An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25


A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
| Quantitative research questions | Quantitative research hypotheses |
|---|---|
| Descriptive research questions | Simple hypothesis |
| Comparative research questions | Complex hypothesis |
| Relationship research questions | Directional hypothesis |
| Non-directional hypothesis | |
| Associative hypothesis | |
| Causal hypothesis | |
| Null hypothesis | |
| Alternative hypothesis | |
| Working hypothesis | |
| Statistical hypothesis | |
| Logical hypothesis | |
| Hypothesis-testing | |
| Qualitative research questions | Qualitative research hypotheses |
| Contextual research questions | Hypothesis-generating |
| Descriptive research questions | |
| Evaluation research questions | |
| Explanatory research questions | |
| Exploratory research questions | |
| Generative research questions | |
| Ideological research questions | |
| Ethnographic research questions | |
| Phenomenological research questions | |
| Grounded theory questions | |
| Qualitative case study questions |
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
| Quantitative research questions | |
|---|---|
| Descriptive research question | |
| - Measures responses of subjects to variables | |
| - Presents variables to measure, analyze, or assess | |
| What is the proportion of resident doctors in the hospital who have mastered ultrasonography (response of subjects to a variable) as a diagnostic technique in their clinical training? | |
| Comparative research question | |
| - Clarifies difference between one group with outcome variable and another group without outcome variable | |
| Is there a difference in the reduction of lung metastasis in osteosarcoma patients who received the vitamin D adjunctive therapy (group with outcome variable) compared with osteosarcoma patients who did not receive the vitamin D adjunctive therapy (group without outcome variable)? | |
| - Compares the effects of variables | |
| How does the vitamin D analogue 22-Oxacalcitriol (variable 1) mimic the antiproliferative activity of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D (variable 2) in osteosarcoma cells? | |
| Relationship research question | |
| - Defines trends, association, relationships, or interactions between dependent variable and independent variable | |
| Is there a relationship between the number of medical student suicide (dependent variable) and the level of medical student stress (independent variable) in Japan during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic? | |
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
| Quantitative research hypotheses | |
|---|---|
| Simple hypothesis | |
| - Predicts relationship between single dependent variable and single independent variable | |
| If the dose of the new medication (single independent variable) is high, blood pressure (single dependent variable) is lowered. | |
| Complex hypothesis | |
| - Foretells relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables | |
| The higher the use of anticancer drugs, radiation therapy, and adjunctive agents (3 independent variables), the higher would be the survival rate (1 dependent variable). | |
| Directional hypothesis | |
| - Identifies study direction based on theory towards particular outcome to clarify relationship between variables | |
| Privately funded research projects will have a larger international scope (study direction) than publicly funded research projects. | |
| Non-directional hypothesis | |
| - Nature of relationship between two variables or exact study direction is not identified | |
| - Does not involve a theory | |
| Women and men are different in terms of helpfulness. (Exact study direction is not identified) | |
| Associative hypothesis | |
| - Describes variable interdependency | |
| - Change in one variable causes change in another variable | |
| A larger number of people vaccinated against COVID-19 in the region (change in independent variable) will reduce the region’s incidence of COVID-19 infection (change in dependent variable). | |
| Causal hypothesis | |
| - An effect on dependent variable is predicted from manipulation of independent variable | |
| A change into a high-fiber diet (independent variable) will reduce the blood sugar level (dependent variable) of the patient. | |
| Null hypothesis | |
| - A negative statement indicating no relationship or difference between 2 variables | |
| There is no significant difference in the severity of pulmonary metastases between the new drug (variable 1) and the current drug (variable 2). | |
| Alternative hypothesis | |
| - Following a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis predicts a relationship between 2 study variables | |
| The new drug (variable 1) is better on average in reducing the level of pain from pulmonary metastasis than the current drug (variable 2). | |
| Working hypothesis | |
| - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory | |
| Dairy cows fed with concentrates of different formulations will produce different amounts of milk. | |
| Statistical hypothesis | |
| - Assumption about the value of population parameter or relationship among several population characteristics | |
| - Validity tested by a statistical experiment or analysis | |
| The mean recovery rate from COVID-19 infection (value of population parameter) is not significantly different between population 1 and population 2. | |
| There is a positive correlation between the level of stress at the workplace and the number of suicides (population characteristics) among working people in Japan. | |
| Logical hypothesis | |
| - Offers or proposes an explanation with limited or no extensive evidence | |
| If healthcare workers provide more educational programs about contraception methods, the number of adolescent pregnancies will be less. | |
| Hypothesis-testing (Quantitative hypothesis-testing research) | |
| - Quantitative research uses deductive reasoning. | |
| - This involves the formation of a hypothesis, collection of data in the investigation of the problem, analysis and use of the data from the investigation, and drawing of conclusions to validate or nullify the hypotheses. | |
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
| Qualitative research questions | |
|---|---|
| Contextual research question | |
| - Ask the nature of what already exists | |
| - Individuals or groups function to further clarify and understand the natural context of real-world problems | |
| What are the experiences of nurses working night shifts in healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic? (natural context of real-world problems) | |
| Descriptive research question | |
| - Aims to describe a phenomenon | |
| What are the different forms of disrespect and abuse (phenomenon) experienced by Tanzanian women when giving birth in healthcare facilities? | |
| Evaluation research question | |
| - Examines the effectiveness of existing practice or accepted frameworks | |
| How effective are decision aids (effectiveness of existing practice) in helping decide whether to give birth at home or in a healthcare facility? | |
| Explanatory research question | |
| - Clarifies a previously studied phenomenon and explains why it occurs | |
| Why is there an increase in teenage pregnancy (phenomenon) in Tanzania? | |
| Exploratory research question | |
| - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated to have a deeper understanding of the research problem | |
| What factors affect the mental health of medical students (areas that have not yet been fully investigated) during the COVID-19 pandemic? | |
| Generative research question | |
| - Develops an in-depth understanding of people’s behavior by asking ‘how would’ or ‘what if’ to identify problems and find solutions | |
| How would the extensive research experience of the behavior of new staff impact the success of the novel drug initiative? | |
| Ideological research question | |
| - Aims to advance specific ideas or ideologies of a position | |
| Are Japanese nurses who volunteer in remote African hospitals able to promote humanized care of patients (specific ideas or ideologies) in the areas of safe patient environment, respect of patient privacy, and provision of accurate information related to health and care? | |
| Ethnographic research question | |
| - Clarifies peoples’ nature, activities, their interactions, and the outcomes of their actions in specific settings | |
| What are the demographic characteristics, rehabilitative treatments, community interactions, and disease outcomes (nature, activities, their interactions, and the outcomes) of people in China who are suffering from pneumoconiosis? | |
| Phenomenological research question | |
| - Knows more about the phenomena that have impacted an individual | |
| What are the lived experiences of parents who have been living with and caring for children with a diagnosis of autism? (phenomena that have impacted an individual) | |
| Grounded theory question | |
| - Focuses on social processes asking about what happens and how people interact, or uncovering social relationships and behaviors of groups | |
| What are the problems that pregnant adolescents face in terms of social and cultural norms (social processes), and how can these be addressed? | |
| Qualitative case study question | |
| - Assesses a phenomenon using different sources of data to answer “why” and “how” questions | |
| - Considers how the phenomenon is influenced by its contextual situation. | |
| How does quitting work and assuming the role of a full-time mother (phenomenon assessed) change the lives of women in Japan? | |
| Qualitative research hypotheses | |
|---|---|
| Hypothesis-generating (Qualitative hypothesis-generating research) | |
| - Qualitative research uses inductive reasoning. | |
| - This involves data collection from study participants or the literature regarding a phenomenon of interest, using the collected data to develop a formal hypothesis, and using the formal hypothesis as a framework for testing the hypothesis. | |
| - Qualitative exploratory studies explore areas deeper, clarifying subjective experience and allowing formulation of a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach. | |
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
| Variables | Unclear and weak statement (Statement 1) | Clear and good statement (Statement 2) | Points to avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Research question | Which is more effective between smoke moxibustion and smokeless moxibustion? | “Moreover, regarding smoke moxibustion versus smokeless moxibustion, it remains unclear which is more effective, safe, and acceptable to pregnant women, and whether there is any difference in the amount of heat generated.” | 1) Vague and unfocused questions |
| 2) Closed questions simply answerable by yes or no | |||
| 3) Questions requiring a simple choice | |||
| Hypothesis | The smoke moxibustion group will have higher cephalic presentation. | “Hypothesis 1. The smoke moxibustion stick group (SM group) and smokeless moxibustion stick group (-SLM group) will have higher rates of cephalic presentation after treatment than the control group. | 1) Unverifiable hypotheses |
| Hypothesis 2. The SM group and SLM group will have higher rates of cephalic presentation at birth than the control group. | 2) Incompletely stated groups of comparison | ||
| Hypothesis 3. There will be no significant differences in the well-being of the mother and child among the three groups in terms of the following outcomes: premature birth, premature rupture of membranes (PROM) at < 37 weeks, Apgar score < 7 at 5 min, umbilical cord blood pH < 7.1, admission to neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and intrauterine fetal death.” | 3) Insufficiently described variables or outcomes | ||
| Research objective | To determine which is more effective between smoke moxibustion and smokeless moxibustion. | “The specific aims of this pilot study were (a) to compare the effects of smoke moxibustion and smokeless moxibustion treatments with the control group as a possible supplement to ECV for converting breech presentation to cephalic presentation and increasing adherence to the newly obtained cephalic position, and (b) to assess the effects of these treatments on the well-being of the mother and child.” | 1) Poor understanding of the research question and hypotheses |
| 2) Insufficient description of population, variables, or study outcomes |
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
| Variables | Unclear and weak statement (Statement 1) | Clear and good statement (Statement 2) | Points to avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Research question | Does disrespect and abuse (D&A) occur in childbirth in Tanzania? | How does disrespect and abuse (D&A) occur and what are the types of physical and psychological abuses observed in midwives’ actual care during facility-based childbirth in urban Tanzania? | 1) Ambiguous or oversimplistic questions |
| 2) Questions unverifiable by data collection and analysis | |||
| Hypothesis | Disrespect and abuse (D&A) occur in childbirth in Tanzania. | Hypothesis 1: Several types of physical and psychological abuse by midwives in actual care occur during facility-based childbirth in urban Tanzania. | 1) Statements simply expressing facts |
| Hypothesis 2: Weak nursing and midwifery management contribute to the D&A of women during facility-based childbirth in urban Tanzania. | 2) Insufficiently described concepts or variables | ||
| Research objective | To describe disrespect and abuse (D&A) in childbirth in Tanzania. | “This study aimed to describe from actual observations the respectful and disrespectful care received by women from midwives during their labor period in two hospitals in urban Tanzania.” | 1) Statements unrelated to the research question and hypotheses |
| 2) Unattainable or unexplorable objectives |
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research Design: Understanding the Differences

As a future professional in the social and education landscape, research design is one of the most critical strategies that you will master to identify challenges, ask questions and form data-driven solutions to address problems specific to your industry.
Many approaches to research design exist, and not all work in every circumstance. While all data-focused research methods are valid in their own right, certain research design methods are more appropriate for specific study objectives.
Unlock our resource to learn more about jump starting a career in research design — Research Design and Data Analysis for the Social Good .
We will discuss the differences between quantitative (numerical and statistics-focused) and qualitative (non-numerical and human-focused) research design methods so that you can determine which approach is most strategic given your specific area of graduate-level study.
Understanding Social Phenomena: Qualitative Research Design
Qualitative research focuses on understanding a phenomenon based on human experience and individual perception. It is a non-numerical methodology relying on interpreting a process or result. Qualitative research also paves the way for uncovering other hypotheses related to social phenomena.
In its most basic form, qualitative research is exploratory in nature and seeks to understand the subjective experience of individuals based on social reality.
Qualitative data is…
- often used in fields related to education, sociology and anthropology;
- designed to arrive at conclusions regarding social phenomena;
- focused on data-gathering techniques like interviews, focus groups or case studies;
- dedicated to perpetuating a flexible, adaptive approach to data gathering;
- known to lead professionals to deeper insights within the overall research study.
You want to use qualitative data research design if:
- you work in a field concerned with enhancing humankind through the lens of social change;
- your research focuses on understanding complex social trends and individual perceptions of those trends;
- you have interests related to human development and interpersonal relationships.
Examples of Qualitative Research Design in Education
Here are just a few examples of how qualitative research design methods can impact education:
Example 1: Former educators participate in in-depth interviews to help determine why a specific school is experiencing a higher-than-average turnover rate compared to other schools in the region. These interviews help determine the types of resources that will make a difference in teacher retention.
Example 2: Focus group discussions occur to understand the challenges that neurodivergent students experience in the classroom daily. These discussions prepare administrators, staff, teachers and parents to understand the kinds of support that will augment and improve student outcomes.
Example 3: Case studies examine the impacts of a new education policy that limits the number of teacher aids required in a special needs classroom. These findings help policymakers determine whether the new policy affects the learning outcomes of a particular class of students.
Interpreting the Numbers: Quantitative Research Design
Quantitative research tests hypotheses and measures connections between variables. It relies on insights derived from numbers — countable, measurable and statistically sound data. Quantitative research is a strategic research design used when basing critical decisions on statistical conclusions and quantifiable data.
Quantitative research provides numerical-backed quantifiable data that may approve or discount a theory or hypothesis.
Quantitative data is…
- often used in fields related to education, data analysis and healthcare;
- designed to arrive at numerical, statistical conclusions based on objective facts;
- focused on data-gathering techniques like experiments, surveys or observations;
- dedicated to using mathematical principles to arrive at conclusions;
- known to lead professionals to indisputable observations within the overall research study.
You want to use quantitative data research design if:
- you work in a field concerned with analyzing data to inform decisions;
- your research focuses on studying relationships between variables to form data-driven conclusions;
- you have interests related to mathematics, statistical analysis and data science.
