
Oxford University Press's Academic Insights for the Thinking World


Long, short, and efficient titles for research articles

A Concise Guide to Communication in Science and Engineering
- By David H. Foster
- September 4 th 2018
The title of a research article has an almost impossible remit. As the freely available representative of the work, it needs to accurately capture what was achieved, differentiate it from other works, and, of course, attract the attention of the reader, who might be searching a journal’s contents list or the return from a database query. The title needs also, in passing, to signal the author’s competence and authority. Getting it right is vital. Success or otherwise is likely to decide whether the article is retrieved, read, and potentially cited by other researchers—crucial for recognition in science.
Is a long title or a short one better? A long title has obvious advantages in communicating content, but if it is too long, it may be difficult to digest, inducing the reader—with little time and commitment—to move on to the next article in his or her search. Conversely, a short title may be easy to digest, but too short to inform, leaving the reader again to move on. These considerations suggest there is an optimum number of words: enough to reflect content, yet not enough to bore.
The traditional recommendation from manuals on scientific writing and from academic publishers is that 10–12 words is about right, certainly no more, although the evidential basis is uncertain. Do authors follow this guidance? I took a sample of 4,000 article titles from the Web of Science database, published by Clarivate Analytics (formerly Thomson Reuters). The articles were from eight research areas: physics, chemistry, mathematics, cell biology, computer science, engineering, psychology, and general and internal medicine. The average or mean title length was 12.3 words, surprisingly close to the 10–12-word recommendation.
This estimate is necessarily subject to sampling error. Furthermore, it depends on the publication year from which the articles are taken. The mean title length of 12.3 words just quoted was for 2012. It was somewhat smaller at 10.9 words in 2002 and smaller still at 10.1 words in 1982. Mean title length also depends on the choice of subject area, the definition of journal article, and the coverage of the database (whose evolution may have contributed to the growth in mean title length). Nevertheless, reassuringly similar values emerged from an analysis of a larger sample of titles taken from the Scopus database, published by Elsevier.
On average, then, title lengths comply with expectations, possibly reflecting the wisdom of crowds, or of editors. Individually, however, title lengths vary enormously, with around 10% having either fewer than five words or more than 20. So, do articles with extreme titles—those whose lengths fall very far from the mean—succeed in attracting the attention of readers?
Here are two very short titles. The first is from a review article published in 2012 in the Annual Review of Psychology :
“Intelligence”
This article has had more than 180 citations, placing it in the top 1% in its subject area and publication year (citations and centiles for subject areas taken from Scopus for the period 2012–18). As a review article in the social sciences, though, it might be expected to be highly cited. The second title is from an original experimental research article published in 2012 in Physical Review Letters , which in spite of its name is not a review journal:
“Orthorhombic BiFeO3”
The topic addressed is less generally accessible, yet this article has had more than 40 citations and is in the top 7% for its area and year.
Importantly, adding more words to these titles to make them more specific does not seem to deliver a proportional gain in information. Consider expanding “Intelligence” to “An Overview of Contributions to Intelligence Research” or changing “Orthorhombic BiFeO3” to “Creation of a new orthorhombic phase of the multiferroic BiFeO3.” The additions, drawn from the article abstracts, just make explicit what is already largely implied.
So, do articles with extreme titles—those whose lengths fall very far from the mean—succeed in attracting the attention of readers?
By contrast with these very short titles, here are two very long ones. The first has 33 words—with hyphens treated as separators—and was published in 2012 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology :
“Cost-effectiveness of transcatheter aortic valve replacement compared with surgical aortic valve replacement in high-risk patients with severe aortic stenosis: Results of the PARTNER (Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valves) trial (Cohort A)”
With more than 120 citations, this article is in the top 1% for its area and year. This performance is not peculiar to general and internal medicine. Articles with very long titles from engineering disciplines can also do well. The second title is from an article published in 2012 in Optics Letters and has about 25 words, depending on definitions:
“Fiber-wireless transmission system of 108 Gb/s data over 80 km fiber and 2×2 multiple-input multiple-output wireless links at 100 GHz W-band frequency”
This article has had more than 110 citations and is in the top 1% for its area and year.
Despite the exceptional lengths of these titles, removing words or phrases, for example, from the first, “Results of the PARTNER . . . (Cohort A)” or, from the second, “at 100 GHz W-band frequency,” seems to result in a disproportionate loss in information and could actually mislead the reader.
Evidently, short titles need not fail to inform and long titles need not promote disengagement. Each can be as effective as the other and lead to high levels of recognition. The implication is that length, on its own, is a poor proxy for something more relevant and fundamental, namely how much the title tells the reader about the work given the number of words it expends.
What is being described here is a kind of efficiency. To paraphrase the statistician and artist Edward Tufte, albeit speaking in a different context, an efficient title is one that maximizes the ratio of the information communicated to its length. Accordingly, the number of words should be immaterial, or almost so. After all, it is what they communicate that really counts.
Featured image credit: Straying Thoughts by Edmund Blair Leighton. Public Domain via Flickr .
David H. Foster is Professor of Vision Systems at the University of Manchester and formerly Director of Research in the School of Electrical & Electronic Engineering. He has served as journal editor or editor in chief for over 30 years and has taught communication in science and engineering at undergraduate, postgraduate, and postdoctoral levels in the UK and elsewhere. He is a Fellow of the Institute of Physics, the Physiological Society, and the Optical Society of America. David is the author of A Concise Guide to Communication in Science and Engineering (OUP, 2017).
- Physics & Chemistry
- Science & Medicine
Our Privacy Policy sets out how Oxford University Press handles your personal information, and your rights to object to your personal information being used for marketing to you or being processed as part of our business activities.
We will only use your personal information to register you for OUPblog articles.
Or subscribe to articles in the subject area by email or RSS
Related posts:

