Standards Alignment
Assessments, professional learning, family engagement, case studies.
NEW EUREKA MATH 2 ® PILOT PACKAGE
Are you looking for new ways to advance equity and build knowledge in your math classroom with high-quality instructional materials? EdReports recently reviewed Eureka Math 2 . Scan the QR code or access the final report .
Check out our special pilot package for only $10 per student.

Shop Online
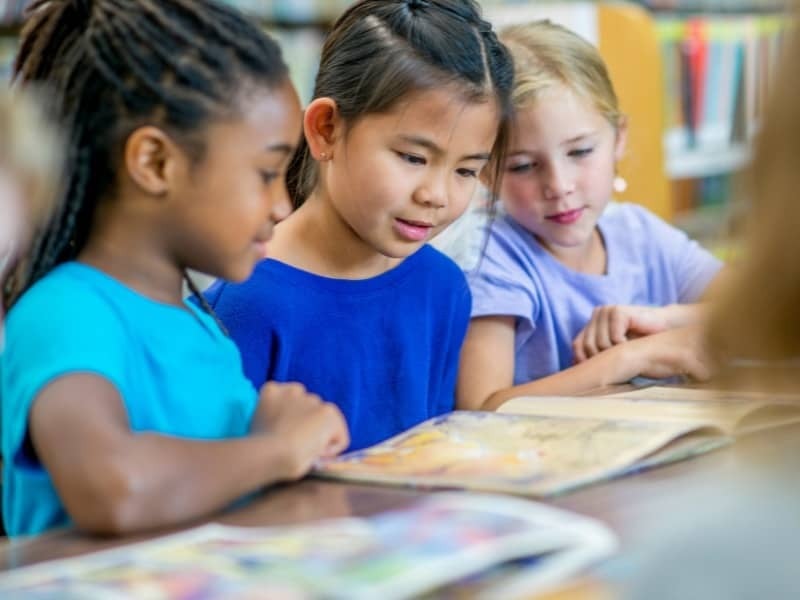

SEE THE SCIENCE OF READING IN ACTION
At Great Minds ® , we’re committed to ensuring our curricula are aligned to the latest research on how students best learn to read, write, and build knowledge.
Explore webinars, blogs, research briefs, and more to discover how we incorporate this important body of research.

FREE CLASSROOM PRINTABLES
At Great Minds®, we’re committed to supporting educators with high-quality curricula and resources.
Explore resources designed to aid students in science and engineering and spark classroom conversation.
Webinar Library
Instructional resources, trending topics, knowledge-building, the science of reading, lesson design, universal design for learning (udl), background knowledge.
Palm Springs, CA
Houston, TX
New Orleans, LA
Eureka Math 2® Curriculum Overview
Exponentially Greater
Eureka Math² ® is a revolutionary Prekindergarten–Algebra I* math program designed to advance equity in the math classroom by helping students build enduring math knowledge.
In Eureka Math² you’ll still find the consistent math models, rigor to support the productive struggle, and coherence across grades that you love from Eureka Math® .
Now you’ll also find digital interactives, increased opportunities for student discourse, and a new level of flexibility to make math instruction exponentially more teachable and engaging.
Eureka Math ²® Undergoes EdReports Review
Eureka Math² was recently reviewed by EdReports for its alignment with the college and career readiness standards. Scan the QR code or access the final report.
The most celebrated math curriculum is now even more joyful to teach and learn
Advancing equity through math instruction.
How can a math curriculum advance equity? By providing teachers with high-quality materials and tools to ensure students build a conceptual understanding of mathematics.
Our Eureka Math² teacher–writers and experts used a research-based approach to craft a new curriculum that ensures students build enduring knowledge.
Learn more about our commitment to accessibility .
Read more about how we’ve incorporated the principles of the Universal Design for Learning to account for learner variance so all students can access grade-level content.
See how lessons and modules are intentionally organized to leverage connections between concepts, and progress conceptual understanding from simple to complex to help students access new learning and problem-solving.