Examples of Quantitative Research Design in Education
Here are just a few examples of how quantitative research design methods may impact education:
Example 1: Researchers compile data to understand the connection between class sizes and standardized test scores. Researchers can determine if and what the relationship is between smaller, intimate class sizes and higher test scores for grade-school children using statistical and data analysis.
Example 2: Professionals conduct an experiment in which a group of high school students must complete a certain number of community service hours before graduation. Researchers compare those students to another group of students who did not complete service hours — using statistical analysis to determine if the requirement increased college acceptance rates.
Example 3: Teachers take a survey to examine an education policy that restricts the number of extracurricular activities offered at a particular academic institution. The findings help better understand the far-reaching impacts of extracurricular opportunities on academic performance.
Making the Most of Research Design Methods for Good: Vanderbilt University’s Peabody College
Vanderbilt University's Peabody College of Education and Human Development offers a variety of respected, nationally-recognized graduate programs designed with future agents of social change in mind. We foster a culture of excellence and compassion and guide you to become the best you can be — both in the classroom and beyond.
At Peabody College, you will experience
- an inclusive, welcoming community of like-minded professionals;
- the guidance of expert faculty with real-world industry experience;
- opportunities for valuable, hands-on learning experiences,
- the option of specializing depending on your specific area of interest.
Explore our monthly publication — Ideas in Action — for an inside look at how Peabody College translates discoveries into action.
Please click below to explore a few of the graduate degrees offered at Peabody College:
- Child Studies M.Ed. — a rigorous Master of Education degree that prepares students to examine the developmental, learning and social issues concerning children and that allows students to choose from one of two tracks (the Clinical and Developmental Research Track or the Applied Professional Track).
- Cognitive Psychology in Context M.S. — an impactful Master of Science program that emphasizes research design and statistical analysis to understand cognitive processes and real-world applications best, making it perfect for those interested in pursuing doctoral studies in cognitive science.
- Education Policy M.P.P — an analysis-focused Master of Public Policy program designed for future leaders in education policy and practice, allowing students to specialize in either K-12 Education Policy, Higher Education Policy or Quantitative Methods in Education Policy.
- Quantitative Methods M.Ed. — a data-driven Master of Education degree that teaches the theory and application of quantitative analysis in behavioral, social and educational sciences.
Connect with the Community of Professionals Seeking to Enhance Humankind at Peabody College
At Peabody College, we equip you with the marketable, transferable skills needed to secure a valuable career in education and beyond. You will emerge from the graduate program of your choice ready to enhance humankind in more meaningful ways than you could have imagined.
If you want to develop the sought-after skills needed to be a force for change in the social and educational spaces, you are in the right place .
We invite you to request more information ; we will connect you with an admissions professional who can answer all your questions about choosing one of these transformative graduate degrees at Peabody College. You may also take this opportunity to review our admissions requirements and start your online application today.

Subscribe to the Blog
← All Posts
Media Inquiries
615-322-6397 Email
Latest Stories
7 quantitative data careers in education that can make a difference, the rewarding outcomes of being a special education teacher, should i earn an m.p.p. degree in education policy 4 questions to ask, keep reading.

Explore Stories by Topic
- M.Ed. Degrees
- Research Design

- Module 1 Resources
- Module 2 Resources
Module 3 Resources
- Library Portal
Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed-Methods Approaches to Research
- Applied Research Methods in Public and Nonprofit Organizations Mitchell Brown, & Kathleen Hale. (2014). Applied Research Methods in Public and Nonprofit Organizations: Vol. First edition. Jossey-Bass.
Please review Chapter 3.
- Research Methodology & Design - Qualitative Research Methods National University Library (2024). Qualitative research methods. This guide features NU Library resources for studying and planning qualitative research methodology and design.
- Research Methodology & Design - Quantitative Research Methods National University Library (2024). Quantitative research methods. This guide features NU Library resources for studying and planning quantitative research methodology and design.
- Doing Qualitative Research Creswell, J. (2015). Doing qualitative research [Video]. Sage Research Methods. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781506363448 This video discusses the characteristics of a qualitative researcher and defines qualitative research. (9:55).
- Top Tips for Conducting Qualitative Research Hein, W. (2020). Top tips for conducting qualitative research [Video]. Sage Research Methods. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781529730708 This video reviews common student research problems, how to identify gaps in your research, figuring out what methods you favor, and challenging research problems. (9:32).
- An Introduction to Reasoning in Qualitative & Quantitative Research Rivas, C. (2017). An introduction to reasoning in qualitative & quantitative research [Video]. Sage Research Methods. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781473992269 This video reviews perspective and reasoning styles, deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, and abductive reasoning. (7:47).
- What Is Best: Quantitative, Qualitative or Mixed Approaches? O'Leary, Z. (2017). What is best: Quantitative, qualitative or mixed approaches? [Video]. Sage Research Methods. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781526400147 This video discusses quantitative, qualitative, and mixed approaches. (10:32).
- An Introduction to Mixed Methods Research Hitchcock, J. (2017). An introduction to mixed methods research [Video]. Sage Research Methods. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781473991712 This video reviews mixed methods research, how it can be used to address complex questions, and more. (16:05).
- SAGE Research Methods: Qualitative vs Quantitative Research – Video Search Result List Spend some time exploring the videos in the search results list provided. This is a great place to start as you complete your own research for your culminating project proposal.
Statistics
- Elementary Statistics: A QuickStudy Digital Reference Guide Rumsey, D. (2020). Elementary Statistics: A QuickStudy Digital Reference Guide. QuickStudy Reference Guides.
- Introductory Statistics Eusea, J., Okwan, P., Belmasrour, R., Patterson, S., & Andrus, S. (2024). Introductory Statistics. Pressbooks.
- Basic Statistics Sandals29, & Leon, A. (2022). Basic Statistics. Pressbooks.
- College Statistics LePine, M. (2022). College Statistics. Pressbooks.
- Statistics for Research Students Fein, E. C., Gilmour, J., Machin, T., & Hendry, L. (2022). Statistics for Research Students. Pressbooks.
- Introduction to Probability and Statistics Pardoe, I. (2022). Introduction to Probability and Statistics. Pressbooks.
- Introduction to Statistics Lumen Learning, & OpenStax (2023). Introduction to Statistics. Pressbooks.
- From Questions To Answers – Statistics For Everyone Roth, A. (2024). From Questions To Answers – Statistics For Everyone. Pressbooks.
Using Artificial Intelligence in Research
Resources .
- Artificial Intelligence: OpenAI, ChatGPT, Large Language Models, and You National University Library (2024). Artificial intelligence: OpenAI, ChatGPT, Large language models, and you. Explore this resource provided by National University to guide the ethical use of AI in your research.
- Using Generative AI Academic Success Center (2024). Using generative AI. Familiarize yourself with the National University Academic Success Center’s resources for using generative AI. Please note that the misuse of AI in courses constitutes a breach of academic integrity as defined by the Student Code of Conduct.
Videos
- Using AI in Research Projects [Cory Lebson]. (2023, October 10). Using AI in Research Projects [Video]. LinkedIn Learning. This course gives tips and techniques for using generative AI to enhance, extend, and improve research projects of all types. (25m). Please make sure you are signed into OKTA prior to accessing the following LinkedIn Learning resources. Faculty, staff, and students have access to LinkedIn Learning and do not need to create an account.
- How to Research and Write Using Generative AI Tools [Dave Birss]. (2023, March 15). How to Research and Write Using Generative AI Tools [Video]. LinkedIn Learning. This course teaches strategies for writing effective prompts for generative AI. (1h 15m). Please make sure you are signed into OKTA prior to accessing the following LinkedIn Learning resources. Faculty, staff, and students have access to LinkedIn Learning and do not need to create an account.
- << Previous: Module 2 Resources
- Next: Library Portal >>
- Last Updated: Jul 12, 2024 9:17 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/EDD825

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods
Published on April 12, 2019 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on June 22, 2023.
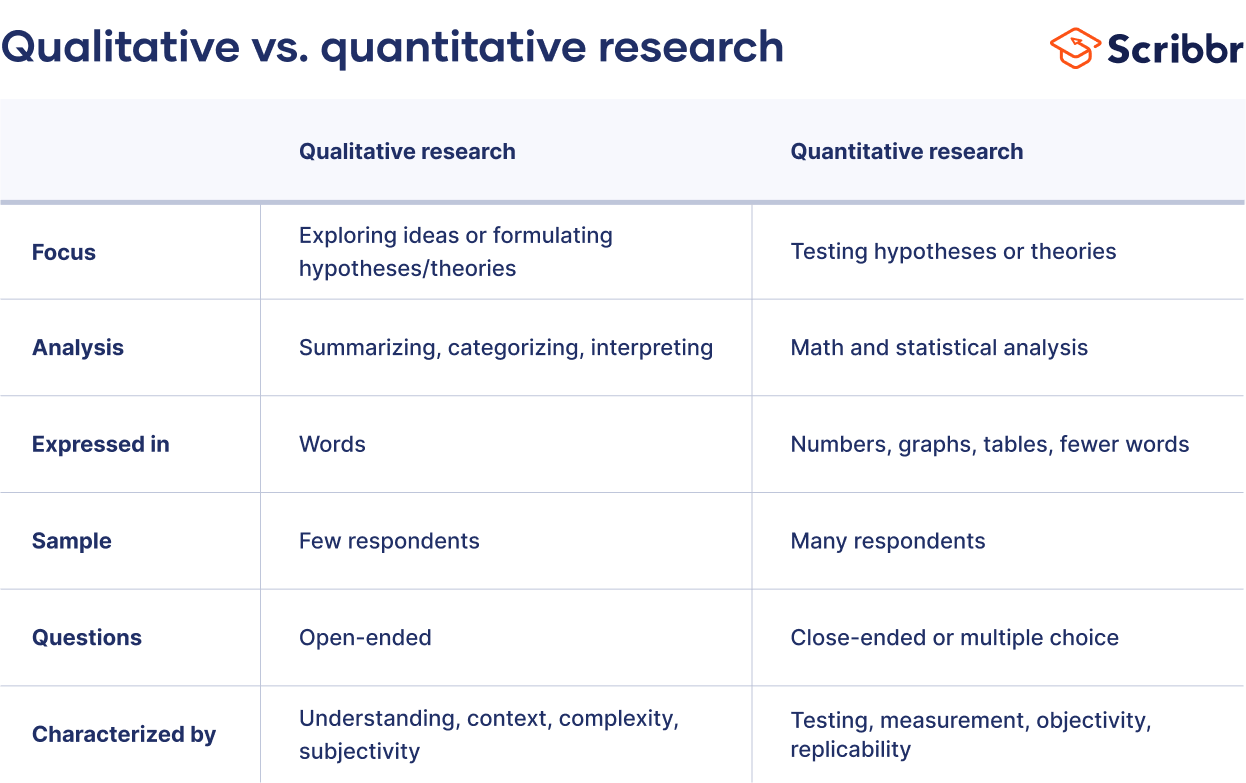
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge.
Common quantitative methods include experiments, observations recorded as numbers, and surveys with closed-ended questions.
Quantitative research is at risk for research biases including information bias , omitted variable bias , sampling bias , or selection bias . Qualitative research Qualitative research is expressed in words . It is used to understand concepts, thoughts or experiences. This type of research enables you to gather in-depth insights on topics that are not well understood.
Common qualitative methods include interviews with open-ended questions, observations described in words, and literature reviews that explore concepts and theories.
Table of contents
The differences between quantitative and qualitative research, data collection methods, when to use qualitative vs. quantitative research, how to analyze qualitative and quantitative data, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative and quantitative research.
Quantitative and qualitative research use different research methods to collect and analyze data, and they allow you to answer different kinds of research questions.
Quantitative and qualitative data can be collected using various methods. It is important to use a data collection method that will help answer your research question(s).
Many data collection methods can be either qualitative or quantitative. For example, in surveys, observational studies or case studies , your data can be represented as numbers (e.g., using rating scales or counting frequencies) or as words (e.g., with open-ended questions or descriptions of what you observe).
However, some methods are more commonly used in one type or the other.
Quantitative data collection methods
- Surveys : List of closed or multiple choice questions that is distributed to a sample (online, in person, or over the phone).
- Experiments : Situation in which different types of variables are controlled and manipulated to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Observations : Observing subjects in a natural environment where variables can’t be controlled.
Qualitative data collection methods
- Interviews : Asking open-ended questions verbally to respondents.
- Focus groups : Discussion among a group of people about a topic to gather opinions that can be used for further research.
- Ethnography : Participating in a community or organization for an extended period of time to closely observe culture and behavior.
- Literature review : Survey of published works by other authors.
A rule of thumb for deciding whether to use qualitative or quantitative data is:
- Use quantitative research if you want to confirm or test something (a theory or hypothesis )
- Use qualitative research if you want to understand something (concepts, thoughts, experiences)
For most research topics you can choose a qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods approach . Which type you choose depends on, among other things, whether you’re taking an inductive vs. deductive research approach ; your research question(s) ; whether you’re doing experimental , correlational , or descriptive research ; and practical considerations such as time, money, availability of data, and access to respondents.
Quantitative research approach
You survey 300 students at your university and ask them questions such as: “on a scale from 1-5, how satisfied are your with your professors?”
You can perform statistical analysis on the data and draw conclusions such as: “on average students rated their professors 4.4”.
Qualitative research approach
You conduct in-depth interviews with 15 students and ask them open-ended questions such as: “How satisfied are you with your studies?”, “What is the most positive aspect of your study program?” and “What can be done to improve the study program?”
Based on the answers you get you can ask follow-up questions to clarify things. You transcribe all interviews using transcription software and try to find commonalities and patterns.
Mixed methods approach
You conduct interviews to find out how satisfied students are with their studies. Through open-ended questions you learn things you never thought about before and gain new insights. Later, you use a survey to test these insights on a larger scale.
