

Research Paper: A step-by-step guide: 3. Thesis Statement & Outline
- 1. Getting Started
- 2. Topic Ideas
- 3. Thesis Statement & Outline
- 4. Appropriate Sources
- 5. Search Techniques
- 6. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
- 7. Evaluating Sources
- 8. Citations & Plagiarism
- 9. Writing Your Research Paper

About Thesis Statements
Qualities of a thesis statement.
Thesis statements:
- state the subject matter and main ideas of a paper.
- appear in the first paragraph and announces what you will discuss in your paper.
- define the scope and focus of your essay, and tells your reader what to expect.
- are not a simple factual statement. It is an assertion that states your claims and that you can prove with evidence.
- should be the product of research and your own critical thinking.
- can be very helpful in constructing an outline for your essay; for each point you make, ask yourself whether it is relevant to the thesis.
Steps you can use to create a thesis statement
1. Start out with the main topic and focus of your essay.
youth gangs + prevention and intervention programs
2. Make a claim or argument in one sentence. It can be helpful to start with a question which you then turn into an argument
Can prevention and intervention programs stop youth gang activities? How? ►►► "Prevention and intervention programs can stop youth gang activities by giving teens something else to do."
3. Revise the sentence by using specific terms.
"Early prevention programs in schools are the most effective way to prevent youth gang involvement by giving teens good activities that offer a path to success."
4. Further revise the sentence to cover the scope of your essay and make a strong statement.
"Among various prevention and intervention efforts that have been made to deal with the rapid growth of youth gangs, early school-based prevention programs are the most effective way to prevent youth gang involvement, which they do by giving teens meaningful activities that offer pathways to achievement and success."
5. Keep your thesis statement flexible and revise it as needed. In the process of researching and writing, you may find new information or refine your understanding of the topic.
You can view this short video for more tips on how to write a clear thesis statement.
An outline is the skeleton of your essay, in which you list the arguments and subtopics in a logical order. A good outline is an important element in writing a good paper. An outline helps to target your research areas, keep you within the scope without going off-track, and it can also help to keep your argument in good order when writing the essay. Once your outline is in good shape, it is much easier to write your paper; you've already done most of the thinking, so you just need to fill in the outline with a paragraph for each point.
To write an outline: The most common way to write an outline is the list format. List all the major topics and subtopics with the key points that support them. Put similar topics and points together and arrange them in a logical order. Include an introduction, a body, and a conclusion.
A list outline should arrange the main points or arguments in a hierarchical structure indicated by Roman numerals for main ideas (I, II, III...), capital letters for subtopics (A, B, C...), Arabic numerals for details (1,2,3...), and lower-case letters for fine details if needed (a,b,c...). This helps keep things organized.
Here is a shortened example of an outline:
Introduction: background and thesis statement
I. First topic
1. Supporting evidence 2. Supporting evidence
II. Second Topic
III. Third Topic
I. Summarize the main points of your paper II. Restate your thesis in different words III. Make a strong final statement
You can see examples of a few different kinds of outlines and get more help at the Purdue OWL .
- << Previous: 2. Topic Ideas
- Next: 4. Appropriate Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2023 12:12 PM
- URL: https://butte.libguides.com/ResearchPaper
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Getting started with your research paper outline
Levels of organization for a research paper outline
First level of organization, second level of organization, third level of organization, fourth level of organization, tips for writing a research paper outline, research paper outline template, my research paper outline is complete: what are the next steps, frequently asked questions about a research paper outline, related articles.
The outline is the skeleton of your research paper. Simply start by writing down your thesis and the main ideas you wish to present. This will likely change as your research progresses; therefore, do not worry about being too specific in the early stages of writing your outline.
A research paper outline typically contains between two and four layers of organization. The first two layers are the most generalized. Each layer thereafter will contain the research you complete and presents more and more detailed information.
The levels are typically represented by a combination of Roman numerals, Arabic numerals, uppercase letters, lowercase letters but may include other symbols. Refer to the guidelines provided by your institution, as formatting is not universal and differs between universities, fields, and subjects. If you are writing the outline for yourself, you may choose any combination you prefer.
This is the most generalized level of information. Begin by numbering the introduction, each idea you will present, and the conclusion. The main ideas contain the bulk of your research paper 's information. Depending on your research, it may be chapters of a book for a literature review , a series of dates for a historical research paper, or the methods and results of a scientific paper.
I. Introduction
II. Main idea
III. Main idea
IV. Main idea
V. Conclusion
The second level consists of topics which support the introduction, main ideas, and the conclusion. Each main idea should have at least two supporting topics listed in the outline.
If your main idea does not have enough support, you should consider presenting another main idea in its place. This is where you should stop outlining if this is your first draft. Continue your research before adding to the next levels of organization.
- A. Background information
- B. Hypothesis or thesis
- A. Supporting topic
- B. Supporting topic
The third level of organization contains supporting information for the topics previously listed. By now, you should have completed enough research to add support for your ideas.
The Introduction and Main Ideas may contain information you discovered about the author, timeframe, or contents of a book for a literature review; the historical events leading up to the research topic for a historical research paper, or an explanation of the problem a scientific research paper intends to address.
- 1. Relevant history
- 2. Relevant history
- 1. The hypothesis or thesis clearly stated
- 1. A brief description of supporting information
- 2. A brief description of supporting information
The fourth level of organization contains the most detailed information such as quotes, references, observations, or specific data needed to support the main idea. It is not typical to have further levels of organization because the information contained here is the most specific.
- a) Quotes or references to another piece of literature
- b) Quotes or references to another piece of literature
Tip: The key to creating a useful outline is to be consistent in your headings, organization, and levels of specificity.
- Be Consistent : ensure every heading has a similar tone. State the topic or write short sentences for each heading but avoid doing both.
- Organize Information : Higher levels of organization are more generally stated and each supporting level becomes more specific. The introduction and conclusion will never be lower than the first level of organization.
- Build Support : Each main idea should have two or more supporting topics. If your research does not have enough information to support the main idea you are presenting, you should, in general, complete additional research or revise the outline.
By now, you should know the basic requirements to create an outline for your paper. With a content framework in place, you can now start writing your paper . To help you start right away, you can use one of our templates and adjust it to suit your needs.
After completing your outline, you should:
- Title your research paper . This is an iterative process and may change when you delve deeper into the topic.
- Begin writing your research paper draft . Continue researching to further build your outline and provide more information to support your hypothesis or thesis.
- Format your draft appropriately . MLA 8 and APA 7 formats have differences between their bibliography page, in-text citations, line spacing, and title.
- Finalize your citations and bibliography . Use a reference manager like Paperpile to organize and cite your research.
- Write the abstract, if required . An abstract will briefly state the information contained within the paper, results of the research, and the conclusion.
An outline is used to organize written ideas about a topic into a logical order. Outlines help us organize major topics, subtopics, and supporting details. Researchers benefit greatly from outlines while writing by addressing which topic to cover in what order.
The most basic outline format consists of: an introduction, a minimum of three topic paragraphs, and a conclusion.
You should make an outline before starting to write your research paper. This will help you organize the main ideas and arguments you want to present in your topic.
- Consistency: ensure every heading has a similar tone. State the topic or write short sentences for each heading but avoid doing both.
- Organization : Higher levels of organization are more generally stated and each supporting level becomes more specific. The introduction and conclusion will never be lower than the first level of organization.
- Support : Each main idea should have two or more supporting topics. If your research does not have enough information to support the main idea you are presenting, you should, in general, complete additional research or revise the outline.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Published on 8 June 2022 by Tegan George .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process . It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation, such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
In the final product, you can also provide a chapter outline for your readers. This is a short paragraph at the end of your introduction to inform readers about the organisational structure of your thesis or dissertation . This chapter outline is also known as a reading guide or summary outline.
Table of contents
How to outline your thesis or dissertation, dissertation and thesis outline templates, chapter outline example, sample sentences for your chapter outline, sample verbs for variation in your chapter outline, frequently asked questions about outlines.
While there are some inter-institutional differences, many outlines proceed in a fairly similar fashion.
- Working Title
- ‘Elevator pitch’ of your work (often written last).
- Introduce your area of study, sharing details about your research question, problem statement , and hypotheses . Situate your research within an existing paradigm or conceptual or theoretical framework .
- Subdivide as you see fit into main topics and sub-topics.
- Describe your research methods (e.g., your scope, population , and data collection ).
- Present your research findings and share about your data analysis methods.
- Answer the research question in a concise way.
- Interpret your findings, discuss potential limitations of your own research and speculate about future implications or related opportunities.
To help you get started, we’ve created a full thesis or dissertation template in Word or Google Docs format. It’s easy adapt it to your own requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template

It can be easy to fall into a pattern of overusing the same words or sentence constructions, which can make your work monotonous and repetitive for your readers. Consider utilising some of the alternative constructions presented below.
Example 1: Passive construction
The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise.
Example 2: IS-AV construction
You can also present your information using the ‘IS-AV’ (inanimate subject with an active verb) construction.
A chapter is an inanimate object, so it is not capable of taking an action itself (e.g., presenting or discussing). However, the meaning of the sentence is still easily understandable, so the IS-AV construction can be a good way to add variety to your text.
Example 3: The I construction
Another option is to use the ‘I’ construction, which is often recommended by style manuals (e.g., APA Style and Chicago style ). However, depending on your field of study, this construction is not always considered professional or academic. Ask your supervisor if you’re not sure.
Example 4: Mix-and-match
To truly make the most of these options, consider mixing and matching the passive voice , IS-AV construction , and ‘I’ construction .This can help the flow of your argument and improve the readability of your text.
As you draft the chapter outline, you may also find yourself frequently repeating the same words, such as ‘discuss’, ‘present’, ‘prove’, or ‘show’. Consider branching out to add richness and nuance to your writing. Here are some examples of synonyms you can use.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
All level 1 and 2 headings should be included in your table of contents . That means the titles of your chapters and the main sections within them.
The contents should also include all appendices and the lists of tables and figures, if applicable, as well as your reference list .
Do not include the acknowledgements or abstract in the table of contents.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, June 08). Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 27 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/outline-thesis-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation table of contents in word | instructions & examples, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples.
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Writing a Top Thesis Outline – Your Comprehensive Guide

