myCBSEguide
- Other Subjects
- Class 11 Psychology Case...

Class 11 Psychology Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Are you struggling to find reliable and up-to-date study resources and Class 11 Psychology case study questions? Look no further than myCBSEguide .
myCBSEguide has all the information you’ll need if you’re seeking for CBSE Class 11 Psychology case study questions. Our team of specialists have created ample of help to Class 11 Psychology students. We have a wide range of Class 11 Psychology case study questions, covering a variety of topics. myCBSEguide is the place to go when you’re having trouble with a topic or just need a little more support pertaining to Class 11 Psychology case study questions.
What is psychology and how does it work?
The word psychology comes from two Greek words: psyche, which means “soul,” and logos, which means “science” or “study of a subject.” As a result, psychology was defined as the study of the soul or mind. Psychology is properly described as a discipline that investigates mental processes, experiences, and behaviour in many circumstances. It does so by employing biological and social scientific tools to collect data in a methodical manner.
Psychology is one of the most popular subjects since it deals with how people think, react, behave, and interact. It is primarily concerned with human behaviour, as well as the thoughts and emotions that influence it. Psychology studies aid students in better understanding themselves and others, as well as developing sound analytical abilities through the use of the scientific method. It also aids pupils in learning how the mind and body operate together. This blog will provide in-depth information on the Psychology Class 11 Psychology syllabus and case study questions asked in Class 11 Psychology examination
The CBSE examination now includes Case Based Questions for Class 11 Psychology. Class 11 Psychology Case Study Questions are simple to understand and will aid in your academic success. On myCBSEguide, you will receive access to the most recent NCERT textbooks for Class 11 Psychology and all other subjects including Class 11 Psychology Case Study Questions, which are created in compliance with the most recent CBSE/NCERT Psychology curriculum and examination format.
Class 11 Psychology Sample case study questions
Our skilled teachers have prepared the crucial case study questions for Class 11 Psychology based on the most recent syllabus and examination norms given by CBSE/ NCERT. It is critical for students in Class 11 Psychology to go over the case study questions. You can tackle the database of Class 11 Psychology case study questions offered by myCBSEguide using the understanding gained from the Class 11 Psychology case study questions and the NCERT Book for Class 11 Psychology. Because these questions are likely to appear on exams, Class 11 Psychology students should know them and practice them on a daily basis.
Class 11 Psychology Sample case study question 1
Socialization is a process by which individuals acquire knowledge, skills and dispositions
which enable them to participate as effective members of group and society. It is a process that continues over the entire life span and through which one learns develops ways of effective
functioning at any stage of development. It forms the basis of social and cultural transmission
from one generation to the next. Its failure in any society may endanger the very existence of that
society. (2+1+1=4)
- Why socialization is necessary in daily life
- What is the age criterion of socialization?
- What is the basis of socialization?
Answer Key:
- Socialization helps individual in acquiring knowledge, skills and aspirations. (2)
- Age criterion of socialization is life span. (1)
- Basis of socialization is social and cultural transmission. (1)
Class 11 Psychology Sample case study question 2
In our eyes, in the outer layer, there is a transparent cornea and a tough sclera that surrounds the rest of the eye. It protects the eye and maintains its shape. The middle layer is called choroid, which is richly supplied with blood vessels. The inner layer is known as retina. It contains photoreceptors (rods and cones) and an elaborate network of interconnecting neurons. The eye is generally compared with a camera. For example, the eye and camera have a lens. The lens divides the eye into two unequal chambers, namely aqueous chamber and vitreous chamber. The aqueous chamber is located between the cornea and the lens. It is smaller in size and is filled with a waterlike substance, called aqueous humor. The vitreous chamber is located between the lens and the retina. It is filled with a jelly like protein, called vitreous humor. These fluids help in holding the lens at its appropriate place and in proper shape. They also allow enough flexibility for the occurrence of accommodation — a process through which the lens changes its shape in order to focus the objects at varying distances. This process is regulated by ciliary muscles, which are attached to the lens. These muscles flatten the lens to focus the distant objects and thicken it to focus the near objects. Like a camera, the eye also has a mechanism to control the amount of light entering into it. Iris is a disc-like coloured membrane lying between the cornea and the lens. It controls the amount of light entering the eye by regulating pupil dilation. In dim light the pupil dilates; in bright light it contracts.
Our eye is made up of _____ layers.
Which muscles serve to flatten the lens so that distant objects can be focused?
- Both a and b
The eye, like a camera, has a system for controlling the amount of light that enters it. Which of the following part of eye serves this purpose?
- None of the given
Class 11 Psychology Curriculum
For Class 11 Psychology students, CBSE/NCERT has created a unique Curriculum to help them gain a foundation and grasp on their learning skills. In Class 11 Psychology, skills-based learning and the development of key concepts begin with a little broader viewpoint. We recognise that young brains are full of questions in the context of Class 11 Psychology , therefore we open up a world full of fascinating learning opportunities and introduce fresh material to our Class 11 Psychology pupils. Class 11 Psychology curriculum is created in such a way that each student masters all of his foundational concepts and achieves higher degrees of brilliance. The chapters covered in the NCERT textbook for class 11 are listed below.
CBSE Class 11 Psychology (Code No. 037) Syllabus
Theory Paper 3 Hours Marks: 70
| What is Psychology? | 27 | 11 | |
| Methods of Enquiry in Psychology | 32 | 13 | |
| Human Development | 26 | 11 | |
| Sensory, Attentional and Perceptual Processes | 18 | 8 | |
| Learning | 20 | 9 | |
| Human Memory | 19 | 8 | |
| Thinking | 14 | 5 | |
| Motivation and Emotion | 14 | 5 | |
myCBSEguide for Class 11 Psychology Case Study questions
myCBSEguide provides ample Class 11 Psychology Case study questions. These Class 11 Psychology Case study questions are significant tools for students across the country, and they have excelled in the country’s educational sector. Let us examine the significance of these Class 11 Psychology Case study questions provided by myCBSEguide:
- Every explanation is accompanied by a relevant problem and answer on myCBSEguide. This makes it easier for Class 11 Psychology students to apply concepts, and the presentation of solutions helps them attain simple problem-solving abilities.
- Through analysis and well-researched insights are offered in a student-friendly style for every class 11 Psychology case study questions. Complex class 11 Psychology case study questions that are presented in detail and in simple terms help class 11 Psychology students to learn faster.
- The NCERT textbooks are directly referenced in CBSE exam papers, and both direct and twisted questions are based on these resources. myCBSEguide follows international level stipulations while adhering to CBSE guidelines; as a result, these class 11 Psychology case study questions are highly suggested by teachers.
- Class 11 Psychology students can benefit from comprehensive myCBSEguide resources, which include previous year’s question papers and answers. Additional tools to promote students’ learning are available on myCBSEguide at all levels in order to increase students’ ability to answer exam papers and offer them more practice.
CBSE Sample papers , question banks, revision notes, and other materials are available through myCBSEguide. You’ll be able to get all you need to help you prepare for your examinations with so much on offer.
So, what do you have to miss? Get started on your exam preparation by downloading myCBSEguide today.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
What Is A Case Study In Psychology?
When people think about psychology studies, they are most likely to think about studies involving several participants split across a number of experimental and control groups. Studies like this are a good way to investigate the effect of a certain treatment or activity, but they are not always the best option. For example, if a scientist is interested in a specific rare disease, they cannot always find enough people with that disease to participate in a useful study. Similarly, one cannot give a group of participants a rare disease (for obvious reasons) and compare them to a group of participants without that disease. For situations like this, there are case studies.
What is a case study?
A case study is, as the name suggests, a study of a single case. For example, if someone has an extremely rare disease, a group of scientists might conduct a case study of that disease rather than attempting to set up an experimental study. In that case study, the researchers might test the effectiveness of a certain drug in treating that disease and carefully document the response of that participant over time.
Of course, the results seen in that one participant will not necessarily apply to all people with that rare disease. However, if the case study shows promising results, that treatment can then be tested in a larger experimental study. If it does not, it indicates that the treatment is not necessarily effective, at least in people that are similar to the original participant in the case study.
Why are case studies useful in psychology?
When people are still learning about psychology, they might think that group studies showing group effects are always better than individual studies showing individual effects. Of course, there is some truth to this notion, as results obtained from a large number of people are likely to be more generalizable than results obtained from a single person. However, this does not mean that we should discount the importance of individual effects.
Consider the following: In studies looking solely at group effects, individual effects can be masked. In other words, certain statistical quirks can lead to the appearance of a group effect despite the fact that no single individual showed that effect. While this is rare, it is possible. For this reason, it is important to consider individual effects. That is why, even in experimental studies examining groups, it can be useful to examine individual effects within that group. This underlines the value of case studies.
Wrapping up
At the end of the day, there are many good reasons that experimental studies examining groups are the most common types of psychological studies. However, case studies are also extremely valuable, particularly when group experiments are less feasible. Just as psychology is a large topic encompassing a wide variety of factors, both case studies and experimental group studies should be used in the larger overall strategy of psychology research.
- Author Details
Joaquín Selva
- Psychology Careers
- Psychology Explained
- Psychology Gear
- Psychology History
- Psychology In Pop Culture
- Psychology News
- Psychology Research

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Psychology /
Psychology Class 11 Chapter 1