It’s also possible to start with a survey to find out the overall trends, followed by interviews to better understand the reasons behind the trends.
Qualitative or quantitative data by itself can’t prove or demonstrate anything, but has to be analyzed to show its meaning in relation to the research questions. The method of analysis differs for each type of data.
Analyzing quantitative data
Quantitative data is based on numbers. Simple math or more advanced statistical analysis is used to discover commonalities or patterns in the data. The results are often reported in graphs and tables.
Applications such as Excel, SPSS, or R can be used to calculate things like:
- Average scores ( means )
- The number of times a particular answer was given
- The correlation or causation between two or more variables
- The reliability and validity of the results
Analyzing qualitative data
Qualitative data is more difficult to analyze than quantitative data. It consists of text, images or videos instead of numbers.
Some common approaches to analyzing qualitative data include:
- Qualitative content analysis : Tracking the occurrence, position and meaning of words or phrases
- Thematic analysis : Closely examining the data to identify the main themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying how communication works in social contexts
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2023, June 22). Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved July 16, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-quantitative-research/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, what is quantitative research | definition, uses & methods, what is qualitative research | methods & examples, mixed methods research | definition, guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Qualitative and Quantitative Research

Related Papers
Jennifer Chase
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare
Anshika Srivastava
Munyaradzi Moyo
Methodological Issues in Management Research: Advances, Challenges, and the Way Ahead
Richa Awasthy
Current paper is an overview of qualitative research. It starts with discussing meaning of research and links it with a framework of experiential learning. Complexity of socio-political environment can be captured with methodologies appropriate to capture dynamism and intricacy of human life. Qualitative research is a process of capturing lived-in experiences of individuals, groups, and society. It is an umbrella concept which involves variety of methods of data collection such as interviews, observations, focused group discussions, projective tools, drawings, narratives, biographies, videos, and anything which helps to understand world of participants. Researcher is an instrument of data collection and plays a crucial role in collecting data. Main steps and key characteristics of qualitative research are covered in this paper. Reader would develop appreciation for methodiness in qualitative research. Quality of qualitative research is explained referring to aspects related to rigor...
IBRAHIM WADEMBERE
Robert Eppel
Research plays a very important role in making sense of the world around us and developing knowledge basis and systems. As such, understanding research methods and paradigms is very important to scholars and researchers if they are to come up with credible and comprehensive research. This paper discusses the differences between qualitative and quantitative research methods and also looks at how the two methods can be similar and how they can be used together. Qualitative research is a scientific and systematic method used to gather data that it not quantifiable (Yin 2018). This type of research, as Marshall (2016)) explains, "refers to the meanings, concepts definitions, characteristics, metaphors, symbols, and description of things". Therefore, as a research method, qualitative research is also used to unearth new trends in thought processes and actions, how people feel about specific circumstances and to get to the heart of issues and how they affect people (Wolcott 2016). Marshall (2016) emphasizes that qualitative research is primarily exploratory research and is used to obtain information such as intentions and motives that helps explain an occurrence. Thus, qualitative research methods help to understand new occurrences or trends and then helps to explain why such things are happening or occurring. Quantitative Research is used to quantify the problem by way of generating numerical data or data that can be transformed into useable statistics (Lichtman 2017). According to Wolcott (2016) quantitative research is used to quantify attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and other defined variables and generalize results from a larger sample population. Thus, quantitative Research uses measurable data to formulate facts and uncover patterns in research to make sense or deductions on how things have unfolded. Therefore, where qualitative data seeks to understand a phenomenon, quantitative methods seek to quantify them and identify variables that can be measured. Qualitative research uses data collecting methods that often require the direct participation of the researcher to gather data and information crucial to the study. Morgan (2017) notes that
Kirathe Wanjiku
Malvin Nana Data IX
Tracie Seidelman
Kezang sherab
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
UNICAF University - Zambia
Ivan Steenkamp
Marsyangdi Journal
Basanta Kandel, PhD
Dr. Mustapha Kulungu
Language Teaching Research
Hossein Nassaji
Fernando Almeida
Rachel Irish Kozicki
Darya Lebedeva
Victoria Clarke
M.Lib.I.Sc. Project, Panjab University, under guidance of Dr. Shiv Kumar
SUBHAJIT PANDA
Psychology Lover
Tinashe Paul
Zeinab NasserEddine
Virginia Njenga
SAI SUSMITHA CHITTETI 1537152
Managing Quality in Qualitative Research
New Directions for Program Evaluation
Sharon Rallis
Canadian journal of psychiatry. Revue canadienne de psychiatrie
David Streiner
Evidence Based Nursing
temitope oludoun
Calvin Moorley
Scholars' Journal
Khim Subedi
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Quantitative and Qualitative Research
- Quantitative vs Qualititave Research
- Searching For Qualitative Research
- Searching for Quantitative Research
- More Resources
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
Research can be done using either qualitative or quantitative data. The decision of which data to use depends on the purpose of the research.
Qualitative Research: Explores an unfamiliar topic, concept, or idea. The data for this research is hard to measure, provided by open ended questionnaires for example. It is presented in the research in descriptive, narrative, exploratory way where a vague topic needs to be clearly defined, explained, the problem should be identified in details.
Quantitative Research: Explores a problem or correlation with variables (measurable data, numbers, or statistics) provided by surveys and questionnaires with closed ended questions for example. Usually uses large samples of data to warrant generalization.
Empirical Research: The terms quantitative and empirical research are often used interchangeably. Empirical research however simply means any form of research that is directly observed. Therefore not all empirical research is quantitative.
| Qualitative Research | Quantitative Research |
|---|---|
| Soft Science | Hard Science |
| Inductive reasoning used to synthesize data | Deductive reasoning used to synthesize data |
| Develops a theory | Tests a theory |
| Basis of knowing - meaning, discovery | Basis of knowing - cause and effect relationships |
| Basic element of analysis - words, narrative | Basic element of analysis - numbers and statistical analysis |
Borrowed from the John M. Pfau Library
Examples of Qualitative Vs. Quantitative
| Research question | Unit of analysis | Goal is to generalize? | Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|
| What is the experience of hope in women with advances ovarian cancer? | Semi-structures interviews with women with advances ovarian cancer (N-20). Identified codes and categories with narrative examples | No | Qualitative |
| What are the experiences of fathers concerning support for their wives/partners during labor? | Unstructured interviews with fathers (5 supportive, 5 non-supportive): results left in narrative form describing themes based on nursing for the whole person theory | No | Qualitative |
| What is the effect of crossing legs on blood pressure measurement? | Blood pressure measurements before and after crossing legs resulting in numbers | Yes | Quantitative |
| What is the impact of a learner-centered hand washing program on a group of 2 graders? | Paper and pencil test resulting in hand washing scores | Yes | Quantitative |
Borrowed from the Ebling Library
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Qualitative Research >>
- The Interprofessional Health Sciences Library
- 123 Metro Boulevard
- Nutley, NJ 07110
- [email protected]
- Student Services
- Parents and Families
- Career Center
- Web Accessibility
- Visiting Campus
- Public Safety
- Disability Support Services
- Campus Security Report
- Report a Problem
- Login to LibApps
- Systematic review
- Open access
- Published: 15 July 2024
Teamwork and implementation of innovations in healthcare and human service settings: a systematic review
- Elizabeth A. McGuier ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6219-6358 1 ,
- David J. Kolko 1 ,
- Gregory A. Aarons 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Allison Schachter 5 , 6 ,
- Mary Lou Klem 7 ,
- Matthew A. Diabes 8 ,
- Laurie R. Weingart 8 ,
- Eduardo Salas 9 &
- Courtney Benjamin Wolk 5 , 6
Implementation Science volume 19 , Article number: 49 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Implementation of new practices in team-based settings requires teams to work together to respond to new demands and changing expectations. However, team constructs and team-based implementation approaches have received little attention in the implementation science literature. This systematic review summarizes empirical research examining associations between teamwork and implementation outcomes when evidence-based practices and other innovations are implemented in healthcare and human service settings.
We searched MEDLINE, CINAHL, APA PsycINFO and ERIC for peer-reviewed empirical articles published from January 2000 to March 2022. Additional articles were identified by searches of reference lists and a cited reference search for included articles (completed in February 2023). We selected studies using quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods to examine associations between team constructs and implementation outcomes in healthcare and human service settings. We used the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool to assess methodological quality/risk of bias and conducted a narrative synthesis of included studies. GRADE and GRADE-CERQual were used to assess the strength of the body of evidence.
Searches identified 10,489 results. After review, 58 articles representing 55 studies were included. Relevant studies increased over time; 71% of articles were published after 2016. We were unable to generate estimates of effects for any quantitative associations because of very limited overlap in the reported associations between team variables and implementation outcomes. Qualitative findings with high confidence were: 1) Staffing shortages and turnover hinder implementation; 2) Adaptive team functioning (i.e., positive affective states, effective behavior processes, shared cognitive states) facilitates implementation and is associated with better implementation outcomes; Problems in team functioning (i.e., negative affective states, problematic behavioral processes, lack of shared cognitive states) act as barriers to implementation and are associated with poor implementation outcomes; and 3) Open, ongoing, and effective communication within teams facilitates implementation of new practices; poor communication is a barrier.
Conclusions
Teamwork matters for implementation. However, both team constructs and implementation outcomes were often poorly specified, and there was little overlap of team constructs and implementation outcomes studied in quantitative studies. Greater specificity and rigor are needed to understand how teamwork influences implementation processes and outcomes. We provide recommendations for improving the conceptualization, description, assessment, analysis, and interpretation of research on teams implementing innovations.

Trial registration
This systematic review was registered in PROSPERO, the international prospective register of systematic reviews. Registration number: CRD42020220168.
Peer Review reports
Contributions to the Literature:
This paper reviews more than 20 years of research on teams and implementation of new practices in healthcare and human service settings.
We concluded with high confidence that adaptive team functioning is associated with better implementation outcomes and problems in team functioning are associated with poorer implementation outcomes. While not surprising, the implementation science literature has lacked clear empirical evidence for this finding.
Use of the provided recommendations will improve the quality of future research on teams and implementation of evidence-based practices.
Healthcare and human service providers (e.g., clinicians, case managers) often work in team-based settings where professionals work collaboratively with one another and service recipients toward shared goals [ 1 , 2 ]. Team-based care is intended to include multiple professionals with varying skills and expertise [ 1 , 3 ]. It requires shared responsibility for outcomes and increases team members’ dependence on one another to complete work [ 1 , 3 , 4 ]. Effective team-based care and higher quality teamwork are associated with improvements in care access and quality, patient safety, patient satisfaction, clinical outcomes, and costs [ 2 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ].
We use the term ‘teamwork’ to refer to an array of team constructs using the input-mediator-outcome-input (IMOI) framework (Fig. 1 ) [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. The IMOI framework recognizes that team interactions are dynamic and complex, with processes unfolding over time and feedback loops between processes, outcomes, and inputs [ 10 ]. Team inputs include team structure and composition, task demands, and contextual features [ 13 ]. Mediators are aspects of team functioning (i.e., what team members think, feel, and do [ 12 ]) through which inputs influence outcomes. These processes and emergent states may be cognitive, affective, or behavioral [ 5 , 14 , 15 , 16 ]. Team effectiveness outcomes are multidimensional and include team performance as well as team viability and the impact of the team on members’ development [ 12 , 17 , 18 , 19 ].
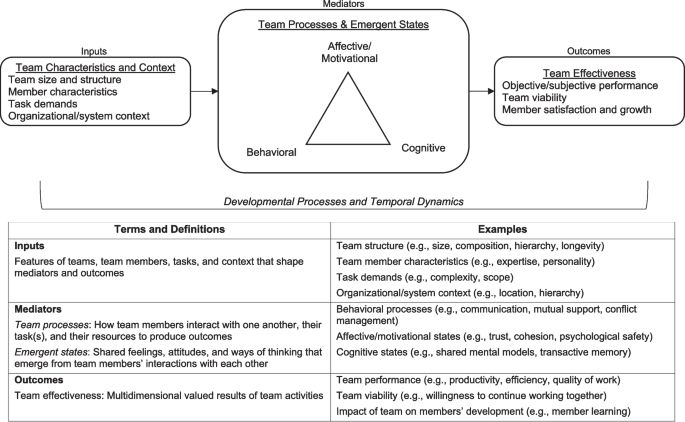
Conceptual model of team effectiveness and key terminology. Figure adapted from “Advancing research on teams and team effectiveness in implementation science: An application of the Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment (EPIS) framework” by E.A. McGuier, D.J. Kolko, N.A. Stadnick, L. Brookman-Frazee, C.B. Wolk, C.T. Yuan, C.S. Burke, & G.A. Aarons, 2023, Implementation Research and Practice , 4 , 26334895231190855. [CC BY-NC]
Implementation of new practices in team-based service settings requires team members to work together to respond to changing demands and expectations. Extensive research has identified barriers and facilitators to implementation of new practices at the individual provider, organization, and system levels; however, the team level has received little empirical attention [ 20 , 21 ]. This is a problem because implementation efforts increasingly rely on teams, and responses to a new practice are likely to be influenced by team characteristics and processes. See McGuier and colleagues [ 20 ] for an overview of team constructs in the context of implementation science and the Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment (EPIS) framework [ 22 , 23 ]. Given increasing use of team-based care and interest in implementation strategies targeting teams, examining how teamwork is associated with implementation processes and outcomes is critical. This systematic review identified and summarized empirical research examining associations between teamwork and implementation outcomes when evidence-based practices (EBPs) and other innovations were implemented in healthcare and human service settings.
This systematic review was registered (PROSPERO; registration number: CRD42020220168) and conducted following the published protocol [ 24 ]. The review was conducted in accordance with PRISMA and SWiM guidance [ 25 , 26 ]; relevant checklists are in Additional File 1.
