
How To Write A Dissertation Or Thesis
8 straightforward steps to craft an a-grade dissertation.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
Writing a dissertation or thesis is not a simple task. It takes time, energy and a lot of will power to get you across the finish line. It’s not easy – but it doesn’t necessarily need to be a painful process. If you understand the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis, your research journey will be a lot smoother.
In this post, I’m going to outline the big-picture process of how to write a high-quality dissertation or thesis, without losing your mind along the way. If you’re just starting your research, this post is perfect for you. Alternatively, if you’ve already submitted your proposal, this article which covers how to structure a dissertation might be more helpful.
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps
- Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is
- Find a unique and valuable research topic
- Craft a convincing research proposal
- Write up a strong introduction chapter
- Review the existing literature and compile a literature review
- Design a rigorous research strategy and undertake your own research
- Present the findings of your research
- Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications

Step 1: Understand exactly what a dissertation is
This probably sounds like a no-brainer, but all too often, students come to us for help with their research and the underlying issue is that they don’t fully understand what a dissertation (or thesis) actually is.
So, what is a dissertation?
At its simplest, a dissertation or thesis is a formal piece of research , reflecting the standard research process . But what is the standard research process, you ask? The research process involves 4 key steps:
- Ask a very specific, well-articulated question (s) (your research topic)
- See what other researchers have said about it (if they’ve already answered it)
- If they haven’t answered it adequately, undertake your own data collection and analysis in a scientifically rigorous fashion
- Answer your original question(s), based on your analysis findings

In short, the research process is simply about asking and answering questions in a systematic fashion . This probably sounds pretty obvious, but people often think they’ve done “research”, when in fact what they have done is:
- Started with a vague, poorly articulated question
- Not taken the time to see what research has already been done regarding the question
- Collected data and opinions that support their gut and undertaken a flimsy analysis
- Drawn a shaky conclusion, based on that analysis
If you want to see the perfect example of this in action, look out for the next Facebook post where someone claims they’ve done “research”… All too often, people consider reading a few blog posts to constitute research. Its no surprise then that what they end up with is an opinion piece, not research. Okay, okay – I’ll climb off my soapbox now.
The key takeaway here is that a dissertation (or thesis) is a formal piece of research, reflecting the research process. It’s not an opinion piece , nor a place to push your agenda or try to convince someone of your position. Writing a good dissertation involves asking a question and taking a systematic, rigorous approach to answering it.
If you understand this and are comfortable leaving your opinions or preconceived ideas at the door, you’re already off to a good start!

Step 2: Find a unique, valuable research topic
As we saw, the first step of the research process is to ask a specific, well-articulated question. In other words, you need to find a research topic that asks a specific question or set of questions (these are called research questions ). Sounds easy enough, right? All you’ve got to do is identify a question or two and you’ve got a winning research topic. Well, not quite…
A good dissertation or thesis topic has a few important attributes. Specifically, a solid research topic should be:
Let’s take a closer look at these:
Attribute #1: Clear
Your research topic needs to be crystal clear about what you’re planning to research, what you want to know, and within what context. There shouldn’t be any ambiguity or vagueness about what you’ll research.
Here’s an example of a clearly articulated research topic:
An analysis of consumer-based factors influencing organisational trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms.
As you can see in the example, its crystal clear what will be analysed (factors impacting organisational trust), amongst who (consumers) and in what context (British low-cost equity brokerage firms, based online).
Need a helping hand?
Attribute #2: Unique
Your research should be asking a question(s) that hasn’t been asked before, or that hasn’t been asked in a specific context (for example, in a specific country or industry).
For example, sticking organisational trust topic above, it’s quite likely that organisational trust factors in the UK have been investigated before, but the context (online low-cost equity brokerages) could make this research unique. Therefore, the context makes this research original.
One caveat when using context as the basis for originality – you need to have a good reason to suspect that your findings in this context might be different from the existing research – otherwise, there’s no reason to warrant researching it.
Attribute #3: Important
Simply asking a unique or original question is not enough – the question needs to create value. In other words, successfully answering your research questions should provide some value to the field of research or the industry. You can’t research something just to satisfy your curiosity. It needs to make some form of contribution either to research or industry.
For example, researching the factors influencing consumer trust would create value by enabling businesses to tailor their operations and marketing to leverage factors that promote trust. In other words, it would have a clear benefit to industry.
So, how do you go about finding a unique and valuable research topic? We explain that in detail in this video post – How To Find A Research Topic . Yeah, we’ve got you covered 😊
Step 3: Write a convincing research proposal
Once you’ve pinned down a high-quality research topic, the next step is to convince your university to let you research it. No matter how awesome you think your topic is, it still needs to get the rubber stamp before you can move forward with your research. The research proposal is the tool you’ll use for this job.
So, what’s in a research proposal?
The main “job” of a research proposal is to convince your university, advisor or committee that your research topic is worthy of approval. But convince them of what? Well, this varies from university to university, but generally, they want to see that:
- You have a clearly articulated, unique and important topic (this might sound familiar…)
- You’ve done some initial reading of the existing literature relevant to your topic (i.e. a literature review)
- You have a provisional plan in terms of how you will collect data and analyse it (i.e. a methodology)
At the proposal stage, it’s (generally) not expected that you’ve extensively reviewed the existing literature , but you will need to show that you’ve done enough reading to identify a clear gap for original (unique) research. Similarly, they generally don’t expect that you have a rock-solid research methodology mapped out, but you should have an idea of whether you’ll be undertaking qualitative or quantitative analysis , and how you’ll collect your data (we’ll discuss this in more detail later).
Long story short – don’t stress about having every detail of your research meticulously thought out at the proposal stage – this will develop as you progress through your research. However, you do need to show that you’ve “done your homework” and that your research is worthy of approval .
So, how do you go about crafting a high-quality, convincing proposal? We cover that in detail in this video post – How To Write A Top-Class Research Proposal . We’ve also got a video walkthrough of two proposal examples here .
Step 4: Craft a strong introduction chapter
Once your proposal’s been approved, its time to get writing your actual dissertation or thesis! The good news is that if you put the time into crafting a high-quality proposal, you’ve already got a head start on your first three chapters – introduction, literature review and methodology – as you can use your proposal as the basis for these.
Handy sidenote – our free dissertation & thesis template is a great way to speed up your dissertation writing journey.
What’s the introduction chapter all about?
The purpose of the introduction chapter is to set the scene for your research (dare I say, to introduce it…) so that the reader understands what you’ll be researching and why it’s important. In other words, it covers the same ground as the research proposal in that it justifies your research topic.
What goes into the introduction chapter?
This can vary slightly between universities and degrees, but generally, the introduction chapter will include the following:
- A brief background to the study, explaining the overall area of research
- A problem statement , explaining what the problem is with the current state of research (in other words, where the knowledge gap exists)
- Your research questions – in other words, the specific questions your study will seek to answer (based on the knowledge gap)
- The significance of your study – in other words, why it’s important and how its findings will be useful in the world
As you can see, this all about explaining the “what” and the “why” of your research (as opposed to the “how”). So, your introduction chapter is basically the salesman of your study, “selling” your research to the first-time reader and (hopefully) getting them interested to read more.
How do I write the introduction chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this post .

Step 5: Undertake an in-depth literature review
As I mentioned earlier, you’ll need to do some initial review of the literature in Steps 2 and 3 to find your research gap and craft a convincing research proposal – but that’s just scratching the surface. Once you reach the literature review stage of your dissertation or thesis, you need to dig a lot deeper into the existing research and write up a comprehensive literature review chapter.
What’s the literature review all about?
There are two main stages in the literature review process:
Literature Review Step 1: Reading up
The first stage is for you to deep dive into the existing literature (journal articles, textbook chapters, industry reports, etc) to gain an in-depth understanding of the current state of research regarding your topic. While you don’t need to read every single article, you do need to ensure that you cover all literature that is related to your core research questions, and create a comprehensive catalogue of that literature , which you’ll use in the next step.
Reading and digesting all the relevant literature is a time consuming and intellectually demanding process. Many students underestimate just how much work goes into this step, so make sure that you allocate a good amount of time for this when planning out your research. Thankfully, there are ways to fast track the process – be sure to check out this article covering how to read journal articles quickly .

Literature Review Step 2: Writing up
Once you’ve worked through the literature and digested it all, you’ll need to write up your literature review chapter. Many students make the mistake of thinking that the literature review chapter is simply a summary of what other researchers have said. While this is partly true, a literature review is much more than just a summary. To pull off a good literature review chapter, you’ll need to achieve at least 3 things:
- You need to synthesise the existing research , not just summarise it. In other words, you need to show how different pieces of theory fit together, what’s agreed on by researchers, what’s not.
- You need to highlight a research gap that your research is going to fill. In other words, you’ve got to outline the problem so that your research topic can provide a solution.
- You need to use the existing research to inform your methodology and approach to your own research design. For example, you might use questions or Likert scales from previous studies in your your own survey design .
As you can see, a good literature review is more than just a summary of the published research. It’s the foundation on which your own research is built, so it deserves a lot of love and attention. Take the time to craft a comprehensive literature review with a suitable structure .
But, how do I actually write the literature review chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this video post .
Step 6: Carry out your own research
Once you’ve completed your literature review and have a sound understanding of the existing research, its time to develop your own research (finally!). You’ll design this research specifically so that you can find the answers to your unique research question.
There are two steps here – designing your research strategy and executing on it:
1 – Design your research strategy
The first step is to design your research strategy and craft a methodology chapter . I won’t get into the technicalities of the methodology chapter here, but in simple terms, this chapter is about explaining the “how” of your research. If you recall, the introduction and literature review chapters discussed the “what” and the “why”, so it makes sense that the next point to cover is the “how” –that’s what the methodology chapter is all about.
In this section, you’ll need to make firm decisions about your research design. This includes things like:
- Your research philosophy (e.g. positivism or interpretivism )
- Your overall methodology (e.g. qualitative , quantitative or mixed methods)
- Your data collection strategy (e.g. interviews , focus groups, surveys)
- Your data analysis strategy (e.g. content analysis , correlation analysis, regression)
If these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these in plain language in other posts. It’s not essential that you understand the intricacies of research design (yet!). The key takeaway here is that you’ll need to make decisions about how you’ll design your own research, and you’ll need to describe (and justify) your decisions in your methodology chapter.
2 – Execute: Collect and analyse your data
Once you’ve worked out your research design, you’ll put it into action and start collecting your data. This might mean undertaking interviews, hosting an online survey or any other data collection method. Data collection can take quite a bit of time (especially if you host in-person interviews), so be sure to factor sufficient time into your project plan for this. Oftentimes, things don’t go 100% to plan (for example, you don’t get as many survey responses as you hoped for), so bake a little extra time into your budget here.
Once you’ve collected your data, you’ll need to do some data preparation before you can sink your teeth into the analysis. For example:
- If you carry out interviews or focus groups, you’ll need to transcribe your audio data to text (i.e. a Word document).
- If you collect quantitative survey data, you’ll need to clean up your data and get it into the right format for whichever analysis software you use (for example, SPSS, R or STATA).
Once you’ve completed your data prep, you’ll undertake your analysis, using the techniques that you described in your methodology. Depending on what you find in your analysis, you might also do some additional forms of analysis that you hadn’t planned for. For example, you might see something in the data that raises new questions or that requires clarification with further analysis.
The type(s) of analysis that you’ll use depend entirely on the nature of your research and your research questions. For example:
- If your research if exploratory in nature, you’ll often use qualitative analysis techniques .
- If your research is confirmatory in nature, you’ll often use quantitative analysis techniques
- If your research involves a mix of both, you might use a mixed methods approach
Again, if these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these concepts and techniques in other posts. The key takeaway is simply that there’s no “one size fits all” for research design and methodology – it all depends on your topic, your research questions and your data. So, don’t be surprised if your study colleagues take a completely different approach to yours.

