- Utility Menu
- Writing Center
- Writing Program
- Senior Thesis Writing Guides
The senior thesis is typically the most challenging writing project undertaken by undergraduate students. The writing guides below aim to introduce students both to the specific methods and conventions of writing original research in their area of concentration and to effective writing process.
- Brief Guides to Writing in the Disciplines
- Course-Specific Writing Guides
- Disciplinary Writing Guides
- Gen Ed Writing Guides

Important Addresses
Harvard College
University Hall Cambridge, MA 02138
Harvard College Admissions Office and Griffin Financial Aid Office
86 Brattle Street Cambridge, MA 02138
Social Links
If you are located in the European Union, Iceland, Liechtenstein or Norway (the “European Economic Area”), please click here for additional information about ways that certain Harvard University Schools, Centers, units and controlled entities, including this one, may collect, use, and share information about you.
- Application Tips
- Navigating Campus
- Preparing for College
- How to Complete the FAFSA
- What to Expect After You Apply
- View All Guides
- Parents & Families
- School Counselors
- Información en Español
- Undergraduate Viewbook
- View All Resources
Search and Useful Links
Search the site, search suggestions, alert: harvard yard closed to the public.
Please note, Harvard Yard gates are currently closed. Entry will only be permitted to those with a Harvard ID via Johnston, Thayer, Widener, Sever and Solomon (Lamont) Gates. Guests are not allowed.
Last Updated: April 25, 2:24pm
Open Alert: Harvard Yard Closed to the Public
Preparing for a senior thesis.

Every year, a little over half of Harvard’s senior class chooses to pursue a senior thesis. While the senior thesis looks a little different from field to field, one thing remains the same: completion of a senior thesis is a serious and challenging endeavor that requires the student to make a genuine intellectual contribution to their field of interest.
The senior thesis is a significant task for students to undertake, but there is a variety of support resources available here at Harvard to ensure that seniors can make the best of their senior thesis experience.

Wandering the library stacks at Widener.
I do most of my research in Widener Library. Hannah Martinez
As a rising senior in the History department, I am planning on pursuing a senior thesis on the history and use of the SAT in college admissions, and I am using the following support systems and resources to research and write my thesis:
- Staff at the History department. Every student within the department is assigned an academic advisor, who is a graduate student studying History at Harvard and knows the support available within the department. My academic advisor has helped me throughout the thesis process by connecting me with potential faculty members to advise my thesis and pick classes with a lighter course load so I can focus on completing my thesis. The Director of Undergraduate Studies in History (the History DUS) has also been pivotal in making sure that I attended a lot of information sessions about what the thesis looks like and how much of a commitment it is.
- History faculty at Harvard! All of my professors in History have been incredibly helpful in teaching me how to write like a historian, how to use primary sources in my essays, and how to undertake a serious research project over the course of a semester. Of course, while the thesis will require me to go far beyond what I’ve ever done before, I feel prepared to take on such a task because of the unwavering support from the History faculty. My mentor, Emma Rothschild, is one of the members of the faculty who has been invaluable in encouraging me to go as far as I am able.
- And last but certainly not least: funding. Funding, whether in term-time of the summer before senior year, is crucial towards making the senior thesis possible. Harvard’s Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships is dedicated to connecting Harvard students to funding sources across the university so they can pursue their research and get paid for it. This summer, I received a grant from the university of almost $2,000 so I am able to travel to libraries, buy books, and potentially take time off of work and do my research. Without such a grant, it would be incredibly difficult for me to do enough research so I can write a thesis this upcoming fall.
As you can see, there are multiple avenues for support and resources here at Harvard so your senior thesis is as easy as possible. While the senior thesis is still a challenging project that will take up a lot of time, Harvard’s resources make it possible for senior students to do their very best in all of their theses. I’m excited to start writing this fall!
Hannah Class of '23 Alumni
Hello! My name is Hannah, and I am a rising senior at Harvard concentrating in History from southeast Los Angeles County.

Student Voices
How the mellon mays undergraduate fellowship propelled my love of archives into academic aspirations.

Beginning my senior thesis: A personal commitment to community and justice
Amy Class of '23 Alumni
Exploring Research at Harvard: Social Studies Edition
Olga Class of '22 Alumni

- Utility Menu
- ARC Scheduler
- Student Employment
- Senior Theses
Doing a senior thesis is an exciting enterprise. It’s often the first time students are engaging in truly original research and trying to develop a significant contribution to a field of inquiry. But as joyful as an independent research process can be, you don’t have to go it alone. It’s important to have support as you navigate such a large endeavor, and the ARC is here to offer one of those layers of support.
Whether or not to write a senior thesis is just the first in a long line of questions thesis writers need to consider. In addition to questions about the topic and scope of your thesis, there are questions about timing, schedule, and support. For example, if you are collecting data, when should data collection start and when should it be completed? What kind of schedule will you write on? How will you work with your adviser? Do you want to meet with your adviser about your progress once a month? Once a week? What other resources can you turn to for information, feedback, and support?
Even though there is a lot to think about and a lot to do, doing a thesis really can be an enjoyable experience! Keep reminding yourself why you chose this topic and why you care about it.
Tips for Tackling Big Projects:
Break the process down into manageable chunks.
- When you’re approaching a big project, it can seem overwhelming to look at the whole thing at once, so it’s essential to identify the smaller steps that will move you towards the completed project.
- Your adviser is best suited to help you break down the thesis process with field-specific advice.
- If you need to refine the breakdown further so it makes sense for you, schedule an appointment with an Academic Coach . An academic coach can help you think through the steps in a way that works for you.
Schedule brief writing sessions at regular times.
- Pre-determine the time, place, and duration.
- Keep it short (15 to 60 minutes).
- Have a clear and reasonable goal for each writing session.
- Make it a regular event (every day, every other day, MWF).
- time is not wasted deciding to write if it’s already in your calendar;
- keeping sessions short reduces the competition from other tasks that are not getting done;
- having an achievable goal for each session provides a sense of accomplishment (a reward for your work);
- writing regularly can turn into a productive habit.
Create accountability structures.
- In addition to having a clear goal for each writing session, it's important to have clear goals for each week and to find someone to communicate these goals to, such as your adviser, a “thesis buddy,” your roommate, etc. Communicating your goals and progress to someone else creates a useful sense of accountability.
- If your adviser is not the person you are communicating your progress to on a weekly basis, then request to set up a structure with your adviser that requires you to check in at less frequent but regular intervals.
- Commit to attending Accountability Hours at the ARC on the same day every week. Making that commitment will add both social support and structure to your week. Use the ARC Scheduler to register for Accountability Hours.
- Set up an accountability group in your department or with thesis writers from different departments.
Create feedback structures.
- It’s important to have a means for getting consistent feedback on your work and to get that feedback early. Work on large projects often lacks the feeling of completeness, so don’t wait for a whole section (and certainly not the whole thesis) to feel “done” before you get feedback on it!
- Your thesis adviser is typically the person best positioned to give you feedback on your research and writing, so communicate with your adviser about how and how often you would like to get feedback.
- If your adviser isn’t able to give you feedback with the frequency you’d like, then fill in the gaps by creating a thesis writing group or exploring if there is already a writing group in your department or lab.
- The Harvard College Writing Center is a great resource for thesis feedback. Writing Center Senior Thesis Tutors can provide feedback on the structure, argument, and clarity of your writing and help with mapping out your writing plan. Visit the Writing Center website to schedule an appointment with a thesis tutor .
Accept that there will be some anxious moments.
- To reduce this source of anxiety, try keeping a separate document where you jot down ideas on how your research questions or central argument might be clarifying or changing as you research and write. Doing this will enable you to stay focused on the section you are working on and to stop worrying about forgetting the new ideas that are emerging.
- You might feel anxious when you realize that you need to update your argument in response to the evidence you have gathered or the new thinking your writing has unleashed. Know that that is OK. Research and writing are iterative processes – new ideas and new ways of thinking are what makes progress possible.
- Breaking down big projects into manageable chunks and mapping out a schedule for working through each chunk is one way to reduce this source of anxiety. It’s reassuring to know you are working towards the end even if you cannot quite see how it will turn out.
- It may be that your thesis or dissertation never truly feels “done” to you, but that’s okay. Academic inquiry is an ongoing endeavor.
Focus on what works for you.
- Just because your roommate wrote 10 pages in a day doesn’t mean that’s the right pace or strategy for you.
- If you are having trouble figuring out what works for you, use the ARC Scheduler to make an appointment with an Academic Coach , who can help you come up with daily, weekly, and semester-long plans.
Use your resources.
- There’s a lot of the thesis writing process that has to be done independently, but there are also a lot of free resources at Harvard to help you do the work.
- If you’re having trouble finding a source, email your question or set up a research consult via Ask a Librarian .
- If you’re looking for additional feedback or help with any aspect of writing, contact the Harvard College Writing Center . The Writing Center has Senior Thesis Tutors who will read drafts of your thesis (more typically, parts of your thesis) in advance and meet with you individually to talk about structure, argument, clear writing, and mapping out your writing plan.
- If you need help with breaking down your project or setting up a schedule for the week, the semester, or until the deadline, use the ARC Scheduler to make an appointment with an Academic Coach .
- If you would like an accountability structure for social support and to keep yourself on track, come to Accountability Hours at the ARC.
Accordion style
- Assessing Your Understanding
- Building Your Academic Support System
- Common Class Norms
- Effective Learning Practices
- First-Year Students
- How to Prepare for Class
- Interacting with Instructors
- Know and Honor Your Priorities
- Memory and Attention
- Minimizing Zoom Fatigue
- Note-taking
- Office Hours
- Perfectionism
- Scheduling Time
- Study Groups
- Tackling STEM Courses
- Test Anxiety
Senior Honors Thesis Timeline
Junior year.
- Decide on a thesis topic or approach.
- Conduct background research to determine the viability of your topic.
- Begin drafting a thesis proposal.
- If required in your major department, submit your thesis proposal in the second semester of your junior year.
- Contact possible faculty advisors and readers.
- Seek funding for your research; note funding deadlines.
- Determine whether your research methods will require IRB approval.
- Make a one-on-one appointment with the reference librarian in your area of focus.
Fall Semester of Senior Year
By the end of september, you should:.
- Finalize your decision to write an honors thesis.
- Finalize your topic and research approach.
- Confirm primary thesis advisor and secondary reader.
- Think about length, breadth, and size of your finished thesis. Consider chapter breakdowns or other forms of presenting the finished product.
- Attend informational meetings and understand all requirements.
- Create your own project timeline and goals.
- Submit Thesis Honors Candidate Form . The chairperson of your major department must sign this form. Must be submitted by the the sixth week of the semester.
- Conduct research in library, lab, or field.
- Meet with librarians for guidance on conducting advanced library or electronic research.
- Gather, record, and categorize information as you find it. Keep accurate bibliographic notes and organized files.
- Keep a journal to record your ideas related to thesis topic and research discoveries.
- Begin writing. You should be able to draft some introductory sections of your thesis, including your hypothesis, governing question, or thesis statement, as well as your literature review, methodology, and definitions of terms.
- Establish a regular meeting time with your primary advisor and provide regular (weekly) progress reports or written drafts to advisors.
- Meet with an ARC writing consultant or join a writing group to help you stay on track.
November and Early December
- Begin to draft a chapter (not necessarily the first chapter.)
- Reassess chapter breakdowns; work on outline of thesis as whole.
- Mid-year assessment: You and your advisor should assess your progress so far to determine if you should continue to pursue the honors thesis in the spring or switch to a senior project or independent study.
- Plan detailed research and writing agenda for winter break. If you are doing a traditional research-based thesis, you should plan to write a substantial amount over break.
Spring Semester of Senior Year
- Submit a draft of your first chapter or section of your thesis to your advisor. Remember to include a bibliography with any draft you submit to your committee members.
- Schedule a meeting with your thesis advisor or thesis committee to discuss your work completed over winter break.
- Plan a new timeline for spring. Plan to have the thesis substantially written BEFORE spring break.
- Continue to send regular progress reports to your committee.
February and March
- Write your thesis section by section and submit drafts to your primary advisor for revision comments.
- Be very careful to cite sources correctly and incorporate them into your writing so as to avoid accidental plagiarism.
- Set a date and time for your defense in April; all three committee members must be present at the defense. Remember to book a room that has everything you need (for example, internet connection or a movie screen).
- You should be rewriting and revising by early April. Now is the time to pay attention to clarity of expression and prose style; you may need to work on major structural changes to your outline or clarify your logic.
- Rewrite and revise according to your advisors' recommendations. Be sure the committee is in agreement on what they expect from you during the revision process.
- Schedule a meeting with your entire committee so there will be no unpleasant surprises during the defense.
- Submit your completed thesis with complete and accurate bibliography to your committee at least two weeks before your defense date.
- Your DEFENSE must take place before finals for you to graduate in May.
- First day of finals: This is the DEADLINE for "Recommendation for Thesis Honors" form to be submitted by your honors thesis advisor to the degree audit coordinator in Dowling Hall.
- Your committee may ask you to correct or rewrite portions of your thesis after the defense but before you submit it to archives.
- Prepare the final document for archives. See the online guide for instructions and specifications.
- Submit your completed manuscript to Digital Collections & Archives.
- Enjoy Senior Week–you’ve earned it.

