Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.

‘My Online Learning Experience as a Student This Fall Has Been Great’

- Share article
This series highlights contributions from students in my classes.
In Part One , Cathy Liu, Julia Yang, Eliseo Angulo Lopez, and Masihullah Shafiq shared their thoughts.
In Part Two , Luis Diaz, Samantha Nicole Vicedo, Cheyenne Lo, and Manpreet Rana contribute their commentaries.
Today, Lyna Nguyen, Nono Loek, and Rachel Anjel “wrap up” this series...
Teachers ‘have been really understanding’
Lyna Nguyen is a junior at Luther Burbank High School in Sacramento, Calif.
My online learning experience as a student this fall has been great. What’s working for me is I like the 40 minutes in class and 40 minutes asynchronous time to work on our assignments. I feel like teachers have been really understanding and helpful of what we’re going through and how difficult it can be. I find it more relaxing for me because everything is organized through Google Classroom, and it puts a little stress off of me because I disliked feeling disorganized and anxious.

What is not working for me is sometimes my time management is off, and it can be a little stressful how teachers assign work really close to the due date of other class assignments. I’d rather have the assignments’ due dates spread out throughout the week. Sometimes, there are technology difficulties, which can interrupt my learning experience. Everything is also online, so it can take a while communicating with teachers. Overall, communication is delayed, and it can be difficult reaching out to teachers and asking for assistance. Even when I need help with a certain assignment, it can be difficult learning and processing information through a screen. Other than that, I appreciate teachers trying their best to make everything work during this pandemic.
‘Internet classes save time’
Nono Loek is a senior at Luther Burbank High School:
In my experience with internet classes, the good far outweighs the bad. Internet classes save time, and saving time is important to me. The studies are structured much better than I expected. I don’t really see a difference between the online and offline structures. Group work is done in separate rooms, and I think it’s not that bad, because we also learn a lot in online classes.
I sometimes miss the interaction with people, making long-lasting friendships, which is extremely important for all of us. At home, it’s hard to force yourself to take a break. I think this pandemic has t probably transformed education. Most of the things we found to be impossible have now proven to be possible.

I actually really enjoy distance learning, but sometimes I want everything to go back to normal. I also like how I don’t have to wake up at 6 every morning. I like that with learning online, I can relax more, as well as think more. What I don’t like about online learning is that it can take me up to a whole school day (6-7 hours) to finish assignments.
‘I understand teachers are trying to keep us safe’
Rachel Anjel is a senior at Luther Burbank High School:
My online experience this year is kind of boring because I don’t really get to see friends in school anymore. And I thought it was going to be fun using Chromebooks. Sometimes it can be difficult because sometimes the Wi-Fi doesn’t work or it can be slow. I sometimes feel bored because I can’t spend or hang out with my friends.
A good thing is that we have this app called FaceTime, so whenever I’m bored, I can just call my friends. We talk and play while we do our homework and have fun. But at the same time, I think having an online school is bad because I hate sitting in my room the whole six hrs. I remember saying I like online school, but now it’s getting boring. I think it would be better if we went to school. But I understand teachers are trying to keep us safe.

Thanks to Lyna, Nono, and Rachel for their contributions!
(This is the final post in a multipart series. You can see Part One here and Part Two here .)
The question-of-the-week:
What has your online learning experience been as a student this fall? What is working for you and why? What is not working for you and why?
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
If you missed any of the highlights from the first eight years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below. The list doesn’t include ones from this current year.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies.
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagment In Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Tech Leader
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

Essays About Online Learning: Top 6 Examples And Prompts
If you are writing essays about online learning, you can start by reading some essay examples and prompts in this article.
People often regard online learning as kids stuck at home, glued to their devices. However, there is so much more to it than this simplistic concept. Many parents may see it as an “easy way out” for students to slack off on their studies while still passing their classes, but online learning has not reached its full potential yet.
It has dramatically impacted how education is handled globally, for better or worse. It has forced teachers to take on extra work , while students say it has helped reduce their stress levels. It is undoubtedly a contentious topic.
If you need help writing an essay about online learning, here are some essay examples you can use for inspiration.
1. Disabled Students Urge Universities To Make Online Learning More Accessible by Lucia Posteraro
2. why are more and more students taking online classes by perry mullins, 3. the benefits of online learning: 7 advantages of online degrees by kelsey miller, 4. why is online learning important by clare scott, 5. is online learning as effective as face-to-face learning by kelli wilkins, 6. i’m a high school student. i don’t want online learning to end. by rory selinger, prompts on essays about online learning, 1. how has online learning affected you, 2. compare and contrast online and in-person classes., 3. what can you learn from an online setup, 4. what is the future of online learning, 5. which is better- online or face-to-face learning, 6. can online learning be sustained long-term.
“Autism may hinder the ability to follow complex conversations, especially with background noise – but Charli’s lectures did not have subtitles. Moreover, extensions for group projects were too short for her extenuating circumstances.’
Posteraro tells the stories of students who want online learning to be more accessible. For example, Charli, a student with autism, was greatly affected by the transition from in-person to online classes during the COVID-19 pandemic. Unfortunately, online learning has not catered to her special needs, so she urges schools to take action to make online education more inclusive. You might also be interested in these essays about knowledge .
“The result of taking online classes is that students who take them become more proficient and comfortable with using computers. Students can learn to connect with one another online and with information in meaningful and useful ways. With that said more and more students are taking online classes because it’s the best way to save money work at your own pace and not have to be stressed about going to class.”
In his essay, Mullins discusses why more students prefer online learning. First, it lessens expenses, as students learn from the comfort of their rooms. Second, it helps students avert the fear of talking to strangers face-to-face, helping them communicate better.
“It’s clear, then, that learning online helps prepare professionals for this shift toward online work. Below, explore what online courses entail, explore seven key benefits, and get the advice you need to determine if online courses are right for you.”
Miller briefly explains what online learning is, then proceeds to discuss its advantages. These include a self-paced schedule, improved communication, and new technical skills. However, he reminds readers that everyone is different; regardless of the benefits, they should only choose online learning if they believe it will work for them.
“Boil it right down and the answer is simple: change is constant. You must move with it. The true beauty of online learning is that it lends itself perfectly to your lifestyle. By its very nature, it can fit around you. Also, no longer are we taught how to do a job, it’s usually a case of figuring it out for yourself—and that’s where online learning can amplify your skills.”
Scott presents the importance of online learning. Similar to Miller, she mentions self-paced, giving students new skills. However, the most important lesson is that change is constant. Online learning exemplifies this precept, and these skills help us move along.
“While both ways of learning have advantages and disadvantages, what is more effective is based off of the student themselves. Students can weigh the costs and benefits between online learning and face-to-face learning. They can decide for themselves what would be best for them. Online learning can be as effective as face-to-face learning if the student is committed to putting their time and effort to study alone.”
Wilkins questions the notion that online learning is inferior to a face-to-face classes. She begins by listing the benefits of online classes, including comfort and easier schedules, as with Miller and Scott. However, she also mentions its disadvantages, such as the possibility of students being distracted and a lack of bonding between classmates. But, of course, it’s all up to the student in the end: they should decide which type of education they prefer.
“One thing I hope people now realize is that education is not a one-size-fits-all model. While the self-disciplined nature of remote learning is not for everyone, it has allowed students like me to flourish unimpeded by the challenges presented by typical classroom settings.”
A 14-year-old student, Selinger wishes to continue her education online as schools return to physical classes amid the pandemic. She discusses the relief she feels from the lack of peer pressure, judgment, and a rigorous schedule. Controlling your study schedule relieves students of pressure, and Selinger believes this is optimal for success. She believes online learning opens a path to be better rather than to “return to normal.”

In this essay, you can write about your experience of online learning. Whether you have had online coursework from school or college or taken an online course for your own interests, we’ve all had some experience learning online. Discuss how you benefited from online learning and the challenges you faced. For a compelling essay, conduct interviews to back up your experience by showing others who felt the same way.
Create an exciting comparative essay between online and in-person learning. You can compare and contrast the experiences and show the positives and negatives of each. Start by making a list or Venn diagram, and organize your essay. Include the structure, advantages, and disadvantages of each method of learning.
Online learning can teach you some skills to succeed in the real world. In this essay, write about the unique skills you can gain from online learning. Perhaps you learn valuable IT skills, virtual note-taking, and basic administrative skills. Then, look into how these skills can benefit you in future studies or when trying to step into a new career path.
We have barely scratched the surface of technology. In this essay, look to the future and imagine how online education will look. Then, research up-and-coming online learning technologies and see what will come next. Will the development of more online learning technology benefit students? Look into this exciting topic for an engaging discussion.
For this topic, writing an excellent argumentative essay is easy. First, from research and your own experience, list the benefits and downsides of each type of learning and determine which is more effective. Then, you can use Google and the essay examples above to support your argument.
Online learning is most commonly used for students who are ill or during situations such as a global pandemic. It is meant to be temporary; however, can schools stick to a completely-online method of instruction? Include some advantages and disadvantages of online learning in your essay.
Tip: If writing an essay sounds like a lot of work, simplify it. Write a simple 5 paragraph essay instead.
If you’re still stuck, check out our general resource of essay writing topics .

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Students’ experience of online learning during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A province‐wide survey study
Lixiang yan.
1 Centre for Learning Analytics at Monash, Faculty of Information Technology, Monash University, Clayton VIC, Australia
Alexander Whitelock‐Wainwright
2 Portfolio of the Deputy Vice‐Chancellor (Education), Monash University, Melbourne VIC, Australia
Quanlong Guan
3 Department of Computer Science, Jinan University, Guangzhou China
Gangxin Wen
4 College of Cyber Security, Jinan University, Guangzhou China
Dragan Gašević
Guanliang chen, associated data.
The data is not openly available as it is restricted by the Chinese government.
Online learning is currently adopted by educational institutions worldwide to provide students with ongoing education during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Even though online learning research has been advancing in uncovering student experiences in various settings (i.e., tertiary, adult, and professional education), very little progress has been achieved in understanding the experience of the K‐12 student population, especially when narrowed down to different school‐year segments (i.e., primary and secondary school students). This study explores how students at different stages of their K‐12 education reacted to the mandatory full‐time online learning during the COVID‐19 pandemic. For this purpose, we conducted a province‐wide survey study in which the online learning experience of 1,170,769 Chinese students was collected from the Guangdong Province of China. We performed cross‐tabulation and Chi‐square analysis to compare students’ online learning conditions, experiences, and expectations. Results from this survey study provide evidence that students’ online learning experiences are significantly different across school years. Foremost, policy implications were made to advise government authorises and schools on improving the delivery of online learning, and potential directions were identified for future research into K‐12 online learning.
Practitioner notes
What is already known about this topic
- Online learning has been widely adopted during the COVID‐19 pandemic to ensure the continuation of K‐12 education.
- Student success in K‐12 online education is substantially lower than in conventional schools.
- Students experienced various difficulties related to the delivery of online learning.
What this paper adds
- Provide empirical evidence for the online learning experience of students in different school years.
- Identify the different needs of students in primary, middle, and high school.
- Identify the challenges of delivering online learning to students of different age.
Implications for practice and/or policy
- Authority and schools need to provide sufficient technical support to students in online learning.
- The delivery of online learning needs to be customised for students in different school years.
INTRODUCTION
The ongoing COVID‐19 pandemic poses significant challenges to the global education system. By July 2020, the UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (2020) reported nationwide school closure in 111 countries, affecting over 1.07 billion students, which is around 61% of the global student population. Traditional brick‐and‐mortar schools are forced to transform into full‐time virtual schools to provide students with ongoing education (Van Lancker & Parolin, 2020 ). Consequently, students must adapt to the transition from face‐to‐face learning to fully remote online learning, where synchronous video conferences, social media, and asynchronous discussion forums become their primary venues for knowledge construction and peer communication.
For K‐12 students, this sudden transition is problematic as they often lack prior online learning experience (Barbour & Reeves, 2009 ). Barbour and LaBonte ( 2017 ) estimated that even in countries where online learning is growing rapidly, such as USA and Canada, less than 10% of the K‐12 student population had prior experience with this format. Maladaptation to online learning could expose inexperienced students to various vulnerabilities, including decrements in academic performance (Molnar et al., 2019 ), feeling of isolation (Song et al., 2004 ), and lack of learning motivation (Muilenburg & Berge, 2005 ). Unfortunately, with confirmed cases continuing to rise each day, and new outbreaks occur on a global scale, full‐time online learning for most students could last longer than anticipated (World Health Organization, 2020 ). Even after the pandemic, the current mass adoption of online learning could have lasting impacts on the global education system, and potentially accelerate and expand the rapid growth of virtual schools on a global scale (Molnar et al., 2019 ). Thus, understanding students' learning conditions and their experiences of online learning during the COVID pandemic becomes imperative.
Emerging evidence on students’ online learning experience during the COVID‐19 pandemic has identified several major concerns, including issues with internet connection (Agung et al., 2020 ; Basuony et al., 2020 ), problems with IT equipment (Bączek et al., 2021 ; Niemi & Kousa, 2020 ), limited collaborative learning opportunities (Bączek et al., 2021 ; Yates et al., 2020 ), reduced learning motivation (Basuony et al., 2020 ; Niemi & Kousa, 2020 ; Yates et al., 2020 ), and increased learning burdens (Niemi & Kousa, 2020 ). Although these findings provided valuable insights about the issues students experienced during online learning, information about their learning conditions and future expectations were less mentioned. Such information could assist educational authorises and institutions to better comprehend students’ difficulties and potentially improve their online learning experience. Additionally, most of these recent studies were limited to higher education, except for Yates et al. ( 2020 ) and Niemi and Kousa’s ( 2020 ) studies on senior high school students. Empirical research targeting the full spectrum of K‐12students remain scarce. Therefore, to address these gaps, the current paper reports the findings of a large‐scale study that sought to explore K‐12 students’ online learning experience during the COVID‐19 pandemic in a provincial sample of over one million Chinese students. The findings of this study provide policy recommendations to educational institutions and authorities regarding the delivery of K‐12 online education.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Learning conditions and technologies.
Having stable access to the internet is critical to students’ learning experience during online learning. Berge ( 2005 ) expressed the concern of the divide in digital‐readiness, and the pedagogical approach between different countries could influence students’ online learning experience. Digital‐readiness is the availability and adoption of information technologies and infrastructures in a country. Western countries like America (3rd) scored significantly higher in digital‐readiness compared to Asian countries like China (54th; Cisco, 2019 ). Students from low digital‐readiness countries could experience additional technology‐related problems. Supporting evidence is emerging in recent studies conducted during the COVID‐19 pandemic. In Egypt's capital city, Basuony et al. ( 2020 ) found that only around 13.9%of the students experienced issues with their internet connection. Whereas more than two‐thirds of the students in rural Indonesia reported issues of unstable internet, insufficient internet data, and incompatible learning device (Agung et al., 2020 ).
Another influential factor for K‐12 students to adequately adapt to online learning is the accessibility of appropriate technological devices, especially having access to a desktop or a laptop (Barbour et al., 2018 ). However, it is unlikely for most of the students to satisfy this requirement. Even in higher education, around 76% of students reported having incompatible devices for online learning and only 15% of students used laptop for online learning, whereas around 85% of them used smartphone (Agung et al., 2020 ). It is very likely that K‐12 students also suffer from this availability issue as they depend on their parents to provide access to relevant learning devices.
Technical issues surrounding technological devices could also influence students’ experience in online learning. (Barbour & Reeves, 2009 ) argues that students need to have a high level of digital literacy to find and use relevant information and communicate with others through technological devices. Students lacking this ability could experience difficulties in online learning. Bączek et al. ( 2021 ) found that around 54% of the medical students experienced technical problems with IT equipment and this issue was more prevalent in students with lower years of tertiary education. Likewise, Niemi and Kousa ( 2020 ) also find that students in a Finish high school experienced increased amounts of technical problems during the examination period, which involved additional technical applications. These findings are concerning as young children and adolescent in primary and lower secondary school could be more vulnerable to these technical problems as they are less experienced with the technologies in online learning (Barbour & LaBonte, 2017 ). Therefore, it is essential to investigate the learning conditions and the related difficulties experienced by students in K‐12 education as the extend of effects on them remain underexplored.
Learning experience and interactions
Apart from the aforementioned issues, the extent of interaction and collaborative learning opportunities available in online learning could also influence students’ experience. The literature on online learning has long emphasised the role of effective interaction for the success of student learning. According to Muirhead and Juwah ( 2004 ), interaction is an event that can take the shape of any type of communication between two or subjects and objects. Specifically, the literature acknowledges the three typical forms of interactions (Moore, 1989 ): (i) student‐content, (ii) student‐student, and (iii) student‐teacher. Anderson ( 2003 ) posits, in the well‐known interaction equivalency theorem, learning experiences will not deteriorate if only one of the three interaction is of high quality, and the other two can be reduced or even eliminated. Quality interaction can be accomplished by across two dimensions: (i) structure—pedagogical means that guide student interaction with contents or other students and (ii) dialogue—communication that happens between students and teachers and among students. To be able to scale online learning and prevent the growth of teaching costs, the emphasise is typically on structure (i.e., pedagogy) that can promote effective student‐content and student‐student interaction. The role of technology and media is typically recognised as a way to amplify the effect of pedagogy (Lou et al., 2006 ). Novel technological innovations—for example learning analytics‐based personalised feedback at scale (Pardo et al., 2019 ) —can also empower teachers to promote their interaction with students.
Online education can lead to a sense of isolation, which can be detrimental to student success (McInnerney & Roberts, 2004 ). Therefore, integration of social interaction into pedagogy for online learning is essential, especially at the times when students do not actually know each other or have communication and collaboration skills underdeveloped (Garrison et al., 2010 ; Gašević et al., 2015 ). Unfortunately, existing evidence suggested that online learning delivery during the COVID‐19 pandemic often lacks interactivity and collaborative experiences (Bączek et al., 2021 ; Yates et al., 2020 ). Bączek et al., ( 2021 ) found that around half of the medical students reported reduced interaction with teachers, and only 4% of students think online learning classes are interactive. Likewise, Yates et al. ( 2020 )’s study in high school students also revealed that over half of the students preferred in‐class collaboration over online collaboration as they value the immediate support and the proximity to teachers and peers from in‐class interaction.
Learning expectations and age differentiation
Although these studies have provided valuable insights and stressed the need for more interactivity in online learning, K‐12 students in different school years could exhibit different expectations for the desired activities in online learning. Piaget's Cognitive Developmental Theory illustrated children's difficulties in understanding abstract and hypothetical concepts (Thomas, 2000 ). Primary school students will encounter many abstract concepts in their STEM education (Uttal & Cohen, 2012 ). In face‐to‐face learning, teachers provide constant guidance on students’ learning progress and can help them to understand difficult concepts. Unfortunately, the level of guidance significantly drops in online learning, and, in most cases, children have to face learning obstacles by themselves (Barbour, 2013 ). Additionally, lower primary school students may lack the metacognitive skills to use various online learning functions, maintain engagement in synchronous online learning, develop and execute self‐regulated learning plans, and engage in meaningful peer interactions during online learning (Barbour, 2013 ; Broadbent & Poon, 2015 ; Huffaker & Calvert, 2003; Wang et al., 2013 ). Thus, understanding these younger students’ expectations is imperative as delivering online learning to them in the same way as a virtual high school could hinder their learning experiences. For students with more matured metacognition, their expectations of online learning could be substantially different from younger students. Niemi et al.’s study ( 2020 ) with students in a Finish high school have found that students often reported heavy workload and fatigue during online learning. These issues could cause anxiety and reduce students’ learning motivation, which would have negative consequences on their emotional well‐being and academic performance (Niemi & Kousa, 2020 ; Yates et al., 2020 ), especially for senior students who are under the pressure of examinations. Consequently, their expectations of online learning could be orientated toward having additional learning support functions and materials. Likewise, they could also prefer having more opportunities for peer interactions as these interactions are beneficial to their emotional well‐being and learning performance (Gašević et al., 2013 ; Montague & Rinaldi, 2001 ). Therefore, it is imperative to investigate the differences between online learning expectations in students of different school years to suit their needs better.
Research questions
By building upon the aforementioned relevant works, this study aimed to contribute to the online learning literature with a comprehensive understanding of the online learning experience that K‐12 students had during the COVID‐19 pandemic period in China. Additionally, this study also aimed to provide a thorough discussion of what potential actions can be undertaken to improve online learning delivery. Formally, this study was guided by three research questions (RQs):
RQ1 . What learning conditions were experienced by students across 12 years of education during their online learning process in the pandemic period? RQ2 . What benefits and obstacles were perceived by students across 12 years of education when performing online learning? RQ3 . What expectations do students, across 12 years of education, have for future online learning practices ?
Participants
The total number of K‐12 students in the Guangdong Province of China is around 15 million. In China, students of Year 1–6, Year 7–9, and Year 10–12 are referred to as students of primary school, middle school, and high school, respectively. Typically, students in China start their study in primary school at the age of around six. At the end of their high‐school study, students have to take the National College Entrance Examination (NCEE; also known as Gaokao) to apply for tertiary education. The survey was administrated across the whole Guangdong Province, that is the survey was exposed to all of the 15 million K‐12 students, though it was not mandatory for those students to accomplish the survey. A total of 1,170,769 students completed the survey, which accounts for a response rate of 7.80%. After removing responses with missing values and responses submitted from the same IP address (duplicates), we had 1,048,575 valid responses, which accounts to about 7% of the total K‐12 students in the Guangdong Province. The number of students in different school years is shown in Figure 1 . Overall, students were evenly distributed across different school years, except for a smaller sample in students of Year 10–12.