Through an intentional integration of digital resources , a focused approach to encouraging student discourse, and by connecting lessons to real-world math, students stay engaged in the learning. Get access to the curriculum .
Through this knowledge-building approach, Eureka Math² helps teachers unlock the greatness in every child.
Watch this guided walk-through of the curriculum to learn more .
Access our state alignment studies to see how Eureka Math 2 supports your mathematics standards .
Interested in piloting Eureka Math 2 in your classroom? Learn more .
The Intersection of Art and Math
While students often think of math as simply numbers, we know that mathematics itself is an art—and math is a key element of artistic compositions throughout history. Eureka Math² brings that connection to center stage by featuring a piece of fine art that has a connection to the math taught in the module. With this focus, the art provides a novel entry point for all learners to engage with while building knowledge of math concepts.
Everything Needed to Teach and Learn Math
Eureka Math² includes print and digital materials designed to engage students and provide teachers with high-quality materials to lead every math lesson with confidence.
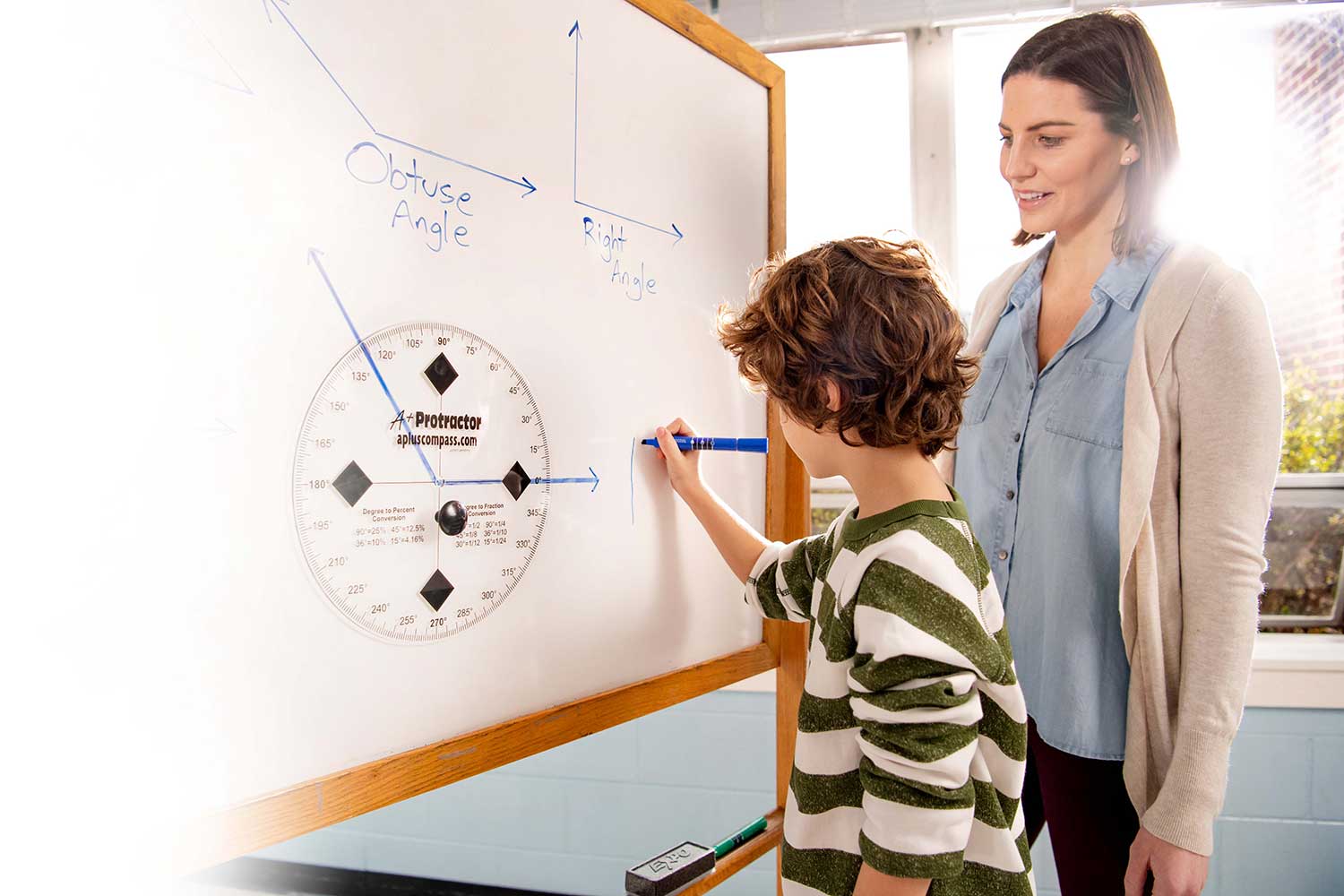

For Teachers
The Teach book is the Teacher Edition and is also available in Spanish for Grade Levels Prekindergarten–Algebra I .