Honors Theses
What this handout is about.
Writing a senior honors thesis, or any major research essay, can seem daunting at first. A thesis requires a reflective, multi-stage writing process. This handout will walk you through those stages. It is targeted at students in the humanities and social sciences, since their theses tend to involve more writing than projects in the hard sciences. Yet all thesis writers may find the organizational strategies helpful.
Introduction
What is an honors thesis.
That depends quite a bit on your field of study. However, all honors theses have at least two things in common:
- They are based on students’ original research.
- They take the form of a written manuscript, which presents the findings of that research. In the humanities, theses average 50-75 pages in length and consist of two or more chapters. In the social sciences, the manuscript may be shorter, depending on whether the project involves more quantitative than qualitative research. In the hard sciences, the manuscript may be shorter still, often taking the form of a sophisticated laboratory report.
Who can write an honors thesis?
In general, students who are at the end of their junior year, have an overall 3.2 GPA, and meet their departmental requirements can write a senior thesis. For information about your eligibility, contact:
- UNC Honors Program
- Your departmental administrators of undergraduate studies/honors
Why write an honors thesis?
Satisfy your intellectual curiosity This is the most compelling reason to write a thesis. Whether it’s the short stories of Flannery O’Connor or the challenges of urban poverty, you’ve studied topics in college that really piqued your interest. Now’s your chance to follow your passions, explore further, and contribute some original ideas and research in your field.
Develop transferable skills Whether you choose to stay in your field of study or not, the process of developing and crafting a feasible research project will hone skills that will serve you well in almost any future job. After all, most jobs require some form of problem solving and oral and written communication. Writing an honors thesis requires that you:
- ask smart questions
- acquire the investigative instincts needed to find answers
- navigate libraries, laboratories, archives, databases, and other research venues
- develop the flexibility to redirect your research if your initial plan flops
- master the art of time management
- hone your argumentation skills
- organize a lengthy piece of writing
- polish your oral communication skills by presenting and defending your project to faculty and peers
Work closely with faculty mentors At large research universities like Carolina, you’ve likely taken classes where you barely got to know your instructor. Writing a thesis offers the opportunity to work one-on-one with a with faculty adviser. Such mentors can enrich your intellectual development and later serve as invaluable references for graduate school and employment.
Open windows into future professions An honors thesis will give you a taste of what it’s like to do research in your field. Even if you’re a sociology major, you may not really know what it’s like to be a sociologist. Writing a sociology thesis would open a window into that world. It also might help you decide whether to pursue that field in graduate school or in your future career.
How do you write an honors thesis?
Get an idea of what’s expected.
It’s a good idea to review some of the honors theses other students have submitted to get a sense of what an honors thesis might look like and what kinds of things might be appropriate topics. Look for examples from the previous year in the Carolina Digital Repository. You may also be able to find past theses collected in your major department or at the North Carolina Collection in Wilson Library. Pay special attention to theses written by students who share your major.
Choose a topic
Ideally, you should start thinking about topics early in your junior year, so you can begin your research and writing quickly during your senior year. (Many departments require that you submit a proposal for an honors thesis project during the spring of your junior year.)
How should you choose a topic?
- Read widely in the fields that interest you. Make a habit of browsing professional journals to survey the “hot” areas of research and to familiarize yourself with your field’s stylistic conventions. (You’ll find the most recent issues of the major professional journals in the periodicals reading room on the first floor of Davis Library).
- Set up appointments to talk with faculty in your field. This is a good idea, since you’ll eventually need to select an advisor and a second reader. Faculty also can help you start narrowing down potential topics.
- Look at honors theses from the past. The North Carolina Collection in Wilson Library holds UNC honors theses. To get a sense of the typical scope of a thesis, take a look at a sampling from your field.
What makes a good topic?
- It’s fascinating. Above all, choose something that grips your imagination. If you don’t, the chances are good that you’ll struggle to finish.
- It’s doable. Even if a topic interests you, it won’t work out unless you have access to the materials you need to research it. Also be sure that your topic is narrow enough. Let’s take an example: Say you’re interested in the efforts to ratify the Equal Rights Amendment in the 1970s and early 1980s. That’s a big topic that probably can’t be adequately covered in a single thesis. You need to find a case study within that larger topic. For example, maybe you’re particularly interested in the states that did not ratify the ERA. Of those states, perhaps you’ll select North Carolina, since you’ll have ready access to local research materials. And maybe you want to focus primarily on the ERA’s opponents. Beyond that, maybe you’re particularly interested in female opponents of the ERA. Now you’ve got a much more manageable topic: Women in North Carolina Who Opposed the ERA in the 1970s and 1980s.
- It contains a question. There’s a big difference between having a topic and having a guiding research question. Taking the above topic, perhaps your main question is: Why did some women in North Carolina oppose the ERA? You will, of course, generate other questions: Who were the most outspoken opponents? White women? Middle-class women? How did they oppose the ERA? Public protests? Legislative petitions? etc. etc. Yet it’s good to start with a guiding question that will focus your research.
Goal-setting and time management
The senior year is an exceptionally busy time for college students. In addition to the usual load of courses and jobs, seniors have the daunting task of applying for jobs and/or graduate school. These demands are angst producing and time consuming If that scenario sounds familiar, don’t panic! Do start strategizing about how to make a time for your thesis. You may need to take a lighter course load or eliminate extracurricular activities. Even if the thesis is the only thing on your plate, you still need to make a systematic schedule for yourself. Most departments require that you take a class that guides you through the honors project, so deadlines likely will be set for you. Still, you should set your own goals for meeting those deadlines. Here are a few suggestions for goal setting and time management:
Start early. Keep in mind that many departments will require that you turn in your thesis sometime in early April, so don’t count on having the entire spring semester to finish your work. Ideally, you’ll start the research process the semester or summer before your senior year so that the writing process can begin early in the fall. Some goal-setting will be done for you if you are taking a required class that guides you through the honors project. But any substantive research project requires a clear timetable.
Set clear goals in making a timetable. Find out the final deadline for turning in your project to your department. Working backwards from that deadline, figure out how much time you can allow for the various stages of production.
Here is a sample timetable. Use it, however, with two caveats in mind:
- The timetable for your thesis might look very different depending on your departmental requirements.
- You may not wish to proceed through these stages in a linear fashion. You may want to revise chapter one before you write chapter two. Or you might want to write your introduction last, not first. This sample is designed simply to help you start thinking about how to customize your own schedule.
Sample timetable
Avoid falling into the trap of procrastination. Once you’ve set goals for yourself, stick to them! For some tips on how to do this, see our handout on procrastination .
Consistent production
It’s a good idea to try to squeeze in a bit of thesis work every day—even if it’s just fifteen minutes of journaling or brainstorming about your topic. Or maybe you’ll spend that fifteen minutes taking notes on a book. The important thing is to accomplish a bit of active production (i.e., putting words on paper) for your thesis every day. That way, you develop good writing habits that will help you keep your project moving forward.
Make yourself accountable to someone other than yourself
Since most of you will be taking a required thesis seminar, you will have deadlines. Yet you might want to form a writing group or enlist a peer reader, some person or people who can help you stick to your goals. Moreover, if your advisor encourages you to work mostly independently, don’t be afraid to ask them to set up periodic meetings at which you’ll turn in installments of your project.
Brainstorming and freewriting
One of the biggest challenges of a lengthy writing project is keeping the creative juices flowing. Here’s where freewriting can help. Try keeping a small notebook handy where you jot down stray ideas that pop into your head. Or schedule time to freewrite. You may find that such exercises “free” you up to articulate your argument and generate new ideas. Here are some questions to stimulate freewriting.
Questions for basic brainstorming at the beginning of your project:
- What do I already know about this topic?
- Why do I care about this topic?
- Why is this topic important to people other than myself
- What more do I want to learn about this topic?
- What is the main question that I am trying to answer?
- Where can I look for additional information?
- Who is my audience and how can I reach them?
- How will my work inform my larger field of study?
- What’s the main goal of my research project?
Questions for reflection throughout your project:
- What’s my main argument? How has it changed since I began the project?
- What’s the most important evidence that I have in support of my “big point”?
- What questions do my sources not answer?
- How does my case study inform or challenge my field writ large?
- Does my project reinforce or contradict noted scholars in my field? How?
- What is the most surprising finding of my research?
- What is the most frustrating part of this project?
- What is the most rewarding part of this project?
- What will be my work’s most important contribution?
Research and note-taking
In conducting research, you will need to find both primary sources (“firsthand” sources that come directly from the period/events/people you are studying) and secondary sources (“secondhand” sources that are filtered through the interpretations of experts in your field.) The nature of your research will vary tremendously, depending on what field you’re in. For some general suggestions on finding sources, consult the UNC Libraries tutorials . Whatever the exact nature of the research you’re conducting, you’ll be taking lots of notes and should reflect critically on how you do that. Too often it’s assumed that the research phase of a project involves very little substantive writing (i.e., writing that involves thinking). We sit down with our research materials and plunder them for basic facts and useful quotations. That mechanical type of information-recording is important. But a more thoughtful type of writing and analytical thinking is also essential at this stage. Some general guidelines for note-taking:
First of all, develop a research system. There are lots of ways to take and organize your notes. Whether you choose to use note cards, computer databases, or notebooks, follow two cardinal rules:
- Make careful distinctions between direct quotations and your paraphrasing! This is critical if you want to be sure to avoid accidentally plagiarizing someone else’s work. For more on this, see our handout on plagiarism .
- Record full citations for each source. Don’t get lazy here! It will be far more difficult to find the proper citation later than to write it down now.
Keeping those rules in mind, here’s a template for the types of information that your note cards/legal pad sheets/computer files should include for each of your sources:
Abbreviated subject heading: Include two or three words to remind you of what this sources is about (this shorthand categorization is essential for the later sorting of your sources).
