Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Conclusion for Research Papers (with Examples)

The conclusion of a research paper is a crucial section that plays a significant role in the overall impact and effectiveness of your research paper. However, this is also the section that typically receives less attention compared to the introduction and the body of the paper. The conclusion serves to provide a concise summary of the key findings, their significance, their implications, and a sense of closure to the study. Discussing how can the findings be applied in real-world scenarios or inform policy, practice, or decision-making is especially valuable to practitioners and policymakers. The research paper conclusion also provides researchers with clear insights and valuable information for their own work, which they can then build on and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
The research paper conclusion should explain the significance of your findings within the broader context of your field. It restates how your results contribute to the existing body of knowledge and whether they confirm or challenge existing theories or hypotheses. Also, by identifying unanswered questions or areas requiring further investigation, your awareness of the broader research landscape can be demonstrated.
Remember to tailor the research paper conclusion to the specific needs and interests of your intended audience, which may include researchers, practitioners, policymakers, or a combination of these.
Table of Contents
What is a conclusion in a research paper, summarizing conclusion, editorial conclusion, externalizing conclusion, importance of a good research paper conclusion, how to write a conclusion for your research paper, research paper conclusion examples.
- How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
A conclusion in a research paper is the final section where you summarize and wrap up your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. The research paper conclusion is not the place to introduce new information or data that was not discussed in the main body of the paper. When working on how to conclude a research paper, remember to stick to summarizing and interpreting existing content. The research paper conclusion serves the following purposes: 1
- Warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend specific course(s) of action.
- Restate key ideas to drive home the ultimate point of your research paper.
- Provide a “take-home” message that you want the readers to remember about your study.

Types of conclusions for research papers
In research papers, the conclusion provides closure to the reader. The type of research paper conclusion you choose depends on the nature of your study, your goals, and your target audience. I provide you with three common types of conclusions:
A summarizing conclusion is the most common type of conclusion in research papers. It involves summarizing the main points, reiterating the research question, and restating the significance of the findings. This common type of research paper conclusion is used across different disciplines.
An editorial conclusion is less common but can be used in research papers that are focused on proposing or advocating for a particular viewpoint or policy. It involves presenting a strong editorial or opinion based on the research findings and offering recommendations or calls to action.
An externalizing conclusion is a type of conclusion that extends the research beyond the scope of the paper by suggesting potential future research directions or discussing the broader implications of the findings. This type of conclusion is often used in more theoretical or exploratory research papers.
Align your conclusion’s tone with the rest of your research paper. Start Writing with Paperpal Now!
The conclusion in a research paper serves several important purposes:
- Offers Implications and Recommendations : Your research paper conclusion is an excellent place to discuss the broader implications of your research and suggest potential areas for further study. It’s also an opportunity to offer practical recommendations based on your findings.
- Provides Closure : A good research paper conclusion provides a sense of closure to your paper. It should leave the reader with a feeling that they have reached the end of a well-structured and thought-provoking research project.
- Leaves a Lasting Impression : Writing a well-crafted research paper conclusion leaves a lasting impression on your readers. It’s your final opportunity to leave them with a new idea, a call to action, or a memorable quote.

Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is essential to leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you create and know what to put in the conclusion of a research paper: 2
- Research Statement : Begin your research paper conclusion by restating your research statement. This reminds the reader of the main point you’ve been trying to prove throughout your paper. Keep it concise and clear.
- Key Points : Summarize the main arguments and key points you’ve made in your paper. Avoid introducing new information in the research paper conclusion. Instead, provide a concise overview of what you’ve discussed in the body of your paper.
- Address the Research Questions : If your research paper is based on specific research questions or hypotheses, briefly address whether you’ve answered them or achieved your research goals. Discuss the significance of your findings in this context.
- Significance : Highlight the importance of your research and its relevance in the broader context. Explain why your findings matter and how they contribute to the existing knowledge in your field.
- Implications : Explore the practical or theoretical implications of your research. How might your findings impact future research, policy, or real-world applications? Consider the “so what?” question.
- Future Research : Offer suggestions for future research in your area. What questions or aspects remain unanswered or warrant further investigation? This shows that your work opens the door for future exploration.
- Closing Thought : Conclude your research paper conclusion with a thought-provoking or memorable statement. This can leave a lasting impression on your readers and wrap up your paper effectively. Avoid introducing new information or arguments here.
- Proofread and Revise : Carefully proofread your conclusion for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Ensure that your ideas flow smoothly and that your conclusion is coherent and well-structured.
Write your research paper conclusion 2x faster with Paperpal. Try it now!
Remember that a well-crafted research paper conclusion is a reflection of the strength of your research and your ability to communicate its significance effectively. It should leave a lasting impression on your readers and tie together all the threads of your paper. Now you know how to start the conclusion of a research paper and what elements to include to make it impactful, let’s look at a research paper conclusion sample.

How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
A research paper conclusion is not just a summary of your study, but a synthesis of the key findings that ties the research together and places it in a broader context. A research paper conclusion should be concise, typically around one paragraph in length. However, some complex topics may require a longer conclusion to ensure the reader is left with a clear understanding of the study’s significance. Paperpal, an AI writing assistant trusted by over 800,000 academics globally, can help you write a well-structured conclusion for your research paper.
- Sign Up or Log In: Create a new Paperpal account or login with your details.
- Navigate to Features : Once logged in, head over to the features’ side navigation pane. Click on Templates and you’ll find a suite of generative AI features to help you write better, faster.
- Generate an outline: Under Templates, select ‘Outlines’. Choose ‘Research article’ as your document type.
- Select your section: Since you’re focusing on the conclusion, select this section when prompted.
- Choose your field of study: Identifying your field of study allows Paperpal to provide more targeted suggestions, ensuring the relevance of your conclusion to your specific area of research.
- Provide a brief description of your study: Enter details about your research topic and findings. This information helps Paperpal generate a tailored outline that aligns with your paper’s content.
- Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on ‘generate’. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline.
- Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion. The outline serves as a guide, ensuring you cover all critical aspects of a strong conclusion, from summarizing key findings to highlighting the research’s implications.
- Refine and enhance: Paperpal’s ‘Make Academic’ feature can be particularly useful in the final stages. Select any paragraph of your conclusion and use this feature to elevate the academic tone, ensuring your writing is aligned to the academic journal standards.
By following these steps, Paperpal not only simplifies the process of writing a research paper conclusion but also ensures it is impactful, concise, and aligned with academic standards. Sign up with Paperpal today and write your research paper conclusion 2x faster .
The research paper conclusion is a crucial part of your paper as it provides the final opportunity to leave a strong impression on your readers. In the research paper conclusion, summarize the main points of your research paper by restating your research statement, highlighting the most important findings, addressing the research questions or objectives, explaining the broader context of the study, discussing the significance of your findings, providing recommendations if applicable, and emphasizing the takeaway message. The main purpose of the conclusion is to remind the reader of the main point or argument of your paper and to provide a clear and concise summary of the key findings and their implications. All these elements should feature on your list of what to put in the conclusion of a research paper to create a strong final statement for your work.
A strong conclusion is a critical component of a research paper, as it provides an opportunity to wrap up your arguments, reiterate your main points, and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here are the key elements of a strong research paper conclusion: 1. Conciseness : A research paper conclusion should be concise and to the point. It should not introduce new information or ideas that were not discussed in the body of the paper. 2. Summarization : The research paper conclusion should be comprehensive enough to give the reader a clear understanding of the research’s main contributions. 3 . Relevance : Ensure that the information included in the research paper conclusion is directly relevant to the research paper’s main topic and objectives; avoid unnecessary details. 4 . Connection to the Introduction : A well-structured research paper conclusion often revisits the key points made in the introduction and shows how the research has addressed the initial questions or objectives. 5. Emphasis : Highlight the significance and implications of your research. Why is your study important? What are the broader implications or applications of your findings? 6 . Call to Action : Include a call to action or a recommendation for future research or action based on your findings.
The length of a research paper conclusion can vary depending on several factors, including the overall length of the paper, the complexity of the research, and the specific journal requirements. While there is no strict rule for the length of a conclusion, but it’s generally advisable to keep it relatively short. A typical research paper conclusion might be around 5-10% of the paper’s total length. For example, if your paper is 10 pages long, the conclusion might be roughly half a page to one page in length.
In general, you do not need to include citations in the research paper conclusion. Citations are typically reserved for the body of the paper to support your arguments and provide evidence for your claims. However, there may be some exceptions to this rule: 1. If you are drawing a direct quote or paraphrasing a specific source in your research paper conclusion, you should include a citation to give proper credit to the original author. 2. If your conclusion refers to or discusses specific research, data, or sources that are crucial to the overall argument, citations can be included to reinforce your conclusion’s validity.
The conclusion of a research paper serves several important purposes: 1. Summarize the Key Points 2. Reinforce the Main Argument 3. Provide Closure 4. Offer Insights or Implications 5. Engage the Reader. 6. Reflect on Limitations
Remember that the primary purpose of the research paper conclusion is to leave a lasting impression on the reader, reinforcing the key points and providing closure to your research. It’s often the last part of the paper that the reader will see, so it should be strong and well-crafted.
- Makar, G., Foltz, C., Lendner, M., & Vaccaro, A. R. (2018). How to write effective discussion and conclusion sections. Clinical spine surgery, 31(8), 345-346.
- Bunton, D. (2005). The structure of PhD conclusion chapters. Journal of English for academic purposes , 4 (3), 207-224.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Paraphrasing in Academic Writing: Answering Top Author Queries
Preflight For Editorial Desk: The Perfect Hybrid (AI + Human) Assistance Against Compromised Manuscripts
You may also like, measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., 9 steps to publish a research paper, what are the different types of research papers.
The past, present, and future of consumer research
- Published: 13 June 2020
- Volume 31 , pages 137–149, ( 2020 )
Cite this article

- Maayan S. Malter ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0383-7925 1 ,
- Morris B. Holbrook 1 ,
- Barbara E. Kahn 2 ,
- Jeffrey R. Parker 3 &
- Donald R. Lehmann 1
45k Accesses
36 Citations
3 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
In this article, we document the evolution of research trends (concepts, methods, and aims) within the field of consumer behavior, from the time of its early development to the present day, as a multidisciplinary area of research within marketing. We describe current changes in retailing and real-world consumption and offer suggestions on how to use observations of consumption phenomena to generate new and interesting consumer behavior research questions. Consumption continues to change with technological advancements and shifts in consumers’ values and goals. We cannot know the exact shape of things to come, but we polled a sample of leading scholars and summarize their predictions on where the field may be headed in the next twenty years.
Similar content being viewed by others

