points. Well-chosen and credible evidence enhances the persuasive power of your speech.
- Transitions: Transitions are phrases or statements that connect different parts of your speech, guiding the audience from one idea to the next. Effective transitions signal the shifts in topics or ideas and help maintain a smooth flow throughout the speech.
- Counterarguments and rebuttals (if applicable): If your speech involves addressing opposing viewpoints or counterarguments, you should acknowledge and address them. Presenting counterarguments makes your speech more persuasive and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Conclusion: The conclusion is the final part of your speech and should bring your message to a satisfying close. Summarize your main points, restate your thesis statement, and leave the audience with a memorable closing thought or call to action.
- Closing statement: This is the final statement that leaves a lasting impression and reinforces the main message of your speech. It can be a call to action, a thought-provoking question, a powerful quote, or a memorable anecdote.
- Delivery and presentation: How you deliver your speech is also an essential element to consider. Pay attention to your tone, body language, eye contact , voice modulation, and timing. Practice and rehearse your speech, and try using the 7-38-55 rule to ensure confident and effective delivery.
While the order and emphasis of these elements may vary depending on the type of speech and audience, these elements provide a framework for organizing and delivering a successful speech.

How to structure a good speech
You know what message you want to transmit, who you’re delivering it to, and even how you want to say it. But you need to know how to start, develop, and close a speech before writing it.
Think of a speech like an essay. It should have an introduction, conclusion, and body sections in between. This places ideas in a logical order that the audience can better understand and follow them. Learning how to make a speech with an outline gives your storytelling the scaffolding it needs to get its point across.
Here’s a general speech structure to guide your writing process:
- Explanation 1
- Explanation 2
- Explanation 3
How to write a compelling speech opener
Some research shows that engaged audiences pay attention for only 15 to 20 minutes at a time. Other estimates are even lower, citing that people stop listening intently in fewer than 10 minutes . If you make a good first impression at the beginning of your speech, you have a better chance of interesting your audience through the middle when attention spans fade.
Implementing the INTRO model can help grab and keep your audience’s attention as soon as you start speaking. This acronym stands for interest, need, timing, roadmap, and objectives, and it represents the key points you should hit in an opening.
Here’s what to include for each of these points:
- Interest : Introduce yourself or your topic concisely and speak with confidence . Write a compelling opening statement using relevant data or an anecdote that the audience can relate to.
- Needs : The audience is listening to you because they have something to learn. If you’re pitching a new app idea to a panel of investors, those potential partners want to discover more about your product and what they can earn from it. Read the room and gently remind them of the purpose of your speech.
- Timing : When appropriate, let your audience know how long you’ll speak. This lets listeners set expectations and keep tabs on their own attention span. If a weary audience member knows you’ll talk for 40 minutes, they can better manage their energy as that time goes on.
- Routemap : Give a brief overview of the three main points you’ll cover in your speech. If an audience member’s attention starts to drop off and they miss a few sentences, they can more easily get their bearings if they know the general outline of the presentation.
- Objectives : Tell the audience what you hope to achieve, encouraging them to listen to the end for the payout.
Writing the middle of a speech
The body of your speech is the most information-dense section. Facts, visual aids, PowerPoints — all this information meets an audience with a waning attention span. Sticking to the speech structure gives your message focus and keeps you from going off track, making everything you say as useful as possible.
Limit the middle of your speech to three points, and support them with no more than three explanations. Following this model organizes your thoughts and prevents you from offering more information than the audience can retain.
Using this section of the speech to make your presentation interactive can add interest and engage your audience. Try including a video or demonstration to break the monotony. A quick poll or survey also keeps the audience on their toes.
Wrapping the speech up
To you, restating your points at the end can feel repetitive and dull. You’ve practiced countless times and heard it all before. But repetition aids memory and learning , helping your audience retain what you’ve told them. Use your speech’s conclusion to summarize the main points with a few short sentences.
Try to end on a memorable note, like posing a motivational quote or a thoughtful question the audience can contemplate once they leave. In proposal or pitch-style speeches, consider landing on a call to action (CTA) that invites your audience to take the next step.

How to write a good speech
If public speaking gives you the jitters, you’re not alone. Roughly 80% of the population feels nervous before giving a speech, and another 10% percent experiences intense anxiety and sometimes even panic.
The fear of failure can cause procrastination and can cause you to put off your speechwriting process until the last minute. Finding the right words takes time and preparation, and if you’re already feeling nervous, starting from a blank page might seem even harder.
But putting in the effort despite your stress is worth it. Presenting a speech you worked hard on fosters authenticity and connects you to the subject matter, which can help your audience understand your points better. Human connection is all about honesty and vulnerability, and if you want to connect to the people you’re speaking to, they should see that in you.
1. Identify your objectives and target audience
Before diving into the writing process, find healthy coping strategies to help you stop worrying . Then you can define your speech’s purpose, think about your target audience, and start identifying your objectives. Here are some questions to ask yourself and ground your thinking :
- What purpose do I want my speech to achieve?
- What would it mean to me if I achieved the speech’s purpose?
- What audience am I writing for?
- What do I know about my audience?
- What values do I want to transmit?
- If the audience remembers one take-home message, what should it be?
- What do I want my audience to feel, think, or do after I finish speaking?
- What parts of my message could be confusing and require further explanation?
2. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is crucial for tailoring your speech effectively. Consider the demographics of your audience, their interests, and their expectations. For instance, if you're addressing a group of healthcare professionals, you'll want to use medical terminology and data that resonate with them. Conversely, if your audience is a group of young students, you'd adjust your content to be more relatable to their experiences and interests.
3. Choose a clear message
Your message should be the central idea that you want your audience to take away from your speech. Let's say you're giving a speech on climate change. Your clear message might be something like, "Individual actions can make a significant impact on mitigating climate change." Throughout your speech, all your points and examples should support this central message, reinforcing it for your audience.
4. Structure your speech
Organizing your speech properly keeps your audience engaged and helps them follow your ideas. The introduction should grab your audience's attention and introduce the topic. For example, if you're discussing space exploration, you could start with a fascinating fact about a recent space mission. In the body, you'd present your main points logically, such as the history of space exploration, its scientific significance, and future prospects. Finally, in the conclusion, you'd summarize your key points and reiterate the importance of space exploration in advancing human knowledge.
5. Use engaging content for clarity
Engaging content includes stories, anecdotes, statistics, and examples that illustrate your main points. For instance, if you're giving a speech about the importance of reading, you might share a personal story about how a particular book changed your perspective. You could also include statistics on the benefits of reading, such as improved cognitive abilities and empathy.
6. Maintain clarity and simplicity
It's essential to communicate your ideas clearly. Avoid using overly technical jargon or complex language that might confuse your audience. For example, if you're discussing a medical breakthrough with a non-medical audience, explain complex terms in simple, understandable language.
7. Practice and rehearse
Practice is key to delivering a great speech. Rehearse multiple times to refine your delivery, timing, and tone. Consider using a mirror or recording yourself to observe your body language and gestures. For instance, if you're giving a motivational speech, practice your gestures and expressions to convey enthusiasm and confidence.
8. Consider nonverbal communication
Your body language, tone of voice, and gestures should align with your message . If you're delivering a speech on leadership, maintain strong eye contact to convey authority and connection with your audience. A steady pace and varied tone can also enhance your speech's impact.
9. Engage your audience
Engaging your audience keeps them interested and attentive. Encourage interaction by asking thought-provoking questions or sharing relatable anecdotes. If you're giving a speech on teamwork, ask the audience to recall a time when teamwork led to a successful outcome, fostering engagement and connection.
10. Prepare for Q&A
Anticipate potential questions or objections your audience might have and prepare concise, well-informed responses. If you're delivering a speech on a controversial topic, such as healthcare reform, be ready to address common concerns, like the impact on healthcare costs or access to services, during the Q&A session.
By following these steps and incorporating examples that align with your specific speech topic and purpose, you can craft and deliver a compelling and impactful speech that resonates with your audience.

Tools for writing a great speech
There are several helpful tools available for speechwriting, both technological and communication-related. Here are a few examples:
- Word processing software: Tools like Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or other word processors provide a user-friendly environment for writing and editing speeches. They offer features like spell-checking, grammar correction, formatting options, and easy revision tracking.
- Presentation software: Software such as Microsoft PowerPoint or Google Slides is useful when creating visual aids to accompany your speech. These tools allow you to create engaging slideshows with text, images, charts, and videos to enhance your presentation.
- Speechwriting Templates: Online platforms or software offer pre-designed templates specifically for speechwriting. These templates provide guidance on structuring your speech and may include prompts for different sections like introductions, main points, and conclusions.
- Rhetorical devices and figures of speech: Rhetorical tools such as metaphors, similes, alliteration, and parallelism can add impact and persuasion to your speech. Resources like books, websites, or academic papers detailing various rhetorical devices can help you incorporate them effectively.
- Speechwriting apps: Mobile apps designed specifically for speechwriting can be helpful in organizing your thoughts, creating outlines, and composing a speech. These apps often provide features like voice recording, note-taking, and virtual prompts to keep you on track.
- Grammar and style checkers: Online tools or plugins like Grammarly or Hemingway Editor help improve the clarity and readability of your speech by checking for grammar, spelling, and style errors. They provide suggestions for sentence structure, word choice, and overall tone.
- Thesaurus and dictionary: Online or offline resources such as thesauruses and dictionaries help expand your vocabulary and find alternative words or phrases to express your ideas more effectively. They can also clarify meanings or provide context for unfamiliar terms.
- Online speechwriting communities: Joining online forums or communities focused on speechwriting can be beneficial for getting feedback, sharing ideas, and learning from experienced speechwriters. It's an opportunity to connect with like-minded individuals and improve your public speaking skills through collaboration.
Remember, while these tools can assist in the speechwriting process, it's essential to use them thoughtfully and adapt them to your specific needs and style. The most important aspect of speechwriting remains the creativity, authenticity, and connection with your audience that you bring to your speech.

5 tips for writing a speech
Behind every great speech is an excellent idea and a speaker who refined it. But a successful speech is about more than the initial words on the page, and there are a few more things you can do to help it land.
Here are five more tips for writing and practicing your speech:
1. Structure first, write second
If you start the writing process before organizing your thoughts, you may have to re-order, cut, and scrap the sentences you worked hard on. Save yourself some time by using a speech structure, like the one above, to order your talking points first. This can also help you identify unclear points or moments that disrupt your flow.
2. Do your homework
Data strengthens your argument with a scientific edge. Research your topic with an eye for attention-grabbing statistics, or look for findings you can use to support each point. If you’re pitching a product or service, pull information from company metrics that demonstrate past or potential successes.
Audience members will likely have questions, so learn all talking points inside and out. If you tell investors that your product will provide 12% returns, for example, come prepared with projections that support that statement.
3. Sound like yourself
Memorable speakers have distinct voices. Think of Martin Luther King Jr’s urgent, inspiring timbre or Oprah’s empathetic, personal tone . Establish your voice — one that aligns with your personality and values — and stick with it. If you’re a motivational speaker, keep your tone upbeat to inspire your audience . If you’re the CEO of a startup, try sounding assured but approachable.
4. Practice
As you practice a speech, you become more confident , gain a better handle on the material, and learn the outline so well that unexpected questions are less likely to trip you up. Practice in front of a colleague or friend for honest feedback about what you could change, and speak in front of the mirror to tweak your nonverbal communication and body language .
5. Remember to breathe
When you’re stressed, you breathe more rapidly . It can be challenging to talk normally when you can’t regulate your breath. Before your presentation, try some mindful breathing exercises so that when the day comes, you already have strategies that will calm you down and remain present . This can also help you control your voice and avoid speaking too quickly.
How to ghostwrite a great speech for someone else
Ghostwriting a speech requires a unique set of skills, as you're essentially writing a piece that will be delivered by someone else. Here are some tips on how to effectively ghostwrite a speech:
- Understand the speaker's voice and style : Begin by thoroughly understanding the speaker's personality, speaking style, and preferences. This includes their tone, humor, and any personal anecdotes they may want to include.
- Interview the speaker : Have a detailed conversation with the speaker to gather information about their speech's purpose, target audience, key messages, and any specific points they want to emphasize. Ask for personal stories or examples they may want to include.
- Research thoroughly : Research the topic to ensure you have a strong foundation of knowledge. This helps you craft a well-informed and credible speech.
- Create an outline : Develop a clear outline that includes the introduction, main points, supporting evidence, and a conclusion. Share this outline with the speaker for their input and approval.
- Write in the speaker's voice : While crafting the speech, maintain the speaker's voice and style. Use language and phrasing that feel natural to them. If they have a particular way of expressing ideas, incorporate that into the speech.
- Craft a captivating opening : Begin the speech with a compelling opening that grabs the audience's attention. This could be a relevant quote, an interesting fact, a personal anecdote, or a thought-provoking question.
- Organize content logically : Ensure the speech flows logically, with each point building on the previous one. Use transitions to guide the audience from one idea to the next smoothly.
- Incorporate engaging stories and examples : Include anecdotes, stories, and real-life examples that illustrate key points and make the speech relatable and memorable.
- Edit and revise : Edit the speech carefully for clarity, grammar, and coherence. Ensure the speech is the right length and aligns with the speaker's time constraints.
- Seek feedback : Share drafts of the speech with the speaker for their feedback and revisions. They may have specific changes or additions they'd like to make.
- Practice delivery : If possible, work with the speaker on their delivery. Practice the speech together, allowing the speaker to become familiar with the content and your writing style.
- Maintain confidentiality : As a ghostwriter, it's essential to respect the confidentiality and anonymity of the work. Do not disclose that you wrote the speech unless you have the speaker's permission to do so.
- Be flexible : Be open to making changes and revisions as per the speaker's preferences. Your goal is to make them look good and effectively convey their message.
- Meet deadlines : Stick to agreed-upon deadlines for drafts and revisions. Punctuality and reliability are essential in ghostwriting.
- Provide support : Support the speaker during their preparation and rehearsal process. This can include helping with cue cards, speech notes, or any other materials they need.
Remember that successful ghostwriting is about capturing the essence of the speaker while delivering a well-structured and engaging speech. Collaboration, communication, and adaptability are key to achieving this.
Give your best speech yet
Learn how to make a speech that’ll hold an audience’s attention by structuring your thoughts and practicing frequently. Put the effort into writing and preparing your content, and aim to improve your breathing, eye contact , and body language as you practice. The more you work on your speech, the more confident you’ll become.
The energy you invest in writing an effective speech will help your audience remember and connect to every concept. Remember: some life-changing philosophies have come from good speeches, so give your words a chance to resonate with others. You might even change their thinking.
Elevate your communication skills
Unlock the power of clear and persuasive communication. Our coaches can guide you to build strong relationships and succeed in both personal and professional life.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
How to write an impactful cover letter for a career change
6 presentation skills and how to improve them, 10+ interpersonal skills at work and ways to develop them, how to be more persuasive: 6 tips for convincing others, the 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills, what is a career statement, and should you write one, a guide on how to find the right mentor for your career, self-management skills for a messy world, asking for a raise: tips to get what you’re worth, similar articles, how to write an executive summary in 10 steps, the importance of good speech: 5 tips to be more articulate, how to pitch ideas: 8 tips to captivate any audience, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, anxious about meetings learn how to run a meeting with these 10 tips, writing an elevator pitch about yourself: a how-to plus tips, how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, how to write a memo: 8 steps with examples, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- How to plan a speech
Planning your speech
- a complete, unabridged guide with multiple examples to help plan a successful speech ☺.
By: Susan Dugdale | Last modified: 06-05-2023
Planning your speech is where your success begins. I do not jest!
In your imagination you may hear yourself being stunning, the audience clapping wildly as they rise to their feet to give you a standing ovation.
You may see yourself being deluged in red roses and offered several speaking contracts. Obviously, they are all lucrative but you choose the one with optional extras: an extended holiday in the South of France …
But first you have to begin at the beginning: planning your speech. Without a plan you are whistling in the wind, dreaming.