The Great Minds ® Digital Platform teacher access provides lesson facilitation slides along with all the same content found in the Teach book.
Achievement Descriptors represent what students should know, and Proficiency Indicators show what knowing looks like.
Pre-Module diagnostic, formative, and summative assessments provide teachers comprehensive visibility into student learning.
Talking Tool and Thinking Tool posters to facilitate mathematical discourse.
Great Minds Data Talks offer accessible data literacy activities that engage students in critical thinking and discourse while interpreting data visualizations. Explore a sample of our Data Talks' Teacher Resources and Student Resources.
Family Math Night Resources provide teachers with ready-made tools that create a rich, productive, engaging Eureka Math 2 family night in your learning community.
For Students
The Learn book is the student edition and is also available in Spanish for Grade Levels Prekindergarten–Algebra I . It provides students with in-class lesson supports, problem sets, and formative assessments ( Exit Tickets and Topic Tickets ).
The Apply book provides students in Grade Levels 1–5 with additional practice for home.
Digital lessons and interactives fuel student discourse.
Math context videos provide students with low floor/high ceiling learning opportunities as they explore real-world math.
Family Math and Practice Partners provide caregivers with guidance on how to best support their mathematicians at home .
Open-middle and open-ended tasks empower students to find their own solution pathways.
Hands-on math manipulatives provide students with kinesthetic learning opportunities .

Supporting Teachers Before , During , and After Implementation
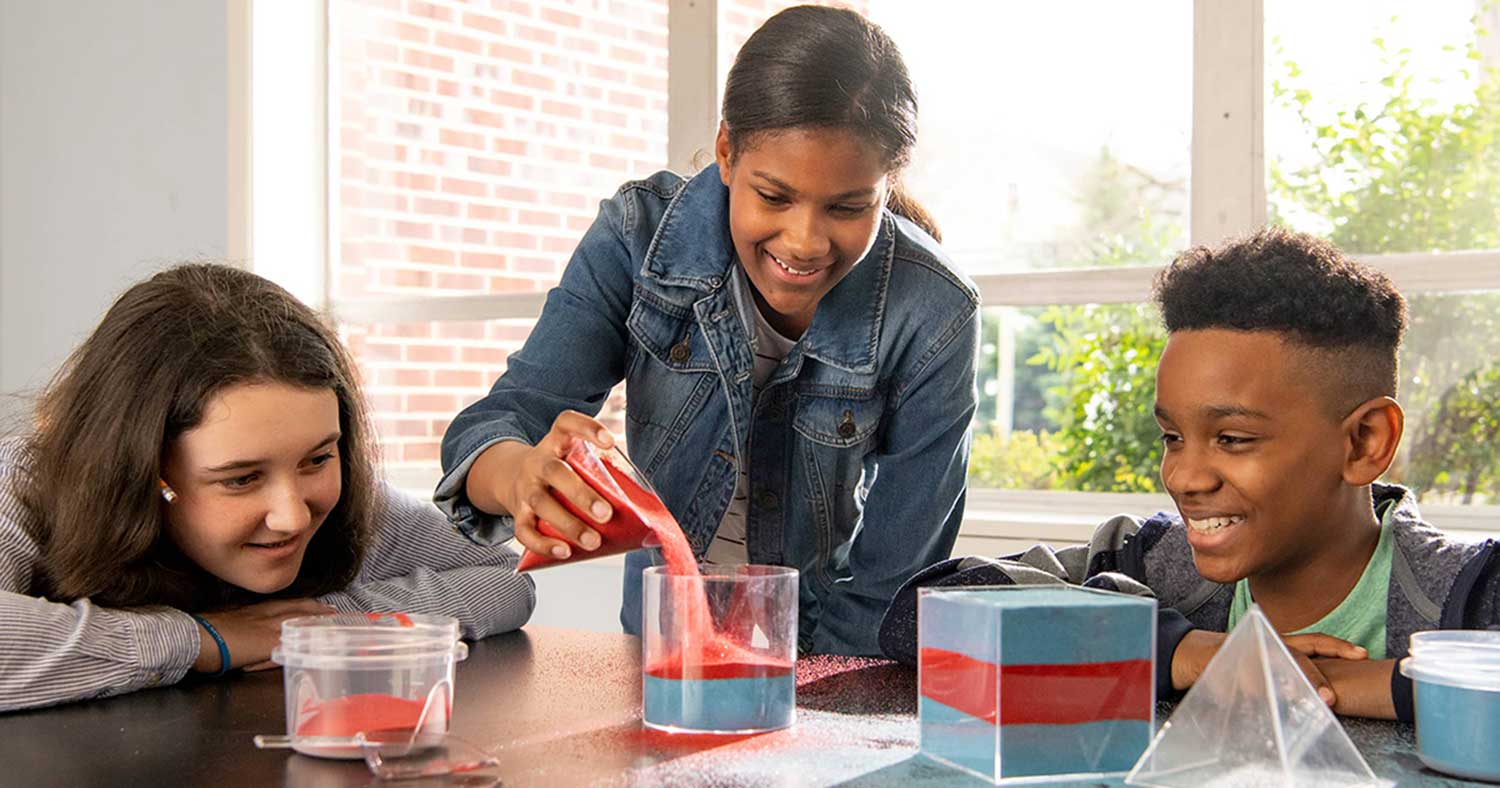

Guidance and Coaching Built into Every Lesson
High-quality curriculum can transform a classroom, but only if teachers have the support they need to implement it. Eureka Math² teacher–writers and experts crafted the curriculum with point-of-use notes to guide teachers on:
- UDL principles
- Language support
- Differentiation
- Instructional choices
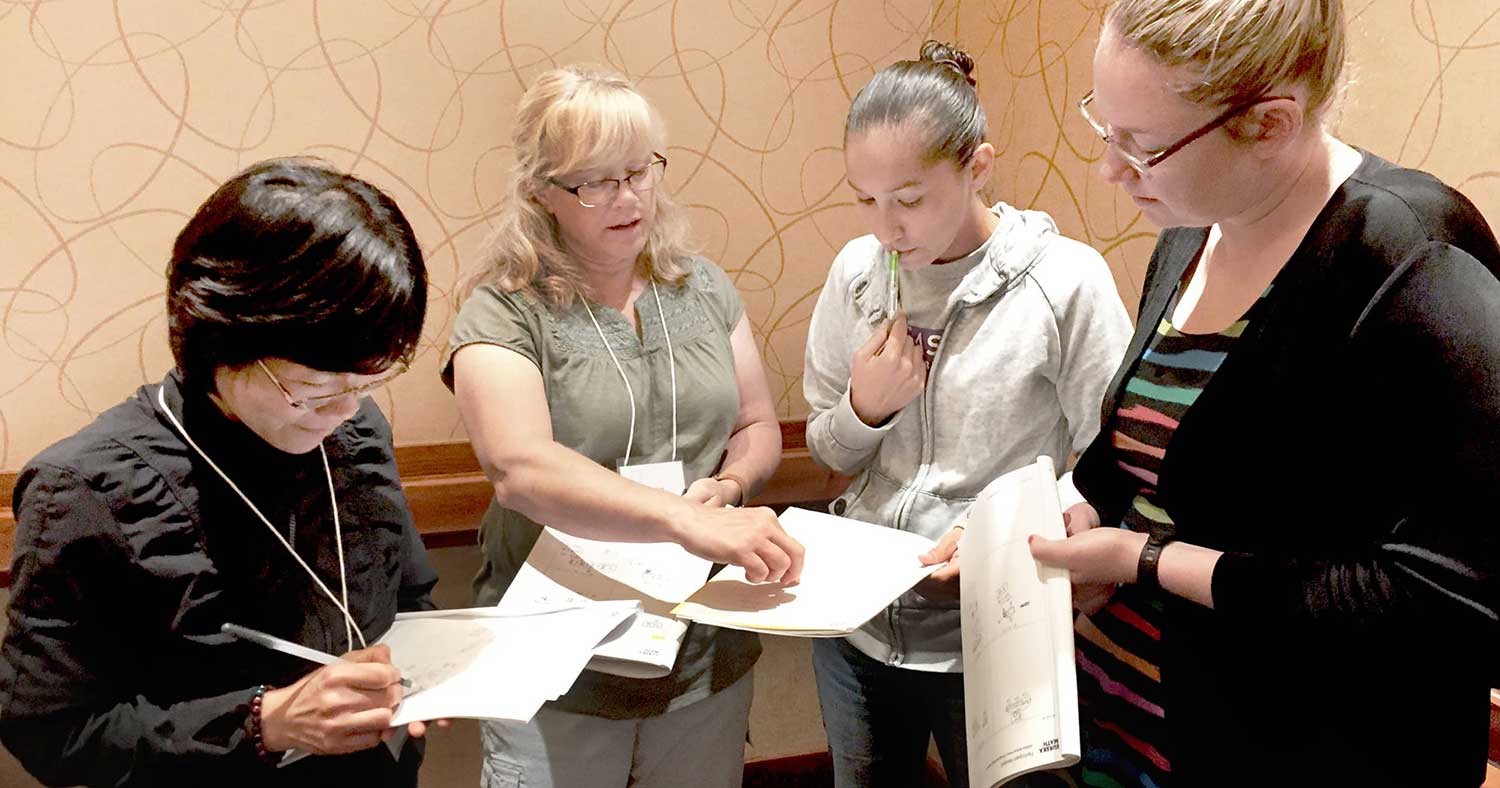

Professional Learning from a Trusted Colleague