The number of students in each school year
Survey design
The survey was designed collaboratively by multiple relevant parties. Firstly, three educational researchers working in colleges and universities and three educational practitioners working in the Department of Education in Guangdong Province were recruited to co‐design the survey. Then, the initial draft of the survey was sent to 30 teachers from different primary and secondary schools, whose feedback and suggestions were considered to improve the survey. The final survey consisted of a total of 20 questions, which, broadly, can be classified into four categories: demographic, behaviours, experiences, and expectations. Details are available in Appendix.
All K‐12 students in the Guangdong Province were made to have full‐time online learning from March 1, 2020 after the outbreak of COVID‐19 in January in China. A province‐level online learning platform was provided to all schools by the government. In addition to the learning platform, these schools can also use additional third‐party platforms to facilitate the teaching activities, for example WeChat and Dingding, which provide services similar to WhatsApp and Zoom. The main change for most teachers was that they had to shift the classroom‐based lectures to online lectures with the aid of web‐conferencing tools. Similarly, these teachers also needed to perform homework marking and have consultation sessions in an online manner.
The Department of Education in the Guangdong Province of China distributed the survey to all K‐12 schools in the province on March 21, 2020 and collected responses on March 26, 2020. Students could access and answer the survey anonymously by either scan the Quick Response code along with the survey or click the survey address link on their mobile device. The survey was administrated in a completely voluntary manner and no incentives were given to the participants. Ethical approval was granted by the Department of Education in the Guangdong Province. Parental approval was not required since the survey was entirely anonymous and facilitated by the regulating authority, which satisfies China's ethical process.
The original survey was in Chinese, which was later translated by two bilingual researchers and verified by an external translator who is certified by the Australian National Accreditation Authority of Translators and Interpreters. The original and translated survey questionnaires are available in Supporting Information. Given the limited space we have here and the fact that not every survey item is relevant to the RQs, the following items were chosen to answer the RQs: item Q3 (learning media) and Q11 (learning approaches) for RQ1, item Q13 (perceived obstacle) and Q19 (perceived benefits) for RQ2, and item Q19 (expected learning activities) for RQ3. Cross‐tabulation based approaches were used to analyse the collected data. To scrutinise whether the differences displayed by students of different school years were statistically significant, we performed Chi‐square tests and calculated the Cramer's V to assess the strengths of the association after chi‐square had determined significance.
For the analyses, students were segmented into four categories based on their school years, that is Year 1–3, Year 4–6, Year 7–9, and Year 10–12, to provide a clear understanding of the different experiences and needs that different students had for online learning. This segmentation was based on the educational structure of Chinese schools: elementary school (Year 1–6), middle school (Year 7–9), and high school (Year 10–12). Children in elementary school can further be segmented into junior (Year 1–3) or senior (Year 4–6) students because senior elementary students in China are facing more workloads compared to junior students due to the provincial Middle School Entry Examination at the end of Year 6.
Learning conditions—RQ1
Learning media.
The Chi‐square test showed significant association between school years and students’ reported usage of learning media, χ 2 (55, N = 1,853,952) = 46,675.38, p < 0.001. The Cramer's V is 0.07 ( df ∗ = 5), which indicates a small‐to‐medium effect according to Cohen’s ( 1988 ) guidelines. Based on Figure 2 , we observed that an average of up to 87.39% students used smartphones to perform online learning, while only 25.43% students used computer, which suggests that smartphones, with widespread availability in China (2020), have been adopted by students for online learning. As for the prevalence of the two media, we noticed that both smartphones ( χ 2 (3, N = 1,048,575) = 9,395.05, p < 0.001, Cramer's V = 0.10 ( df ∗ = 1)) and computers ( χ 2 (3, N = 1,048,575) = 11,025.58, p <.001, Cramer's V = 0.10 ( df ∗ = 1)) were more adopted by high‐school‐year (Year 7–12) than early‐school‐year students (Year 1–6), both with a small effect size. Besides, apparent discrepancies can be observed between the usages of TV and paper‐based materials across different school years, that is early‐school‐year students reported more TV usage ( χ 2 (3, N = 1,048,575) = 19,505.08, p <.001), with a small‐to‐medium effect size, Cramer's V = 0.14( df ∗ = 1). High‐school‐year students (especially Year 10–12) reported more usage of paper‐based materials ( χ 2 (3, N = 1,048,575) = 23,401.64, p < 0.001), with a small‐to‐medium effect size, Cramer's V = 0.15( df ∗ = 1).

Learning media used by students in online learning
Learning approaches
School years is also significantly associated with the different learning approaches students used to tackle difficult concepts during online learning, χ 2 (55, N = 2,383,751) = 58,030.74, p < 0.001. The strength of this association is weak to moderate as shown by the Cramer's V (0.07, df ∗ = 5; Cohen, 1988 ). When encountering problems related to difficult concepts, students typically chose to “solve independently by searching online” or “rewatch recorded lectures” instead of consulting to their teachers or peers (Figure 3 ). This is probably because, compared to classroom‐based education, it is relatively less convenient and more challenging for students to seek help from others when performing online learning. Besides, compared to high‐school‐year students, early‐school‐year students (Year 1–6), reported much less use of “solve independently by searching online” ( χ 2 (3, N = 1,048,575) = 48,100.15, p <.001), with a small‐to‐medium effect size, Cramer's V = 0.21 ( df ∗ = 1). Also, among those approaches of seeking help from others, significantly more high‐school‐year students preferred “communicating with other students” than early‐school‐year students ( χ 2 (3, N = 1,048,575) = 81,723.37, p < 0.001), with a medium effect size, Cramer's V = 0.28 ( df ∗ = 1).

Learning approaches used by students in online learning
Perceived benefits and obstacles—RQ2
Perceived benefits.
The association between school years and perceived benefits in online learning is statistically significant, χ 2 (66, N = 2,716,127) = 29,534.23, p < 0.001, and the Cramer's V (0.04, df ∗ = 6) indicates a small effect (Cohen, 1988 ). Unsurprisingly, benefits brought by the convenience of online learning are widely recognised by students across all school years (Figure 4 ), that is up to 75% of students reported that it is “more convenient to review course content” and 54% said that they “can learn anytime and anywhere” . Besides, we noticed that about 50% of early‐school‐year students appreciated the “access to courses delivered by famous teachers” and 40%–47% of high‐school‐year students indicated that online learning is “helpful to develop self‐regulation and autonomy” .

Perceived benefits of online learning reported by students
Perceived obstacles
The Chi‐square test shows a significant association between school years and students’ perceived obstacles in online learning, χ 2 (77, N = 2,699,003) = 31,987.56, p < 0.001. This association is relatively weak as shown by the Cramer's V (0.04, df ∗ = 7; Cohen, 1988 ). As shown in Figure 5 , the biggest obstacles encountered by up to 73% of students were the “eyestrain caused by long staring at screens” . Disengagement caused by nearby disturbance was reported by around 40% of students, especially those of Year 1–3 and 10–12. Technological‐wise, about 50% of students experienced poor Internet connection during their learning process, and around 20% of students reported the “confusion in setting up the platforms” across of school years.

Perceived obstacles of online learning reported by students
Expectations for future practices of online learning – RQ3
Online learning activities.
The association between school years and students’ expected online learning activities is significant, χ 2 (66, N = 2,416,093) = 38,784.81, p < 0.001. The Cramer's V is 0.05 ( df ∗ = 6) which suggests a small effect (Cohen, 1988 ). As shown in Figure 6 , the most expected activity for future online learning is “real‐time interaction with teachers” (55%), followed by “online group discussion and collaboration” (38%). We also observed that more early‐school‐year students expect reflective activities, such as “regular online practice examinations” ( χ 2 (3, N = 1,048,575) = 11,644.98, p < 0.001), with a small effect size, Cramer's V = 0.11 ( df ∗ = 1). In contrast, more high‐school‐year students expect “intelligent recommendation system …” ( χ 2 (3, N = 1,048,575) = 15,327.00, p < 0.001), with a small effect size, Cramer's V = 0.12 ( df ∗ = 1).

Students’ expected online learning activities
Regarding students’ learning conditions, substantial differences were observed in learning media, family dependency, and learning approaches adopted in online learning between students in different school years. The finding of more computer and smartphone usage in high‐school‐year than early‐school‐year students can probably be explained by that, with the growing abilities in utilising these media as well as the educational systems and tools which run on these media, high‐school‐year students tend to make better use of these media for online learning practices. Whereas, the differences in paper‐based materials may imply that high‐school‐year students in China have to accomplish a substantial amount of exercise, assignments, and exam papers to prepare for the National College Entrance Examination (NCEE), whose delivery was not entirely digitised due to the sudden transition to online learning. Meanwhile, high‐school‐year students may also have preferred using paper‐based materials for exam practice, as eventually, they would take their NCEE in the paper format. Therefore, these substantial differences in students’ usage of learning media should be addressed by customising the delivery method of online learning for different school years.
Other than these between‐age differences in learning media, the prevalence of smartphone in online learning resonates with Agung et al.’s ( 2020 ) finding on the issues surrounding the availability of compatible learning device. The prevalence of smartphone in K‐12 students is potentially problematic as the majority of the online learning platform and content is designed for computer‐based learning (Berge, 2005 ; Molnar et al., 2019 ). Whereas learning with smartphones has its own unique challenges. For example, Gikas and Grant ( 2013 ) discovered that students who learn with smartphone experienced frustration with the small screen‐size, especially when trying to type with the tiny keypad. Another challenge relates to the distraction of various social media applications. Although similar distractions exist in computer and web‐based social media, the level of popularity, especially in the young generation, are much higher in mobile‐based social media (Montag et al., 2018 ). In particular, the message notification function in smartphones could disengage students from learning activities and allure them to social media applications (Gikas & Grant, 2013 ). Given these challenges of learning with smartphones, more research efforts should be devoted to analysing students’ online learning behaviour in the setting of mobile learning to accommodate their needs better.
The differences in learning approaches, once again, illustrated that early‐school‐year students have different needs compared to high‐school‐year students. In particular, the low usage of the independent learning methods in early‐school‐year students may reflect their inability to engage in independent learning. Besides, the differences in help seeking behaviours demonstrated the distinctive needs for communication and interaction between different students, that is early‐school‐year students have a strong reliance on teachers and high‐school‐year students, who are equipped with stronger communication ability, are more inclined to interact with their peers. This finding implies that the design of online learning platforms should take students’ different needs into account. Thus, customisation is urgently needed for the delivery of online learning to different school years.
In terms of the perceived benefits and challenges of online learning, our results resonate with several previous findings. In particular, the benefits of convenience are in line with the flexibility advantages of online learning, which were mentioned in prior works (Appana, 2008 ; Bączek et al., 2021 ; Barbour, 2013 ; Basuony et al., 2020 ; Harvey et al., 2014 ). Early‐school‐year students’ higher appreciation in having “access to courses delivered by famous teachers” and lower appreciation in the independent learning skills developed through online learning are also in line with previous literature (Barbour, 2013 ; Harvey et al., 2014 ; Oliver et al., 2009 ). Again, these similar findings may indicate the strong reliance that early‐school‐year students place on teachers, while high‐school‐year students are more capable of adapting to online learning by developing independent learning skills.
Technology‐wise, students’ experience of poor internet connection and confusion in setting up online learning platforms are particularly concerning. The problem of poor internet connection corroborated the findings reported in prior studies (Agung et al., 2020 ; Barbour, 2013 ; Basuony et al., 2020 ; Berge, 2005 ; Rice, 2006 ), that is the access issue surrounded the digital divide as one of the main challenges of online learning. In the era of 4G and 5G networks, educational authorities and institutions that deliver online education could fall into the misconception of most students have a stable internet connection at home. The internet issue we observed is particularly vital to students’ online learning experience as most students prefer real‐time communications (Figure 6 ), which rely heavily on stable internet connection. Likewise, the finding of students’ confusion in technology is also consistent with prior studies (Bączek et al., 2021 ; Muilenburg & Berge, 2005 ; Niemi & Kousa, 2020 ; Song et al., 2004 ). Students who were unsuccessfully in setting up the online learning platforms could potentially experience declines in confidence and enthusiasm for online learning, which would cause a subsequent unpleasant learning experience. Therefore, both the readiness of internet infrastructure and student technical skills remain as the significant challenges for the mass‐adoption of online learning.
On the other hand, students’ experience of eyestrain from extended screen time provided empirical evidence to support Spitzer’s ( 2001 ) speculation about the potential ergonomic impact of online learning. This negative effect is potentially related to the prevalence of smartphone device and the limited screen size of these devices. This finding not only demonstrates the potential ergonomic issues that would be caused by smartphone‐based online learning but also resonates with the aforementioned necessity of different platforms and content designs for different students.
A less‐mentioned problem in previous studies on online learning experiences is the disengagement caused by nearby disturbance, especially in Year 1–3 and 10–12. It is likely that early‐school‐year students suffered from this problem because of their underdeveloped metacognitive skills to concentrate on online learning without teachers’ guidance. As for high‐school‐year students, the reasons behind their disengagement require further investigation in the future. Especially it would be worthwhile to scrutinise whether this type of disengagement is caused by the substantial amount of coursework they have to undertake and the subsequent a higher level of pressure and a lower level of concentration while learning.
Across age‐level differences are also apparent in terms of students’ expectations of online learning. Although, our results demonstrated students’ needs of gaining social interaction with others during online learning, findings (Bączek et al., 2021 ; Harvey et al., 2014 ; Kuo et al., 2014 ; Liu & Cavanaugh, 2012 ; Yates et al., 2020 ). This need manifested differently across school years, with early‐school‐year students preferring more teacher interactions and learning regulation support. Once again, this finding may imply that early‐school‐year students are inadequate in engaging with online learning without proper guidance from their teachers. Whereas, high‐school‐year students prefer more peer interactions and recommendation to learning resources. This expectation can probably be explained by the large amount of coursework exposed to them. Thus, high‐school‐year students need further guidance to help them better direct their learning efforts. These differences in students’ expectations for future practices could guide the customisation of online learning delivery.
Implications
As shown in our results, improving the delivery of online learning not only requires the efforts of policymakers but also depend on the actions of teachers and parents. The following sub‐sections will provide recommendations for relevant stakeholders and discuss their essential roles in supporting online education.
Technical support
The majority of the students has experienced technical problems during online learning, including the internet lagging and confusion in setting up the learning platforms. These problems with technology could impair students’ learning experience (Kauffman, 2015 ; Muilenburg & Berge, 2005 ). Educational authorities and schools should always provide a thorough guide and assistance for students who are experiencing technical problems with online learning platforms or other related tools. Early screening and detection could also assist schools and teachers to direct their efforts more effectively in helping students with low technology skills (Wilkinson et al., 2010 ). A potential identification method involves distributing age‐specific surveys that assess students’ Information and Communication Technology (ICT) skills at the beginning of online learning. For example, there are empirical validated ICT surveys available for both primary (Aesaert et al., 2014 ) and high school (Claro et al., 2012 ) students.
For students who had problems with internet lagging, the delivery of online learning should provide options that require fewer data and bandwidth. Lecture recording is the existing option but fails to address students’ need for real‐time interaction (Clark et al., 2015 ; Malik & Fatima, 2017 ). A potential alternative involves providing students with the option to learn with digital or physical textbooks and audio‐conferencing, instead of screen sharing and video‐conferencing. This approach significantly reduces the amount of data usage and lowers the requirement of bandwidth for students to engage in smooth online interactions (Cisco, 2018 ). It also requires little additional efforts from teachers as official textbooks are often available for each school year, and thus, they only need to guide students through the materials during audio‐conferencing. Educational authority can further support this approach by making digital textbooks available for teachers and students, especially those in financial hardship. However, the lack of visual and instructor presence could potentially reduce students’ attention, recall of information, and satisfaction in online learning (Wang & Antonenko, 2017 ). Therefore, further research is required to understand whether the combination of digital or physical textbooks and audio‐conferencing is appropriate for students with internet problems. Alternatively, suppose the local technological infrastructure is well developed. In that case, governments and schools can also collaborate with internet providers to issue data and bandwidth vouchers for students who are experiencing internet problems due to financial hardship.
For future adoption of online learning, policymakers should consider the readiness of the local internet infrastructure. This recommendation is particularly important for developing countries, like Bangladesh, where the majority of the students reported the lack of internet infrastructure (Ramij & Sultana, 2020 ). In such environments, online education may become infeasible, and alternative delivery method could be more appropriate, for example, the Telesecundaria program provides TV education for rural areas of Mexico (Calderoni, 1998 ).
Other than technical problems, choosing a suitable online learning platform is also vital for providing students with a better learning experience. Governments and schools should choose an online learning platform that is customised for smartphone‐based learning, as the majority of students could be using smartphones for online learning. This recommendation is highly relevant for situations where students are forced or involuntarily engaged in online learning, like during the COVID‐19 pandemic, as they might not have access to a personal computer (Molnar et al., 2019 ).
Customisation of delivery methods
Customising the delivery of online learning for students in different school years is the theme that appeared consistently across our findings. This customisation process is vital for making online learning an opportunity for students to develop independent learning skills, which could help prepare them for tertiary education and lifelong learning. However, the pedagogical design of K‐12 online learning programs should be differentiated from adult‐orientated programs as these programs are designed for independent learners, which is rarely the case for students in K‐12 education (Barbour & Reeves, 2009 ).
For early‐school‐year students, especially Year 1–3 students, providing them with sufficient guidance from both teachers and parents should be the priority as these students often lack the ability to monitor and reflect on learning progress. In particular, these students would prefer more real‐time interaction with teachers, tutoring from parents, and regular online practice examinations. These forms of guidance could help early‐school‐year students to cope with involuntary online learning, and potentially enhance their experience in future online learning. It should be noted that, early‐school‐year students demonstrated interest in intelligent monitoring and feedback systems for learning. Additional research is required to understand whether these young children are capable of understanding and using learning analytics that relay information on their learning progress. Similarly, future research should also investigate whether young children can communicate effectively through digital tools as potential inability could hinder student learning in online group activities. Therefore, the design of online learning for early‐school‐year students should focus less on independent learning but ensuring that students are learning effective under the guidance of teachers and parents.
In contrast, group learning and peer interaction are essential for older children and adolescents. The delivery of online learning for these students should focus on providing them with more opportunities to communicate with each other and engage in collaborative learning. Potential methods to achieve this goal involve assigning or encouraging students to form study groups (Lee et al., 2011 ), directing students to use social media for peer communication (Dabbagh & Kitsantas, 2012 ), and providing students with online group assignments (Bickle & Rucker, 2018 ).
Special attention should be paid to students enrolled in high schools. For high‐school‐year students, in particular, students in Year 10–12, we also recommend to provide them with sufficient access to paper‐based learning materials, such as revision booklet and practice exam papers, so they remain familiar with paper‐based examinations. This recommendation applies to any students who engage in online learning but has to take their final examination in paper format. It is also imperative to assist high‐school‐year students who are facing examinations to direct their learning efforts better. Teachers can fulfil this need by sharing useful learning resources on the learning management system, if it is available, or through social media groups. Alternatively, students are interested in intelligent recommendation systems for learning resources, which are emerging in the literature (Corbi & Solans, 2014 ; Shishehchi et al., 2010 ). These systems could provide personalised recommendations based on a series of evaluation on learners’ knowledge. Although it is infeasible for situations where the transformation to online learning happened rapidly (i.e., during the COVID‐19 pandemic), policymakers can consider embedding such systems in future online education.
Limitations
The current findings are limited to primary and secondary Chinese students who were involuntarily engaged in online learning during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Despite the large sample size, the population may not be representative as participants are all from a single province. Also, information about the quality of online learning platforms, teaching contents, and pedagogy approaches were missing because of the large scale of our study. It is likely that the infrastructures of online learning in China, such as learning platforms, instructional designs, and teachers’ knowledge about online pedagogy, were underprepared for the sudden transition. Thus, our findings may not represent the experience of students who voluntarily participated in well‐prepared online learning programs, in particular, the virtual school programs in America and Canada (Barbour & LaBonte, 2017 ; Molnar et al., 2019 ). Lastly, the survey was only evaluated and validated by teachers but not students. Therefore, students with the lowest reading comprehension levels might have a different understanding of the items’ meaning, especially terminologies that involve abstract contracts like self‐regulation and autonomy in item Q17.
In conclusion, we identified across‐year differences between primary and secondary school students’ online learning experience during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Several recommendations were made for the future practice and research of online learning in the K‐12 student population. First, educational authorities and schools should provide sufficient technical support to help students to overcome potential internet and technical problems, as well as choosing online learning platforms that have been customised for smartphones. Second, customising the online pedagogy design for students in different school years, in particular, focusing on providing sufficient guidance for young children, more online collaborative opportunity for older children and adolescent, and additional learning resource for senior students who are facing final examinations.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
There is no potential conflict of interest in this study.
ETHICS STATEMENT
The data are collected by the Department of Education of the Guangdong Province who also has the authority to approve research studies in K12 education in the province.
Supporting information
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62077028, 61877029), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong (2020B0909030005, 2020B1212030003, 2020ZDZX3013, 2019B1515120010, 2018KTSCX016, 2019A050510024), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou (201902010041), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (21617408, 21619404).
SURVEY ITEMS
Yan, L , Whitelock‐Wainwright, A , Guan, Q , Wen, G , Gašević, D , & Chen, G . Students’ experience of online learning during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A province‐wide survey study . Br J Educ Technol . 2021; 52 :2038–2057. 10.1111/bjet.13102 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
- Aesaert, K. , Van Nijlen, D. , Vanderlinde, R. , & van Braak, J. (2014). Direct measures of digital information processing and communication skills in primary education: Using item response theory for the development and validation of an ICT competence scale . Computers & Education , 76 , 168–181. 10.1016/j.compedu.2014.03.013 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Agung, A. S. N. , Surtikanti, M. W. , & Quinones, C. A. (2020). Students’ perception of online learning during COVID‐19 pandemic: A case study on the English students of STKIP Pamane Talino . SOSHUM: Jurnal Sosial Dan Humaniora , 10 ( 2 ), 225–235. 10.31940/soshum.v10i2.1316 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, T. (2003). Getting the mix right again: An updated and theoretical rationale for interaction . The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning , 4 ( 2 ). 10.19173/irrodl.v4i2.149 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Appana, S. (2008). A review of benefits and limitations of online learning in the context of the student, the instructor and the tenured faculty . International Journal on E‐learning , 7 ( 1 ), 5–22. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bączek, M. , Zagańczyk‐Bączek, M. , Szpringer, M. , Jaroszyński, A. , & Wożakowska‐Kapłon, B. (2021). Students’ perception of online learning during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A survey study of Polish medical students . Medicine , 100 ( 7 ), e24821. 10.1097/MD.0000000000024821 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbour, M. K. (2013). The landscape of k‐12 online learning: Examining what is known . Handbook of Distance Education , 3 , 574–593. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbour, M. , Huerta, L. , & Miron, G. (2018). Virtual schools in the US: Case studies of policy, performance and research evidence. In Society for information technology & teacher education international conference (pp. 672–677). Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education (AACE). [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbour, M. K. , & LaBonte, R. (2017). State of the nation: K‐12 e‐learning in Canada, 2017 edition . http://k12sotn.ca/wp‐content/uploads/2018/02/StateNation17.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbour, M. K. , & Reeves, T. C. (2009). The reality of virtual schools: A review of the literature . Computers & Education , 52 ( 2 ), 402–416. [ Google Scholar ]
- Basuony, M. A. K. , EmadEldeen, R. , Farghaly, M. , El‐Bassiouny, N. , & Mohamed, E. K. A. (2020). The factors affecting student satisfaction with online education during the COVID‐19 pandemic: An empirical study of an emerging Muslim country . Journal of Islamic Marketing . 10.1108/JIMA-09-2020-0301 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berge, Z. L. (2005). Virtual schools: Planning for success . Teachers College Press, Columbia University. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bickle, M. C. , & Rucker, R. (2018). Student‐to‐student interaction: Humanizing the online classroom using technology and group assignments . Quarterly Review of Distance Education , 19 ( 1 ), 1–56. [ Google Scholar ]
- Broadbent, J. , & Poon, W. L. (2015). Self‐regulated learning strategies & academic achievement in online higher education learning environments: A systematic review . The Internet and Higher Education , 27 , 1–13. [ Google Scholar ]
- Calderoni, J. (1998). Telesecundaria: Using TV to bring education to rural Mexico (Tech. Rep.). The World Bank. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cisco . (2018). Bandwidth requirements for meetings with cisco Webex and collaboration meeting rooms white paper . http://dwz.date/dpbc [ Google Scholar ]
- Cisco . (2019). Cisco digital readiness 2019 . https://www.cisco.com/c/m/en_us/about/corporate‐social‐responsibility/research‐resources/digital‐readiness‐index.html#/ (Library Catalog: www.cisco.com). [ Google Scholar ]
- Clark, C. , Strudler, N. , & Grove, K. (2015). Comparing asynchronous and synchronous video vs. text based discussions in an online teacher education course . Online Learning , 19 ( 3 ), 48–69. [ Google Scholar ]
- Claro, M. , Preiss, D. D. , San Martín, E. , Jara, I. , Hinostroza, J. E. , Valenzuela, S. , Cortes, F. , & Nussbaum, M. (2012). Assessment of 21st century ICT skills in Chile: Test design and results from high school level students . Computers & Education , 59 ( 3 ), 1042–1053. 10.1016/j.compedu.2012.04.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences . Routledge Academic. [ Google Scholar ]
- Corbi, A. , & Solans, D. B. (2014). Review of current student‐monitoring techniques used in elearning‐focused recommender systems and learning analytics: The experience API & LIME model case study . IJIMAI , 2 ( 7 ), 44–52. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dabbagh, N. , & Kitsantas, A. (2012). Personal learning environments, social media, and self‐regulated learning: A natural formula for connecting formal and informal learning . The Internet and Higher Education , 15 ( 1 ), 3–8. 10.1016/j.iheduc.2011.06.002 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garrison, D. R. , Cleveland‐Innes, M. , & Fung, T. S. (2010). Exploring causal relationships among teaching, cognitive and social presence: Student perceptions of the community of inquiry framework . The Internet and Higher Education , 13 ( 1–2 ), 31–36. 10.1016/j.iheduc.2009.10.002 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gašević, D. , Adesope, O. , Joksimović, S. , & Kovanović, V. (2015). Externally‐facilitated regulation scaffolding and role assignment to develop cognitive presence in asynchronous online discussions . The Internet and Higher Education , 24 , 53–65. 10.1016/j.iheduc.2014.09.006 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gašević, D. , Zouaq, A. , & Janzen, R. (2013). “Choose your classmates, your GPA is at stake!” The association of cross‐class social ties and academic performance . American Behavioral Scientist , 57 ( 10 ), 1460–1479. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gikas, J. , & Grant, M. M. (2013). Mobile computing devices in higher education: Student perspectives on learning with cellphones, smartphones & social media . The Internet and Higher Education , 19 , 18–26. [ Google Scholar ]
- Harvey, D. , Greer, D. , Basham, J. , & Hu, B. (2014). From the student perspective: Experiences of middle and high school students in online learning . American Journal of Distance Education , 28 ( 1 ), 14–26. 10.1080/08923647.2014.868739 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kauffman, H. (2015). A review of predictive factors of student success in and satisfaction with online learning . Research in Learning Technology , 23 . 10.3402/rlt.v23.26507 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuo, Y.‐C. , Walker, A. E. , Belland, B. R. , Schroder, K. E. , & Kuo, Y.‐T. (2014). A case study of integrating interwise: Interaction, internet self‐efficacy, and satisfaction in synchronous online learning environments . International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning , 15 ( 1 ), 161–181. 10.19173/irrodl.v15i1.1664 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee, S. J. , Srinivasan, S. , Trail, T. , Lewis, D. , & Lopez, S. (2011). Examining the relationship among student perception of support, course satisfaction, and learning outcomes in online learning . The Internet and Higher Education , 14 ( 3 ), 158–163. 10.1016/j.iheduc.2011.04.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu, F. , & Cavanaugh, C. (2012). Factors influencing student academic performance in online high school algebra . Open Learning: The Journal of Open, Distance and e‐Learning , 27 ( 2 ), 149–167. 10.1080/02680513.2012.678613 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lou, Y. , Bernard, R. M. , & Abrami, P. C. (2006). Media and pedagogy in undergraduate distance education: A theory‐based meta‐analysis of empirical literature . Educational Technology Research and Development , 54 ( 2 ), 141–176. 10.1007/s11423-006-8252-x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Malik, M. , & Fatima, G. (2017). E‐learning: Students’ perspectives about asynchronous and synchronous resources at higher education level . Bulletin of Education and Research , 39 ( 2 ), 183–195. [ Google Scholar ]
- McInnerney, J. M. , & Roberts, T. S. (2004). Online learning: Social interaction and the creation of a sense of community . Journal of Educational Technology & Society , 7 ( 3 ), 73–81. [ Google Scholar ]
- Molnar, A. , Miron, G. , Elgeberi, N. , Barbour, M. K. , Huerta, L. , Shafer, S. R. , & Rice, J. K. (2019). Virtual schools in the US 2019 . National Education Policy Center. [ Google Scholar ]
- Montague, M. , & Rinaldi, C. (2001). Classroom dynamics and children at risk: A followup . Learning Disability Quarterly , 24 ( 2 ), 75–83. [ Google Scholar ]
- Montag, C. , Becker, B. , & Gan, C. (2018). The multipurpose application Wechat: A review on recent research . Frontiers in Psychology , 9 , 2247. 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02247 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Moore, M. G. (1989). Editorial: Three types of interaction . American Journal of Distance Education , 3 ( 2 ), 1–7. 10.1080/08923648909526659 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muilenburg, L. Y. , & Berge, Z. L. (2005). Student barriers to online learning: A factor analytic study . Distance Education , 26 ( 1 ), 29–48. 10.1080/01587910500081269 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muirhead, B. , & Juwah, C. (2004). Interactivity in computer‐mediated college and university education: A recent review of the literature . Journal of Educational Technology & Society , 7 ( 1 ), 12–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- Niemi, H. M. , & Kousa, P. (2020). A case study of students’ and teachers’ perceptions in a finnish high school during the COVID pandemic . International Journal of Technology in Education and Science , 4 ( 4 ), 352–369. 10.46328/ijtes.v4i4.167 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Oliver, K. , Osborne, J. , & Brady, K. (2009). What are secondary students’ expectations for teachers in virtual school environments? Distance Education , 30 ( 1 ), 23–45. 10.1080/01587910902845923 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pardo, A. , Jovanovic, J. , Dawson, S. , Gašević, D. , & Mirriahi, N. (2019). Using learning analytics to scale the provision of personalised feedback . British Journal of Educational Technology , 50 ( 1 ), 128–138. 10.1111/bjet.12592 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramij, M. , & Sultana, A. (2020). Preparedness of online classes in developing countries amid covid‐19 outbreak: A perspective from Bangladesh. Afrin, Preparedness of Online Classes in Developing Countries amid COVID‐19 Outbreak: A Perspective from Bangladesh (June 29, 2020) .
- Rice, K. L. (2006). A comprehensive look at distance education in the k–12 context . Journal of Research on Technology in Education , 38 ( 4 ), 425–448. 10.1080/15391523.2006.10782468 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shishehchi, S. , Banihashem, S. Y. , & Zin, N. A. M. (2010). A proposed semantic recommendation system for elearning: A rule and ontology based e‐learning recommendation system. In 2010 international symposium on information technology (Vol. 1, pp. 1–5).
- Song, L. , Singleton, E. S. , Hill, J. R. , & Koh, M. H. (2004). Improving online learning: Student perceptions of useful and challenging characteristics . The Internet and Higher Education , 7 ( 1 ), 59–70. 10.1016/j.iheduc.2003.11.003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Spitzer, D. R. (2001). Don’t forget the high‐touch with the high‐tech in distance learning . Educational Technology , 41 ( 2 ), 51–55. [ Google Scholar ]
- Thomas, R. M. (2000). Comparing theories of child development. Wadsworth/Thomson Learning. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. (2020, March). Education: From disruption to recovery . https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse (Library Catalog: en.unesco.org)
- Uttal, D. H. , & Cohen, C. A. (2012). Spatial thinking and stem education: When, why, and how? In Psychology of learning and motivation (Vol. 57 , pp. 147–181). Elsevier. [ Google Scholar ]
- Van Lancker, W. , & Parolin, Z. (2020). Covid‐19, school closures, and child poverty: A social crisis in the making . The Lancet Public Health , 5 ( 5 ), e243–e244. 10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30084-0 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, C.‐H. , Shannon, D. M. , & Ross, M. E. (2013). Students’ characteristics, self‐regulated learning, technology self‐efficacy, and course outcomes in online learning . Distance Education , 34 ( 3 ), 302–323. 10.1080/01587919.2013.835779 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, J. , & Antonenko, P. D. (2017). Instructor presence in instructional video: Effects on visual attention, recall, and perceived learning . Computers in Human Behavior , 71 , 79–89. 10.1016/j.chb.2017.01.049 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilkinson, A. , Roberts, J. , & While, A. E. (2010). Construction of an instrument to measure student information and communication technology skills, experience and attitudes to e‐learning . Computers in Human Behavior , 26 ( 6 ), 1369–1376. 10.1016/j.chb.2010.04.010 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organization . (2020, July). Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): Situation Report‐164 (Situation Report No. 164). https://www.who.int/docs/default‐source/coronaviruse/situation‐reports/20200702‐covid‐19‐sitrep‐164.pdf?sfvrsn$=$ac074f58$_$2
- Yates, A. , Starkey, L. , Egerton, B. , & Flueggen, F. (2020). High school students’ experience of online learning during Covid‐19: The influence of technology and pedagogy . Technology, Pedagogy and Education , 9 , 1–15. 10.1080/1475939X.2020.1854337 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