A thesis paper outline is a simple way of ensuring that each of your paragraphs serves a specific purpose in your paper. All students need to master this writing tool as it helps you organize your work.
What is a Thesis Outline?
A thesis outline is an organizational tool that writers use in their academic and professional thesis papers. Like a blueprint for your essay, it forms the foundation of the entire writing process. It is used to structure the main ideas into a list of easy and quick to follow contents.
Creating a thesis outline is vital in the following ways:
It gives a precise organization of the ideas Identifies parts of the paper that need special attention It singles out sections that need to be reduced or omitted Helps create connections and transitions where necessary It enables a student to fit the ideas systematically
Having a clearly defined thesis statement is better than a thousand thesis writers being dispatched at your disposal.
Thesis Outline Template
Now, what will make or break your master’s thesis outline or senior thesis outline is understanding its structure. It is not enough to have what to write but how to register it as well. That is why you need this template when writing a thesis outline.
Thesis Outline Format
A conventional thesis paper will have the following sections:
- Introduction (contains the background and thesis statement)
- The body paragraphs
- The conclusion
To attain this thesis structure’s best, you have to understand each part’s significance and how it contributes to the overall thesis paper. Let us look at how to write a thesis outline while delving deep into every section.
Thesis topic outline
A topic is described as the trigger button of your paper. It will determine whether your reader will have the interest to read your thesis or not. Therefore, when you are thinking about your thesis topic, consider the following:
- It should be brief and to the point (Do not explain or illustrate, just state)
- Use the keywords provided in the assignment for your topic
- AVOID using punctuations at the end
- It should be an eye-catcher and act as a bait
For you to have a good thesis topic, it should offer a solution. Nobody wants to spend his precious time on a paper that does not address a prevailing societal problem.
- How to do a thesis statement outline
The thesis statement is written in the introductory paragraph. Since this is the main idea for your paper, there is no room for error. Start with an attention-grabber that will lead the reader to your thesis statement.
Example of an attention grabber : Did you know that the average person who stays at home every day consumes over 10 tons of calories in a week?
Sample thesis statement : Excess calorie is a contributing factor to the high obesity rates patients witnessed in hospitals.
When creating a thesis statement outline, ensure that it relates to your introductory paragraph’s first two or three statements. Let it come out clearly so that the reader is prepared for what is coming next in the paper’s body.
They are made up of arguments in support of the thesis statement. This section carries a lot of weight as it either persuades or turns off the reader. Here is an outline for thesis paper body paragraphs:
Identify the main points Look for supporting ideas or evidence Have a list of transitional words from one section to another
The body of a thesis consists of the Literature Review, Research Methods, Results, and Discussion. It is recommended to begin with the literature review first before proceeding to the other two sections.
Since the Discussion is the longest part of the thesis, ensure that you gather all the necessary information needed to furnish it. In this part, you will need to identify the following aspects of your research process:
- Limitations of your study,
- Explanations for unexpected results, and
- Identify any questions that remain unanswered.
Every argument should be crystal clear to prevent any doubt or object on the part of the reader.
- The Conclusion
Though it appears last, it is one of the most critical sections of your thesis. It is the chapter that shows whether you achieved your research objectives or not. In this part, you can point out the following:
Point out the challenges you encountered in your study Your lessons from the research Make recommendations for future research
The conclusion should be a point where you identify whether every hypothesis was met or objective was achieved. It is vital to note that this chapter should short and clear to the end. Now that you have argued your case make this as your final nail to the coffin.
How To Make a Thesis Outline – Step By Step Guide
A superb outline can ease your research process and make your thesis writing process quick and easy. When you are thinking of creating a thesis paper outline, consider the following steps:
Read and understand the question first. If your tutor has given you a topic or question for your thesis, ensure that you digest it well to understand what is required of you. It will help to align your thesis outline correctly. Check for similar thesis outlines on the same topic. You can Google for any reliable thesis outline example that is similar to your topic of research. By doing this, you will get a rough idea of what is expected of you. Consult with your professor on the thesis outline format for your institution. Different institutions have varying structures, and thus, you need to use one that matches your institution’s house style. Do not rush into creating the outline. Before you draft your strategy, ensure that you have all the essentials at your fingertips first. Since this will be your guiding principle, it should be devoid of any errors or bogus steps.
After setting your house in order, writing your thesis paper is now time for the real task.
If you did not know how to create a thesis outline, we hope that this writing guide has served that purpose for you. Nevertheless, we also have a thesis writing service that offers students with online assistance.
Get help with thesis outline at affordable rates today. You can also find a master thesis outline example from gurus who have been in this business for decades. What is holding you now?

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Research Paper Outline with Examples
You sometimes have to submit an essay outline or a research proposal checklist for a research project before you do most of the actual research to show that you have understood the assignment, defined a good research question or hypothesis, and contemplated the structure of your research paper. You can find various templates and examples for such outlines, which usually begin with “put your thesis statement/research question at the top” and then ask you to decide whether to add your supporting ideas/points in “alphanumeric,” “decimal,” or “full-sentence” style.
That is certainly one useful (if not overly formalized) way of using outlining to prepare to draft an academic text. But here we want to talk about how to make an outline after you have done a research project or thesis work and are not quite sure how to put everything together into a written thesis to hand in or a research paper manuscript to submit to a journal.
What is a research paper outline?
Creating a research project outline entails more than just listing bullet points (although you can use bullet points and lists in your outline). It includes how to organize everything you have done and thought about and want to say about your work into a clear structure you can use as the basis for your research paper.
There are two different methods of creating an outline: let’s call these “abstract style” and “paper style.” These names reflect how briefly you summarize your work at this initial point, or show how extensive and complicated the methods and designs you used and the data you collected are. The type of outline you use also depends on how clear the story you want to tell is and how much organizing and structuring of information you still need to do before you can draft your actual paper.