Complete bibliographic citation:
- author, title, publisher, copyright date, and page numbers for published works
- box and folder numbers and document descriptions for archival sources
- complete web page title, author, address, and date accessed for online sources
Notes on facts, quotations, and arguments: Depending on the type of source you’re using, the content of your notes will vary. If, for example, you’re using US Census data, then you’ll mainly be writing down statistics and numbers. If you’re looking at someone else’s diary, you might jot down a number of quotations that illustrate the subject’s feelings and perspectives. If you’re looking at a secondary source, you’ll want to make note not just of factual information provided by the author but also of their key arguments.
Your interpretation of the source: This is the most important part of note-taking. Don’t just record facts. Go ahead and take a stab at interpreting them. As historians Jacques Barzun and Henry F. Graff insist, “A note is a thought.” So what do these thoughts entail? Ask yourself questions about the context and significance of each source.
Interpreting the context of a source:
- Who wrote/created the source?
- When, and under what circumstances, was it written/created?
- Why was it written/created? What was the agenda behind the source?
- How was it written/created?
- If using a secondary source: How does it speak to other scholarship in the field?
Interpreting the significance of a source:
- How does this source answer (or complicate) my guiding research questions?
- Does it pose new questions for my project? What are they?
- Does it challenge my fundamental argument? If so, how?
- Given the source’s context, how reliable is it?
You don’t need to answer all of these questions for each source, but you should set a goal of engaging in at least one or two sentences of thoughtful, interpretative writing for each source. If you do so, you’ll make much easier the next task that awaits you: drafting.
The dread of drafting
Why do we often dread drafting? We dread drafting because it requires synthesis, one of the more difficult forms of thinking and interpretation. If you’ve been free-writing and taking thoughtful notes during the research phase of your project, then the drafting should be far less painful. Here are some tips on how to get started:
Sort your “evidence” or research into analytical categories:
- Some people file note cards into categories.
- The technologically-oriented among us take notes using computer database programs that have built-in sorting mechanisms.
- Others cut and paste evidence into detailed outlines on their computer.
- Still others stack books, notes, and photocopies into topically-arranged piles.There is not a single right way, but this step—in some form or fashion—is essential!
If you’ve been forcing yourself to put subject headings on your notes as you go along, you’ll have generated a number of important analytical categories. Now, you need to refine those categories and sort your evidence. Everyone has a different “sorting style.”
Formulate working arguments for your entire thesis and individual chapters. Once you’ve sorted your evidence, you need to spend some time thinking about your project’s “big picture.” You need to be able to answer two questions in specific terms:
- What is the overall argument of my thesis?
- What are the sub-arguments of each chapter and how do they relate to my main argument?
Keep in mind that “working arguments” may change after you start writing. But a senior thesis is big and potentially unwieldy. If you leave this business of argument to chance, you may end up with a tangle of ideas. See our handout on arguments and handout on thesis statements for some general advice on formulating arguments.
Divide your thesis into manageable chunks. The surest road to frustration at this stage is getting obsessed with the big picture. What? Didn’t we just say that you needed to focus on the big picture? Yes, by all means, yes. You do need to focus on the big picture in order to get a conceptual handle on your project, but you also need to break your thesis down into manageable chunks of writing. For example, take a small stack of note cards and flesh them out on paper. Or write through one point on a chapter outline. Those small bits of prose will add up quickly.
Just start! Even if it’s not at the beginning. Are you having trouble writing those first few pages of your chapter? Sometimes the introduction is the toughest place to start. You should have a rough idea of your overall argument before you begin writing one of the main chapters, but you might find it easier to start writing in the middle of a chapter of somewhere other than word one. Grab hold where you evidence is strongest and your ideas are clearest.
Keep up the momentum! Assuming the first draft won’t be your last draft, try to get your thoughts on paper without spending too much time fussing over minor stylistic concerns. At the drafting stage, it’s all about getting those ideas on paper. Once that task is done, you can turn your attention to revising.
Peter Elbow, in Writing With Power, suggests that writing is difficult because it requires two conflicting tasks: creating and criticizing. While these two tasks are intimately intertwined, the drafting stage focuses on creating, while revising requires criticizing. If you leave your revising to the last minute, then you’ve left out a crucial stage of the writing process. See our handout for some general tips on revising . The challenges of revising an honors thesis may include:
Juggling feedback from multiple readers
A senior thesis may mark the first time that you have had to juggle feedback from a wide range of readers:
- your adviser
- a second (and sometimes third) faculty reader
- the professor and students in your honors thesis seminar
You may feel overwhelmed by the prospect of incorporating all this advice. Keep in mind that some advice is better than others. You will probably want to take most seriously the advice of your adviser since they carry the most weight in giving your project a stamp of approval. But sometimes your adviser may give you more advice than you can digest. If so, don’t be afraid to approach them—in a polite and cooperative spirit, of course—and ask for some help in prioritizing that advice. See our handout for some tips on getting and receiving feedback .
Refining your argument
It’s especially easy in writing a lengthy work to lose sight of your main ideas. So spend some time after you’ve drafted to go back and clarify your overall argument and the individual chapter arguments and make sure they match the evidence you present.
Organizing and reorganizing
Again, in writing a 50-75 page thesis, things can get jumbled. You may find it particularly helpful to make a “reverse outline” of each of your chapters. That will help you to see the big sections in your work and move things around so there’s a logical flow of ideas. See our handout on organization for more organizational suggestions and tips on making a reverse outline
Plugging in holes in your evidence
It’s unlikely that you anticipated everything you needed to look up before you drafted your thesis. Save some time at the revising stage to plug in the holes in your research. Make sure that you have both primary and secondary evidence to support and contextualize your main ideas.
Saving time for the small stuff
Even though your argument, evidence, and organization are most important, leave plenty of time to polish your prose. At this point, you’ve spent a very long time on your thesis. Don’t let minor blemishes (misspellings and incorrect grammar) distract your readers!
Formatting and final touches
You’re almost done! You’ve researched, drafted, and revised your thesis; now you need to take care of those pesky little formatting matters. An honors thesis should replicate—on a smaller scale—the appearance of a dissertation or master’s thesis. So, you need to include the “trappings” of a formal piece of academic work. For specific questions on formatting matters, check with your department to see if it has a style guide that you should use. For general formatting guidelines, consult the Graduate School’s Guide to Dissertations and Theses . Keeping in mind the caveat that you should always check with your department first about its stylistic guidelines, here’s a brief overview of the final “finishing touches” that you’ll need to put on your honors thesis:
- Honors Thesis
- Name of Department
- University of North Carolina
- These parts of the thesis will vary in format depending on whether your discipline uses MLA, APA, CBE, or Chicago (also known in its shortened version as Turabian) style. Whichever style you’re using, stick to the rules and be consistent. It might be helpful to buy an appropriate style guide. Or consult the UNC LibrariesYear Citations/footnotes and works cited/reference pages citation tutorial
- In addition, in the bottom left corner, you need to leave space for your adviser and faculty readers to sign their names. For example:
Approved by: _____________________
Adviser: Prof. Jane Doe
- This is not a required component of an honors thesis. However, if you want to thank particular librarians, archivists, interviewees, and advisers, here’s the place to do it. You should include an acknowledgments page if you received a grant from the university or an outside agency that supported your research. It’s a good idea to acknowledge folks who helped you with a major project, but do not feel the need to go overboard with copious and flowery expressions of gratitude. You can—and should—always write additional thank-you notes to people who gave you assistance.
- Formatted much like the table of contents.
- You’ll need to save this until the end, because it needs to reflect your final pagination. Once you’ve made all changes to the body of the thesis, then type up your table of contents with the titles of each section aligned on the left and the page numbers on which those sections begin flush right.
- Each page of your thesis needs a number, although not all page numbers are displayed. All pages that precede the first page of the main text (i.e., your introduction or chapter one) are numbered with small roman numerals (i, ii, iii, iv, v, etc.). All pages thereafter use Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.).
- Your text should be double spaced (except, in some cases, long excerpts of quoted material), in a 12 point font and a standard font style (e.g., Times New Roman). An honors thesis isn’t the place to experiment with funky fonts—they won’t enhance your work, they’ll only distract your readers.
- In general, leave a one-inch inch margin on all sides. However, for the copy of your thesis that will be bound by the library, you need to leave a 1.25-inch margin on the left.
How do I defend my honors thesis?
Graciously, enthusiastically, and confidently. The term defense is scary and misleading—it conjures up images of a military exercise or an athletic maneuver. An academic defense ideally shouldn’t be a combative scene but a congenial conversation about the work’s merits and weaknesses. That said, the defense probably won’t be like the average conversation that you have with your friends. You’ll be the center of attention. And you may get some challenging questions. Thus, it’s a good idea to spend some time preparing yourself. First of all, you’ll want to prepare 5-10 minutes of opening comments. Here’s a good time to preempt some criticisms by frankly acknowledging what you think your work’s greatest strengths and weaknesses are. Then you may be asked some typical questions:
- What is the main argument of your thesis?
- How does it fit in with the work of Ms. Famous Scholar?
- Have you read the work of Mr. Important Author?
NOTE: Don’t get too flustered if you haven’t! Most scholars have their favorite authors and books and may bring one or more of them up, even if the person or book is only tangentially related to the topic at hand. Should you get this question, answer honestly and simply jot down the title or the author’s name for future reference. No one expects you to have read everything that’s out there.
- Why did you choose this particular case study to explore your topic?
- If you were to expand this project in graduate school, how would you do so?
Should you get some biting criticism of your work, try not to get defensive. Yes, this is a defense, but you’ll probably only fan the flames if you lose your cool. Keep in mind that all academic work has flaws or weaknesses, and you can be sure that your professors have received criticisms of their own work. It’s part of the academic enterprise. Accept criticism graciously and learn from it. If you receive criticism that is unfair, stand up for yourself confidently, but in a good spirit. Above all, try to have fun! A defense is a rare opportunity to have eminent scholars in your field focus on YOU and your ideas and work. And the defense marks the end of a long and arduous journey. You have every right to be proud of your accomplishments!

Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Atchity, Kenneth. 1986. A Writer’s Time: A Guide to the Creative Process from Vision Through Revision . New York: W.W. Norton.
Barzun, Jacques, and Henry F. Graff. 2012. The Modern Researcher , 6th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Elbow, Peter. 1998. Writing With Power: Techniques for Mastering the Writing Process . New York: Oxford University Press.
Graff, Gerald, and Cathy Birkenstein. 2014. “They Say/I Say”: The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing , 3rd ed. New York: W.W. Norton and Company.
Lamott, Anne. 1994. Bird by Bird: Some Instructions on Writing and Life . New York: Pantheon.
Lasch, Christopher. 2002. Plain Style: A Guide to Written English. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press.
Turabian, Kate. 2018. A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, Dissertations , 9th ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

The Senior Thesis
From the outset of their time at Princeton, students are encouraged and challenged to develop their scholarly interests and to evolve as independent thinkers.
The culmination of this process is the senior thesis, which provides a unique opportunity for students to pursue original research and scholarship in a field of their choosing. At Princeton, every senior writes a thesis or, in the case of some engineering departments, undertakes a substantial independent project.
Integral to the senior thesis process is the opportunity to work one-on-one with a faculty member who guides the development of the project. Thesis writers and advisers agree that the most valuable outcome of the senior thesis is the chance for students to enhance skills that are the foundation of future success, including creativity, intellectual engagement, mental discipline and the ability to meet new challenges.
Many students develop projects from ideas sparked in the classes they’ve taken; others fashion their topics on the basis of long-standing personal passions. Most thesis writers encounter the intellectual twists and turns of any good research project, where the questions emerge as they proceed, often taking them in unexpected directions.
Planning for the senior thesis starts in earnest in the junior year, when students complete a significant research project known as the junior paper. Students who plan ahead can make good use of the University's considerable resources, such as receiving University funds to do research in the United States or abroad. Other students use summer internships as a launching pad for their thesis. For some science and engineering projects, students stay on campus the summer before their senior year to get a head start on lab work.
Writing a thesis encourages the self-confidence and high ambitions that come from mastering a difficult challenge. It fosters the development of specific skills and habits of mind that augur well for future success. No wonder generations of graduates look back on the senior thesis as the most valuable academic component of their Princeton experience.
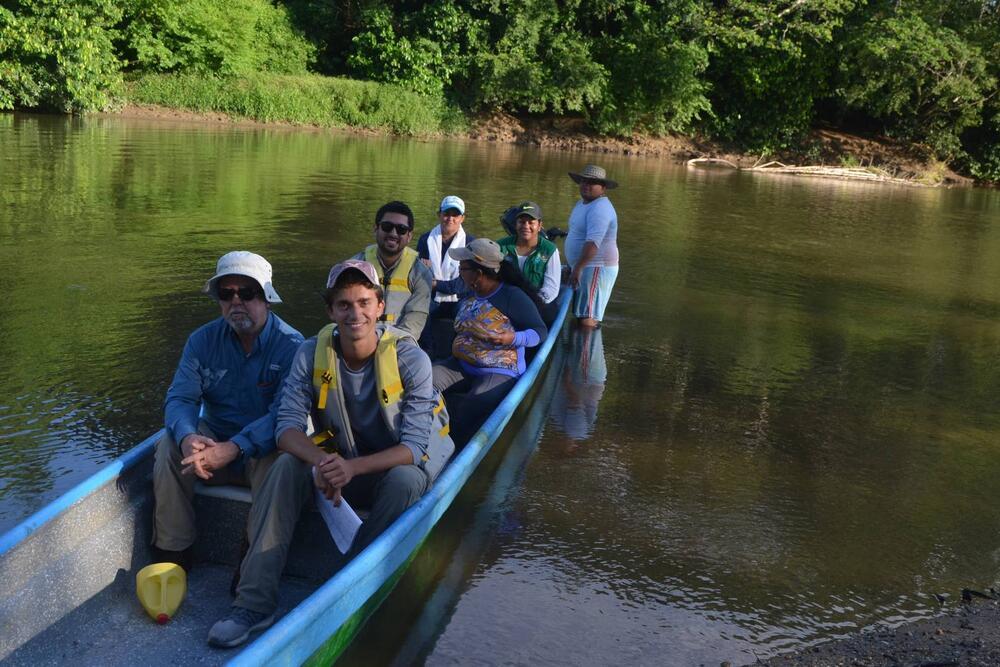
Navigating Colombia’s Magdalena River, One Story At A Time
For his senior thesis, Jordan Salama, a Spanish and Portuguese major, produced a nonfiction book of travel writing about the people and places along Colombia’s main river, the Magdalena.

