myCBSEguide
- Class 9 Science Case...

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you are wondering how to solve class 9 science case study questions, then myCBSEguide is the best platform to choose. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions.
You can find a wide range of solved case studies on myCBSEguide, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand the application of various concepts in real-life situations.
The rationale behind Science
Science is crucial for Class 9 students’ cognitive, emotional, and psychomotor development. It encourages curiosity, inventiveness, objectivity, and aesthetic sense.
In the upper primary stage, students should be given a variety of opportunities to engage with scientific processes such as observing, recording observations, drawing, tabulating, plotting graphs, and so on, whereas in the secondary stage, abstraction and quantitative reasoning should take a more prominent role in science teaching and learning. As a result, the concept of atoms and molecules as matter’s building units, as well as Newton’s law of gravitation, emerges.
Science is important because it allows Class 9 Science students to understand the world around us. It helps to find out how things work and to find solutions to problems at the Class 9 Science level. Science is also a source of enjoyment for many people. It can be a hobby, a career, or a source of intellectual stimulation.
Case study questions in Class 9 Science
The inclusion of case study questions in Class 9 science CBSE is a great way to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving. By working through real-world scenarios, Class 9 Science students will be better prepared to tackle challenges they may face in their future studies and careers. Class 9 Science Case study questions also promote higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and synthesis. In addition, case study questions can help to foster creativity and innovation in students. As per the recent pattern of the Class 9 Science examination, a few questions based on case studies/passages will be included in the CBSE Class 9 Science Paper. There will be a paragraph presented, followed by questions based on it.
Examples of Class 9 science class case study questions
Class 9 science case study questions have been prepared by myCBSEguide’s qualified teachers. Class 9 case study questions are meant to evaluate students’ knowledge and comprehension of the material. They are not intended to be difficult, but they will require you to think critically about the material. We hope you find Class 9 science case study questions beneficial and that they assist you in your exam preparation.
The following are a few examples of Class 9 science case study questions.
Class 9 science case study question 1
- due to its high compressibility
- large volumes of a gas can be compressed into a small cylinder
- transported easily
- all of these
- shape, volume
- volume, shape
- shape, size
- size, shape
- the presence of dissolved carbon dioxide in water
- the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- the presence of dissolved Nitrogen in the water
- liquid particles move freely
- liquid have greater space between each other
- both (a) and (b)
- none of these
- Only gases behave like fluids
- Gases and solids behave like fluids
- Gases and liquids behave like fluids
- Only liquids are fluids
Answer Key:
- (d) all of these
- (a) shape, volume
- (b) the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- (c) both (a) and (b)
- (c) Gases and liquids behave like fluids
Class 9 science case study question 2
- 12/32 times
- 18 g of O 2
- 18 g of CO 2
- 18 g of CH 4
- 1 g of CO 2
- 1 g of CH 4 CH 4
- 2 moles of H2O
- 20 moles of water
- 6.022 × 1023 molecules of water
- 1.2044 × 1025 molecules of water
- (I) and (IV)
- (II) and (III)
- (II) and (IV)
- Sulphate molecule
- Ozone molecule
- Phosphorus molecule
- Methane molecule
- (c) 8/3 times
- (d) 18g of CH 4
- (c) 1g of H 2
- (d) (II) and (IV)
- (c) phosphorus molecule
Class 9 science case study question 3
- collenchyma
- chlorenchyma
- It performs photosynthesis
- It helps the aquatic plant to float
- It provides mechanical support
- Sclerenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Epithelial tissue
- Parenchyma tissues have intercellular spaces.
- Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners.
- Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues.
- Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles, muscles
- (I) and (II)
- (III) and (I)
- Transpiration
- Provides mechanical support
- Provides strength to the plant parts
- None of these
- (a) Collenchyma
- (b) help aquatic plant to float
- (b) Sclerenchyma
- (d) Only (III)
- (c) provide strength to plant parts
Cracking Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
There is no one definitive answer to Class 9 Science case study questions. Every case study is unique and will necessitate a unique strategy. There are, nevertheless, certain general guidelines to follow while answering case study questions.
- To begin, double-check that you understand the Class 9 science case study questions. Make sure you understand what is being asked by reading it carefully. If you’re unclear, seek clarification from your teacher or tutor.
- It’s critical to read the Class 9 Science case study material thoroughly once you’ve grasped the question. This will provide you with a thorough understanding of the problem as well as the various potential solutions.
- Brainstorming potential solutions with classmates or other students might also be beneficial. This might provide you with multiple viewpoints on the situation and assist you in determining the best solution.
- Finally, make sure your answer is presented simply and concisely. Make sure you clarify your rationale and back up your claim with evidence.
A look at the Class 9 Science Syllabus
The CBSE class 9 science syllabus provides a strong foundation for students who want to pursue a career in science. The topics are chosen in such a way that they build on the concepts learned in the previous classes and provide a strong foundation for further studies in science. The table below lists the topics covered in the Class 9 Science syllabus of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). As can be seen, the Class 9 science syllabus is divided into three sections: Physics, Chemistry and Biology. Each section contains a number of topics that Class 9 science students must study during the course.
CBSE Class 9 Science (Code No. 086)
Theme: Materials Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour Definition of matter; solid, liquid and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of state-melting (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation. Nature of matter: Elements, compounds and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids and suspensions. Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of constant proportions, Atomic and molecular masses. Mole concept: Relationship of mole to mass of the particles and numbers. Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, valency, the chemical formula of common compounds. Isotopes and Isobars.
Theme: The World of the Living Unit II: Organization in the Living World Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number. Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Theme: Moving Things, People and Ideas Unit III: Motion, Force and Work Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, derivation of equations of motion by graphical method; elementary idea of uniform circular motion. Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration. Elementary idea of conservation of Momentum. Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall. Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy. Work, energy and power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy. Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Theme: Food Unit IV: Food Production Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
PRESCRIBED BOOKS:
- Science-Textbook for class IX-NCERT Publication
- Assessment of Practical Skills in Science-Class IX – CBSE Publication
- Laboratory Manual-Science-Class IX, NCERT Publication
- Exemplar Problems Class IX – NCERT Publication
myCBSEguide: A true helper
There are numerous advantages to using myCBSEguide to achieve the highest results in Class 9 Science.
- myCBSEguide offers high-quality study materials that cover all of the topics in the Class 9 Science curriculum.
- myCBSEguide provides practice questions and mock examinations to assist students in the best possible preparation for their exams.
- On our myCBSEguide app, you’ll find a variety of solved Class 9 Science case study questions covering a variety of topics and concepts. These case studies are intended to help you understand how certain principles are applied in real-world settings
- myCBSEguide is that the study material and practice problems are developed by a team of specialists who are always accessible to assist students with any questions they may have. As a result, students may be confident that they will receive the finest possible assistance and support when studying for their exams.
So, if you’re seeking the most effective strategy to study for your Class 9 Science examinations, myCBSEguide is the place to go!
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Class 9 Science Case Study Questions play a crucial role in the field of science education as they provide real-life scenarios for students to analyze, apply their knowledge, and develop problem-solving skills. This article aims to present a comprehensive collection of case study questions for Class 9 Science , covering various topics and concepts.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

CBSE Class 9 Science Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. The CBSE Class 9 Science Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends.
If you want to want to prepare all the tough, tricky & difficult questions for your upcoming exams, this is where you should hang out. CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 will provide you with detailed, latest, comprehensive & confidence-inspiring solutions to the maximum number of Case Study Questions covering all the topics from your NCERT Text Books !
Table of Contents
CBSE Class 9th SCIENCE Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
Case study questions provide students with real-life scenarios that require critical thinking and application of scientific concepts. They help students understand the practical application of scientific principles and develop problem-solving skills in various scientific disciplines.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
Inboard exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. For Science subjects, there would be 5 case-based sub-part questions, wherein a student has to attempt 4 sub-part questions.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Tissues
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Gravitation
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Sound
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
The above Case studies for Class 9 Science will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Science Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for the benefit of Class 10 students.
Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions
Benefits of Case Studies in Science Education
Case studies offer several advantages over traditional teaching methods. Here are some key benefits:
- Real-World Application : Case studies present authentic scenarios, enabling students to understand how scientific concepts are applied in real-life situations.
- Critical Thinking : Analyzing case studies requires students to think critically, make connections, and apply scientific knowledge to solve problems.
- Interdisciplinary Approach : Case studies often involve multiple scientific disciplines, fostering an interdisciplinary understanding of complex issues.
- Engagement and Active Learning : Case studies actively engage students in the learning process, promoting active participation, discussion, and collaboration.
- Skill Development : Case studies develop essential skills such as analytical thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication of scientific concepts.
Importance of Practicing Case Study Questions
Practicing case study questions is crucial for Class 9 Science students to enhance their understanding and application of scientific concepts. Here’s why it is important:
- Application of Knowledge : Case studies allow students to apply their theoretical knowledge to practical situations, bridging the gap between theory and real-world scenarios.
- Developing Analytical Skills : Analyzing case studies improves students’ ability to identify relevant information, make connections, and draw logical conclusions.
- Problem-Solving Skills : Case studies present complex problems that require students to think critically and develop effective problem-solving strategies.
- Enhanced Exam Performance : Practicing case study questions familiarizes students with the format and types of questions they may encounter in exams, leading to improved performance.
Subjects Covered in the Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
The case study questions for Class 9 Science cover the following subjects:
- Motion and Forces
- Light and Reflection
- Electricity
- Matter and Its Properties
- Atoms and Molecules
- Structure of the Atom
- Chemical Reactions
- Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Diversity in Living Organisms
- Natural Resources
Tips for Approaching Case Study Questions
To tackle case study questions effectively, consider the following tips:
- Read Carefully : Pay close attention to the details provided in the case study, as they hold crucial information for solving the problem.
- Analyze Methodically : Break down the problem into smaller components and analyze each part systematically.
- Apply Relevant Concepts : Identify the scientific principles relevant to the case study and apply them appropriately.
- Consider Multiple Perspectives : Explore different angles and viewpoints while proposing solutions, taking into account various scientific factors.
- Provide Justifications : Support your answers with scientific explanations and logical reasoning to strengthen your responses.