Step 7: Present your findings
Once you’ve completed your analysis, it’s time to present your findings (finally!). In a dissertation or thesis, you’ll typically present your findings in two chapters – the results chapter and the discussion chapter .
What’s the difference between the results chapter and the discussion chapter?
While these two chapters are similar, the results chapter generally just presents the processed data neatly and clearly without interpretation, while the discussion chapter explains the story the data are telling – in other words, it provides your interpretation of the results.
For example, if you were researching the factors that influence consumer trust, you might have used a quantitative approach to identify the relationship between potential factors (e.g. perceived integrity and competence of the organisation) and consumer trust. In this case:
- Your results chapter would just present the results of the statistical tests. For example, correlation results or differences between groups. In other words, the processed numbers.
- Your discussion chapter would explain what the numbers mean in relation to your research question(s). For example, Factor 1 has a weak relationship with consumer trust, while Factor 2 has a strong relationship.
Depending on the university and degree, these two chapters (results and discussion) are sometimes merged into one , so be sure to check with your institution what their preference is. Regardless of the chapter structure, this section is about presenting the findings of your research in a clear, easy to understand fashion.
Importantly, your discussion here needs to link back to your research questions (which you outlined in the introduction or literature review chapter). In other words, it needs to answer the key questions you asked (or at least attempt to answer them).
For example, if we look at the sample research topic:
In this case, the discussion section would clearly outline which factors seem to have a noteworthy influence on organisational trust. By doing so, they are answering the overarching question and fulfilling the purpose of the research .

For more information about the results chapter , check out this post for qualitative studies and this post for quantitative studies .
Step 8: The Final Step Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications
Last but not least, you’ll need to wrap up your research with the conclusion chapter . In this chapter, you’ll bring your research full circle by highlighting the key findings of your study and explaining what the implications of these findings are.
What exactly are key findings? The key findings are those findings which directly relate to your original research questions and overall research objectives (which you discussed in your introduction chapter). The implications, on the other hand, explain what your findings mean for industry, or for research in your area.
Sticking with the consumer trust topic example, the conclusion might look something like this:
Key findings
This study set out to identify which factors influence consumer-based trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms. The results suggest that the following factors have a large impact on consumer trust:
While the following factors have a very limited impact on consumer trust:
Notably, within the 25-30 age groups, Factors E had a noticeably larger impact, which may be explained by…
Implications
The findings having noteworthy implications for British low-cost online equity brokers. Specifically:
The large impact of Factors X and Y implies that brokers need to consider….
The limited impact of Factor E implies that brokers need to…
As you can see, the conclusion chapter is basically explaining the “what” (what your study found) and the “so what?” (what the findings mean for the industry or research). This brings the study full circle and closes off the document.

Let’s recap – how to write a dissertation or thesis
You’re still with me? Impressive! I know that this post was a long one, but hopefully you’ve learnt a thing or two about how to write a dissertation or thesis, and are now better equipped to start your own research.
To recap, the 8 steps to writing a quality dissertation (or thesis) are as follows:
- Understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is – a research project that follows the research process.
- Find a unique (original) and important research topic
- Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal
- Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter
- Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review
- Undertake your own research
- Present and interpret your findings
Once you’ve wrapped up the core chapters, all that’s typically left is the abstract , reference list and appendices. As always, be sure to check with your university if they have any additional requirements in terms of structure or content.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

20 Comments
thankfull >>>this is very useful
Thank you, it was really helpful
unquestionably, this amazing simplified way of teaching. Really , I couldn’t find in the literature words that fully explicit my great thanks to you. However, I could only say thanks a-lot.
Great to hear that – thanks for the feedback. Good luck writing your dissertation/thesis.
This is the most comprehensive explanation of how to write a dissertation. Many thanks for sharing it free of charge.
Very rich presentation. Thank you
Thanks Derek Jansen|GRADCOACH, I find it very useful guide to arrange my activities and proceed to research!
Thank you so much for such a marvelous teaching .I am so convinced that am going to write a comprehensive and a distinct masters dissertation
It is an amazing comprehensive explanation
This was straightforward. Thank you!
I can say that your explanations are simple and enlightening – understanding what you have done here is easy for me. Could you write more about the different types of research methods specific to the three methodologies: quan, qual and MM. I look forward to interacting with this website more in the future.
Thanks for the feedback and suggestions 🙂
Hello, your write ups is quite educative. However, l have challenges in going about my research questions which is below; *Building the enablers of organisational growth through effective governance and purposeful leadership.*
Very educating.
Just listening to the name of the dissertation makes the student nervous. As writing a top-quality dissertation is a difficult task as it is a lengthy topic, requires a lot of research and understanding and is usually around 10,000 to 15000 words. Sometimes due to studies, unbalanced workload or lack of research and writing skill students look for dissertation submission from professional writers.
Thank you 💕😊 very much. I was confused but your comprehensive explanation has cleared my doubts of ever presenting a good thesis. Thank you.
thank you so much, that was so useful
Hi. Where is the excel spread sheet ark?
could you please help me look at your thesis paper to enable me to do the portion that has to do with the specification
my topic is “the impact of domestic revenue mobilization.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples, & Template
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program.
Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you’ve ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating to know where to begin.
Your department likely has guidelines related to how your dissertation should be structured. When in doubt, consult with your supervisor.
You can also download our full dissertation template in the format of your choice below. The template includes a ready-made table of contents with notes on what to include in each chapter, easily adaptable to your department’s requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
- In the US, a dissertation generally refers to the collection of research you conducted to obtain a PhD.
- In other countries (such as the UK), a dissertation often refers to the research you conduct to obtain your bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

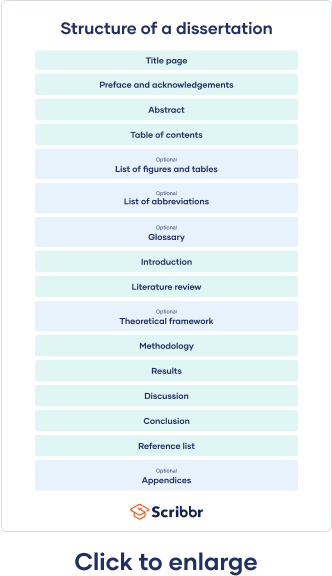
Table of contents
Dissertation committee and prospectus process, how to write and structure a dissertation, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your dissertation, free checklist and lecture slides.
When you’ve finished your coursework, as well as any comprehensive exams or other requirements, you advance to “ABD” (All But Dissertation) status. This means you’ve completed everything except your dissertation.
Prior to starting to write, you must form your committee and write your prospectus or proposal . Your committee comprises your adviser and a few other faculty members. They can be from your own department, or, if your work is more interdisciplinary, from other departments. Your committee will guide you through the dissertation process, and ultimately decide whether you pass your dissertation defense and receive your PhD.
Your prospectus is a formal document presented to your committee, usually orally in a defense, outlining your research aims and objectives and showing why your topic is relevant . After passing your prospectus defense, you’re ready to start your research and writing.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The structure of your dissertation depends on a variety of factors, such as your discipline, topic, and approach. Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an overall argument to support a central thesis , with chapters organized around different themes or case studies.
However, hard science and social science dissertations typically include a review of existing works, a methodology section, an analysis of your original research, and a presentation of your results , presented in different chapters.
Dissertation examples
We’ve compiled a list of dissertation examples to help you get started.
- Example dissertation #1: Heat, Wildfire and Energy Demand: An Examination of Residential Buildings and Community Equity (a dissertation by C. A. Antonopoulos about the impact of extreme heat and wildfire on residential buildings and occupant exposure risks).
- Example dissertation #2: Exploring Income Volatility and Financial Health Among Middle-Income Households (a dissertation by M. Addo about income volatility and declining economic security among middle-income households).
- Example dissertation #3: The Use of Mindfulness Meditation to Increase the Efficacy of Mirror Visual Feedback for Reducing Phantom Limb Pain in Amputees (a dissertation by N. S. Mills about the effect of mindfulness-based interventions on the relationship between mirror visual feedback and the pain level in amputees with phantom limb pain).
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. In some cases, your acknowledgements are part of a preface.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150 to 300 words long. Though this may seem very short, it’s one of the most important parts of your dissertation, because it introduces your work to your audience.
Your abstract should:
- State your main topic and the aims of your research
- Describe your methods
- Summarize your main results
- State your conclusions
Read more about abstracts
The table of contents lists all of your chapters, along with corresponding subheadings and page numbers. This gives your reader an overview of your structure and helps them easily navigate your document.
Remember to include all main parts of your dissertation in your table of contents, even the appendices. It’s easy to generate a table automatically in Word if you used heading styles. Generally speaking, you only include level 2 and level 3 headings, not every subheading you included in your finished work.
Read more about tables of contents
While not usually mandatory, it’s nice to include a list of figures and tables to help guide your reader if you have used a lot of these in your dissertation. It’s easy to generate one of these in Word using the Insert Caption feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
Similarly, if you have used a lot of abbreviations (especially industry-specific ones) in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
In addition to the list of abbreviations, if you find yourself using a lot of highly specialized terms that you worry will not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary. Here, alphabetize the terms and include a brief description or definition.
Read more about glossaries
The introduction serves to set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance. It tells the reader what to expect in the rest of your dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving the background information needed to contextualize your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of your research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your research questions and objectives
- Outline the flow of the rest of your work
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant. By the end, the reader should understand the what, why, and how of your research.
Read more about introductions
A formative part of your research is your literature review . This helps you gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic.
Literature reviews encompass:
- Finding relevant sources (e.g., books and journal articles)
- Assessing the credibility of your sources
- Critically analyzing and evaluating each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g., themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps) to strengthen your overall point
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing sources. Your literature review should have a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear justification for your own research. It may aim to:
- Address a gap in the literature or build on existing knowledge
- Take a new theoretical or methodological approach to your topic
- Propose a solution to an unresolved problem or advance one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework. Here, you define and analyze the key theories, concepts, and models that frame your research.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to critically assess its credibility. Your methodology section should accurately report what you did, as well as convince your reader that this was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- The overall research approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative ) and research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment )
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Any tools and materials you used (e.g., computer programs, lab equipment)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses , or themes, but avoid including any subjective or speculative interpretation here.
Your results section should:
- Concisely state each relevant result together with relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Briefly state how the result relates to the question or whether the hypothesis was supported
- Report all results that are relevant to your research questions , including any that did not meet your expectations.
Additional data (including raw numbers, full questionnaires, or interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix. You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results. Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is your opportunity to explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research question. Here, interpret your results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. Refer back to relevant source material to show how your results fit within existing research in your field.
Some guiding questions include:
- What do your results mean?
- Why do your results matter?
- What limitations do the results have?
If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your dissertation’s conclusion should concisely answer your main research question, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your central argument and emphasizing what your research has contributed to the field.
In some disciplines, the conclusion is just a short section preceding the discussion section, but in other contexts, it is the final chapter of your work. Here, you wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you found, with recommendations for future research and concluding remarks.
It’s important to leave the reader with a clear impression of why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known? Why is your research necessary for the future of your field?
Read more about conclusions
It is crucial to include a reference list or list of works cited with the full details of all the sources that you used, in order to avoid plagiarism. Be sure to choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your dissertation. Each style has strict and specific formatting requirements.
Common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA , but which style you use is often set by your department or your field.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
Your dissertation should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents such as interview transcripts or survey questions can be added as appendices, rather than adding them to the main body.
Read more about appendices
Making sure that all of your sections are in the right place is only the first step to a well-written dissertation. Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing and proofreading, as grammar mistakes and sloppy spelling errors can really negatively impact your work.
Dissertations can take up to five years to write, so you will definitely want to make sure that everything is perfect before submitting. You may want to consider using a professional dissertation editing service , AI proofreader or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect prior to submitting.
After your written dissertation is approved, your committee will schedule a defense. Similarly to defending your prospectus, dissertation defenses are oral presentations of your work. You’ll present your dissertation, and your committee will ask you questions. Many departments allow family members, friends, and other people who are interested to join as well.
After your defense, your committee will meet, and then inform you whether you have passed. Keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality; most committees will have resolved any serious issues with your work with you far prior to your defense, giving you ample time to fix any problems.
As you write your dissertation, you can use this simple checklist to make sure you’ve included all the essentials.
Checklist: Dissertation
My title page includes all information required by my university.
I have included acknowledgements thanking those who helped me.
My abstract provides a concise summary of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of my key results or arguments.
I have created a table of contents to help the reader navigate my dissertation. It includes all chapter titles, but excludes the title page, acknowledgements, and abstract.
My introduction leads into my topic in an engaging way and shows the relevance of my research.
My introduction clearly defines the focus of my research, stating my research questions and research objectives .
My introduction includes an overview of the dissertation’s structure (reading guide).
I have conducted a literature review in which I (1) critically engage with sources, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, (2) discuss patterns, themes, and debates in the literature, and (3) address a gap or show how my research contributes to existing research.
I have clearly outlined the theoretical framework of my research, explaining the theories and models that support my approach.
I have thoroughly described my methodology , explaining how I collected data and analyzed data.
I have concisely and objectively reported all relevant results .
I have (1) evaluated and interpreted the meaning of the results and (2) acknowledged any important limitations of the results in my discussion .
I have clearly stated the answer to my main research question in the conclusion .
I have clearly explained the implications of my conclusion, emphasizing what new insight my research has contributed.
I have provided relevant recommendations for further research or practice.
If relevant, I have included appendices with supplemental information.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
I have listed every source in a reference list at the end of my dissertation.
I have consistently followed the rules of my chosen citation style .
I have followed all formatting guidelines provided by my university.
Congratulations!
The end is in sight—your dissertation is nearly ready to submit! Make sure it's perfectly polished with the help of a Scribbr editor.
If you’re an educator, feel free to download and adapt these slides to teach your students about structuring a dissertation.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation Binding and Printing | Options, Tips, & Comparison
- Example of a dissertation abstract
- Figure and Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Purpose and structure of an advisory report
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Shorten your abstract or summary
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What is your plagiarism score?
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- How to Hook Your Readers with a Compelling Topic Sentence
Is a Thesis Writing Format Easy? A Comprehensive Guide to Thesis Writing
- The Complete Guide to Copy Editing: Roles, Rates, Skills, and Process
- How to Write a Paragraph: Successful Essay Writing Strategies
- Everything You Should Know About Academic Writing: Types, Importance, and Structure
- Concise Writing: Tips, Importance, and Exercises for a Clear Writing Style
How to Write a PhD Thesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Success
- How to Use AI in Essay Writing: Tips, Tools, and FAQs
- Copy Editing Vs Proofreading: What’s The Difference?
How Much Does It Cost To Write A Thesis? Get Complete Process & Tips
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips

Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
Writing a PhD thesis is a complicated and demanding process that involves rigorous research, detailed analysis, and structured writing. This guide provides an extensive overview of each step required to craft a successful PhD thesis, offering essential insights and strategies that benefit novice and seasoned researchers.
Step 1: Understand the Requirements
The initial step in crafting your PhD thesis is to thoroughly understand its specific requirements, which can vary widely between disciplines and institutions. A thesis must contribute new knowledge to its field, necessitating a deep familiarity with the expected structure, depth of analysis, and submission formalities. Your university guidelines should state how many words in a PhD thesis are needed within your discipline—usually ranging from 60,000 to 80,000 words.
Step 2: Choose Your Topic Wisely
Selecting a suitable topic is crucial and should be approached with great care. Your subject should interest you, fill a research gap, and be feasible within your available time and resources. Extensive preliminary reading and discussions with advisors are crucial at this stage to refine your topic and formulate precise research questions.
Step 3: Develop a Detailed Proposal
A detailed proposal acts as your thesis roadmap, outlining your research questions, the study's significance, methodologies, and a preliminary literature review. This document guides your research trajectory and is a reference point throughout your project.
Step 4: Conduct Rigorous Research
The research phase forms the backbone of your thesis. It involves systematic data collection, comprehensive literature review, and meticulous analysis. Effective research methods are crucial, and keeping organised, detailed records during this phase will facilitate a smoother writing process later on.
Step 5: Start Writing Early
Begin writing early in the research process. Starting with less complex sections like the literature review or methodology can help clarify your thoughts and identify gaps in your research. Early writing reduces the burden as the thesis deadline approaches.
Step 6: Structure Your Thesis
A PhD thesis usually has an introduction, a literature review, a methodology, findings, a discussion, a conclusion, and a list of references. Each section serves a distinct purpose: the introduction presents your research question and its significance, while the conclusion synthesises your findings and highlights their importance. But, how long is a PhD thesis typically? It usually ranges from 100 to 300 pages, varying by field and the nature of the research conducted.
Step 7: Seek Feedback Regularly
Regular feedback from your supervisor and peers is invaluable. Sharing drafts of chapters as you complete them ensures you remain on the correct path and integrates diverse perspectives that can enhance your work.
Step 8: Revise Thoroughly
Revision is a critical phase in which good writing is refined into excellent writing. Use feedback to enhance your arguments, clarify points, and refine your prose. Expect multiple rounds of revisions and be prepared to rework sections as needed.
Step 9: Proofread and Edit
Comprehensive proofreading and editing are crucial to ensure your thesis is error-free. Consider employing PhD thesis help from a PhD thesis writing service if needed. These professionals can provide detailed feedback and help polish your document to perfection.
Step 10: Prepare for the Viva
The final step is the viva, where you'll present your research to a panel of experts in your field. Thorough preparation, including a deep understanding of your research and readiness for potential questions, is essential. This presentation is your opportunity to highlight the significance and rigour of your work.
The Importance of a High-Quality PhD Thesis
A high-quality PhD thesis is not just a requirement for completing your doctorate; it significantly contributes to your field of study. Furthermore, it highlights your ability to conduct independent research, contribute original insights, and communicate complex ideas clearly and effectively. The calibre of your thesis can influence your academic and professional future, impacting job opportunities, postdoctoral positions, and the ability to publish your work in reputable journals.
Seeking Professional Help: Sources and Providers
When crafting your PhD thesis, seeking professional help can be a wise decision. Support can come from various sources:
University Resources : Most universities offer writing centres and libraries with professionals skilled in research methodologies, writing, and editing. PhD Thesis Writing Services : Specialised services can provide comprehensive help throughout the writing process. These services employ experienced PhD thesis writers familiar with the nuances of doctoral writing across various disciplines. Independent Consultants : Expert consultants or freelance PhD thesis writers can offer personalised guidance and feedback, focusing on specific areas of your thesis where you need extra help.
The Advantages of Professional PhD Thesis Help
Opting for professional PhD thesis help offers several advantages:
- Expert Guidance : Professional writers and editors bring expertise that can help you improve your thesis. They understand the academic standards and can help ensure your thesis meets them.
- Time Management : With the help of a PhD thesis writing service, you can manage your time more effectively. Professionals can speed up the research, writing, and revision processes, allowing you to focus on other important academic or personal commitments.
- Reduced Stress : The process of writing a PhD thesis can be stressful. Having a professional by your side can alleviate much of this stress by ensuring you are on the right track and providing reassurance through expert feedback.
Key Takeaways
A high-quality PhD thesis is the masterpiece of your academic career, thus requiring meticulous attention to detail and a deep understanding of your research topic. When asking, "How many words are in a PhD thesis?" it's important to note that quality and depth of research often matter more than the word count.
Utilising professional help, whether through university resources, dedicated PhD thesis writing services, or independent consultants, can provide invaluable support. These professionals enhance the quality of your work and help streamline the entire thesis process, allowing you to present a polished, scholarly work that stands out in your field. By investing in professional help, you invest in your academic success and future career prospects.

How to Tell if a Source is Reliable
Writing services.
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Thesis and Dissertation: Getting Started