Information sources and search strategy
We searched the following databases: MEDLINE (Ovid), CINAHL (Ebsco), APA PsycINFO (Ovid), and ERIC (Ebsco). Database searches were run on August 7, 2020, and again on March 8, 2022. For all searches, a publication date from 2000 to current was applied; there were no language restrictions (see [ 24 ]). An experienced health sciences librarian (MLK) designed the Ovid MEDLINE search and translated that search for use in the other databases (see additional file in [ 24 ]). The search strings consisted of controlled vocabulary (when available) and natural language terms representing concepts of teamwork and implementation science or innovation or evidence-based practice. Results were downloaded to an EndNote (version X9.3.3) library and duplicate records removed [ 27 ]. Additional relevant articles were identified by hand searches of reference lists of included articles, a cited reference search for included articles in the Web of Science (Clarivate) bibliographic database (completed in February 2023), and requests sent to implementation science listservs and centers for suggestions of relevant articles.
Eligibility criteria
We included empirical journal articles describing studies using quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods. Study protocols, reviews, and commentaries were excluded. All studies were conducted in healthcare or human service settings (e.g., hospitals, clinics, child welfare) and described the implementation of a practice to improve patient care. Studies of interventions to improve teamwork (e.g., team building interventions) and studies of teams created to implement the innovation (e.g., quality improvement teams, implementation support teams) were excluded. Eligible studies assessed at least one team construct and described its influence on implementation processes and outcomes.
Changes from protocol
Several changes were made from our systematic review protocol (PROSPERO CRD42020220168; [ 24 ]). Specifically, during the full-text review stage, we broadened the scope from team functioning (i.e., processes and states) to include team structure and performance because of the small number of studies that assessed and reported specific processes or states. This change increased the number of included studies. Similarly, because implementation outcomes were often inconsistently defined and poorly reported [ 28 , 29 , 30 ], we broadened our scope to include studies that identified team constructs as implementation determinants (i.e., barriers/facilitators) without explicitly defining and measuring an implementation outcome. Because of changes in university access to bibliographic databases, the cited reference search was performed in the Web of Science only instead of the Web of Science and Scopus. This bibliographic database indexes more than 21,000 scientific journals [ 31 ]. Lastly, because of time and resource constraints, we did not search conference abstracts or contact authors for unreported data.
Selection process and data extraction
Title/abstract screening and review of full-text articles were conducted by pairs of trained independent reviewers in DistillerSR. Conflicts were resolved through re-review, discussion between reviewers, and when needed, discussion with a senior team member (EAM). A final review of all included articles was conducted by EAM. Relevant data from each article was extracted into an Excel spreadsheet by one reviewer (AS). A second reviewer (EAM) conducted a line-by-line review and verification. Our data extraction form was informed by existing forms and guides (e.g., [ 32 , 33 ]). For each included study, we extracted information on measures of teamwork and implementation-relevant outcomes, characteristics of the setting, teams, and participants, analysis methods, and results. For quantitative studies, we recorded correlation coefficients and/or regression coefficients as standardized metrics of association. For qualitative studies, we recorded themes [ 33 ].
Quality and risk of bias assessment
The Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) [ 34 ] was used to evaluate quality and risk of bias for each included study. Multiple publications from the same study were evaluated separately because they reported different outcomes. Consistent with Powell and colleagues [ 35 ], quality evaluations were only made for the components of the study relevant to our question. Quality evaluations were conducted by two independent reviewers (EAM, MAD) with discrepancies resolved through consensus discussion. After completing the MMAT, the reviewers jointly categorized each article as high, moderate, or low quality. High quality studies were those with affirmative responses to all MMAT questions. Moderate quality studies had at least one minor methodological problem, and low-quality studies had serious flaws (e.g., qualitative studies with poor coherence between data, analysis, and conclusions; quantitative studies with biased samples and/or inappropriate statistical analyses).
We rated the relevance of each publication to our research question as high, moderate, or low. Highly relevant studies reported implementation of a well-defined innovation, thoroughly described team constructs and implementation outcomes, and clearly linked team constructs to implementation outcomes. Most studies rated as low relevance provided very limited information about teamwork and/or implementation outcomes. Studies that only described barriers/facilitators were rated as low or moderate relevance. Ratings were conducted by two independent reviewers (EAM, CBW) with discrepancies resolved through consensus discussion.
Data synthesis
We conducted a narrative synthesis of included studies following guidelines for synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) [ 36 ]. We prioritized reporting of high quality, highly relevant studies. Studies categorized as low quality and/or low relevance were not included in the synthesis but are included in the description of study characteristics to convey the breadth of the literature. We organized studies based on the IMOI framework (i.e., team inputs, processes/states, and outputs) and organized studies of processes/states by affective, behavioral, and cognitive constructs when possible. Because of the heterogeneity in team constructs and implementation outcomes, we were unable to quantitatively synthesize results using meta-analysis or formally investigate heterogeneity; this challenge is common in implementation science systematic reviews [ 30 ]. We assessed the strength of the overall body of evidence with GRADE for quantitative studies [ 37 ] and GRADE-CERQual for qualitative studies [ 38 , 39 ]. GRADE results in ratings of high, moderate, low, or very low quality of evidence for each outcome of interest. GRADE-CERQual results in ratings of high, moderate, low, or very low confidence in each review finding. GRADE ratings were made independently with discrepancies resolved through consensus discussion; GRADE-CERQual ratings were made through iterative discussions as recommended [ 39 ]. All ratings and decisions were made by the first and senior authors.
Search results
Our initial search, after removal of duplicates, yielded 7181 results. The second search (August 2020-March 2022) captured an additional 1341 results. The cited reference search yielded 1961 results. A total of 10,489 results were included in title/abstract review. Figure 2 provides a PRISMA flow diagram for included studies. After full-text review, 58 articles from 55 studies were included in analyses [ 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 , 97 ].
PRISMA flow diagram of included articles. From: Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021;372:n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71 . For more information, visit: http://www.prisma-statement.org/
As shown in Fig. 3 , publications on teamwork and implementation have increased substantially since 2000. Three articles on this topic (5%) were published between 2000 and 2007, 14 (24%) between 2008 and 2015, and 41 (71%) between 2016 and early 2023.
Included articles by year of publication
Study characteristics
Interrater agreement was good for assessment of study quality (81% agreement on MMAT questions) and ratings of relevance (88% agreement). There were 20 high quality articles, 23 moderate quality articles, and 15 low quality articles. Fourteen articles were rated as high relevance, 22 as moderate, and 22 as low relevance. Only 4 were rated as both high quality and high relevance. We report study characteristics for all 58 eligible articles. Our narrative synthesis includes 32 articles categorized as moderate/high quality and moderate/high relevance; it excludes 26 articles categorized as low quality and/or relevance.
Studies were conducted in inpatient healthcare ( n = 22), outpatient/ambulatory healthcare ( n = 21), mental health settings ( n = 9), and other settings (e.g., residential facilities, multiple settings; n = 6). There were 33 qualitative, 15 quantitative, and 10 mixed methods studies. All quantitative studies were descriptive observational studies.
Most studies examined team processes/states ( n = 53); fewer examined team inputs ( n = 27). Only two studies examined a team effectiveness outcome. The most common implementation outcomes were fidelity ( n = 16) and other specified implementation outcomes (e.g., “extent of use,” “implementation success”) ( n = 15). Less frequently identified implementation outcomes included adoption ( n = 5), sustainment ( n = 4), reach ( n = 4), and perceptions of the innovation (e.g., acceptability, appropriateness, feasibility; n = 3). Approximately one-third of studies ( n = 21) did not report specific implementation outcomes but described implementation determinants (i.e., barriers and facilitators).
Synthesis: team inputs & implementation outcomes
Team inputs examined in studies included team stability/instability and staffing shortages, aspects of team structure and composition, interdependence, and hierarchy and professional roles. Quantitative findings are presented in Table 1 . A CERQual Summary of Qualitative Findings related to team inputs is shown in Table 2 . A CERQual Evidence Profile is provided in Additional File 2 (Table A1).
Team stability/instability and staffing shortages
Team stability/instability (i.e., consistency in membership over time) was examined in one mixed methods study [ 48 , 49 ] and three qualitative studies [ 70 , 81 , 94 ]. A study of surgical teams found variations in membership stability but no association between stability and “implementation success” (i.e., composite measure based on number of uses of new technique, proportion of uses, and changes in use) [ 48 , 49 ]. The authors suggested that stability facilitates the development of team coordination but that selecting small and exclusive teams may limit the spread of innovations within the organization. Another study found that a dedicated and stable team in which members were selected and trained together in the use of a new surgical technique led to quicker uptake and better integration into practice, theorizing that dedicated and stable teams increased trust, motivation, and collaborative problem-solving [ 81 ]. However, dedicated teams were difficult to sustain, and some sites instead used rotating team members from a larger pool of trained staff. In rural primary care, stability of team members facilitated sustainment of memory care clinics [ 70 ]. Lastly, another study in primary care found mixed perceptions of stable vs. rotating staff when adding a new team role (i.e., health coach); some team members liked rotating through different roles while others wanted more stability [ 94 ]. Across studies, we found that dedicated and stable team members facilitate implementation while instability in team membership is a barrier to implementation (moderate confidence).
Qualitative studies identified staffing shortages and turnover on teams as barriers to implementation [ 50 , 67 , 75 , 78 , 92 ]. In Veterans Health Administration (VA) clinics, “inadequate staffing posed an insurmountable barrier,” hindering communication and delivery of optimal care during the implementation of the patient-centered medical home (PCMH) model [ 92 ]. Similarly, staff shortages, turnover, and high workloads hindered guideline implementation in Kenyan hospitals [ 75 ]. Two studies found negative impacts of staffing shortages and turnover on sustainment. Staff turnover contributed to discontinuity in Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) team members [ 78 ], and appropriate staffing (i.e., ensuring manageable workloads) and blocking time for team members were identified as critical to sustainment of a team-based model in the VA [ 67 ]. We found that staffing shortages and turnover hinder implementation (high confidence).
Team structure/composition
Studies examined multiple aspects of team structure and composition, specifically team size, workload, longevity (i.e., how long team members had worked together), history of change, and team member characteristics. Team size was examined in two studies of DBT. In a mixed methods study, team size was positively correlated with fidelity, and qualitative data suggested that team size may increase as a result of successful implementation [ 47 ]. In contrast, another study found that DBT team size was not associated with the number of DBT components adopted and was negatively associated with reach, suggesting reach may reflect high workloads [ 72 ]. In VA mental health clinics, team workload (i.e., number of patients seen) was negatively associated with sustainment of trauma-focused therapies [ 68 ]. In these studies, team longevity and history of change were not associated with implementation outcomes [ 47 , 68 ]. Team member characteristics, specifically team member competency/expertise, experience, and commitment/engagement, were identified as facilitators of implementation in some qualitative studies [ 40 , 70 , 81 , 84 , 95 ].
Overall, few findings could be made from quantitative studies examining team structure and composition. Two studies of team size found mixed results, and workload, longevity, and history of change were examined in only one study each. Across qualitative studies, we found team member competency/expertise, experience, and commitment/engagement facilitate implementation (moderate confidence).
Team interdependence
One quantitative study examined team interdependence [ 65 ]. In multidisciplinary child abuse teams implementing a mental health screening/referral protocol, task interdependence (i.e., reliance on team members to share resources and coordinate workflows) was positively associated with reach but not time to adoption. Outcome interdependence (i.e., extent to which outcomes are evaluated at the team vs. individual level) was significantly negatively correlated with time to adoption but not reach. Neither task nor outcome interdependence were associated with team members’ perceptions of acceptability, appropriateness, or feasibility of the innovation [ 65 ]. Because only one study examined interdependence, no review findings were made.
Hierarchy & professional roles
Hierarchy, power distributions, and rigid roles were identified as barriers to implementation in several qualitative studies [ 50 , 53 , 74 , 97 ]. Flatter hierarchies (i.e., more equal distribution of power and authority) supported guideline implementation in pediatric primary care; practices with low compliance to guidelines had more hierarchical relationships while practices with high compliance had more shared decision-making [ 97 ]. In a setting with hierarchy and rigid division of roles, nurses trained in an innovation reported concern that their decisions would be questioned by physicians without expertise in the innovation but more authority [ 74 ]. Similarly, in surgical teams, rigid professional roles and a hierarchical team culture constrained open discussion and created contention over how and when a “time-out” should be completed, resulting in inconsistent use and poor fidelity [ 50 , 53 ]. Across studies, we found that in multidisciplinary settings, rigid professional roles, hierarchical relationships, and power differentials are barriers to implementation (moderate confidence).
Summary of team inputs & implementation outcomes
There was no overlap among team input variables and implementation outcomes examined in quantitative studies (Table 1 ). Accordingly, we were unable to generate estimates of effects or ratings of evidence quality. Qualitative review findings are shown in Table 2 . We found: 1) Dedicated and stable team members facilitate implementation while instability in team membership is a barrier to implementation (moderate confidence); 2) Staffing shortages and turnover hinder implementation (high confidence); 3) Team member competency/expertise, experience, and commitment/engagement facilitate implementation (moderate confidence); and 4) In multidisciplinary settings, rigid professional roles, hierarchical relationships, and power differentials are barriers to implementation (moderate confidence).
Synthesis: team processes/states & implementation outcomes
Studies examined overall team functioning as well as specific affective states, behavioral processes, and cognitive states. Quantitative findings are presented in Table 3 , and a GRADE Evidence Profile is provided in Additional File 2 (Table A2). A CERQual Summary of Qualitative Findings related to team processes and states is shown in Table 4 . A CERQual Evidence Profile is provided in Additional File 2 (Table A3).