Recent Comments
This describes the key points to decide an attractive journal title very clearly. The discussion is based on the thorough survey of recent publication and the presentation is very convincing with quantified statistical figures. I highly recommend this to anybody including the well-established academics.
Creating a good title is an art in itself – but it can be learned. The key techniques are summarized here very nicely: “Make it clear and remove the fluff” (my words). For more advice, go to David Foster’s excellent book, “A concise guide …” (see bottom of page). Good reading! One thing I would like to add: In my feeling, a short title implies that the paper is more fundamental, more general in its scope, and more accessible (my favourite title is “On Seeing Sidelong” by Gerry Lettvin, which is on peripheral vision). When, instead, the paper is rather narrow, I will be disappointed and think of it lowly. Conversely, I go to the longer titles when I search for something more specific. Of course that comes down – algorithmically so to say – to “an efficient title is one that maximizes the ratio of the information communicated to its length”. But it suggests that the optimum number of words is not independent of content and, rather, correlates with the content’s generality.
Comments are closed.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Saudi J Anaesth
- v.13(Suppl 1); 2019 Apr
Writing the title and abstract for a research paper: Being concise, precise, and meticulous is the key
Milind s. tullu.
Department of Pediatrics, Seth G.S. Medical College and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
This article deals with formulating a suitable title and an appropriate abstract for an original research paper. The “title” and the “abstract” are the “initial impressions” of a research article, and hence they need to be drafted correctly, accurately, carefully, and meticulously. Often both of these are drafted after the full manuscript is ready. Most readers read only the title and the abstract of a research paper and very few will go on to read the full paper. The title and the abstract are the most important parts of a research paper and should be pleasant to read. The “title” should be descriptive, direct, accurate, appropriate, interesting, concise, precise, unique, and should not be misleading. The “abstract” needs to be simple, specific, clear, unbiased, honest, concise, precise, stand-alone, complete, scholarly, (preferably) structured, and should not be misrepresentative. The abstract should be consistent with the main text of the paper, especially after a revision is made to the paper and should include the key message prominently. It is very important to include the most important words and terms (the “keywords”) in the title and the abstract for appropriate indexing purpose and for retrieval from the search engines and scientific databases. Such keywords should be listed after the abstract. One must adhere to the instructions laid down by the target journal with regard to the style and number of words permitted for the title and the abstract.
Introduction
This article deals with drafting a suitable “title” and an appropriate “abstract” for an original research paper. Because the “title” and the “abstract” are the “initial impressions” or the “face” of a research article, they need to be drafted correctly, accurately, carefully, meticulously, and consume time and energy.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ] Often, these are drafted after the complete manuscript draft is ready.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 9 , 10 , 11 ] Most readers will read only the title and the abstract of a published research paper, and very few “interested ones” (especially, if the paper is of use to them) will go on to read the full paper.[ 1 , 2 ] One must remember to adhere to the instructions laid down by the “target journal” (the journal for which the author is writing) regarding the style and number of words permitted for the title and the abstract.[ 2 , 4 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 12 ] Both the title and the abstract are the most important parts of a research paper – for editors (to decide whether to process the paper for further review), for reviewers (to get an initial impression of the paper), and for the readers (as these may be the only parts of the paper available freely and hence, read widely).[ 4 , 8 , 12 ] It may be worth for the novice author to browse through titles and abstracts of several prominent journals (and their target journal as well) to learn more about the wording and styles of the titles and abstracts, as well as the aims and scope of the particular journal.[ 5 , 7 , 9 , 13 ]
The details of the title are discussed under the subheadings of importance, types, drafting, and checklist.
Importance of the title
When a reader browses through the table of contents of a journal issue (hard copy or on website), the title is the “ first detail” or “face” of the paper that is read.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 13 ] Hence, it needs to be simple, direct, accurate, appropriate, specific, functional, interesting, attractive/appealing, concise/brief, precise/focused, unambiguous, memorable, captivating, informative (enough to encourage the reader to read further), unique, catchy, and it should not be misleading.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 9 , 12 ] It should have “just enough details” to arouse the interest and curiosity of the reader so that the reader then goes ahead with studying the abstract and then (if still interested) the full paper.[ 1 , 2 , 4 , 13 ] Journal websites, electronic databases, and search engines use the words in the title and abstract (the “keywords”) to retrieve a particular paper during a search; hence, the importance of these words in accessing the paper by the readers has been emphasized.[ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 12 , 14 ] Such important words (or keywords) should be arranged in appropriate order of importance as per the context of the paper and should be placed at the beginning of the title (rather than the later part of the title, as some search engines like Google may just display only the first six to seven words of the title).[ 3 , 5 , 12 ] Whimsical, amusing, or clever titles, though initially appealing, may be missed or misread by the busy reader and very short titles may miss the essential scientific words (the “keywords”) used by the indexing agencies to catch and categorize the paper.[ 1 , 3 , 4 , 9 ] Also, amusing or hilarious titles may be taken less seriously by the readers and may be cited less often.[ 4 , 15 ] An excessively long or complicated title may put off the readers.[ 3 , 9 ] It may be a good idea to draft the title after the main body of the text and the abstract are drafted.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]
Types of titles
Titles can be descriptive, declarative, or interrogative. They can also be classified as nominal, compound, or full-sentence titles.
Descriptive or neutral title
This has the essential elements of the research theme, that is, the patients/subjects, design, interventions, comparisons/control, and outcome, but does not reveal the main result or the conclusion.[ 3 , 4 , 12 , 16 ] Such a title allows the reader to interpret the findings of the research paper in an impartial manner and with an open mind.[ 3 ] These titles also give complete information about the contents of the article, have several keywords (thus increasing the visibility of the article in search engines), and have increased chances of being read and (then) being cited as well.[ 4 ] Hence, such descriptive titles giving a glimpse of the paper are generally preferred.[ 4 , 16 ]
Declarative title
This title states the main finding of the study in the title itself; it reduces the curiosity of the reader, may point toward a bias on the part of the author, and hence is best avoided.[ 3 , 4 , 12 , 16 ]
Interrogative title
This is the one which has a query or the research question in the title.[ 3 , 4 , 16 ] Though a query in the title has the ability to sensationalize the topic, and has more downloads (but less citations), it can be distracting to the reader and is again best avoided for a research article (but can, at times, be used for a review article).[ 3 , 6 , 16 , 17 ]
From a sentence construct point of view, titles may be nominal (capturing only the main theme of the study), compound (with subtitles to provide additional relevant information such as context, design, location/country, temporal aspect, sample size, importance, and a provocative or a literary; for example, see the title of this review), or full-sentence titles (which are longer and indicate an added degree of certainty of the results).[ 4 , 6 , 9 , 16 ] Any of these constructs may be used depending on the type of article, the key message, and the author's preference or judgement.[ 4 ]
Drafting a suitable title
A stepwise process can be followed to draft the appropriate title. The author should describe the paper in about three sentences, avoiding the results and ensuring that these sentences contain important scientific words/keywords that describe the main contents and subject of the paper.[ 1 , 4 , 6 , 12 ] Then the author should join the sentences to form a single sentence, shorten the length (by removing redundant words or adjectives or phrases), and finally edit the title (thus drafted) to make it more accurate, concise (about 10–15 words), and precise.[ 1 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 9 ] Some journals require that the study design be included in the title, and this may be placed (using a colon) after the primary title.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 14 ] The title should try to incorporate the Patients, Interventions, Comparisons and Outcome (PICO).[ 3 ] The place of the study may be included in the title (if absolutely necessary), that is, if the patient characteristics (such as study population, socioeconomic conditions, or cultural practices) are expected to vary as per the country (or the place of the study) and have a bearing on the possible outcomes.[ 3 , 6 ] Lengthy titles can be boring and appear unfocused, whereas very short titles may not be representative of the contents of the article; hence, optimum length is required to ensure that the title explains the main theme and content of the manuscript.[ 4 , 5 , 9 ] Abbreviations (except the standard or commonly interpreted ones such as HIV, AIDS, DNA, RNA, CDC, FDA, ECG, and EEG) or acronyms should be avoided in the title, as a reader not familiar with them may skip such an article and nonstandard abbreviations may create problems in indexing the article.[ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 9 , 12 ] Also, too much of technical jargon or chemical formulas in the title may confuse the readers and the article may be skipped by them.[ 4 , 9 ] Numerical values of various parameters (stating study period or sample size) should also be avoided in the titles (unless deemed extremely essential).[ 4 ] It may be worthwhile to take an opinion from a impartial colleague before finalizing the title.[ 4 , 5 , 6 ] Thus, multiple factors (which are, at times, a bit conflicting or contrasting) need to be considered while formulating a title, and hence this should not be done in a hurry.[ 4 , 6 ] Many journals ask the authors to draft a “short title” or “running head” or “running title” for printing in the header or footer of the printed paper.[ 3 , 12 ] This is an abridged version of the main title of up to 40–50 characters, may have standard abbreviations, and helps the reader to navigate through the paper.[ 3 , 12 , 14 ]
Checklist for a good title
Table 1 gives a checklist/useful tips for drafting a good title for a research paper.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 12 ] Table 2 presents some of the titles used by the author of this article in his earlier research papers, and the appropriateness of the titles has been commented upon. As an individual exercise, the reader may try to improvise upon the titles (further) after reading the corresponding abstract and full paper.
Checklist/useful tips for drafting a good title for a research paper
Some titles used by author of this article in his earlier publications and remark/comment on their appropriateness
The Abstract
The details of the abstract are discussed under the subheadings of importance, types, drafting, and checklist.
Importance of the abstract
The abstract is a summary or synopsis of the full research paper and also needs to have similar characteristics like the title. It needs to be simple, direct, specific, functional, clear, unbiased, honest, concise, precise, self-sufficient, complete, comprehensive, scholarly, balanced, and should not be misleading.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 13 , 17 ] Writing an abstract is to extract and summarize (AB – absolutely, STR – straightforward, ACT – actual data presentation and interpretation).[ 17 ] The title and abstracts are the only sections of the research paper that are often freely available to the readers on the journal websites, search engines, and in many abstracting agencies/databases, whereas the full paper may attract a payment per view or a fee for downloading the pdf copy.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 10 , 11 , 13 , 14 ] The abstract is an independent and stand-alone (that is, well understood without reading the full paper) section of the manuscript and is used by the editor to decide the fate of the article and to choose appropriate reviewers.[ 2 , 7 , 10 , 12 , 13 ] Even the reviewers are initially supplied only with the title and the abstract before they agree to review the full manuscript.[ 7 , 13 ] This is the second most commonly read part of the manuscript, and therefore it should reflect the contents of the main text of the paper accurately and thus act as a “real trailer” of the full article.[ 2 , 7 , 11 ] The readers will go through the full paper only if they find the abstract interesting and relevant to their practice; else they may skip the paper if the abstract is unimpressive.[ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 13 ] The abstract needs to highlight the selling point of the manuscript and succeed in luring the reader to read the complete paper.[ 3 , 7 ] The title and the abstract should be constructed using keywords (key terms/important words) from all the sections of the main text.[ 12 ] Abstracts are also used for submitting research papers to a conference for consideration for presentation (as oral paper or poster).[ 9 , 13 , 17 ] Grammatical and typographic errors reflect poorly on the quality of the abstract, may indicate carelessness/casual attitude on part of the author, and hence should be avoided at all times.[ 9 ]
Types of abstracts
The abstracts can be structured or unstructured. They can also be classified as descriptive or informative abstracts.
Structured and unstructured abstracts
Structured abstracts are followed by most journals, are more informative, and include specific subheadings/subsections under which the abstract needs to be composed.[ 1 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 13 , 17 , 18 ] These subheadings usually include context/background, objectives, design, setting, participants, interventions, main outcome measures, results, and conclusions.[ 1 ] Some journals stick to the standard IMRAD format for the structure of the abstracts, and the subheadings would include Introduction/Background, Methods, Results, And (instead of Discussion) the Conclusion/s.[ 1 , 2 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 17 , 18 ] Structured abstracts are more elaborate, informative, easy to read, recall, and peer-review, and hence are preferred; however, they consume more space and can have same limitations as an unstructured abstract.[ 7 , 9 , 18 ] The structured abstracts are (possibly) better understood by the reviewers and readers. Anyway, the choice of the type of the abstract and the subheadings of a structured abstract depend on the particular journal style and is not left to the author's wish.[ 7 , 10 , 12 ] Separate subheadings may be necessary for reporting meta-analysis, educational research, quality improvement work, review, or case study.[ 1 ] Clinical trial abstracts need to include the essential items mentioned in the CONSORT (Consolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials) guidelines.[ 7 , 9 , 14 , 19 ] Similar guidelines exist for various other types of studies, including observational studies and for studies of diagnostic accuracy.[ 20 , 21 ] A useful resource for the above guidelines is available at www.equator-network.org (Enhancing the QUAlity and Transparency Of health Research). Unstructured (or non-structured) abstracts are free-flowing, do not have predefined subheadings, and are commonly used for papers that (usually) do not describe original research.[ 1 , 7 , 9 , 10 ]
The four-point structured abstract: This has the following elements which need to be properly balanced with regard to the content/matter under each subheading:[ 9 ]
Background and/or Objectives: This states why the work was undertaken and is usually written in just a couple of sentences.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 ] The hypothesis/study question and the major objectives are also stated under this subheading.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 ]
Methods: This subsection is the longest, states what was done, and gives essential details of the study design, setting, participants, blinding, sample size, sampling method, intervention/s, duration and follow-up, research instruments, main outcome measures, parameters evaluated, and how the outcomes were assessed or analyzed.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 ]
Results/Observations/Findings: This subheading states what was found, is longer, is difficult to draft, and needs to mention important details including the number of study participants, results of analysis (of primary and secondary objectives), and include actual data (numbers, mean, median, standard deviation, “P” values, 95% confidence intervals, effect sizes, relative risks, odds ratio, etc.).[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 ]
Conclusions: The take-home message (the “so what” of the paper) and other significant/important findings should be stated here, considering the interpretation of the research question/hypothesis and results put together (without overinterpreting the findings) and may also include the author's views on the implications of the study.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 ]
The eight-point structured abstract: This has the following eight subheadings – Objectives, Study Design, Study Setting, Participants/Patients, Methods/Intervention, Outcome Measures, Results, and Conclusions.[ 3 , 9 , 18 ] The instructions to authors given by the particular journal state whether they use the four- or eight-point abstract or variants thereof.[ 3 , 14 ]
Descriptive and Informative abstracts
Descriptive abstracts are short (75–150 words), only portray what the paper contains without providing any more details; the reader has to read the full paper to know about its contents and are rarely used for original research papers.[ 7 , 10 ] These are used for case reports, reviews, opinions, and so on.[ 7 , 10 ] Informative abstracts (which may be structured or unstructured as described above) give a complete detailed summary of the article contents and truly reflect the actual research done.[ 7 , 10 ]
Drafting a suitable abstract
It is important to religiously stick to the instructions to authors (format, word limit, font size/style, and subheadings) provided by the journal for which the abstract and the paper are being written.[ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 13 ] Most journals allow 200–300 words for formulating the abstract and it is wise to restrict oneself to this word limit.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 22 ] Though some authors prefer to draft the abstract initially, followed by the main text of the paper, it is recommended to draft the abstract in the end to maintain accuracy and conformity with the main text of the paper (thus maintaining an easy linkage/alignment with title, on one hand, and the introduction section of the main text, on the other hand).[ 2 , 7 , 9 , 10 , 11 ] The authors should check the subheadings (of the structured abstract) permitted by the target journal, use phrases rather than sentences to draft the content of the abstract, and avoid passive voice.[ 1 , 7 , 9 , 12 ] Next, the authors need to get rid of redundant words and edit the abstract (extensively) to the correct word count permitted (every word in the abstract “counts”!).[ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 13 ] It is important to ensure that the key message, focus, and novelty of the paper are not compromised; the rationale of the study and the basis of the conclusions are clear; and that the abstract is consistent with the main text of the paper.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 9 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 , 22 ] This is especially important while submitting a revision of the paper (modified after addressing the reviewer's comments), as the changes made in the main (revised) text of the paper need to be reflected in the (revised) abstract as well.[ 2 , 10 , 12 , 14 , 22 ] Abbreviations should be avoided in an abstract, unless they are conventionally accepted or standard; references, tables, or figures should not be cited in the abstract.[ 7 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 13 ] It may be worthwhile not to rush with the abstract and to get an opinion by an impartial colleague on the content of the abstract; and if possible, the full paper (an “informal” peer-review).[ 1 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 11 , 17 ] Appropriate “Keywords” (three to ten words or phrases) should follow the abstract and should be preferably chosen from the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) list of the U.S. National Library of Medicine ( https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/search ) and are used for indexing purposes.[ 2 , 3 , 11 , 12 ] These keywords need to be different from the words in the main title (the title words are automatically used for indexing the article) and can be variants of the terms/phrases used in the title, or words from the abstract and the main text.[ 3 , 12 ] The ICMJE (International Committee of Medical Journal Editors; http://www.icmje.org/ ) also recommends publishing the clinical trial registration number at the end of the abstract.[ 7 , 14 ]
Checklist for a good abstract
Table 3 gives a checklist/useful tips for formulating a good abstract for a research paper.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 , 22 ]
Checklist/useful tips for formulating a good abstract for a research paper
Concluding Remarks
This review article has given a detailed account of the importance and types of titles and abstracts. It has also attempted to give useful hints for drafting an appropriate title and a complete abstract for a research paper. It is hoped that this review will help the authors in their career in medical writing.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgement
The author thanks Dr. Hemant Deshmukh - Dean, Seth G.S. Medical College & KEM Hospital, for granting permission to publish this manuscript.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example
Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example
Table of Contents