Our math team members have crafted a series of professional development sessions and personalized coaching bundles to support both teachers new to Eureka Math² and experienced implementers.
Flexible lessons allow teachers to focus on the needs of their students.

Do you have any questions you would want to ask our experts? Check out our Frequently Asked Questions for answers to our most-received queries. Are there other questions you have? We’re here to help.

See how our curricula leverage a similar learning design to help students build enduring knowledge.
Every child is capable of greatness.
- Job Openings
- Digital Support
- Print Support
- Media Inquiries
Let’s Connect
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- System Status
- CA Residents: Do Not Sell My Info
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 14 Answer Key
Engage ny eureka math 1st grade module 2 lesson 14 answer key, eureka math grade 1 module 2 lesson 14 sprint answer key.
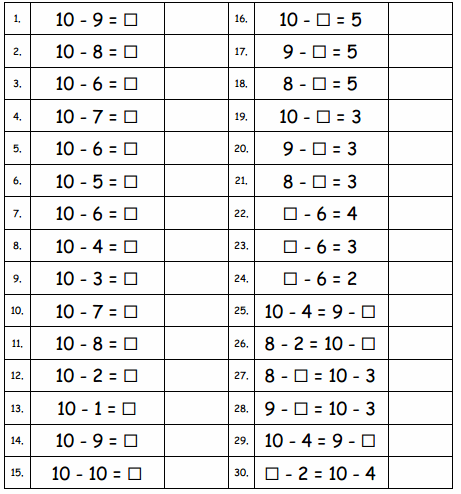
Question 1. 10 – 9 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 2. 10 – 8 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two.