Consumer Behavior Research Methods

Consumer dynamics: theories, methods, and emerging directions
Understanding effect sizes in consumer psychology
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Beginning in the late 1950s, business schools shifted from descriptive and practitioner-focused studies to more theoretically driven and academically rigorous research (Dahl et al. 1959 ). As the field expanded from an applied form of economics to embrace theories and methodologies from psychology, sociology, anthropology, and statistics, there was an increased emphasis on understanding the thoughts, desires, and experiences of individual consumers. For academic marketing, this meant that research not only focused on the decisions and strategies of marketing managers but also on the decisions and thought processes on the other side of the market—customers.
Since then, the academic study of consumer behavior has evolved and incorporated concepts and methods, not only from marketing at large but also from related social science disciplines, and from the ever-changing landscape of real-world consumption behavior. Its position as an area of study within a larger discipline that comprises researchers from diverse theoretical backgrounds and methodological training has stirred debates over its identity. One article describes consumer behavior as a multidisciplinary subdiscipline of marketing “characterized by the study of people operating in a consumer role involving acquisition, consumption, and disposition of marketplace products, services, and experiences” (MacInnis and Folkes 2009 , p. 900).
This article reviews the evolution of the field of consumer behavior over the past half century, describes its current status, and predicts how it may evolve over the next twenty years. Our review is by no means a comprehensive history of the field (see Schumann et al. 2008 ; Rapp and Hill 2015 ; Wang et al. 2015 ; Wilkie and Moore 2003 , to name a few) but rather focuses on a few key thematic developments. Though we observe many major shifts during this period, certain questions and debates have persisted: Does consumer behavior research need to be relevant to marketing managers or is there intrinsic value from studying the consumer as a project pursued for its own sake? What counts as consumption: only consumption from traditional marketplace transactions or also consumption in a broader sense of non-marketplace interactions? Which are the most appropriate theoretical traditions and methodological tools for addressing questions in consumer behavior research?
2 A brief history of consumer research over the past sixty years—1960 to 2020
In 1969, the Association for Consumer Research was founded and a yearly conference to share marketing research specifically from the consumer’s perspective was instituted. This event marked the culmination of the growing interest in the topic by formalizing it as an area of research within marketing (consumer psychology had become a formalized branch of psychology within the APA in 1960). So, what was consumer behavior before 1969? Scanning current consumer-behavior doctoral seminar syllabi reveals few works predating 1969, with most of those coming from psychology and economics, namely Herbert Simon’s A Behavioral Model of Rational Choice (1955), Abraham Maslow’s A Theory of Human Motivation (1943), and Ernest Dichter’s Handbook of Consumer Motivations (1964). In short, research that illuminated and informed our understanding of consumer behavior prior to 1969 rarely focused on marketing-specific topics, much less consumers or consumption (Dichter’s handbook being a notable exception). Yet, these works were crucial to the rise of consumer behavior research because, in the decades after 1969, there was a shift within academic marketing to thinking about research from a behavioral or decision science perspective (Wilkie and Moore 2003 ). The following section details some ways in which this shift occurred. We draw on a framework proposed by the philosopher Larry Laudan ( 1986 ), who distinguished among three inter-related aspects of scientific inquiry—namely, concepts (the relevant ideas, theories, hypotheses, and constructs); methods (the techniques employed to test and validate these concepts); and aims (the purposes or goals that motivate the investigation).
2.1 Key concepts in the late - 1960s
During the late-1960s, we tended to view the buyer as a computer-like machine for processing information according to various formal rules that embody economic rationality to form a preference for one or another option in order to arrive at a purchase decision. This view tended to manifest itself in a couple of conspicuous ways. The first was a model of buyer behavior introduced by John Howard in 1963 in the second edition of his marketing textbook and quickly adopted by virtually every theorist working in our field—including, Howard and Sheth (of course), Engel-Kollat-&-Blackwell, Franco Nicosia, Alan Andreasen, Jim Bettman, and Joel Cohen. Howard’s great innovation—which he based on a scheme that he had found in the work of Plato (namely, the linkages among Cognition, Affect, and Conation)—took the form of a boxes-and-arrows formulation heavily influenced by the approach to organizational behavior theory that Howard (University of Pittsburgh) had picked up from Herbert Simon (Carnegie Melon University). The model represented a chain of events
where I = inputs of information (from advertising, word-of-mouth, brand features, etc.); C = cognitions (beliefs or perceptions about a brand); A = Affect (liking or preference for the brand); B = behavior (purchase of the brand); and S = satisfaction (post-purchase evaluation of the brand that feeds back onto earlier stages of the sequence, according to a learning model in which reinforced behavior tends to be repeated). This formulation lay at the heart of Howard’s work, which he updated, elaborated on, and streamlined over the remainder of his career. Importantly, it informed virtually every buyer-behavior model that blossomed forth during the last half of the twentieth century.
To represent the link between cognitions and affect, buyer-behavior researchers used various forms of the multi-attribute attitude model (MAAM), originally proposed by psychologists such as Fishbein and Rosenberg as part of what Fishbein and Ajzen ( 1975 ) called the theory of reasoned action. Under MAAM, cognitions (beliefs about brand attributes) are weighted by their importance and summed to create an explanation or prediction of affect (liking for a brand or preference for one brand versus another), which in turn determines behavior (choice of a brand or intention to purchase a brand). This took the work of economist Kelvin Lancaster (with whom Howard interacted), which assumed attitude was based on objective attributes, and extended it to include subjective ones (Lancaster 1966 ; Ratchford 1975 ). Overall, the set of concepts that prevailed in the late-1960s assumed the buyer exhibited economic rationality and acted as a computer-like information-processing machine when making purchase decisions.
2.2 Favored methods in the late-1960s
The methods favored during the late-1960s tended to be almost exclusively neo-positivistic in nature. That is, buyer-behavior research adopted the kinds of methodological rigor that we associate with the physical sciences and the hypothetico-deductive approaches advocated by the neo-positivistic philosophers of science.
Thus, the accepted approaches tended to be either experimental or survey based. For example, numerous laboratory studies tested variations of the MAAM and focused on questions about how to measure beliefs, how to weight the beliefs, how to combine the weighted beliefs, and so forth (e.g., Beckwith and Lehmann 1973 ). Here again, these assumed a rational economic decision-maker who processed information something like a computer.
Seeking rigor, buyer-behavior studies tended to be quantitative in their analyses, employing multivariate statistics, structural equation models, multidimensional scaling, conjoint analysis, and other mathematically sophisticated techniques. For example, various attempts to test the ICABS formulation developed simultaneous (now called structural) equation models such as those deployed by Farley and Ring ( 1970 , 1974 ) to test the Howard and Sheth ( 1969 ) model and by Beckwith and Lehmann ( 1973 ) to measure halo effects.
2.3 Aims in the late-1960s
During this time period, buyer-behavior research was still considered a subdivision of marketing research, the purpose of which was to provide insights useful to marketing managers in making strategic decisions. Essentially, every paper concluded with a section on “Implications for Marketing Managers.” Authors who failed to conform to this expectation could generally count on having their work rejected by leading journals such as the Journal of Marketing Research ( JMR ) and the Journal of Marketing ( JM ).
2.4 Summary—the three R’s in the late-1960s
Starting in the late-1960s to the early-1980s, virtually every buyer-behavior researcher followed the traditional approach to concepts, methods, and aims, now encapsulated under what we might call the three R’s —namely, rationality , rigor , and relevance . However, as we transitioned into the 1980s and beyond, that changed as some (though by no means all) consumer researchers began to expand their approaches and to evolve different perspectives.
2.5 Concepts after 1980
In some circles, the traditional emphasis on the buyer’s rationality—that is, a view of the buyer as a rational-economic, decision-oriented, information-processing, computer-like machine for making choices—began to evolve in at least two primary ways.
First, behavioral economics (originally studied in marketing under the label Behavioral Decision Theory)—developed in psychology by Kahneman and Tversky, in economics by Thaler, and applied in marketing by a number of forward-thinking theorists (e.g., Eric Johnson, Jim Bettman, John Payne, Itamar Simonson, Jay Russo, Joel Huber, and more recently, Dan Ariely)—challenged the rationality of consumers as decision-makers. It was shown that numerous commonly used decision heuristics depart from rational choice and are exceptions to the traditional assumptions of economic rationality. This trend shed light on understanding consumer financial decision-making (Prelec and Loewenstein 1998 ; Gourville 1998 ; Lynch Jr 2011 ) and how to develop “nudges” to help consumers make better decisions for their personal finances (summarized in Johnson et al. 2012 ).
Second, the emerging experiential view (anticipated by Alderson, Levy, and others; developed by Holbrook and Hirschman, and embellished by Schmitt, Pine, and Gilmore, and countless followers) regarded consumers as flesh-and-blood human beings (rather than as information-processing computer-like machines), focused on hedonic aspects of consumption, and expanded the concepts embodied by ICABS (Table 1 ).
2.6 Methods after 1980
The two burgeoning areas of research—behavioral economics and experiential theories—differed in their methodological approaches. The former relied on controlled randomized experiments with a focus on decision strategies and behavioral outcomes. For example, experiments tested the process by which consumers evaluate options using information display boards and “Mouselab” matrices of aspects and attributes (Payne et al. 1988 ). This school of thought also focused on behavioral dependent measures, such as choice (Huber et al. 1982 ; Simonson 1989 ; Iyengar and Lepper 2000 ).
The latter was influenced by post-positivistic philosophers of science—such as Thomas Kuhn, Paul Feyerabend, and Richard Rorty—and approaches expanded to include various qualitative techniques (interpretive, ethnographic, humanistic, and even introspective methods) not previously prominent in the field of consumer research. These included:
Interpretive approaches —such as those drawing on semiotics and hermeneutics—in an effort to gain a richer understanding of the symbolic meanings involved in consumption experiences;
Ethnographic approaches — borrowed from cultural anthropology—such as those illustrated by the influential Consumer Behavior Odyssey (Belk et al. 1989 ) and its discoveries about phenomena related to sacred aspects of consumption or the deep meanings of collections and other possessions;
Humanistic approaches —such as those borrowed from cultural studies or from literary criticism and more recently gathered together under the general heading of consumer culture theory ( CCT );
Introspective or autoethnographic approaches —such as those associated with a method called subjective personal introspection ( SPI ) that various consumer researchers like Sidney Levy and Steve Gould have pursued to gain insights based on their own private lives.
These qualitative approaches tended not to appear in the more traditional journals such as the Journal of Marketing , Journal of Marketing Research , or Marketing Science . However, newer journals such as Consumption, Markets, & Culture and Marketing Theory began to publish papers that drew on the various interpretive, ethnographic, humanistic, or introspective methods.
2.7 Aims after 1980
