Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved June 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Jun 18, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews


Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
| Annotated Bibliography | Literature Review | |
| Purpose | List of citations of books, articles, and other sources with a brief description (annotation) of each source. | Comprehensive and critical analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. |
| Focus | Summary and evaluation of each source, including its relevance, methodology, and key findings. | Provides an overview of the current state of knowledge on a particular subject and identifies gaps, trends, and patterns in existing literature. |
| Structure | Each citation is followed by a concise paragraph (annotation) that describes the source’s content, methodology, and its contribution to the topic. | The literature review is organized thematically or chronologically and involves a synthesis of the findings from different sources to build a narrative or argument. |
| Length | Typically 100-200 words | Length of literature review ranges from a few pages to several chapters |
| Independence | Each source is treated separately, with less emphasis on synthesizing the information across sources. | The writer synthesizes information from multiple sources to present a cohesive overview of the topic. |
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to structure an essay, leveraging generative ai to enhance student understanding of..., what’s the best chatgpt alternative for academic writing, how to write a good hook for essays,..., addressing peer review feedback and mastering manuscript revisions..., how paperpal can boost comprehension and foster interdisciplinary..., what is the importance of a concept paper..., how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding....
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 18 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
- Library Homepage
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide: Literature Reviews?
- Literature Reviews?
- Strategies to Finding Sources
- Keeping up with Research!
- Evaluating Sources & Literature Reviews
- Organizing for Writing
- Writing Literature Review
- Other Academic Writings
What is a Literature Review?
So, what is a literature review .
"A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available or a set of summaries." - Quote from Taylor, D. (n.d)."The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting it".
- Citation: "The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting it"
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Each field has a particular way to do reviews for academic research literature. In the social sciences and humanities the most common are:
- Narrative Reviews: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific research topic and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weaknesses, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section that summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Book review essays/ Historiographical review essays : A type of literature review typical in History and related fields, e.g., Latin American studies. For example, the Latin American Research Review explains that the purpose of this type of review is to “(1) to familiarize readers with the subject, approach, arguments, and conclusions found in a group of books whose common focus is a historical period; a country or region within Latin America; or a practice, development, or issue of interest to specialists and others; (2) to locate these books within current scholarship, critical methodologies, and approaches; and (3) to probe the relation of these new books to previous work on the subject, especially canonical texts. Unlike individual book reviews, the cluster reviews found in LARR seek to address the state of the field or discipline and not solely the works at issue.” - LARR
What are the Goals of Creating a Literature Review?
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
- Baumeister, R.F. & Leary, M.R. (1997). "Writing narrative literature reviews," Review of General Psychology , 1(3), 311-320.
When do you need to write a Literature Review?
- When writing a prospectus or a thesis/dissertation
- When writing a research paper
- When writing a grant proposal
In all these cases you need to dedicate a chapter in these works to showcase what has been written about your research topic and to point out how your own research will shed new light into a body of scholarship.
Where I can find examples of Literature Reviews?
Note: In the humanities, even if they don't use the term "literature review", they may have a dedicated chapter that reviewed the "critical bibliography" or they incorporated that review in the introduction or first chapter of the dissertation, book, or article.
- UCSB electronic theses and dissertations In partnership with the Graduate Division, the UC Santa Barbara Library is making available theses and dissertations produced by UCSB students. Currently included in ADRL are theses and dissertations that were originally filed electronically, starting in 2011. In future phases of ADRL, all theses and dissertations created by UCSB students may be digitized and made available.
Where to Find Standalone Literature Reviews
Literature reviews are also written as standalone articles as a way to survey a particular research topic in-depth. This type of literature review looks at a topic from a historical perspective to see how the understanding of the topic has changed over time.
- Find e-Journals for Standalone Literature Reviews The best way to get familiar with and to learn how to write literature reviews is by reading them. You can use our Journal Search option to find journals that specialize in publishing literature reviews from major disciplines like anthropology, sociology, etc. Usually these titles are called, "Annual Review of [discipline name] OR [Discipline name] Review. This option works best if you know the title of the publication you are looking for. Below are some examples of these journals! more... less... Journal Search can be found by hovering over the link for Research on the library website.
Social Sciences
- Annual Review of Anthropology
- Annual Review of Political Science
- Annual Review of Sociology
- Ethnic Studies Review
Hard science and health sciences:
- Annual Review of Biomedical Data Science
- Annual Review of Materials Science
- Systematic Review From journal site: "The journal Systematic Reviews encompasses all aspects of the design, conduct, and reporting of systematic reviews" in the health sciences.
- << Previous: Overview
- Next: Strategies to Finding Sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 5, 2024 11:44 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucsb.edu/litreview
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Literature review

How to write a literature review in 6 steps
How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.

How to write a systematic literature review [9 steps]
How do you write a systematic literature review? What types of systematic literature reviews exist and where do you use them? Learn everything you need to know about a systematic literature review in this guide

What is a literature review? [with examples]
Not sure what a literature review is? This guide covers the definition, purpose, and format of a literature review.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
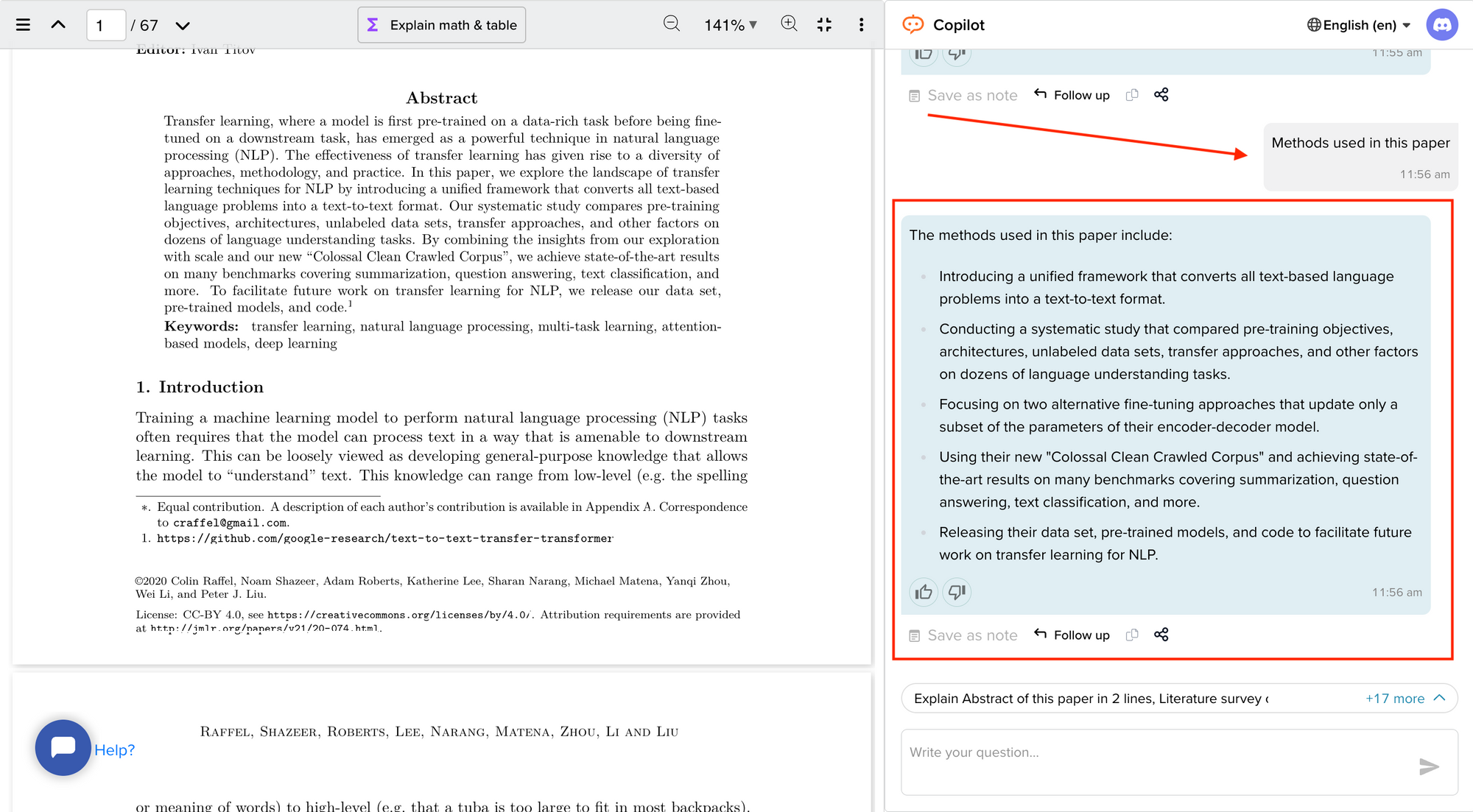
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

What’s the state of hiring researchers in science? Share your insights with Nature
Career News 19 JUN 24

How researchers and their managers can build an actionable career-development plan
Career Column 17 JUN 24

Tiny beauty: how I make scientific art from behind the microscope
Career Feature 17 JUN 24

Three ways to recognize hidden labour in research
Nature Index 13 JUN 24

‘It can feel like there’s no way out’ — political scientists face pushback on their work
News Feature 19 JUN 24

How climate change is hitting Europe: three graphics reveal health impacts
News 18 JUN 24

Twelve scientist-endorsed tips to get over writer’s block
Career Feature 13 JUN 24
ZJU 100 Young Professor
Promising young scholars who can independently establish and develop a research direction.
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Zhejiang University

Qiushi Chair Professor
Distinguished scholars with notable achievements and extensive international influence.
Research Postdoctoral Fellow - MD
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Postdoctoral position for EU project ARTiDe: A novel regulatory T celltherapy for type 1 diabetes
Development of TCR-engineered Tregs for T1D. Single-cell analysis, evaluate TCRs. Join INEM's cutting-edge research team.
Paris, Ile-de-France (FR)
French National Institute for Health Research (INSERM)
Postdoc or PhD position: the biology of microglia in neuroinflammatory disease
Join Our Team! Investigate microglia in neuroinflammation using scRNAseq and genetic tools. Help us advance CNS disease research at INEM!
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2024 9:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
What Is A Literature Review?
A plain-language explainer (with examples).
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) & Kerryn Warren (PhD) | June 2020 (Updated May 2023)
If you’re faced with writing a dissertation or thesis, chances are you’ve encountered the term “literature review” . If you’re on this page, you’re probably not 100% what the literature review is all about. The good news is that you’ve come to the right place.
Literature Review 101
- What (exactly) is a literature review
- What’s the purpose of the literature review chapter
- How to find high-quality resources
- How to structure your literature review chapter
- Example of an actual literature review
What is a literature review?
The word “literature review” can refer to two related things that are part of the broader literature review process. The first is the task of reviewing the literature – i.e. sourcing and reading through the existing research relating to your research topic. The second is the actual chapter that you write up in your dissertation, thesis or research project. Let’s look at each of them:
Reviewing the literature
The first step of any literature review is to hunt down and read through the existing research that’s relevant to your research topic. To do this, you’ll use a combination of tools (we’ll discuss some of these later) to find journal articles, books, ebooks, research reports, dissertations, theses and any other credible sources of information that relate to your topic. You’ll then summarise and catalogue these for easy reference when you write up your literature review chapter.
The literature review chapter
The second step of the literature review is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or thesis structure ). At the simplest level, the literature review chapter is an overview of the key literature that’s relevant to your research topic. This chapter should provide a smooth-flowing discussion of what research has already been done, what is known, what is unknown and what is contested in relation to your research topic. So, you can think of it as an integrated review of the state of knowledge around your research topic.

What’s the purpose of a literature review?
The literature review chapter has a few important functions within your dissertation, thesis or research project. Let’s take a look at these:
Purpose #1 – Demonstrate your topic knowledge
The first function of the literature review chapter is, quite simply, to show the reader (or marker) that you know what you’re talking about . In other words, a good literature review chapter demonstrates that you’ve read the relevant existing research and understand what’s going on – who’s said what, what’s agreed upon, disagreed upon and so on. This needs to be more than just a summary of who said what – it needs to integrate the existing research to show how it all fits together and what’s missing (which leads us to purpose #2, next).
Purpose #2 – Reveal the research gap that you’ll fill
The second function of the literature review chapter is to show what’s currently missing from the existing research, to lay the foundation for your own research topic. In other words, your literature review chapter needs to show that there are currently “missing pieces” in terms of the bigger puzzle, and that your study will fill one of those research gaps . By doing this, you are showing that your research topic is original and will help contribute to the body of knowledge. In other words, the literature review helps justify your research topic.
Purpose #3 – Lay the foundation for your conceptual framework
The third function of the literature review is to form the basis for a conceptual framework . Not every research topic will necessarily have a conceptual framework, but if your topic does require one, it needs to be rooted in your literature review.
For example, let’s say your research aims to identify the drivers of a certain outcome – the factors which contribute to burnout in office workers. In this case, you’d likely develop a conceptual framework which details the potential factors (e.g. long hours, excessive stress, etc), as well as the outcome (burnout). Those factors would need to emerge from the literature review chapter – they can’t just come from your gut!
So, in this case, the literature review chapter would uncover each of the potential factors (based on previous studies about burnout), which would then be modelled into a framework.
Purpose #4 – To inform your methodology
The fourth function of the literature review is to inform the choice of methodology for your own research. As we’ve discussed on the Grad Coach blog , your choice of methodology will be heavily influenced by your research aims, objectives and questions . Given that you’ll be reviewing studies covering a topic close to yours, it makes sense that you could learn a lot from their (well-considered) methodologies.
So, when you’re reviewing the literature, you’ll need to pay close attention to the research design , methodology and methods used in similar studies, and use these to inform your methodology. Quite often, you’ll be able to “borrow” from previous studies . This is especially true for quantitative studies , as you can use previously tried and tested measures and scales.