Table of Contents:
- Abstract-Style Outline Format
- Paper-Style Outline Format
Additional Tips for Outlining a Research Paper in English
Abstract-style research paper outline format.
A research paper outline in abstract style consists, like the abstract of a research paper , of short answers to the essential questions that anyone trying to understand your work would ask.
- Why did you decide to do what you did?
- What exactly did you do?
- How did you do it?
- What did you find?
- What does it mean?
- What should you/we/someone else do now?
These questions form the structure of not only a typical research paper abstract but also a typical article manuscript. They will eventually be omitted and replaced by the usual headers, such as Introduction/Background, Aim, Methods, Results, Discussion, Conclusions, etc. Answering these key questions for yourself first (with keywords or short sentences) and then sticking to the same structure and information when drafting your article will ensure that your story is consistent and that there are no logical gaps or contradictions between the different sections of a research paper .
If you draft this abstract outline carefully, you can use it as the basis for every other part of your paper. You reduce it even more, down to the absolute essential elements, to create your manuscript title ; you choose your keywords on the basis of the summary presented here; and you expand it into the introduction , methods , results , and discussion sections of your paper without contradicting yourself or losing the logical thread.
Research Paper Outline Example (Abstract style)
Let’s say you did a research project on the effect of university online classes on attendance rates and create a simple outline example using these six questions:
1. Why did you decide to do what you did?
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, many university courses around the world have been moved online, at least temporarily. Since students have been saving time on commuting, I wondered if attendance rates have increased overall.
2. What exactly did you do?
I compared attendance scores for courses that were taught both before (offline) and during (online) the COVID-19 pandemic at my university.
3. How did you do it?
I selected five popular subjects (business, law, medicine, psychology, art & design) and one general course per subject; then I contacted the professors in charge and asked them to provide me with anonymized attendance scores.
4. What did you find?
Attendance did not significantly change for medicine and law, but slightly dropped for the other three subjects. I found no difference between male and female students.
5. What does it mean?
Even though students saved time on traveling between their homes and the campus during the COVID-19 pandemic, they did not attend classes more consistently; in some subjects, they missed more classes than before.
6. What should you/we/someone else do now?
Since I do not have any other information about the students, I can only speculate on potential explanations. Next, I will put together a questionnaire to assess how students have been coping with online classes and how the experiences from this time can benefit university teaching and learning in general.
Note that you could have made the same outline using just keywords instead of full sentences. You could also have added more methodological details or the results of your statistical analysis. However, when you can break everything down to the absolute essentials like this, you will have a good foundation upon which to develop a full paper.
However, maybe your study just seems too complicated. So you look at these questions and then at your notes and data and have no idea how to come up with such simple answers. Or maybe things went in a completely different direction since you started writing your paper, so now you are no longer sure what the main point of your experiments was and what the main conclusion should be. If that is how you feel right now, then outlining your paper in “paper style” might be the right method for you.
Paper-Style Research Paper Outline Format
The purpose of a paper-style outline is the same as that of an abstract-style outline: You want to organize your initial thoughts and plans, the methods and tools you used, all the experiments you conducted, the data you collected and analyzed, as well as your results, into a clear structure so that you can identify the main storyline for your paper and the main conclusions that you want the reader to take from it.
First, take as much space as you need and simply jot down everything in your study you planned to do, everything you did, and everything you thought about based on your notes, lab book, and earlier literature you read or used. Such an outline can contain all your initial ideas, the timeline of all your pilots and all your experiments, the reasons why you changed direction or designed new experiments halfway through your study, all the analyses you ever did, all the feedback and criticism you already got from supervisors and seniors or during conference presentations, and all the ideas you have for future work. If this is your thesis or your first publication, then your first outline might look quite messy – and that is exactly why you need to structure your paper before trying to write everything up.
So you have finally remembered all you have done in your study and have written everything down. The next step is to realize that you cannot throw all of this at the reader and expect them to put it together. You will have to create a story that is clear and consistent, contains all the essential information (and leaves out any that is not), and leads the reader the same way the abstract outline does, from why over what and how to what you found and what it all means .
This does not mean you should suppress results that did not come out as intended or try to make your study look smoother. But the reader does not really need to know all the details about why you changed your research question after your initial literature search or some failed pilots. Instead of writing down the simple questions we used for the abstract outline, to organize your still messy notes, write down the main sections of the manuscript you are trying to put together. Additionally, include what kinds of information needs to go where in your paper’s structure.
1. Introduction Section:
What field is your research part of?
What other papers did you read before deciding on your topic?
Who is your target audience and how much information do your readers need to understand where you are coming from?
Can you summarize what you did in two sentences?
Did you have a clear hypothesis? If not, what were the potential outcomes of your work?
2. Methods Section:
List all the methods, questionnaires, and tests you used.
Are your methods all standard in the field or do you need to explain them?
List everything chronologically or according to topics, whatever makes more sense. Read more about writing the Methods section if you need help with this important decision.
3. Results Section:
Use the same timeline or topics you introduced in the method section.
Make sure you answer all the questions you raised in the introduction.
Use tables, graphs, and other visualizations to guide the reader.
Don’t present results of tests/analyses that you did not mention in the methods.
4. Discussion/Conclusion Section:
Summarize quickly what you did and found but don’t repeat your results.
Explain whether your findings were to be expected, are new and surprising, are in line with the existing literature, or are contradicting some earlier work.
Do you think your findings can be generalized? Can they be useful for people in certain professions or other fields?
Does your study have limitations? What would you do differently next time?
What future research do you think should be done based on your findings?
5. Conclusion Statement/Paragraph:
This is your take-home message for the reader. Make sure that your conclusion is directly related to your initial research question.
Now you can simply reorganize your notes (if you use computer software) or fill in the different sections and cross out information on your original list. When you have used all your jotted notes, go through your new outline and check what is still missing. Now check once more that your conclusion is related to your initial research question. If that is the case, you are good to go. You can now either break your outline down further and shorten it into an abstract, or you can expand the different outline sections into a full article.
If you are a non-native speaker of English, then you might take notes in your mother language or maybe in different languages, read literature in your mother language, and generally not think in English while doing your research. If your goal is to write your thesis or paper in English, however, then our advice is to only use your mother language when listing keywords at the very beginning of the outlining process (if at all). As soon as you write down full sentences that you want to go into your paper eventually, you can save yourself a lot of work, avoid mistakes later in the process, and train your brain (which will help you immensely the next time you write an academic text), if you stick to English.
Another thing to keep in mind is that starting to write in full sentences too early in the process means that you might need to omit some passages (maybe even entire paragraphs) when you later decide to change the structure or storyline of your paper. Depending on how much you enjoy (or hate) writing in English and how much effort it costs you, having to throw away a perfectly fine paragraph that you invested a lot of time in can be incredibly frustrating. Our advice is therefore to not spend too much time on writing and to not get too attached to exact wording before you have a solid outline that you then only need to fill in and expand into a full paper.
Once you have finished drafting your paper, consider using professional proofreading and English editing service to revise your paper and prepare it for submission to journals. Wordvice offers a paper editing service , manuscript editing service , dissertation editing service , and thesis editing service to polish and edit your research work and correct any errors in style or formatting.
And while you draft your article, make use of Wordvice AI, a free AI Proofreader that identifies and fixes errors in punctuation, spelling, and grammar in any academic document.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Making an Outline
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
An outline is a formal system used to develop a framework for thinking about what should be the organization and eventual contents of your paper. An outline helps you predict the overall structure and flow of a paper.
Why and How to Create a Useful Outline. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Importance of...
Writing papers in college requires you to come up with sophisticated, complex, and sometimes very creative ways of structuring your ideas . Taking the time to draft an outline can help you determine if your ideas connect to each other, what order of ideas works best, where gaps in your thinking may exist, or whether you have sufficient evidence to support each of your points. It is also an effective way to think about the time you will need to complete each part of your paper before you begin writing.
A good outline is important because :
- You will be much less likely to get writer's block . An outline will show where you're going and how to get there. Use the outline to set goals for completing each section of your paper.
- It will help you stay organized and focused throughout the writing process and help ensure proper coherence [flow of ideas] in your final paper. However, the outline should be viewed as a guide, not a straitjacket. As you review the literature or gather data, the organization of your paper may change; adjust your outline accordingly.
- A clear, detailed outline ensures that you always have something to help re-calibrate your writing should you feel yourself drifting into subject areas unrelated to the research problem. Use your outline to set boundaries around what you will investigate.
- The outline can be key to staying motivated . You can put together an outline when you're excited about the project and everything is clicking; making an outline is never as overwhelming as sitting down and beginning to write a twenty page paper without any sense of where it is going.
- An outline helps you organize multiple ideas about a topic . Most research problems can be analyzed from a variety of perspectives; an outline can help you sort out which modes of analysis are most appropriate to ensure the most robust findings are discovered.
- An outline not only helps you organize your thoughts, but it can also serve as a schedule for when certain aspects of your writing should be accomplished . Review the assignment and highlight the due dates of specific tasks and integrate these into your outline. If your professor has not created specific deadlines, create your own deadlines by thinking about your own writing style and the need to manage your time around other course assignments.
How to Structure and Organize Your Paper. Odegaard Writing & Research Center. University of Washington; Why and How to Create a Useful Outline. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Lietzau, Kathleen. Creating Outlines. Writing Center, University of Richmond.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Approaches
There are two general approaches you can take when writing an outline for your paper:
The topic outline consists of short phrases. This approach is useful when you are dealing with a number of different issues that could be arranged in a variety of different ways in your paper. Due to short phrases having more content than using simple sentences, they create better content from which to build your paper.
The sentence outline is done in full sentences. This approach is useful when your paper focuses on complex issues in detail. The sentence outline is also useful because sentences themselves have many of the details in them needed to build a paper and it allows you to include those details in the sentences instead of having to create an outline of short phrases that goes on page after page.
II. Steps to Making the Outline
A strong outline details each topic and subtopic in your paper, organizing these points so that they build your argument toward an evidence-based conclusion. Writing an outline will also help you focus on the task at hand and avoid unnecessary tangents, logical fallacies, and underdeveloped paragraphs.
- Identify the research problem . The research problem is the focal point from which the rest of the outline flows. Try to sum up the point of your paper in one sentence or phrase. It also can be key to deciding what the title of your paper should be.
- Identify the main categories . What main points will you analyze? The introduction describes all of your main points; the rest of your paper can be spent developing those points.
- Create the first category . What is the first point you want to cover? If the paper centers around a complicated term, a definition can be a good place to start. For a paper that concerns the application and testing of a particular theory, giving the general background on the theory can be a good place to begin.
- Create subcategories . After you have followed these steps, create points under it that provide support for the main point. The number of categories that you use depends on the amount of information that you are trying to cover. There is no right or wrong number to use.
Once you have developed the basic outline of the paper, organize the contents to match the standard format of a research paper as described in this guide.
III. Things to Consider When Writing an Outline
- There is no rule dictating which approach is best . Choose either a topic outline or a sentence outline based on which one you believe will work best for you. However, once you begin developing an outline, it's helpful to stick to only one approach.
- Both topic and sentence outlines use Roman and Arabic numerals along with capital and small letters of the alphabet arranged in a consistent and rigid sequence. A rigid format should be used especially if you are required to hand in your outline.
- Although the format of an outline is rigid, it shouldn't make you inflexible about how to write your paper. Often when you start investigating a research problem [i.e., reviewing the research literature], especially if you are unfamiliar with the topic, you should anticipate the likelihood your analysis could go in different directions. If your paper changes focus, or you need to add new sections, then feel free to reorganize the outline.
- If appropriate, organize the main points of your outline in chronological order . In papers where you need to trace the history or chronology of events or issues, it is important to arrange your outline in the same manner, knowing that it's easier to re-arrange things now than when you've almost finished your paper.
- For a standard research paper of 15-20 pages, your outline should be no more than few pages in length . It may be helpful as you are developing your outline to also write down a tentative list of references.
Muirhead, Brent. “Using Outlines to Improve Online Student Writing Skills.” Journal on School Educational Technology 1, (2005): 17-23; Four Main Components for Effective Outlines. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; How to Make an Outline. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Kartawijaya, Sukarta. “Improving Students’ Writing Skill in Writing Paragraph through an Outline Technique.” Curricula: Journal of Teaching and Learning 3 (2018); Organization: Informal Outlines. The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; Organization: Standard Outline Form. The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; Outlining. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University; Plotnic, Jerry. Organizing an Essay. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Reverse Outline. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Reverse Outlines: A Writer's Technique for Examining Organization. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Using Outlines. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
A Disorganized Outline Means a Disorganized Paper!
If, in writing your paper, it begins to diverge from your outline, this is very likely a sign that you've lost your focus. How do you know whether to change the paper to fit the outline, or, that you need to reconsider the outline so that it fits the paper? A good way to check your progress is to use what you have written to recreate the outline. This is an effective strategy for assessing the organization of your paper. If the resulting outline says what you want it to say and it is in an order that is easy to follow, then the organization of your paper has been successful. If you discover that it's difficult to create an outline from what you have written, then you likely need to revise your paper.
- << Previous: Choosing a Title
- Next: Paragraph Development >>
- Last Updated: May 25, 2024 4:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
APA Research Paper Outline: Examples and Template
Table of contents
- 1 Why Is Research Paper Format Necessary?
- 2.1 Purpose of research paper outline
- 2.2 APA outline example
- 3.1 APA paper outline example
- 3.2 Introduction:
- 3.4 Conclusion:
- 4 The Basic APA Outline Format
- 5 APA Style Outline Template Breakdown
- 6.1 APA Research Paper Outline Example
- 6.2 APA Paper Outline Format Example
- 7.1 First Paragraph: Hook and Thesis
- 7.2 Main Body
- 7.3 Conclusion
- 7.4 Decimal APA outline format example
- 7.5 Decimal APA outline format layout
- 8.1 A definite goal
- 8.2 Division
- 8.3 Parallelism
- 8.4 Coordination
- 8.5 Subordination
- 8.6 Avoid Redundancy
- 8.7 Wrap it up in a good way
- 8.8 Conclusion
Formatting your paper in APA can be daunting if this is your first time. The American Psychological Association (APA) offers a guide or rules to follow when conducting projects in the social sciences or writing papers. The standard APA fromat a research paper outline includes a proper layout from the title page to the final reference pages. There are formatting samples to create outlines before writing a paper. Amongst other strategies, creating an outline is the easiest way to APA format outline template.
Why Is Research Paper Format Necessary?
Consistency in the sequence, structure, and format when writing a research paper encourages readers to concentrate on the substance of a paper rather than how it is presented. The requirements for paper format apply to student assignments and papers submitted for publication in a peer-reviewed publication. APA paper outline template style may be used to create a website, conference poster, or PowerPoint presentation . If you plan to use the style for other types of work like a website, conference poster, or even PowerPoint presentation, you must format your work accordingly to adjust to requirements. For example, you may need different line spacing and font sizes. Follow the formatting rules provided by your institution or publication to ensure its formatting standards are followed as closely as possible. However, to logically structure your document, you need a research paper outline in APA format. You may ask: why is it necessary to create an outline for an APA research paper?
Concept & Purposes of Research Paper Outline
A path, direction, or action plan! Writing short essays without a layout may seem easy, but not for 10,000 or more words. Yet, confusing a table of contents with an outline is a major issue. The table of contents is an orderly list of all the chapters’ front matter, primary, and back matter. It includes sections and, often, figures in your work, labeled by page number. On the other hand, a research APA-style paper outline is a proper structure to follow.
Purpose of research paper outline
An outline is a formalized essay in which you give your own argument to support your point of view. And when you write your apa outline template, you expand on what you already know about the topic. Academic writing papers examine an area of expertise to get the latest and most accurate information to work on that topic. It serves various purposes, including:
- APA paper outline discusses the study’s core concepts.
- The research paper outlines to define the link between your ideas and the thesis.
- It provides you with manageable portions that you can handle.
- The research paper’s APA outline enables the detection of structural faults or gaps.
- As shown in the example, it must clearly comprehend the subject at hand.
APA outline example