Overall team functioning
Nine studies examined quantitative associations between overall team functioning and implementation outcomes. Team functioning was positively associated with intervention fidelity in 2 of 3 studies. One study examined implementation of transition programs for adolescents with chronic health conditions in 29 teams. More positive team climate, measured by the Team Climate Inventory (i.e., shared vision, participative safety, task orientation, support for innovation), at study start was associated with greater improvements in quality of chronic care delivery one year later [ 45 ]. Additionally, improvements in team climate were associated with greater improvement in care delivery [ 45 ]. These findings were consistent across teams working with different patient populations, suggesting the influence of team climate generalizes across teams and settings [ 45 ]. Greater team climate for innovation was also associated with greater fidelity (i.e., implementation of more program elements) among DBT teams [ 47 ]. In contrast, no significant associations were found between team climate and fidelity to a multifaceted cardiovascular disease management intervention, with qualitative data suggesting variation in the influence of teamwork across practices [ 77 ]. There was no overlap in the metrics of association reported in these studies; therefore, we were unable to generate an estimate of the effect of team functioning on fidelity. The quality of the evidence for fidelity was rated very low because of serious methodological limitations, serious inconsistency, and very serious imprecision due to the small number of studies.
Three studies examined associations between teamwork and adoption, with no significant associations found. The first study found that teamwork climate (i.e., perceived quality of collaboration between personnel) was not significantly associated with adoption of a comprehensive safety program in intensive care units, although there were associations between adoption and organizational constructs (e.g., lower safety climate, more management support) [ 59 ]. In a study of DBT teams, neither positive nor negative team functioning was associated with the number of DBT modes adopted [ 72 ]. The third study assessed relational coordination (i.e., shared goals, communication, respect) in primary care practices implementing patient engagement strategies. Relational coordination was high across practices initially and did not differ for practices with high vs. low adoption, although it increased over time in practices with high adoption [ 83 ]. There was no overlap in the metrics of association reported in these studies; therefore, we were unable to generate an estimate of the effect of team functioning on adoption. The quality of the evidence was rated very low because of serious methodological limitations and very serious imprecision due to the small number of studies.
Reach and sustainment were each examined in one quantitative study. DBT teams with more negative functioning had greater reach, suggesting that reach may reflect high workloads; positive functioning was not associated with reach [ 72 ]. In VA mental health clinics, team functioning was positively correlated with sustainment of evidence-based trauma-focused psychotherapies and significantly associated with sustainment after controlling for covariates [ 68 ]. Two studies examined other implementation outcomes. One found that better team functioning was associated with greater implementation of changes to improve access to care in VA clinics [ 62 ]. In the other, primary care practices reporting better teamwork were more likely to be in later stages of transformation to PCMHs than practices with poorer teamwork [ 88 ]. Because of the small number of studies examining reach, sustainment, and other implementation outcomes, we were unable to generate estimates of effects or ratings of evidence quality for these outcomes.
Our qualitative review findings are based on 12 studies describing how team functioning influenced implementation processes and outcomes. There was considerable variation across studies in how team functioning was defined and what implementation outcomes were examined. Most findings were based on relatively thin and superficial data. Studies occurred in a variety of healthcare settings with varying resources and implemented diverse interventions. We found with high confidence that 1) Adaptive team functioning, characterized by positive affective states (e.g., trust, mutual respect, belonging), effective behavior processes (e.g., frequent communication and coordination), and shared cognitive states (e.g., clear roles, shared mental models of how to provide care), facilitates implementation and is associated with better implementation outcomes; and 2) Problems in team functioning, including negative affective states (e.g., tension, lack of trust), problematic behavioral processes (e.g., conflict, competition, poor communication), and a lack of shared cognitive states (e.g., unclear roles, lack of shared awareness, competing goals), act as barriers to implementation and are associated with poor implementation outcomes.
Affective states
Specific affective states were examined in one quantitative study, three mixed methods studies, and one qualitative study. There was no overlap in the associations between affective states and implementation outcomes reported in quantitative studies (Table 3 ). In a study of multidisciplinary teams responding to child abuse, affective integration (i.e., liking, trust, respect) was positively associated with acceptability, appropriateness, and feasibility but not time to adoption or reach [ 65 ]. In DBT teams, cohesion was associated with fidelity, and qualitative data indicated that liking one’s team members and having a shared team identity were critical to effective implementation [ 47 ]. Another study of DBT teams described conflicts and lack of safety and trust within teams resulting in their dissolution [ 78 ].
Edmondson and colleagues found that psychological safety and ease of speaking up (i.e., interpersonal climate that allows members to share questions and concerns) were associated with implementation success [ 48 , 49 ]. In teams with low psychological safety, lower-status team members were hesitant to speak up, hindering change and proficiency in the new practice [ 49 ]. Psychological safety was closely related to learning behavior within the team, including speaking up with questions and concerns [ 48 , 49 ]. From the mixed methods and qualitative studies, we found that trust, cohesion, and psychological safety within teams facilitate implementation by contributing to team members’ willingness to speak up and share experiences and feedback. Negative affective states, fear of judgment, conflict, and lack of safety hinder implementation (moderate confidence).
Behavioral processes
Specific behavioral processes, including communication, learning behavior, and coordination, were examined in two quantitative studies, two mixed methods studies, and five qualitative studies. There was no overlap in the associations between behavioral processes and implementation outcomes reported in quantitative studies (Table 3 ).
Only one study reported quantitative findings for communication. Communication in DBT teams was positively associated with fidelity [ 47 ]. Qualitative studies frequently identified communication as a determinant of implementation (Table 4 ). From qualitative studies, we found that open, ongoing, and effective communication within teams facilitates implementation of new practices; poor communication is a barrier (high confidence).
Quantitative associations between team learning behavior and implementation outcomes were reported in three studies. Team learning behavior in child abuse teams was positively correlated with acceptability and feasibility; it was not associated with appropriateness, time to adoption, or reach [ 65 ]. Learning behavior was positively associated with knowledge and use of innovations in nursing teams [ 91 ] and with implementation success in surgical teams [ 48 ]. Because each of these studies examined different implementation outcomes, we were unable to generate an estimate of the effect of learning behavior or rate evidence quality.
Inter-team communication, specifically speaking up and learning from other teams (i.e., boundary spanning), was identified as a critical part of team learning processes associated with successful implementation [ 48 ]. Communication beyond the team was also identified as a facilitator of implementation in two qualitative studies [ 47 , 75 ]. We found that communication beyond the team facilitates implementation by providing opportunities for team learning (low confidence).
Lastly, two qualitative studies examined coordination among healthcare teams [ 40 , 95 ]. Findings were somewhat ambiguous and based on thin data. We found with low confidence that poor coordination among healthcare professionals interferes with providing high-quality care and can be a barrier to implementation of new approaches (low confidence).
Cognitive states
Specific cognitive states were examined in two quantitative studies. There was no overlap in the associations between cognitive states and implementation outcomes reported (Table 3 ). The first study found no significant associations between shared goals and implementation outcomes [ 65 ]. The second study found that greater team knowledge and skills were associated with greater implementation of key changes to improve access to care; team problem recognition was not associated with implementation [ 62 ].
Two studies reported qualitative findings related to shared goals. In VA mental health teams, shared mission differentiated teams with sustained high reach of EBPs from those with low reach [ 84 ]. Commitment to a shared goal consistent with the EBP supported sustainment [ 84 ]. Similarly, shared goals and vision were identified as a facilitator of DBT programs [ 47 ]. We found that shared goals, mission, and vision within teams facilitate implementation and sustainment (low confidence).
Summary of team processes/states & implementation outcomes
There was very little overlap in the reported associations between team processes/states and implementation outcomes (Table 3 ). We were unable to generate estimates of effects for any associations. When there was sufficient overlap to rate evidence quality, the evidence was rated very low quality (Table A2, Additional File 2).
Qualitative review findings are shown in Table 4 . We found the following: 1) Adaptive team functioning, characterized by positive affective states (e.g., trust, mutual respect, belonging), effective behavior processes (e.g., frequent communication and coordination), and shared cognitive states (e.g., clear roles, shared mental models of how to provide care), facilitates implementation and is associated with better implementation outcomes (high confidence); 2) Problems in team functioning, including negative affective states (e.g., tension, lack of trust), problematic behavioral processes (e.g., conflict, competition, poor communication), and a lack of shared cognitive states (e.g., unclear roles, lack of shared awareness, competing goals), act as barriers to implementation and are associated with poor implementation outcomes (high confidence); 3) Trust, cohesion, and psychological safety within teams facilitate implementation by contributing to team members’ willingness to speak up and openly share experiences and feedback. Negative affective states, fear of judgment, conflict, and lack of safety hinder implementation (moderate confidence); 4) Open, ongoing, and effective communication within teams facilitates implementation of new practices; poor communication is a barrier (high confidence); 5) Communication beyond the team facilitates implementation by providing opportunities for team learning (low confidence); 6) Poor coordination among healthcare professionals interferes with providing high-quality care and can be a barrier to implementation of new approaches (low confidence); and 7) Shared goals, mission, and vision within teams facilitate implementation and sustainment (low confidence).
Synthesis: team effectiveness outcomes & implementation outcomes
Team effectiveness outcomes are multidimensional and include performance (i.e., productivity, efficiency, and quality of the team’s work), team viability, and the impact of the team on members’ development [ 12 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Only two studies examined associations between team effectiveness and implementation outcomes. Quantitative findings are presented in Table 5 . One quantitative study found that team members’ ratings of team performance were associated with innovation acceptability, appropriateness, and feasibility; performance was not associated with time to adoption or reach [ 65 ]. One qualitative study found that positive outcomes for team members (e.g., increased comfort working together, greater knowledge) were associated with sustainment [ 70 ]. No studies examined associations of team viability and implementation outcomes.
Summary of team effectiveness outcomes & implementation outcomes
Only one quantitative study examined associations between a dimension of team effectiveness and implementation outcomes (Table 5 ). Accordingly, we were unable to generate ratings of evidence quality or estimates of any effects. Similarly, because there was only one qualitative study, we were unable to make a review finding.
This systematic review summarizes over 20 years of empirical literature on the associations between teamwork and implementation outcomes in the context of implementation of new practices in health and human services. Consistent with increased attention to teams and reliance on team-based models of care, as well as the growth of implementation science, studies increased substantially over time. We included studies that used quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods, yielding a total of 58 articles representing 55 studies. Included studies spanned naturalistic implementation evaluations and planned implementation research.
Key findings with high confidence were: 1) Staffing shortages and turnover hinder implementation, 2) Adaptive team functioning, characterized by positive affective states, effective behavior processes, and shared cognitive states, facilitates implementation and is associated with better implementation outcomes. Problems in team functioning, including negative affective states, problematic behavioral processes, and a lack of shared cognitive states, act as barriers to implementation and are associated with poor implementation outcomes, and 3) Open, ongoing, and effective communication within teams facilitates implementation of new practices; poor communication is a barrier. Our results generally align with conventional wisdom and scientific research outside of healthcare, increasing confidence in the findings. Team effectiveness and change management research in other types of organizations and settings (e.g., military, aviation, space exploration) [ 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 , 102 , 103 ] is largely converging.
Overall, the literature was heterogeneous, and many studies lacked specificity regarding team composition and implementation activities and outcomes. Teamwork was defined and measured inconsistently and with limited precision across studies, which hindered our ability to draw conclusions about how teams influence implementation processes and outcomes. There was also poor measurement and reporting of implementation outcomes in many studies, consistent with a recent review of research on implementation outcomes [ 28 , 29 ]. Many studies used broad measures encompassing multiple dimensions of teamwork. Among studies that assessed specific team processes and states, there was very little overlap across constructs assessed. Qualitative studies identified a rich array of specific team processes and states; research to confirm the presence of these factors in other settings and determine their associations with implementation outcomes is needed.
In Table 6 , we summarize the limitations of existing research on teams and implementation and provide recommendations for future research. Notably, increased specificity and rigor in how teamwork is conceptualized and assessed is needed to advance our understanding of how teamwork affects implementation processes and outcomes. Limited inclusion of teams and team constructs in implementation theories, models, and frameworks has likely contributed to the neglect of teams in implementation science [ 20 ]. Updates to theories, models, and framework should consider integrating teams and team-level constructs [ 20 ]. In addition, there are well-established theories of team effectiveness that could inform hypotheses about how specific team constructs affect implementation [ 104 , 105 , 106 , 107 ].
There is considerable room for improvement in the definition and description of teams and analysis of data from teams. Describing the structure and purpose of teams, as well as interdependencies within the team, can help differentiate teams from groups of individuals who do not constitute a team, an important conceptual distinction that can be difficult to discern in study descriptions. Reporting of sampling and recruitment procedures for teams and team-level response rates is needed. For quantitative studies, use of standardized, validated measures of teamwork constructs is recommended. Researchers should be careful to base inferences about teams on team-level data. Lastly, future research should follow recommendations for improving measurement and reporting of implementation outcomes [ 29 , 108 ] and consider the multilevel context of teams in theory, measurement, analysis, and interpretation of results [ 109 ].
Limitations
As with all systematic reviews, it is possible that we failed to identify some relevant articles or data. We did not search gray literature or conference abstracts or contact authors for unreported data. Our organization of studies by the IMOI framework is likely imperfect given the broad array of team constructs included and poor reporting in many studies. We included diverse innovations intended to improve patient care, including specific EBPs, clinical practice guidelines, models of care, care bundles, procedural changes, and technological innovations. This diversity in objects of implementation reflects ongoing debates about the necessary strength of evidence for objects of implementation and varying thresholds in different contexts [ 110 ]. In this review, high quality studies tended to involve clinical interventions with strong research evidence (e.g., DBT) and clinics in structured and often team-based healthcare systems (e.g., VA). Diversity of innovations and settings provides greater external validity for our findings but may mask some findings specific to certain innovations or settings.
We only included studies of existing teams providing clinical services, however, many studies provided limited descriptions of teams, and in some cases the distinction between clinical teams and implementation/quality improvement teams was unclear. There is increasing attention to use of teams in implementation frameworks [ 20 , 111 ] and evidence that functioning of implementation teams matters [ 112 , 113 ]. Research on the composition and functioning of implementation teams is an important area for future research.