- Updated on
- Nov 23, 2022

Psychology class 11 chapter 1 is an interesting and riveting chapter that answers some of the questions which we have always had like what exactly is,” Psychology all about?”, ” What is its application in our everyday life?.” The answers to the above questions will unfold in the given blog where all the crucial topics of Psychology Class 11 chapter 1 have been covered.
This Blog Includes:
Psychology class 11 chapter 1: concepts, psychology as a discipline, psychology as a natural science, understanding mind and behaviour, popular notions about psychology, structuralism , functionalism, behaviourism, gestalt psychology, psychoanalysis, humanistic perspective, cognitive perspective, cognitive psychology, biological psychology, neuropsychology, developmental psychology, social psychology, cultural psychology, environmental psychology, health psychology, clinical psychology, counselling psychology, industrial/organisational psychology, educational psychology, sports psychology, other emerging fields of psychology, development of psychology in india, themes of research and application, basic v/s applied psychology, music and fine art, architecture and engineering, mass communication, types of psychologists at work, psychology in everyday life, ppt on what is psychology, ncert solutions for psychology class 11 chapter 1.
Psychology is defined formally as a science that studies mental processes, experiences and behaviours in different contexts. We will further understand the meaning of mental processes, behaviours and experiences in detail
- Mental Processes are usually used when we think or to solve a problem, to know or remember something. One level at which these mental processes are reflected in brain activity. Unlike the brain, our mind does not have a physical structure or a definite location.
- Experiences are subjective in nature which are studied by psychologists. One important thing about experiences is that we cannot directly observe or know someone else’s experience, only the experiencing person can be aware or conscious of her or his experiences.
- Behaviours are responses or reactions we make or activities we engage in. Behaviours may be simple or complex, short or enduring. Some behaviours are overt which means they can be outwardly seen or sensed by an observer whereas some behaviours are covert which means that they cannot be easily spotted and seen by other people
Psychology is a discipline that studies about human behaviour, mental processes, experiences in different contexts:
- It makes us understand how our mind works and how certain mental processes result in a specific type of behaviour.
- Natural Science
- Social Science
Psychology as a Natural Science largely focuses on biological principles to explain human behaviour.
- It assumes that all behavioural phenomena have causes which can be discovered if we can collect data systematically under controlled conditions.
- The main aim of the researcher is to understand the cause and effect relationship so that an accurate prediction of the behavioural phenomena can be made.
- Psychologists use hypothetical deductive model to prove their hypothesis
- By the application of this model,many psychologists gave theories on topics like Motivation, Memory etc.
Psychology as a Social Science
Psychology as a Social Science focuses on how behavioural phenomena can be explained in terms of interaction that takes place between the person and the socio-cultural context of which he/she is a part
- Studies human behavior in social context
- Humans are not only impacted by their socio-cultural contexts,they also create them as well.
- Focuses on humans and communities as social beings in relation to their social culture and physical environment.
It is true that the mind cannot exist without the brain but the mind is a separate entity:
- Earlier it was believed that there is no relationship between mind and body but now as per various researches in neuroscience prove that there is indeed a relationship between mind and Behaviour
- A new discipline called Psychoneuroimmunology has emerged in recent times which primarily explains the significant role of the mind in strengthening our immune system.
- Common sense does not always equate with Psychological studies
- Common sense is based on hindsight. Psychology as a science looks for patterns of behaviour which can be predicted and not explained after the behaviour occurs.
- Common Sense tells us that an individual is not able to perform the best in front audience but Psychological studies have shown that if you have practiced well,you may actually perform better than expected because the presence of others helps in enhancing performance.
Also Read: Motivation and Emotion Class 11 Notes
The Evolution of Psychology
The evolution of Psychology can be traced way back to 1879 when the first experimental laboratory was established in Leipzig, Germany by Wilhelm Wundt and he was interested in the study of conscious experience and wanted to analyse building blocks of the mind. Due to the fact that Psychologists during Wundt’s time started analysing the structure of the mind through introspection, they were also called structuralists. Later on, this approach was taken over by a functionalist approach. Introduced by an American psychologist, William James, the functionalist approach utilised the study of the human mind instead of focusing on the structure of the mind.
- It was proposed by Wilhelm Wundt and structuralism is considered the oldest school of psychology.
- Structuralists were interested in the analysis of the human mind and its structure
- They were interested in conscious experience and wanted to study the building blocks of the mind
- They used the introspection method to study mental processes and experiences
- Functionalism school of psychology was proposed by William James
- They focused on what the mind does and the function of consciousness in adjustment to the environment
- According to functionalists, Consciousness is an ongoing mental process that cannot be broken down into parts.
- This school of psychology was proposed by John B.Watson who viewed Psychology as a science of behaviour in terms of stimuli and responses.
- Our response to stimulus in the environment are the basic building blocks of our personality
- Watson emphasized on observable and verifiable response to stimuli and he was profoundly interested in the study of learning
- This school of psychology was in contrast to structuralism and it was founded in Germany by Wertheimer, Kohler and Koffka.
- It primarily focused on perceptual Organization (Organization of what we see)
- As per Gestalt Psychology, we look at the world, our Perceptual experience is more than its components.
- For example, when we look at a chair. We do not see four wooden legs but we recognise it completely as a table
- It was proposed by Dr Sigmund Freud
- As per this school of psychology, human behaviour is viewed as a dynamic manifestation of unconscious desires and conflicts about which we are not completely aware at present.
- Practical implementation of this school of psychology helps us to understand and cure psychological disorders.
- Humanistic Perspective was proposed by Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow
- It laid emphasis on the free will of human beings and their actions are not predetermined by any force.
- As per this school of psychology, human beings strive to grow and unleash their true potential which lies within them.
- All human beings have an innate tendency to attain a state of self-actualization and the nature of human activities is that they are goal-oriented.
- It was proposed by Jean Piaget and Vygotsky.
- This approach is considered as a fusion of the Gestalt Approach and Structuralism
- Lays emphasis on cognition which means thinking, understanding, perceiving, memorising etc
- They view the human mind as an information processing system just like a computer and mind receives, processes, transforms, stores and retrieves information.
Must Read: Thinking Class 11 Psychology Notes
Psychology Class 11 Chapter 1: Branches

Various fields of specialization in psychology have emerged over the years which have been comprehensively elucidated below-
- It investigates mental processes involved in the acquisition, storage, manipulation and transformation of information received from the environment along with its use and communication
- Major cognitive processes are attention, perception, memory, problem solving and decision-making etc.
- Focuses on the relationship between the behavior and physical system, including the brain and the rest of the nervous system, immune system and genetics
- Psychologists and Neuroscientists are working together and studying the role of neurotransmitters which are responsible for neural communication in different areas of the brain and associated mental functions.
- Comprehensive research is carried out on people with the normal functioning of the brain and as well as on people with damaged brains by use of advanced and recent technologies like EEG, PET etc.
- It studies the physical, social and psychological changes that occur at different stages and ages over life-span, from conception to old age.
- This branch of Psychology explores how people are affected by their social environments, how people think about the world around them and how they try to impact people around them.
- Topics such as Prosocial behaviour, Attitude Formation, Prejudice are of keen interest to social Psychologists
- Lays emphasis on the role of culture in attaining a deep understanding of human behaviour, thought and emotion.
- The main assumption of Cultural Psychology is that human behaviour is not only a reflection of human-biological potential but also a product of culture.
- It studies the interaction of physical factors such as temperature, humidity, pollution and natural disasters on human behaviour.
- The influence of the physical arrangement of the workplace on health, the emotional state is understood in environmental Psychology
- It lays emphasis on the role of psychological factors such as anxiety, stress, fear in the development, prevention and treatment of illness
- Areas of keen interest for a health Psychologist are coping with stress, promotion of health-enhancing factors etc.
- Clinical Psychology deals with the causes, treatment and prevention of some of the major psychological disorders like anxiety, depression, eating disorders and chronic substance abuse.
- Counselling Psychology aims to improve everyday functioning by helping people solve problems of their daily life and effectively cope up with challenging situations.
- This branch of Psychology mainly deals with both the employees and the organization which have employed them. They are focused on training employees, improving work conditions and developing selection criteria for employees.
- It lays emphasis on understanding how people of all ages understand and learn things. Educational Psychologists mainly develop instructional methods and materials used to train people both in Educational and work settings.
- Sports Psychology focuses on the application of Psychological principles to improve the performance of athletes.
Psychology has always been of multidisciplinary nature and because of this nature of Psychology, various other fields of Psychology have emerged which are described as follows-
- Political Psychology
- Aviation Psychology
- Space Psychology
- Forensic Psychology
- Military Psychology
- Community Psychology
- Managerial Psychology
- Indian philosophical tradition was already known to practice various mental processes and reflections on human consciousness, self, mind-body relations, and a variety of mental functions. But when it comes to the modern study of the human mind, such evolutionary study was highly influenced by the Western school of thought only.
- The first offical experiment with Modern Psychology in India happened in 1916 at the Calcutta University where Dr. N.N. Sengupta initiated the first modern experiments on Psychological fields.
- Departments of Psychology in the Universities of Mysore and Patna were other early centres of teaching and research in psychology.
- Durganand Sinha in his book ‘Psychology in a Third World Country: The Indian Experience’ categorises the evolution of Indian Psychology as the pre-independence phase, and the 1960s phase.
Themes that provide Direction to research and application of Psychology are mentioned as follows-
- Psychology, like other sciences, attempts to develop principles of behaviour and mental processes.
- Human Behaviour is a function of both the attributes of persons and environment
- Human Behaviour is caused
- Understanding of human behaviour is culturally constructed
- Human Behaviour can be controlled and modified through the application of psychological principles.
- Basic Psychology provides us with theories and principles that form the basis of application of Psychology
- Applied Psychology provides us with different contexts in which the theories and principles derived from research can be meaningfully applied.
Must Read: Learning Class 11 Notes
Psychology And Other Disciplines
Psychology shares its knowledge with literature, art, science, commerce, music etc. Some of the Major disciplines linked to the field of psychology are discussed below-
Music and Psychology are complementary in nature which means that they go hand in hand as they help in uplifting mood and productivity at work as well.
Psychology and Architecture go hand in hand as well. One of the important jobs of an architect is to provide a physical space that satisfies their client mentally and aesthetically.
Mass Communication is related to Psychology as well as the impact of media on the formation of attitudes on children and their behaviour is a domain where both of these disciplines come together.
- Computer Science
Psychologists work at various human service areas and these are described below-
- Clinical Psychologists mainly deal with patients who suffer from severe psychological disorders such as Depression, Schizophrenia, Anxiety, Eating Disorders etc.
- Counselling Psychologists help clients deal with everyday challenges and interpersonal issues such as career problems, self-esteem issues, Relationship and family problems etc.
- Organizational Psychologist Helps employees improve upon their overall well-being along with their productivity and also they focus on making such a kind of workplace environment which is very enriching for the employees.
There is no denial about the fact that Psychology plays a crucial role in our everyday life.
- Helps in solving our day to day problems in very effective and efficient manner
- Principles and methods of Psychology help us in analysing and understanding our relationship with others
- Helps us in attaining self-awareness and thus,that helps in improving our decision-making
- Various methods and techniques of Psychology helps us in improving our learning and memorising abilities
- Thus, Psychology indeed plays a crucial role in our lives.
Various schools of psychology like structuralism, functionalism, Humanism, Gestalt Psychology aptly explain the evolution of psychology.
Everyday application of Psychology helps us in decision making, problem-solving, enhancing our learning and memorising ability, attaining self-awareness etc.
The best branch of psychology in the given case is Forensic Psychology.
Behaviour refers to any response of an organism that can be measured. Any covert or overt action/reaction a person does can be observed in some ways. A person running to catch a train is an example of overt behaviour. The working of human memory or problem-solving might be thought of as behaviour, even though they cannot be observed directly but must be inferred from their product.
The popular theories of human behaviour are based on common sense and may or may not be true if investigated scientifically. Common sense is based on hindsight. Psychology as science looks for patterns of behaviour that can be predicted and not explained after the behaviour occurs. Dweck’s study on children (who gave up too easily when faced with difficult problems or failures) is worth mentioning here. Common sense tells us to give them easy problems, first in order to increase their success rate so that their confidence goes up. Dweck found that children who had always succeeded because they were given easy problems could not cope up with difficult problems and gave up faster in comparison to those who had the experience of both success and failure and were taught to put more effort to deal with difficult problems. Such studies prove that predictions based on empirical studies are reliable and valid.
Psychology is located at the intersection of many fields of knowledge pertaining to human functioning. It contributes to the growth of other disciplines and draws subject matter from them as well. In the study of brain and behaviour, psychology shares its knowledge with neurology, physiology, biology, medicine and computer science. In studying the meaning, growth and development of human behaviour in a socio-cultural context, psychology shares its knowledge with anthropology, sociology, social work, political science and economics.
Must Read: Human Development Notes for Class 11
This was all about Psychology Class 11 Chapter 1 notes. Worried about how to revise at the last moment for exams? Don’t worry! We at Leverage Edu are here for you to provide all the required notes to help you revise faster and ace your examinations.
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
You cleared all the doubts
Hey, We are glad to know that you have found our blog on Psychology Class 11 Chapter 1 Notes helpful. Here are some more blogs that can help you out with your Class 11 syllabus: https://leverageedu.com/blog/psychology-class-11/ https://leverageedu.com/blog/learning-class-11-psychology-notes/ https://leverageedu.com/blog/thinking-class-11-psychology-notes/
Being a good human person
IM SOO THANKFUL ABOUT THIS WEBSITE. It litteraly explained me everything so easily and helped me to make notes which i understood everything of!!
Can u pls provide pdf of these notes