How do I find articles for my literature review?
Finding quality journal articles is essential to crafting a rock-solid literature review. As you probably already know, not all research is created equally, and so you need to make sure that your literature review is built on credible research .
We could write an entire post on how to find quality literature (actually, we have ), but a good starting point is Google Scholar . Google Scholar is essentially the academic equivalent of Google, using Google’s powerful search capabilities to find relevant journal articles and reports. It certainly doesn’t cover every possible resource, but it’s a very useful way to get started on your literature review journey, as it will very quickly give you a good indication of what the most popular pieces of research are in your field.
One downside of Google Scholar is that it’s merely a search engine – that is, it lists the articles, but oftentimes it doesn’t host the articles . So you’ll often hit a paywall when clicking through to journal websites.
Thankfully, your university should provide you with access to their library, so you can find the article titles using Google Scholar and then search for them by name in your university’s online library. Your university may also provide you with access to ResearchGate , which is another great source for existing research.
Remember, the correct search keywords will be super important to get the right information from the start. So, pay close attention to the keywords used in the journal articles you read and use those keywords to search for more articles. If you can’t find a spoon in the kitchen, you haven’t looked in the right drawer.
Need a helping hand?
How should I structure my literature review?
Unfortunately, there’s no generic universal answer for this one. The structure of your literature review will depend largely on your topic area and your research aims and objectives.
You could potentially structure your literature review chapter according to theme, group, variables , chronologically or per concepts in your field of research. We explain the main approaches to structuring your literature review here . You can also download a copy of our free literature review template to help you establish an initial structure.
In general, it’s also a good idea to start wide (i.e. the big-picture-level) and then narrow down, ending your literature review close to your research questions . However, there’s no universal one “right way” to structure your literature review. The most important thing is not to discuss your sources one after the other like a list – as we touched on earlier, your literature review needs to synthesise the research , not summarise it .
Ultimately, you need to craft your literature review so that it conveys the most important information effectively – it needs to tell a logical story in a digestible way. It’s no use starting off with highly technical terms and then only explaining what these terms mean later. Always assume your reader is not a subject matter expert and hold their hand through a journe y of the literature while keeping the functions of the literature review chapter (which we discussed earlier) front of mind.

Example of a literature review
In the video below, we walk you through a high-quality literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction. This will give you a clearer view of what a strong literature review looks like in practice and hopefully provide some inspiration for your own.
Wrapping Up
In this post, we’ve (hopefully) answered the question, “ what is a literature review? “. We’ve also considered the purpose and functions of the literature review, as well as how to find literature and how to structure the literature review chapter. If you’re keen to learn more, check out the literature review section of the Grad Coach blog , as well as our detailed video post covering how to write a literature review .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

16 Comments
Thanks for this review. It narrates what’s not been taught as tutors are always in a early to finish their classes.
Thanks for the kind words, Becky. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This website is amazing, it really helps break everything down. Thank you, I would have been lost without it.
This is review is amazing. I benefited from it a lot and hope others visiting this website will benefit too.
Timothy T. Chol [email protected]
Thank you very much for the guiding in literature review I learn and benefited a lot this make my journey smooth I’ll recommend this site to my friends
This was so useful. Thank you so much.
Hi, Concept was explained nicely by both of you. Thanks a lot for sharing it. It will surely help research scholars to start their Research Journey.
The review is really helpful to me especially during this period of covid-19 pandemic when most universities in my country only offer online classes. Great stuff
Great Brief Explanation, thanks
So helpful to me as a student
GradCoach is a fantastic site with brilliant and modern minds behind it.. I spent weeks decoding the substantial academic Jargon and grounding my initial steps on the research process, which could be shortened to a couple of days through the Gradcoach. Thanks again!
This is an amazing talk. I paved way for myself as a researcher. Thank you GradCoach!
Well-presented overview of the literature!
This was brilliant. So clear. Thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
How to Write a Literature Review
What is a literature review.
- What Is the Literature
- Writing the Review
A literature review is much more than an annotated bibliography or a list of separate reviews of articles and books. It is a critical, analytical summary and synthesis of the current knowledge of a topic. Thus it should compare and relate different theories, findings, etc, rather than just summarize them individually. In addition, it should have a particular focus or theme to organize the review. It does not have to be an exhaustive account of everything published on the topic, but it should discuss all the significant academic literature and other relevant sources important for that focus.
This is meant to be a general guide to writing a literature review: ways to structure one, what to include, how it supplements other research. For more specific help on writing a review, and especially for help on finding the literature to review, sign up for a Personal Research Session .
The specific organization of a literature review depends on the type and purpose of the review, as well as on the specific field or topic being reviewed. But in general, it is a relatively brief but thorough exploration of past and current work on a topic. Rather than a chronological listing of previous work, though, literature reviews are usually organized thematically, such as different theoretical approaches, methodologies, or specific issues or concepts involved in the topic. A thematic organization makes it much easier to examine contrasting perspectives, theoretical approaches, methodologies, findings, etc, and to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of, and point out any gaps in, previous research. And this is the heart of what a literature review is about. A literature review may offer new interpretations, theoretical approaches, or other ideas; if it is part of a research proposal or report it should demonstrate the relationship of the proposed or reported research to others' work; but whatever else it does, it must provide a critical overview of the current state of research efforts.
Literature reviews are common and very important in the sciences and social sciences. They are less common and have a less important role in the humanities, but they do have a place, especially stand-alone reviews.
Types of Literature Reviews
There are different types of literature reviews, and different purposes for writing a review, but the most common are:
- Stand-alone literature review articles . These provide an overview and analysis of the current state of research on a topic or question. The goal is to evaluate and compare previous research on a topic to provide an analysis of what is currently known, and also to reveal controversies, weaknesses, and gaps in current work, thus pointing to directions for future research. You can find examples published in any number of academic journals, but there is a series of Annual Reviews of *Subject* which are specifically devoted to literature review articles. Writing a stand-alone review is often an effective way to get a good handle on a topic and to develop ideas for your own research program. For example, contrasting theoretical approaches or conflicting interpretations of findings can be the basis of your research project: can you find evidence supporting one interpretation against another, or can you propose an alternative interpretation that overcomes their limitations?
- Part of a research proposal . This could be a proposal for a PhD dissertation, a senior thesis, or a class project. It could also be a submission for a grant. The literature review, by pointing out the current issues and questions concerning a topic, is a crucial part of demonstrating how your proposed research will contribute to the field, and thus of convincing your thesis committee to allow you to pursue the topic of your interest or a funding agency to pay for your research efforts.
- Part of a research report . When you finish your research and write your thesis or paper to present your findings, it should include a literature review to provide the context to which your work is a contribution. Your report, in addition to detailing the methods, results, etc. of your research, should show how your work relates to others' work.
A literature review for a research report is often a revision of the review for a research proposal, which can be a revision of a stand-alone review. Each revision should be a fairly extensive revision. With the increased knowledge of and experience in the topic as you proceed, your understanding of the topic will increase. Thus, you will be in a better position to analyze and critique the literature. In addition, your focus will change as you proceed in your research. Some areas of the literature you initially reviewed will be marginal or irrelevant for your eventual research, and you will need to explore other areas more thoroughly.
Examples of Literature Reviews
See the series of Annual Reviews of *Subject* which are specifically devoted to literature review articles to find many examples of stand-alone literature reviews in the biomedical, physical, and social sciences.
Research report articles vary in how they are organized, but a common general structure is to have sections such as:
- Abstract - Brief summary of the contents of the article
- Introduction - A explanation of the purpose of the study, a statement of the research question(s) the study intends to address
- Literature review - A critical assessment of the work done so far on this topic, to show how the current study relates to what has already been done
- Methods - How the study was carried out (e.g. instruments or equipment, procedures, methods to gather and analyze data)
- Results - What was found in the course of the study
- Discussion - What do the results mean
- Conclusion - State the conclusions and implications of the results, and discuss how it relates to the work reviewed in the literature review; also, point to directions for further work in the area
Here are some articles that illustrate variations on this theme. There is no need to read the entire articles (unless the contents interest you); just quickly browse through to see the sections, and see how each section is introduced and what is contained in them.
The Determinants of Undergraduate Grade Point Average: The Relative Importance of Family Background, High School Resources, and Peer Group Effects , in The Journal of Human Resources , v. 34 no. 2 (Spring 1999), p. 268-293.
This article has a standard breakdown of sections:
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Some discussion sections
First Encounters of the Bureaucratic Kind: Early Freshman Experiences with a Campus Bureaucracy , in The Journal of Higher Education , v. 67 no. 6 (Nov-Dec 1996), p. 660-691.
This one does not have a section specifically labeled as a "literature review" or "review of the literature," but the first few sections cite a long list of other sources discussing previous research in the area before the authors present their own study they are reporting.
- Next: What Is the Literature >>
- Last Updated: Jan 11, 2024 9:48 AM
- URL: https://libguides.wesleyan.edu/litreview