Online Education Essay: Distance Education & E-Learning
Online education has emerged as a dynamic and versatile alternative, providing learners with unprecedented access to a wealth of resources and opportunities. Let’s explore here, Online Education Essay
Online education, also known as e-learning or distance learning, is an innovative approach to acquiring knowledge and skills using digital technology and the Internet as the main medium of instruction.
This allows learners to remotely access educational content, interact with teachers, and collaborate with peers, overcoming geographic barriers and traditional classroom limitations.
Online education has experienced significant growth and development in recent years, changing the way people of all ages and backgrounds approach learning.
Online education essay explores the transformative power, benefits, challenges, and future prospects of online education in the modern era.
The importance of online education in today’s world cannot be overstated. The key points that highlight its importance are, such as…
Accessibility : Online education makes learning accessible to audiences around the world, overcoming geographic barriers. This allows people in remote and underserved areas to access quality education.
Flexibility : In an increasingly fast-paced world, online education offers flexibility in when and where you learn. This takes into account different schedules and lifestyles, including those of professionals and parents.
Lifelong learning : Online education promotes lifelong learning. Learners can gain new skills and knowledge at every stage of their lives and accelerate their personal and professional development.
Cost-effective : It often proves to be more cost-effective than traditional education. Learners can save on transportation, accommodation, and textbooks. This affordability increases access to education.
Customization : Online platforms allow you to personalize your learning experience and adapt content to your individual needs and speed. This improves comprehension and memory.
Technological advances : Integrating cutting-edge technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI) enriches the online learning experience and prepares learners for the digital age.
Pandemic response : The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the critical role of online education in ensuring continuity of learning during a crisis. This has become an important part of the education resilience toolkit.
Global collaboration : Online education fosters international collaboration and diverse perspectives. Learners can interact with peers and instructors from around the world, enriching their educational experience.
Employability : Many online courses and degrees are designed to be industry-relevant. Learners will gain skills that are directly applicable to their career goals.
Sustainability : Online education contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing the carbon footprint associated with commuting to a physical campus.
Overview of the components that typically make up the structure of online education.
1. Platform or institution website
Online education experiences often begin with a platform or institution’s website. This website serves as a central hub where learners can access information about available courses, enrollment, and resources.
2. Registration and Registration
Learners typically begin by enrolling in a course or program online. Registration may include creating an account, providing personal information, and selecting a course.
3. Course catalog
Online education platforms typically maintain a catalog of available courses and programs. Learners can search this catalog to find courses that match their interests and goals.
4. Course structure
Each course or program has its own structure and may include modules, units, and lessons. The course structure describes the order in which content is presented and the learning objectives for each section.
5. Learning resources
Online courses typically offer a variety of learning materials, including video lectures, text-based content, multimedia, and downloadable resources. These materials can be accessed through the Platform’s interface.
6. Interactive elements
Many online courses include interactive elements to engage learners, such as discussion forums, quizzes, assignments, and group projects. Learners can use these tools to communicate with instructors and other students.
7. Evaluation and scoring
Online courses include assessments to assess learner understanding of the material. Evaluation methods vary but include quizzes, exams, essays, peer reviews, and participation grades.
8. Support and help
Online learners often have access to technical and academic support. Depending on the platform, support can be provided via email, chat, or help desk.
9. Track your progress
Many platforms offer tools that allow learners to track their progress throughout a course. Learners can monitor completed assignments, upcoming deadlines, and overall course progress.
10. Certifications and references
Upon successfully completing a course or program, learners can receive a certificate, degree, or digital badge. You can add these credentials to your resume or share them on your professional profile.
11. Community and Commitment
Online education often focuses on building a sense of community among learners. To encourage participation, you can offer discussion forums, virtual meetings, and networking opportunities.
12. Privacy and security
The platform focuses on privacy and security, ensuring that learners’ personal information is protected. It will typically outline your privacy policy and data processing practices.
13. Frequently Asked Questions and Help Center
Many platforms offer a section where learners can find answers to frequently asked questions. You can provide a comprehensive help center or knowledge base.
14. Feedback and improvements
Platforms often seek feedback from learners to improve their online education experience. This feedback can be used to improve the content, functionality, and usability of your course.

The Evolution of Online Education
The evolution of online education has been a dynamic journey marked by significant advances in technology and changes in educational paradigms.
Early experiments (1960s-1970s)
The concept of online education dates back to the 1960s when educational institutions such as the University of Illinois began experimenting with computer-based education. Early efforts focused on delivering educational content via mainframe computers and teleprinters.
Emergence of the Internet (1980s-1990s)
The development of the World Wide Web in the late 1980s and early 1990s laid the foundation for modern online education. Educational institutions began to explore the potential of the Internet to provide course materials and facilitate communication.
First online courses (1990s)
The first online courses, often referred to as “virtual classrooms” or “e-learning,” appeared in the mid-1990s. These courses included text-based content and basic discussion forums. Learning Management
Systems (LMS) (late 1990s to 2000s)
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, learning management systems (LMS) such as Blackboard and Moodle were developed. LMS platforms have given teachers the tools to create, manage, and deliver online courses.
Multimedia integration (2000s)
As Internet bandwidth improved, online courses began to incorporate multimedia elements such as videos, animations, and interactive simulations. This has enriched the learning experience and made online education more engaging.
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) (2010s)
In the 2010s, MOOCs emerged, allowing students to take courses from famous universities for free. His MOOC platforms such as Coursera, edX, and Udacity have reached millions of learners around the world.
Personalization and adaptive learning (since 2010)
Online education platforms are beginning to implement personalized learning paths and adaptive technology. Algorithms analyze learner progress and tailor content to individual needs.
Blended learning (since 2010)
Blended learning models that combine online and in-person instruction are becoming increasingly popular in K-12 and higher education. This approach provides flexibility while maintaining personal interaction.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) (since 2010)
Advances in VR and AR technology are being integrated into online education to provide immersive learning experiences. Learners can explore virtual environments and simulations.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic (2020)
The global pandemic has forced schools and universities to close to prevent the spread of the virus, forcing a rapid shift to online education. This has accelerated the adoption of online learning and highlighted the need for a robust digital infrastructure.
Hybrid and distance learning (2020s)
Many institutions will continue to offer online and hybrid learning options even after in-person classes resume. Remote work and online education are becoming more integrated into daily life.
Continuous innovation (ongoing)
As technology advances, online education continues to evolve. Artificial intelligence, data analytics, and learning analytics are playing an increasingly important role in the design of online learning experiences.
Benefits of Online Education
Challenges in Online Education (Online education essay)
Technological Advancements in Online Learning (Online education essay)
Advances in technology have revolutionized the online learning landscape, improving the educational experience and expanding its possibilities. The main technological advances in online learning are as…
Learning Management System (LMS)
LMS platforms such as Moodle, Blackboard, and Canvas provide a central hub for course management, content delivery, and communication between instructors and students.
Mobile learning (M-Learning)
Mobile apps and responsive design make learning more accessible as learners can access course materials and participate in learning activities on their smartphones and tablets.
Video conferences and webinars
Tools like Zoom and Microsoft Teams make it easy to conduct live virtual classes and webinars, facilitating real-time interaction between instructors and learners.
Gamification
Gamification techniques such as badges, leaderboards, and interactive quizzes make learning more engaging and motivate learners to progress through course content.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR)
VR and AR technology provide an immersive learning experience, allowing learners to explore virtual environments and interact with their 3D objects, making it ideal for training in fields such as medicine, engineering, and aviation.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
AI-powered tools analyze learner data and provide personalized recommendations, including adaptive learning paths and targeted resources to address individual needs.
Big data and learning analytics
Big data analytics provides insights into learner behavior and performance, helping educators make data-driven decisions and improve course design and instruction.
Cloud computing
Cloud-based platforms store and deliver course content, making it accessible from anywhere and ensuring scalability for institutions and course providers.
Open Educational Resources (OER)
OER repositories provide free, open-licensed educational materials such as textbooks, videos, and assessments, reducing costs for learners.
Blockchain credentials
Blockchain technology is used to issue and verify digital credentials, making it easier to verify the authenticity of degrees, certificates, and badges earned online.
Chatbots and virtual assistants
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide instant support to learners by answering questions and guiding them through course content.
Peer learning platform
Online platforms facilitate peer-to-peer learning through features such as discussion forums, group projects, and collaboration tools.
Language processing and translation tools
Language processing technology and translation tools help you deliver courses in multiple languages and support diverse learning groups.
Accessibility tools
Assistive technologies such as screen readers and closed captioning make online education more accessible to people with disabilities.
Cyber security measures
Robust cybersecurity measures protect online learning platforms and learner data from cyber threats, ensuring the privacy and security of online education.
The Future of Online Education (Online education essay)
The future of online education holds tremendous growth and innovation. Advances in technology such as augmented reality and artificial intelligence provide immersive and personalized learning experiences.
Learning analytics provides deep insights and allows educators to tailor instruction to individual needs. The global reach of online education is expanding, providing access to high-quality courses to learners in underserved areas.
Moreover, online education will increasingly complement traditional classrooms and create hybrid learning environments. Continuing education and lifelong learning are becoming the norm as the lines between work and study blur.
The future of online education promises increased accessibility, flexibility, and relevance in a rapidly evolving knowledge-based world.
Online Education Best Practices (Online education essay)
Best practices in online education are essential to ensuring an effective and engaging digital learning experience. Clear communication between teachers and students, as well as between colleagues, is very important.
Well-structured courses with structured content, intuitive navigation, and regular updates accelerate student success. Encouraging active participation through discussions, collaborative projects, and peer feedback fosters a sense of community.
Flexibility in assessment and learning paths accommodates the diverse needs of learners. Timely feedback and support, as well as technical troubleshooting assistance, will enhance your learning process.
Additionally, educators must continually adapt to evolving online tools and teaching methods to ensure that online education is accessible, engaging, and effective.
We hope this online education essay covers all aspects of distance learning and e-learning and helps you understand this type of education.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
My Online Learning Experience Essay Example
Although online school has flexibility and benefits, in- person school is more beneficial because there is increased teacher communication, students perform better at school, and it is more active and involved.
Some people mention that online school has various benefits and flexibility. Citing the article, 5 Key Benefits of Online High School by ICON, it says, “Online education provides an unparalleled flexibility that allows for a customized experience. With self-directed learning and no mandatory live classes, you can play to your strengths.” Online school allows students to learn freely, without any pressure from in- person school and teachers. Students can learn at the comfort of their home, which most likely could make school more enjoyable and relaxing. According to the same article written by ICON they say, “For some students, a traditional school can be incredibly uncomfortable, sparking social anxiety, behavioral problems, and mental health issues. Why not remove the barriers and keep the educational content with online classes?” When kids are at risk of developing a mental illness because of in- person school, online school is a great way to avoid any possibilities of mental illness. Online school can help students become more comfortable with handling school and staying out of harm’s way from mental illness. Online school also provides more comfort and stability while being at home in their own alleviation. However online school has many benefits, in-person school allows more opportunities.
Even though online school has some positives, in-person school involves more teacher communication and association. According to the College Times, Miranda Cyr quotes, “’It’s much easier to form a relationship with the professor,” Nardizzi says. “Online, I usually don’t get to know my professor or only correspond with them via email so it doesn’t feel like a real relationship, especially as a lot of teachers can be great resources or future references.’” When in in-person school, students always need assistance and help. For online school, students and teachers are communicating through email, it is certainly more difficult to have a good relationship. In the Article, My College Guide, it explains, “Online learning can’t adequately replicate the relationship and human experience that develops in a face-to-face learning environment. When a professor is physically in front of you, you can read his or her body language, mannerisms, gestures, tone, volume and so on. These things help you to interpret and recall the information being presented. You are also able to engage in natural, spontaneous conversations with classmates that can enrich the learning experience.” When there is a teacher always there to help and assist students with assignments, tests, etc., it is more comforting to know that there is always help around. The stress and pressure to do things independently can get overwhelming, and it’s remarkably more suitable to have help near. In- person school can help kids have a better relationship with teachers, helping them accomplish more.
Next, students perform and accomplish more in in-person school. To speak from experience, I had to do online school for the last term of my 8th grade school year. At the beginning, I enjoyed not having to follow the same schedule every day. It was nice to sleep in and do schoolwork in my pj’s and in my bed. However, after a few weeks I started to fall behind, and I would procrastinate all my assignments because I had “so much time”. This was not the case, however. Because of all of the procrastination and delay, I was so stressed due to all the work I had to get done in a period of time. I did well in the end, but this story does show how easy it is to fall behind and not be able to catch up. It was way too easy to procrastinate. In the article, How Effective is Online Learning? What the Research Does and Doesn’t Tell Us by Susanna Loeb, she explains, “It is not surprising that in-person courses are, on average, more effective. Being in person with teachers and other students creates social pressures and benefits that can help motivate students to engage.” When students aren’t interested and engaged to learn, it is harder for them to perform well. Being at home makes it too easy to put work aside and procrastinate.
Lastly, in-person school is more active and involved. There are many things that go on at in-person school including, sports, clubs, student government, etc. Online school stops students from having the crucial social life the true high school, college, and elementary school experience. According to the College Times they reason, “I prefer in-person classes mainly because of the more hands-on learning approach that I think in-person classes have,” Nardizzi says. “It’s much easier to be distant and detached from the course, your classmates and the professor in an online class.” In-person courses hold the student accountable for remaining active and alert during class time.” In-person school helps students be aware of their priorities and duties. When at school, students are more present and engaged in the classroom. In the article USA Today, Erin Richards tells a story about a girl named Ruby Rodriguez. She says, “Virtual learning might be keeping Ruby, 14, and her family safer during a public health crisis. But it has made it exponentially harder for her to stay motivated and learn. Her online classes are lecture-heavy, repetitive and devoid of student conversation.” Online school is filled with repetitive days and lack of attention to do schoolwork. Being at school helps students stay more alert to their tasks to be more involved in school.
To conclude, in- person school is more beneficial because there is increased teacher communication, students perform better at school, and it is more active and involved. Face to face school is crucial for college students, elementary students, and high school students to be successful. School is more enjoyable when students can be social and can be with each other on a day to day basis. In-person school helps students grow, become better and obtain knowledge.
Related Samples
- Persuasive Essay Sample: The SHSAT Should Be Abolished
- Experience Essay about Gap Year
- Essay about TOK Exhibition
- Should Mobile Phones be Banned in Schools? Essay Example
- Essay Sample about UCLA
- Experience Essay on STEM Membership
- Essay Example on Studying Astronomy
- The Importance of Standardized Testing Argumentative Essay
- Year-Round School Persuasive Essay Example
- Persuasive Essay on School Uniforms Should Be Banned In School
Didn't find the perfect sample?