What's on this page:
How to plan a speech step by step:
- gathering the information to write your speech
- brainstorming : what is a brainstorm, examples of brainstorms, getting started, with full step by step explanations and examples
- how to shape material to fit an audience, the speech setting, and time allocation
- an example speech outline
- how and why to research
- how to meet varying learning style needs: visual, auditory, and kinesthetic
- links to other useful pages: how to rehearse, make cue-cards...
Planning your speech from the start
A note about these notes.
These notes are general guidelines for ALL types of speeches. I know they are long.
(Actually that's an understatement! They are very long.)
I also know if you take the time to go through them they'll give you a solid introduction to thorough speech preparation.
They cover the basics of good presentation planning, research, writing and rehearsal: aspects you’ll want to consider regardless of the type of speech you’re giving.
Gathering your information
Once you have information about:
- WHY you are going to speak (the purpose of your speech),
- WHO you are going to speak to (your audience),
- WHAT your general or specific subject matter is,
- HOW long the speech is to be,
- and WHERE it is...,
you are ready to make a rough or draft outline.
This will be your guide for writing.
You may alter the outline as you go along, as better or different ideas occur to you and that’s OK. It shows you’re flexible and thinking but before we can change anything we have to have something to start with.
To get to the outline stage in the speech planning process we first need to collect up all the "why", "who", "what", "when", "how", and "where" information needed. And that begins with a brainstorm * .
* What is a brainstorm?
A brainstorm is the name given to a commonly used, and effective, technique for generating lots of ideas on a topic, or theme, fast.
Using a heading as a prompt to get you thinking, you quickly note everything you can think of relating to it. You do not edit yourself. You simply let the ideas flow until you can think of no more, making no judgements about whether it's a good idea, a silly idea, or a right or wrong one.
Ultimately, some will be more useful than others. You will sort through and order them later. However, the first step in the brainstorming process, is to accept everything you think of without hesitation. Stopping to decide what's OK and what's not breaks the flow.
If you'd like to see what a completed brainstorm looks like I have examples of them on my site. You'll see they provided the ideas that were then used to write the example speeches.
- one for a maid of honor speech
- one for a 50th wedding anniversary speech
- and another for a farewell speech for a colleague
Return to Top
Brainstorm to begin planning your speech
The brainstorm you are going to do is about making sure you thoroughly understand everything you possibly can about the speech you intend to give.
On a large piece of paper or in a word document write these headings with enough space between them for notes.
WHY are you giving this speech?
What is the purpose of the speech? Do you intend to inspire? To motivate? To entertain? To inform? Or perhaps you want to combine several, like to inform, motivate and inspire?
Knowing what you want your audience to think, feel and do as a result of listening to your speech is the WHY underpinning your presentation. It will help guide what content you use and how you structure it.
WHO is your audience?
Write down as much as you know about the audience.
This will give you ideas about what they will want to hear and be interested in. It will also be your guide when it comes to shaping your material. (More about this later!)
For now, make notes covering:
- the number of people expected to be in your audience,
- their age group,
- ethnicity, if appropriate,
- and the common, or uniting factors they share,
- and specific interests they may have.
Why is knowing who you're talking to vital?

Find out more about why being in harmony with your audience is so important. Check out building rapport.
Examples of WHY, WHO, WHAT...brainstorm notes

Meet Martha Brown. She's fictional. I've made her, and the presentation she's preparing for up, to show you how the brainstorming part of the planning process works.
Martha's been asked to give a motivational speech to a group of women whose background is similar to her own. She, too, came from a family who struggled financially.
Today she is one of the few amongst her relatives who has maintained a marriage, raised children and has a successful business. Her small catering firm specializes in delivering beautifully presented gourmet meals and finger food on demand.
The organizer of the event wants her to share her life story as a guide or inspiration.
Martha is conscious of her good fortune but also knows the starting point, or the seed, lay within her. She desired the change of circumstances so much she enabled them to happen.
WHY is Martha giving this presentation?
What's the principal purpose behind Martha's speech? What does she want her audience to think, feel or do as a result of listening to her?
Let's put ourselves in her shoes.
She wants to:
- motivate and inspire her audience
- give them hope
- show them there is a way out of the circumstances they find themselves in
WHO is Martha's audience?
These are Martha's notes covering the key points about her audience.
- Approximately 25 people ( number )
- Mostly mid to late 30s (age)
- All women (gender)
- Mixed ethnic background but all speak English (ethnicity)
- City dwellers (uniting factor)
- Mostly work inside the home (uniting factor)
- Many have children (uniting factor)
- Interested in achieving work/life balance for themselves and their families and in particular a better financial situation (interest/uniting factor)
- All belong to the same church group (uniting factor)
WHAT are you going to talk about?
Write down the title and/or type of speech you have been asked to prepare. Now using your notes from the WHO section of your brainstorm, begin another set.
This time you are looking to see how WHAT you're going to talk about can be specifically shaped to meet and serve the interests of your audience.
Let's look at an example of WHAT
How does martha shape her life story to fit her audience.
She doesn't want to overwhelm them with information so they can’t think straight or digest it. That will turn them off.
They will think it’s too difficult and beyond them. They may listen, be interested, but they won’t identify with it.
She wants them to feel they can take from her experience and use it to enrich their own lives.
Her notes for WHAT may look like this:
- S peech Title How to win a future for your family when the kids need feeding and the bills want paying.
- Content - main points
- I am like you – I get too busy to plan ahead, I have a tendency to deal with what or whoever squeals loudest, I get tired …
- Before and after – life before I made the decision to start my own business – life after I made the decision. Comparisons – several examples.
- The hardest part of making the decision and acting on it was … Examples.
- The best part of making the decision … Examples. People who inspired me to act.
- What I’ve learned in the process about my family, others and myself … Examples.
- How I keep myself inspired … goal setting, listening and learning from others
- The future – a possible way forward for you, the women in the audience listening.
It’s not a speech yet but you can see the beginnings of its shape and how she’s used her knowledge of the audience to ensure giving them something they’ll enjoy listening to and identify with.
How? (How long will I speak for? How will I deliver my speech?)
There are two important 'hows' to consider.
1. How long have I got to speak?
The first is HOW long have I got to speak.
The time allocation you have been given will determine what you put into your speech and what you will leave out.
If you have a relatively short time, 3-5 minutes, you will need to either focus on one major topic with examples to illustrate or settle for covering a maximum of three lightly.
The purpose of your speech and your audience will help you make the most relevant choice. A longer time gives you more freedom to develop several ideas/themes fully.
2. How will I deliver my presentation?
The second 'how' relates to the method of presentation. HOW will you deliver this speech?
For example:
- Will this be a speech told with humor?
- Will you have a 'show and tell'? (This is when you take objects relevant to your speech to illustrate your points. It could be photographs or other items if they are suitable to transport.)
- Could you give a demonstration?
Shaping delivery to meet different learning styles
When you consider this 'how' bear in mind the different needs of your audience. Most people have a preferred mode for receiving information. That is their learning style.
Some people understand well through listening. They are called 'auditory'.
Some people get most of their understanding through looking. They are called 'visual'.
Others receive and understand information best when they can touch, feel or do what is being explained to them. These are the 'kinesthetics'.
Most of us have a preference for one or two modes. For instance, I am 'auditory' and 'visual'. I want to hear and see.
A considerate speaker tries to include all three modes (learning styles) in their speech.
(For more on catering for learning styles with examples see the foot of the page.)
Delivery and time are yoked together
How you to choose to deliver your presentation is governed by the time you have available. If it is short, you may have to leave out a 'show and tell' or a demonstration but you will always be able to include something to meet all three modes satisfactorily.
'HOW' example from Martha's brainstorm notes
Let’s return to Martha’s Notes to see what she does with the 'how' segment of her brainstorm.
How long? Time available = 10 minutes. (Maybe a little more but that depends on the rest of the agenda of the meeting and how well it flows. Could be some space for questions from the audience and answer.)
How to present? Definitely with humor! Also take some fliers, business cards and samples of finger food along. These can be available for people to pick up at the end of the presentation.
WHEN will this speech be given?
WHEN has two aspects you'll want to take into consideration.
The first is the actual date you have to have it ready for delivery. That lets you know how much time you have for preparation. Is it three weeks, six weeks, or two days?
You'll use that information to plan your workflow. For example, allocating yourself one week to get your preliminary outline and any research required, completed.
The second aspect is the actual time of day and season you deliver a speech. This can have an impact on what you do and say.
For example: You can use an early bird start in the middle of winter on a wet Monday morning effectively by acknowledging the efforts people have made to be there, and by making sure the heaters are on and there's hot coffee available.
Finding ways of tying in what is happening in the 'here and now' is a good way to connect with your audience.
A word of warning : Be conscious about presenting difficult or challenging material when people are either both tired and hungry (just before lunch or dinner) or when they’ve just eaten! Concentration spans are not at their best in either situation. If possible save this type of content for a mid-morning or afternoon slot.
Martha’s Notes, WHEN: 2.45pm, Wednesday, 2nd August – Summer heat
WHERE will this presentation take place?
The environment/room/space you are to speak can play a big role in shaping the final presentation of your speech.
Points to consider are:
- Where will I be in relation to the audience?
- Will they see me easily?
- Will they hear me easily?
- Do I need a microphone?
- Is there a place to put notes if I’m using them?
- Where can I set up my samples for people to take them easily?
- Are there power points if I want to use any electronic devices?
- Do I have to provide everything I want to use (e.g.: computer, screen, leads…)?
Many fully prepared, beautifully rehearsed speeches fail because insufficient thought has gone into where they are to take place.
It’s no fun when people can neither see nor hear you or the carefully thought through demonstration is stymied through lack of an electric socket in the right place!
Martha’s Notes, WHERE: Church meeting room. It can seat everybody comfortably and there’s room for a table to put out a display of fliers and trays of food, paper napkins etc. Arrange the chairs in a horseshoe or semi-circle so everybody can see clearly.
Pulling the brainstorm notes together in an outline
Once you've worked your way through making notes under your WHY, WHO, WHAT, HOW, WHEN, and WHERE headings, you're ready for the next step.
That's picking and choosing, then re-ordering and re-writing the material you've taken from the WHAT and HOW segments of your brainstorm until you're satisfied it flows well and meets your speech purpose.
After you’ve completed outlining your speech, you’ll be ready to do any extra research required, and then you’re on to the task of writing your speech.
Martha's completed outline
Here's Martha’s Finished Outline as an example.
Speech length : 15 minutes with extra time for a 'Question and Answer' session at the end of the presentation.
Speech title : How to win a future for your family when the kids need feeding, and the bills want paying
Introduction (2.5 minutes): Thanks for coming today … Summer heat, we’d all rather be at beach reading a book under a sun umbrella….etc. But I hope I’ve got something for you that’ll more than make up for it. I look around the hall and I see a lot of women just like me: women, who work hard, love their families, etc., … want the best for them.
(Insert anecdotal humor, perhaps a small personal story about credit cards. For instance, the only way I could manage them was to banish them the bottom drawer of the filing cabinet. Or use them to test how sharp my scissors were.)
Main Idea 1 (3 minutes): Introduce business and what it is.
Explain how it functions on a daily basis. Briefly outline long-term goals.
(Quick show-and-tell with flyers and food. Invite people to sample at end and ask questions.)
Main idea 2 (3.5 minutes): My life before the business (tie to women in audience). My life after business started. What I have achieved. The hardest part about starting, staying in business. The best part about starting, staying in business. People who have inspired me.
Main idea 3 (3.5 minutes): What I’ve learned in the process about my family, others and myself … Examples. How I keep myself inspired … goal setting, listening and learning from others
Summary : (2.5 minutes): Very quick round up of principal points. The future – the way forward for you, the women in the audience listening. Invite questions if time. Remind them about the fliers and the food! Thank organizers.
Summary - Core speech planning questions
That’s it! Very short, sweet and simple.
There’s nothing magical about planning your speech. It's just methodical: one-step-after-another. If you find yourself flustered go back to the core brainstorm headings and ask yourself the key questions once more.
- WHY am I giving this presentation? What is my purpose?What do I want my audience to do, think, or feel as a result of having heard me speak?
- WHO is this speech for?
- WHAT am I going to tell them that’s relevant and interesting?
- HOW long is the speech expected to be?
- HOW am I going to present it?
- WHEN is the speech for? (Date, day, time, season)
- WHERE is the speech going to happen? (Hall, outdoors, stadium…)
Write your answers down and let them be your guide.
Remember this is not your finished speech.
It’s your outline * : a map of what you’re going to cover.
Don’t spend too much time trying to get it perfect. You’ll want that energy for researching, writing and rehearsing!
And guess what is coming up next?
* If you'd like more about outlining a speech, including a printable outline template to use, go to sample speech outline .
Getting from planning to delivery
Here are links to articles on:
- how to research your speech . The reasons for research are discussed under the heading below -"When and What to Research"
- how to write your speech
- how to prepare and use cue cards. The benefits of using cue cards over reading from a word-for-word script are enormous. Because you are freed from having to focus on your notes you can interact with your audience directly. Your speech becomes more spontaneous and "in-the-moment".
- how to use story telling to enrich your speech . Do consider weaving your personal stories into your speech. They add tremendous audience appeal.
- how to use props. If you're planning a "show and tell" type speech, this page is essential reading.
- how to rehearse. Rehearsal will lift your speech from ordinary to extraordinary. You'll find out privately where the glitches are, rather than publicly. It gives you an opportunity to refine your delivery. I think it's absolutely essential!
When and what to research
If you already know your subject thoroughly, inside out, back to front and sideways, there will be no need to research and you can skip this part of planning your speech.
BUT if you don’t, the outline should point up the gaps needing to be filled with specific information.
In our example it there seems little need for Martha to do any further research, as this speech is her personal story.
However, there are a number of ways she could strengthen her speech and add real benefits for her audience.
For example: she could bring along fliers from local training institutions providing courses especially geared for women setting up business on their own or she could provide a list of business women in the community willing to mentor and advise women in start-ups. A reading list would be helpful, as would a resource list.
All of these ideas need researching before presenting.
Careful research adds authority to your work. It shows care, thought and dedication to getting it right. Your audience will appreciate and respect you for it.
NB. If you are presenting material as fact rather than as opinion, check it! Make sure you know rather than think you know. If you can’t find out, then say so.
PS. Remember those modes or preferred learning styles?
Did you pick how Martha planned to meet each of them in her outline?
For the 'auditory' learners she would tell her story using her voice in a lively, interesting-to-listen-to way! Nothing turns an auditory focused person's ears off faster than a monotone drawl.
For the 'visual' people, she would provide fliers and food to see. Plus her appearance and body language would 'say' to them, this is a vibrant, purpose-filled person who loves what she does.
And lastly, she would use 'word pictures' to illustrate the points she made in her speech. The 'visual' would literally 'see' where she was coming from by using their imagination to recreate her images in their own minds!
For the 'kinesthetics', Martha planned to actively tell her story. She would use vivid 'action' words describing how she did things.
Example: ' I started a business.' is bland. It doesn't communicate any of the effort or feelings involved.
By contrast: ' I started my own business. What a journey! I know you've watched your children learning to walk. Well, that was me! I fell. I skinned my knees and bruised myself. I got up, took two steps and crashed again...'
You get the idea. This is action, living and real.
The 'kinesthetic' folk will appreciate and know what she is talking about.
Additionally, Martha's fliers and food will appeal too. They can hold them, actively read the fliers and taste the food.
Lastly, they will be aware of what Martha does while she's talking to them. Is she conveying energy, excitement and action in her body language? If so, she'll have them with her!
- Return to the top of planning your speech page
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs

How to Write a Speech: My Simple 6-Step Formula

Ed Darling 9 min read
What you’ll learn:
- Why great speechwriting requires a structure.
- My exact 6-step speech structure you can steal.
- How to start and end your speech strong.

How to write a speech, the easiest way possible.
How? By following a simple frame-work that’s powerful and versatile.
Whether you have a work presentation, keynote talk, or best man’s speech – by the end of this article, you’ll know exactly how to write a speech, and in what order.
I’m Ed, a public speaking coach and co-founder of Project Charisma . I help professionals, leaders and business owners to speak in public, and this is the #1 speech framework that I share with all of my clients.
I ’ll walk you through the process of how to write a speech step-by-step , explaining each section as we go. I’ll also give you some examples of how this would look in different types of speech.
The first step is something 99% of people miss.
PS. Check out our specific speech guides on:
Delivering a Business Pitch
Giving a Best Man Speech
Step 1. Find your speech's "Golden Thread"
The first lesson in how to write a speech is setting a clear objective from the get-go — so that what you write doesn’t end up being vague or convoluted.
Afterall, If you don’t know exactly what your speech is about, neither will your audience.
To avoid this, we’re going to begin by defining our “Golden Thread”.
This is the key idea, insight or message that you want to get across. Like a thread, it will run throughout your speech, linking each section together in a way that’s clear and coherent.
To help you figure out your Golden Thread, try answering these two questions:
- If you had to summarise your speech into a single sentence, what would that be?
- If your audience could leave remembering only one thing, what would that be?
Golden Thread examples: A work presentation: “Customer referrals can be our our super-power”
A motivational speech: “Don’t let circumstances define you”
For a wedding/event speech: “Enjoy the journey together”
Speech Writing Tip:
Your Golden Thread isn’t something you share with the audience. You don’t start your speech by saying it out loud. Rather, it’s something we define in the preparation phase to clarify your own thoughts and ensure everything that comes next makes sense.
That said, your Golden Thread may double-up as the perfect speech title, or memorable catch-phrase. In which case it’s fine to use it within your speech as a way to drive-home the overall message.
Think of MLKs famous “I have a dream” speech . The Golden Thread would be his dream of a future with equality — a core idea which ran throughout the speech. But the exact phrase “I have a dream” was also spoken and repeated for effect.
Ready to feel confident while speaking in public? Join our next 1-Day Public Speaking Masterclass

Step 2. Start with your Hook
Now we get into the nitty-gritty of how to write a speech.
The Hook is the first thing you will actually say to the audience – usually within the first 10-30 seconds of your speech.
Most people start a speech by introducing themselves and their topic:
“Hello everyone, I’m John from accounting, today I’ll be talking about our quarterly figures” .
It’s predictable, it’s unimaginative, it’s starting with a yawn instead of a bang.
Instead, we’re going to open the speech with a hook that gets people sitting up and listening.
A hook can be anything that captures attention, including a:
- Relevant quote
- Interesting statistic
- Intriguing question
- Funny anecdote
- Powerful statement
Watch how Apollo Robbins opens his TED talk with a question-hook to engage the audience.
Whichever type of hook you use, it needs to be short, punchy and ideally something that builds intrigue in your audience’s mind. Depending on the type of speech, your hook might be humorous, dramatic, serious or thoughtful.
For an in-depth guide on how to write a speech with a great hook, I highly recommend our article on 9 Killer Speech Openers.
H ook examples:
A work presentation: “What if I told you we could increase revenue by 35%, without any additional ad-spend?”
A motivational speech: “At the age of 30, my life was turned upside down – I was jobless, directionless, and depressed”
For a wedding/event speech: “Love is a fire. But whether it is going to warm your hearth or burn down your house, you can never tell! – so said Joan Crawford”
Speech Hook Tip:
Don’t rush into things. Hooks work infinitely better when you pause just before speaking, and again just after.
Step 3. The Speech Introduction
We’ve captured attention and have the whole room interested. The next step is to formally introduce ourselves, our speech, and what the audience can expect to hear.
Depending on the situation, you can use your introduction as an opportunity to build credibility with your audience. If they don’t know you, it’s worth explaining who you are, and why you’re qualified to be speaking on this topic.
The more credibility you build early on, the more engagement you’ll have throughout the speech. So consider mentioning expertise, credentials and relevant background.
In other situations where people already know you, there may be less need for this credibility-building. In which case, keep it short and sweet.
Intro examples:
A work presentation: “Good morning everyone, I’m Jenny from the Marketing department. For the past few months I’ve been tracking our referrals with a keen-eye. Today, I want to show you the numbers, and explain my plan double our referrals in the next 6 months”
A motivational speech: “Ladies and gentlemen, at the age of 40 I’m a speaker, an author and a teacher – but my life could have turned out very differently. Today, I want to share with you my story of overcoming adversity.”
For a wedding/event speech: “Good afternoon everyone, I’m Luke the Best Man. I can’t promise anything quite as poetic as that quote, but I’d like to say a few words for the Bride and Groom”.
Speech Intro Tip:
In certain situations, your introduction can also be a time to give thanks – to the event organisers, hosts, audience, etc. But always keep this brief, and keep focused on your message.
Step 4. The Speech Body
The body of the speech is where you share your main stories, ideas or points. The risk for many speakers here is that they start meandering.
One point leads to another, which segues into a story, then a tangents off to something else, and before we know it, everyone’s confused – definitely not how to write a speech.
Remember, clarity is key.
For this reason, wherever possible you should aim to split the body of your speech into three distinct sections.
Why three? Because humans tend to process information more effectively when it comes in triads . Making it easier for you to remember, and easier for your audience to follow.
The most obvious example of this is the classic beginning, middle and end structure in storytelling .
You can also use past, present and future as a way to take people on a journey from “where we used to be, what happens now, and what the vision is going forwards”.
Or even more simple, break things up into:
- Three stories
- Three challenges
- Three case-studies
- Three future goals
Of course, It’s not always possible to structure speeches into three sections. Sometimes there’s just more information that you need to cover – such as with a technical presentation or sales pitch.
In this case, I recommend thinking in terms of chapters, and aiming for a maximum of 5-7. Ensure that each “chapter” or section is clearly introduced and explained, before moving on to the next. The more content you cover, the greater the need for clarity.
Body examples:
A work presentation: “We’ve discovered that referrals happen when we get three things right: building the relationship, delighting the customer, and making the ask – let’s look at each of these stages.
A motivational speech: “I don’t believe our past has to dictate our future, but in order to tell my story, let me take you back to the very beginning.” For a wedding/event speech: “Of all the most embarrassing, undignified, and downright outrageous stories I could think of involving the Groom, I’ve whittled it down to three, which I think sum up why this marriage is destined for a long and happy future. It starts back in high-school…”
Speech Body Tip:
I mention “chapters” because when reading a book, there’s a moment to reflect after each chapter as we turn the page. In the same way, when speaking, make sure to give your audience a moment to process what you’ve just said at the end of each section, before moving on to your next point.
Ready to speak with confidence ? Explore our training options...
Step 5. the conclusion.
Now it’s time to bring everything together, guiding your audience to the key conclusions you want them to take away.
Depending on your speech, this could be an idea, an insight, a moral, or a message. But whatever it is, now is your time to say it in a clear and compelling way.
Watch David Eagleman use a thought-provoking metaphor and rhetorical question to wrap up his TED talk on senses.
This final conclusion should always link back to your Golden Thread, making sense of everything that’s come before it.
Answer the following questions as prompts (you could even say one of these out-loud to lead into your conclusion)
- What is the message I want to leave you with?
- What have we learned from all this?
- What is the key take-away?
Conclusion examples:
A work presentation: “So what have we learned? When we get each of these steps right, our customers are eager to give us referrals, and those referrals usually result in more happy clients.”
A motivational speech: “My journey has had many ups and downs, but if there’s one lesson I’ve learned – it’s that our circumstances don’t dictate our direction, that we can come back from failure, and find a way to win” For a wedding/event speech: “So what can I say about the Bride and Groom? They’re clearly made for each other and if history is anything to go by, their future will be full of many more stories and adventures.”
Speech Conclusion Tip:
Never use your conclusion to apologise for yourself, explain a whole new idea, or be overly thankful to everyone for watching. Keep it professional, and keep it focused on hammering-home the main idea of the speech.
6. The Call To Action, or Call To Thought
You’ve concluded your message and summarised your main points. At this point, most people think the speech is done.
Not so fast — there’s one final key step we need to take, the Call to Action .
If you’ve followed the steps so far on how to write a speech, your audience should have been listening, learning, and hopefully now feel inspired by your words.
We’ve built up the potential for some kind of action , and now all that’s left is to direct that energy into a clear “next step” they can take.
Imagine your audience are thinking “what should I do with this information”?
Your CTA is the direct answer to that question.
It should be clear, simple and ideally – something they can act on quickly. For instance, you may request the audience to download an app you’ve discussed, connect with you online, sign up for a service, or come and speak with you afterwards.
Not every speech suits a CTA however, which is where the CTT comes in.
This is a great variation I picked up from Justin Welsh which stands for “ Call to Thought ”. It’s a more nuanced action – typically asking people to reflect on an idea, consider a specific issue, or think differently about something.
C TA/CTT examples:
A work presentation (CTA): “As an immediate next step to get us started, I’d like everyone to reach out to your current clients this week, and ask them to refer one new customer. We’ll be tracking the results, and rewarding the winning referral rain-maker!”
A motivational speech (CTC): “So ask yourself, where are you allowing circumstances to hold you back, and how could your life change if you took a new direction?”
For a wedding/event speech (CTA): “With that said, I’d like to raise a toast to the Bride and Groom. Now enjoy the day, and get yourself a drink at the bar!”
Speech CTA/CTT Tip:
Once you’ve stated your CTA/CTT, the only thing left to do is thank people and finish. Don’t be tempted to back-track and start repeating any of your points. It’s time to get off stage!
How to write a speech using this framework.
Without a framework to guide you, it’s easy to get lost in analysis-paralysis, or worse, create a speech which gets everyone ELSE lost.
Now that you’re armed with this foolproof formula and know exactly how to write a speech, you can approach the situation with confidence .
- Define your speeches Golden Thread.
- Hook your audience in the first 10-30 seconds.
- Introduce yourself while building credibility.
- Divide your body into three clear sections.
- Conclude your main points and drive-home the message.
- Leave them with an inspiring CTA/CTT.
Even as an inexperienced speaker, by following this formula you’ll come across with the clarity and credibility of a professional.
R emember, public speaking is simply a skillset that requires practice . The more you use this speech framework, watch other speakers in action, and gain practical experience, the more your communication skills will naturally develop.
I hope learning how to write a speech using this frame-work makes the process of writing your next speech a breeze.
Need any further help with how to write a speech? Feel free to reach out.
Head Coach and co-founder at Project Charisma.
Join 350+ leaders getting my weekly tips on confidence and charisma... 👇
Navigation:.
Home About Success Stories Contact Privacy Policy
Work with Ed:
1-to-1 Coaching 1-Day Masterclass Team Training
Follow/Connect:
Get started:, copyright © 2023 project charisma ltd. all rights reserved..
Speech And Debate
Speech Writing
Last updated on: Feb 9, 2023
How to Write a Speech - Outline With Example
By: Cordon J.
Reviewed By: Rylee W.
Published on: Sep 8, 2020

Giving a speech for a class, event or work can be nerve-wracking. However, writing an effective speech can boost your confidence level.
A speech is an effective medium to communicate your message and speech writing is a skill that has its advantages even if you are a student or a professional.
With careful planning and paying attention to small details, you can write a speech that will inform, persuade, entertain or motivate the people you are writing for.
If this is your first speech. Take all the time you need.
Like other skills, you can learn speech writing too.
Give yourself enough time to write and practice it several times for the best possible results.