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
- Class 11 Psychology Chapter 1 Important Questions
Class 11 Psychology Chapter 1 Important Questions What is Psychology designed for CBSE 2024-25. Get here important questions and Extra Question Answers of 11th Psychology chapter 1 along with the NCERT question answers.
Class 11 Psychology Chapter 1 Extra Question Answers
- Class 11 Psychology Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Psychology Chapter 1 MCQ Answers
- Class 11 Psychology all Chpaters Solutions
- Class 11 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
Humanistic psychology could be a psychological perspective that emphasizes the study of the entire person. Humanistic psychologists observe human behavior not only through the eyes of the observer, but through the eyes of the person doing the behaving. An example of humanistic psychology may be a therapist seeing a client for the primary time for a therapy session and utilizing Maslow’s hierarchy of must determine where the client was on the hierarchy and to work out what needs were and weren’t being met.
Humanistic psychology could be a perspective that emphasizes viewing the full individual and stresses concepts like powerfulness, self-efficacy, and self-actualization. instead of concentrating on dysfunction, humanistic psychology strives to assist people fulfill their potential and maximize their well-being.
Define Constructivism. Constructivism is that the theory that says learners construct knowledge instead of just passively soak up information. As people experience the globe and reflect upon those experiences, they build their own representations and incorporate new information into their pre-existing knowledge (schemas).
Constructivism relies on the concept that individuals actively construct or make their own knowledge, which reality is decided by your experiences as a learner. Basically, learners use their previous knowledge as a foundation and hinge upon it with new things that they learn.
Write short notes on Biological psychology. Biological psychology, also called psychological science, is that the study of the biology of behavior; it focuses on the system nervous, hormones and genetics. Biological psychology examines the connection between mind and body, neural mechanisms, and therefore the influence of heredity on behavior.
Download App for Class 11

Biological psychology as a field emerged from a spread of scientific and philosophical traditions within the 18th and 19th centuries. within the Principles of Psychology (1890), William James argued that the scientific study of psychology should be grounded in an understanding of biology.
What are the 7 principles of ethics in psychology? This approach – that specialize in the appliance of seven mid-level principles to cases (non-maleficence, beneficence, health maximization, efficiency, respect for autonomy, justice, proportionality) – is presented during this paper.
Developmental psychology is that the scientific study of how and why humans grow, changes, and adapt across the course of their lives. Originally concerned with infants and kids, the sphere has expanded to incorporate adolescence, adult development, aging, and also the entire lifespan.
What does one understand by Industrial psychology? Industrial psychology refers to the applied organizational psychology accustomed study, analyze and understand human behavior within the workplace, mainly how business works and the way employees function. psychological science uses a variety of scientific methods, including quantitative and qualitative research.
Explain Educational psychology. Educational psychology is that the study of how people learn, including teaching methods, instructional processes, and individual differences in learning. The goal is to grasp how people learn and retain information.
Following are the points which shows the link between mind and behaviour:
- Using positive visualization techniques and feeling positive emotions, one can give birth to significant changes in bodily processes.
- Use of representational process, i.e. images generated by an individual in her/his mind, are wont to cure various sorts of phobias.
- A new discipline called Psychoneuroimmunology has emerged which emphasizes the role played by the mind in strengthening the system.
- One example which shows mind behaviour relationship may be a person with blocked arteries was made to visualize that blood was flowing through her/ his blocked arteries. After practicing this over a period of your time, significant relief was obtained by these patients because the degree of blockage became significantly less.
Psychology is that the scientific study and usage of observable behavior and mental processes of organisms. the topic matter of psychology is, affect, behavior, and cognition. The affect for psychology is that the actual mental processes that make up: moods, feeling, and spirit. humanistic psychology, a movement in psychology supporting the idea that humans, as individuals, are unique beings and may be recognized and treated intrinsically by psychologists and psychiatrists. The movement grew con to the 2 mainstream 20th-century trends in psychology, behaviorism and psychoanalysis. The humanistic approach emphasizes the private worth of the individual, the centrality of human values, and therefore the creative, active nature of kinsfolk.
The approach is optimistic and focuses on the noble human capacity to beat hardship, pain and despair. Sensitivity training at an area of employment is an example of the humanistic perspective. Individuals are taught to value and respect their coworkers for who they’re, irrespective of differences. This results in stronger workplace relationships and a more inclusive work environment.

Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education


- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes PDF Download (Handwritten & Short Notes)
Free pdf download.
SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
The NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes in PDF prepare students in advance to perform better in the board and competitive examinations. Therefore, the students studying Psychology should definitely use Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes in PDF because it will help them cover their full NCERT Psychology Syllabus with ease.
It is possible with the notes because the revision notes are prepared to keep in mind the cruciality of time for the students. Subject matter experts of Selfstudys have crafted the Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes in PDF after analysing the whole NCERT 12 Psychology books and syllabus. Links to download are mentioned here on this page which will aid students to access the PDF of Psychology revision notes anytime they want.
Chapter wise Class 11 NCERT Psychology Notes
Chapters of Class 11 Psychology are a bit complicated and so, it requires rigorous revisions from time to time to understand the concepts of the chapters. Hence, in favour of students, our subject matter experts have prepared the Chapter wise Class 11 NCERT Psychology Notes which are organised in chapter wise manner and topic-wise manner.
By using the NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes PDF students can stay organised and do their study precisely, therefore, our team has bundled the NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes in individual PDF files.
What Is Psychology Class 11 Notes
Methods Of Enquiry In Psychology Class 11 Notes
The Bases Of Human Behaviour Class 11 Notes
Human Development Class 11 Notes
Sensory, Attentional And Perceptual Processes Class 11 Notes
Learning Class 11 Notes
Human Memory Class 11 Notes
Thinking Class 11 Notes
Motivation And Emotion Class 11 Notes
NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes PDF Download Process
If you are looking for the NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes PDF then go through the download process, mentioned below -
- Open the Selfstudys website and click on the Navigation button
- Click on NCERT Books & Solutions to expand it further
- Now, click on NCERT Notes to open a new page
- Choose Class 11th from the given options
- Now, search or Click on Psychology to access the Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes in a chapter-wise format.
What are NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes and Why It Is Popular?
NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes is a study tool which contains a collection of short summaries of subtopics, definitions, and key points. The Notes are an easily absorbable document that helps students to improve their grip on the topics explained. Due to this reason, it is one of the most popular study resources used by lakhs of students to prepare for their board examinations and competitive examinations.
NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes PDF is prepared by those teachers who have years of experience in teaching and they know how to shorten the long definitions so that a reader can easily remember them.