You can order a custom paper by our expert writers
- Open supplemental data
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, insights into students’ experiences and perceptions of remote learning methods: from the covid-19 pandemic to best practice for the future.

- 1 Minerva Schools at Keck Graduate Institute, San Francisco, CA, United States
- 2 Ronin Institute for Independent Scholarship, Montclair, NJ, United States
- 3 Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
This spring, students across the globe transitioned from in-person classes to remote learning as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. This unprecedented change to undergraduate education saw institutions adopting multiple online teaching modalities and instructional platforms. We sought to understand students’ experiences with and perspectives on those methods of remote instruction in order to inform pedagogical decisions during the current pandemic and in future development of online courses and virtual learning experiences. Our survey gathered quantitative and qualitative data regarding students’ experiences with synchronous and asynchronous methods of remote learning and specific pedagogical techniques associated with each. A total of 4,789 undergraduate participants representing institutions across 95 countries were recruited via Instagram. We find that most students prefer synchronous online classes, and students whose primary mode of remote instruction has been synchronous report being more engaged and motivated. Our qualitative data show that students miss the social aspects of learning on campus, and it is possible that synchronous learning helps to mitigate some feelings of isolation. Students whose synchronous classes include active-learning techniques (which are inherently more social) report significantly higher levels of engagement, motivation, enjoyment, and satisfaction with instruction. Respondents’ recommendations for changes emphasize increased engagement, interaction, and student participation. We conclude that active-learning methods, which are known to increase motivation, engagement, and learning in traditional classrooms, also have a positive impact in the remote-learning environment. Integrating these elements into online courses will improve the student experience.
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically changed the demographics of online students. Previously, almost all students engaged in online learning elected the online format, starting with individual online courses in the mid-1990s through today’s robust online degree and certificate programs. These students prioritize convenience, flexibility and ability to work while studying and are older than traditional college age students ( Harris and Martin, 2012 ; Levitz, 2016 ). These students also find asynchronous elements of a course are more useful than synchronous elements ( Gillingham and Molinari, 2012 ). In contrast, students who chose to take courses in-person prioritize face-to-face instruction and connection with others and skew considerably younger ( Harris and Martin, 2012 ). This leaves open the question of whether students who prefer to learn in-person but are forced to learn remotely will prefer synchronous or asynchronous methods. One study of student preferences following a switch to remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic indicates that students enjoy synchronous over asynchronous course elements and find them more effective ( Gillis and Krull, 2020 ). Now that millions of traditional in-person courses have transitioned online, our survey expands the data on student preferences and explores if those preferences align with pedagogical best practices.
An extensive body of research has explored what instructional methods improve student learning outcomes (Fink. 2013). Considerable evidence indicates that active-learning or student-centered approaches result in better learning outcomes than passive-learning or instructor-centered approaches, both in-person and online ( Freeman et al., 2014 ; Chen et al., 2018 ; Davis et al., 2018 ). Active-learning approaches include student activities or discussion in class, whereas passive-learning approaches emphasize extensive exposition by the instructor ( Freeman et al., 2014 ). Constructivist learning theories argue that students must be active participants in creating their own learning, and that listening to expert explanations is seldom sufficient to trigger the neurological changes necessary for learning ( Bostock, 1998 ; Zull, 2002 ). Some studies conclude that, while students learn more via active learning, they may report greater perceptions of their learning and greater enjoyment when passive approaches are used ( Deslauriers et al., 2019 ). We examine student perceptions of remote learning experiences in light of these previous findings.
In this study, we administered a survey focused on student perceptions of remote learning in late May 2020 through the social media account of @unjadedjade to a global population of English speaking undergraduate students representing institutions across 95 countries. We aim to explore how students were being taught, the relationship between pedagogical methods and student perceptions of their experience, and the reasons behind those perceptions. Here we present an initial analysis of the results and share our data set for further inquiry. We find that positive student perceptions correlate with synchronous courses that employ a variety of interactive pedagogical techniques, and that students overwhelmingly suggest behavioral and pedagogical changes that increase social engagement and interaction. We argue that these results support the importance of active learning in an online environment.
Materials and Methods
Participant pool.
Students were recruited through the Instagram account @unjadedjade. This social media platform, run by influencer Jade Bowler, focuses on education, effective study tips, ethical lifestyle, and promotes a positive mindset. For this reason, the audience is presumably academically inclined, and interested in self-improvement. The survey was posted to her account and received 10,563 responses within the first 36 h. Here we analyze the 4,789 of those responses that came from undergraduates. While we did not collect demographic or identifying information, we suspect that women are overrepresented in these data as followers of @unjadedjade are 80% women. A large minority of respondents were from the United Kingdom as Jade Bowler is a British influencer. Specifically, 43.3% of participants attend United Kingdom institutions, followed by 6.7% attending university in the Netherlands, 6.1% in Germany, 5.8% in the United States and 4.2% in Australia. Ninety additional countries are represented in these data (see Supplementary Figure 1 ).
Survey Design
The purpose of this survey is to learn about students’ instructional experiences following the transition to remote learning in the spring of 2020.
This survey was initially created for a student assignment for the undergraduate course Empirical Analysis at Minerva Schools at KGI. That version served as a robust pre-test and allowed for identification of the primary online platforms used, and the four primary modes of learning: synchronous (live) classes, recorded lectures and videos, uploaded or emailed materials, and chat-based communication. We did not adapt any open-ended questions based on the pre-test survey to avoid biasing the results and only corrected language in questions for clarity. We used these data along with an analysis of common practices in online learning to revise the survey. Our revised survey asked students to identify the synchronous and asynchronous pedagogical methods and platforms that they were using for remote learning. Pedagogical methods were drawn from literature assessing active and passive teaching strategies in North American institutions ( Fink, 2013 ; Chen et al., 2018 ; Davis et al., 2018 ). Open-ended questions asked students to describe why they preferred certain modes of learning and how they could improve their learning experience. Students also reported on their affective response to learning and participation using a Likert scale.
The revised survey also asked whether students had responded to the earlier survey. No significant differences were found between responses of those answering for the first and second times (data not shown). See Supplementary Appendix 1 for survey questions. Survey data was collected from 5/21/20 to 5/23/20.
Qualitative Coding
We applied a qualitative coding framework adapted from Gale et al. (2013) to analyze student responses to open-ended questions. Four researchers read several hundred responses and noted themes that surfaced. We then developed a list of themes inductively from the survey data and deductively from the literature on pedagogical practice ( Garrison et al., 1999 ; Zull, 2002 ; Fink, 2013 ; Freeman et al., 2014 ). The initial codebook was revised collaboratively based on feedback from researchers after coding 20–80 qualitative comments each. Before coding their assigned questions, alignment was examined through coding of 20 additional responses. Researchers aligned in identifying the same major themes. Discrepancies in terms identified were resolved through discussion. Researchers continued to meet weekly to discuss progress and alignment. The majority of responses were coded by a single researcher using the final codebook ( Supplementary Table 1 ). All responses to questions 3 (4,318 responses) and 8 (4,704 responses), and 2,512 of 4,776 responses to question 12 were analyzed. Valence was also indicated where necessary (i.e., positive or negative discussion of terms). This paper focuses on the most prevalent themes from our initial analysis of the qualitative responses. The corresponding author reviewed codes to ensure consistency and accuracy of reported data.
Statistical Analysis
The survey included two sets of Likert-scale questions, one consisting of a set of six statements about students’ perceptions of their experiences following the transition to remote learning ( Table 1 ). For each statement, students indicated their level of agreement with the statement on a five-point scale ranging from 1 (“Strongly Disagree”) to 5 (“Strongly Agree”). The second set asked the students to respond to the same set of statements, but about their retroactive perceptions of their experiences with in-person instruction before the transition to remote learning. This set was not the subject of our analysis but is present in the published survey results. To explore correlations among student responses, we used CrossCat analysis to calculate the probability of dependence between Likert-scale responses ( Mansinghka et al., 2016 ).
Table 1. Likert-scale questions.
Mean values are calculated based on the numerical scores associated with each response. Measures of statistical significance for comparisons between different subgroups of respondents were calculated using a two-sided Mann-Whitney U -test, and p -values reported here are based on this test statistic. We report effect sizes in pairwise comparisons using the common-language effect size, f , which is the probability that the response from a random sample from subgroup 1 is greater than the response from a random sample from subgroup 2. We also examined the effects of different modes of remote learning and technological platforms using ordinal logistic regression. With the exception of the mean values, all of these analyses treat Likert-scale responses as ordinal-scale, rather than interval-scale data.
Students Prefer Synchronous Class Sessions
Students were asked to identify their primary mode of learning given four categories of remote course design that emerged from the pilot survey and across literature on online teaching: live (synchronous) classes, recorded lectures and videos, emailed or uploaded materials, and chats and discussion forums. While 42.7% ( n = 2,045) students identified live classes as their primary mode of learning, 54.6% ( n = 2613) students preferred this mode ( Figure 1 ). Both recorded lectures and live classes were preferred over uploaded materials (6.22%, n = 298) and chat (3.36%, n = 161).
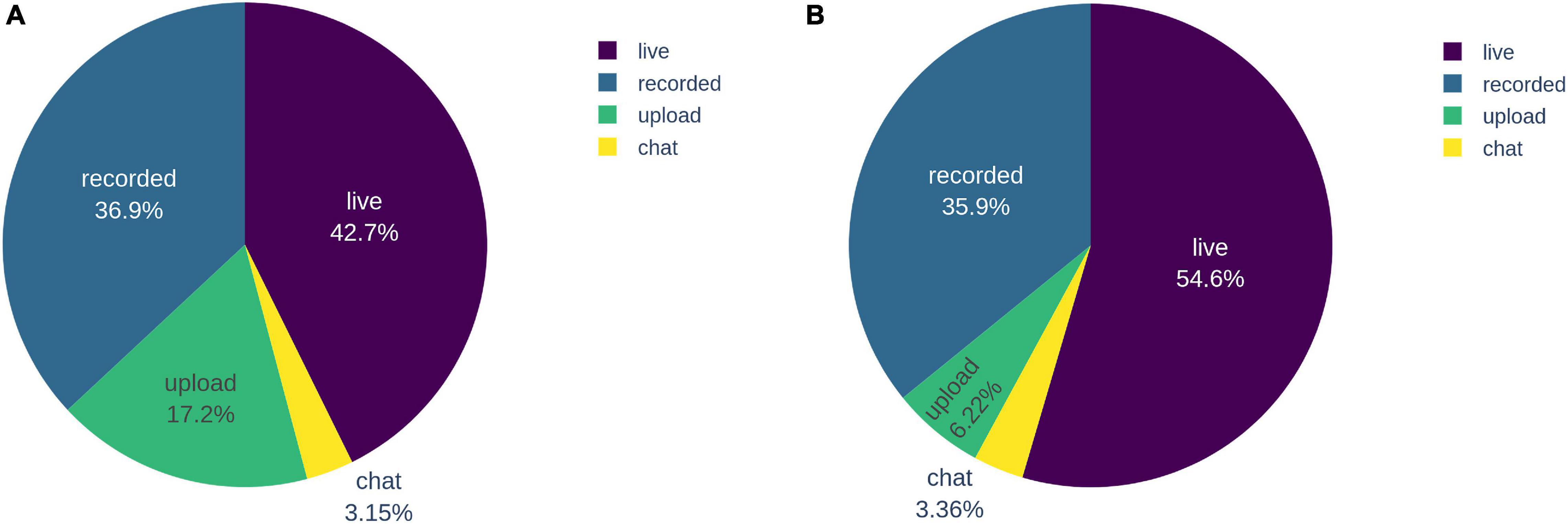
Figure 1. Actual (A) and preferred (B) primary modes of learning.
In addition to a preference for live classes, students whose primary mode was synchronous were more likely to enjoy the class, feel motivated and engaged, be satisfied with instruction and report higher levels of participation ( Table 2 and Supplementary Figure 2 ). Regardless of primary mode, over two-thirds of students reported they are often distracted during remote courses.
Table 2. The effect of synchronous vs. asynchronous primary modes of learning on student perceptions.
Variation in Pedagogical Techniques for Synchronous Classes Results in More Positive Perceptions of the Student Learning Experience
To survey the use of passive vs. active instructional methods, students reported the pedagogical techniques used in their live classes. Among the synchronous methods, we identify three different categories ( National Research Council, 2000 ; Freeman et al., 2014 ). Passive methods (P) include lectures, presentations, and explanation using diagrams, white boards and/or other media. These methods all rely on instructor delivery rather than student participation. Our next category represents active learning through primarily one-on-one interactions (A). The methods in this group are in-class assessment, question-and-answer (Q&A), and classroom chat. Group interactions (F) included classroom discussions and small-group activities. Given these categories, Mann-Whitney U pairwise comparisons between the 7 possible combinations and Likert scale responses about student experience showed that the use of a variety of methods resulted in higher ratings of experience vs. the use of a single method whether or not that single method was active or passive ( Table 3 ). Indeed, students whose classes used methods from each category (PAF) had higher ratings of enjoyment, motivation, and satisfaction with instruction than those who only chose any single method ( p < 0.0001) and also rated higher rates of participation and engagement compared to students whose only method was passive (P) or active through one-on-one interactions (A) ( p < 0.00001). Student ratings of distraction were not significantly different for any comparison. Given that sets of Likert responses often appeared significant together in these comparisons, we ran a CrossCat analysis to look at the probability of dependence across Likert responses. Responses have a high probability of dependence on each other, limiting what we can claim about any discrete response ( Supplementary Figure 3 ).
Table 3. Comparison of combinations of synchronous methods on student perceptions. Effect size (f).
Mann-Whitney U pairwise comparisons were also used to check if improvement in student experience was associated with the number of methods used vs. the variety of types of methods. For every comparison, we found that more methods resulted in higher scores on all Likert measures except distraction ( Table 4 ). Even comparison between four or fewer methods and greater than four methods resulted in a 59% chance that the latter enjoyed the courses more ( p < 0.00001) and 60% chance that they felt more motivated to learn ( p < 0.00001). Students who selected more than four methods ( n = 417) were also 65.1% ( p < 0.00001), 62.9% ( p < 0.00001) and 64.3% ( p < 0.00001) more satisfied with instruction, engaged, and actively participating, respectfully. Therefore, there was an overlap between how the number and variety of methods influenced students’ experiences. Since the number of techniques per category is 2–3, we cannot fully disentangle the effect of number vs. variety. Pairwise comparisons to look at subsets of data with 2–3 methods from a single group vs. 2–3 methods across groups controlled for this but had low sample numbers in most groups and resulted in no significant findings (data not shown). Therefore, from the data we have in our survey, there seems to be an interdependence between number and variety of methods on students’ learning experiences.
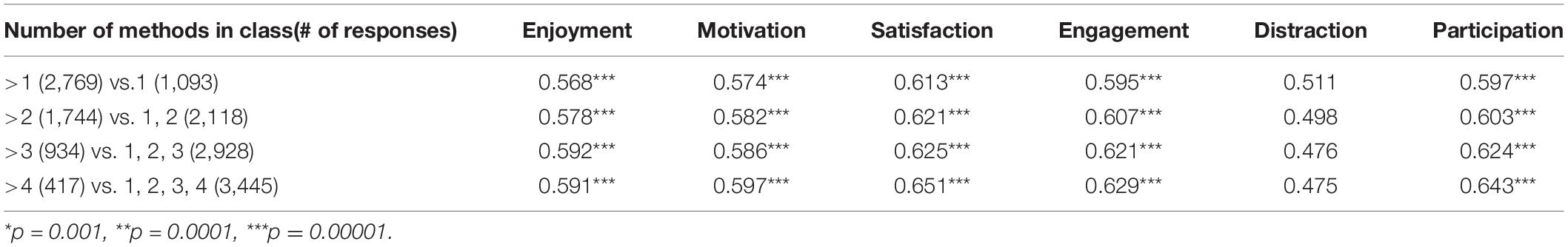
Table 4. Comparison of the number of synchronous methods on student perceptions. Effect size (f).
Variation in Asynchronous Pedagogical Techniques Results in More Positive Perceptions of the Student Learning Experience
Along with synchronous pedagogical methods, students reported the asynchronous methods that were used for their classes. We divided these methods into three main categories and conducted pairwise comparisons. Learning methods include video lectures, video content, and posted study materials. Interacting methods include discussion/chat forums, live office hours, and email Q&A with professors. Testing methods include assignments and exams. Our results again show the importance of variety in students’ perceptions ( Table 5 ). For example, compared to providing learning materials only, providing learning materials, interaction, and testing improved enjoyment ( f = 0.546, p < 0.001), motivation ( f = 0.553, p < 0.0001), satisfaction with instruction ( f = 0.596, p < 0.00001), engagement ( f = 0.572, p < 0.00001) and active participation ( f = 0.563, p < 0.00001) (row 6). Similarly, compared to just being interactive with conversations, the combination of all three methods improved five out of six indicators, except for distraction in class (row 11).
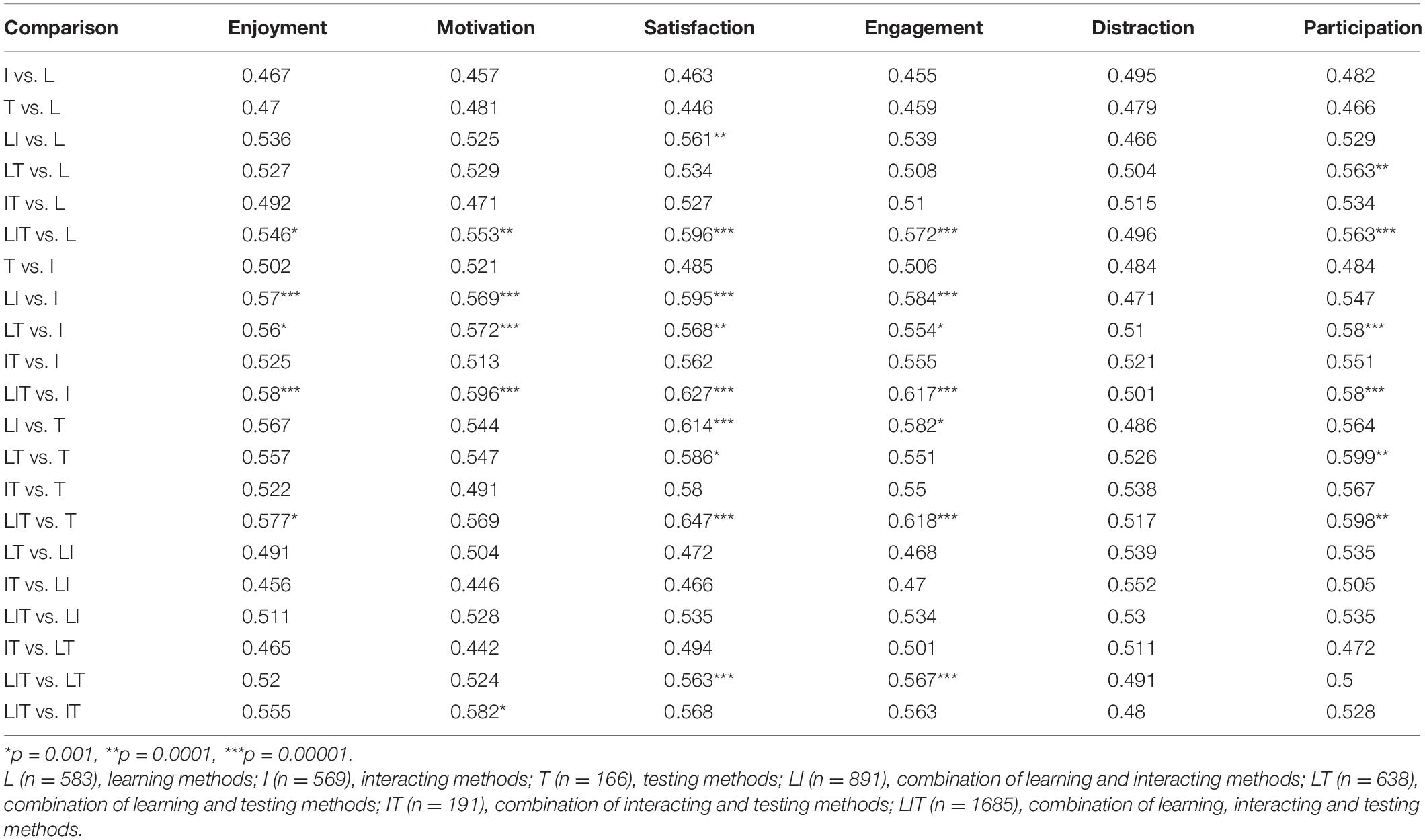
Table 5. Comparison of combinations of asynchronous methods on student perceptions. Effect size (f).
Ordinal logistic regression was used to assess the likelihood that the platforms students used predicted student perceptions ( Supplementary Table 2 ). Platform choices were based on the answers to open-ended questions in the pre-test survey. The synchronous and asynchronous methods used were consistently more predictive of Likert responses than the specific platforms. Likewise, distraction continued to be our outlier with no differences across methods or platforms.
Students Prefer In-Person and Synchronous Online Learning Largely Due to Social-Emotional Reasoning
As expected, 86.1% (4,123) of survey participants report a preference for in-person courses, while 13.9% (666) prefer online courses. When asked to explain the reasons for their preference, students who prefer in-person courses most often mention the importance of social interaction (693 mentions), engagement (639 mentions), and motivation (440 mentions). These students are also more likely to mention a preference for a fixed schedule (185 mentions) vs. a flexible schedule (2 mentions).
In addition to identifying social reasons for their preference for in-person learning, students’ suggestions for improvements in online learning focus primarily on increasing interaction and engagement, with 845 mentions of live classes, 685 mentions of interaction, 126 calls for increased participation and calls for changes related to these topics such as, “Smaller teaching groups for live sessions so that everyone is encouraged to talk as some people don’t say anything and don’t participate in group work,” and “Make it less of the professor reading the pdf that was given to us and more interaction.”
Students who prefer online learning primarily identify independence and flexibility (214 mentions) and reasons related to anxiety and discomfort in in-person settings (41 mentions). Anxiety was only mentioned 12 times in the much larger group that prefers in-person learning.
The preference for synchronous vs. asynchronous modes of learning follows similar trends ( Table 6 ). Students who prefer live classes mention engagement and interaction most often while those who prefer recorded lectures mention flexibility.
Table 6. Most prevalent themes for students based on their preferred mode of remote learning.
Student Perceptions Align With Research on Active Learning