Literature Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain what literature reviews are and offer insights into the form and construction of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
Introduction
OK. You’ve got to write a literature review. You dust off a novel and a book of poetry, settle down in your chair, and get ready to issue a “thumbs up” or “thumbs down” as you leaf through the pages. “Literature review” done. Right?
Wrong! The “literature” of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic, not necessarily the great literary texts of the world. “Literature” could be anything from a set of government pamphlets on British colonial methods in Africa to scholarly articles on the treatment of a torn ACL. And a review does not necessarily mean that your reader wants you to give your personal opinion on whether or not you liked these sources.
What is a literature review, then?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper?
The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Why do we write literature reviews?
Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Who writes these things, anyway?
Literature reviews are written occasionally in the humanities, but mostly in the sciences and social sciences; in experiment and lab reports, they constitute a section of the paper. Sometimes a literature review is written as a paper in itself.
Let’s get to it! What should I do before writing the literature review?
If your assignment is not very specific, seek clarification from your instructor:
- Roughly how many sources should you include?
- What types of sources (books, journal articles, websites)?
- Should you summarize, synthesize, or critique your sources by discussing a common theme or issue?
- Should you evaluate your sources?
- Should you provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history?
Find models
Look for other literature reviews in your area of interest or in the discipline and read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or ways to organize your final review. You can simply put the word “review” in your search engine along with your other topic terms to find articles of this type on the Internet or in an electronic database. The bibliography or reference section of sources you’ve already read are also excellent entry points into your own research.
Narrow your topic
There are hundreds or even thousands of articles and books on most areas of study. The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to get a good survey of the material. Your instructor will probably not expect you to read everything that’s out there on the topic, but you’ll make your job easier if you first limit your scope.
Keep in mind that UNC Libraries have research guides and to databases relevant to many fields of study. You can reach out to the subject librarian for a consultation: https://library.unc.edu/support/consultations/ .
And don’t forget to tap into your professor’s (or other professors’) knowledge in the field. Ask your professor questions such as: “If you had to read only one book from the 90’s on topic X, what would it be?” Questions such as this help you to find and determine quickly the most seminal pieces in the field.
Consider whether your sources are current
Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. In the sciences, for instance, treatments for medical problems are constantly changing according to the latest studies. Information even two years old could be obsolete. However, if you are writing a review in the humanities, history, or social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be what is needed, because what is important is how perspectives have changed through the years or within a certain time period. Try sorting through some other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to consider what is currently of interest to scholars in this field and what is not.
Strategies for writing the literature review
Find a focus.
A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time. No. As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. Do they present one or different solutions? Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? Do they reveal a trend in the field? A raging debate? Pick one of these themes to focus the organization of your review.
Convey it to your reader
A literature review may not have a traditional thesis statement (one that makes an argument), but you do need to tell readers what to expect. Try writing a simple statement that lets the reader know what is your main organizing principle. Here are a couple of examples:
The current trend in treatment for congestive heart failure combines surgery and medicine. More and more cultural studies scholars are accepting popular media as a subject worthy of academic consideration.
Consider organization
You’ve got a focus, and you’ve stated it clearly and directly. Now what is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc., that your review needs to include? And in what order should you present them? Develop an organization for your review at both a global and local level:
First, cover the basic categories
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews also must contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper. The following provides a brief description of the content of each:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing the body
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario:
You’ve decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you’ve just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale’s portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980’s. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Now consider some typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
- By trend: A better way to organize the above sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Under this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a “chronological” and a “thematic” approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.But more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as “evil” in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the “methods” of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed. Once you’ve decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
- Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
- History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
Begin composing
Once you’ve settled on a general pattern of organization, you’re ready to write each section. There are a few guidelines you should follow during the writing stage as well. Here is a sample paragraph from a literature review about sexism and language to illuminate the following discussion:
However, other studies have shown that even gender-neutral antecedents are more likely to produce masculine images than feminine ones (Gastil, 1990). Hamilton (1988) asked students to complete sentences that required them to fill in pronouns that agreed with gender-neutral antecedents such as “writer,” “pedestrian,” and “persons.” The students were asked to describe any image they had when writing the sentence. Hamilton found that people imagined 3.3 men to each woman in the masculine “generic” condition and 1.5 men per woman in the unbiased condition. Thus, while ambient sexism accounted for some of the masculine bias, sexist language amplified the effect. (Source: Erika Falk and Jordan Mills, “Why Sexist Language Affects Persuasion: The Role of Homophily, Intended Audience, and Offense,” Women and Language19:2).
Use evidence
In the example above, the writers refer to several other sources when making their point. A literature review in this sense is just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence to show that what you are saying is valid.
Be selective
Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the review’s focus, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological.
Use quotes sparingly
Falk and Mills do not use any direct quotes. That is because the survey nature of the literature review does not allow for in-depth discussion or detailed quotes from the text. Some short quotes here and there are okay, though, if you want to emphasize a point, or if what the author said just cannot be rewritten in your own words. Notice that Falk and Mills do quote certain terms that were coined by the author, not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. But if you find yourself wanting to put in more quotes, check with your instructor.
Summarize and synthesize
Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each paragraph as well as throughout the review. The authors here recapitulate important features of Hamilton’s study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study’s significance and relating it to their own work.
Keep your own voice
While the literature review presents others’ ideas, your voice (the writer’s) should remain front and center. Notice that Falk and Mills weave references to other sources into their own text, but they still maintain their own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with their own ideas and their own words. The sources support what Falk and Mills are saying.
Use caution when paraphrasing
When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author’s information or opinions accurately and in your own words. In the preceding example, Falk and Mills either directly refer in the text to the author of their source, such as Hamilton, or they provide ample notation in the text when the ideas they are mentioning are not their own, for example, Gastil’s. For more information, please see our handout on plagiarism .
Revise, revise, revise
Draft in hand? Now you’re ready to revise. Spending a lot of time revising is a wise idea, because your main objective is to present the material, not the argument. So check over your review again to make sure it follows the assignment and/or your outline. Then, just as you would for most other academic forms of writing, rewrite or rework the language of your review so that you’ve presented your information in the most concise manner possible. Be sure to use terminology familiar to your audience; get rid of unnecessary jargon or slang. Finally, double check that you’ve documented your sources and formatted the review appropriately for your discipline. For tips on the revising and editing process, see our handout on revising drafts .
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Jones, Robert, Patrick Bizzaro, and Cynthia Selfe. 1997. The Harcourt Brace Guide to Writing in the Disciplines . New York: Harcourt Brace.
Lamb, Sandra E. 1998. How to Write It: A Complete Guide to Everything You’ll Ever Write . Berkeley: Ten Speed Press.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
Troyka, Lynn Quittman, and Doug Hesse. 2016. Simon and Schuster Handbook for Writers , 11th ed. London: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Contact & Directions
- Climate Statement
- Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Adjunct Faculty
- Non-Senate Instructors
- Researchers
- Psychology Grads
- Affiliated Grads
- New and Prospective Students
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Programs & Events
- Psi Chi / Psychology Club
- Prospective PhD Students
- Current PhD Students
- Area Brown Bags
- Colloquium Series
- Anderson Distinguished Lecture Series
- Speaker Videos
- Undergraduate Program
- Academic and Writing Resources
Writing Research Papers
- Writing a Literature Review
When writing a research paper on a specific topic, you will often need to include an overview of any prior research that has been conducted on that topic. For example, if your research paper is describing an experiment on fear conditioning, then you will probably need to provide an overview of prior research on fear conditioning. That overview is typically known as a literature review.
Please note that a full-length literature review article may be suitable for fulfilling the requirements for the Psychology B.S. Degree Research Paper . For further details, please check with your faculty advisor.
Different Types of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews come in many forms. They can be part of a research paper, for example as part of the Introduction section. They can be one chapter of a doctoral dissertation. Literature reviews can also “stand alone” as separate articles by themselves. For instance, some journals such as Annual Review of Psychology , Psychological Bulletin , and others typically publish full-length review articles. Similarly, in courses at UCSD, you may be asked to write a research paper that is itself a literature review (such as, with an instructor’s permission, in fulfillment of the B.S. Degree Research Paper requirement). Alternatively, you may be expected to include a literature review as part of a larger research paper (such as part of an Honors Thesis).
Literature reviews can be written using a variety of different styles. These may differ in the way prior research is reviewed as well as the way in which the literature review is organized. Examples of stylistic variations in literature reviews include:
- Summarization of prior work vs. critical evaluation. In some cases, prior research is simply described and summarized; in other cases, the writer compares, contrasts, and may even critique prior research (for example, discusses their strengths and weaknesses).
- Chronological vs. categorical and other types of organization. In some cases, the literature review begins with the oldest research and advances until it concludes with the latest research. In other cases, research is discussed by category (such as in groupings of closely related studies) without regard for chronological order. In yet other cases, research is discussed in terms of opposing views (such as when different research studies or researchers disagree with one another).
Overall, all literature reviews, whether they are written as a part of a larger work or as separate articles unto themselves, have a common feature: they do not present new research; rather, they provide an overview of prior research on a specific topic .
How to Write a Literature Review
When writing a literature review, it can be helpful to rely on the following steps. Please note that these procedures are not necessarily only for writing a literature review that becomes part of a larger article; they can also be used for writing a full-length article that is itself a literature review (although such reviews are typically more detailed and exhaustive; for more information please refer to the Further Resources section of this page).
Steps for Writing a Literature Review
1. Identify and define the topic that you will be reviewing.
The topic, which is commonly a research question (or problem) of some kind, needs to be identified and defined as clearly as possible. You need to have an idea of what you will be reviewing in order to effectively search for references and to write a coherent summary of the research on it. At this stage it can be helpful to write down a description of the research question, area, or topic that you will be reviewing, as well as to identify any keywords that you will be using to search for relevant research.
2. Conduct a literature search.
Use a range of keywords to search databases such as PsycINFO and any others that may contain relevant articles. You should focus on peer-reviewed, scholarly articles. Published books may also be helpful, but keep in mind that peer-reviewed articles are widely considered to be the “gold standard” of scientific research. Read through titles and abstracts, select and obtain articles (that is, download, copy, or print them out), and save your searches as needed. For more information about this step, please see the Using Databases and Finding Scholarly References section of this website.
3. Read through the research that you have found and take notes.
Absorb as much information as you can. Read through the articles and books that you have found, and as you do, take notes. The notes should include anything that will be helpful in advancing your own thinking about the topic and in helping you write the literature review (such as key points, ideas, or even page numbers that index key information). Some references may turn out to be more helpful than others; you may notice patterns or striking contrasts between different sources ; and some sources may refer to yet other sources of potential interest. This is often the most time-consuming part of the review process. However, it is also where you get to learn about the topic in great detail. For more details about taking notes, please see the “Reading Sources and Taking Notes” section of the Finding Scholarly References page of this website.
4. Organize your notes and thoughts; create an outline.
At this stage, you are close to writing the review itself. However, it is often helpful to first reflect on all the reading that you have done. What patterns stand out? Do the different sources converge on a consensus? Or not? What unresolved questions still remain? You should look over your notes (it may also be helpful to reorganize them), and as you do, to think about how you will present this research in your literature review. Are you going to summarize or critically evaluate? Are you going to use a chronological or other type of organizational structure? It can also be helpful to create an outline of how your literature review will be structured.
5. Write the literature review itself and edit and revise as needed.
The final stage involves writing. When writing, keep in mind that literature reviews are generally characterized by a summary style in which prior research is described sufficiently to explain critical findings but does not include a high level of detail (if readers want to learn about all the specific details of a study, then they can look up the references that you cite and read the original articles themselves). However, the degree of emphasis that is given to individual studies may vary (more or less detail may be warranted depending on how critical or unique a given study was). After you have written a first draft, you should read it carefully and then edit and revise as needed. You may need to repeat this process more than once. It may be helpful to have another person read through your draft(s) and provide feedback.
6. Incorporate the literature review into your research paper draft.
After the literature review is complete, you should incorporate it into your research paper (if you are writing the review as one component of a larger paper). Depending on the stage at which your paper is at, this may involve merging your literature review into a partially complete Introduction section, writing the rest of the paper around the literature review, or other processes.
Further Tips for Writing a Literature Review
Full-length literature reviews
- Many full-length literature review articles use a three-part structure: Introduction (where the topic is identified and any trends or major problems in the literature are introduced), Body (where the studies that comprise the literature on that topic are discussed), and Discussion or Conclusion (where major patterns and points are discussed and the general state of what is known about the topic is summarized)
Literature reviews as part of a larger paper
- An “express method” of writing a literature review for a research paper is as follows: first, write a one paragraph description of each article that you read. Second, choose how you will order all the paragraphs and combine them in one document. Third, add transitions between the paragraphs, as well as an introductory and concluding paragraph. 1
- A literature review that is part of a larger research paper typically does not have to be exhaustive. Rather, it should contain most or all of the significant studies about a research topic but not tangential or loosely related ones. 2 Generally, literature reviews should be sufficient for the reader to understand the major issues and key findings about a research topic. You may however need to confer with your instructor or editor to determine how comprehensive you need to be.
Benefits of Literature Reviews
By summarizing prior research on a topic, literature reviews have multiple benefits. These include:
- Literature reviews help readers understand what is known about a topic without having to find and read through multiple sources.
- Literature reviews help “set the stage” for later reading about new research on a given topic (such as if they are placed in the Introduction of a larger research paper). In other words, they provide helpful background and context.
- Literature reviews can also help the writer learn about a given topic while in the process of preparing the review itself. In the act of research and writing the literature review, the writer gains expertise on the topic .
Downloadable Resources
- How to Write APA Style Research Papers (a comprehensive guide) [ PDF ]
- Tips for Writing APA Style Research Papers (a brief summary) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – literature review) [ PDF ]
Further Resources
How-To Videos
- Writing Research Paper Videos
- UCSD Library Psychology Research Guide: Literature Reviews
External Resources
- Developing and Writing a Literature Review from N Carolina A&T State University
- Example of a Short Literature Review from York College CUNY
- How to Write a Review of Literature from UW-Madison
- Writing a Literature Review from UC Santa Cruz
- Pautasso, M. (2013). Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review. PLoS Computational Biology, 9 (7), e1003149. doi : 1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
1 Ashton, W. Writing a short literature review . [PDF]
2 carver, l. (2014). writing the research paper [workshop]. , prepared by s. c. pan for ucsd psychology.
Back to top
- Research Paper Structure
- Formatting Research Papers
- Using Databases and Finding References
- What Types of References Are Appropriate?
- Evaluating References and Taking Notes
- Citing References
- Writing Process and Revising
- Improving Scientific Writing
- Academic Integrity and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Writing Research Papers Videos

Writing a Literature Review
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- Peer Review
- Citation/Style Guides
Reference & Instruction Librarian

What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is not:
- just a summary of the sources
- a grouping of broad, unrelated sources
- a compilation of everything that has been written on a particular topic
- literature criticism (think English) or a book review.
So, what is it then?
A literature review :
- Surveys all of the scholarship that has been written about a particular topic (your research question).
- Provides a description , summary , and evaluation of each scholarly work.
- Synthesizes and organizes the previous research by comparing and contrasting the findings or methodology of those previous writings.
"A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. Occasionally, you will be asked to write one as a separate assignment, ..., but more often, it is part of the introduction to an essay, research report, or thesis. In writing the literature review, you aim to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic and their strengths and weaknesses. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available or a set of summaries."
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings that are related directly to your research question. That is, it represents the literature that provides background information on your topic and shows a correspondence between those writings and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand-alone work or the introduction to a more extensive research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
Where Can I Find a Lit Review?
The Literature Review portion of a scholarly article is usually close to the beginning. It often follows the introduction , or may be combined with the introduction. The writer may discuss his or her research question first, or may choose to explain it while surveying previous literature.
If you are lucky, there will be a section heading that includes " literature review ". If not, look for the section of the article with the most citations or footnotes .
Searching In Databases
Resources on the web.
- Writing a Literature Review Brendan Rapple, Boston College Libraries
- Next: Steps for Conducting a Lit Review >>
- Last Updated: Jun 18, 2024 1:28 PM
- URL: https://westlibrary.txwes.edu/writing_a_literature_review
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Functional connectivity changes in the brain of adolescents with internet addiction: A systematic literature review of imaging studies
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Child and Adolescent Mental Health, Department of Brain Sciences, Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, University College London, London, United Kingdom
Roles Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Behavioural Brain Sciences Unit, Population Policy Practice Programme, Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, University College London, London, United Kingdom
- Max L. Y. Chang,
- Irene O. Lee