This research paper outline example will guide you in formatting the layout for a clear direction to work on. It eliminates the inconsistency along with lacking proper substance in the paper.
Understanding the APA Outline Format
It would not be wrong to say there is no standard outline format. The official publishing handbook does not give precise guidelines for preparing an outline. But, it requires certain basic guidelines to follow regarding typeface, font size, structure, margins, etc.
APA paper outline example
Moreover, the final shape of your work relies on your instructor’s specifications and your particular preferences for APA citation format. Though, it would be better to follow some standards for formatting your outline, for instance:
Times New Roman is a widely accessible standard typeface for an APA essay format in 12-point font. However, serif and sans serif fonts like Arial and Georgia are acceptable in font size 11pt.
The text of your paper format should be double-spaced.
The primary headlines use Roman and Arabic numerals to write an outline.
Headings & Subheadings
While writing an APA essay, there are particular standards for utilizing headings in your outline: I – Main headings are numbered by Roman numerals like I, II, III, IV A – Subheadings are numbered with Capital letters (A, B, C, D) 1 – The APA outline uses Arabic numerals (1-9 type numbers) within those subheadings. a – Below Arabic number subheadings, lower-case letters are used (a, b, a). [1] – Headings below those subheadings use Arabic numbers enclosed in parenthesis.
APA format offers a standard layout for each paper, such as
- 1-inch margins on the top, bottom, left, and right.
- The page number on the upper right corner.
The structure of writing an outline consists of three major sections:
- Introduction
Introduction:
This section highlights crucial background information.
Explain the primary points that support your ideas.
Conclusion:
- Summarize your key arguments.
- Explain how these concepts support your ultimate stance, as shown in APA outline example below.
An outline in APA has three common formats that vary in the numeric sequence of all. To make it easier for you, we have compiled all three templates. You can format your document using these examples for added coherence and structure.
The Basic APA Outline Format

APA Style Outline Template Breakdown
Numbering the APA style format follows five levels of headings that use different alphabets and numbers. For instance, I – Headings use Roman numerals like I, II, and III. A – CAPITAL ALPHABETS”, such as A, B, C, etc. 1 – Headings and subheadings use Arabic numbers (1, 2, 3). a – If there are further headings (the fourth level), use lower-case alphabets. [1] – Headings below that (the fifth level) use Arabic numerals enclosed in parentheses, such as [1], [2], [3].
Full Sentence Outline Format
As the name specifies, the full-sentence style outline format requires every line to be a proper sentence. Full-sentence APA style outline is best recommended for essays and speeches. It gives your writing process an idea or a logical path to follow.
APA Research Paper Outline Example
If you are looking for how to write a research paper outline APA in Full Sentence Format, here is an example:
Full Sentence APA format heading utilizes Roman numerals I, II, and III. Every heading must be a full sentence. Here is an APA style paper outline template for the full-sentence format that will clear all your confusion on how to write an outline in full-sentence format.

APA Paper Outline Format Example
I. Introduction
III. Conclusion
Decimal Outline Format
The decimal outline format for APA research papers differs from other formats. The decimal APA style is simple and uses paragraphs for structure. It contains three main paragraphs, introduction, main body, and conclusion.

First Paragraph: Hook and Thesis
- The first paragraph is a sentence or two that introduces the central concept of your article.
- Introduce your topic or subject of study where your research is applicable as a context for further research.
- Explain why the mentioned issue is essential or relevant to the audience.
- A thesis statement is a claim that you make throughout your whole essay.
- The topic phrase is the first point in any writing to support a thesis statement.
- Give an explanation or provide evidence to support your point.
- Provide verifiable facts, figures, and/or citations from credible sources in your writing. It helps in the substantiating assertion.
- Include as many supporting statements and related evidence in your decimal outline.
Finally, when you write an outline, provide a concluding remark to support your claims.
Decimal APA outline format example
1.0 The main heading 1.1 Subheading under the main heading 1.2 Second digit is represented by subheadings under the main headings 1.2.1 Further division adds another digit in decimal format 1.2.2 You can number them as per the number of paragraphs or points, or lines An easy way to write in decimal APA outline format is to remember the structure, i.e.; 1.1.1 = Heading.Paragraph.Sentence/point under paragraph.”
Decimal APA outline format layout
1.0 Main heading 1.1 First paragraph for first heading. 1.2 Second paragraph for first heading. 1.2.1 First point or sentence for the second paragraph. 2.0 Second heading 2.1 Second heading, first paragraph. 2.2 Second heading, second paragraph. 2.2.1 Second, heading, second paragraph, first sentence, or point. 3.0 Decimal working 3.1 You must remember that each digit represents a segment. 3.2 It is easier to remember the placement of numbers. 3.2.1 First digit represents the heading 3.2.2 Second digit represents the paragraph under the main heading <3.2.3 The third digit represents any point or sentence under the paragraph.
Tips for Writing an Outline: Organize Your Ideas
You may feel it is easier to write without outlines, but once you start writing, organizing your ideas or thoughts becomes hard. Even if you have some fantastic ideas, producing an engaging story is practically hard. If you are not first creating an outline or conceptual guides while writing a research paper, you may lose track. A well-written outline is essential in completing your paper and maintaining quality. Establishing your point in paper writing is easy if you create an outline first. You can find an APA research paper outline template that best suits your requirement. Moreover, these tips can help you polish your writing. These tips and sample papers can help you write outstanding outlines without making any hassle.
A definite goal
For better expression, make a list of primary objectives on a title page in a single phrase or less. Your goal should be specific and measurable. If it is too broad or imprecise, you will not achieve anything. If you are working on a large paper format that covers a variety of themes or topics, you may have a more general purpose in mind. But, if you plan to write an essay, the aim should be as specific and clear as possible to be effective.
Breaking things up rather than allowing them to become verbose is known as the division rule. Make sure that each subsection in the document corresponds to its parent heading. If it doesn’t compare to the section, removing it or moving it to another location is better.
Parallelism
It is mainly related to the consistency and structure of the document. It keeps your paper’s layout tidy and also ensures relevancy. For instance, if you begin one heading with a verb, make sure all other headings and subheadings also start with a verb.
Coordination
Having headings aligned is critical to creating a well-organized outline. This rule also applies to subheadings, which is a good thing. If one title is less important than another, consider changing your layout by incorporating it into a subsection instead.
Subordination
Subordination deals with maintaining a connection between your paper’s headings and subheadings. It helps in the proper sequencing of headings and subheadings. Headings should be broad at the outset. At the same time, the subheadings become more particular as they go further into the document.
Avoid Redundancy
While writing a paper outline, look through it many times and cross out any items that aren’t necessary or have no significance. While outlining, make sure to be specific and concise. It will prevent you from adding information that does not supporting your final essay. Remove all the extra information and points while c that weighs you down while you write.
Wrap it up in a good way
Creating an outline does not only help in writing a coherent term paper, but it also helps in ending with precise understanding. Be considerate of your audience’s time and effort when you write an outline in APA, and ensure it serves its purpose. If you still have any doubts about formatting your paper outline, you can use this APA-style research paper outline template to write your document. We have provided Outline Format Example for every style.
People find it hard to write an outline in APA, but if you are aware of the requirements and structure, it’s no breeze. Sometimes, your instructor may alter your paper format by introducing or removing existing sections. As a result, if you come across any templates for an outline in APA, pay close attention to them. If you are looking for a quick answer to how to outline an APA paper, here’s a standard logical sequence of typical parts to include when writing an outline in APA:
- Thesis statement
- Techniques employed
- Body of paper
- Conclusions section
- List of references
A well-written outline is an excellent tool for presenting an outstanding paper. Including the key components while writing an outline for a research paper is necessary.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Outline – Types, Example, Template
Research Paper Outline – Types, Example, Template
Table of Contents