In 1974, consumer research finally got its own journal with the launch of the Journal of Consumer Research ( JCR ). The early editors of JCR —especially Bob Ferber, Hal Kassarjian, and Jim Bettman—held a rather divergent attitude about the importance or even the desirability of managerial relevance as a key goal of consumer studies. Under their influence, some researchers began to believe that consumer behavior is a phenomenon worthy of study in its own right—purely for the purpose of understanding it better. The journal incorporated articles from an array of methodologies: quantitative (both secondary data analysis and experimental techniques) and qualitative. The “right” balance between theoretical insight and substantive relevance—which are not in inherent conflict—is a matter of debate to this day and will likely continue to be debated well into the future.
2.8 Summary—the three I’s after 1980
In sum, beginning in the early-1980s, consumer research branched out. Much of the work in consumer studies remained within the earlier tradition of the three R’s—that is, rationality (an information-processing decision-oriented buyer), rigor (neo-positivistic experimental designs and quantitative techniques), and relevance (usefulness to marketing managers). Nonetheless, many studies embraced enlarged views of the three major aspects that might be called the three I’s —that is, irrationality (broadened perspectives that incorporate illogical, heuristic, experiential, or hedonic aspects of consumption), interpretation (various qualitative or “postmodern” approaches), and intrinsic motivation (the joy of pursuing a managerially irrelevant consumer study purely for the sake of satisfying one’s own curiosity, without concern for whether it does or does not help a marketing practitioner make a bigger profit).
3 The present—the consumer behavior field today
3.1 present concepts.
In recent years, technological changes have significantly influenced the nature of consumption as the customer journey has transitioned to include more interaction on digital platforms that complements interaction in physical stores. This shift poses a major conceptual challenge in understanding if and how these technological changes affect consumption. Does the medium through which consumption occurs fundamentally alter the psychological and social processes identified in earlier research? In addition, this shift allows us to collect more data at different stages of the customer journey, which further allows us to analyze behavior in ways that were not previously available.
Revisiting the ICABS framework, many of the previous concepts are still present, but we are now addressing them through a lens of technological change (Table 2 )
. In recent years, a number of concepts (e.g., identity, beliefs/lay theories, affect as information, self-control, time, psychological ownership, search for meaning and happiness, social belonging, creativity, and status) have emerged as integral factors that influence and are influenced by consumption. To better understand these concepts, a number of influential theories from social psychology have been adopted into consumer behavior research. Self-construal (Markus and Kitayama 1991 ), regulatory focus (Higgins 1998 ), construal level (Trope and Liberman 2010 ), and goal systems (Kruglanski et al. 2002 ) all provide social-cognition frameworks through which consumer behavior researchers study the psychological processes behind consumer behavior. This “adoption” of social psychological theories into consumer behavior is a symbiotic relationship that further enhances the theories. Tory Higgins happily stated that he learned more about his own theories from the work of marketing academics (he cited Angela Lee and Michel Pham) in further testing and extending them.
3.2 Present Methods
Not only have technological advancements changed the nature of consumption but they have also significantly influenced the methods used in consumer research by adding both new sources of data and improved analytical tools (Ding et al. 2020 ). Researchers continue to use traditional methods from psychology in empirical research (scale development, laboratory experiments, quantitative analyses, etc.) and interpretive approaches in qualitative research. Additionally, online experiments using participants from panels such as Amazon Mechanical Turk and Prolific have become commonplace in the last decade. While they raise concerns about the quality of the data and about the external validity of the results, these online experiments have greatly increased the speed and decreased the cost of collecting data, so researchers continue to use them, albeit with some caution. Reminiscent of the discussion in the 1970s and 1980s about the use of student subjects, the projectability of the online responses and of an increasingly conditioned “professional” group of online respondents (MTurkers) is a major concern.
Technology has also changed research methodology. Currently, there is a large increase in the use of secondary data thanks to the availability of Big Data about online and offline behavior. Methods in computer science have advanced our ability to analyze large corpuses of unstructured data (text, voice, visual images) in an efficient and rigorous way and, thus, to tap into a wealth of nuanced thoughts, feelings, and behaviors heretofore only accessible to qualitative researchers through laboriously conducted content analyses. There are also new neuro-marketing techniques like eye-tracking, fMRI’s, body arousal measures (e.g., heart rate, sweat), and emotion detectors that allow us to measure automatic responses. Lastly, there has been an increase in large-scale field experiments that can be run in online B2C marketplaces.
3.3 Present Aims
Along with a focus on real-world observations and data, there is a renewed emphasis on managerial relevance. Countless conference addresses and editorials in JCR , JCP , and other journals have emphasized the importance of making consumer research useful outside of academia—that is, to help companies, policy makers, and consumers. For instance, understanding how the “new” consumer interacts over time with other consumers and companies in the current marketplace is a key area for future research. As global and social concerns become more salient in all aspects of life, issues of long-term sustainability, social equality, and ethical business practices have also become more central research topics. Fortunately, despite this emphasis on relevance, theoretical contributions and novel ideas are still highly valued. An appropriate balance of theory and practice has become the holy grail of consumer research.
The effects of the current trends in real-world consumption will increase in magnitude with time as more consumers are digitally native. Therefore, a better understanding of current consumer behavior can give us insights and help predict how it will continue to evolve in the years to come.
4 The future—the consumer behavior field in 2040
The other papers use 2030 as a target year but we asked our survey respondents to make predictions for 2040 and thus we have a different future target year.
Niels Bohr once said, “Prediction is very difficult, especially if it’s about the future.” Indeed, it would be a fool’s errand for a single person to hazard a guess about the state of the consumer behavior field twenty years from now. Therefore, predictions from 34 active consumer researchers were collected to address this task. Here, we briefly summarize those predictions.
4.1 Future Concepts
While few respondents proffered guesses regarding specific concepts that would be of interest twenty years from now, many suggested broad topics and trends they expected to see in the field. Expectations for topics could largely be grouped into three main areas. Many suspected that we will be examining essentially the same core topics, perhaps at a finer-grained level, from different perspectives or in ways that we currently cannot utilize due to methodological limitations (more on methods below). A second contingent predicted that much research would center on the impending crises the world faces today, most mentioning environmental and social issues (the COVID-19 pandemic had not yet begun when these predictions were collected and, unsurprisingly, was not anticipated by any of our respondents). The last group, citing the widely expected profound impact of AI on consumers’ lives, argued that AI and other technology-related topics will be dominant subjects in consumer research circa 2040.
While the topic of technology is likely to be focal in the field, our current expectations for the impact of technology on consumers’ lives are narrower than it should be. Rather than merely offering innumerable conveniences and experiences, it seems likely that technology will begin to be integrated into consumers’ thoughts, identities, and personal relationships—probably sooner than we collectively expect. The integration of machines into humans’ bodies and lives will present the field with an expanding list of research questions that do not exist today. For example, how will the concepts of the self, identity, privacy, and goal pursuit change when web-connected technology seamlessly integrates with human consciousness and cognition? Major questions will also need to be answered regarding philosophy of mind, ethics, and social inequality. We suspect that the impact of technology on consumers and consumer research will be far broader than most consumer-behavior researchers anticipate.
As for broader trends within consumer research, there were two camps: (1) those who expect (or hope) that dominant theories (both current and yet to be developed) will become more integrated and comprehensive and (2) those who expect theoretical contributions to become smaller and smaller, to the point of becoming trivial. Both groups felt that current researchers are filling smaller cracks than before, but disagreed on how this would ultimately be resolved.
4.2 Future Methods
As was the case with concepts, respondents’ expectations regarding consumer-research methodologies in 2030 can also be divided into three broad baskets. Unsurprisingly, many indicated that we would be using many technologies not currently available or in wide use. Perhaps more surprising was that most cited the use of technology such as AI, machine-learning algorithms, and robots in designing—as opposed to executing or analyzing—experiments. (Some did point to the use of technologies such as virtual reality in the actual execution of experiments.) The second camp indicated that a focus on reliable and replicable results (discussed further below) will encourage a greater tendency for pre-registering studies, more use of “Big Data,” and a demand for more studies per paper (versus more papers per topic, which some believe is a more fruitful direction). Finally, the third lot indicated that “real data” would be in high demand, thereby necessitating the use of incentive-compatible, consequential dependent variables and a greater prevalence of field studies in consumer research.
As a result, young scholars would benefit from developing a “toolkit” of methodologies for collecting and analyzing the abundant new data of interest to the field. This includes (but is not limited to) a deep understanding of designing and implementing field studies (Gerber and Green 2012 ), data analysis software (R, Python, etc.), text mining and analysis (Humphreys and Wang 2018 ), and analytical tools for other unstructured forms of data such as image and sound. The replication crisis in experimental research means that future scholars will also need to take a more critical approach to validity (internal, external, construct), statistical power, and significance in their work.
4.3 Future Aims
While there was an air of existential concern about the future of the field, most agreed that the trend will be toward increasing the relevance and reliability of consumer research. Specifically, echoing calls from journals and thought leaders, the respondents felt that papers will need to offer more actionable implications for consumers, managers, or policy makers. However, few thought that this increased focus would come at the expense of theoretical insights, suggesting a more demanding overall standard for consumer research in 2040. Likewise, most felt that methodological transparency, open access to data and materials, and study pre-registration will become the norm as the field seeks to allay concerns about the reliability and meaningfulness of its research findings.
4.4 Summary - Future research questions and directions
Despite some well-justified pessimism, the future of consumer research is as bright as ever. As we revised this paper amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, it was clear that many aspects of marketplace behavior, consumption, and life in general will change as a result of this unprecedented global crisis. Given this, and the radical technological, social, and environmental changes that loom on the horizon, consumer researchers will have a treasure trove of topics to tackle in the next ten years, many of which will carry profound substantive importance. While research approaches will evolve, the core goals will remain consistent—namely, to generate theoretically insightful, empirically supported, and substantively impactful research (Table 3 ).
5 Conclusion