- Published: June 4, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022
- Peer Review
- Reader Comments
Internet usage has seen a stark global rise over the last few decades, particularly among adolescents and young people, who have also been diagnosed increasingly with internet addiction (IA). IA impacts several neural networks that influence an adolescent’s behaviour and development. This article issued a literature review on the resting-state and task-based functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies to inspect the consequences of IA on the functional connectivity (FC) in the adolescent brain and its subsequent effects on their behaviour and development. A systematic search was conducted from two databases, PubMed and PsycINFO, to select eligible articles according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Eligibility criteria was especially stringent regarding the adolescent age range (10–19) and formal diagnosis of IA. Bias and quality of individual studies were evaluated. The fMRI results from 12 articles demonstrated that the effects of IA were seen throughout multiple neural networks: a mix of increases/decreases in FC in the default mode network; an overall decrease in FC in the executive control network; and no clear increase or decrease in FC within the salience network and reward pathway. The FC changes led to addictive behaviour and tendencies in adolescents. The subsequent behavioural changes are associated with the mechanisms relating to the areas of cognitive control, reward valuation, motor coordination, and the developing adolescent brain. Our results presented the FC alterations in numerous brain regions of adolescents with IA leading to the behavioural and developmental changes. Research on this topic had a low frequency with adolescent samples and were primarily produced in Asian countries. Future research studies of comparing results from Western adolescent samples provide more insight on therapeutic intervention.
Citation: Chang MLY, Lee IO (2024) Functional connectivity changes in the brain of adolescents with internet addiction: A systematic literature review of imaging studies. PLOS Ment Health 1(1): e0000022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022
Editor: Kizito Omona, Uganda Martyrs University, UGANDA
Received: December 29, 2023; Accepted: March 18, 2024; Published: June 4, 2024
Copyright: © 2024 Chang, Lee. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting information files.
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
The behavioural addiction brought on by excessive internet use has become a rising source of concern [ 1 ] since the last decade. According to clinical studies, individuals with Internet Addiction (IA) or Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) may have a range of biopsychosocial effects and is classified as an impulse-control disorder owing to its resemblance to pathological gambling and substance addiction [ 2 , 3 ]. IA has been defined by researchers as a person’s inability to resist the urge to use the internet, which has negative effects on their psychological well-being as well as their social, academic, and professional lives [ 4 ]. The symptoms can have serious physical and interpersonal repercussions and are linked to mood modification, salience, tolerance, impulsivity, and conflict [ 5 ]. In severe circumstances, people may experience severe pain in their bodies or health issues like carpal tunnel syndrome, dry eyes, irregular eating and disrupted sleep [ 6 ]. Additionally, IA is significantly linked to comorbidities with other psychiatric disorders [ 7 ].
Stevens et al (2021) reviewed 53 studies including 17 countries and reported the global prevalence of IA was 3.05% [ 8 ]. Asian countries had a higher prevalence (5.1%) than European countries (2.7%) [ 8 ]. Strikingly, adolescents and young adults had a global IGD prevalence rate of 9.9% which matches previous literature that reported historically higher prevalence among adolescent populations compared to adults [ 8 , 9 ]. Over 80% of adolescent population in the UK, the USA, and Asia have direct access to the internet [ 10 ]. Children and adolescents frequently spend more time on media (possibly 7 hours and 22 minutes per day) than at school or sleeping [ 11 ]. Developing nations have also shown a sharp rise in teenage internet usage despite having lower internet penetration rates [ 10 ]. Concerns regarding the possible harms that overt internet use could do to adolescents and their development have arisen because of this surge, especially the significant impacts by the COVID-19 pandemic [ 12 ]. The growing prevalence and neurocognitive consequences of IA among adolescents makes this population a vital area of study [ 13 ].
Adolescence is a crucial developmental stage during which people go through significant changes in their biology, cognition, and personalities [ 14 ]. Adolescents’ emotional-behavioural functioning is hyperactivated, which creates risk of psychopathological vulnerability [ 15 ]. In accordance with clinical study results [ 16 ], this emotional hyperactivity is supported by a high level of neuronal plasticity. This plasticity enables teenagers to adapt to the numerous physical and emotional changes that occur during puberty as well as develop communication techniques and gain independence [ 16 ]. However, the strong neuronal plasticity is also associated with risk-taking and sensation seeking [ 17 ] which may lead to IA.
Despite the fact that the precise neuronal mechanisms underlying IA are still largely unclear, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) method has been used by scientists as an important framework to examine the neuropathological changes occurring in IA, particularly in the form of functional connectivity (FC) [ 18 ]. fMRI research study has shown that IA alters both the functional and structural makeup of the brain [ 3 ].
We hypothesise that IA has widespread neurological alteration effects rather than being limited to a few specific brain regions. Further hypothesis holds that according to these alterations of FC between the brain regions or certain neural networks, adolescents with IA would experience behavioural changes. An investigation of these domains could be useful for creating better procedures and standards as well as minimising the negative effects of overt internet use. This literature review aims to summarise and analyse the evidence of various imaging studies that have investigated the effects of IA on the FC in adolescents. This will be addressed through two research questions:
- How does internet addiction affect the functional connectivity in the adolescent brain?
- How is adolescent behaviour and development impacted by functional connectivity changes due to internet addiction?
The review protocol was conducted in line with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (see S1 Checklist ).
Search strategy and selection process
A systematic search was conducted up until April 2023 from two sources of database, PubMed and PsycINFO, using a range of terms relevant to the title and research questions (see full list of search terms in S1 Appendix ). All the searched articles can be accessed in the S1 Data . The eligible articles were selected according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria used for the present review were: (i) participants in the studies with clinical diagnosis of IA; (ii) participants between the ages of 10 and 19; (iii) imaging research investigations; (iv) works published between January 2013 and April 2023; (v) written in English language; (vi) peer-reviewed papers and (vii) full text. The numbers of articles excluded due to not meeting the inclusion criteria are shown in Fig 1 . Each study’s title and abstract were screened for eligibility.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g001
Quality appraisal
Full texts of all potentially relevant studies were then retrieved and further appraised for eligibility. Furthermore, articles were critically appraised based on the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations) framework to evaluate the individual study for both quality and bias. The subsequent quality levels were then appraised to each article and listed as either low, moderate, or high.
Data collection process
Data that satisfied the inclusion requirements was entered into an excel sheet for data extraction and further selection. An article’s author, publication year, country, age range, participant sample size, sex, area of interest, measures, outcome and article quality were all included in the data extraction spreadsheet. Studies looking at FC, for instance, were grouped, while studies looking at FC in specific area were further divided into sub-groups.
Data synthesis and analysis
Articles were classified according to their location in the brain as well as the network or pathway they were a part of to create a coherent narrative between the selected studies. Conclusions concerning various research trends relevant to particular groupings were drawn from these groupings and subgroupings. To maintain the offered information in a prominent manner, these assertions were entered into the data extraction excel spreadsheet.
With the search performed on the selected databases, 238 articles in total were identified (see Fig 1 ). 15 duplicated articles were eliminated, and another 6 items were removed for various other reasons. Title and abstract screening eliminated 184 articles because they were not in English (number of article, n, = 7), did not include imaging components (n = 47), had adult participants (n = 53), did not have a clinical diagnosis of IA (n = 19), did not address FC in the brain (n = 20), and were published outside the desired timeframe (n = 38). A further 21 papers were eliminated for failing to meet inclusion requirements after the remaining 33 articles underwent full-text eligibility screening. A total of 12 papers were deemed eligible for this review analysis.
Characteristics of the included studies, as depicted in the data extraction sheet in Table 1 provide information of the author(s), publication year, sample size, study location, age range, gender, area of interest, outcome, measures used and quality appraisal. Most of the studies in this review utilised resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging techniques (n = 7), with several studies demonstrating task-based fMRI procedures (n = 3), and the remaining studies utilising whole-brain imaging measures (n = 2). The studies were all conducted in Asiatic countries, specifically coming from China (8), Korea (3), and Indonesia (1). Sample sizes ranged from 12 to 31 participants with most of the imaging studies having comparable sample sizes. Majority of the studies included a mix of male and female participants (n = 8) with several studies having a male only participant pool (n = 3). All except one of the mixed gender studies had a majority male participant pool. One study did not disclose their data on the gender demographics of their experiment. Study years ranged from 2013–2022, with 2 studies in 2013, 3 studies in 2014, 3 studies in 2015, 1 study in 2017, 1 study in 2020, 1 study in 2021, and 1 study in 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.t001
(1) How does internet addiction affect the functional connectivity in the adolescent brain?
The included studies were organised according to the brain region or network that they were observing. The specific networks affected by IA were the default mode network, executive control system, salience network and reward pathway. These networks are vital components of adolescent behaviour and development [ 31 ]. The studies in each section were then grouped into subsections according to their specific brain regions within their network.
Default mode network (DMN)/reward network.
Out of the 12 studies, 3 have specifically studied the default mode network (DMN), and 3 observed whole-brain FC that partially included components of the DMN. The effect of IA on the various centres of the DMN was not unilaterally the same. The findings illustrate a complex mix of increases and decreases in FC depending on the specific region in the DMN (see Table 2 and Fig 2 ). The alteration of FC in posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) in the DMN was the most frequently reported area in adolescents with IA, which involved in attentional processes [ 32 ], but Lee et al. (2020) additionally found alterations of FC in other brain regions, such as anterior insula cortex, a node in the DMN that controls the integration of motivational and cognitive processes [ 20 ].
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g002
The overall changes of functional connectivity in the brain network including default mode network (DMN), executive control network (ECN), salience network (SN) and reward network. IA = Internet Addiction, FC = Functional Connectivity.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.t002
Ding et al. (2013) revealed altered FC in the cerebellum, the middle temporal gyrus, and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) [ 22 ]. They found that the bilateral inferior parietal lobule, left superior parietal lobule, and right inferior temporal gyrus had decreased FC, while the bilateral posterior lobe of the cerebellum and the medial temporal gyrus had increased FC [ 22 ]. The right middle temporal gyrus was found to have 111 cluster voxels (t = 3.52, p<0.05) and the right inferior parietal lobule was found to have 324 cluster voxels (t = -4.07, p<0.05) with an extent threshold of 54 voxels (figures above this threshold are deemed significant) [ 22 ]. Additionally, there was a negative correlation, with 95 cluster voxels (p<0.05) between the FC of the left superior parietal lobule and the PCC with the Chen Internet Addiction Scores (CIAS) which are used to determine the severity of IA [ 22 ]. On the other hand, in regions of the reward system, connection with the PCC was positively connected with CIAS scores [ 22 ]. The most significant was the right praecuneus with 219 cluster voxels (p<0.05) [ 22 ]. Wang et al. (2017) also discovered that adolescents with IA had 33% less FC in the left inferior parietal lobule and 20% less FC in the dorsal mPFC [ 24 ]. A potential connection between the effects of substance use and overt internet use is revealed by the generally decreased FC in these areas of the DMN of teenagers with drug addiction and IA [ 35 ].
The putamen was one of the main regions of reduced FC in adolescents with IA [ 19 ]. The putamen and the insula-operculum demonstrated significant group differences regarding functional connectivity with a cluster size of 251 and an extent threshold of 250 (Z = 3.40, p<0.05) [ 19 ]. The molecular mechanisms behind addiction disorders have been intimately connected to decreased striatal dopaminergic function [ 19 ], making this function crucial.
Executive Control Network (ECN).
5 studies out of 12 have specifically viewed parts of the executive control network (ECN) and 3 studies observed whole-brain FC. The effects of IA on the ECN’s constituent parts were consistent across all the studies examined for this analysis (see Table 2 and Fig 3 ). The results showed a notable decline in all the ECN’s major centres. Li et al. (2014) used fMRI imaging and a behavioural task to study response inhibition in adolescents with IA [ 25 ] and found decreased activation at the striatum and frontal gyrus, particularly a reduction in FC at inferior frontal gyrus, in the IA group compared to controls [ 25 ]. The inferior frontal gyrus showed a reduction in FC in comparison to the controls with a cluster size of 71 (t = 4.18, p<0.05) [ 25 ]. In addition, the frontal-basal ganglia pathways in the adolescents with IA showed little effective connection between areas and increased degrees of response inhibition [ 25 ].
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g003
Lin et al. (2015) found that adolescents with IA demonstrated disrupted corticostriatal FC compared to controls [ 33 ]. The corticostriatal circuitry experienced decreased connectivity with the caudate, bilateral anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), as well as the striatum and frontal gyrus [ 33 ]. The inferior ventral striatum showed significantly reduced FC with the subcallosal ACC and caudate head with cluster size of 101 (t = -4.64, p<0.05) [ 33 ]. Decreased FC in the caudate implies dysfunction of the corticostriatal-limbic circuitry involved in cognitive and emotional control [ 36 ]. The decrease in FC in both the striatum and frontal gyrus is related to inhibitory control, a common deficit seen with disruptions with the ECN [ 33 ].
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), ACC, and right supplementary motor area (SMA) of the prefrontal cortex were all found to have significantly decreased grey matter volume [ 29 ]. In addition, the DLPFC, insula, temporal cortices, as well as significant subcortical regions like the striatum and thalamus, showed decreased FC [ 29 ]. According to Tremblay (2009), the striatum plays a significant role in the processing of rewards, decision-making, and motivation [ 37 ]. Chen et al. (2020) reported that the IA group demonstrated increased impulsivity as well as decreased reaction inhibition using a Stroop colour-word task [ 26 ]. Furthermore, Chen et al. (2020) observed that the left DLPFC and dorsal striatum experienced a negative connection efficiency value, specifically demonstrating that the dorsal striatum activity suppressed the left DLPFC [ 27 ].
Salience network (SN).
Out of the 12 chosen studies, 3 studies specifically looked at the salience network (SN) and 3 studies have observed whole-brain FC. Relative to the DMN and ECN, the findings on the SN were slightly sparser. Despite this, adolescents with IA demonstrated a moderate decrease in FC, as well as other measures like fibre connectivity and cognitive control, when compared to healthy control (see Table 2 and Fig 4 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g004
Xing et al. (2014) used both dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) and insula to test FC changes in the SN of adolescents with IA and found decreased structural connectivity in the SN as well as decreased fractional anisotropy (FA) that correlated to behaviour performance in the Stroop colour word-task [ 21 ]. They examined the dACC and insula to determine whether the SN’s disrupted connectivity may be linked to the SN’s disruption of regulation, which would explain the impaired cognitive control seen in adolescents with IA. However, researchers did not find significant FC differences in the SN when compared to the controls [ 21 ]. These results provided evidence for the structural changes in the interconnectivity within SN in adolescents with IA.
Wang et al. (2017) investigated network interactions between the DMN, ECN, SN and reward pathway in IA subjects [ 24 ] (see Fig 5 ), and found 40% reduction of FC between the DMN and specific regions of the SN, such as the insula, in comparison to the controls (p = 0.008) [ 24 ]. The anterior insula and dACC are two areas that are impacted by this altered FC [ 24 ]. This finding supports the idea that IA has similar neurobiological abnormalities with other addictive illnesses, which is in line with a study that discovered disruptive changes in the SN and DMN’s interaction in cocaine addiction [ 38 ]. The insula has also been linked to the intensity of symptoms and has been implicated in the development of IA [ 39 ].
“+” indicates an increase in behaivour; “-”indicates a decrease in behaviour; solid arrows indicate a direct network interaction; and the dotted arrows indicates a reduction in network interaction. This diagram depicts network interactions juxtaposed with engaging in internet related behaviours. Through the neural interactions, the diagram illustrates how the networks inhibit or amplify internet usage and vice versa. Furthermore, it demonstrates how the SN mediates both the DMN and ECN.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g005
(2) How is adolescent behaviour and development impacted by functional connectivity changes due to internet addiction?
The findings that IA individuals demonstrate an overall decrease in FC in the DMN is supported by numerous research [ 24 ]. Drug addict populations also exhibited similar decline in FC in the DMN [ 40 ]. The disruption of attentional orientation and self-referential processing for both substance and behavioural addiction was then hypothesised to be caused by DMN anomalies in FC [ 41 ].
In adolescents with IA, decline of FC in the parietal lobule affects visuospatial task-related behaviour [ 22 ], short-term memory [ 42 ], and the ability of controlling attention or restraining motor responses during response inhibition tests [ 42 ]. Cue-induced gaming cravings are influenced by the DMN [ 43 ]. A visual processing area called the praecuneus links gaming cues to internal information [ 22 ]. A meta-analysis found that the posterior cingulate cortex activity of individuals with IA during cue-reactivity tasks was connected with their gaming time [ 44 ], suggesting that excessive gaming may impair DMN function and that individuals with IA exert more cognitive effort to control it. Findings for the behavioural consequences of FC changes in the DMN illustrate its underlying role in regulating impulsivity, self-monitoring, and cognitive control.
Furthermore, Ding et al. (2013) reported an activation of components of the reward pathway, including areas like the nucleus accumbens, praecuneus, SMA, caudate, and thalamus, in connection to the DMN [ 22 ]. The increased FC of the limbic and reward networks have been confirmed to be a major biomarker for IA [ 45 , 46 ]. The increased reinforcement in these networks increases the strength of reward stimuli and makes it more difficult for other networks, namely the ECN, to down-regulate the increased attention [ 29 ] (See Fig 5 ).
Executive control network (ECN).
The numerous IA-affected components in the ECN have a role in a variety of behaviours that are connected to both response inhibition and emotional regulation [ 47 ]. For instance, brain regions like the striatum, which are linked to impulsivity and the reward system, are heavily involved in the act of playing online games [ 47 ]. Online game play activates the striatum, which suppresses the left DLPFC in ECN [ 48 ]. As a result, people with IA may find it difficult to control their want to play online games [ 48 ]. This system thus causes impulsive and protracted gaming conduct, lack of inhibitory control leading to the continued use of internet in an overt manner despite a variety of negative effects, personal distress, and signs of psychological dependence [ 33 ] (See Fig 5 ).
Wang et al. (2017) report that disruptions in cognitive control networks within the ECN are frequently linked to characteristics of substance addiction [ 24 ]. With samples that were addicted to heroin and cocaine, previous studies discovered abnormal FC in the ECN and the PFC [ 49 ]. Electronic gaming is known to promote striatal dopamine release, similar to drug addiction [ 50 ]. According to Drgonova and Walther (2016), it is hypothesised that dopamine could stimulate the reward system of the striatum in the brain, leading to a loss of impulse control and a failure of prefrontal lobe executive inhibitory control [ 51 ]. In the end, IA’s resemblance to drug use disorders may point to vital biomarkers or underlying mechanisms that explain how cognitive control and impulsive behaviour are related.