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The resources in this section are designed to provide guidance for the first steps of the thesis or dissertation writing process. They offer tools to support the planning and managing of your project, including writing out your weekly schedule, outlining your goals, and organzing the various working elements of your project.
Weekly Goals Sheet (a.k.a. Life Map) [Word Doc]
This editable handout provides a place for you to fill in available time blocks on a weekly chart that will help you visualize the amount of time you have available to write. By using this chart, you will be able to work your writing goals into your schedule and put these goals into perspective with your day-to-day plans and responsibilities each week. This handout also contains a formula to help you determine the minimum number of pages you would need to write per day in order to complete your writing on time.
Setting a Production Schedule (Word Doc)
This editable handout can help you make sense of the various steps involved in the production of your thesis or dissertation and determine how long each step might take. A large part of this process involves (1) seeking out the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding specific document formatting requirements, (2) understanding research protocol limitations, (3) making note of deadlines, and (4) understanding your personal writing habits.
Creating a Roadmap (PDF)
Part of organizing your writing involves having a clear sense of how the different working parts relate to one another. Creating a roadmap for your dissertation early on can help you determine what the final document will include and how all the pieces are connected. This resource offers guidance on several approaches to creating a roadmap, including creating lists, maps, nut-shells, visuals, and different methods for outlining. It is important to remember that you can create more than one roadmap (or more than one type of roadmap) depending on how the different approaches discussed here meet your needs.
PhD Thesis Guide
This phd thesis guide will guide you step-by-step through the thesis process, from your initial letter of intent to submission of the final document..
All associated forms are conveniently consolidated in the section at the end.
Deadlines & Requirements
Students should register for HST.ThG during any term in which they are conducting research towards their thesis. Regardless of year in program students registered for HST.ThG in a regular term (fall or spring) must meet with their research advisor and complete the Semi-Annual PhD Student Progress Review Form to receive credit.
Years 1 - 2
- Students participating in lab rotations during year 1, may use the optional MEMP Rotation Registration Form , to formalize the arrangement and can earn academic credit by enrolling in HST.599.
- A first letter of intent ( LOI-1 ) proposing a general area of thesis research and research advisor is required by April 30th of the second year of registration.
- A second letter of intent ( LOI-2 ) proposing a thesis committee membership and providing a more detailed description of the thesis research is required by April 30th of the third year of registration for approval by the HST-IMES Committee on Academic Programs (HICAP).
Year 4
- Beginning in year 4, (or after the LOI-2 is approved) the student must meet with their thesis committee at least once per semester.
- Students must formally defend their proposal before the approved thesis committee, and submit their committee approved proposal to HICAP by April 30 of the forth year of registration.
- Meetings with the thesis committee must be held at least once per semester.
HST has developed these policies to help keep students on track as they progress through their PhD program. Experience shows that students make more rapid progress towards graduation when they interact regularly with a faculty committee and complete their thesis proposal by the deadline.
| September 2023 | April 30, 2025 | April 30, 2026 | April 30, 2027 |
| September 2022 | April 30, 2024 | April 30, 2025 | April 30, 2026 |
| September 2021 | April 30, 2023 | April 30, 2024 | April 30, 2025 |
| September 2020 | April 30, 2022 | April 30, 2023 | April 30, 2024 |
Getting Started
Check out these resources for finding a research lab.
The Thesis Committee: Roles and Responsibilities
Students perform doctoral thesis work under the guidance of a thesis committee consisting of at least three faculty members from Harvard and MIT (including a chair and a research advisor) who will help guide the research. Students are encouraged to form their thesis committee early in the course of the research and in any case by the end of the third year of registration. The HST IMES Committee on Academic Programs (HICAP) approves the composition of the thesis committee via the letter of intent and the thesis proposal (described below).
Research Advisor
The research advisor is responsible for overseeing the student's thesis project. The research advisor is expected to:
- oversee the research and mentor the student;
- provide a supportive research environment, facilities, and financial support;
- discuss expectations, progress, and milestones with the student and complete the Semi-Annual PhD Student Progress Review Form each semester;
- assist the student to prepare for the oral qualifying exam;
- guide the student in selecting the other members of the thesis committee;
- help the student prepare for, and attend, meetings of the full thesis committee, to be held at least once per semester;
- help the student prepare for, and attend, the thesis defense;
- evaluate the final thesis document.
The research advisor is chosen by the student and must be a faculty member of MIT* or Harvard University and needs no further approval. HICAP may approve other individuals as research advisor on a student-by-student basis. Students are advised to request approval of non-faculty research advisors as soon as possible. In order to avoid conflicts of interest, the research advisor may not also be the student's academic advisor. In the event that an academic advisor becomes the research advisor, a new academic advisor will be assigned.
The student and their research advisor must complete the Semi-Annual PhD Student Progress Review during each regular term in order to receive academic credit for research. Download Semi Annual Review Form
*MIT Senior Research Staff are considered equivalent to faculty members for the purposes of research advising. No additional approval is required.
Thesis Committee Chair
Each HST PhD thesis committee is headed administratively by a chair, chosen by the student in consultation with the research advisor. The thesis committee chair is expected to:
- provide advice and guidance concerning the thesis research;
- oversee meetings of the full thesis committee, to be held at least once per semester;
- preside at the thesis defense;
- review and evaluate the final thesis document.
The thesis committee chair must be well acquainted with the academic policies and procedures of the institution granting the student's degree and be familiar with the student's area of research. The research advisor may not simultaneously serve as thesis committee chair.
For HST PhD students earning degrees through MIT, the thesis committee chair must be an MIT faculty member. A select group of HST program faculty without primary appointments at MIT have been pre-approved by HICAP to chair PhD theses awarded by HST at MIT in cases where the MIT research advisor is an MIT faculty member.**
HST PhD students earning their degree through Harvard follow thesis committee requirements set by the unit granting their degree - either the Biophysics Program or the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS).
** List of non-MIT HST faculty approved to chair MIT thesis proposals when the research advisor is an MIT faculty member.
In addition to the research advisor and the thesis committee chair, the thesis committee must include one or more readers. Readers are expected to:
- attend meetings of the full thesis committee, to be held at least once per semester;
- attend the thesis defense;
Faculty members with relevant expertise from outside of Harvard/MIT may serve as readers, but they may only be counted toward the required three if approved by HICAP.
The members of the thesis committee should have complementary expertise that collectively covers the areas needed to advise a student's thesis research. The committee should also be diverse, so that members are able to offer different perspectives on the student's research. When forming a thesis committee, it is helpful to consider the following questions:
- Do the individuals on the committee collectively have the appropriate expertise for the project?
- Does the committee include at least one individual who can offer different perspectives on the student's research? The committee should include at least one person who is not closely affiliated with the student's primary lab. Frequent collaborators are acceptable in this capacity if their work exhibits intellectual independence from the research advisor.
- If the research has a near-term clinical application, does the committee include someone who can add a translational or clinical perspective?
- Does the committee conform to HST policies in terms of number, academic appointments, and affiliations of the committee members, research advisor, and thesis committee chair as described elsewhere on this page?
[Friendly advice: Although there is no maximum committee size, three or four is considered optimal. Committees of five members are possible, but more than five is unwieldy.]
Thesis Committee Meetings
Students must meet with their thesis committee at least once each semester beginning in the fourth year of registration. It is the student's responsibility to schedule these meetings; students who encounter difficulties in arranging regular committee meetings can contact Julie Greenberg at jgreenbe [at] mit.edu (jgreenbe[at]mit[dot]edu) .
The format of the thesis committee meeting is at the discretion of the thesis committee chair. In some cases, the following sequence may be helpful:
- The thesis committee chair, research advisor, and readers meet briefly without the student in the room;
- The thesis committee chair and readers meet briefly with the student, without the advisor in the room;
- The student presents their research progress, answers questions, and seeks guidance from the members of the thesis committee;
Please note that thesis committee meetings provide an important opportunity for students to present their research and respond to questions. Therefore, it is in the student's best interest for the research advisor to refrain from defending the research in this setting.
Letters of Intent
Students must submit two letters of intent ( LOI-1 and LOI-2 ) with applicable signatures.
In LOI-1, students identify a research advisor and a general area of thesis research, described in 100 words or less. It should include the area of expertise of the research advisor and indicate whether IRB approval (Institutional Review Board; for research involving human subjects) and/or IACUC approval (Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee; for research involving vertebrate animals) will be required and, if so, from which institutions. LOI-1 is due by April 30 of the second year of registration and and should be submitted to HICAP, c/o Traci Anderson in E25-518.
In LOI-2, students provide a description of the thesis research, describing the Background and Significance of the research and making a preliminary statement of Specific Aims (up to 400 words total). In LOI-2, a student also proposes the membership of their thesis committee. In addition to the research advisor, the proposed thesis committee must include a chair and one or more readers, all selected to meet the specified criteria . LOI-2 is due by April 30th of the third year of registration and should be submitted to HICAP, c/o Traci Anderson in E25-518.
LOI-2 is reviewed by the HST-IMES Committee on Academic Programs (HICAP) to determine if the proposed committee meets the specified criteria and if the committee members collectively have the complementary expertise needed to advise the student in executing the proposed research. If HICAP requests any changes to the proposed committee, the student must submit a revised LOI-2 for HICAP review by September 30th of the fourth year of registration. HICAP must approve LOI-2 before the student can proceed to presenting and submitting their thesis proposal. Any changes to the thesis committee membership following HICAP approval of LOI-2 and prior to defense of the thesis proposal must be reported by submitting a revised LOI-2 form to HICAP, c/o tanderso [at] mit.edu (Traci Anderson) . After final HICAP approval of LOI-2, which confirms the thesis committee membership, the student may proceed to present their thesis proposal to the approved thesis committee, as described in the next section.
Students are strongly encouraged to identify tentative thesis committee members and begin meeting with them as early as possible to inform the direction of their research. Following submission of LOI-2, students are required to hold at least one thesis committee meeting per semester. Students must document these meetings via the Semi- Annual PhD Student Progress Review form in order to receive a grade reflecting satisfactory progress in HST.ThG.
Thesis Proposal and Proposal Presentation
For MEMP students receiving their degrees through MIT, successful completion of the Oral Qualifying Exam is a prerequisite for the thesis proposal presentation. For MEMP students receiving their degrees through Harvard, the oral qualifying exam satisfies the proposal presentation requirement.
Proposal Document
Each student must present a thesis proposal to a thesis committee that has been approved by HICAP via the LOI-2 and then submit a full proposal package to HICAP by April 30th of the fourth year of registration. The only exception is for students who substantially change their research focus after the fall term of their third year; in those cases the thesis proposal must be submitted within three semesters of joining a new lab. Students registering for thesis research (HST.THG) who have not met this deadline may be administratively assigned a grade of "U" (unsatisfactory) and receive an academic warning.
The written proposal should be no longer than 4500 words, excluding references. This is intended to help students develop their proposal-writing skills by gaining experience composing a practical proposal; the length is comparable to that required for proposals to the NIH R03 Small Research Grant Program. The proposal should clearly define the research problem, describe the proposed research plan, and defend the significance of the work. Preliminary results are not required. If the proposal consists of multiple aims, with the accomplishment of later aims based on the success of earlier ones, then the proposal should describe a contingency plan in case the early results are not as expected.
Proposal Presentation
The student must formally defend the thesis proposal before the full thesis committee that has been approved by HICAP.
Students should schedule the meeting and reserve a conference room and any audio visual equipment they may require for their presentation. To book a conference room in E25, please contact Joseph Stein ( jrstein [at] mit.edu (jrstein[at]mit[dot]edu) ).
Following the proposal presentation, students should make any requested modifications to the proposal for the committee members to review. Once the committee approves the proposal, the student should obtain the signatures of the committee members on the forms described below as part of the proposal submission package.
[Friendly advice: As a professional courtesy, be sure your committee members have a complete version of your thesis proposal at least one week in advance of the proposal presentation.]
Submission of Proposal Package
When the thesis committee has approved the proposal, the student submits the proposal package to HICAP, c/o Traci Anderson in E25-518, for final approval. HICAP may reject a thesis proposal if it has been defended before a committee that was not previously approved via the LOI-2.
The proposal package includes the following:
- the proposal document
- a brief description of the project background and significance that explains why the work is important;
- the specific aims of the proposal, including a contingency plan if needed; and
- an indication of the methods to be used to accomplish the specific aims.
- signed research advisor agreement form(s);
- signed chair agreement form (which confirms a successful proposal defense);
- signed reader agreement form(s).
Thesis Proposal Forms
- SAMPLE Title Page (doc)
- Research Advisor Agreement Form (pdf)
- Chair Agreement Form (pdf)
- Reader Agreement Form (pdf)
Thesis Defense and Final Thesis Document
When the thesis is substantially complete and fully acceptable to the thesis committee, a public thesis defense is scheduled for the student to present his/her work to the thesis committee and other members of the community. The thesis defense is the last formal examination required for receipt of a doctoral degree. To be considered "public", a defense must be announced to the community at least five working days in advance. At the defense, the thesis committee determines if the research presented is sufficient for granting a doctoral degree. Following a satisfactory thesis defense, the student submits the final thesis document, approved by the research advisor, to Traci Anderson via email (see instructions below).
[Friendly advice: Contact jrstein [at] mit.edu (Joseph Stein) at least two weeks before your scheduled date to arrange for advertising via email and posters. A defense can be canceled for insufficient public notice.]
Before the Thesis Defense
Committee Approves Student to Defend: The thesis committee, working with the student and reviewing thesis drafts, concludes that the doctoral work is complete. The student should discuss the structure of the defense (general guidelines below) with the thesis committee chair and the research advisor.
Schedule the Defense: The student schedules a defense at a time when all members of the thesis committee will be physical present. Any exceptions must be approved in advance by the IMES/HST Academic Office.
Reserve Room: It is the student's responsibility to reserve a room and any necessary equipment. Please contact imes-reservation [at] mit.edu (subject: E25%20Room%20Reservation) (IMES Reservation) to reserve rooms E25-140, E25-141, E25-119/121, E25-521.
Final Draft: A complete draft of the thesis document is due to the thesis committee two weeks prior to the thesis defense to allow time for review. The thesis should be written as a single cohesive document; it may include content from published papers (see libraries website on " Use of Previously Published Material in a Thesis ") but it may not be a simple compilation of previously published materials.
Publicize the Defense: The IMES/HST Academic Office invites the community to attend the defense via email and a notice on the HST website. This requires that the student email a thesis abstract and supplemental information to jrstein [at] mit.edu (Joseph Stein) two weeks prior to the thesis defense. The following information should be included: Date and time, Location, (Zoom invitation with password, if offering a hybrid option), Thesis Title, Names of committee members, with academic and professional titles and institutional affiliations. The abstract is limited to 250 words for the poster, but students may optionally submit a second, longer abstract for the email announcement.
Thesis Defense Guidelines
Public Defense: The student should prepare a presentation of 45-60 minutes in length, to be followed by a public question and answer period of 15–30 minutes at discretion of the chair.
Committee Discussion: Immediately following the public thesis presentation, the student meets privately with the thesis committee and any other faculty members present to explore additional questions at the discretion of the faculty. Then the thesis committee meets in executive session and determines whether the thesis defense was satisfactory. The committee may suggest additions or editorial changes to the thesis document at this point.
Chair Confirms Pass: After the defense, the thesis committee chair should inform Traci Anderson of the outcome via email to tanderso [at] mit.edu (tanderso[at]mit[dot]edu) .

Submitting the Final Thesis Document
Please refer to the MIT libraries thesis formatting guidelines .
Title page notes. Sample title page from the MIT Libraries.
Program line : should read, "Submitted to the Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology, in partial fulfillment of the the requirements for the degree of ... "
Copyright : Starting with the June 2023 degree period and as reflected in the MIT Thesis Specifications , all students retain the copyright of their thesis. Please review this section for how to list on your title page Signature Page: On the "signed" version, only the student and research advisor should sign. Thesis committee members are not required to sign. On the " Accepted by " line, please list: Collin M. Stultz, MD, PhD/Director, Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology/ Nina T. and Robert H. Rubin Professor in Medical Engineering and Science/Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science.
The Academic Office will obtain Professor Stultz's signature.
Thesis Submission Components. As of 4/2021, the MIT libraries have changed their thesis submissions guidelines and are no longer accepting hard copy theses submissions. For most recent guidance from the libraries: https://libguides.mit.edu/mit-thesis-faq/instructions
Submit to the Academic Office, via email ( tanderso [at] mit.edu (tanderso[at]mit[dot]edu) )
pdf/A-1 of the final thesis should include an UNSIGNED title page
A separate file with a SIGNED title page by the student and advisor, the Academic Office will get Dr. Collin Stultz's signature.
For the MIT Library thesis processing, fill out the "Thesis Information" here: https://thesis-submit.mit.edu/
File Naming Information: https://libguides.mit.edu/
Survey of Earned Doctorates. The University Provost’s Office will contact all doctoral candidates via email with instructions for completing this survey.
Links to All Forms in This Guide
- MEMP Rotation Form (optional)
- Semi-Annual Progress Review Form
- Letter of Intent One
- Letter of Intent Two
Final Thesis
- HST Sample thesis title page (signed and unsigned)
- Sample thesis title page (MIT Libraries)