The Class 9 Science Case Study Questions provided in this article serve as a valuable resource for students seeking to enhance their scientific knowledge and problem-solving skills. By practicing these case studies, students can develop a deeper understanding of scientific concepts and their practical applications. Embrace this opportunity to engage with real-world scenarios and strengthen your scientific acumen.
Q1: Are the Class 9 Science Case Study Questions aligned with the official curriculum?
Yes, the Class 9 Science Case Study Questions presented in this article are aligned with the official curriculum. They cover relevant topics and concepts that students need to study for their exams.
Q2: Can practicing case study questions alone guarantee success in Class 9 Science exams?
Practicing case study questions is an important part of exam preparation, but it should be complemented with a thorough understanding of the subject matter. It is advisable to study the concepts in detail, refer to textbooks, and engage in other learning activities to achieve success in exams.
Q3: Where I Can get Class 9 Science Case Study Questions ?
You can practice Class 9 Science Case Study Questions on schools.studyrate.in for free.
You Might Also Like
Class 9 mcq questions for chapter 3 atoms and molecules with answers, class 9 mcq questions for chapter 9 force and laws of motion with answers, class 9 science case study questions chapter 8 motion, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Expert

Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science PDF Download
Download PDF Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams Exam 2023-24. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions .

Case study questions are based on real or hypothetical scenarios that require students to analyze, evaluate, and apply scientific concepts to solve problems or make informed decisions. They often present a detailed context, providing students with the opportunity to demonstrate their understanding of the subject matter beyond basic recall.
Table of Contents
Class 9 Science: Case Study Questions
The inclusion of case study questions in Class 9 science CBSE is a great way to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving. By working through real-world scenarios, Class 9 Science students will be better prepared to tackle challenges they may face in their future studies and careers. Class 9 Science Case study questions also promote higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and synthesis. In addition, case study questions can help to foster creativity and innovation in students. As per the recent pattern of the Class 9 Science examination, a few questions based on case studies/passages will be included in the CBSE Class 9 Science Paper. There will be a paragraph presented, followed by questions based on it.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Tissues
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Gravitation
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Sound
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
You can find a wide range of solved case studies on cbseexperts, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand the application of various concepts in real-life situations.
Class 9 Science Syllabus
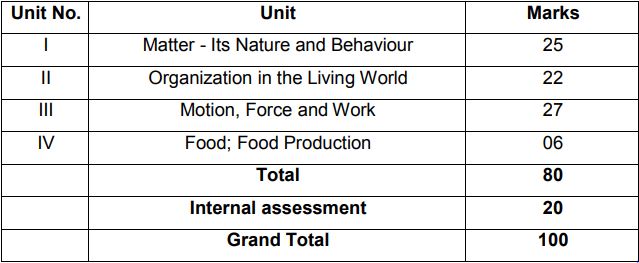
Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour
Definition of matter; solid, liquid, and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of statementing (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation.
Nature of matter: Elements, compounds, and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids, and suspensions. Physical and chemical changes (excluding separating the components of a mixture).
Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of Chemical Combination, Chemical formula of common compounds, Atomic and molecular masses.
Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, Valency, Atomic Number and Mass Number, Isotopes and Isobars.
Unit II: Organization in the Living World
Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number.
Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Unit III: Motio n, Force, and Work
Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, elementary idea of uniform circular motion.
Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration.
Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall. Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy.
Work, Energy and Power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy (excluding commercial unit of Energy).
Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Unit IV: Food Production
Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
Books for Class 9 Science Exams

Benefits of Case Study Questions
- Enhancing Analytical Skills : Case study questions challenge students to analyze complex scenarios, identify relevant information, and derive meaningful insights. By engaging with these questions, students develop critical analytical skills that are essential for scientific thinking and problem-solving.
- Promoting Critical Thinking : Case study questions encourage students to think critically and evaluate different perspectives. They require students to reason, make logical deductions, and justify their answers with supporting evidence. This process helps in honing their critical thinking abilities, enabling them to approach problems from multiple angles.
- Encouraging Practical Application of Concepts : By presenting real-world or hypothetical situations, case study questions promote the application of scientific concepts in practical scenarios. This application-based approach fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter and helps students see the relevance of what they learn in the classroom to everyday life.
Case study questions of Class 9 Science provide students with an opportunity to apply their knowledge, enhance analytical skills, and think critically. By understanding the format, benefits, and effective strategies for answering case study questions, students can excel in this form of assessment. While challenges may arise, practicing time management, improving information extraction skills, and enhancing observation abilities will enable students to overcome these obstacles and perform well. Embracing case study questions as a valuable learning tool can contribute to a holistic understanding of scientific concepts and foster problem-solving abilities.
1. What is the purpose of case study questions in Class 9 Science?
Case study questions serve the purpose of evaluating a student’s understanding of scientific concepts, their ability to apply knowledge in real-life situations, and their analytical and critical thinking skills.
2. How can case study questions help improve analytical skills?
Case study questions require students to analyze complex scenarios, identify relevant information, and derive meaningful insights. Regular practice with such questions can significantly enhance analytical skills.
3. Are case study questions difficult to answer?
Case study questions can be challenging due to their comprehensive nature and the need for critical thinking. However, with practice and effective strategies, students can develop the skills necessary to answer them effectively.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Cbse board result 2024.
- CBSE 10th Result 2024
- CBSE 12th Result 2024
- JAC Board Result 2024
- CG Board Result 2024
- UK Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 9 Study Material
CBSE Class 9 Science Important Case Study Questions with Answers for Term 2 Exam 2022 (PDF)
Check important case study questions of cbse class 9 science to prepare for the cbse term 2 exam 2022. all these questions have been put together by subject experts..

CBSE Class 9 Term 2 Exam 2022: Important case based questions for CBSE Class 9 Science are provided here students to prepare for the upcoming Term 2 Exam 2022. All the questions provided below are curated by the subject experts. These questions are really helpful to revise important concepts and prepare the case study questions for the exam. Answers to all questions have been provided for reference. So, students should practice the chapter-wise questions to clearly understand the right way to attempt the case based questions. Download the chapter-wise questions in PDF.
Check some of the important case study questions below:
Q. Read the following and answer the questions :
A student was asked by his teacher to verify the law of conservation of mass in the laboratory. He prepared 5% aqueous solutions of NaCl and Na 2 SO 4 . He mixed 10 mL of both these solutions in a conical flask. He weighed the flask on a balance. He then stirred the flask with a rod and weighed it after sometime. There was no change in mass.
- Was the student able to verify the law of conservation of mass?
- If not, what was the mistake committed by him?
- In your opinion, what he should have done?
- What is the molar mass of Na 2 SO 4 ?
- No, he could not verify the law of conservation of mass in-spite of the fact that there was no change in mass.
- No chemical reaction takes place between NaCl and Na 2 SO 4 . This means that no reaction actually took place in the flask.
- He should have performed the experiment by using aqueous solutions of BaCl 2 and Na 2 SO 4 . A chemical reaction takes place in this case and a white precipitate of BaSO 4 is formed.
- Will the weight of the precipitate be the same as that of the reactants before mixing?
- If not, what she should have done?
- Which law of chemical combination does this support?
- State the law of conservation of mass.
- No, it will not be the same.
- She should have weighed the total contents of the beaker after the reaction and not the precipitate alone.
- It supports the law of conservation of mass.
- Mass can neither be created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction.
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- SSC GD Result 2024
- WBBSE Result 2024
- wbbse.wb.gov.in Result 2024
- WB Board 10th Result 2024 Jagran Josh
- WB Madhyamik Toppers 2024
- wbresults.nic.in Result 2024
- West Bengal Madhyamik Supplementary Exam 2024
- CGBSE Result 2024
- AP SSC Results 2024 Manabadi by Jagran Josh
- AP SSC Topper List 2024
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 9
Latest Education News
Who Won Yesterday IPL Match: GT vs RCB, Match 52, Check All Details and Latest Points Table
Fastest 50s In IPL History: किसने जड़ा है आईपीएल इतिहास का सबसे तेज़ अर्द्धशतक? देखें पूरी लिस्ट
Personality Test: Your Sleeping Position Reveals Your Hidden Personality Traits
HBSE 10th Result 2024: हरियाणा बोर्ड 10वीं का रिजल्ट bseh.org.in पर जल्द, देखें लेटेस्ट अपडेट
HPBOSE 10th Result 2024: कल सुबह 10 बजे जारी हो सकता है हिमाचल प्रदेश 10वीं का रिजल्ट, hpbose.org पर मिलेगा Direct Link
HP Board 10th Result 2024 Date and Time Soon: Check Latest Updates at hpbose.org
Assam HS Result 2024 Likely Soon, Download AHSEC Mark Sheet at ahsec.assam.gov.in and Check Latest Updates Here
HNGU Result OUT at ngu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Result PDF
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: Only Extremely Observant Can Spot The Teapot In This Park In 8 Seconds!
Gujarat University Result 2024 OUT at gujaratuniversity.ac.in: Direct Link to Download The UG and PG Marksheets
Updated List of Fastest 100 in IPL (2008 - 2024)
IPL 2024 Live Streaming: मोबाइल या टीवी कहां और कैसे देखें आईपीएल का LIVE टेलीकास्ट?
IPL 2024: IPL इतिहास में सबसे तेज गेंद फेंकने वाले गेंदबाज कौन है?
Lok Sabha election 2024: केंद्रीय गृह मंत्री Amit Shah कितनी संपत्ति के मालिक है? देखें पूरी Net Worth
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Only Highly Detail-Oriented Can Spot The Number 6 Among 9's In 6 Seconds!
Most Sixes In IPL 2024: आईपीएल में चौकों-छक्कों की रेस में कौन सबसे आगे? देखें पूरी लिस्ट
Seek and Find Puzzle: Can You Find the Timepiece in This Family Vacation Scene?
Australia T20 World Cup Squad 2024: Complete List of Team Players and Name
Teams With Most ICC Trophies: Check the List of Cricket Teams With Most ICC Tournament Wins In History
Pakistan T20 World Cup Squad 2024: Complete List of Team Players and Name
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science - Pdf PDF Download
Cbse case study questions for class 9 science.