At any given moment in time, the focal concepts, methods, and aims of consumer-behavior scholarship reflect both the prior development of the field and trends in the larger scientific community. However, despite shifting trends, the core of the field has remained constant—namely, to understand the motivations, thought processes, and experiences of individuals as they consume goods, services, information, and other offerings, and to use these insights to develop interventions to improve both marketing strategy for firms and consumer welfare for individuals and groups. Amidst the excitement of new technologies, social trends, and consumption experiences, it is important to look back and remind ourselves of the insights the field has already generated. Effectively integrating these past findings with new observations and fresh research will help the field advance our understanding of consumer behavior.
Beckwith, N. E., & Lehmann, D. R. (1973). The importance of differential weights in multiple attribute models of consumer attitude. Journal of Marketing Research, 10 (2), 141–145.
Article Google Scholar
Belk, R. W., Wallendorf, M., & Sherry Jr., J. F. (1989). The sacred and the profane in consumer behavior: theodicy on the odyssey. Journal of Consumer Research, 16 (1), 1–38.
Dahl, R. A., Haire, M., & Lazarsfeld, P. F. (1959). Social science research on business: product and potential . New York: Columbia University Press.
Ding, Y., DeSarbo, W. S., Hanssens, D. M., Jedidi, K., Lynch Jr., J. G., & Lehmann, D. R. (2020). The past, present, and future of measurements and methods in marketing analysis. Marketing Letters, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11002-020-09527-7 .
Farley, J. U., & Ring, L. W. (1970). An empirical test of the Howard-Sheth model of buyer behavior. Journal of Marketing Research, 7 (4), 427–438.
Farley, J. U., & Ring, L. W. (1974). “Empirical” specification of a buyer behavior model. Journal of Marketing Research, 11 (1), 89–96.
Google Scholar
Fishbein, M., & Ajzen, I. (1975). Belief, attitude, intention, and behavior: an introduction to theory and research . Reading: Addison-Wesley.
Gerber, A. S., & Green, D. P. (2012). Field experiments: design, analysis, and interpretation . New York: WW Norton.
Gourville, J. T. (1998). Pennies-a-day: the effect of temporal reframing on transaction evaluation. Journal of Consumer Research, 24 (4), 395–408.
Higgins, E. T. (1998). Promotion and prevention: regulatory focus as a motivational principle. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 30 , 1–46.
Howard, J. A., & Sheth, J. (1969). The theory of buyer behavior . New York: Wiley.
Huber, J., Payne, J. W., & Puto, C. (1982). Adding asymmetrically dominated alternatives: violations of regularity and the similarity hypothesis. Journal of Consumer Research, 9 (1), 90–98.
Humphreys, A., & Wang, R. J. H. (2018). Automated text analysis for consumer research. Journal of Consumer Research, 44 (6), 1274–1306.
Iyengar, S. S., & Lepper, M. R. (2000). When choice is demotivating: can one desire too much of a good thing? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79 (6), 995–1006.
Johnson, E. J., Shu, S. B., Dellaert, B. G., Fox, C., Goldstein, D. G., Häubl, G., et al. (2012). Beyond nudges: tools of a choice architecture. Marketing Letters, 23 (2), 487–504.
Kruglanski, A. W., Shah, J. Y., Fishbach, A., Friedman, R., Chun, W. Y., & Sleeth-Keppler, D. (2002). A theory of goal systems. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 34 , 311–378.
Lancaster, K. (1966). A new theory of consumer behavior. Journal of Political Economy, 74 , 132–157.
Laudan, L. (1986). Methodology’s prospects. In PSA: Proceedings of the Biennial Meeting of the Philosophy of Science Association, 1986 (2), 347–354.
Lynch Jr., J. G. (2011). Introduction to the journal of marketing research special interdisciplinary issue on consumer financial decision making. Journal of Marketing Research, 48 (SPL) Siv–Sviii.
MacInnis, D. J., & Folkes, V. S. (2009). The disciplinary status of consumer behavior: a sociology of science perspective on key controversies. Journal of Consumer Research, 36 (6), 899–914.
Markus, H. R., & Kitayama, S. (1991). Culture and the self: implications for cognition, emotion, and motivation. Psychological Review, 98 (2), 224–253.
Payne, J. W., Bettman, J. R., & Johnson, E. J. (1988). Adaptive strategy selection in decision making. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 14 (3), 534–552.
Prelec, D., & Loewenstein, G. (1998). The red and the black: mental accounting of savings and debt. Marketing Science, 17 (1), 4–28.
Rapp, J. M., & Hill, R. P. (2015). Lordy, Lordy, look who’s 40! The Journal of Consumer Research reaches a milestone. Journal of Consumer Research, 42 (1), 19–29.
Ratchford, B. T. (1975). The new economic theory of consumer behavior: an interpretive essay. Journal of Consumer Research, 2 (2), 65–75.
Schumann, D. W., Haugtvedt, C. P., & Davidson, E. (2008). History of consumer psychology. In Haugtvedt, C. P., Herr, P. M., & Kardes, F. R. eds. Handbook of consumer psychology (pp. 3-28). New York: Erlbaum.
Simonson, I. (1989). Choice based on reasons: the case of attraction and compromise effects. Journal of Consumer Research, 16 (2), 158–174.
Trope, Y., & Liberman, N. (2010). Construal-level theory of psychological distance. Psychological Review, 117 (2), 440–463.
Wang, X., Bendle, N. T., Mai, F., & Cotte, J. (2015). The journal of consumer research at 40: a historical analysis. Journal of Consumer Research, 42 (1), 5–18.
Wilkie, W. L., & Moore, E. S. (2003). Scholarly research in marketing: exploring the “4 eras” of thought development. Journal of Public Policy & Marketing, 22 (2), 116–146.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Columbia Business School, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Maayan S. Malter, Morris B. Holbrook & Donald R. Lehmann
The Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Barbara E. Kahn
Department of Marketing, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA
Jeffrey R. Parker
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Maayan S. Malter .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Malter, M.S., Holbrook, M.B., Kahn, B.E. et al. The past, present, and future of consumer research. Mark Lett 31 , 137–149 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11002-020-09526-8
Download citation
Published : 13 June 2020
Issue Date : September 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11002-020-09526-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Consumer behavior
- Information processing
- Judgement and decision-making
- Consumer culture theory
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Conclusion
Definition:
A research paper conclusion is the final section of a research paper that summarizes the key findings, significance, and implications of the research. It is the writer’s opportunity to synthesize the information presented in the paper, draw conclusions, and make recommendations for future research or actions.
The conclusion should provide a clear and concise summary of the research paper, reiterating the research question or problem, the main results, and the significance of the findings. It should also discuss the limitations of the study and suggest areas for further research.
Parts of Research Paper Conclusion
The parts of a research paper conclusion typically include:
Restatement of the Thesis
The conclusion should begin by restating the thesis statement from the introduction in a different way. This helps to remind the reader of the main argument or purpose of the research.
Summary of Key Findings
The conclusion should summarize the main findings of the research, highlighting the most important results and conclusions. This section should be brief and to the point.
Implications and Significance
In this section, the researcher should explain the implications and significance of the research findings. This may include discussing the potential impact on the field or industry, highlighting new insights or knowledge gained, or pointing out areas for future research.
Limitations and Recommendations
It is important to acknowledge any limitations or weaknesses of the research and to make recommendations for how these could be addressed in future studies. This shows that the researcher is aware of the potential limitations of their work and is committed to improving the quality of research in their field.
Concluding Statement
The conclusion should end with a strong concluding statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. This could be a call to action, a recommendation for further research, or a final thought on the topic.
How to Write Research Paper Conclusion
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion:
- Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study.
- Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results of your research. This can be done by highlighting the most important aspects of your research and the evidence that supports them.
- Discuss the implications: Discuss the implications of your findings for the research area and any potential applications of your research. You should also mention any limitations of your research that may affect the interpretation of your findings.
- Provide a conclusion : Provide a concise conclusion that summarizes the main points of your paper and emphasizes the significance of your research. This should be a strong and clear statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
- Offer suggestions for future research: Lastly, offer suggestions for future research that could build on your findings and contribute to further advancements in the field.
Remember that the conclusion should be brief and to the point, while still effectively summarizing the key findings and implications of your research.
Example of Research Paper Conclusion
Here’s an example of a research paper conclusion:
Conclusion :
In conclusion, our study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Our findings suggest that there is a significant association between social media use and increased levels of anxiety and depression among college students. This highlights the need for increased awareness and education about the potential negative effects of social media use on mental health, particularly among college students.
Despite the limitations of our study, such as the small sample size and self-reported data, our findings have important implications for future research and practice. Future studies should aim to replicate our findings in larger, more diverse samples, and investigate the potential mechanisms underlying the association between social media use and mental health. In addition, interventions should be developed to promote healthy social media use among college students, such as mindfulness-based approaches and social media detox programs.
Overall, our study contributes to the growing body of research on the impact of social media on mental health, and highlights the importance of addressing this issue in the context of higher education. By raising awareness and promoting healthy social media use among college students, we can help to reduce the negative impact of social media on mental health and improve the well-being of young adults.
Purpose of Research Paper Conclusion
The purpose of a research paper conclusion is to provide a summary and synthesis of the key findings, significance, and implications of the research presented in the paper. The conclusion serves as the final opportunity for the writer to convey their message and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
The conclusion should restate the research problem or question, summarize the main results of the research, and explain their significance. It should also acknowledge the limitations of the study and suggest areas for future research or action.
Overall, the purpose of the conclusion is to provide a sense of closure to the research paper and to emphasize the importance of the research and its potential impact. It should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the main findings and why they matter. The conclusion serves as the writer’s opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
When to Write Research Paper Conclusion
The conclusion of a research paper should be written after the body of the paper has been completed. It should not be written until the writer has thoroughly analyzed and interpreted their findings and has written a complete and cohesive discussion of the research.
Before writing the conclusion, the writer should review their research paper and consider the key points that they want to convey to the reader. They should also review the research question, hypotheses, and methodology to ensure that they have addressed all of the necessary components of the research.
Once the writer has a clear understanding of the main findings and their significance, they can begin writing the conclusion. The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, and should reiterate the main points of the research while also providing insights and recommendations for future research or action.
Characteristics of Research Paper Conclusion
The characteristics of a research paper conclusion include:
- Clear and concise: The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, summarizing the key findings and their significance.
- Comprehensive: The conclusion should address all of the main points of the research paper, including the research question or problem, the methodology, the main results, and their implications.