A task-related fMRI study found that the decrease in FC between the left DLPFC and dorsal striatum was congruent with an increase in impulsivity in adolescents with IA [ 26 ]. The lack of response inhibition from the ECN results in a loss of control over internet usage and a reduced capacity to display goal-directed behaviour [ 33 ]. Previous studies have linked the alteration of the ECN in IA with higher cue reactivity and impaired ability to self-regulate internet specific stimuli [ 52 ].
Salience network (SN)/ other networks.
Xing et al. (2014) investigated the significance of the SN regarding cognitive control in teenagers with IA [ 21 ]. The SN, which is composed of the ACC and insula, has been demonstrated to control dynamic changes in other networks to modify cognitive performance [ 21 ]. The ACC is engaged in conflict monitoring and cognitive control, according to previous neuroimaging research [ 53 ]. The insula is a region that integrates interoceptive states into conscious feelings [ 54 ]. The results from Xing et al. (2014) showed declines in the SN regarding its structural connectivity and fractional anisotropy, even though they did not observe any appreciable change in FC in the IA participants [ 21 ]. Due to the small sample size, the results may have indicated that FC methods are not sensitive enough to detect the significant functional changes [ 21 ]. However, task performance behaviours associated with impaired cognitive control in adolescents with IA were correlated with these findings [ 21 ]. Our comprehension of the SN’s broader function in IA can be enhanced by this relationship.
Research study supports the idea that different psychological issues are caused by the functional reorganisation of expansive brain networks, such that strong association between SN and DMN may provide neurological underpinnings at the system level for the uncontrollable character of internet-using behaviours [ 24 ]. In the study by Wang et al. (2017), the decreased interconnectivity between the SN and DMN, comprising regions such the DLPFC and the insula, suggests that adolescents with IA may struggle to effectively inhibit DMN activity during internally focused processing, leading to poorly managed desires or preoccupations to use the internet [ 24 ] (See Fig 5 ). Subsequently, this may cause a failure to inhibit DMN activity as well as a restriction of ECN functionality [ 55 ]. As a result, the adolescent experiences an increased salience and sensitivity towards internet addicting cues making it difficult to avoid these triggers [ 56 ].
The primary aim of this review was to present a summary of how internet addiction impacts on the functional connectivity of adolescent brain. Subsequently, the influence of IA on the adolescent brain was compartmentalised into three sections: alterations of FC at various brain regions, specific FC relationships, and behavioural/developmental changes. Overall, the specific effects of IA on the adolescent brain were not completely clear, given the variety of FC changes. However, there were overarching behavioural, network and developmental trends that were supported that provided insight on adolescent development.
The first hypothesis that was held about this question was that IA was widespread and would be regionally similar to substance-use and gambling addiction. After conducting a review of the information in the chosen articles, the hypothesis was predictably supported. The regions of the brain affected by IA are widespread and influence multiple networks, mainly DMN, ECN, SN and reward pathway. In the DMN, there was a complex mix of increases and decreases within the network. However, in the ECN, the alterations of FC were more unilaterally decreased, but the findings of SN and reward pathway were not quite clear. Overall, the FC changes within adolescents with IA are very much network specific and lay a solid foundation from which to understand the subsequent behaviour changes that arise from the disorder.
The second hypothesis placed emphasis on the importance of between network interactions and within network interactions in the continuation of IA and the development of its behavioural symptoms. The results from the findings involving the networks, DMN, SN, ECN and reward system, support this hypothesis (see Fig 5 ). Studies confirm the influence of all these neural networks on reward valuation, impulsivity, salience to stimuli, cue reactivity and other changes that alter behaviour towards the internet use. Many of these changes are connected to the inherent nature of the adolescent brain.
There are multiple explanations that underlie the vulnerability of the adolescent brain towards IA related urges. Several of them have to do with the inherent nature and underlying mechanisms of the adolescent brain. Children’s emotional, social, and cognitive capacities grow exponentially during childhood and adolescence [ 57 ]. Early teenagers go through a process called “social reorientation” that is characterised by heightened sensitivity to social cues and peer connections [ 58 ]. Adolescents’ improvements in their social skills coincide with changes in their brains’ anatomical and functional organisation [ 59 ]. Functional hubs exhibit growing connectivity strength [ 60 ], suggesting increased functional integration during development. During this time, the brain’s functional networks change from an anatomically dominant structure to a scattered architecture [ 60 ].
The adolescent brain is very responsive to synaptic reorganisation and experience cues [ 61 ]. As a result, one of the distinguishing traits of the maturation of adolescent brains is the variation in neural network trajectory [ 62 ]. Important weaknesses of the adolescent brain that may explain the neurobiological change brought on by external stimuli are illustrated by features like the functional gaps between networks and the inadequate segregation of networks [ 62 ].
The implications of these findings towards adolescent behaviour are significant. Although the exact changes and mechanisms are not fully clear, the observed changes in functional connectivity have the capacity of influencing several aspects of adolescent development. For example, functional connectivity has been utilised to investigate attachment styles in adolescents [ 63 ]. It was observed that adolescent attachment styles were negatively associated with caudate-prefrontal connectivity, but positively with the putamen-visual area connectivity [ 63 ]. Both named areas were also influenced by the onset of internet addiction, possibly providing a connection between the two. Another study associated neighbourhood/socioeconomic disadvantage with functional connectivity alterations in the DMN and dorsal attention network [ 64 ]. The study also found multivariate brain behaviour relationships between the altered/disadvantaged functional connectivity and mental health and cognition [ 64 ]. This conclusion supports the notion that the functional connectivity alterations observed in IA are associated with specific adolescent behaviours as well as the fact that functional connectivity can be utilised as a platform onto which to compare various neurologic conditions.
Limitations/strengths
There were several limitations that were related to the conduction of the review as well as the data extracted from the articles. Firstly, the study followed a systematic literature review design when analysing the fMRI studies. The data pulled from these imaging studies were namely qualitative and were subject to bias contrasting the quantitative nature of statistical analysis. Components of the study, such as sample sizes, effect sizes, and demographics were not weighted or controlled. The second limitation brought up by a similar review was the lack of a universal consensus of terminology given IA [ 47 ]. Globally, authors writing about this topic use an array of terminology including online gaming addiction, internet addiction, internet gaming disorder, and problematic internet use. Often, authors use multiple terms interchangeably which makes it difficult to depict the subtle similarities and differences between the terms.
Reviewing the explicit limitations in each of the included studies, two major limitations were brought up in many of the articles. One was relating to the cross-sectional nature of the included studies. Due to the inherent qualities of a cross-sectional study, the studies did not provide clear evidence that IA played a causal role towards the development of the adolescent brain. While several biopsychosocial factors mediate these interactions, task-based measures that combine executive functions with imaging results reinforce the assumed connection between the two that is utilised by the papers studying IA. Another limitation regarded the small sample size of the included studies, which averaged to around 20 participants. The small sample size can influence the generalisation of the results as well as the effectiveness of statistical analyses. Ultimately, both included study specific limitations illustrate the need for future studies to clarify the causal relationship between the alterations of FC and the development of IA.
Another vital limitation was the limited number of studies applying imaging techniques for investigations on IA in adolescents were a uniformly Far East collection of studies. The reason for this was because the studies included in this review were the only fMRI studies that were found that adhered to the strict adolescent age restriction. The adolescent age range given by the WHO (10–19 years old) [ 65 ] was strictly followed. It is important to note that a multitude of studies found in the initial search utilised an older adolescent demographic that was slightly higher than the WHO age range and had a mean age that was outside of the limitations. As a result, the results of this review are biased and based on the 12 studies that met the inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Regarding the global nature of the research, although the journals that the studies were published in were all established western journals, the collection of studies were found to all originate from Asian countries, namely China and Korea. Subsequently, it pulls into question if the results and measures from these studies are generalisable towards a western population. As stated previously, Asian countries have a higher prevalence of IA, which may be the reasoning to why the majority of studies are from there [ 8 ]. However, in an additional search including other age groups, it was found that a high majority of all FC studies on IA were done in Asian countries. Interestingly, western papers studying fMRI FC were primarily focused on gambling and substance-use addiction disorders. The western papers on IA were less focused on fMRI FC but more on other components of IA such as sleep, game-genre, and other non-imaging related factors. This demonstrated an overall lack of western fMRI studies on IA. It is important to note that both western and eastern fMRI studies on IA presented an overall lack on children and adolescents in general.
Despite the several limitations, this review provided a clear reflection on the state of the data. The strengths of the review include the strict inclusion/exclusion criteria that filtered through studies and only included ones that contained a purely adolescent sample. As a result, the information presented in this review was specific to the review’s aims. Given the sparse nature of adolescent specific fMRI studies on the FC changes in IA, this review successfully provided a much-needed niche representation of adolescent specific results. Furthermore, the review provided a thorough functional explanation of the DMN, ECN, SN and reward pathway making it accessible to readers new to the topic.
Future directions and implications
Through the search process of the review, there were more imaging studies focused on older adolescence and adulthood. Furthermore, finding a review that covered a strictly adolescent population, focused on FC changes, and was specifically depicting IA, was proven difficult. Many related reviews, such as Tereshchenko and Kasparov (2019), looked at risk factors related to the biopsychosocial model, but did not tackle specific alterations in specific structural or functional changes in the brain [ 66 ]. Weinstein (2017) found similar structural and functional results as well as the role IA has in altering response inhibition and reward valuation in adolescents with IA [ 47 ]. Overall, the accumulated findings only paint an emerging pattern which aligns with similar substance-use and gambling disorders. Future studies require more specificity in depicting the interactions between neural networks, as well as more literature on adolescent and comorbid populations. One future field of interest is the incorporation of more task-based fMRI data. Advances in resting-state fMRI methods have yet to be reflected or confirmed in task-based fMRI methods [ 62 ]. Due to the fact that network connectivity is shaped by different tasks, it is critical to confirm that the findings of the resting state fMRI studies also apply to the task based ones [ 62 ]. Subsequently, work in this area will confirm if intrinsic connectivity networks function in resting state will function similarly during goal directed behaviour [ 62 ]. An elevated focus on adolescent populations as well as task-based fMRI methodology will help uncover to what extent adolescent network connectivity maturation facilitates behavioural and cognitive development [ 62 ].
A treatment implication is the potential usage of bupropion for the treatment of IA. Bupropion has been previously used to treat patients with gambling disorder and has been effective in decreasing overall gambling behaviour as well as money spent while gambling [ 67 ]. Bae et al. (2018) found a decrease in clinical symptoms of IA in line with a 12-week bupropion treatment [ 31 ]. The study found that bupropion altered the FC of both the DMN and ECN which in turn decreased impulsivity and attentional deficits for the individuals with IA [ 31 ]. Interventions like bupropion illustrate the importance of understanding the fundamental mechanisms that underlie disorders like IA.
The goal for this review was to summarise the current literature on functional connectivity changes in adolescents with internet addiction. The findings answered the primary research questions that were directed at FC alterations within several networks of the adolescent brain and how that influenced their behaviour and development. Overall, the research demonstrated several wide-ranging effects that influenced the DMN, SN, ECN, and reward centres. Additionally, the findings gave ground to important details such as the maturation of the adolescent brain, the high prevalence of Asian originated studies, and the importance of task-based studies in this field. The process of making this review allowed for a thorough understanding IA and adolescent brain interactions.
Given the influx of technology and media in the lives and education of children and adolescents, an increase in prevalence and focus on internet related behavioural changes is imperative towards future children/adolescent mental health. Events such as COVID-19 act to expose the consequences of extended internet usage on the development and lifestyle of specifically young people. While it is important for parents and older generations to be wary of these changes, it is important for them to develop a base understanding of the issue and not dismiss it as an all-bad or all-good scenario. Future research on IA will aim to better understand the causal relationship between IA and psychological symptoms that coincide with it. The current literature regarding functional connectivity changes in adolescents is limited and requires future studies to test with larger sample sizes, comorbid populations, and populations outside Far East Asia.
This review aimed to demonstrate the inner workings of how IA alters the connection between the primary behavioural networks in the adolescent brain. Predictably, the present answers merely paint an unfinished picture that does not necessarily depict internet usage as overwhelmingly positive or negative. Alternatively, the research points towards emerging patterns that can direct individuals on the consequences of certain variables or risk factors. A clearer depiction of the mechanisms of IA would allow physicians to screen and treat the onset of IA more effectively. Clinically, this could be in the form of more streamlined and accurate sessions of CBT or family therapy, targeting key symptoms of IA. Alternatively clinicians could potentially prescribe treatment such as bupropion to target FC in certain regions of the brain. Furthermore, parental education on IA is another possible avenue of prevention from a public health standpoint. Parents who are aware of the early signs and onset of IA will more effectively handle screen time, impulsivity, and minimize the risk factors surrounding IA.
Additionally, an increased attention towards internet related fMRI research is needed in the West, as mentioned previously. Despite cultural differences, Western countries may hold similarities to the eastern countries with a high prevalence of IA, like China and Korea, regarding the implications of the internet and IA. The increasing influence of the internet on the world may contribute to an overall increase in the global prevalence of IA. Nonetheless, the high saturation of eastern studies in this field should be replicated with a Western sample to determine if the same FC alterations occur. A growing interest in internet related research and education within the West will hopefully lead to the knowledge of healthier internet habits and coping strategies among parents with children and adolescents. Furthermore, IA research has the potential to become a crucial proxy for which to study adolescent brain maturation and development.
Supporting information
S1 checklist. prisma checklist..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.s001
S1 Appendix. Search strategies with all the terms.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.s002
S1 Data. Article screening records with details of categorized content.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.s003
Acknowledgments
The authors thank https://www.stockio.com/free-clipart/brain-01 (with attribution to Stockio.com); and https://www.rawpixel.com/image/6442258/png-sticker-vintage for the free images used to create Figs 2 – 4 .
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar
- 2. Association AP. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. 5 ed. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
- 10. Stats IW. World Internet Users Statistics and World Population Stats 2013 [ http://www.internetworldstats.com/stats.htm .
- 11. Rideout VJR M. B. The common sense census: media use by tweens and teens. San Francisco, CA: Common Sense Media; 2019.
- 37. Tremblay L. The Ventral Striatum. Handbook of Reward and Decision Making: Academic Press; 2009.
- 57. Bhana A. Middle childhood and pre-adolescence. Promoting mental health in scarce-resource contexts: emerging evidence and practice. Cape Town: HSRC Press; 2010. p. 124–42.
- 65. Organization WH. Adolescent Health 2023 [ https://www.who.int/health-topics/adolescent-health#tab=tab_1 .
- Case report
- Open access
- Published: 18 June 2024
Gossypiboma larynx: a rare cause of post-tracheostomy stridor—case report and review of literature
- Gagan S. Prakash 1 ,
- Vikyath Satish ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4954-2620 2 ,
- Bharath Raju 3 ,
- Neema Jayachamarajapura Onkaramurthy 4 &
- Sathya Prakash 5
Journal of Medical Case Reports volume 18 , Article number: 293 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
84 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Gossypiboma, a retained surgical sponge with a foreign body reaction, is an unusual but serious complication seen in open abdominal surgeries. It is exceptionally rare following head and neck surgeries. Here, we present a case of Gossypiboma of the upper airway following tracheostomy.
Case presentation
A 32-year-old male presented with stridor and difficulty breathing one-month post-tracheostomy after a severe head injury following a road traffic accident. A neck radiograph was unremarkable, and a computed tomography (CT) scan of the neck showed a well-defined homogenous curvilinear membrane extending from the hypopharynx to the upper trachea. Bronchoscopic evaluation of the larynx and upper trachea revealed a retained surgical sponge, which was retrieved. The patient’s breathing improved drastically post intervention.
Gossypiboma may go undetected in radiographs and may also present atypically as a homogenous membrane on a CT scan of the neck. Though rare, retained surgical items can have profound medicolegal and professional consequences on physicians. Hence, a strong clinical suspicion and vigilance for gossypiboma is necessary for patients presenting with respiratory distress post-tracheostomy.
Peer Review reports
Referred to euphemistically as Gossypiboma, the term denotes a mass lesion due to a retained surgical sponge surrounded by foreign-body reaction [ 1 ]. Retained sponges in adults occur most commonly in the abdomen (56%), pelvis (18%), and thorax (11%), but their incidence in head and neck surgeries/procedures is exceedingly rare [ 2 ], and clinicians face difficulty in early diagnosis. Failure in early diagnosis can lead to increased morbidity and mortality, given its potential to cause stridor and severe hypoxemia. We report a rare case of a retained surgical sponge in the larynx of a patient post-tracheostomy. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of Gossypiboma in the upper airway.
A 32-year-old male with no medical history who had undergone tracheostomy for a traumatic head injury one month ago returned to the hospital with complaints of exertional dyspnea and difficulty in breathing following tracheostomy decannulation. Physical examination revealed stridor, and differential causes like post-intubation/tracheostomy tracheal stenosis, pseudo-membrane, granulation tissue, and synechiae were suspected. The patient also complained of a foreign body sensation in the throat and an inability to expectorate secretions. He was clinically stable but had an elevated leukocyte count (13,400 cells/mm 3 ) and was treated conservatively with steroids, antibiotics, and albuterol nebulization.
Since the chest radiograph was unremarkable, a CT scan of the neck was performed to delineate the pathology. It unveiled a well-defined homogenous curvilinear soft tissue density in the hypopharynx, larynx, and upper trachea (Fig. 1 ). Meanwhile, the patient developed an irritant cough and severe dyspnea at rest and underwent fiberoptic bronchoscopy for further management.