- Manuscript Preparation
Know How to Structure Your PhD Thesis
- 4 minute read
Table of Contents
In your academic career, few projects are more important than your PhD thesis. Unfortunately, many university professors and advisors assume that their students know how to structure a PhD. Books have literally been written on the subject, but there’s no need to read a book in order to know about PhD thesis paper format and structure. With that said, however, it’s important to understand that your PhD thesis format requirement may not be the same as another student’s. The bottom line is that how to structure a PhD thesis often depends on your university and department guidelines.
But, let’s take a look at a general PhD thesis format. We’ll look at the main sections, and how to connect them to each other. We’ll also examine different hints and tips for each of the sections. As you read through this toolkit, compare it to published PhD theses in your area of study to see how a real-life example looks.
Main Sections of a PhD Thesis
In almost every PhD thesis or dissertation, there are standard sections. Of course, some of these may differ, depending on your university or department requirements, as well as your topic of study, but this will give you a good idea of the basic components of a PhD thesis format.
- Abstract : The abstract is a brief summary that quickly outlines your research, touches on each of the main sections of your thesis, and clearly outlines your contribution to the field by way of your PhD thesis. Even though the abstract is very short, similar to what you’ve seen in published research articles, its impact shouldn’t be underestimated. The abstract is there to answer the most important question to the reviewer. “Why is this important?”
- Introduction : In this section, you help the reviewer understand your entire dissertation, including what your paper is about, why it’s important to the field, a brief description of your methodology, and how your research and the thesis are laid out. Think of your introduction as an expansion of your abstract.
- Literature Review : Within the literature review, you are making a case for your new research by telling the story of the work that’s already been done. You’ll cover a bit about the history of the topic at hand, and how your study fits into the present and future.
- Theory Framework : Here, you explain assumptions related to your study. Here you’re explaining to the review what theoretical concepts you might have used in your research, how it relates to existing knowledge and ideas.
- Methods : This section of a PhD thesis is typically the most detailed and descriptive, depending of course on your research design. Here you’ll discuss the specific techniques you used to get the information you were looking for, in addition to how those methods are relevant and appropriate, as well as how you specifically used each method described.
- Results : Here you present your empirical findings. This section is sometimes also called the “empiracles” chapter. This section is usually pretty straightforward and technical, and full of details. Don’t shortcut this chapter.
- Discussion : This can be a tricky chapter, because it’s where you want to show the reviewer that you know what you’re talking about. You need to speak as a PhD versus a student. The discussion chapter is similar to the empirical/results chapter, but you’re building on those results to push the new information that you learned, prior to making your conclusion.
- Conclusion : Here, you take a step back and reflect on what your original goals and intentions for the research were. You’ll outline them in context of your new findings and expertise.
Tips for your PhD Thesis Format
As you put together your PhD thesis, it’s easy to get a little overwhelmed. Here are some tips that might keep you on track.
- Don’t try to write your PhD as a first-draft. Every great masterwork has typically been edited, and edited, and…edited.
- Work with your thesis supervisor to plan the structure and format of your PhD thesis. Be prepared to rewrite each section, as you work out rough drafts. Don’t get discouraged by this process. It’s typical.
- Make your writing interesting. Academic writing has a reputation of being very dry.
- You don’t have to necessarily work on the chapters and sections outlined above in chronological order. Work on each section as things come up, and while your work on that section is relevant to what you’re doing.
- Don’t rush things. Write a first draft, and leave it for a few days, so you can come back to it with a more critical take. Look at it objectively and carefully grammatical errors, clarity, logic and flow.
- Know what style your references need to be in, and utilize tools out there to organize them in the required format.
- It’s easier to accidentally plagiarize than you think. Make sure you’re referencing appropriately, and check your document for inadvertent plagiarism throughout your writing process.
PhD Thesis Editing Plus
Want some support during your PhD writing process? Our PhD Thesis Editing Plus service includes extensive and detailed editing of your thesis to improve the flow and quality of your writing. Unlimited editing support for guaranteed results. Learn more here , and get started today!

- Publication Process
Journal Acceptance Rates: Everything You Need to Know

- Publication Recognition
How to Make a PowerPoint Presentation of Your Research Paper
You may also like.

Page-Turner Articles are More Than Just Good Arguments: Be Mindful of Tone and Structure!

A Must-see for Researchers! How to Ensure Inclusivity in Your Scientific Writing

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a PhD Thesis: 13 Tips For PhD Thesis Writing

Completing a successful PhD research thesis is extremely challenging, and how to write a PhD thesis is often a question in students’ minds. Fret not, there are many ways to make the process of PhD thesis writing less bumpy. This article will provide some PhD thesis writing tips to simplify the writing process and help you complete your thesis on time, while keeping your sanity mostly intact.
Only about 50% of students enrolled in a PhD program ever complete it 1 . They drop out at many different points during the process for many different reasons. Some leave because the course work is too difficult or time consuming. Some leave for personal or financial reasons. One common cause of non-completion, or late completion, is the daunting spectre of PhD thesis writing.
PhD thesis writing tips: How to overcome the challenge of writing your PhD thesis
First, remember that although writing a PhD thesis is difficult, this can be accomplished. Here are some things to consider that will increase your confidence and make the task of PhD thesis writing a bit less scary.
- Create an outline before you start writing – The most effective way to keep your work organized is to first create an outline based on the PhD thesis structure required by your university. Using an outline for your PhD paper writing has tremendous benefits. It creates a handy space to keep and organize all the little snippets of information and questions you will have during your preparation. It allows you to effectively plan your work and manage your time and makes the actual writing much easier. A thesis is shaped more than written, and an outline provides it the required PhD thesis structure.
- Follow all university guides – Be careful to ensure that you are meeting all the requirements of your university. This includes everything from topic selection to structure to writing style. It is extremely frustrating to spend a lot of time and effort on a section only to have to do it over because you didn’t follow the proper guidelines. Read all relevant material from your university over and over until you have it memorized. Then, check it again.
- Section order – It is usually best not to do your PhD thesis writing in chronological order. For researchers, the easiest parts to write are usually the Method and Results. So, gain some confidence first and write the Introduction and Conclusion last to tie it all together.
- Work extensively with your supervisor – Don’t forget that in the process of PhD thesis writing, help is right there when you ask for it. Do not hesitate to ask for guidance from your supervisor, advisors, or other committee members when you get stuck. Clear and regular communication with these important resources can save you untold heartache during the PhD research and thesis writing processes. This should not be a solo exercise; they have all been where you are now.
- Plan carefully, create rough drafts, and refine 2 – This is so important and basic to all academic research that it bears repeating. You will not write the final PhD thesis on your first try. Do not become frustrated, trust the process.
- Produce quality writing – Make sure your ideas flow easily and are clear and easy to read. This is not a strong skill for most beginning researchers, but it’s a skill that can be learned with a lot of practice. Therefore, edit, edit, and edit some more. If you need it, there are many places to get PhD thesis writing help and assistance.
- Details matter – Pay attention to the small things, especially with the document formatting. If you start out using the proper format, you will be saving a tremendous amount of time and grief later.
- Avoid plagiarism – Quote accurately, otherwise paraphrase. There is no excuse for being a lazy writer. Consider using a smart tool or service to check for plagiarism during your PhD thesis editing process to make sure you did not unintentionally copy any material.
- Rein in the references – Use a database, such as EndNote or Mendeley, to keep them organized and under control; check and double check citations and references with the bibliography to ensure they all match. Don’t forget to use the PhD thesis style required by your university.
- Keep it simple – Remember, this is only the start of your career, not your ultimate work 3 ; perfectionism can be a disaster.
- Make consistent progress – Try to write at least a little every day; check quotations and references when writing seems too difficult. 3
- Keep your reader in mind – As with all writing, your PhD thesis is meant to be read, so be considerate of those who read it; be concise, include all necessary data/information to support your argument but nothing extra. Strive to be understood and avoid unnecessary words.
- Be persistent and eager – Writing a doctoral thesis becomes easier if you are consistent and dedicated. All other things being equal, your attitude will ultimately determine your success. Have patience and work hard. Create work you will be proud of for a lifetime.
- Cassuto, L. Ph.D. attrition: How much is too much? The Chronicle of Higher Education. https://www.chronicle.com/article/ph-d-attrition-how-much-is-too-much/?cid=gen_sign_in [Accessed 20 July 2022]
- Curl, I. 10 tips for writing a PhD thesis. Times Higher Education. https://www.timeshighereducation.com/blog/10-tips-writing-phd-thesis [Accessed 20 July 2022]
- Thomas, K. Finishing your PhD thesis: 15 top tips from those in the know. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/higher-education-network/blog/2014/aug/27/finishing-phd-thesis-top-tips-experts-advice [Accessed 20 July 2022]
A PhD thesis includes several key components, that are essential for the work to be considered seriously. These may vary depending on the research field and specific requirements of the institution, but generally include: · an introduction that presents the research question and context, · a literature review that surveys existing knowledge and research, · a methodology section describing the research design and methods employed, · a presentation of findings or results, · a discussion section interpreting the results and their implications, and · a conclusion that summarizes the main findings and contributions. Additionally, appendices may contain supplementary materials such as data, charts, or technical details.
The time required for writing a PhD thesis can vary significantly depending on factors such as the research topic, the individual’s research progress, the specific requirements of the institution, and the researcher’s writing process. On average, it can take several months to a few years to complete a PhD thesis. The research, data collection, and analysis stages can span several years, with the PhD thesis writing phase itself often lasting several months. Here, AI writing assistants like Paperpal, designed for academics, can help you write better. Explore Paperpal and see the difference for yourself!
To select a suitable topic for your PhD thesis, start by identifying your research interests and areas of expertise. Consider the gaps or unresolved questions in your field of study and explore potential research avenues and read extensively in your area of interest. Consult with your advisor or mentors, who can offer guidance and help narrow down your options. Once you have a tentative topic, conduct a literature review to ensure its novelty and feasibility. It’s important to choose a topic that aligns with your passion, has potential for meaningful contribution, and is feasible given available resources and time constraints.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Confusing Elements of a Research Paper That Trip Up Most Academics
- How to Present Data and Statistics in Your Research Paper: Language Matters
- 3 Easy Ways for Researchers to Improve Their Academic Vocabulary
- What is an Expository Essay and How to Write It
How to Respond to Peer Reviewer Comments [Do’s and Dont’s for Authors]
5 steps to reduce the length of the research paper without losing content, you may also like, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., 9 steps to publish a research paper, self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how..., 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., 8 most effective ways to increase motivation for..., how to make your thesis supervision work for..., how to write a conclusion for research papers..., ethical research practices for research with human subjects, 5 reasons for rejection after peer review.
9 Writing Tips for PhD Students
Boost your writing skills as a PhD student with these 9 essential tips. From creating a schedule to seeking feedback, learn how to improve your academic writing.
Jun 12, 2024
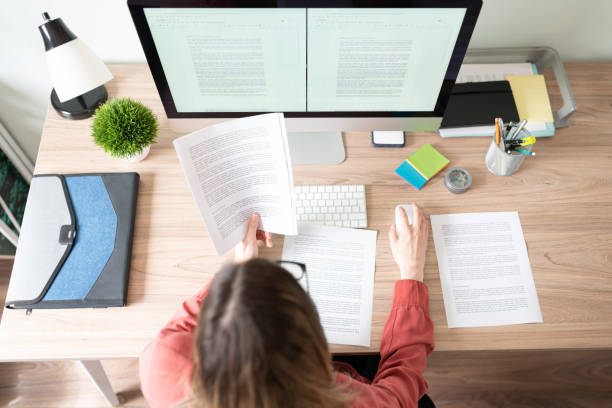