Research Paper Title
Research Paper Title is the name or heading that summarizes the main theme or topic of a research paper . It serves as the first point of contact between the reader and the paper, providing an initial impression of the content, purpose, and scope of the research . A well-crafted research paper title should be concise, informative, and engaging, accurately reflecting the key elements of the study while also capturing the reader’s attention and interest. The title should be clear and easy to understand, and it should accurately convey the main focus and scope of the research paper.
Examples of Research Paper Title
Here are some Good Examples of Research Paper Title:
- “Investigating the Relationship Between Sleep Duration and Academic Performance Among College Students”
- “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Employment: A Systematic Review”
- “The Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Interventions for Anxiety: A Meta-Analysis”
- “Exploring the Effects of Social Support on Mental Health in Patients with Chronic Illness”
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Depression: A Randomized Controlled Trial”
- “The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Consumer Behavior: A Systematic Review”
- “Investigating the Link Between Personality Traits and Leadership Effectiveness”
- “The Effect of Parental Incarceration on Child Development: A Longitudinal Study”
- “Exploring the Relationship Between Cultural Intelligence and Cross-Cultural Adaptation: A Meta-Analysis”
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction for Chronic Pain Management”.
- “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health: A Meta-Analysis”
- “The Impact of Climate Change on Global Crop Yields: A Longitudinal Study”
- “Exploring the Relationship between Parental Involvement and Academic Achievement in Elementary School Students”
- “The Ethics of Genetic Editing: A Review of Current Research and Implications for Society”
- “Understanding the Role of Gender in Leadership: A Comparative Study of Male and Female CEOs”
- “The Effect of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial”
- “The Impacts of COVID-19 on Mental Health: A Cross-Cultural Comparison”
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Online Learning Platforms: A Case Study of Coursera”
- “Exploring the Link between Employee Engagement and Organizational Performance”
- “The Effects of Income Inequality on Social Mobility: A Comparative Analysis of OECD Countries”
- “Exploring the Relationship Between Social Media Use and Mental Health in Adolescents”
- “The Impact of Climate Change on Crop Yield: A Case Study of Maize Production in Sub-Saharan Africa”
- “Examining the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Anxiety Disorders: A Meta-Analysis”
- “An Analysis of the Relationship Between Employee Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment”
- “Assessing the Impacts of Wilderness Areas on Local Economies: A Case Study of Yellowstone National Park”
- “The Role of Parental Involvement in Early Childhood Education: A Review of the Literature”
- “Investigating the Effects of Technology on Learning in Higher Education”
- “The Use of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Opportunities and Challenges”
- “A Study of the Relationship Between Personality Traits and Leadership Styles in Business Organizations”.
How to choose Research Paper Title
Choosing a research paper title is an important step in the research process. A good title can attract readers and convey the essence of your research in a concise and clear manner. Here are some tips on how to choose a research paper title:
- Be clear and concise: A good title should convey the main idea of your research in a clear and concise manner. Avoid using jargon or technical language that may be confusing to readers.
- Use keywords: Including keywords in your title can help readers find your paper when searching for related topics. Use specific, descriptive terms that accurately describe your research.
- Be descriptive: A descriptive title can help readers understand what your research is about. Use adjectives and adverbs to convey the main ideas of your research.
- Consider the audience : Think about the audience for your paper and choose a title that will appeal to them. If your paper is aimed at a specialized audience, you may want to use technical terms or jargon in your title.
- Avoid being too general or too specific : A title that is too general may not convey the specific focus of your research, while a title that is too specific may not be of interest to a broader audience. Strive for a title that accurately reflects the focus of your research without being too narrow or too broad.
- Make it interesting : A title that is interesting or provocative can capture the attention of readers and draw them into your research. Use humor, wordplay, or other creative techniques to make your title stand out.
- Seek feedback: Ask colleagues or advisors for feedback on your title. They may be able to offer suggestions or identify potential problems that you hadn’t considered.
Purpose of Research Paper Title
The research paper title serves several important purposes, including:
- Identifying the subject matter : The title of a research paper should clearly and accurately identify the topic or subject matter that the paper addresses. This helps readers quickly understand what the paper is about.
- Catching the reader’s attention : A well-crafted title can grab the reader’s attention and make them interested in reading the paper. This is particularly important in academic settings where there may be many papers on the same topic.
- Providing context: The title can provide important context for the research paper by indicating the specific area of study, the research methods used, or the key findings.
- Communicating the scope of the paper: A good title can give readers an idea of the scope and depth of the research paper. This can help them decide if the paper is relevant to their interests or research.
- Indicating the research question or hypothesis : The title can often indicate the research question or hypothesis that the paper addresses, which can help readers understand the focus of the research and the main argument or conclusion of the paper.
Advantages of Research Paper Title
The title of a research paper is an important component that can have several advantages, including:
- Capturing the reader’s attention : A well-crafted research paper title can grab the reader’s attention and encourage them to read further. A captivating title can also increase the visibility of the paper and attract more readers.
- Providing a clear indication of the paper’s focus: A well-written research paper title should clearly convey the main focus and purpose of the study. This helps potential readers quickly determine whether the paper is relevant to their interests.
- Improving discoverability: A descriptive title that includes relevant keywords can improve the discoverability of the research paper in search engines and academic databases, making it easier for other researchers to find and cite.
- Enhancing credibility : A clear and concise title can enhance the credibility of the research and the author. A title that accurately reflects the content of the paper can increase the confidence readers have in the research findings.
- Facilitating communication: A well-written research paper title can facilitate communication among researchers, enabling them to quickly and easily identify relevant studies and engage in discussions related to the topic.
- Making the paper easier to remember : An engaging and memorable research paper title can help readers remember the paper and its findings. This can be especially important in fields where researchers are constantly inundated with new information and need to quickly recall important studies.
- Setting expectations: A good research paper title can set expectations for the reader and help them understand what the paper will cover. This can be especially important for readers who are unfamiliar with the topic or the research area.
- Guiding research: A well-crafted research paper title can also guide future research by highlighting gaps in the current literature or suggesting new areas for investigation.
- Demonstrating creativity: A creative research paper title can demonstrate the author’s creativity and originality, which can be appealing to readers and other researchers.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Make a Research Paper Title with Examples
What is a research paper title and why does it matter?
A research paper title summarizes the aim and purpose of your research study. Making a title for your research is one of the most important decisions when writing an article to publish in journals. The research title is the first thing that journal editors and reviewers see when they look at your paper and the only piece of information that fellow researchers will see in a database or search engine query. Good titles that are concise and contain all the relevant terms have been shown to increase citation counts and Altmetric scores .
Therefore, when you title research work, make sure it captures all of the relevant aspects of your study, including the specific topic and problem being investigated. It also should present these elements in a way that is accessible and will captivate readers. Follow these steps to learn how to make a good research title for your work.
How to Make a Research Paper Title in 5 Steps
You might wonder how you are supposed to pick a title from all the content that your manuscript contains—how are you supposed to choose? What will make your research paper title come up in search engines and what will make the people in your field read it?
In a nutshell, your research title should accurately capture what you have done, it should sound interesting to the people who work on the same or a similar topic, and it should contain the important title keywords that other researchers use when looking for literature in databases. To make the title writing process as simple as possible, we have broken it down into 5 simple steps.
Step 1: Answer some key questions about your research paper
What does your paper seek to answer and what does it accomplish? Try to answer these questions as briefly as possible. You can create these questions by going through each section of your paper and finding the MOST relevant information to make a research title.
Step 2: Identify research study keywords
Now that you have answers to your research questions, find the most important parts of these responses and make these your study keywords. Note that you should only choose the most important terms for your keywords–journals usually request anywhere from 3 to 8 keywords maximum.
Step 3: Research title writing: use these keywords
“We employed a case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years to assess how waiting list volume affects the outcomes of liver transplantation in patients; results indicate a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and negative prognosis after the transplant procedure.”
The sentence above is clearly much too long for a research paper title. This is why you will trim and polish your title in the next two steps.
Step 4: Create a working research paper title
To create a working title, remove elements that make it a complete “sentence” but keep everything that is important to what the study is about. Delete all unnecessary and redundant words that are not central to the study or that researchers would most likely not use in a database search.
“ We employed a case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years to assess how the waiting list volume affects the outcome of liver transplantation in patients ; results indicate a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and a negative prognosis after transplant procedure ”
Now shift some words around for proper syntax and rephrase it a bit to shorten the length and make it leaner and more natural. What you are left with is:
“A case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years assessing the impact of waiting list volume on outcome of transplantation and showing a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and a negative prognosis” (Word Count: 38)
This text is getting closer to what we want in a research title, which is just the most important information. But note that the word count for this working title is still 38 words, whereas the average length of published journal article titles is 16 words or fewer. Therefore, we should eliminate some words and phrases that are not essential to this title.
Step 5: Remove any nonessential words and phrases from your title
Because the number of patients studied and the exact outcome are not the most essential parts of this paper, remove these elements first:
“A case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years assessing the impact of waiting list volume on outcomes of transplantation and showing a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and a negative prognosis” (Word Count: 19)
In addition, the methods used in a study are not usually the most searched-for keywords in databases and represent additional details that you may want to remove to make your title leaner. So what is left is:
“Assessing the impact of waiting list volume on outcome and prognosis in liver transplantation patients” (Word Count: 15)
In this final version of the title, one can immediately recognize the subject and what objectives the study aims to achieve. Note that the most important terms appear at the beginning and end of the title: “Assessing,” which is the main action of the study, is placed at the beginning; and “liver transplantation patients,” the specific subject of the study, is placed at the end.
This will aid significantly in your research paper title being found in search engines and database queries, which means that a lot more researchers will be able to locate your article once it is published. In fact, a 2014 review of more than 150,000 papers submitted to the UK’s Research Excellence Framework (REF) database found the style of a paper’s title impacted the number of citations it would typically receive. In most disciplines, articles with shorter, more concise titles yielded more citations.
Adding a Research Paper Subtitle
If your title might require a subtitle to provide more immediate details about your methodology or sample, you can do this by adding this information after a colon:
“ : a case study of US adult patients ages 20-25”
If we abide strictly by our word count rule this may not be necessary or recommended. But every journal has its own standard formatting and style guidelines for research paper titles, so it is a good idea to be aware of the specific journal author instructions , not just when you write the manuscript but also to decide how to create a good title for it.
Research Paper Title Examples
The title examples in the following table illustrate how a title can be interesting but incomplete, complete by uninteresting, complete and interesting but too informal in tone, or some other combination of these. A good research paper title should meet all the requirements in the four columns below.
Tips on Formulating a Good Research Paper Title
In addition to the steps given above, there are a few other important things you want to keep in mind when it comes to how to write a research paper title, regarding formatting, word count, and content:
- Write the title after you’ve written your paper and abstract
- Include all of the essential terms in your paper
- Keep it short and to the point (~16 words or fewer)
- Avoid unnecessary jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords that capture the content of your paper
- Never include a period at the end—your title is NOT a sentence
Research Paper Writing Resources
We hope this article has been helpful in teaching you how to craft your research paper title. But you might still want to dig deeper into different journal title formats and categories that might be more suitable for specific article types or need help with writing a cover letter for your manuscript submission.
In addition to getting English proofreading services , including paper editing services , before submission to journals, be sure to visit our academic resources papers. Here you can find dozens of articles on manuscript writing, from drafting an outline to finding a target journal to submit to.
- Share on twitter
- Share on facebook
Long research titles ‘have lower impact’
Lengthy titles of journal papers are a turn-off for fellow academics and lead to fewer citations, claims new analysis .
- Share on linkedin
- Share on mail

