

Jeanette Winterson: Novelist and Professor of Creative Writing
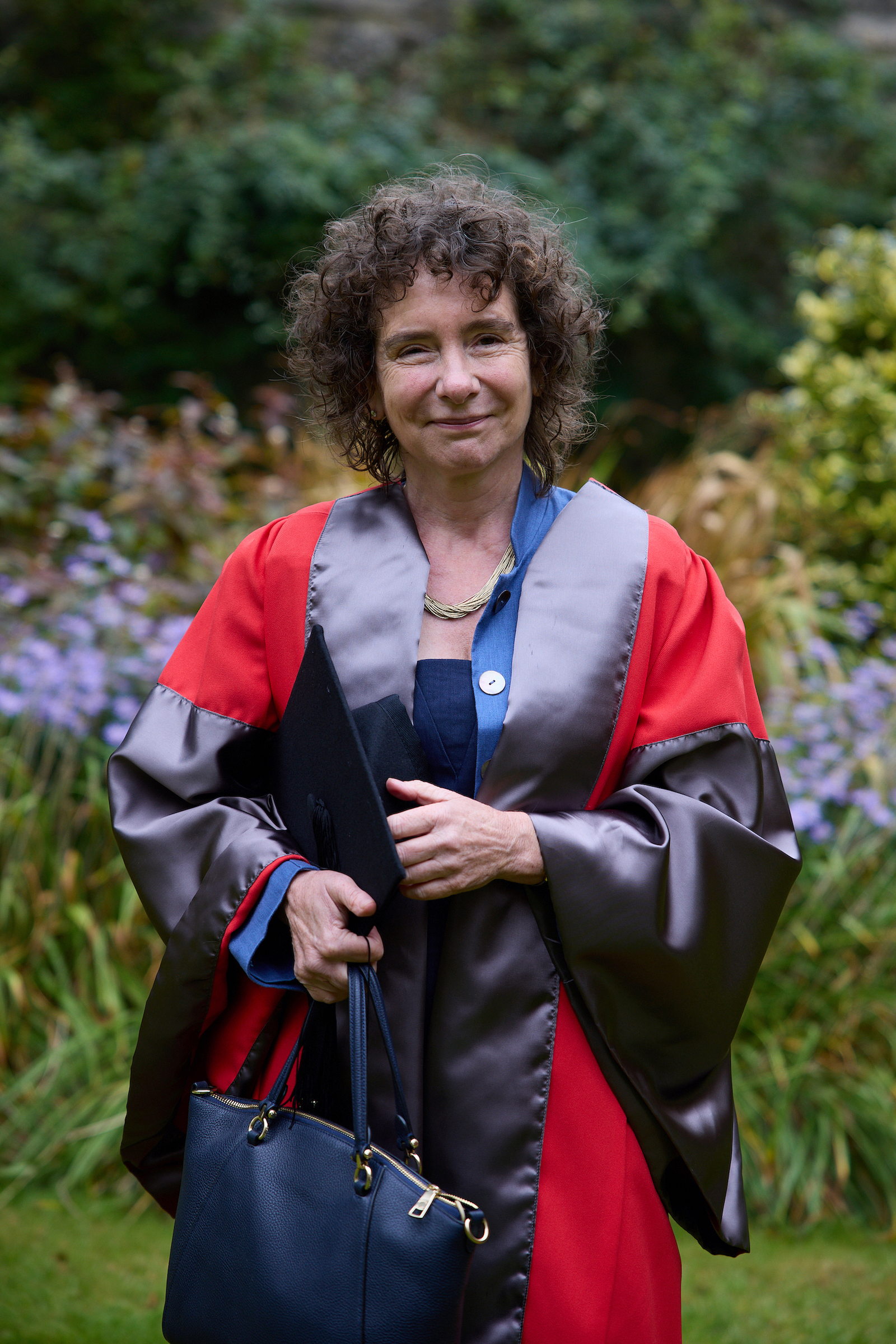

Photo credit Ian Wallman, 2021 Encaenia
Although we were not able to interview Jeanette for this project, her career and writings are a source of inspiration for many current, future, and former English students. You might like to listen to an interview with Jeanette on the occasion of receiving an honorary degree in 2021.
Return to the main gallery , or browse the Stories Bookshelf .
Books by Jeanette:

Oranges are Not the Only Fruit

Frankissstein
Emory College of Arts and Sciences Creative Writing Program
Home » People » Core Faculty
- Core Faculty

Jericho Brown
Charles howard candler professor of english and creative writing, interim director, creative writing program, english and creative writing, [email protected].

Kimberly Belflower
Advanced assistant professor of dramatic writing, creative writing program/department of theater and dance, [email protected], 404-727-0524.

Heather Christle
Assistant professor of english and creative writing, [email protected].

[email protected]
404-727-7987.

Tayari Jones
Charles howard candler professor of english and creative writing, [email protected], 404-727-4683.

Hank Klibanoff
Professor of practice, [email protected], 404-712-4584.

Joseph Skibell
Professor of english and creative writing, [email protected], 404-727-0840.

Tiphanie Yanique
[email protected], more information about....
- Visiting Faculty
- Current Fellows
- Fellowship Positions

- Bodleian Libraries
- Oxford LibGuides
- Creative Writing
Creative Writing: Home
Free online resources, purpose of this guide.
This guide is intended for students on Certificate, Diploma and Degree courses studying Creative Writing, although students and researchers from other fields may find it useful.
Finding books
Oxford has a wide range of books (including ebooks and print books) for Creative Writing. For more detailed info about finding books visit the books tab on this guide.
- SOLO Search SOLO, the University's resource discovery tool, for print and ebooks at Oxford. You can search by author, title or subject and limit to a specific library or online resources.
- SOLO user guide If you need help with SOLO, take a look at this guide for tips on searching, managing results and using your SOLO account.
Key journals
You can search for individual journal articles in SOLO by searching for the author and/or article title and/or subject keywords.
In addition, you can search for a particular journal or newspaper (e.g. Nature, English Historical Review, The Guardian) by entering the title in SOLO or via e-Journals A-Z.
- e-Journals A-Z A full, browsable list of ejournals available at Oxford.
Below are a few key journals for Creative Writing. See the journals tab of this guide for more information.
- New Writing International journal for the practice and theory of creative writing
- Poets and Writers magazine
Key databases
Oxford subscribes to many scholarly databases. They can be used to locate journal articles, conference proceedings, books, patents, images, data and more. You can find some of the key databases for Creative Writing below. Take a look at the ' Databases ' tab of this guide for more information.
- Databases A-Z A full, browsable list of Oxford's online databases.
- ProQuest One Literature more... less... ProQuest One Literature brings together primary texts, literary criticism, reference works, and more. It includes more than 500,000 works of poetry, prose and plays, as well as full-text literary and interdisciplinary journals, book reviews, and dissertations. Primary texts are mostly works in English, but there is also literature in German and Spanish, including the following collections: Teatro Español del Siglo de Oro, Schillers Werke, Kafkas Werke, Goethes Werke, Digitale Bibliothek Deutscher Klassiker, Die Deutsche Lyrik in Reclams Universal-Bibliothek, Bertolt Brechts Werke, and Latin American Women Writers. Works in English include poetry, drama and fiction across all periods, including the following specific collections: African American Poetry, African Writers Series, American Drama 1714–1915, Black Short Fiction and Folklore, Black Women Writers, Canadian Poetry, Caribbean Literature, Early American Fiction 1789-1875, Early English Prose Fiction, Eighteenth-Century Fiction, the Faber Poetry Library, Irish Women Poets of the Romantic Period, Latino Literature, Scottish Women Poets of the Romantic Period, Southeast Asian Literature in English, and more. As well as searchable, the database can be browsed by author, collection, movement. ProQuest One Literature also includes the Annual Bibliography of English Language and Literature (ABELL), indexing journals, book chapters, conference proceedings, and dissertations from 1892 onwards, with regular monthly updates of newly indexed material. ProQuest One Literature replaces Literature Online (LION) and includes all of LION’s content. This resource is partly paid for by the Drue Heinz Fund.
- Arts & Humanities Citation Index (ISI) more... less... Alternative name: Web of Science. Arts & Humanities Citation Index is a multidisciplinary index covering the journal literature of the arts and humanities. It fully covers 1,144 of the world's leading arts and humanities journals, and it indexes individually selected, relevant items from over 6,800 major science and social science journals.
There are many scholarly resources which are freely available on the web. Key free web resources are listed below and on the ' Free Online Resources " tab.
- The Poetry Archive A searchable collection of recordings of English-language poets reading their work.
- Open Learn: Creative Writing The Open University provides free educational resources online in a range of subjects.
Rewley House Continuing Education Library

The Library
Contact info
Rewley House Continuing Education Library Rewley House 1 Wellington Square Oxford OX1 2JA
Tel.01865 270454
Email [email protected]
LIbrary news
Related guides.
- English Language and Literature by English Faculty Library EFL Last Updated Apr 24, 2024 1830 views this year
- English Literature for Continuing Education short courses by Rebeca Otazua Last Updated Mar 2, 2024 771 views this year
- Finding English Faculty Library Items by English Faculty Library EFL Last Updated Feb 19, 2024 218 views this year
Key Libraries
Here are some of the key libraries for Creative Writing. A full list of libraries is on the Bodleian Libraries website :
- Continuing Education Library The Rewley House Library is your home library and buys many of the books for your course.
- English Faculty Library The EFL holds the main teaching collections for English Literature
- Next: Books >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 11:21 AM
- URL: https://libguides.bodleian.ox.ac.uk/creative-writing
Website feedback
Accessibility Statement - https://visit.bodleian.ox.ac.uk/accessibility
Google Analytics - Bodleian Libraries use Google Analytics cookies on this web site. Google Analytics anonymously tracks individual visitor behaviour on this web site so that we can see how LibGuides is being used. We only use this information for monitoring and improving our websites and content for the benefit of our users (you). You can opt out of Google Analytics cookies completely (from all websites) by visiting https://tools.google.com/dlpage/gaoptout
© Bodleian Libraries 2021. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Licence

Creative Writing
Whether you want to write your first novel or create a poem that captures a specific emotion or experience, this dynamic workshop-style seminar is a step toward finding your voice and pushing your boundaries as a creative writer. Through personalized exercises led by published authors, develop skills in the genre of your choosing while exploring important craft challenges such as dialogue, imagery, narrative structure, word choice, theme, and storytelling technique. Share your work and receive valuable feedback from your peers and instructor as you push yourself to think creatively and try new techniques.
- Oxford Academia
- Oxford Academia at Yale University
This site uses cookies. Find out more about cookies and how you can refuse them.
New membership are not allowed.
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- What Is Creative Writing? The ULTIMATE Guide!