Homogenous curvilinear soft tissue density in the hypopharynx, larynx, and upper trachea causing mild to moderate luminal narrowing seen on CT scan of the neck
During fiberoptic bronchoscopy, a greyish strand of glistening thick inspissated mass projecting across the vocal cords in the anterior commissure was observed. The scope was passed distally beyond the cords, and the band-like structure adhered to the anterior tracheal wall at the tracheostomy site. The cords appeared normal, with no granulation tissue or narrowing at the tracheostomy site. The tracheobronchial tree was inspected, and a thorough tracheobronchial toileting was performed. Upon withdrawal of the scope, the initial band-like structure in the larynx was not visualized anymore. Suspecting distal dislodgement, the entire tracheobronchial tree was re-visualized, revealing no band-like structure. Assuming it was a mucus strand that the patient coughed up and ingested, the bronchoscope was withdrawn. The patient complained of foreign body sensation in the throat during the visualization of the pharynx, where a thick greyish-black slimy mass was retrieved (Fig. 2 ). After thorough cleaning and examination, it was revealed to be a ribbon gauze piece covered with mucus. Following the procedure and removal of the gossypiboma, the patient improved clinically and was discharged the following day.

Gossypiboma retrieved from the larynx by bronchoscopy
Gossypiboma is a well-accepted “never event” of the National Quality Forum, USA, and is also part of patient safety guidelines by the Health Department of the UK [ 3 ]. The incidence of Gossypiboma varies by surgical site and is exceedingly rare in the head and neck region. In 2005, the Joint Commission designated retained surgical items as a sentinel event requiring immediate root cause analysis investigation and response.
To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of a gossypiboma in the larynx. Most cases go unreported due to fear of litigation and are perceived to taint a professional career. The principle of “res ipsa loquitor” (let the act speak for itself) applies to such incidents and warrants a root cause analysis.
The most probable cause for the retained sponge was the surgical gauze used to guard the tracheostomy site. Typically, a gauze is tied around the tracheostomy tube for a good seal and to prevent air leaks. Here, the patient was shifted between multiple departments, which probably lead to the missing of the fact that the gauze was packed at the tracheostomy site in the first place. It is possible that the gauze got buried under the skin post-decannulation and slowly dislodged into the trachea over time. Despite the patient’s effort to cough it up, the gauze was lodged in the larynx as one end was embedded at the tracheotomy site. The gauze was dislodged and retrieved at the end of the bronchoscopy procedure. Gossypiboma larynx presents itself earlier than at other sites and is associated with an imminent risk of airway compromise, hence warranting early intervention.
Radiographs are the most commonly used modality to detect gossypibomas. In an unremarkable radiograph, imaging modalities like CT, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and Positron emission tomography (PET) aid in the diagnosis.
Established methods to prevent retained surgical items during surgery, such as gauze counting, the pack of five approach, the Swiss cheese model, flattening the hierarchy of surgeons, and the use of a checklist have proven effective in lowering surgical mortality and litigation. However, owing to its exceedingly rare occurrence, sparse guidelines and studies exist on the prevention of gossypiboma in stomas.
While the use of a radio-opaque marker-tagged surgical sponge [ 4 ] is universal in most Western surgical centers, its use is inconsistent in developing countries, especially outside major operating rooms. Surgical sponges tagged with a radiofrequency identification (RFID) chip and a handheld detector have a near-total detection rate, specificity, and sensitivity [ 5 ]. Lastly, effective communication and documentation between members of the multi-disciplinary [ 2 ] team can prevent the occurrence of a gossypiboma.
Gossypiboma larynx is a rare albeit reversible cause of stridor in patients undergone tracheostomy. Gossypiboma may go undetected in radiographs and may also present atypically as a homogenous curvilinear membrane on a CT scan of the neck, an exceedingly rare finding. Early evaluation by bronchoscopy should be undertaken in the event of a diagnostic dilemma, which would aid in the definitive diagnosis and prove therapeutic. The primary goal is to establish hospital protocols for gossypiboma and use newer technology to avoid such “never events” from occurring.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
Computed tomography
Magnetic resonance imaging
Positron emission tomography
Radiofrequency identification
Aminian A. Gossypiboma: a case report. Cases J. 2008;1(1):220.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wan W, Le T, Riskin L, Macario A. Improving safety in the operating room: a systematic literature review of retained surgical sponges. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2009;22:207–14.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hariharan D, Lobo DN. Retained surgical sponges, needles and instruments. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2013;95:87–92.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Takigami I, Itoh Y, Itokazu M, Shimizu K. Radio-opaque marker of a surgical sponge appearing as an intra-articular foreign body after total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128(10):1167–8.
Macario A, Morris D, Morris S. Initial clinical evaluation of a handheld device for detecting retained surgical gauze sponges using radiofrequency identification technology. Arch Surg. 2006;141(7):659–62.
Download references
Acknowledgements
No relevant funding sources served as financial support for this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of General Surgery, Bronx Care Health System, Bronx, NY, USA
Gagan S. Prakash
Department of Pulmonology and Critical Care, Apollo Hospitals, 21/2 14th Main Jayanagar 1st Block, Bangalore, Karnataka, 560011, India
Vikyath Satish
Department of Neurosurgery, Rutgers-Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital, New Brunswick, NJ, USA
Bharath Raju
Department of Internal Medicine, Columbia College of Physicians and Surgeons, NYC Health and Hospitals/Harlem Hospital Center, Harlem, NY, USA
Neema Jayachamarajapura Onkaramurthy
Department of Thoracic Anesthesia, SDS and Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Chest Diseases, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Sathya Prakash
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
A preliminary draft was prepared by VS, after discussing it with GSP and SP. GSP participated in critical input for manuscript content and editing. SP supervised the draft preparation, critical input for manuscript content, and reviewed the manuscript. BR and JON edited the manuscript for the important scientific content. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Vikyath Satish .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The Institutional Review Board Ethical Committee clearance and Informed consent from the study participant was obtained.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Prakash, G.S., Satish, V., Raju, B. et al. Gossypiboma larynx: a rare cause of post-tracheostomy stridor—case report and review of literature. J Med Case Reports 18 , 293 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04490-7
Download citation
Received : 20 December 2022
Accepted : 01 March 2024
Published : 18 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04490-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bronchoscopy
- Foreign body
- Gossypiboma
- Laryngeal membrane
- Surgical gauze
- Tracheostomy
Journal of Medical Case Reports
ISSN: 1752-1947
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Evidence-based green human resource management: a systematic literature review.