Writing is crucial in a PhD journey. It's how doctoral students communicate research findings, contribute to their field, and demonstrate expertise. From research proposals to the final dissertation, writing plays a vital role in a PhD student's success. However, many PhD students face challenges when writing effectively and using data efficiently.
One main challenge present is the volume of writing required. Students must produce substantial, high-quality paperwork while juggling other responsibilities. Complex subject matter and strict academic conventions make writing daunting and time-consuming.
Another challenge is developing a distinct, persuasive writing style. Doctoral-level writing demands sophistication and clarity in simple language. Students must articulate complex ideas in simple language, engage with literature, and make original contributions. This is challenging, especially for non-native English speakers or those with limited academic writing experience.
Despite these challenges, strong writing skills are essential for PhD success and beyond. Effective academic writing also enables students to communicate findings, secure funding, publish, and establish expertise. To help navigate these challenges and improve writing skills, we've identified 9 key tips:
- Start writing early
- Create a writing schedule
- Break down writing tasks
- Read extensively in your field
- Seek feedback from others
- Edit and revise repeatedly
- Develop your own writing style
- Practice writing in different formats
- Take care of yourself
By learning and implementing these strategies, PhD students can overcome writing obstacles, hone skills, and increase success in doctoral programs and future careers. The present chapter and following sections will explore each tip in detail, providing practical advice and examples to help you become a more confident, productive writer.
1. Start writing early
One of the most important tips for PhD students is to start writing early in their doctoral journey. Many students make the mistake of waiting until they have completed all their research or until they feel fully prepared before they begin writing.
Starting to write early, even if it's just rough drafts or exploratory pieces, offers several benefits:
- It helps you clarify your thoughts and identify areas that need further research or development.
- It allows you to receive early feedback from your supervisor or peers, which can guide your research and writing process.
- It gives you ample time to revise and polish your work, ensuring that your final product is of the highest quality.
To start writing early, try the following strategies:
- Set aside dedicated writing time each day or week, even if it's just for 30 minutes.
- Begin with low-stakes writing tasks, such as brainstorming or freewriting, to overcome initial hesitation.
- Write short pieces, such as blog posts or conference abstracts, to build momentum and confidence.
- Share your early drafts with trusted colleagues or mentors for constructive feedback.
Remember, the goal of early writing is not perfection but rather progress. By starting early and writing regularly, we hope you'll develop a strong foundation for your PhD writing and set yourself up for success in the long run.
2. Create a writing schedule
Creating a consistent writing schedule is crucial for PhD students to make steady progress and complete their writing projects. A writing schedule helps you prioritize writing, allocate sufficient time, and establish a regular habit.
To create an effective writing schedule, consider these tips best advice:
- Some write best in the morning, others in the afternoon or evening
- Determine how much time you can dedicate to writing, considering other commitments
- Divide larger projects into manageable tasks that can be completed in a single session
- Treat scheduled writing time as non-negotiable
- Communicate your schedule to others and minimize distractions
- Adjust your schedule when necessary to accommodate unexpected demands or opportunities
Use tools and strategies to support your writing schedule:
- Use a calendar or planner to block out writing time and track progress
- Try the Pomodoro Technique: write in focused 25-minute intervals with short breaks
- Join a writing group or find an accountability partner to stay motivated
By creating and sticking to a consistent writing schedule, you'll begin to build a strong writing habit and make significant progress on your PhD writing projects over time.
Easily pronounces technical words in any field
3. Break down writing tasks
Breaking down large writing and research tasks into smaller, manageable chunks is essential for PhD students. When one page faced with a daunting project, like a dissertation or journal article, it's easy to feel overwhelmed by the scope of the work.
Tips for breaking down writing tasks:
- Include main sections, subsections, and key points
- Use the outline as a roadmap while writing
- Break each section into actionable tasks
- Example: Instead of "write literature review," use "read and summarize five key articles," "identify themes and gaps," and "draft introduction"
- Focus on completing the most critical tasks first
- Move on to less crucial ones later
- Assign realistic deadlines for each task
- Consider available time and task complexity
- Acknowledge progress and celebrate accomplishments
- Maintain motivation and build momentum
Benefits of breaking down writing tasks:
- Make the writing process more manageable
- Focus on one small task at a time
- Track progress and identify areas needing more resources
- Maintain motivation through small wins
Remember, writing a thesis is a process. By breaking it down into smaller steps, for example, you can make steady progress towards completing your PhD thesis writing projects.
4. Read extensively in your field

Reading extensively is crucial for PhD students to produce high-quality, well-informed writing. By staying current with the latest research, data, and scholarship, you ensure your thesis writing is grounded in up-to-date knowledge and contributes to academic conversations.
Strategies for effective reading:
- Block out time specifically for reading
- Treat this time as a priority and protect it from distractions
- Focus on the most important and relevant sources
- Use citation tracking and keyword searches to identify key articles and books
- Note main arguments, methodologies, and findings
- Use a consistent note-taking system to keep notes organized and accessible
- Actively engage with sources
- Look for patterns, themes, and gaps in the literature
- Consider how your research fits into the scholarly conversation
- Share reading with colleagues, mentors, or classmates
- Engage in discussions about key ideas and implications
- Deepen your understanding and generate new insights
Benefits of extensive reading:
- Develop a broad and deep understanding of your research area
- Identify key debates, methodologies, and findings
- Situate your research within the scholarly landscape
- Generate new ideas and research questions based on gaps and opportunities
Remember, reading is an ongoing learning process throughout your PhD journey. Make reading a regular habit and priority to ensure your writing is informed by current and relevant scholarship.
5. Seek feedback from others
Seeking feedback from others is essential for PhD students to improve writing quality, identify areas for improvement, and gain new perspectives.
Strategies for seeking and incorporating feedback:
- Share early drafts and ideas throughout the writing process
- Seek feedback from those with relevant expertise, such as supervisors, committee members, or scholars in your field
- Consider feedback from peers or writing groups for fresh perspectives
- Clarify what type of input you're looking for, whether it's on the overall argument and structure or specific sections
- Approach feedback with an open and receptive mindset
- Remember the goal is to improve your writing and strengthen your work
- Assess and incorporate feedback that aligns with your overall goals and vision
- Consider each suggestion carefully before making changes
Benefits of seeking and incorporating feedback:
- Identify strengths and weaknesses in your writing
- Gain new insights and perspectives to enrich your work
- Improve clarity, coherence, and persuasiveness
- Develop relationships and networks with other scholars
Remember, seeking feedback is a hallmark of good scholarship. By actively seeking and incorporating feedback, for example, you can take your writing to the next level and produce valuable contributions to your subject field.
6. Edit and revise repeatedly
Here's the edited version:
Editing and revising are critical for PhD students. No matter how carefully you plan and first draft your writing, there's always room for improvement. By editing and revising repeatedly, you ensure your writing is clear, concise, and effective in communicating your ideas.
Strategies for effective editing and revising:
- Step away from your writing for a day or two after completing a draft
- Approach your work with fresh eyes to identify areas for improvement
- Identify awkward or unclear phrases and areas where writing doesn't flow smoothly
- One round: focus on overall structure and argument
- Another round: focus on improving clarity and concision of sentences
- Utilize grammar and spell checkers, style guides , and citation manuals
- Catch errors and ensure adherence to academic conventions
- Use feedback to guide revisions and strengthen writing
Benefits of editing and revising repeatedly:
- Improve clarity and coherence
- Eliminate errors and inconsistencies
- Strengthen arguments and analysis
- Ensure polished and professional writing
Remember, editing and revising are ongoing processes. Build in time for multiple rounds of revision, approaching each round with a specific sense of focus and goal to take your writing from good to great.
7. Develop your writing style
Developing your unique writing style is important for becoming an effective and confident writer as a PhD student. While academic writing of course has conventions, structure and expectations, there's room for individuality and creativity in expressing your ideas.
Tips for developing your writing style:
- Note how authors structure arguments, use language and tone, and engage readers
- Try analogies, varying sentence lengths, or incorporating personal anecdotes
- See what feels natural and effective for you
- Reflect your unique perspective and personality
- Focus on expressing ideas in a way that feels authentic to you
- Aim for clarity and concision, regardless of individual style
- Use simple, direct language and avoid jargon or complex sentence structures
- Developing your writing style takes time and practice
- The more you write, the more you'll find your unique voice and style
Benefits of developing your writing style:
- Make your writing engaging and memorable
- Communicate ideas more effectively
- Stand out from other scholars in your field
- Feel more confident and authentic in your writing
Remember, developing your writing style is an ongoing process. It's okay to experiment and make mistakes. By staying true to your voice and perspective while being open to feedback and growth, you can cultivate a unique writing style.
8. Practice writing in different formats

As a PhD student, you'll write in various formats, from abstracts to dissertation chapters. Practicing these formats develops versatility and prepares you for diverse writing tasks throughout the university and the rest of your career.
Tips for practicing different formats:
- Read examples and note key features and requirements
- Write a conference abstract or book review before a full journal article
- Submit proposals for conferences or workshops
- Participate in writing groups or collaborations
- Use feedback to identify areas for improvement
- Note what you learned and found challenging
- Set goals for future tasks and track your growth
Benefits of practicing different formats:
- Develop versatility and adaptability as a writer
- Prepare for diverse writing tasks throughout your career
- Improve your ability to communicate ideas to different audiences and contexts
- Increase your confidence and competence
Becoming skilled in multiple formats takes time and practice. Don't be discouraged if early attempts feel challenging. With persistence and a growth mindset, you can develop the skills and confidence to tackle any writing task.
9.Take care of yourself
Taking care of yourself is crucial for PhD students throughout the paper writing process. Writing a paper can be mentally and emotionally demanding, leading to stress and burnout if you don't prioritize your well-being.
Strategies for self-care:
- Be realistic about what you can accomplish
- Remember that writing is a process with setbacks and challenges
- Take regular breaks during writing sessions
- Prioritize activities that help you recharge, like exercise or hobbies
- Reach out to your supervisor, peers, or mental health professionals
- Acknowledge and celebrate your writing successes, no matter how small
- Recognize your progress to stay motivated
- Prioritize relationships, health, and other aspects of life alongside writing
Benefits of self-care:
- Maintain motivation and enthusiasm
- Prevent burnout and emotional exhaustion
- Produce higher-quality writing with a clear mind
- Model good self-care practices for others
Taking care of yourself is a necessity for long-term success and your complete well-being as a writer and scholar. Prioritize your needs and seek support to thrive personally and professionally during a specific time in your PhD journey.
Developing strong writing skills is essential for success in a PhD program and beyond.
Follow these nine key tips to overcome academic writing challenges and become a confident, productive writer.
Start writing early to avoid the blank page and maintain momentum. Create a detailed outline and schedule to break down tasks and stay on track. Read extensively to ensure enough research supports your ideas and arguments.
Seek feedback from others at every stage to identify areas for improvement and gain new perspectives. Edit and revise repeatedly, focusing on different aspects in each round.
Develop your writing style by experimenting with techniques, finding your authentic voice, and using active voice. Practice writing in various formats to prepare for expected tasks throughout your career.
Take care of yourself during the writing process. Set realistic goals, take breaks, and seek support when stuck. Remember, writing is a journey. Every word brings you closer to your goal.
Follow these tips and maintain a growth mindset to navigate academic writing challenges and produce a compelling, well-researched thesis that contributes to your field. Don't let the blank page intimidate you – start writing today and watch your ideas come to life!
Writing Skills
PhD Students
Recent articles

10 Best Universities in Canada
Glice Martineau
Jun 17, 2024
Best Universities
World University Rankings
Top Ranked Universities
Universities in Canada

Top 10 Universities in the United Kingdom
Amethyst Rayne
British Universities
Best Universities in the UK
UK Education System

Top 10 Universities in New Zealand
Kate Windsor
Jun 18, 2024
New Zealand education
Best universities in New Zealand
International student guide
Study abroad in New Zealand
Top universities in New Zealand
New Zealand universities

How to Ask a Professor to be Your Advisor? 5 Practical Tips
Jun 19, 2024
professor-student relationship
graduate school
academic advisor
- Composition Studies
- Writing Processes
PhD Thesis Writing Process: A Systematic Approach—How to Write Your Literature Review
- January 2018
- Creative Education 09(16):2912-2919
- 09(16):2912-2919
- This person is not on ResearchGate, or hasn't claimed this research yet.
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Lutfi Hardiyanto
- Herinto Sidik Iriansyah
- Sri Rahayu Pudjiastuti
- JOSEPH MAUNDU (MBA)
- Ernesto Jr. L. Bastida

- Freddy Prasetyo
- Dadan Dasari
- Jack Franke
- Yelfiza Yelfiza
- Siska Siska
- Faiqotun Naylah