Case based questions for Class 9 Science involve exploring a real-world situation through scientific analysis and inquiry. These questions allow students to make connections between science concepts and the world around them, as well as develop critical thinking skills. For example, a case study may involve challenging a student to determine the cause of an illness in a local population by researching the disease, its symptoms, and the local environment. Through this exercise, students learn how to identify a problem, break it down into parts, and come up with a solution that is supported by evidence. This type of question helps students to understand how science is at the centre of solving real-world problems.
Chapter Wise Case Based Questions for Class 9 Science
Chapter-wise case-based questions for Class 9 Science are a set of questions based on specific chapters or topics covered in the science textbook. These questions are designed to help students apply their understanding of scientific concepts to real-world situations and events.
The CBSE Class 9 Case Based Questions can be accessed from Chapetrwise Links provided below:
Chapter 1: Matter In Our Surroundings
Chapter 2: is matter around us pure.
- Case Based Questions: Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Chapter 3: Atoms And Molecules
- Case Based Questions: Atoms And Molecules
Chapter 4: Structure Of The Atom
- Case Based Questions: Structure Of The Atom
Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit Of Life
- Case Based Questions: The Fundamental Unit Of Life- 1
- Case Based Questions: The Fundamental Unit Of Life- 2
Chapter 6: Tissues
- Case Based Questions: Tissues- 1
- Case Based Questions: Tissues- 2
Chapter 7: Motion
- Case Based Questions: Motion-1
- Case Based Questions: Motion- 2
Chapter 8: Force And Laws Of Motion
- Case Based Questions: Force And Laws Of Motion
Chapter 9: Gravitation
- Case Based Questions: Gravitation
Chapter 10: Work And Energy
- Case Based Questions: Work And Energy- 1
- Case Based Questions: Work And Energy- 2
Chapter 11: Diversity In Living Organisms
Chapter 12: sound, chapter 13: natural resources, chapter 14: improvement in food resource, chapter 15: why do we fall ill.
- Case Based Questions: Why Do We Fall Ill?
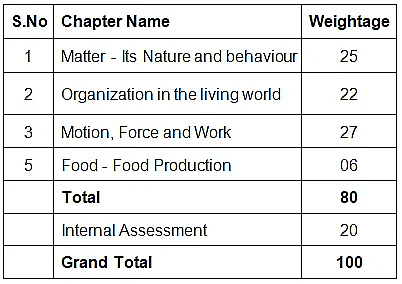
Weightage of Case Based Questions in Class 9 Science
Why are Case Study Questions important in Science Class 9?
- Enhance critical thinking: Case study questions require students to analyze a real-life scenario and think critically to identify the problem and come up with possible solutions. This enhances their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Apply theoretical concepts: Case study questions allow students to apply theoretical concepts that they have learned in the classroom to real-life situations. This helps them to understand the practical application of the concepts and reinforces their learning.
- Develop decision-making skills: Case study questions challenge students to make decisions based on the information provided in the scenario. This helps them to develop their decision-making skills and learn how to make informed decisions.
- Improve communication skills: Case study questions often require students to present their findings and recommendations in written or oral form. This helps them to improve their communication skills and learn how to present their ideas effectively.
- Enhance teamwork skills: Case study questions can also be done in groups, which helps students to develop teamwork skills and learn how to work collaboratively to solve problems.
In summary, case study questions are important in Class 9 because they enhance critical thinking, apply theoretical concepts, develop decision-making skills, improve communication skills, and enhance teamwork skills. They provide a practical and engaging way for students to learn and apply their knowledge and skills to real-life situations.
Class 9 Science Curriculum at Glance
The Class 9 Science curriculum in India covers a wide range of topics and concepts. Here is a brief overview of the Science curriculum at a glance:
- Physics: The Physics section includes topics such as motion, force, work and energy, sound, and light.
- Chemistry: The Chemistry section includes topics such as matter, atoms and molecules, structure of the atom, and chemical reactions.
- Biology: The Biology section includes topics such as cell structure and functions, tissues, diversity in living organisms, natural resources, and environmental management.
- Practical Work: The Science curriculum also includes practical work, where students perform experiments to observe and understand scientific phenomena.
The Class 9 Science curriculum is designed to provide a strong foundation in science and prepare students for higher education in the field. The curriculum is structured to develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills, and to promote the application of scientific concepts in real-life situations. The curriculum is also designed to help students prepare for competitive exams and develop a strong scientific base for future academic and professional pursuits.
Students can also access Case Based Questions of all subjects of CBSE Class 9
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Maths
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Social Science
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 English
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Hindi
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Sanskrit

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Case Based Questions for Class 9 Science
Are case-based questions on the class 9 science exam.
Yes, case-based questions are often included in science exams at the class 9 level as they test students' ability to apply their scientific knowledge and skills to real-world situations.
How are case-based questions different from traditional science questions?
Traditional science questions typically focus on testing students' knowledge of specific facts, concepts, and theories. Case-based questions, on the other hand, require students to use their knowledge and understanding to analyze and interpret real-world situations and make informed decisions.
How can students prepare for case-based questions in science?
To prepare for case-based questions in science, students should practice analyzing data and interpreting scientific experiments. They should also work on developing their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Top Courses for Class 9
Faqs on cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf, study material, cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf, video lectures, past year papers, semester notes, practice quizzes, extra questions, previous year questions with solutions, sample paper, shortcuts and tricks, mock tests for examination, objective type questions, viva questions, important questions.

CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science - Pdf Free PDF Download
Importance of cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf, cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf notes, cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf class 9, study cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 13 - Why Do We Fall ill

CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter-13 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
Important questions science class 9 chapter 13 are prepared by the experts of Vedantu. Students are provided with ultimate study materials to perform better in the examination. Science chapter 13 why do we fall ill of class 9 deals with the health of a human being. It teaches the importance to stay healthy and prevent us from falling sick. It focuses on the significance of staying fit and healthy. It casts light on the importance of daily hygiene to keep diseases at bay. Register Online for Class 9 Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in your examination. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions ,they can download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions for other chapters:

Study Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 - Why Do We Fall Ill
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. Which one of the following is not important for individual health?
Living in clean space
Good economic condition
Social equality and harmony
Living in a large and well-furnished house.
Ans: a. Living in clean space
2. ‘Penicillin’, a lifesaving antibiotic, was discovered by
Alexander Fleming
Edward Jenner
H.G. Khorana
William Harvey.
Ans: a. Alexander Fleming
3. Making anti-viral drugs is more difficult than making anti-bacterial medicines because-
Viruses make use of host machinery.
Viruses are on the border line of living and non-living
Viruses have very few biochemical mechanisms of their own
Viruses have a protein coat.
Ans: c. Viruses have very few biochemical mechanisms of their own.
4. Which one of the following deficiency disease?
Ans: c. Goitre
5. The chemical that kill or stop the growing of certain kinds of microbes are called-
Antibiotics
Ans: c. antibiotics
6. Choose the wrong statement –
High blood pressure is caused by excessive weight and lack of exercise.
Cancers can be caused by genetic abnormalities.
Peptic ulcers are caused by eating acidic food.
Acne is not caused by staphylococci.
Ans: d. Acne is not caused by staphylococci.
7. Rabies occurs through the bite of.
Female Anopheles Mosquito
Female culex mosquito
Ans: c. Rabid dog
8. AIDS is caused by –
Ans: b. Virus
9. Identify a protozoan disease –
Ans: d. Amoebiasis
10. If you live in a overcrowded and poorly ventilated house, it is possible that you may suffer from which of the following diseases.
Air borne diseases
Ans: c. Air borne diseases
11. The symptom of goitre is
Swelling of eye
Swelling of the thyroid gland
Swelling of the liver
Swelling of the limbs.
Ans: b. Swelling of the thyroid gland
12. Which one of the following does not help in the prevention of AIDS?
Use of disposable syringes.
Safe sex practiced between single partners.
Proper screening of blood before transfusion
Using same syringe again and again
Ans: d. Using same syringe again and again
13. You are aware of Polio Eradication Programme in your city. Children are vaccinated because –
vaccination kills polio causing micro-organisms
Prevents the entry of polio causing micro-organisms
It creates immunity in the body.
all the above.
Ans: c. It creates immunity in the body.
14. ‘BCG’ vaccine is given to infants for protection against –
Tuberculosis
Ans: c. Pneumonia
15. Which one is not sexually transmitted disease?
Ans: d. Diabetes.
16. Which one of the following causes kala-azar?
Trypanosome
Ans: c. Leishmania
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. State any two conditions essential for good health.
Ans: The two conditions essential for good health are:
i. Clean and Hygienic surroundings
ii. A sound physical, mental and social state
2. State any two conditions essential for being free of disease.
Ans: The two conditions essential for being free of disease are:
i. Personal as well as domestic hygiene
ii. Consuming a balanced diet
3. Are the answers to the above questions necessarily the same or different? Why?
Ans: The answers to the above questions are different as a person may be disease free but does not have a good physical, mental or social state which lead to a poor health.
4. How many times did you fall ill in the last one year? What were the illnesses?
a. Think of one change you could make in your habits in order to avoid any of/most of the above illnesses.
Ans: I fell ill twice last year. I had suffered from viral fever and typhoid.
In order to prevent myself from getting infected again in future, I will avoid street food especially those cooked at unhygienic places and are kept uncovered. Also, I will drink filtered or boiled water.
b. Think of one change you would wish for in your surroundings in order to avoid any of/most of the above illnesses.
Ans: In order to prevent myself from getting infected again in future, I shall keep my surroundings cleaner than earlier and also maintain my personal hygiene.
5. A doctor/nurse/health-worker is exposed to more sick people than others in the community. Find out how she/he avoids getting sick herself/himself.
Ans: A doctor/nurse/health-worker is exposed to more sick people than others in the community, still they prevent themselves from getting sick as they take proper care of their personal hygiene as well as domestic hygiene. Also, they maintain clean and immune surroundings to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
6. A baby is not able to tell her/his caretakers that she/he is sick. What would help us to find out
a. that the baby is sick?
Ans: If the baby is crying continuously and remains restless for a long time despite providing comfort then he/she might be sick.
b. What is the sickness?
Ans: We should observe the symptoms and its severity to diagnose the sickness.
7. Under which of the following conditions is a person most likely to fall sick?
(a) when she is recovering from malaria.
(b) when she has recovered from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox.