The first, and most robust, conclusion is that incorporation of active-learning methods correlates with more positive student perceptions of affect and engagement. We can see this clearly in the substantial differences on a number of measures, where students whose classes used only passive-learning techniques reported lower levels of engagement, satisfaction, participation, and motivation when compared with students whose classes incorporated at least some active-learning elements. This result is consistent with prior research on the value of active learning ( Freeman et al., 2014 ).
Though research shows that student learning improves in active learning classes, on campus, student perceptions of their learning, enjoyment, and satisfaction with instruction are often lower in active-learning courses ( Deslauriers et al., 2019 ). Our finding that students rate enjoyment and satisfaction with instruction higher for active learning online suggests that the preference for passive lectures on campus relies on elements outside of the lecture itself. That might include the lecture hall environment, the social physical presence of peers, or normalization of passive lectures as the expected mode for on-campus classes. This implies that there may be more buy-in for active learning online vs. in-person.
A second result from our survey is that student perceptions of affect and engagement are associated with students experiencing a greater diversity of learning modalities. We see this in two different results. First, in addition to the fact that classes that include active learning outperform classes that rely solely on passive methods, we find that on all measures besides distraction, the highest student ratings are associated with a combination of active and passive methods. Second, we find that these higher scores are associated with classes that make use of a larger number of different methods.
This second result suggests that students benefit from classes that make use of multiple different techniques, possibly invoking a combination of passive and active methods. However, it is unclear from our data whether this effect is associated specifically with combining active and passive methods, or if it is associated simply with the use of multiple different methods, irrespective of whether those methods are active, passive, or some combination. The problem is that the number of methods used is confounded with the diversity of methods (e.g., it is impossible for a classroom using only one method to use both active and passive methods). In an attempt to address this question, we looked separately at the effect of number and diversity of methods while holding the other constant. Across a large number of such comparisons, we found few statistically significant differences, which may be a consequence of the fact that each comparison focused on a small subset of the data.
Thus, our data suggests that using a greater diversity of learning methods in the classroom may lead to better student outcomes. This is supported by research on student attention span which suggests varying delivery after 10–15 min to retain student’s attention ( Bradbury, 2016 ). It is likely that this is more relevant for online learning where students report high levels of distraction across methods, modalities, and platforms. Given that number and variety are key, and there are few passive learning methods, we can assume that some combination of methods that includes active learning improves student experience. However, it is not clear whether we should predict that this benefit would come simply from increasing the number of different methods used, or if there are benefits specific to combining particular methods. Disentangling these effects would be an interesting avenue for future research.
Students Value Social Presence in Remote Learning
Student responses across our open-ended survey questions show a striking difference in reasons for their preferences compared with traditional online learners who prefer flexibility ( Harris and Martin, 2012 ; Levitz, 2016 ). Students reasons for preferring in-person classes and synchronous remote classes emphasize the desire for social interaction and echo the research on the importance of social presence for learning in online courses.
Short et al. (1976) outlined Social Presence Theory in depicting students’ perceptions of each other as real in different means of telecommunications. These ideas translate directly to questions surrounding online education and pedagogy in regards to educational design in networked learning where connection across learners and instructors improves learning outcomes especially with “Human-Human interaction” ( Goodyear, 2002 , 2005 ; Tu, 2002 ). These ideas play heavily into asynchronous vs. synchronous learning, where Tu reports students having positive responses to both synchronous “real-time discussion in pleasantness, responsiveness and comfort with familiar topics” and real-time discussions edging out asynchronous computer-mediated communications in immediate replies and responsiveness. Tu’s research indicates that students perceive more interaction with synchronous mediums such as discussions because of immediacy which enhances social presence and support the use of active learning techniques ( Gunawardena, 1995 ; Tu, 2002 ). Thus, verbal immediacy and communities with face-to-face interactions, such as those in synchronous learning classrooms, lessen the psychological distance of communicators online and can simultaneously improve instructional satisfaction and reported learning ( Gunawardena and Zittle, 1997 ; Richardson and Swan, 2019 ; Shea et al., 2019 ). While synchronous learning may not be ideal for traditional online students and a subset of our participants, this research suggests that non-traditional online learners are more likely to appreciate the value of social presence.
Social presence also connects to the importance of social connections in learning. Too often, current systems of education emphasize course content in narrow ways that fail to embrace the full humanity of students and instructors ( Gay, 2000 ). With the COVID-19 pandemic leading to further social isolation for many students, the importance of social presence in courses, including live interactions that build social connections with classmates and with instructors, may be increased.
Limitations of These Data
Our undergraduate data consisted of 4,789 responses from 95 different countries, an unprecedented global scale for research on online learning. However, since respondents were followers of @unjadedjade who focuses on learning and wellness, these respondents may not represent the average student. Biases in survey responses are often limited by their recruitment techniques and our bias likely resulted in more robust and thoughtful responses to free-response questions and may have influenced the preference for synchronous classes. It is unlikely that it changed students reporting on remote learning pedagogical methods since those are out of student control.
Though we surveyed a global population, our design was rooted in literature assessing pedagogy in North American institutions. Therefore, our survey may not represent a global array of teaching practices.
This survey was sent out during the initial phase of emergency remote learning for most countries. This has two important implications. First, perceptions of remote learning may be clouded by complications of the pandemic which has increased social, mental, and financial stresses globally. Future research could disaggregate the impact of the pandemic from students’ learning experiences with a more detailed and holistic analysis of the impact of the pandemic on students.
Second, instructors, students and institutions were not able to fully prepare for effective remote education in terms of infrastructure, mentality, curriculum building, and pedagogy. Therefore, student experiences reflect this emergency transition. Single-modality courses may correlate with instructors who lacked the resources or time to learn or integrate more than one modality. Regardless, the main insights of this research align well with the science of teaching and learning and can be used to inform both education during future emergencies and course development for online programs that wish to attract traditional college students.
Global Student Voices Improve Our Understanding of the Experience of Emergency Remote Learning
Our survey shows that global student perspectives on remote learning agree with pedagogical best practices, breaking with the often-found negative reactions of students to these practices in traditional classrooms ( Shekhar et al., 2020 ). Our analysis of open-ended questions and preferences show that a majority of students prefer pedagogical approaches that promote both active learning and social interaction. These results can serve as a guide to instructors as they design online classes, especially for students whose first choice may be in-person learning. Indeed, with the near ubiquitous adoption of remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic, remote learning may be the default for colleges during temporary emergencies. This has already been used at the K-12 level as snow days become virtual learning days ( Aspergren, 2020 ).
In addition to informing pedagogical decisions, the results of this survey can be used to inform future research. Although we survey a global population, our recruitment method selected for students who are English speakers, likely majority female, and have an interest in self-improvement. Repeating this study with a more diverse and representative sample of university students could improve the generalizability of our findings. While the use of a variety of pedagogical methods is better than a single method, more research is needed to determine what the optimal combinations and implementations are for courses in different disciplines. Though we identified social presence as the major trend in student responses, the over 12,000 open-ended responses from students could be analyzed in greater detail to gain a more nuanced understanding of student preferences and suggestions for improvement. Likewise, outliers could shed light on the diversity of student perspectives that we may encounter in our own classrooms. Beyond this, our findings can inform research that collects demographic data and/or measures learning outcomes to understand the impact of remote learning on different populations.
Importantly, this paper focuses on a subset of responses from the full data set which includes 10,563 students from secondary school, undergraduate, graduate, or professional school and additional questions about in-person learning. Our full data set is available here for anyone to download for continued exploration: https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId= doi: 10.7910/DVN/2TGOPH .
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics Statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
GS: project lead, survey design, qualitative coding, writing, review, and editing. TN: data analysis, writing, review, and editing. CN and PB: qualitative coding. JW: data analysis, writing, and editing. CS: writing, review, and editing. EV and KL: original survey design and qualitative coding. PP: data analysis. JB: original survey design and survey distribution. HH: data analysis. MP: writing. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank Minerva Schools at KGI for providing funding for summer undergraduate research internships. We also want to thank Josh Fost and Christopher V. H.-H. Chen for discussion that helped shape this project.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2021.647986/full#supplementary-material
Aspergren, E. (2020). Snow Days Canceled Because of COVID-19 Online School? Not in These School Districts.sec. Education. USA Today. Available online at: https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/education/2020/12/15/covid-school-canceled-snow-day-online-learning/3905780001/ (accessed December 15, 2020).
Google Scholar
Bostock, S. J. (1998). Constructivism in mass higher education: a case study. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 29, 225–240. doi: 10.1111/1467-8535.00066
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Bradbury, N. A. (2016). Attention span during lectures: 8 seconds, 10 minutes, or more? Adv. Physiol. Educ. 40, 509–513. doi: 10.1152/advan.00109.2016
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Chen, B., Bastedo, K., and Howard, W. (2018). Exploring best practices for online STEM courses: active learning, interaction & assessment design. Online Learn. 22, 59–75. doi: 10.24059/olj.v22i2.1369
Davis, D., Chen, G., Hauff, C., and Houben, G.-J. (2018). Activating learning at scale: a review of innovations in online learning strategies. Comput. Educ. 125, 327–344. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2018.05.019
Deslauriers, L., McCarty, L. S., Miller, K., Callaghan, K., and Kestin, G. (2019). Measuring actual learning versus feeling of learning in response to being actively engaged in the classroom. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 116, 19251–19257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821936116
Fink, L. D. (2013). Creating Significant Learning Experiences: An Integrated Approach to Designing College Courses. Somerset, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Freeman, S., Eddy, S. L., McDonough, M., Smith, M. K., Okoroafor, N., Jordt, H., et al. (2014). Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111, 8410–8415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319030111
Gale, N. K., Heath, G., Cameron, E., Rashid, S., and Redwood, S. (2013). Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 13:117. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-13-117
Garrison, D. R., Anderson, T., and Archer, W. (1999). Critical inquiry in a text-based environment: computer conferencing in higher education. Internet High. Educ. 2, 87–105. doi: 10.1016/S1096-7516(00)00016-6
Gay, G. (2000). Culturally Responsive Teaching: Theory, Research, and Practice. Multicultural Education Series. New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Gillingham, and Molinari, C. (2012). Online courses: student preferences survey. Internet Learn. 1, 36–45. doi: 10.18278/il.1.1.4
Gillis, A., and Krull, L. M. (2020). COVID-19 remote learning transition in spring 2020: class structures, student perceptions, and inequality in college courses. Teach. Sociol. 48, 283–299. doi: 10.1177/0092055X20954263
Goodyear, P. (2002). “Psychological foundations for networked learning,” in Networked Learning: Perspectives and Issues. Computer Supported Cooperative Work , eds C. Steeples and C. Jones (London: Springer), 49–75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4471-0181-9_4
Goodyear, P. (2005). Educational design and networked learning: patterns, pattern languages and design practice. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 21, 82–101. doi: 10.14742/ajet.1344
Gunawardena, C. N. (1995). Social presence theory and implications for interaction and collaborative learning in computer conferences. Int. J. Educ. Telecommun. 1, 147–166.
Gunawardena, C. N., and Zittle, F. J. (1997). Social presence as a predictor of satisfaction within a computer mediated conferencing environment. Am. J. Distance Educ. 11, 8–26. doi: 10.1080/08923649709526970
Harris, H. S., and Martin, E. (2012). Student motivations for choosing online classes. Int. J. Scholarsh. Teach. Learn. 6, 1–8. doi: 10.20429/ijsotl.2012.060211
Levitz, R. N. (2016). 2015-16 National Online Learners Satisfaction and Priorities Report. Cedar Rapids: Ruffalo Noel Levitz, 12.
Mansinghka, V., Shafto, P., Jonas, E., Petschulat, C., Gasner, M., and Tenenbaum, J. B. (2016). CrossCat: a fully Bayesian nonparametric method for analyzing heterogeneous, high dimensional data. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17, 1–49. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-69765-9_7
National Research Council (2000). How People Learn: Brain, Mind, Experience, and School: Expanded Edition. Washington, DC: National Academies Press, doi: 10.17226/9853
Richardson, J. C., and Swan, K. (2019). Examining social presence in online courses in relation to students’ perceived learning and satisfaction. Online Learn. 7, 68–88. doi: 10.24059/olj.v7i1.1864
Shea, P., Pickett, A. M., and Pelz, W. E. (2019). A Follow-up investigation of ‘teaching presence’ in the suny learning network. Online Learn. 7, 73–75. doi: 10.24059/olj.v7i2.1856
Shekhar, P., Borrego, M., DeMonbrun, M., Finelli, C., Crockett, C., and Nguyen, K. (2020). Negative student response to active learning in STEM classrooms: a systematic review of underlying reasons. J. Coll. Sci. Teach. 49, 45–54.
Short, J., Williams, E., and Christie, B. (1976). The Social Psychology of Telecommunications. London: John Wiley & Sons.
Tu, C.-H. (2002). The measurement of social presence in an online learning environment. Int. J. E Learn. 1, 34–45. doi: 10.17471/2499-4324/421
Zull, J. E. (2002). The Art of Changing the Brain: Enriching Teaching by Exploring the Biology of Learning , 1st Edn. Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing.
Keywords : online learning, COVID-19, active learning, higher education, pedagogy, survey, international
Citation: Nguyen T, Netto CLM, Wilkins JF, Bröker P, Vargas EE, Sealfon CD, Puthipiroj P, Li KS, Bowler JE, Hinson HR, Pujar M and Stein GM (2021) Insights Into Students’ Experiences and Perceptions of Remote Learning Methods: From the COVID-19 Pandemic to Best Practice for the Future. Front. Educ. 6:647986. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.647986
Received: 30 December 2020; Accepted: 09 March 2021; Published: 09 April 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Nguyen, Netto, Wilkins, Bröker, Vargas, Sealfon, Puthipiroj, Li, Bowler, Hinson, Pujar and Stein. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Geneva M. Stein, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Covid-19 and Beyond: From (Forced) Remote Teaching and Learning to ‘The New Normal’ in Higher Education
Advertisement
Exploring students’ learning experience in online education: analysis and improvement proposals based on the case of a Spanish open learning university
- Cultural and Regional Perspectives
- Open access
- Published: 27 August 2021
- Volume 69 , pages 3367–3389, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Pablo Rivera-Vargas ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9564-2596 1 , 2 ,
- Terry Anderson 3 &
- Cristina Alonso Cano 1
12k Accesses
18 Citations
10 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Not surprisingly, the number of online universities continues to expand—especially in Covid-19 times. These institutions all offer “online education” with diverse institutional, technological, and pedagogical processes. However, a fundamental element has to do with the experience of the students, and how they adapt to the educational model of the online university in which they are studying. In this article, we present the main results of the case-study developed in one of the most historical and relevant virtual universities in an international context. We have explored and analysed the process of adaptation to the educational model by the student body, and their perceptions of their interactions with the pedagogical, institutional, and technological elements designed to support their learning. Qualitative and quantitative methods are used to gather and analyse the data. From 1715 students who participated in the survey and the perceptions of 30 students individually interviewed, the results show positive evaluations regarding the integration and adoption of technological competencies, and also, that the online education generally serves as a responsive model to the emergent needs of the learner. However, the results also show that students have important concerns regarding the pedagogical and institutional support provided.
Similar content being viewed by others