Our systematic review findings indicate that teamwork matters for implementation. However, greater specificity and rigor are needed to advance our understanding of how teamwork influences implementation processes and outcomes. We provide recommendations for improving the conceptualization, description, assessment, analysis, and interpretation of research on teams implementing new practices.
Availability of data and materials
All data cited in this review came from published papers and are therefore already available. The data created as part of the review process are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Mitchell P, Wynia M, Golden R, McNellis B, Okun S, Webb CE, et al. Core principles and values of effective team-based health care. NAM Perspectives. 2012. Available from: https://nam.edu/perspectives-2012-core-principles-values-of-effective-team-based-health-care/ Cited 2020 Sep 23
Reiss-Brennan B, Brunisholz KD, Dredge C, Briot P, Grazier K, Wilcox A, et al. Association of integrated team-based care with health care quality, utilization, and cost. JAMA. 2016;316(8):826–34.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Katkin JP, Kressly SJ, Edwards AR, Perrin JM, Kraft CA, Richerson JE, et al. Guiding principles for team-based pediatric care. Pediatrics. 2017;140(2):e20171489.
Lipton HL. Home is where the health is: Advancing team-based care in chronic disease management. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(21):1945–8.
Dinh JV, Traylor AM, Kilcullen MP, Perez JA, Schweissing EJ, Venkatesh A, et al. Cross-disciplinary care: A systematic review on teamwork processes in health care. Small Group Research. 2020;51(1):125–66.
Article Google Scholar
Fiscella K, McDaniel SH. The complexity, diversity, and science of primary care teams. Am Psychol. 2018;73(4):451–67.
Herbert JL, Bromfield LM. A quasi-experimental study of the Multi-Agency Investigation & Support Team (MIST): A collaborative response to child sexual abuse. Child Abuse Negl. 2020;27:104827.
Google Scholar
Reiss-Brennan B. Mental Health Integration: Normalizing Team Care. J Prim Care Community Health. 2014;5(1):55–60.
Schmutz J, Manser T. Do team processes really have an effect on clinical performance? A systematic literature review. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110(4):529–44.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ilgen DR, Hollenbeck JR, Johnson M, Jundt D. Teams in organizations: From input-process-output models to IMOI models. Annu Rev Psychol. 2005;56:517–43.
Kozlowski SWJ, Bell BS. Work groups and teams in organization. In: Borman WC, Ilgen DR, Klimoski RJ, editors. Handbook of Psychology (Vol 12): Industrial and Organizational Psychology. New York: Wiley-Blackwell. 2003. p. 333–75. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118133880.hop212017 Cited 2020 Apr 10
Mathieu JE, Maynard MT, Rapp T, Gilson L. Team effectiveness 1997–2007: A review of recent advancements and a glimpse into the future. J Manag. 2008;34(3):410–76.
Cordery JL, Tian AW. Team Design. In: The Wiley Blackwell Handbook of the Psychology of Team Working and Collaborative Processes. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. 2017;p. 103–28. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118909997.ch5 Cited 2021 Apr 2
Kozlowski SWJ, Bell BS. Work groups and teams in organizations: Review update. In: Schmitt N, Highhouse S, editors. Handbook of Psychology (Vol 12): Industrial and Organizational Psychology. 2nd ed. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley; 2013. p. 111.
Kozlowski SWJ, Ilgen DR. Enhancing the effectiveness of work groups and teams. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2006;7(3):77–124.
Marks MA, Mathieu JE, Zaccaro SJ. A temporally based framework and taxonomy of team processes. AMR. 2001;26(3):356–76.
Hackman JR. A normative model of work team effectiveness. Arlington, VA: Office of Naval Research; 1983. Available from: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/citations/ADA136398 Cited 2022 May 16
Mathieu JE, Hollenbeck JR, van Knippenberg D, Ilgen DR. A century of work teams in the Journal of Applied Psychology. J Appl Psychol. 2017;102(3):452–67.
Rosen MA, Dietz AS. Team performance measurement. In: The Wiley Blackwell Handbook of the Psychology of Team Working and Collaborative Processes. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2017. p. 479–502.
Chapter Google Scholar
McGuier EA, Kolko DJ, Stadnick NA, Brookman-Frazee L, Wolk CB, Yuan CT, et al. Advancing research on teams and team effectiveness in implementation science: An application of the Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment (EPIS) framework. Implementation Research and Practice. 2023;1(4):26334895231190856.
Williams NJ, Beidas RS. Annual research review: The state of implementation science in child psychology and psychiatry: A review and suggestions to advance the field. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2019;60:430–50.
Aarons GA, Hurlburt M, Horwitz SM. Advancing a conceptual model of evidence-based practice implementation in public service sectors. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2011;38(1):4–23.
Moullin JC, Dickson KS, Stadnick NA, Rabin B, Aarons GA. Systematic review of the Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment (EPIS) framework. Implement Sci. 2019;14(1):1.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
McGuier EA, Kolko DJ, Klem ML, Feldman J, Kinkler G, Diabes MA, et al. Team functioning and implementation of innovations in healthcare and human service settings: a systematic review protocol. Syst Rev. 2021;10(1):189.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339. Available from: http://www.bmj.com/content/339/bmj.b2535 Cited 2020 Apr 1
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;29(372):n71.
Bramer WM, Giustini D, de Jonge GB, Holland L, Bekhuis T. De-duplication of database search results for systematic reviews in EndNote. J Med Libr Assoc. 2016;104(3):240–3.
Lengnick-Hall R, Gerke DR, Proctor EK, Bunger AC, Phillips RJ, Martin JK, et al. Six practical recommendations for improved implementation outcomes reporting. Implement Sci. 2022;17(1):16.
Proctor EK, Bunger AC, Lengnick-Hall R, Gerke DR, Martin JK, Phillips RJ, et al. Ten years of implementation outcomes research: a scoping review. Implement Sci. 2023;18(1):31.
Chapman A, Rankin NM, Jongebloed H, Yoong SL, White V, Livingston PM, et al. Overcoming challenges in conducting systematic reviews in implementation science: a methods commentary. Syst Rev. 2023;12(1):116.
Pranckutė R. Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The Titans of Bibliographic Information in Today’s Academic World. Publications. 2021;9(1):12.
Effective Practice and Organisation of Care (EPOC). Data collection form. EPOC Resources for review authors. Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services. 2013. Available from: http://epoc.cochrane.org/epoc-specific-resources-review-authors .
Noyes J, Lewin S. Extracting qualitative evidence. In: Noyes J, Booth A, Hannes K, Harden A, Harris J, Lewin S, et al., editors. Supplementary Guidance for Inclusion of Qualitative Research in Cochrane Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 1 (updated August 2011). Cochrane Collaboration Qualitative Methods Group; 2011. Available from: http://cqrmg.cochrane.org/supplemental-handbook-guidance
Hong QN, Pluye P, Fàbregues S, Bartlett G, Boardman F, Cargo M, et al. Improving the content validity of the mixed methods appraisal tool: a modified e-Delphi study. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019;1(111):49-59.e1.
Powell BJ, Patel SV, Haley AD, Haines ER, Knocke KE, Chandler S, Determinants of implementing evidence-based trauma-focused interventions for children and youth: A systematic review. Adm Policy Ment Health, et al. cited 2020 Feb 20. Available from: 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10488-019-01003-3 .
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Campbell M, McKenzie JE, Sowden A, Katikireddi SV, Brennan SE, Ellis S, et al. Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: reporting guideline. BMJ. 2020;16(368):l6890.
Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction—GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2011;64(4):383–94.
Lewin S, Bohren M, Rashidian A, Munthe-Kaas H, Glenton C, Colvin CJ, et al. Applying GRADE-CERQual to qualitative evidence synthesis findings—paper 2: how to make an overall CERQual assessment of confidence and create a Summary of Qualitative Findings table. Implementation Sci. 2018;13(1):11–23.
Lewin S, Booth A, Glenton C, Munthe-Kaas H, Rashidian A, Wainwright M, et al. Applying GRADE-CERQual to qualitative evidence synthesis findings: introduction to the series. Implementation Sci. 2018;13(1):1–10.
Adjognon OL, Shin MH, Steffen MJA, Moye J, Solimeo S, Sullivan JL. Factors affecting primary care implementation for older veterans with multimorbidity in Veterans Health Administration (VA). Health Serv Res. 2021;56(S1):1057–68.
Alidina S, Chatterjee P, Zanial N, Alreja SS, Balira R, Barash D, et al. Improving surgical quality in low-income and middle-income countries: why do some health facilities perform better than others? BMJ Qual Saf. 2021;30(12):937–49.
Boltey EM, Iwashyna TJ, Hyzy RC, Watson SR, Ross C, Costa DK. Ability to predict team members’ behaviors in ICU teams is associated with routine ABCDE implementation. J Crit Care. 2019;51:192–7.
Chenoweth L, Jeon YH, Stein-Parbury J, Forbes I, Fleming R, Cook J, et al. PerCEN trial participant perspectives on the implementation and outcomes of person-centered dementia care and environments. Int Psychogeriatr. 2015;27(12):2045–57.
Costa DK, Valley TS, Miller MA, Manojlovich M, Watson SR, McLellan P, et al. ICU team composition and its association with ABCDE implementation in a quality collaborative. J Crit Care. 2018;44:1–6.
Cramm JM, Strating MMH, Nieboer AP. The role of team climate in improving the quality of chronic care delivery: a longitudinal study among professionals working with chronically ill adolescents in transitional care programmes. BMJ Open. 2014;4(5):e005369.
DePuccio MJ, Gaughan AA, Sova LN, MacEwan SR, Walker DM, Gregory ME, et al. An examination of the barriers to and facilitators of implementing nurse-driven protocols to remove indwelling urinary catheters in acute care hospitals. The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety. 2020;46(12):691–8.
Ditty MS, Landes SJ, Doyle A, Beidas RS. It takes a village: A mixed method analysis of inner setting variables and Dialectical Behavior Therapy implementation. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2015;42(6):672–81.
Edmondson AC. Speaking up in the operating room: How team leaders promote learning in interdisciplinary action teams. J Manage Stud. 2003;40(6):1419–52.
Edmondson AC, Bohmer RM, Pisano GP. Disrupted routines: Team learning and new technology implementation in hospitals. Adm Sci Q. 2001;46(4):685–716.
Gillespie BM, Chaboyer W, Wallis M, Fenwick C. Why isn’t “time out” being implemented? An exploratory study. Qual Saf Health Care. 2010;19(2):103–6.
Gillespie BM, Harbeck E, Lavin J, Gardiner T, Withers TK, Marshall AP. Using normalisation process theory to evaluate the implementation of a complex intervention to embed the surgical safety checklist. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):170.
Gillespie BM, Marshall AP, Gardiner T, Lavin J, Withers TK. Impact of workflow on the use of the Surgical Safety Checklist: a qualitative study: Surgical Safety Checklist and work flow. ANZ J Surg. 2016;86(11):864–7.
Gillespie BM, Withers TK, Lavin J, Gardiner T, Marshall AP. Factors that drive team participation in surgical safety checks: a prospective study. Patient Saf Surg. 2016;10(3):1–9.
Gosling AS. Clinical team functioning and IT innovation: A study of the diffusion of a point-of-care online evidence system. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2003;10(3):244–51.
Graetz I, Huang J, Brand R, Shortell SM, Rundall TG, Bellows J, et al. The impact of electronic health records and teamwork on diabetes care quality. American Journal of Managed Care. 2015;21(12):878–84.
PubMed Google Scholar
Haider S, Ali RF, Ahmed M, Humayon AA, Sajjad M, Ahmad J. Barriers to implementation of emergency obstetric and neonatal care in rural Pakistan. Sawyer A, editor. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(11):e0224161.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Harvey C, Killaspy H, Martino S, White S, Priebe S, Wright C, et al. A comparison of the implementation of Assertive Community Treatment in Melbourne, Australia and London. England Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2011;20(2):151–61.
Harvey C, Killaspy H, Martino S, Johnson S. Implementation of Assertive Community Treatment in Australia: Model fidelity, patient characteristics and staff experiences. Community Ment Health J. 2012;48(5):652–61.
Hsu YJ, Marsteller JA. Who applies an intervention to influence cultural attributes in a quality improvement collaborative? J Patient Saf. 2020;16(1):1–6.
Irimu GW, Greene A, Gathara D, Kihara H, Maina C, Mbori-Ngacha D, et al. Explaining the uptake of paediatric guidelines in a Kenyan tertiary hospital – mixed methods research. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14(1):119.
Lall D, Engel N, Devadasan N, Horstman K, Criel B. Team-based primary health care for non-communicable diseases: complexities in South India. Health Policy Plan. 2020;35(Supplement_2):ii22-34.
Lukas CV, Mohr D, Meterko M. Team effectiveness and organizational context in the implementation of a clinical innovation. Qual Manag Health Care. 2009;18(1):25–39.
Mariani E, Vernooij-Dassen M, Koopmans R, Engels Y, Chattat R. Shared decision-making in dementia care planning: barriers and facilitators in two European countries. Aging Ment Health. 2017;21(1):31–9.
Martinez RN, Hogan TP, Balbale S, Lones K, Goldstein B, Woo C, et al. Sociotechnical perspective on implementing clinical video telehealth for veterans with spinal cord injuries and disorders. Telemedicine and e-Health. 2017;23(7):567–76.
McGuier EA, Aarons GA, Byrne KA, Campbell KA, Keeshin B, Rothenberger SD, et al. Associations between teamwork and implementation outcomes in multidisciplinary cross-sector teams implementing a mental health screening and referral protocol. Implementation Science Communications. 2023;4(1):13.
Meloncelli N, Barnett A, de Jersey S. Staff resourcing, guideline implementation and models of care for gestational diabetes mellitus management. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020;60(1):115–22.