Embracing the Classics to Inform Policymaking for Public Education
For her senior thesis, Emma Treadwayconsiders how the basic tenets of Stoicism — a school of philosophy that dates from 300 BCE — can teach students to engage empathetically with the world and address inequities in the classroom.

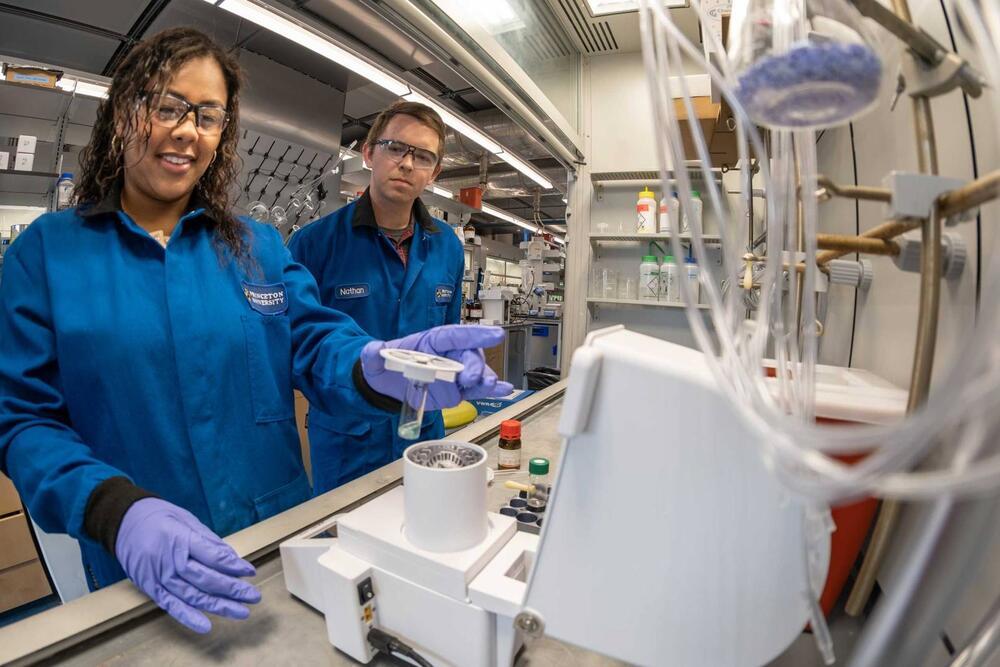
Creating A Faster, Cheaper and Greener Chemical Reaction
One way to make drugs more affordable is to make them cheaper to produce. For her senior thesis research, Cassidy Humphreys, a chemistry major with a passion for medicine, took on the challenge of taking a century-old formula at the core of many modern medications — and improving it.

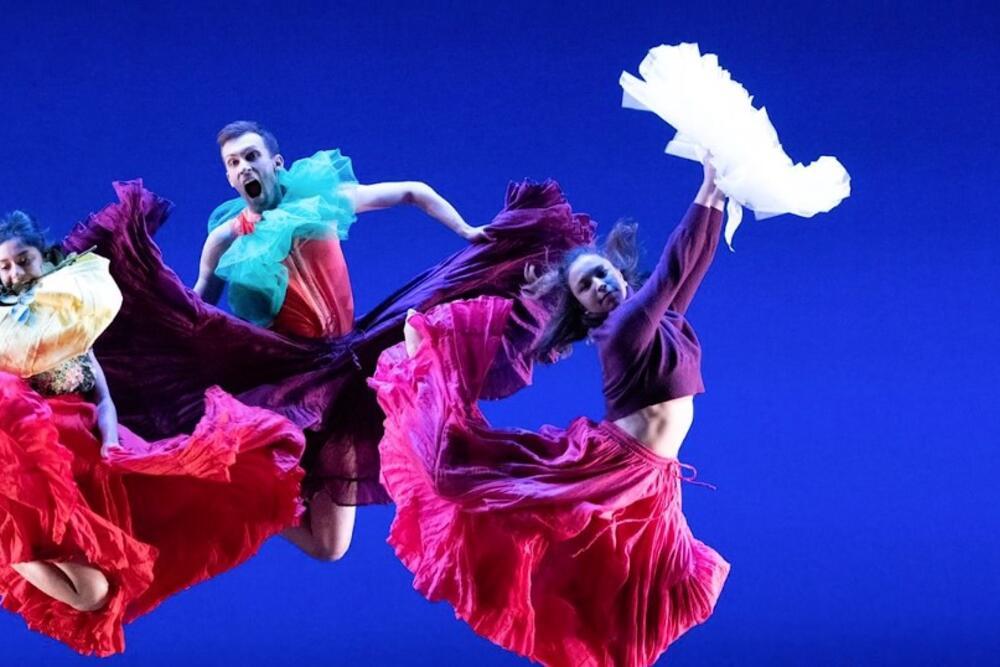
The Humanity of Improvisational Dance
Esin Yunusoglu investigated how humans move together and exist in a space — both on the dance floor and in real life — for the choreography she created as her senior thesis in dance, advised by Professor of Dance Susan Marshall.

From the Blog
The infamous senior thesis, revisiting wwii: my senior thesis, independent work in its full glory, advisers, independent work and beyond.

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
Preparing for your Senior Thesis Before your Senior Year: Tips on Finding a Thesis Adviser

If you’re caught up on some of my earlier posts , you’ll remember that I’ve been working on my Junior Papers all year, ultimately gearing up towards the independent work that my senior thesis will require. However, as an underclass student, I was definitely unclear about what the senior thesis process would entail. I thought it was something I wouldn’t have to worry about until my last year at Princeton when, in reality, it starts much earlier than that (scary!!).
Every thesis process is different depending on your department, so I can’t speak for all of them. However, in the Woodrow Wilson School, students start preparing for their theses during their junior year (in some majors, it starts even earlier!). For example, at the beginning and end of the fall semester, I attended information sessions that taught me what to expect from senior year and how to prepare for my thesis. The meetings helped me realize that I had to start looking for a thesis adviser. Although some students wait until the end of junior year or the beginning of senior year to choose an adviser, I plan to do research over the summer, and in order to apply for funding, it is helpful to have an adviser in mind early on.
Every student who writes a thesis must choose a thesis adviser. Some seniors I have spoken to have said that it’s helpful to meet with multiple potential advisers before selecting the one you wish to work with. For me, this presents a strange yet exciting power dynamic that I have never encountered before: for the first time, the student has a sense of agency and the ability to make their own decisions about a project from the very beginning.
So, what should I have in mind as I meet with potential advisers? How do I even select the potential advisers? I have compiled some advice below that I’ve received from various seniors.
Decide on a thesis topic. It doesn’t have to be a well-thought-out plan; it just needs to exist in some basic form. You shouldn’t select an adviser without a thesis topic! See tip number two to understand why.
Look through the list of faculty members in your department. Each faculty member should have a short description of themselves and their research interests next to their name. Use this description to select a few professors whose interests match up with yours/your thesis topic.
Email the professors. Make sure you have options before you make your final decision. Meet with each professor and explain your thesis topic. Go to the meeting prepared with some notes about your topic to show that you’re serious about it and that you’ve done some preliminary research.
Ask questions about their expectations! Is the professor an active adviser, or are they more hands-off? How often would the professor want to meet with you during your senior year? It is important to understand their expectations so that you aren’t blindsided senior year.
Make sure the professor is aware that you are meeting with other professors. Just as it is important to know the professor’s expectations of you, it is important they know your expectations of them. Transparency is so important during this process. Be clear from the beginning so that the professor knows nothing is set in stone yet.
The senior thesis process can feel far away and daunting, but as a junior, it isn’t as far away as it seems. Keeping these helpful tips in mind will give you a head start and make the process a lot less stressful!
— Andrea Reino, Social Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr


Senior Thesis
A senior thesis is more than a big project write-up. It is documentation of an attempt to contribute to the general understanding of some problem of computer science, together with exposition that sets the work in the context of what has come before and what might follow. In computer science, some theses involve building systems, some involve experiments and measurements, some are theoretical, some involve human subjects, and some do more than one of these things. Computer science is unusual among scientific disciplines in that current faculty research has many loose ends appropriate for undergraduate research.
Senior thesis projects generally emerge from collaboration with faculty. Students looking for senior thesis projects should tell professors they know, especially professors whose courses they are taking or have taken, that they are looking for things to work on. See the page on CS Research for Undergrads . Ideas often emerge from recent papers discussed in advanced courses. The terms in which some published research was undertaken might be generalized, relaxed, restricted, or applied in a different domain to see if changed assumptions result in a changed solution. Once a project gets going, it often seems to assume a life of its own.
To write a thesis, students may enroll in Computer Science 91r one or both terms during their senior year, under the supervision of their research advisor. Rising seniors may wish to begin thinking about theses over the previous summer, and therefore may want to begin their conversations with faculty during their junior spring—or even try to stay in Cambridge to do summer research.
An information session for those interested in writing a senior thesis is held towards the end of each spring semester. Details about the session will be posted to the [email protected] email list.
Students interested in commercializing ideas in their theses may wish to consult Executive Dean Fawwaz Habbal about patent protection. See Harvard’s policy for information about ownership of software written as part of your academic work.
Thesis Supervisor
You need a thesis supervisor. Normally this is a Harvard Computer Science faculty member. Joint concentrators (and, in some cases, non-joint concentrators) might have a FAS/SEAS Faculty member from a different field as their thesis supervisor. Exceptions to the requirement that the thesis supervisor is a CS or FAS/SEAS faculty member must be approved by the Director of Undergraduate Studies. For students whose advisor is not a Harvard CS faculty member, note that at least one of your thesis readers must be a Harvard CS faculty member, and we encourage you to talk with this faculty member regularly to help ensure that your thesis is appropriately relevant for Harvard Computer Science.
It’s up to you and your supervisor how frequently you meet and how engaged the supervisor is in your thesis research. However, we encourage you to meet with your supervisor at least several times during the Fall and Spring, and to agree on deadlines for initial results, chapter outlines, drafts, etc.
Thesis Readers
The thesis is evaluated by the thesis readers. Thesis readers must be either:
Two Harvard CS faculty members/affiliates ; or:
Three readers, at least one of whom is a Harvard CS faculty member and the others are ordinarily teaching faculty members of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences or SEAS who are generally familiar with the research area.
The thesis supervisor is one of the readers.
The student is responsible for finding the other readers, but you can talk with your supervisor for suggestions of possible readers.
Exceptions to these thesis reader requirements must be approved by the Directors of Undergraduate Studies.
For joint concentrators, the other concentration may have different procedures for thesis readers; if you have any questions or concerns about thesis readers, please contact the Directors of Undergraduate Studies.
Senior Thesis Seminar
Computer Science does not have a Senior Thesis seminar course.
However, we do run an informal optional series of Senior Thesis meetings in the Fall to help with the thesis writing process, focused on topics such as technical writing tips, work-shopping your senior thesis story, structure of your thesis, and more. Pay attention to your email in the Fall for announcements about this series of meetings.
The thesis should contain an informative abstract separate from the body of the thesis. This abstract should clearly state what the contribution of the thesis is–which parts are expository, whether there are novel results, etc. We also recommend the thesis contain an introduction that is at most 5 pages in length that contains an “Our contributions” section which explains exactly what the thesis contributed, and which sections in the thesis these are elaborated on. At the degree meeting, the Committee on Undergraduate Studies in Computer Science will review the thesis abstract, the reports from the three readers and the student’s academic record; it will have access to the thesis. The readers (and student) are told to assume that the Committee consists of technical professionals who are not necessarily conversant with the subject matter of the thesis so their reports (and abstract) should reflect this audience.
The length of the thesis should be as long as it needs to be to present its arguments, but no longer!
There are no specific formatting guidelines. For LaTeX, some students have used this template in the past . It is set up to meet the Harvard PhD Dissertation requirements, so it is meeting requirements that you as CS Senior Thesis writers don’t have.
Thesis Timeline for Seniors
(The timeline below is for students graduating in May. For off-cycle students, the same timeline applies, but offset by one semester. The thesis due date for March 2025 graduates is Friday November 22, 2024 at 2pm. The thesis deadline for May 2024 graduates is Friday March 29th Monday April 1st at 2pm.
Please be aware that students writing a joint thesis must meet the requirements of both departments–so if there are two different due dates for the thesis, you are expected to meet the earlier date.
Senior Fall (or earlier) Find a thesis supervisor, and start research.
October/November/December Start writing.
All fourth year concentrators are contacted by the Office of Academic Programs and those planning to submit a senior thesis are requested to supply certain information, including name of advisor and a tentative thesis title. You may use a different title when you submit your thesis; you do not need to tell us your updated title before then. If Fall 2024 is your final term, please fill out this form . If May 2024 is your final term, please fill out this form .
Early February The student should provide the name and contact information for the readers (see above), together with assurance that they have agreed to serve.
Mid-March Thesis supervisors are advised to demand a first draft. (A common reaction of thesis readers is “This would have been an excellent first draft. Too bad it is the final thesis—it could have been so much better if I had been able to make some suggestions a couple of weeks ago.")
April 1, 2024 * Thesis is due by 2:00 pm. Electronic copies in PDF format should be delivered by the student to all three readers and to [email protected] (which will forward to the Director of Undergraduate Studies) on or before that date. An electronic copy should also be submitted via the SEAS online submission tool on or before that date. SEAS will keep this electronic copy as a non-circulating backup. During this online submission process, the student will also have the option to make the electronic copy publicly available via DASH, Harvard’s open-access repository for scholarly work. Please note that the thesis will NOT be published to ProQuest. More information can be found on the SEAS Senior Thesis Submission page.
The two or three readers will receive a rating sheet to be returned to the Office of Academic Programs before the beginning of the Reading Period, together with their copy of the thesis and any remarks to be transmitted to the student.
Late May The Office of Academic Programs will send students their comments after the degree meeting to decide honors recommendations.
Thesis Extensions and Late Submissions
Thesis extensions Thesis extensions will be granted in extraordinary circumstances, such as hospitalization or grave family emergency, with the support of the thesis advisor and resident dean and the agreement of all readers. For joint concentrators, the other concentration should also support the extension. To request an extension, please have your advisor or resident dean email [email protected] , ideally several business days in advance, so that we may follow up with readers. Please note that any extension must be able to fall within our normal grading, feedback, and degree recommendation deadline, so extensions of more than a few days are usually impossible.
Late submissions Late submission of thesis work should be avoided. Work that is late will ordinarily not be eligible for thesis prizes like the Hoopes Prize. Theses submitted late will ordinarily be penalized one full level of honors (highest honors, high honors, honors, no honors) per day late or part thereof, including weekends, so a thesis submitted two days and one minute late is ordinarily ineligible to receive honors. Penalties will be waived only in extraordinary cases, such as documented medical illness or grave family emergency; students should consult with the Directors of Undergraduate Studies in that event. Missed alarm clocks, crashed computers, slow printers, corrupted files, and paper jams are not considered valid causes for extensions.
Thesis Examples
Recent thesis examples can be found on the Harvard DASH (Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard) repository here . Examples of Mind, Brain, Behavior theses are here .
Spectral Sparsification: The Barrier Method and its Applications
- Martin Camacho, Advisor: Jelani Nelson
Good Advice Costs Nothing and it’s Worth the Price: Incentive Compatible Recommendation Mechanisms for Exploring Unknown Options
- Perry Green, Advisor: Yiling Chen
Better than PageRank: Hitting Time as a Reputation Mechanism
- Brandon Liu, Advisor: David Parkes
Tree adjoining grammar at the interfaces
- Nicholas Longenbaugh, Advisor: Stuart Shieber
SCHUBOT: Machine Learning Tools for the Automated Analysis of Schubert’s Lieder
- Dylan Nagler, Advisor: Ryan Adams
Learning over Molecules: Representations and Kernels
- Jimmy Sun, Advisor: Ryan Adams
Towards the Quantum Machine: Using Scalable Machine Learning Methods to Predict Photovoltaic Efficacy of Organic Molecules
- Michael Tingley, Advisor: Ryan Adams
Yale College Undergraduate Admissions
- A Liberal Arts Education
- Majors & Academic Programs
- Teaching & Advising
- Undergraduate Research
- International Experiences
- Science & Engineering Faculty Features
- Residential Colleges
- Extracurriculars
- Identity, Culture, Faith
- Multicultural Open House
- Virtual Tour
- Bulldogs' Blogs
- First-Year Applicants
- International First-Year Applicants
- QuestBridge First-Year Applicants
- Military Veteran Applicants
- Transfer Applicants
- Eli Whitney: Nontraditional Applicants
- Non-Degree & Alumni Auditing Applicants
- What Yale Looks For
- Putting Together Your Application
- Selecting High School Courses
- Application FAQs
- First-Generation College Students
- Rural and Small Town Students
- Choosing Where to Apply
- Inside the Yale Admissions Office Podcast
- Visit Campus
- Virtual Events
- Connect With Yale Admissions
- The Details
- Estimate Your Cost
- QuestBridge
Search form
Writing a senior thesis: is it worth it.