Picking a pithy title for your research paper could significantly improve its impact, new analysis suggests.
While many researchers might not worry too much about finding a memorable or eye-catching title for a new journal paper, a recently published study indicates that a longer and more convoluted title could seriously harm its chances of doing well.
According to an examination of the titles of around 155,000 journal articles submitted to the UK’s most recent research excellence framework ( REF ), papers with briefer titles tend to be cited more frequently.
Across 10 of the 11 units of assessment covering 36 disciplines in the 2014 REF, “citations significantly decline with title length”, according to the paper, “An analysis of the titles of papers submitted to the UK REF in 2014: authors, disciplines, and stylistic details”, by John Hudson, professor of economics at the University of Bath , in a recent edition of the journal Scientometrics .
That effect was more marked in certain subjects, including clinical medicine, biology and physics, and less so in disciplines such as computer science and economics, according to the study.
“A longer title generally means a paper is less likely to receive citations,” Professor Hudson told Times Higher Education .
Using a question mark in a journal paper’s title reduces the number of citations it received, he added.
However, using a colon tended to improve the citations received by a paper, Professor Hudson said.
“With a colon you have to divide up the title into two parts, so you have two messages for readers,” he said, noting that a dual title could broaden the appeal of a paper.
Overall, the discipline with the longest journal titles on average was public health, whose titles averaged 117 characters including spaces, followed by clinical medicine (113) and agriculture (110). The shortest titles tended to come in social sciences and humanities, such as economics (66 characters), Classics (69) and English language (74).
Political scientists and law academics were most likely to use question marks in their journal titles (almost a fifth of papers in these disciplines used them) but these were used by less than 1 per cent of papers submitted in maths and electrical engineering.
The average number of authors per paper differed significantly between disciplines ; physics papers had 131 co-authors on average, but for history, philosophy and theology the average was 1.1 in each case, the study found.
Consistent with previous studies, those papers with multiple authorship tended to receive higher citation rates, but numerous authors also led to longer titles, Professor Hudson said.
Those longer titles may be the result of negotiation between numerous authors, he suggested.
“If they are compromising on titles, are they compromising on other aspects of research?” Professor Hudson said.
Disciplinary variation in the number of authors per paper also highlighted how it had been much more difficult for academics in certain disciplines to generate the four pieces of work required for the 2014 REF – a factor policymakers might wish to consider when finalising future research audits, he added.
Register to continue
Why register?
- Registration is free and only takes a moment
- Once registered, you can read 3 articles a month
- Sign up for our newsletter
Or subscribe for unlimited access to:
- Unlimited access to news, views, insights & reviews
- Digital editions
- Digital access to THE’s university and college rankings analysis
Already registered or a current subscriber? Login
Related articles

Twitter taunts over REF omission rile professor
Politics scholar angered by what he claims was ‘ruthless’ attempt to discredit him by citing non-inclusion in UK’s research excellence framework

Could refusal to reveal graduate premium lead to a fraud charge?
David Palfreyman considers how secretiveness about the benefits a graduate might expect might fall foul of trading regulations

Can the research excellence framework run on metrics?
An Elsevier analysis explores the viability of a ‘smarter and cheaper’ model

Scientists oppose retractions for racism, sexism and fraud
Poll of researchers finds little support for pulling scholarly papers of those found guilty of objectionable personal behaviour

New Zealand reviews ‘urgently needed but light on detail’
New government announces evaluations of science and universities after scrapping predecessor’s efforts to do likewise

Forget book deals if REF open access rules proceed, warn scholars
Researchers say precariously employed academics will lose out if universities are required to stump up fees for open access

Australia set to pass new research sharing rules
Despite explicit exemption for fundamental research, Greens warn that new regime will stymie collaboration ‘outside Aukus bubble’
Featured jobs

6 Important Tips on Writing a Research Paper Title
When you are searching for a research study on a particular topic, you probably notice that articles with interesting, descriptive research titles draw you in. By contrast, research paper titles that are not descriptive are usually passed over, even though you may write a good research paper with interesting contents. This shows the importance of coming up with a good title for your research paper when drafting your own manuscript.
Importance of a Research Title
The research title plays a crucial role in the research process, and its importance can be summarized as follows:
Why do Research Titles Matter?
Before we look at how to title a research paper, let’s look at a research title example that illustrates why a good research paper should have a strong title.
Imagine that you are researching meditation and nursing, and you want to find out if any studies have shown that meditation makes nurses better communicators. You conduct a keyword search using the keywords “nursing”, “communication”, and “meditation.” You come up with results that have the following titles:
- Benefits of Meditation for the Nursing Profession: A Quantitative Investigation
- Why Mindful Nurses Make the Best Communicators
- Meditation Gurus
- Nurses on the Move: A Quantitative Report on How Meditation Can Improve Nurse Performance
All four of these research paper titles may describe very similar studies—they could even be titles for the same study! As you can see, they give very different impressions.
- Title 1 describes the topic and the method of the study but is not particularly catchy.
- Title 2 partly describes the topic, but does not give any information about the method of the study—it could simply be a theoretical or opinion piece.
- Title 3 is somewhat catchier but gives almost no information at all about the article.
- Title 4 begins with a catchy main title and is followed by a subtitle that gives information about the content and method of the study.
As we will see, Title 4 has all the characteristics of a good research title.
Characteristics of a Good Research Title
According to rhetoric scholars Hairston and Keene, making a good title for a paper involves ensuring that the title of the research accomplishes four goals as mentioned below:
- It should predict the content of the research paper .
- It should be interesting to the reader .
- It should reflect the tone of the writing .
- It should contain important keywords that will make it easier to be located during a keyword search.
Let’s return to the examples in the previous section to see how to make a research title.
As you can see in the table above, only one of the four example titles fulfills all of the criteria of a suitable research paper title.
Related: You’ve chosen your study topic, but having trouble deciding where to publish it? Here’s a comprehensive course to help you identify the right journal .
Tips for Writing an Effective Research Paper Title
When writing a research title, you can use the four criteria listed above as a guide. Here are a few other tips you can use to make sure your title will be part of the recipe for an effective research paper :
- Make sure your research title describes (a) the topic, (b) the method, (c) the sample, and (d) the results of your study. You can use the following formula:
[ Result ]: A [ method ] study of [ topic ] among [ sample ] Example : Meditation makes nurses perform better: a qualitative study of mindfulness meditation among German nursing students
- Avoid unnecessary words and jargons. Keep the title statement as concise as possible. You want a title that will be comprehensible even to people who are not experts in your field. Check our article for a detailed list of things to avoid when writing an effective research title .
- Make sure your title is between 5 and 15 words in length.
- If you are writing a title for a university assignment or for a particular academic journal, verify that your title conforms to the standards and requirements for that outlet. For example, many journals require that titles fall under a character limit, including spaces. Many universities require that titles take a very specific form, limiting your creativity.
- Use a descriptive phrase to convey the purpose of your research efficiently.
- Most importantly, use critical keywords in the title to increase the discoverability of your article.

Resources for Further Reading
In addition to the tips above, there are many resources online that you can use to help write your research title. Here is a list of links that you may find useful as you work on creating an excellent research title:
- The University of Southern California has a guide specific to social science research papers: http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/title
- The Journal of European Psychology Students has a blog article focusing on APA-compliant research paper titles: http://blog.efpsa.org/2012/09/01/how-to-write-a-good-title-for-journal-articles/
- This article by Kristen Hamlin contains a step-by-step approach to writing titles: http://classroom.synonym.com/choose-title-research-paper-4332.html
Are there any tips or tricks you find useful in crafting research titles? Which tip did you find most useful in this article? Leave a comment to let us know!
- Hairston, M., & Keene, M. 2003. Successful writing . 5th ed. New York: Norton.
- University of Southern California. 2017. Organizing your social sciences research paper: choosing a title . [Online] Available at: http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/title
Thank you so much:) Have a nice day!
Thank you so much, it helped me.. God bless..
Thank you for the excellent article and tips for creating a research work, because I always forget about such an essential element as the keywords when forming topics. In particular, I have found a rapid help with the formation of informative and sound titles that also conforms to the standards and requirements.
I am doing a research work on sales girls or shop girls using qualititative method. Basicly I am from Pakistan and writing on the scenario of mycountry. I am really confused about my research title can you kindly give some suggestions and give me an approperaite tilte

Hi Zubair, Thank you for your question. However, the information you have provided is insufficient for drafting an appropriate title. Information on what exactly you intend to study would be needed in order to draft a meaningful title. Meanwhile, you can try drafting your own title after going through the following articles our website: https://www.enago.com/academy/top-10-tips-on-choosing-an-attractive-research-title/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/writing-a-good-research-title-things-to-avoid/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/write-irresistible-research-paper-title/ We would be happy to give you feedback and suggest changes if required. Did you get a chance to install our free Mobile App? https://www.enago.com/academy/mobile-app/ . Make sure you subscribe to our weekly newsletter https://www.enago.com/academy/subscribe-now/ .
thanks for helping me like this!!
Thank you for this. It helped me improve my research title. I just want to verify to you the title I have just made. “Ensuring the safety: A Quantitative Study of Radio Frequency Identification system among the selected students of ( school’s name ).
(I need your reply asap coz we will be doing the chap. 1 tomorrow. Thank u in advance. 🙂 )
I am actually doing a research paper title. I want to know more further in doing research title. Can you give me some tips on doing a research paper?
Hi Joan, Thank you for your question. We are glad to know that you found our resources useful. Your feedback is very valuable to us. You can try drafting your own title after going through the following articles on our website: https://www.enago.com/academy/top-10-tips-on-choosing-an-attractive-research-title/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/writing-a-good-research-title-things-to-avoid/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/write-irresistible-research-paper-title/
We would be happy to give you feedback and suggest changes if required. Did you get a chance to install our free Mobile App? https://www.enago.com/academy/mobile-app/ . Make sure you subscribe to our weekly newsletter https://www.enago.com/academy/subscribe-now/ .
That really helpful. Thanks alot
Thank you so much. It’s really help me.
Thanks for sharing this tips. Title matters a lot for any article because it contents Keywords of article. It should be eye-catchy. Your article is helpful to select title of any article.
nice blog that you have shared
This blog is very informative for me. Thanks for sharing.
nice information that you have shared
i’m found in selecting my ma thesis title ,so i’m going to do my final research after the proposal approved. Your post help me find good title.
I need help. I need a research title for my study about early mobilization of the mechanically ventilated patients in the ICU. Any suggestions would be highly appreciated.
Thank you for posting your query on the website. When writing manuscripts, too many scholars neglect the research title. This phrase, along with the abstract, is what people will mostly see and read online. Title research of publications shows that the research paper title does matter a lot. Both bibliometrics and altmetrics tracking of citations are now, for better or worse, used to gauge a paper’s “success” for its author(s) and the journal publishing it. Interesting research topics coupled with good or clever yet accurate research titles can draw more attention to your work from peers and the public alike. You can check through the following search results for titles on similar topics: https://www.google.com/search?q=early+mobilization+of+the+mechanically+ventilated+patients+in+the+icu&rlz=1C1GCEU_enIN907IN907&oq=&aqs=chrome.0.69i59.4920093j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8 .
We hope this would be helpful in drafting an attractive title for your research paper.
Please let us know in case of any other queries.
I’ve been surfing online more than 3 hours these days, but I never found any interesting article like yours. It is lovely worth enough for me. In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers made just right content material as you did, the internet will be much more helpful than ever before.
Wonderful article! We will bee linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an very long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say fantastic blog!
In case the topic is new research before you’re writing. And then to stand out, you end up being different.and be inclined to highlight yourself.
There are many free directories, and more paid lists.
To be honest your article is informative. I search many site to know about writing but I didn’t get the information I needed. I saw your site and I read it. I got some new information from here. I think some of your tips can be applied to those too! Thank you so very much for such informative and useful content.
Nice and well written content you have shared with us. thanks a lot!
Thanks for sharing these tips… Rockwide
Its helpful. a person can grab knowledge through it.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.