Miller CJ, Kim B, Connolly SL, Spitzer EG, Brown M, Bailey HM, et al. Sustainability of the Collaborative Chronic Care Model in outpatient mental health teams three years post-Implementation: A qualitative analysis. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2023;50(1):151–9.
Mohr DC, Rosen CS, Schnurr PP, Orazem RJ, Noorbaloochi S, Clothier BA, et al. The influence of team functioning and workload on sustainability of trauma-focused evidence-based psychotherapies. PS. 2018;69(8):879–86.
Morgan D, Kosteniuk J, O’Connell ME, Kirk A, Stewart NJ, Seitz D, et al. Barriers and facilitators to development and implementation of a rural primary health care intervention for dementia: a process evaluation. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):709.
Morgan D, Kosteniuk J, O’Connell ME, Seitz D, Elliot V, Bayly M, et al. Factors influencing sustainability and scale-up of rural primary healthcare memory clinics: perspectives of clinic team members. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22(1):148.
Munce SEP, Graham ID, Salbach NM, Jaglal SB, Richards CL, Eng JJ, et al. Perspectives of health care professionals on the facilitators and barriers to the implementation of a stroke rehabilitation guidelines cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):440.
Navarro-Haro MV, Harned MS, Korslund KE, DuBose A, Chen T, Ivanoff A, et al. Predictors of adoption and reach following Dialectical Behavior Therapy Intensive Training™. Community Ment Health J. 2019;55(1):100–11.
Newbould L, Ariss S, Mountain G, Hawley MS. Exploring factors that affect the uptake and sustainability of videoconferencing for healthcare provision for older adults in care homes: a realist evaluation. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021;21(1):13.
Nyondo-Mipando AL, Woo Kinshella ML, Bohne C, Suwedi-Kapesa LC, Salimu S, Banda M, et al. Barriers and enablers of implementing bubble Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): Perspectives of health professionals in Malawi. Ameh CA, editor. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(2):e0228915.
Nzinga J, Mbindyo P, Mbaabu L, Warira A, English M. Documenting the experiences of health workers expected to implement guidelines during an intervention study in Kenyan hospitals. Implementation Sci. 2009;4(1):44.
Papoutsi C, Poots A, Clements J, Wyrko Z, Offord N, Reed JE. Improving patient safety for older people in acute admissions: implementation of the Frailsafe checklist in 12 hospitals across the UK. Age Ageing. 2018;47(2):311–7.
Patel B, Usherwood T, Harris M, Patel A, Panaretto K, Zwar N, et al. What drives adoption of a computerised, multifaceted quality improvement intervention for cardiovascular disease management in primary healthcare settings? A mixed methods analysis using normalisation process theory. Implementation Sci. 2018;13(1):140.
Popowich AD, Mushquash AR, Pearson E, Schmidt F, Mushquash CJ. Barriers and facilitators affecting the sustainability of dialectical behaviour therapy programmes: A qualitative study of clinician perspectives. Couns Psychother Res. 2020;20(1):68–80.
Prom MC, Canelos V, Fernandez PJ, Gergen Barnett K, Gordon CM, Pace CA, et al. Implementation of integrated behavioral health care in a large medical center: Benefits, challenges, and recommendations. J Behav Health Serv Res. 2021;48(3):346–62.
Provost S, Pineault R, Grimard D, Pérez J, Fournier M, Lévesque Y, et al. Implementation of an integrated primary care cardiometabolic risk prevention and management network in Montréal: does greater coordination of care with primary care physicians have an impact on health outcomes? Health Promot Chronic Dis Prev Can. 2017;37(4):105–13.
Randell R, Honey S, Alvarado N, Greenhalgh J, Hindmarsh J, Pearman A, et al. Factors supporting and constraining the implementation of robot-assisted surgery: a realist interview study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(6):e028635.
Robbins J, McAlearney AS. Encouraging employees to speak up to prevent infections: Opportunities to leverage quality improvement and care management processes. Am J Infect Control. 2016;44(11):1224–30.
Rodriguez HP, Poon BY, Wang E, Shortell SM. Linking practice adoption of patient engagement strategies and relational coordination to patient-reported outcomes in accountable care organizations. Milbank Q. 2019;97(3):692–735.
Sayer NA, Rosen CS, Bernardy NC, Cook JM, Orazem RJ, Chard KM, et al. Context matters: Team and organizational factors associated with reach of evidence-based psychotherapies for PTSD in the Veterans Health Administration. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2017;44(6):904–18.
Shin MH, Montano ARL, Adjognon OL, Harvey KLL, Solimeo SL, Sullivan JL. Identification of implementation strategies using the CFIR-ERIC matching tool to mitigate barriers in a primary care model for older veterans. Gerontologist. 2022;63(3):439–50.
Sopcak N, Aguilar C, O’Brien MA, Nykiforuk C, Aubrey-Bassler K, Cullen R, et al. Implementation of the BETTER 2 program: a qualitative study exploring barriers and facilitators of a novel way to improve chronic disease prevention and screening in primary care. Implementation Sci. 2016;11(1):158.
Steinmo SH, Michie S, Fuller C, Stanley S, Stapleton C, Stone SP. Bridging the gap between pragmatic intervention design and theory: using behavioural science tools to modify an existing quality improvement programme to implement “Sepsis Six.” Implementation Sci. 2016;11(1):14.
Stout S, Zallman L, Arsenault L, Sayah A, Hacker K. Developing high-functioning teams: Factors associated with operating as a “real team” and implications for patient-centered medical home development. Inquiry. 2017;12(54):0046958017707296.
Svensson B, Hansson L, Markström U, Lexén A. What matters when implementing Flexible Assertive Community Treatment in a Swedish healthcare context: A two-year implementation study. Int J Ment Health. 2017;46(4):284–98.
Tadyanemhandu C, van Aswegen H, Ntsiea V. Barriers and facilitators to implementation of early mobilisation of critically ill patients in Zimbabwean and South African public sector hospitals: a qualitative study. Disabil Rehabil. 2021;44(22):6699–709.
Timmermans O, Van Linge R, Van Petegem P, Van Rompaey B, Denekens J. A contingency perspective on team learning and innovation in nursing: Team learning and innovation in nursing teams. J Adv Nurs. 2013;69(2):363–73.
Tuepker A, Kansagara D, Skaperdas E, Nicolaidis C, Joos S, Alperin M, et al. “We’ve not gotten even close to what we want to do”: A qualitative study of early patient-centered medical home implementation. J GEN INTERN MED. 2014;29(S2):614–22.
van Bruggen S, Kasteleyn MJ, Rauh SP, Meijer JS, Busch KJG, Numans ME, et al. Experiences with tailoring of primary diabetes care in well-organised general practices: a mixed-methods study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):1218.
Van der Wees PJ, Friedberg MW, Guzman EA, Ayanian JZ, Rodriguez HP. Comparing the implementation of team approaches for improving diabetes care in community health centers. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14(1):608.
von Meyenfeldt EM, van Nassau F, de Betue CTI, Barberio L, Schreurs WH, Marres GMH, et al. Implementing an enhanced recovery after thoracic surgery programme in the Netherlands: a qualitative study investigating facilitators and barriers for implementation. BMJ Open. 2022;12(1):e051513.
Wakefield BJ, Lampman MA, Paez MB, Stewart GL. Care management and care coordination within a patient-centered medical home. J Nurs Admin. 2020;50(11):565–70.
Wiener-Ogilvie S, Huby G, Pinnock H, Gillies J, Sheikh A. Practice organisational characteristics can impact on compliance with the BTS/SIGN asthma guideline: Qualitative comparative case study in primary care. BMC Fam Pract. 2008;9(1):32.
Errida A, Lotfi B. The determinants of organizational change management success: Literature review and case study. International Journal of Engineering Business Management. 2021;1(13):18479790211016270.
Phillips J, Klein JD. Change management: From theory to practice. TechTrends. 2023;67(1):189–97.
Rousseau DM, ten Have S. Evidence-based change management. Organ Dyn. 2022;51(3):100899.
Goodwin GF, Blacksmith N, Coats MR. The science of teams in the military: Contributions from over 60 years of research. Am Psychol. 2018;73(4):322–33.
DiazGranados D, Woods JJ, Wilder A, Curtis MT. Team dynamics in the air: A review of team research relevant to aviation. Human factors in aviation and aerospace. 2023. p. 199–215.
Salas E, Tannenbaum SI, Kozlowski SWJ, Miller CA, Mathieu JE, Vessey WB. Teams in space exploration: A new frontier for the science of team effectiveness. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2015;24(3):200–7.
Hackman JR. From causes to conditions in group research. J Organ Behav. 2012;33(3):428–44.
Tannenbaum SI, Salas E. Teams that work: The seven drivers of team effectiveness. Illustrated. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2020. p. 272.
Book Google Scholar
Tuckman BW. Developmental sequence in small groups. Psychol Bull. 1965;63:384–99.
Salas E, Stagl KC, Burke CS. 25 years of team effectiveness in organizations: Research themes and emerging needs. In: International Review of Industrial and Organizational Psychology 2004. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. 2004; p. 47–91. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1002/0470013311.ch2 Cited 2022 May 16
Proctor EK, Silmere H, Raghavan R, Hovmand P, Aarons G, Bunger A, et al. Outcomes for implementation research: Conceptual distinctions, measurement challenges, and research agenda. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2011;38(2):65–76.
Lengnick-Hall R, Williams NJ, Ehrhart MG, Willging CE, Bunger AC, Beidas RS, et al. Eight characteristics of rigorous multilevel implementation research: a step-by-step guide. Implement Sci. 2023;18(1):52.
Wensing M, Sales A, Aarons GA, Xu D (Roman), Wilson P. Evidence for objects of implementation in healthcare: considerations for Implementation Science and Implementation Science Communications. Implementation Sci. 2022;17(1):83.
Damschroder LJ, Reardon CM, Widerquist MAO, Lowery J. The updated Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research based on user feedback. Implement Sci. 2022;17(1):75.
Shortell SM, Marsteller JA, Lin M, Pearson ML, Wu SY, Mendel P, et al. The role of perceived team effectiveness in improving chronic illness care. Med Care. 2004;42(11):1040–8.
Yakovchenko V, Morgan TR, Chinman MJ, Powell BJ, Gonzalez R, Park A, et al. Mapping the road to elimination: a 5-year evaluation of implementation strategies associated with hepatitis C treatment in the veterans health administration. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):1348.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Thank you to Ikzzui Chu, Jamie Feldman, Grace Kinkler, Rachael Park, and Jaely Wright for their assistance with article screening.
This work was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health grants MH123729 (EAM), MH124914 (DJK), and MH126231 (GAA), the National Cancer Institute U01CA275118 (GAA), National Institute on Drug Abuse R01DA049891 (GAA), the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality grant R18HS026862 (CBW), and the Collaboration and Conflict Research Lab at Carnegie Mellon University Tepper School of Business. The content of this manuscript does not represent the views of funding agencies and is solely the responsibility of the authors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, 3811 O’Hara Street, Pittsburgh, PA, 15213, USA
Elizabeth A. McGuier & David J. Kolko
Department of Psychiatry, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA, USA
Gregory A. Aarons
ACTRI Dissemination and Implementation Science Center, UC San Diego, La Jolla, CA, USA
Child and Adolescent Services Research Center, San Diego, CA, USA
Department of Psychiatry, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Allison Schachter & Courtney Benjamin Wolk
Penn Implementation Science Center at the Leonard Davis Institute of Health Economics, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Health Sciences Library System, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
Mary Lou Klem
Tepper School of Business, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
Matthew A. Diabes & Laurie R. Weingart
Department of Psychological Sciences, Rice University, Houston, TX, USA
Eduardo Salas
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
EAM conceptualized and developed the protocol for this review, participated in article screening, data extraction, quality appraisal, and analysis, and led manuscript development and writing. DJK, GAA, LRW, ES, and CBW provided guidance and input into the protocol and methods and interpretation of results. AS participated in article screening, data extraction, and preparation of supplementary files. MLK developed the search strategy and conducted database searches. MAD participated in quality appraisal. DJK, GAA, LRW, ES, and CBW reviewed multiple drafts of the manuscript and provided critical input and editing. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Elizabeth A. McGuier .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
GAA is a Co-Editor-in-Chief of Implementation Science and on the Editorial Board of Implementation Science Communications ; all decisions on this paper were made by another editor. The authors declare that they have no other competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
McGuier, E.A., Kolko, D.J., Aarons, G.A. et al. Teamwork and implementation of innovations in healthcare and human service settings: a systematic review. Implementation Sci 19 , 49 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-024-01381-9
Download citation
Received : 18 January 2024
Accepted : 07 July 2024
Published : 15 July 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-024-01381-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Implementation outcomes
Implementation Science
ISSN: 1748-5908
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Sydney.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- The Ultimate Guide to Market Research
- Quantitative Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Your ultimate guide to quantitative research.
12 min read You may be already using quantitative research and want to check your understanding, or you may be starting from the beginning. Here’s an exploration of this research method and how you can best use it for maximum effect for your business.
You may be already using quantitative research and want to check your understanding, or you may be starting from the beginning. Here’s an exploration of this research method and how you can best use it for maximum effect for your business.
What is quantitative research?
Quantitative is the research method of collecting quantitative data – this is data that can be converted into numbers or numerical data, which can be easily quantified, compared, and analysed.
Quantitative research deals with primary and secondary sources where data is represented in numerical form. This can include closed-question poll results, statistics, and census information or demographic data .
Quantitative data tends to be used when researchers are interested in understanding a particular moment in time and examining data sets over time to find trends and patterns.
To collect numerical data, surveys are often employed as one of the main research methods to source first-hand information in primary research . Qualitative research can also come from third-party research studies .
Quantitative research is widely used in the realms of social sciences, such as biology, chemistry, psychology, economics, sociology, and marketing .