At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a range of summer school programmes that have become extremely popular amongst students of all ages. The subject of creative writing continues to intrigue many academics as it can help to develop a range of skills that will benefit you throughout your career and life.
Nevertheless, that initial question is one that continues to linger and be asked time and time again: what is creative writing? More specifically, what does it mean or encompass? How does creative writing differ from other styles of writing?
During our Oxford Summer School programme , we will provide you with in-depth an immersive educational experience on campus in the colleges of the best university in the world. However, in this guide, we want to provide a detailed analysis of everything to do with creative writing, helping you understand more about what it is and why it could benefit you to become a creative writer.
The best place to start is with a definition.
What is creative writing?
The dictionary definition of creative writing is that it is original writing that expresses ideas and thoughts in an imaginative way. [1] Some academics will also define it as the art of making things up, but both of these definitions are too simplistic in the grand scheme of things.
It’s challenging to settle on a concrete definition as creative writing can relate to so many different things and formats. Naturally, as the name suggests, it is all built around the idea of being creative or imaginative. It’s to do with using your brain and your own thoughts to create writing that goes outside the realms of what’s expected. This type of writing tends to be more unique as it comes from a personal place. Each individual has their own level of creativity, combined with their own thoughts and views on different things. Therefore, you can conjure up your own text and stories that could be completely different from others.
Understanding creative writing can be challenging when viewed on its own. Consequently, the best way to truly understand this medium is by exploring the other main forms of writing. From here, we can compare and contrast them with the art of creative writing, making it easier to find a definition or separate this form of writing from others.
What are the main forms of writing?
In modern society, we can identify five main types of writing styles [1] that will be used throughout daily life and a plethora of careers:
- Narrative Writing
- Descriptive Writing
- Persuasive Writing
- Expository Writing
- Creative Writing
Narrative writing refers to storytelling in its most basic form. Traditionally, this involves telling a story about a character and walking the readers through the journey they go on. It can be a long novel or a short story that’s only a few hundred words long. There are no rules on length, and it can be completely true or a work of fiction.
A fundamental aspect of narrative writing that makes it different from other forms is that it should includes the key elements of storytelling. As per UX Planet, there are seven core elements of a good story or narrative [2] : the plot, characters, theme, dialogue, melody, decor and spectacle. Narrative writing will include all of these elements to take the ready on a journey that starts at the beginning, has a middle point, but always comes to a conclusion. This style of writing is typically used when writing stories, presenting anecdotes about your life, creating presentations or speeches and for some academic essays.
Descriptive writing, on the other hand, is more focused on the details. When this type of writing is used, it’s focused on capturing the reader’s attention and making them feel like they are part of the story. You want them to live and feel every element of a scene, so they can close their eyes and be whisked away to whatever place or setting you describe.
In many ways, descriptive writing is writing as an art form. Good writers can be given a blank canvas, using their words to paint a picture for the audience. There’s a firm focus on the five senses all humans have; sight, smell, touch, sound and taste. Descriptive writing touches on all of these senses to tell the reader everything they need to know and imagine about a particular scene.
This is also a style of writing that makes good use of both similes and metaphors. A simile is used to describe something as something else, while a metaphor is used to show that something is something else. There’s a subtle difference between the two, but they both aid descriptive writing immensely. According to many writing experts, similes and metaphors allow an author to emphasise, exaggerate, and add interest to a story to create a more vivid picture for the reader [3] .
Looking at persuasive writing and we have a form of writing that’s all about making yourself heard. You have an opinion that you want to get across to the reader, convincing them of it. The key is to persuade others to think differently, often helping them broaden their mind or see things from another point of view. This is often confused with something called opinionative writing, which is all about providing your opinions. While the two seem similar, the key difference is that persuasive writing is built around the idea of submitting evidence and backing your thoughts up. It’s not as simple as stating your opinion for other to read; no, you want to persuade them that your thoughts are worth listening to and perhaps worth acting on.
This style of writing is commonly used journalistically in news articles and other pieces designed to shine a light on certain issues or opinions. It is also typically backed up with statistical evidence to give more weight to your opinions and can be a very technical form of writing that’s not overly emotional.
Expository writing is more focused on teaching readers new things. If we look at its name, we can take the word exposure from it. According to Merriam-Webster [4] , one of the many definitions of exposure is to reveal something to others or present them with something they otherwise didn’t know. In terms of writing, it can refer to the act of revealing new information to others or exposing them to new ideas.
Effectively, expository writing focuses on the goal of leaving the reader with new knowledge of a certain topic or subject. Again, it is predominately seen in journalistic formats, such as explainer articles or ‘how-to’ blogs. Furthermore, you also come across it in academic textbooks or business writing.
This brings us back to the centre of attention for this guide: what is creative writing?
Interestingly, creative writing is often seen as the style of writing that combines many of these forms together in one go. Narrative writing can be seen as creative writing as you are coming up with a story to keep readers engaged, telling a tale for them to enjoy or learn from. Descriptive writing is very much a key part of creative writing as you are using your imagination and creative skills to come up with detailed descriptions that transport the reader out of their home and into a different place.
Creative writing can even use persuasive writing styles in some formats. Many writers will combine persuasive writing with a narrative structure to come up with a creative way of telling a story to educate readers and provide new opinions for them to view or be convinced of. Expository writing can also be involved here, using creativity and your imagination to answer questions or provide advice to the reader.
Essentially, creative writing can combine other writing types to create a unique and new way of telling a story or producing content. At the same time, it can include absolutely none of the other forms at all. The whole purpose of creative writing is to think outside the box and stray from traditional structures and norms. Fundamentally, we can say there are no real rules when it comes to creative writing, which is what makes it different from the other writing styles discussed above.
What is the purpose of creative writing?
Another way to understand and explore the idea of creative writing is to look at its purpose. What is the aim of most creative works of writing? What do they hope to provide the reader with?
We can look at the words of Bryanna Licciardi, an experienced creative writing tutor, to understand the purpose of creative writing. She writes that the primary purpose is to entertain and share human experiences, like love or loss. Writers attempt to reveal the truth with regard to humanity through poetics and storytelling. [5] She also goes on to add that the first step of creative writing is to use one’s imagination.
When students sign up to our creative writing courses, we will teach them how to write with this purpose. Your goal is to create stories or writing for readers that entertain them while also providing information that can have an impact on their lives. It’s about influencing readers through creative storytelling that calls upon your imagination and uses the thoughts inside your head. The deeper you dive into the art of creative writing, the more complex it can be. This is largely because it can be expressed in so many different formats. When you think of creative writing, your instinct takes you to stories and novels. Indeed, these are both key forms of creative writing that we see all the time. However, there are many other forms of creative writing that are expressed throughout the world.
What are the different forms of creative writing?
Looking back at the original and simple definition of creative writing, it relates to original writing in a creative and imaginative way. Consequently, this can span across so many genres and types of writing that differ greatly from one another. This section will explore and analyse the different types of creative writing, displaying just how diverse this writing style can be – while also showcasing just what you’re capable of when you learn how to be a creative writer.
The majority of students will first come across creative writing in the form of essays . The point of an essay is to present a coherent argument in response to a stimulus or question. [6] In essence, you are persuading the reader that your answer to the question is correct. Thus, creative writing is required to get your point across as coherently as possible, while also using great descriptive writing skills to paint the right message for the reader.
Moreover, essays can include personal essays – such as writing a cover letter for work or a university application. Here, great creativity is needed to almost write a story about yourself that captivates the reader and takes them on a journey with you. Excellent imagination and persuasive writing skills can help you tell your story and persuade those reading that you are the right person for the job or university place.
Arguably, this is the most common way in which creative writing is expressed. Fictional work includes novels, novellas, short stories – and anything else that is made up. The very definition of fiction by the Cambridge Dictionary states that it is the type of book or story that is written about imaginary characters and events not based on real people and facts. [7] As such, it means that your imagination is called upon to create something out of nothing. It is a quintessential test of your creative writing skills, meaning you need to come up with characters, settings, plots, descriptions and so much more.
Fictional creative writing in itself takes on many different forms and can be completely different depending on the writer. That is the real beauty of creative writing; you can have entirely different stories and characters from two different writers. Just look at the vast collection of fictional work around you today; it’s the perfect way to see just how versatile creative writing can be depending on the writer.
Similarly, scripts can be a type of creative writing that appeals to many. Technically, a script can be considered a work of fiction. Nevertheless, it depends on the script in question. Scripts for fictional television shows, plays or movies are obviously works of fiction. You, the writer, has come up with the characters and story of the show/play/movie, bringing it all to life through the script. But, scripts can also be non-fictional. Creating a play or movie that adapts real-life events will mean you need to write a script based on something that genuinely happened.
Here, it’s a perfect test of creative writing skills as you take a real event and use your creative talents to make it more interesting. The plot and narrative may already be there for you, so it’s a case of using your descriptive writing skills to really sell it to others and keep readers – or viewers – on the edge of their seats.
A speech is definitely a work of creative writing. The aim of a speech can vary depending on what type of speech it is. A politician delivering a speech in the House of Commons will want to get a point across to persuade others in the room. They’ll need to use creative writing to captivate their audience and have them hanging on their every word. A recent example of a great speech was the one by Sir David Attenborough at the recent COP26 global climate summit. [8] Listening to the speech is a brilliant way of understanding how creative writing can help get points across. His speech went viral around the world because of how electrifying and enthralling it is. The use of many descriptive and persuasive words had people hanging onto everything he said. He really created a picture and an image for people to see, convincing them that the time is now to work on stopping and reversing climate change.
From this speech to a completely different one, you can see creative writing at play for speeches at weddings and other jovial events. Here, the purpose is more to entertain guests and make them laugh. At the same time, someone giving a wedding speech will hope to create a lovely story for the guests to enjoy, displaying the true love that the married couple share for one another. Regardless of what type of speech an individual is giving, creative writing skills are required for it to be good and captivating.
Poetry & Songs
The final example of creative writing is twofold; poetry and songs. Both of these formats are similar to one another, relying on creativity to deliver a combination of things. Poetry can take so many forms and styles, but it aims to inspire readers and get them thinking. Poems often have hidden meanings behind them, and it takes a great deal of imagination and creativity to come up with these meanings while also creating a powerful poem. Some argue that poetry is the most creative of all creative writing forms.
Songwriting is similar in that you use creativity to come up with lyrics that can have powerful meanings while also conjuring up a story for people. The best songwriters will use lyrics that stay in people’s minds and get them thinking about the meaning behind the song. If you lack imagination and creativity, you will never be a good songwriter.
In truth, there are so many other types and examples of creative writing that you can explore. The ones listed above are the most common and powerful, and they all do a great job of demonstrating how diverse creative writing can be. If you can hone your skills in creative writing, it opens up many opportunities for you in life. Primarily, creative writing focuses on fictional pieces of work, but as you can see, non-fiction also requires a good deal of creativity.
What’s needed to make a piece of creative writing?
Our in-depth analysis of creative writing has led to a point where you’re aware of this style of writing and its purpose, along with some examples of it in the real world. The next question to delve into is what do you need to do to make a piece of creative writing. To phrase this another way; how do you write something that comes under the creative heading rather than another form of writing?
There is an element of difficulty in answering this question as creative writing has so many different types and genres. Consequently, there isn’t a set recipe for the perfect piece of creative writing, and that’s what makes this format so enjoyable and unique. Nevertheless, we can discover some crucial elements or principles that will help make a piece of writing as creative and imaginative as possible:
A target audience
All creative works will begin by defining a target audience. There are many ways to define a target audience, with some writers suggesting that you think about who is most likely to read your work. However, this can still be challenging as you’re unsure of the correct demographic to target. Writer’s Digest makes a good point of defining your target audience by considering your main motivation for writing in the first place. [9] It’s a case of considering what made you want to start writing – whether it’s a blog post, novel, song, poem, speech, etc. Figuring out your motivation behind it will help you zero in on your target audience.
Defining your audience is vital for creative writing as it helps you know exactly what to write and how to write it. All of your work should appeal to this audience and be written in a way that they can engage with. As a simple example, authors that write children’s stories will adapt their writing to appeal to the younger audience. Their stories include lots of descriptions and words that children understand, rather than being full of long words and overly academic writing.
Establishing the audience lets the writer know which direction to take things in. As a result, this can aid with things like character choices, plot, storylines, settings, and much more.
A story of sorts
Furthermore, great works of creative writing will always include a story of sorts. This is obvious for works such as novels, short stories, scripts, etc. However, even for things like poems, songs or speeches, a story helps make it creative. It gives the audience something to follow, helping them make sense of the work. Even if you’re giving a speech, setting a story can help you create a scene in people’s minds that makes them connect to what you’re saying. It’s a very effective way of persuading others and presenting different views for people to consider.
Moreover, consider the definition of a story/narrative arc. One definition describes it as a term that describes a story’s full progression. It visually evokes the idea that every story has a relatively calm beginning, a middle where tension, character conflict and narrative momentum builds to a peak and an end where the conflict is resolved. [10]
Simplifying this, we can say that all works of creative writing need a general beginning, middle and end. It’s a way of bringing some sort of structure to your writing so you know where you are going, rather than filling it with fluff or waffle.
A good imagination
Imagination is a buzzword that we’ve used plenty of times throughout this deep dive into creative writing. Every creative writing course you go on will spend a lot of time focusing on the idea of using your imagination. The human brain is a marvellously powerful thing that holds the key to creative freedom and expressing yourself in new and unique ways. If you want to make something creative, you need to tap into your imagination.
People use their imagination in different ways; some will be able to conjure up ideas for stories or worlds that exist beyond our own. Others will use theirs to think of ways of describing things in a more creative and imaginative way. Ultimately, a good imagination is what sets your work apart from others within your genre. This doesn’t mean you need to come up with the most fantastical novel of all time to have something classified as creative writing. No, using your imagination and creativity can extend to something as simple as your writing style.
Ultimately, it’s more about using your imagination to find your own personal flair and creative style. You will then be able to write unique pieces that stand out from the others and keep audiences engaged.
How can creative writing skills benefit you?
When most individuals or students consider creative writing, they imagine a world where they are writing stories for a living. There’s a common misconception that creative writing skills are only beneficial for people pursuing careers in scriptwriting, storytelling, etc. Realistically, enhancing ones creative writing skills can open up many windows of opportunity throughout your education and career.
- Improve essay writing – Naturally, creative writing forms a core part of essays and other written assignments in school and university. Improving your skills in this department can help a student get better at writing powerful essays and achieving top marks. In turn, this can impact your career by helping you get better grades to access better jobs in the future.
- Become a journalist – Journalists depend on creative writing to make stories that capture audiences and have people hanging on their every word. You need high levels of creativity to turn a news story into something people are keen to read or watch.
- Start a blog – In modern times, blogging is a useful tool that can help people find profitable and successful careers. The whole purpose of a blog is to provide your opinions to the masses while also entertaining, informing and educating. Again, having a firm grasp of creative writing skills will aid you in building your blog audience.
- Write marketing content – From advert scripts to content on websites, marketing is fuelled by creative writing. The best marketers will have creative writing skills to draw an audience in and convince them to buy products. If you can learn to get people hanging on your every word, you can make it in this industry.
These points all demonstrate the different ways in which creative writing can impact your life and alter your career. In terms of general career skills, this is one that you simply cannot go without.
How to improve your creative writing
One final part of this analysis of creative writing is to look at how students can improve. It begins by reading as much as you can and taking in lots of different content. Read books, poems, scripts, articles, blogs – anything you can find. Listen to music and pay attention to the words people use and the structure of their writing. It can help you pick up on things like metaphors, similes, and how to use your imagination. Of course, writing is the key to improving; the more you write, the more creative you can get as you will start unlocking the powers of your brain.
Conclusion: What is creative writing
In conclusion, creative writing uses a mixture of different types of writing to create stories that stray from traditional structures and norms. It revolves around the idea of using your imagination to find a writing style that suits you and gets your points across to an audience, keeping them engaged in everything you say. From novels to speeches, there are many forms of creative writing that can help you in numerous career paths throughout your life.
[1] SkillShare: The 5 Types of Writing Styles with Examples
[2] Elements of Good Story Telling – UX Planet
[3] Simile vs Metaphor: What’s the Difference? – ProWritingAid
[4] Definition of Exposure by Merriam-Webster
[5] The Higher Purpose of Creative Writing | by Terveen Gill
[6] Essay purpose – Western Sydney University
[7] FICTION | meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary
[8] ‘Not fear, but hope’ – Attenborough speech in full – BBC News
[9] Writer’s Digest: Who Is Your Target Reader?
[10] What is a Narrative Arc? • A Guide to Storytelling Structure
125 Stanford Stories
70 years of great writing.