On this Page
You have a message that you want people to hear or you are preparing a speech for a particular situation such as a commemorative speech.
No matter what the case, it is important to ensure that the speech is well structured or else you will fail to deliver your effective message. And you don’t want that, do you?
You can also explore our complete guide to write a commemorative speech . Make sure to give the article a thorough read.
How to Create a Speech Outline?
Want to write a speech your audience will remember? A speech outline is a thing you should start with.
‘How to write a speech outline?’
A speech outline is very important in helping you sound more authoritative and in control. As you write your speech outline you will have to focus on how you will introduce yourself, your topic, and the points that you will be going to cover.
A speech outline will save a lot of your time and will help you organize your thoughts. It will make sure the speech is following a proper structure and format.
Before you start writing your own speech you need to know:
- WHO you are writing the speech for
- WHAT the speech will be going to cover
- HOW long it needs to be e.g if it is a 5-minute speech (then how many words in a 5-minute speech)
These speech tips will help you get on the right track from the start. Here is an example of how you can craft a speech outline.
Preparation
- Choose your topic and the main points that your speech will cover. Know your audience and get to know what they are looking for. Pay attention to their needs
- Define the purpose of the speech and properly organize it
Introduction
- A strong statement to grab the reader’s attention
- Refine the thesis statement
- State something that establishes credibility
- Provide your main idea and include some supporting statements.
- Examples and further details (if needed)
- Summarize the main points of the speech
- Closing statement
- Call to action

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How to Write an Effective Speech?
‘How to write a graduation speech?’
‘How to write a speech for school?’
‘How to write a speech about yourself?’
Get your answers in the below sections.
Just like essays, the speech also follows three sections: Introduction, the main body, and conclusion.
However, unlike essays, a speech must be written to be heard as opposed to just being read. It is important to write a speech in a way that can grab the reader’s attention and helps in painting a mental image.
It is the opening statement of a speech. It is important to know how to start a speech that can grab the attention of the audience.
‘How to write a speech introduction?’
It should include a hook-grabber statement about your topic. It should end with a strong transition from a big idea of the introduction to the main body of the essay. Some great ways to begin your speech are, to begin with, a rhetorical question, a quote, or another strong statement.
Make sure the introduction is not more than one paragraph. This will ensure you do not spend much time on the background before getting to the main idea of the topic.
The introduction is a great chance to make sure your opening is memorable as this is the point when your audience will make up their mind about you.
The Main body
The majority of the speech should be spent presenting your thesis statement and supporting ideas in an organized way.
Avoid rambling as it will immediately lose your audience’s attention. No need to share everything, instead pick some points and stick to them throughout your speech.
Organize your points in a logical manner so they support and build on each other. Add as many points as needed to support the overall message of your speech.
State each point clearly and provide all the required information, facts, statistics, and evidence, to clarify each of your points.
It is a good idea to include your personal experiences to make your speech more interesting and memorable.
Another important thing to be kept in mind is the use of transition. The purpose of adding transition words is to improve the overall flow of the information and help the reader to understand the speech structure. Words like next, then, after, before, at that moment, etc. are the most commonly used transition words to make the whole writing less choppy and more interesting.
The conclusion should restate and summarize all the main points of the speech. Because the audience will most likely remember what they have heard last. Beautifully wrap up the whole speech and give something for the audience to think about.
For an extra element, close your speech by restating the introduction statement so it feels like a complete package.
A good approach to conclude your speech is to introduce a call to action. Encourage your audience to participate in the solution to the problem that you are discussing. Give your audience some direction on how they can participate.
Practice and more practice is key to a great speech so it is important that you read your speech and listen to yourself. When writing, take care of the required length also.
Speech Topics - Engaging Topics to Choose From
You feel relief when your teacher says you are free to choose your speech topic. Feel free to write about anything you want. The problem is students still feel stuck in choosing an effective speech topic. If you are one of them, here is a list of the best speech ideas to help you get through the process.
- What role do cats play in human’s lives
- How to improve communication disorders
- World’s fastest-growing country
- Today’s world pollution rate
- How to improve interpersonal skills
- Are paper books better than e-books
- Should the death penalty be abolished
- Should prisoners be allowed to vote
- Should voting be made compulsory
- Is it better to live together before marriage
These are some of the interesting topics that you can consider. However, if you are still not sure about the topic of your speech, you can explore our article on informative speech topics and pick any of your choices.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Speech Example
Stressing over on how to write a good speech? Speech examples are sure to be your best friend for effective speech writing and its effortless delivery.
Here is a sample speech example to help you get through your own speech writing process. Explore this example and get the answer on how to give a good speech.
Get Professional Help for Your Speech
If you are good at public speaking but lack writing skills or you do not have enough time to follow the mentioned points and write a speech, don't worry.
You can always contact us at 5StarEssays.com.
We have a highly qualified and amazing team of expert writers who can help you if you want to buy speeches online with high-quality content.
Contact our " write my essay " service with your requirements. Our essay writer will provide you with quality material that your audience will remember for a long time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best introduction for a speech.
The best way to open a speech’s introduction is, to begin with, a story. Tell an inspiring story to your audience and connect it with your personal narrative.
What is the first step of speech writing?
The first step of writing a speech is to choose a topic. Choosing a good topic is important to have an engaging and great speech.
What are the five steps in speech writing?
Here are the five steps involved in writing a speech.
- Choose a topic.
- Investigate your audience.
- Built an outline.
- Rehearse the speech.
- Revise and finalize.
What are the types of speech delivery?
Here are the types of speech delivery.
- Extemporaneous
What are the two P’s required for good speech delivery?
The two P’s required for proper speech delivery are Preparation and Practice.

Cordon. is a published author and writing specialist. He has worked in the publishing industry for many years, providing writing services and digital content. His own writing career began with a focus on literature and linguistics, which he continues to pursue. Cordon is an engaging and professional individual, always looking to help others achieve their goals.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Informative Speech Topics - Interesting Ideas By Experts

- Commemorative Speech: Guide to Craft an Engaging Speech

- Persuasive Speech Topics - 150+ Topics for Students

- 50+ Demonstration Speech Ideas for Your Next Great Speech

- Impromptu Speech Topics - 150+ Interesting Ideas

- Debate Topics (2024) - Top 200+ Compelling Topics

- 100+ Motivational Speech Topics for an Inspirational Speech

- Extemporaneous Speech - How to Write One Successfully?

- Graduation Speech - Write Your Best Graduation Speech

People Also Read
- narrative essay outline
- solve math problems
- writing a descriptive essay conclusion
- types of sentences
- how to cite a research paper
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved
The Ultimate Guide to Structuring a Speech
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking , Speech Writing

Some speakers are great writers. Some are great at delivery. And some are good at both.
The problem is that even if you are one of those speakers who can write good content as well as deliver well, if your speech is not structured properly, your message’s effectiveness will plummet. Structuring your speech is necessary as it makes it easy for your audience to understand its contents.
I’ve seen it time and again (including with myself) – speakers come on stage and start off really well…but somewhere the audience gets lost.
Have you ever been in this situation? This is probably because the speech is not structured properly. A well-structured speech helps navigate your audience through your message. And that is why it’s so important.
Without it, your speech will be scattery and not be held together, leaving the audience the same way – scattered.
Writer, Daniel Pink , put it well when he said:
Give the speech a beginning, a middle and an end. You don’t have to take the audience by the hand and walk them through each step. And you don’t have to proceed chronologically. But having that structure in your head will give your speech a shape. And it will provide your audience some guideposts about where you’ve been and where you’re going.

3 Things to Keep in Mind for a Good Speech Structure
Here are some things to keep in mind while writing your speech.
Don’t write like you write. Write like you talk
This one is tricky, especially if you’re a seasoned writer as opposed to a seasoned speaker. I learned this when I was giving my first few speeches. I was writing my speeches like a writer, not like a speaker.
That means to say that my speech was written in a way that would sound great if someone read it on paper. But when I would deliver it on stage, it wouldn’t be that good.
Nowadays, when I sit down to write a speech, I keep re-reading the words to see what they would sound like out loud. This makes me edit my speech to make it sound more natural and conversational and less “article-types”.
Don’t use fancy language.
This is not a grammar essay. When we talk with our friends, we tend to use shorter, more crisp sentences with simple language…which is exactly how we should write our speech.
You can also be informal when you speak. So no need to be worried if you’re not following every grammatical rule out there. Using informal language (to an extent) helps to make you sound more natural and makes your speech more conversational.
Writing a conversational speech might not be as easy as it sounds, and that’s why we have just the right video for you. From writing a conversational speech to delivering it, this video will definitely help you through the process.
Keep the speech simple
I stress this a lot. But it’s mainly because so many speakers (who are starting out) try and make their speech very fancy!
Keeping your speech simple, in language and thought, will make it that much easier to structure your speech and thus, that much easier for the audience to consume your speech.
It sounds like a piece of cake when we put it like that, and you might think that simply avoiding jargon or using more visuals will make your speech easy to follow.
Still, there are just three tips you need to know to keep a speech simple: Know your audience, focus on the outcome and finally, use a narrative structure. This video will tell you just how to use these three tips to your advantage.
When you write your speech draft, relook at it and see what words or sentences you can cut. It’s best to simplify…which brings us to our next point:
Focus on one idea

Keep your speech centered around one thought or idea. If you try to cram too much into your speech, it can get cluttered. But more importantly, the audience won’t remember much of your speech anyway!
If you talk about 4-5 ideas, they’re quite likely to remember none. But if you focus on just one idea, you can structure your whole speech around that, and it will be much easier for the audience to consume your speech and remember your idea.
You can use a simple method to make sure that your speech does not have any redundancies and you do not overwhelm your audience. This framework is called the “what? so what? now what?” framework. We put out a video you can watch explaining how to use this framework for any public speaking event and has some extra tips on how to deliver a concise and clear speech.
Step by Step Guide to Structuring a Speech
Here is a step-by-step guide to writing a great speech structure, which is broken down into two parts, that is, preparation and writing.
Preparation
1. audience.
This includes researching your audience in order to better understand them and their interests. With proper audience research in place, one can adapt the speech as per the beliefs, interests, and level of understanding of the audience.
Audience research mainly entails their educational background, profession, ethnicity, sex, age group, etc. But besides this, we should strive to also understand the knowledge the audience has on the topic that we are speaking about.
One way of researching your audience can be by sending a questionnaire to them before your speech. If that is not possible, try and speak to the host or the person who invited you to speak. They will probably have valuable insights into the crowd you are about to address.
Another way is by reaching the venue early, greeting the audience, and asking them questions to better understand them. However, with this method, you are required to be spontaneous and make changes which could be quite last-minute.
This is an essential step to writing a speech that is relevant and will resonate with your audience.
This video has several additional tips on collecting information about the audience, what kind of questions need to be asked, and even some last resorts that might work when all else fails!
This includes knowing the purpose of your speech and what exactly you want to convey to the audience. I have attended some presentations where at the end of the speech, I was wondering what the speaker was trying to convey because the purpose of the speech was not clear at all.
On a broader level, the purpose of your speech can be to inform, persuade, or entertain the audience. It is crucial to know which category your speech falls into. On a narrower level, we need to ask ourselves, “What do we want the listeners to take away from my speech?”.
Once we have this down, all our efforts should be focused on driving that point.
Ethos mainly includes establishing credibility and convincing your audience that you are trustworthy. It is important to establish credibility from the start of the talk or it might be difficult for the audience to accept what you say.
In order to identify ethos, one can ask oneself questions like “Why should I give this particular speech?”, “How can I get the audience to believe me with the contents of the speech?”.
Once ethos is established, the audience is likely to listen to you more attentively and be persuaded.
4. Research
Delivering a good speech is not just about speaking or writing a good speech but also confidence in your ability to deliver it. This confidence stems from thorough research which gives your speech authenticity and credibility.
Including statistics in your speech and the sources from where you have picked up the information can prove helpful. Moreover, if you are willing to go the extra mile, doing primary research in your speech can also help you gain insight and a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Moreover, it will make your research stand out and add to your ethos.
1. Narrative
There are different narrative styles when it comes to speeches. It helps us story-tell much more effectively and helps our audience retain a lot of the information.
Choosing the right narrative style is important as it also helps us understand the type of structure we should follow. I’m noting down a few narrative styles for you to get inspiration from, but we have written extensively on the topic which you can check out here: 9 Storytelling Approaches For Your Next Speech or Presentation .
Nested Loops
In this, three stories or more stories are told but none of these stories are completed. Once the gist of all the three stories is given, we start closing the loop in reverse order, that is by finishing the last story first and so on.
This is a better way of gaining the audience’s interest and attention as psychologists believe that people remember interrupted tasks better than the complete ones.
In Medias Res
In this, the narrative is started in the heat of the action rather than starting from the beginning. Basically, you launch your story right into the action–providing the snippets of how you got there. This works because you take your audience to the most titillating part which makes them inquisitive to know how you got there.
In this, you shift between hope and reality where you and your brand promise to bridge the gap between the ideal and contemporary situations. Basically providing a ray of hope to all the problems in one’s life. Through an emotional appeal the speaker fuels a desire for change among the audience.
Rags to Riches
This is a narrative style where the protagonist has struggled and suffered greatly because of his/her background but later reaches success. This narrative instills hope in people and makes them relatable to the failures or difficulties faced in life.
I’ve written an entire article on speech outlines which you can read so I’m not going to spend too much time here.
A basic outline of a speech broken down into a good ol’ Intro-Body-Conclusion:
The Opening – While it’s important to have a strong opening , your opening should seamlessly tie into your premise which is basically the core and the main reason for your speech.
The Body – The body, while being the larger chunk of your speech, shouldn’t be just that – a large chunk. Break the body up! Split your ideas within the core message of your speech and transition smoothly through each idea so your audience can digest what you’re trying to communicate.
The Conclusion – Here is where many new speakers fall short. While you must focus on having a bang ending , tell the audience what you want them to do! Give them a clear indication or a ‘call-to-action’.
3. Transition
Speech transitions are words or phrases that help you to move from one topic to another without breaking the flow of the speech. A speech without transitions can seem disorganized and confusing to an audience. There are different types of speech transitions, as given below.
Counterpoints This particular transition is used while talking about contradicting ideas. Phrases such as on the other hand, contrary to what was said earlier, at the same time, on the flip side, etc. can be used to make this transition.
Important Ideas Having a transition for the important ideas in your speech can make them stand out and gain attention causing the audience to listen attentively. These transitions can include pausing before the important statement to make an impact or slowing down the pace of your speech while making the important statement. Posing a question before starting the main idea of the presentation can also put emphasis on it.
Processes While speaking about the steps on how to achieve something or the process of something, numerical transitions can be simpler for the audience to follow. For instance, firstly, secondly, lastly, etc.
Example While giving an example of something, transitional phrases such as for instance, take the case of, to better understand this…, etc. can be used to maintain the flow of the presentation.
Here’s a detailed article written on the different types of transitions along with an example for each, which is titled Effective Speech Transitions: How to Make Your Speech Flow .
The content is the main matter of the speech which is divided into 3 parts, namely, beginning, body, and conclusion.
The Beginning
How you start your speech introduction is, of course, very important. It’s what will grip the audience. They say that people have judged you as soon as you go up on stage, so it’s crucial to catch their attention quickly.
There is no right way to start your speech, but when writing it, make sure you spend some time crafting a good beginning.
Most speakers start with a story, or ask the audience to close their eyes and imagine something, or start with some sort of outstanding fact.
The point is that the beginning should be something that sets the tone for your speech and gets your audience into the mood you want them to be in. There is no set rule as to how long your introduction should be – it can be a few lines or even just a sentence.
To learn more about how to begin your speech with powerful openers, read our extensively written article on 15 Powerful Speech Opening Lines (And How to Create Your Own)
Here’s the meat of your idea.
This is where you get into what your speech is really about. Again, if you’ve focused on too many ideas, the body gets cluttered up and it becomes hard for the audience to consume the speech. So, focus on that one idea that you want to communicate.
Talk about a personal story, throw in some researched facts, show the twists and turns. I like to use the statement-problem-solution approach. I start off with the idea, then I move on to what the problem with it is, and finally to the solution.
This might be hard to explain since every speech is different, so I rather show it to you instead.
Email me at [email protected] and I will send across a speech drafted by one of my speech mentors. It really drives home the idea of how you can structure your speech in an effective manner.
The best is for the last.
Remember, the audience does not tend to remember much of a speech.
So in the end, try to summarize your idea and give the audience some sort of actionable takeaway. That means that you should give the audience something that they can try or change about themselves right this very moment (or at least in the near future) so they can see the benefits of your idea.
Again, this is subjective for different speeches. But the basic idea is to repeat your idea towards the end so it sticks with your audience and gives them something to take away.
This video on 5 powerful speech-ending lines (And how to use them), displays some memorable speech endings and also gives tips on how to deliver a closing line of equal caliber on your own.
After forming the first draft of your speech, editing requires you to go through your speech and remove any kind of repetition or errors that you come across.
Editing mercilessly is the key to delivering a good speech. Anything that strays from your core message should be edited. Making sure that there is clarity in your speech is also crucial in order to avoid confusion among the audience.
While editing, the aim should be to make the speech concise by eliminating words that do not add meaning to the sentence, removing paragraphs if the meaning is conveyed fine without them, and using shorter and simpler words rather than using complex words.
Types of Speech Structures
These are some of the speech structure types that you might relate your speech to:
The ‘3 Anecdotes’ Structure
This structure implies that you start your speech off with an introduction by hinting at your main idea and then use the body to tell 3 different stories supporting that idea.
For example, if you were talking about the importance of confidence, give the audience 3 anecdotes of how you missed out on opportunities because you were not confident. Each story can address a different sub-idea within the main idea.
Again, this does not mean that you talk about multiple things, it just means that you are really fleshing out your main idea. These types of speeches work well when you want to tackle a singular idea from different angles.