- Research guides
Writing an Educational Research Paper
Research paper sections, customary parts of an education research paper.
There is no one right style or manner for writing an education paper. Content aside, the writing style and presentation of papers in different educational fields vary greatly. Nevertheless, certain parts are common to most papers, for example:
Title/Cover Page
Contains the paper's title, the author's name, address, phone number, e-mail, and the day's date.
Not every education paper requires an abstract. However, for longer, more complex papers abstracts are particularly useful. Often only 100 to 300 words, the abstract generally provides a broad overview and is never more than a page. It describes the essence, the main theme of the paper. It includes the research question posed, its significance, the methodology, and the main results or findings. Footnotes or cited works are never listed in an abstract. Remember to take great care in composing the abstract. It's the first part of the paper the instructor reads. It must impress with a strong content, good style, and general aesthetic appeal. Never write it hastily or carelessly.
Introduction and Statement of the Problem
A good introduction states the main research problem and thesis argument. What precisely are you studying and why is it important? How original is it? Will it fill a gap in other studies? Never provide a lengthy justification for your topic before it has been explicitly stated.
Limitations of Study
Indicate as soon as possible what you intend to do, and what you are not going to attempt. You may limit the scope of your paper by any number of factors, for example, time, personnel, gender, age, geographic location, nationality, and so on.

Methodology
Discuss your research methodology. Did you employ qualitative or quantitative research methods? Did you administer a questionnaire or interview people? Any field research conducted? How did you collect data? Did you utilize other libraries or archives? And so on.
Literature Review
The research process uncovers what other writers have written about your topic. Your education paper should include a discussion or review of what is known about the subject and how that knowledge was acquired. Once you provide the general and specific context of the existing knowledge, then you yourself can build on others' research. The guide Writing a Literature Review will be helpful here.
Main Body of Paper/Argument
This is generally the longest part of the paper. It's where the author supports the thesis and builds the argument. It contains most of the citations and analysis. This section should focus on a rational development of the thesis with clear reasoning and solid argumentation at all points. A clear focus, avoiding meaningless digressions, provides the essential unity that characterizes a strong education paper.
After spending a great deal of time and energy introducing and arguing the points in the main body of the paper, the conclusion brings everything together and underscores what it all means. A stimulating and informative conclusion leaves the reader informed and well-satisfied. A conclusion that makes sense, when read independently from the rest of the paper, will win praise.
Works Cited/Bibliography
See the Citation guide .
Education research papers often contain one or more appendices. An appendix contains material that is appropriate for enlarging the reader's understanding, but that does not fit very well into the main body of the paper. Such material might include tables, charts, summaries, questionnaires, interview questions, lengthy statistics, maps, pictures, photographs, lists of terms, glossaries, survey instruments, letters, copies of historical documents, and many other types of supplementary material. A paper may have several appendices. They are usually placed after the main body of the paper but before the bibliography or works cited section. They are usually designated by such headings as Appendix A, Appendix B, and so on.
- << Previous: Choosing a Topic
- Next: Find Books >>
- Last Updated: Dec 5, 2023 2:26 PM
- Subjects: Education
- Tags: education , education_paper , education_research_paper
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 26 August 2015
Papers with shorter titles get more citations
- Boer Deng
Nature ( 2015 ) Cite this article
5185 Accesses
11 Citations
1064 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Research management
Intriguing correlation mined from 140,000 papers.
To William Shakespeare, brevity was the soul of wit. For scientists, it may be even more valuable, as conciseness seems to correlate with how frequently a research paper is cited.
Adrian Letchford and his colleagues at the University of Warwick in Coventry, UK, analysed the titles of 140,000 of the most highly cited peer-reviewed papers published between 2007 and 2013 as listed on Scopus , a research-paper database. They compared the lengths of the papers’ titles with the number of times each paper was cited by other peer-reviewed papers— a statistic sometimes used as a crude measure of importance.
As they report in Royal Society Open Science 1 , “journals which publish papers with shorter titles receive more citations per paper”.
The impetus for the current study came from a desire to pen better papers, says Letchford, and to see whether good writing is rewarded in research. “As scientists, we’re all cursed,” when it comes to writing, Letchford says, as researchers hone their specialised knowledge but often cannot explain themselves to readers outside their own field.
Journal factors
Previous research has come to conflicting conclusions on the link between title length and citations 2 , 3 . And Letchford admits that their paper is merely a 'proof of concept' that does not show that shorter titles lead to more citations.
Among the possible confounding factors is that not all journals have the same standards for title lengths. Papers published in Science , which average more than 30 citations, are limited to titles of 90 characters, whereas the Public Library of Science journals, where papers generally attract fewer citations, allow up to 250. To account for some of these differences, Letchford also compared the number of citations for papers published in the same journal and found that the pattern held true.
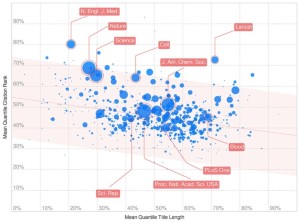
However, Letchford and his team did not investigate the possible effect of factors such as subject matter, seniority of authorship or other aspects of a paper that affect its citation rate. John Mingers, a bibliometrician at the University of Kent's business school in Canterbury, UK, says that even if there is a relationship between title length and frequency of citation, a more rigorous analysis might have found the importance of that association to be very slight. There might simply be more citations in fields where it is standard to write shorter titles, for example. “They have used a large dataset, which is good, but there are problems, and what you can conclude from these results is very limited,” he says.
Shorter is sweeter
Regardless of whether they influence citations, clear, tightly constructed titles are in authors’ best interests, says Karl Ziemelis, Nature ’s chief physical sciences editor, as they can improve the chances of a paper being discovered by readers and encourage them not to pass it over. “I find that snappier ones catch my attention more,” agrees Meghan Byrne, a senior editor at PLoS One .
John Ioannidis, an epidemiologist at Stanford University in California, who studies scientific publishing, says the work is “a cute paper, but I don’t really trust the results to be conclusive”.
He adds, “I will continue to struggle finding appropriate titles for my papers without worrying about whether the title length may affect their citations.”
But the study has already influenced at least one piece of writing. Given their findings, Letchford says that the research team spent quite some time on naming their paper.
“After all that, we thought, ‘we’d better give it a good title,’” he says.
They chose "The advantage of short paper titles".

Letchford, A. et al. R. Soc. Open Sci. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsos.150266 (2015).
Jamali, H. R. & Nikzad, M. Scientometrics 88 , 653–661 (2011).
Article Google Scholar
Jacques, T. S. & Sebire, N. J. J. R. Soc. Med. Short Rep. http://dx.doi.org/10.1258/shorts.2009.100020 (2010).
Download references
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Additional information
Tweet Follow @NatureNews
Related links
Related links in nature research.
‘Sleeping beauty’ papers slumber for decades 2015-May-25
Bibliometrics: The Leiden Manifesto for research metrics 2015-Apr-22
The focus on bibliometrics makes papers less useful 2015-Jan-13
Scientists: your number is up 2012-May-30
Related external links
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Deng, B. Papers with shorter titles get more citations. Nature (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2015.18246
Download citation
Published : 26 August 2015
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2015.18246
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Authorship and citation cultural nature in density functional theory from solid state computational packages.
- Marie Dumaz
- Reese Boucher
- Aldo H. Romero
Scientometrics (2021)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Titles in research articles and doctoral dissertations: cross-disciplinary and cross-generic perspectives
- Published: 29 February 2024
Cite this article
- Jialiang Hao ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0006-5980-4451 1 , 2
115 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Although titles are often regarded as a minimal aspect of academic discourse, they play a crucial role in knowledge construction across various disciplines and genres. This study examined four features of titles, namely, title length, punctuation usage, structure, and content information, with a corpus comprising 1600 titles of research articles (RAs) from top journals and doctoral dissertations (DDs) from prestigious universities across four soft and hard science disciplines. The results confirm disciplinary and generic variations within the titles of these two critical academic genres. Titles in linguistics and medicine are generally longer than those in economics and computer science (CS). Slightly more titles in hard disciplines contain punctuation than do those in soft disciplines. The average title length of RAs is longer than that of DDs, and more RA titles than DD titles have punctuation in all four disciplines, with no apparent difference in the punctuation variety across the two genres, except for CS titles. Nominal group titles and compound titles are the two most common types, and prepositional phrase titles are the least common in all four disciplines and genres. The content information in titles is different in each discipline and genre. These findings are partially congruent with those of previous studies, indicating the significance of further investigating titles across disciplines and genres.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
More diversity, more complexity, but more flexibility: research article titles in TESOL Quarterly, 1967–2022
Gianna Kexin Jiang & Yajun Jiang