Imagination flourishes in Stanford’s Creative Writing Program
“Minds grow by contact with other minds. The bigger the better, as clouds grow toward thunder by rubbing together.” — Wallace Stegner
The novelist Wallace Stegner came to Stanford in 1946 to teach writing. He found a campus swollen with returning GIs and war workers. This cohort – later known as the Greatest Generation – had interesting stories to tell. At Stanford, Stegner developed a program of workshops, community and freedom to write that would nurture these writers’ talents and those of generations to come.
The Stegner Fellowships, as Stanford’s two-year writers’ fellowships are now called, are perhaps the best-known facet of Stanford’s Creative Writing Program . Stegner Fellows have gone on to become Pulitzer Prize winners (N. Scott Momaday, Larry McMurtry, Adam Johnson ), poets laureate of the United States (Robert Pinsky, Philip Levine) and bestselling novelists (Scott Turow). Diverse in origin, they have brought new understanding of their own countries and cultures through literature ( NoViolet Bulawayo ). Many have returned to Stanford to teach new generations (Johnson, Kenneth Fields, Tobias Wolff).
The milieu in which the Stegner Fellows flourish also nourishes the creative gifts of hundreds of Stanford undergraduates each year. Creative writing workshops and tutorials are among Stanford’s most sought-after courses. That’s unsurprising when one considers the value that Stanford puts on output, on expressing one’s ideas.
“We hated the idea that someone would come to this great university and think it’s either/or — ‘I’m going to be a science student, or I’m going to be a creative writer.’ We made the minor so people would know they didn’t have to make that choice.” — Eavan Boland , director of the Stanford Creative Writing Program
“It’s the art of imagination. It’s a muscle that students want to activate,” explained Tom Kealey, a lecturer in the Creative Writing Program.
Nearly all of Stanford’s creative writing courses are open to undergraduates across the curriculum, though some, like the one-on-one Levinthal Tutorials, require a manuscript review. Nearly 70 percent of Stanford’s English majors have emphases in creative writing, whether in poetry or prose. There is also a creative writing minor. Its new Fiction into Film option culminates in the Hoffs-Roach Tutorial, in which students complete a 100-page screenplay. Another popular option is to take four or five writing courses as an informal emphasis.
The creative nonfiction courses are popular with students in the sciences, Kealey said: “Many want to make sense of their lives by creating narratives.”
Lectures about the craft of writing are also very popular. Professor Elizabeth Tallent teaches a course each spring, Development of the Short Story , that can attract up to 100 students.
The newest member of the program’s distinguished faculty is novelist Chang-Rae Lee , who comes to Stanford in fall 2016.
Informal workshops such as Poets’ House and Art of Writing offer an introduction to creative writing across disciplines. Innovative courses seek to explore new literary forms and to bring appreciation of writing to more people in new ways.
Stanford’s creative writing program was the first to offer a course in completing a graphic novel , a popular class repeated every other year. It gives undergraduate awards for environmental writing, an important aspect of Wallace Stegner’s legacy .
In spring 2015, program director Eavan Boland led a free online course on Ten Premodern Poems by Women that drew more than 1,000 participants from 105 countries. For the course, the office of the Vice Provost of Teaching and Learning enhanced Stanford’s OpenEdX platform to allow participants to submit narrative responses and even poems, an innovation that will help future online humanities courses.
Watch the creation of the Creative Writing Program’s latest graphic novel in this video.
CalArts offers a variety of unique programs at the undergraduate and graduate level within its six world-renowned Schools—Art, Critical Studies, Dance, Film/Video, Music and Theater.
Undergraduate core courses are the foundation of BFA studies at CalArts, providing a strong general education and opportunities to deepen every student's artistic practice.
- Interdisciplinary
- International Engagement Opportunities
- Open Learning
- Coursera for Campus
- Academic Calendar
- Course Catalog
- Academic Requirements
- Archived Catalogs
Explore is your first stop if you are considering applying to CalArts. Here you can find information about your program(s) of interest, events the Institute is hosting or attending, a virtual campus map, and much more. Your journey to CalArts starts here.
- Application Process
- Application Deadlines
- International Applicants
- Transfer Applicants
- Academic Transcripts
- Letters of Recommendation
- Critical Studies
Center for Integrated Media
- Campus Tours and Information Sessions
- Open Houses
- Accepted Students
- Submit Enrollment Deposit
- Admissions FAQ
- Meet Our Counselors
- Tuition and Fees
- Cost of Attendance
- Net Price Calculator
- Estimated Multi-Year Tuition Schedule
- Health Insurance
- For BFA Students
- For Graduate Students
- Outside Private Scholarships
- International Students
- Federal Work Study
- Student Employment
- Policies & Eligibility
- Self-Service Proxy
- Financial Literacy Resources
- Understanding Your Award
- How to Pay Tuition
- Payment and Refund Deadlines
- Payment Options
- Access Tuition Statement
- Residence Life
- Dining Options
- Student Union
- Campus Maps
- Santa Clarita Tip Sheet
- Health and Wellness
- Disability Services
- Academic Support
- International Student Support
- Sexual Respect
- Office Of Community Rights And Responsibilities
- Basic Needs Center
- Career Fair
- Internship Program
- Bridges to Industry Program
- Campus Safety
- Covid Updates
- Board of Trustees
- Mission and Values
- Strategic Framework
- Equity and Diversity (IDEA)
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Facts and Figures
- Accreditation
- Consumer Information
- The Herb Alpert Award in the Arts
- Land Acknowledgment
- Institutional Effectiveness
- Giving Opportunities
- Planned Giving
- Impact Stories
- How to Give
- Industry Partnerships
- Advancement Staff
- Annual Report
- Scholarship Impact
- Alumni Council
- Alumni Events
- Benefits and Discounts
- Stay Connected
- Get Involved
- Professional Development Resources
- Parents & Families
- CalArts News
- Event Publicity
- Social Media
- Publications
- Events Calendar
CalArts is located in Santa Clarita, Calif., 30 miles north of Los Angeles. Explore the local area and community.
Offering innovative continuing education arts courses designed to meet the needs of both emerging artists and lifelong learners.
- Request Info
Creative Writing
- Program Faculty
- Writing Now Reading Series
- Next Words Reading Series
2-Year Program
The CalArts MFA Creative Writing is unique in the field for the way it combines a dedication to experimental practice and a resolutely non-genre tracking curriculum . These commitments are intertwined: unlike in many MFA programs our students are free to pursue their imaginative and experimental impulses into whatever genre their work takes them—including into hybrid genre forms of their own. This is all in keeping to CalArts’s foundational commitment to experiment and interdisciplinarity. Students who come to our program regularly engage in substantial projects in multiple genres across their coursework and beyond. In other words, each student designs their own path through our curriculum, engaging with what questions of genre and practice inform their work as it develops. All this gives special import to the work each student does with their mentor during their time in our program. Students meet with their mentors multiple times each semester to discuss their plan of study, their creative work, and larger questions related to a life in writing and to connections between writing, other art forms, and intellectual endeavors. Our commitment to the mentor relationship is foundational to the pedagogy of CalArts.
While our program is non-tracking we do offer four optional emphases that help guide our students through our curriculum and the course offerings of other schools and programs in the Institute. We call these emphases our Concentrations . These non-required Concentrations are Image + Text , Writing and Performativity , Writing and its Publics and Documentary Strategies . Image + Text traces the relationship of the written word and the visual image, including the cinematic, the static image, and the materiality of language. Writing and Performativity offers students an array of courses focused on the creative and critical practices of performative writing. Writing and Its Publics deals with the public face of writing, be it publishing, community-based work, or writing for various art audiences, while Documentary Strategies takes on a wide array of artistic engagements with documentation, witnessing, and archives of all kinds. Students whose work and interests closely engage one of these four areas can formalize that engagement by declaring an official Concentration, which may be advantageous in their professional lives after the MFA.
In the Creative Writing Program, our core courses attend closely to questions of form and aesthetics, as well as to the historical and critical contexts of literary work. Most classes combine workshopping of student-generated work with discussion of assigned texts. While not all classes are offered every year, over the two-year program all students will take a wide selection, honing their individual visions and practices while experimenting with new forms and subjects. Writing students also benefit from being able to take courses for elective credit in the MA Program in Aesthetics and Politics, as well as other MFA/upper-level BFA courses throughout the Institute.
Full Curriculum
Detailed curriculum and academic requirements can be found in the online course catalog.
View Curriculum Requirements
Ready to Begin?
Request Information
Interdisciplinary Opportunities
In addition to CalArts' rich and diverse community and naturally collaborative atmosphere, the Institute provides several programs of study that can be pursued concurrently with a student's chosen metier.
The Center for Integrated Media concentration is designed specifically for MFA students whose creative use of technology—in particular digital media—goes beyond their primary areas of study.
Home • Programs • Creative Writing • MFA
School of Critical Studies
661-253-7803 phone 661-255-0177 fax Room E123J
Santa Clara University
The jesuit university in silicon valley.
- Creative Writing Minor
- College of Arts and Sciences
- Academic Programs
The Creative Writing Program offers students a coherent course of study in poetry, fiction, and creative nonfiction.
The creative writing minor is firmly grounded within the liberal arts tradition, integrating courses in poetry, fiction, screenwriting, and creative nonfiction writing within their broader literary and cultural context.
Introductory courses familiarize students with the practice and theory of creative writing. Advanced courses offer a workshop setting in which students write and critique one another’s work. Electives focus on particular genres of creative writing, such as Lifewriting, Fantasy and Science Fiction, and Screenwriting. All creative writing courses incorporate some study of literature as well as close attention to students’ own creative writing.
English majors who complete the Creative Writing minor may use their Creative Writing track courses for both the major and the minor.
*English majors who complete the Creative Writing minor may use their Creative Writing track courses for both the major and the minor.
Two Introductory Courses:
- English 71 . Fiction Writing
English 72. Poetry Writing
Two Sections of the Practicum Course:
- English 91. Literary Review Practicum
One Advanced Course:
- English 171. Advanced Fiction Writing or English 172. Advanced Poetry Writing (may not double dip)
Three Electives From the Following:
- English 73. Lifewriting
- English 74. New Forms for Creative Writing
- English 170. Writing for Children and Young Adults
- English 171. Advanced Fiction Writing
- English 172. Advanced Poetry Writing
- English 173. Screenwriting
- English 175. Creative Nonfiction
- English 176. Creative Writing and Social Justice
- English 177. Writing Genre Fiction
- English 178. Creative Writing and Performing
- English 179W. Playwriting
- English 179. Advanced Playwriting
All SCU students have the opportunity to work on the University’s literary magazine. Published twice a year, the Review includes fiction, essays, poetry, book reviews, art and photography from the Santa Clara University Community and the Bay Area. In the Literary Magazine Practicum, one-unit courses offered every quarter, students discuss submissions.
Each year three department literary prizes for undergraduates are given: the McCann Prize for the best short story, the Shipsey Prize for the best poem or group of poems, and the Academy of American Poets “Tamara Verga Poetry Prize” for the best poem or group of poems. In addition, SCU participates in the Ina Coolbrith Memorial Poetry Prize, choosing three finalists to compete with other California university undergraduates. The winning manuscripts receive cash awards and maybe published in the Santa Clara Review.
The Writing Forward Reading Series brings creative writers with international, national, and regional reputations to the Santa Clara University campus for readings, classroom discussions, informal meetings with students, and interviews with the Santa Clara Review literary/arts magazine. This collaborative program between the English Department’s Creative Writing Program and the student-run Santa Clara Review is grounded in the Department’s and University’s commitment to involving undergraduate students in research collaboration with faculty, and is dedicated to reaching out to both the campus and local communities.
Poets and writers brought to campus include Robert Hass (U.S. Poet Laureate, Pulitzer Prize), Carolyn Forché (Yale Younger Poets, NEA and Lannan grants), Khaled Hosseini (NYT Bestseller List, SCU alumnus), Viet Thanh Nguyen (Pulitzer Prize, MacArthur Grant), Tobias Wolff (Pen/Faulkner Award, National Medal of the Arts), Reyna Grande (American Book Award, International Latino Book Award), Gerald Stern (National Book Award, Guggenheim), Juan Felipé Herrera (American Book Award, National Book Critics Circle Award, US Poet Laureate), Dana Gioia (American Book Award, Chair of NEA), Rigoberto Gonzalez (American Book Award, Guggenheim), Raina Leon (Cave Canem and MacDowell Fellow), Jim Shepard (Guggenheim Award, The Story Prize) Alexandra Teague (Stegner and NEA Fellowships), Norma Cantú (MLA Distinguished Scholar Award), and Cheryl Dumesnil (Agnes Lynch Starrett Prize, SCU alumna).
Students majoring or minoring in English and/or Creative Writing and those working on the Santa Clara Review from a variety of majors are actively engaged in planning, inviting, and organizing the series, in close collaboration with faculty. This involvement gives undergraduates hands-on experience with the fields of writing, publishing, and public relations, while also ensuring that the series continues to speak to our campus population. The faculty-student collaboration that undergirds the series is also mirrored in interdisciplinary collaboration on campus and in community collaboration off campus.
In the last few years, over two dozen SCU students who have studied Creative Writing have been accepted into M.A., M.F.A., and Ph.D. programs in Creative Writing at University of Virginia, University of Iowa, Syracuse University, New York University, San Francisco State, University of Denver, University of Montana, University of Arizona, Bennington College, UC Davis, Brown University, San Diego State University, San Jose State University, USC, among others. Several have received prestigious fellowships and teaching assistantships to these universities. English major alumni include Neal Jimenez, who won first prize at the Sundance Film Festival for his film, Waterdance, and Jeff Brazil, who won a Pulitzer Prize in Journalism.
- Jerald Enos - Theater and Dance
- Francisco Jimenez, Tonia Riviello - Modern Languages
- Diane Dreher, Ron Hansen, Claudia MonPere McIsaac - English
Kirk Glaser, Claudia MonPere McIsaac, Cory Wade, Juan Velasco
Fiction and Screenwriting:
Kirk Glaser, Ron Hansen, David Keaton, Claudia MonPere McIsaac, Tim Myers, Juan Velasco
Nonfiction:
Simone Billings, Diane Dreher
For more information, contact:
Kirk Glaser
Director Creative Writing Program (408) 554-4384 Direct (408) 554-4837 Fax [email protected]