Problem-Solution Approach
This is the approach I use a lot. What it basically means is that you start off your body by emphasizing the issue at hand. Really build it up to make the audience believe that this really is a problem!
Put in facts, use your own story and make your problem feel like the audience’s problem as well (does that make sense?).
When you introduce the solution, show how it has benefited you as well as how it can benefit the audience. This also makes it easier to add an actionable takeaway at the end.
These types of speeches are great when you have to persuade or convince your audience about a particular matter.
Bed Time Story

This follows the flow of a classic story. Start with an intro. This is where you build up the narrative by setting the scene (try not to say “once upon a time” since it’s become too clichéd).
Then, flesh out the idea. This is where you introduce the hero, the villain, and the plot twist.
Eventually, you end with a happy ending. These types of speeches are great for people who are speaking to an audience with a low attention span, like children. However, if done correctly, it can be a great speech for adults as well!
In addition to this, there are several other speech structures you can use depending on the suitability of your topic. Read the details of the various other types of speech structures (with examples) in this article called Structuring a Speech Right: 7 Simple Tips
Demonstration of the idea of your speech
Many times, when you have to make a presentation, you may have to demonstrate a product, feature, service or idea of some sort.
When doing this, don’t just jump into whatever it is you’re demonstrating. As Simon Sinek says, “talk about the WHY” of whatever it is you’re talking about. Then move on to the “HOW” of it and eventually the “WHAT” of it.
This will help you demonstrate more effectiveness rather than just talking about what you have to present. If you want to know more about “Starting with the WHY”, you can check out Simon Sinek’s best-selling book “Start with the Why”.
There are several ways to structure a speech, and there isn’t really a right or wrong way to do so. As long as you feel it’s simple and easy enough for your audience to understand, you’re good to go.
Structuring your speech is important in order to make the audience better understand the matter of the speech and also to maintain their attention and interest. The message of an unstructured speech cannot reach the audience, as the speaker is confused most of the time regarding what topic to present.
A structured speech also helps the speaker to stay calm and not stray from the topic of the presentation. If you’re still not convinced writing a speech is useful, read this article on 9 Reasons Why Writing A Speech Is Important which will change your mind.
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.

Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Grow » thrive, 7 steps to writing a great speech.
These seven steps will help you write a memorable and effective speech.

If you’re preparing for a presentation, the work really begins when you sit down to write your speech. A great speech will engage the audience and can lead to greater personal and professional success. Here are seven steps to writing an effective speech.
Know what your core message is
When preparing to write a speech, you want to start by thinking about the core message you want to share. Your core message should be a topic you’re knowledgeable and passionate about and one that’s relevant to your audience.
The topic should be delivered in a way that’s easy to understand and concise. Ideally, your audience should be able to explain what the speech was about in just one or two sentences.
Think about your audience
Next, you want to learn as much as possible about your audience because this will inform how you deliver the speech. The language you use and the examples you share will depend on the audience you’re speaking to.
As you learn more about your audience, you want to consider the circumstances that brought them together. Are they gathering for a business conference, or is it for a charity event? How big will the audience be, and how knowledgeable are they about the subject you’re speaking on?
[Read more: How to Give a Great Presentation ]
Do your research
The amount of research you complete will depend on how familiar you are with your topic. But even if it’s a topic you know inside and out, it’s a good idea to do at least some research. This will help you gather new information and come up with unique and fresh ideas.
The amount of research you complete will depend on how familiar you are with your topic. But even if it’s a topic you know inside and out, it’s a good idea to do at least some research.
Come up with an outline
Now it’s time to organize your information and ideas into a detailed outline. Organizing your information will make it easier once it’s time to sit down and write the speech. Your outline should include three main parts:
- Introduction : The introduction sets the stage for the information you’ll be sharing. It’s a good idea to start with a story that will catch your audience’s attention. From there, you can outline what you’ll be sharing and the conclusion you’ll reach.
- Body : The body of your speech is where you’ll highlight the overarching points you’re trying to make. But be careful not to throw too much information at your audience — two to three main points are enough.
- Conclusion : During the conclusion, you’ll summarize your core message and what the audience should take away from the speech. Look for ways to end your speech on a strong note, so the audience understands why this topic matters and how they can take action.
Write a draft
Once you have an outline, you can begin drafting your speech. Don’t try to make your speech perfect during the drafting stage — just try to get your ideas on paper. You can come back to revise and improve your speech later.
Choose a presentation tool
If you’re speaking in a professional setting, you’ll likely want to compliment your speech with a presentation tool like PowerPoint. Using a slide deck is a great way to add a visual element to your speech that will further engage the audience. Using a template can make it easier to develop a well-designed slide deck.
[Read more: 6 Business Presentation Tools for Small Businesses ]
Practice and revise
Great speeches take time to write, so you should plan to practice and revise your speech as needed. You can practice your speech in front of a friend or family member, ask for their feedback, and then adjust your speech accordingly.
As you’re revising, focus on using conversational language and short sentences. Look for any areas that are too general or vague, and try to come up with specific examples that will back up your core message.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Become a small business member and save!
Become an integral voice in the world’s largest business organization when you join the U.S. Chamber of Commerce as a small business member. Members also receive exclusive discounts from B2B partners, including a special offer from FedEx that can help your business save hundreds a year on shipping. Become a member today and start saving!
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more personal success tips
5 tools that can help boost productivity for remote entrepreneurs, 5 simple steps to finding a mentor, 9 tips for becoming a great mentor.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
Get in touch with us – here
- About Ginger
- About Leadership
- All programmes and courses
- Purpose-Driven Leadership
- Storytelling Mastery
- 1-2-1 training/coaching
- Elevate your Influence
- Executive Presence
- Present with Influence
- Public Speaking Foundations
- Assertive Communications
- Boosting Visibility and Confidence
- Building Your Personal Brand
- Clear & Concise Communications
- Courageous Communications
- Fearless Feedback
- High-Impact Communications
- Messages that Stand Out From the Crowd
- The Essentials of Storytelling for Business
- Virtually Brilliant for Online Communicators
- hello@gingerleadershipcomms.com
- +44 (0) 207 3888 645
Speech Writing: How to write a speech in 5 steps

Every great speech starts with an idea, be it for school or work or a TED talk about your area of speciality. We investigate how to get all those ideas from your head to a written speech and then back to your heart. Author of “ How to be Brilliant at Public Speaking “, Sarah Lloyd-Hughes explains the five steps of speech writing…
Even heads of state and other renowned orators have help in writing a speech. They often have professional speech writers to provide them with great content, but you too can learn not only how to talk but also how to write a speech like a pro.
Here are 5 steps that we take our speakers through when they’re writing a speech – and it’s the same process as we use for writing TED style talks.
Speech writing step 1: Get focused
TED talks famously focus on ‘one idea worth spreading’ and this is what helps them to retain their power. Before you write a single line, figure out what the ONE idea is that you’ll shape your talk around.
When your talk has a single focus you’ll see huge benefits:
- Clarity: For yourself and your audience.
- Easy to pass on: Popular talks, like Simon Sinek’s TED talk ‘ How great leaders inspire action ‘ or Ken Robinson’s TED favourite ‘ Do schools kill creativity? ‘ are utterly focused and easy to pass on because they have just one idea.
- Powerful: When you’re digging in one hole you get deeper, likewise with your talk you can go further with one idea.
- Memorability: Audiences these days are overwhelmed with ideas and information. You need to be much simpler than you think to stand a chance of your message being remembered.
To find your ‘idea worth spreading’ takes a little time and skill, which is why we’ve devised a complete programme for speakers who are interested in writing World Class Speeches , like the finest TED speakers.
But if you’re just looking for a place to start, these questions will help you get going:
- What do I want to say?
- What effect am I trying to have by speaking?
- If I can only put across one message in my speech, what will that be?
- What is my broader purpose in speaking?
You’re looking for one idea that is clear, interesting and hasn’t been heard before. Good luck!
Speech writing step 2: Think about your audience
Ironically, most speakers completely fail to think about their audience! Yet the best speakers are intimately aware of the needs, questions and doubts facing their audience.
Ask: To whom am I speaking? Before you start writing you first must ask yourself Who is my audience and what are they seeking ? Writing a speech for a group of human rights activists would be very different to a speech for business managers. Technology engineers might have a totally different perspective on your subject than a room full of English professors. Thinking deeply about your audience’s needs is the quality of a public speaker I call Empathy. It’s an important starting point on your speech writing journey.
Ask: Why should they listen to you? Great speech writing is grounded in purpose and message. Consider what qualifies you to speak; what you have to offer the audience that they would not be able to hear from anyone else (we all have something).
Ask: What do you want to leave your audience with? As a result of your Empathetic investigations, what would be your desired outcome as a result of the speech? Decide what your main message will be and continually return to that primary point as you compose your speech. This keeps the audience (and you) focused. As Winston Churchill said: “If you have an important point to make, don’t try to be subtle or clever. Use a pile driver. Hit the point once. Then come back and hit it again. Then hit it a third time with a tremendous whack. ”
Speech writing step 3: Build up your speech
Now you have a clear focus to your speech and an idea of how to communicate that clearly to your audience. That’s the skeleton of the speech. It’s now time to fill in that skeleton with meaty content:
- Brain Storming. Make lists of all the things you want to speak about. Once listed, it will be easier to cut or rearrange your points.
- Categorize for the win. Brainstorming should lead to a nice list with several categories. Speech writing is all about organization and finding what fits best with your audience and their needs. Think of these categories as stepping stones. Leaving a gap too large between any two stones and they will turn into stumbling blocks will sinking you and your audience. Speech writing is not very much different than writing a paper; thesis statement, support of the thesis, and a conclusion.
- Edit for the jewels . Look for the key moments in your speech that will stimulate the hearts, minds and even stomachs of your audience. Seek the most vivid experiences and stories that you can use to make your point – these are what will make your speech stand out from all the other public speaking our there.
Speech writing step 4: Create a journey
Another key skill of speech writing is to get the right information in the right order. Think of your speech like a journey up a mountain:
Get ready for the trip (introduction).
- The beginning of your speech is the place where you grab the attention of the audience and get them ready to go on a journey with you. For them to travel up your mountain with you they need to know where you’re going together, why it’s an interesting journey to go on and why you are a credible guide to lead them there.
Pass some interesting sights on the way (main body).
- Keep an audience engaged for an entire speech by raising the stakes, or raising the tension as you progress through the speech. Think about contrasts between the ‘good’ and the ‘evil’ of your subject matter and contrast the two with stories, facts, ideas or examples.
- Here you might write multiple sections to your speech, to help you stay focused. You might like to write an introduction, main body, and conclusion for each section also. All sections don’t have to be the same length. Take time to decide and write about the ones that need the most emphasis.
Reach your summit (climax).
- The climax is the moment of maximum emotional intensity that most powerfully demonstrates your key message. Think of the key ‘Ahah!’ moment that you want to take your audience to. This is the moment where you reach the top of your mountain and marvel at the view together. It’s a powerful, but underused speech writing tool.
A speedy descent (the close).
- Once you’ve hit your climax, the story is almost over. We don’t want to go all the way down the mountain with you, we’d much rather get airlifted off the top of the mountain whilst we still have the buzz of reaching our goal. This is what great speech writing manages time and again.
- Strangely enough the close can be the hardest part of speech writing. Here’s where you get to hit home your action point – the key thing you want your audience to do differently as a result of listening to your speech. Often the close is where speakers undermine the power of the rest of their speech. So, write a memorable conclusion that captures the essence of your speech, give it some punch, and stick to it!
Speech writing step 5: Test your material
Practice your speech several times so that you can feel comfortable with the material. Try the speech out on camera or to a friend to see which parts are most powerful and which you can take the red pen to.
However skilled you are (or not) at speech writing, remember that you are the magic that makes the speech work. It’s your authentic voice that will shine to the audience them and inspire them towards your message.
Follow these speech writing tips, give it some practice and you’ll be sure to be a speech writing winner.
But I’ve collected my years of experience working with world-class conference speakers and TED speakers and distilled it into a simple guidebook that you can access now for just £20 (+VAT) .
Ginger Leadership Communications
This showcase of inspiring female speakers is part of Ginger’s work with game changing leaders.