Adoption of online mathematics learning in Ugandan government universities during the COVID-19 pandemic: pre-service teachers’ behavioural intention and challenges
Geofrey Kansiime & Marjorie Sarah Kabuye Batiibwe
Exploring the role of social media in collaborative learning the new domain of learning
Jamal Abdul Nasir Ansari & Nawab Ali Khan

Online learning in higher education: exploring advantages and disadvantages for engagement
Amber D. Dumford & Angie L. Miller
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Online education has undergone profound transformations in recent times. Its evolution and configuration has gone hand in hand with changes that societies themselves have experienced with pervasive effects of the digital and networked society. These changes intensified during 2020 with the pandemic and its consequences.
The research presented in this article is from a case study developed at the Open University of Catalonia (UOC), located in Spain OUC was founded as an online university and has 25 years’ experience in offering online education. The main objective of the research was to explore and understand the academic and personal trajectories of the students during their educational experiences, with a focus on their interaction with the main pedagogical and technological elements that make up the online education system and their adaptation to the online education model used by the University. Considering this context, the two research questions that we answer in this article are:
What are the most relevant aspects for the student body when evaluating their online educational experience?
How can the educational experiences of virtual students in online universities be improved?
In order to answer these questions, and before presenting the methodological process carried out together with the results and main conclusions, two central dimensions of the work are analysed. First, the possibilities and limits of online learning, and second, a scan of the research literature on the nature and challenges faced by online students.
Although this research was carried out prior to the pandemic, we consider that its results are useful in identifying some of the possibilities and limitations that this form of education so as to improve the online educational experience of students from traditional, blended and online universities.
Online education: possibilities and limits for learning
The definition of “Online Education” has gone through substantive transits. Although its definitions and approaches are varied, the present literature defines it as a mode that is essentially carried out in virtual learning environments (VLE), through the internet and with active use of digital devices (Anderson & Rivera-Vargas, 2020 ; Bates, 2019 ; Lee, 2019 ). Its emergence and consolidation must be understood not only as an evolution of traditional distance education, but also as a modality capable of dealing with the new formative demands of a technologically infused world (Lee, 2019 ) and a networked and connected society (Selwyn, 2019 ).
At the same time, the consolidation of the digital society, and the recent consequences and responses to the Covid-19 pandemic have reduced the distance between traditional face-to-face education and online education. Although their target audiences are still essentially different, traditional universities have undergone substantial virtualization processes, gradually leaving behind their analog heritage (Rivera-Vargas & Cobo Romaní, 2019 ). In addition, virtual universities have opted to offer, in their own virtual learning environments, some of those distinctive features of face-to-face education—including in some cases occasional face-to-face gatherings. An example of this is the continuing effort of virtual universities to strengthen the constructivist and collaborative character of their educational programming. Unlike early models of distance education that focussed on independent study (Fallon & Brown, 2016 ; Moore, 1989 ) and instructivist pedagogies (Zawacki-Richter & Anderson, 2014 ) online education now provides a platform and thus an educational teaching model with the affordances to create and sustain simultaneous and accessible learning communities anywhere at any time.
Online education has also defended its role as an inclusive educational modality that enables and facilitates access to higher education and the development of digital competences. Research efforts such as Sangrà et al ( 2012 ), and Hills ( 2017 ) show that the active use of electronic and digital media and devices in online education can facilitate access, development and improvement of the quality of education. Simultaneously to formal curriculum delivery, Chu ( 2010 ) and Anderson & Rivera-Vargas ( 2020 ) argue that online education provides and standardizes the technological and digital competencies of the students using the same virtual environment. This reduces the potential digital divide across multiple intersectional dimensions including gender, social class, physical disability, geographical location, and age (Chu, 2010 ).
It is important to highlight that these characteristics of online education, have coexisted for years with opposing critical views—some that question their effectiveness in real contexts rather than their global conceptualization. These highlights, for example, the limitations of mediated human contact and the need for the student to have high levels of personal motivation to be successful (Anderson & Rivera-Vargas, 2020 ; Kocdar et al., 2018 ). A problem also arises when the design of a virtual environment and learning activities is limited to the organization and dissemination of electronic resources (for example posting lectures online) and is not built on an ecological support of active learning (Davis et al., 2018 ).
In this sense, one of the most researched and most relevant aspects of the online education experience are efforts to increase student motivation in their educational process, through autonomy in learning, through effective use of digital tools, and through an active and interactive relationship between and amongst students and teachers. Guri-Rosenblit and Gros ( 2011 ) highlight the potential horizontal nature of this pedagogical relationship, giving relevance to the support that the student receives from the teaching staff and the institution as a whole. At the same time, Palloff & Pratt ( 2013 ), Kocdar et al., ( 2018 ) and Pilkington ( 2018 ) highlight the importance of helping students achieve autonomy and self-regulation so as, to motivate and thus enrich their educational experience.
In the next section, we delve more deeply into the importance of the student body in the educational model of online university education.
The student in virtual learning environments
The development and large-scale accessibility to digital technologies and resources, together with the need for lifelong learning motivate why many people decide to pursue their university education in virtual environments (Jung, 2011 ; Pilkington, 2018 ). Many of these students cannot access traditional learning centres, with conventional face-to-face models, due to physical or economic constraints. However, they still need to acquire specific knowledge and skills that are applicable to their personal and professional lives (McKnight et al., 2016 ). In addition, it is usually students with professional experience and digital skills, who generally seek an education that allows them to integrate their previous knowledge, with new skills and knowledge (Jung, 2011 ; Sánchez-Gelabert et al., 2020 ) while adapting to their emergent needs in their professional and personal lives.
From a constructivist viewpoint, Anderson ( 2016 ) and Vuopala et al ( 2016 ) maintain that the learning process with digital tools is or at least can be, fundamentally collaborative. Students create knowledge through interaction between themselves, the teacher, and their environment, that allows and indeed forces them to assume the leading role in their learning process. The demographic characteristics of the student body engaged in online learning are heterogeneous. Jung ( 2011 ) and Murphy and Stewart ( 2017 ) noted that the majority of the first wave of online education students made contact with the computer and with digital technologies in late youth or adult life (late twentieth century and early twenty-first century). That is, these students came from a campus-based educational environment where the teacher was the leader of the process, who set the timetable and dictated how knowledge would be acquired.
The following generations of virtual students are made up of a great variety of ages, the majority coming from a regulated formation focused on the transmission of knowledge made by the teacher, but who more prone to proactivity (Murphy & Stewart, 2017 ). Thus, they are more accustomed to collaboration between equals, to be more democratic, more diverse and be involved in less hierarchical telematic relationships. Although there are differences and varying needs among online students according to their culture, the disciplines they choose to study and their age, they show many common characteristics in their identity and performance when learning in these environments (Kocdar et al., 2018 ; McKnight et al., 2016 ). Perhaps the most striking commonality, although not surprising, is that the majority enrol for the first time in online education, without knowing what it is to be an online student, without knowing what to do, what it entails, how to perform optimally and without having received any training (Jung, 2011 ; Pilkington, 2018 ). Despite this, most are able to adapt and learn due to the flexible context, transference of digital skills from social and professional contexts, having the individual responsibility for their time and the ability to access educational resources until the completion of their course (Pilkington, 2018 ).
When referring to the online student, there is a tendency to highlight those actions that describe their predisposition to participate in online learning environments (Sánchez-Gelabert et al., 2020 ). This is important if we take into account the multiple transformations that have occurred in the educational field during the last decades (Lee, 2019 ). In fact, the figure of the student in virtual environments as an apprentice with a higher level of autonomy, not only emerges as a consequence of the development and use of digital technologies in educational contexts, but also emerges from previous efforts aimed at positioning the student as a leading actor in the teaching and learning processes, and as a result strengthens their autonomous learning (Farrell & Brunton, 2020 ). Palloff & Pratt ( 2013 ), for example, suggest the profile of the successful online student, that although emergent and mediated through the use of computers, is marked by the abilities and skills to manage the tools and resources of these learning environments. The student also gains skills and competencies that facilitate their autonomous learning. Palloff & Pratt ( 2013 ) identify these characteristics of the online students:
Ease of sharing their work, points of view, and experiences with others in order to build virtual communities.
Improvement in written communication skills, in order to relate to others online and to develop social capital by exposing personal and communication skills.
Ability to self-motivate and self-discipline, given the flexibility of the courses.
Commitment to the course, investing a significant amount of time and effort.
Adaptability—a critical position in their learning process.
Understanding that reflection is part of the learning process and that learning is a transformative experience.
The use of digital technologies in the teaching and learning process aims to partially remedy the deficiencies of the traditional teaching and learning model used on campus and formally used in older distance education models (Alqurashi, 2019 ). In this way, inserting strategies that encourage the student to work autonomously, reinforce their self-control and support leaving behind the conception of student as passive, dependent, rigid, solitary, and non-reflective are critically important (Murphy & Stewart, 2017 ; Sánchez-Gelabert et al., 2020 ).
Method and context
Context of the open university of catalonia.
This case study focuses on the Open University of Catalonia (UOC). This institution was founded in 1995 during the period of the initial internet expansion. The UOC sought to be an academic environment adapted to the characteristics of modern society (UOC, 2009 ). It is recognized as one of the first universities in the world that has supported its teaching and learning model with the integral use of a virtual learning environment (VLE) or a learning management system (LMS) (Grau-Valldosera & Minguillón, 2014 ).
During the 2019–2020 academic year, the UOC had 56500 active students, of which 40500 were undertaking bachelor’s degrees studies, and 16000 were undertaking master’s degrees studies. From its foundation (1995) until December 2020, there have been a total of 89300 Bachelor’s degrees, and master’s degrees graduates, Footnote 1 spread over 134 countries around the world (UOC, 2020 ).
According to the institutional report for the 2018–2019 academic year (UOC, 2020 ), the typical student who begins studies at the UOC combines studies with work (81.70%), works in the private sector (67.40%), is studying to progress professionally (61.10%) and opts for the UOC in order to reconcile studies, work, and other responsibilities (50.40%) (UOC, 2020 ). Finally, it should be noted that the UOC has been increasing its international prestige in recent years. The latest version of the university ranking created by the Times Higher Education journal (THE, 2021 ), has placed the UOC in the following quality dimensions: among the top 150 young universities; the second-best Spanish university under 50 years old; the best online university in Ibero-America; and among the top 601–800 global universities. Footnote 2
Approach to the educational model
The UOC's educational model is focused on extending the learning possibilities of the student. To this end, it offers a wide diversity of strategies, resources, and pedagogical work dynamics, based on support of the teaching team and on interaction with classmates, who try to empathize with their needs and lifestyles (UOC, 2020 ). The model supports students learning as they work and communicate on the network (Sánchez-Gelabert et al, 2020 ).
The UOC’s educational model, it is based on the integration of four fundamental elements (Grau-Valldosera & Minguillón, 2014 ; UOC, 2009 , 2020 ):
The commitment to a horizontal and collaborative relationship between students and teachers.
The promotion of student autonomy and self-regulation, placing these at the center of their learning process.
Human support of the student, instantiated by three roles:
“Consultant”: providing pedagogical and subject matter support on a course-by-course basis
“Tutor”: providing institutional pastoral support throughout the students’ enrolment Footnote 3
“Technological support department”: providing technical support and accompaniment
Resources and content (spaces, tools and didactic materials with active use of digital technologies).
In addition, the UOC supports its pedagogical commitment with evaluative flexibility and the creation of a learning environment that favours interactivity and cooperation between students, and between students and the university (Sánchez-Gelabert et al., 2020 ). It is a model focused on accommodating the contemporary students as active participants in their learning processes (Kocdar et al., 2018 ). Footnote 4
Methodological design
In this research, a sequential mixed methods approach (qualitative first) has been used, complementing the use of qualitative methods with quantitative information collection and analysis techniques (Goetz & LeCompte, 1988 ). At the analytical level, an interpretative view is assumed, because it emphasizes the concern for the local and for the generation of a knowledge that is relevant and that emerges within these environments. This has also allowed us to observe how the students from an online university interact with educational transformations, and what realities and subjects they recognize (Anderson & Rivera-Vargas, 2020 ). The study focuses on how reality is generated through ordinary actions. We explore how students, beyond the technology itself, create and recreate learning contexts from their interaction with digital technologies (Laux et al., 2016 ). Thus, the research can be considered a multi-method, single case study (Stake, 1995 ) bounded by undergraduate students enrolled in the Open University of Catalonia (Spain).
Information collection tool
Individual active interviews were conducted (Denzin, 2001 ; Holstein & Gubrium, 2020 ) with students, academics and institutional representatives of the UOC. In this type of active interview, the interaction between the interviewer and the interviewee tends to be symmetrical, that is, both having an active role. We used semi-structured interviews with topics and questions derived directly from the objectives of the research (Denzin, 2001 ), but also left room for participants to expand and shape the conversations. Table 1 shows the main topics developed in the interview.
At the quantitative level, based on the statements and discourses obtained in the analysis of the interviews, a questionnaire was designed (Goetz & LeCompte, 1988 ). These complements and triangulate the information obtained in the qualitative phase, and at the same time provide a more representative reflection of the experiences of those interviewed. To ensure the content validity of the questionnaire, the initial 40 questions were validated through expert judgment. Seven experts from the field of online university education and distance education participated, from Spain (3), Canada (2), UK (1) and Chile (1). This process was carried out through validation matrices, where each expert responded individually with a Yes or No to the validity conditions of each question. Of the 40 questions, 35 obtained a quality assessment of over 75%, while 5 questions that were evaluated under 75%, sere dropped in the final evaluation instrument. Thus, the final instrument was made up of 35 questions, which included closed multiple-choice responses, and Likert scales. Footnote 5
The internal consistency of the instrument was calculated and interpreted using data from a test application. The results, α = 0.60, indicated a «good» internal reliability for scales between 0.6 and 0.8 points (Cohen et al., 2007 ). The test application process that led to the final design of the questionnaire spanned two months. The data from questionnaire were downloaded and saved in an IBM SPSS 25.0 (2017) spreadsheet with consideration for the ethical aspects corresponding to anonymity and data security compliance. The questionnaire was administrated using the online platform of the UOC Office of Planning and Quality.
Sample and participants
The research targetted students in undergraduate degree programmes, with current enrolment at the time of the research (course 2016–2017), and who have had at least two consecutive years of experience at the UOC. The process was divided into two phases. In the first, essentially qualitative phase three undergraduate degree programmes were reviewed these were: computer engineering, psychology, and business administration and management (BAM). This choice was not arbitrary, since these three studies are the oldest (Computer Engineering) and with the highest number of students (Psychology, and BAM) (UOC, 2009 , 2020 ). In addition, each of these undergraduate degree programmes belong to a different knowledge area (Table 1 ). Finally, 30 individual active interviews of students across the three selected degree programmes were carried out (10 students from each). These students were selected based on three criteria:
Had completed at least two full years at the UOC
Have passed all the subjects enrolled
Voluntarily to participate in this investigation. An invitation was sent to all students who met the first two criteria. Each of the 30 interviewees responded with an email confirming their personal interest in participating in this investigation.
In the second, quantitative phase, the complementary questionnaire (Goetz & LeCompte, 1988 ) was provided to all 7885 students belonging to the 15 undergraduate studies that made up the UOC’s enrolment in 2016. The questionnaire was completed by 1715 (21.75%) of students (which fits a 3% accepted error and a confidence level of 99%).
Analysis procedure
The analysis of the qualitative information used discourse analysis by grouping and categorizing the responses from the interviewees. We selected this type of analysis from Wetherell & Potter ( 1998 ), because it poses discourse as a social practice, and not just as a set of statements. In the words of Iñiguez & Antaki ( 1994 ) we extracted “a set of linguistic practices that maintain and promote certain social relationships” (1994: 63).
In the qualitative information coding and treatment phase, the transcripts were grouped according to the three-degree studies considered (computer engineering, psychology, and BAM). Then, the codified process was developed from the interview guideline. Subsequently, the units of meaning created in each degree were grouped into a single frame of group narrations. This work reduced the volume of data, highlighting those collective narratives directly and indirectly linked with the research objectives. By systematically reading the codes, selected citations and their context, we searched for patterns, themes and regularities, as well as contrasts, paradoxes and irregularities (Denzin, 2001 ; Denzin et al., 2016 ). From this, we proceeded to relate the codes, grouping and regrouping them until they made sense in order to create consolidated discourses. The regrouping of narratives generated a new analytical sense, allowing in this way, new interpretative schemes (Wetherell & Potter, 1998 ). This work gave rise to four categories:

Assimilation of digital competences
Flexibility and adaptation to the UOC model
Virtual learning environments
Students’ support
Once the categories were organized, they were analysed according to a combined model, in which the content of the narratives was worked on, also considering their discursive form, recovering analytical resources from the repertoire model of Wetherell & Potter ( 1998 ).
For the analysis of the quantitative information, the data was analysed using SPSS software, using descriptive analysis techniques. The classification and tabulation was made according to the Knowledge Areas in which the UOC organizes the degree studies, shown in Table 2 .
Finally, in the last phase, analytical triangulation and discussion was carried out using both the qualitative and quantitative information obtained. The coherence and correlation between both types of information was analyzed, identifying the most significant similarities and differences.
Analysis of results
The results presented below have been organized based on the development of the four emerging categories mentioned in the previous section. Each of the four categories were addressed using triangulation of data, including the constructed discourse, quotations from the interviewed student body, and descriptive results of the supplied questionnaire, illustrated in tables, that have been grouped according to the Knowledge Areas described in Table 1 .
One of the main results of this research was to determine if the online education experience itself provided powerful and sustainable digital skills to students. This is significant because it was not a goal established in the pedagogical models proposed by UOC (UOC, 2009 , 2020 ), nor in the initial expectations of this research.
An important part of the student body considers this process of assimilation of skills in digital technologies as an added value to the formative experience, as affirmed by this fifty-two-year-old student of Psychology:
You are using the virtual campus, then an application, and then you have to create one of these, etc. At first it is difficult to understand the mechanics of them, but once you manage to do it for the first time, everything flows and is faster (Psychology student).
Although a significant majority of the students stated that they had some level of digital competence prior to joining the UOC, almost all of the participants interviewed acknowledged that they now use digital technologies more actively and reflectively in other areas of their work and leisure activities. This they attribute to their formative experience using e-Learning tools.
Results obtained from the questionnaire, confirm results gathered from individual interviews. As we see in Fig. 1 , students from all areas of knowledge acquired new technological skills.
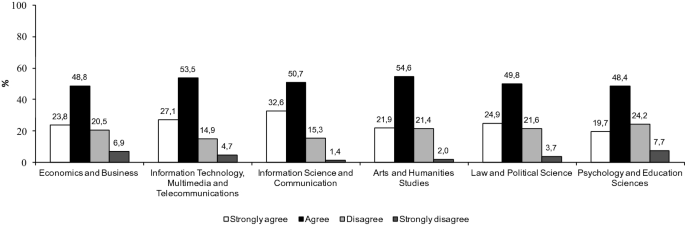
I consider that studying at the UOC using online education technologies has allowed me to gain new technological competences. According to discipline (%)
As might be expected, we see a trend (Fig. 2 ) towards more perceived value of online education skills acquired in older ages. Beyond this, the evidence shows that age differentiates students when it comes to assimilating competences in digital technologies during the online education experience.
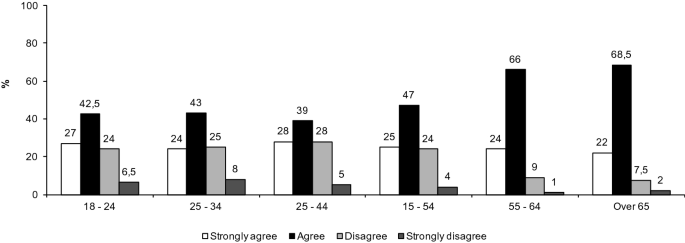
I consider that studying at the UOC under the online education modality has allowed me to assimilate new technological competences. According to Age (%)
Complementing this data, we found from students’ comments, that variables such as: experience with digital technologies, gender, age, degree of study, do not negatively affect the academic interaction between classmates, nor their learning performance in VLE. This is in line with Chu’s ( 2010 ) argument that online education experience may reduce the digital divide between ages, genders and disciplines.
However, the main obstacle to interaction with colleagues is more related to the lack of concrete experience in the virtual campus of the UOC, as this student of BAM states.
You can quickly find out who is harder to study with online. If you are a new student, everything is slower (when you have to work in a group), they also fill the forum with questions, send you some personal messages, etc. The key is in the years (level of experience) you have been in the UOC, if you have several, then you do everything right. This goes beyond the age or sex of the people, or other aspects (BAM Student).
Thus, the increased participation in VLEs, in addition to favouring the assimilation of new digital skills, is valued by the student body as an action that tends to reduce the digital divide between students.
Flexibility and adaptation to the model
In this second dimension, students’ evaluations of the online education educational model proposed by the UOC are revealed. At the same time, the compatibility of the model with their own lifestyles is analysed. The flexibility of the learning model (Sangrà et al., 2012 ), together with the largely asynchronous character (Jung, 2011 ), allowed for continuing studies while engaged in often busy professional and personal lives. According to Anderson ( 2016 ), Anderson & Rivera-Vargas ( 2020 ) this generates greater commitment and leadership of the student in their own learning process:
Studying from my house and doing other activities at the time of day that suits me best, is fundamental for me. Otherwise, (using a face-to-face model) I couldn’t work or have a personal life (Psychology Student). Because of my work, I have a free schedule at very unusual times. That’s when I can take advantage of studying and doing evaluative activities. Having this autonomy and leading my learning process, is what, in fact, allows me to be committed to my studies and motivates me to continue (Computer Engineering Student).
Complementing this discourse, the results of the questionnaire reaffirm that students across the UOC's Knowledge Areas consider that the online education educational model at the UOC allows them to combine their studies with the usual organization of their time, and also, with their personal and professional life (Table 3 ).
The results also reflect that many virtual students of the UOC opt for online education because their lifestyle prevents them from attending university institutions with face-to-face instructional models:
In order to get a job promotion, for me it was important to finish my studies, but studying in person was impossible. So, I looked for distance education alternatives and the truth is that it works very well for me. So far, I have not had to change my routine in any way (Computer Engineering Student).
As can be seen in Fig. 3 , this sentiment is felt beyond the field of study or knowledge areas.
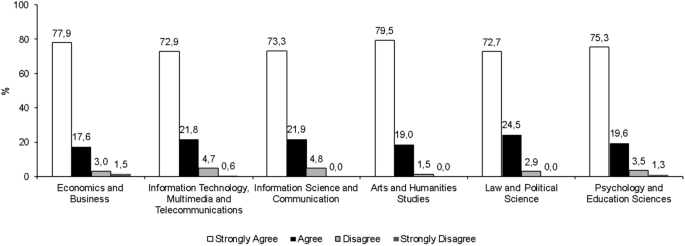
With the lifestyle I have, it was very difficult for me to study in person. (%)
One of the central aspects of the UOC's educational model is its permanent evaluation component, based on Continuous Evaluation Tests (CET). This flexible evaluative model, which aims to promote the autonomy and leadership of students in their educational process (Sánchez-Gelabert et al., 2020 ; UOC, 2020 ), represents the main reason why students choose to complete their university education in the online education system (Fig. 4 ).
If the continuous assessment model did not exist (through the CET), I could not study at the UOC (%)
However, beyond the fact that the student recognizes the flexibility of the UOC's educational model, there are aspects such as “personal academic organization and planning” that are recognized as difficult challenges to solve. This is significant, given the importance of enhancing the self-regulation and autonomy of students throughout their educational process (Pilkington, 2018 ; UOC, 2020 ). In this sense, beyond the flexibility of the evaluation model (considering evaluation and pedagogical tools), students also find that due to other commitments of their lifestyle, it is often difficult for them to plan and fulfil their academic responsibilities.
The model is flexible, and it is assumed that you can self-manage everything, but in practice, it does not stop having a very intense lifestyle. I finish each semester overwhelmed and pushing my academic abilities to the limit (BAM Student).
In general, we found that students organize and submit their evaluation work without sufficient time, and without much space for reflection and content review. In the opinion of the interviewees themselves, this has as a consequence for many, that, it is not possible to complete the courses with high levels of academic quality.
In this third section, the perceptions and the assessment of the structure and design of the virtual campus, are presented. The student perception of the virtual campus, where most student interaction action takes place, is generally positive. It is recognized that it is a friendly environment and that the applications and tools provide an effective learning space. One student explains:
Without having much previous experience in these environments (VLE), the truth is that I have always found that the (virtual) campus of the UOC is easy to manage. It is quite instinctive. In addition, the fact that you can give it your own design, makes it more representative of your own identity (Psychology Student).
Most students had positive opinions of the design, technical performance and operations of the virtual campus, however we found (Table 4 ) that the assessments of the students tend to vary depending on the area of knowledge and the variable that is evaluated. For example, students in the knowledge areas: law and political sciences (7.94), and Arts and Humanities (8.16), give a very good general assessment of the virtual campus. While for the students of the knowledge areas: computer science, multimedia and telecommunications (7.67), and Information Sciences (7.38), the assessment tends to be less favourable. Table 4 also shows that generally students generally rate positively access to materials, assessment activities, and communications with consultants, tutors, student services and peers. There are however small differences between knowledge areas.
Generally, we note that the two aspects with worse valued are related to the communication mechanisms of the campus, both for communication with institutional departments (7.19), and communication between students (7.36). The two most valued aspects of the virtual campus are: access to pedagogical materials of the subjects (7.95) and access to continuous evaluation tests (8).
- Student support
A successful student's support from UOC staff is probably one of the most important aspect of UOC's educational model (Sánchez-Gelabert et al, 2020 ). Both the interview and survey results show that although a small majority of students report satisfaction with tutors and consultants, there is a large portion of students who express dissatisfaction with these support roles (see Table 5 ). When we are asking about the feedback that students receive from the Consultants, the interviewees value it as weak and inefficient, recognizing how frustrating this is.
In general, you spend a lot of time doing your work, so you expect relatively clear feedback. But nothing, just a note, you do not know the reasons behind it. It seems to me very insincere (BAM Student). Corrections should be returned so that you can see how you have done in your work and what criteria were used to evaluate them, because if not, in the end, the only thing you look at is whether you have passed or not (Psychology Student).
In relation to the performance of Tutors, many participating students consider that their efforts are not very resolute when it comes to managing and solving certain problems:
In the three years that I have been at the UOC, I have only managed to contact my tutor 2 times and I will have written more than 20 emails. It is very frustrating, although I confess that at least it is good to know that they exist, that, in case of emergency, you can still count on them. In fact, if this role did not exist, surely people would ask for it (BAM Student).
In any virtual environment, the supportive role of human contacts remains critical to student success (Tait, 2014 ). As seen in Table 5 this area of support is problematic for many students as revealed in the questionnaire. For example, if the four indicators of the Likert scale are grouped in only two: “positive” (“Good” and “Very good”) and “negative” (“Bad” and “Very bad”), we observe that except for “Arts and Humanities Studies” the results in general, are equally split between positive and negative evaluations.
As we see in Table 4 , dimensions such as technological management, adaptation to the educational model and flexibility of its evaluation model, present generally positive evaluations from the students. However, when assessing two of the most relevant actors in the process of student's accompaniment and support, as shown in Table 5 , the results are not so positive. The only exception is given in the area of “Arts and Humanities Studies”, where the assessment of the performance of tutors and consultants is substantively positive. Meanwhile, in the five remaining areas of knowledge, there is a symmetry between the sum of the indicators “Very good—Good” and “Very bad—Bad”, highlighting even, the cases of the areas of “Law and Political Science” and “Studies in Psychology and Educational Sciences” where the sum of the negative evaluations exceeds 50% of the total, both in the case of Consultants and Tutors.
For me, the tutor’s performance has been very bad. At first, I did not know how the virtual campus worked, I did not know what and how many subjects I had to do. I did not even know if it made much sense to do college at my age. I wrote several emails, asking for your guidance. He never answered me (Psychology Student).
This is lack of communication was also identified by students from other areas of knowledge, where although the opinion on the performance of the consultants and tutors is better, we have been able to recognize multiple manifestations that openly criticize their performance.
Since I entered the UOC, I had to do everything by myself. I have never felt that a consultant oriented me well pedagogically, even his feedback tends to be monosyllabic. From the tutor, I have nothing to say, in three years, I still do not know who he is (BAM Student).
This data shows that the pedagogical support to the student, which represents one of the most significant aspects of online education (Almusharraf & Khahro, 2020 ; Sánchez-Gelabert et al., 2020 ; UOC, 2020 ) is not satisfactory for large numbers of students. These assessments of the role of the “Consultants” and “Tutors” reveal some significant weaknesses in the UOC’s educational model.
Discussion and conclusions
In this section, we will answer the two questions that guided the research.
Regarding the first question: “ From the perception of the students of the Open University of Catalonia, Identify and analyse which are the most relevant aspects for the student body when evaluating their online educational experience ?” The development of the empirical phase of this research has allowed us to identify four categories that have been relevant to students during their online university education. Next, we will contrast the evidence that supports these categories with the literature on the subject that we presented in the first part of this article.
We find that participation in virtual environments had a significant side effect of providing opportunity to learn and assimilate digital competences (Hills, 2017 ). Thus, participation in a virtual environment has benefits that go beyond subject matter learning objectives. Further, these benefits have become critical for both personal and professional advancement as communications and networking applications become increasingly important in both commercial and social realms. As Anderson & Rivera-Vargas ( 2020 ) argue, these benefits are seen across all age groups suggesting generally positive outcomes.
This outcome highlights that the students carry out their university education through online education because it gives them the possibility of making their studies compatible with the normal development of their professional and personal lives (Guri-Rosenblit & Gros, 2011 ; Pilkington, 2018 ). This critical capacity of increasing access is well known in the literature and widely supported among students of different ages in this study. We find that one of the major reasons why students opt for online education is due to the enhanced flexibility of the model as compared to attendance in traditional university institutions with a face-to-face approach (Anderson & Rivera-Vargas 2020 ). In relation to the mechanisms of evaluation of learning, students prefer the continuous evaluations tests (CET) to learge summative examinations, because is suits their lifestyle (allowing for more flexible time-shifting. However, similar to expressed in Kocdar et al ( 2018 ) the student’s question being overworked in certain subjects leading to lack of time for reflection and application of new knowledge.
The virtual campus
In general terms, and similar to the evidence that Sánchez-Gelabert et al. ( 2020 ) presented, students made positive evaluations of their experience of the technological platform and technical support, especially in those aspects of essentially educational including: access to pedagogical materials and to Continuous Evaluation Tests. However, contrary to what Fallon and Brown ( 2016 ) suggested, the lowest scores were obtained in those dimensions that evaluated the virtual contact tools between the students with the University (at a pedagogical, institutional, and technical level) and among the students themselves.
The student’s support
One of the most central aspects in determining the success of the online educational experience is the quality of interactions with human staff (Palloff & Pratt, 2013 ; Pilkington, 2018 ; Anderson & Rivera-Vargas 2020 ). In the case of the UOC, pedagogical and institutional accompaniment to the student body is supposed to continue throughout their educational experience, whereas it is absent or provided on a course by course basis in most other open universities (Davis et al., 2018 ). In this way, this university gives responsibility to both tutors and consultants, to provide student support (UOC, 2009 ). UOC contends that this has been authentic and sustainable model (intact since 2010) (UOC, 2020 ). However, the results show that there are medium to high levels of dissatisfaction with these resources as assessed by the students. This is an important factor, considering the efforts made by this educational institution to promote the students' interactive experience during their university studies. There are strong pedagogical rationale documenting the value of this type of continuous support (Sánchez-Gelabert et al., 2020 ), but it seems at UOC that the realization of this value is at best uncertain. This study reveals the need to first measure and then design ways to make this support more effective. This diagnosis should be accentuated when evaluating the performance of tutors and consultants.
Regarding the second question: “ From the analysis of the results of this research: how to improve the educational experience of virtual students in online universities ?”
As we have seen, the educational model of the UOC works well in general and has a good evaluation by the student body. However, there are some aspects that require adjustments or at least a revision. Based on this, and bearing in mind the results of this study, some initiatives are proposed below that could be considered by online universities to improve the educational experience of their students.
Firstly, the assimilation of digital skills during their own online education experience is an aspect recognized and well valued by the student body. These are instrumental skills, which are necessary to make adequate use of the virtual campus. However, at different moments of the research, the students raised the need for their educational experience to further strengthen the comprehensive and reflective processes. Given this, the main suggestion in this dimension is to go beyond an instrumental learning and promote the assimilation of reflective and critical skills of the student body on the use of digital technologies. For example, it would be useful to make students literate about the potential of the use of data in education, incorporating in the educational process the possibility of working and generating new knowledge (both individually and in groups). Self-care strategies could also be strengthened in relation to learning to properly organize the time they spend exposed and connected to digital screens. It could be useful in this sense to propose the development of learning activities outside the virtual campus, or directly in communities that are not virtual nor online.
Secondly, although the evaluation proposal based on CET is one of the strengths of the UOC’s educational model, an important part of the student body claims the need to reduce the time they dedicate to performing the multiple tasks that it entails. Given this, a commitment to the project-based learning model (PBL), could fit in and solve this demand of the student body to have more time for reflection and the application of the new knowledge assimilated in a subject. There is already a set of PBL, DIY, Maker experiences, implemented with substantive successes in other online university institutions (Lasauskiene and Rauduvaite, 2015 ; Chu et al., 2017 ). In most cases, these are initiatives that, through projects, have connected the study plan of the subjects with real social problems of interest to the students. It is a strategy that, in addition to being flexible, makes it possible to strengthen the bond of the student body with their own learning trajectory (Miño-Puigcercós et al., 2019 ).
Thirdly, the results show the need to generate alternative strategies, that favor the accompaniment of the student, taking into account their diverse learning needs and socio-cultural characteristics (Tait, 2014 ). However, the support from the human actors—tutors and consultants present a significant number of students expressing dissatisfaction with the service levels. At the same time, provision of this service incurs both financial and opportunity costs in addition to time commitments required of both students and staff. Thus, choice of type and level of support is critical. A first step in decision making is to accurately measure the current function of the service within the delivery system (Oregon et al., 2018 ).
A second step, given the current post-pandemic scenario is to look at innovative models from other industries in which service is provided by machines (for example driver-less cars, chat bot customer service, self-service banking and automated tax returns, etc.). This growing set of digital tools used effectively by online universities may provide pedagogical, institutional, and technical support to students (chatbots, web tools, student access to their own and comparative student data analytics), which according to Salmon ( 2013 ), could favour the experience of the student body in virtual learning environments in addition to extending their expertise and exposure to digital technologies.
Finally, the study provides useful information for UOC, but also to other virtual universities and traditional face-to-face mode universities that are experimenting important changes given the accelerated virtualization caused by the Covid-19 pandemic (Dhawan, 2020 ). The results also can assist the wider online educational community by examining, in detail, an innovative model for online learning. Thus, each institution can reflect on their own level of support and service to students and costs of doing so.
Data availability
We will make the data available.
See more details here: https://www.uoc.edu/portal/en/metodologia-online-qualitat/fets-xifres/index.html.
See more details here: https://www.timeshighereducation.com/world-university-rankings/open-university-catalonia.
This role is relatively unique amongst online universities in that the term ‘tutor’ is often used elsewhere to refer to faculty who engage only with the student as they are enrolled in a particular course (similar to consultant role above), not as here, where they are engaged with the student throughout their enrolment at the university (Sánchez-Gelabert et al., 2020 ).
For more information on the UOC's educational model see https://www.uoc.edu/portal/en/metodologia-online-qualitat/model-educatiu/index.html .
See the final version of the questionnaire, before it was digitized and included in the UOC’s institutional platform, and sent to the student body: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1frnPPJsiTBULI92RQgx1jI4bcaAQB4GN/view?usp=sharing .
Almusharraf, N., & Khahro, S. (2020). Students satisfaction with online learning experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 15 (21), 246–267. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v15i21.15647
Article Google Scholar
Alqurashi, E. (2019). Predicting student satisfaction and perceived learning within online learning environments. Distance Education, 40 (1), 133–148. https://doi.org/10.1080/01587919.2018.1553562
Anderson, T. (2016). Theories for learning with emerging technologies. In G. Veletsianos (Ed.), Emergence and innovation in digital learning: Foundations and applications (pp. 35–50). Athabasca University Press.
Google Scholar
Anderson, T., & Rivera-Vargas, P. (2020). A critical look at educational technology from a distance education perspective. Digital Education Review . https://doi.org/10.1344/der.2020.37.208-229
Bates, A. W. (2019). Teaching in a digital age . University of British Columbia.
Chu, R. J. C. (2010). How family support and Internet self-efficacy influence the effects of e-Learning among higher aged adults–analyses of gender and age differences. Computers & Education, 55 (1), 255–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2010.01.011
Chu, S. K. W., Zhang, Y., Chen, K., Chan, C. K., Lee, C. W. Y., Zou, E., & Lau, W. (2017). The effectiveness of wikis for project-based learning in different disciplines in higher education. The Internet and Higher Education, 33 , 49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2017.01.005
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2007). Research methods in education. Routledge . https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203224342
Davis, D., Chen, G., Hauff, C., & Houben, G. J. (2018). Activating learning at scale: A review of innovations in online learning strategies. Computers & Education, 125 , 327–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2018.05.019
Denzin, N., & Giardina, M. (2016). Qualitative inquiry through a critical lens . Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Denzin, N. (2001). The reflexive interview and a performative social science. Qualitative Research, 1 (1), 23–46. https://doi.org/10.1177/146879410100100102
Dhawan, S. (2020). Online learning: A panacea in the time of COVID-19 crisis. Journal of Educational Technology Systems, 49 (1), 5–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047239520934018
Fallon, C., & Brown, S. (2016). E-learning standards: A guide to purchasing, developing, and deploying standards-conformant e-Learning . CRC Press.
Farrell, O., & Brunton, J. (2020). A balancing act: A window into online student engagement experiences. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 17 (25), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-020-00199-x
Goetz, J.P. & LeCompte, M.D. (1988). Etnografía y diseño cualitativo en investigación educativa. Evaluación del diseño etnográfico [ Ethnography and qualitative design in educational research. Ethnographic design evaluation ]. Morata.
Grau-Valldosera, J., & Minguillón, J. (2014). Rethinking dropout in online higher education: The case of the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 15 (1), 291–308. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v15i1.1628
Guri-Rosenblit, S., & Gros, B. (2011). e-Learning: Confusing terminology, research gaps and inherent challenges. Journal of Distance Education, 25 (1), 1–17.
Hills, H. (2017). Individual preferences in e-Learning . Routledge.
Holstein, J. A., & Gubrium, J. F. (2020). Interviewing as a form of narrative practice. In D. Silverman (Ed.). Qualitative research (pp. 69–85). Sage.
Íñiguez, L., & Antaki, C. (1994). Discourse analysis in social psychology. Boletín De Psicología, 44 , 57–75.
Jung, I. (2011). The dimensions of e-Learning quality: From the learner’s perspective. Educational Technology Research and Development, 59 (4), 445–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-010-9171-4
Kocdar, S., Karadeniz, A., Bozkurt, A., & Buyuk, K. (2018). Measuring self-regulation in self-paced open and distance learning environments. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 19 (1), 25–43. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v19i1.3255
Lasauskiene, J., & Rauduvaite, A. (2015). Project-based learning at university: Teaching experiences of lecturers. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 197 , 788–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.07.182
Laux, D., Luse, A., & Mennecke, B. E. (2016). Collaboration, connectedness, and community: An examination of the factors influencing student persistence in virtual communities. Computers in Human Behavior, 57 , 452–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.12.046
Lee, K. (2019). Rewriting a history of open universities. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 20 (4), 21–35. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v20i3.4070
McKnight, K., O’Malley, K., Ruzic, R., Horsley, M. K., Franey, J. J., & Bassett, K. (2016). Teaching in a digital age: How educators use technology to improve student learning. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 48 (3), 194–211. https://doi.org/10.1080/15391523.2016.1175856
Miño-Puigcercós, R., Domingo Coscollola, M., & Sancho Gil, J. M. (2019). Transforming the teaching and learning culture in higher education from a DIY perspective. Educación XX1, 22 (1), 139–160. https://doi.org/10.5944/educxx1.20057
Moore, M. (1989). Editorial: Three types of interaction. American Journal of Distance Education, 3 (2), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/1080/08923648909526659
Murphy, C. A., & Stewart, J. C. (2017). On-campus students taking online courses: Factors associated with unsuccessful course completion. The Internet and Higher Education, 34 , 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2017.03.001
Oregon, E., McCoy, L., & Carmon-Johnson, L. (2018). Case analysis: Exploring the application of using rich media technologies and social presence to decrease attrition in an online graduate program. Journal of Educators Online, 15 (2), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.9743/JEO.2018.15.2.7
Palloff, R., & Pratt, K. (2013). Lessons from the cyberspace classroom. The realities of online teaching (2nd ed.). Jossey-Bass.
Pilkington, C. (2018). A Playful approach to fostering motivation in a distance education computer programming course: Behaviour change and student perceptions. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 19 (3), 282–298. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v19i3.3664
Rivera-Vargas, P., & Cobo Romaní, C. (2019). La universidad en la sociedad digital: entre la herencia analógica y la socialización del conocimiento [The university in the digital society: between the analogic heritage and the socialization of knowledge]. Revista de Docencia Universitaria, 17 (1), 17–32. https://doi.org/10.4995/redu.2019.11276
Salmon, G. (2013). E-tivities: The key to active online learning . Routledge.
Sánchez-Gelabert, A., Valente, R., & Duart, J. M. (2020). Profiles of online students and the impact of their university experience. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 21 (3), 230–249. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v21i3.4784
Sangrà, A., Vlachopoulus, D., & Cabrera, N. (2012). Building an inclusive definition of e-Learning: An approach to the conceptual framework. The International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, 13 (2), 145–159. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v13i2.1161
Selwyn, N. (2019). Whats is digital sociology? Polity Press.
Stake, R. E. (1995). The art of case study research . Sage.
Tait, A. (2014). From place to virtual space: Reconfiguring student support for distance and e-learning in the digital age. Open Praxis, 6 (1), 5–16. https://doi.org/10.5944/openpraxis.6.1.102
Times Higher Education. (2021). World University Ranking. Open university of Catalonia ranking . Times Higher Education. Retrieved from: https://www.timeshighereducation.com/world-university-rankings/open-university-catalonia
UOC. (2009). The UOC educational model: Evolution and perspectives. Universitat Oberta de Catalunya . Retrieved from: http://www.uoc.edu/portal/_resources/ES/documents/innovacio/modelo_educativo.pdf
UOC. (2020). Report of the 2018–2019 academic year. We grow in research, we share knowledge . Universitat Oberta de Catalunya. Retrieved from: https://www.uoc.edu/portal/_resources/ES/documents/memories/1819/memoria-UOC-2018-2019_es.pdf
Vuopala, E., Hyvönen, P., & Järvelä, S. (2016). Interaction forms in successful collaborative learning in virtual learning environments. Active Learning in Higher Education, 17 (1), 25–38. https://doi.org/10.1177/1469787415616730
Wetherell, M., & Potter, J. (1998). Discourse analysis and identification of interpretive repertoires. In A. Gordo, & J. Linaza (Eds.), Psychology, discourse and power: qualitative methodologies, critical perspectives (pp. 63–78). Edvisor.
Zawacki-Richter, O., & Anderson, T. (Eds.). (2014). Online distance education: Towards a research agenda . Athabasca University Press.
Download references
Acknowledgements
National Agency for Research and Development (ANID—Chile).
Open Access funding provided thanks to the CRUE-CSIC agreement with Springer Nature. This study was supported by National Agency for Research and Development (CONICYT) Grant No.72090564.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Teaching and Learning and Educational Organization, Universidad de Barcelona, Passeig de la Vall d’Hebron, 171. Edifici de Llevant, 2nd floor, 08035, Barcelona, Spain
Pablo Rivera-Vargas & Cristina Alonso Cano
Facultad de Educación y Ciencias Sociales, Universidad Andrés Bello, Fernández Concha 700, Las Condes, Santiago, Región Metropolitana, Chile
Pablo Rivera-Vargas
Athabasca University, 10005 93 St. Edmonton, Athabasca, AB T5H1W6, Canada
Terry Anderson
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pablo Rivera-Vargas .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
The authors have the informed consent of the thirty students interviewed.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
The research has not involved human or animal experiments. Individual interviews have been conducted with thirty students. The interviews have been transcribed, processed, and subsequently anonymized in the analysis and presentation of results phase.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Rivera-Vargas, P., Anderson, T. & Cano, C.A. Exploring students’ learning experience in online education: analysis and improvement proposals based on the case of a Spanish open learning university. Education Tech Research Dev 69 , 3367–3389 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-021-10045-0
Download citation
Accepted : 15 August 2021
Published : 27 August 2021
Issue Date : December 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-021-10045-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Online education
- Autonomous learning
- Digital divide
- Competences in digital technologies
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
✍️Essay on Online Classes: Samples in 100, 150, 200 Words
- Updated on
- Oct 20, 2023

Online classes, also known as virtual classes, have over time revolutionized education. They are known for providing students with the flexibility to access educational content and at the same time interact with professors in the comfort of their homes. With time, this mode of learning has gained huge popularity due to its accessibility and the ability to cater to diverse learning styles.

In this digital age, online classes have become a fundamental part of education, enabling all individuals to acquire knowledge, skills etc. Are you looking to gain some more information about online classes? Well, you have come to the right place. Here you will get to read some samples of online classes.
Table of Contents
- 1 What are Online Classes?
- 2 Essay on Online Classes in 100 Words
- 3 Essay on Online Classes in 150 Words
- 4 Essay on Online Classes in 200 Words
Also Read: Online Courses
What are Online Classes?
Online classes are educational courses or learning programs which are conducted over the Internet. They provide students with the opportunity to study and complete their coursework remotely from the comfort of their homes. Online classes are a part of formal education. They can be taken in schools or colleges or can be offered by various online learning platforms.
Online classes may include a variety of digital resources as well as tools. These may include quizzes, assignments, video lectures, discussion forums, connecting with friends via email, chat video calls etc. This type of learning offers the student flexibility in terms of when and where they can access their coursework and study. It is also helpful for those who study part-time have busy schedules and prefer remote learning.
With the onset of COVID-19 , online classes became a huge hit hence the evolution of online classes. It offers one with different levels of education, skill training and much more.
Essay on Online Classes in 100 Words
Online classes have become a central aspect of modern education. They offer flexibility, accessibility, and convenience, allowing students to learn from the comfort of their homes. The rise of online classes was accelerated during the COVID-19 pandemic, making a shift from traditional classrooms to virtual learning environments.
However, there are many disadvantages to online classes. Students may struggle with distractions, lack of in-person interaction, and technical issues. Additionally, they have opened up new avenues for global collaboration and lifelong learning. In an increasingly digital world, online classes are likely to remain a significant part of education.
Essay on Online Classes in 150 Words
Online classes have become a prevalent mode of education, especially in the past two years. These digital platforms offer several advantages. First, they provide flexibility, allowing students to learn from the comfort of their homes. This is especially beneficial for those with busy schedules or who are studying part-time.
Second, online classes often offer a wider range of courses, enabling learners to explore diverse subjects. Additionally, these classes promote self-discipline and time management skills as students must regulate their own study routines.
However, there are challenges associated with online learning. Technical issues can disrupt classes, and the lack of face-to-face interaction may hinder social development. It can also be isolating for some students.
In conclusion, online classes offer convenience and a variety of courses, but they also present challenges related to technology and socialization. The future of education likely involves a blend of traditional and online learning methods, catering to diverse learning needs.
Also Read: Online Learning
Essay on Online Classes in 200 Words
Online classes have become a prevalent mode of education. However, this shift has brought about both advantages and challenges.
One significant benefit of online classes is accessibility. They allow students from diverse backgrounds and locations to access quality education without any constraints. This inclusivity promotes diversity and global learning experiences. Additionally, online classes often offer flexible schedules, enabling students to balance their studies with other responsibilities.
However, online classes present challenges too. Technical issues and a lack of face-to-face interaction can hinder effective learning. Students may even struggle with self-discipline and motivation, leading to a decline in academic performance. Moreover, the absence of physical facilities like libraries and laboratories can limit hands-on learning opportunities.
In conclusion, online classes have revolutionized education by providing accessibility and flexibility. Yet, they also pose challenges related to technical issues, motivation, and practical experiences.
Related Articles
Every student has their own pace of study, and this is where distance learning’s benefits really shine. You can go at your own speed in online classes, go over the material as needed, and complete the work in a method that best suits your learning preferences.
Online courses can be successful provided they are well-designed and delivered, just like any other course or programme. However, this depends from person to person as not every student is meant for online classes.
In online education, students get to study online using a computer/laptop and only need a proper internet connection.
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay-writing page and follow Leverage Edu !
Malvika Chawla
Malvika is a content writer cum news freak who comes with a strong background in Journalism and has worked with renowned news websites such as News 9 and The Financial Express to name a few. When not writing, she can be found bringing life to the canvasses by painting on them.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- Essay Samples
- College Essay
- Writing Tools
- Writing guide

Creative samples from the experts
↑ Return to Essay Samples
Argumentative Essay: Online Learning and Educational Access
Conventional learning is evolving with the help of computers and online technology. New ways of learning are now available, and improved access is one of the most important benefits available. People all around the world are experiencing improved mobility as a result of the freedom and potential that online learning provides, and as academic institutions and learning organisations adopt online learning technologies and remote-access learning, formal academic education is becoming increasingly legitimate. This essay argues the contemporary benefits of online learning, and that these benefits significantly outweigh the issues, challenges and disadvantages of online learning.
Online learning is giving people new choices and newfound flexibility with their personal learning and development. Whereas before, formal academic qualifications could only be gained by participating in a full time course on site, the internet has allowed institutions to expand their reach and offer recognized courses on a contact-partial, or totally virtual, basis. Institutions can do so with relatively few extra resources, and for paid courses this constitutes excellent value, and the student benefits with greater educational access and greater flexibility to learn and get qualified even when there lots of other personal commitments to deal with.
Flexibility is certainly one of the most important benefits, but just as important is educational access. On top of the internet’s widespread presence in developed countries, the internet is becoming increasingly available in newly developed and developing countries. Even without considering the general informational exposure that the internet delivers, online academic courses and learning initiatives are becoming more aware of the needs of people from disadvantaged backgrounds, and this means that people from such backgrounds are in a much better position to learn and progress than they used to be.
The biggest argument that raises doubt over online learning is the quality of online courses in comparison to conventional courses. Are such online courses good enough for employers to take notice? The second biggest argument is the current reality that faces many people from disadvantaged backgrounds, despite the improvements made in this area in recent years – they do not have the level of basic access needed to benefit from online learning. In fact, there are numerous sources of evidence that claim disadvantaged students are not receiving anywhere near the sort of benefits that online learning institutions and promoters are trying to instigate. Currently there are many organisations, campaigns and initiatives that are working to expand access to higher education. With such high participation, it can be argued that it is only a matter of time before the benefits are truly realised, but what about the global online infrastructure?
There is another argument that is very difficult to dispel, and that is the response of different types of students to the online learning paradigm. Evidence shows that there are certain groups of students that benefit from college distance learning much more than other groups. In essence, students must be highly motivated and highly disciplined if they are to learn effectively in their own private environment.