By creating a well-structured research paper outline, writers can easily organize their thoughts and ideas and ensure that their final paper is clear, concise, and effective. In this article, we will explore the essential components of a research paper outline and provide some tips and tricks for creating a successful one.
Research Paper Outline
Research paper outline is a plan or a structural framework that organizes the main ideas , arguments, and supporting evidence in a logical sequence. It serves as a blueprint or a roadmap for the writer to follow while drafting the actual research paper .
Typically, an outline consists of the following elements:
- Introduction : This section presents the topic, research question , and thesis statement of the paper. It also provides a brief overview of the literature review and the methodology used.
- Literature Review: This section provides a comprehensive review of the relevant literature, theories, and concepts related to the research topic. It analyzes the existing research and identifies the research gaps and research questions.
- Methodology: This section explains the research design, data collection methods, data analysis, and ethical considerations of the study.
- Results: This section presents the findings of the study, using tables, graphs, and statistics to illustrate the data.
- Discussion : This section interprets the results of the study, and discusses their implications, significance, and limitations. It also suggests future research directions.
- Conclusion : This section summarizes the main findings of the study and restates the thesis statement.
- References: This section lists all the sources cited in the paper using the appropriate citation style.
Research Paper Outline Types
There are several types of outlines that can be used for research papers, including:
Alphanumeric Outline
This is a traditional outline format that uses Roman numerals, capital letters, Arabic numerals, and lowercase letters to organize the main ideas and supporting details of a research paper. It is commonly used for longer, more complex research papers.
I. Introduction
- A. Background information
- B. Thesis statement
- 1 1. Supporting detail
- 1 2. Supporting detail 2
- 2 1. Supporting detail
III. Conclusion
- A. Restate thesis
- B. Summarize main points
Decimal Outline
This outline format uses numbers to organize the main ideas and supporting details of a research paper. It is similar to the alphanumeric outline, but it uses only numbers and decimals to indicate the hierarchy of the ideas.
- 1.1 Background information
- 1.2 Thesis statement
- 1 2.1.1 Supporting detail
- 1 2.1.2 Supporting detail
- 2 2.2.1 Supporting detail
- 1 2.2.2 Supporting detail
- 3.1 Restate thesis
- 3.2 Summarize main points
Full Sentence Outline
This type of outline uses complete sentences to describe the main ideas and supporting details of a research paper. It is useful for those who prefer to see the entire paper outlined in complete sentences.
- Provide background information on the topic
- State the thesis statement
- Explain main idea 1 and provide supporting details
- Discuss main idea 2 and provide supporting details
- Restate the thesis statement
- Summarize the main points of the paper
Topic Outline
This type of outline uses short phrases or words to describe the main ideas and supporting details of a research paper. It is useful for those who prefer to see a more concise overview of the paper.
- Background information
- Thesis statement
- Supporting detail 1
- Supporting detail 2
- Restate thesis
- Summarize main points
Reverse Outline
This is an outline that is created after the paper has been written. It involves going back through the paper and summarizing each paragraph or section in one sentence. This can be useful for identifying gaps in the paper or areas that need further development.
- Introduction : Provides background information and states the thesis statement.
- Paragraph 1: Discusses main idea 1 and provides supporting details.
- Paragraph 2: Discusses main idea 2 and provides supporting details.
- Paragraph 3: Addresses potential counterarguments.
- Conclusion : Restates thesis and summarizes main points.
Mind Map Outline
This type of outline involves creating a visual representation of the main ideas and supporting details of a research paper. It can be useful for those who prefer a more creative and visual approach to outlining.
- Supporting detail 1: Lack of funding for public schools.
- Supporting detail 2: Decrease in government support for education.
- Supporting detail 1: Increase in income inequality.
- Supporting detail 2: Decrease in social mobility.
Research Paper Outline Example
Research Paper Outline Example on Cyber Security:
A. Overview of Cybersecurity
- B. Importance of Cybersecurity
- C. Purpose of the paper
II. Cyber Threats
A. Definition of Cyber Threats
- B. Types of Cyber Threats
- C. Examples of Cyber Threats
III. Cybersecurity Measures
A. Prevention measures
- Anti-virus software
- Encryption B. Detection measures
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Security Operations Center (SOC) C. Response measures
- Incident Response Plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Disaster Recovery Plan
IV. Cybersecurity in the Business World
A. Overview of Cybersecurity in the Business World
B. Cybersecurity Risk Assessment
C. Best Practices for Cybersecurity in Business
V. Cybersecurity in Government Organizations
A. Overview of Cybersecurity in Government Organizations
C. Best Practices for Cybersecurity in Government Organizations
VI. Cybersecurity Ethics
A. Definition of Cybersecurity Ethics
B. Importance of Cybersecurity Ethics
C. Examples of Cybersecurity Ethics
VII. Future of Cybersecurity
A. Overview of the Future of Cybersecurity
B. Emerging Cybersecurity Threats
C. Advancements in Cybersecurity Technology
VIII. Conclusion
A. Summary of the paper
B. Recommendations for Cybersecurity
- C. Conclusion.
IX. References
A. List of sources cited in the paper
B. Bibliography of additional resources
Introduction
Cybersecurity refers to the protection of computer systems, networks, and sensitive data from unauthorized access, theft, damage, or any other form of cyber attack. B. Importance of Cybersecurity The increasing reliance on technology and the growing number of cyber threats make cybersecurity an essential aspect of modern society. Cybersecurity breaches can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. C. Purpose of the paper This paper aims to provide an overview of cybersecurity, cyber threats, cybersecurity measures, cybersecurity in the business and government sectors, cybersecurity ethics, and the future of cybersecurity.
A cyber threat is any malicious act or event that attempts to compromise or disrupt computer systems, networks, or sensitive data. B. Types of Cyber Threats Common types of cyber threats include malware, phishing, social engineering, ransomware, DDoS attacks, and advanced persistent threats (APTs). C. Examples of Cyber Threats Recent cyber threats include the SolarWinds supply chain attack, the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack, and the Microsoft Exchange Server hack.
Prevention measures aim to minimize the risk of cyber attacks by implementing security controls, such as firewalls, anti-virus software, and encryption.
- Firewalls Firewalls act as a barrier between a computer network and the internet, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic to prevent unauthorized access.
- Anti-virus software Anti-virus software detects, prevents, and removes malware from computer systems.
- Encryption Encryption involves the use of mathematical algorithms to transform sensitive data into a code that can only be accessed by authorized individuals. B. Detection measures Detection measures aim to identify and respond to cyber attacks as quickly as possible, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM), and security operations centers (SOCs).
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS) IDS monitors network traffic for signs of unauthorized access, such as unusual patterns or anomalies.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) SIEM combines security information management and security event management to provide real-time monitoring and analysis of security alerts.
- Security Operations Center (SOC) SOC is a dedicated team responsible for monitoring, analyzing, and responding to cyber threats. C. Response measures Response measures aim to mitigate the impact of a cyber attack and restore normal operations, such as incident response plans (IRPs), business continuity plans (BCPs), and disaster recovery plans (DRPs).
- Incident Response Plan IRPs outline the procedures and protocols to follow in the event of a cyber attack, including communication protocols, roles and responsibilities, and recovery processes.
- Business Continuity Plan BCPs ensure that critical business functions can continue in the event of a cyber attack or other disruption.
- Disaster Recovery Plan DRPs outline the procedures to recover from a catastrophic event, such as a natural disaster or cyber attack.
Cybersecurity is crucial for businesses of all sizes and industries, as they handle sensitive data, financial transactions, and intellectual property that are attractive targets for cyber criminals.
Risk assessment is a critical step in developing a cybersecurity strategy, which involves identifying potential threats, vulnerabilities, and consequences to determine the level of risk and prioritize security measures.
Best practices for cybersecurity in business include implementing strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, regularly updating software and hardware, training employees on cybersecurity awareness, and regularly backing up data.
Government organizations face unique cybersecurity challenges, as they handle sensitive information related to national security, defense, and critical infrastructure.
Risk assessment in government organizations involves identifying and assessing potential threats and vulnerabilities, conducting regular audits, and complying with relevant regulations and standards.
Best practices for cybersecurity in government organizations include implementing secure communication protocols, regularly updating and patching software, and conducting regular cybersecurity training and awareness programs for employees.
Cybersecurity ethics refers to the ethical considerations involved in cybersecurity, such as privacy, data protection, and the responsible use of technology.
Cybersecurity ethics are crucial for maintaining trust in technology, protecting privacy and data, and promoting responsible behavior in the digital world.
Examples of cybersecurity ethics include protecting the privacy of user data, ensuring data accuracy and integrity, and implementing fair and unbiased algorithms.
The future of cybersecurity will involve a shift towards more advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and quantum computing.
Emerging cybersecurity threats include AI-powered cyber attacks, the use of deepfakes and synthetic media, and the potential for quantum computing to break current encryption methods.
Advancements in cybersecurity technology include the development of AI and machine learning-based security tools, the use of blockchain for secure data storage and sharing, and the development of post-quantum encryption methods.
This paper has provided an overview of cybersecurity, cyber threats, cybersecurity measures, cybersecurity in the business and government sectors, cybersecurity ethics, and the future of cybersecurity.
To enhance cybersecurity, organizations should prioritize risk assessment and implement a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes prevention, detection, and response measures. Additionally, organizations should prioritize cybersecurity ethics to promote responsible behavior in the digital world.
C. Conclusion
Cybersecurity is an essential aspect of modern society, and organizations must prioritize cybersecurity to protect sensitive data and maintain trust in technology.
for further reading
X. Appendices
A. Glossary of key terms
B. Cybersecurity checklist for organizations
C. Sample cybersecurity policy for businesses
D. Sample cybersecurity incident response plan
E. Cybersecurity training and awareness resources
Note : The content and organization of the paper may vary depending on the specific requirements of the assignment or target audience. This outline serves as a general guide for writing a research paper on cybersecurity. Do not use this in your assingmets.
Research Paper Outline Template
- Background information and context of the research topic
- Research problem and questions
- Purpose and objectives of the research
- Scope and limitations
II. Literature Review
- Overview of existing research on the topic
- Key concepts and theories related to the research problem
- Identification of gaps in the literature
- Summary of relevant studies and their findings
III. Methodology
- Research design and approach
- Data collection methods and procedures
- Data analysis techniques
- Validity and reliability considerations
- Ethical considerations
IV. Results
- Presentation of research findings
- Analysis and interpretation of data
- Explanation of significant results
- Discussion of unexpected results
V. Discussion
- Comparison of research findings with existing literature
- Implications of results for theory and practice
- Limitations and future directions for research
- Conclusion and recommendations
VI. Conclusion
- Summary of research problem, purpose, and objectives
- Discussion of significant findings
- Contribution to the field of study
- Implications for practice
- Suggestions for future research
VII. References
- List of sources cited in the research paper using appropriate citation style.
Note : This is just an template, and depending on the requirements of your assignment or the specific research topic, you may need to modify or adjust the sections or headings accordingly.
Research Paper Outline Writing Guide
Here’s a guide to help you create an effective research paper outline:
- Choose a topic : Select a topic that is interesting, relevant, and meaningful to you.
- Conduct research: Gather information on the topic from a variety of sources, such as books, articles, journals, and websites.
- Organize your ideas: Organize your ideas and information into logical groups and subgroups. This will help you to create a clear and concise outline.
- Create an outline: Begin your outline with an introduction that includes your thesis statement. Then, organize your ideas into main points and subpoints. Each main point should be supported by evidence and examples.
- Introduction: The introduction of your research paper should include the thesis statement, background information, and the purpose of the research paper.
- Body : The body of your research paper should include the main points and subpoints. Each point should be supported by evidence and examples.
- Conclusion : The conclusion of your research paper should summarize the main points and restate the thesis statement.
- Reference List: Include a reference list at the end of your research paper. Make sure to properly cite all sources used in the paper.
- Proofreading : Proofread your research paper to ensure that it is free of errors and grammatical mistakes.
- Finalizing : Finalize your research paper by reviewing the outline and making any necessary changes.
When to Write Research Paper Outline
It’s a good idea to write a research paper outline before you begin drafting your paper. The outline will help you organize your thoughts and ideas, and it can serve as a roadmap for your writing process.
Here are a few situations when you might want to consider writing an outline:
- When you’re starting a new research project: If you’re beginning a new research project, an outline can help you get organized from the very beginning. You can use your outline to brainstorm ideas, map out your research goals, and identify potential sources of information.
- When you’re struggling to organize your thoughts: If you find yourself struggling to organize your thoughts or make sense of your research, an outline can be a helpful tool. It can help you see the big picture of your project and break it down into manageable parts.
- When you’re working with a tight deadline : If you have a deadline for your research paper, an outline can help you stay on track and ensure that you cover all the necessary points. By mapping out your paper in advance, you can work more efficiently and avoid getting stuck or overwhelmed.
Purpose of Research Paper Outline
The purpose of a research paper outline is to provide a structured and organized plan for the writer to follow while conducting research and writing the paper. An outline is essentially a roadmap that guides the writer through the entire research process, from the initial research and analysis of the topic to the final writing and editing of the paper.
A well-constructed outline can help the writer to:
- Organize their thoughts and ideas on the topic, and ensure that all relevant information is included.
- Identify any gaps in their research or argument, and address them before starting to write the paper.
- Ensure that the paper follows a logical and coherent structure, with clear transitions between different sections.
- Save time and effort by providing a clear plan for the writer to follow, rather than starting from scratch and having to revise the paper multiple times.
Advantages of Research Paper Outline
Some of the key advantages of a research paper outline include:
- Helps to organize thoughts and ideas : An outline helps to organize all the different ideas and information that you want to include in your paper. By creating an outline, you can ensure that all the points you want to make are covered and in a logical order.
- Saves time and effort : An outline saves time and effort because it helps you to focus on the key points of your paper. It also helps you to identify any gaps or areas where more research may be needed.
- Makes the writing process easier : With an outline, you have a clear roadmap of what you want to write, and this makes the writing process much easier. You can simply follow your outline and fill in the details as you go.
- Improves the quality of your paper : By having a clear outline, you can ensure that all the important points are covered and in a logical order. This makes your paper more coherent and easier to read, which ultimately improves its overall quality.
- Facilitates collaboration: If you are working on a research paper with others, an outline can help to facilitate collaboration. By sharing your outline, you can ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Why and How to Create a Useful Outline