How to Write an Effective Speech Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The Speaker Lab
- March 8, 2024
Table of Contents
Mastering the art of speaking starts with crafting a stellar speech outline. A well-structured outline not only clarifies your message but also keeps your audience locked in.
In this article, you’ll learn how to mold outlines for various speech types, weaving in research that resonates and transitions that keep listeners on track. We’ll also show you ways to spotlight crucial points and manage the clock so every second counts. When it’s time for final prep, we’ve got smart tips for fine-tuning your work before stepping into the spotlight.
Understanding the Structure of a Speech Outline
An effective speech outline is like a map for your journey as a speaker, guiding you from start to finish. Think of it as the blueprint that gives shape to your message and ensures you hit all the right notes along the way.
Tailoring Your Outline for Different Speech Types
Different speeches have different goals: some aim to persuade, others inform or celebrate. Each type demands its own structure in an outline. For instance, a persuasive speech might highlight compelling evidence while an informative one focuses on clear explanations. Crafting your outline with precision means adapting it to fit these distinct objectives.
Incorporating Research and Supporting Data
Your credibility hinges on solid research and data that back up your claims. When writing your outline, mark the places where you’ll incorporate certain pieces of research or data. Every stat you choose should serve a purpose in supporting your narrative arc. And remember to balance others’ research with your own unique insights. After all, you want your work to stand out, not sound like someone else’s.
The Role of Transitions in Speech Flow
Slick transitions are what turn choppy ideas into smooth storytelling—think about how bridges connect disparate land masses seamlessly. They’re not just filler; they carry listeners from one thought to another while maintaining momentum.
Incorporate transitions that feel natural yet keep people hooked. To keep things smooth, outline these transitions ahead of time so nothing feels left up to chance during delivery.
Techniques for Emphasizing Key Points in Your Outline
To make certain points pop off the page—and stage—you’ll need strategies beyond bolding text or speaking louder. Use repetition wisely or pause strategically after delivering something significant. Rather than go impromptu, plan out what points you want to emphasize before you hit the stage.
Timing Your Speech Through Your Outline
A watchful eye on timing ensures you don’t overstay—or undercut—your moment under the spotlight. The rhythm set by pacing can be pre-determined through practice runs timed against sections marked clearly in outlines. Practice will help ensure that your grand finale isn’t cut short by surprise.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
Depending on the type of speech you’re giving, your speech outline will vary. The key ingredients—introduction, body, and conclusion—are always there, but nuances like tone or message will change with each speaking occasion.
Persuasive Speeches: Convincing With Clarity
When outlining a persuasive speech, arrange your arguments from strong to strongest. The primacy effect works wonders here, so make sure to start off with a strong point. And just when they think they’ve heard it all, hit them with an emotional story that clinches the deal.
You might start by sharing startling statistics about plastic pollution before pivoting to how individuals can make a difference. Back this up with data on successful recycling programs which demonstrate tangible impact, a technique that turns facts into fuel for action.
Informative Speeches: Educating Without Overwhelming
An informative speech shouldn’t feel like drinking from a fire hose of facts and figures. Instead, lay out clear subtopics in your outline and tie them together with succinct explanations—not unlike stepping stones across a stream of knowledge.
If you’re talking about breakthroughs in renewable energy technology, use bullet points to highlight different innovations then expand upon their potential implications one at a time so the audience can follow along without getting lost in technical jargon or complexity.
Ceremonial Speeches: Creating Moments That Matter
In a ceremonial speech you want to capture emotion. Accordingly, your outline should feature personal anecdotes and quotes that resonate on an emotional level. However, make sure to maintain brevity because sometimes less really is more when celebrating milestones or honoring achievements.
Instead of just going through a hero’s whole life story, share the powerful tales of how they stepped up in tough times. This approach hits home for listeners, letting them feel the impact these heroes have had on their communities and sparking an emotional bond.
Incorporating Research in Your Speech Outline
When you’re crafting a speech, the backbone of your credibility lies in solid research and data. But remember, it’s not just about piling on the facts. It’s how you weave them into your narrative that makes listeners sit up and take notice.
Selecting Credible Sources
Finding trustworthy sources is like going on a treasure hunt where not all that glitters is gold. To strike real gold, aim for academic journals or publications known for their rigorous standards. Google Scholar or industry-specific databases are great places to start your search. Be picky. Your audience can tell when you’ve done your homework versus when you’ve settled for less-than-stellar intel.
You want to arm yourself with evidence so compelling that even skeptics start nodding along. A well-chosen statistic from a reputable study does more than decorate your point—it gives it an ironclad suit of armor.
Organizing Information Effectively
Your outline isn’t just a roadmap; think of it as scaffolding that holds up your argument piece by piece. Start strong with an eye-opening factoid to hook your audience right off the bat because first impressions matter—even in speeches.
To keep things digestible, group related ideas together under clear subheadings within your outline. Stick to presenting data that backs up each key idea without wandering down tangential paths. That way, everyone stays on track.
Making Data Relatable
Sure, numbers don’t lie but they can be hard to connect to. If you plan on using stats in your speech, make them meaningful by connecting them to relatable scenarios or outcomes people care about deeply. For instance, if you’re talking health statistics, relate them back to someone’s loved ones or local hospitals. By making the personal connection for your audience, you’ll get their attention.
The trick is using these nuggets strategically throughout your talk, not dumping them all at once but rather placing each one carefully where its impact will be greatest.
Imagine your speech as a road trip. Without smooth roads and clear signs, the journey gets bumpy, and passengers might miss the scenery along the way. That’s where transitions come in. They’re like your speech’s traffic signals guiding listeners from one point to another.
Crafting Seamless Bridges Between Ideas
Transitions are more than just linguistic filler. They’re strategic connectors that carry an audience smoothly through your narrative. Start by using phrases like “on top of this” or “let’s consider,” which help you pivot naturally between points without losing momentum.
To weave these seamlessly into your outline, map out each major turn beforehand to ensure no idea is left stranded on a tangent.
Making Use of Transitional Phrases Wisely
Be cautious: overusing transitional phrases can clutter up your speech faster than rush hour traffic. Striking a balance is key—think about how often you’d want to see signposts on a highway. Enough to keep you confident but not so many that it feels overwhelming.
Pick pivotal moments for transitions when shifting gears from one major topic to another or introducing contrasting information. A little direction at critical junctures keeps everyone onboard and attentive.
Leveraging Pauses as Transition Tools
Sometimes silence speaks louder than words, and pauses are powerful tools for transitioning thoughts. A well-timed pause lets ideas resonate and gives audiences time to digest complex information before moving forward again.
This approach also allows speakers some breathing room themselves—the chance to regroup mentally before diving into their next point with renewed vigor.
Connecting Emotional Threads Throughout Your Speech
Last but not least, don’t forget emotional continuity, that intangible thread pulling heartstrings from start-to-finish. Even if topics shift drastically, maintaining an underlying emotional connection ensures everything flows together cohesively within the larger tapestry of your message.
Techniques for Emphasizing Key Points in Your Speech Outline
When you’re crafting your speech outline, shine a spotlight on what matters most so that your audience doesn’t miss your key points.
Bold and Italicize for Impact
You wouldn’t whisper your punchline in a crowded room. Similarly, why let your main ideas get lost in a sea of text? Use bold or italics to give those lines extra weight. This visual cue signals importance, so when you glance at your notes during delivery, you’ll know to emphasize those main ideas.
Analogies That Stick
A good analogy is like super glue—it makes anything stick. Weave them into your outline and watch as complex concepts become crystal clear. But remember: choose analogies that resonate with your target audience’s experiences or interests. The closer home it hits, the longer it lingers.
The Power of Repetition
If something’s important say it again. And maybe even once more after that—with flair. Repetition can feel redundant on paper, but audiences often need to hear critical messages several times before they take root.
Keep these strategies in mind when you’re ready to dive into your outline. You’ll transform those core ideas into memorable insights before you know it.
Picture this: you’re delivering a speech, and just as you’re about to reach the end, your time’s up. Ouch! Let’s make sure that never happens. Crafting an outline is not only about what to say but also how long to say it.
Finding Balance in Section Lengths
An outline isn’t just bullet points; it’s a roadmap for pacing. When outlining your speech, make sure to decide how much time you’d like to give each of your main points. You might even consider setting specific timers during rehearsals to get a real feel for each part’s duration. Generally speaking, you should allot a fairly equal amount of time for each to keep things balanced.
The Magic of Mini Milestones
To stay on track, a savvy speaker will mark time stamps or “mini milestones” on their outline. These time stamps give the speaker an idea of where should be in their speech by the time, say, 15 minutes has passed. If by checkpoint three you should be 15 minutes deep and instead you’re hitting 20 minutes, it’s time to pick up the pace or trim some fat from earlier sections. This approach helps you stay on track without having to glance at the clock after every sentence.
Utilizing Visual Aids and Multimedia in Your Outline
Pictures speak louder than words, especially when you’re on stage. Think about it: How many times have you sat through a presentation that felt like an eternity of endless bullet points? Now imagine if instead, there was a vibrant image or a short video clip to break up the monotony—it’s game-changing. That’s why integrating visual aids and multimedia into your speech outline isn’t just smart. It’s crucial for keeping your audience locked in.
Choosing Effective Visuals
Selecting the right visuals is not about flooding your slides with random images but finding those that truly amplify your message. Say you’re talking about climate change. In this case, a graph showing rising global temperatures can hit hard and illustrate your chosen statistic clearly. Remember, simplicity reigns supreme; one powerful image will always trump a cluttered collage.
Multimedia Magic
Videos are another ace up your sleeve. They can deliver testimonials more powerfully than quotes or transport viewers to places mere descriptions cannot reach. But be warned—timing is everything. Keep clips short and sweet because no one came to watch a movie—they came to hear you . You might highlight innovations using short video snippets, ensuring these moments serve as compelling punctuations rather than pauses in your narrative.
The Power of Sound
We often forget audio when we think multimedia, yet sound can evoke emotions and set tones subtly yet effectively. Think striking chords for dramatic effect or nature sounds for storytelling depth during environmental talks.
Audiences crave experiences they’ll remember long after they leave their seats. With well-chosen visuals and gripping multimedia elements woven thoughtfully into every section of your speech outline, you’ll give them exactly that.
Rehearsing with Your Speech Outline
When you’re gearing up to take the stage, your speech outline is a great tool to practice with. With a little preparation, you’ll give a performance that feels both natural and engaging.
Familiarizing Yourself with Content
To start off strong, get cozy with your outline’s content. Read through your outline aloud multiple times until the flow of words feels smooth. This will help make sure that when showtime comes around, you can deliver those lines without tripping over tough transitions or complex concepts.
Beyond mere memorization, understanding the heart behind each point allows you to speak from a place of confidence. You know this stuff—you wrote it. Now let’s bring that knowledge front and center in an authentic way.
Mimicking Presentation Conditions
Rehearsing under conditions similar to those expected during the actual presentation pays off big time. Are you going to stand or roam about? Will there be a podium? Think about these details and simulate them during rehearsal because comfort breeds confidence—and we’re all about boosting confidence.
If technology plays its part in your talk, don’t leave them out of rehearsals either. The last thing anyone needs is tech trouble during their talk.
Perfecting Pace Through Practice
Pacing matters big time when speaking. Use timed rehearsals to nail down timing. Adjust speed as needed but remember: clarity trumps velocity every single time.
You want people hanging onto every word, which is hard to do if you’re talking so fast they can barely make out what you’re saying. During rehearsals, find balance between pacing and comprehension; they should go hand-in-hand.
Finalizing Your Speech Outline for Presentation
You’ve poured hours into crafting your speech, shaping each word and idea with precision. Now, it’s time to tighten the nuts and bolts. Finalizing your outline isn’t just about dotting the i’s and crossing the t’s. It’s about making sure your message sticks like a perfectly thrown dart.
Reviewing Your Content for Clarity
Your first task is to strip away any fluff that might cloud your core message. Read through every point in your outline with a critical eye. Think of yourself as an editor on a mission to cut out anything that doesn’t serve a purpose. Ask yourself if you can explain each concept clearly without needing extra words or complex jargon. If not, simplify.
Strengthening Your Argument
The meat of any good presentation lies in its argument, the why behind what you’re saying. Strengthen yours by ensuring every claim has iron-clad backing—a stat here, an expert quote there. Let this be more than just facts tossed at an audience; weave them into stories they’ll remember long after they leave their seats.
Crafting Memorable Takeaways
Audiences may forget details but never how you made them feel—or think. Embed memorable takeaways throughout your outline so when folks step out into fresh air post-talk, they carry bits of wisdom with them.
This could mean distilling complex ideas down to pithy phrases or ending sections with punchy lines that resonate. It’s these golden nuggets people will mine for later reflection.
FAQs on Speech Outlines
How do you write a speech outline.
To craft an outline, jot down your main ideas, arrange them logically, and add supporting points beneath each.
What are the 3 main parts of a speech outline?
An effective speech has three core parts: an engaging introduction, a content-rich body, and a memorable conclusion.
What are the three features of a good speech outline?
A strong outline is clear, concise, and structured in logical sequence to maximize impact on listeners.
What is a working outline for a speech?
A working outline serves as your blueprint while preparing. It’s detailed but flexible enough to adjust as needed.
Crafting a speech outline is like drawing your map before the journey. It starts with structure and flows into customization for different types of talks. Remember, research and evidence are your compass—they guide you to credibility. Transitions act as bridges, connecting one idea to another smoothly. Key points? They’re landmarks so make them shine.
When delivering your speech, keep an eye on the clock and pace yourself so that every word counts.
Multimedia turns a good talk into a great show. Rehearsing polishes that gem of a presentation until it sparkles.
Last up: fine-tuning your speech outline means you step out confident, ready to deliver something memorable because this isn’t just any roadmap—it’s yours.
- Last Updated: March 5, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
Speech Writing
Speech Examples
20+ Outstanding Speech Examples for Your Help

