Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Electricity
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 12 electricity, case study: 1, case study: 2, case study:3.
Thus, heat produced is directly proportional to the square of the electric current, directly proportional to the resistance of the resistor and the time for which electric current flows through the circuit. This heating effect is used in many applications. The heating effect is also used for producing light. In case of electric bulb, the filament produces more heat energy which is emitted in the form of light. And hence filament are made from tungsten which is having high melting point.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, west bengal board class 6 math solution, west bengal board class 6 maths chapter 24 solutions নানা দিক থেকে ঘনবস্তু (perspective/পরিপ্রেক্ষিত), ncert class 7 mathematics third chapter data handling exercise 3.1 3.2 3.3 solutions, west bengal board class 6 maths chapter 27 solutions ভগ্নাংশ, দশমিক ভগ্নাংশ, শতকরা ও অনুপাতের তুল্যতা.

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 12 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Electricity Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
The heating effect of current is obtained by the transformation of electrical energy into heat energy. Just as mechanical energy used to overcome friction is covered into heat, in the same way, electrical energy is converted into heat energy when an electric current flows through a resistance wire. The heat produced in a conductor, when a current flows through it is found to depend directly on (a) strength of current (b) resistance of the conductor (c) time for which the current flows. The mathematical expression is given by H = I 2 Rt. The electrical fuse, electrical heater, electric iron, electric geyser, etc. all are based on the heating effect of current.
(i) What are the properties of heating elements? (a) High resistance, high melting point (b) Low resistance, high melting point (c) Low resistance, high melting point (d) Low resistance, low melting point.
Answer: (b) Low resistance, high melting point
(ii) What are the properties of an electric fuse? (a) Low resistance, low melting point (b) High resistance, high melting point. (c) High resistance, low melting point (d) Low resistance, high melting point
Answer: (c) High resistance, low melting point
(iii) When the current is doubled in a heating device and time is halved, the heat energy produced is
| (a) doubled | (b) halved |
| (c) four times | (d) one fourth times |
Answer: (a) doubled
(iv) A fuse wire melts at 5 A. It is is desired that the fuse wire of same material melt at 10 A. The new radius of the wire is
| (a) 4 times | (b) 2 times |
| (c) 6 times | (d) 8 times |
Answer: (b) 2 times
(v) When a current of 0.5 A passes through a conductor for 5 min and the resistance of conductor is 10 ohm, the amount of heat produced is
| (a) 250 J | (b) 5000J |
| (c) 750J | (d) 1000J |
Answer: (c) 750J
Question 2:
The relationship between potential difference and the current was first established by George Simon Ohm. This relationship is known as Ohm’s law. According to this law, the current passed through a conductor is proportional to the potential difference applied between its ends provided the temperature remains constant i.e. I ∝ V or V = IR where R is the constant for the conductor and it is known as the resistance of the conductor. Although Ohm’s law has been found valid over a large class of materials, there are some materials that do not hold Ohm’s law.
2.1) Name the law which is illustrated by the VI graph. (a) Lenz law (b) Faraday’s law (c) Ohm’s law (d) Newton’s law
Answer(c) Ohm’s law
2.2) By increasing the voltage across a conductor, the (a) current will decrease (b) current will increase (c) resistance will increase (d) resistance will decrease
Answer(b) current will increase
2.3) When a battery of 9 V is connected across a conductor and the current flows is 0.1 A, the resistance is (a) 9 Ohm (b) 0.9 Ohm (c) 90 Ohm (d) 900 Ohm
Answer(c) 90 Ohm
2.4) If both the potential difference and resistance in a circuit are doubled then : (a) current remains same (b) current becomes double (c) current becomes zero (d) current becomes half
Answer(a) current remains same
2.5) Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is doubled. The current will become : (a) double (b) half (c) one fourth (d) 4 time
Answer(b) half
Case Study 3
3.1) The current passing through an electric kettle has been doubled. The heat produced will become : (a) half (b) double (c) four times (d) one fourth
Answer(c) four times
3.2) The heat produced in a wire of resistance ‘a’ when a current ‘b’ flows through it in time ‘c’ is given by : (a) a 2 bc (b) abc 2 (c) ab 2 c (d) abc
Answer(c) ab2c
3.3) What are the properties of heating element ? (a) high resistance, high melting point (b) low resistance, high melting point (c) low resistance, high melting point (d) low resistance, low melting point
Answer (a) high resistance, high melting point
3.4) Calculate the heat produced when 96,000 coulombs of charge is transferred in one hour through a potential difference of 50 volts. (a) 4788 J (b) 4788 kJ (c) 478 kJ (d) 478 J
Answer (b) 4788 kJ
3.5) Which of the following characteristic is not suitable for a fuse wire ? (a) thin and short (b) low melting point (c) thick and short (d) high resistance
Answer (c) thick and short
Case Study 4
Substance through which charges cannot pass is called insulators. Glass, pure water, and all gases are insulators. Insulators are also called dielectrics. In insulators, the electrons are strongly bound to their atoms and cannot get themselves freed. Thus, free electrons are absent in insulators. Insulators can easily be charged by friction. This is due to the reason that when an electric charge is given to an insulator, it is unable to move freely and remains localized. But this does not mean that conductors cannot be charged. A metal rod can be charged by rubbing it with silk if it is held in a handle of glass or amber
4.1) Calculate the current in a wire if a 1500 C charge is passed through it in 5 minutes. (a) 2 A (b) 5 A (c) 3 A (d) 4 A
Answer (b) 5 A
4.2) Electrons and conventional current flows in : (a) The same direction (b) The opposite direction (c) Any direction (d) Can’t say
Answer (b) The opposite direction
4.3) If the current passing through a lamp is 5 A, what charge passes in 10 second ? (a) 0.5 C (b) 3 C (c) 5 C (d) 50 C
Answer (d) 50 C
4.4) One-coulomb charge is equivalent to the charge contained in : (a) 6.2 × 10 19 electrons (b) 2.6 × 10 18 electrons (c) 2.65 × 10 19 electrons (d) 6.25 × 10 18 electrons
Answer (d) 6.25 × 1018 electrons
4.5) When an electric lamp is connected to 12 V battery, it draws a current of 0.5 A. The power of the lamp is : (a) 0.5 W (b) 6 W (c) 12 W (d) 24 W
Answer (b) 6 W
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Assertion reason questions class 10 science chapter 15 our environment, extra questions of class 10 maths chapter 11 constructions pdf download.

Best Olympiad Books for Class 10th- Science Maths English and more.
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 12 Electricity PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity Case Study Questions, by practicing these Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 12 Electricity
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
The heating effect of current is obtained by the transformation of electrical energy into heat energy. Just as mechanical energy used to overcome friction is covered into heat, in the same way, electrical energy is converted into heat energy when an electric current flows through a resistance wire. The heat produced in a conductor, when a current flows through it is found to depend directly on (a) strength of current (b) resistance of the conductor (c) time for which the current flows. The mathematical expression is given by H = I 2 Rt. The electrical fuse, electrical heater, electric iron, electric geyser, etc. all are based on the heating effect of current.
(i) What are the properties of heating elements? (a) High resistance, high melting point (b) Low resistance, high melting point (c) Low resistance, high melting point (d) Low resistance, low melting point.
Answer: (b) Low resistance, high melting point
(ii) What are the properties of an electric fuse? (a) Low resistance, low melting point (b) High resistance, high melting point. (c) High resistance, low melting point (d) Low resistance, high melting point
Answer: (c) High resistance, low melting point
(iii) When the current is doubled in a heating device and time is halved, the heat energy produced is
| (a) doubled | (b) halved |
| (c) four times | (d) one fourth times |
Answer: (a) doubled
(iv) A fuse wire melts at 5 A. It is is desired that the fuse wire of same material melt at 10 A. The new radius of the wire is
| (a) 4 times | (b) 2 times |
| (c) 6 times | (d) 8 times |
Answer: (b) 2 times
(v) When a current of 0.5 A passes through a conductor for 5 min and the resistance of conductor is 10 ohm, the amount of heat produced is
| (a) 250 J | (b) 5000J |
| (c) 750J | (d) 1000J |
Answer: (c) 750J
Question 2:
The relationship between potential difference and the current was first established by George Simon Ohm. This relationship is known as Ohm’s law. According to this law, the current passed through a conductor is proportional to the potential difference applied between its ends provided the temperature remains constant i.e. I ∝ V or V = IR where R is the constant for the conductor and it is known as the resistance of the conductor. Although Ohm’s law has been found valid over a large class of materials, there are some materials that do not hold Ohm’s law.
2.1) Name the law which is illustrated by the VI graph. (a) Lenz law (b) Faraday’s law (c) Ohm’s law (d) Newton’s law
Answer(c) Ohm’s law
2.2) By increasing the voltage across a conductor, the (a) current will decrease (b) current will increase (c) resistance will increase (d) resistance will decrease
Answer(b) current will increase
2.3) When a battery of 9 V is connected across a conductor and the current flows is 0.1 A, the resistance is (a) 9 Ohm (b) 0.9 Ohm (c) 90 Ohm (d) 900 Ohm
Answer(c) 90 Ohm
2.4) If both the potential difference and resistance in a circuit are doubled then : (a) current remains same (b) current becomes double (c) current becomes zero (d) current becomes half
Answer(a) current remains same
2.5) Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is doubled. The current will become : (a) double (b) half (c) one fourth (d) 4 time
Answer(b) half
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
- Bihar Board
James Dyson Award
Sanskriti university, srm university.
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Important Case Study Questions
Chapter wise important case study questions cbse class 10 science: cbse class 10 science board exam 2024 is just around the corner and students are working hard to score maximum marks. check these case study questions from class 10 science to ace your examination this year also download the solutions from the pdf attached towards the end. .