1. Introduction
1.1. state of the art of ghrm, 1.2. previous reviews of ghrm, 1.3. aims of the research, 2.1. identification: information sources and search strategies, 2.1.1. information sources, 2.1.2. search strategies, 2.2. screening: selection process and criteria, 2.3. included: data processing and analyzing, 3. results and discussion, 3.1. general overview of ghrm literature, 3.1.1. publications by years, 3.1.2. publications by sources, 3.1.3. publications by contexts, 3.1.4. publications by methodologies, 3.2. ghrm research foci and trends, 3.2.1. bibliographic coupling analysis, 3.2.2. keyword evolution analysis, 3.3. ghrm conceptualizations and research framework, 3.3.1. dimensions and measurements of ghrm, 3.3.2. theoretical bases of ghrm, 3.3.3. framework of ghrm, 3.4. recommendation for practitioners and researchers, 3.4.1. context and trend of ghrm, 3.4.2. access and approach to ghrm, 3.4.3. mechanism and innovation in ghrm, 4. conclusions, 4.1. summary of the research, 4.2. contribution of the research, 4.3. limitations and proposed solutions, author contributions, institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
- Jackson, S.E.; Renwick, D.W.; Jabbour, C.J.; Muller-Camen, M. State-of-the-art and future directions for green human resource management: Introduction to the special issue. Ger. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2011 , 25 , 99–116. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Panda, T.K.; Kumar, A.; Jakhar, S.; Luthra, S.; Garza-Reyes, J.A.; Kazancoglu, I.; Nayak, S.S. Social and environmental sustainability model on consumers’ altruism, green purchase intention, green brand loyalty and evangelism. J. Clean. Prod. 2020 , 243 , 118575. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mensah, J. Sustainable development: Meaning, history, principles, pillars, and implications for human action: Literature review. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2019 , 5 , 1653531. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zeng, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L. Local government environmental regulatory pressures and corporate environmental strategies: Evidence from natural resource accountability audits in China. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022 , 31 , 3060–3082. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pham, N.T.; Tučková, Z.; Jabbour, C.J.C. Greening the hospitality industry: How do green human resource management practices influence organizational citizenship behavior in hotels? A mixed-methods study. Tour. Manag. 2019 , 72 , 386–399. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Han, H. Consumer behavior and environmental sustainability in tourism and hospitality: A review of theories, concepts, and latest research. J. Sustain. Tour. 2021 , 29 , 1021–1042. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- González-Benito, J.; González-Benito, Ó. A study of determinant factors of stakeholder environmental pressure perceived by industrial companies. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2010 , 19 , 164–181. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Manaktola, K.; Jauhari, V. Exploring consumer attitude and behaviour towards green practices in the lodging industry in India. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2007 , 19 , 364–377. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Garcés-Ayerbe, C.; Rivera-Torres, P.; Murillo-Luna, J.L. Stakeholder pressure and environmental proactivity: Moderating effect of competitive advantage expectations. Manag. Decis. 2012 , 50 , 189–206. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Song, W.; Yu, H. Green innovation strategy and green innovation: The roles of green creativity and green organizational identity. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2018 , 25 , 135–150. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- do Paço, A.; Shiel, C.; Alves, H. A new model for testing green consumer behaviour. J. Clean. Prod. 2019 , 207 , 998–1006. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Singh, S.K.; El-Kassar, A.-N. Role of big data analytics in developing sustainable capabilities. J. Clean. Prod. 2019 , 213 , 1264–1273. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; Santos, F.C.A. The central role of human resource management in the search for sustainable organizations. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2008 , 19 , 2133–2154. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Renwick, D.W.; Redman, T.; Maguire, S. Green human resource management: A review and research agenda. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2013 , 15 , 1–14. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Evans, P.A. The strategic outcomes of human resource management. Hum. Resour. Manag. 1986 , 25 , 149–167. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Benevene, P.; Buonomo, I. Green human resource management: An evidence-based systematic literature review. Sustainability 2020 , 12 , 5974. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; Santos, F.C.A. Relationships between human resource dimensions and environmental management in companies: Proposal of a model. J. Clean. Prod. 2008 , 16 , 51–58. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jackson, S.E.; Seo, J. The greening of strategic HRM scholarship. Organ. Manag. J. 2010 , 7 , 278–290. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Renwick, D.; Redman, T.; Maguire, S. Green HRM: A review, process model, and research agenda. Univ. Sheff. Manag. Sch. Discuss. Pap. 2008 , 1 , 1–46. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L. Green human resource management and green supply chain management: Linking two emerging agendas. J. Clean. Prod. 2016 , 112 , 1824–1833. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Milliman, J.; Clair, J. Best environmental HRM practices in the US. In Greening People ; Greenleaf Publishing: Sheffield, UK, 1996; pp. 49–74. [ Google Scholar ]
- Renwick, D.W.S.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Muller-Camen, M.; Redman, T.; Wilkinson, A. Contemporary developments in Green (environmental) HRM scholarship. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2016 , 27 , 114–128. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- James, P. Total Quality Environmental Management and Human Resource Management. In Greening People ; Greenleaf Publishing: Sheffield, UK, 1996; pp. 33–47. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dutta, D.S. Greening people: A strategic dimension. ZENITH Int. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. Res. 2012 , 2 . Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2382034 (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; Santos, F.C.A.; Nagano, M.S. Contributions of HRM throughout the stages of environmental management: Methodological triangulation applied to companies in Brazil. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2010 , 21 , 1049–1089. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gholami, H.; Rezaei, G.; Saman, M.Z.M.; Sharif, S.; Zakuan, N. State-of-the-art Green HRM System: Sustainability in the sports center in Malaysia using a multi-methods approach and opportunities for future research. J. Clean. Prod. 2016 , 124 , 142–163. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ren, S.; Tang, G.; E Jackson, S. Green human resource management research in emergence: A review and future directions. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2018 , 35 , 769–803. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Appelbaum, E.; Bailey, T.; Berg, P.; Kalleberg, A.L. Manufacturing Advantage: Why High-Performance Work Systems Pay off ; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 25–63. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991 , 17 , 99–120. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Barney, J.B. Resource-based theories of competitive advantage: A ten-year retrospective on the resource-based view. J. Manag. 2001 , 27 , 643–650. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Freeman, R.E. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach ; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Connelly, B.L.; Certo, S.T.; Ireland, R.D.; Reutzel, C.R. Signaling theory: A review and assessment. J. Manag. 2011 , 37 , 39–67. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Edwards, J.R. An examination of competing versions of the person-environment fit approach to stress. Acad. Manag. J. 1996 , 39 , 292–339. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Edwards, J.R.; Shipp, A.J. The relationship between person-environment fit and outcomes: An integrative theoretical framework. In Perspectives on Organizational Fit ; Psychology Press: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 209–258. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dumont, J.; Shen, J.; Deng, X. Effects of green HRM practices on employee workplace green behavior: The role of psychological green climate and employee green values. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2017 , 56 , 613–627. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Shafaei, A.; Nejati, M.; Mohd Yusoff, Y. Green human resource management: A two-study investigation of antecedents and outcomes. Int. J. Manpow. 2020 , 41 , 1041–1060. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Al-Hawari, M.A.; Quratulain, S.; Melhem, S.B. How and when frontline employees’ environmental values influence their green creativity? Examining the role of perceived work meaningfulness and green HRM practices. J. Clean. Prod. 2021 , 310 , 127598. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zaid, A.A.; Jaaron, A.A.; Bon, A.T. The impact of green human resource management and green supply chain management practices on sustainable performance: An empirical study. J. Clean. Prod. 2018 , 204 , 965–979. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yu, W.; Chavez, R.; Feng, M.; Wong, C.Y.; Fynes, B. Green human resource management and environmental cooperation: An ability-motivation-opportunity and contingency perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020 , 219 , 224–235. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fachada, J.; Rebelo, T.; Lourenço, P.; Dimas, I.; Martins, H. Green Human Resource Management: A Bibliometric Analysis. Adm. Sci. 2022 , 12 , 95. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yong, J.Y.; Yusliza, M.-Y.; Fawehinmi, O.O. Green human resource management: A systematic literature review from 2007 to 2019. Benchmarking: Int. J. 2020 , 27 , 2005–2027. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pham, N.T.; Hoang, H.T.; Phan, Q.P.T. Green human resource management: A comprehensive review and future research agenda. Int. J. Manpow. 2020 , 41 , 845–878. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tanova, C.; Bayighomog, S.W. Green human resource management in service industries: The construct, antecedents, consequences, and outlook. Serv. Ind. J. 2022 , 42 , 412–452. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Mendy, J.; Rahman, M. A Systematic Literature Review of GHRM: Organizational Sustainable Performance Reimagined Using a New Holistic Framework. Sustainability 2023 , 15 , 7513. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Singh, S.K.; Del Giudice, M.; Chierici, R.; Graziano, D. Green innovation and environmental performance: The role of green transformational leadership and green human resource management. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020 , 150 , 119762. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tang, G.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Paillé, P.; Jia, J. Green human resource management practices: Scale development and validity. Asia Pac. J. Hum. Resour. 2018 , 56 , 31–55. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Shah, M. Green human resource management: Development of a valid measurement scale. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2019 , 28 , 771–785. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Guerci, M.; Montanari, F.; Scapolan, A.; Epifanio, A. Green and nongreen recruitment practices for attracting job applicants: Exploring independent and interactive effects. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2016 , 27 , 129–150. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cop, S.; Alola, U.V.; Alola, A.A. Perceived behavioral control as a mediator of hotels’ green training, environmental commitment, and organizational citizenship behavior: A sustainable environmental practice. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020 , 29 , 3495–3508. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L. Uncovering the influence mechanism between top management support and green procurement: The effect of green training. J. Clean. Prod. 2020 , 251 , 119674. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pfeffer, J.; Sutton, R.I. Evidence-based management. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2006 , 84 , 62–74. Available online: https://hbr.org/2006/01/evidence-based-management (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021 , 88 , 105906. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tranfield, D.; Denyer, D.; Smart, P. Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br. J. Manag. 2003 , 14 , 207–222. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021 , 372 , n160. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pahlevan-Sharif, S.; Mura, P.; Wijesinghe, S.N. A systematic review of systematic reviews in tourism. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2019 , 39 , 158–165. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Perianes-Rodriguez, A.; Waltman, L.; Van Eck, N.J. Constructing bibliometric networks: A comparison between full and fractional counting. J. Informetr. 2016 , 10 , 1178–1195. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Bahuguna, P.C.; Srivastava, R.; Tiwari, S. Two-decade journey of green human resource management research: A bibliometric analysis. Benchmarking Int. J. 2023 , 30 , 585–602. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yu, D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S. A bibliometric analysis of research on multiple criteria decision making. Curr. Sci. 2018 , 114 , 747–758. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. A tale of two databases: The use of Web of Science and Scopus in academic papers. Scientometrics 2020 , 123 , 321–335. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.; Karmakar, M.; Leta, J.; Mayr, P. The journal coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics 2021 , 126 , 5113–5142. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- López-Concepción, A.; Gil-Lacruz, A.I.; Saz-Gil, I. Stakeholder engagement, Csr development and Sdgs compliance: A systematic review from 2015 to 2021. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2022 , 29 , 19–31. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wagner, M. ‘Green’human resource benefits: Do they matter as determinants of environmental management system implementation? J. Bus. Ethics 2013 , 114 , 443–456. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Leal Filho, W.; Azul, A.M.; Wall, T.; Vasconcelos, C.R.; Salvia, A.L.; do Paço, A.; Shulla, K.; Levesque, V.; Doni, F.; Alvarez-Castañón, L. COVID-19: The impact of a global crisis on sustainable development research. Sustain. Sci. 2021 , 16 , 85–99. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chen, C.; Feng, Y.; Shen, B. Managing Labor Sustainability in Digitalized Supply Chains: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2022 , 14 , 3895. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tuan, L.T. Promoting employee green behavior in the Chinese and Vietnamese hospitality contexts: The roles of green human resource management practices and responsible leadership. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2022 , 105 , 103253. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Haddock-Millar, J.; Sanyal, C.; Müller-Camen, M. Green human resource management: A comparative qualitative case study of a United States multinational corporation. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2016 , 27 , 192–211. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Ureña Espaillat, H.J.; Briones Penalver, A.J.; Bernal Conesa, J.A. Influencing responsible green innovation in Dominican agribusiness performance. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2022 , 29 , 675–685. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ojo, A.O. Motivational factors of pro-environmental behaviors among information technology professionals. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2022 , 16 , 1853–1876. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yong, J.Y.; Yusliza, M.-Y.; Ramayah, T.; Fawehinmi, O. Nexus between green intellectual capital and green human resource management. J. Clean. Prod. 2019 , 215 , 364–374. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Visualizing bibliometric networks. In Measuring Scholarly Impact: Methods and Practice ; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 285–320. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bellucci, M.; Marzi, G.; Orlando, B.; Ciampi, F. Journal of Intellectual Capital: A review of emerging themes and future trends. J. Intellect. Cap. 2021 , 22 , 744–767. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Masri, H.A.; Jaaron, A.A. Assessing green human resources management practices in Palestinian manufacturing context: An empirical study. J. Clean. Prod. 2017 , 143 , 474–489. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, W.G.; Choi, H.-M.; Phetvaroon, K. The effect of green human resource management on hotel employees’ eco-friendly behavior and environmental performance. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019 , 76 , 83–93. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Guerci, M.; Longoni, A.; Luzzini, D. Translating stakeholder pressures into environmental performance—The mediating role of green HRM practices. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2016 , 27 , 262–289. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Nejati, M.; Rabiei, S.; Jabbour, C.J.C. Envisioning the invisible: Understanding the synergy between green human resource management and green supply chain management in manufacturing firms in Iran in light of the moderating effect of employees’ resistance to change. J. Clean. Prod. 2017 , 168 , 163–172. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ogbeibu, S.; Chiappetta Jabbour, C.J.; Burgess, J.; Gaskin, J.; Renwick, D.W. Green talent management and turnover intention: The roles of leader STARA competence and digital task interdependence. J. Intellect. Cap. 2022 , 23 , 27–55. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bazrkar, A.; Moshiripour, A. Corporate practices of green human resources management. Foresight STI Gov. 2021 , 15 , 97–105. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ghouri, A.M.; Mani, V.; Khan, M.R.; Khan, N.R.; Srivastava, A.P. Enhancing business performance through green human resource management practices: An empirical evidence from Malaysian manufacturing industry. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2020 , 69 , 1585–1607. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Khatoon, A.; Khan, N.A.; Parvin, F.; Wahid, M.S.; Jamal, M.T.; Azhar, S. Green HRM: Pathway towards environmental sustainability using AHP and FAHP in a nascent parsimony. Int. J. Manpow. 2022 , 43 , 805–826. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Marrucci, L.; Daddi, T.; Iraldo, F. The contribution of green human resource management to the circular economy and performance of environmental certified organisations. J. Clean. Prod. 2021 , 319 , 128859. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Muisyo, P.K.; Qin, S. Enhancing the FIRM’S green performance through green HRM: The moderating role of green innovation culture. J. Clean. Prod. 2021 , 289 , 125720. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Muisyo, P.K.; Qin, S.; Ho, T.H.; Julius, M.M. The effect of green HRM practices on green competitive advantage of manufacturing firms. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2022 , 33 , 22–40. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Muisyo, P.; Su, Q.; Ho, T.H.; Julius, M.M.; Usmani, M.S. Implications of green HRM on the firm’s green competitive advantage: The mediating role of enablers of green culture. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2022 , 33 , 308–333. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ojo, A.O.; Tan, C.N.-L.; Alias, M. Linking green HRM practices to environmental performance through pro-environment behaviour in the information technology sector. Soc. Responsib. J. 2022 , 18 , 1–18. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Paillé, P.; Valéau, P.; Renwick, D.W. Leveraging green human resource practices to achieve environmental sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2020 , 260 , 121137. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yong, J.Y.; Yusliza, M.Y.; Ramayah, T.; Seles, B.M.R.P. Testing the stakeholder pressure, relative advantage, top management commitment and green human resource management linkage. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2022 , 29 , 1283–1299. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Teixeira, A.A.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L. Relationship between green management and environmental training in companies located in Brazil: A theoretical framework and case studies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012 , 140 , 318–329. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Shields, J.; Brown, M.; Kaine, S.; Dolle-Samuel, C.; North-Samardzic, A.; McLean, P.; Johns, R.; O’Leary, P.; Plimmer, G.; Robinson, J. Managing Employee Performance & Reward: Concepts, Practices, Strategies ; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pinzone, M.; Guerci, M.; Lettieri, E.; Huisingh, D. Effects of ‘green’training on pro-environmental behaviors and job satisfaction: Evidence from the Italian healthcare sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2019 , 226 , 221–232. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ogbeibu, S.; Emelifeonwu, J.; Senadjki, A.; Gaskin, J.; Kaivo-oja, J. Technological turbulence and greening of team creativity, product innovation, and human resource management: Implications for sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2020 , 244 , 118703. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Amrutha, V.; Geetha, S. Linking organizational green training and voluntary workplace green behavior: Mediating role of green supporting climate and employees’ green satisfaction. J. Clean. Prod. 2021 , 290 , 125876. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Paillé, P.; Valéau, P. “I don’t owe you, but I am committed”: Does felt obligation matter on the effect of green training on employee environmental commitment? Organ. Environ. 2021 , 34 , 123–144. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jose Chiappetta Jabbour, C. How green are HRM practices, organizational culture, learning and teamwork? A Brazilian study. Ind. Commer. Train. 2011 , 43 , 98–105. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Daily, B.F.; Bishop, J.W.; Massoud, J.A. The role of training and empowerment in environmental performance: A study of the Mexican maquiladora industry. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2012 , 32 , 631–647. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bos-Nehles, A.C.; Van Riemsdijk, M.J.; Kees Looise, J. Employee perceptions of line management performance: Applying the AMO theory to explain the effectiveness of line managers’ HRM implementation. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2013 , 52 , 861–877. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gerhart, B. Human resources and business performance: Findings, unanswered questions, and an alternative approach. Manag. Rev. 2005 , 16 , 174–185. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10419/78948 (accessed on 1 June 2023). [ CrossRef ]