Writing Resources
Beyond one-to-one consultations , the Howe Writing Center (HWC) offers a number of resources to help Miami students grow as writers.
Use the Howe Writing Center Handouts as reference sheets when you take writing classes. There are 30 Handouts in total covering such topics as the writing process, working with sources, and grammar & punctuation. For writing related to specific majors, see the Disciplinary Writing Guides prepared by the Howe Center for Writing Excellence (HCWE).
We also want to help you refine your writing practice and encourage you toward your best work. Our compilation of digital tools for writing can give you new ways of approaching the writing process. Creative writers are especially welcome to pass their writing by us ( quite a few of our consultants are creative writers! ) and browse our list of publication venues .

Types of Writing
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Business Writing
- Cover Letters (For Resumes)
- Email Etiquette
- Fulbright Applications
- Literature Reviews
- Narrative Essays
- Personal Statements (for Graduate School)
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Research Stories
- Rhetorical Analyses
- Scientific/Technical Reports
- Writer's Letters
- Writing for a General Audience
Writing Process
- Writing Process Overview
- Generating Ideas
- Developing Ideas
- Supporting an Argument
- Introductions
- Thesis Statements
- Conclusions
- Reverse Outlining
- Revision Strategies
- Editing for Clear Style
Using Sources
- Plagiarism Prevention (Quoting, Summarizing, and Paraphrasing)
- Reliable Sources
- Source Integration
Grammar & Punctuation
- Apostrophes
- Hyphens and Dashes
- Parentheses
- Quotes and Quotation Marks
- Semicolons and Colons
- Sentence Combination
- Voice (Active and Passive)
Citation Resources
- Citation Styles
- How to get the Most Out of Citation Guides
Howe Writing Center
151 S. Campus Ave King Library Oxford, OH 45056 [email protected] 513-529-6100
Popular Destinations
- Consultation Appointments
- Howe Center for Writing Excellence
- Howe Writing Across the Curriculum
- University Libraries
- Academic Integrity
2022 Writing Program Certificate of Excellence