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Important Case Study Questions: While the CBSE Board exam for Class 10 students are ongoing, the CBSE Class 10 Science board exam 2024 is to be held on March 2, 2024. With the exams just a few days away, CBSE Class 10th Board exam candidates are rushing to prepare the remaining syllabus, practising their weak portions, trying to revise the important questions from the past year papers, practise questions, etc.
Why are CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions Important?
- Section A : 20 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B : 6 Very Short Answer type questions carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C : 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D : 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E : 3 Case Based/ Source Based units of assessment (4 marks each) with sub-parts.
How to solve case study questions in CBSE Class 10 Science?
- Read the case given and the associated questions carefully.
- Read the questions attentively and analyse what they are asking.
- Apply your subject knowledge and theories in the given case to decide what the correct answers should be.
1.A chemical reaction is a representation of chemical change in terms of symbols and formulae of reactants and products. There are various types of chemical reactions like combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, oxidation and reduction reactions. Reactions in which heat is released along with the formation of products are called exothermic chemical reactions. All combustion reactions are exothermic reactions.
(i) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the
(a) combination reaction
(b) decomposition reaction
(c) displacement reaction
(d) double displacement reaction
(ii) A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and yellow residue is left behind. The yellow residue left is of
(a) lead nitrate
(b) nitrogen oxide
(c) lead oxide
(d) oxygen gas
(iii) Which of the following reactions represents a combination reaction?
(a) CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca (OH)2 (aq)
(b) CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2(g)
(c) Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
(d) 2FeSO4(s) → Fe2O3 (s) +SO2(g) + SO3(g)
(iv) Complete the following statements by choosing correct type of reaction for X and Y.
Statement 1: The heating of lead nitrate is an example of ‘X’ reaction.
Statement 2: The burning of magnesium is an example of ‘Y’ reaction.
(a)X-Combination,Y-Decomposition
(b)X-Decomposition,Y-Combination
(c)X-Combination,Y-Displacement
(d) X- Displacement, Y-Decomposition
2.The earlier concept of oxidation and reduction is based on the addition or removal of oxygen or hydrogen elements so, in terms of oxygen and hydrogen, oxidation is addition of oxygen to a substance and removal of hydrogen from a substance. On the other hand, reduction is addition of hydrogen to a substance and removal of oxygen from a substance. The substance which gives oxygen to another substance or removes hydrogen from another substance in an oxidation reaction is known as oxidising agent, while the substance which gives hydrogen to another substance or removes oxygen from another substance in a reduction reaction is known as reducing agent. For example,
(i) A redox reaction is one in which
(a) both the substances are reduced
(b) both the substances are oxidised
(c) an acid is neutralised by the base
(d) one substance is oxidised while the other is reduced.
(ii) In the reaction, H2S+Cl2⟶S+2HCl
(a) H2S is the reducing agent.
(b) HCl is the oxidising agent.
(c) H2S is the oxidising agent.
(d) Cl2 is the reducing agent.
(iii) Which of the following processes does not involve either oxidation or reduction?
(a) Formation of slaked lime from quicklime.
(b) Heating mercuric oxide.
(c) Formation of manganese chloride from manganese oxide (MnO2).
(d) Formation of zinc from zinc blende.
(iv) Mg+CuO⟶MgO+Cu
Which of the following is wrong relating to the above reaction?
(a) CuO gets reduced
(b) Mg gets oxidised.
(c) CuO gets oxidised.
(d) It is a redox reaction.
3.A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lemon on the vessel, the surface is cleaned, and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that which reacts with the acid present in lemon to form a salt which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
1.Which of the following acids is present in lemon?
(a) Formic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Citric acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid
2.The nature of copper oxide is
d) amphoteric
3.Name the salt formed in the above reaction
a) copper carbonate
b) copper chloride
c)copper citrate
d) copper citrate
4.The phenomenon of copper getting tarnished is
a) corrosion
b) rancidity
c) displacement
d)none of these
4.Metals as we know, are very useful in all fields, industries in particular. Non-metals are no less in any way. Oxygen present in air is essential for breathing as well as for combustion. Non-metals form a large number of compounds which are extremely useful, e.g., ammonia, nitric acid, sulphuric acid, etc. Non-metals are found to exist in three states of matter. Only solid non-metals are expected to be hard however, they have low density and are brittle. They usually have low melting and boiling points and are poor conductors of electricity.
i.____________ is a non-metal but is lustrous
A.Phosphorus
ii.Which of the following is known as 'King of chemicals'?
C. Sulphuric acid
D. Nitric acid
iii.Which of the following non-metals is a liquid?
iv.Hydrogen is used
A.for the synthesis of ammonia
B. for the synthesis of methyl alcohol
C.nitrogenous fertilizers
D. all of these
5.Nisha observed that the bottoms of cooking utensils were turning black in colour while the flame of her stove was yellow in colour. Her daughter suggested cleaning the air holes of the stove to get a clean, blue flame. She also told her mother that this would prevent the fuel from getting wasted.
a) Identify the reasons behind the sooty flame arising from the stove.
b) Can you distinguish between saturated and unsaturated compounds by burning them? Justify your answer.
c) Why do you think the colour of the flame turns blue once the air holes of the stove are cleaned?
6.Blood transport food, Oxygen and waste materials in our bodies. It consists of plasma as a fluid medium. A pumping organ [heart] is required to push the blood around the body. The blood flows through the chambers of the heart in a specific manner and direction. While flowing throughout the body, blood exerts a pressure against the wall or a vessel.
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Very narrow and have high resistance
- Much wide and have low resistance
- Very narrow and have low resistance
- Much wide and have high resistance
- It is a hollow muscular organ
- It is four chambered having three auricles and one ventricle.
- It has different chambers to prevent O2 rich blood from mixing with the blood containing CO2
- Both A & C
- Blood = Plasma + RBC + WBC + Platelets
- Plasma = Blood – RBC
- Lymph = Plasma + RBC
- Serum = Plasma + RBC + WBC
7.A brain is displayed at the Allen Institute for Brain Science. The human brain is a 3-pound (1.4-kilogram) mass of jelly-like fats and tissues—yet it's the most complex of all known living structures The human brain is more complex than any other known structure in the universe. Weighing in at three pounds, on average, this spongy mass of fat and protein is made up of two overarching types of cells—called glia and neurons— and it contains many billions of each. Neurons are notable for their branch-like projections called axons and dendrites, which gather and transmit electrochemical signals. Different types of glial cells provide physical protection to neurons and help keep them, and the brain, healthy. Together, this complex network of cells gives rise to every aspect of our shared humanity. We could not breathe, play, love, or remember without the brain.
1)Animals such as elephants, dolphins, and whales actually have larger brains, but humans have the most developed cerebrum. It's packed to capacity inside our skulls and is highly folded. Why our brain is highly folded?
- b) Learning
3)Which among these protects our brain?
a)Neurotransmitter
b) Cerebrospinal fluid
d) Grey matter
4.Ram was studying in his room. Suddenly he smells something burning and sees smoke in the room. He rushes out of the room immediately. Was Ram’s action voluntary or involuntary? Why?
8.Preeti is very fond of gardening. She has different flowering plants in her garden. One day a few naughty children entered her garden and plucked many leaves of Bryophyllum plant and threw them here and there in the garden. After few days, Preeti observed that new Bryophyllum plants were coming out from the leaves which fell on the ground.
1.What does the incident sited in the paragraph indicate?
(a). Bryophyllum leaves have special buds that germinate to give rise to new plant.
(b). Bryophyllum can propagate vegetatively through leaves.
(c). Bryophyllum is a flowering plant that reproduces only asexually
(d). Both (a) and (b).
2.Which of the following plants can propagate vegetatively through leaves like Bryophyllum?
3.Do you think any other vegetative part of Bryophyllum can help in propagation? If yes, then which part?
(c) Flowers
4.Which of the following plant is artificially propagated (vegetatively) by stem cuttings in horticultural practices?
(b)Snakeplant
(d)Water hyacinth
9.The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of the population.
1) What are common signs of sexual maturation in boys?
a) Broadening of shoulders
b) Development of mammary glands
c) Broadening of waist
d) High pitch of voice
2) Common sign of sexual maturation in girls is
a) Low pitch voice
b) Appearance of moustache and beard
c) Development of mammary glands
d) Broadening of shoulders
3) Which contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body?
b) Diaphragms
c) Oral pills
d) Both a) and b)
4) What should be maintained for healthy society?
a) Rate of birth and death rate
b) Male and female sex ratio
c) Child sex ratio
d) None of these
10.Pea plants can have smooth seeds or wrinkled seeds. One of the phenotypes is completely dominant over the other. A farmer decides to pollinate one flower of a plant with smooth seeds using pollen from a plant with wrinkled seeds. The resulting pea pod has all smooth seeds.
i) Which of the following conclusions can be drawn?
(1) The allele for smooth seeds is dominated over that of wrinkled seeds.
(2) The plant with smooth seeds is heterozygous.
(3) The plant with wrinkled seeds is homozygous.
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ii) Which of the following crosses will give smooth and wrinkled seeds in same proportion?
(a) RR X rr
(b) Rr X rr
(d) rr X rr
iii) Which of the following cross can be used to determine the genotype of a plant with dominant phenotype?
(a) RR X RR
(b) Rr X Rr
(c) Rr X RR
(d) RR X rr
iv) On crossing of two heterozygous smooth seeded plants (Rr), a total of 1000 plants were obtained in F1 generation. What will be the respective number of smooth and wrinkled seeds obtained in F1 generation?
(a) 750, 250
(b) 500, 500
(C) 800, 200
(d) 950, 50
11.Food chains are very important for the survival of most species.When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases.The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers.Primary producers or autotrophs,can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds,whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun’s light is necessary for photosynthesis,most life could not exist if the sun disappeared.Even so,it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life,chemotrophs,that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents,thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
1.If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem,what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy?
(d)It will depend on the type of the terrestrial plant
2.Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of
(a)Energy is by directional and matter is repeatedly circulating
(b)Energy is repeatedly circulating and matter is unidirectional
(c)Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating
(d)Energy is multidirectional and matter is bidirectional
3.Raj is eating curd/yoghurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
(a)First trophic level
(b)Second trophic level
(c)Third trophic level
(d)Fourth trophic level
4.Which of the following, limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain
(a)Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
(b)Less availability of food
(c)Polluted air
5.The decomposers are not included in the food chain. The correct reason for the same is because decomposers
(a) Act at every trophic level at the food chain
(b) Do not breakdown organic compounds
(c) Convert organic material to inorganic forms
(d) Release enzymes outside their body to convert organic material to inorganic forms
12.Shyam participated in a group discussion in his inter school competition on the practical application of light and was very happy to win an award for his school. That very evening his father gave treat to celebrate Shyam’s win. Shyam while sitting saw an image of a person sitting at his backside in his curved plate and could see that person’s mobile drop in the flower bed. Person was not aware until Shyam went and informed him. He thanked Shyam for his clever move.
a)From which side of his plate Shyam observed the incident –
i)outward curved
ii)inward curved
iii)plane surface
b)Part of plate from which Shyam observed the incident acted like a-
i)concave mirror
ii)convex mirror
iii)plane mirror
c)The nature of the size of the image formed in above situation is –
i)real, inverted and magnified
ii)same size , laterally inverted
iii)virtual, erect and diminished
iv)real , inverted and diminished
d)Magnification of the image formed by convex mirror is –
more than 1
iii)equal to 1
iv)less than 1
- The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is
(a) at focus
(c) at optical center
- When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is
(a)real and smaller
(b) virtual and smaller
(c) virtual and inverted
- The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus ofconvex lens is
(a) highly magnified
(b) point in size
- When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is
(b) between F and optical center
(c) at infinity
(d) none of the above
14.One of the wires in domestic circuits supply, usually with a red insulation cover, is called live wire. with black insulation is called neutral wire. The earth wire, which has insulation of green colour, is usually connected to a metal plate deep in the earth near the house appliances that has a metallic body. Overloading contact, in such a situation the current in the circuit abruptly increases. circuit prevents damage to the appliances and the circuit due to overloading.
1 When do we say that an electrical appliance
2 Mention the function of earth wire in electrical line
3 How is an electric fuse connected in a domestic circuit?
4 When overloading and short circuiting are said to occur?
5 What is a live wire?
15.Light of all the colours travel at the same speed in vacuum for all wavelengths. But in any transparent medium(glass or water), the light of different colours travels at different speeds for different wavelengths, which means that the refractive index of a particular medium is different for different wavelengths. As there is a difference in their speeds, the light of different colours bend through different angles. The speed of violet colour is maximum and the speed of red colour is minimum in glass so, the red light deviates least and violet colour deviates most. Hence, higher the wavelength of a colour of light, smaller the refractive index and less is the bending of light.
(i)Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of Light of different colours of white light in air?
(a) Red light moves fastest.
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light.
(c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed.
(d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light.
(ii)Which of the following is the correct order of wavelength?
(a) Red> Green> Yellow
(b) Red> Violet> Green
(c) Yellow> Green> Violet
(d) Red> Yellow> Orange
(iii)Which of the following is the correct order of speed of light in glass?
(a) Red> Green> Blue
(b) Blue> Green> Red
(c) Violet> Red> Green
(d) Green> Red> Blue
(iv)Which colour has maximum frequency?
16.The region around a magnet where magnetism acts is represented by the magnetic field.The force of magnetism is due to moving charge or some magnetic material. Like stationary charges produce an electric field proportional to the magnitude of charge, moving charges produce magnetic fields proportional to the current. In other words, a current carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. The subatomic particles in the conductor, like the electrons moving in atomic orbitals, are responsible for the production of magnetic fields. The magnetic field lines around a straight conductor (straight wire) carrying current are concentric circles whose centres lie on the wire.
1)The magnetic field associated with a current carrying straight conductor is in anti- clockwise direction. If the conductor was held horizontally along east west direction,what is the direction of current through it?
2)Name and state the rule applied to determine the direction of magnetic field in a straight current carrying conductor.
3)Ramus performs an experiment to study the magnetic effect of current around a current carrying straight conductor with the help of a magnetic compass. He reports that
a)The degree of deflection of magnetic compass increases when the compass is moved away from the conductor.
b)The degree of deflection of the magnetic compass increases when the current through the conductor is increased.
Which of the above observations of the student appears to be wrong and why?
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science CBSE Chapter Wise PDF
Related resources to prepare for CBSE 10th Science Board Exam 2024
- CBSE class 10 Science syllabus 2024
- NCERT Book for Class 10th Science 2023-2024 (PDF)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- CBSE Class 10 Science sample paper
- Previous Year Questions of CBSE Class 10 Science
- CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Physics Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Biology Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Topper Answer Sheet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Practice Paper 2023 with Answers
- Class 10 CBSE Admit Card 2023-24
- CBSE Class 10 Date Sheet 2023
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2023 - 2024
- CBSE Class 10 DELETED Syllabus 2023-24
- CBSE Class 10th Sample Paper 2022-23: Download Sample Question Papers and Marking Scheme
- CBSE Class 10 Previous Year Question Papers for 2022-23
- CBSE Class 10 Important Questions and Answers for 2023-24 of ALL Chapters
- CBSE Class 10 Practice Papers: All Subjects
- CBSE Topper Answer Sheet Class 10: Model Answer Paper Download PDF
- CBSE Class 10 Mock Tests: All Subjects
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- UGC NET Exam 2024 Cancelled
- UPSC Question Paper 2024
- UPSC Exam Analysis 2024
- UPSC Prelims Cut Off 2024
- Bihar BEd Admit Card 2024
- CSIR NET Admit Card 2024
- NTA NET Admit Card 2024
- APSC SO Result 2024
- APSC SO Admit Card 2024
- UPSC CSE Admit Card 2024
- CBSE Class 10 QnA
Latest Education News
Optical Illusion: Can You Spot the Hidden Frog in This Bedroom? Test Your Observation Skills Now!
Can You Find The Hidden Car In This Mind-Bending Optical Illusion In 12 Seconds?
Rajasthan BSTC Deled Admit Card 2024 Live Update: जारी होने वाला है राजस्थान प्री डीएलएड परीक्षा का एडमिट कार्ड
RMPSSU Result 2024 OUT at rmpssu.ac.in; Download UG and PG Marksheet
No More App Switching! WhatsApp Testing In-App Dialer for Direct Calls
JK NMMS 2024 Exam to be Held on July 8, Check Eligibility and Paper Pattern Here
Seek and Find Puzzle: Only the Experts Can Untangle the Tresses By Finding the Hidden Comb
Today’s T20 World Cup Match (22 June) - IND vs BAN: Team Squad, Match Time, Where to Watch Live and Stadium
NIOS Result 2024 Class 12 Declared at results.nios.ac.in, Steps to Access Here
Dr MGR Medical University Result 2024 OUT at tnmgrmu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
PRSU Result 2024 OUT at prsu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
HNGU Result 2024 OUT at ngu.ac.in, Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
IND vs BAN Head to Head in T20 World Cup History: Stats, Records and Results
Sarguja University Result 2024 OUT: संत गहिरा गुरु विश्वविद्यालय सरगुजा यूनिवर्सिटी रिजल्ट sggcg.in पर जारी, इस लिंक से डाउनलोड करें मार्कशीट
Bihar Sakshamta Pariksha 2024 Phase 2: बिहार बोर्ड ने स्थगित की 26 से 28 जून को होने वाली सक्षमता परीक्षा, जानें नई तारीखों के बारे में अपडेट
Spot the 3 Differences Between Grandfather Cooking Pictures in 33 Seconds
उत्तर प्रदेश का सबसे अधिक शहरी क्षेत्र वाला जिला कौन-सा है, जानें
T20 World Cup Points Table 2024: Team Standings, Group Ranking and Net Run Rate
Most Runs In T20 World Cup 2024
CSIR NET 2024 Exam Postponed: Check NTA Official Notice for June Rescheduled Examination
myCBSEguide
- Case Study Questions Class...
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Download Case study questions for CBSE class 10 Science in PDF format from the myCBSEguide App . We have the new pattern case study-based questions for free download. Class 10 Science case study questions
This article will guide you through:
What are case study questions?
- Sample Papers with Case Study questions
- Class 10 Science Case Study question examples
- How to get case-based questions for free?
- How to attempt the case-based questions in Science?
Questions based on case studies are some real-life examples. The questions are asked based on a given paragraph i.e. Case Study. Usually, 4-5 questions are asked on the basis of the given passage. In most cases, these are either MCQs or assertion & reason type questions. Let’s take an example to understand. There is one paragraph on how nitrogen is generated in the atmosphere. On the basis of this paragraph, the board asks a few objective-type questions. In other words, it is very similar to the unseen passages given in language papers. But the real cases may be different. So, read this article till the end to understand it thoroughly.
What is CBE?
CBSE stands for competency-based education. The case study questions are part of this CBE. The purpose of CBE is to demonstrate the learning outcomes and attain proficiency in particular competencies.
Questions on Real-life Situations
As discussed the case study questions are based on real-life situations. Especially for grade 10 science, it is very essential to have the practical knowledge to solve such questions. Here on the myCBSEguide app, we have given many such case study paragraphs that are directly related to real-life implications of the knowledge.
Sample Papers with Case Study Questions
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App . There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions. In some cases, you will find that the question is not asked directly from the passage but is based on the concept that is discussed there. That’s why it is very much important to understand the background of the case study paragraph.
CBSE Case Study Sample Papers
You can download CBSE case study sample papers from the myCBSEguide App or Student Dashboard. Here is the direct link to access it.
Case Study Question Bank
As we mentioned that case study questions are coming in your exams for the last few years. You can get them in all previous year question papers issued by CBSE for class 1o Science. Here is the direct link to get them too.
Class 10 Science Case Study Question Examples
As you have already gone through the four questions provided in the CBSE model question paper , we are proving you with other examples of the case-based questions in the CBSE class 10 Science. If you wish to get similar questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App and access the Sample question papers with case study-type questions.
Case-based Question -1
Read the following and answer any four questions: Salt of a strong acid and strong base is neutral with a pH value of 7. NaCl common salt is formed by a combination of hydrochloride and sodium hydroxide solution. This is the salt that is used in food. Some salt is called rock salt bed of rack salt was formed when seas of bygone ages dried up. The common salt thus obtained is an important raw material for various materials of daily use, such as sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
- Phosphoric acid
- Carbonic acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Blue vitriol
- Washing soda
- Baking soda
- Bleaching powder
Case-based Question -2
- V 1 + V 2 + V 3
- V 1 – V 2 +V 2
- None of these
- same at every point of the circuit
- different at every point of the circuit
- can not be determined
- 20 3 Ω 203Ω
- 15 2 Ω 152Ω
Case-based Question -3
- pure strips
- impure copper
- refined copper
- none of these
- insoluble impurities
- soluble impurities
- impure metal
- bottom of cathode
- bottom of anode
How to Attempt the Case-Based Questions in Science?
Before answering this question, let’s read the text given in question number 17 of the CBSE Model Question Paper.
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
See, there are only two sentences and CBSE is asking you 5 questions based on these two sentences. Now let’s check the first questions given there.
Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by a) Breathing b) Tissue respiration c) Organ respiration d) Digestion of food
Now let us know if you can relate the question to the paragraph directly. The two sentences are about energy and how it is obtained. But neither the question nor the options have any similar text in the paragraph.
So the conclusion is, in most cases, you will not get direct answers from the passage. You will get only an idea about the concept. If you know it, you can answer it but reading the paragraph even 100 times is not going to help you.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Science Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
3 thoughts on “Case Study Questions Class 10 Science”
Where is the answer
Class 10 Science MCQ
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 12 Electricity
Please refer to Chapter 12 Electricity Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 12 Electricity
Case/Passage – 1
Two tungston lamps with resistances R1 and R2 respectively at full incandescence are connected first in parallel and then in series, in a lighting circuit of negaligible internal resistance. It is given that: R 1 > R 2 .
Question: Which lamp will glow more brightly when they are connected in parallel? (a) Bulb having lower resistance (b) Bulb having higher resistance (c) Both the bulbs (d) None of the two bulbs
Question: Which lamp will glow more brightly when they are connected in series? (a) Bulb having lower resistance (b) Bulb having higher resistance (c) Both the bulbs (d) None of the two bulbs
Question: If the lamp of resistance R 2 now burns out and the lamp of resistance R1 alone is plugged in, will the illumination increase or decrease? (a) Illumination will remain same (b) Illumination will increase (c) Illumination will decrease (d) None
Question: If the lamp of resistance R 1 now burns out, how will the illumination produced change? (a) Net illumination will increase (b) Net illumination will decrease (c) Net illumination will remain same (d) Net illumination will reduced to zero
Question: Would physically bending a supply wire cause any change in the illumination? (a) Illumination will remain same (b) Illumination will increase (c) Illumination will decrease (d) It is not possible to predict from the given datas
Case/Passage – 2
The rate at which electric energy is dissipated or consumed in an electric circuit. This is termed as electric power, P = IV, According to Ohm’s law V = IR We can express the power dissipated in the alternative forms P =I 2 R=V 2 /R
If 100W – 220V is written on the bulb then it means that the bulb will consume 100 joule in one second if used at the potential difference of 220 volts. The value of electricity consumed in houses is decided on the basis of the total electric energy used. Electric power tells us about the electric energy used per second not the total electric energy. The total energy used in a circuit = power of the electric circuit × time.
Question: Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit? (a) I 2 R (b) IR 2 (c) VI (d) V 2 /R
Question: Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in sereis and then in parallel in an electric circuit. The ratio of heat produced in series and in parallel combinations would be– (a) 1 : 2 (b) 2 : 1 (c) 1 : 4 (d) 4 : 1
Question: In an electrical circuit, two resistors of 2Ω and 4Ω respectively are connected in series to a 6V battery. The heat dissipated by the 4Ω resistor in 5s will be (a) 5 J (b) 10 J (c) 20 J (d) 30 J
Question: In an electrical circuit three incandescent bulbs. A, B and C of rating 40 W, 60 W and 100 W, respectively are connected in parallel to an electric source. Which of the following is likely to happen regarding their brightness? (a) Brightness of all the bulbs will be the same (b) Brightness of bulb A will be the maximum (c) Brightness of bulb B will be more than that of A (d) Brightness of bulb C will be less than that of B
Question: An electric bulb is rated 220V and 100W. When it is operated on 110V, the power consumed will be– (a) 100 W (b) 75 W (c) 50 W (d) 25 W
Case/Passage – 3
Answer the following questions based on the given circuit.
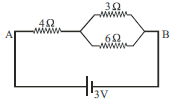
Question: The equivalent resistance between points A and B is (a) 7Ω (b) 6Ω (c) 13Ω (d) 5Ω
Question: The potential drop across the 3Ω resistor is (a) 1 V (b) 1.5 V (c) 2 V (d) 3 V
Question: The current flowing through in the given circuit is (a) 0.5 A (b) 1.5 A (c) 6 A (d) 3 A
Case/Passage – 4
Answer the following questions based on the given circuit.
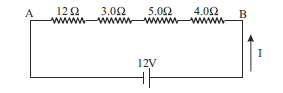
Question: The current through each resistor is (a) 1 A (b) 2.3 A (c) 0.5 A (d) 0.75 A
Question: The equivalent resistance between points A and B, is (a) 12 Ω (b) 36 Ω (c) 32 Ω (d) 24 Ω
Question: The potential drop across the 12Ω resistor is (a) 12 V (b) 6 V (c) 8 V (d) 0.5 V
Case/Passage – 5
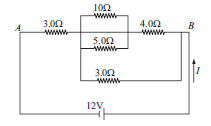
Question: The equivalent resistance between points A and B (a) 6.2 Ω (b) 5.1 Ω (c) 13.33 Ω (d) 1.33 Ω
Question: The current through the 4.0 ohm resistor is (a) 5.6 A (b) 0.98 A (c) 0.35 A (d) 0.68 A
Question: The current through the battery is (a) 2.33 A (b) 3.12 A (c) 4.16 A (d) 5.19 A
Case/Passage – 6
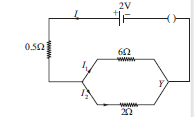
Question: The total resistance of the circuit is (a) 2 Ω (b) 4 Ω (c) 1.5 Ω (d) 0.5 Ω
Question: The current flowing through 6Ω resistor is (a) 0.50 A (b) 0.75 A (c) 0.80 A (d) 0.25
Question: The current flowing through 0.5Ω resistor is (a) 1 A (b) 1.5 A (c) 3 A (d) 2.5 A
Case/Passage – 7
Ohm’s law gives the relationship between current flowing through a conductor with potential difference across it provided the physical conditions and temperature remains constant. The electric current flowing in a circuit can be measured by an ammeter. Potential difference is measured by voltmeter connected in parallel to the battery or cell. Resistances can reduce current in the circuit. A variable resistor or rheostat is used to vary the current in the circuit.
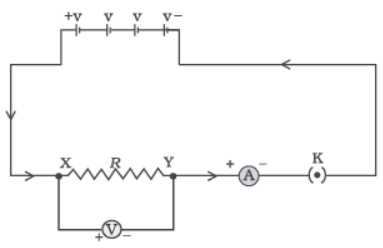
Question. Which type of conductor is represented by the graph given alongside?
(a) Non-ohmic conductor like thermistor (b) Non-ohmic conductor like metal filament (c) Ohmic conductor like copper (d) None of these
Question. What is the slope of graph in (i) equal to? (a) V (b) I (c) R (d) VI
Question. Which of the following is the factor on which resistance of a conductor does not depend? (a) Length (b) Area (c) Temperature (d) Pressur
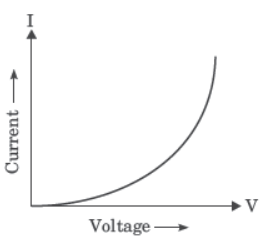
Question. What type of conductor is represented by the following graph?
(a) Non-ohmic conductor like thermistor (b) Non-ohmic conductor like metal filament (c) Ohmic conductor like copper (d) None of these
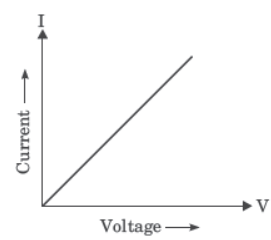
Question. What type of conductors are represented by the following graph?
Study this table related to material and their resistivity and answer the questions that follow.
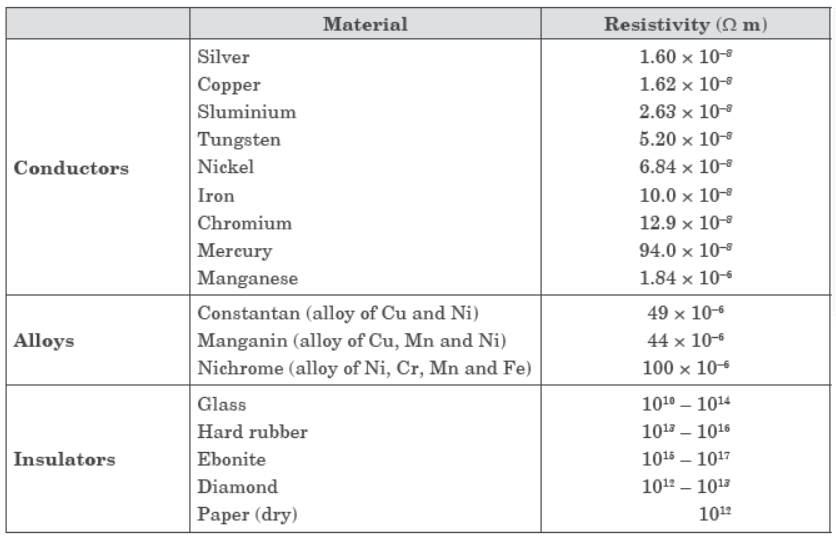
Question. Which of the following is used in transmission wires? (a) Cr (b) Al (c) Zn (d) Fe
Question. Which is the best conducting metal? (a) Cu (b) Ag (c) Au (d) Hg
Question. Which of the following is used as a filament in electric bulbs? (a) Nichrome (b) Tungsten (c) Manganese (d) Silver
Question. What is the range of resistivity in metals, good conductors of electricity? (a) 10–8 to 10–6 Wm (b) 10–6 to 10–4 Wm (c) 1010 to 1014 Wm (d) 1012 to 1014 Wm
Question. Which property of the alloy makes it useful in heating devices like electric iron, toasters, immersion rods, etc.? (a) Higher resistivity (b) Do not oxidise at low temperature (c) Do not reduce at high temperature (d) Oxidise at high temperature

Related Posts

The Heart of a Tree Summary by Henry Cuyler Bunner
Class 10 maths all formulas.