What is the Importance of Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes?
- Helps In Recalling the Studied Topics: We all know that revision helps recall the studied topics, and it becomes much more important when you are studying subjects like Psychology. Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes is intentionally prepared to keep in mind the need of students in remembering the topics studied.
- Timely Revision Helps Reduce Anxiety And Stress: Revising the Psychology topics timely: during regular classes or exam preparation helps students deal with stress and reduces anxiety. Since with the help of Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes students can deal with such disturbing situations, they can better perform in the examinations.
- Using Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes Boosts Confidence in Students: Having confidence in Psychology can help you to perform better in the examination. But it is only possible if you have completed your CBSE Syllabus and you are well aware of all the topics that are discussed in Psychology. Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes help you build that confidence as it contains the details about every single topic in a brief.
- Assists in Identifying Weak and Strongest Areas in the Subject: If you use the Blurting technique to revise the Class 11 Psychology, you will find that there are some weak and strongest areas in the subject. How to use Blurting techniques to revise has been discussed below. By using the Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes, you can work on the weak areas to improve them.
3 Revision Techniques To Use NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes PDF
- Revise, Sleep, & Repeat: Research says that taking a short nap of about 20 or 30 minutes improves memory. So, revising, Sleeping, & repeating the same process time and again helps in improving memory or recall power so, use this revision technique to use the NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes PDF.
- Pomodoro is a way for distracted students: The Pomodoro technique is a great way to revise, and it works very well for those students who struggle with concentrating on a single task for a longer period of time. Thus, students can use this technique to use the NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes PDF to revise the whole Psychology syllabus.
- Blurting, a new trend to revise: So far, you understood the two most popular ways to revise the concepts of Psychology you have studied, but Blurting is a revision technique that you can use. Blurting revision techniques include reading your Psychology notes aloud. Only reading helps so much to remember. Once, you do this technique, make sure you test yourself by writing down everything you have remembered so far during your Class 11 Psychology revision time.
When To Use Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes in PDF That Will Add Value To Your Life?
The revision notes of Class 11 can add great value to your academic life if you know when to use them. Therefore, in this section, we have mentioned the crucial moments you should use NCERT Psychology Class 11 Notes PDF.
- At the time of classroom study: The Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes in PDF is an ideal study resource to use at the time of classroom study. It is so because generally, one chapter of Psychology will take some time to complete so when it is the second or third class for the same Psychology chapter use the revision notes of Class 11 Psychology to recall whatever you have studied in the previous classes. It will make the previous learning fresh and will enable you to take more interest in the study as you can better understand the topics now.
- While doing the weekly revision: All the students studying in Class 11 should do weekly revision as it helps them keep track of whatever they have studied in the entire week as well as helps them refresh all the learnings.
- During board exam preparation: All the board candidates who have prepared a timetable to dedicate to the board exam preparation should use the Class 11 Psychology NCERT Notes. Using the Class 11 Psychology notes at that time will help the students to strengthen their grip on the topics which will help them score better marks in the board examination.
- While preparing for competitive exams: Class 11 Psychology isn’t limited to the board exams only, there are several competitive exams in which Psychology plays a crucial role; students can use the NCERT Psychology Class 11 Notes PDF while preparing for competitive exams. It will help them better prepare for the subject.
- During last-minute preparation: About one day before the examination using the NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes can add great value to the student’s overall preparation. Using the Psychology Notes during the last-minute preparation gives instant recall to all the topics of Psychology. It will also help them ease their stress as they will get some confidence by doing this.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


Last few days of free access to Embibe
Click on Get Started to access Learning Outcomes today

Share this article

Table of Contents
Latest updates.

1 Million Means: 1 Million in Rupees, Lakhs and Crores

Ways To Improve Learning Outcomes: Learn Tips & Tricks

Visual Learning Style for Students: Pros and Cons

NCERT Books for Class 6 Social Science 2024 – Download PDF

CBSE Syllabus for Class 9 Social Science 2023-24: Download PDF

CBSE Syllabus for Class 8 Maths 2024: Download PDF

NCERT Books for Class 6 Maths 2025: Download Latest PDF

CBSE Class 10 Study Timetable 2024 – Best Preparation Strategy

CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2025 – Download PDF

CBSE Syllabus for Class 11 2025: Download PDF
Tag cloud :.
- entrance exams
- engineering
- ssc cgl 2024
- Written By Sankavi_E
- Last Modified 16-06-2023
CBSE Class 11 Psychology 2022-23
CBSE Class 11 Psychology 2022-23: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) introduced Psychology as an elective subject in the CBSE Class 11 curriculum. Students will learn new and exciting concepts in their academic year. The syllabus is carefully designed to help students understand the behaviours and mental processes of human beings.
As per the new assessment scheme of 2022-23, CBSE Class 11 Psychology will be conducted once a year due to the single exam format. CBSE Class 11 is a crucial year for students because it lays the groundwork for all important topics covered in the following class. It is critical to study hard in Class 11 to get good grades and prepare for competitive exams. Students must carefully check all the details about Psychology as it is a scoring subject from an exam point of view. In this article, students will learn about Psychology CBSE Class 11 and its various aspects.

Class 11 CBSE Psychology Highlights
Before we jump into further details about the subject, students can get an overview of CBSE Class 11 Psychology from the table below:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Name of the Subject | CBSE Class 11 Psychology |
| Conducting Body | The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) |
| Exam Level | Matriculate/School Level |
| CBSE official Website | |
| NCERT official Website |
CBSE Class 11 Psychology Exam Pattern 2022-23
The important topics of Class 11 Psychology are mentioned below. Carefully go through the latest marking scheme of the Psychology syllabus to prepare for the exams accordingly:
| Units | Topics | No. of periods | Marks |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | What is Psychology? | 27 | 11 |
| II | Methods of Enquiry in Psychology | 32 | 13 |
| IV | Human Development | 26 | 11 |
| V | Sensory, Attentional and Perceptual Processes | 18 | 8 |
| VI | Learning | 20 | 9 |
| VII | Human Memory | 19 | 8 |
| VIII | Thinking | 14 | 5 |
| IX | Motivation and Emotion | 14 | 5 |
| Total | 170 | 70 |
Check the chapter-wise weightage of CBSE Class 11 Psychology practicals from the below-mentioned table:
| CBSE Class 11 Psychology – Chapters (Practicals) | Marks Weightage |
|---|---|
| Practicals file | 5 |
| Project file | 5 |
| Viva Voce | 5 |
| Experiment | 15 |
| Total marks | 30 |
Psychology Textbook Class 11 CBSE
The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) released the Psychology textbook Class 11 CBSE , covering the latest syllabus proposed by CBSE. NCERT books explain concepts with illustrations and in simple language. As it is comprehensible, it helps students easily relate to and encourages the spirit of learning.
It is a reliable source to prepare for the board examination. With the help of the CBSE Class 11 Psychology book, students can cover the entire syllabus. The questions for CBSE Class 11 board exams will be prepared from the NCERT books. Therefore, students must focus on the NCERT books for CBSE Class 11 Psychology to score well in the examination:
| CBSE Class 11 Psychology Books – In English Medium | CBSE Class 11 Psychology Books – In Hindi Medium |
|---|---|