501 E. High Street Oxford, OH 45056
- Online: Miami Online
- Main Operator 513-529-1809
- Office of Admission 513-529-2531
- Vine Hotline 513-529-6400
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/emergency
1601 University Blvd. Hamilton, OH 45011
- Online: E-Campus
- Main Operator 513-785-3000
- Office of Admission 513-785-3111
- Campus Status Line 513-785-3077
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/regionals/emergency
4200 N. University Blvd. Middletown, OH 45042
- Main Operator 513-727-3200
- Office of Admission 513-727-3216
- Campus Status 513-727-3477
7847 VOA Park Dr. (Corner of VOA Park Dr. and Cox Rd.) West Chester, OH 45069
- Main Operator 513-895-8862
- From Middletown 513-217-8862
Chateau de Differdange 1, Impasse du Chateau, L-4524 Differdange Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
- Main Operator 011-352-582222-1
- Email [email protected]
- Website https://miamioh.edu/luxembourg
217-222 MacMillan Hall 501 E. Spring St. Oxford, OH 45056, USA
- Main Operator 513-529-8600
Initiatives
- Miami THRIVE Strategic Plan
- Miami Rise Strategic Plan
- Boldly Creative
- Annual Report
- Moon Shot for Equity
- Miami and Ohio
- Majors, Minors, and Programs
- Inclusive Excellence
- Employment Opportunities
- University Safety and Security
- Parking, Directions, and Maps
- Equal Opportunity
- Consumer Information
- Land Acknowledgement
- Privacy Statement
- Title IX Statement
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- Annual Security and Fire Safety Report
- Report a Problem with this Website
- Policy Library
Duration: 2 years part-time
Starts: October 2024
Applications will close at 7pm BST on:
- Thursday 6 June 2024, or when all places have been filled (whichever is sooner).
Please read the application guidance notes before applying.
Course Director: Dr John Ballam
Sign up to receive news and updates about the course.
Undergraduate Diploma in Creative Writing
Course details.
With expert tuition and small class sizes, this course gives keen writers the opportunity to explore and develop their craft.
Our two-year, part-time Diploma allows you to strengthen your ability in four major areas of literary activity — prose, poetry, drama and analytical reading — as well as the chance to specialise in the genre of your choice.
There are two ways to study. The in-person pathway ( Option 1 ) takes place on weekends in Oxford and offers a rich combination of seminars, one-to-one tutorials and group discussions. The online pathway ( Option 2 ) with a summer school in Oxford, replicates the in-person structure exactly, using a variety of media to offer a stimulating and challenging learning environment.
For both study options, the chance to have your work read and analysed by a supportive, suitably skilled peer group is one of the great benefits of the course, offering fresh perspectives and insights on your writing. At the same time, we emphasise the importance of individual voice and vision, and there will be ample time for one-to-one, in-depth discussion of your work.
Many of our former students have had work accepted for publication during or after their time with us. A significant number have progressed to Creative Writing MAs and MFA programmes at a range of universities, including Oxford University’s Master's in Creative Writing.
Watch our recent webinar
During this webinar our Course Director, Dr John Ballam, provided an overview of the course, including the different study options, outlined what to include in your application, and answered a range of questions from those who attended. Watch a recording of the event below.
- 0:00 Welcome
- 2:20 Course overview and content
- 16:44 Study options explained
- 27:07 How you will be assessed
- 28:55 Benefits of studying with Oxford University
- 31:27 How to apply
- 35:55 Contact details and how to get in touch
- 36:46 Q&A session
To stay informed of future events, sign up to receive course news .
Quick links
Who is this course for, how you will study.
- Course content and assessment
- IT requirements and study skills
- Teaching staff and contact information
- Application details – how to apply, fees, award and credit transfer
English language requirements
Pathways and other levels of study
We are looking for enthusiastic writers with a strong commitment to improving their craft, an awareness of literary areas and a degree of articulacy in discussing them, and the capacity for intellectual and imaginative development. This is an intensive and challenging course, and you will need to consider carefully whether you can offer the high level of commitment required. You will want to devote at least 12 hours a week to your writing outside of timetabled classes.
You don’t need formal qualifications. You must already be active as a writer, but it is not essential to have been published. Our students come from many backgrounds, and typically range in age from their 18 to 80. Some have previous experience of literary study, but again, this is not essential.
If you apply, we will ask you to submit a small portfolio of your work. Admission is selective and would be based on your portfolio and an interview.
There are two study options for the Diploma in Creative Writing.
Option 1:
Most terms you will attend four Saturday day schools, four per term in terms 1-5, two in term 6, which usually run from 9am - 5pm at Ewert House in Summertown, Oxford. Should circumstances dictate, the teaching can be moved online (either fully or partly).
In the day schools you will take part in:
- seminars, involving practical writing activities and lively group discussions;
- group discussions of each other’s work. This is because the value of group activity as a catalyst for the creative imagination is a central tenet of the course.
You will also attend one Sunday day school each term, which is paired with one of the Saturday schools. At the Sunday sessions, visiting writers, speakers and tutors provide a wide range of voices to counterpoint and amplify the insights and opinions of the Diploma’s regular teaching team. You can hear readings by well-known writers from all genres, and engage in discussions with them, as well as enjoying related workshop sessions.
There is a seven-day summer school (residence possible) at the end of the first year of study, in June, which provides an unparalleled opportunity to concentrate on living and working your craft. The summer school is a vibrant culmination to your first year, allowing dedicated time and space for your writing. Sessions for the whole group are balanced by individual sessions which allow you to focus on areas of your choice. There is time set aside for uninterrupted writing, and guidance will be given, as a group and individually, about how best to focus your efforts during the summer vacation so that you can get the most out of your second year.
The summer school is an integral part of the course and included in the course fee. It usually starts at lunchtime on a Saturday in June and finishes at lunchtime on the Friday. From Sunday, each day begins at 9.30 am and continues to 7pm, with breaks for tea/coffee and lunch.
Accommodation, should you require it for the summer school, is not included in your tuition fee but it may be possible to book accommodation for that period subject to availability.
Due to UK immigration and visa rules, Option 1 is normally more suitable for UK nationals and others who do not need a student visa or immigration permission to study in the UK, whereas Option 2 is normally suitable for all nationals. Please see www.ox.ac.uk/students/visa for more visa and immigration information.
Option 2:
The online study option repeats the course structure exactly as outlined above, but instead of in-person day schools in Oxford, nearly all of the work you do will be through online media and resources. Each of the first five terms is comprised of ten weekly units focusing on individual aspects of the writer’s craft. Term 6 has five units instead of ten, mirroring the in-person option above. Each weekly unit has:
- experiments and exercises in reading, critiquing and practical writing activities as well as lively group discussions in focused study forums wherein your tutor is an active participant;
- group discussions in forums centred on each other’s work. This is because the value of group activity as a catalyst for the creative imagination is a central tenet of the course.
There is a two-week residential summer school at the end of the first year of study, which provides an unparalleled opportunity to concentrate on living and working your craft. This is an integral part of the course. Please note accommodation is not included in the course fee.
The summer school is a vibrant culmination to your first year, allowing dedicated time and space for your writing. Sessions for the whole group are balanced by individual sessions shortly before or during the summer school which allow you to focus on areas of your choice. There is time set aside for uninterrupted writing, and guidance will be given, as a group and individually, about how best to focus your efforts during the summer vacation so that you can get the most out of your second year. Every day begins with a plenary lecture by a visiting speaker – most often these are professional writers in various media. There are eight two-hour in-person classes with your tutors one week, and seven in the other week. As well as your classes, you can spend your free time getting to know the world's most famous university city, visit Oxford’s outstanding museums and art galleries, gardens and enjoy tours of ‘literary/historical’ sites, concerts and theatre trips and so on in the evenings.
Throughout the course, whichever study option you take, you will be producing your own work (see below for more details). For each assignment, there is usually a one-to-one tutorial with a specialist in this type of writing, making an unrivalled opportunity for focused, developmental discussion of your own work in progress. Remember that you will need to devote a considerable amount of time to your writing outside the timetabled sessions — you should plan for at least 12 hours each week.
Course content
Year 1 teaching.
The first term provides an introduction to the three main genres: prose, poetry and drama. From the outset you will be able to engage in practical activity and wide-ranging group discussions of aims, techniques and issues.
All good writers must first be skilled readers. Developing your strengths as a critical, intelligent reader allows you to consider and articulate the ways in which various kinds of writing work. In the second term, you can refine and develop your analytical skills with three weeks of Reading for Writers, followed by seven weeks of close attention to the structures and approaches of prose fiction.
The third term concentrates on how to address the challenges of writing poetry and stage drama.
Year 2 teaching
Year 2 allows you to consolidate and broaden the advances in skill, confidence and analytical ability you will have made in Year 1.
Term 4 provides in-depth concentration on short and long fiction, while Term 5 focuses on advanced Reading for Writers (three weeks) and further high-level consideration of the craft of poetry. Term 6 gives students up-to-the-minute experience of how to write broadcast drama.
Each term you will have two tutorials of around 45 minutes each. These one-to-one sessions allow time for concentrated appraisal of your work in progress, giving you feedback on the strengths of your work as well as those areas which may need improvement. The tutorials focus on work you have produced in relation to the genres studied during that term. This means that as early as Term 1 you have considerable freedom of choice to engage with prose, poetry or drama (though you should expect to engage with more than one category in that term). For those students pursuing Option 1 (in person) tutorials can be arranged in person or online; for those pursing Option 2 (online) all tutorials are online except for those at or around the summer school, where some will be online and others in-person, as circumstances permit.
Space for specialisation
At the end of both years you will be able to work more extensively in your own area of interest, producing a portfolio of around 6,000 words in the case of prose, or 30pp of drama, or around 300 lines of poetry. Your second-year portfolio is allocated four term weeks for concentrated attention, guided by a preliminary tutorial discussion of the content you are proposing, and a review tutorial on completion of the project.
You will be assessed on:
- Two pieces of writing submitted each term. These are tied to that term’s seminar activities and are each expected to be about 2,000 words of prose, 15 pages of drama, or about 100 lines of poetry.
- The end-of-year portfolio submission, which will be around three times this length for prose and poetry, double this length for drama.
If you have not recently been involved in assessment of this kind, do not regard it as a barrier. Tutors and other specialist staff will be happy to offer advice and guidance at any time during the course.
IT requirements
To study at this level you are expected to have some IT skills, access to a computer and the internet. Your course requires you to engage with the Virtual Learning Environment for course materials and uses the Department’s online assignment submission system. Students need to have regular access to a computer and the internet, and some level of experience and skill including the use of Microsoft Word or similar word-processing package, email and internet browser such as Firefox or Google Chrome .
The computer you use should meet our recommended minimum computer specification .
Study skills
The course team will provide both academic and pastoral support, including guidance on the development of effective study skills for students returning to study after a break. Additional support is available at a Departmental level by the Widening Access Assistant, who can be contacted on +44 (0)1865 280355 or via email at [email protected] .
Before the start of the Michaelmas (autumn) term, we offer an Award-Bearing Course Preparation Study Day focusing on Academic Reading and Writing, which is free for students enrolled on our award-bearing courses. This can help students gain the confidence to read and follow academic assignment instructions and to respond to essay questions; and it discusses how to manage your time effectively, and how to locate and cite sources.
The Department also runs a programme of Study Skills workshops and weekly classes (available at a reduced rate to current students), designed to enable you to develop and improve the skills needed for effective study. If you have any questions about ‘Award-Bearing Course Preparation Study Day’ or any Study Skills course, please email [email protected] or telephone +44 (0)1865 270286.
Teaching staff
Course director.
John Ballam is the author of two collections of poems, six stage plays, four screenplays, two novels and numerous reviews, articles and academic works. His best-known title is his memoir The Road to Harmony (1999; newest edn. 2013). He has been a script consultant/screenwriter for several major film producers in Hollywood, London and Mumbai. His latest work is a novel entitled The Mary House , published in NYC in 2019.
Potential tutors
Contact information
Course Director, Dr John Ballam +44 (0)1865 280885 [email protected]
For queries on applications and admissions: +44 (0)1865 270286 [email protected]
For general guidance and advice, credit transfer, special needs provision and sources of funding: +44 (0)1865 280355 [email protected]
For information about Study Skills courses: +44 (0)1865 280892 [email protected]
How to apply
Please click on the ‘Apply’ button which will automatically notify us that you want a link to the online application form. We will email you that link together with a code to waive the application fee, and guidance on completing and submitting your application.
You will need to upload the following documents as part of your application:
- a sample of your work: approximately 2000 words of prose fiction or dramatic dialogue, or about half a dozen poems
- a statement of between 300 and 400 words explaining why you wish to enrol on the course, and stating which pathway you are applying for.
- proof of English language ability if a non-native English speaker. Further information on English language requirements can be found here . Please note that candidates are required to have the higher-level score.
- contact details for one referee
If possible, your referee should be someone who can comment on your academic ability and background, but where this is not appropriate, please choose a referee who can vouch for your motivation, commitment and potential. A reference from a family member is not acceptable.
Admissions decisions will be based on an assessment of knowledge, relevant experience, academic ability, potential and suitability for a course of study. We welcome applicants without traditional qualifications, including those with relevant career or life skills.
Selection criteria
Even if a course has no specific academic entry requirements then: (a) assessment of an applicant’s academic ability and suitability for the course of study will still take place and (b) since applications for many courses often significantly exceed places available, each application will be judged against the gathered field of applicants for each course each year.
The University is committed to promoting diversity, equality, inclusion, and widening access, including during the admissions process. We fully endorse the Equality Policy and our admissions procedures are kept under regular review to ensure compliance with this policy.
Short-listed applicants will be invited for interview.
The final decision on admission to the course rests with the Department.
Award and credit transfer
An Undergraduate Diploma will be awarded on completion of the course. You will be invited to receive your Diploma at the annual Awards Ceremony of the Department for Continuing Education, held at Oxford’s Sheldonian Theatre.
Students who successfully complete this two-year course will be awarded an Oxford University Undergraduate Diploma in Creative Writing. The Diploma carries a Credit Accumulation and Transfer Scheme (CATS) rating of 120 points at FHEQ Level 5. Outstanding performance will qualify for a Distinction. These credit points are widely recognised in terms of credit for transfer to other higher education institutions, including the Open University and modular universities such as Oxford Brookes University.
Opportunities vary for the transfer of credit, so students who are considering taking this course in order to transfer credit are advised to discuss the possibilities with the Course Administrator on [email protected] or [email protected] .
Learn more about the Credit Accumulation and Transfer Scheme (CATS points) .
The fee for Option 1 in 2024-25 is £3,620 (Home, Islands, and Republic of Ireland students) or £6,210 (Overseas students). An option to pay the fee in instalments may be available.
The fee for Option 2 in 2024-25 is £3,620 (Home, Islands, and Republic of Ireland students) or £6,210 (Overseas students). An option to pay the fee in instalments may be available.
Please be aware that fees will usually increase annually.
Information for applicants from the EU, EEA and Switzerland
On 11 May 2021 the UK Council for International Student Affairs published new regulations and guidance to be used in assessing the fee status of students commencing courses in August 2021 and later. We will be using this guidance to carry out fee status assessments for students commencing courses in 2021/22 and later, including students from the EU, EEA and Switzerland.
If you are an EU national and do not live in the UK then you are likely to be charged Overseas fees. Students with settled and pre-settled status in the UK and some other categories of students who work in the UK can qualify for Home fee status as long as they meet the residence criteria.
Students from outside the UK/Republic of Ireland
If you are from outside the UK/Republic of Ireland, you will be classed either as an ‘Overseas’ or 'Islands' student.
Information on financial support can be found on our website here .
Please check the information on the specific English language requirements for this course. Applicants are required to have the higher level scores.
The Department for Continuing Education offers day and weekend courses, weekly learning programmes and summer schools in English literature, creative writing and film studies.
In the undergraduate programme, as well as the Diploma in Creative Writing, we offer the Certificate in English Literature and the Certificate of Higher Education . At postgraduate level we offer an MSt in Creative Writing and MSt in Literature and Arts , along with the DPhil in Literature and Arts .
If you are planning on embarking on a new career as a result of your studies, or hope to progress in your current field, you can access help and advice through the University Careers Service .
Return to top
Terms & conditions for applicants and students
Information on financial support