Old Man at the Bridge Summary by Ernest Miller Hemingway
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity 2024-25
- Class 10 Important Question
- Chapter 12: Electricity

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter-12 Electricity Important Questions with Answers - Free PDF Download
Class 10 is an essential stage in every student's career. Their performance in Class 10 acts as a base for their future studies. So it's important to score well in Class 10. The most important and challenging subject in Class 10 is Science and many students seem to get confused here and lose marks. If students want a successful career in future, then they can't afford to lose marks in this stage of their life. It's important to understand every chapter in science thoroughly to score good marks. Chapter 12 of Class 10 Science which is about electricity is one of the difficult chapters. A student who is incapable of understanding this chapter must practice Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 . These important questions of Electricity Class 10 can make the students through on the concepts of this chapter. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions, they can download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions for other chapters:
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions | ||
Sl.No | Chapter No | Chapter Name |
1 | Chapter 1 |
|
2 | Chapter 2 |
|
3 | Chapter 3 |
|
4 | Chapter 4 |
|
5 | Chapter 5 |
|
6 | Chapter 6 |
|
7 | Chapter 7 |
|
8 | Chapter 8 |
|
9 | Chapter 9 |
|
10 | Chapter 10 |
|
11 | Chapter 11 |
|
12 | Chapter 12 | Electricity |
13 | Chapter 13 |
|
14 | Chapter 14 |
|
15 | Chapter 15 |
|
16 | Chapter 16 |
|