People also read
The 10 Key Steps for Perfect Speech Writing
Understanding the Speech Format - Detailed Guide & Examples
How to Start A Speech - 13 Interesting Ideas & Examples
Common Types of Speeches that Every Speechwriter Should Know
Good Impromptu Speech Topics for Students
Entertaining Speech Topics for Your Next Debate
How to Write a Special Occasion Speech: Types, Tips, and Examples
Introduction Speech - A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
How to Write the Best Acceptance Speech for Your Audience?
Presentation Speech - An Ultimate Writing Guide
Commemorative Speech - Writing Guide, Outline & Examples
Farewell Speech - Writing Tips & Examples
How to Write an Extemporaneous Speech? A Step-by-Step Guide
Crafting the Perfect Graduation Speech: A Guide with Examples
Public speaking can be daunting for students. They often struggle to start, engage the audience, and be memorable. It's a fear of forgetting words or losing the audience's interest.
This leads to anxiety and self-doubt. Students wonder, "Am I boring them? Will they remember what I say? How can I make my speech better?"
The solution lies in speech examples. In this guide, we'll explore these examples to help students create captivating and memorable speeches with confidence.
So, keep reading to find helpful examples!
- 1. Speech Examples
- 2. Tips to Write a Good Speech
Speech Examples
Talking in front of a bunch of audiences is not as easy as it seems. But, if you have some good content to deliver or share with the audience, the confidence comes naturally.
Before you start writing your speech, it is a good idea that you go through some good speech samples. The samples will help to learn how to start the speech and put information into a proper structure.
Speech Examples for Students
Speech writing is a huge part of academic life. These types of writing help enhance the creative writing skills of students.
Here is an amazing farewell speech sample for students to learn how to write an amazing speech that will captivate the audience.
Below, you will find other downloadable PDF samples.
Speech Examples for Students
Every school and college has a student council. And every year, students elect themselves to be a part of the student council. It is mandatory to impress the student audience to get their votes. And for that, the candidate has to give an impressive speech.
Here are some speech examples pdf for students.
Speech Examples For Public Speaking
Speech Examples About Yourself
Speech Examples Short
Speech Examples For College Students
Speech For Student Council
Speech Examples Introduction
Speech Example For School
Persuasive Speech Examples
The main purpose of a speech is to persuade the audience or convince them of what you say. And when it comes to persuasive speech , the sole purpose of speech becomes more specific.
Persuasive Speech Example
Informative Speech Examples
Informative speeches are intended to inform the audience. These types of speeches are designed to provide a detailed description of the chosen topic.
Below we have provided samples of informative speech for you.
Informative Speech Example
Informative Speech Sample
Entertainment Speech Examples
Entertainment speeches are meant to entertain the audience. These types of speeches are funny, as well as interesting. The given speech samples will help you in writing an entertaining speech.
Entertainment Speech Example
Entertainment Speech Sample
Argumentative Speech Examples
Making a strong argument that is capable of convincing others is always difficult. And, when it comes to making a claim in an argumentative speech, it becomes more difficult.
Check out the argumentative speech sample that demonstrates explicitly how an argumentative speech needs to be written.
Argumentative Speech Example
Demonstration Speech Examples
The demonstrative speeches are intended to demonstrate or describe the speech topic in depth. Get inspired by the demonstrative speech sample given below and write a captivating demonstrative speech.
Demonstration Speech Example
Demonstration Speech Sample
Motivational Speech Examples
Motivational speeches are designed to motivate the audience to do something. Read out the sample motivational speech given below and learn the art of motivational speech writing.
Impromptu Speech Examples
Impromptu speech writing makes you nervous as you are not good at planning and organization?
Check out the sample impromptu speech and learn to make bullet points of your thoughts and plan your speech properly.
Graduation Speech Examples
Are you graduating soon and need to write a graduation farewell speech?
Below is a sample graduation speech for your help.
Wedding Speech Examples
“My best friend’s wedding is next week, and I’m the maid of honor. She asked me to give the maid of honor speech, but I’m not good at expressing emotions. I’m really stressed. I don’t know what to do.”
If you are one of these kinds of people who feel the same way, this sample is for you. Read the example given below and take help from it to write a special maid of honor speech.
Best Man Speech Examples
Father of The Bride Speech Example
Speech Essay Example
A speech essay is a type of essay that you write before writing a proper speech. It helps in organizing thoughts and information.
Here is a sample of speech essays for you to understand the difference between speech format and speech essay format.
Tips to Write a Good Speech
Reading some famous and incredible sample speeches before writing your own speech is really a good idea. The other way to write an impressive speech is to follow the basic tips given by professional writers.
- Audience Analysis: Understand your audience's interests, knowledge, and expectations. Tailor your speech to resonate with them.
- Clear Purpose: Define a clear and concise purpose for your speech. Ensure your audience knows what to expect right from the beginning.
- Engaging Opening: Start with a captivating hook – a story, question, quote, or surprising fact to grab your audience's attention.
- Main Message: Identify and convey your main message or thesis throughout your speech.
- Logical Structure: Organize your speech with a clear structure, including an introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Transitions: Use smooth transitions to guide your audience through different parts of your speech.
- Conversational Tone: Use simple, conversational language to make your speech accessible to everyone.
- Timing: Respect the allocated time and write the speech accordingly. An overly long or short speech can diminish the audience's engagement.
- Emotional Connection: Use storytelling and relatable examples to evoke emotions and connect with your audience.
- Call to Action (if appropriate): Encourage your audience to take action, change their thinking, or ponder new ideas.
- Practice Natural Pace: Speak at a natural pace, avoiding rushing or speaking too slowly.
So, now you know that effective communication is a powerful tool that allows you to inform, persuade, and inspire your audience. Throughout this blog, we've provided you with numerous examples and invaluable tips to help you craft a compelling speech.
And for those moments when you require a professionally written speech that truly stands out, remember that our team is here to help. We can rescue you from writer's block and deliver an outstanding speech whenever you need it.
With our professional essay writing service , you can be confident in your ability to communicate your message effectively and leave a lasting impact.
So, don't hesitate – place order now and buy speech that will truly captivate your audience.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Column: Lauren Boebert is her own best asset — and worst enemy — as she fights to stay in Congress

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
Lauren Boebert was preaching to the faithful, prowling the stage of a megachurch and delivering a sermon — filled with Scripture and references to Christ and Satan — taken straight from the Book of Grievance.
She spit fire.
At President Biden and denizens of the Beltway swamp. At those criminally prosecuting former President Trump . At politicians presuming to substitute their judgment for God’s. And, not least, at the “sellouts” within her own Republican Party.
“Every time that dirty four-letter word called ‘compromise’ comes up,” Boebert fumed, “it’s always Republicans stepping away from their principles, their platform, your priorities and siding with socialists, communists and Marxists.”
The darkened sanctuary of the Rez Church filled with claps, whoops and cries of “yes!”

Columnist Mark Z. Barabak joins candidates for various offices as they hit the campaign trail in this momentous election year.
With her swaggering persona, distinctly non-Washington wardrobe and gleeful trampling of protocols — heckling Biden during his State of the Union speech , toting a pistol in defiance of the capital’s tough gun laws — Boebert made herself into one of the most prominent faces of a feral breed of conservatives attacking Congress from within.
It didn’t play so well back home.
Despite her district’s solidly Republican leaning, Boebert very nearly lost her seat after a single term, to a Democrat who assailed her headline-hunting and “angertainment” approach to office. Facing a tough rematch, she abruptly decamped this year to a district clear on the other side of Colorado, where the Republican faces five opponents in a June 25 primary — many with deep roots in the region.

“This is where I grew up,” conservative activist Deborah Flora pointedly stated as Boebert scribbled notes alongside her at a breakfast forum in Castle Rock, a fast-growing exurb on the far edge of Denver’s sprawling metropolitan area. “This is where I raised my children.”
“I promise not to embarrass you,” another opponent, Logan County Commissioner Jerry Sonnenberg, chimed in. “I promise not to humiliate you.”
Sonnenberg wasn’t any more specific. He didn’t have to be.
In September, Boebert was tossed out of a Denver showing of the musical “Beetlejuice” after vaping, carrying on and getting handsy with her date. The scene was captured on camera and the PG-13 clip went viral, turning the 37-year-old lawmaker into a national punchline.
Worse, from a political standpoint, the off-color episode raised doubts about Boebert’s judgment and impetuous nature, and badly undermined her image as a family-minded conservative and devout Christian.
She has apologized repeatedly, though at times Boebert seems less than contrite.
Rallying a few hundred supporters at the Rez Church in Loveland, she assailed the $95-billion military aid package Biden just signed into law , calling the emergency relief for Ukraine and others a shameful product of Republican treachery and Democratic deceit.
“More political theater in Washington, D.C.,” she sniped. “If there’s any theater to criticize, I think it’s that one.”
The response was knowing laughter and a smattering of applause.
“Praise the Lord for his mercy,” Boebert added after a beat.
“And yours.”
Boebert is, in many ways, her own greatest political asset.
She’s a charismatic campaigner, filling a room with her slight 5-foot frame and a fusillade of attacks that issue forth in a high-volume, highly caffeinated rat-a-tat: against “open borders,” a “woke and weaponized federal government,” “the corruption of the Biden crime family,” say-one-thing-do-another Republicans.
“When I go to D.C., it isn’t to have fancy dinners with lobbyists and special-interest groups,” she told several dozen Republican regulars at the Castle Rock breakfast. “That is not a representative. That’s a welfare recipient.”
When Boebert moves about, she’s swarmed by selfie-seeking fans, reflecting the celebrity that’s turned her into a national personality and built a formidable fundraising base. (The $3.4 million and counting that Boebert has raised so far is several times more than her Republican opponents combined.)
But the reputation preceding her also makes Boebert her own worst enemy.

It’s not just the “Beetlejuice” episode. Details of her nasty divorce, including a restraining order against Boebert’s ex-husband, have been splattered across the media. In February, the oldest of Boebert’s four sons was arrested and charged with identity theft and other crimes.
She cited the personal shambles as the reason she switched districts, moving from western to eastern Colorado. “I wanted a fresh start for my boys,” Boebert said in an interview — though she could have very well stayed in her old district, which is roughly the size of Pennsylvania, and still put some distance between herself and her ex-husband.
Some voters question whether Boebert, with all her mess, is worth the trouble.
Larry, a 73-year-old retired postal worker, showed up at the fairgrounds in Castle Rock to look over the congressional field and eye Boebert in person. (He declined to state his last name to avoid being hassled for giving his opinion.)
“I like her voting record and the way she stands up to Democrats,” Larry said, as he added creamer to his coffee. “But I’m not sure about her leaving her district. And as a devout Christian, from a moral standpoint, I don’t like her antics at the theater in Denver.”
For some, however, Boebert’s don’t-give-a-flip attitude and not-in-the-least-conventional biography — she’s a high school dropout and became a grandmother at age 36 — make her authentic in a way most politicians aren’t.
Bill Bennett brought his French bulldog, Donald J. Tank, to see Boebert when she dropped by a coffee shop in Elizabeth, farm country about 15 miles east of Castle Rock. Portraits of livestock and multiple crosses filled the small space, which barely contained the 75 or so who crowded in.
Bennett, a 61-year-old civil contractor who switched from independent to Republican when Trump became president, wasn’t the least fazed by Boebert’s unruly escapades.
“She’s a total bad-ass. A total bad-ass,” he said, holding a Boebert for Congress sign in one hand and Tank’s leash in the other, “and I love that. We need strength and she’s got backbone. We need backbone in the Republican Party. I can’t stress that enough.”
In fact, Boebert may perhaps best be described as a Republican in name only, an epithet she frequently hurls at others; her allegiance is to Trump and the MAGA movement, not the expectations or designs of the Grand Old Party.
Boebert’s special guest in Elizabeth was Texas Rep. Ronny Jackson, a fellow traveler in the GOP’s burn-down-the-House caucus, who drove straight from Amarillo — a six-hour trip — to lend his support. Boasting of his contrarian approach, Jackson described his political “superpower” as not giving “a damn what anyone says about me.”
Boebert smiled broadly and clapped enthusiastically.
Whoever wins the GOP primary is virtually certain to be the next representative from Colorado’s 4th Congressional District. ( The incumbent, Ken Buck , unexpectedly stepped down in March; a caretaker is running in a separate contest to fill the final few months of his term.)
Unlike Boebert’s old district, which includes the posh mountain resorts of Aspen and Telluride, the new one is as flat and Republican as neighboring Kansas . There’s a broad streak of Christian conservatism, more akin to the South or Midwest than the rest of Colorado. Farming and ranching, not apres-ski, are the major industries.
In short, this is Trump Country.
In 2020, the former president won the 4th District by nearly three times his margin in Boebert’s old district. That makes Trump’s support for Boebert vitally important. He’s showcased in one of her TV spots — “Lauren, you’re gonna do fantastically” — and his son Donald Jr. appeared alongside her at church in Loveland, after campaigning for Boebert in her former district last summer.
Past a small forest of American flags, past tables of Trump merchandise and two armed policemen standing guard, Trump Jr. performed more than 30 minutes of political stand-up, mocking Biden (“this dips— has the nuclear codes?”) and making light of the Jan. 6 attack on the Capitol, before turning to the business at hand.
He acknowledged Boebert’s relatively recent arrival to the district, but said she “obviously made a mark in D.C., because they’re going after her like you wouldn’t believe. That’s a good thing. That, in and of itself, is probably the only endorsement you need. If the D.C. swamp people — especially the Republicans — dislike you, that’s probably a no-brainer.”
Boebert may be a newcomer, but having the most money and highest name recognition (for good and ill) makes her the candidate to beat. Running against a lone rival or two would be one thing. But with multiple candidates splitting the Republican vote, Boebert’s standing with the MAGA base — which may be 35% or more of the primary electorate — could be enough to send her back to Washington.
“It’s an environment that gives her a lot of advantages,” said Seth Masket, head of the University of Denver’s Center on American Politics, who’s closely followed the race. “But it doesn’t guarantee a win.”
The question is whether Boebert can stay out of her own way — and keep out of any more trouble — between now and the June primary.
“I do live large,” she said, unabashedly, in a conversation between campaign stops. “I live fast. I am very spontaneous.”
So put that down as a maybe.
More to Read

Granderson: What Katie Britt’s misleading, melodramatic speech revealed about the Republican Party
March 11, 2024
Letters to the Editor: ‘I see myself in Katie Britt’ — what liberal critics missed in the senator’s response

Column: Kari Lake talked smack about John McCain. Now she wants to take it back
Feb. 25, 2024
Get the latest from Mark Z. Barabak
Focusing on politics out West, from the Golden Gate to the U.S. Capitol.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.