(c) when she is on a four-day fast after recovering from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox. Why?
Ans: A person is most likely to fall sick when she is on a four-day fast after recovering from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox because during her fast she must have consumed a limited diet and hence less nutrition is given to her body. Also, she is at a high risk of getting infected from chicken-pox while taking care of someone suffering from it. Therefore, we can state that her health is poor and she is very likely to fall sick again.
8. Under which of the following conditions are you most likely to fall sick?
(a) when you are taking examinations.
(b) when you have travelled by bus and train for two days.
(c) when your friend is suffering from measles. Why?
Ans: We are most likely to fall sick when our friend is suffering from measles since measles is an infectious/communicable disease which can be easily spread from person to person.
9. How are acute diseases different from chronic diseases?
Ans: Acute disease are diseases which are sudden but severe and last for short periods of time. For example: Malaria, Jaundice, etc.
Chronic disease are diseases which develop gradually over a period of time and are long lasting causing damage to the organs of the body. For example: Cancer, Diabetes, etc.
10. What is the full form of AIDS? Name the causal organism.
Ans: The full form of AIDS is Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. AIDS is caused by HIV – Human Immunodeficiency virus.
11. Define the following terms:
Ans: Health is defined as a sound state of physical, mental and social well-being and it does not relate to the absence of disease.
(b) disease.
Ans: Disease refers to the malfunctioning of the organs or parts of the body due to internal dysfunctions or external factors.
12. What are non-communicable diseases? Give examples.
Ans: Non-communicable diseases are non-infectious diseases which cannot be spread from one person to another and are long-lasting.
For example – Diabetes, cancer.
13. Define carriers. Give two examples.
Ans: Carriers are the organisms that carry disease causing agents and has the ability to spread the disease amongst healthy individuals without showing any sign of disease
For example – Housefly, female insect Anopheles.
14. Why do children need vaccination?
Ans: Vaccination is important for children because it protects them from getting infected by deadly diseases like tetanus, polio and also prevents the spread of these diseases from child to child.
15. How can we prevent influenza?
Ans: Influenza is an air-borne disease, therefore it can be prevented by maintaining a distance from the others and washing your hands regularly.
16. State giving reasons whether the following statements are correct or not.
Health is only the absence of any physical disease.
Ans: This statement is incorrect because health is a state of sound physical, mental and social well-being. Hence, being disease free does not ensure that the person has a good health.
Children need not be immunized.
Ans: This statement is incorrect because there is a need to immunize children as their immune system is not fully developed and so they are more susceptible to diseases.
17. What is peptic ulcer?
Ans: Peptic ulcer is a disease in which ulcers or sores are formed on the lining of your stomach or duodenum and the person suffers from pain due to acidity.
18. What are the different types of diseases? Explain them.
Ans: Diseases are broadly classified into two types –
Communicable or infectious disease – Those diseases which are spread from one person to another in contact and it generally lasts for a short term. It can be spread through air, water, food, physical contact and insects.
For example: Chicken pox, malaria, cholera, etc.
Non-communicable or non- infectious diseases – Those diseases which cannot be spread from person to person and are long-lasting. For example - arthritis, marasmus etc.
19. Which bacterium causes peptic ulcers? Who discovered the above pathogen?
Ans: Helicobacter pylori bacterium causes peptic ulcers and it was discovered by Robin Warren and Barry Marshall.
20. Name the target organs for the following disease-
Hepatitis targets ______________
Fits or unconsciousness targets __________________
Pneumonia targets _________________
Fungal disease targets ______________
21. How are diseases diagnosed by physician?
Ans: When a person is infected from a disease, it may cause malfunctioning of organs or body parts which produces external symptoms of diseases. On the basis of the symptoms and physical examination of the person, the disease is diagnosed by the physician.
22. Who discovered ‘vaccine’ for the first time? Name two diseases which can be prevented by using vaccine.
Ans: Vaccine was discovered by a surgeon, Edward Jenner. Two diseases which can be prevented by using vaccines are polio and tetanus.
23. Name the approaches generally adopted to treat infectious diseases.
Ans: Infectious diseases can be treated by two ways:
By reducing its effect using medications that may reduce its symptoms.
By killing its cause using antibiotics.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
1. Why are we normally advised to take bland and nourishing food when we are sick?
Ans: When we are sick, our body becomes fragile and our digestion process also becomes poor. Hence, we are advised to take bland and nourishing food when we are sick because we need complete nourishment for faster recovery.
2. What are the different means by which infectious diseases are spread?
Ans: Infectious diseases can spread by the following means:
Through contaminated food and water
Through atmosphere
Through vectors or carriers (housefly, mosquito etc)
Through direct skin contact or sexual contact
Through cuts or wounds
3. What precautions can you take in your school to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases?
Ans: To reduce the incidence of infectious diseases, I would take the following precautions in my school:
Maintain distance from an infected person
Keep my surroundings clean
Wash my hands regularly.
I would not consume open/uncovered food materials
4. What is immunisation?
Ans: Immunisation is a method in which an immunized person develops resistance towards a specific disease.
In this method weak or dead microbes of a specific disease are injected into the body such that they develop memory lymphocytes (WBCs) but do not cause disease. For example: vaccination against polio, tetanus etc.
5. What are the immunisation programmes available at the nearest health centre in your locality? Which of these diseases are the major health problems in your area?
Ans: The immunisation programmes available at the nearest health centre in our locality are as follows:
For infants: DPT, polio, measles
For children: TT, TAB, smallpox
Hepatitis-B for pregnant women
The diseases like typhoid, measles, smallpox, polio are the major health problems in our area.
6. List any three reasons why you would think that you are sick and ought to see a doctor. If only one of these symptoms were present, would you still go to the doctor? Why or why not?
Ans: If we have continuous headache, stomach ache, loose motions, fever, cough and cold, then we would consult a doctor. If only one of these symptoms were present continuously for a period of time then also we will go to see the doctor as it may be the initial signs of a severe disease.
7. In which of the following case do you think the long-term effects on your health are likely to be most unpleasant?
if you get jaundice
if you get lice
if you get acne.
Ans: If I suffer from jaundice, I believe that its long-term effects on our health are likely to be most unpleasant because the symptoms severely affect our body parts and the internal organs and persist for a long time.
8. Conduct a survey in your neighbourhood to find out what the three most common diseases are. Suggest three steps that could be taken by your local authorities to bring down the incidence of these diseases.
Ans: Three most common diseases in my locality are diarrhoea, malaria and tuberculosis.
To bring down the incidence of these diseases I would suggest the following steps:
Supply of safe drinking water and closed drains.
Hygienic and clean environment.
Eradication of mosquitoes
Immunisation or vaccination camps
9. Why are antibiotics not effective for viral disease.
Ans: Viruses are different from bacteria. They do not have cell walls which can be attacked by antibodies. Thus, antibodies are ineffective against viral disease. Antibiotics tend to break the bacterial cell wall and block the bacterial pathways. Thus, they are effective on bacterial infections.
10. What is inflammation? What are the changes occur during inflammation?
Ans: Inflammation is a process carried by the immune system in which it recruits many cells to the affected tissue during an injury or burn to kill the disease-causing germs and protect the tissue from external pathogens.
During this process, swelling, pain and redness may develop.
11. Why do some children fall ill more frequently than others living in the same locality?
Ans: It is the immune system which protects our body from various diseases and infections. Children tend to fall ill more frequently because they have a poor or not a well-developed immune system.
A balanced diet, proper sleep and exercise would help children develop a strong immune system.
12. How can the disease be prevented?
Ans: Diseases can be prevented by taking the following measures–
By avoiding crowded places
By maintaining public hygiene
By washing our hands regularly
By consuming a balanced diet and maintaining personal hygiene.
By immunization.
13. Give two examples for each of the following:
Chronic Diseases
Ans: Chronic diseases – Diabetes, arthritis
Infectious Diseases
Ans: Infectious diseases – Chicken pox, Influenza
Non-infectious Diseases.
Ans: Non-infectious diseases – asthma, obesity
14. Give difference between vaccines and antibiotics.
Ans: Difference between vaccines and antibiotics is stated as follows:
15. The body of a patient has lost its power of fighting against infections. Which disease may the patient be suffering from? Name the pathogen and describe any two modes of its transmission from the patient to other person.
Ans: The patient is suffering from AIDS, i.e., Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
AIDS is caused by HIV – Human Immunodeficiency virus.
Two modes of transmission are
By sexual contact with an infected person.
By the use of an infected syringe or needle.
16. What are the conditions favouring for air-bone diseases?
Ans: Conditions favouring for air-borne infections -
Close contact with the infected person.
Over – crowding
Poor – Ventilation
17. What are the various dimensions of health?
Ans: Various dimensions of health are as follows–
Physical Dimensions- It implies perfect functioning of all the organs and parts of the body.
Mental Dimensions – It implies a state of mental balance, harmony and peace between the individual and his environment.
Social Dimensions – A person is socially sound if he shares a good bond with his surroundings and the people around him, i.e., if he has a good job, a good house, a happy family, helpful friends.
18. What are the causes of diseases?
Ans: Causes of diseases are –
Microorganisms – Bacteria, virus, fungi, protozoa and worms cause most of the communicable diseases.
Malfunctioning of parts of the body or body organs.
Nutritional deficiency.
Genetic factors.
Polluted environment.
19. Give the schedule of immunization for infants and children up to six years.
Ans: The schedule of immunization for infants and children up to six years is given below:
20. Explain giving reasons –
Balanced diet is necessary for maintaining health body.
Ans: Balanced diet contains all the nutrients required for maintaining proper health as well as they are needed for growth and repair of the damaged cells.
Health of an organism depends upon the surrounding environmental conditions.
Ans: Surrounding environmental conditions plays an important role in the maintenance of health. For example we feel uneasy if –
Our surroundings are dirty and the garbage is not collected or disposed off.
Drains are not cleaned and water gets collected in the streets or open spaces.
21. What is immunization, immune system, immunity?
Immune system is a system which protects the body against pathogens which may lead to infections.
Immunity refers to our body’s power to resist and overcome infection.
22. Name the agents and the diseases caused by them?
Ans: A list of agents and the disease caused by them is given below:
What are the different aspects of maintaining good health?