Related Chapters
Study Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 – Electricity
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. Which two circuit components are connected in parallel in the following circuit diagram?
(a) \[{{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}\] and ${{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}$ only
(b) ${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}$ only
(c) ${{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}$ and ${\text{V}}$ only
(d) ${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}$ and ${\text{V}}$only
Ans: (a) The two circuit components that are connected parallel in the circuit diagram is and ${R_2}$ only.
2. A metallic conductor has loosely bound electrons called free electrons. The metallic conductor is
(a) negatively charged
(b) positively charged
(c) neutral
(d) Either positively charged or negatively charged
Ans: (c) The metallic conductor is neutral.
3. Which of the following expressions does not represent the electric power in the circuit?
(a) ${\text{VI}}$.
(b) ${{\text{I}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{/R}}$
(c) ${{\text{V}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{/R}}$
(d) ${{\text{I}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{R}}$
Ans: (b) The expression which does not represent the electric power in the circuit is ${I^2}/R$ .
4. Resistivity of a metallic wise depends on
(a) its length
(b) its shape
(c) its thickness
(d) nature of material
Ans: (d) Resistivity of a metallic wire depends on the nature of the material.
5. If the current I through a resistor is increased by \[{\mathbf{100}}\% \] the increased in power dissipation will be (assume temperature remain unchanged)
(a) \[{\mathbf{100}}\% \]
(b) \[{\mathbf{200}}\% \]
(c) \[{\mathbf{300}}\% \]
(d) \[{\mathbf{400}}\% \]
Ans: (c) The increase in power dissipation will be \[300\% \] .
6. For the circuit arrangement shown below, a student would observe.
(a) Some reading in both ammeter and voltmeter.
(b) No reading in either the ammeter or the voltmeter.
(c) Some reading in the ammeter but no reading in the voltmeter.
(d) Some reading in the voltmeter but no reading in the ammeter.
Ans: (c) A student will observe some reading in the ammeter but no reading in the voltmeter.
7. A wire of resistance $R$ is cut into five equal pieces. These pieces are connected in parallel and the equivalent resistances of the combination are $R'$ . Then the ratio $\dfrac{R}{{R'}}$ is
(a) $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{5}}}$
(b) ${\text{5}}$
(c) $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{{\text{25}}}}$
(d) ${\text{25}}$
Ans: (d)The ratio $\dfrac{R}{{R'}}$ is $25$ .
8. The resistance of the conductor is $R$ . If its length is doubled, then its new resistance will be
Ans: (c) The new resistance is $4R$ .
9. A student carries out an experiment and plots the V-I graph of three samples of nichrome wire with resistances ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ respectively as shown in the figure. Which of the following is live?
(a) ${R_3} > {R_2} > {R_1}$
(b) ${R_2} > {R_3} > {R_1}$
(c) ${R_1} > {R_2} > {R_3}$
(d) ${R_1} = {R_2} = {R_3}$
Ans: (a)According to the graph , ${R_3} > {R_2} > {R_1}$
10. The nature of the graph between potential difference and the electric current flowing through a conductor is
(a)parabolic
(b) circle
(c) straight line
(d) hyperbolic
Ans: (c)The nature of the graph between potential difference and the electric current flowing through a conductor is a straight line.
11. An electric heater is salted at $1500$ w. How much heat is produced per hour?
(i) $5400$ J
(ii) $54000$ J
(iii) $5.4 \times {10^5}$
(iv) $5.4 \times {10^6}$.
Ans: (iv) The electric heater produces $5.4 \times {10^6}$ J per hour.
12. A student says that the resistance of two wires of the same length and same area of cross section is the same. This statement is correct if
(a) Both wires are of different materials
(b) Both wires are made of the same material and are at different temperatures.
(c) Both wires are made of the same material and are at the same temperature.
(d) Both wires are made of different materials and are at the same temperature.
Ans: This statement is correct if (c)The resistance of two wires of the same length and same area of cross section is the same if both wires are made of the same material and are at the same temperature.
13. In an experiment ohm, s law a student obtained a graph as shown in the diagram. The value of resistance of the resistor is
(a) $0.1\Omega $
(b) $1.0\Omega $
(c) $10\Omega $
(d) $100\Omega $
Ans: (d) The value of resistance of the resistor is $100\Omega $ .
14. Work done to move $1$ coulomb charge from one point to another point on a charged conductor having potential $10$ volt is
(a) $1$ Joule
(b) $10$ Joule
(c) zero
(d) $100$ Joule
Ans: (c) Work done to move $1$ coulomb charge from one point to another point on a charged conductor having potential $10$ volt is zero.
15. Three resistors are shown in the figure. The resistance of the combination is
(a)$3\Omega $
(b) $6\Omega $
(c) $9\Omega $
(d) $7\Omega $
Ans: (c) The resistance of the combination is $9\Omega $ .
16. Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference between across a conductor.
Ans: A device that helps to maintain a potential difference between conductors is the battery.
17. What determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current?
Ans: The rate at which energy is delivered by a current is determined by electric power.
18. A wire of resistance $R$ is cut into five equal pieces. These pieces are connected inparallel and the equivalent resistances of the combination are $R'$ . Then the ratio $\dfrac{R}{{R'}}$ is
(a) $\dfrac{1}{5}$
(c) $\dfrac{1}{{25}}$
Ans: (d)A wire of resistance ${\text{R}}$ is cut into five equal pieces. These pieces are connected inparallel and the equivalent resistances of the combination are ${\text{R'}}$. In this cases, the ratio$\dfrac{R}{{R'}}$ is $25$ .
19. Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit?
(a) ${I^2}R$
(b) $I{R^2}$
(c) $VI$
(d) ${V^2}/R$
Ans: (b) The term that does not represent electrical power in a circuit is $I{R^2}$ .
20. An electric bulb is rated $220$ V and $100$ W. When it is operated on $110$ V, the power consumed will be:
(a) $220$ W
(b) $75$ W
(c) $50$ W
(d) $25$ W
Ans: (d)The power consumed will be $25$ W.
21. Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in series and then parallel in a circuit across the same potential difference. The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combination would be:
Ans: (c) The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combination will be $1:4$ .
22. A wire of resistance $R$ is bent in the form of a closed circle, what is the resistance across a diameter of the circle?
Ans: The resistance across a diameter of the circle
23. A charge of $6$ C is moved between two points $P$ and $Q$ having, potential $10$ V and $5$ V respectively. Find the amount of work done.
Ans: The amount of work done, $W = q({V_2} - {V_1})\;$
$\; = {\text{ }}6\left( {10 - 5} \right)$
\[ = {\text{ }}30\] joule
24. Name the physical quantity whose SI unit is JC
Ans: The physical quantity whose SI unit is JC is Potential.
25. Why are copper wires used as connecting wires?
Ans: Copper wires are used as connecting wires because in case of copper the electrical resistivity for it is low.
26. A wire of resistivity $p$ is stretched to double its length. What is its new resistivity?
Ans: When a wire of resistivity ${\text{p}}$ is stretched to double its length, then the new resistivity remains the same because resistivity depends on the nature of material.
27. What is the resistance of the connecting wire?
Ans: The resistance of a connecting wire made of a good conductor is extremely low.
28. What is the resistance of an ammeter?
Ans: An ammeter's resistance is very minimal, and in an ideal ammeter, it is zero.
29. What is the resistance of a Voltmeter?
Ans: An ideal voltmeter's internal resistance is infinite.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. How does use of fuse wire protect electrical appliances?
Ans: When a large quantity of current passes through the circuit, the temperature of the wire rises and the fuse wire melts. This prevents current from flowing into the house's other circuits, saving electrical appliances.
2. Calculate the resistance of an electric bulb which allows a $10$A current when connected to a $220$ V power source?
Ans: It is given from the question that an electric bulb allows a $10$A current when connected to a $220$ V power source.
\[I = 10\] A ,
\[V = 220\]V
\[R = \dfrac{V}{I}\]
\[ = \dfrac{{220}}{{10}}\]
\[ = 22\] ohm
3. (i) Identify the $V - I$ graphs for ohmic and non-ohmic materials.
Ans: The $V - I$ graphs for ohmic and non-ohmic materials respectively can be represented as shown below:
(ii) Give one example of each.
Ans: (ii) Some examples of ohmic material are Copper, Nichrome and some examples of Non-ohmic material are Diode, Transistor.
4. What do the following symbols represent in a circuit? Write the name and one function of each?
Ans: (i) It symbolises a battery that maintains a potential difference across the circuit element to allow current to flow.
Ans: It's an ammeter that measures how much current is flowing across a circuit.
5. Define the term “volt”?
Ans: If $1$joule of energy is transferred between two points A and $B$, the potential difference between them is one volt. In an electric circuit, work is done to move one coulomb of charge from one point to another field.
6. Why does the connecting rod of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does?
Ans: As its resistance is lower than that of the heating element, the connecting cord of an electric heater does not glow. As a result, the heating element produces more heat than the connecting cord, and it glows
7. A number of \[n\] resistors each of resistance \[R\] are first connected in series and then in parallel. What is the ratio of the total effective resistance of the circuit is series combination and parallel combination?
Ans: Total effective resistance of the circuit when in series combination \[{R_s} = nR\]
And for parallel combination is \[{R_p} = \dfrac{R}{n}\] and
$\dfrac{{{R_s}}}{{{R_p}}} = \dfrac{{nR}}{{\dfrac{R}{n}}}$
The ratio will be ${n^2}$ .
8. Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit consisting of \[3\] V battery, \[5\] ohm, \[3\Omega \] and \[1\Omega \] resistor, an ammeter and a plug key, all connected in series.
Ans: The circuit diagram of a circuit consisting of \[3\] V battery, \[5\] ohm, \[3\Omega \] and \[1\Omega \] resistor, an ammeter and a plug key, all connected in series can be represented as show below,
9. A copper wire has diameter \[0.5\] mm and Resistivity of \[1.6 \times {10^{ - 8}}\Omega m\] What is the length of this wire to make its resistance ? How much does the resistance change if diameter is doubled?
Ans: Diameter of the copper wire, $D = 0.5 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ m
$P = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 8}}$
$R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A}$
$ = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{{\pi {r^2}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{4\rho l}}{{\pi {D^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow l = \dfrac{{\pi R{D^2}}}{{4\rho }}$
$l = \dfrac{{3.14 \times 10 \times {{(5 \times {{10}^{ - 4}})}^2}}}{{4 \times 1.62 \times {{10}^{ - 8}}}}$
$ = 121.14$
Length of the wire, $l = 121.14$ m
New $R' = \dfrac{{4\rho l}}{{\pi {{(D')}^2}}}$
$ = \dfrac{1}{4}\dfrac{{4\rho l}}{{\pi {D^2}}}$
$ = \dfrac{1}{4}R$
Length of the wire to make its resistance $10\Omega $ is $121.14$m and when the diameter is doubled the new resistance will be one fourth that of the old one.
10. Alloys are used in electrical heating devices rather than pure metals. Give a reason.
Ans: Alloys are utilised in electricity heating devices rather than pure metals because alloys have a higher resistivity and hence produce more heat. Furthermore, alloy is non-combustible (or oxidises easily at higher temperature).
11. On what factor does the resistance of a conductor depend?
Ans: The factors on which Resistance depends are:-
(a) Length of the conductor
(b) Area of cross - section
(c) Temperature
(d) Nature of material
12. Calculate the number of electrons consisting of one coulomb of charge?
Ans: Let $x = $ no. of electrons
Charge on $1$ electron $ = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}$ C , that is
$x = \dfrac{1}{{1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}$
$x = 6.25 \times {10^{18}}$
The number of electrons consisting of one coulomb of charge is $6.25 \times {10^{18}}$ .
13. What does an electric circuit mean?
Ans: An electric circuit is a current route that is both continuous and closed. Current can flow through an electric circuit if it is complete.
14. Define the unit of current.
Ans: The ampere is the SI unit for electric current. If $1$ coulomb charge flows per second across a conductor cross-section, the current is said to be $1$ ampere.
15. Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
Ans: The charge on one electron $ = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}$ coulomb.
Number of electrons in one coulomb of charge$ = \dfrac{1}{{1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}$
$ = 6.25 \times {10^{18}}$
16. What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is \[1\] v?
Ans: If $1$ joule of labour is required to move a charge of $1$ coulomb from one location to another, the potential difference between the two points is said to be $1$ volt.
17. Ammeter burns out when connected in parallel. Give reasons.
Ans: When a low-resistance wire is connected in series, a huge quantity of current travels through it, causing it to be burned, or short-circuited.
18. Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel:
(a) Equivalent resistance of \[1\Omega \] and \[{10^6}\Omega \]
Ans: When the resistances are connected in a parallel arrangement, the resultant resistance is given by:
$\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + \cdots $
$\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{1} + \dfrac{1}{{{{10}^6}}}$
$ = 1 + {10^{ - 6}}$
$R = 1\Omega $
The equivalent resistance is $1\Omega $ .
(b) Equivalent resistance of \[1\Omega \] , \[{10^3}\Omega \] and \[{10^6}\Omega \]
Ans: $\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{1} + \dfrac{1}{{{{10}^3}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{{10}^6}}}$
$ = 1 + {10^{ - 3}} + {10^{ - 6}}$
19. An electric iron of resistance \[20\] takes a current of \[5\] A. Calculate the heat developed in \[30\] s.
Ans: Resistance of electric iron, $R = 20\Omega $ , current, $I = 5$ A and time $ = 30$ s.
Heat generated $H = {I^2}Rt$
$ = {5^2} \times 20 \times 30$
$ = 15000$ j
The heat developed in $30$ second is $15000$ j .
20. Compute the heat generated while transferring \[96000\] coulomb of charge in one hour through a potential difference of \[50\] V
Ans: The given information is as shown below,
Charge transferred, $Q = 96000$
Potential Difference, $V = 50$ V.
Heat generated, $H = VQ$
$ = 50 \times 96000$
$ = 4800000$ j
$ = 4.8 \times {10^6}$ j
The heat generated while transferring $96000$ coulomb of charge in one hour
through a potential difference of $50$ V is $4.8 \times {10^6}$ j
21. An electric motor takes \[5\] A from a \[220\] V line. Determine the power of the motor and energy consumed in \[2\] h.
Ans: Given that current drawn by electric motor $I = 5$ A.
The line voltage $V = 220$ V
Time, $t = 2$ h
Power of motor , $P = VI$
$ = 220 \times 5$
$ = 1100$ W and
the energy consumed $E = Pt$
$ = 2 \times 1100$
$ = 2.2$ KWh
The power of the motor and energy consumed in $2$ h are $1100$ W and $2.2$ kWh respectively.
22. How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points?
Ans: A voltmeter is connected in parallel to the resistance across the place where the potential difference is to be determined.
23. When a \[12\] v battery is connected across an unknown resistor, there is a current of \[2.5\] mA in the circuit. Find the value of the resistance of the resistor.
Ans: Given that Voltage of battery, $V = 12$ V,
Current, $I = 2.5$ mA
$ = 2.5 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ A
Resistance, $R = V/I$
$ = \dfrac{{12}}{{2.5 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
$ = 4800\Omega $
The value of the resistance of the resistor is $4800\Omega $ .
24. Several electric bulbs designed to be used on a \[220\] V electric supply line, are rated \[10\] W. How many lamps can be connected in parallel with each other across the two wires of \[220\] V line if the maximum allowable current is \[5\] A?
Ans: The given information is as shown below
Each bulb is rated as $10$ W, $220$ V,
It draws current, $I = P/V$
$ = \dfrac{{10}}{{220}}$ V
$ = 1/22$ A.
The maximum allowable current is $5$ A and all lamps are connected in parallel. Therefore the maximum number of bulbs joined in parallel with each other $ = 5 \times 22$whichis$110$.
25. Two lamps, one rated \[100\] W at \[220\] V, and the other \[60\] W at \[220\] V are connected in parallel to electric mains supply. What current is drawn from the line if the supply voltage is \[220\] V?
Ans: Current drawn by ${1^{st}}$lamp rated $100$ W at $220$ , $V = P/V$
\[ = 100/220\]
\[ = 5/11\] A.
Current drawn by ${2^{nd}}$lamp rated $60$ W at \[220\] , \[V = 60/220\]\[ = 3/11\;\]A.
In parallel arrangement the total current \[ = {\text{ }}3/11 + {\text{ }}5/11\]
\[ = {\text{ }}8/11\]
\[ = {\text{ }}0.73\] A.
Current drawn from the line if the supply voltage is $220$ V is $0.73$ A .
26. Which uses more energy, a \[250\] W TV set in \[1\] hour, or a \[1200\] W toaster in \[10\] minutes?
Ans: Energy used by a TV set of power $250$ W in $1$ hour $ = Pt$
Energy used by toaster of power \[1200\] W in \[10\] minute \[\left( {10/60h} \right) = {\text{ }}200\] Wh.
A $250$ W TV set in $1$ hour uses more energy.
27. An electric heater of resistance \[8\] draws \[15\] A from the service mains for \[2\] hours. Calculate the rate at which heat is developed in the heater.
Ans: Resistance of electric heater, \[R{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}8\Omega \],
current, \[I{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}15\] A.
Rate at which heat developed in the heater $ = \dfrac{{{I^2}Rt}}{t}$
$ = 1800$ W.
The rate at which heat is developed in the heater is $1800$ W.
28. In the given figure what is the ratio of current in \[A\]
Ans: Observe that it I clearly known to us that $V = IR$
$\dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{{I_2}}} = \dfrac{R}{{2R}}$
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}$
The ratio of current is$1/2$.
29. Two wires of equal cross sectional area, one of copper and other of managing have the same resistance. Which one will be longer?
Ans: Using the equation $\rho = \dfrac{{RA}}{l}$ , where $\rho $ is the resistivity, $R$ is the resistance and $A$ the area
We can see that copper wire has a lower resistance than manganin, hence copper will last longer.
30. A Rectangular block of iron has dimensions $L \times L \times b$ . What is the resistance of the block measured between the two square ends? Given $p$ resistivity.
Ans: $R = \dfrac{{pb}}{{{L^2}}}$is the resistance of the block measured between the two square ends
31. Three equal resistances are connected in series then in parallel. What will be the ratio of their Resistances?
Ans: ${R_{series}} = 3R$
${R_{parallel}} = R/3$
The ratio of Resistances is $9$ .
32. Justify for any pair of resistance the equivalent resistance equivalent resistance in parallel.
Ans: As $R = V/I$
From the graph for any pair of resistance the equivalent resistance in series is greater than equivalent resistance in parallel.
$A = $ Series, $B = $ Parallel
33. How many bulbs of \[81\] should be joined in parallel to draw a current of \[2\] A from a battery of \[4\] V?
Ans: $R = V/I$
$ = 2\Omega $
let $n$ be the number of bulbs.
$1/R = 1/{R_1} + 1/{R_2} + \cdots + 1/{R_n} = \dfrac{n}{8}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{n}{8}$
$ \Rightarrow n = 4$
Number of bulbs are $4$ .
34. Two cubes \[A\] and \[B\] are of the same material. The side of \[B\] is thrice as that of \[A\] . Find the ratio \[{R_A}/{R_B}\] .
Ans: The value of ${R_A} = \dfrac{{pL}}{A}$ and
${R_B} = \dfrac{{p3L}}{{9A}}$
${R_A}:{R_B} = 3:1$
35. If there are $3 \times {10^{11}}$ electrons are flowing through the filament of the bulb for two minutes. Find the current flowing through the circuit. Charge on one electron $1.6 \times {10^{19}}$
Ans: Observe as shwn below,
Using the equation
$ = 3 \times {10^{11}} \times 1.6 \times {10^{19}}$C
$ = 4.8 \times {10^8}$C
$ = \dfrac{{4.8 \times {{10}^8}}}{{2 \times 60}}$
$ = 4 \times {10^7}$ A
The current flowing through the circuit is $4 \times {10^7}$ A.
36. A nichrome wire of resistivity $100$ W m and copper wire of resistivity $1.62$ M ohm-m of the same length and same area of cross section are connected in series , current is passed through them, why does the nichrome wire get heated first?
Ans: Looking at the equation
$Q = {I^2}RT$
$Q = {I^2}(pL/A)t$
Henceforth, because nichrome wire has a higher resistance than copper wire, it must be heated first.
37. What is represented by joule/coulomb?
Ans: The potential difference is represented by the joule/coulomb.
38. A charge of $2$ C moves between two plates, maintained at a p.d of $IV$ . What is the energy acquired by the charge?
Ans: The energy acquired by the charge, $W = QV$
The energy acquired is $2$ J
39. Which has more resistance: $100$ W bulb or $60$ W bulb?
Ans: As, it is clearly known that$R \propto \dfrac{1}{P}$, thus the resistance of $60$ W bulb is more.
40. What happens to the current in a circuit if its resistance is doubled?
Ans: As current and resistance are inversely proportional, the current is reduced to half of its previous value.
41. What happens to the resistance of a circuit if the current through it is doubled?
Ans: Resistance is unaffected since the circuit's resistance is independent of the current flowing through it.
42. How does the resistance of a wire depend upon its radius?
Ans: As $R \propto \dfrac{1}{A}$
$ \Rightarrow R \propto V$
Resistance of a wire is directly proportional to its radius.
43. Two wires are of the same length, same radius, but one of them is of copper and the other is of iron. Which will have more resistance.
Ans: Since \[R{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}p1/A\] ,
but A and I are the same. It is solely determined by resistivity, hence iron has a higher resistance.
44. Two wires of same material and same length have radii $R$ and $r$ Compare their resistances.
Ans: Suppose $R$ and $r$ are resistances, then $R = r$ as $p$ and $I$ are the same.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
1. Two metallic wires A and B are connected, wire A has length I and radius $r$ , while wire B has length $2l$ and radius $2r$ . Find the ratio of total resistance of series combination and the resistance of wire $A$ , if both the wires are of the same material?
Ans: Observe as shown below,
Resistance of metallic wire $A$ , ${R_1} = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A}$
Resistance of metallic wire $B$ , ${R_2} = \dfrac{{\rho 2l}}{{4\pi {r^2}}}$
Total resistance in series is $R = {R_1} + {R_2}$
$ = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{{\pi {r^2}}} + \dfrac{{2\rho l}}{{4\pi {r^2}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{3\rho l}}{{2\pi {r^2}}}$
The ratio of the total resistance is series to the resistance of $A$ is
$\dfrac{R}{{{R_1}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\rho l}}{{\pi {r^2}}}}}{{\dfrac{{3\rho l}}{{2\pi {r^2}}}}}$
The ratio of the total resistance is series to the resistance of $A$ is $2/3$ .
2. Should the heating element of an electric iron be made of iron, silver or nichrome wire? Justify giving three reasons?
Ans: The following reasons can be found, why the heating element of an electric iron is composed of nichrome wire.
(1) Due to the high resistance, the passage of current generates additional heat.
(2) High melting point.
(3) At high temperatures, it does not easily oxidised (or burn).
3. (a) Define electric resistance of a conductor?
Ans: A conductor's electric resistance is defined as the resistance it provides to the flow of current.
That is $R = V/I$ and its S.I. unit is ohm , $\Omega $ .
(b) A wire of length $L$ and resistance $R$ is stretched so that its length is doubled and the area of the cross section is halved. How will its
(i) resistance change
Ans: It is clearly known that resistance, $R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A}$
New length $L' = 2L$ and
$A' = \dfrac{A}{2}$
Therefore ${R^1} = \dfrac{{\rho L'}}{{A'}}$
Therefore, the resistance of a wire becomes 4 times its original resistance.
(ii) resistivity change?
Ans: The size of a wire has no bearing on its resistance. As a result, resistance does not vary.
4. Two resistors of resistance $R$ and $2R$ are connected in parallel in an electric circuit. Calculate the ratio of the electric power consumed by $R$ and $2R$ ?
Ans: Power consumed by $R$ , ${\rho _1} = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$
Power consumed by$2R$ , ${\rho _2} = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{{2R}}$
Ratio $\dfrac{{{\rho _1}}}{{{\rho _2}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}}}{{\dfrac{{{V^2}}}{{2R}}}}$
The ratio of the electric power consumed by $R$ and $2R$ is $2:1$ .
5. The length of different metallic wires but of same area of cross section and made of the same material are given below
Wire | Length |
$A$ | $1\,m$ |
$B$ | $1.5\,m$ |
$C$ | $2.0\,m$ |
(i) Out of these two wires which wire has higher resistance.
Ans: As $R \propto l$ (length of the conductor) and since length of wire $C$ is more than $A$ and $B$ , wire $C$ has higher resistance.
(ii) Which wire has higher electrical resistance? Justify your answer.
Ans: The electrical resistivity of a wire is determined by the nature of the material, not by its dimensions. As a result, the resistivity of all wires is the same as the substance of all wires.
6. Two resistors of resistances $R$ and $2R$ are connected in series with an electrical circuit? Calculate the ratio of the electric power consumed by $R$ and $2R$ ?
Ans: It is clearly known thatElectric power consumed by $R$ , ${P_1} = {I^2}R$
Also, electric power consumed by $2R$ , ${P_2} = {I^2}2R$
$\dfrac{{{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}} = 1/2$
The ratio of the electric power consumed by $R$ and $2R$ is$1:2$.
7. Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in series and then in parallel in an electric circuit. the ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations would be
Ans: (c)Let resistance of each wire is $R$
In series, resistance is $ = 2R$
Heat produced, ${H_1} = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{{2R}}t$
In parallel total resistance $ = R/2$
Heat produced, ${H_2} = \left( {\dfrac{{{V^2}}}{{\dfrac{R}{2}}}} \right)t$
$ = \dfrac{{2{V^2}}}{R}t$
${H_2} = 4{H_1}$
$\dfrac{{{H_1}}}{{{H_2}}} = 1/4$
The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations is $1:4$ .
8. Calculate the following of a circuit shown in the figure.
(i) effective resistance
Ans: Effective resistance, $R = {R_1} + {R_2}$
$ = 5 + 10$
The effective resistance is $15\Omega $ .
(ii) current
Ans: Current, $I = V/R$
The current is $0.133$ A.
(iii) Potential difference across $10\Omega $ resistor
Ans: Potential difference across $10\Omega $
$ = \dfrac{2}{{15}} \times 10$
The potential difference across $10\Omega $ is $1.33$ volt.
9. A Piece of wire of resistance $20\Omega $ is drawn out so that its length is increased to twice its original length to calculate the resistance of the wire is the new situation?
Ans: Resistance of wire$ = 20\Omega $
As $R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A}$
And as length of a wire is increased, its area of cross- section decreases, and volume of the wire remains constant.
$R' = \dfrac{{\rho l'}}{{A'}}$
$ = \dfrac{{4\rho l}}{{A'}}$
$\dfrac{{R'}}{R} = \dfrac{4}{1}$
$ \Rightarrow R' = 80$
The resistance of the wire is the new situation is $80\Omega $ .
10. A battery made of $5$ cells each of $2$ V and have internal resistance $0.1\Omega ,0.2\Omega ,$$0.3\Omega ,0.4\Omega $ and \[0.5\Omega \] is connected across \[10\Omega \] resistance. Draw a circuit diagram and calculate the current flowing through$10\Omega $resistance?
Ans: The internal resistance , \[0.1 + 0.2 + 0.3 + 0.4 + 0.5 = 1.5\Omega \]
Total resistance \[ = 1.5 + 10\]
\[ = 11.5\]
\[I = V/R\]
\[ = 10/11.5\]
\[I = {\text{ }}0.869\] A
Current flowing through $10\Omega $ resistance is $0.869$ A.
11. In the circuit diagram given here Calculate-
(a) The total effective resistance
Ans: As resistances are in parallel
$\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}}$
$ = \dfrac{1}{2} + \dfrac{1}{5} + \dfrac{1}{{10}}$
$ = \dfrac{8}{{10}}$
$R = \dfrac{{10}}{8}$
Total effective resistance is $\dfrac{{10}}{8}\Omega $
(b) The total current
Ans: Total current, $I = V/R$
$ = \dfrac{6}{{10/8}}$
The total current is $4.8$ A.
(c) The current through each resistor.
Ans: From the circuit diagram, ${I_1},{I_2}$ and ${I_3}$ be the current through $2\Omega ,5\Omega $ and $10\Omega $ respectively
Therefore, ${I_1} = \dfrac{V}{{{R_1}}}$
${I_2} = \dfrac{V}{{{R_2}}}$
${I_3} = \dfrac{V}{{{R_3}}}$
Current through each$2\Omega ,5\Omega $ and $10\Omega $ is $3$ A ,$1.2$ A, and $0.6$ A respectively.
12. You have two circuits Compare the power used in \[2\Omega \] resistor in each case.
(i) a \[6V\] battery is series with \[1\Omega \] and \[2\Omega \] resistor
Ans: Potential difference, $V = 6V$
${R_1} = 1\Omega $
${R_2} = 2\Omega $
Total Resistor $ = {R_1} + {R_2}$
$I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
$ = \dfrac{6}{3}$
${P_1} = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$
The power used in $2\Omega $resistor is $8$ W.
(ii) a \[4V\] battery in parallel with \[12\Omega \] and \[2\Omega \] resistor
Ans: Potential difference, $V = 4V$
${R_1} = 12\Omega $
${P_2} = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$
The ratio of both power is $1:1$ .
13. How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a \[6\] volt battery?
Charge, $Q = 1C$
Energy = total work done
\[ = {\text{ }}Q{\text{ }}x{\text{ }}V\]
\[ = {\text{ }}1x6\]
\[ = {\text{ }}6\] joule.
Energy given to each coulomb of charge passing through a $6$ volt battery is $6$ joules.
14. On what factor does the resistance of a conductor depend?
Ans: A conductor's resistance is determined by the following factors:
(i) length of conductor
(ii) Area of cross-section
(iii) Temperature
(iv) Conductors are made from a variety of materials.
15. Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or a thin wire of the same material, when connected to the same source? Why?
Ans: When linked to the same source, current flows more freely through a thick wire than via a small wire of the same material. It's because resistance rises as thickness decreases.
16. Let the resistance of an electric component remain constant while the potential difference across the two ends of the component decreases to half of its former value. What change will occur in the current through it?
Ans: T he electrical component's resistance R remains unchanged, but the potential difference across its ends falls to half of its original value. As a result of Ohm's law, new current is reduced to half of its initial value.
17. Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
Ans: The following reasons are why the coils of electric toasters and electric irons are built of an alloy rather than a pure metal:
(i) An alloy's resistivity is higher than that of pure metal.
(ii) An alloy does not rust quickly at high temperatures.
18. Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit consisting of a battery of three cells of \[2V\] , each, a \[5\Omega \] resistor, \[8\Omega \] resistors and a \[12\Omega \] and a plug key, all connected in series.
Ans: The diagram of circuit is as follows
19. An electric lamp of \[100\Omega \] , a toaster of resistance \[50\Omega \] and a water filter of resistance \[500\Omega \] are connected in parallel to a \[220V\] source. What is the resistance of an electric iron connected to the same source that takes as much current as all three appliances, and what is the current through it?
Ans: It can be found from the question, voltage, $V = 220V$
${R_1} = 100\Omega $
${R_2} = 50\Omega $
${R_3} = 500\Omega $
\[1/R = 1/100 + 1/50 + 1/500\]
\[R{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}500/16\]
\[ = {\text{ }}31.25\Omega \]
The resistance of electric iron, which draws as much current as all three appliances take together is $31.25\Omega $ .
Current passing through electric iron, \[I = V/R\]
\[ = 220/31.25\]
\[ = 7.04\] A.
That is the current passing is $7.04$ A.
20. What is (a) the highest total resistance that can be secured by a combination of four resistance of \[4\Omega ,8\Omega ,12\Omega \] and \[24\Omega \] ?
Ans: When all four resistances must be connected in series, the highest resistance is achieved. In that instance, the outcome
$R = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + {R_4}$
\[ = {\text{ }}4 + 8 + 12 + 24\]
\[ = {\text{ }}48\Omega \]
The highest resistance is \[48\Omega \] .
(b) The lowest total resistance that can be secured by a combination of four resistance of \[4\Omega ,8\Omega ,12\Omega \] and \[24\Omega \] ?
Ans: All four resistances must be connected in parallel to produce the lowest resistance.
$1/R = 1/{R_1} + 1/{R_2} + 1/{R_3} + 1/{R_4}$
\[ = {\text{ }}1/4{\text{ }} + 1/8{\text{ }} + 1/12{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}1/24\]
\[ = {\text{ }}12/24\]
The lowest resistance is $2\Omega $ .
21. Why does the cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does?
Ans: When connected to the voltage source, the cord of a heater and the cord of an electric heater are connected in series and carry the same current.
Because the resistance of the cord is so low in comparison to the resistance of the heater element.
As a result, the amount of heat created in the cord is extremely low, but significantly higher in the heater element. As a result, the heating element glows, but the cord does not.
22. A copper wire has diameter \[0.5\] mm and resistivity of \[1.6 \times {10^{ - 8}}\] m. What will be the length of this wire to make its resistance \[10\] ? How much does the resistance change if the diameter is doubled?
Ans: The diameter of wire, d = 0.5 mm,
Resistivity, $\rho = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 8}}$
resistance $R = {\text{ }}10{\text{ }}\Omega $
\[R = \rho L/A\]
$L = \dfrac{{\pi {D^2}R}}{{4\rho }}$
\[ = \dfrac{{22 \times {{(5 \times {{10}^{ - 4}})}^2}}}{{7 \times 4 \times 1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 8}}}}\]
\[ = {\text{ }}122.5\] m
As resistance is inversely proportional to the cross-section area of wire, when the diameter is doubled for a given length of material, the resistance reduces.
23. A battery of \[9V\] is connected in series with resistance of \[0.2\Omega ,0.3\Omega ,0.4\Omega ,0.5\Omega \] and \[12\Omega \]respectively. How much current would flow through the \[12\] resistor?
Ans: Potential difference $V = 9V$ .
Total resistance \[ = {\text{ }}0.2{\text{ }} + 0.3{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}0.5{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}0.5{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}12{\text{ }}\]
\[ = {\text{ }}13.4{\text{ }}\Omega \]
Current in the circuit \[I{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}V/R{\text{ }}\]
\[ = {\text{ }}9{\text{ }}V{\text{ }}/{\text{ }}13.{\text{ }}4{\text{ }}\] A.
\[ = {\text{ }}0.67\]
In a series circuit the same current flows through all the resistance, hence current of \[0.67\] A will flow through \[12{\text{ }}\Omega \] resistor.
24. How many \[176\Omega \] resistors (in parallel) are required to carry \[5\] A on a \[220\] V line?
Ans: Let the resistors of \[176\Omega \] be joined in parallel.
Their combined resistance,
\[1/R = 1/176 + 1/176 \ldots \ldots \] times
\[ = n/176\;\] or
$ \Rightarrow R = 176/n\Omega $
Given that \[V = 220V\] and
\[I = 5\] A
\[R = V/I\]
\[ = 176/n\]
\[ = 220/5\]
\[ = 44\Omega \;\;\;\;\;\;\]
\[n{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}176/44{\text{ }}\]
\[ = {\text{ }}4\] ,
A number of $4$ resistors should be joined in parallel.
25. Show how you would connect three resistors, each of resistance \[6\Omega \] so that the combination has resistance of
(i) \[9\Omega \]
Ans: From the question, ${R_1} = {R_2}$
Join three resistors as below to get net resistance of $9\Omega $ :
(ii) \[4\Omega \]
Ans: Join three resistors as below to get \[4\Omega \] net resistance :
26. A hot plate of an electric oven connected to a \[220V\] line has two resistance coils \[A\] and \[B\] . Each of \[24\Omega \] resistances, which may be used separately, in series or in parallel. What are the currents in the three cases?
Ans: From the question, potential difference\[V = {\text{ }}220{\text{ }}V\] .
Resistance of coil $A = $ Resistance of coil \[B\]
\[ = 24{\text{ }}\Omega \]
When coil is used separately, the circuit \[I = V/R\]
\[ = 220V/24\Omega \]
\[ = {\text{ }}9.2{\text{ }}A\]
The current is\[9.2{\text{ }}A\].
When coils are used in series total resistance $R = {R_1} + {R_2}$
\[ = 24 + 24\]
\[ = 48\Omega \]
The current flowing, \[I = V/R\]
\[ = 220V/48\Omega \]
\[ = 4.6\] A
The current is $4.6$ A.
Two coils are joined in parallel.
Total resistance \[R = {\text{ }}1/24{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}1/24\]
\[ = {\text{ }}2/24\]
\[R = 12{\text{ }}\Omega \] .
Current \[I = V/R\]
\[ = 220V/12\Omega \]
\[ = 18.3\] A.
The current is $18.3$ A.
27. Compare the power used in the \[2\Omega \] resistor in each of the following circuits:
(i) a \[6\] volt battery in series with \[1\Omega \] and \[2\Omega \] resistors and,
Ans: Suppose a \[2\Omega \] resistor is joined to a $6$ V battery in series with \[1\Omega \] and \[2\Omega \] resistors.
Total resistance \[R = 2 + 1 + 2\]
\[ = 5\Omega \]
Current \[I = 6V/5\Omega \]
\[ = 1.2\] A
Power used in $2A$ resistor \[ = {I^2}R\]
\[ = 2.88\] W
Power used is $2.88$ W.
(ii) a \[4V\] battery in parallel with \[12\Omega \] and \[2\Omega \] resistors.
Ans: Suppose \[2\Omega \] resistor is joined to a $4V$ battery in parallel with \[12\Omega \] resistor and \[2\Omega \] resistors,
the current flowing in \[2\Omega = 4V/2\Omega \]
Power used in \[2\Omega \] resistor \[ = {I^2}R\]
\[ = 8\] W
Ratio \[ = 2.88/8\]
\[ = 0.36:1\;\]
The ratio of power used is \[0.36:1\] .
28. In the given figure what is ratio of ammeter reading when \[J\] is connected to \[A\] and then to \[B\]
Ans: Connect $J$ to $A$ , then
\[ = 0.6A\]
When $J$ is connected to $B$\[V = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4\]
Ratio of ammeter reading when J is connected to $A$ and then to $B$ is $3:10$ .
29. Given a resistor each of resistors \[R\] . How will you combine them to get the
(i) maximum effective resistance?
Ans: For maximum resistance $R = nr$ , this is the same as combining a series of numbers.
(ii) minimum effective resistance? What is the ratio of the maximum to minimum resistance?
Ans: For minimum resistance $R' = r/n$ , this is the same as combining a series of numbers.The ratio of the maximum to minimum resistance is $R/R' = {n^2}$.
30. A wire of length \[L\] and resistance \[R\] is stretched so that its length is doubled. How will its
(a) Resistance change
Ans: The resistance of a wire is determined by its length, cross-sectional area, and resistivity as\[{\text{R = }}\dfrac{{{{\rho l}}}}{{\text{A}}}\]
Hence, if the length is doubled and area is halved, then we have
$\dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_1}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\rho {l_2}}}{{{A_2}}}}}{{\dfrac{{\rho {l_1}}}{{{A_1}}}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{{l_2}{A_1}}}{{{l_1}{A_2}}}$
Therefore, ${R_2} = 4{R_1}$
Hence, resistance of the wire becomes four times the original value.
(b) Resistively change?
Ans: The substance from which wire is formed has a property called wire resistivity. As a result, changing the wire's size has no effect on its resistivity.
31. Two students perform the experiments on series and parallel combinations of two given resistors \[{R_1}\] and \[{R_2}\] and plot the following \[V - I\] graphs.
Ans: Both students are correct because
\[AV/A1 = \;\] resistance $R$ and
\[A1/AV = l/R\;\]
The term "series" refers to high resistance, while "parallel" refers to low resistance.
32. A household uses the following electric appliances. Calculate the electricity bill of the household for the month of June if the cost per unit of electric energy is Rs. \[3.00\]
(i) Refrigerator of rating \[4\] for ten hours each day.
Ans: Month of June has \[30\] days.
Refrigerator of $400$ W is running $2$ hours each day.
Total hours it is run in $30$ days \[ = 2 \times 30\]
\[ = 60\] h
Energy consumed in kWh is \[ = 400{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}60/1000{\text{ }}\]
\[ = {\text{ }}24\] kWh
(ii) Two electric fans of rating \[80\]each for twelve hours each day.
Ans: Two electric fans of \[80\] W are run \[12\] hours each day.
Total hours they are run in \[30\] days \[ = 12 \times 30\]
Energy consumed in kWh is \[ = 2 \times 80 \times 360/1000\]
$ = 57.6$ kWh
(iii) Six electric tubes of rating \[18\] W each for 6 hours each day.
Ans: Six electric tubes each of \[18\] W are run $6$ hours daily.
Total hours it is run in $30$ days \[ = 6 \times 30\]
\[ = 180\] h
Energy consumed in kWh is \[ = 6 \times 18 \times 180/1000\]
\[ = 19.44\] kWh
Net energy consumed in the month of June is \[ = 24 + 57.6 + 19.44\]
\[ = 101.04\] kWh
Thus, the electric bill is \[ = 3 \times 101.04\]
\[ = Rs303.12\]
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. Two wires \[A\] and \[B\] are of equal length, different cross sectional areas and made of the same metal.
(a) (i) Name the property which is same for both the wires,
Ans: Resistivity - As resistivity is a property of a substance, it is constant for both wires.
(ii) Name the property which is different for both the wires.
Ans: Resistances - As the cross sectional areas of each wires are different, they are treated as separate objects.
(b) If the resistance of wire \[A\] is four times the resistance of wire \[B\] , calculate
(i) the ratio of the cross sectional areas of the wires and
Ans: Since \[R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A}\]
For wire $A$ , ${R_1} = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{{{A_1}}}$
For wire $B$ , ${R_2} = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{{{A_2}}}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_1}}} = \dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}}\]
Since ${R_1} = 4{R_2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} = 1:4$
\[\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} = \dfrac{{\pi {r_1}^2}}{{\pi {r_2}^2}}\]
\[ = {\left( {\dfrac{{{r_1}}}{{{r_2}}}} \right)^2}\]
Ratio is \[{\left( {\dfrac{{{r_1}}}{{{r_2}}}} \right)^2}\] .
(ii) The ratio of the radii of the wire.
Ans: \[{\left( {\dfrac{{{r_1}}}{{{r_2}}}} \right)^2} = 1/4\]
Ratio is $1:2$ .
2. (a) State ohm’s law?
Ans: If the temperature and other physical conditions of the conductor stay constant, the electric current flowing through the conductor is precisely proportional to the potential difference across the conductor's end.
(b) The value of \[(I)\] current flowing through a conductor for the corresponding values of \[(V)\] potential difference are given below
${\text{I}}$ (Amperes) | $0.5$ | $1.0$ | $1.5$ | $2.5$ | $3$ |
${\text{V}}$ (Volts) | $1$ | $2$ | $3$ | $4.5$ | $5$ |
Plot a graph between \[V\] and \[I\] and also calculate resistance.
Ans: Along $x$ -axis \[IV = 1\] cm
The resistance is $1.67\Omega $ .
3. (a) Define electrical energy with S.I. unit?
Ans: The effort done by a source of electricity to sustain current in a circuit is known as electrical energy. The joule is its SI unit.
(b) A household uses the following electric appliance; Calculate the electricity bill of the household for the month of June if the cost per unit of electric energy is Rs. \[3.00\] .
(i) Refrigerator of rating \[400\] w for ten hour each day.
Ans: Electricity consumed by refrigerator in one day $ = $ power $ \times $ time
\[ = 400 \times \;10\]
\[ = {\text{ }}4000\] Wh
\[ = 4\] kwh
Therefore the electricity consumed is $4$ KWh.
(ii) Two electric fans of rating \[80\] w each for twelve hours each day.
Ans: Electricity consumed by $2$ electric fans in $1$ day, power $ \times $ time
\[ = 2 \times 80 \times 12\]
\[ = {\text{ }}1.92\] kwh
Therefore the electricity consumed is $1.92$ KWh.
(iii) Six electric tubes of rating \[18\] w each for 6hours each day.
Ans : Electricity consumed by $6$ electric tubes in $1$ day \[ = 6 \times 18 \times \;6\]
\[ = {\text{ }}0.648\] kwh
Therefore the electricity consumed is $0.648$ KWh.
Total energy consumed in one day \[ = 4 + 1.92 + 0.648\]
\[ = 6.548\] kwh
Total energy consumed in one month \[ = 6.568 \times 30\]
\[ = 197.04\] kwh
Cost of $1$ unit (kwh) $ = $ Rs \[3.00\]
Cost of \[197.04\] kwh \[ = 197.04 \times 3\]
Electricity bill \[ = Rs591.12\]
The electricity bill of the household for the month of June is Rs. $591.12$.
4. Redraw the circuit of question \[1\] , putting in an ammeter to measure the current through the resistors and a voltmeter to measure the potential difference across the \[12\Omega \] resistors. What would be the reading in the ammeter and voltmeter?
Ammeter $A$ has been joined in series with circuit and voltmeter $V$ is joined in parallel to $12$ ohms resistor.
Total voltage of battery \[V = 3x2\]
\[ = 6\] V.
Total resistance \[R = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}\]
\[ = 5\Omega + 8\Omega + 12\Omega \]
\[ = 25\Omega \]
Ammeter reading \[ = I\]
\[ = 6/25\]
\[ = 0.24\] A.
Voltmeter reading \[ = {\text{ }}IR\]
\[ = 0.24{\text{ }}x{\text{ }}12\]
\[ = 2.88\] V.
The reading in the ammeter and voltmeter is $0.24$ A and $2.88$ V respectively.
5. What are the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery instead of connecting them in series?
Ans: The following are the benefits of connecting electrical equipment in parallel with the battery rather than in series:
(i) Each connecting electrical device will have the same voltage, and the device will take current according to its resistance.
(ii) It is possible to use separate on/off switches.
(iii) As the total resistance in the parallel circuit falls, a large current can be pulled from the cell.
(iv) Even if one electrical gadget is broken, other devices continue to function normally.
6. How can three resistors of resistance \[2\Omega ,3\Omega \]and \[6\Omega \] be connected to give a total resistance of
(a) \[4\Omega \]
Ans: If we connect resistance of $3\Omega $ and $6\Omega $ in parallel and resistance of $2\Omega $ is connected in series with the combination, then total resistance of combination is $4\Omega $ .
(b) \[9\Omega \]
Ans: If all the three resistance are joined in parallel the resulting resistance will be $3\Omega $ .
7. The value of current \[I\] flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference \[V\] across the resistor are given below:
${\text{I}}$ (amperes) | $0.5$ | $1.0$ | $2.0$ | $3.0$ | $4.0$ |
${\text{V}}$ (volts) | $1.6$ | $3.4$ | $6.7$ | $10.2$ | $13.2$ |
Plot a graph between \[V\] and \[I\] and calculate the resistance of that resistor.
Ans: From the given data the \[I - V\] graph is a straight line as shown below:
Resistance of resistor \[R{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{V_A} - {V_B}/{1_A} - {1_B}\]
\[ = {\text{ }}12{\text{ }}V{\text{ }}--{\text{ }}6{\text{ }}V/{\text{ }}3.6{\text{ }}A{\text{ }}--{\text{ }}1.8{\text{ }}A\]
\[ = {\text{ }}6V/{\text{ }}1.8{\text{ }}A{\text{ }}\]
\[ = {\text{ }}3.3{\text{ }}\Omega \]
8. Explain the following:
(a) Why is tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps?
Ans: For the filament of electric lamps, we need a robust metal with a high melting point. Because of its high melting point, tungsten is utilised only for electric lamp filament.
(b) Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters and electric irons, made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
Ans: Electric heating device conductors are composed of an alloy because it has a higher resistance than pure metal and a higher melting point, which prevents it from oxidising at high temperatures.
(c) Why is the series arrangement not used for domestic circuits?
Ans: As the current to all appliances remains constant despite varying resistance, each appliance cannot be turned on or off independently.
(d) How does the resistance of wire vary with its area of cross-section?
Ans: As resistance of a wire is inversely proportional to its cross-section area, the resistance will decrease when the area of cross section increases.
(e) Why are copper and aluminum wires usually employed for electric transmission?
Ans: As copper and aluminium wires are good conductors with low resistance, they are commonly utilised for electrical transmission. They can also be drawn into thin wires since they are ductil
Important Questions of Chapter 12 Class 10 Science - Free PDF Download
Students who are weak in Science and do not have a strong core knowledge might find the chapter electricity quite confusing. This chapter is full of theories and diagrams which confuse students and act as a barrier in their way of achieving good marks. Students must plan to avoid this situation so that they can score the highest possible marks in the final exams. The best way to overcome this problem is a continuous practice. Students can solve some of Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions regularly. They must induct these practice hours in their preparation schedule. So that every day some time is given to revise and practice. This will make the students efficient and thorough.
Students who are unable to solve the questions must take the help of Important Questions of Electricity Class 10 with Solutions which is available on Vedantu for free. Students can download these questions in PDF format. The downloaded CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions act as a guide in preparation for the final exams.
Class 10 Science Ch 12 Important Questions
Students will learn about the concepts and theories of electricity when they will study Chapter 12 of Class 10. They will gain a detailed knowledge of this chapter after practising Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12. Some of the knowledge that the students will learn are as follows:
Electricity
Electricity is considered as a set of physical phenomena which are associated with the presence and motion of electric charge. It is also believed that electricity is somehow related to magnetism which is why both are part of a phenomenon which is called the phenomenon of electromagnetism. This was described in Maxwell's equations. There are many other phenomena which are related to electricity such as lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others.
An electric field gets produced, when there is some kind of presence of positive or negative charge. The positive and negative charges are considered as electric charges. When the electric charge moves it is known as Electric current, and it produces a magnetic field nearby.
Attributes of Electricity
There are two primary attributes of electricity: voltage and current. They both have different properties and are quite different from each other, but only in electronic circuits, they are interrelated. Absence of any of these attributes can harm the circuit operation and ruin it. Let's discuss both these attributes:
Voltage is considered as a force which is responsible for making the current flow in a circuit. Voltage gets measured in volts. In order to get a better understanding of voltage, try to think of a water faucet, in which voltage can get compared to the pressure at which the water is coming out of the faucet. A slow-flowing stream from a faucet resembles a low voltage circuit. In contrast, a high flowing stream resembles a high voltage circuit. A voltage is a mandatory requirement for a current to flow.
The movement of electrical charges is termed as current. When electrons flow through an electronic circuit, it generates a current. Current is measured in terms of amperes (amp). Here also we can take the example of a water faucet to understand the concept of current. It is assumed that the current is at a high level when more water flows in an hour through the faucet, whereas when the flowing water level is low, the current is also low. After the rain, you must have seen that river flows faster than the usual speed because the current remains high at that point of time as more amount of water passes during rains.
Conductors and Insulators
Another thing that students are going to learn while practising the Electricity Class 10 Important Questions is about the significant classification of elements which is done on the basis of their conductivity of electric charge, i.e. conductors and insulators.
Conductors:
In simple terms, conductors is the name given to those materials which allow electricity to flow through them easily without any difficulties. The conductors' property that makes them capable of allowing electricity to flow through them is termed as conductivity. When electrons start flowing in the conductors, they start to produce an electric current. The force which is required for the current to move through the conductor is known as the voltage. Some examples of conductors are copper, gold and iron. Let's discuss some properties of a Conductor.
Materials which are considered as conductors have a minimal resistance because electricity flows through them.
The inductance of the electric conductor occurs when there is a high voltage drop in the conductor.
Inside a perfect conductor, the electric field is considered to be zero. It is zero because it helps to keep the electrons calm so that they don’t accelerate.
There is no electric charge inside the material which is considered as a conductor.
Insulators are considered to be materials within which free flow of electrons from one particle of the element to the other particle is interrupted. If a certain amount of charge is transferred to such an element at a given point of time, then the charge does not get distributed in the surface and remains at the same position. The most common process to charge these elements is by rubbing or charging it through induction. Some examples of insulators are wood, plastic and glass. Let's discuss some properties of insulators:
There are no free electrons in such material because all the electrons are tightly held with each other.
The ability of these materials to stop the electric current from passing through them is known as resistance.
Dielectric length of insulators is vast. Dielectric strength is considered as the maximum electric field that an insulator can handle without suffering an electrical breakdown.
High air permeability is a feature of good insulators as they allow air to pass through their pores.
Important Questions for Electricity Class 10
To give the students an overview of the Important Questions of Chapter 12 Class 10 Science , we are listing here some of the questions which are most likely to come in the exams:
What is Electricity?
What are the attributes of electricity?
Write the SI unit of resistivity.
What do you mean by electric current? Mention and define the SI unit of electric current.
What do you understand by electrical resistivity of a material? Describe an experiment which will show the factors on which the resistance of a conducting wire depends.
What do you understand by a conductor? State its properties.
What do you understand by an insulator? State its properties.
Differentiate between indicator and conductor.
State the difference between electric energy and power.
Mention the commercial unit of electric energy.
Convert the unit of electric energy into joules.
Benefits of Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions offer significant advantages for board exam preparation.
Vedantu's team conducts thorough research to compile a list with a high probability of exam inclusion.
Expert reviews from seasoned professionals with extensive experience ensure accuracy.
Questions adhere to the CBSE board format, providing students insight into exam patterns.
Detailed and explanatory solutions accompany these important questions for comprehensive understanding.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 Science Study Materials |
|
|
|
|
|
These important questions serve as a valuable reference, elucidating key concepts and aiding comprehensive exam preparation. Whether unravelling Ohm's Law or comprehending circuit configurations, these important questions offer understanding. For students grappling with scientific complexities, relying on "Electricity Class 10 Important Questions" proves beneficial, promising improved comprehension and heightened confidence. This resource is not just a tool for academic success but a key to unlocking one's potential in understanding and excelling in the captivating subject of electricity.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity 2024-25
1. How will Vedantu’s important questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 will help you to score well?
Ans: Vedantu’s important questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 helps the students by providing an excellent exam strategy to prepare for the board examinations. Science is an essential subject for students who are aspiring for various competitive exams like JEE, NEET, etc in future. Every student aspiring to excel in the board examinations requires deep knowledge and thorough understanding of this subject. Therefore, the important questions for CBSE Class 10 Science help the students in preparing for their exams. All the questions present in these materials are framed under the latest CBSE curriculum and guidelines.
2. Can I download the important questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 from Vedantu website for free?
Ans: Yes, the download option is available on Vedantu website and mobile application for Class 10 Science Chapter 12. Any student can download these study materials from Vedantu website in PDF format at absolutely free of cost. These are high-quality study materials created by our in-house subject matter experts as per the latest CBSE curriculum and guidelines.
3. Define electricity.
Ans: Electricity is one of the most important aspects of our society. Electricity is a set of physical phenomena that has been shaping up our civilization ever since the wake of the industrial revolution all over the entire industries and businesses. Today, life without electricity would be unimaginable and would lead to total chaos if we somehow lose this important source of energy.
4. What are the topics and subtopics covered under this chapter of Class 10 Science?
Resistivity and Resistance
Factors that affect the Resistance of a Conductor
Parallel and Series Combination of Resistors and their applications
Heating Effect of Electric Current and its Applications
Electric Power
The interrelation between P, V, I and R
5. Define the following terms-
Potential difference
Ans: One volt- One volt is defined as the potential difference between two points in a conductor that carries current. Here, one joule of work is done to locomote a charge from one place to the other. It is the SI unit of potential difference.
Potential Difference- Potential difference is defined as the work done to move a charge from one point to another in a current-carrying conductor. The formula of potential difference is 1 volt- 1 joule/ 1coulomb. A voltmeter is used to measure the potential difference. A voltmeter is connected parallelly in a circuit.
6. Define resistance.
Ans: Resistance is defined as the internal property of a substance that offers obstruction to the current flowing through it. The electric resistance of a substance is inversely proportional to its area of cross-section (A) and directly proportional to its length (l). This means when the area will increase the resistance will decrease and vice-versa. And if the length increases, the resistance will also increase.
The formula is: R=⍴*L/A
Here R is the resistance, L is the length, A is the Area and ⍴ is a constant. The SI unit of resistance is the ohm.
7. Define resistivity.
Ans: The resistivity can be defined as the resistance offered by a current-carrying conductor that has an area of cross-section equal to one centimetre square with a length equal to one centimetre. This means it is the resistance of a one-centimetre cube of the current-carrying conductor. The formula for resistivity is ⍴=R*L/A
Here R is the resistance, L is the length and A is the area. The SI unit of resistivity is ohm*metre. To study more about resistivity, students can download the Important Questions free of cost from the Vedantu website or mobile app.
8. Define ohm’s law.
Ans: Ohm’s law states that the potential difference (V) across a current-carrying conductor is directly proportional to the current (I) flowing through it. Mathematically, V ∝ I or V= IR.
Here, V is the potential difference, I is the current and R is a constant called resistance of the conductor. Ohm’s law is followed by both electrolytic conductors as well as metallic objects.
9. Define Joule’s law of heating.
Ans: Joule’s law of heating states that the heat generated in a current-carrying resistor is directly proportional to the square of the current, resisting capability of the resistor and time till which the current flows through the resistor. The formula of Joule’s Law of Heating is given as
H= I square RT. Here, H is the heat produced in the resistor, I is current, R is the resistance and T is the time during which the current flows in the resistor. The SI unit of heat is Joule.
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity

| Study Reference for Class 10 Chapter 12 Electricity |
|---|
| |
| Conductors | Silver | 1.60 × 10 |
| Copper | 1.62 × 10 | |
| Aluminium | 2.63 × 10 | |
| Tungsten | 5.20 × 10 | |
| Nickel | 6.84 × 10 | |
| Iron | 10.0 × 10 | |
| Chromium | 12.9 × 10 | |
| Mercury | 94.0 × 10 | |
| Manganese | 1.84 × 10 | |
| Constantan (alloy of Cu and Ni) | 49 × 10 | |
| Alloys | Manganin (alloy of Cu, Mn and Ni) | 44 × 10 |
| Nichrome (alloy of Ni, Cr, Mn and Fe) | 100 × 10 | |
| Glass | 10 − 10 | |
| Insulators | Hard rubber | 10 − 10 |
| Ebonite | 10 − 10 | |
| Diamond | 10 − 10 | |
| Paper (dry) | 10 |

| (amperes ) | |||||
| (volts) |
| (volts) | |||||
| (amperes ) |

Chapter 12 Electricity Class 10 NCERT Solutions
Ncert solutions for class 10 science chapters:.
What is the resistance of a Voltmeter?
What does an electric circuit mean, what is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is 1v, how is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points, why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of alloy rather than pure metals, contact form.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
September 27, 2019 by Rama Krishna
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity : In this article, we will provide you all the necessary information regarding NCERT solutions for class 10 science physics chapter 12 electricity. Working on CBSE class 10 physics electricity questions and answers will help candidates to score good marks in-class tests as well as in the CBSE Class 10 board exam.
Electricity class 10 NCERT solutions will not only help in board exam preparation but also helps in clearing the competitive exams like Engineering. Also, candidates can find electricity class 10 numericals with solutions which helps candidates solving their assignments. Read on to find out everything NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity .
Before getting into the details of NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity, let’s have an overview of the list of topics and subtopics under Electricity class 10 NCERT solutions :
- Electricity
- Electric Current And Circuit
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- Circuit Diagram
- Factors On Which The Resistance Of A Conductor Depends
- Resistance Of A System Of Resistors
- Heating Effect Of Electric Current
- Electric Power
Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity PDF in Hindi Medium as well as in English Medium for CBSE, Uttarakhand, Bihar, MP Board, Gujarat Board, and UP Board students, who are using NCERT Books based on updated CBSE Syllabus for the session 2019-20.
- विद्युत कक्षा 10 विज्ञान हिंदी में
- Class 10 Electricity Important Questions
- Electricity Class 10 Notes
- Electricity NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Class 10 Science Electricity Mind Map
Ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 12 intext questions.
Page Number: 200
Question 1 What does an electric circuit mean ? Answer: A continuous and closed path along which an electric current flows is called an electric circuit.
Question 2 Define the unit of current. Answer: Unit of current is ampere. If one coulomb of charge flows through any section of a conductor in one second then the current through it is said to be one ampere. I = \(\frac { Q }{ t }\) or 1 A = I C s -1
Question 3 Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge. Answer: Charge on one electron, e = 1.6 x 10 -19 C Total charge, Q = 1 C Number of electrons, n = \(\frac { Q }{ e }\) = \(\frac { 1C }{ 1.6x{ 10 }^{ -19 } }\) = 6.25 x 10 18
Page Number: 202
Question 1 Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor. Answer: A battery.
Question 2 What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is IV? Answer: The potential difference between two points is said to be 1 volt if 1 joule of work is done in moving 1 coulomb of electric charge from one point to the other.
Question 3 How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V battery ? Answer: Energy given by battery = charge x potential difference or W = QV = 1C X 6V = 6J.
Page Number: 209
Question 1 On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend ? OR List the factors on which the resistance of a conductor in the shape of a wire depends. [CBSE2018] Answer: The resistance of a conductor depends (i) on its length (ii) on its area of cross-section and (iii) on the nature of its material.
Question 2 Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or a thin wire of the same material, when connected to the same source ? Why ? Answer: The current will flow more easily through a thick wire than a thin wire of the same material. Larger the area of cross-section of a conductor, more is the ease with which the electrons can move through the conductor. Therefore, smaller is the resistance of the conductor.
Question 3 Let the resistance of an electrical component remains constant while the potential difference across the two ends of the component decreases to half of its former value. What change will occur in the current through it ? Answer: When potential difference is halved, the current through the component also decreases to half of its initial value. This is according to ohm’s law i.e., V ∝ I.
Question 4 Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons are made of an-alloy rather than a pure metal ? OR Why are alloys commonly used in electric heating devices? Given reason. [CBSE 2018] Answer: The coils of electric toasters, electric irons and other heating devices are made of an alloy rather than a pure metal because (i) the resistivity of an alloy is much higher than that of a pure metal, and (ii) an alloy does not undergo oxidation (or burn) easily even at high temperature, when it is red hot.
Question 5 Use the data in Table 12.2 (in NCERT Book on Page No. 207) to answer the following : (i) Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor ? (ii) Which material is the best conductor ? Answer: (i) Resistivity of iron = 10.0 x 10 -8 Ω m Resistivity of mercury = 94.0 x 10 -8 Ω m. Thus iron is a better conductor because it has lower resistivity than mercury. (ii) Because silver has the lowest resistivity (= 1.60 x 10 -8 Ω m), therefore silver is the best conductor.
Page Number: 213
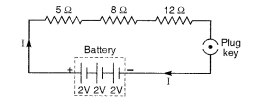
Page Number: 216
Question 1 Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel : (i) 1 Ω and 106 Ω, (if) 1 Ω and 103 Ω and 106 Ω. Answer: When the resistances are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance is smaller than the smallest individual resistance. (i) Equivalent resistance < 1 Ω. (ii) Equivalent resistance < 1 Ω.
Question 3 What are the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery instead of connecting them in series ? Answer: Advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery are :
- In parallel circuits, if an electrical appliance stops working due to some defect, then all other appliances keep working normally.
- In parallel circuits, each electrical appliance has its own switch due to which it can be turned on turned off independently, without affecting other appliances.
- In parallel circuits, each electrical appliance gets the same voltage (220 V) as that of the power supply line.
- In the parallel connection of electrical appliances, the overall resistance of the household circuit is reduced due to which the current from the power supply is high.
Page Number: 218
Question 1 Why does the cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does ? Solution: Heat generated in a circuit is given by I 2 R t. The heating element of an electric heater made of nichrome glows because it becomes red-hot due to the large amount of heat produced on passing current because of its high resistance, but the cord of the electric heater made of copper does not glow because negligible heat is produced in it by passing current because of its extremely low resistance.
Question 2 Compute the heat generated while transferring 96000 coulomb of charge in one hour through a potential difference of 50 V. Solution: Here, Q = 96,000 C, t =1 hour = 1 x 60 x 60 sec = 3,600 s, V = 50 V Heat generated, H = VQ = 50Vx 96,000 C = 48,00,000 J = 4.8 x 10 6 J
Question 3 An electric iron of resistance 20Ω takes a current of 5 A. Calculate the heat developed in 30 s. Solution: Here, R = 20 Ω, i = 5 A, t = 3s Heat developed, H = I 2 R t = 25 x 20 x 30 = 15,000 J = 1.5 x 10 4 J
Page Number: 220
Question 1 What determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current ? Answer: Resistance of the circuit determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current.
Question 2 An electric motor takes 5 A from a 220 V line. Determine the power of the motor and the energy consumed in 2 h. Answer: Here, I = 5 A, V = 220 V, t = 2h = 7,200 s Power, P = V I = 220 x 5 = 1100 W Energy consumed = P x t = 100 W x 7200 s = 7,20,000 J = 7.2 x 10 5 J
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Textbook Chapter End Questions
Question 1 A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into five equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this combination is R’, then the ratio R/R’ is : (a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 25 }\) (b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) (c) 5 (d) 25 Answer: (d) 25
Question 2 Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit? (a) I 2 R (b) IR 2 (c) VI (d) \(\frac { { v }^{ 2 } }{ 2 }\) Answer: (fa) IR2
Question 3 An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. When it is operated on 110 V, the power consumed will be : (a) 100 W (b) 75 W (c) 50 W (d) 25 W Answer: (d) 25 W
Question 4 Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in series and then parallel in a circuit across the same potential difference. The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations would be : (a) 1 : 2 (b) 2 : 1 (c) 1 : 4 (d) 4 : 1 Answer: (c) 1 : 4
Question 5 How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points ? Answer: A voltmeter is connected in parallel to measure the potential difference between two points.
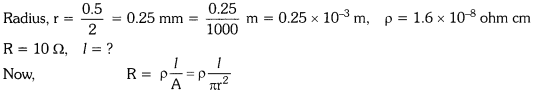
Question 8 When a 12 V battery is connected across an unknown resistor, there is a current of 2.5 mA in the circuit. Find the value of the resistance of the resistor. Solution: Here, V = 12 V and I = 2.5 mA = 2.5 x 10 -3 A ∴ Resistance, R = \(\frac { V }{ I }\) = \(\frac { 12V }{ 2.5\times { 10 }^{ 3 }A }\) = 4,800 Ω = 4.8 x 10 -3 Ω
Question 9 A battery of 9V is connected in series with resistors of 0.2 O, 0.3 O, 0.4 Q, 0.5 Q and 12 £1, respectively. How much current would flow through the 12 Q resistor? Solution: Total resistance, R = 0.2 Ω + 0.3 Ω + 0.4 Ω + 0.5 Ω + 12 Ω – 13.4 Ω Potential difference, V = 9 V Current through the series circuit, I = \(\frac { V }{ R }\) = \(\frac { 12V }{ 13.4\Omega }\) = 0.67 A ∵ There is no division of current in series. Therefore current through 12 Ω resistor = 0.67 A.
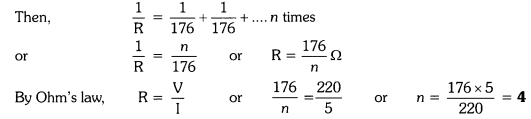
Question 11 Show how you would connect three resistors, each of resistance 6 Ω, so that the combination has a resistance of (i) 9 Ω, (ii) 4Ω Solution: Here, R 1 = R 2 = R 3 = 6 Ω.
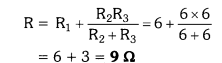
Question 12 Several electric bulbs designed to be used on a 220 V electric supply line, are rated 10 W. How many lamps can be connected in parallel with each other across the two wires of 220 V line if the maximum allowable current is 5 A ? Solution: Here, current, I = 5 A, voltage, V = 220 V ∴ Maxium power, P = I x V = 5 x 220 = 1100W Required no. of lamps \( =\frac { Max.Power }{ Power\quad of\quad 1\quad lamp } \quad =\quad \frac { 1100 }{ 10 } =110\) ∴ 110 lamps can be connected in parallel.
Question 16 Which uses more energy, a 250 W TV set in 1 hr, or a 1200 W toaster in 10 minutes ? Solution: Energy used by 250 W TV set in 1 hour = 250 W x 1 h = 250 Wh Energy used by 1200 W toaster in 10 minutes = 1200 W x 10 min = 1200 x \(\frac { 10 }{ 60 }\) = 200 Wh 60 Thus, the TV set uses more energy than the toaster.
Question 17 An electric heater of resistance 8 Ω draws 15 A from the service mains 2 hours. Calculate the rate at which heat is developed in the heater. Solution: Here, R = 8 Ω, 1 = 15 A, t = 2 h The rate at which heat is developed in the heater is equal to the power. Therefore, P = I 2 R = (15) 2 x 8 = 1800 Js -1
Question 18 Explain the following: (i) Why is tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps ? (ii) Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters and electric irons, made of an alloy rather than a pure metal ? (in) Why is the series arrangement not used for domestic circuits ? (iv) How does the resistance of a wire vary with its area of cross-section ? (v) Why are copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electricity transmission? Answer: (i) The tungsten is used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps because it has a very high melting point (3300°C). On passing electricity through tungsten filament, its temperature reaches to 2700°C and it gives heat and light energy without being melted. (ii) The conductors of electric heating devices such as bread-toasters and electric irons, are made of an alloy rather than a pure metal because the resistivity of an alloy is much higher than that of pure metal and an alloy does not undergo oxidation (or burn) easily even at high temperature. (iii) The series arrangement is not used for domestic circuits because in series circuit, if one electrical appliance stops working due to some defect, than all other appliances also stop working because the whole circuit is broken. (iv) The resistance of a wire is inversely proportional to its area of cross-section, i.e., Resistance R ∝ (1/πr 2 ). If the area of cross section of a conductor of fixed length is increased, then resistance decreases because there are more free electrons for movement in conductor. (v) Copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electricity transmission because they have very low resistances. So, they do not become too hot on passing electric current.
Electric current, potential difference and electric current, Ohms law, Resistance, Resistivity factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends; Series combination of resistors, parallel combination of resistors; and its application on daily life; Heating effect of Electric current, electric Power, Interrelation between P, V, and R.
| CBSE | |
| NCERT | |
| Class 10 | |
| Science | |
| Chapter 12 | |
| Electricity | |
| 41 | |
Formulae Handbook for Class 10 Maths and Science