- Mellyatul Aini

- Qais Faryadi
- J Res Int Educ

- John W Creswell
- Jose L. Galvan
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
- What is a PhD?
Written by Mark Bennett
A PhD is a doctoral research degree and the highest level of academic qualification you can achieve. The degree normally takes between three and four years of full-time work towards a thesis offering an original contribution to your subject.
This page explains what a PhD is, what it involves and what you need to know if you’re considering applying for a PhD research project , or enrolling on a doctoral programme .
The meaning of a PhD
The PhD can take on something of a mythic status. Are they only for geniuses? Do you have to discover something incredible? Does the qualification make you an academic? And are higher research degrees just for people who want to be academics?
Even the full title, ‘Doctor of Philosophy’, has a somewhat mysterious ring to it. Do you become a doctor? Yes, but not that kind of doctor. Do you have to study Philosophy? No (not unless you want to) .
So, before going any further, let's explain what the term 'PhD' actually means and what defines a doctorate.
What does PhD stand for?
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is one of the highest level academic degrees that can be awarded. PhD is an abbreviation of the Latin term (Ph)ilosophiae (D)octor. Traditionally the term ‘philosophy’ does not refer to the subject but its original Greek meaning which roughly translates to ‘lover of wisdom’.
What is a doctorate?
A doctorate is any qualification that awards a doctoral degree. In order to qualify for one you need to produce advanced work that makes a significant new contribution to knowledge in your field. Doing so earns you the title 'Doctor' – hence the name.
So, is a PhD different to a doctorate? No. A PhD is a type of doctorate .
The PhD is the most common type of doctorate and is awarded in almost all subjects at universities around the world. Other doctorates tend to be more specialised or for more practical and professional projects.
Essentially, all PhDs are doctorates, but not all doctorates are PhDs.
Do you need a Masters to get a PhD?
Not necessarily. It's common for students in Arts and the Humanities to complete an MA (Master of Arts) before starting a PhD in order to acquire research experience and techniques. Students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) don't always need an MS/MSc (Master of Science) to do a PhD as you'll gain training in lab techniques and other skills during your undergraduate degree.
Whether a Masters is a requirement for a PhD also varies by country. Australian PhDs may require a Masters as the equivalent of their own 'honours year' (where students work on research). US PhD programmes often include a Masters.
We have a whole guide dedicated to helping you decide whether a PhD without a Masters is the right route for you.
The origin of the PhD
Despite its name, the PhD isn't actually an Ancient Greek degree. Instead it's a much more recent development. The PhD as we know it was developed in nineteenth-century Germany, alongside the modern research university.
Higher education had traditionally focussed on mastery of an existing body of scholarship and the highest academic rank available was, appropriately enough, a Masters degree.
As the focus shifted more onto the production of new knowledge and ideas, the PhD degree was brought in to recognise those who demonstrated the necessary skills and expertise.
The PhD process – what's required to get a PhD?
The typical length of a PhD is three to four years full-time, or five to six years part-time.
Unlike most Masters courses (or all undergraduate programmes), a PhD is a pure research degree. But that doesn’t mean you’ll just spend years locked away in a library or laboratory. In fact, the modern PhD is a diverse and varied qualification with many different components.
Whereas the second or third year of a taught degree look quite a lot like the first (with more modules and coursework at a higher level) a PhD moves through a series of stages.
A typical PhD normally involves:
- Carrying out a literature review (a survey of current scholarship in your field).
- Conducting original research and collecting your results .
- Producing a thesis that presents your conclusions.
- Writing up your thesis and submitting it as a dissertation .
- Defending your thesis in an oral viva voce exam.
These stages vary a little between subjects and universities, but they tend to fall into the same sequence over the three years of a typical full-time PhD.
The first year of a PhD
The beginning of a PhD is all about finding your feet as a researcher and getting a solid grounding in the current scholarship that relates to your topic.
You’ll have initial meetings with your supervisor and discuss a plan of action based on your research proposal.
The first step in this will almost certainly be carrying out your literature review . With the guidance of your supervisor you’ll begin surveying and evaluating existing scholarship. This will help situate your research and ensure your work is original.
Your literature review will provide a logical jumping off point for the beginning of your own research and the gathering of results . This could involve designing and implementing experiments, or getting stuck into a pile of primary sources.
The year may end with an MPhil upgrade . This occurs when PhD students are initially registered for an MPhil degree and then ‘upgraded’ to PhD candidates upon making sufficient progress. You’ll submit material from your literature review, or a draft of your research findings and discuss these with members of your department in an upgrade exam . All being well, you’ll then continue with your research as a PhD student.
PhDs in other countries
The information on the page is based on the UK. Most countries follow a similar format, but there are some differences. In the USA , for example, PhD students complete reading assignments and examinations before beginning their research. You can find out more in our guides to PhD study around the world .
The second year of a PhD
Your second year will probably be when you do most of your core research. The process for this will vary depending on your field, but your main focus will be on gathering results from experiments, archival research, surveys or other means.
As your research develops, so will the thesis (or argument) you base upon it. You may even begin writing up chapters or other pieces that will eventually form part of your dissertation .
You’ll still be having regular meetings with your supervisor. They’ll check your progress, provide feedback on your ideas and probably read any drafts your produce.
The second year is also an important stage for your development as a scholar. You’ll be well versed in current research and have begun to collect some important data or develop insights of your own. But you won’t yet be faced with the demanding and time-intensive task of finalising your dissertation.
So, this part of your PhD is a perfect time to think about presenting your work at academic conferences , gaining teaching experience or perhaps even selecting some material for publication in an academic journal. You can read more about these kinds of activities below.
The third year of a PhD
The third year of a PhD is sometimes referred to as the writing up phase.
Traditionally, this is the final part of your doctorate, during which your main task will be pulling together your results and honing your thesis into a dissertation .
In reality, it’s not always as simple as that.
It’s not uncommon for final year PhD students to still be fine-tuning experiments, collecting results or chasing up a few extra sources. This is particularly likely if you spend part of your second year focussing on professional development.
In fact, some students actually take all or part of a fourth year to finalise their dissertation. Whether you are able to do this will depend on the terms of your enrolment – and perhaps your PhD funding .
Eventually though, you are going to be faced with writing up your thesis and submitting your dissertation.
Your supervisor will be very involved in this process. They’ll read through your final draft and let you know when they think your PhD is ready for submission.
All that’s left then is your final viva voce oral exam. This is a formal discussion and defence of your thesis involving at least one internal and external examiner. It’s normally the only assessment procedure for a PhD. Once you’ve passed, you’ve done it!
Looking for more information about the stages of a PhD?
How do you go about completing a literature review? What's it like to do PhD research? And what actually happens at an MPhil upgrade? You can find out more in our detailed guide to the PhD journey .
Doing a PhD – what's it actually like?
You can think of the ‘stages’ outlined above as the basic ‘roadmap’ for a PhD, but the actual ‘journey’ you’ll take as a research student involves a lot of other sights, a few optional destinations and at least one very important fellow passenger.
Carrying out research
Unsurprisingly, you’ll spend most of your time as a PhD researcher… researching your PhD. But this can involve a surprisingly wide range of activities.
The classic image of a student working away in the lab, or sitting with a pile of books in the library is true some of the time – particularly when you’re monitoring experiments or conducting your literature review.
Your PhD can take you much further afield though. You may find yourself visiting archives or facilities to examine their data or look at rare source materials. You could even have the opportunity to spend an extended period ‘in residence’ at a research centre or other institution beyond your university.
Research is also far from being a solitary activity. You’ll have regular discussions with your supervisor (see below) but you may also work with other students from time to time.
This is particularly likely if you’re part of a larger laboratory or workshop group studying the same broad area. But it’s also common to collaborate with students whose projects are more individual. You might work on shorter projects of joint interest, or be part of teams organising events and presentations.
Many universities also run regular internal presentation and discussion groups – a perfect way to get to know other PhD students in your department and offer feedback on each other’s work in progress.
Working with your supervisor
All PhD projects are completed with the guidance of at least one academic supervisor . They will be your main point of contact and support throughout the PhD.
Your supervisor will be an expert in your general area of research, but they won’t have researched on your exact topic before (if they had, your project wouldn’t be original enough for a PhD).
As such, it’s better to think of your supervisor as a mentor, rather than a teacher.
As a PhD student you’re now an independent and original scholar, pushing the boundaries of your field beyond what is currently known (and taught) about it. You’re doing all of this for the first time, of course. But your supervisor isn’t.
They’ll know what’s involved in managing an advanced research project over three years (or more). They’ll know how best to succeed, but they’ll also know what can go wrong and how to spot the warning signs before it does.
Perhaps most importantly, they’ll be someone with the time and expertise to listen to your ideas and help provide feedback and encouragement as you develop your thesis.
Exact supervision arrangements vary between universities and between projects:
- In Science and Technology projects it’s common for a supervisor to be the lead investigator on a wider research project, with responsibility for a laboratory or workshop that includes several PhD students and other researchers.
- In Arts and Humanities subjects, a supervisor’s research is more separate from their students’. They may supervise more than one PhD at a time, but each project is essentially separate.
It’s also becoming increasingly common for PhD students to have two (or more) supervisors. The first is usually responsible for guiding your academic research whilst the second is more concerned with the administration of your PhD – ensuring you complete any necessary training and stay on track with your project’s timetable.
However you’re supervised, you’ll have regular meetings to discuss work and check your progress. Your supervisor will also provide feedback on work during your PhD and will play an important role as you near completion: reading your final dissertation draft, helping you select an external examiner and (hopefully) taking you out for a celebratory drink afterwards!
Professional development, networking and communication
Traditionally, the PhD has been viewed as a training process, preparing students for careers in academic research.
As such, it often includes opportunities to pick up additional skills and experiences that are an important part of a scholarly CV. Academics don’t just do research after all. They also teach students, administrate departments – and supervise PhDs.
The modern PhD is also viewed as a more flexible qualification. Not all doctoral graduates end up working in higher education. Many follow alternative careers that are either related to their subject of specialism or draw upon the advanced research skills their PhD has developed.
PhD programmes have begun to reflect this. Many now emphasise transferrable skills or include specific training units designed to help students communicate and apply their research beyond the university.
What all of this means is that very few PhD experiences are just about researching and writing up a thesis.
The likelihood is that you’ll also do some (or all) of the following during your PhD:
The work is usually paid and is increasingly accompanied by formal training and evaluation.
Conference presentation
As a PhD student you’ll be at the cutting edge of your field, doing original research and producing new results. This means that your work will be interest to other scholars and that your results could be worth presenting at academic conferences .
Doing this is very worthwhile, whatever your career plans. You’ll develop transferrable skills in public speaking and presenting, gain feedback on your results and begin to be recognised as an expert in your area.
Conferences are also great places to network with other students and academics.
Publication
As well as presenting your research, you may also have the opportunity to publish work in academic journals, books, or other media. This can be a challenging process.
Your work will be judged according to the same high standards as any other scholar’s and will normally go through extensive peer review processes. But it’s also highly rewarding. Seeing your work ‘in print’ is an incredible validation of your PhD research and a definite boost to your academic CV.
Public engagement and communication
Academic work may be associated with the myth of the ‘ivory tower’ – an insular community of experts focussing on obscure topics of little interest outside the university. But this is far from the case. More and more emphasis is being placed on the ‘impact’ of research and its wider benefits to the public – with funding decisions being made accordingly.
Thankfully, there are plenty of opportunities to try your hand at public engagement as a PhD student. Universities are often involved in local events and initiatives to communicate the benefits of their research, ranging from workshops in local schools to public lectures and presentations.
Some PhD programmes include structured training in order to help students with activities such as the above. Your supervisor may also be able to help by identifying suitable conferences and public engagement opportunities, or by involving you in appropriate university events and public engagement initiatives.
These experiences will be an important part of your development as a researchers - and will enhance the value of your PhD regardless of your career plans.
What is a PhD for – and who should study one?
So, you know what a PhD actually is, what’s involved in completing one and what you might get up to whilst you do. That just leaves one final question: should you do a PhD?
Unfortunately, it’s not a question we can answer for you.
A PhD is difficult and uniquely challenging. It requires at least three years of hard work and dedication after you’ve already completed an undergraduate degree (and probably a Masters degree too).
You’ll need to support yourself during those years and, whilst you will be building up an impressive set of skills, you won’t be directly progressing in a career.
But a PhD is also immensely rewarding. It’s your chance to make a genuine contribution to the sum of human knowledge and produce work that other researchers can (and will) build on in future. However obscure your topic feels, there’s really no such thing as a useless PhD.
A PhD is also something to be incredibly proud of. A proportionately tiny number of people go on to do academic work at this level. Whatever you end up doing after your doctorate you’ll have an impressive qualification – and a title to match. What’s more, non-academic careers and professions are increasingly recognising the unique skills and experience a PhD brings.
Other PhDs - do degree titles matter?
The PhD is the oldest and most common form of higher research degree, but a few alternatives are available. Some, such as the DPhil are essentially identical to a PhD. Others, such as the Professional Doctorate or DBA are slightly different. You can find out more in our guide to types of PhD .
Is a PhD for me?
There’s more advice on the value of a PhD – and good reasons for studying one – elsewhere in this section. But the following are some quick tips if you’re just beginning to consider a PhD.
Speak to your lecturers / tutors
The best people to ask about PhD study are people who’ve earned one. Ask staff at your current or previous university about their experience of doctoral research – what they enjoyed, what they didn’t and what their tips might be.
If you’re considering a PhD for an academic career, ask about that too. Are job prospects good in your field? And what’s it really like to work at a university?
Speak to current PhD students
Want to know what it’s like studying a PhD right now? Or what it’s like doing research at a particular university? Ask someone who knows.
Current PhD students were just like you a year or two ago and most will be happy to answer questions.
If you can’t get in touch with any students ‘face to face’, pop over to the Postgraduate Forum – you’ll find plenty of students there who are happy to chat about postgraduate research.
Take a look at advertised projects and programmes
This may seem like a strange suggestion. After all, you’re only going to study one PhD, so what’s the point of reading about lots of others?
Well, looking at the details of different PhD projects is a great way to get a general sense of what PhD research is like. You’ll see what different PhDs tend to have in common and what kinds of unique opportunity might be available to you.
And, with thousands of PhDs in our database , you’re already in a great place to start.
Read our other advice articles
Finally, you can also check out some of the other advice on the FindAPhD website. We’ve looked at some good (and bad) reasons for studying a PhD as well as the value of a doctorate to different career paths.
More generally, you can read our in-depth look at a typical PhD journey , or find out more about specific aspects of doctoral study such as working with a supervisor or writing your dissertation .
We add new articles all the time – the best way to stay up to date is by signing up for our free PhD opportunity newsletter .
Ready to find your PhD?
Head on over to our PhD search listings to learn what opportunities are on offer within your discipline.
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

What happens during a typical PhD, and when? We've summarised the main milestones of a doctoral research journey.