Psychology Class 11 CBSE Syllabus 2022-23
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) proposes the Psychology CBSE Class 11 Syllabus . It has a total of nine chapters which are designed to develop ideas about the human mind and behaviour among students. The main objective of the CBSE Class 11 Psychology Syllabus is to encourage students to become perceptive, socially aware and self-reflective.
CBSE Class 11 is a crucial stage in a student’s life, and therefore, CBSE has crafted the syllabus to build the foundation and prepare the students for higher studies. Students must cover the entire syllabus to ace the examination and prepare for higher education. Before commencing the preparation, students must develop ideas about the topics and sub-topics in Psychology Class 11 CBSE Syllabus.
CBSE Class 11 Psychology Syllabus
Students can check the Psychology CBSE Class 11 syllabus from the table below:
| Psychology Class 11 CBSE Syllabus – in English Medium | Psychology Class 11 CBSE Syllabus – in Hindi Medium |
|---|---|
| Chapter 1: What is Psychology? | अध्याय 1: मनोविज्ञान क्या है? |
| Chapter 2: Methods of Enquiry in Psychology | अध्याय 2: मनोविज्ञान में जांच के तरीके |
| Chapter 3: The Bases of Human Behavior | अध्याय 3: मानव व्यवहार के मामले |
| Chapter 4: Human Development | अध्याय 4: मानव विकास |
| Chapter 5: Sensory, Attentional and Perceptual Processes | अध्याय 5: संवेदी, चौकस और अवधारणात्मक प्रक्रियाएं |
| Chapter 6: Learning | अध्याय 6: अधिगम |
| Chapter 7: Human Memory | अध्याय 7: मानव स्मृति |
| Chapter 8: Thinking | अध्याय 8: चिंतन |
| Chapter 9: Motivation and Emotion | अध्याय 9: अभिप्रेरणा और संवेगा |
CBSE Class 11 Psychology Course Structure 2022-23
Students preparing for CBSE Class 11 Psychology must know the course structure. A fair understanding of the course helps students to strategise their preparation for the examination:
| Units | Details | Periods |
|---|---|---|
| Unit I | What is Psychology? The topics in this unit are: Introduction What is Psychology? Psychology as a Discipline Psychology as a Natural Science Psychology as a Social Science Understanding Mind and Behaviour Popular Notions about the Discipline of Psychology Evolution of Psychology Development of Psychology in India Branches of Psychology Psychology and Other Disciplines Psychology in Everyday Life | 27 Periods |
| Unit II | Methods of Enquiry in Psychology The topics in this unit are: Introduction Goals of Psychological Enquiry Steps in Conducting Scientific Research Alternative Paradigms of Research Nature of Psychological Data Some Important Methods in Psychology Observational Method Experimental Method Correlational Research Survey Research Psychological Testing Case Study Analysis of Data Quantitative Method Qualitative Method Limitations of Psychological Enquiry Ethical Issues | 32 Periods |
| Unit IV | Human Development The topics in this unit are: Introduction Meaning of Development Life-Span Perspective on Development Factors Influencing Development Context of Development Overview of Developmental Stages Prenatal Stage Infancy Childhood Challenges of Adolescence Adulthood and Old Age | 26 Periods |
| Unit V | Sensory, Attentional and Perceptual Processes The topics in this unit are: Introduction Knowing the world Nature and varieties of Stimulus Sense Modalities Functional limitation of sense organs Attentional Processes Selective Attention Sustained Attention Perceptual Processes Processing Approaches in Perception The Perceiver Principles of Perceptual Organisation Perception of Space, Depth and Distance Monocular Cues and Binocular Cues Perceptual Constancies Illusions Socio-Cultural Influences on Perception | 18 Periods |
| Unit VI | Learning The topics in this unit are: Introduction Nature of Learning Paradigms of Learning Classical Conditioning Determinants of Classical Conditioning Operant/Instrumental Conditioning Determinants of Operant Conditioning Key Learning Processes Observational Learning Cognitive Learning Verbal Learning Skill Learning Factors Facilitating Learning Learning Disabilities | 20 Periods |
| Unit VII | Human Memory The topics in this unit are: Introduction Nature of Memory Information Processing Approach: The Stage Model Memory Systems: Sensory, Short-term and Long term Memories Levels of Processing Types of Long-term Memory Declarative and Procedural; Episodic and Semantic Nature and Causes of Forgetting Forgetting due to Trace Decay, Interference and Retrieval Failure Enhancing Memory Mnemonics using Images and Organisation | 19 Periods |
| Unit VIII | Thinking The topics in this unit are: Introduction Nature of Thinking Building Blocks of Thought The Processes of Thinking Problem Solving Reasoning Decision-making Nature and Process of Creative Thinking Nature of Creative Thinking Process of Creative Thinking Thought and Language Development of Language and Language Use | 14 Periods |
| Unit IX | Motivation and Emotion The topics in this unit are: Introduction Nature of Motivation Types of Motives Biological Motives Psychosocial Motives Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Nature of Emotions Expression of Emotions Culture and Emotional Expression Culture and Emotional Labelling Managing Negative Emotions Enhancing Positive Emotions | 14 Periods |
| Practical (Projects, experiments, small studies, etc.) 30 marks The students shall be required to undertake one project and conduct two experiments. The project would involve the use of different methods of enquiry like observation, survey, interview, questionnaire, small studies related to the topics covered in the course (e.g. Human development, Learning, Memory, Motivation, Perception, Attention and Thinking). Experiments could focus on cause-and-effect relationship. Practical Examination Practical (Experiments) file 05 Marks Project file 05 Marks Viva Voce (Project and experiments) 05 Marks One experiment 15 Marks (05 Marks for conduct of practical and 10 Marks for reporting) Total 30 Marks | 60 Period | |
Psychology Class 11 Question Paper Design 2022-23
Students preparing for Psychology Class 11 examination must know the question paper design ahead of the exams to score well and achieve excellent results. Below we have mentioned the question paper design for the academic year 2022-23 to help students prepare for their exams:
| Time: 3 Hours | Maximum Marks: 70 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| S. No. | Competencies | Total Marks | % Weightage |
| 1 | Remembering and Understanding: Exhibiting memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers; Demonstrating understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions and stating main ideas | 25 | 35% |
| 2 | Applying: Solving problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. | 31 | 45% |
| 3 | Formulating, Analysing, Evaluating and Creating: Examining and breaking information into parts by identifying motives or causes; Making inferences and finding evidence to support generalizations; Presenting and defending opinions by making judgments about information, validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria; Compiling information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions. | 14 | 20% |
| Total | 70 | 100% | |
How Does Embibe Help in Class 11 Psychology Preparation?
Acing the CBSE Class 11 Psychology examination is tough, and its preparation can be quite stressful for many. Here, Embibe comes to the rescue! Students can better understand the latest syllabus and exam pattern of the CBSE Class 11 Psychology from Embibe. Students can take the mock test, check sample papers and NCERT solutions provided at Embibe to improve their preparation.
Students can understand their knowledge on the subject, the time they consume to answer the question compared to the actual time, behavioural loopholes and suggestions to improve the behavioural loopholes etc., from our mock test series. Utilising the resources provided at Embibe reduces the time consumed for the preparation. Thus, students can revise and score well in the examinations.
CBSE Class 11 Psychology Preparation Tips
CBSE Class 11 Psychology preparation tips help students complete the syllabus and ace the examinations. The preparation tips created by our experts are listed as follows:
- Understand Psychology CBSE Class 11 syllabus and check topics and the sub-topics. Getting familiar with the syllabus helps students effectively strategise their preparation.
- Make a habit of studying for 5 hours a day. Take proper rest and breaks to stop yourself from draining your energy.
- Prepare a timetable considering the difficult and easy topics included in the syllabus. Following the timetable helps students keep track and complete the syllabus at the estimated time.
- Revise daily as it helps you retain the concept for a long time. Also, regular revision helps you spend less time on the topics already covered.
- Develop the habit of making notes. It helps the students understand the concepts better. Making notes in bullet point format will also help have a quick revision just before the examination.

FAQs on CBSE Class 11 Psychology
Ans: It is not difficult to ace the CBSE Class 11 Psychology examination if the student understands the syllabus and strategises the preparation.
Ans: CBSE Class 11 Psychology has nine chapters namely- What is Psychology?, Methods of Enquiry in Psychology, The Bases of Human Behavior, Human Development, Sensory, Attentional and Perceptual Processes, Learning, Human Memory, Thinking and Motivation and Emotion.
Ans: Students can find all the details about Psychology Class 11 on Embibe.
Ans: Students can download the textbook from this page or from the official website.
Ans: Students can take the Class 11 Psychology mock test embibe to understand their knowledge on their subject and get familiar with the exam pattern.
Related Articles
1 Million Means: 1 million in numerical is represented as 10,00,000. The Indian equivalent of a million is ten lakh rupees. It is not a...
Ways To Improve Learning Outcomes: With the development of technology, students may now rely on strategies to enhance learning outcomes. No matter how knowledgeable a...
Visual Learning Style: We as humans possess the power to remember those which we have caught visually in our memory and that too for a...
NCERT Books for Class 6 Social Science 2024: Many state education boards, including the CBSE, prescribe the NCRET curriculum for classes 1 to 12. Thus,...
CBSE Syllabus for Class 9 Social Science: The Central Board of Secondary Education releases the revised CBSE Class 9 Social Science syllabus. The syllabus is...
CBSE Syllabus for Class 8 Maths 2023-24: Students in CBSE Class 8 need to be thorough with their syllabus so that they can prepare for the...
NCERT Books for Class 6 Maths 2025: The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) textbooks are the prescribed set of books for schools...
CBSE Class 10 Study Timetable: The CBSE Class 10 is the board-level exam, and the Class 10th students will appear for the board examinations for...
CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2025: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) conducts the Class 10 exams every year. Students in the CBSE 10th Class...
CBSE Syllabus for Class 11 2025: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has published the Class 11 syllabus for all streams on its official...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water – A Precious Resource
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water – A Precious Resource: In this chapter, students will study about the importance of water. There are three...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 2024: Respiration in Organisms
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms: NCERT solutions are great study resources that help students solve all the questions associated...
Factors Affecting Respiration: Definition, Diagrams with Examples
In plants, respiration can be regarded as the reversal of the photosynthetic process. Like photosynthesis, respiration involves gas exchange with the environment. Unlike photosynthesis, respiration...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants: The chapter 'Reproduction' in Class 7 Science discusses the different modes of reproduction in...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11: Chapter 11 of Class 7 Science deals with Transportation in Animals and Plants. Students need to ensure...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15: Light
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15: The NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 15 is Light. It is one of the most basic concepts. Students...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13: Chapter 13 in class 7 Science is Motion and Time. The chapter concepts have a profound impact...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 14: Electric Current and its Effects
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 14: One of the most important chapters in CBSE Class 7 is Electric Current and its Effects. Using...
General Terms Related to Spherical Mirrors
General terms related to spherical mirrors: A mirror with the shape of a portion cut out of a spherical surface or substance is known as a...
Animal Cell: Definition, Diagram, Types of Animal Cells
Animal Cell: An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell with membrane-bound cell organelles without a cell wall. We all know that the cell is the fundamental...
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science 2024 – Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science: The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) publishes NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science as a comprehensive...
NCERT Books for Class 12 Chemistry 2024: Download PDF
NCERT Books for class 12 Chemistry: NCERT publishes chemistry class 12 books every year. The NCERT chemistry class 12 books are essential study material for...
CBSE Class 9 Mock Tests 2025: Attempt Online Mock Test Series (Subject-wise)
We all have heard at least once that the secret to success is practice. Some of you could say it's a cliché, but those who...
NCERT Books for Class 10 Maths 2025: Download Latest PDF
NCERT Books for Class 10 Maths: The NCERT Class 10 Maths Book is a comprehensive study resource for students preparing for their Class 10 board exams....
Arc of a Circle: Definition, Properties, and Examples
Arc of a circle: A circle is the set of all points in the plane that are a fixed distance called the radius from a fixed point...
CBSE Class 10 Mock Test 2025: Practice Latest Test Series
CBSE Class 10 Mock Test 2025: Students' stress is real due to the mounting pressure of scoring good marks and getting into a renowned college....
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 2024: Science and Maths
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 2024: Students appearing for the CBSE Class 10 board exam must go through NCERT Solutions to prepare for the exams...