- Future-oriented : The conclusion should provide insights and recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the research.
- Impressive : The conclusion should leave a lasting impression on the reader, emphasizing the importance of the research and its potential impact.
- Objective : The conclusion should be based on the evidence presented in the research paper, and should avoid personal biases or opinions.
- Unique : The conclusion should be unique to the research paper and should not simply repeat information from the introduction or body of the paper.
Advantages of Research Paper Conclusion
The advantages of a research paper conclusion include:
- Summarizing the key findings : The conclusion provides a summary of the main findings of the research, making it easier for the reader to understand the key points of the study.
- Emphasizing the significance of the research: The conclusion emphasizes the importance of the research and its potential impact, making it more likely that readers will take the research seriously and consider its implications.
- Providing recommendations for future research or action : The conclusion suggests practical recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the study.
- Providing closure to the research paper : The conclusion provides a sense of closure to the research paper, tying together the different sections of the paper and leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
- Demonstrating the writer’s contribution to the field : The conclusion provides the writer with an opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
Limitations of Research Paper Conclusion
While the conclusion of a research paper has many advantages, it also has some limitations that should be considered, including:
- I nability to address all aspects of the research: Due to the limited space available in the conclusion, it may not be possible to address all aspects of the research in detail.
- Subjectivity : While the conclusion should be objective, it may be influenced by the writer’s personal biases or opinions.
- Lack of new information: The conclusion should not introduce new information that has not been discussed in the body of the research paper.
- Lack of generalizability: The conclusions drawn from the research may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, limiting the generalizability of the study.
- Misinterpretation by the reader: The reader may misinterpret the conclusions drawn from the research, leading to a misunderstanding of the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
How to write a strong conclusion for your research paper
Last updated
17 February 2024
Reviewed by
Writing a research paper is a chance to share your knowledge and hypothesis. It's an opportunity to demonstrate your many hours of research and prove your ability to write convincingly.
Ideally, by the end of your research paper, you'll have brought your readers on a journey to reach the conclusions you've pre-determined. However, if you don't stick the landing with a good conclusion, you'll risk losing your reader’s trust.
Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper involves a few important steps, including restating the thesis and summing up everything properly.
Find out what to include and what to avoid, so you can effectively demonstrate your understanding of the topic and prove your expertise.
- Why is a good conclusion important?
A good conclusion can cement your paper in the reader’s mind. Making a strong impression in your introduction can draw your readers in, but it's the conclusion that will inspire them.
- What to include in a research paper conclusion
There are a few specifics you should include in your research paper conclusion. Offer your readers some sense of urgency or consequence by pointing out why they should care about the topic you have covered. Discuss any common problems associated with your topic and provide suggestions as to how these problems can be solved or addressed.
The conclusion should include a restatement of your initial thesis. Thesis statements are strengthened after you’ve presented supporting evidence (as you will have done in the paper), so make a point to reintroduce it at the end.
Finally, recap the main points of your research paper, highlighting the key takeaways you want readers to remember. If you've made multiple points throughout the paper, refer to the ones with the strongest supporting evidence.
- Steps for writing a research paper conclusion
Many writers find the conclusion the most challenging part of any research project . By following these three steps, you'll be prepared to write a conclusion that is effective and concise.
- Step 1: Restate the problem
Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper.
When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
- Step 2: Sum up the paper
After you've restated the problem, sum up the paper by revealing your overall findings. The method for this differs slightly, depending on whether you're crafting an argumentative paper or an empirical paper.
Argumentative paper: Restate your thesis and arguments
Argumentative papers involve introducing a thesis statement early on. In crafting the conclusion for an argumentative paper, always restate the thesis, outlining the way you've developed it throughout the entire paper.
It might be appropriate to mention any counterarguments in the conclusion, so you can demonstrate how your thesis is correct or how the data best supports your main points.
Empirical paper: Summarize research findings
Empirical papers break down a series of research questions. In your conclusion, discuss the findings your research revealed, including any information that surprised you.
Be clear about the conclusions you reached, and explain whether or not you expected to arrive at these particular ones.
- Step 3: Discuss the implications of your research
Argumentative papers and empirical papers also differ in this part of a research paper conclusion. Here are some tips on crafting conclusions for argumentative and empirical papers.
Argumentative paper: Powerful closing statement
In an argumentative paper, you'll have spent a great deal of time expressing the opinions you formed after doing a significant amount of research. Make a strong closing statement in your argumentative paper's conclusion to share the significance of your work.
You can outline the next steps through a bold call to action, or restate how powerful your ideas turned out to be.
Empirical paper: Directions for future research
Empirical papers are broader in scope. They usually cover a variety of aspects and can include several points of view.
To write a good conclusion for an empirical paper, suggest the type of research that could be done in the future, including methods for further investigation or outlining ways other researchers might proceed.
If you feel your research had any limitations, even if they were outside your control, you could mention these in your conclusion.
After you finish outlining your conclusion, ask someone to read it and offer feedback. In any research project you're especially close to, it can be hard to identify problem areas. Having a close friend or someone whose opinion you value read the research paper and provide honest feedback can be invaluable. Take note of any suggested edits and consider incorporating them into your paper if they make sense.
- Things to avoid in a research paper conclusion
Keep these aspects to avoid in mind as you're writing your conclusion and refer to them after you've created an outline.
Dry summary
Writing a memorable, succinct conclusion is arguably more important than a strong introduction. Take care to avoid just rephrasing your main points, and don't fall into the trap of repeating dry facts or citations.
You can provide a new perspective for your readers to think about or contextualize your research. Either way, make the conclusion vibrant and interesting, rather than a rote recitation of your research paper’s highlights.
Clichéd or generic phrasing
Your research paper conclusion should feel fresh and inspiring. Avoid generic phrases like "to sum up" or "in conclusion." These phrases tend to be overused, especially in an academic context and might turn your readers off.
The conclusion also isn't the time to introduce colloquial phrases or informal language. Retain a professional, confident tone consistent throughout your paper’s conclusion so it feels exciting and bold.
New data or evidence
While you should present strong data throughout your paper, the conclusion isn't the place to introduce new evidence. This is because readers are engaged in actively learning as they read through the body of your paper.
By the time they reach the conclusion, they will have formed an opinion one way or the other (hopefully in your favor!). Introducing new evidence in the conclusion will only serve to surprise or frustrate your reader.
Ignoring contradictory evidence
If your research reveals contradictory evidence, don't ignore it in the conclusion. This will damage your credibility as an expert and might even serve to highlight the contradictions.
Be as transparent as possible and admit to any shortcomings in your research, but don't dwell on them for too long.
Ambiguous or unclear resolutions
The point of a research paper conclusion is to provide closure and bring all your ideas together. You should wrap up any arguments you introduced in the paper and tie up any loose ends, while demonstrating why your research and data are strong.
Use direct language in your conclusion and avoid ambiguity. Even if some of the data and sources you cite are inconclusive or contradictory, note this in your conclusion to come across as confident and trustworthy.
- Examples of research paper conclusions
Your research paper should provide a compelling close to the paper as a whole, highlighting your research and hard work. While the conclusion should represent your unique style, these examples offer a starting point:
Ultimately, the data we examined all point to the same conclusion: Encouraging a good work-life balance improves employee productivity and benefits the company overall. The research suggests that when employees feel their personal lives are valued and respected by their employers, they are more likely to be productive when at work. In addition, company turnover tends to be reduced when employees have a balance between their personal and professional lives. While additional research is required to establish ways companies can support employees in creating a stronger work-life balance, it's clear the need is there.
Social media is a primary method of communication among young people. As we've seen in the data presented, most young people in high school use a variety of social media applications at least every hour, including Instagram and Facebook. While social media is an avenue for connection with peers, research increasingly suggests that social media use correlates with body image issues. Young girls with lower self-esteem tend to use social media more often than those who don't log onto social media apps every day. As new applications continue to gain popularity, and as more high school students are given smartphones, more research will be required to measure the effects of prolonged social media use.
What are the different kinds of research paper conclusions?
There are no formal types of research paper conclusions. Ultimately, the conclusion depends on the outline of your paper and the type of research you’re presenting. While some experts note that research papers can end with a new perspective or commentary, most papers should conclude with a combination of both. The most important aspect of a good research paper conclusion is that it accurately represents the body of the paper.
Can I present new arguments in my research paper conclusion?
Research paper conclusions are not the place to introduce new data or arguments. The body of your paper is where you should share research and insights, where the reader is actively absorbing the content. By the time a reader reaches the conclusion of the research paper, they should have formed their opinion. Introducing new arguments in the conclusion can take a reader by surprise, and not in a positive way. It might also serve to frustrate readers.
How long should a research paper conclusion be?
There's no set length for a research paper conclusion. However, it's a good idea not to run on too long, since conclusions are supposed to be succinct. A good rule of thumb is to keep your conclusion around 5 to 10 percent of the paper's total length. If your paper is 10 pages, try to keep your conclusion under one page.
What should I include in a research paper conclusion?
A good research paper conclusion should always include a sense of urgency, so the reader can see how and why the topic should matter to them. You can also note some recommended actions to help fix the problem and some obstacles they might encounter. A conclusion should also remind the reader of the thesis statement, along with the main points you covered in the paper. At the end of the conclusion, add a powerful closing statement that helps cement the paper in the mind of the reader.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Consumer Research: Examples, Process and Scope