Stay in touch with the Diploma in Creative Writing
Diploma in creative writing info session, tahmina maula, daisy mcnally, roger bannister's fourth challenge, literature, creative writing and film studies, mst in creative writing.
Visit the Health Advisories website for the latest vaccination and mask information and to Report a Case.
Questions about FAFSA and CADAA?
Visit our Financial Aid and Scholarship Office for updated information, workshops and FAQs.
Department of English and Comparative Literature
MFA Program
Our Program and Literary Community
A 44 semester-unit, 2-year studio/research program:
- A dual-genre program with concentrations in fiction, creative nonfiction , poetry, and playwriting/screenwriting.
- Curriculum includes writing workshops in primary and secondary genres, literature seminars, professional training courses, and internships.
- First Year: All applicants are considered for six Graduate Steinbeck Fellowships (covers in-state tuition).
- Second Year : Students can apply to be Teaching Associates in the English Department with a salary and tuition remittance.
- Connie L. Lurie Distinguished Visiting Author-in-Residence . Don George, Andrew Sean Greer, Nayomi Munaweera, and Faith Adiele (Spring 2020). Past visitors include: Vendela Vida, Cristina García, Ursula K. Le Guin, Ishmael Reed, Kim Addonizio, Simon Winchester, Tim Cahill, and Daniel Alarcón.
- Reed Magazine , the oldest student-run literary journal west of the Mississippi.
- Center for Literary Arts holds readings, discussions, and master classes with writers of exceptional voice and vision in San Jose since 1986. Guests since 2007 include E.L. Doctorow, Denis Johnson, ZZ Packer, Mary Roach, Salman Rushdie, Tracy K. Smith, Juan Felipe Herrera, Joy Harjo, T. C. Boyle, Viet Thanh Nguyen, William Finnegan, Paul Beatty, Marilyn Chin (Fall 2019), and Jonathan Franzen (Fall 2019).
Fall admission opens October 1.
Admission is based on a writing sample in the primary genre, in which the student will complete a full-length thesis. Students must declare a primary and a secondary genre to apply for admission.
- MFA Admission requirements
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Choose Our MFA Program?
- Be part of workshops and literature seminars (averaging 15-16 students) taught by actively publishing, available faculty .
- Courses are taught in-person and via online modalities, and are offered weekly in the late afternoons and evenings to fit your busy schedule.
- Apply for a fellowship! All applicants are automatically eligible to be considered for one of six full in-state tuition Graduate Steinbeck Fellowships in their first year.
- Take advantage of a plethora of opportunities, such as joining the editorial staff of REED Magazine , an award-winning student-edited annual literary journal.
- Become a teaching assistant. Teaching opportunities while completing the degree through the department’s Graduate Assistant and Teaching Associate programs .
- Hear from renowned authors in events presented by the Center for Literary Arts and from our annual Lurie Visiting Author-in-Residence who teaches a graduate workshop each Spring. Come join our supportive literary and social community !
Reading List
For the MFA exam you should be prepared to cite approximately 8 works in the primary (approximately 4 per essay) and 4 works in the secondary on our reading list.
Past MFA Events
From MFA Theses Readings to Legacy of Poetry, you can find recordings and slide decks from our past events!
Nick Taylor , Director of Creative Writing (408) 924-5087 Faculty Offices 106 [email protected]
April 26, 2024
The following messages have been shared with the Emory community or with members of the media.
Media requests should be directed to [email protected] .
Campus Update: May 1 Events
May 2, 2024
Expression-related events occurred in multiple locations on Emory’s Atlanta campus on Wednesday, May 1, including Asbury Circle, Cannon Chapel, the Oxford Road building and the Quad.
On Wednesday afternoon, protestors entered Emory’s Oxford Road building and disrupted its operations. Due to these disruptions, Emory closed the building and Open Expression Observers asked all individuals to leave. The protestors complied. When the protestors exited the building, several dozen of them remained just outside the building, opened three small tents and continued their protest. Open Expression Observers requested that they remove the tents and depart. When the protestors did not comply, Emory Police Department officers repeated the request, at which time the protestors complied. The protesters then moved to the Emory Quad, where the protest continued for several hours before concluding.
During the protest at the Oxford Road building, some individuals watching the event were asked to leave the area because of safety concerns. Later that evening, a group of counter-protesters also arrived on the Quad. More information on how counter-protesting is managed by Open Expression Observers can be found here .
In an unrelated incident, at 3:35 p.m., Emory University notified our community about a police emergency at Glenn Memorial United Methodist Church and instructed people to avoid the area. A suspicious package was found near the church and Glenn School. Emory Police requested assistance from DeKalb Police to investigate. Law enforcement officers determined the package did not pose a threat and Emory issued an all-clear at 4:03 p.m.
Recent Arrest and Campus Safety
April 30, 2024
Updated May 3, 2024, to reflect new information
This update shares information about two incidents that occurred on Sunday as well as the steps Emory is taking to address community safety.
On Sunday, April 28, the Emory Police Department (EPD) issued criminal trespass warnings to six individuals, four of whom were suspected of committing recent acts of vandalism on campus. This information was released by EPD that day, and EPD confirmed that none of these individuals are affiliated with Emory.
Separately, EPD shared this evening the following statement regarding an arrest later that day:
The Emory Police Department Tuesday announced the arrest of a convicted felon who crossed state lines to come to campus.
EPD arrested Derek Zika, from Statesville, North Carolina, on the Emory Quad Sunday afternoon. He was carrying knives and an Oleoresin Capsicum spray (pepper spray) canister.
He was charged with criminal trespass, obstructing a law enforcement officer, possession of a weapon in a school safety zone, criminal trespass and crossing state lines with weapons, intoxicants or drugs. He was transported to the Dekalb County Jail.
Police obtained a search warrant and inspected Zika’s vehicle Monday evening. Inside the vehicle police found an axe, a hatchet and two knives in a bag with survival gear.
Emory Police Chief Burt Buchtinec thanks community members who alerted the department to the individual being on campus.
We understand that this information comes at a sensitive time. It is our responsibility to communicate the facts that impact community safety as they become available.
We have in place or are taking the following measures to further enhance the safety of our community:
- We have added more lighting and additional cameras covering key campus locations. These cameras are monitored 24/7 by the Emory Police Department.
- We have increased officer patrols, the visibility of uniformed officers on campus, and other security measures. These efforts are especially focused on the Quad and are extended to the broader campus.
- We have limited building entry to individuals with card access.
- We are working with individual students who have needs related to exams and other academic accommodations.
Emory is continuously working to take appropriate measures to keep our community safe. We depend on a strong collaboration between EPD and other law enforcement agencies. We support their efforts to assist in keeping Emory safe.
We know that potential adverse impacts to Emory Commencement are a shared concern for many members of our community. We look forward to celebrating the Class of 2024 at Commencement and will share details of any necessary changes in future communications.
If you need immediate police assistance, call 911. As always, if you need help on campus, the following resources are available 24/7:
- Emergency/non-emergency support: 404.727.6111 (or 911 ) | TDD/TTY: 404.320.1024
- Need support? Visit resources for victims and survivors.
- Request a virtual escort using the Friend Walk option in our Emory Safe app .
- Email (non-emergency): [email protected]
- Share a confidential tip: 404.727.TIPS or 404.727.8477
- Need a SafeRide? Call 404.727.7555 from 9 p.m. to 5 a.m.
- Need counseling? Students, visit Counseling and Psychological Services | Faculty and staff, visit the Faculty Staff Assistance Program .
- Locked out? Call 404.727.6111 | TDD/TTY: 404.320.1024 , 24 hours a day.
Please remember that Emory has support resources available to assist you.
Message from President Fenves
April 29, 2024
Dear Emory Community,
Over the past week, Emory has experienced unprecedented protests and disruptions. We are not alone. Nationwide, universities are grappling with events that have deeply shaken our respective communities. I have heard from many of you, and I want you to know that I am listening. I understand your concerns, your fears, your frustrations, and your outrage. As we enter the final week of the academic year, I am focused on protecting our campuses, supporting peaceful expression for all members of our community, and finding ways to foster healing and rebuild trust.
I would like to use this message to update you on last Thursday’s events.
Based on the information we had early Thursday morning, we determined that the individuals who constructed the encampment on our Quad were not members of our community. It is clear to us now that this information was not fully accurate, and I apologize for that mischaracterization. My goal was to remove a growing encampment, as allowing such an encampment would have been highly disruptive, affecting everything from classes and exams to our ability to hold Commencement. I remain firm that such encampments cannot be permitted at Emory.
Let me be clear: I am devastated that members of our community were caught up in law enforcement activity enforcing the removal of the encampment. The videos of these interactions are deeply distressing. I take Thursday’s events very seriously and we are launching a thorough review of them so that we can develop recommendations to improve how we keep our community safe. This review will include how Emory engages external law enforcement agencies.
I am committed to supporting our students and faculty who wish to express their views peacefully. We will not tolerate conduct that undermines these efforts. I know that many members of our community are focused on their classes, research, exams, and upcoming graduation. We are working hard to keep our campus as free from disruption as possible so that these important core functions of the university can carry forward at the highest level.
Gregory L. Fenves President
Message from the Emory Police Department
April 28, 2024
Emory police officers on Sunday issued criminal trespass warnings to six individuals, four of whom were suspected in last night’s criminal activity on campus. None of the individuals are affiliated with Emory. They were all escorted off campus property.
On Saturday, a group of individuals disrupted peaceful protests and vandalized several campus structures, including spray-painting hateful messages on Convocation Hall.
The police investigation into this incident continues and further charges may be pending. Chief Burt Buchtinec thanks the community members who alerted police with descriptions of the individuals.
On Friday and again yesterday, hundreds of students and faculty assembled peacefully on our Atlanta campus for student-led protests. Our open expression team worked closely with the student organizers of the events to facilitate their peaceful expression, and that partnership worked as it is supposed to.
That changed last night.
Late in the evening, as students and faculty were assembled on the Quad, several individuals rapidly approached Convocation Hall and spray-painted hateful messages on the building’s exterior walls. Several other structures were also vandalized. These individuals brazenly disrupted what had been a peaceful protest. Many on the Quad, including those participating in the protest, condemned the action as the work of individuals from outside our community. Last night’s incidents follow similar vandalism that occurred on the Quad last Monday. The Emory Police Department is coordinating with other law enforcement agencies to investigate these crimes.
With the events of this week, it has become clear: Emory is navigating a divide between individuals who wish to express themselves peacefully and those who seek to use our campus as a platform to promote discord. Incidents like this—perpetrated by those who aim to disrupt and divide us—must be rejected and condemned at Emory.