Ans: Different aspects for maintaining good health-
Community health – Keeping our surrounding clean and hygienic contributes to our personal health.
Maintaining personal hygiene by washing our hands continuously and avoiding close contact and overcrowded places.
Regular exercise and a proper sleep are very necessary to keep the mind and body fit. Also, relaxation is very essential for good health.
Optimum nutrition through a balanced diet is essential for maintenance of good health. One should avoid the consumption of junk food to maintain good health.
CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
The importance of health.
Health is the state of being well enough to function well physically, mentally as well as socially. Health cannot be achieved entirely on our own because it depends on the surrounding the organism.
The surrounding has a great impact on the health of a human being. Human beings live in a society. Consider what would happen if there is no garbage collector to collect the garbage and everyone throw garbage around their houses. Within a few days, the place will start to stink and everyone will fall sick. This will have a huge impact on the physical, mental as well as on the social health of the people living in that area.
We need food to stay healthy and fit. Food can be earned by doing work. For this, there should be opportunities to do work. One also needs to stay happy to be healthy. Happiness can cure many illnesses and it gives mental as well as physical fitness to the body. Social equality and harmony also play a very pivotal role in the health of an individual.
The Difference Between Staying Healthy and Disease Free
Disease means being uncomfortable. When we see a person suffering from a disease we can find a particular cause for the discomfort. But whereas when a person is not in a good health we cannot find the actual suffering from any disease.
In simple words, not being diseased is not the same as being healthy. When we think about good health then we think about societies and also communities. On the other hand, when we think about a disease we always think about the suffering of an individual.
Types of Disease
There are two types of disease. One is an acute disease and the other one is a chronic disease. The disease which lasts for a very short period is known as acute diseases. Common cold or viral fever is an example of an acute disease.
The diseases which last for a very long period are known as a chronic disease. Chronic diseases can also last for a lifetime. The infections causing elephantiasis which is very common in the parts of India and Africa is an example of chronic disease.
Any disease can have a great effect on the health of an individual. An acute disease that gets over in a very short period does not have a major impact on the health of a human being. Whereas chronic diseases which take a very long period sometimes the whole life have a very great impact on the body. Chronic disease disrupts the mental health of the individual.
Causes of a Disease
There are two types of causes of disease. One is the infectious cause and the other is the non-infectious cause. It is very crucial to keep public health as well as community health in mind when one thinks about the cause of the disease. When microbes or microorganisms are the reason behind a disease then that disease is known as infectious disease.
The microbes spread in the community and also the disease they cause also spreads with them. Conductivities are an example of an infectious disease. On the other hand, some diseases are not caused by infectious agents such as microorganisms. Such diseases are called non-infectious diseases. The causes of non-infectious diseases vary with the situation.
For example, cancer is a type of non-infectious disease because it is caused by genetic abnormalities. High blood pressure is also an example of a non-infectious disease because it is caused by excessive weight and lack of exercise.
The prevention, treatment, and causes of disease at the community level will be different for different diseases.
Means of Spread of a Disease
Diseases can be spread in very different ways. Different diseases are spread in different ways. Some diseases spread through water. When the excreta from someone suffering from an infectious gut disease such as cholera gets mixed with the drinking water then the person drinking that water gets cholera.
The microbes causing cholera will enter the body of the person drinking and will have a huge impact on the health of the human being. Such diseases are usually spread when there are no safe drinking water supplies.
The sexual act is one of the closest physical contacts between two people. Infectious diseases like AIDS or Syphilis are transmitted by sexual contact from an infected partner. AIDS can also spread through the blood to blood contact with the infected person. It can also spread from an infected mother to the baby during the pregnancy or through breastfeeding. Casual physical contact such as handshakes, hugs, or wrestling can also cause communicable disease if a healthy person comes in contact with an infected person.
Humans live in an environment that is full of various creatures. Many diseases are spread through various animals to humans. Some animals carry infectious agents from a sick person to another potential host. Such animals are the intermediaries and are called vectors. Mosquitoes are the vectors that transfer the disease from an infected person to a healthy person.
Principles of Treatment
One way to treat disease will be to reduce the effect of the disease and the other way will be to kill the cause of the disease. In the first case, we provide with required treatment that will reduce the symptoms of the disease. The symptoms usually occur because of the inflammation. For example, when we have a fever we take medicines and take bed rest.
The other way is to kill the microbes causing the disease. Microbes can be classified into different categories like viruses, bacteria, fungi, or protozoa. These microbes causing illness are killed by using anti-bacterial medicines or anti-viral medicines. It is hard to make an antiviral drug but it is easy to make an anti-bacterial drug.
Viruses have few biochemical mechanisms. They enter the cell of a human being and use the machinery for their life process. This means there are few virus-specific targets to aim at.
Despite these limitations are very few effective antiviral drugs because of the development in medical science. There are anti-viral drugs to keep HIV infections under control.
Why Study Important Questions class 9 from Vedantu?
Vedantu is one of the best education platforms where all the study materials are procured by experts. Why do we fall ill class 9 important questions are prepared by Vedantu especially for the students to get a clear concept of the topics.
Vedantu's important questions for class 9 chapter 13 tell the students about what type of questions they should expect to face in their exams. All the questions provided by us are available online as well as online. One can go through the notes and also the questions to practice and get a revision anytime.
The important questions for class 9 are prepared by the most experienced teachers of Vedantu also help every student to revise for the upcoming exams. Students can practice with questions to score good marks in the upcoming examination. Why do we fall ill class 9 important questions are provided to the students for their better understanding.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 9

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 13 - Why Do We Fall ill
1. Write a Short Note on Peptic Ulcers.
Ans: For many long years people use to think that peptic ulcers are caused because of the lifestyle reasons of an individual. Peptic ulcers are a disease that causes acidity related pain as well as bleeding in the stomach and duodenum. This leads to indigestion in the stomach of the individual suffering from peptic ulcers.
Everyone used to think that too much stress led to a lot of acid secretion in the stomach which causes peptic ulcers. Then two Australians discovered that a bacterium named Helicobacter pylori was responsible for causing peptic ulcers in the stomach.
Robin Warren born in 1937 and Barry Marshall born in 1951 who was a young clinical fellow made this discovery. A peptic ulcer is not a chronic disease. It is a disease that can be cured in a short period with antibiotics.
2. Write in Brief about Immunization.
Ans: The traditional Indian as well as the Chinese medicinal systems sometimes deliberately rubbed the skin crusts from smallpox victims into the skin of the healthy person. This was done to create a resistance against the disease into the body of the healthy person.
Two centuries ago an English physician named Edward Jenner realized that maids who have cowpox did not catch smallpox. Cowpox is a very mild disease. Jenner then deliberately gave cowpox to people and found out that it was a resistance to smallpox.
This happened because the smallpox virus was very closely related to the cowpox virus. ‘Cow’ is ‘Vacca’ in Latin and cowpox is ‘vaccinia’ and this is how the word ‘vaccination’ came into usage.
3. Name any two groups of microorganisms from which antibiotics could be extracted.
Ans: Antibiotics are pharmaceutical drugs, produced to destroy or prevent the growth of the disease-causing bacteria in the human and animal body. Bacteria and Fungi are two groups of microorganisms that help make antibiotics. Various variants of bacteria and fungi are used in making antibiotics merged along with different chemicals that can effectively treat a particular illness. Antibiotics are of numerous types like tablets, syrups, and capsules and are consumed in different manners.
4. Why are we advised to take bland and nourishing food when we are sick?
Ans: Sickness results in weak digestion and low immunity, so doctors recommend us to take bland food that is easy on our stomach and nourishing food that refuels our immune system. Fruits and other edibles rich in vitamins are also suggested for a rapid recovery. It is essential to take easy-to-digest and fulfilling food along with the prescribed medicines for a quick recovery. Though the type of food intake may differ for certain illnesses.
5. Why is AIDS considered to be a ‘Syndrome’ and not a disease?
Ans: AIDs stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. If a person suffers from AIDS, then they experience symptoms like fever, weakness, weight loss, etc. A syndrome refers to a set of health issues that combine to make a disease. Hence, due to the regular symptoms of certain health problems AIDS is considered to be a syndrome and not a disease. It is to be noted that various treatments have been discovered that ease the symptoms but AIDS cannot be fully cured.
6. Why are antibiotics not effective for viral diseases?
Ans: Antibiotics are medicines formed using chemicals and extracts from bacteria and fungi used to treat various illnesses. Antibiotics treat bacterial infections by destroying the cell walls of the bacteria. Viruses do not have a cell wall which is why viral diseases cannot be treated with antibiotics. One can recover from viral diseases by building the immune system by eating healthy. The medicines help with certain symptoms but nourishing food is the main requirement in assisting the body fight the viruses responsible for the disease.
7. Why do we fall ill (Chapter 13 of Class 9 Science, Important question)?
Ans: We often suffer from acute diseases like the common cold and so on owing to the attacks of viruses or bacteria, lack of public health services, and inadequate nourishment. It is essential to look after ourselves and take preventive measures to avoid falling sick. Medicinal science has grown to provide us with various vaccines for deadly diseases while other common diseases can be treated with medicines and healthy food and sanitary habits.
CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall ill
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (biology) Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall ill are given below. In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 9 science textbook. Class 9 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 13 provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free from our app.
Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Textbook Questions and Answers
INTEXT QUESTIONS
PAGE NO. 178
Question 1: State any two conditions essential for good health.
Answer: ‘Health’ is a state of being well enough to function well physically, mentally and socially. Therefore, for good health. (i) One should be disease free. (ii) There should be social equality and harmony which are essential for individual health particularly for social and mental health.
Question 2: State any two conditions essential for being free of disease.
Answer: The twoconditions essential for being free of diseases are:
(i) Personal hygiene and cleanliness are necessary to stay away from diseases.
(ii) Individuals should take a balanced diet that contains carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, fibres, and proper quantity of water.
Question 3: Are the answers to the above questions necessarily the same or different? Why?
Answer: No. The answers to the above questions may not necessarily be the same. This is because a disease free state is not the same as being healthy. Good health is the ability of an individual to realise his or her full potential. Individuals can have poor health without having any identifiable disease. Also, health is related to society and community, whereas having a disease is about an individual sick person. Hence, the conditions for good health and for being disease free can be same or even different.