What is Consumer Research?
Consumer research is a part of market research in which inclination, motivation and purchase behavior of the targeted customers are identified. Consumer research helps businesses or organizations understand customer psychology and create detailed purchasing behavior profiles.
It uses research techniques to provide systematic information about what customers need. Using this information brands can make changes in their products and services, making them more customer-centric thereby increasing customer satisfaction. This will in turn help to boost business.
LEARN ABOUT: Market research vs marketing research
An organization that has an in-depth understanding about the customer decision-making process, is most likely to design a product, put a certain price tag to it, establish distribution centers and promote a product based on consumer research insights such that it produces increased consumer interest and purchases.
For example, A consumer electronics company wants to understand, thought process of a consumer when purchasing an electronic device, which can help a company to launch new products, manage the supply of the stock, etc. Carrying out a Consumer electronics survey can be useful to understand the market demand, understand the flaws in their product and also find out research problems in the various processes that influence the purchase of their goods. A consumer electronics survey can be helpful to gather information about the shopping experiences of consumers when purchasing electronics. which can enable a company to make well-informed and wise decisions regarding their products and services.
LEARN ABOUT: Test Market Demand
Consumer Research Objectives
When a brand is developing a new product, consumer research is conducted to understand what consumers want or need in a product, what attributes are missing and what are they looking for? An efficient survey software really makes it easy for organizations to conduct efficient research.
Consumer research is conducted to improve brand equity. A brand needs to know what consumers think when buying a product or service offered by a brand. Every good business idea needs efficient consumer research for it to be successful. Consumer insights are essential to determine brand positioning among consumers.
Consumer research is conducted to boost sales. The objective of consumer research is to look into various territories of consumer psychology and understand their buying pattern, what kind of packaging they like and other similar attributes that help brands to sell their products and services better.
LEARN ABOUT: Brand health
Consumer Research Model
According to a study conducted, till a decade ago, researchers thought differently about the consumer psychology, where little or no emphasis was put on emotions, mood or the situation that could influence a customer’s buying decision.
Many believed marketing was applied economics. Consumers always took decisions based on statistics and math and evaluated goods and services rationally and then selected items from those brands that gave them the highest customer satisfaction at the lowest cost.
However, this is no longer the situation. Consumers are very well aware of brands and their competitors. A loyal customer is the one who would not only return to repeatedly purchase from a brand but also, recommend his/her family and friends to buy from the same brand even if the prices are slightly higher but provides an exceptional customer service for products purchased or services offered.
Here is where the Net Promoter Score (NPS) helps brands identify brand loyalty and customer satisfaction with their consumers. Net Promoter Score consumer survey uses a single question that is sent to customers to identify their brand loyalty and level of customer satisfaction. Response to this question is measured on a scale between 0-10 and based on this consumers can be identified as:
Detractors: Who have given a score between 0-6.
Passives: Who have given a score between 7-8.
Promoters: Who have given a score between 9-10.
Consumer market research is based on two types of research method:
1. Qualitative Consumer Research
Qualitative research is descriptive in nature, It’s a method that uses open-ended questions , to gain meaningful insights from respondents and heavily relies on the following market research methods:
Focus Groups: Focus groups as the name suggests is a small group of highly validated subject experts who come together to analyze a product or service. Focus group comprises of 6-10 respondents. A moderator is assigned to the focus group, who helps facilitate discussions among the members to draw meaningful insights
One-to-one Interview: This is a more conversational method, where the researcher asks open-ended questions to collect data from the respondents. This method heavily depends on the expertise of the researcher. How much the researcher is able to probe with relevant questions to get maximum insights. This is a time-consuming method and can take more than one attempt to gain the desired insights.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Interview
Content/ Text Analysis: Text analysis is a qualitative research method where researchers analyze social life by decoding words and images from the documents available. Researchers analyze the context in which the images are used and draw conclusions from them. Social media is an example of text analysis. In the last decade or so, inferences are drawn based on consumer behavior on social media.
Learn More: How to conduct Qualitative Research
2.Quantitative Consumer Research
In the age of technology and information, meaningful data is more precious than platinum. Billion dollar companies have risen and fallen on how well they have been able to collect and analyze data, to draw validated insights.
Quantitative research is all about numbers and statistics. An evolved consumer who purchases regularly can vouch for how customer-centric businesses have become today. It’s all about customer satisfaction , to gain loyal customers. With just one questions companies are able to collect data, that has the power to make or break a company. Net Promoter Score question , “On a scale from 0-10 how likely are you to recommend our brand to your family or friends?”
How organic word-of-mouth is influencing consumer behavior and how they need to spend less on advertising and invest their time and resources to make sure they provide exceptional customer service.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Targeting
Online surveys , questionnaires , and polls are the preferred data collection tools. Data that is obtained from consumers is then statistically, mathematically and numerically evaluated to understand consumer preference.
Learn more: How to carry out Quantitative Research
Consumer Research Process
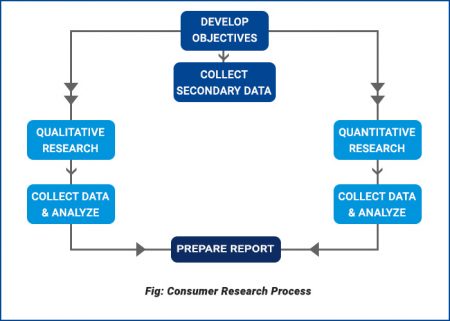
The process of consumer research started as an extension of the process of market research . As the findings of market research is used to improve the decision-making capacity of an organization or business, similar is with consumer research.
LEARN ABOUT: Market research industry
The consumer research process can be broken down into the following steps:
- Develop research objectives: The first step to the consumer research process is to clearly define the research objective, the purpose of research, why is the research being conducted, to understand what? A clear statement of purpose can help emphasize the purpose.
- Collect Secondary data: Collect secondary data first, it helps in understanding if research has been conducted earlier and if there are any pieces of evidence related to the subject matter that can be used by an organization to make informed decisions regarding consumers.
- Primary Research: In primary research organizations or businesses collect their own data or employ a third party to collect data on their behalf. This research makes use of various data collection methods ( qualitative and quantitative ) that helps researchers collect data first hand.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
- Collect and analyze data: Data is collected and analyzed and inference is drawn to understand consumer behavior and purchase pattern.
- Prepare report: Finally, a report is prepared for all the findings by analyzing data collected so that organizations are able to make informed decisions and think of all probabilities related to consumer behavior. By putting the study into practice, organizations can become customer-centric and manufacture products or render services that will help them achieve excellent customer satisfaction.
LEARN ABOUT: market research trends
After Consumer Research Process
Once you have been able to successfully carry out the consumer research process , investigate and break paradigms. What consumers need should be a part of market research design and should be carried out regularly. Consumer research provides more in-depth information about the needs, wants, expectations and behavior analytics of clients.
By identifying this information successfully, strategies that are used to attract consumers can be made better and businesses can make a profit by knowing what consumers want exactly. It is also important to understand and know thoroughly the buying behavior of consumers to know their attitude towards brands and products.
The identification of consumer needs, as well as their preferences, allows a business to adapt to new business and develop a detailed marketing plan that will surely work. The following pointers can help. Completing this process will help you:
- Attract more customers
- Set the best price for your products
- Create the right marketing message
- Increase the quantity that satisfies the demand of its clients
- Increase the frequency of visits to their clients
- Increase your sales
- Reduce costs
- Refine your approach to the customer service process .
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Research
Consumer Research Methods
Consumers are the reason for a business to run and flourish. Gathering enough information about consumers is never going to hurt any business, in fact, it will only add up to the information a business would need to associate with its consumers and manufacture products that will help their business refine and grow.
Following are consumer research methods that ensure you are in tandem with the consumers and understand their needs:
The studies of customer satisfaction
One can determine the degree of satisfaction of consumers in relation to the quality of products through:
- Informal methods such as conversations with staff about products and services according to the dashboards.
- Past and present questionnaires/ surveys that consumers might have filled that identify their needs.
T he investigation of the consumer decision process
It is very interesting to know the consumer’s needs, what motivates them to buy, and how is the decision-making process carried out, though:
- Deploying relevant surveys and receiving responses from a target intended audience .
Proof of concept
Businesses can test how well accepted their marketing ideas are by:
- The use of surveys to find out if current or potential consumer see your products as a rational and useful benefit.
- Conducting personal interviews or focus group sessions with clients to understand how they respond to marketing ideas.
Knowing your market position
You can find out how your current and potential consumers see your products, and how they compare it with your competitors by:
- Sales figures talk louder than any other aspect, once you get to know the comparison in the sales figures it is easy to understand your market position within the market segment.
- Attitudes of consumers while making a purchase also helps in understanding the market hold.
Branding tests and user experience
You can determine how your customers feel with their brands and product names by:
- The use of focus groups and surveys designed to assess emotional responses to your products and brands.
- The participation of researchers to study the performance of their brand in the market through existing and available brand measurement research.
Price changes
You can investigate how your customers accept or not the price changes by using formulas that measure the revenue – multiplying the number of items you sold, by the price of each item. These tests allow you to calculate if your total income increases or decreases after making the price changes by:
- Calculation of changes in the quantities of products demanded by their customers, together with changes in the price of the product.
- Measure the impact of the price on the demand of the product according to the needs of the client.
Social media monitoring
Another way to measure feedback and your customer service is by controlling your commitment to social media and feedback. Social networks (especially Facebook) are becoming a common element of the commercialization of many businesses and are increasingly used by their customers to provide information on customer needs, service experiences, share and file customer complaints . It can also be used to run surveys and test concepts. If handled well, it can be one of the most powerful research tools of the client management . I also recommend reading: How to conduct market research through social networks.
Customer Research Questions
Asking the right question is the most important part of conducting research. Moreover, if it’s consumer research, questions should be asked in a manner to gather maximum insights from consumers. Here are some consumer research questions for your next research:
- Who in your household takes purchasing decisions?
- Where do you go looking for ______________ (product)?
- How long does it take you to make a buying decision?
- How far are you willing to travel to buy ___________(product)?
- What features do you look for when you purchase ____________ (product)?
- What motivates you to buy_____________ (product)?
See more consumer research survey questions:
Customer satisfaction surveys
Voice of customer surveys
Product surveys
Service evaluation surveys
Mortgage Survey Questions
Importance of Consumer Research
Launching a product or offering new services can be quite an exciting time for a brand. However, there are a lot of aspects that need to be taken into consideration while a band has something new to offer to consumers.
LEARN ABOUT: User Experience Research
Here is where consumer research plays a pivotal role. The importance of consumer research cannot be emphasized more. Following points summarizes the importance of consumer research:
- To understand market readiness: However good a product or service may be, consumers have to be ready to accept it. Creating a product requires investments which in return expect ROI from product or service purchases. However, if a market is mature enough to accept this utility, it has a low chance of succeeding by tapping into market potential . Therefore, before launching a product or service, organizations need to conduct consumer research, to understand if people are ready to spend on the utility it provides.
- Identify target consumers: By conducting consumer research, brands and organizations can understand their target market based on geographic segmentation and know who exactly is interested in buying their products. According to the data or feedback received from the consumer, research brands can even customize their marketing and branding approach to better appeal to the specific consumer segment.
LEARN ABOUT: Marketing Insight
- Product/Service updates through feedback: Conducting consumer research, provides valuable feedback from consumers about the attributes and features of products and services. This feedback enables organizations to understand consumer perception and provide a more suitable solution based on actual market needs which helps them tweak their offering to perfection.
Explore more: 300 + FREE survey templates to use for your research
MORE LIKE THIS