- Hart, S.L. A natural-resource-based view of the firm. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1995 , 20 , 986–1014. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Emerson, R.M. Social Exchange Theory. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 1976 , 2 , 335–362. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/2946096 (accessed on 1 June 2023). [ CrossRef ]
- Ashforth, B.E.; Mael, F. Social identity theory and the organization. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1989 , 14 , 20–39. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Adubor, N.V.; Adeniji, A.A.; Salau, O.P.; Olajugba, O.J.; Onibudo, G.O. Exploring Green Human Resource Adoption and Corporate Sustainability in Nigerian Manufacturing Industry. Sustainability 2022 , 14 , 12635. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Moin, M.F.; Omar, M.K.; Wei, F.; Rasheed, M.I.; Hameed, Z. Green HRM and psychological safety: How transformational leadership drives follower’s job satisfaction. Curr. Issues Tour. 2021 , 24 , 2269–2277. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Farooq, R.; Zhang, Z.; Talwar, S.; Dhir, A. Do green human resource management and self-efficacy facilitate green creativity? A study of luxury hotels and resorts. J. Sustain. Tour. 2022 , 30 , 824–845. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; Jugend, D.; de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.; Gunasekaran, A.; Latan, H. Green product development and performance of Brazilian firms: Measuring the role of human and technical aspects. J. Clean. Prod. 2015 , 87 , 442–451. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Song, W.; Yu, H.; Xu, H. Effects of green human resource management and managerial environmental concern on green innovation. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2021 , 24 , 951–967. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gim, G.C.; Ooi, S.K.; Teoh, S.T.; Lim, H.L.; Yeap, J.A. Green human resource management, leader–member exchange, core self-evaluations and work engagement: The mediating role of human resource management performance attributions. Int. J. Manpow. 2022 , 43 , 682–700. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yong, J.Y.; Yusliza, M.Y.; Ramayah, T.; Chiappetta Jabbour, C.J.; Sehnem, S.; Mani, V. Pathways towards sustainability in manufacturing organizations: Empirical evidence on the role of green human resource management. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020 , 29 , 212–228. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mousa, S.K.; Othman, M. The impact of green human resource management practices on sustainable performance in healthcare organisations: A conceptual framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2020 , 243 , 118595. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Muisyo, P.K.; Qin, S.; Julius, M.M.; Ho, T.H.; Ho, T.H. Green HRM and employer branding: The role of collective affective commitment to environmental management change and environmental reputation. J. Sustain. Tour. 2022 , 30 , 1897–1914. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Rehman, S.U.; Kraus, S.; Shah, S.A.; Khanin, D.; Mahto, R.V. Analyzing the relationship between green innovation and environmental performance in large manufacturing firms. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021 , 163 , 120481. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Karatepe, O.M.; Hsieh, H.; Aboramadan, M. The effects of green human resource management and perceived organizational support for the environment on green and non-green hotel employee outcomes. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2022 , 103 , 103202. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Saeed, B.B.; Afsar, B.; Hafeez, S.; Khan, I.; Tahir, M.; Afridi, M.A. Promoting employee’s proenvironmental behavior through green human resource management practices. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019 , 26 , 424–438. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fawehinmi, O.; Yusliza, M.Y.; Mohamad, Z.; Noor Faezah, J.; Muhammad, Z. Assessing the green behaviour of academics: The role of green human resource management and environmental knowledge. Int. J. Manpow. 2020 , 41 , 879–900. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Rubel, M.R.B.; Kee, D.M.H.; Rimi, N.N. The influence of green HRM practices on green service behaviors: The mediating effect of green knowledge sharing. Empl. Relat. Int. J. 2021 , 43 , 996–1015. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chaudhary, R. Green human resource management and employee green behavior: An empirical analysis. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020 , 27 , 630–641. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hameed, Z.; Khan, I.U.; Islam, T.; Sheikh, Z.; Naeem, R.M. Do green HRM practices influence employees’ environmental performance? Int. J. Manpow. 2020 , 41 , 1061–1079. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Rizvi, Y.S.; Garg, R. The simultaneous effect of green ability-motivation-opportunity and transformational leadership in environment management: The mediating role of green culture. Benchmarking Int. J. 2021 , 28 , 830–856. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Umrani, W.A.; Channa, N.A.; Ahmed, U.; Syed, J.; Pahi, M.H.; Ramayah, T. The laws of attraction: Role of green human resources, culture and environmental performance in the hospitality sector. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2022 , 103 , 103222. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- He, J.; Morrison, A.M.; Zhang, H. Being sustainable: The three-way interactive effects of CSR, green human resource management, and responsible leadership on employee green behavior and task performance. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2021 , 28 , 1043–1054. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ren, S.; Tang, G.; Jackson, S.E. Effects of Green HRM and CEO ethical leadership on organizations’ environmental performance. Int. J. Manpow. 2021 , 42 , 961–983. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Roscoe, S.; Subramanian, N.; Jabbour, C.J.; Chong, T. Green human resource management and the enablers of green organisational culture: Enhancing a firm’s environmental performance for sustainable development. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2019 , 28 , 737–749. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ahmed, M.; Guo, Q.; Qureshi, M.A.; Raza, S.A.; Khan, K.A.; Salam, J. Do green HR practices enhance green motivation and proactive environmental management maturity in hotel industry? Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021 , 94 , 102852. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cabral, C.; Jabbour, C.J.C. Understanding the human side of green hospitality management. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020 , 88 , 102389. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Islam, M.A.; Jantan, A.H.; Yusoff, Y.M.; Chong, C.W.; Hossain, M.S. Green Human Resource Management (GHRM) practices and millennial employees’ turnover intentions in tourism industry in malaysia: Moderating role of work environment. Glob. Bus. Rev. 2020 . [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- O’Donohue, W.; Torugsa, N. The moderating effect of ‘Green’HRM on the association between proactive environmental management and financial performance in small firms. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2016 , 27 , 239–261. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Yusliza, M.-Y.; Norazmi, N.A.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Fernando, Y.; Fawehinmi, O.; Seles, B.M.R.P. Top management commitment, corporate social responsibility and green human resource management: A Malaysian study. Benchmarking: Int. J. 2019 , 26 , 2051–2078. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, L. Corporate ambidexterity: Uncovering the antecedents of enduring sustainable performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2022 , 365 , 132740. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pinzone, M.; Guerci, M.; Lettieri, E.; Redman, T. Progressing in the change journey towards sustainability in healthcare: The role of ‘Green’HRM. J. Clean. Prod. 2016 , 122 , 201–211. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Database | Search Terms | Eligible Criteria Set in Automatic Filters |
|---|---|---|
| N = Initial Records (searching date) | n = Records marked as ineligible | |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY = (“green hr*” OR “green human resource*” OR “green attract*” OR “green recruit*” OR “green select*” OR “green train*” OR “green performance manag*” OR “green performance apprais*” OR “green pay*” OR “green compensat*” OR “green reward” OR “green employee*”) N = 963 (19/04/2023) | Publication years: 2022 Document type: Article Source type: Journal Publication stage: Final Subject Area: Business, Management, and Accounting Language: English n = 636 (excluded) |
| Web of Science Core Collection | TS = (“green hr*” OR “green human resource*” OR “green attract*” OR “green recruit*” OR “green select*” OR “green train*” OR “green performance manag*” OR “green performance apprais*” OR “green pay*” OR “green compensat*” OR “green reward” OR “green employee*”) N = 796 (19/04/2023) | Publication years: 2022 Document type: Article Publication stage: Final Language: English Citation Topics Meso: Management Research Area: Business Economics, Environmental Sciences Ecology, Social Sciences Other Topics n = 406 (excluded) |
| RQs | Evidence from GHRM Literature | New Findings of GHRM |
|---|---|---|
| RQ1. What is the status quo of empirical GHRM research? | 1. Significant growth varies in research disciplines; | 1. Attention from not only HRM but also across disciplines; |
| 2. Conducted context: mainly in Asia, developing economies, and the service and manufacturing sectors; | 2. Lack of evidence in the primary sector; lack of industrial description for the manufacturing sector; | |
| 3. Research clusters: theory implementing and framework extension, linking with employees, linking with an organization; | 3. Three main research streams; | |
| 4. Keyword trends: pro-environmental behavior, green creativity, and competitive advantage appeared in recent studies. | 4. Recent interests are employee-related issues. | |
| RQ2. How has GHRM been conceptualized, and how have theories been in empirical research? | 1. GHRM dimensions: most studies adopted bundled GHRMPs, and GT is among the most examined GHRMP aspect; bundled GHRMPs and GT were found positively relates to desired outcomes in most cases; | 1. Preference showed in bundled GHRMPs and GT, which show a high possibility of having positive effects; comparisons between GHRMPs were rarely made; |
| 2. Theory application: around half of the studies were based on a single theory; AMO theory was used most, followed by RBV, SET, and SIT; some recent studies used multiple theories. | 2. Tendency of using multiple theories and conducting research from different perspectives. | |
| RQ3. What suggestions can be offered for future GHRM development based on the evidence? | 1. Research that adopted the same measurement scales for GHRM constructs show similar choices in the design of GHRM dimensions; 2. Research that applied the same theories had similar inclinations of construct levels (organizational vs. employee level). | 1. Selection of GHRM dimensions influences the choice of measurement scales; 2. Theory applications interrelated with constructs choice and framework design. |
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Lau, T.C. Evidence-Based Green Human Resource Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2023 , 15 , 10941. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151410941
Xie H, Lau TC. Evidence-Based Green Human Resource Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability . 2023; 15(14):10941. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151410941
Xie, Huirong, and Teck Chai Lau. 2023. "Evidence-Based Green Human Resource Management: A Systematic Literature Review" Sustainability 15, no. 14: 10941. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151410941
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources.
What kinds of literature reviews are written? Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified.
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it ...
Definition. A literature review is an assessment of the sources in a chosen topic of research. In a literature review, you're expected to report on the existing scholarly conversation, without adding new contributions. If you are currently writing one, you've come to the right place. In the following paragraphs, we will explain: the objective ...
Most literature reviews are embedded in articles, books, and dissertations. In most research articles, there are set as a specific section, usually titled, "literature review", so they are hard to miss.But, sometimes, they are part of the narrative of the introduction of a book or article. This section is easily recognized since the author is engaging with other academics and experts by ...
What is a literature review? [with examples] Not sure what a literature review is? This guide covers the definition, purpose, and format of a literature review.
As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter. Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter.
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
The word "literature review" can refer to two related things that are part of the broader literature review process. The first is the task of reviewing the literature - i.e. sourcing and reading through the existing research relating to your research topic. The second is the actual chapter that you write up in your dissertation, thesis or ...
A literature review is much more than an annotated bibliography or a list of separate reviews of articles and books. It is a critical, analytical summary and synthesis of the current knowledge of a topic. Thus it should compare and relate different theories, findings, etc, rather than just summarize them individually. ...
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or ...
the literature review journey, this chapter is designed to help you understand the process and skills involved in navigating the literature and reaching your ultimate destination. Learning Outcomes By the end of this chapter you should be able to: • explain what a literature review is.
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
A literature review is an overview of the previously published works on a topic. The term can refer to a full scholarly paper or a section of a scholarly work such as a book, or an article. Either way, a literature review is supposed to provide the researcher /author and the audiences with a general image of the existing knowledge on the topic ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources that provides an overview of a particular topic. Literature reviews are a collection of the most relevant and significant publications regarding that topic in order to provide a comprehensive look at what has been said on the topic and by whom. The basic components of a literature review include:
An "express method" of writing a literature review for a research paper is as follows: first, write a one paragraph description of each article that you read. Second, choose how you will order all the paragraphs and combine them in one document. Third, add transitions between the paragraphs, as well as an introductory and concluding ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings that are related directly to your research question. That is, it represents the literature that provides background information on your topic and shows a correspondence between those writings and your research question.
Internet usage has seen a stark global rise over the last few decades, particularly among adolescents and young people, who have also been diagnosed increasingly with internet addiction (IA). IA impacts several neural networks that influence an adolescent's behaviour and development. This article issued a literature review on the resting-state and task-based functional magnetic resonance ...
Currently, there is a scarcity of cases and diagnostic data regarding ectopic adrenocortical adenomas, particularly in relation to their impact on gonadal function and localization diagnostic techniques. We report a typical case of ectopic adrenocortical adenomas and the data of treatment follow-up, and review the literature of 31 available cases of ectopic adrenocortical adenomas.
Review Findings This review summarizes a 2-day meeting of patient partners, clinicians, researchers, and lung associations to discuss the interplay between cognitive and physical function in people with chronic lung diseases.
Gossypiboma, a retained surgical sponge with a foreign body reaction, is an unusual but serious complication seen in open abdominal surgeries. It is exceptionally rare following head and neck surgeries. Here, we present a case of Gossypiboma of the upper airway following tracheostomy. A 32-year-old male presented with stridor and difficulty breathing one-month post-tracheostomy after a severe ...
This article investigates the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on logistics and supply chain processes through a two-phase analysis. First, a literature review maps the existing studies, published from 2021 to 2023 (101 papers), offering a view of the multiple challenges faced by supply chains during the pandemic emergency. The literature analysis makes use of descriptive statistics, thematic ...
To better understand the empirical development of green human resource management (GHRM) research and theories and to provide evidence-based suggestions, the article conducts a systematic review of evidence-based studies within the academic field of GHRM. The review follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Protocol 2020 to select GHRM-focused and ...