This is a distinctly emotional and challenging time. We continue to gather the facts so that we can update you on the steps we are taking to address this week’s events. As we engage in important conversations about how we move forward, we must not allow hatred to overwhelm the many peaceful and thoughtful voices at Emory.
I am dedicated to keeping this campus safe as community members finish classes, continue their research, sit for exams, and prepare for Commencement.
April 26, 2024
I’m writing to follow up on yesterday’s messages regarding the protests at Emory. The encampment that was set up yesterday in the early morning on the Quad in front of the Commencement stage was quickly cleared by law enforcement and a number of arrests were made. Following these events, students gathered outside Convocation Hall to organize a protest. Throughout the afternoon, Emory students and community members assembled peacefully on the Quad. The afternoon events were monitored by open expression observers and Emory Police Department (EPD) officers were on site to provide support as needed. Early yesterday evening, a large group of protestors left the Quad and gathered outside the Candler School of Theology. Some protestors pinned police officers against the building’s glass doors, threw objects at them, and attempted to gain access to the building. These actions against officers prompted an increased law enforcement presence on campus. Protestors then returned to the Quad and eventually dispersed. No further arrests were made. I am saddened by what took place at Emory yesterday. To watch these highly organized, outside protestors arrive on campus in vans, construct an encampment, and overtake the Quad just days after it was vandalized with hateful and threatening messages was deeply disturbing. I also know that some of the videos are shocking, and I am horrified that members of our community had to experience and witness such interactions. The fact that members of our community were arrested upsets me even more and is something that I take very seriously. To the best of our ability, we are working with law enforcement agencies to assist detained community members and expedite their release. Yesterday’s events echo similar incidents that have taken place at universities nationwide. I understand that the ongoing effects of the war in Israel and Gaza, including the humanitarian crisis engulfing the Palestinian people and the hostage crisis involving Israeli civilians, continue to stir painful emotions. At the same time, the construction of the Atlanta Public Safety Training Center engenders fierce debate across our city. As Emory community members continue to express themselves and protest, we are committed to working with students and faculty, open expression observers, and the EPD to facilitate their peaceful expression. However, we will not tolerate vandalism, violence, or any attempt to disrupt our campus through the construction of encampments. These actions are counter to our values, and they disrupt the core purpose of the university and its educational and research missions. Today, once again, Emory staff from Facilities Management have returned to the Quad to repair the damage caused by a group of individuals who did not have this community’s best interests in mind. Dedicated staff members will then resume the work of preparing our facilities as we welcome thousands of families, parents, and guests to campus for our Commencement ceremonies. As we approach finals, the end of the academic year, and Commencement, I recognize that there is disagreement on difficult issues and there will continue to be debate. But I also know we can express our views and beliefs without diminishing the experiences and accomplishments of others. That will be our challenge in the days ahead and I know it is one that this community will rise to meet. Sincerely,
Message from VP for Public Safety Cheryl Elliott
I'm writing to share further information about the events that took place on our Atlanta campus earlier today and the actions taken by the Emory Police Department (EPD).
At 7:41 a.m. a few dozen protestors arrived on campus. When they arrived, these individuals ignored and pushed past EPD officers stationed on the Quad and set up tents in an area where equipment and materials were staged for Commencement. Based on their actions and refusal to confirm their connection to Emory, EPD made the assessment that these individuals were not Emory community members. Officers with the Atlanta Police Department and Georgia State Patrol were then called to provide further assistance. Around this time, several social media accounts announced a protest and occupation of the Quad and issued a public call for non-Emory community members to join them.
EPD issued multiple warnings at different intervals advising individuals in the encampment that they were trespassing on private property and instructing them to leave. When those requests were ignored, Atlanta Police and Georgia State Patrol officers assisted EPD with dispersing the crowd and taking individuals into custody for criminal trespass.
During this process and the subsequent confrontations, objects were thrown at police officers. To our knowledge at this time, an individual attacked a non-EPD officer and appears to have been tased. Video of this incident has been widely shared on social media. Based on current information, this individual is not a member of the Emory community. Due to the direct assault of officers, law enforcement released chemical irritants into the ground to assist with crowd control.
As of this message, we have been notified that 28 individuals have been arrested, including 20 Emory community members, some of whom have been released. We are working with responding agencies to expedite the release of any Emory community members who remain in custody.
Our primary goal today was clearing the Quad of a disruptive encampment while holding individuals accountable to the law.
Cheryl Elliott Vice President for Public Safety
Early this morning, several dozen protestors entered our Atlanta campus and set up an encampment on the Quad. These individuals are largely not affiliated with Emory and were disrupting the university as our students finish classes and prepare for finals. This is completely unacceptable. In response to this encampment, the Emory Police Department notified these individuals that they were trespassing. When they refused to leave, law enforcement cleared the Quad. I ask each of you to use judgment and show compassion for everyone with whom you share this community. It is essential that we preserve an atmosphere of respect on our campuses at all times. We will provide additional updates moving forward.
- University Announcements
- News Releases
Recent News
Download emory news photo.
By downloading Emory news media, you agree to the following terms of use:
Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License
By exercising the Licensed Rights (defined below), You accept and agree to be bound by the terms and conditions of this Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License ("Public License"). To the extent this Public License may be interpreted as a contract, You are granted the Licensed Rights in consideration of Your acceptance of these terms and conditions, and the Licensor grants You such rights in consideration of benefits the Licensor receives from making the Licensed Material available under these terms and conditions.
Section 1 – Definitions.
- Adapted Material means material subject to Copyright and Similar Rights that is derived from or based upon the Licensed Material and in which the Licensed Material is translated, altered, arranged, transformed, or otherwise modified in a manner requiring permission under the Copyright and Similar Rights held by the Licensor. For purposes of this Public License, where the Licensed Material is a musical work, performance, or sound recording, Adapted Material is always produced where the Licensed Material is synched in timed relation with a moving image.
- Copyright and Similar Rights means copyright and/or similar rights closely related to copyright including, without limitation, performance, broadcast, sound recording, and Sui Generis Database Rights, without regard to how the rights are labeled or categorized. For purposes of this Public License, the rights specified in Section 2(b)(1)-(2) are not Copyright and Similar Rights.
- Effective Technological Measures means those measures that, in the absence of proper authority, may not be circumvented under laws fulfilling obligations under Article 11 of the WIPO Copyright Treaty adopted on December 20, 1996, and/or similar international agreements.
- Exceptions and Limitations means fair use, fair dealing, and/or any other exception or limitation to Copyright and Similar Rights that applies to Your use of the Licensed Material.
- Licensed Material means the artistic or literary work, database, or other material to which the Licensor applied this Public License.
- Licensed Rights means the rights granted to You subject to the terms and conditions of this Public License, which are limited to all Copyright and Similar Rights that apply to Your use of the Licensed Material and that the Licensor has authority to license.
- Licensor means the individual(s) or entity(ies) granting rights under this Public License.
- Share means to provide material to the public by any means or process that requires permission under the Licensed Rights, such as reproduction, public display, public performance, distribution, dissemination, communication, or importation, and to make material available to the public including in ways that members of the public may access the material from a place and at a time individually chosen by them.
- Sui Generis Database Rights means rights other than copyright resulting from Directive 96/9/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 March 1996 on the legal protection of databases, as amended and/or succeeded, as well as other essentially equivalent rights anywhere in the world.
- You means the individual or entity exercising the Licensed Rights under this Public License. Your has a corresponding meaning.
Section 2 – Scope.
- reproduce and Share the Licensed Material, in whole or in part; and
- produce and reproduce, but not Share, Adapted Material.
- Exceptions and Limitations . For the avoidance of doubt, where Exceptions and Limitations apply to Your use, this Public License does not apply, and You do not need to comply with its terms and conditions.
- Term . The term of this Public License is specified in Section 6(a) .
- Media and formats; technical modifications allowed . The Licensor authorizes You to exercise the Licensed Rights in all media and formats whether now known or hereafter created, and to make technical modifications necessary to do so. The Licensor waives and/or agrees not to assert any right or authority to forbid You from making technical modifications necessary to exercise the Licensed Rights, including technical modifications necessary to circumvent Effective Technological Measures. For purposes of this Public License, simply making modifications authorized by this Section 2(a)(4) never produces Adapted Material.
- Offer from the Licensor – Licensed Material . Every recipient of the Licensed Material automatically receives an offer from the Licensor to exercise the Licensed Rights under the terms and conditions of this Public License.
- No downstream restrictions . You may not offer or impose any additional or different terms or conditions on, or apply any Effective Technological Measures to, the Licensed Material if doing so restricts exercise of the Licensed Rights by any recipient of the Licensed Material.
- No endorsement . Nothing in this Public License constitutes or may be construed as permission to assert or imply that You are, or that Your use of the Licensed Material is, connected with, or sponsored, endorsed, or granted official status by, the Licensor or others designated to receive attribution as provided in Section 3(a)(1)(A)(i) .
Other rights .
- Moral rights, such as the right of integrity, are not licensed under this Public License, nor are publicity, privacy, and/or other similar personality rights; however, to the extent possible, the Licensor waives and/or agrees not to assert any such rights held by the Licensor to the limited extent necessary to allow You to exercise the Licensed Rights, but not otherwise.
- Patent and trademark rights are not licensed under this Public License.
- To the extent possible, the Licensor waives any right to collect royalties from You for the exercise of the Licensed Rights, whether directly or through a collecting society under any voluntary or waivable statutory or compulsory licensing scheme. In all other cases the Licensor expressly reserves any right to collect such royalties.