39 Insightful Publications

Embibe Is A Global Innovator

Innovator Of The Year Education Forever

Interpretable And Explainable AI

Revolutionizing Education Forever

Best AI Platform For Education

Enabling Teachers Everywhere

Decoding Performance

Leading AI Powered Learning Solution Provider

Auto Generation Of Tests

Disrupting Education In India

Problem Sequencing Using DKT

Help Students Ace India's Toughest Exams

Best Education AI Platform

Unlocking AI Through Saas

Fixing Student’s Behaviour With Data Analytics

Leveraging Intelligence To Deliver Results

Brave New World Of Applied AI

You Can Score Higher

Harnessing AI In Education

Personalized Ed-tech With AI

Exciting AI Platform, Personalizing Education

Disruptor Award For Maximum Business Impact

Top 20 AI Influencers In India

Proud Owner Of 9 Patents

Innovation in AR/VR/MR

Best Animated Frames Award 2024
Trending Searches
Previous year question papers, sample papers.
Adaptive Practice with Solutions To Help You Ace Important Topics for 11th CBSE

Practice Unlimited 11th CBSE Questions With Hints & Solutions
Enter mobile number.
By signing up, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Psychology Chapter 1 What is Psychology?
June 3, 2024 by Bhagya
NCERT Text Book Questions Solved
Question 1. What is behaviour? Give examples of overt and covert behaviour? Answer: Behaviour refers to any response of an organism that can be measured. Any covert or overt action/reaction a person does that can be observed in some ways. A person running to catch train is an example of overt behaviour. The working of human memory or problem solving might be thought of as behaviour, even though they cannot be observed directly but must be inferred from their product.
Read more about NCERT Psychology Class 11
Question 2. How can you distinguish scientific psychology from the popular notions about the discipline of Psychology? Answer: The popular theories of human behaviour are based on common sense and may or may not be true if investigated scientifically.
- Common sense based on hind sight. Psychology as a science looks for patterns of behaviour which can be predicted and not explained after the behaviour occurs.
- Dweck’s study on children (who gave up too easily when faced with difficult problems or failures) is worth mentioning here.
- Commonsense tells us to give them easy problems, first in order to increase their success rate so that their confidence goes up.
- Dweck found that children who had always succeeded because they were given easy problems could not cope up with difficult problems and gave up faster in comparison to those who had experience of both success and failure and were taught to put more effort to deal with difficult problems.Such studies prove that predictions based on empirical studies are reliable and valid.
Question 3. Give a brief account of the evolution of psychology. Answer: Psychology as a modem discipline has a short history but a long past. It grew out of ancient philosophy. It emerges as a scientific discipline in the following phases: 1. Structuralism: It is the oldest school/approach to psychology, and it was proposed by William Wundt. Structuralists were interested in analysis of human mind and its structure.
- They were interested in conscious experience and wanted to study the building blocks of mind.
- They used introspective method to study mental processes and experiences.
2. Functionalism: It is an approach to psychology, developed by an American Psychologist William James.
- They (Functionalists) emphasised on what the mind does and the function of consciousness in adjustment to the environment
- According to them consciousness is an on-going stream of mental process, it can’t be broken down into parts.
- They also used introspective method to study mental processes and experiences.
3. Behaviourism: Proposed by John B. Watson who viewed psychology as the science of behaviour and behaviour could be described objectively in terms of stimuli and responses (S-R).
- This approach proposed that mentalist concepts such as consciousness, image or mind cannot be measured or studied objectively and scientifically.
- Watson emphasised on observable and verifiable response to stimuli.
- He was influenced by Pavlov’s classical conditioning and was interested in the study of learning.
4. Gestalt Psychology: This approach was a revolt against structuralism, founded in Germany by Wertheimer, Kohler and Koffka
- It focused on perceptual organisation (organisation of what we see) and they also demonstrated the laws of perceptual organisation.
- Structuralist wanted to break down perception into elements but Gestalt stated that when we look at the world, our perceptual experience is more than the sum of the components of the perceptions i.e. we give meaning to perception.
- For example, when we look at a table we do not see four wooden legs and trapezoid plain surface above it but we recognise it as a table.
5. Psychoanalysis: This approach was proposed by Dr. Sigmund Freud.
- He viewed human behaviour as a dynamic manifestation of unconscious desires and conflicts of which we are not aware at present.
- He used psychoanalysis as a system to understand and cure psychological disorders.
6. Humanism: It was advocated by Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow.
- They emphasised on the free will of human beings i.e. people are free to do whatever they choose to do. Their actions are not predetermined by any force.
- They said that human beings strive to grow and unfold their inner potential i.e. what they are capable of doing.
- According to them all individuals have innate tendency to self actualise and all human activities are goal directed and worthwhile.
7. Cognitive Perspective/Cortstructivism: This perspective is a combination of Gestalt approach and structuralist approach. This approach focuses on cognition i.e. how we know the world through thinking understanding, perceiving, memorising and problem solving etc.
- Jean Piaget and Vygotsky are the pioneers of this approach.
- Cognitive psychologists view the human mind as an information processing system like a computer.
- Mind is considered to receive, process, transform, store and retrieve information.
- Mind is dynamic and human beings actively construct their minds as they interact with the social and physical environment and interaction between adults and children.
Question 4. What are the problems for which collaboration of psychologists with other disciplines can be fruitful? Take any two problems to explain. Answer: Psychology is located at the intersection of many fields of knowledge pertaining to human functioning.
- It contributes to the growth of other disciplines and draws subject-matter from them as well.
- In the study of brain and behaviour psychology shares its knowledge with neurology, physiology, biology, medicine and computer science.
- In studying the meaning, growth and the development of human behaviour in a socio-cultural context, psychology shares its knowledge with anthropology, sociology, social work, political science and economics.
Question 5. Differentiate between (a) a psychologist and a psychiatrist (b) a counsellor and a clinical psychologist. Answer: (a) Psychologist —A psychologist is someone who possesses the knowledge of psychology and holds recognized degree in the field; they work in diverse areas, like teaching, counselling, community etc. Psychiatrist—They are qualified medical-practitioners who are concerned with psychological well-being of individuals. Clinical Psychologist and psychiatrist are different in the qualification and in roles. Clinical Psychologist cannot administer or prescribe drugs whereas psychiatrists are medical professionals and trained in administering medicine/drugs to treat mental disorders. (b) Counsellor —A counsellor provides advice to the persons who suffer from motivational and emotional problems, they provide vocational guidance also. Clinical psychologist—A clinical psychologist also helps people with behavioural, mental and emotional problems.
- They are post- graduate in Psychology and are specialised professionals.
- They provide therapy for various mental disorders, anxiety, fear or stress of any type.
- They use interview and administer psychological tests to diagnose the client’s problem.
Question 6. Describe some of the areas of everyday life where understanding of psychology can be put to practice. Answer:
- Psychology is not only a subject that satisfies curiosities of our mind about human nature, but it is also a subject that offers solutions to a variety of problems. It ranges from personal to family, a community or even national and international dimensions.
- The solution of these problems may involve political, economic and social reforms; however, these problems are a result of unhealthy thinking, negative attitude towards people and self and undesirable patterns of behaviour.
- A psychological analysis of these problems helps both in having a deeper understanding of these problems and also finding effective solutions.
- Psychology enables an individual to understand oneself in a balanced and positive way without being reactionary, in order to deal with everyday challenges and meet with personal expectations.
- Therefore, understanding of psychology enables a person to build stronger relationships at community level and improve individual strength.
Question 7. How can knowledge of the field of environmental psychology be used to promote environment friendly behaviour? Answer: Environmental psychology studies the interaction between natural and man-made environment and human behaviour.
- The knowledge of environmental psychology can help us prevent big disasters.
- We can learn to modify our behaviour to prevent any unwanted and painful outcome.
- For example, if we know the hazards of growing population, we can certainly apply some measure to stop population growth.
Question 8. In terms of helping solve an important social problem such as crime, which branch of psychology do you think is most suitable. Identify the field and discuss the concerns of the psychologists working in this field. Answer: The branch of social psychology is the most suitable for solving problems like crime. It explores through thought process of people and their influence on other. Social psychologists are concerned with topics like attitude, conformity, obedience to authority, social motivation, inter-group relations, etc. In answering such questions the knowledge of psychology for Lawer and a criminologist is also very essential. If they have the knowledge of psychology they can understand how well a witness remembers the incident? How well can he/she report such facts when taking the witness stand in the court.
NCERT Solutions Psychology Entrepreneurship Indian Economic Development Humanities
Also Read: Exercises to induce period
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
Have an account?