Question 1: Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor. Answer: Cell or battery eliminator.
Question 2: What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is 1 V? Answer: As we know that V = W / q Thus, the potential difference between two points is one volt when one joule of work is done to carry a charge of one coulomb between the two points in the electric field.
More Resources for CBSE Class 10
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Sanskrit
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Foundation of IT
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
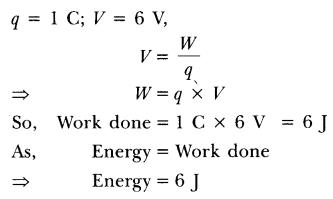
Question 1: On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend Answer: Resistance of a conductor depends upon: (i) Resistivity of the material. (ii) Length of the conductor. (iii) Cross-sectional area of the conductor.
Question 2: Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or thin wire of the same material when connected to the same source? Why Answer: The current flows more easily through a thick wire than through a thin wire because the resistance of thick wire is less than that of a thin wire as R ∝ 1/A.
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity PDF
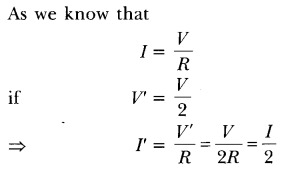
Question 4: Why are the coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal Answer: The coils of electric toaster and electric iron are made of an alloy rather than a pure metal because of the following reasons; (i) The resistivity of an alloy is higher than that of a pure metal. (ii) It has high melting point and does not oxidise.
Question 5: Use the data in Table 12.2 of NCERT book to answer the following: (a) Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor? (b) Which material is the best conductor? ‘ Answer: (a) Iron because its resistivity is less than mercury. (b) Silver is the best conductor as it has least resistivity.
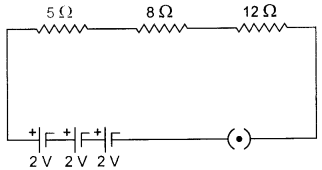
Question 1: Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel. (a) 1 Ω and 10 6 Ω (b) 1 Ω , 10 3 Ω and 10 6 Ω Answer: Equivalent resistance in parallel combination of resistors is always less than the least resistance of any resistor in the circuit. Hence, in both the given cases, the equivalent resistance is less than 1 Ω.
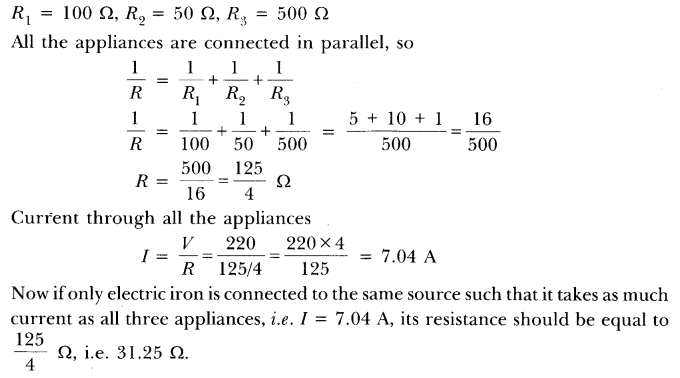
Question 3: What are the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery instead of connecting them in series ? Answer: Advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel:
- When the appliances are connected in parallel with the battery, each appliance gets the same potential difference as that-of battery which is not possible in series connection.
- Each appliance has different resistances and requires different currents to operate properly. This is possible only in parallel connection, as in series connection, same current flows through all devices, irrespective of their resistances.
- If one appliance fails to work, other will continue to work properly.
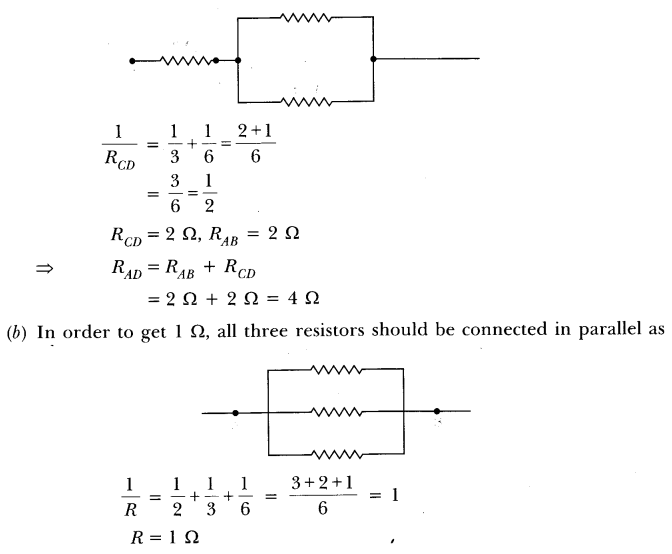
Question 1: Why does the cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does? Answer: The cord of an electric heater is made up of metallic wire such as copper or aluminum which has low resistance while the heating element is made up of an alloy which has more resistance than its constituent metals. Also heat produced ‘H’ is H = I 2 Rt Thus, for the same current H oc R, so for more resistance, more heat is produced by heating element and it glows.
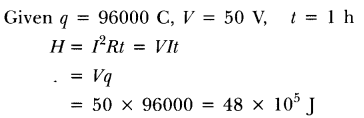
Question 3: An electric iron of resistance 20 Q takes a current of 5 A. Calculate the heat developed in 30 s. Answer: Given R = 20 Ω, I = 5 A, t = 30 s H = I 2 Rt = (5) 2 x 20 x 30 = 15000 J = 1.5 x 10 4 J
Question 1: What determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current? Answer: Electric power determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current.
Question 2: An electric motor takes 5 A from a 220 V line. Determine the power of the motor and the energy consumed in 2 h. Answer: Given I = 5 A, V = 220 V, t = 2 h Power, p = VI = 220 x 5 = 1100 W Energy consumed = Vlt = Pt = 1100 x 2 = 2200 Wh
Textbook Questions

Question 2: Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit? (a) I 2 R (b) IR 2 (c) VI (d) V 2/ R Answer: (b) P = V 2/ R = I 2 R = VI Option (b) does not represent electrical power.
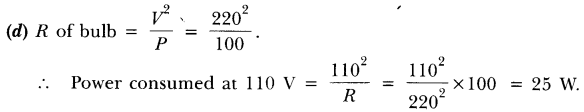
Question 5: How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points? Answer: A voltmeter is connected in parallel across any two points in a circuit to measure the potential difference between them with its +ve terminal to the point at higher potential and -ve terminal to the point at lower potential of the source.
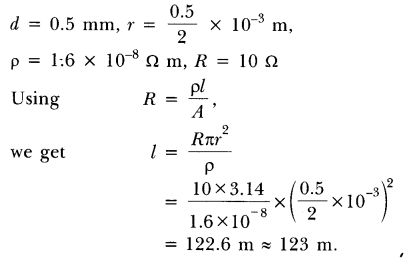
Question 16: Which uses more energy, a 250 W TV set in 1 hr, or a 1200 W toaster in 10 minutes? Answer: Energy consumed by 250 W TV set in 1 h = 250 x 1 = 250 Wh. Energy consumed by 1200 W toaster in 10 min = 1200 X 1/6 = 200 Wh. ∴ Energy consumed by TV set is more than the energy consumed by toaster in the given timings.
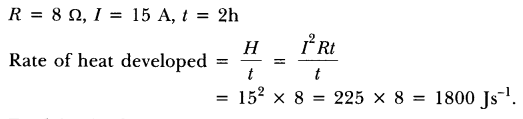
Question 18: Explain the following. (a) Why is the tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps? (b) Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters and electric irons, made of an alloy rather than a pure metal? (c) Why is the series arrangement not used for domestic circuits? (d) How does the resistance of a wire vary with its area of cross-section? (e) Why are copper and aluminum wires usually employed for electricity transmission? Answer: (a) It has high melting point and emits light at a high temperature. (b) It has more resistivity and less temperature coefficient of resistance. (c) (i) All appliances do not get same potential in series arrangement. (ii) All appliances cannot be individually operated. (d) R ∝ =1 / Area of cross – section. (e) They are very good conductors of electricity.
Short Answer Type Questions
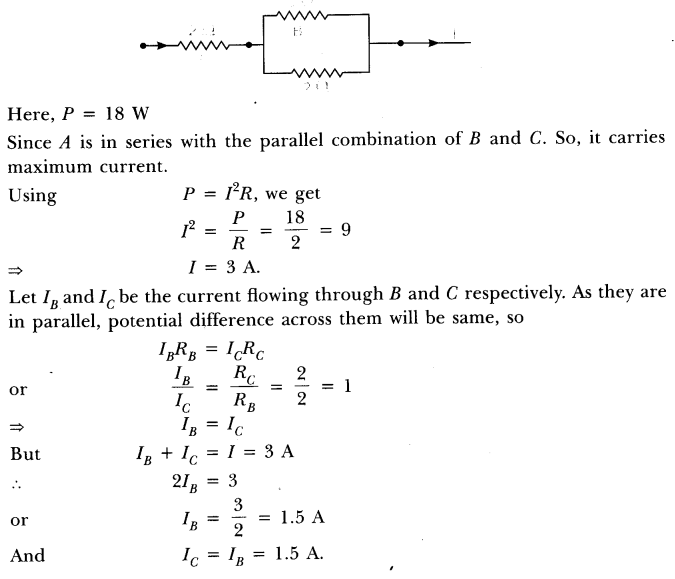
Question 2: Should the resistance of an ammeter be low or high? Give reason. Answer: The resistance of an ammeter should be low so that it will not disturb the magnitude of current flowing through the circuit when connected in series in a circuit.
Question 3: How does use of a fuse wire protect electrical appliances? Answer: The fuse wire is always connected in series with the live wire or electrical devices. If the flow of current exceeds the specified preset value due to some reason, the heat produced melts it and disconnects the circuit or the device from the mains. In this way, fuse wire protects the electrical appliances.
Question 6: Why is parallel arrangement used in domestic wiring? Answer: Parallel arrangement is used in domestic wiring because (i) Each appliance gets the same voltage as that of the mains supply. (ii) If one component is switched off, others can work properly. (iii) Fault in any branch of the circuit can be easily identified.
Question 7: B 1, B 2 and B 3 are three identical bulbs connected as shown in figure. When all the three bulbs glow, a current of 3A is recorded by the ammeter A.
Long Answer Type Questions

Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) [1 Mark each]
Question 4. An ammeter has 20 divisions between 0 mark and 2A mark on its scale. The least count of ammeter is (a) 0.01A (b) 0.2A (c) 0.1A (d) 1A Answer: (c) Number of divisions = 20 Maximum reading of ammeter = 2 A Least count of ammeter = 2/20 = 1/10 = 0.1 A
Question 5. A student finds that there are 20 divisions between zero mark and 1V mark of a voltmeter. The least count of voltmeter is (a) 0.1 V (b) 0.01 V (c) 0.05 V (d) 1.0 V Answer: (c) Number of divisions = 20 Maximum reading of the voltmeter = 1 V Least count of voltmeter = 1/20 = 0.05 V
Question 7. Which of the following is the correct method to connect the ammeter and voltmeter with resistance in the circuit to verify Ohm’s law? [CCE 2012] (a) Ammeter and voltmeter in series (b) Ammeter in series and voltmeter in parallel (c) Ammeter in parallel and voltmeter in series (d) Ammeter and voltmeter in parallel Answer: (b) In a circuit, ammeter should be connected in series, while voltmeter in parallel.
Question 8. In an experiment on studying the dependence of the current I flowing through a given resistor on the potential difference V applied across it, a student has to change the value of the current. For doing this, he should change the (a) number of cells used (b) resistor itself (c) ammeter used in the circuit (d) Voltmeter used in the circuit Answer: (a) If we change the number of cells in electric circuit, the potential difference will change and as a result current flowing in the circuit changes.
Question 9. A milliammeter had graduations marked 0, 100, 200, 300, 400 and 500. The space between 0 mark and 100 mark is divided into 20 divisions. If the pointer of the milliammeter is indicating the seventh graduation after 300 mark, the current flowing in the circuit is (a) 335 mA (b) 330 mA (c) 331mA (d) 340 mA Answer: (a) Number of divisions = 20 Least count of milliammeter = (100-0) / 20 = 5 mA Milliammeter reading = 300 + 7 x 5 = 335 mA
Question 10. If a student while studying the dependence of current on the potential difference keeps the circuit closed for a long time to measure the current and potential difference, then (a) ammeter’s zero error will change (b) ammeter will give more reading (c) voltmeter will show constantly higher readings (d) resistor will get heated up and its value will change Answer: (d) If the circuit is closed for a long time, then current flows in it for a long time which results that the resistor is heated.
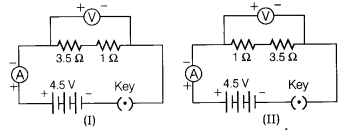
Question 12. When parallel resistors are of three different values, the potential difference across its terminals is [CCE 2015] (a) greatest across smallest resistance (b) greatest across largest resistance (c) equal across each resistance (d) least across the smallest resistance Answer: (c) Potential difference across each resistor is same in parallel combination of resistors.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity (Hindi Medium)

Electricity Study of Electric Charges at Rest and in Motion
Charge Something associated with the matter due to which it produces and experiences electric and magnetic effects. Resides on the outer surface of the conductor. Q = ne S.I. unit coulomb (C)
Electric Current (I) The time rate of flow of charge (Q) through any cross-section I = \(\frac{Q}{t}\) S.I. unit ampere (A)
Types of Current Direct Current Current whose magnitude and direction does not vary with time.
Alternating Current Current whose magnitude and direction periodically changes with time.
Electric Potential Work done per unit charge V = \(\frac{W}{Q}\) S.I. unit volt
Ohm’s law: If the physical conditions remain same, current I ∝ V => V = IR R-electric resistance Substances which obey ohm’s law called ohmic and that do not obey called non-ohmic substances.
Dependence of Resistance
On length (l) and area of cross-section (A) R ∝ l ∝ \(\frac{1}{A}\) R = \(\rho \frac{l}{A}\) ρ = resistivity Resistivity depends on the material of the conductor only.
On Temperature R t = R 0 ( 1 + αt) α = temperature coefficient of resistance
Resistance (R): Obstruction offered to flow of electrons. SI unit ohm Resistance, R ∝ \(\frac{\ell^{2}}{m}\) l = length and m = mass of conducting wire
After stretching, if length increases by n times then resistance will increase by n 2 times i.e., R 2 = n 2 R 1 . Similarly if radius be reduced to \(\frac{1}{n}\) times then area of cross-section decreases \(\frac{1}{n^{2}}\) times so the resistance becomes n 4 times i.e.. R 2 = n 4 R 1 After stretching, if length of a conductor increases by x%, then resistance will increase by 2x% (valid only if x< 10%).
- Using n conductors of equal resistance, the number of possible combinations is 2 n-1 .
- If the resistances of n conductors are totally different, then the number of possible combinations will be 2 n .
- If n identical resistances are first connected in series and then in parallel, the ratio of the equivalent resistance is given by \(\frac{R_{s}}{R_{p}}=\frac{n^{2}}{1}\)
- If a wire of resistance R is cut in n equal parts and then these parts are collected to form a bundle, then equivalent resistance of combination will be \(\frac{\mathrm{R}}{\mathrm{n}^{2}}\)
- If equivalent resistance of R 1 and R 2 in series and parallel be R s and R p respectively, then R 1 = \(\frac{1}{2}\left[\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{s}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{s}}^{2}-4 \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{s}} \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{p}}}\right]\) and R 2 = \(=\frac{1}{2}\left[\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{s}}-\sqrt{\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{s}}^{2}-4 \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{s}} \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{p}}}\right]\)
Grouping of Resistances
Series Grouping of Resistances Equivalent resistance, resistance, R s = R 1 + R 2 + … + R n In this case same current flows through each resistance but potential difference in the ratio of resistance
Parallel Grouping of Resistances \(\frac{1}{R_{P}}=\frac{1}{R_{1}}+\frac{1}{R_{2}}+\ldots+\frac{1}{R_{n}}\) In this case same potential across each resistance but current distributes in the reverse ratio of their resistances
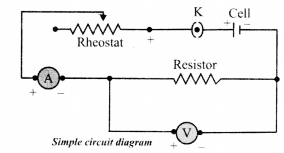
Heating Effect of Electric Current As current flows through a conductor, the free electrons lose energy which is converted into heat. Joule’s heating law H ∝ I 2 H ∝ R H ∝ t H = I 2 Rt = VIt
Practical Applications
- Electric heater, electric iron and water heater, etc. work on the principle of heating effect of current
- Electric bulb glows when electric current flows through the filament of the bulb
Electric Power Rate at which electric energy is dissipated or consumed in a circuit, P = VI , or P = I 2 R = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^{2}}{\mathrm{R}}\)
Watt is a smaller unit of power, its other bigger units are kilowatt (KW), Megawatt (MW) and Horsepower (HP) 1 KW = 10 3 W 1 MW = 10 6 W 1 hp =746 W The commercial unit of electrical energy is 1 Kwh. 1 Kwh = 3.6 × 10 6 J
LED It is a device which glows even if a weak electric current is allowed to flow through it
Now that you are provided all the necessary information regarding Electricity class 10 NCERT solutions and we hope this detailed article on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity is helpful. If you have any doubt regarding this article or NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity, leave your comments in the comment section below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Chapters
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
Free Resources
Quick Resources

- Neet Online Test Pack
12th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் subjects.