Question 3. 10 – 6 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 6 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from ten then we got four.
Question 4. 10 – 7 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 5. 10 – 6 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 6 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from ten then we got four.
Question 6. 10 – 5 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 5 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from ten then we got five.
Question 7. 10 – 6 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 6 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from ten then we got four.
Question 8. 10 – 4 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 4 = 6 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract four from ten then we got six.
Question 9. 10 – 3 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 3 = 7 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract three from ten then we got seven.
Question 10. 10 – 7 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 11. 10 – 8 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two.
Question 12. 10 – 2 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 2 = 8 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract two from ten then we got eight.
Question 13. 10 – 1 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 1 = 9 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract one from ten then we got nine.
Question 14. 10 – 9 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 15. 10 – 10 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 10 = 0 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract ten from ten then we got zero.
Question 16. 10 – ☐ = 5 Answer: 10 – 5 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from ten then we got five.
Question 17. 9 – ☐ = 5 Answer: 9 – 4 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract four from nine then we got five.
Question 18. 8 – ☐ = 5 Answer: 8 – 3 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract three from eight then we got five.
Question 19. 10 – ☐ = 3 Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 20. 9 – ☐ = 3 Answer: 9 – 6 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from nine then we got three.
Question 21. 8 – ☐ = 3 Answer: 8 – 5 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from eight then we got three.
Question 22. ☐ – 6 = 4 Answer: 10 – 6 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from ten then we got four.
Question 23. ☐ – 6 = 3 Answer: 9 – 6 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from nine then we got three.
Question 24. ☐ – 6 = 2 Answer: 8 – 6 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from eight then we got two.
Question 25. 10 – 4 = 9 – ☐ Answer: 10 – 4 = 9 – 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract four from ten then we got six. Subtract three from nine then we got six. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 26. 8 – 2 = 10 – ☐ Answer: 8 – 2 = 10 – 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract two from eight then we got six. Subtract four from ten then we got six. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 27. 8 – ☐ = 10 – 3 Answer: 8 – 1 = 10 – 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract one from eight then we got seven. Subtract three from ten then we got seven. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 28. 9 – ☐ = 10 – 3 Answer: 9 – 2 = 10 – 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract two from nine then we got seven. Subtract three from ten then we got seven. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 29. 10 – 4 = 9 – ☐ Answer: 10 – 4 = 9 – 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract four from ten then we got six. Subtract three from nine then we got six. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 30. ☐ – 2 = 10 – 4 Answer: 8 – 2 = 10 – 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract two from eight then we got six. Subtract four from ten then we got six. Both are equal number sentences.
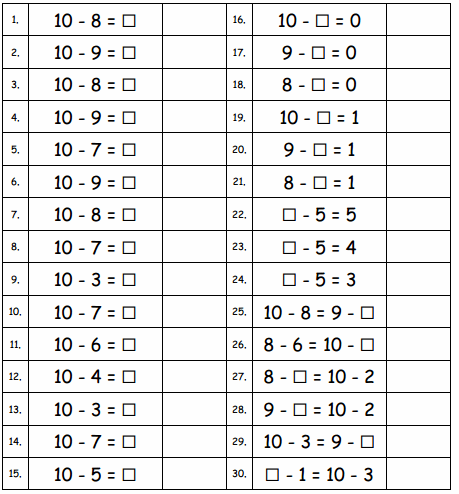
Question 1. 10 – 8 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two.
Question 2. 10 – 9 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 3. 10 – 8 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two.
Question 4. 10 – 9 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 5. 10 – 7 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 6. 10 – 9 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 7. 10 – 8 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two.