PSYCHOLOGY ,CHAPTER-2 , CLASS 11
Social studies, other.
14 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
METHOD OF INTENSE STUDY OF JUST ONE INDIVIDUAL IS
NATURALISTIC OBSERVATION
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
IN AN EXPERIMENT, THE _________________ VARIABLE IS TESTED BY THE RESEARCHER TO OBSERVE ITS EFFECT(S) ON THE _________________ VARIABLE.
INDEPENDENT, DEPENDENT
FIRST , SECOND
DEPENDENT, INDEPENDENT
RESEARCH,SEARCH
A TYPE OF OBSERVATION CONDUCTED IN THE PARTICIPANTS' NORMAL ENVIRONMENT WITHOUT INTERFERENCE FROM THE RESEARCHERS.
CONTROLLED OBSERVATION
THIS IS A METHOD OF RESEARCH WHERE AN INVESTIGATOR MANIPULATES ONE OR MORE FACTORS (INDEPENDENT VARIABLES) TO OBSERVE THE EFFECT ON SOME BEHAVIOR OR MENTAL PROCESS (THE DEPENDENT VARIABLE).
EXPERIMENTS
OBSERVATIONAL
CORRELATION
THE ADVANTAGE OF THIS DESCRIPTIVE METHOD OF RESEARCH IS THAT IT CREATES AN IMMENSE AMOUNT OF DATA TO BE GATHERED QUICKLY AND INEXPENSIVELY.
IDENTIFY THE TYPE OF RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN WEIGHT AND PRICE.
THE PRICE IS NEVER 0 ON THE GRAPH
AS WEIGHT INCREASES, PRICE INCREASES
THERE IS A NEGATIVE LINEAR CORRELATION BETWEEN WEIGHT AND PRICE
THE PRICE GETS HIGH AT THE END OF THE GRAPH
INDEPENDENT VARIABLE IS TO DEPENDENT VARIABLE AS _________ IS TO ____________.
HYPOTHESIS-CONCLUSION
EFFECT-CAUSE
CONCLUSION-HYPOTHESIS
CAUSE-EFFECT
THE MAIN RULE OF NATURALISTIC OBSERVATION.
SETTING UP DEPENDENT AND INDEPENDENT VARIABLE
RESEARCH AND FIND ENOUGH PARTICIPANTS
NOT DISTURBING PARTICIPANTS IN THE STUDIES
GETTING ENOUGH DIFFERENT AGE GROUPS FOR STUDY
IF I WANT TO GATHER HOW ALL STUDENTS ARE FEELING ABOUT REMOTE LEARNING SO FAR, WHICH METHOD WOULD MAKE THE MOST SENSE?
EXPERIMENTAL
IN EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES WHICH GROUP RECEIVES NOTHING? IN OTHER WORDS, THEY DO NOT GET THE VARIABLE THAT IS UNDER STUDY.
EXPERIMENTAL GROUP
CONTROL GROUP
IDENTIFY THE SITUATIONAL VARIABLES.
PRIOR EXPERIENCE AND KNOWLEDGE OF THE SUBJECT, INTELLIGENCE
INDEPENDENT AND DEPENDENT VARIABLE
TIME.NOISE,TEMPRATURE
EXTRENOUS VARIABLE
VALIDITY IS__________
THE EXTENT THE TESTS MEASURES WHAT IT AIMS TO MEASURE
CONSISTENCY OF TESTS RESULTS
AVERAGE SCORES OR VALUES
UNIFORMITY IN INSTRUCTIONS , ADMINITRATIONS,SCORING
PHYSICAL INFORMATION INCLUDES
ECOLOGICAL CONDITIONS
HOUSING CONDITIONS
FINANCIAL CONDITIONS
ALL OF THE ABOVE
A PSYCHOLOGICAL TEST IS A ________AND __________TOOL TO ASSESS THE INDIVIDUALS ABILITIES
STANDARDISED , VALID
STANDARDISED , OBJECTIVE
STANDARDISED , RELIABLE
STANDARDISED , STRUCTURED
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone
Important Questions and Answers
- 1 mark Questions and Answers
- 2 marks Questions and Answers
- 3 marks Questions and Answers
Chapter wise Questions and Answers
- Chapter 1: What is Psychology
- Chapter 1: What is Psychology - Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
- Chapter 2: Methods of Enquiry in Psychology
- Chapter 2: Methods of Enquiry in Psychology - Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
- Chapter 3: The Bases of Human Behaviour
- Chapter 4: Human Development
- Chapter 5: Sensory, Attentional and Perceptional Processes
- Chapter 6: Learning
- Chapter 7: Human Memory
- Chapter 8: Thinking
- Chapter 9: Motivation and Emotion
List of Questions and Answers
1.In terms of helping solve an important social problem such as discrimination , the branch of psychology which is most suitable is______________. (a) Educational (b) Clinical (c) Social (d) Industrial (Chapter 1: What is Psychology)
Ans: (c) Social
2.The introspective report in an experiment is given by____________ . (a) Experimenter (b) Subject (c) Both the experimenter and subject (d) None of the above (Chapter 1 - What is Psychology?)
Ans: (b) Subject
3.In Psychology the words Psyche and logos are made up of two words which mean: (a) Psychology is the science of soul (b) Psychology is the science of conscience experience (c) Psychology is the science of behaviour (d) None of the above (Chapter 1 - What is Psychology?)
Ans: a) Psychology is the science of soul
4.________ established the first experimental laboratory in Leipzig, Germany. (a) Dr. N.N. Sengupta (b) Wilhelm Wundt (c) Dweck (d) None of the above (Chapter 1 - What is Psychology?)
Ans: b) Wilhelm Wundt
5.Where was the first laboratory of modern psychology established? (a) Moscow (b) Leipzig (c) New york (d) Calcutta (Chapter 1 - What is Psychology?)
Ans: b) Leipzig
6.The psychology in which behaviours are studied in a social situation is called: (a) Social Psychology (b) General Psychology (c) Abnormal Psychology (d) Clinical Psychology (Chapter 1 - What is Psychology?)
Ans: a) Social Psychology
7. The first psychology laboratory was established in the year (a) 1915 (b) 1922 (c) 1986 (d) None of the above (Chapter 1 - What is Psychology?)
Ans: a) 1915
8. _____________ studies the changes that occur from infancy to old age. (a) Developmental Psychology (b) Biological Psychology (c) Cognitive Psychology (d) Health Psychology (Chapter 1 - What is Psychology?)
Ans: a) Developmental Psychology
9.________________ work with persons who suffer from motivational and emotional problems. (a) Counselling psychologists (b) Clinical psychologists (c) Community psychologists (d) Organisational psychologists (Chapter 1 - What is Psychology?)
Ans: a) Counselling psychologists
10.Name the psychologist who said psychology as a study of behaviour or responses which can be measured and studied objectively. (a) Sigmund Freud (b) William James (c) John Watson (d) None of the above (Chapter 1 - What is Psychology?)
Ans: a) Sigmund Freud
11.___________ first proposed the famous equation B = f(P,E) (a) Kurt Lewin (b) William James (c) John Watson (d) None of the above (Chapter 1 - What is Psychology?)
Ans: a) Kurt Lewin
12.Name the psychologist who founded psychoanalysis. (a) Sigmund Freud (b) William James (c) John Watson (d) None of the above (Chapter 1 - What is Psychology?)
More Questions and Answers Coming Soon.
Previous Page
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Psychology - What is Psychology
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Q1: What is behaviour? Give examples of overt and covert behaviour. Ans: Behaviour is a response or a reaction of an individual or an activity in which the individual is engaged in. It is the result of a stimulus in the environment or an internal change. Behaviours may be simple or complex and overt or covert. Examples of overt behaviour (i) Blinking of eyes when a stone is hurled at a person (ii) Withdrawing the hand immediately after touching a hot pan Examples of covert behaviour (i) The twitching of hand muscles while playing a game of chess. (ii) Pounding of heart during an interview. Q2: How can you distinguish scientific psychology from the popular notions about the discipline of psychology? Ans: Scientific psychology can be distinguished from the popular notions about the discipline of psychology on the basis of the following characteristics:
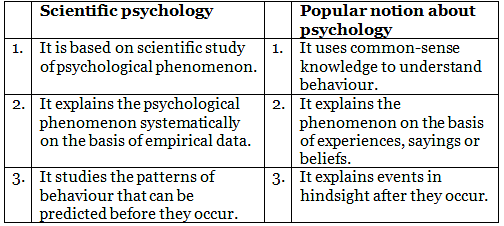
Q3: Give a brief account of the evolution of psychology. Ans: The evolution of psychology was an outcome of ancient philosophy. It later varied with the development of different approaches of psychological study. The formal beginning of modern psychology took place in 1879 with the establishment of an experimental laboratory in Leipzig by Wilhelm Wundt.
- The initial approach to study psychology was based on introspection or structuralism in which the individuals were asked to describe their experiences.
- It was followed by functionalism that studied the working of the mind and the impact of behaviour upon people's interaction with their environment.
- Gestalt psychology emerged as a reaction to structuralism in the early 20th century and focused on the organisation of the perceptual experiences.
- Another reaction was the development of behaviourism that studied behaviour or responses in a measurable and objective form.
- This was followed by psychoanalysis of Sigmund Freud that viewed human behaviour as a dynamic manifestation of unconscious desires, conflicts and their gratification.
- In contrast, the humanistic perspective emphasised the free will of human beings and their natural striving to grow and unfold their inner potential.
- Further, Cognitive perspective was a combination of Gestalt approach and structuralismand focused on how anindividual perceived the world.
- Later, Constructivism viewed human beings as activelyconstructing their minds through the exploration of physical and the social world.
- It was followed by Vygotsky's view that human mind develops through social and cultural processes in which the mind is perceived as culturally constructed by joint interaction between children and adults.
Therefore, the evolution of psychology passed through various stages and levels. Starting from the roots of philosophy, it took a new direction and included numerous theories of structuralism, functionalism, behaviourism, constructivism, etc. However, in contemporary era the discipline of psychology has grown into a scientific discipline, which deals with various processes underlying human experiences and behaviours. Q4: What are the problems for which collaboration of psychologists with other disciplines can be fruitful? Take any two problems to explain. Ans: The problems for which collaboration of psychologists with other disciplines can be fruitful are as follows:
- While dealing with a criminal case, it is important for a lawyer or a criminologist to understand the psychology of a witness or the criminal. It is also necessary to decide the degree of punishment valid for a crime. Thus, it is important for a lawyer or a criminologist to have the knowledge of psychology in order to regulate the legal system of a country.
- It is important for an architect or an engineer to satisfy his/her customers by providing with mental and physical space in a building. Further, an engineer should also consider the human habits while construction. Thus, they need to have a psychological knowledge in order to understand the needs and demands of their customers.
Q5: Differentiate between (a) a psychologist and a psychiatrist (b) a counsellor and a clinical psychologist. Ans: (a) The difference between a psychologist and a psychiatrist are mentioned below:
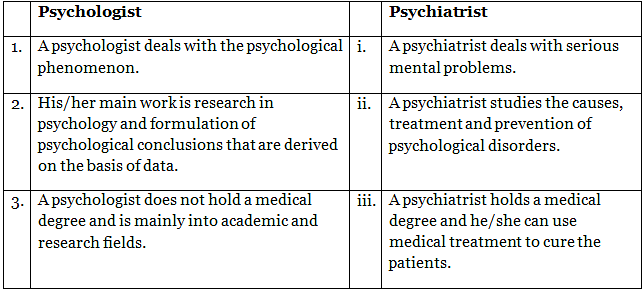
Q6: Describe some of the areas of everyday life where understanding of psychology can be put to practice. Ans: Some of the areas of everyday life where understanding of psychology can be put into practice are as follows:
- Psychology helps to understand various personal problems like family, marriage and work sphere. It also helps to deal with larger problems related to community and society.
- Psychology enables an individual to understand oneself in a balanced and positive way without being reactionary, in order to deal with everyday challenges and meet with personal expectations.
- Understanding of psychology further helps in analysing the various social, economic and political problems that affect an individual's life and their solution at individual and collective level.
- Psychology helps in understanding the cause of violence and need for cooperation that makes people wise, which improves the societal relationships by avoiding conflict, frustration and aggression.
- Psychological analysis also enables in decision-making for various spheres and cultivating healthy lifestyles.
Therefore, the understanding of psychology enables a person to build stronger relationships at community level and improves the strength at individual level in order to meet daily challenges and obstacles. Q7: How can knowledge of the field of environmental psychology be used to promote environment-friendly behaviour? Ans: The knowledge of environmental psychology is helpful to promote environment friendly behaviour because:
- It studies the interaction of physical factors such as temperature, humidity, pollution and natural disaster on human behaviour.
- It analyses the influence of physical arrangements at work place on the health, emotional state and interpersonal relations of the individual.
- Issues like disposal of waste, population explosion, conservation of energy etc. are related with behaviour of human beings as well as its consequence.
- Thus, an understanding of human behaviour in relation to environment generates awareness and inculcates safe environmental practices.
Q8: In terms of helping solve an important social problem such as crime, which branch of psychology do you think is most suitable? Identify the field and discuss the concerns of the psychologists working in this field. Ans: The branch of social psychology is most suitable for the purpose of solving social problems like crime. It explores the thought process of people and their influence upon others and evaluates the impact of social environment upon the actions of an individual. Social psychologists are concerned with topics like attitudes, conformity and obedience to authority, interpersonal attraction, helpful behaviour, prejudice, aggression, social motivation and inter-group relations.
| |66 docs|20 tests |
Top Courses for Humanities/Arts
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Psychology - What is Psychology
| 1. What is the scope of psychology? |
| 2. How does psychology differ from psychiatry? |
| 3. What are the major schools of thought in psychology? |
| 4. How is psychology applied in everyday life? |
| 5. What are the career opportunities in psychology? |
| Views | |
| Rating | |
study material
Important questions, mock tests for examination, semester notes, past year papers, practice quizzes, objective type questions, shortcuts and tricks, extra questions, sample paper, viva questions, video lectures, previous year questions with solutions.