கணினி பயன்பாடுகள்

கணினி அறிவியல்
வணிகக் கணிதம் மற்றும் புள்ளியியல்.

கணினி தொழில்நுட்பம்

கணக்குப்பதிவியல்

English Subjects

Computer Science

Business Maths and Statistics

Accountancy

Computer Applications

Computer Technology

11th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

9th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

Social Science

சமூக அறிவியல்
6th standard stateboard question papers & study material.

10th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

7th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

8th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

கணிதம் - old

12th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Introductory Micro and Macroeconomics

Business Studies

Indian Society

Physical Education

Bio Technology


Engineering Graphics

Entrepreneurship

Hindi Elective

Home Science

Legal Studies

Political Science

11th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Mathematics

Enterprenership

Applied Mathematics
10th standard cbse subject question paper & study material.

9th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

8th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

7th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

6th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

School Exams

Tamil Nadu State Board Exams

Scholarship Exams

Study Materials , News and Scholarships

Stateboard Tamil Nadu

Free Online Tests

Educational News

Scholarships

Entrance Exams India

Video Materials

10th Standard CBSE
Class 10th Science - Electricity Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023

Class 10th Science - Electricity Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023 Study Materials Sep-09 , 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 10 Science Subject - Electricity, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.

A PHP Error was encountered
Severity: Warning
Message: in_array() expects parameter 2 to be array, null given
Filename: material/details.php
Line Number: 1436
Message: Use of undefined constant EXAM - assumed 'EXAM' (this will throw an Error in a future version of PHP)
Line Number: 1438
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Electricity case study questions with answer key.
Final Semester - June 2015
The rate of flow of charge is called electric current. The SI unit of electric current is Ampere (A). The direction of flow of current is always opposite to the direction of flow of electrons in the current. The electric potential is defined as the amount of work done in bringing a unit positive test charge from infinity to a point in the electric field. The amount of work done in bringing a unit positive test charge from one point to another point in an electric field is defined as potential difference. \(\begin{equation} V_{A B}=V_{B}-V_{A}=\frac{W_{B A}}{q} \end{equation}\) The SI unit of potential and potential difference is volt. (i) The 2 C of charge is flowing through a conductor in 100 rns, the current in the circuit is
(ii) Which of the following is true? (a) Current flows from positive terminal ofthe cell to the negative terminal of the cell outside the cell. (b) The negative charge moves from lower potential to higher potential. (c) The direction of flow of current in same as the direction of flow of positive charge. (d) All of these (iii) The potential difference between the two terminals of a battery, if 100 joules of work is required to transfer 20 coulombs of charge from one terminal of the battery to other is
(iv) The number of electrons flowing per second in a conductor if 1A current is passing through it
(v) The voltage can be written as
The relationship between potential difference and current was first established by George Simon Ohm called Ohm's law. According to this law, the current through a metallic conductor is proportional to the potential difference applied between its ends, provided the temperature remain constant i.e. I \(\begin{equation} \propto \end{equation}\) V or V = IR; where R is constant for the conductor and it is called resistance of the conductor. Although Ohm's law has been found valid over a large class of materials, there do exist materials and devices used in electric circuits where the proportionality of V and I does not hold. (i) If both the potential difference and the resistance in a circuit are doubled, then
(ii) For a conductor, the graph between V and I is there. Which one is the correct?
(iii) The slope of V - I graph (V on x-axis and I on y-axis) gives
(iv) When battery of 9 V is connected across a conductor and the current flows is 0.1 A, the resistance is
(v) By increasing the voltage across a conductor, the
The obstruction offered by a conductor in the path of flow of current is called resistance. The SI unit of resistance is ohm ( \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) ). It has been found that the resistance of a conductor depends on the temperature of the conductor. As the temperature increases the resistance also increases. But the resistance of alloys like mangnin, constantan and nichrome is almost unaffected by temperature. The resistance of a conductor also depends on the length of conductor and the area of cross-section of the conductor. More be the length, more will be the resistance, more be the area of cross-section, lesser will be the resistance. (i) Which of the following is not will desired in material being used for making electrical wires?
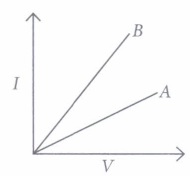
| < T | > T |
| = T |
(iii) Two wires of same material one of length L and area of cross-section A, other is of length 2L and area A/2 . Which of the following is correct?
| = R | = 4R |
| = 4R | = 2R |
(iv) For the same conducting wire (a) resistance is higher in summer (b) resistance is higher in winter (c) resistance is same is summer or in winter (d) none of these (v) A wire of resistance 20 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) is cut into 5 equal pieces. The resistance of each part is
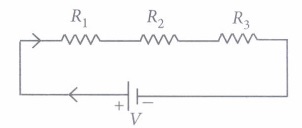
| = V = V | + V + V |
| + V + V = 3V | + V + V |
(ii) When the three resistors each of resistance R ohm, connected in series, the equivalent resistance is
(iii) There is a wire oflength 20 cm and having resistance 20 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) cut into 4 equal pieces and then joined in series. The equivalent resistance is
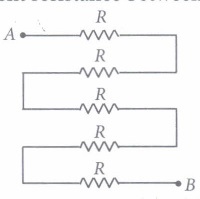
| = 2I = 3I | = 4I = 3I |
| = I = 3I | = 2I = I |
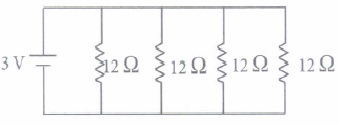
Several resistors may be combined to form a network. The combination should have two end points to connect it with a battery or other circuit elements. When the resistances are connected in series, the current in each resistance is same but the potential difference is different in each resistor. When the resistances are connected in parallel, the voltage drop across each resistance is same but the current is different in each resistor. (i) The household circuits are connected in
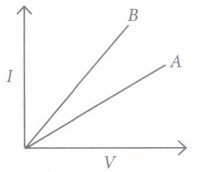
(v) Two resistances 10 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) and 3 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) are connected in parallel across a battery. If there is a current of 0.2 A in 10 .Q resistor, the voltage supplied by battery is
The heating effect of current is obtained by transformation of electrical energy in heat energy. Just as mechanical energy used to overcome friction is covered into heat, in the same way, electrical energy is converted into heat energy when an electric current flows through a resistance wire. The heat produced in a conductor, when a current flows through it is found to depend directly on (a) strength of current (b) resistance of the conductor (c) time for which the current flows. The mathematical expression is given by H = I 2 Rt. The electrical fuse, electrical heater, electric iron, electric geyser etc. all are based on the heating effect of current. (i) What are the properties of heating element? (a) High resistance, high melting point (b) Low resistance, high melting point (c) Low resistance, high melting point (d) Low resistance, low melting point. (ii) What are the properties of electric fuse? (a) Low resistance, low melting point (b) High resistance, high melting point. (c) High resistance, low melting point (d) Low resistance, high melting point (iii) When the current is doubled in a heating device and time is halved, the heat energy produced is
(iv) A fuse wire melts at 5 A. It is is desired that the fuse wire of same material melt at 10 A. The new radius of the wire is
(v) When a current of 0.5 A passes through a conductor for 5 min and the resistance of conductor is 10 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) , the amount of heat produced is
The electrical energy consumed by an electrical appliance is given by the product of its power rating and the time for which it is used. The SI unit of electrical energy is Joule. Actually, Joule represents a very small quantity of energy and therefore it is inconvenient to use where a large quantity of energy is involved. So for commercial purposes we use a bigger unit of electrical energy which is called kilowatt hour. 1 kilowatt-hour is equal to 3.6 x 106 joules of electrical energy. (i) The energy dissipated by the heater is E. When the time of operating the heater is doubled, the energy dissipated is
(ii) The power of a lamp is 60 W The energy consumed in 1 minute is
(iii) The electrical refrigerator rated 400 W operates 8 hours a day. The cost of electrical energy is \(\begin{equation} ₹ \end{equation}\) 5 per kWh. Find the cost of running the refrigerator for one day?
| 32 | 16 |
| 8 | 4 |
(iv) Calculate the energy transformed by a 5 A current flowing through a resistor of 2 \(\begin{equation} \Omega \end{equation}\) for 30 minutes?
(v) Which of the following is correct? (a) 1 watt hour = 3600 J (b) lkWh = 36x10 6 J (c) Energy (in kWh) = power (in W) x time (in hr) (d) \(\begin{equation} \text { Energy (in kWh) }=\frac{V(\text { volt }) \times I(\text { ampere }) \times t(\text { sec })}{1000} \end{equation}\)
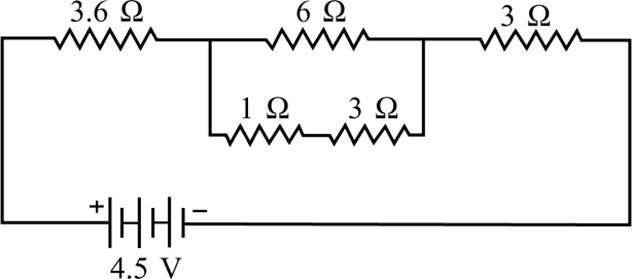
(i) Total resistance of parallel combination is : (a) 2.4 Ω (b) 3 Ω (c) 6 Ω (d) 2 Ω (ii) Equivalent resistance of total circuit is : (a) 5 Ω (b) 9 Ω (c) 11 Ω (d) 13 Ω (iii) Total current in the circuit is : (a) 2 A (b) 4.5 A (c) 0.5 A (d) 10 A (iv) Current in 6 ohm resistance is (a) 0.3 A (b) 0.2 A (c) 4 A (d) 6 A (v) Potential across 3.6 ohm resistance will be : (a) 1.8 V (b) 2.6 V (c) 9 V (d) 4.5 V
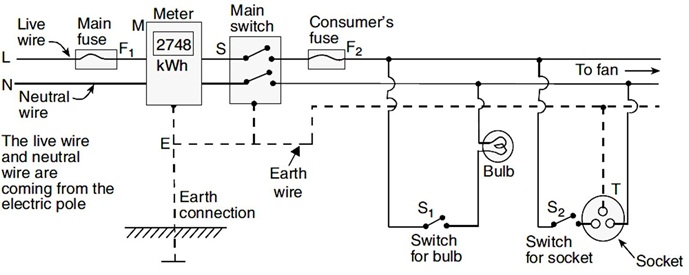
*****************************************
- Previous Class 10th Science - Our Environment Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 202...
- Next Class 10th Science - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Case Study Questions a...
10th Standard CBSE Science free Online practice tests
Metals and non-metals - practice test 1.
10 Questions
Acids, Bases and Salts - Practice Test 1
Chemical reactions and equations - practice test 1, reviews & comments about class 10th science - electricity case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.

Write your Comment

10th Standard CBSE Science Videos
CBSE 10th Science Sample Model Question Paper with Answer Key 2023
10th Standard CBSE Science Usefull Links

- 10th Standard
Other 10th Standard CBSE Subjects

Other 10th Standard CBSE Science Study material
Class 10th science - our environment case ... click to view, class 10th science - magnetic effects of ... click to view, class 10th science - electricity case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 10th science - human eye and ... click to view, class 10th science - light reflection and ... click to view, class 10th science - heredity and evolution ... click to view, class 10th science - how do organisms ... click to view, class 10th science - life processes case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 10th science - periodic classification of ... click to view, class 10th science - carbon and its ... click to view, class 10th science - metals and non-metals ... click to view, class 10th science - acids, bases and ... click to view, class 10th science - chemical reactions and ... click to view, 10th standard cbse science board exam model question paper iii 2019-2020 click to view, 10th standard cbse science board exam model question paper ii 2019-2020 click to view, register & get the solution for class 10th science - electricity case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity In-Text Question With Detailed Solution
- Last modified on: 3 years ago
- Reading Time: 23 Minutes
NCERT In-Text Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity In-Text Solution will help students to score good in class tests as well as in the CBSE Class 10 Board Exam. The solution provided below will also help students to clear their concepts about electricity.
Before getting into the in-text questions, let’s have a look on the topics covered in this chapter under CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity
Topics covered in electricity are:
- Electric Charge and Electric Current
- Electric Potential and Potential Difference
- Circuit Diagram
- Ohm’s Law
- Factors on Which Resistance of A Conductor Depends
- Combination of resistors
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Electric Power
Don’t forget to check the important links for CBSE Class 10 Electricity Given at the end of this page.
INTEXT QUESTIONS PAGE NO. 200
1. What does an electric circuit mean?
2. Define the unit of current.
3.Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
INTEXT QUESTIONS PAGE NO. 202
1.Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor.
2.What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is 1 V?
3.How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V battery?
INTEXT QUESTIONS PAGE NO. 209
1.On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend?
2.Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or a thin wire of the same material, when connected to the same source? Why?
3.Let the resistance of an electrical component remains constant while the potential difference across the two ends of the component decreases to half of its former value. What change will occur in the current through it?
4.Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
5.(a) Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor?
(b) Which material is the best conductor?
INTEXT QUESTIONS PAGE NO. 213
1.Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit consisting of a battery of three cells of 2 V each, a 5 Ω resistor, an 8 Ω resistor, and a 12 Ω resistor, and a plug key, all connected in series.

2.Redraw the circuit of question 1, putting in an ammeter to measure the current through the resistors and a voltmeter to measure potential difference across the 12 Ω resistor. What would be the readings in the ammeter and the voltmeter?

INTEXT QUESTIONS PAGE NO. 216
1. Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel − (a) 1 Ω and 10 6 Ω, (b) 1 Ω and 10 3 Ω and 10 6 Ω.

2. An electric lamp of 100 Ω, a toaster of resistance 50 Ω, and a water filter of resistance 500 Ω are connected in parallel to a 220 V source. What is the resistance of an electric iron connected to the same source that takes as much current as all three appliances, and what is the current through it?

3.What are the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery instead of connecting them in series?
4.How can three resistors of resistances 2 Ω, 3 Ω and 6 Ω be connected to give a total resistance of (a) 4 Ω, (b) 1 Ω?

5.What is (a) the highest, (b) the lowest total resistance that can be secured by combinations of four coils of resistance 4 Ω, 8 Ω, 12 Ω, 24 Ω?

INTEXT QUESTIONS PAGE NO. 218
1.Why does the cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does?
2.Compute the heat generated while transferring 96000 coulomb of charge in one hour through a potential difference of 50 V.

3. An electric iron of resistance 20 Ω takes a current of 5 A. Calculate the heat developed in 30 s.
INTEXT QUESTIONS PAGE NO. 220
1.What determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current?
2.An electric motor takes 5 A from a 220 V line. Determine the power of the motor and the energy consumed in 2 h.
Important links on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity NCERT Solution
CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity NCERT Exemplar Solution
Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Science Electricity Solution
Also Check:
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 2
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 4
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 7
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 14
- MCQs on CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Electricity Case Study Based Questions Class 10
Students who are studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to get the knowledge about the Electricity Case Study Based Questions. Case based questions are generally based on the seen passages from the chapter Electricity. Through solving the case based questions, students can understand each and every concept.
With the help of Electricity Case Study Based Questions, students don’t need to memorise each answer. As answers for these case studies are already available in the given passage. Questions are asked through MCQs so student’s won’t take time to mark the answers. These multiple choice questions can help students to score the weightage of Electricity.
Electricity Case Study Based Questions with Solutions
Selfstudys provides case studies for the Class 10 Science chapter Electricity with solutions. The Solutions can be helpful for students to refer to if there is a doubt in any of the case studies problems. The solutions from the Selfstudys website are easily accessible and free of cost to download. This accessibility can help students to download case studies from anywhere with the help of the Internet.
Electricity Case Study Based Questions with solutions are in the form of PDF. Portable Document Format (PDF) can be downloaded through any of the devices: smart phone, laptop. Through this accessibility, students don't need to carry those case based questions everywhere.
Features of Electricity Case Study Based Questions
Before solving questions, students should understand the basic details of Electricity. Here are the features of case based questions on Electricity are:
- These case based questions start with short or long passages. In these passages some concepts included in the chapter can be explained.
- After reading the passage, students need to answer the given questions. These questions are asked in the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ).
- These case based questions are a type of open book test. These case based questions can help students to score well in the particular subject.
- These Electricity Case Study Based Questions can also be asked in the form of CBSE Assertion and Reason .
Benefits of Solving Electricity Case Study Based Questions
According to the CBSE board, some part of the questions are asked in the board exam question papers according to the case studies. As some benefits of solving Electricity Case Study Based Questions can be obtained by the students. Those benefits are:
- Through solving case studies students will be able to understand every concept included in the chapter Electricity
- Passages included in the case study are seen passages, so students don’t need to struggle for getting answers. As these questions and answers can be discussed by their concerned teacher.
- Through these students can develop their observation skills. This skill can help students to study further concepts clearly.
- Case studies covers all the concepts which are included in the Electricity
How to Download Electricity Case Based Questions?
Students studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to solve questions based on case study. It is necessary for students to know the basic idea of Electricity Case Study Based Questions. Students can obtain the basic idea of case based questions through Selfstudys website. Easy steps to download it are:
- Open Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which is visible in the navigation bar.
- A pop-up menu will appear, Select case study from the list.
- New page will appear, select 10 from the list of classes.
- Select Science from the subject list.
- And in the new page, you can access the Electricity Case Study Based Questions.
Tips to solve Electricity Case Study Questions-
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Electricity Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science.
- Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
- Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
- Identify the questions and give the answers according to the case given.
- Read the passage again, so that you can easily answer the complex questions.
- Answer according to the options given below the questions provided in the Electricity Case Study Based Questions.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- CBSE- Electricity
- Sample Questions
Electricity-Sample Questions
- STUDY MATERIAL FOR CBSE CLASS 10 PHYSICS
- Chapter 1 - Electricity
- Chapter 2 - Human Eye and the Colourful World
- Chapter 3 - Light- Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 4 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 5 - Sources of Energy
Electricity Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity covers each topic of the chapter. These questions aim at providing a better understanding of the chapter to the students and can be downloaded in PDF format. These important question bank help students in clearing their doubts so that they can score well in the exam.
While preparing for exams, students should practise these important questions of Class 10 Science to understand the concepts better. Solving important questions of Class 10 Science Chapter 12 will teach students time management skills and enhance their problem-solving skills. Also, students may come across a few of these questions in the board exam.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers
We have compiled the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers Pdf free download covering the entire syllabus. Practice MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science with Answers on a daily basis and score well in exams. Refer to the Electricity Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.
Electricity Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
1. When electric current is passed, electrons move from: (a) high potential to low potential. (b) low potential to high potential. (c) in the direction of the current. (d) against the direction of the current.