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Why create an outline? There are many reasons, but in general, it may be helpful to create an outline when you want to show the hierarchical relationship or logical ordering of information. For research papers, an outline may help you keep track of large amounts of information. For creative writing, an outline may help organize the various plot threads and help keep track of character traits. Many people find that organizing an oral report or presentation in outline form helps them speak more effectively in front of a crowd. Below are the primary reasons for creating an outline.
- Aids in the process of writing
- Helps you organize your ideas
- Presents your material in a logical form
- Shows the relationships among ideas in your writing
- Constructs an ordered overview of your writing
- Defines boundaries and groups
How do I create an outline?
- Determine the purpose of your paper.
- Determine the audience you are writing for.
- Develop the thesis of your paper.
- Brainstorm : List all the ideas that you want to include in your paper.
- Organize : Group related ideas together.
- Order : Arrange material in subsections from general to specific or from abstract to concrete.
- Label : Create main and sub headings.
Remember: creating an outline before writing your paper will make organizing your thoughts a lot easier. Whether you follow the suggested guidelines is up to you, but making any kind of outline (even just some jotting down some main ideas) will be beneficial to your writing process.

- Foundations
- Write Paper
Search form
- Experiments
- Anthropology
- Self-Esteem
- Social Anxiety

- Research Paper >
Research Paper Outline Examples
Below are examples of research paper outlines. Creating an outline is the first thing you should do before starting on your research paper.
This article is a part of the guide:
- Example of a Paper
- Write a Hypothesis
- Introduction
- Example of a Paper 2
Browse Full Outline
- 1 Write a Research Paper
- 2 Writing a Paper
- 3.1 Write an Outline
- 3.2 Outline Examples
- 4.1 Thesis Statement
- 4.2 Write a Hypothesis
- 5.2 Abstract
- 5.3 Introduction
- 5.4 Methods
- 5.5 Results
- 5.6 Discussion
- 5.7 Conclusion
- 5.8 Bibliography
- 6.1 Table of Contents
- 6.2 Acknowledgements
- 6.3 Appendix
- 7.1 In Text Citations
- 7.2 Footnotes
- 7.3.1 Floating Blocks
- 7.4 Example of a Paper
- 7.5 Example of a Paper 2
- 7.6.1 Citations
- 7.7.1 Writing Style
- 7.7.2 Citations
- 8.1.1 Sham Peer Review
- 8.1.2 Advantages
- 8.1.3 Disadvantages
- 8.2 Publication Bias
- 8.3.1 Journal Rejection
- 9.1 Article Writing
- 9.2 Ideas for Topics
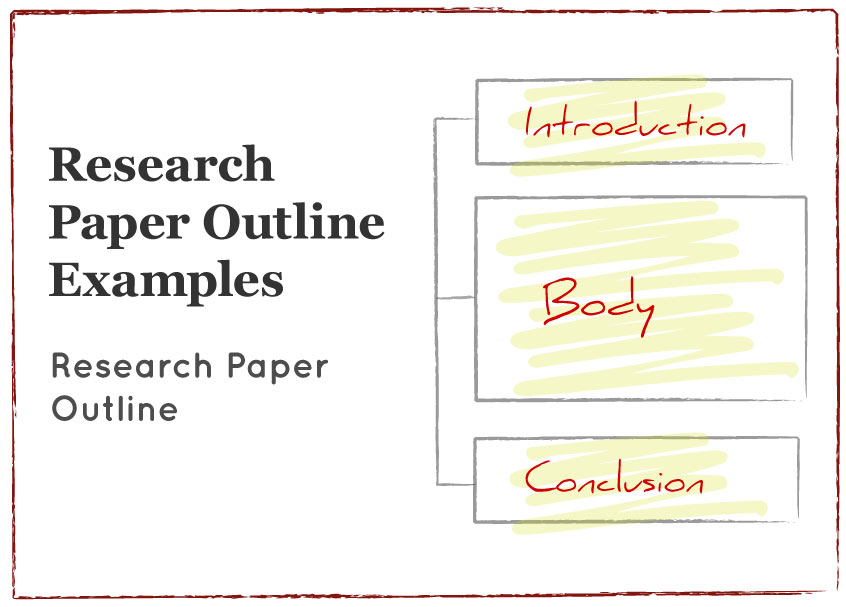
Once you've decided what topic you will be writing about, the next thing you should pay attention to is the scope of your paper or what you will be including in your discussion . The broader your topic is, the more difficult it is to discuss the full details. This is why you should establish early on the scope and limitations of your paper which will provide the foundation for your research paper outline.
Basically, your outline will constitute three main sections: the Introduction, the Body and the Conclusion. But to make sure your paper is complete, consult your instructor for specific parts they wants to be included in your research paper . Sample outlines for research papers will follow. But first, let’s discuss the main sections of your paper and what information each should cover.