NCERT Solutions - What is Psychology Free PDF Download
Importance of ncert solutions - what is psychology, ncert solutions - what is psychology notes, ncert solutions - what is psychology humanities/arts questions, study ncert solutions - what is psychology on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Class 11 Psychology Sample case study question 1. Socialization is a process by which individuals acquire knowledge, skills and dispositions. which enable them to participate as effective members of group and society. It is a process that continues over the entire life span and through which one learns develops ways of effective.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
1. Descriptive methods include the use of surveys, naturalistic observation, and clinical methods to describe behaviour and mental processes; these help us to reach the goal of description. 2. Correlational methods are used to study the relationships between variables; these help us to reach the goal of prediction. 3.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright ...
Methods of Enquiry in Psychology: Class 11 Notes, PDF, Important Questions and Answers, Notes and Summary, Extra Questions. Read Now. ... Case study. It is an in-depth study of a particular case. It employs multiple methods for collecting information such as interviews, observations and psychological tests from a variety of respondents who in ...
A case study psychology example could be that a researcher wants to study the onset of severe anxiety by a teenager following a natural disaster. The three most common types of case studies are ...
This type of observation is conducted in hospitals, homes, schools, day care centers, etc. However, many a times you might need to control certain factors that determine behaviour as they are not the focus of your study. For this reason, many of the studies in psychology are conducted in the laboratory.
Case study in psychology refers to the use of a descriptive research approach to obtain an in-depth analysis of a person, group, or phenomenon. A variety of techniques may be employed including personal interviews, direct-observation, psychometric tests, and archival records.In psychology case studies are most often used in clinical research to describe rare events and conditions, which ...
A case study is, as the name suggests, a study of a single case. For example, if someone has an extremely rare disease, a group of scientists might conduct a case study of that disease rather than attempting to set up an experimental study. In that case study, the researchers might test the effectiveness of a certain drug in treating that ...
Psychology Class 11 Chapter 1: Concepts. YouTube: 2 Minute Classroom. Psychology is defined formally as a science that studies mental processes, experiences and behaviours in different contexts. We will further understand the meaning of mental processes, behaviours and experiences in detail. Mental Processes are usually used when we think or to ...
Psychology is that the scientific study and usage of observable behavior and mental processes of organisms. the topic matter of psychology is, affect, behavior, and cognition. The affect for psychology is that the actual mental processes that make up: moods, feeling, and spirit. humanistic psychology, a movement in psychology supporting the ...
NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes PDF Download Process. If you are looking for the NCERT Class 11 Psychology Notes PDF then go through the download process, mentioned below -. Open the Selfstudys website and click on the Navigation button. Click on NCERT Books & Solutions to expand it further. Now, click on NCERT Notes to open a new page.
The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) released the Psychology textbook Class 11 CBSE, covering the latest syllabus proposed by CBSE. NCERT books explain concepts with illustrations and in simple language. As it is comprehensible, it helps students easily relate to and encourages the spirit of learning.
EduRev's Psychology Class 11 Course for Humanities/Arts is designed to introduce students to the fascinating world of psychology. The course covers various topics such as human behaviour, emotions, senses, and perception. It also delves into the study of mental processes, including thinking, memory, and learning. Through this course, students will develop a deeper understanding of the ...
In waking consciousness, we perceive time, place and events as real, meaningful and familiar. • Psychology is a social science because it studies the behaviour of human beings in their social tests cultural context. • Psychology as a social science discipline focuses on humans as social beings. • It focuses on the individual and ...
Question 3. Give a brief account of the evolution of psychology. Answer: Psychology as a modem discipline has a short history but a long past. It grew out of ancient philosophy. It emerges as a scientific discipline in the following phases: 1. Structuralism: It is the oldest school/approach to psychology, and it was proposed by William Wundt.
2.State two points of difference between Speed tests and Power tests. (Chapter 2: Methods of Enquiry in Psychology) Ans: Speed Test. Power Test. In a speed test, there is a time limit within which the test taker is required to answer all the items. Power test assesses the underlying ability (or power) of the individuals by allowing them ...
PSYCHOLOGY ,CHAPTER-2 , CLASS 11 quiz for 11th grade students. Find other quizzes for Social Studies and more on Quizizz for free! PSYCHOLOGY ,CHAPTER-2 , CLASS 11 quiz for 11th grade students. ... CASE STUDY. SURVEY. OBSERVATIONAL. CORRELATION. 5. Multiple Choice. Edit. 30 seconds. 1 pt.
Chapter wise questions and answers,extra questions and answers , NCERT solutions for class 11 Psychology What is Psychology?, Methods of Enquiry in Psychology, The bases of human behaviour, human development, sensory, attentional and perceptional processes, learning, human memory, thinking, motivation and emotion.All about CBSE Class 11 Psychology important questions, 1 mark questions, class ...
Social psychologists are concerned with topics like attitudes, conformity and obedience to authority, interpersonal attraction, helpful behaviour, prejudice, aggression, social motivation and inter-group relations. The document NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Psychology - What is Psychology is a part of the Humanities/Arts Course Psychology Class ...
class 11 case studies ( by myself ).docx - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The case describes a 6-year-old boy in foster care who is overfamiliar, struggles to focus, is physically inappropriate, and has difficulty with speech and self-care tasks. His symptoms are consistent