The PhD thesis is the most important part of a doctoral degree. This page will introduce you to what you need to know about the PhD dissertation.

This page will give you an idea of what to expect from your routine as a PhD student, explaining how your daily life will look at you progress through a doctoral degree.
Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a PhD in the USA.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAPhD account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest PhD news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite projects, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .

Tips for surviving the first year of your PhD
Even a marathon begins with first steps, and so it makes sense to master motivation, set healthy habits and get writing early to reap the reward of a polished dissertation at the end of the PhD journey, writes Andreï Kostryka
Andreï V. Kostyrka

Created in partnership with

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} The secrets to success as a provost
Using non verbal cues to build rapport with students, emotionally challenging research and researcher well-being, augmenting the doctoral thesis in preparation for a viva, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
The first year of a PhD programme can be overwhelming. The success of a dissertation in many fields depends on the polish, iterations and revisions the research has undergone. So, what you do, what habits and routines you set up in the first year, will make a difference to the result at the end.
The first year is also crucial for learning – not least because neuroplasticity wanes as one grows older (as does the amount of time before the defence ). First-year doctoral students might be exempt from research-related events such as conferences, brown-bag seminars and faculty talks, yet there is no time for complacency.
Here are insider tips for making the most of the first 12 months.
Start writing as soon as possible
Do not let provocative articles that explain how to write a PhD dissertation in three months delay the start of your writing. Unless you are John von Neumann or Paul Erdős (which you are not), it is impossible to write a proficient thesis in three or even six months.
- How to write an abstract for a research paper
- How to structure your PhD thesis
- What is your academic writing temperament?
Your early writing does not have to be grandiose or purposeful. It can begin with any thought related to your topic of study. In applied sciences, a good starting point is describing an output table or interpreting a few plots in simple language, as most applied research articles include a Discussion section where findings are explained in layman’s terms. If your work is more theoretical, any attempt at a derivation or a proof is valuable. Even a well-crafted email to your adviser can become the foundation stone. Generate as much material as possible, and you will have plenty to choose from for the thesis.
Iterations take time and effort. Reflection and re-evaluation are essential for shaping one’s ideas.
Give yourself the earliest opportunity to pick up the language appropriate for academia by receiving criticism and suggestions on your writing. Your first research poster will probably look amateurish, and your first empirical analysis will likely yield mixed conclusions – but this is not a cause for concern. Babies learn to walk by trying, falling, getting up and trying again.
Remember that chapters are not the endgame
Your PhD should reflect a deeper understanding of the subject, and this does not come overnight. It results from pumping large volumes of information into one’s head and allowing it to roam among the neurons.
Attend conferences, seminars and courses outside the university to hone your skills because the chapters are not the final goal. Presentations at informal seminars in front of one’s colleagues are a reliable way to build horizontal networks with postdocs, other students and specialists.
Keep a research diary
Document your methods, results and ideas in a research diary. If you are not writing the thesis in your native language, jot down ideas in your preferred language. A notebook of ideas is invaluable during meetings with your supervisor. It is easier for them to give feedback on clearly written statements.
Communication with your supervisor, positive or negative, can be a part of the research diary. It often takes extra effort to prove to a professor that their ideas need refinement. Reinforce your points with plots, tables and other printed material that will help you cast your mind back after a couple of years. Professors may lag behind the state of the art if the subject is outside their research interests – read the best practices in the field, take notes and share them during discussions.
Back up your work
Always make backups, even after small steps, because old versions and old results are valuable if you need to retrace your train of thought. The most convenient option is setting up a trustworthy cloud synchronisation service that automatically saves everything you write and stores multiple versions. If you do not trust those providers, synchronise your working folder with an external storage device every week or set up a self-hosted home cloud. Remember the 3-2-1 principle: have three versions of your data – two on different physical media and one on the server of your choice.
Work in small increments
List small tasks for each day and set deadlines for yourself. It is normal to work harder on some days and make less effort on others. The flexibility of a PhD researcher’s job allows you to get the most out of your rushes of inspiration.
Punctuate stints of work with exercise breaks. Health directly impacts the clarity of thinking, so set a timer to stretch out and do sit-ups every hour (for example). There might be swimming pools, gyms or sports classes nearby. Student groups often organise collective events (like hiking or yoga) and provide free tickets for cultural events.
What to do when motivation flags
Other academic activities on campus may be more engaging than writing the thesis. With summer schools, conferences and workshops, it is easy to lose track of time and neglect your work. Writer’s block is another reason to postpone writing . Certain PhD students focus on teaching, believing that their foremost duty is to be helpful teaching assistants or exam invigilators.
Everything takes time, even if one considers Hofstadter’s law , which is why we present a list of tips on what to prioritise to free up time that would otherwise be wasted on non-thesis-related tasks.
- Write in plain text and do the formatting last.
- Get a distraction-free plain-text editor that autosaves your input and restores it, even after a power outage.
- Type long passages instead of hand-writing to eliminate the need for retyping.
- Create figures using preferably free and open-source software; avoid relying on Microsoft Office.
- Use specialised software like JabRef or Zotero to arrange bibliographies and citations.
- Do not tolerate software quirks. Demand the right to install open-source tools from your IT team without needing support tickets.
- Do not try to solve bureaucratic or logistical problems outside your competence; there are non-research university personnel for those.
Writer’s block or frustration can result from stress. Being stuck at a certain point and without the courage to move forward is not uncommon in any job, including research positions. Should the stress pile up to the extent that it causes physical or mental unwellness, contact a healthcare provider and do not hesitate to book an appointment with a psychologist.
One possible remedy for writer’s block is switching to literature review. Prior reading is essential for smooth writing. The more you learn, the more you can say about the subject. Alternatively, you may try to process measurement data, prove a lemma, create a plot or engage in any other part of research that does not involve writing out words.
Finally, get enough sleep (at least on average). Force yourself to stop working in the evening and go home. If the crickets start chirping when you are still at your office, it is a sign to clock off.
Andreï V. Kostyrka is a postdoctoral researcher in the department of economics and management at the University of Luxembourg.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
The secrets to success as a provost
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, the podcast: bringing an outsider’s eye to primary sources, a diy guide to starting your own journal, formative, summative or diagnostic assessment a guide, harnessing the power of data to drive student success.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Most dissertations are 100 to 300 pages in length. All dissertations should be divided into appropriate sections, and long dissertations may need chapters, main divisions, and even subdivisions. Students should keep in mind that GSAS and many departments deplore overlong and wordy dissertations.
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps. Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is. Find a unique and valuable research topic. Craft a convincing research proposal. Write up a strong introduction chapter. Review the existing literature and compile a literature review.
Dissertations typically include a literature review section or chapter. Create a list of books, articles, and other scholarly works early in the process, and continue to add to your list. Refer to the works cited to identify key literature. And take detailed notes to make the writing process easier.
A Guide to Writing a PhD Thesis. A PhD thesis is a work of original research all students are requiured to submit in order to succesfully complete their PhD. The thesis details the research that you carried out during the course of your doctoral degree and highlights the outcomes and conclusions reached. The PhD thesis is the most important ...
You create a tiny text using a five-paragraph structure: The first sentence addresses the broad context. This locates the study in a policy, practice or research field. The second sentence establishes a problem related to the broad context you have set out. It often starts with "But", "Yet" or "However".
it deliberates and defines the various parts of methodology, results and PhD conclusion writing process and elucidates the "how to do" in a very unpre-tentious and understanding manner. As thus, this paper summarises the var-ious steps of thesis methodology, results and conclusion writing to pilot the PhD students. This road map is a useful ...
1) To help PhD candidates in writing scientifically correct PhD thesis. 2) To describe PhD thesis writing process. 3) To assist PhD candidates to understand what PhD means. 4. Methodology The methodology applied in this research was descriptive as it discusses and de-scribes the various parts of PhD thesis and explains the how to do of them in a
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
The task of writing a PhD thesis is top of mind for many aspiring scholars. After all, completing one is no small task. ... How to write a PhD thesis: a step-by-step guide . 5 minute read. Transitioning to a PhD: common struggles and how to overcome them. What I have learned on the journey towards commercialising my PhD.
Think carefully about your writing. Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense. Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency.
Step 1: Understand the Requirements. The initial step in crafting your PhD thesis is to thoroughly understand its specific requirements, which can vary widely between disciplines and institutions. A thesis must contribute new knowledge to its field, necessitating a deep familiarity with the expected structure, depth of analysis, and submission ...
Writing a PhD dissertation or thesis is probably the most chall enging task that a young scholar attempts to do. We have traveled this journey ... Use seven active steps to state the social science issue you wish to study for your dissertation/thesis as a research problem.
Thesis and Dissertation: Getting Started. The resources in this section are designed to provide guidance for the first steps of the thesis or dissertation writing process. They offer tools to support the planning and managing of your project, including writing out your weekly schedule, outlining your goals, and organzing the various working ...
This PhD Thesis Guide will guide you step-by-step through the thesis process, from your initial letter of intent to submission of the final document. ... This is intended to help students develop their proposal-writing skills by gaining experience composing a practical proposal; the length is comparable to that required for proposals to the NIH ...
into a PhD thesis | that is another story. It is all about writing a successful thesis and enjoying the viva. Let's get started! 2 Writing a thesis At the point of writing up, PhD students are unlikely to have written many theses: typically one to document an undergraduate nal year project and possibly another one at Master level.
Work with your thesis supervisor to plan the structure and format of your PhD thesis. Be prepared to rewrite each section, as you work out rough drafts. Don't get discouraged by this process. It's typical. Make your writing interesting. Academic writing has a reputation of being very dry.
What is the Process of Writing a PhD Thesis? 1. Choosing a Research Topic. The first step in writing a PhD thesis is selecting a research topic. This topic should be original, significant, and ...
A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words ( 100 to 300 pages in length) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) - from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion. The structure of a dissertation will vary depending on discipline (humanities, social ...
2) Analogue Introduction: Start your introduction with a comparison so that. your reader is eager to know the differences. 3) Narrative Introduction: Start your introduction with an eye-catching ...
The most difficult step in writing a PhD thesis is getting started. Lack of academic writing skills and uncertainty about PhD thesis writing guidelines leads to procrastination, self-doubt, and anxiety. This article lists writing tips for PhD students to write a great first draft of their PhD thesis.
Strive to be understood and avoid unnecessary words. Be persistent and eager - Writing a doctoral thesis becomes easier if you are consistent and dedicated. All other things being equal, your attitude will ultimately determine your success. Have patience and work hard. Create work you will be proud of for a lifetime.
minimum of ten days for all members of the thesis committee to review the thesis. Step 1: Prepare the content of your presentation. The content of your presentation is the mirror of your thesis ...
Remember, writing a thesis is a process. By breaking it down into smaller steps, for example, you can make steady progress towards completing your PhD thesis writing projects. 4. Read extensively in your field. Reading extensively is crucial for PhD students to produce high-quality, well-informed writing.
7) One of the best referencing styles in thesis writing is the American Psycho-. logical Association (APA) style (which will be discussed later). 8) When doing a literature review, read the ...
The second year of a PhD. Your second year will probably be when you do most of your core research. The process for this will vary depending on your field, but your main focus will be on gathering results from experiments, archival research, surveys or other means.. As your research develops, so will the thesis (or argument) you base upon it. You may even begin writing up chapters or other ...
How to write a PhD thesis: a step-by-step guide . 5 minute read. Evidence synthesis: what every student (and researcher) should know . 4 minute read. 1 The secrets to success as a provost. 2 Using non verbal cues to build rapport with students. 3 Emotionally challenging research and researcher well-being. 4