Section 3 – License Conditions.
Your exercise of the Licensed Rights is expressly made subject to the following conditions.
Attribution .
If You Share the Licensed Material, You must:
- identification of the creator(s) of the Licensed Material and any others designated to receive attribution, in any reasonable manner requested by the Licensor (including by pseudonym if designated);
- a copyright notice;
- a notice that refers to this Public License;
- a notice that refers to the disclaimer of warranties;
- a URI or hyperlink to the Licensed Material to the extent reasonably practicable;
- indicate if You modified the Licensed Material and retain an indication of any previous modifications; and
- indicate the Licensed Material is licensed under this Public License, and include the text of, or the URI or hyperlink to, this Public License.
- You may satisfy the conditions in Section 3(a)(1) in any reasonable manner based on the medium, means, and context in which You Share the Licensed Material. For example, it may be reasonable to satisfy the conditions by providing a URI or hyperlink to a resource that includes the required information.
- If requested by the Licensor, You must remove any of the information required by Section 3(a)(1)(A) to the extent reasonably practicable.
Section 4 – Sui Generis Database Rights.
Where the Licensed Rights include Sui Generis Database Rights that apply to Your use of the Licensed Material:
- for the avoidance of doubt, Section 2(a)(1) grants You the right to extract, reuse, reproduce, and Share all or a substantial portion of the contents of the database, provided You do not Share Adapted Material;
- if You include all or a substantial portion of the database contents in a database in which You have Sui Generis Database Rights, then the database in which You have Sui Generis Database Rights (but not its individual contents) is Adapted Material; and
- You must comply with the conditions in Section 3(a) if You Share all or a substantial portion of the contents of the database.
Section 5 – Disclaimer of Warranties and Limitation of Liability.
- Unless otherwise separately undertaken by the Licensor, to the extent possible, the Licensor offers the Licensed Material as-is and as-available, and makes no representations or warranties of any kind concerning the Licensed Material, whether express, implied, statutory, or other. This includes, without limitation, warranties of title, merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, non-infringement, absence of latent or other defects, accuracy, or the presence or absence of errors, whether or not known or discoverable. Where disclaimers of warranties are not allowed in full or in part, this disclaimer may not apply to You.
- To the extent possible, in no event will the Licensor be liable to You on any legal theory (including, without limitation, negligence) or otherwise for any direct, special, indirect, incidental, consequential, punitive, exemplary, or other losses, costs, expenses, or damages arising out of this Public License or use of the Licensed Material, even if the Licensor has been advised of the possibility of such losses, costs, expenses, or damages. Where a limitation of liability is not allowed in full or in part, this limitation may not apply to You.
- The disclaimer of warranties and limitation of liability provided above shall be interpreted in a manner that, to the extent possible, most closely approximates an absolute disclaimer and waiver of all liability.
Section 6 – Term and Termination.
- This Public License applies for the term of the Copyright and Similar Rights licensed here. However, if You fail to comply with this Public License, then Your rights under this Public License terminate automatically.
Where Your right to use the Licensed Material has terminated under Section 6(a) , it reinstates:
- automatically as of the date the violation is cured, provided it is cured within 30 days of Your discovery of the violation; or
- upon express reinstatement by the Licensor.
- For the avoidance of doubt, the Licensor may also offer the Licensed Material under separate terms or conditions or stop distributing the Licensed Material at any time; however, doing so will not terminate this Public License.
- Sections 1 , 5 , 6 , 7 , and 8 survive termination of this Public License.
Section 7 – Other Terms and Conditions.
- The Licensor shall not be bound by any additional or different terms or conditions communicated by You unless expressly agreed.
- Any arrangements, understandings, or agreements regarding the Licensed Material not stated herein are separate from and independent of the terms and conditions of this Public License.
Section 8 – Interpretation.
- For the avoidance of doubt, this Public License does not, and shall not be interpreted to, reduce, limit, restrict, or impose conditions on any use of the Licensed Material that could lawfully be made without permission under this Public License.
- To the extent possible, if any provision of this Public License is deemed unenforceable, it shall be automatically reformed to the minimum extent necessary to make it enforceable. If the provision cannot be reformed, it shall be severed from this Public License without affecting the enforceability of the remaining terms and conditions.
- No term or condition of this Public License will be waived and no failure to comply consented to unless expressly agreed to by the Licensor.
- Nothing in this Public License constitutes or may be interpreted as a limitation upon, or waiver of, any privileges and immunities that apply to the Licensor or You, including from the legal processes of any jurisdiction or authority.
Creative Commons is not a party to its public licenses. Notwithstanding, Creative Commons may elect to apply one of its public licenses to material it publishes and in those instances will be considered the “Licensor.” The text of the Creative Commons public licenses is dedicated to the public domain under the CC0 Public Domain Dedication . Except for the limited purpose of indicating that material is shared under a Creative Commons public license or as otherwise permitted by the Creative Commons policies published at creativecommons.org/policies , Creative Commons does not authorize the use of the trademark “Creative Commons” or any other trademark or logo of Creative Commons without its prior written consent including, without limitation, in connection with any unauthorized modifications to any of its public licenses or any other arrangements, understandings, or agreements concerning use of licensed material. For the avoidance of doubt, this paragraph does not form part of the public licenses.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Creative Writing. There are plenty of opportunities to get involved in creative writing whilst a student within the Faculty and a number of our academics are also published authors. Oxford's English Faculty also has some of the country's leading poets among its lecturers. Our academics, the Professor of Poetry and other invited guests give ...
Undergraduate Diploma in Creative Writing (choose from two study options including one mostly online) MSt in Creative Writing ... five members of the University of Oxford's English Faculty will guide you through some of its highlights, from Tolkien and Lewis to Pullman and modern feminist fantasy. Sat 08 Jun 2024; 9:45am - 5:15pm; Available.
Giving to the English Faculty. Meet our Alumni. Contact us. Jeanette Winterson: Novelist and Professor of Creative Writing. Photo credit Ian Wallman, 2021 Encaenia ... St Cross Building, Manor Road, Oxford, OX1 3UL email: [email protected] or tel: +44 (0)1865 271055. powered by oxford mosaic.
MSt in Creative Writing About the course The MSt in Creative Writing is a two-year, part-time master's degree course offering a unique combination of high contact hours, genre specialisation, and critical and creative breadth. The emphasis of the course is cross-cultural and cross-genre, pointing up the needs and challen ges of the contemporar ...
The gateway to Open Educational Resources and other freely available resources created or selected by tutors of the University of Oxford Department for Continuing Education. An aggregator of free, downloadable courses from the world's leading universities, including many courses relating to Creative Writing.
Abrams is an award-winning author and journalist and a lecturer in creative writing at Oxford University. She is a long-standing tutor on the Oxford Masters in Creative Writing and a writing mentor for the Oxford Centre for Life Writing. From 2017-2020 she was the Royal Literary Fund Writing Fellow at Brasenose College.
Assistant Professor of English and Creative Writing. English and Creative Writing. [email protected]. 404-727-7987.
They can be used to locate journal articles, conference proceedings, books, patents, images, data and more. You can find some of the key databases for Creative Writing below. Take a look at the ' Databases ' tab of this guide for more information. Databases A-Z. A full, browsable list of Oxford's online databases. ProQuest One Literature.
Part-time study in creative writing. Develop your creativity with an Oxford University short course or award programme. ... In this day school, five members of the University of Oxford's English Faculty will guide you through some of its highlights, from Tolkien and Lewis to Pullman and modern feminist fantasy. Sat 08 Jun 2024; 9:45am - 5:15pm;
Oxford Academia at Yale University. Whether you want to write your first novel or create a poem that captures a specific emotion or experience, this dynamic workshop-style seminar is a step toward finding your voice and pushing your boundaries as a creative writer. Through personalized exercises led by published authors, develop skills in the ...
Essentially, creative writing can combine other writing types to create a unique and new way of telling a story or producing content. At the same time, it can include absolutely none of the other forms at all. The whole purpose of creative writing is to think outside the box and stray from traditional structures and norms.
Harriet Doerr '77 returned to Stanford in her 70s to finish her undergraduate degree, then stayed on as a Stegner Fellow. The work she began as a re-entry student, Stones for Ibarra, won a 1984 National Book Award. Poet Eavan Boland is professor of English at Stanford and director of the Creative Writing Program.
2-Year Program. The CalArts MFA Creative Writing is unique in the field for the way it combines a dedication to experimental practice and a resolutely non-genre tracking curriculum. These commitments are intertwined: unlike in many MFA programs our students are free to pursue their imaginative and experimental impulses into whatever genre their ...
View the profiles of MSt in Creative Writing tutors ... Clare is a member of Oxford University's English Faculty and Director of the Kellogg College Centre for Creative Writing. ... Born and raised in Hong Kong, Chan is Senior Lecturer in Creative Writing (Poetry) at Oxford Brookes University. Chan's second poetry collection, Bright Fear ...
The Writing Forward Reading Series brings creative writers with international, national, and regional reputations to the Santa Clara University campus for readings, classroom discussions, informal meetings with students, and interviews with the Santa Clara Review literary/arts magazine.This collaborative program between the English Department's Creative Writing Program and the student-run ...
Beyond one-to-one consultations, the Howe Writing Center (HWC) offers a number of resources to help Miami students grow as writers. Use the Howe Writing Center Handouts as reference sheets when you take writing classes. There are 30 Handouts in total covering such topics as the writing process, working with sources, and grammar & punctuation.
Students who successfully complete this two-year course will be awarded an Oxford University Undergraduate Diploma in Creative Writing. The Diploma carries a Credit Accumulation and Transfer Scheme (CATS) rating of 120 points at FHEQ Level 5. Outstanding performance will qualify for a Distinction.
Master of Fine Arts in Creative Writing Information. Questions about FAFSA and CADAA? Visit our Financial Aid and Scholarship Office for updated information, ... Nick Taylor, Director of Creative Writing (408) 924-5087 Faculty Offices 106 [email protected]. Current Students. Advising Forms; Advisors; Awards and Scholarships; Careers ...
Creative Commons is not a party to its public licenses. Notwithstanding, Creative Commons may elect to apply one of its public licenses to material it publishes and in those instances will be considered the "Licensor." The text of the Creative Commons public licenses is dedicated to the public domain under the CC0 Public Domain Dedication.