The introduction should contain your thesis statement or the topic of your research as well as the purpose of your study. You may include here the reason why you chose that particular topic or simply the significance of your research paper's topic. You may also state what type of approach it is that you'll be using in your paper for the entire discussion of your topic. Generally, your Introduction should orient your readers to the major points the rest of the paper will be covering, and how.

The body of your paper is where you will be presenting all your arguments to support your thesis statement. Remember the “Rule of 3” which states that you should find 3 supporting arguments for each position you take. Start with a strong argument, followed by a stronger one, and end with the strongest argument as your final point.
The conclusion is where you form a summary of all your arguments so you can arrive at your final position. Explain and reiterate why you've ended up with the said conclusion.
As mentioned earlier, here are some sample outlines for research papers:
Thesis Topic: A Study on Factors Affecting the Infant Feeding Practices of Mothers in Las Pinas City
- Statement of the Problem
- Definition of Terms
- Theoretical Framework
- Type of Research
- Respondents
- Questionnaire
- Review of Related Literature
- Scope and Limitations
- Significance of the Study
- Benefits of Breastfeeding
- WHO Recommendations
- The International Code of Marketing of Breast Milk Substitutes
- The Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative
- The Innocenti Declaration on the Protection, Promotion and Support of Breastfeeding
- National Situationer
- The Milk Code
- BFHI in the Philippines
- Milk Code Violations
- Formula Feeding
- Factors Influencing the Decision Regarding Infant Feeding Method
- Area Situationer
- Socio-economic Demographic Profile of Mothers
- Information Regarding Current (Youngest) Infant
- Exclusive Breastfeeding
- Mixed Feeding
- Previous Infant Feeding Practices
- Maternal Knowledge
- Correlation Tests
- Analytical Summary
- Thesis Reworded
- Recommendations
Topic: Asbestos Poisoning
- Definition of Asbestos Poisoning
- Symptoms of Asbestos Poisoning
- Effects of Asbestos Poisoning
- How to Deal with Asbestos Hazards
Topic: Shakespeare Adapted from AResearchGuide.com .
- Life of Anne Hathaway
- Reference in Shakespeare's Poems
- Romeo and Juliet
- The Tempest
- Much Ado About Nothing
- Richard III
- Other Poems
- Last Two Plays
- Concluding Statement

- Psychology 101
- Flags and Countries
- Capitals and Countries
Explorable.com (Jan 6, 2009). Research Paper Outline Examples. Retrieved May 28, 2024 from Explorable.com: https://explorable.com/research-paper-outline-examples
You Are Allowed To Copy The Text
The text in this article is licensed under the Creative Commons-License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) .
This means you're free to copy, share and adapt any parts (or all) of the text in the article, as long as you give appropriate credit and provide a link/reference to this page.
That is it. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).
Related articles
Want to stay up to date follow us, check out the official book.
Learn how to construct, style and format an Academic paper and take your skills to the next level.

(also available as ebook )
Save this course for later
Don't have time for it all now? No problem, save it as a course and come back to it later.
Footer bottom
- Privacy Policy

- Subscribe to our RSS Feed
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter

How to Write an Explanatory Essay
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Published: May 24, 2024
A study from the English Language Teaching Educational Journal found that students encounter difficulty in organizing thoughts, generating ideas, and understanding writing processes when writing essays [1]. These are all key components of putting together a good explanatory essay. If this sounds like you, then don’t worry.
With the right approach, you can seamlessly combine all these components. This guide will give you a simple step-by-step strategy for writing an explanatory essay. It’ll also give you handy writing tips and tool suggestions, like utilizing artificial intelligence.
With this guide, you’ll be able to write an explanatory essay with confidence.
1. Develop a strong thesis statement
Crafting a strong thesis statement is the cornerstone of any well-written explanatory essay. It sets the stage for what your essay will cover and clarifies the main point you’re going to explain. Here’s how to create a thesis:
- Find the main idea : Start by pinpointing the key concept or question you want to explain. Develop a clear purpose for the essay. This will guide your research and writing process for your explanatory paper. Use other reputable explanatory essay examples to guide your ideas. This may involve exploring other explanatory essay topics within the same field.
- Be specific : A vague thesis can confuse readers. So, make sure your statement is clear. If you’re explaining a complex process, break it down to its key points. After that, break it into a clear, concise statement that’s easy to understand.
- Reflect objectivity : Explanatory essays educate and inform. They do not argue a point. So, your thesis should take an unbiased stance on the topic. It should present the facts as they are, not as you interpret them.
- Use tools like the Smodin Writer : Smodin Writer does all the heavy lifting by leveraging the power of artificial intelligence. With it, you can generate an essay with a thesis statement. How, you ask? Through its dedicated thesis generator . It can create a statement that’s both strong and relevant. Plus, it can pull in all the most interesting information based on your topic to further enrich your thesis statement.
Make your thesis clear, informative, and neutral. This sets a strong foundation for an effective explanatory essay. Next, let’s look at how to gather the information you’ll need to support this thesis effectively.
2. Research and gather information
You need to conduct thorough research that will back your thesis with credible sources and relevant evidence. This will make your explanatory essay both informative and persuasive. Here’s a step-by-step guide to conducting effective research:
- Start with a plan: Put together an explanatory essay outline that includes the information you need to support your thesis. The plan should list the best sources, like academic journals, books, reputable websites, or scholarly articles.
- Use credible sources: They ensure the accuracy of your essay. Libraries, academic databases, and certified websites are excellent places to find trustworthy information.
- Seek detailed information: Look for the most current sources that explain your topic well and provide unique insights related to or opposing your thesis statement. This depth is crucial for explaining complex ideas clearly and thoroughly in your explanatory papers. Pay attention to the explanatory essay structure to guide your topic of choice (more on this later).
- Gather relevant evidence: Collect data, stats, and examples. They should directly support your main points. Make sure this evidence is directly related to your topic and enhances your narrative.
- Employ digital tools: Tools like Smodin’s Research Assistant can accelerate your research process. Smodin’s tools can help you find detailed information quickly, ensuring that the data you use is up-to-date and relevant.
- Document your sources: As you conduct research, keep a meticulous record of where your information comes from. This practice will help you make an accurate bibliography. It can save you time when you need to refer back to details or verify facts. Again, this is something that’s covered thanks to Smodin’s Citation Machine.
- Evaluate your findings: Critically assess the information you collect. Ensure it provides a balanced view and covers the necessary aspects of your topic to give a comprehensive overview of your essay.
By following these steps, you can gather a rich pool of information that provides a strong backbone for your explanatory essay. Now, you can start structuring your findings into well-organized body paragraphs.
3. Structure body paragraphs
Once you’ve gathered relevant evidence through thorough research, it’s time to organize it. You should put it into well-structured body paragraphs that follow a logical flow. Here’s how to structure each body paragraph for a strong explanatory essay:
- Decide how many paragraphs to use : It will depend on your topic’s complexity and the needed detail. Typically, three to five paragraphs are suitable, but longer essays may require more. An explanatory essay example on your topic of choice will be helpful.
- Start with a topic sentence : Each body paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. This sentence will act as a roadmap for the paragraph, giving the reader a sense of what to expect.
- Provide supporting evidence : After the topic sentence, share the evidence from your research. Ensure the evidence is relevant and directly supports the paragraph’s topic sentence.
- Give a detailed explanation : Follow the evidence with an analysis or explanation that ties it back to the thesis statement. This step is crucial for maintaining logical flow throughout your body paragraphs.
- Use linking words : They connect body paragraphs smoothly, ensuring the reader can follow your argument.
- End each body paragraph with a closing sentence : It should sum up the point and move to the next idea.
Following this structure will help your body paragraphs support your thesis. These paragraphs will also offer a clear, detailed explanation of your essay topic. Strong body paragraphs are essential to maintain objectivity in your writing.
4. Maintain objectivity
An explanatory essay aims to inform and educate, which makes maintaining objectivity crucial. Staying neutral lets readers form their own opinions based on facts. This ensures the writing is both reliable and informative. Here’s how to maintain objectivity:
- Avoid personal opinions: Your goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Refrain from injecting your personal opinion or biases. Instead, stick to presenting factual information that supports the thesis.
- Use relevant evidence: As mentioned, ground your arguments with relevant evidence from credible sources. Back up your main points with data and use research findings and verified details. This will make the explanatory article trustworthy.
- Provide a balanced view: In cases with multiple perspectives, offer a balanced view. Cover each side fairly. Even if one view prevails in consensus, acknowledging others gives readers a broader understanding.
- Adopt neutral language: Be careful with word choice and tone. Neutral language implies words that don’t encourage or illustrate bias. This helps avoid emotionally charged phrases and keeps the writing objective.
- Cite sources accurately: Proper citation of sources provides accountability for the evidence presented. This transparency builds credibility and shows you’ve conducted research thoroughly. It’s also worth noting that different intuitions have different citation styles like APA and Chicago, which is important to note before starting your essay.
- Review for biases: After drafting your essay, review it with an eye for biases. Ensure no part leans too much on one viewpoint. And, don’t dismiss an opposing perspective without cause.
Maintaining objectivity enhances the clarity and reliability of explanatory writing. Let’s now focus on crafting an introduction and conclusion that bookend your work effectively.
5. Craft an effective introduction and conclusion
A good introduction and a strong conclusion frame your explanatory essay. They give context at the start and reinforce the main points at the end. Here’s how to craft an effective introduction and conclusion.
In the introduction:
- Hook your reader in the introduction : Use an interesting fact, a compelling quote, or a surprising statistic.
- Provide background information : Be brief and offer only the essential context the reader needs to fully understand the topic. This should give the audience a foundational understanding before diving deeper into your main points.
- Include the thesis statement : Clearly state your thesis near the end of the introduction. This statement will outline the essay’s direction and give readers a preview of the body paragraphs.
In the conclusion:
- Summarize the key points : Start your explanatory essay conclusion with a summary. It should cover the main points from the body paragraphs. This summary should help readers recall and reinforce the information they’ve just read.
- Restate the thesis : Repeat your thesis again but in a new way. Explain how the evidence from the body paragraphs supported or clarified it.
- Provide a conclusion : End the essay with a statement that wraps up the argument. This statement should resonate with the reader. It should leave them with an impression that stresses the topic’s importance.
An effective introduction and conclusion give the essay structure and coherence. They guide readers from start to finish. The next step is revising and editing your entire essay for clarity and precision.
6. Revise and check clarity
Revising and editing are key in writing. They make sure your essay is clear, joined, and polished. Here’s how to refine your writing using an explanatory essay checklist and proven academic writing techniques:
- Take a break: Before diving into revisions, step away from your essay for a few hours or even a day. This break will help you return with fresh eyes, making it easier to spot errors or inconsistencies.
- Follow an essay checklist: Create or use a checklist to ensure your essay has all the needed parts. It needs a strong intro with a clear thesis, well-structured body paragraphs, good sources, and a short conclusion. Check that your arguments follow a logical flow and that all relevant evidence is directly linked to your thesis statement.
- Check for clarity and conciseness: Academic writing needs clarity. So, make sure each paragraph and sentence conveys your point. Don’t use unnecessary jargon or overly complex language. Keep sentences concise while maintaining detailed explanations of your main points.
- Verify facts and citations: Make sure all facts, data, and quotes in the essay are accurate. Also, check that they are cited in the required academic style (e.g. MLA, APA). Improper citations can undermine the credibility of your writing.
- Review the grammar and style: Look for common grammar mistakes, punctuation errors, and awkward phrasing. Reading the essay aloud can help catch odd sentence structures or confusing wording.
- Seek feedback: Share your essay with a peer or use online tools to get constructive criticism. A second perspective can highlight issues you might have missed.
These editing steps will help you produce a polished essay that clearly explains your main points and holds up to academic scrutiny.
Explanatory Essay Format
Understanding the explanatory essay format is key to a well-structured and logical paper. Here’s a basic breakdown of the format for an explanatory essay:
Introduction paragraph
- Begin with an interesting sentence to capture the reader’s attention.
- Give a short intro. It should set the topic and outline the essay’s purpose.
- Present a clear thesis statement summarizing the main idea of the entire essay.
Body paragraphs
- Organize the body paragraphs around logical subtopics related to the essay topic.
- Start each body paragraph with a topic sentence that aligns with the thesis.
- Show evidence from good sources. Also, give key details for each main point.
- Incorporate a robust concluding statement per paragraph that drives home your point and links to the ideas in the next paragraph/section.
- Summarize the key points.
- Provide a final statement that reinforces the main idea without introducing new information.
- Craft a concluding statement that leaves your teacher or professor with a lasting impression.
Following this essay outline ensures that your paper has a clear flow. This makes it easy for readers to understand and follow your argument.
Write Better Explanatory Essays With Smodin
Explanatory essays can be overwhelming. Presenting a solid argument, keeping your professor or teacher interested, and remembering conventions like citations can be a real headache.
But, a strong thesis and thorough research make them easier. Well-structured body paragraphs also help deliver a clear, insightful essay that maintains objectivity. Just remember to revise and check for accuracy!
AI-powered platforms like Smodin simplify and enhance the process of writing explanatory essays.
Smodin’s tools help craft clear and well-structured essays that meet any of your academic standards. With Smodin’s advanced research capabilities, you can gather detailed and relevant information quickly. This will save you time and improve your work.
- Plagiarism Checker : Ensure your essay maintains originality with Smodin’s plagiarism detection tool. This feature helps maintain academic integrity by checking your work against vast databases.
- Auto Citation : Cite your sources accurately without the hassle. Smodin’s auto-citation tool ensures your references are in the right format and meet your academic institution’s rules.
- Text Shortener : If your explanatory essay is too long, use Smodin’s AI writer as an essay shortener. It will help you cut your content without losing key details. This helps keep your essay clear and relevant.
- Text Rewriter : Helps paraphrase existing content, ensuring uniqueness and a fresh perspective.
- Summarizer : The Summarizer boils down long articles into short summaries. They are perfect for making an efficient outline or conclusion.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
Thesis outline typically follows a standard format and includes the following sections: Title page: This page includes the thesis title, author's name, department, university, and the date of submission. Abstract: This section is a brief summary of the thesis, highlighting the main points and conclusions. It usually contains around 150-300 words.
Here is a shortened example of an outline: Introduction: background and thesis statement. Body. I. First topic. A. Point A. 1. Supporting evidence 2. Supporting evidence. a. Detail. II. Second Topic. III. Third Topic. Conclusion. I. Summarize the main points of your paper II. Restate your thesis in different words III. Make a strong final statement
Thesis Paper Outline (Word) A thesis paper outline example is a draft that details all the key points that would normally go in a thesis paper. Such an example has an introduction, the content body and a conclusion in rough draft. These would later be used by the writer in composing the actual thesis paper.
The outline is the skeleton of your research paper. Simply start by writing down your thesis and the main ideas you wish to present. This will likely change as your research progresses; therefore, do not worry about being too specific in the early stages of writing your outline. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile.
Example 1: Passive construction. The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise. Example: Passive construction.
A thesis paper outline is a simple way of ensuring that each of your paragraphs serves a specific purpose in your paper. All students need to master this writing tool as it helps you organize your work. ... Thesis Outline Format. A conventional thesis paper will have the following sections: Title; Introduction (contains the background and ...
3. Results Section: Use the same timeline or topics you introduced in the method section. Make sure you answer all the questions you raised in the introduction. Use tables, graphs, and other visualizations to guide the reader. Don't present results of tests/analyses that you did not mention in the methods. 4.
Think through the sequence in which you will present your topic and ideas. Structure the research paper outline in a way that allows a clear and continuous narrative that is easy to understand. For example, the introduction must be concise and engaging and must clearly introduce the research topic. The main paragraphs must focus on the research ...
Here are some additional tips to keep in mind when writing a research paper outline: 1. Pick a topic of your interest. Make sure the scope of the topic is not too broad or too narrow. 2. Formulate a thesis statement. 3. Gather all relevant ideas that give support to your thesis statement. 4.
Once you have developed the basic outline of the paper, organize the contents to match the standard format of a research paper as described in this guide. III. Things to Consider When Writing an Outline. There is no rule dictating which approach is best. Choose either a topic outline or a sentence outline based on which one you believe will ...
If you are looking for how to write a research paper outline APA in Full Sentence Format, here is an example: A. For subheadings, you use capital alphabets A, B, C. B. Subheadings must complement, lead, or link to the paper's main idea. 1. Arabic numerals are used for headings under subheadings like 1, 2, and 3. 2.
Outline a paragraph to support each point in the thesis. Begin each with a topic sentence that sequentially addresses points in the thesis. For example, the first body paragraph in an essay using the thesis above may be: " 'Rosemary's Baby' was among the first films to successfully use several cinematic elements to create atmospheric horror."
This type of outline involves creating a visual representation of the main ideas and supporting details of a research paper. It can be useful for those who prefer a more creative and visual approach to outlining. Example: Introduction: Provides background information and states the thesis statement. Body :
This outline is most often used when preparing a traditional essay. Select the "Sample Outlines" PDF in the Media Box above to download the sample of this outline. Decimal Outlines. The decimal outline is similar in format to the alphanumeric outline. The added benefit is a system of decimal notation that clearly shows how every level of the ...
Brainstorm: List all the ideas that you want to include in your paper. Organize: Group related ideas together. Order: Arrange material in subsections from general to specific or from abstract to concrete. Label: Create main and sub headings. Remember: creating an outline before writing your paper will make organizing your thoughts a lot easier.
Below are examples of research paper outlines. Creating an outline is the first thing you should do before starting on your research paper. ... As mentioned earlier, here are some sample outlines for research papers: Sample #1. Thesis Topic: A Study on Factors Affecting the Infant Feeding Practices of Mothers in Las Pinas City. Introduction.
For a master's, get ready to craft 12,000-50,000 words; for a Ph.D., your dissertation may look like a book of 70,000-100,000 words! It stands to reason that such a substantial academic paper can't be of the same structure as a standard college essay or thesis. Here's a more detailed outline structure for your dissertation:
Now, using this essay writing guide, let's explore how to create a well-structured introduction in ten steps. Each step is crucial in writing an essay introduction that captures attention and presents the thesis. Start with a hook: Begin with something that is engaging. Use a startling fact, a quote from a well-known figure, or a riveting ...
Here's a basic breakdown of the format for an explanatory essay: Introduction paragraph. Begin with an interesting sentence to capture the reader's attention. Give a short intro. It should set the topic and outline the essay's purpose. Present a clear thesis statement summarizing the main idea of the entire essay. Body paragraphs