A lexical and syntactic study of research article titles in Library Science and Scientometrics
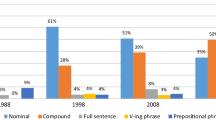
A diachronic comparative study of research article titles in linguistics and literature journals
Xuechun Xiang & Jing Li
This paper follows US conventions.
https://www.scimagojr.com/journalrank.php
The impact factor is from the 2022 Journal Citation Reports .
https://www.topuniversities.com/university-rankings/world-university-rankings/2022
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/74/2014/09/guidelines-for-the-PhD-dissertation.pdf
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the american psychological association (7th ed.). American Psychological Association.
Google Scholar
Anthony, L. (2001). Characteristic features of research article titles in computer science. IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication, 44 (3), 187–194. https://doi.org/10.1109/47.946464
Article Google Scholar
Bahadoran, Z., Mirmiran, P., Kashfi, K., & Ghasemi, A. (2019). The principles of biomedical scientific writing: Title. International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, 17 , e98326. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijem.98326
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ball, R. (2009). Scholarly communication in transition: The use of question marks in the titles of scientific articles in medicine, life sciences and physics 1966–2005. Scientometrics, 79 (3), 667–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-007-1984-5
Berkenkotter, C., & Huckin, T. N. (1995). News value in scientific journal articles. In C. Berkenkotter & T. N. Huckin (Eds.), Genre knowledge in disciplinary communication: Cognition, culture, power (pp. 27–44). Routledge.
Bramoullé, Y., & Ductor, L. (2018). Title length. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 150 , 311–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2018.01.014
Braticevic, M. N., Babic, I., Abramovic, I., Jokic, A., & Horvat, M. (2020). Title does matter: A cross-sectional study of 30 journals in the medical laboratory technology category. Biochemia Medica, 30 (1), 128–133. https://doi.org/10.11613/bm.2020.010708
Bunton, D. (2002). Generic moves in PhD theses introductions. In J. Flowerdew (Ed.), Academic discourse (pp. 57–75). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315838069
Chapter Google Scholar
Chen, X., & Liu, H. (2023). Academic “click bait”: A diachronic investigation into the use of rhetorical part in pragmatics research article titles. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 66 , 101306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2023.101306
Cheng, S. W., Kuo, C.-W., & Kuo, C.-H. (2012). Research article titles in applied linguistics. Journal of Academic Language and Learning, 6 (1), A1–A14.
Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: looks matter! Indian Pediatrics, 53 (3), 235–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-016-0827-y
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Diao, J. (2021). A lexical and syntactic study of research article titles in library science and scientometrics. Scientometrics, 126 , 6041–6058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-021-04018-6
El-Dakhs, D. A. S. (2018). Why are abstracts in PhD theses and research articles different? A genre-specific perspective. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 36 , 48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2018.09.005
Finlay, C. S., Sugimoto, C. R., Li, D., & Russell, T. G. (2012). LIS dissertation titles and abstracts (1930–2009): Where have all the librar* gone? The Library Quarterly, 82 (1), 29–46. https://doi.org/10.1086/662945
Fox, C. W., & Burns, C. S. (2015). The relationship between manuscript title structure and success: Editorial decisions and citation performance for an ecological journal. Ecology and Evolution, 5 , 1970–1980. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.1480
Gesuato, S. (2008). Encoding of information in titles: Academic practices across four genres in linguistics. In C. Taylor (Ed.), Ecolingua. The role of E-corpora in translation and language learning (pp. 127–157). EUT Edizioni Università di Trieste.
Gnewuch, M., & Wohlrabe, K. (2017). Title characteristics and citations in economics. Scientometrics, 110 (3), 1573–1578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-2216-7
Goodman, R. A., Thacker, S. B., & Siegel, P. Z. (2001). What’s in a title? A descriptive study of article titles in peer-reviewed medical journals. Science Editor, 24 (3), 75–78.
Guo, S., Zhang, G., Ju, Q., Chen, Y., Chen, Q., & Li, L. (2015). The evolution of conceptual diversity in economics titles from 1890 to 2012. Scientometrics, 102 , 2073–2088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1501-6
Habibzadeh, F., & Yadollahie, M. (2010). Are shorter article titles more attractive for citations? Cross-sectional study of 22 scientific journals. Croatian Medical Journal, 51 (2), 165–170. https://doi.org/10.3325/cmj.2010.51.165
Haggan, M. (2004). Research paper titles in literature, linguistics and science: Dimensions of attractions. Journal of Pragmatics, 36 , 293–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-2166(03)00090-0
Hallock, R. M., & Dillner, K. M. (2016). Should title lengths really adhere to the American Psychological Association’s twelve word limit? American Psychologist, 71 (3), 240–242. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0040226
Hartley, J. (2005). To attract or to inform: What are titles for? Journal Technical Writing & Communication, 35 , 203–213. https://doi.org/10.2190/NV6E-FN3N-7NGN-TWQT
Hartley, J. (2007a). Planning that title: Practices and preferences for titles with colons in academic articles. Library & Information Science Research, 29 (4), 553–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lisr.2007.05.002
Hartley, J. (2007b). Colonic titles! The Write Stuff, 16 (4), 147–149.
Hyland, K. (2004). Disciplinary interactions: Metadiscourse in L2 postgraduate writing. Journal of Second Language Writing, 13 , 133–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2004.02.001
Article ADS Google Scholar
Hyland, K., & Tse, P. (2005). Hooking the reader: A corpus study of evaluative that in abstracts. English for Specific Purposes, 24 (2), 123–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2004.02.002
Hyland, K., & Zou, H. (2022). Titles in research articles. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 56 , 101094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2022.101094
Jacques, T. S., & Sebire, N. J. (2009). The impact of article titles on citation hits: An analysis of general and specialist medical journals. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Short Reports, 1 (2), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1258/shorts.2009.100020
Jalilifar, A. (2010). Writing titles in applied linguistics: A comparative study of theses and research articles. Taiwan International ESP Journal, 2 (1), 27–52.
Jalilifar, A., Hayati, A., & Mayahi, N. (2010). An exploration of generic tendencies in Applied Linguistics titles. Journal of Faculty of Letters and Humanities, 5 (16), 35–57.
Jamali, H. R., & Nikzad, M. (2011). Article title type and its relation with the number of downloads and citations. Scientometrics, 88 (2), 653–661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-011-0412-z
Jiang, F. K., & Hyland, K. (2023). Titles in research articles: Changes across time and discipline. Learned Publishing, 36 , 239–248. https://doi.org/10.1002/leap.1498
Jiang, G. K., & Jiang, Y. (2023). More diversity, more complexity, but more flexibility: Research article titles in TESOL Quarterly , 1967–2022. Scientometrics, 128 , 3959–3980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-023-04738-x
Kawase, T. (2015). Metadiscourse in the introductions of PhD theses and research articles. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 20 , 114–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2015.08.006
Kawase, T. (2018). Rhetorical structure of the introductions of applied linguistics PhD theses. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 31 , 18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2017.12.005
Kerans, M. E., Marshall, J., Murray, A., & Sabaté, S. (2020). Research article title content and form in high-ranked international clinical medicine journals. English for Specific Purposes, 60 , 127–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2020.06.001
Kerans, M. E., Murray, A., & Sabaté, S. (2016). Content and phrasing in titles of original research and review articles in 2015: Range of practice in four clinical journals. Publications, 4 (2), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications4020011
Koutsantoni, D. (2006). Rhetorical strategies in engineering research articles and research theses: Advanced academic literacy and relations of power. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 5 (1), 19–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2005.11.002
Lewison, G., & Hartley, J. (2005). What’s in a title? Numbers of words and the presence of colons. Scientometrics, 63 (2), 341–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-005-0216-0
Article CAS Google Scholar
Li, Z., & Xu, J. (2019). The evolution of research article titles: The case of Journal of Pragmatics 1978–2018. Scientometrics, 121 , 1619–1634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-019-03244-3
Méndez, D. I., ÁngelesAlcaraz, M., & Salager-Meyer, F. (2014). Titles in English-medium Astrophysics research articles. Scientometrics, 98 (3), 2331–2351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-013-1174-6
Milojevic, S. (2017). The length and semantic structure of article titles—evolving disciplinary practices and correlations with impact. Frontiers in Research Metrics and Analysis, 2 , 2. https://doi.org/10.3389/frma.2017.00002
Morales, O. A., Perdomo, B., Cassany, D., Tovar, R. M., & Izarra, É. (2020). Linguistic structures and functions of thesis and dissertation titles in dentistry. Lebende Sprachen, 65 (1), 49–73. https://doi.org/10.1515/les-2020-0003
Moslehi, S., & Kafipour, R. (2022). Syntactic structure and rhetorical combinations of Iranian English research article titles in medicine and applied linguistics: A cross-disciplinary study. Frontiers in Education, 7 , 935274. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2022.935274
Nagano, R. L. (2015). Research article titles and disciplinary conventions: A corpus study of eight disciplines. Journal of Academic Writing, 5 , 133–144. https://doi.org/10.18552/joaw.v5i1.168
Nair, L. B., & Gibbert, M. (2016). What makes a “good” title and (how) does it matter for citations? A review and general model of article title attributes in management science. Scientometrics, 107 (3), 1331–1359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-1937-y
Nieuwenhuis, J. (2023). Another article titled “Should I Stay or Should I Go?” or, the mass production of academic research titles. The Information Society, 39 (2), 123–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/01972243.2022.2152916
Paiva, C., Lima, J., & Paiva, B. (2012). Articles with short titles describing the results are cited more often. Clinics, 67 (5), 509–513. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2012(05)17
Paltridge, B. (2002). Thesis and dissertation writing: An examination of published advice and actual practice. English for Specific Purposes, 21 (2), 125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0889-4906(00)00025-9
Paré, A. (2019). Re-writing the doctorate: New contexts, identities, and genres. Journal of Second Language Writing, 43 , 80–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2018.08.004
Paré, A., Starke-Meyerring, D., & McAlpine, L. (2009). The dissertation as multi-genre: Many readers, many readings. In C. Bazerman, A. Bonini, & D. Figueiredo (Eds.), Genre in a changing world (pp. 179–193). The WAC Clearinghouse and Parlor Press.
Pearson, W. S. (2020). Research article titles in written feedback on English as a second language writing. Scientometrics, 123 , 997–1019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03388-7
Pearson, W. S. (2021). Quoted speech in linguistics research article titles: Patterns of use and effects on citations. Scientometrics, 126 , 3421–3442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03827-5
Qiu, X., & Ma, X. (2019). Disciplinary enculturation and authorial stance: comparison of stance features among master’s dissertations, doctoral theses, and research articles. Ibérica, 38 , 327–348.
Sahragard, R., & Meihami, H. (2016). A diachronic study on the information provided by the research titles of applied linguistics journals. Scientometrics, 108 , 1315–1331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-2049-4
Salager-Meyer, F., Alcaraz-Ariza, M. A., & Briceño, M. L. (2013). Titling and authorship practices in medical case reports: A diachronic study (1840–2009). Communication & Medicine, 10 (1), 63–80. https://doi.org/10.1558/cam.v10i1.63
Soler, V. (2007). Writing titles in science: An exploratory study. English for Specific Purposes, 26 (1), 90–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2006.08.001
Soler, V. (2011). Comparative and contrastive observations on scientific titles written in English and Spanish. English for Specific Purposes, 30 (2), 124–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2010.09.002
Soler, V. (2018). Estudio exploratorio de títulos de tesis doctorales redactados en lengua Española [Exploratory study of Ph.D. thesis titles written in Spanish]. Lebende Sprachen, 63 (2), 374–392. https://doi.org/10.1515/les-2018-0022
Swales, J. (1990). Genre analysis: English in academic and research setting . Cambridge University Press.
Swales, J. (2004). Research genres: Explorations and applications. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press . https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139524827
Swales, J., & Feak, C. B. (2012). Academic writing for graduate students . Ann Arbor, MI, The University of Michigan Press.
Book Google Scholar
Taş, E. E. I. (2008). A corpus-based analysis of genre-specific discourse of research: The PhD thesis and the research article in ELT. Doctorate thesis at Middle East Technical University (Turkey) . http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.633.4476&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Thompson, P. (2005). Points of focus and position: Intertextual reference in PhD theses. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 4 (4), 307–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2005.07.006
Thompson, P. (2013). Thesis and dissertation writing. In B. Paltridge & S. Starfield (Eds.), The handbook of English for specific purposes (pp. 283–299). West Essex.
Wang, Y., & Bai, Y. (2007). A corpus-based syntactic study of medical research article titles. System, 35 , 388–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2007.01.005
Whissell, C. (2012). The trend toward more attractive and informative titles: American psychologist 1946–2010. Psychological Reports, 110 (2), 427–444. https://doi.org/10.2466/17.28.pr0.110.2.427-444
Whissell, C. (2013). Titles in highly ranked multidisciplinary psychology journals 1966–2011: More words and punctuation marks allow for the communication of more information. Psychological Reports, 113 (3), 969–986. https://doi.org/10.2466/28.17.PR0.113x30z5
Xiang, X., & Li, J. (2020). A diachronic comparative study of research article titles in linguistics and literature journals. Scientometrics, 122 , 847–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-019-03329-z
Xiao, W., & Sun, S. (2020). Dynamic lexical features of PhD theses across disciplines: A text mining approach. Journal of Quantitative Linguistics, 27 (2), 114–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/09296174.2018.1531618
Xie, S. (2020). English research article titles: Cultural and disciplinary perspectives. SAGE Open, 10 (2), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244020933614
Yang, W. (2019). A diachronic keyword analysis in research article titles and cited article titles in applied linguistics from 1990 to 2016. English Text Construction, 12 (1), 84–102. https://doi.org/10.1075/etc.00019.yan
Yitzhaki, M. (2002). Relation of the title length of a journal article to the length of the article. Scientometrics, 54 , 435–447. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016038617639
Zhou, H., & Jiang, F. K. (2023). “The study has clear limitations”: Presentation of limitations in conclusion sections of PhD dissertations and research articles in applied linguistics. English for Specific Purposes, 71 , 34–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2023.02.001
Download references
Acknowledgements
The researcher thanks the handling editor and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments, which significantly contributed to enhancing the quality of the manuscript.
This research was supported and funded by the Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (Program No. 23JK0100).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Xi’an International Studies University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China
Jialiang Hao
Weinan Normal University, Weinan, Shaanxi, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jialiang Hao .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author has no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Hao, J. Titles in research articles and doctoral dissertations: cross-disciplinary and cross-generic perspectives. Scientometrics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-024-04941-4
Download citation
Received : 10 July 2023
Accepted : 09 January 2024
Published : 29 February 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-024-04941-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Research articles
- Doctoral dissertations
- Disciplines
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
How Long Should a Research Paper Be? Data from 61,519 Examples
I analyzed a random sample of 61,519 full-text research papers, uploaded to PubMed Central between the years 2016 and 2021, in order to answer the questions:
What is the typical overall length of a research paper? and how long should each section be?
I used the BioC API to download the data (see the References section below).
Here’s a summary of the key findings
1- The median length of a research paper is 4,133 words (equivalent to 166 sentences or 34 paragraphs), excluding the abstract and references, with 90% of papers being between 2,023 and 8,284 words.
2- A typical article is divided in the following way:
- Introduction section: 14.6% of the total word count.
- Methods section: 29.7% of the total word count.
- Results section: 26.2% of the total word count.
- Discussion section: 29.4% of the total word count.
Notice that the Materials and methods is the longest section of a professionally written article. So always write this section in enough depth to provide the readers with the necessary details that allow them to replicate your study if they wanted to without requiring further information.
Overall length of a research paper
Let’s start by looking at the maximum word count allowed in some of the well-known journals. Note that the numbers reported in this table include the Abstract , Figure legends and References unless otherwise specified:
[1] excluding figure legends [2] excluding references
⚠ Note A review paper is either a systematic review or a meta-analysis, and an original research paper refers to either an observational or an experimental study conducted by the authors themselves.
Notice the large variability between these journals: The maximum number of words allowed ranges between 3,000 and 9,000 words.
Next, let’s look at our data.
Here’s a table that describes the length of a research paper in our sample:
90% of research papers have a word count between 2,023 and 8,284. So it will be a little weird to see a word count outside of this range.
Our data also agree that a typical review paper is a little bit longer than a typical original research paper but not by much (3,858 vs 3,708 words).
Length of each section in a research article
The median article with an IMRaD structure (i.e. contains the following sections: Introduction , Methods , Results and Discussion ) is in general characterized by a short 553 words introduction. And the methods, results and discussion sections are about twice the size of the introduction:
For more information, see:
- How Long Should a Research Title Be? Data from 104,161 Examples
- How Long Should the Abstract Be? Data 61,429 from Examples
- How Long Should the Introduction of a Research Paper Be? Data from 61,518 Examples
- How Long Should the Methods Section Be? Data from 61,514 Examples
- How Long Should the Results Section Be? Data from 61,458 Examples
- How Long Should the Discussion Section Be? Data from 61,517 Examples
- Length of a Conclusion Section: Analysis of 47,810 Examples
- Comeau DC, Wei CH, Islamaj Doğan R, and Lu Z. PMC text mining subset in BioC: about 3 million full text articles and growing, Bioinformatics , btz070, 2019.
How Long Should A Research Paper Be?