Before coming to Yale, I thought a thesis was the main argument of a paper. I quickly learned that an undergraduate thesis is about fifty times harder and fifty pages longer than any thesis arguments I wrote in high school. At Yale, every senior has some sort of senior requirement, but thesis projects vary by department. Some departments require students to do a semester-long project, where you write a longer paper (25-35 pages) or expand, through writing, the research you’ve been working on (mostly applies to STEM majors). In some departments you can take two senior seminars and complete a longer project at the end of the semester. And other departments have an option to complete a year-long thesis: you spend your senior year (and in some cases your junior year), intensely researching and writing about a topic you choose or create yourself.
Both my departments––English and Ethnicity, Race, and Migration––offer all three of these options, and each student decides what they think is best for them. As a double major, I had the additional option to write an even longer thesis combining both my majors, but that seemed like way too much work––especially since I would have to take two senior thesis classes at the same time. Instead, I chose a year-long thesis for ER&M that combined my literary interests with various theoretical frameworks and the two senior seminars for English. This spring I’m taking my second seminar. Really, I chose the option to torture myself for a whole year, the end result being a minimum of 50 pages of innovative thinking and writing. I wanted to rise to the challenge, proving to myself I could do it. But there also seemed to be the pressure of “this is what everyone in the major does,” and a “thesis is proof that you actually learned.” Although these sentiments influenced my decision to complete a thesis, I know a long research paper does not validate my education or work as a scholar the last four years. It is not the end all be all.
My senior thesis focuses on Caribbean literature - specifically, two novels written by Caribbean women that really look at what it means to come from an immigrant family, to move, and to find yourself in completely new spaces. These experiences are all too relatable to my own life as a second-generation woman of color with immigrant parents enrolled at Yale. In my writing, I focus on how these women make sense of “home” (a very broad and complicated topic, I know), and what their stories tell us about the diasporic experience in general. The project is very personal to me, and I chose it because I wanted to understand my family’s history and their task in making “home” in the U.S., whatever that means. But because it’s so personal, it’s also been really difficult. I’ve experienced a lot of writer’s block or often felt unmotivated and judgmental towards my work. I’ve realized how difficult it is to devote your time and energy to such a long process––not only is it research heavy, but you have to write and rewrite drafts, constantly adjusting to make sure you’re being as clear as possible. Really, writing a thesis is like writing a portion of a book. And that’s crazy! You’re writing two or three whole chapters of academic work as an undergraduate student.
The process is definitely not for everyone, and I’ve certainly thought “Why did I want to do this again?” But what’s really kept me going is the support from my advisors and friends. The ER&M department faculty does an amazing job of providing us mentorship, revisions, and support throughout the process; my advisor has served as my editor but also the person who reminds me most that this work is important, as I often forget that. It also helps to have many friends and people in the major also writing their theses. I’ve found different spaces to just have a thesis study hall or working time, with other people also struggling through. Recently, I submitted my first full draft (note: it was kind of unfinished but it’s okay because it’s a draft!), and it was crazy to think that I wrote 50+ pages, most of which are just my own original thoughts and analysis on two books that have almost no scholarship written about them. It was a relief for sure. This week I will be taking a full break from it, but it reminded me of why I began this journey. It reminded me of all the people who’ve supported me along the way, and how I really couldn’t have done it without them. And now, I’m really looking forward to how good it will feel to turn in my fully written thesis mid-April. I’ve realized that this project shouldn’t be about making it good for Yale’s standard, but for myself, for my family, and for the people who believe in this work as much as I do.
More Posts by Gianna

Senior Bucket List: All the things I had to do before I left Yale/New Haven

Meet Rhythmic Blue!

Medieval Manuscripts and the Beinecke Library

How I Navigated My Double Major

Rating Boba in New Haven

Quarantine Birthdays

Welcome to the Trumbutt!!!!

Yale IMs: Intramural Sports #MOORAH
Reimagining Virtual Relationships


The Senior Thesis
From the outset of their time at Princeton, students are encouraged and challenged to develop their scholarly interests and to evolve as independent thinkers.
The culmination of this process is the senior thesis, which provides a unique opportunity for students to pursue original research and scholarship in a field of their choosing. At Princeton, every senior writes a thesis or, in the case of some engineering departments, undertakes a substantial independent project.
Integral to the senior thesis process is the opportunity to work one-on-one with a faculty member who guides the development of the project. Thesis writers and advisers agree that the most valuable outcome of the senior thesis is the chance for students to enhance skills that are the foundation of future success, including creativity, intellectual engagement, mental discipline and the ability to meet new challenges.
Many students develop projects from ideas sparked in the classes they’ve taken; others fashion their topics on the basis of long-standing personal passions. Most thesis writers encounter the intellectual twists and turns of any good research project, where the questions emerge as they proceed, often taking them in unexpected directions.
Planning for the senior thesis starts in earnest in the junior year, when students complete a significant research project known as the junior paper. Students who plan ahead can make good use of the University's considerable resources, such as receiving University funds to do research in the United States or abroad. Other students use summer internships as a launching pad for their thesis. For some science and engineering projects, students stay on campus the summer before their senior year to get a head start on lab work.
Writing a thesis encourages the self-confidence and high ambitions that come from mastering a difficult challenge. It fosters the development of specific skills and habits of mind that augur well for future success. No wonder generations of graduates look back on the senior thesis as the most valuable academic component of their Princeton experience.
Navigating Colombia’s Magdalena River, One Story At A Time
For his senior thesis, Jordan Salama, a Spanish and Portuguese major, produced a nonfiction book of travel writing about the people and places along Colombia’s main river, the Magdalena.

Embracing the Classics to Inform Policymaking for Public Education
For her senior thesis, Emma Treadwayconsiders how the basic tenets of Stoicism — a school of philosophy that dates from 300 BCE — can teach students to engage empathetically with the world and address inequities in the classroom.

Creating A Faster, Cheaper and Greener Chemical Reaction
One way to make drugs more affordable is to make them cheaper to produce. For her senior thesis research, Cassidy Humphreys, a chemistry major with a passion for medicine, took on the challenge of taking a century-old formula at the core of many modern medications — and improving it.

The Humanity of Improvisational Dance
Esin Yunusoglu investigated how humans move together and exist in a space — both on the dance floor and in real life — for the choreography she created as her senior thesis in dance, advised by Professor of Dance Susan Marshall.