PAGE NO. 180
Question 1: List any three reasons why you would think that you are sick and ought to see a doctor. If only one of these symptoms were present would you still go to the doctor? Why not?
Answer: Common symptoms, which indicate sickness are: (i) Headache, (ii) Cough and (iii) Loose motion.
Even seeing one symptoms. I will go to doctor.
Reason: A single symptom is the sign of a disease. On delaying, it may lead to serious illness. For example, headache may mean meningitis.
Question 2: In which of the following case do you think the long – term effects on your health are likely to be most unpleasant?
- If you get jaundice.
- If you get lice.
- If you get acne.
Answer: Jaundice because it is a chronic disease and takes long time to be cured. Moreover, jaundice affects the whole body and it takes long time to be healthy.
PAGE NO. 186
Question 1: Why are we normally advised to tale bland and nourishing food when we are sick?
Answer: Infectious disease show a lack of success of the immune system of the body. For the functioning of immune system properly, sufficient nourishment and easily digestible food is necessary for a sick person.
Question 2: What are the different means by which infectious diseases are spread?
Answer: Diseases can be spread through various means such as air, water, sexual contact, blood, and vector.
(i) Certain disease-causing micro-organisms are expelled in air by coughing, sneezing, talking, etc. These micro-organisms can travel through dust particles or water droplets in air to reach other people. For example, tuberculosis, pneumonia, etc. spread through air.
(ii) Sometimes causal micro-organisms get mixed with drinking water and spread water borne diseases. Cholera for example is water borne disease.
(iii) Sexual act between two people can lead to the transfer of diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhoea, AIDS, etc.
(iv) Certain diseases such as AIDS can spread via blood to blood contact during blood transfusion or pregnancy.
(v) Certain diseases spread by animals called vectors. For example mosquitoes spread malaria.
Question 3: What precautions could you take in your school to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases?
Answer: Precautions to reduce incidence of infectious diseases are:
(i) Preventing over crowing classes, (ii) Providing safe drinking water, (iii) Cleanliness in the school premises and also in the classroom, (iv) Use of handkerchief or towel while an infected student in sneezing or coughing, (v) Use of clean toilets, (vi) Not to allows water to stagnate in school or around the school to avoid mosquito breeding, (vii) To get vaccinated whenever programmers organized in the for inoculation against various diseases. (viii) Not eating food exposed to flies, mosquitoes etc.
Question 4: What is immunization?
Answer: Introduction of mild type of infection (microbes) or killed infectious microbes into the body by vaccination / by other means to activate the immune system against a particular infection / disease is called immunization.
Question 5: What is the immunization programme available at the nearest health center in your locality?
Which of these diseases are the major health problems in your area?
Answer: Immunization programme (i) BCG vaccine against tuberculosis. (ii) Polio drops against polio. (iii) Vaccination against chicken pox. (iv) Vaccination against Hepatitis. (v) DPT vaccination against diptheria, pertusis (whooping cough) and tetanus. (vi) Immunisation against measles.
Major health problems are (i) Hepatitis, (ii) Chicken pox, (iii) Tuberculosis, and (iv) Tetanus
Question 1. How many times did you fall ill in the last one year? What were the illnesses? (a) Think of one change you could make in your habits in order to avoid any of/ most of the above illnesses. (b) Think of one change you would wish for in your surroundings in order to avoid any of/most of the above illness.
Answer: The illness was 2-3 times, common-cold, occurred in a year. (a) One change I would make in my habits in order to avoid the above illness is that I would take a proper diet rich in vitamin C and would avoid too cold food. (b) The surroundings should be neat, and clean,
Question 2. A doctor/nurse/health worker is exposed to more sick people than others in the community. Find out how she/he avoids getting sick herself/himself?
Answer: A doctor/nurse/health worker when exposed to sick people they keep their nose and mouth covered, take care of hygiene, wash hands with soap before drinking water or eating food. They use mask, gloves, etc to avoid direct contact with the person suffering from infectious diseases.
Question 3. Conduct a survey in your neighbourhood to find out what the three most common diseases are. Suggest three steps that could be taken by your local authorities to bring down the incidence of these diseases.
Answer: The following three are the most common diseases in any neighbourhood: Cold and cough, loose motions, and malaria. Some of the preventive measures that can be taken are:
(a) By drinking fresh, uncontaminated, and clean water. (b) By maintaining hygienic-sanitary conditions. (c) By educating people about various preventive measures with the help of posters, and pamphlets.
Question 4. A baby is not able to tell bis/her.caretakers that she/he is sick. What would help us to find out (a) that the baby is sick? (b) what is the sickness?
Answer: (a) The symptoms like body temperature, fever, cough, cold, loose-motions, non-stop crying improper or no food intake etc. would help up to find that the baby is sick. (b) The symptoms could help us to find out the sickness of the body.
Question 5. Under which of the following conditions is a person most likely to fall sick? (a) When she is recovering from malaria. (b) When she has recovered from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox. (c) When she is on a four-day fast after recovering from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox. Why?
Answer: (c) When she is on a four-day fast after recovering from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox.
As the person is not taking a proper diet which is required for her proper health and healing of the body. Her chances of getting chicken-pox also high as her body’s immunity have lowered.
Question 6. Under which of the following conditions are you most likely to fall sick? (a) When you are taking examinations. (b) When you have travelled by bus and train for two days. (c) When your friend is suffering from measles. Why?
Answer: (c) When your friend is suffering from measles, as it is an infectious disease.
A person can most likely fall sick when his/her friend is suffering from measles. It is a highly contagious disease and can easily be transferred through air and respiration. It is always better to stay away from your friend who is affected with measles, else even you may get infected with the disease.
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall ill?
CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 13 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 PDF
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 9
- NCERT 9 Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
Ncert solutions for class 9 science updated for 2023-24 free chapterwise pdf download.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science help students to clear any doubts instantly and efficiently. These NCERT Solutions guide students to learn the important concepts which are included in the CBSE Class 9 Science syllabus. Students are required to solve the exercise questions included in the textbook to create a proper understanding of the topics.
While solving the textbook questions, doubts arise among students. The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 come in handy at such times, as they include precise explanations and detailed answers to those questions. These CBSE Science NCERT Solutions for Class 9 cover solutions to all the important chapters included in the textbook, like Matter, Atoms, Tissues, Living Organisms, Motion, Force, Laws of Motion, Gravitation, Energy and Work, Sound, Natural Resources, etc.
Along with answers to the textbook questions, these solutions provide you with extra questions, exemplar problems, the important questions from previous year question papers, sample papers , worksheets, MCQs, short answering questions, descriptive type questions, their solutions, as well as tips and tricks.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter-Wise PDFs
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science are provided in a format for better accessibility to the students. These solutions serve as an important studying tool for students who are preparing for their board examinations and assignments.

NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Book Chapter Brief
Chapter 1: matter in our surrounding.
The Class 9 science textbook starts with the chapter “Matter in Our Surroundings”. Everything that we see around us is made up of material which is called matter. These things occupy space and have mass. Earlier, Indian philosophers had classified matter into 5 basic elements called Panch Tatva – air, water, earth, sky and fire. Now, modern scientists have come up with 2 types of classification, i.e., based on physical property and chemical nature. In this chapter, students will learn about the physical properties of matter .
The matter is made up of particles and these particulars are very small. The particles of matter have space between them, they are continuously moving and attract each other. The matter around us exists in 3 different states – solids, liquids and gases. These states of matter arise due to variation in the characteristic of the particles of matter. All the 3 states of matters have been explained in-depth with the help of activities. Further, the textbook explains that the state of matter is inter-convertible. The state of matter can be changed by changing temperature or pressure. The phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapour at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation. The rate of evaporation depends upon the surface area exposed to the atmosphere, the temperature, the humidity and the wind speed. Evaporation also causes cooling.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding :
Definition of matter; solid, liquid and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of state – melting (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding at BYJU’S:
- Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes – Chapter 1
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings
Chapter 2: Is Matter Around Us Pure?
This chapter of NCERT Class 9 Science students will teach about mixtures, solutions, properties of solutions, separation of mixtures, and physical and chemical changes. Along with this, they will also learn about compounds and their properties, the difference between mixtures and compounds, the classification of matter, etc.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure? :
Nature of matter: Elements, compounds and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids and suspensions. Physical and chemical changes (excluding separating the components of a mixture).
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure? at BYJU’S:
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure? Notes
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 2 – Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 2 – Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Chapter 3: Atoms and Molecules
In NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 3, students will learn the laws of chemical combination , atoms and molecules. They will get to know how to write a chemical formula, molecular mass and mole concepts and some numerical problems related to these concepts.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules :
Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of Chemical Combination, Chemical formula of common compounds, Atomic and molecular masses.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules, at BYJU’S:
- Atoms And Molecules Class 9 Notes – Chapter 3
- Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 – Atoms and Molecules
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 3 – Atoms And Molecules
Chapter 4: Structure of the Atom
This chapter of NCERT Class 9 Science deals with the various atomic models of atoms that were proposed by different scientists. In addition to it, this chapter also covers electrons’ distribution in different orbits, calculation of valency , atomic number and mass number.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom :
Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, Valency, Atomic Number and Mass Number, Isotopes and Isobars.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom at BYJU’S:
- Structure of the Atom Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 4
- Important Questions of CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 4 – Structure of the Atom
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 4 – Structure of the Atom
Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit of Life
This chapter is related to Biology. In this chapter, students will get to know that the cell is the fundamental unit of life. The whole chapter revolves around the cell and its structural organisation, in which students will learn about the plasma membrane , cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm and structure of an animal cell.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life :
Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life at BYJU’S:
- The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 5
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 5 – The Fundamental Unit of Life
Chapter 6: Tissues
This chapter pertains to the basic definition of tissue and then elaborates on Plant and Animal tissue with proper diagrams. Students will get to know the different types of plant and animal tissues with a detailed explanation of each.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues :
Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 6 Tissues at BYJU’S:
- Tissues Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 6
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 6 – Tissues
Chapter 7: Diversity in Living Organism
This chapter deals with the classification of plants and animals. Students get to know that all living organisms are divided into 5 kingdoms namely Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia. It also describes the classification and evolution, the hierarchy of classification.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organism at BYJU’S:
- Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 7
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 7 – Diversity in Living Organisms
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 7 – Diversity In Living Organisms
Chapter 8: Motion
NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 8 describes motion, the speed with direction, rate of change of velocity , and graphical representation of motion. Also, students will find the 3 equations of motion and numerical problems related to them. Overall, this chapter will be a mix of theory as well as the numerical part.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion :
Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, elementary idea of uniform circular motion.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 8 Motion at BYJU’S:
- CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 8 – Motion
Chapter 9: Force and Law of Motion
This chapter explains the 3 laws of motion with the help of diagrams and examples. Below are the 3 laws of motion:
- First law of motion: An object continues to be in a state of rest or of uniform motion along a straight line unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
- Second law of motion: The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of the force .