15 Best Customer Experience Software of 2024
May 2, 2024

Journey Orchestration Platforms: Top 11 Platforms in 2024

Top 12 Employee Pulse Survey Tools Unlocking Insights in 2024
May 1, 2024

Taking Action in CX – Tuesday CX Thoughts
Apr 30, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Author Interviews
- Research Curations
- Author Guidelines
- Open Access
- Submission Site
- Why Submit?
- About Journal of Consumer Research
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Bernd Schmitt
June Cotte
Markus Giesler
Andrew Stephen
About the Journal
The Journal of Consumer Research publishes scholarly research that describes and explains consumer behavior.

Latest articles
Latest posts on x, visit the new jcr website.
The new JCR website highlights our community of consumer researchers and the important work we do. Visit consumerresearcher.com and find interviews with authors, resources for teachers, and much more.
Explore the website now
Why Publish with JCR ?
Award-winning articles.
Read our award-winning articles, including the Best Article Award winner as chosen by the members of the JCR Policy Board after receiving nominations from the Editorial Review Board. JCR also awards the Robert Ferber Award and Robert Ferber Honorable Mention. The Robert Ferber Award competition is held annually in honor of one of the founders and the second editor of the Journal of Consumer Research .
Read award-winning articles
High-Impact Articles
To highlight the impact of the journal, we have organized a collection of some of the most read, most cited, and most discussed articles from recent years.
Explore the collection
From the OUPblog

How drawing pictures can help us understand wine
Find out more

Why morning people seek more variety

The science behind ironic consumption

Read all posts from JCR on the OUPblog
Explore all past posts

Recommend to your library
Fill out our simple online form to recommend Journal of Consumer Research to your library.
Recommend now

Email alerts
Register to receive table of contents email alerts as soon as new issues of Journal of Consumer Research are published online.

Developing countries initiative
Your institution could be eligible to free or deeply discounted online access to Journal of Consumer Research through the Oxford Developing Countries Initiative.
Related Titles
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1537-5277
- Print ISSN 0093-5301
- Copyright © 2024 Journal of Consumer Research Inc.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research. For most college-level research papers, two or three well-developed paragraphs is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, more paragraphs may be required in describing the key findings and their significance.
Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with important opportunities to demonstrate to the reader your understanding of the research problem. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key findings in your analysis that advance new understanding about the research problem, that are unusual or unexpected, or that have important implications applied to practice.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger significance of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly re-emphasize your answer to the "So What?" question by placing the study within the context of how your research advances past research about the topic.
- Identifying how a gap in the literature has been addressed . The conclusion can be where you describe how a previously identified gap in the literature [first identified in your literature review section] has been addressed by your research and why this contribution is significant.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers an opportunity to elaborate on the impact and significance of your findings. This is particularly important if your study approached examining the research problem from an unusual or innovative perspective.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing or contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Bunton, David. “The Structure of PhD Conclusion Chapters.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 4 (July 2005): 207–224; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
The general function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Do this by clearly summarizing the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem you investigated in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found in the literature. However, make sure that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings. This reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your paper.
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- Present your conclusions in clear, concise language. Re-state the purpose of your study, then describe how your findings differ or support those of other studies and why [i.e., what were the unique, new, or crucial contributions your study made to the overall research about your topic?].
- Do not simply reiterate your findings or the discussion of your results. Provide a synthesis of arguments presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem and the overall objectives of your study.
- Indicate opportunities for future research if you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper. Highlighting the need for further research provides the reader with evidence that you have an in-depth awareness of the research problem but that further investigations should take place beyond the scope of your investigation.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is presented well:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data [this is opposite of the introduction, which begins with general discussion of the context and ends with a detailed description of the research problem].
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have conducted will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way. If asked to think introspectively about the topics, do not delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply, not to guess at possible outcomes or make up scenarios not supported by the evidence.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Although an effective conclusion needs to be clear and succinct, it does not need to be written passively or lack a compelling narrative. Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following:
- If your essay deals with a critical, contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem proactively.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action that, if adopted, could address a specific problem in practice or in the development of new knowledge leading to positive change.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion already noted in your paper in order to lend authority and support to the conclusion(s) you have reached [a good source would be from your literature review].
- Explain the consequences of your research in a way that elicits action or demonstrates urgency in seeking change.
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to emphasize the most important finding of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point by drawing from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you presented in your introduction, but add further insight derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results from your study to recast it in new or important ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a succinct, declarative statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid
Failure to be concise Your conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too lengthy often have unnecessary information in them. The conclusion is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, and other forms of analysis that you make. Strategies for writing concisely can be found here .
Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from the general [the field of study] to the specific [the research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from a specific discussion [your research problem] back to a general discussion framed around the implications and significance of your findings [i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In short, the conclusion is where you should place your research within a larger context [visualize your paper as an hourglass--start with a broad introduction and review of the literature, move to the specific analysis and discussion, conclude with a broad summary of the study's implications and significance].
Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. These are problems, deficiencies, or challenges encountered during your study. They should be summarized as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative or unintended results [i.e., findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section and discuss their implications in the discussion section of your paper. In the conclusion, use negative results as an opportunity to explain their possible significance and/or how they may form the basis for future research.
Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits within your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize briefly and succinctly how it contributes to new knowledge or a new understanding about the research problem. This element of your conclusion may be only a few sentences long.
Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives in the social and behavioral sciences change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine the original objectives in your introduction. As these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you presumably should know a good deal about it [perhaps even more than your professor!]. Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority as a researcher by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches that...." The overall tone of your conclusion should convey confidence to the reader about the study's validity and realiability.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin Madison; Miquel, Fuster-Marquez and Carmen Gregori-Signes. “Chapter Six: ‘Last but Not Least:’ Writing the Conclusion of Your Paper.” In Writing an Applied Linguistics Thesis or Dissertation: A Guide to Presenting Empirical Research . John Bitchener, editor. (Basingstoke,UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), pp. 93-105; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining that they are reaching the end of your paper. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. This why the conclusion rarely has citations to sources. If you have new information to present, add it to the discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no new information is introduced, the conclusion, along with the discussion section, is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; the conclusion is where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate that you understand the material that you’ve presented, and position your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic, including describing how your research contributes new insights to that scholarship.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: May 1, 2024 9:25 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Ready to level up your insights?
Get ready to streamline, scale and supercharge your research. Fill out this form to request a demo of the InsightHub platform and discover the difference insights empowerment can make. A member of our team will reach out within two working days.
Cost effective insights that scale
Quality insight doesn't need to cost the earth. Our flexible approach helps you make the most of research budgets and build an agile solution that works for you. Fill out this form to request a call back from our team to explore our pricing options.
- What is InsightHub?
- Data Collection
- Data Analysis
- Data Activation
- Research Templates
- Information Security
- Our Expert Services
- Support & Education
- Consultative Services
- Insight Delivery
- Research Methods
- Sectors We Work With
- Meet the team
- Advisory Board
- Press & Media
- Book a Demo
- Request Pricing

Embark on a new adventure. Join Camp InsightHub, our free demo platform, to discover the future of research.

Read a brief overview of the agile research platform enabling brands to inform decisions at speed in this PDF.
InsightHub on the Blog
- Surveys, Video and the Changing Face of Agile Research
- Building a Research Technology Stack for Better Insights
- The Importance of Delegation in Managing Insight Activities
- Common Insight Platform Pitfalls (and How to Avoid Them)
- Support and Education
- Insight Delivery Services

Our services drive operational and strategic success in challenging environments. Find out how.

Close Connections bring stakeholders and customers together for candid, human conversations.
Services on the Blog
- Closing the Client-Agency Divide in Market Research
- How to Speed Up Fieldwork Without Compromising Quality
- Practical Ways to Support Real-Time Decision Making
- Developing a Question Oriented, Not Answer Oriented Culture
- Meet the Team

The FlexMR credentials deck provides a brief introduction to the team, our approach to research and previous work.

We are the insights empowerment company. Our framework addresses the major pressures insight teams face.
Latest News
- Insight as Art Shortlisted for AURA Innovation Award
- FlexMR Launch Video Close Connection Programme
- VideoMR Analysis Tool Added to InsightHub
- FlexMR Makes Shortlist for Quirks Research Supplier Award
- Latest Posts
- Strategic Thinking
- Technology & Trends
- Practical Application
- Insights Empowerment
- View Full Blog Archives

Discover how to build close customer connections to better support real-time decision making.

What is a market research and insights playbook, plus discover why should your team consider building one.
Featured Posts
- Five Strategies for Turning Insight into Action
- How to Design Surveys that Ask the Right Questions
- Scaling Creative Qual for Rich Customer Insight
- How to Measure Brand Awareness: The Complete Guide
- All Resources
- Client Stories
- Whitepapers
- Events & Webinars
- The Open Ideas Panel
- InsightHub Help Centre
- FlexMR Client Network

The insights empowerment readiness calculator measures your progress in building an insight-led culture.