You must have known what research looks like. It has a particular structure that should be followed at any cost since it is the criteria for writing a research paper . Several questions come into the mind of students such as how to write a research paper, how long should a research paper be, etc.
That’s why we have brought a series of research writing and addressing different questions related to it. This blog aims to answer queries about the duration your research should ideally take, including insights on how to write an 8-page paper effectively. Although it depends upon the guidelines given by your teacher, there is also a standard length of research writing. Let’s dive in and learn everything about the ideal word count of any research.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper is an essay that is based on your investigational work you have completed or will complete on just one or many specific topics of a specific discipline. Research or investigation essays are lengthy depending on the scope and extensive nature of the topic.
It’s just an analysis of the topic from your own perspective. A student or a reader present facts and their theories in front of the audience to inform them about the specific subject matter. If you dont know how long is a research paper, here we will take you on a deeper tour to help you understand these essays thoroughly.
What is the Standard Length of a Research Paper?
Discussing the standard length of a paper, it’s important to note that it varies depending on the specific instructions given to each student and the structural requirements related to their chosen finance research topics . It is never a fixed one for all types of papers yet, there are some conditions and possibilities because of which the word count varies.
Research that has a thesis statement only requires 2 to 3 arguments to be proved and will be summed up in 500 to 700 words. After providing the introduction and a little background on the research, you can directly shift to mentioning the arguments and claims so you may prove the statement and complete the research.
Some research requires detailed analysis and interpretation of the findings. This kind of paper has several stages such as introduction, background, thesis statement, objective, research questions, literature review, research methodology, data collection, discussion, findings, conclusion, and bibliography. Such research easily crosses 5000 words because it is important to discuss everything about the topic.
So it entirely depends upon the structure you are following to write the research. It could be as long as just 500 words, or 5000 words, and even more. It all varies therefore you must be prepared for writing a paper no matter how long it should be.
How long is introduction in research paper?
Many students wonder how long should an introduction be in a research paper? The simple answer to this query is as short as possible that justify the requirements and employ all the methods that are necessary for coveying your message.
Typically, a standard length of introductory paragraph is 300-500 words. If your topic needs more than the standard word count than always ask for suggestion from your professor on first priority. We hope now you know how long should an introduction be for a research paper.
Why Considering Length of a Research Paper is Important
Identifying the length of research is important because of so many reasons. You might have never realized the significance of considering how long a paper should be, so here we go with some of the vital reasons.
1. Going Extra May Ruin Your Research
You cannot write more than is required in research. If you are doing so then you are automatically ignoring the quality measures of writing a paper. If you are writing more than words than is required then there are chances you are going to submit a poor quality research work.
2. Sticking to the Guidelines is Important
When your guidelines have mentioned 1000 words maximum and you are submitting research of 2000 words, you already know what wrong you have done. If you are not sticking to the guidelines it will result in deduction of marks, fall in grades, and repetition of the class course.
3. Having a Balance is Good
It is necessary to keep a balance between the word count of all the headings. Without this much-needed balance, you might end up submitting a poor paper that has a longer introduction, and a shorter explanation of the findings. That’s why attaining a balance is important in your research word count.
4. Delivering Quality Research is the Criteria
When you are delivering quality content, you will be appreciated no matter what. If you consider the length of your research, you are one step forward in delivering quality research work to your teacher.
How Long Should a Research Paper Be?
This question is valid and one of the frequently asked questions by the students of high school and college. It is also important to know before you start working on your paper. Don’t forget to read the instructions provided by your teacher, however, we have more suggestions for you regarding the length of the research.
1. It All Depends On Your Teacher First
Your teacher indeed decides what should be the ideal length of your research. They have given some guidelines to you and you need to follow them. The teachers always know the best and they will suggest to you how long your essay should be.
Some teachers have kept a certain word limit for the paper while others provide you complete freedom to write as long as you want. It is necessary to figure out what’s best for your research. In high schools, a standard length of any research is a maximum of 7 to 8 pages while the minimum should be 5 pages.
2. Check How Much Length is Required to Justify Your Statement
Sometimes it is based on the thesis for research paper . From the part of the abstract to the conclusion, there must be a balance between the word count of every heading. It is your responsibility as a writer to track the word count when you are trying to justify your thesis by giving several arguments and claims.
If you have decided how many arguments it will take to prove your thesis, then you have already finalized the length of your research. All you have to do is prepare everything in advance and see if you are proving your point within 5 or 8 pages.
3. It Shouldn’t Miss Any Point
A researcher must be discussing all the standard details that could justify the purpose of writing the paper. It must have all the headings properly discussed. Since all the points must be 100% clear in the research, deciding on a word limit in the very beginning could be a little hard.
But it is not impossible to identify by making an outline and checking how many pages will be covered in writing about a certain topic. All you have to do is take care that no point is missing in the research. Cutting the research short and trying to discuss facts to the exact point won’t help unless you are entirely explaining every aspect as required.
How Long a Research Paper Should be in Words?
You have learned something about the ideal length of research. When it comes to the word count, the criterion is a bit different. For example, if you need a Ph.D. research paper help , you must know the word count, typically between 70,000 to 80,000 words. As you suggest a specific word count for every heading, it is easier to guess how many words are required to summarize every title.
1. Assign Word Count To Each Heading
It is easier to assign a specific word count to every heading and then see what’s the total word length of the paper. For instance, you have to decide how many words will be used to cover your introduction section. A literature review is a second longer part after the discussion in every research so it is necessary to make an outline in advance and see what is the ideal length of every heading.
By giving a suggested word count to each heading you will make a clear pathway to follow during the complete research. It will be automatically easier for you to see how many words will be written to explain everything in your research thoroughly.
There are several sections in research that require certain word counts. Let’s see what word count is usually subjected to every heading.
An abstract for a research paper is the first main part that summarizes the research from the beginning to the conclusion. It contains the thesis, methodology, findings, and conclusion. So to explain the complete research in a few sentences, roughly 100 to 200 words will be required. So you may keep in mind the word count for an abstract is a maximum of 200 words.
● Introduction
An introduction is also a major part of the research and it is easily covered within 300 words maximum. Nothing else is required to explain terminologies or theories in this section. However, there are many opinion on this topic and each have different answers. That’s the prime reason students spend day and night on google looking for answers on their questions such as how long should introduction be for research paper. In short, 300 to 500 words are more than enough to state your thoughts in an into section and persuade your readers.
● Literature Review
The literature review is the second-longest section in any research. It contains a reference to the past research done in a similar field by other researchers. Every research must have 5 to 8 or even more past papers discussed in it. Therefore the ideal word count for this section is 500 to 1000 words.
● Methodology
The methodology section also has subcategories in which you have to explain the method of research, data collection, population, research implications, research Instrument, etc. It will take around 300 to 400 words and 100 words extra if you are discussing a theoretical framework too.
● Discussion and Interpretation
This is the longest part of any research since you have to explain all the findings and tell your readers how successfully you have managed to prove your thesis. This part is as long as 500 to 1000 or even 1500 words depending upon the results and the explanation required.
● Conclusion
A conclusion is a not so lengthy part of the paper. It is usually done within only 100 or 150 words maximum. It is that simple and thus it doesn’t need so many words to finish the argument and put a full stop.
2. Form a Paper Outline
Forming a paper outline in advance will also help you in understanding how many words you may need to cover every heading. This is one of the best ideas for assigning a particular word count to every heading of the paper.
As you’ll create a paper outline, you will get an instant idea of how many words you have to write in total to complete the research. Following this strategy will surely help you won’t be puzzled later during the writing process.
3. Ask Your Instructor
It is always a good idea to ask your teacher or instructor before following any word count technique. They have assigned you a paper so they can provide you with a better guideline to write your paper. It is the easiest method of identifying the word count of your research as it’s something recommended by an expert. Your job will become much easier and simpler by just seeking advice from your teacher.
How Long a Research Paper Should be for Middle School?
A middle school student is just starting with the research work and they are at the initial stages of learning how to conduct research. To understand how long a paper should be for middle school, you need to do some work.
1. Seek Expert Help
It is always better to seek help from an expert to decide the word limit of your essay when you’re a high school student. It could be your teacher or any senior student who will help you and guide how many pages you should write for your research. It is suggested to write 4 to 5 pages when you are a middle school student in writing a paper.
2. Do Research
It is always important to do some research and find out what’s best for your paper. Google is always open to helping students in learning new things without any limit. You can open the Google search engine, write down your query in the search bar and click on it.
Next, you will have everything to read and understand how a paper for middle school will work. By doing so you will automatically get an in-depth idea of crafting research for the initial level project.
After analyzing everything you can easily guess what should be the length of any research written by a middle school student. In pages, it is suggested to write 3 to 5 pages, but in words, it is recommended to write 400 to 500 words only. You can also hire a professional paper writing service to aid you in the process.
As it’s a new thing for the students to perform, they might get nervous easily. That’s why starting slow and taking baby steps towards learning research writing will help a lot.
How long Should a Research Paper be for High School?
High school is a different stage than middle school. You are mature, better at studies, and even more creative than before. This stage comes with its challenges and one of them is writing the research. If you are a new high school student we bet you don’t know much about paper writing at this level.
When a high school student writes a research paper, it’s usually written within 500 to 1000 words. It could be more than this word count or just 5 to 6 pages. The teacher’s instructions do matter a lot in this aspect and without them, you can’t understand the criteria of research writing. It takes a lot of research, consultation, and creativity to write a paper that stands out. The competition is even tougher in high schools so you know how tough it can get to write a research paper fast .
Your research will decide if you are going to pass the school or not. Many students stay stuck in a class because they are incapable of submitting a brilliant research paper. Most of the time it’s because they don’t know the standard guidelines for writing a paper.
They usually end up ignoring the pattern, writing incorrect information, or exceeding or limiting the length assigned for the research. So it’s better to keep in mind what is the better approach for research writing and how a high school student can learn to write it.
How Long Should a Research Paper be for College?
Have you ever thought about how long your research should be when you have finally reached college? It is the final stage of your education and writing research in this phase will require a lot of preparation. In college, you have to write the longest research papers because it is the standard of a paper written by a college student.
So how exactly long should research be for college? It starts with roughly 3000 words and goes up to 15000 words. 15000 words is a lot but students who are working on their thesis need a lot of details to justify and complete their research. Without doing this they are not getting passed at any cost so now you know why it is so important.
Different sections of the paper require their particular word count. It is sometimes difficult to identify but your teachers will always be there to guide you. Sometimes students are given the entire freedom to keep their essay length on their own. It helps them understand how easily they can prove their thesis either in a few or a lot of pages.