- Third law of motion: To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, and they act on two different bodies.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Law of Motion :
Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 9 Force and Law of Motion at BYJU’S:
- Force and Laws Of Motion Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 9
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 9 – Force and Laws Of Motion
Chapter 10: Gravitation
In chapter 10 of NCERT Class 9 Science, students will learn the universal law of gravitation and its importance, free fall, mass, weight, thrust and pressure, Archimedes’ principle and relative density. Students will also find numerical problems related to these topics.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation :
Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall.
Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 10 Gravitation at BYJU’S:
- Gravitation Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 10
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 10 – Gravitation
Chapter 11: Work and Energy
In this chapter, the concept of work is defined with different activities, numerical and examples. The chapter also deals with energy and its different forms. Examples are given to explain all types of energy. The chapter ends with the topic “rate of doing work”.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy :
Work, Energy and Power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy (excluding commercial unit of Energy).
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 11 Work and Energy at BYJU’S:
- Work And Energy Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 11
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 11 – Work And Energy
Chapter 12: Sound
Chapter 12 of CBSE Class 9 Science, deals with concepts such as the production of sound, propagation of sound, the reflection of sound, range of hearing, applications of ultrasound, and the structure of the human ear . A few numericals are also there in the chapter which can only be solved after understanding the concepts. So, students must grasp and study the chapter carefully.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound :
Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 12 Sound at BYJU’S:
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound Notes
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 – Sound
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 12 – Sound
Chapter 13: Why Do We Fall Ill?
NCERT Class 9 Science chapter 13 deals with health issues and different types of diseases. It covers topics like; Health and its failure , disease and its cause, infectious diseases. This chapter is added to make students aware of different types of diseases so that they take care of their health and be fit and healthy.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill? at BYJU’S:
- Why Do We Fall Ill? Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 13
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill?
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill?
Chapter 14: Natural Resources
We are blessed with natural resources. These are essential to meet the basic requirements of all forms of life on Earth. So, this chapter has been included by NCERT to provide knowledge on the types of resources available on the Earth. This chapter deals with the topics like air, water, soil, the biogeochemical cycle and the ozone layer, its importance and how humans are polluting them.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 14 Natural Resources at BYJU’S:
- Natural Resources Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 14
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 14 – Natural Resources
Chapter 15: Improvement in Food Resources
The last chapter of NCERT Class 9 Science covers topics like Improvement in crop yields, manure, fertilizer, storage of grains, and animal husbandry . This chapter provides knowledge regarding agriculture, farming and dairy.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources at BYJU’S:
- Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 15
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 – Improvement in Food Resources
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 15 – Improvement In Food Resources
To download the complete book in PDF format, visit NCERT Science Book Class 9 . For more practice tests and mock tests, sign up on BYJU’S the learning app. Apart from Science, get NCERT Solutions for all the subjects. Students can download worksheets, assignments, NCERT Books , notes and study materials for exam preparation and for a better understanding of the topics.
CBSE Class 9 Science Evaluation Scheme (Theory) –
Features of ncert 9 th class science book solutions.
The book has a wide variety of features which are listed below:
- CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions are available to everyone for free.
- Covers all the exercise problems from the Class 9 textbook.
- Consists of extra questions, exemplar problems, the important questions from previous year question papers and sample papers, worksheets, MCQs, short answering questions, descriptive type questions, their solutions and tips and tricks.
- CBSE Class 9 Science Solutions files are available for download in PDF format for easy access.
- Diagrams are included to help students visualize the topics.
- Most effective solutions are given which can help to score well in the exams.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
How many chapters are there in the ncert solutions for class 9 science , can i expect the questions from ncert solutions for class 9 science to be asked in the annual exam, is the ncert solutions for class 9 science sufficient for the exam preparation, why should students refer to the ncert solutions for class 9 science , leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Very good app
I am a subscriber and my feedback is that it really helped me to understand how the question’s answers came. Thank you Byju’s
Very nice app
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 9 Science The Fundamental Unit of Life
Case study questions class 9 science chapter 5 the fundamental unit of life.
CBSE Class 9 Case Study Questions Science The Fundamental Unit of Life. Important Case Study Questions for Class 9 Exam. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions The Fundamental Unit of Life.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science – The Fundamental Unit of Life
All living Organisms are made up of cells and these cells perform all the functions essential for the survival of the Organism eg. Respiration, digestion, excretion etc. In Unicellular organisms, a single cell carries out all these functions and in multicellular organisms different group of cells carry out different functions.
Cells were first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. He observed the cells in a cork slice with the help of a primitive microscope. Leeuwenhoek (1674), with the improved microscope, discovered the free living cells in pond water for the first time. It was Robert Brown in 1831 who discovered the nucleus in the cell. Purkinje in 1839 coined the term ‘protoplasm’ for the fluid substance of the cell.
(1) Who discovered the cell?
(a) Robert Hooke
(b) Leeuwenhoek
(c) Robert Brown
(d) T. Schwann
(2) Who discovered the nucleus in the cell?
(3) Who coined the term ‘Protoplasm’?
(d) Purkinje
(4) What is protoplasm?
(a) Unit of life
(b) Cell organelle
(c) Fluid substance of the cell.
(d) Cytoplasm
(5) Which of these statement is true about the cell?
(a) All organism are made up of cell
(b) Cell is the basic unit of life
(c) Cell is responsible for different metabolic functions
(d) All above
The cell theory, that all the plants and animals are composed of cells and that the cell is the basic unit of life, was presented by two biologists, German zoologist Schleiden (1838) and British zoologist Schwann (1839). The cell theory was further expanded by Virchow (1855) by suggesting that all cells arise from pre-existing cells. With the discovery of the electron microscope in 1940, it was possible to observe and understand the complex structure of the cell and its various organelles.
(1) Theodore Schwann was a _____
(a) British zoologist
(b) German zoologist
(c) British botanist
(d) German botanist
(2) Matthias Schleiden was a _____
(a) German zoologist
(b) British zoologist
(c) German botanist
(d) British botanist
(3) Which of these scientists formulated the cell theory?
(a) Schleiden and Schwann
(b) Rudolf Virchow
(c) Robert Koch
(d) Antony Von Leeuwenhoek
(4) Which scientist was the first to explain that new cells arise from pre-existing cells?
(a) Antony Von Leeuwenhoek
(b) Matthias Schleiden
(c) Rudolph Virchow
(d) Theodore Schwann
(5) Which of these scientists did not contribute to the cell theory?
(a) Robert Koch
(c) Theodore Schwann
(d) Rudolph Virchow
Plasma membrane or Cell membrane is the outermost covering of the cell that separates the contents of the cell from its external environment. The plasma membrane is flexible and is made up of organic molecules called lipids and proteins. The flexibility of the cell membrane also enables the cell to engulf in food and other material from its external environment. Such processes are known as endocytosis.The plasma membrane allows or permits the entry and exit of some materials in and out of the cell. It also prevents movement of some other materials. The cell membrane, therefore, is called a selectively permeable membrane.
Some substances like carbon dioxide or oxygen can move across the cell membrane by a process called diffusion. There is spontaneous movement of a substance from a region of high concentration to a region where its concentration is low. Similar thing happens in cells – some substance like CO2 (carbon dioxide is cellular waste and requires to be excreted out by the cell) accumulates in high concentrations inside the cell. In the cell’s external environment, the concentration of CO2 is low as compared to that inside the cell. As soon as there is a difference of concentration of CO2 inside and outside a cell, CO2 moves out of the cell, from a region of high concentration, to a region of low concentration outside the cell by the process of diffusion.
Water obeys the law of diffusion. The movement of water molecules through such a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. The movement of water across the plasma membrane is also affected by the amount of substance dissolved in water. Thus, osmosis is the net diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane toward a higher solute concentration.
(1) The plasma membrane is made up of ___________
(a) Proteins
(c) Proteins and Lipids (Lipoproteins)
(d) none of above
(2) Which of the following substance is known as cellular waste?
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) None of above
(3) The movement of a substance from the region of higher concentration to the region where its concentration is lower is called as _____________
(a) Osmosis
(b) Diffusion
(c) Excretion of CO2 (carbon dioxide)
(4) Why cell membrane is known as selectively permeable membrane?
(5) What is mean by diffusion?
(6) Define Osmosis.
(d) Cell membrane allows or permits the entry and exit of some materials in and out of the cell. It also prevents movement of some other materials. Hence it is called as selectively permeable membrane.
(e) It is spontaneous movement of a substance from a region of high concentration to a region where its concentration is low. For example, some substances like carbon dioxide or oxygen can move across the cell membrane by a process called diffusion.
Plant cells, in addition to the plasma membrane, have another rigid outer covering called the cell wall. The cell wall lies outside the plasma membrane. The plant cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose. Cellulose is a complex substance and provides structural strength to plants. When a living plant cell loses water through osmosis there is shrinkage or contraction of the contents of the cell away from the cell wall. This phenomenon is known as plasmolysis.
(1) Which of the following is the main constituent of cell wall?
(c) Lipoproteins
(d) Cellulose
(2) Which of the following is outer most covering of the plant cell?
(a) Cell membrane
(b) Plasma membrane
(c) Cell wall
(3) Choose the correct set of statements from the following.
Statement 1 – Cell wall lies outside the plasma membrane.
Statement 2 – Cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose.
Statement 3 – Cellulose is a complex substance and provides structural strength to plants.
Statement 4 – Cell wall lies outside the plasma membrane.