From the Blog
The infamous senior thesis, revisiting wwii: my senior thesis, independent work in its full glory, advisers, independent work and beyond.
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
fa51e2b1dc8cca8f7467da564e77b5ea
- Make a Gift
- Join Our Email List
- Advising Senior Theses
Every thesis writer and thesis project is unique, and arguably the single most important thing that you can do as a thesis adviser is to get to know your student well and to be supportive and attentive as they work towards their spring deadline. The amount of structure that different concentrations offer their students can also have a significant impact on how you think about your role as an adviser. In some cases you may feel like an extension of the department’s undergraduate office, encouraging your student to follow its well-articulated pathway towards completion and nudging your student to heed (albeit perhaps with some discretion) its recommended proposal or draft deadlines. In other cases you may be the one responsible for translating the concentration’s somewhat vague guidelines into an actionable roadmap of recommended thresholds and dates. It’s well worth establishing a healthy line of communication with the concentration’s undergraduate office (and with anyone else involved in advising your student’s academic work) from the start of your advising relationship.
Regardless of the precise structure and obligations surrounding your position as an adviser, there are a number of things which you can do to help just about any student have a meaningful, and successful, experience with the senior thesis. Here are five key contributions which you can make:
Manage expectations
In an ideal world, every student would enter the thesis process fully prepared for every aspect of scholarly work. They all would know how to ask an analytical question suitable for a 60- or 100-page paper, how to find relevant data, how to draw lucid figures, how to format every footnote or methods section, … . Likewise, we might wish that every thesis topic lent itself equally well to the particular constraints of Harvard’s resources and academic calendar. If only that essential cache of Russian manuscripts existed in a published English translation in Widener! If only this experimental protocol took two weeks rather than four months! In reality, however, every thesis involves some compromise—perhaps significant compromise. One of your most important jobs as a thesis adviser is to roleplay your student’s future audience, and to help your student understand that the most successful theses ask questions that are not only meaningful, but that can be answered at least somewhat plausibly by the set of skills, resources, and time that is available to a Harvard undergraduate. Insofar as a student is determined to tackle a dissertation-sized question, the adviser can at least remind the student that it will be important to frame the results as a “partial” answer or a “contribution towards” an answer in the introduction.
Encourage self-knowledge
As with the previous point about managing expectations, it is important that an adviser be able to remind their student that the senior thesis is not, and will not be, the moment when students magically become “better” people than they already are. Students who have been night owls during their first three years of college are unlikely to transform miraculously into the type of scholars who rise at 6am and write 1000 words before breakfast—no matter how much they yearn to emulate some academic role model. Students who have participated actively in a sport or other extracurricular are unlikely to be able to simply recoup those hours for thesis work—cutting back three hours/week at The Crimson is at least as likely to translate into three more hours spent bantering in the dining hall as it is into three hours spent poring over the administrative structure of the Byzantine Empire. The point is that students can benefit from being reminded that they already know how to do the kind of work expected of them on the thesis, and that it may be counterproductive—if not downright unhealthy—to hold themselves to new or arbitrary standards.
Motivate to start writing early
With relatively few exceptions, most of the writing projects assigned in college are sufficiently modest that students can wait to start writing until they have figured out the full arc of what they want to say and how they want to say it. It’s possible, in other words, to plan and hold the entirety of a five-page essay in one’s head. This is simply not true of a senior thesis. Theses require the author to take a leap of faith—to start writing before the research is done and long before they know exactly what they want to say. Students may be reluctant to do this, fearing that they might “waste” precious time drafting a section of a chapter that ultimately doesn’t fit in the final thesis. You can do your student a world of good by reminding them that there is no such thing as wasted writing. In a project as large as a thesis, writing is not merely about reporting one’s conclusions—it is the process through which students come to figure out what their conclusions might be, and which lines of research they will need to pursue to get there.
Model strategies
While academic research and writing can and should be a creative endeavor, it is also undeniably true that even professional scholars draw upon a relatively constrained set of well-known strategies when framing their work. How many different ways, after all, are there to say that the conventional wisdom on a topic has ignored a certain genre of evidence? Or that two competing schools of thought actually agree more than they disagree? Or that fiddling with one variable has the power to reframe an entire discussion? Students may struggle to see how to plug their research into the existing scholarly conversation around their topic. Showing them models or templates that demystify the ways in which scholars frame their interventions can be enormously powerful.
Keep contact and avoid the "shame spiral"
As noted above, the senior thesis is a long process, and while it’s rarely a good idea for students to change their work habits in an effort to complete it, it is important that they be working early and often. Occasionally students do become overwhelmed by the scope of the project, and begin to feel defeated by the incremental nature of progress they are making. Even a good week of work may yield only a couple of pages of passable writing. Ideally a student feeling overwhelmed would come to their adviser for some help putting things into perspective. But for a student used to having a fair amount of success, the struggles involved in a senior thesis may be disorienting, and they may worry that they are “disappointing” you. For some, this will manifest as a retreat from your deadlines and oversight—even as they outwardly project confidence. They may begin bargaining with themselves in ways that only serve to sink them deeper into a sense of panic or shame. (“I’m long past the deadline for my first ten pages—but if I give my adviser a really brilliant fifteen-page section, he won’t mind! Surely I can turn these four pages into fifteen if I stay up all night!”) One of the best things that you can do as an adviser is keep contact with your student and make sure to remind them that your dynamic is not one of “approval” or “disapproval.” It is important that they maintain a healthy and realistic approach to the incremental process of completing the thesis over several months.
For more information...
The Art of Thesis Writing: A handout for students
Harvard's Academic Resource Center on Senior Theses
Senior Thesis Tutors at the Harvard College Writing Center
- Designing Your Course
- In the Classroom
- Getting Feedback
- Equitable & Inclusive Teaching
- Writing Letters of Recommendation
- Teaching and Your Career
- Teaching Remotely
- Tools and Platforms
- The Science of Learning
- Bok Publications
- Other Resources Around Campus

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Senior Thesis Writing Guides. The senior thesis is typically the most challenging writing project undertaken by undergraduate students. The writing guides below aim to introduce students both to the specific methods and conventions of writing original research in their area of concentration and to effective writing process. The senior thesis is ...
2 Q: Why should I write a Senior Thesis? A: While writing a thesis is one way to become eligible for honors, and the only way to become eligible for the summa cum laude level of honors, the best motivations are a love of research and/or a burning question. You should not consider a Senior Thesis if your primary motivations are not intellectually based, but are instead more practical—i.e ...
A senior thesis in literature, on the other hand, will likely involve studying a movement, trope, author, or theme, and your sources will involve a combination of fiction, historical context, literary criticism, and literary theory. At many schools, a thesis ranges from 80 to 125 pages. At other universities, as few as 25 pages might fill the ...
senior thesis is not simply a much longer term paper. It is not simply an independent project carried out under the general guidance of an advisor. It does not simply require more research, more evidence, and more writing. Rather, your thesis requires more methodology. In a nutshell, that is what this handbook is meant to provide.
The senior thesis is a significant task for students to undertake, but there is a variety of support resources available here at Harvard to ensure that seniors can make the best of their senior thesis experience. Wandering the library stacks at Widener. I do most of my research in Widener Library.
The senior thesis will be, for most of you, the longest and most ambitious critical, scholarly or creative work you have done so far; plan early, set aside time, and save your energy so as to get the most out of it. Meet regularly with your advisor(s) throughout the fall term, as well as in early spring. If you have
The Writing Center has Senior Thesis Tutors who will read drafts of your thesis (more typically, parts of your thesis) in advance and meet with you individually to talk about structure, argument, clear writing, and mapping out your writing plan. If you need help with breaking down your project or setting up a schedule for the week, the semester ...
Director of Studies to write a thesis that exceeds 20,000 words. Typical theses run somewhere in the range of 15,000-20,000 words. • All candidates for an honors degree in History & Literature must prepare a senior thesis. Students who do not complete a thesis are not eligible to graduate with honors in History & Literature.
Fall Semester of Senior Year By the end of September, you should: Finalize your decision to write an honors thesis. Finalize your topic and research approach. Confirm primary thesis advisor and secondary reader. Think about length, breadth, and size of your finished thesis. Consider chapter breakdowns or other forms of presenting the finished ...
The EPS Senior Thesis Guide Updated March 17, 2021 1 The EPS Senior Thesis Guide . A Note to Students: Completing a senior thesis will likely be the most challenging and rewarding experience of your undergraduate career. Students undertake thesis research and writing for various reasons—to see if
A Social Studies thesis needs to be between 20,000 and 30,000 words long, which roughly works out to about 80-120 pages in length. While this may sound intimidating, the reality is that most students end up somewhere over the wordcount and end up hav- ing to edit their content back down.
4. Do focused, or prompted, freewriting. Sometimes freewriting works better with a focus and/or a running start. Consider using the following sentence stems as prompts for your freewriting. Complete the sentence and continue writing from there. 1.
A senior thesis is an original research project undertaken during one's senior year at Harvard College. The thesis project requires research into the theories and past research relevant to the project, analysis of data, either original or existing, and a written final product. The thesis should be a project that can be feasibly completed in 7 ...
What this handout is about. Writing a senior honors thesis, or any major research essay, can seem daunting at first. A thesis requires a reflective, multi-stage writing process. This handout will walk you through those stages. It is targeted at students in the humanities and social sciences, since their theses tend to involve more writing than ...
Integral to the senior thesis process is the opportunity to work one-on-one with a faculty member who guides the development of the project. Thesis writers and advisers agree that the most valuable outcome of the senior thesis is the chance for students to enhance skills that are the foundation of future success, including creativity, intellectual engagement, mental discipline and the ability ...
A Guide to Writing a Senior Thesis in Linguistics | page 1 Time Management Tips Start writing as soon as possible! Don't put off writing your thesis until you know exactly what your results are—if you do that, you won't have enough time left to finish your project We recommend starting your abstract, introduction and literature review .
The Department provides seniors with a comprehensive guide on the senior thesis process and expectations. This will be helpful as you familiarize yourself with the expectations, format, and structure of senior theses at Harvard. The Department has compiled advice from past thesis writers. You may find it helpful to share this with the student ...
Writing a senior essay is a very daunting task. For my major - political science - the senior paper needs to be 25 pages minimum. This paper has the potential of being the longest paper you'll write during your entire Yale undergraduate career and so, preparation is necessary. A great resource offered by Yale to undergrads writing their ...
The meetings helped me realize that I had to start looking for a thesis adviser. Although some students wait until the end of junior year or the beginning of senior year to choose an adviser, I plan to do research over the summer, and in order to apply for funding, it is helpful to have an adviser in mind early on.
Senior Thesis Seminar . Computer Science does not have a Senior Thesis seminar course. However, we do run an informal optional series of Senior Thesis meetings in the Fall to help with the thesis writing process, focused on topics such as technical writing tips, work-shopping your senior thesis story, structure of your thesis, and more.
Before coming to Yale, I thought a thesis was the main argument of a paper. I quickly learned that an undergraduate thesis is about fifty times harder and fifty pages longer than any thesis arguments I wrote in high school. At Yale, every senior has some sort of senior requirement, but thesis projects vary by department. Some departments require students to do a semester-long
Integral to the senior thesis process is the opportunity to work one-on-one with a faculty member who guides the development of the project. Thesis writers and advisers agree that the most valuable outcome of the senior thesis is the chance for students to enhance skills that are the foundation of future success, including creativity, intellectual engagement, mental discipline and the ability ...
As noted above, the senior thesis is a long process, and while it's rarely a good idea for students to change their work habits in an effort to complete it, it is important that they be working early and often. Occasionally students do become overwhelmed by the scope of the project, and begin to feel defeated by the incremental nature of ...
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
177 likes, 1 comments - universityofthearts on April 27, 2024: "Spring? Do you mean thesis season? Emely Gonzalez '27 (Dance) was at the School of Dance Festival of ...