Research teams collect data that is significant to proving or disproving a hypothesis research question – known as the research objective. When they collect quantitative data, researchers will aim to use a sample size that is representative of the total population of the target market they’re interested in.
Then the data collected will be manually or automatically stored and compared for insights.
Free Download: Improve your market research with our Ultimate Guide to Market Research eBook
Qualitative vs quantitative research
While the quantitative research definition focuses on numerical data, qualitative research is defined as data that supplies non-numerical information.
Quantitative research focuses on the thoughts, feelings, and values of a participant , to understand why people act in the way they do . They result in data types like quotes, symbols, images, and written testimonials.
These data types tell researchers subjective information, which can help us assign people into categories, such as a participant’s religion, gender , social class, political alignment, likely favoured products to buy, or their preferred training learning style.
For this reason, qualitative research is often used in social research, as this gives a window into the behaviour and actions of people.
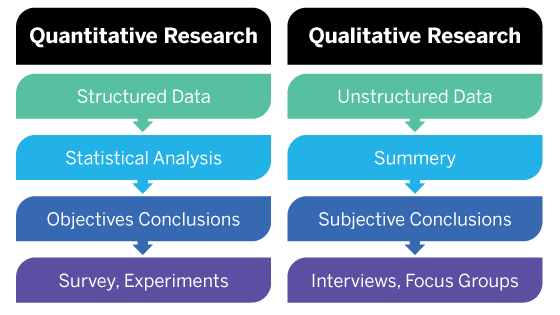
In general, if you’re interested in measuring something or testing a hypothesis, use quantitative methods. If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods.
However, quantitative and qualitative research methods are both recommended when you’re looking to understand a point in time, while also finding out the reason behind the facts.
Quantitative research data collection methods
Quantitative research methods can use structured research instruments like:
- Surveys : A survey is a simple-to-create and easy-to-distribute research method , which helps gather information from large groups of participants quickly. Traditionally, paper-based surveys can now be made online, so costs can stay quite low.
Quantitative questions tend to be closed questions that ask for a numerical result, based on a range of options, or a yes/no answer that can be tallied quickly.
- Face-to-face or phone interviews: Interviews are a great way to connect with participants , though they require time from the research team to set up and conduct.
Researchers may also have issues connecting with participants in different geographical regions . The researcher uses a set of predefined close-ended questions, which ask for yes/no or numerical values.
- Polls: Polls can be a shorter version of surveys , used to get a ‘flavour’ of what the current situation is with participants. Online polls can be shared easily, though polls are best used with simple questions that request a range or a yes/no answer.
Quantitative data is the opposite of qualitative research, another dominant framework for research in the social sciences, explored further below.
Quantitative data types
Quantitative research methods often deliver the following data types:
- Test Scores
- Percent of training course completed
- Performance score out of 100
- Number of support calls active
- Customer Net Promoter Score (NPS)
When gathering numerical data, the emphasis is on how specific the data is, and whether they can provide an indication of what ‘is’ at the time of collection. Pre-existing statistical data can tell us what ‘was’ for the date and time range that it represented
Quantitative research design methods (with examples)
Quantitative research has a number of quantitative research designs you can choose from:
Descriptive
This design type describes the state of a data type is telling researchers, in its native environment. There won’t normally be a clearly defined research question to start with. Instead, data analysis will suggest a conclusion , which can become the hypothesis to investigate further.
Examples of descriptive quantitative design include:
- A description of child’s Christmas gifts they received that year
- A description of what businesses sell the most of during Black Friday
- A description of a product issue being experienced by a customer
Correlational
This design type looks at two or more data types, the relationship between them, and the extent that they differ or align. This does not look at the causal links deeper – instead statistical analysis methods looks at the variables in a natural environment.
Examples of correlational quantitative design include:
- The relationship between a child’s Christmas gifts and their perceived happiness level
- The relationship between a business’ sales during Black Friday and the total revenue generated over the year
- The relationship between a customer’s product issue and the reputation of the product
Causal-Comparative/Quasi-Experimental
This design type looks at two or more data types and tries to explain any relationship and differences between them, using a cause-effect analysis. The research is carried out in a near-natural environment, where information is gathered from two groups – a naturally occurring group that matches the original natural environment, and one that is not naturally present.
This allows for causal links to be made, though they might not be correct, as other variables may have an impact on results.
Examples of causal-comparative/quasi-experimental quantitative design include:
- The effect of children’s Christmas gifts on happiness
- The effect of Black Friday sales figures on the productivity of company yearly sales
- The effect of product issues on the public perception of a product
Experimental Research
This design type looks to make a controlled environment in which two or more variables are observed to understand the exact cause and effect they have. This becomes a quantitative research study, where data types are manipulated to assess the effect they have. The participants are not naturally occurring groups, as the setting is no longer natural. A quantitative research study can help pinpoint the exact conditions in which variables impact one another.
Examples of experimental quantitative design include:
- The effect of children’s Christmas gifts on a child’s dopamine (happiness) levels
- The effect of Black Friday sales on the success of the company
- The effect of product issues on the perceived reliability of the product
Quantitative research methods need to be carefully considered, as your data collection of a data type can be used to different effects. For example, statistics can be descriptive or correlational (or inferential). Descriptive statistics help us to summarise our data, while inferential statistics help infer conclusions about significant differences.
Advantages of quantitative research
- Easy to do : Doing quantitative research is more straightforward, as the results come in numerical format, which can be more easily interpreted.
- Less interpretation : Due to the factual nature of the results, you will be able to accept or reject your hypothesis based on the numerical data collected.
- Less bias : There are higher levels of control that can be applied to the research, so bias can be reduced , making your data more reliable and precise.
Disadvantages of quantitative research
- Can’t understand reasons: Quantitative research doesn’t always tell you the full story, meaning you won’t understand the context – or the why, of the data you see, why do you see the results you have uncovered?
- Useful for simpler situations: Quantitative research on its own is not great when dealing with complex issues. In these cases, quantitative research may not be enough.
How to use quantitative research to your business’s advantage
Quantitative research methods may help in areas such as:
- Identifying which advert or landing page performs better
- Identifying how satisfied your customers are
- How many customers are likely to recommend you
- Tracking how your brand ranks in awareness and customer purchase intent
- Learn what consumers are likely to buy from your brand.
6 steps to conducting good quantitative research
Businesses can benefit from quantitative research by using it to evaluate the impact of data types. There are several steps to this:
- Define your problem or interest area : What do you observe is happening and is it frequent? Identify the data type/s you’re observing.
- Create a hypothesis : Ask yourself what could be the causes for the situation with those data types.
- Plan your quantitative research : Use structured research instruments like surveys or polls to ask questions that test your hypothesis.
- Data Collection : Collect quantitative data and understand what your data types are telling you. Using data collected on different types over long time periods can give you information on patterns.
- Data analysis : Does your information support your hypothesis? (You may need to redo the research with other variables to see if the results improve)
- Effectively present data : Communicate the results in a clear and concise way to help other people understand the findings.
How Qualtrics products can enhance & simplify the quantitative research process
The Qualtrics XM system gives you an all-in-one, integrated solution to help you all the way through conducting quantitative research. From survey creation and data collection to statistical analysis methods and data reporting, it can help all your internal teams gain insights from your numerical data.
Quantitative methods are catered to your business through templates or advanced survey designs. While you can manually collect data and conduct data analysis in a spreadsheet program, this solution helps you automate the process of quantitative research, saving you time and administration work.
Using computational techniques helps you to avoid human errors, and participant results come in are already incorporated into the analysis in real-time.
Our key tools, Stats IQ™ and Driver IQ™ make analysing numerical data easy and simple. Choose to highlight key findings based on variables or highlight statistically insignificant findings. The choice is yours.
Some examples of your workspace in action, using drag and drop to create fast data visualisations quickly:
Find out how Qualtrics XM solution can help improve research team’s quantitative methods
Related resources
Market intelligence tools 10 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, business research methods 12 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, business research 10 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This chapter uses an emphasis on research design to discuss qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research as three major approaches to research in the social sciences. The first major section considers the role ... Qualitative and Quantitative Research through side-by-side comparisons of a number of key features in these two approaches ...
Quantitative research is an inquiry into an identified problem, based on testing a theory, measured with numbers, and analyzed using statistical techniques. The goal of quantitative methods is to determine whether the predictive generalizations of a theory hold true. By contrast, a study based upon a qualitative process of inquiry has the goal ...
Quantitative and qualitative methods are the engine behind evidence-based outcomes. For decades, one of the popular phenomena that troubled young researchers is that which appropriate research ...
observation that "good qualitative research has equaled, if not exceeded, quantitative research in status, relevance, and methodological rigor" (p. 574). Several principles guide the thinking and ... Qualitative research methods are not "routinized", meaning there are many different ways to think about qualitative research and
ArticlePDF Available. Strengths and Limitations of Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methods. September 2017. September 2017. 3 (9):369-387. DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.887089. Authors: Fernando ...
Quantitative and qualitative research design represent the two sides of a coin in research project and Hammed (2020) citing Guba (1982) illustrated the axiomatic differences between the two ...
Chapter 2. tive and Qualitative Research: An Overview of ApproachesEuclid SeeramIn Chap. 1, the nature and scope of research were outlined and included an overview of quantit. tive and qualitative research and a brief description of research designs. In this chapter, both quantitative and qualitative research will be described in a.
1 Introduction: qualitative and quantitative methods, presentations, and practices Teaching in research methods courses for undergraduates, postgraduates and newer researchers is commonly supported or guided through textbooks with explanations of 'qualitative' and 'quantitative' methods and cases of how these methods are employed.
Qualitative Research seeks to understand human experiences, perception, social processes and subcultures. These research methods are not reducible to numbers and categories. The data that is collected in qualitative research can be taken from observations in the field, recording and transcripts, dairies, or other documents.
Lacking in both approaches, however, is a clear empirical answer as to whether the variables in our statistical and theoretical arguments are actually "doing the work" in raising a country's susceptibility to a civil war onset. This is where case narratives can play an especially valuable role. 2. Choosing Narratives.
data collection, analysis, and interpretation. The selection of a research approach includes the research problem or issue being addressed, the researchers' persona. experiences, and the audiences for the study. Thus, in this book, philosophical assumptions, research approaches, research designs, and research methods are four key terms ...
Qualitative research is a type of scientific research. In general terms, scientific research consists of an investigation that: • seeks answers to a question. • systematically uses a predefined set of procedures to answer the question. • collects evidence. • produces findings that were not determined in advance.
DATA COLLECTION METHODS: SOME TIPS AND COMPARISONS. In the previous chapter, we identified two broad types of evaluation methodologies: quantitative and qualitative. In this section, we talk more about the debate over the relative virtues of these approaches and discuss some of the advantages and disadvantages of different types of instruments.
This paper will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative and quantitative research approaches and methods, evaluating their usefulness as well as any ethical considerations in relation to problem-solving instruction in science education curriculum with indication of the dominant approaches in the area.
To interpret means to assign significance or coher-ent meaning. In quantitative research, meaning comes from using numbers (e.g.,percentages or sta-tistical coefficients),and we explain how the numer-ical data relate to the hypotheses. Qualitative studies rarely include tables with numbers.
Chapter 3 of the dissertation provides the reader with a detailed description of the components of the method that will be used in the research. This chapter helps the reader to judge if the method used in the research provided an adequate opportunity to examine the research questions and hypotheses.
Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes.2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed ...
Mixed-methods research is a flexible approach, where the research design is determined by what we want to find out rather than by any predetermined epistemological position. In mixed-methods research, qualitative or quantitative components can predominate, or both can have equal status. 1.4. Units and variables.
Quantitative research. Quantitative research is 'explaining phenom enon by collection numerical data that are. analyzed using mathematically based methods (in particular statistics)' (Aliaga and ...
ssessing quality in the QRC. The Postscript describes the core attributes of quality in our qual-itative research approach: the importance of coherence, the iterative processes of inductive and deductiv. reasoning, and reflexivity. The Postscript complements the quality assessment criteria which we includ.
We will discuss the differences between quantitative (numerical and statistics-focused) and qualitative (non-numerical and human-focused) research design methods so that you can determine which approach is most strategic given your specific area of graduate-level study.. Understanding Social Phenomena: Qualitative Research Design. Qualitative research focuses on understanding a phenomenon ...
This video reviews common student research problems, how to identify gaps in your research, figuring out what methods you favor, and challenging research problems. (9:32). An Introduction to Reasoning in Qualitative & Quantitative Research
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge. Quantitative research. Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions.
Quantitative research seeks explanatory laws; qualitative research aims 1 fat in-depth description. Qualitative research measures what it assumes to be a static reality in hopes of developing universal laws. Qualitative research is an exploration of what is assumed to be a dynamic reality.
Research can be done using either qualitative or quantitative data. The decision of which data to use depends on the purpose of the research. Qualitative Research: Explores an unfamiliar topic, concept, or idea.The data for this research is hard to measure, provided by open ended questionnaires for example.
Since then, researchers have started to question the fundamental nature of quantitative research, as it couldn't address the questions of meanings and understandings. Qualitative research was, therefore, considered as an alternative method offering richer interpretations and understanding of lived realities.
We selected studies using quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods to examine associations between team constructs and implementation outcomes in healthcare and human service settings. We used the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool to assess methodological quality/risk of bias and conducted a narrative synthesis of included studies.
Additionally, the work developed intends to be a fundamental reference for the accomplishment of a research study, in which the researcher intends to adopt a qualitative or quantitative methodology.
The iterative design cycle: Steps 1 and 3 involve summative research (done with either quantitative or qualitative methods), while step 2 involves formative research (done with qualitative methods). The first and third stages of the iterative design cycle are summative — they are intended to provide an overall assessment of a design.
Qualitative vs quantitative research. While the quantitative research definition focuses on numerical data, qualitative research is defined as data that supplies non-numerical information. Quantitative research focuses on the thoughts, feelings, and values of a participant, to understand why people act in the way they do. They result in data ...