2. The heating element of an electric iron is made up of: (a) copper (b) nichrome (c) aluminium (d) iron

3. The electrical resistance of insulators is (a) high (b) low (c) zero (d) infinitely high
4. Electrical resistivity of any given metallic wire depends upon (a) its thickness (b) its shape (c) nature of the material (d) its length

6. Electric power is inversely proportional to (a) resistance (b) voltage (c) current (d) temperature
MCQ Chapter Electricity Class 10 Question 7. What is the commercial unit of electrical energy? (a) Joules (b) Kilojoules (c) Kilowatt-hour (d) Watt-hour
8. Three resistors of 1 Ω, 2 ft and 3 Ω are connected in parallel. The combined resistance of the three resistors should be (a) greater than 3 Ω (b) less than 1 Ω (c) equal to 2 Ω (d) between 1 Ω and 3 Ω

9. An electric bulb is connected to a 220V generator. The current is 0.50 A. What is the power of the bulb? (a) 440 W (b) 110 W (c) 55 W (d) 0.0023 W
Answer: b Explaination: Here, V = 220 V, I = 0.50 A ∴ Power (P) = VI = 220 x 0.50 = 110 W
10. The resistivity of insulators is of the order of (a) 10 -8 Ω -m (b) 10 1 Ω -m (c) 10 -6 Ω -m (d) 10 6 Ω -m
11. 1 kWh = ……….. J (a) 3.6 × 10 -6 J (b) \(\frac{1}{3.6}\) × 10 6 J (c) 3.6 × 10 6 J (d) \(\frac{1}{3.6}\) × 10 -6 J
12. Which of the following gases are filled in electric bulbs? (a) Helium and Neon (b) Neon and Argon (c) Argon and Hydrogen (d) Argon and Nitrogen
13. 100 J of heat is produced each second in a 4Ω resistor. The potential difference across the resistor will be: (a) 30 V (b) 10 V (c) 20 V (d) 25 V
14. Electric potential is a: (a) scalar quantity (b) vector quantity (c) neither scalar nor vector (d) sometimes scalar and sometimes vector
Electricity Question 15. 1 mV is equal to: (a) 10 volt (b) 1000 volt (c) 10 -3 volt (d) 10 -6 volt
Electricity MCQ Question 16. Coulomb is the SI unit of: (a) charge (b) current (c) potential difference (d) resistance
Fill in the Blanks
1. The SI unit of current is ……… . 2. According to ……… Law, the potential difference across the ends of a resistor is directly proportional to the ……… through it, provided its remains constant. 3. The resistance of a conductor depends directly on its ……… , inversely on its ……… and also on the ……… of the conductor. 4. The SI unit of resistivity is ……… . 5. If the potential difference across the ends of a conductor is doubled, the current flowing through it, gets ……… .
1. ampere 2. Ohm’s, current, temperature 3. length, area of cross-section, material 4. ohm-metre (Ω m) 5. doubled
Hope the information shed above regarding NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, feel free to reach us so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
2 thoughts on “MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers”
It was very helpful for me … it helped me to understand the chapter in a better way …the whole chapter was covered in this questions ..Now I think that I am fully prepared for the test …thanks allot
Mastery app thanks
Comments are closed.
- Class 11-12
- Counsellors
- Professionals
- Study Abroad
- Psychometric Test
Share Chat 10th Question Paper Science Download
- Question Paper
- June 22, 2024
Share Chat 10th Question Paper Science : With the help of our website, which has an extensive collection of Previous Paper of Class 10 CBSE Board , you may successfully prepare for your Class 10 CBSE Board Exam. Get access to a large selection of past exam questions that have been carefully chosen to cover subjects related to the Class 10 CBSE Board course . Download practice tests in several formats, such as multiple-choice questions (MCQs) and descriptive questions, to help you prepare for exams and increase your confidence. With the help of our platform, you can revise with concentrate and recognize important themes and question formulation trends . Get ongoing help and direction to help you prepare for and pass the CBSE Board Exam .
Introduction : Share Chat 10th Question Paper Science
- Download : Share Chat 10th Question Paper Science with Solution
Syllabus : Share Chat 10th Question Paper Science
Exam pattern : share chat 10th question paper science, significance of share chat 10th question paper science, tips for good preparation : share chat 10th question paper science, faqs : share chat 10th question paper science.
The Class 10 CBSE Science exam features a comprehensive have a look at of essential ideas in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. It emphasizes the application of medical standards to actual-world conditions, fostering essential thinking and trouble-fixing capabilities . The curriculum ambitions to broaden a scientific temperament and curiosity, encouraging college students to question, test, and explore. With a robust foundation in technology, college students are well-organized for numerous profession paths in fields which include engineering, medicine, research, and era. The significance of lifelong learning is also highlighted, making sure students stay updated with ongoing scientific advancements.
Educational Scheme
Numerous medical topics, inclusive of as physics, chemistry, and biology, are blanketed within the Class 10 Science curriculum. Students gain analytical and important questioning competencies as they work with theories, experiments, and real-international applications. In order to prepare students for future academic endeavors and real-global packages within the fields of science and technology, learners broaden a radical understanding of clinical principles through theoretical examine and palms-on activities.
Learning Goals
The learning goal is to equip students with a comprehensive understanding of scientific principles and processes, enabling them to apply critical thinking skills and problem-solving strategies to real-world situations.
Practical Implementations
Practical implementations in technological know-how education encompass palms-on experiments, projects, and real-global applications that make stronger theoretical principles. Students interact in laboratory activities, fieldwork, and simulations to deepen their understanding of scientific standards and increase trouble-fixing abilties. Through sensible studying experiences, freshmen gain perception into the software of scientific information in diverse contexts, preparing them for destiny educational pastimes and careers in technology and technology . These sports promote important thinking, creativity, and collaboration, nurturing a nicely-rounded technique to scientific inquiry and exploration.
Significance
The importance of science training lies in its capability to domesticate a scientifically literate society ready with the abilties and understanding to cope with complicated worldwide challenges. By fostering crucial questioning, trouble-solving, and inquiry-based totally gaining knowledge of, science schooling empowers people to make informed choices, innovate, and make a contribution to improvements in various fields. Furthermore, a strong foundation in technology promotes economic development, environmental sustainability, and public health tasks. Ultimately, technology schooling plays a important position in shaping the future through inspiring interest, fostering medical reasoning, and selling a deeper understanding of the natural global.
As the Class 10 CBSE Science test draws to a close, it’s important to review the key ideas in Biology, Chemistry, and Physics while highlighting the application of knowledge to practical settings. The critical thinking and problem-solving abilities that this course has fostered have helped students acquire the scientific temperament and curiosity that are necessary for investigating and comprehending the natural world. A solid background in science also leads to a variety of job options in engineering, medicine, research, and technology, underscoring the significance of lifelong learning to keep up with rapidly advancing scientific fields.
Download : Share Chat 10th Question Paper Science 2023 with Solution
| Question Paper | |
|---|---|

The CBSE Class 10 Science theory exam will be of 80 marks and will be conducted for 3 hours. Students will also get an additional 15 minutes to read the question paper.
There will be 39 questions in total, broken down into 5 areas on the CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper :
| Section | Type of Questions | Marks |
|---|---|---|
| Section A: Objective Type | Multiple Choice | 20 |
| Section B: Short Answer I | Brief Answers | 12 |
| Section C: Short Answer II | Detailed Responses | 21 |
| Section D: Long Answer | Elaborate Explanations | 15 |
| Section E: Case Study | Analytical Responses | 12 |
Here is a comprehensive breakdown of the CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper’s structure:
Internal Assessment
The significance of Share Chat 10th Question Paper Science lies in their ability to serve as valuable study resources for candidates preparing for the CBSE Board examination. Here are some key reasons why these question papers are important:
Exam Blueprint Revealed:
The actual exam is modeled by these papers . You can learn a lot about the arrangement of the questions, the relative importance of the various areas on the syllabus, and even the degree of difficulty by carefully examining them. This enables you to customize your study and give priority to the subjects that need greater attention.
Improving Your Skills:
Using past year papers for practice is similar to taking practice exams in a real exam setting. You get to put your speed, accuracy, and conceptual understanding to the test in a virtual setting. This assists in determining your areas of strength and weakness prior to the exam, enabling you to improve your strategy and reinforce your comprehension of important subjects.
Building Exam Stamina:
The Class 10 CBSE Board exam may have a time limit, therefore success depends on your ability to manage your time well. You can improve your endurance and time management abilities for the test by using previous year’s papers. You can learn to pace yourself, prioritize questions , and stay away from becoming bogged down on any one problem by practicing in a timed environment.
Increasing Confidence:
Completing last year’s papers successfully boosts your self-assurance and eases exam anxiety. Observing that you can appropriately respond to questions validates your understanding and inspires you to keep trying. Your overall exam performance is significantly impacted by this positive reinforcement.
Finding Recurring Patterns:
Although the precise questions won’t be asked again, reviewing previous exams frequently identifies patterns in the subjects and question types that are asked again. This enables you to create focused strategies for answering the kinds of questions you might encounter on the actual exam by anticipating their types.
It’s like having a secret weapon when you use the Share Chat 10th Question Paper Science in your preparing approach . They sharpen your abilities, give you confidence boosts, and offer priceless insights, all of which considerably raise your chances of succeeding on test day.
Recognize the test and syllabus:
Visit the CBSE Board website to download the official announcement and curriculum. Recognize the format of the exam (number of sections, weighted scores, time allotment). Learn everything there is to know about the subjects included on the curriculum for each area.
Create a Timetable and Study Plan:
Make a realistic study schedule with time allotted for each section based on the syllabus and your preferred method of learning . Establish study times on a daily or weekly basis, and try your best to maintain them. Be adaptable and make necessary changes to your plan, but consistency is essential.
Establish a Robust Base:
Pay close attention to the fundamental ideas in each area, paying particular attention. Learn the fundamental, shortcuts, and approaches to solving problems .
Make Use of Educational Resources
Make use of top-notch study resources, such as online courses, textbooks, and coaching materials (if necessary). Exam patterns and time management exercises can be learned by looking at previous year’s question papers and practice exams.
Consistent Practice:
Every day, complete practice questions from different sources. Prioritize precision while progressively picking up speed. Examine your errors and determine what needs to be improved.
By following these tips and dedicating yourself to consistent preparation, you can significantly increase your chances of success in the Share Chat 10th Question Paper Science Exam. Remember, the key is to start early, work hard, and stay focused on your goal.
Q1: What topics are covered in the Class 10 Science exam?
A1: The exam covers physics, chemistry, and biology topics outlined in the curriculum, including motion, forces, chemical reactions, life processes, and more.
Q2: How is the Class 10 Science exam structured?
A2: The exam typically consists of multiple-choice questions, short answer questions, and long answer questions, covering theoretical concepts and practical applications.
Q3: Are practicals included in the Science exam?
A3: Yes, practical assessments are an integral part of the Science exam. Students are evaluated on their experimental skills, observations, and ability to draw conclusions.
Q4: How can I prepare effectively for the Class 10 Science exam?
A4: Practice solving sample papers, previous years’ question papers, and engage in regular revision of key concepts. Focus on understanding fundamental principles and their applications.
Q5: What is the marking scheme for the Class 10 Science exam?
A5: Marks distribution varies, but typically, theoretical questions carry more weightage compared to practicals. It’s essential to understand the marking scheme provided by the examination board.
People Also Viewed
Class 10 Physics Notes Download PDF
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Chemistry PDF
Class 10 Biology Notes Download PDF
Class 11 Chemistry Sample Paper 2020-21 PDF
Class 10 Chemistry Notes Download PDF
Class 11 Chemistry Sample Paper 2022-23 PDF
Accountancy Model Question Paper 2023 Class 11 with Answers
Class 10 Practical Sample Paper Download PDF
Class 11 Accounts Sample Paper with Solution PDF-
Most Recent Posts
Biology Class 12 Term 2 Sample Paper 2022
8th Class Guess Paper 2016 English & Sample Paper | 2017, 2020, 2021
Second Term English Question Paper: Download
Bstc Question Paper Download
Class 11 Physics Sample Paper 2022-23 Download
10th Tamil Model Question Paper
Class 12 Biology Syllabus 2024 Download PDF
NTA CUET PG 2024 Answer Key: cuetpg.samarth.ac.in 2024
10th Maths Guide: Previous Year Question Papers, With Answers
Most Popular Article's
| Professional Courses After 12th For Bio-Math Students? Best Courses After 12th For Bio Math Group Course List ? |
Career Counselling & Services
Psychometric Tests:
21st Century Skills & Learning Test:
Most Popular Links
AMU Class 9 Entrance Question Paper 2019 PDF
Talathi Bharti tcs pattern question paper | TCS Paper
UP police online mock test free: Download, Solved
NTSE Sample Papers PDF Download with Solution
Polytechnic English Question Paper 1st Year
CRPF Previous Year Question Paper
EMRS lab attendant question paper: Download
UP Board 12th English Paper Pdf Download
CTET Question Paper 2022 PDF Download
10th Class Ka English Ka paper 2018
- Privacy Policy
- Refund & Cancellation
- Content Writer Jobs
- Counselling Blogs
PSYCHOMERIC TEST
- Ideal Career Test
- Skill Based Career Test
- Stream Selector
- Engineering Branch Selector
- Humanities Career Selector
- Commerce Career Selector
- Professional Skill Index
- Educator Professional Skills
- Institute Blogs
- Counselling Services For School
- Counselling Services For 9th Class
- Counselling Services For 10th Class
- Counselling Services For 11th Class
- Counselling Services For 12th Class
- Competitive Exam Calendars
- Engineering Entrance Exam
- Medical Entrance Exam
- Management Entrance Exam
- Psychometric Career Tests
- Study in India
- Knowledge Base
- Career Options
- CareerGuide Profile
- Certification Courses
- Know Your Community
- Counsellor Jobs
- Post Counsellor Jobs
- Exclusive Interviews
- Impact Stories
- Inspirational Stories
LET'S BE FRIENDS
Engineering Exams
- JEE ADVANCE
Manav Rachna University
- MRU Chandigarh
- MRU University
- MRU Course , Admissions
- MRU Scholarship
- MRU CampurLife
Sharda University
- About Sharda
- Sharda University Fees
- Sharda University MBBS Fees
- Sharda University B.Tech Fees
- Sharda University MBA Fees
- Sharda University Ranking
- Sharda University Noida
- Sharda University Placements
- Sharda University Student Login
Lovely Professional University
- LPU Courses , Admission
- LPUNEST Syllabus
- LPU Ranking
- LPU B.Tech Fees
- LPU MBA Fees
Chandigarh University
- About Chandigarh University
- CU Course , Admissions
- Chandigarh University Fees
- Chandigarh University Ranking
- Chandigarh University B.Tech Fees
- Chandigarh University MBA Fees
- Chandigarh University Hostel fees
- Chandigarh University Campus
- Chandigarh University Online
- UPES Dehradun
- UPES B.Tech Fees
- UPES Dehradun Entrance Exam
- UPES Dehradun Fees
- UPES Dehradun Placements
- UPES Campus
- UPES MBA Fees
Top Searches
- Top BBA Colleges In India
- Top BBA colleges in Mumbai
- Top Private BBA Colleges In Delhi
- Top BBA colleges in Bangalore
- Top Colleges for BBA in Hyderabad
- Top BBA Colleges In Pune
- Top BBA Colleges in Chennai
- Top BBA Colleges in Indore
- TOP BBA COLLEGES IN JAIPUR
- JEE MAIN 2023
- JEE FULL FORM
- JEE MAIN 2023 EXAM PATTERN
- JEE MAIN 2023 EXAM DATE
- JEE MAIN 2023 RESULT
- JEE MAIN 2023 CUT-OFF
- JEE MAIN COLLEGE PREDICTOR
- JEE MAIN ANSWER KEY 2023
- JEE MAIN 2023 COUNSELLING
Jee Advance
- JEE ADVANCE 2023
- JEE ADVANCE EXAM PATTERN
- JEE ADVANCE 2023 EXAM DATE
- JEE ADVANCE 2023 RESULT
- JEE ADVANCE CUT-OFF
MOST SEARCHED
- MBA Full Form
- IAS Full Form
- MBBS Full Form
- BSC Full Form
- IIT Full Form
- IMPS Full Form
- NASA Full Form
- PHD Full Form
- IIM Full Form
- IIIT Full Form
- BCA Full Form
- LLB Full Form
- CISF Full Form
- CDS Full Form
- For 9th class
- Skill Based Career Test |
- Basic Plan |
- Advance Plan |
- Video Counselling Plan |
- Mentorship Plan
- For 10th class
- Stream Selector Test |
- Ideal Career Test |
- For 11th class
- Engineering Branch Selector |
- Humanities Career Selector |
- Commerce Career Selector |
- Video Counselling Plan|
- For 12th class
- Professional Skill Index Test |
- For Masters
- For Working Professionals
- Video Counselling Plan
- Online Courses
- Data Science Courses |
- Digital Marketing Courses |
- Designing Courses |
- Back End Development Courses |
- Web Development Courses |
- Business Courses
STUDY ABROAD
- Study in USA |
- Study in Europe |
- Study in UK |
- Study in Australia |
- Study in New Zealand |
- Study in Singapore |
- Study in Canada |
- Study in Dubai |
- Study in Hong Kong |
- Study in Ireland

Copyright © CareerGuide.com
Build Version:- 1.0.0.0
WhatsApp us
MAT ANSWER KEY, SYLLABUS, SAMPLE PAPER
Request a call back.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. Case study: 1. We can see that, as the applied voltage is increased the current through the wire also increases.
Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Question 1: The heating effect of current is obtained by the transformation of electrical energy into heat energy. Just as mechanical energy used to overcome friction is covered into heat, in the same way, electrical energy is converted into heat energy when an electric current flows through a resistance wire.
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Electricity Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. 10th Standard CBSE. Reg.No. : Science. Time : 00:30:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 16. The rate of flow of charge is called electric current. The SI unit of electric current is Ampere (A). The direction of flow of current is always opposite to the direction of flow ...
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity. Question 1: The electrical energy consumed by an electrical appliance is given by the product of its power rating and the time for which it is used. The SI unit of electrical energy is Joule (as shown in figure). Actually, Joule represents a very small quantity of energy and ...
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Question 1: The heating effect of current is obtained by the transformation of electrical energy into heat energy. Just as mechanical energy used to overcome friction is covered into heat, in the same way ...
The Chapter wise Important case study based questions with their solved answers in CBSE Class 10 Science can be accessed from the table below: CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions ...
The switch if OFF. Q2. A current of 10 A flows through a conductor for two minutes. ( i ) Calculate the amount of charge passed through any area of cross section of the conductor. ( ii ) If the charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10 − 19 C , then calculate the total number of electrons flowing.
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App. There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions.
Case Study Questions Chapter 12 Electricity. Case/Passage - 1. Two tungston lamps with resistances R1 and R2 respectively at full incandescence are connected first in parallel and then in series, in a lighting circuit of negaligible internal resistance. It is given that: R1 > R2.
H= I square RT. Here, H is the heat produced in the resistor, I is current, R is the resistance and T is the time during which the current flows in the resistor. The SI unit of heat is Joule. Get chapter-wise important questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with answers on Vedantu.
CBSE Class 10th - SCIENCE : Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution. In board exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Electricity Case Study Questions (CSQ's) Practice Tests. Timed Tests. Select the number of questions for the test: Select the number of questions for the test: TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem ...
Accurate answers of all the Case-based questions given in the PDF. Case Study class 10 Science solutions are prepared by subject experts referring to the CBSE Syllabus of class 10. Free to download in Portable Document Format (PDF) so that students can study without having access to the internet.
Important Questions of Electricity Class 10 Science Chapter 12. Question 1. A current of 10 A flows through a conductor for two minutes. (i) Calculate the amount of charge passed through any area of cross section of the conductor. (ii) If the charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10 -19 C, then calculate the total number of electrons flowing.
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity. December 19, 2021 March 19, 2023 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce. ... Environment and Natural Resources Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 12 Political Science Chapter 6;
Chapter 12 Electricity NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science will prepare students to do better during immense pressure and make much easier to memorize topics faster and frame better answers. Your marks play an important role in shaping future thus these NCERT Solutions will become your comprehensive guide in easy learning and evaluating ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Textbook Chapter End Questions. Question 1. A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into five equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this combination is R', then the ratio R/R' is : (a) 125.
10th Standard CBSE. Science. Time : 01:35:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 75. Case Study. The rate of flow of charge is called electric current. The SI unit of electric current is Ampere (A). The direction of flow of current is always opposite to the direction of flow of electrons in the current. The electric potential is defined as the amount of work ...
Answer. An electric circuit consists of electric devices, switching devices, source of electricity, etc. that are connected by conducting wires. 2. Define the unit of current. Answer. The unit of electric current is ampere (A). 1 A is defined as the flow of 1 C of charge through a wire in 1 s.
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Electricity Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science. Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs). Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
Calculate the energy consumed (in kWh) in the month of February. 13. A torch bulb is rated at 3V and 600mA. Calculate it's. (a) Power b) Resistance c) Energy consumed if it is lighted for 4 Hrs. 14. State and derive joule's law. An electric iron consumes energy at rate of 420w when heating is at maximum rate and 180 w when heating is at ...
Answer: (a) Electric bulbs are generally filled with some inert gas like nitrogen or argon. This enables to prolong the life of the filament of electric bulb. (b) Here radius of wire r = 0.01 cm = 0.01 × 10 -2 m, resistance R = 10 Ω and resistivity ρ = 50 × 10 -8 Ω/m. 33. (a)Define electric power.
Answers. 1. ampere. 2. Ohm's, current, temperature. 3. length, area of cross-section, material. 4. ohm-metre (Ω m) 5. doubled. Hope the information shed above regarding NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 ...
#cbse #resistance #electricity #physics #potential #education #physics
Overview. The Class 10 CBSE Science exam features a comprehensive have a look at of essential ideas in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. It emphasizes the application of medical standards to actual-world conditions, fostering essential thinking and trouble-fixing capabilities.The curriculum ambitions to broaden a scientific temperament and curiosity, encouraging college students to question ...