(a) Statement 1 & 3
(b) Statement 1 & 2
(c) Statement 3 & 4
(d) All statement are correct
(4) What is mean by plasmolysis?
(5) What is the reason behind structural strength of plant cell?
(4) When living plant cell loses water through osmosis there is contraction of the contents of the cell away from the cell wall. This phenomenon is called as plasmolysis.
(5) The plant cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose. Cellulose is a complex substance and provides structural strength to plants.
Every cell has a membrane around it to keep its own contents separate from the external environment. Large and complex cells, including cells from multicellular organisms, need a lot of chemical activities to support their complicated structure and function. To keep these activities of different kinds separate from each other, these cells use membrane-bound little structures within themselves. The cytoplasm is the jelly like fluid content inside the plasma membrane which contains many specialised cell organelles. Such as Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi apparatus, Lysosomes, Ribosomes, Nucleus, Chloroplast, Mitochondria and Plastids.Each of these organelles performs a specific function for the cell. Some of these organelles are visible only with an electron microscope. They are important because they carry out some very crucial functions in cells.
(1) Identify the statement which is true for cells.
Statement 1 – Some cell organelles are visible only with an electron microscope.
Statement 2 – Cytoplasm is jelly like fluid present inside the cell.
Statement 3 – Cell organelles perform all the functions in cell.
Statement 4 – Every cell has a membrane around it to keep its own contents separate from the external environment.
(b) Statement 2 & 4
(c) Statement 1 & 4
(d) All statement are true.
(2) A suitable term for the various components of cells is ________
(b) cell organelles
(c) chromosomes
(3) The jelly-like fluid substance present in cells is called __________
(a) Protoplasm
(b) Chromosome
(c) Chloroplast
(4) What is cell organelles?
(5) Enlist the any five cell organelles.
(4) Cell organelles are the specialized organelles present with in the cells these organelles are involved in carrying out essential functions.
(5) Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi apparatus, Lysosomes, Ribosomes, Nucleus, Chloroplast, Mitochondria and Plastids.
The endoplasmic reticulum is a large network of membrane-bound tubes and sheets. It looks like long tubules or round or oblong bags (vesicles). It is discovered by Porter and Thompson. The ER membrane is similar in structure to the plasma membrane. There are two types of ER– rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). RER looks rough under a microscope because it has particles called ribosomes attached to its surface. The ribosomes, which are present in all active cells, are the sites of protein manufacture. The manufactured proteins are then sent to various places in the cell depending on need, using the ER. The SER helps in the manufacture of fat molecules, or lipids, important for cell function. Some of these proteins and lipids help in building the cell membrane. This process is known as membrane biogenesis. Some other proteins and lipids function as enzymes and hormones. Although the ER varies greatly in appearance in different cells, it always forms a network system.
(1) Who discovered endoplasmic reticulum?
(a) Porter and Thompson
(b) Robert Brown
(c) Robert Hooke
(d) Koshland
(2) Which are the components of endoplasmic reticulum__________
(a) Cisternae, tubules and vesicles.
(b) Cisternae, chromatids and vacuoles
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of the above
(3) Endoplasmic reticulum membrane which is associated with ribosomes is called_______
(a) ER lumen
(b) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(c) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Endosome
(4) Enlist the types of Endoplasmic Reticulum.
(5) Define membrane biogenesis?
(4) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum and Rough endoplasmic reticulum
(5) The SER helps in the manufacture of fat molecules, or lipids, important for cell function. Some of these proteins and lipids help in building the cell membrane. This process is known as membrane biogenesis.
The Golgi apparatus, first described by Camilo Golgi, consists of a system of membrane-bound vesicles (flattened sacs) arranged approximately parallel to each other in stacks called cisterns. These membranes often have connections with the membranes of ER and therefore constitute another portion of a complex cellular membrane system. The material synthesised near the ER is packaged and dispatched to various targets inside and outside the cell through the Golgi apparatus. Its functions include the storage, modification and packaging of products in vesicles. In some cases, complex sugars may be made from simple sugars in the Golgi apparatus. The Golgi apparatus is also involved in the formation of lysosomes
(d) Camilo Golgi
(2) A system of membrane-bound flattened sacs arranged approximately parallel to each other in stacks are called as _________
(a) Cisterns
(b) Vesicles
(c) Golgi complex
(d) Vacuoles
(3) Membrane bound flattened sacs is termed as _________
(4) Enlist the function of Golgi apparatus.
(5) Name the cell organelles which is involved in the formation of lysosomes?
(4) Functions of Golgi apparatus:
- Storage, modification and packaging of products
- Involved in formation of lysosomes
(5) Golgi apparatus
It’s a suggestion that tries to give all the questions in mcq types in case/paragraph-based questions or if you are putting question-based kindly put only very short answer types questions like one word or one sentence it’s more helpful to all. Rest it’s really good information and provides ideas to us.
Ok Dibya, We will design this page
tomorrow is my science final papper. this case study is come in my papper than i am very happy.
This very helpful casebased questions Thanku for this
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Class 7 maths worksheets, worksheet on rational number for class 7, sikkim scert class 5 english chapter 4d a walk in the dark solution, sikkim scert class 5 english chapter 5a picture reading solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion
- Last modified on: 2 years ago
- Reading Time: 3 Minutes
Case Study/Passage Based Questions:
Question 1:
Read the following paragraph and any four questions from (i) to (v).
Distance is the length of the actual path covered by an object, irrespective of its direction of motion. Displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of an object in a given direction. Distance is a scalar quantity. Displacement is a vector quantity. Distance covered can never be negative. It is always positive or zero. Displacement may be positive, negative or zero.
(i) ______________ is the actual path covered by an object. (a) Speed (b) Motion (c) Velocity (d) Distance
(ii) _______________ is the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of an object. (a) Displacement (b) Acceleration (c) Distance (d) Motion
(iii) Which of the following is a scalar quantity? (a) Displacement (b) Distance (c) Velocity (d) Acceleration
(iv) Distance covered ____________ (a) can never be negative. (b) can never be positive. (c) can never be zero. (d) can be positive or negative.
(v) Which of the following is vector quantity? (a) Displacement (b) Velocity (c) Acceleration (d) All of these
Other Chapters:
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:5MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of Atom In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then questions based…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given,…
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Class 9 science case study question 1. Read the passage and answer any four questions: Gases are highly compressible as compared to solids and liquids. The liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinder that we get in our home for cooking or the oxygen supplied to hospitals in cylinders is compressed gas.
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then questions based … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science ...
This article aims to present a comprehensive collection of case study questions for Class 9 Science, covering various topics and concepts. Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th. CBSE Class 9 Science Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in ...
Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill; Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources; Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources; You can find a wide range of solved case studies on cbseexperts, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand ...
CBSE Class 9 Science Sample Paper with Solutions for Term 2 Exam 2022. Check some of the important case study questions below: Q. Read the following and answer the questions: A student was asked ...
Case based questions for Class 9 Science involve exploring a real-world situation through scientific analysis and inquiry. These questions allow students to make connections between science concepts and the world around them, as well as develop critical thinking skills. For example, a case study may involve challenging a student to determine ...
February 4, 2022 February 4, 2022 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill. ... Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings; An Imperial Capital - Vijayanagara Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 12 History Chapter 7 ...
Important questions science class 9 chapter 13 are prepared by the experts of Vedantu. Students are provided with ultimate study materials to perform better in the examination. Science chapter 13 why do we fall ill of class 9 deals with the health of a human being. It teaches the importance to stay healthy and prevent us from falling sick.
Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Textbook Questions and Answers. INTEXT QUESTIONS. PAGE NO. 178. Question 1: State any two conditions essential for good health. Answer: 'Health' is a state of being well enough to function well physically, mentally and socially. Therefore, for good health. (i) One should be disease free.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill, renders students with accurate solutions to all the exercise questions provided in the NCERT Class 9 textbook that aligns with the CBSE Board. Here, students are provided with the best study material, the NCERT Class 9 Solutions, which are executed by a team of subject-matter ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Force and Laws of Motion. Case 1: (1) Newton's first law of motion states that a body at rest will remain at rest position only and a body which is in motion continues to be in motion unless otherwise they are acted upon by an external force. In other words, all objects resist a changein their ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the correct option: 1. The disease that affects our lungs is. (a) AIDS (b) rabies. (c) polio (d) tuberculosis. 2. The BCG vaccine is given for the immunity against. (a) hepatitis (b) jaundice.
We provide solutions for the questions given in Class 9 Science textbook as per CBSE Board guidelines from the latest NCERT book for Class 9 Science. The topics and sub-topics in Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall ill. 13.1 Health and its Failure. 13.1.1 THE SIGNIFICANCE OF 'HEALTH'. 13.1.2 PERSONAL AND COMMUNITY ISSUES BOTH MATTER FOR HEALTH.
The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Science Class 9 CBSE 13 (Why do we fall Ill) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while ...
The answers to the NCERT books are the best study material for students. Listed below are the chapter-wise NCERT Science Class 9 Solutions CBSE. • Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings. • Chapter 2: Is Matter around us Pure. • Chapter 3: Atoms and Molecules. • Chapter 4: Structure of the Atom.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science, latest edition, is available in PDF format, which can easily be downloaded. All questions are solved in detail and given here in a chapter-wise format. Visit BYJU'S to download the free NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science 2023-24 PDF.
Case Study 1: 1.) A matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Pen, paper, clips, sand, air, ice, etc. are different forms of matter. Every matter is made up of small particles. These particles are so tiny that they can't be seen with naked eyes. Let's see about the different characteristics of particles of matter.
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions is given here. Students can click on the links of the particular chapter for which they are finding the solutions. Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure. Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules. Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom. Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Work and Energy. (1) Work done by force acting on an object is equal to the magnitude of the force multiplied by the distance moved in the direction of the force. Work has only magnitude and no direction. Work done is negative when the force acts opposite to the direction of displacement.
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given,…
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - The Fundamental Unit of Life. CASE 1. All living Organisms are made up of cells and these cells perform all the functions essential for the survival of the Organism eg. Respiration, digestion, excretion etc. In Unicellular organisms, a single cell carries out all these functions and in multicellular ...
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. Here we are providing case study questions for class 9 science chapter 12 sound. Students are suggested to go through each and every case study questions for better understanding of the chapter. Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1:
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given,…