Question 8. 10 – 7 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 11. 10 – 6 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 6 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from ten then we got four.
Question 12. 10 – 4 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 4 = 6 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract four from ten then we got six.
Question 13. 10 – 3 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 3 = 7 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract three from ten then we got seven.
Question 14. 10 – 7 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 15. 10 – 5 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 5 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from ten then we got five.
Question 16. 10 – ☐ = 0 Answer: 10 – 10 = 0 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract ten from ten then we got zero.
Question 17. 9 – ☐ = 0 Answer: 9 – 9 = 0 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from nine then we got zero.
Question 18. 8 – ☐ = 0 Answer: 8 – 8 = 0 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from eight then we got zero.
Question 19. 10 – ☐ = 1 Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 20. 9 – ☐ = 1 Answer: 9 – 8 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from nine then we got one.
Question 21. 8 – ☐ = 1 Answer: 8 – 7 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from eight then we got one.
Question 22. ☐ – 5 = 5 Answer: 10 – 5 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from ten then we got five.
Question 23. ☐ – 5 = 4 Answer: 9 – 5 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from nine then we got four.
Question 24. ☐ – 5 = 3 Answer: 8 – 5 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from eight then we got three.
Question 25. 10 – 8 = 9 – ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 9 – 7 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two. Subtract seven from nine then we got two. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 26. 8 – 6 = 10 – ☐ Answer: 8 – 6 = 10 -8 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from eight then we got two. Subtract eight from ten then we got two. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 27. 8 – ☐ = 10 – 2 Answer: 8 – 0 = 10 – 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract zero from eight then we got eight. Subtract two from ten then we got eight. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 28. 9 – ☐ = 10 – 2 Answer: 9 – 1 = 10 – 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract one from nine then we got eight. Subtract two from ten then we got eight. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 29. 10 – 3 = 9 – ☐ Answer: 10 – 3 = 9 – 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract three from ten then we got seven. Subtract two from nine then we got seven. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 30. ☐ – 1 = 10 – 3 Answer: 8 – 1 = 10 – 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract one from eight then we got seven. Subtract three from ten then we got seven. Both are equal number sentences.
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 14 Problem Set Answer Key
Question 1. Match the pictures with the number sentences.
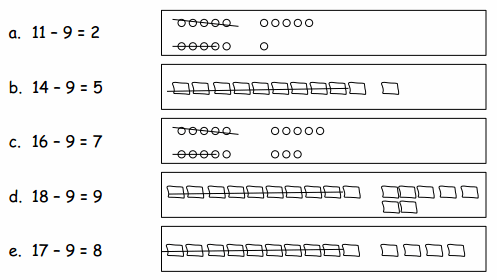
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 14 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 14 Homework Answer Key
Circle 10 and subtract. Make a number bond.
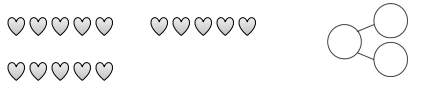
Question 6. Complete the number bond, and write the number sentence that helped you.
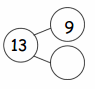
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Download the Eureka Math Solutions for Grades Pre K -12 in PDF format and make your toggling between homework and classroom quite seamless. Learn, Practice, and Succeed using the Extra Practice, Assessment Tests, Chapter Test, Review Tests available in all the Chapterwise Eureka Math Answers. ... FAQs on Eureka Math Answers for Grades Pre K, K ...
A Story of Units 1•2 G1-M2-Lesson 8 1. Solve. Make math drawings using the ten-frame to show how you made ten to solve. 8 + 8 = 𝟏𝟏𝟏𝟏+ = a new expression, 10 + 6. 2. Make math drawings using ten-frames to solve. Circle the true number sentences. Write an X to show number sentences that are not true.
Lesson 4 Answer Key 2• 8 Lesson 4 Problem Set 1. 2 parallel lines of different lengths drawn 2. 2 parallel lines of the same length drawn 3. a. Both pairs of sides highlighted b. 1 pair of sides highlighted c. Both pairs of sides highlighted d. Both pairs of sides highlighted and boxes drawn around all 4 angles e. 1 pair of sides highlighted f.