For newcomers in college unsure about the ideal length for research papers, utilizing Google is a great option to delve deeper into the nuances of research writing. It’s particularly helpful in exploring various guidelines related to history research topics . A lot of content is already published on the web which teaches the students almost everything they need.
We hope you know how long is a research paper, no matter if you are writing one for your middle school, high school, or college. All of them have different requirements and basic criteria that should be followed. We also hope this blog has helped you learn everything about deciding the word count or overall length of your research.
Our comment section is always open for your discussion and feedback. If you want to get in touch with us or discuss the topic more, just leave a comment in the given box. We would love to hear from our readers and see what they have in their minds after reading our blog.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Calculate Your Order Price
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score
- Home New Posts Forum List Trending New Threads New Media Spy
- WikiPost Latest summaries Watched WikiPosts
- Support FAQ and Rules Contact Us
What's the longest research/critical paper you've ever written?
- Thread starter irain
- Start date Dec 17, 2006
- Sort by reaction score
- MacRumors Community
- Community Discussion
macrumors regular
- Dec 17, 2006
What's the longest one you've ever written? I, for one, have just completed a 20-page research paper for my Honors Asian-Studies class (prep-class for AP U.S. History). My topic was on whether or not Japan should become a nuclear power.
macrumors 601
21 pages. I hope I never have to do anything like that ever again ever.
depends on how you define "written" and "research" but my degree project (graphic design BFA) was a book (actually one book in 12 volumes) totaling about 3000 pages with one image per page. it was not linguistic "writing," but it was a visual language and it was research. as far as actual "words" i did a 25 page paper a while back.
macrumors 6502a
I don't really remember, but I think I did: a 20 page English paper on John Constable (Romantic painter) for junior year English in highschool a 20 page Economics paper on how subsidies of US agricultural products affect developing countries, differently affect people within those countries, and how it affects the US itself. I did this for junior year economics in college. And I think I did another, but I totally can't remember (fried from finals).
gauchogolfer
Macrumors 603.
My PhD dissertation was a tidy 160 pages, not like those 400-pagers that some people put out. That's the most I've written.
macrumors 68000
macrumors 68030
I can't imagine writing that much. I don't think I've ever done more than like a 7 page paper.
AvSRoCkCO1067
Macrumors 65816.
325328950235 pages.
I once wrote a 10 page paper on the Tuatara (rare branch of reptile species). I did that when I was in 6th grade (12 y/o)
not that this counts but I wrote a 25-30 page genetics lab report on: Restriction Endonuclease, lysase (I think), Transcription, Translation, E.coli, Plasmid DNA, Amphicilin (sp), another antibiotic that starts with a K, can't remember name, and transformation. Basically we cut a plasmid DNA added in a resistance gene, then transformed it into the E.coli making it resistant to antibiotics.
eva01 said: not that this counts but I wrote a 25-30 page genetics lab report on: Restriction Endonuclease, lysase (I think), Transcription, Translation, E.coli, Plasmid DNA, Amphicilin (sp), another antibiotic that starts with a K, can't remember name, and transformation. Basically we cut a plasmid DNA added in a resistance gene, then transformed it into the E.coli making it resistant to antibiotics. Click to expand...
Leareth said: oh I remember this lab exercise from my molecular genetics class... did you run the gels to prove that there was a genetic change beside the survival in antibiotic growth medium? Click to expand...
macrumors Pentium
Probably not too long at all, certainly not 20+ pages. If I'm writing about something I really care about, I can go on and on. In high school, I wrote a research paper about violence in videogames and their effect (or lack thereof) on the people who play them, and since I love videogames and believe that violence does not have negative effects, I was able to go on and on, producing a pretty long research paper, and it was good too, because I got an A on it (I never get As in English). But if it's a topic that was just randomly assigned to me and I couldn't care less about it, I'm lucky to get 5 pages and a B
eva01 said: yes we did southern blots before transformation and after. And of multiple colonies, since of course some colonies may have gotten a mutation randomly. It was a very fun lab I think my Introduction and materials and methods was 14 pages alone. Click to expand...
macrumors 6502
- Dec 18, 2006
macrumors 604
steelphantom
Probably around 10 pages or so...
20 pages when I was in 6th grade. Crazy.
irain said: What's the longest one you've ever written? I, for one, have just completed a 20-page research paper for my Honors Asian-Studies class (prep-class for AP U.S. History). My topic was on whether or not Japan should become a nuclear power. Click to expand...
macrumors member
mac users = very intelligent.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computation and Language
Title: realm: reference resolution as language modeling.
Abstract: Reference resolution is an important problem, one that is essential to understand and successfully handle context of different kinds. This context includes both previous turns and context that pertains to non-conversational entities, such as entities on the user's screen or those running in the background. While LLMs have been shown to be extremely powerful for a variety of tasks, their use in reference resolution, particularly for non-conversational entities, remains underutilized. This paper demonstrates how LLMs can be used to create an extremely effective system to resolve references of various types, by showing how reference resolution can be converted into a language modeling problem, despite involving forms of entities like those on screen that are not traditionally conducive to being reduced to a text-only modality. We demonstrate large improvements over an existing system with similar functionality across different types of references, with our smallest model obtaining absolute gains of over 5% for on-screen references. We also benchmark against GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, with our smallest model achieving performance comparable to that of GPT-4, and our larger models substantially outperforming it.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here's a summary of the key findings. 1. The median title was 14 words long (equivalent to 103 characters), and 90% of titles in the sample were between 6 and 25 words. 2. The 10-year trend shows an increase in title length from an average of 103 characters in 2012 to 111 characters in 2021. 3.
Here are two very short titles. The first is from a review article published in 2012 in the Annual Review of Psychology: "Intelligence". This article has had more than 180 citations, placing it in the top 1% in its subject area and publication year (citations and centiles for subject areas taken from Scopus for the period 2012-18). As a ...
The title and abstracts are the only sections of the research paper that are often freely available to the readers on the journal websites, search engines, and in many abstracting agencies/databases, whereas the full paper may attract a payment per view or a fee for downloading the pdf copy.[1,2,3,7,8,10,11,13,14] The abstract is an independent ...
The most effective titles are no more than 10 to 12 words and provide an overall view of the paper's significance rather than the detailed contents of the paper. BMJ 7: The title should be informative and, for research papers, a subtitle with the study design (for example, "a phase III clinical trial" or "a systematic review and meta ...
Research Paper Title. Research Paper Title is the name or heading that summarizes the main theme or topic of a research paper.It serves as the first point of contact between the reader and the paper, providing an initial impression of the content, purpose, and scope of the research.A well-crafted research paper title should be concise, informative, and engaging, accurately reflecting the key ...
Shorten the text to make it more concise, while still remaining descriptive. Repeat this process until you have a title of fewer than 15 words. 2. A good title is easily searchable. Most readers ...
Step 4: Create a working research paper title. To create a working title, remove elements that make it a complete "sentence" but keep everything that is important to what the study is about. Delete all unnecessary and redundant words that are not central to the study or that researchers would most likely not use in a database search.
A review of more than 150,000 papers submitted to the United Kingdom's Research Excellence Framework (REF) database in 2014 found the style of a paper's title impacted the number of citations ...
Full-sentence Title: It is the longest type, and it includes . more information about the results (e.g., emphasis on a . ... Haggan, M. Research paper titles in literature, linguistics.
A paper might be rejected simply because the title and the content of the paper do not match. The title is the first thing that reviewers read, so you don't want to mislead them. In fact the title tends to be the benchmark against which reviewers assess the content of the paper. Example 1: The first 3-4 words of all these titles give no ...
Shorter titles are indicative of well-thought-out papers with simple yet effective conclusions. As the research of Carlo Galli and Stefano Guizzardi points out, many academics have claimed that shorter titles can increase citations by making papers stand out amongst others. Their study found that titles with over 30 words had far fewer citations.
Picking a pithy title for your research paper could significantly improve its impact, new analysis suggests. ... Overall, the discipline with the longest journal titles on average was public health, whose titles averaged 117 characters including spaces, followed by clinical medicine (113) and agriculture (110). The shortest titles tended to ...
Key points. Article titles have been getting longer in all disciplines over the past 20 years, with 11-15 words now. being the most common length. There are some differences between journal ...
Make sure your research title describes (a) the topic, (b) the method, (c) the sample, and (d) the results of your study. You can use the following formula: [ Result ]: A [ method] study of [ topic] among [ sample] Example: Meditation makes nurses perform better: a qualitative study of mindfulness meditation among German nursing students. Avoid ...
Titles are a crucial feature of research papers and have become increasingly important with changes in publishing practices and the explosion of published research. As a result, novice writers seeking to get their work noticed in international journals might benefit from a clear understanding of the features of research titles and an awareness ...
Articles with shorter titles tend to get cited more often than those with longer headers, concludes a study published today, which examined 140,000 papers published between 2007 and 2013. It appears in the journal Royal Society Open Science. (See below for a list of the five longest, and five shortest, titles included in the study.)
Contains the paper's title, the author's name, address, phone number, e-mail, and the day's date. Abstract. ... This is generally the longest part of the paper. It's where the author supports the thesis and builds the argument. ... Education research papers often contain one or more appendices. An appendix contains material that is appropriate ...
As they report in Royal Society Open Science 1, "journals which publish papers with shorter titles receive more citations per paper". The impetus for the current study came from a desire to ...
The average length of Econ titles is the shortest in both genres, and that of Med titles is the longest. From the cross-generic perspective, the average length of RA titles was longer than that of DD titles across all disciplines selected. ... Research paper titles in literature, linguistics and science: Dimensions of attractions. Journal of ...
1- The median length of a research paper is 4,133 words (equivalent to 166 sentences or 34 paragraphs), excluding the abstract and references, with 90% of papers being between 2,023 and 8,284 words. 2- A typical article is divided in the following way: Introduction section: 14.6% of the total word count.
When. 12 March 2021. The longest title of a book consists of 27,978 characters, and was achieved by N. Srinivasan (India) in Chennai, India, on 12 March 2021. The title contains 4,558 words with a main header of "Stock Price Prediction, a referential approach on how to predict the stock price using..." going on to list the various tools ...
In college, you have to write the longest research papers because it is the standard of a paper written by a college student. So how exactly long should research be for college? It starts with roughly 3000 words and goes up to 15000 words. 15000 words is a lot but students who are working on their thesis need a lot of details to justify and ...
1. Dec 18, 2006. #18. My longest paper was a measly 8 pages on "No Child Left Behind" for my Honors Freshman English class last year at Penn State. I had a hard time thinking of enough crap to fill 8 pages! I don't know how some of you guys can write these 20+ (and in some cases over 100! ) page papers!
In comparison, Mathematics papers and the Nature portfolio showed the least LLM modification (up to 6.3%). Moreover, at an aggregate level, our analysis reveals that higher levels of LLM-modification are associated with papers whose first authors post preprints more frequently, papers in more crowded research areas, and papers of shorter lengths.
The integration and deployment of large language model (LLM)-based intelligent agents have been fraught with challenges that compromise their efficiency and efficacy. Among these issues are sub-optimal scheduling and resource allocation of agent requests over the LLM, the difficulties in maintaining context during interactions between agent and LLM, and the complexities inherent in integrating ...
Reference resolution is an important problem, one that is essential to understand and successfully handle context of different kinds. This context includes both previous turns and context that pertains to non-conversational entities, such as entities on the user's screen or those running in the background. While LLMs have been shown to be extremely powerful for a variety of tasks, their use in ...