Follow Us on Social Media
Get more free essays

Send via email
Most useful resources for students:.
- Free Essays Download
- Writing Tools List
- Proofreading Services
- Universities Rating
Contributors Bio

Find more useful services for students
Free plagiarism check, professional editing, online tutoring, free grammar check.
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Personal Growth and Development — Reflective My Learning Experience
Reflective My Learning Experience
- Categories: Personal Growth and Development
About this sample

Words: 595 |
Published: Mar 19, 2024
Words: 595 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Introduction.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 647 words
1 pages / 673 words
1 pages / 676 words
2 pages / 785 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Personal Growth and Development
Embracing the journey to be your best self is a pursuit that resonates deeply with individuals across cultures and generations. This essay embarks on an exploration of the concept of self-improvement, delving into its [...]
Kohlberg, Lawrence. 'The Philosophy of Moral Development: Moral Stages and the Idea of Justice.' Harper & Row, 1981.Rest, James R. 'Development in Judging Moral Issues.' University of Minnesota, 1979.Turiel, Elliot. 'The [...]
Help.open.ac.uk. (2019). Friends and family: When study gets difficult - Help Centre - Open University. Available at: Jou
Advantages of living alone essay delves into the liberating and transformative experience of residing independently. Living alone provides individuals with a unique opportunity to embrace autonomy, personal growth, and [...]
As a child, teen, and adult we go through many stages of changes and developments from our physical stature to our emotional stages. Even the way we think can sometimes go from wanting to be an artist when we grow up to wanting [...]
In life, we encounter numerous experiences that leave a lasting impact on our personal growth and development. These singular experiences, defined as those unique and significant moments that shape our lives, have the power to [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
AI Index Report
Welcome to the seventh edition of the AI Index report. The 2024 Index is our most comprehensive to date and arrives at an important moment when AI’s influence on society has never been more pronounced. This year, we have broadened our scope to more extensively cover essential trends such as technical advancements in AI, public perceptions of the technology, and the geopolitical dynamics surrounding its development. Featuring more original data than ever before, this edition introduces new estimates on AI training costs, detailed analyses of the responsible AI landscape, and an entirely new chapter dedicated to AI’s impact on science and medicine.
Read the 2024 AI Index Report
The AI Index report tracks, collates, distills, and visualizes data related to artificial intelligence (AI). Our mission is to provide unbiased, rigorously vetted, broadly sourced data in order for policymakers, researchers, executives, journalists, and the general public to develop a more thorough and nuanced understanding of the complex field of AI.
The AI Index is recognized globally as one of the most credible and authoritative sources for data and insights on artificial intelligence. Previous editions have been cited in major newspapers, including the The New York Times, Bloomberg, and The Guardian, have amassed hundreds of academic citations, and been referenced by high-level policymakers in the United States, the United Kingdom, and the European Union, among other places. This year’s edition surpasses all previous ones in size, scale, and scope, reflecting the growing significance that AI is coming to hold in all of our lives.
Steering Committee Co-Directors

Ray Perrault
Steering committee members.

Erik Brynjolfsson

John Etchemendy

Katrina Ligett

Terah Lyons

James Manyika

Juan Carlos Niebles

Vanessa Parli

Yoav Shoham

Russell Wald
Staff members.

Loredana Fattorini

Nestor Maslej
Letter from the co-directors.
A decade ago, the best AI systems in the world were unable to classify objects in images at a human level. AI struggled with language comprehension and could not solve math problems. Today, AI systems routinely exceed human performance on standard benchmarks.
Progress accelerated in 2023. New state-of-the-art systems like GPT-4, Gemini, and Claude 3 are impressively multimodal: They can generate fluent text in dozens of languages, process audio, and even explain memes. As AI has improved, it has increasingly forced its way into our lives. Companies are racing to build AI-based products, and AI is increasingly being used by the general public. But current AI technology still has significant problems. It cannot reliably deal with facts, perform complex reasoning, or explain its conclusions.
AI faces two interrelated futures. First, technology continues to improve and is increasingly used, having major consequences for productivity and employment. It can be put to both good and bad uses. In the second future, the adoption of AI is constrained by the limitations of the technology. Regardless of which future unfolds, governments are increasingly concerned. They are stepping in to encourage the upside, such as funding university R&D and incentivizing private investment. Governments are also aiming to manage the potential downsides, such as impacts on employment, privacy concerns, misinformation, and intellectual property rights.
As AI rapidly evolves, the AI Index aims to help the AI community, policymakers, business leaders, journalists, and the general public navigate this complex landscape. It provides ongoing, objective snapshots tracking several key areas: technical progress in AI capabilities, the community and investments driving AI development and deployment, public opinion on current and potential future impacts, and policy measures taken to stimulate AI innovation while managing its risks and challenges. By comprehensively monitoring the AI ecosystem, the Index serves as an important resource for understanding this transformative technological force.
On the technical front, this year’s AI Index reports that the number of new large language models released worldwide in 2023 doubled over the previous year. Two-thirds were open-source, but the highest-performing models came from industry players with closed systems. Gemini Ultra became the first LLM to reach human-level performance on the Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) benchmark; performance on the benchmark has improved by 15 percentage points since last year. Additionally, GPT-4 achieved an impressive 0.97 mean win rate score on the comprehensive Holistic Evaluation of Language Models (HELM) benchmark, which includes MMLU among other evaluations.
Although global private investment in AI decreased for the second consecutive year, investment in generative AI skyrocketed. More Fortune 500 earnings calls mentioned AI than ever before, and new studies show that AI tangibly boosts worker productivity. On the policymaking front, global mentions of AI in legislative proceedings have never been higher. U.S. regulators passed more AI-related regulations in 2023 than ever before. Still, many expressed concerns about AI’s ability to generate deepfakes and impact elections. The public became more aware of AI, and studies suggest that they responded with nervousness.
Ray Perrault Co-director, AI Index
Our Supporting Partners

Analytics & Research Partners

Stay up to date on the AI Index by subscribing to the Stanford HAI newsletter.
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
Fall 2024 CSCI Special Topics Courses
Cloud computing.
Meeting Time: 09:45 AM‑11:00 AM TTh Instructor: Ali Anwar Course Description: Cloud computing serves many large-scale applications ranging from search engines like Google to social networking websites like Facebook to online stores like Amazon. More recently, cloud computing has emerged as an essential technology to enable emerging fields such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Machine Learning. The exponential growth of data availability and demands for security and speed has made the cloud computing paradigm necessary for reliable, financially economical, and scalable computation. The dynamicity and flexibility of Cloud computing have opened up many new forms of deploying applications on infrastructure that cloud service providers offer, such as renting of computation resources and serverless computing. This course will cover the fundamentals of cloud services management and cloud software development, including but not limited to design patterns, application programming interfaces, and underlying middleware technologies. More specifically, we will cover the topics of cloud computing service models, data centers resource management, task scheduling, resource virtualization, SLAs, cloud security, software defined networks and storage, cloud storage, and programming models. We will also discuss data center design and management strategies, which enable the economic and technological benefits of cloud computing. Lastly, we will study cloud storage concepts like data distribution, durability, consistency, and redundancy. Registration Prerequisites: CS upper div, CompE upper div., EE upper div., EE grad, ITI upper div., Univ. honors student, or dept. permission; no cr for grads in CSci. Complete the following Google form to request a permission number from the instructor ( https://forms.gle/6BvbUwEkBK41tPJ17 ).
CSCI 5980/8980
Machine learning for healthcare: concepts and applications.
Meeting Time: 11:15 AM‑12:30 PM TTh Instructor: Yogatheesan Varatharajah Course Description: Machine Learning is transforming healthcare. This course will introduce students to a range of healthcare problems that can be tackled using machine learning, different health data modalities, relevant machine learning paradigms, and the unique challenges presented by healthcare applications. Applications we will cover include risk stratification, disease progression modeling, precision medicine, diagnosis, prognosis, subtype discovery, and improving clinical workflows. We will also cover research topics such as explainability, causality, trust, robustness, and fairness.
Registration Prerequisites: CSCI 5521 or equivalent. Complete the following Google form to request a permission number from the instructor ( https://forms.gle/z8X9pVZfCWMpQQ6o6 ).
Visualization with AI
Meeting Time: 04:00 PM‑05:15 PM TTh Instructor: Qianwen Wang Course Description: This course aims to investigate how visualization techniques and AI technologies work together to enhance understanding, insights, or outcomes.
This is a seminar style course consisting of lectures, paper presentation, and interactive discussion of the selected papers. Students will also work on a group project where they propose a research idea, survey related studies, and present initial results.
This course will cover the application of visualization to better understand AI models and data, and the use of AI to improve visualization processes. Readings for the course cover papers from the top venues of AI, Visualization, and HCI, topics including AI explainability, reliability, and Human-AI collaboration. This course is designed for PhD students, Masters students, and advanced undergraduates who want to dig into research.
Registration Prerequisites: Complete the following Google form to request a permission number from the instructor ( https://forms.gle/YTF5EZFUbQRJhHBYA ). Although the class is primarily intended for PhD students, motivated juniors/seniors and MS students who are interested in this topic are welcome to apply, ensuring they detail their qualifications for the course.
Visualizations for Intelligent AR Systems
Meeting Time: 04:00 PM‑05:15 PM MW Instructor: Zhu-Tian Chen Course Description: This course aims to explore the role of Data Visualization as a pivotal interface for enhancing human-data and human-AI interactions within Augmented Reality (AR) systems, thereby transforming a broad spectrum of activities in both professional and daily contexts. Structured as a seminar, the course consists of two main components: the theoretical and conceptual foundations delivered through lectures, paper readings, and discussions; and the hands-on experience gained through small assignments and group projects. This class is designed to be highly interactive, and AR devices will be provided to facilitate hands-on learning. Participants will have the opportunity to experience AR systems, develop cutting-edge AR interfaces, explore AI integration, and apply human-centric design principles. The course is designed to advance students' technical skills in AR and AI, as well as their understanding of how these technologies can be leveraged to enrich human experiences across various domains. Students will be encouraged to create innovative projects with the potential for submission to research conferences.
Registration Prerequisites: Complete the following Google form to request a permission number from the instructor ( https://forms.gle/Y81FGaJivoqMQYtq5 ). Students are expected to have a solid foundation in either data visualization, computer graphics, computer vision, or HCI. Having expertise in all would be perfect! However, a robust interest and eagerness to delve into these subjects can be equally valuable, even though it means you need to learn some basic concepts independently.
Sustainable Computing: A Systems View
Meeting Time: 09:45 AM‑11:00 AM Instructor: Abhishek Chandra Course Description: In recent years, there has been a dramatic increase in the pervasiveness, scale, and distribution of computing infrastructure: ranging from cloud, HPC systems, and data centers to edge computing and pervasive computing in the form of micro-data centers, mobile phones, sensors, and IoT devices embedded in the environment around us. The growing amount of computing, storage, and networking demand leads to increased energy usage, carbon emissions, and natural resource consumption. To reduce their environmental impact, there is a growing need to make computing systems sustainable. In this course, we will examine sustainable computing from a systems perspective. We will examine a number of questions: • How can we design and build sustainable computing systems? • How can we manage resources efficiently? • What system software and algorithms can reduce computational needs? Topics of interest would include: • Sustainable system design and architectures • Sustainability-aware systems software and management • Sustainability in large-scale distributed computing (clouds, data centers, HPC) • Sustainability in dispersed computing (edge, mobile computing, sensors/IoT)
Registration Prerequisites: This course is targeted towards students with a strong interest in computer systems (Operating Systems, Distributed Systems, Networking, Databases, etc.). Background in Operating Systems (Equivalent of CSCI 5103) and basic understanding of Computer Networking (Equivalent of CSCI 4211) is required.
- Future undergraduate students
- Future transfer students
- Future graduate students
- Future international students
- Diversity and Inclusion Opportunities
- Learn abroad
- Living Learning Communities
- Mentor programs
- Programs for women
- Student groups
- Visit, Apply & Next Steps
- Information for current students
- Departments and majors overview
- Departments
- Undergraduate majors
- Graduate programs
- Integrated Degree Programs
- Additional degree-granting programs
- Online learning
- Academic Advising overview
- Academic Advising FAQ
- Academic Advising Blog
- Appointments and drop-ins
- Academic support
- Commencement
- Four-year plans
- Honors advising
- Policies, procedures, and forms
- Career Services overview
- Resumes and cover letters
- Jobs and internships
- Interviews and job offers
- CSE Career Fair
- Major and career exploration
- Graduate school
- Collegiate Life overview
- Scholarships
- Diversity & Inclusivity Alliance
- Anderson Student Innovation Labs
- Information for alumni
- Get engaged with CSE
- Upcoming events
- CSE Alumni Society Board
- Alumni volunteer interest form
- Golden Medallion Society Reunion
- 50-Year Reunion
- Alumni honors and awards
- Outstanding Achievement
- Alumni Service
- Distinguished Leadership
- Honorary Doctorate Degrees
- Nobel Laureates
- Alumni resources
- Alumni career resources
- Alumni news outlets
- CSE branded clothing
- International alumni resources
- Inventing Tomorrow magazine
- Update your info
- CSE giving overview
- Why give to CSE?
- College priorities
- Give online now
- External relations
- Giving priorities
- Donor stories
- Impact of giving
- Ways to give to CSE
- Matching gifts
- CSE directories
- Invest in your company and the future
- Recruit our students
- Connect with researchers
- K-12 initiatives
- Diversity initiatives
- Research news
- Give to CSE
- CSE priorities
- Corporate relations
- Information for faculty and staff
- Administrative offices overview
- Office of the Dean
- Academic affairs
- Finance and Operations
- Communications
- Human resources
- Undergraduate programs and student services
- CSE Committees
- CSE policies overview
- Academic policies
- Faculty hiring and tenure policies
- Finance policies and information
- Graduate education policies
- Human resources policies
- Research policies
- Research overview
- Research centers and facilities
- Research proposal submission process
- Research safety
- Award-winning CSE faculty
- National academies
- University awards
- Honorary professorships
- Collegiate awards
- Other CSE honors and awards
- Staff awards
- Performance Management Process
- Work. With Flexibility in CSE
- K-12 outreach overview
- Summer camps
- Outreach events
- Enrichment programs
- Field trips and tours
- CSE K-12 Virtual Classroom Resources
- Educator development
- Sponsor an event
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Neural and Evolutionary Computing
Title: learning from offline and online experiences: a hybrid adaptive operator selection framework.
Abstract: In many practical applications, usually, similar optimisation problems or scenarios repeatedly appear. Learning from previous problem-solving experiences can help adjust algorithm components of meta-heuristics, e.g., adaptively selecting promising search operators, to achieve better optimisation performance. However, those experiences obtained from previously solved problems, namely offline experiences, may sometimes provide misleading perceptions when solving a new problem, if the characteristics of previous problems and the new one are relatively different. Learning from online experiences obtained during the ongoing problem-solving process is more instructive but highly restricted by limited computational resources. This paper focuses on the effective combination of offline and online experiences. A novel hybrid framework that learns to dynamically and adaptively select promising search operators is proposed. Two adaptive operator selection modules with complementary paradigms cooperate in the framework to learn from offline and online experiences and make decisions. An adaptive decision policy is maintained to balance the use of those two modules in an online manner. Extensive experiments on 170 widely studied real-value benchmark optimisation problems and a benchmark set with 34 instances for combinatorial optimisation show that the proposed hybrid framework outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. Ablation study verifies the effectiveness of each component of the framework.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Lyna Nguyen is a junior at Luther Burbank High School in Sacramento, Calif. My online learning experience as a student this fall has been great. What's working for me is I like the 40 minutes in ...
In his essay, Mullins discusses why more students prefer online learning. First, it lessens expenses, as students learn from the comfort of their rooms. Second, it helps students avert the fear of talking to strangers face-to-face, helping them communicate better. 3.
Emerging evidence on students' online learning experience during the COVID‐19 pandemic has identified several major concerns, ... and exam papers to prepare for the National College Entrance Examination (NCEE), whose delivery was not entirely digitised due to the sudden transition to online learning. Meanwhile, high‐school‐year students ...
Online learning has been widely adopted during the COVID-19 pandemic to ensure the continuation of K-12 education. Student success in K-12 online education is substantially lower than in conventional schools. Students experienced various difficulties related to the delivery of online learning. What this paper adds Provide empirical evidence for ...
Customization: Online platforms allow you to personalize your learning experience and adapt content to your individual needs and speed.This improves comprehension and memory. Technological advances: Integrating cutting-edge technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI) enriches the online learning experience and prepares learners for the digital age.
Some people mention that online school has various benefits and flexibility. Citing the article, 5 Key Benefits of Online High School by ICON, it says, "Online education provides an unparalleled flexibility that allows for a customized experience. With self-directed learning and no mandatory live classes, you can play to your strengths."
This spring, students across the globe transitioned from in-person classes to remote learning as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. This unprecedented change to undergraduate education saw institutions adopting multiple online teaching modalities and instructional platforms. We sought to understand students' experiences with and perspectives on those methods of remote instruction in order to ...
Not surprisingly, the number of online universities continues to expand—especially in Covid-19 times. These institutions all offer "online education" with diverse institutional, technological, and pedagogical processes. However, a fundamental element has to do with the experience of the students, and how they adapt to the educational model of the online university in which they are ...
Online education in the post-COVID era. Barbara B. Lockee. Nature Electronics 4 , 5-6 ( 2021) Cite this article. 138k Accesses. 204 Citations. 337 Altmetric. Metrics. The coronavirus pandemic ...
There are advantages and disadvantages of using online learning to teach in the nursing field. The main advantages of online learning are flexibility and active learning (Kenny.) The flexibility offered by online classes is unmatched. Based on personal experience, I can tell you that you can work almost anywhere and at any time.
Essay on Online Classes in 150 Words. Online classes have become a prevalent mode of education, especially in the past two years. These digital platforms offer several advantages. First, they provide flexibility, allowing students to learn from the comfort of their homes. This is especially beneficial for those with busy schedules or who are ...
Online Learning Essay. Sort By: Page 1 of 50 - About 500 essays. Decent Essays. Online Learning: The Benefits Of Online And Mobile Learning ... Learning in a group is an important way to help students gain experience and share diverse perspectives in critical thinking and deeper understanding of the learned material. Students in an online ...
This essay argues the contemporary benefits of online learning, and that these benefits significantly outweigh the issues, challenges and disadvantages of online learning. Online learning is giving people new choices and newfound flexibility with their personal learning and development. Whereas before, formal academic qualifications could only ...
217. A UNESCO report says schools' heavy focus on remote online learning during the pandemic worsened educational disparities among students worldwide. Amira Karaoud/Reuters. By Natalie Proulx ...
Pages: 1 (417 words) Views: 274. Download. The digital age has ushered in a new era of education, with online classes becoming a significant part of the learning landscape. As a participant in this virtual realm, I have had the opportunity to explore a novel way of acquiring knowledge and skills. In this essay, I will share my online class ...
Online learning provides flexibility, accessibility, and global interaction, while face-to-face education fosters immediate feedback, social interaction, and mentorship. The choice between these modes depends on individual preferences, learning styles, and circumstances. Ultimately, a hybrid approach that combines the strengths of both online ...
As a college student, I have had the privilege of engaging in a multitude of learning experiences, both inside and outside the classroom. In this reflective essay, I will delve into the transformative moments and the valuable lessons I have learned, highlighting the impact they have had on my personal and intellectual development.
Category: Education. Topic: Online Courses, Student, Study. Pages: 1 (448 words) Views: 760. Grade: 4.5. Download. Stressful aspects surround online learning that I have experienced. This is my experience as a student essay where I will show negative sides for students of online learning. Do not use plagiarized sources.
In order to bridge the course theory and practice, I will elaborate on two personal learning reflections that I have experienced during the course. My first learning experience is based on tutorial five and lecture six of this course. During this tutorial, I practiced a negotiation exercise based on a conflicting florist, grocer, and baker.
Mission. The AI Index report tracks, collates, distills, and visualizes data related to artificial intelligence (AI). Our mission is to provide unbiased, rigorously vetted, broadly sourced data in order for policymakers, researchers, executives, journalists, and the general public to develop a more thorough and nuanced understanding of the complex field of AI.
This paper explores how instructors can leverage generative AI to create personalized learning experiences for students that transform teaching and learning. We present a range of AI-based exercises that enable novel forms of practice and application including simulations, mentoring, coaching, and co-creation.
The newly introduced Online Master's in Artificial Intelligence (MSAI) program at the University of Texas at Austin is strategically designed to meet the dynamic needs of the AI sector while placing a strong emphasis on ethical considerations. Throughout the program, students are immersed in challenging coursework, including a compulsory "Ethics in AI" course that underscores
CSCI 5980 Cloud ComputingMeeting Time: 09:45 AM‑11:00 AM TTh Instructor: Ali AnwarCourse Description: Cloud computing serves many large-scale applications ranging from search engines like Google to social networking websites like Facebook to online stores like Amazon. More recently, cloud computing has emerged as an essential technology to enable emerging fields such as Artificial ...
In many practical applications, usually, similar optimisation problems or scenarios repeatedly appear. Learning from previous problem-solving experiences can help adjust algorithm components of meta-heuristics, e.g., adaptively selecting promising search operators, to achieve better optimisation performance. However, those experiences obtained from previously solved problems, namely offline ...
Publication of accepted submissions: Reviews, meta-reviews, and any discussion with the authors will be made public for accepted papers (but reviewer, area chair, and senior area chair identities will remain anonymous). Camera-ready papers will be due in advance of the conference. All camera-ready papers must include a funding disclosure.
For more than 50 years, Title IX has paved the way for tremendous strides in access to education for millions of students across the country. Every student deserves educational opportunity free from discrimination. ... The final regulations advance Title IX's promise of ensuring that no person experiences sex discrimination, including sex-based ...