As the creator of Engage NY Math and Eureka Math, Great Minds is the only place where you can get print editions of the PK-12 curriculum.Our printed materials are available in two configurations: Learn, Practice, Succeed, or student workbooks, teacher editions, assessment and fluency materials. The Learn, Practice, Succeed configuration is available for grades K-8 and offers teachers ...
Eureka Math. Eureka Math® Grade 1 Module 3 TEKS EDITION Answer Key. ... A STORY OF UNITS TEKS EDITION Lesson 2 Answer Key 1 • 3 Module 3: Ordering and Comparing Length Measurements as Numbers 199 ... Homework 1. 1 2. 7 cm; 8 cm 3. 1 4. Model drawn; 11 + 4 = 15 or 15 − 11 = 4; 4 cm
K.G.1 K.G.2 K.G.4 K.MD.3 A Two-Dimensional Flat Shapes Lesson 1: Find and describe flat triangles, squares, rectangles, hexagons, and circles using informal language without naming . Lesson 2: Explain decisions about classifications of triangles into categories using variants and non-examples. Identify shapes as triangles.
Lesson 1: Find and describe flat triangles, squares, rectangles, hexagons, and circles using informal language without naming. •Homework Helper 2 GK-M2-Lesson 1 Draw a line from the shape to its matching object. This shape has no corners or straight lines. It is round like a clock. I see shapes all around me! This shape has four sides that
Bundle options are available for all of our materials (print, digital, PD, etc.). Prices vary by grade and size of class set. Certain grade-levels do not include all packets due to the nature of the grade-level content. Student workbooks are available in class sets of 20, 25, and 30. Prices vary by size of class set.
McGraw Hill Math Grade 8 Lesson 10.2 Answer Key Powers McGraw Hill Math Grade 8 Lesson 10.1 Answer Key Multiplying and Dividing Exponents McGraw Hill Math Grade 4 Chapter 11 Test Answer Key
For Math Grades 6-12, the answers are included in the "Teacher Materials" documents available on the module landing pages. If you navigate to a Math grade level, you can click on the module number in the dynamic "Curriculum Map" on the left to navigate to a module landing page.
Here you'll find curriculum files, lesson plans, core and supplemental materials, video series and more. Use the filters on the left to refine your results. Math ... Eureka Math Equip is the first adaptive diagnostic assessment built for Eureka Math . This suite of digital resources helps teachers identify and...
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 1 Lesson 2For more Eureka Math (EngageNY) videos and other resources, please visit http://EMBARC.onlinePLEASE leave a mes...
bigstock-rear-view-of-students-raising-423365522-1200px.jpg. The New York State Education Department discontinued support for the EngageNY.org website on July 7, 2022. The NYSED encourages educators to download any EngageNY content they wish to use in the future from our archive sites below. All ELA and mathematics curriculum files will be ...
Now, with expert-verified solutions from Eureka Math, Algebra 1 Modules 1, 2, and 3 1st Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Eureka Math, Algebra 1 Modules 1, 2, and 3 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step.
Through an intentional integration of digital resources, a focused approach to encouraging student discourse, and by connecting lessons to real-world math, students stay engaged in the learning. Get access to the curriculum. Through this knowledge-building approach, Eureka Math² helps teachers unlock the greatness in every child.
December 5, 2023 / By Prasanna. Eureka Math Grade 1 Answer Key provided facilitates learning outside the classroom. The Solutions provided bridge the gap between the way maths was once taught. Eureka Math Grade 1 Answers help you to understand the mathematical concepts much easier as well as to enhance problem-solving skills.
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 14 Homework Answer Key. Circle 10 and subtract. Make a number bond. Question 1. 15 - 9 = ___ Answer: 15 - 9 = 6 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. In the above image we can observe a number sentence 15 - 9 = 6.