Mark Z. Barabak is a political columnist for the Los Angeles Times, focusing on California and the West. He has covered campaigns and elections in 49 of the 50 states, including a dozen presidential contests and scores of mayoral, legislative, gubernatorial and congressional races. He also reported from the White House and Capitol Hill during the George H.W. Bush and Clinton administrations.
More From the Los Angeles Times

World & Nation
Trump says Biden is running a ‘Gestapo’ administration. It’s his latest reference to Nazi Germany
May 5, 2024

Calmes: Donald Trump’s terrible, horrible, no good, very bad second term

Column: Watch your step, Democrats. O.C.’s purple shine hides a red underbelly
May 4, 2024

As protests roil college campuses, young voters’ support for Biden hangs in the balance
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
- Speechwriting
How to Write a Persuasive Speech
Last Updated: December 10, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Patrick Muñoz . Patrick is an internationally recognized Voice & Speech Coach, focusing on public speaking, vocal power, accent and dialects, accent reduction, voiceover, acting and speech therapy. He has worked with clients such as Penelope Cruz, Eva Longoria, and Roselyn Sanchez. He was voted LA's Favorite Voice and Dialect Coach by BACKSTAGE, is the voice and speech coach for Disney and Turner Classic Movies, and is a member of Voice and Speech Trainers Association. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,526,655 times.
A persuasive speech is a speech intended to convince the audience to do something. Whether you want to get people to vote, stop littering, or change their minds about an important issue, persuasive speeches are an effective way to sway an audience. There are many elements that go into a successful persuasive speech. But, with some preparation and practice, you can deliver a powerful speech.
Preparing to Write

- Especially if your topic is a controversial one, it's a good idea to know the arguments on all sides of the issue. [1] X Research source Whatever argument you are making, you'll be more persuasive if you can address the views of the opposing side.
- Spend some time reading books or articles about your topic. You can go to the library and ask a librarian for help finding books, or just go online and find some articles. Make sure to use reliable sources, like major news organizations, or academic books or articles.
- Opinion-oriented sources, like editorials, talk radio, or partisan cable news, can be valuable for finding out what other people think about your topic. But, don't rely on them as your only source of information. They can be very biased. If you use them at all, make sure to read a variety of viewpoints on the matter, not just one side.

- For example, if your topic is recycling, it's important to know a lot about recycling. But, your speech will need to reflect exactly what you hope the audience will do. Are you trying to get people to vote in favor of a citywide recycling program? Or are you trying to convince them to sort out their glass and cans and put them in a separate bin? These will be different speeches, so having the goal spelled out early will help you craft your message.

- An audience that knows little about your topic will need more background information and simpler language. An audience made up of experts on the topic would likely find such a simple speech boring.
- Likewise, an audience that already supports your view on a topic will be easier to persuade to take some action. You won't need to convince them you are right, but only that they need to do something. By contrast, an audience that does not agree with you will need persuasion to even consider your point of view.
- For example, imagine you want to convince your audience to support a city-wide recycling program. If they already think recycling is important, you only need to convince them of the value of this specific program. But, if they don't care about recycling or oppose it, you will need to first convince them that recycling is worthwhile.

- Ethos. These are appeals to the audience's ethics or morals. For example: "Recycling is the right thing to do. Wasting our limited resources steals from future generations, which is immoral."
- Pathos. These are appeals to the audience's emotions. For example: "Think of the animals that lose their homes every day because of trees being chopped down. If we recycled more, we could save these beautiful forests."
- Logos. These are appeals to the audiences logic or intellect. For example: "We know that there is a limited supply of natural resources. We can make this supply last longer by recycling."
- You can rely on any one or some combination.

- The number of points you can make to support your position will be determined by how much time you have to speak.
- As a rule of thumb, three to four supporting points is usually a good number. [2] X Research source
- For example, in the speech about recycling, your three main points might be: 1. Recycling saves resources, 2. Recycling reduces the amount of garbage, and 3. Recycling is cost-effective.
Writing your Speech

- An attention grabber. This could be a statement (or sometimes a visual) that gets your audience's attention. It can be a good idea to be a little startling or dramatic at the opening of your speech. For example, you might start with information (or pictures) showing how a nearby landfill is nearly full to capacity.
- A link to the audience. This is a means of showing that you have something in common with the audience. Show that you have a similar background or share an emotional connection of some kind. This will really depend on knowing your audience. For example, if you are a parent, speaking to other parents, you might emphasize the concern for your own children's future. If you share a common interest or ideological position with your audience, you can emphasize that.
- Your credentials. This is a means of showing that you are knowledgeable or an authority on the topic of the speech. Highlight the research you've done on your topic. If you have any personal or professional experience with the topic, be sure to emphasize that, too. In the recycling example, you might say "I've invested many hours studying the recycling issue and the types of programs available in other cities."
- Your goal. Explain to the audience what you hope the speech will accomplish. For example: "I hope by the end of my talk that you will agree that we need a city wide recycling program."
- A road map. Finally, tell the audience what the main points of the speech will be. For example, "I believe we must start a recycling program for these three reasons...."

- Arrange these points logically. Don't jump from one point to the next, and then back again. Instead, complete an argument, then move on to another that flows logically from it. [4] X Research source
- Use credible sources from your research to back the points you are making. Even if your point is more emotional (pathos), introducing some factual information will make your argument stronger. For example "Each year, 40,000 acres of beautiful forests are destroyed to make paper, according to a study from the American Recycling Institute."
- Use real life examples that the audience can relate to. Even an argument based on facts and logic (logos) should relate to the audience's lives and interests. For example: "In these hard economic times, I know many of you are afraid that a recycling program will mean a costly increase in taxes. But, the city of Springfield started a program like this one three years ago. So far they've seen an increase in revenue as a result of the program. Many residents have seen a decrease in their taxes as a result."

- Make sure that you describe opposing views fairly and objectively. Consider whether someone who actually holds that view would approve of the way you are describing their position. If you aren't sure, find someone who thinks that way and ask!
- For example, you would not want to say: "opponents of recycling just don't care if we waste our precious resources, or our money." That's not a fair description of their opinion.
- Instead, you might say: "opponents of recycling are concerned that the cost might be much higher than just using new materials," and then go on to offer an argument about why recycling might be the more cost-effective option.

- Don't just restate, verbatim, what you've already said. Instead, use this as an opportunity to reinforce the way your main points support your call to action. For example: "To sum up, I've shown you (points a, b, and c). These three undeniable facts point to a city-wide recycling program as the most sensible and ethical step we can take in helping create a more sustainable future. Please, join me in voting 'yes' on this program in November."
Delivering your Speech

- Try practicing in front of a mirror, so that you can see how you are delivering the speech. This can help you notice your facial expressions and body language. These can help or hinder your ability to get your message across.
- For example, you might notice you are slouching, or that that you fidget with your collar. These actions suggest to an audience that you aren't confident.
- Better still, record yourself with a video camera and watch the tape afterwards. This can help you see (and hear) where your delivery needs improvement. [5] X Research source It has the benefit of providing audio, and also won't distract you as much as a mirror when you're speaking.
- Once you've practiced on your own a few times, try giving the speech to a small group of friends or family members. Ask for their feedback on your message and delivery.

- Generally speaking, this will mean dressing professionally. But, the degree of formality will vary. A speech to a film club to convince them to show your film won't require the same degree of formality as speaking to the executives of a movie distribution company. For the executives, you would want to wear a suit. For the film club, that might be overdoing it.

- Be friendly and make eye contact with the audience.
- Move around, where appropriate, but don't fidget or pick at your clothes or hair.
- Don't read the speech. It's okay to use a few notes to keep yourself on track, but your speech should be mostly memorized.
- Roll with the punches. If you make a mistake, don't let it derail your whole speech. This might be an opportunity to use a little humor. Then, move on.

- For example, if you want them to contact the mayor, demanding a recycling program, don't just ask them to do it. Give them stamped, addressed envelopes to send a letter, or cards with the mayor's phone number and email address. If you do this, many more people are likely to follow through.
Patrick Muñoz
Speak from your heart and connect with your audience. Look them in the eyes and really talk to them. Make sure you're comfortable delivering your speech and that you use a warm, confident tone.
Sample Template

Community Q&A
- Look around at the audience, making eye contact, especially during pauses in your speech. If you're feeling nervous about this, pick out a single person in the audience and pretend you are speaking only to them. After a little while, pick someone else, and repeat. [6] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Speak forward, projecting your voice toward the audience with confidence. Do not speak down toward the floor. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Try to cite sources for statistics and use credible, non-biased sources. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Avoid being confrontational, when possible. Don't be sarcastic or mocking when discussing viewpoints other than your own. This can be alienating to your audience, even those who may agree with you. Thanks Helpful 55 Not Helpful 17
- Don't be pompous or arrogant during your speech. Be humble, and be open to questions, suggestions, and feedback. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://grammar.yourdictionary.com/style-and-usage/steps-for-writing-a-persuasive-speech.html
- ↑ http://www.best-speech-topics.com/writing-a-persuasive-speech.html
- ↑ https://www.speechanddebate.org/wp-content/uploads/Tips-for-Writing-a-Persuasive-Speech.pdf
- ↑ https://www.comm.pitt.edu/structuring-speech
- ↑ https://www.leonardoenglish.com/blog/recording-yourself-in-english
- ↑ https://www.zenbusiness.com/blog/eyecontact/
About This Article

To write a persuasive speech, start with a strong opening that will make your reader want to pay attention, including an attention grabber, your credentials, the essay's goal, and a road map for the essay. Next, offer persuasive evidence or reasons why the reader should support your viewpoint. Arrange these points logically, use credible sources, and employ some real life examples. Additionally, address counter-arguments to show that you’re looking at the topic from all sides. Finally, conclude by clearly letting the audience know how to put your ideas into action. To learn how to involve your audience when you deliver your speech, keep reading. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Evan Murphree
Feb 8, 2022
Did this article help you?
Dianka Pradhan
Jun 28, 2019
Brittany Grech
Mar 27, 2017
Mavis Agyeiwaa Kyei
Oct 27, 2020
Jun 5, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

COMMENTS
Create an outline: Develop a clear outline that includes the introduction, main points, supporting evidence, and a conclusion. Share this outline with the speaker for their input and approval. Write in the speaker's voice: While crafting the speech, maintain the speaker's voice and style.
Tell them (Body of your speech - the main ideas plus examples) Tell them what you told them (The ending) TEST before presenting. Read aloud several times to check the flow of material, the suitability of language and the timing. Return to top. A step by step guide for writing a great speech.
How to Write a Speech in 5 Steps. 1. Make an Outline. Just like in essay writing, writing a speech outline will help surface key points. This doesn't need to be overly complicated. Most speeches contain three main sections. The intro, which might feature personal stories that illustrate the subject or problem you're addressing; the body of ...
For example, people use one writing tool to put the speech's theme in a 15-20 word short poem or memorable paragraph, then build your speech around it. 3. Have a Clear Structure. When your speech has a clear structure to it your speech becomes more memorable. When writing your speech, have a clear path and a destination.
Second Part: Describes a possible solution or set of solutions. Third Part: Summarizes how the solutions will solve the problem. 3. Write in the same tone as you speak. One of the most important public speaking tips is to remember that you are writing something that you will be speaking out loud for people to hear.
5. Use concrete details and visual aids. Use concrete details to support your points. Brief stories, interesting examples, or factual data can help to engage your audience and convey the truth of your purpose. Consider using visual aids to further support your speech. Images can be powerful and engaging.
After you've completed outlining your speech, you'll be ready to do any extra research required, and then you're on to the task of writing your speech. Martha's completed outline. Here's Martha's Finished Outline as an example. Speech length: 15 minutes with extra time for a 'Question and Answer' session at the end of the presentation.
8. Conclude your speech with a call-to-action. As you near the end of your speech, your audience should be excited by your topic and ready to act. Encourage your audience to find out more and participate in a solution to the problem you have described by telling them how they can do so.
Giving a Best Man Speech. Step 1. Find your speech's "Golden Thread". The first lesson in how to write a speech is setting a clear objective from the get-go — so that what you write doesn't end up being vague or convoluted. Afterall, If you don't know exactly what your speech is about, neither will your audience.
Choose your topic and the main points that your speech will cover. Know your audience and get to know what they are looking for. Pay attention to their needs. Define the purpose of the speech and properly organize it. Introduction. A strong statement to grab the reader's attention. Refine the thesis statement.
Here is a step-by-step guide to writing a great speech structure, which is broken down into two parts, that is, preparation and writing. ... If you're still not convinced writing a speech is useful, read this article on 9 Reasons Why Writing A Speech Is Important which will change your mind.
For you as the speaker, it's much easier (and more powerful) to tell a story that you lived versus one you read in a book. 2. Write out your speech from beginning to end. As Grant Baldwin discusses in this video on preparing your talk, you want to write out your talk to have a basic structure: beginning, middle, and end.
A great speech will engage the audience and can lead to greater personal and professional success. Here are seven steps to writing an effective speech. Know what your core message is. When preparing to write a speech, you want to start by thinking about the core message you want to share. Your core message should be a topic you're ...
2. Include a hook, thesis, and road map of your speech in the introduction. It's common to begin a speech with an attention-grabbing device, such as an anecdote, rhetorical question, or quote. [8] After getting the audience's attention, state your thesis, then preview the points your speech will cover.
Speech writing step 1: Get focused. TED talks famously focus on 'one idea worth spreading' and this is what helps them to retain their power. Before you write a single line, figure out what the ONE idea is that you'll shape your talk around. When your talk has a single focus you'll see huge benefits: Clarity: For yourself and your audience.
1. Be clear on the occasion. It's important to know what kind of speech you're giving and why your audience is gathering to hear it in order to get started on the right foot. [1] Understand if your speech is meant to be a personal narrative, informative, persuasive or ceremonial. [2] Personal narrative.
A successful speech is one that engages the audience and expresses a subject or set of topics clearly. Writing and delivering an effective speech could help to advance your career by developing and displaying strong communication, leadership and interpersonal skills.In this article, we explain steps and tips for how to write an effective speech that illustrates your subject and captures your ...
When outlining your speech, make sure to decide how much time you'd like to give each of your main points. You might even consider setting specific timers during rehearsals to get a real feel for each part's duration. Generally speaking, you should allot a fairly equal amount of time for each to keep things balanced.
Writing a speech. Overview. The purpose of a speech is often to inform or persuade an audience. Speeches are usually written to be spoken directly to an audience and can be used to entertain, influencing the listeners that the viewpoint of the speaker is correct. Speeches can also be used to encourage the audience to take action or to change ...
Here are 26 different techniques for beginning your speech: 1. Use a quote. One method of starting a speech and gaining the audience's attention is to use a famous or relatable quote. This approach can give your audience context for your topic and connect it to something they recognize. For instance, if you plan to give a speech on a political ...
Choose how to keep your speech on point. Decide whether you want to write out your speech or to outline the speech on index cards. Consider your comfort level with the topic. If you know the topic well and can improvise easily, then use index cards. Use 1 card for the introduction. This card should include your opening statement.
Tips to Write a Good Speech. Reading some famous and incredible sample speeches before writing your own speech is really a good idea. The other way to write an impressive speech is to follow the basic tips given by professional writers. Audience Analysis: Understand your audience's interests, knowledge, and expectations. Tailor your speech to ...
The process of speech planning in the brain is a complex, multi-step process involving various brain regions working in coordination. It includes several key stages: Conceptualization
In a new district, the fiery Colorado congresswoman enjoys a solid base among the GOP's MAGA wing. But some are put off by her indiscretions and messy personal life.
3. Address the counter-argument. Although it is not strictly necessary, your argument may be stronger if one or more of your supporting points addresses the views of the opposing side. This gives you a chance to address your audience's possible objections and make your argument stronger.