The MRX Lab podcast explores new and novel ideas from the insights industry in 10 minutes or less.
Featured Stories
- Specsavers Informs Key Marketing Decisions with InsightHub
- The Coventry Panel Helps Maintain Award Winning CX
- Isagenix Customer Community Steers New Product Launch
- Curo Engage Residents with InsightHub Community
- Research Methods /
Consumer Research - Definitions, Examples and Benefits
Emily james, how to tell your insights’ story.
If you search "storytelling in insight" on any search engine, you get lots of results as to WHY we s...
Charlotte Duff
- Insights Empowerment (29)
- Practical Application (169)
- Research Methods (283)
- Strategic Thinking (191)
- Survey Templates (7)
- Tech & Trends (386)
When it comes to how market research is perceived by those outside of the insights industry, most stakeholders see market research as simply a way to create the best products and services for their own customers. And while that is a part of it, there is a lot more to market and consumer research than that.
Consumer research is the path to take when businesses wish to better themselves and direct their endeavours towards success. Whether that is creating new or refining current business strategies, finding the pain points in their customer experience, or even creating new internal policies and processes to become more efficient than ever before. All of these use cases contribute to building the best version of the brand and business as long as stakeholders are relying on quality insights.
In this guide, we’ll discuss:
1. The definition of consumer research 2. The power of consumer research 3. The benefits of consumer research 4. How behaviour influences innovation 5. How to spot behavioural trends and patterns 6. How to conduct consumer research 7. The tools and types of consumer research 8. Best practices for consumer research 9. Examples of good consumer research
This is one of our longer articles, so if you’re looking for something specific then you can use the quick navigation links above to jump to each section of the guide.
What is Consumer Research?
Consumer research has cultivated a very unique reputation for being the way to gain information about a brand’s consumers. With dedicated consumer insights, brands and stakeholders can make sure that they are creating not only the right products but also the right business strategies and communicating in the right way to immerse consumers in their brand experience. And because of this success, the term consumer research has become synonymous with market research. Consumer research is the first thing that typically comes to mind when stakeholders are asked to think about market research and its popular use cases.
The phrase ‘consumer research’ is typically used interchangeably with ‘customer research’ across all industries, with the term ‘consumer’ here taken to mean ‘those who consume the brand’s experience, product and services'. So in this context, consumers and customers are one and the same.
Definition, Reputation and Importance
Based on the above concept, consumer research is market research that is specifically focussed on exploring the attitudes, opinions and experiences of a business’ current customers and/or potential future customers.
This reputation has come around for a reason, because market researchers are very good at what they do. We have made sure that we can recruit and engage participants with the best of them, with our efforts leading to unique research experiences that generate high-quality insights that influence key decisions across entire industries.
The Power of Consumer Research
Consumer research is incredibly powerful. Conducting consumer research in the right way can save struggling businesses from abject failure, and drive moderately successful businesses into the history books under the definition of ‘success’.
Consumer research was one of the first use cases of early market research. In a review of early consumer research, Helgeson et al. states that, “In 1950, seven percent of the articles reviewed were consumer research articles. By 1981, 34 percent of the articles were consumer research articles.” This accelerated growth of articles and information gathering about the topic of consumer behaviour so early on in the evolution of consumer and market research can be attributed to the creation of the journals of Consumer Research and Advances in Consumer Research in the 1970s.
The increase in interest and development in consumer behaviour indicates that many businesses started feeling the power of consumer research from the very beginning. For example, in the 1950s, Ford Motor Company conducted a ten-year-long consumer research project that resulted in the ‘Edsel’, a completely customisable car that truly served the customers’ needs and was supposed to revolutionise the industry. Ford used focus groups, in-depth interviews and ‘motivational research’ to help design the perfect car for the consumer, and with his results it’s fair to assume that at some point in that 10 year-long project, Ford and his insight team cam not the revelation that he could not satisfy every consumer’s need in one single car, which is how the ‘customisable’ option came into being.
While this car never ended up coming to market (due to cost and an underperformance issue), Ford still learnt about a concept that most businesses still struggle with now - the power of consumer insights can transform a business when given the chance, but insights are nothing without the ability and resources to act on them.
Since then, consumer research has undergone significant evolution since Ford attempted to use it to revolutionise the automotive industry, with technological advancements especially in the past decade allowing insight experts to innovate creatively and come up with ways to overcome traditional challenges and reap many of the benefits in one fell swoop.
Benefits of Consumer Research
With the power, importance and reputation of consumer research outlined for all to see, it’s time to explore the impacts and benefits. The power of consumer research impacts two very specific areas and audiences:
1. Understanding Customer Behaviour for Innovation
Now that businesses are in the practice of discovering the next new thing and understand the evolution they will have to undertake in order to stay relevant to their target audience, they are on the right track to truly understand the power of consumer research and insights. Innovation happens every day, but successful innovation happens only when fuelled with the right insights at the right time.
Those insights are gathered directly from the mouths of consumers. Conducting consumer research to gain insights directly from the source allows for no mistakes and helps insight teams to form a complete picture of the brand’s consumers - their likes, dislikes, their demographic information, their common experiences and most obnoxious pain points, all at the very least.
Each insight gained is like a puzzle piece that, when all put together in the right way, paints the picture of the consumer’s experience, opinions and needs, and how the brand is working to serve those needs.
There are numerous ways to act on the insights gathered. Some brand stakeholders take these consumer insights and use them to create customer personas - a character that represents a segment of their consumer base - which can then be used in storytelling efforts as return characters. The more these personas are used, the more they’re recognised by stakeholders across the business and kept in mind when key decisions arise. This is one example of how relevant innovation can occur organically on a daily basis. However, it’s important that when using these personas that the persona itself is kept up to date and accurate when representing their particular segment . Use continuous insight generation to help the persona evolve as the segment does. Ultimately, as long as the method used helps the insights reach more stakeholders across the business efficiently, and influences those daily decision-making processes, insight teams and board members can use any tactic to communicate insights.
‘‘With our customer panel, we are able to amplify the voice of our customers across the organisation to make sure all teams are staying customer-focused.” - Lisa Hulme-Vickerstaff, Head of Insight at Lowell
2. Spotting Trends, Patterns and Needs
Understanding present and past consumer backgrounds, needs, experiences and opinions are one thing, but their behavioural patterns and what incites their actions is typically quite another.
Conducting consumer research to monitor and track consumer behaviour is crucial to stakeholders who need authentic insights to use in their decision-making processes both present and future. Since the very beginning, insight teams have relied on traditional methods such as surveys and focus groups to generate the right data and hunt the ‘why’ behind consumer actions and perceptions, but there is one fundamental issue that most insight experts struggle to overcome - the common gap present between what consumers say they do and what they would actually do in any given scenario.
Consumers typically think they would act in a logical way when imagining a scenario, but when placed in that scenario itself, faced with the real pressures, they would act more emotionally and instinctually, which is hard to communicate in a written or spoken response based in theory.
Tracking to understand a consumer’s actual behaviour will bolster the business’ insight generation efforts, almost eradicating that gap altogether and helping them track those behaviours more effectively. If it doesn’t eradicate the gap, then those insights will at least provide some insight into why that gap is there so insight experts can account for it in the future. This type of research is typically conducted in a long-term research experience that insight teams take on can use to generate continuous insights and observations on consumers’ actions over their words. Using documentary qualitative data, stakeholders have access to a previously under-utilised resource that better informs key decisions.
How to Conduct Consumer Research
When thinking about the best way to conduct consumer research, the eternal dilemma of the consumer perception-action gap mentioned before is one that will plague all insight experts until we discover a way to account for that gap.
This is something that insight professionals have wrestled with for decades after the initial discovery, and while there have been advancements (such as the development of system 1 and system 2 behavioural theories), there has never been a definite answer or path to follow in order to navigate this particular challenge. However, there is a multitude of tools and methods at insight teams’ disposal, and picking the right one for their research experience will determine their success.
Tools and Types of Consumer Research
Qualitative and Quantitative Research is the first obvious answer to how to conduct consumer research. Since the inception of data and insights, market research professionals have created a myriad of tools, methods and tactics to help create the insights industry, home to the insight experts who are here to help businesses and stakeholders understand themselves, their consumers and their future. Through this, we have developed numerous research methods, from the humble survey and in-depth interview to the more modern online methods such as mobile ethnography that help deeply connect consumers, researchers and stakeholders from around the world in mere seconds.
There are numerous market research methods that fall into the category of quantitative or qualitative research, and many more insight platforms on the market dedicated to hosting more traditional research experiences for stakeholders who want to use this traditional line of research to better understand their customers in a formal research setting.
Motivational research is the second consumer research technique to mention, mainly because it was one of the first dedicated market research techniques developed that incorporated psychoanalytical tactics to help insight teams better understand consumer behaviour. Developed by Ernest Dichter in the 1940s, this method was designed with the core belief that individuals don’t always behave in a way that reflects their views, so researchers could use this method to expose their true, unconscious beliefs. The tools used to conduct this research initially were in-depth interviews, but now we can expand this to include other tools such as video focus groups (with break out options for individual questioning), question boards, and more creative qualitative tools that allow insight teams to connect with participants on both an individual and a group level for comparison.
One of the ways that insight experts can conduct motivational research or more traditional research experiences in a formal, structured environment is to create an online dedicated customer community. These are crucial to the success of businesses, whether they are looking to create a positively impactful customer experience, future-proof their primary products and services, benchmark themselves against their direct competitors, or even innovate processes and policies internally to help them become a more efficient and reliable version of themselves. Online customer communities have been called a brand’s secret weapon when building up brand loyalty and skyrocketing themselves to the forefront of their industry.
Market research has taken a lot of tactics and advice from the field of behaviour , whether that’s from behavioural science , behavioural economics , psychology, sociology, or anthropology. These studies of human behaviour in many aspects of life can be directly implemented into market research studies. With insight professionals struggling to understand the unconscious biases impacting consumers’ everyday lives, it’s no wonder that we have turned to these traditionally academic pursuits to help light the way. Insight teams are now using actions to de-bias research data or mitigate the presence of bias during data collection whether that’s from the consumers or researchers.
Behavioural science methods have stretched into most modern forms of market research, including social media intelligence and passive data collection methods such as geolocation and biometric wearable research, with this data being sent to insight teams to analyse and better understand consumer actions over perceptions.
Social media intelligence allows stakeholders to understand how consumers behave in a more informal setting than online customer communities, where consumers can communicate with each other on topics of their own devising without the sense of being observed by insight professionals. Social media platforms can be used similar to dedicated online customer research communities, with insight experts using the brand’s channel to spark topics if they do desire and to communicate with consumers through their comments section and direct messaging, but these platforms are already recruited with a significant amount of consumers that have already started sharing their opinions and experiences with the brand. Social media teams will be able to work well with research teams on this as they will have been dealing with both complaints and recommendations from consumers across the globe.
But, however comfortable digital natives find themselves discussing and connecting with each other online, this is a far from a natural setting. The anonymity or customisability provided by this online setting means that consumers can pretend to be who they’re not. While most of them will have a profile on one website that is completely authentic, they can also create alter egos or different personas to help fulfil or explore a different aspect of themselves or who they want to be. So with this danger outlined from the beginning, insight teams can still take good advantage of this platform of already recruited consumers to understand more about their behaviour, needs opinions and experiences with the brand.
Passive data collection methods are worth considering when it comes to consumer research, geolocation and biometric data as stated before are easily available now with the commercialisation of smartphones and smart watches. Geolocation data can be obtained through brand apps on smartphones, and then used to understand when a consumer interacts with a brand, how frequently they interact, and what they are focussed on when interacting with the brand (e.g. the products/services they buy can be gained from the receipts or documented on the consumer’s profile in their order history).
Biometric data has been historically a little difficult to gain access to since it's been categorised as more personal data than consumer data. But now with smart watches acting as trackers for fitness apps and recording data such as pulse rate, certain insight professionals who have access to that data can cross-examine the geolocation data from the tracker with the pulse rate data to understand how their consumers feel when they come across their store, their products, etc. and this unconscious reaction could help them build better customer experiences that get their heart rate pumping.
Best Practices: Tactics and Techniques
So, once the tools and types of consumer research have been picked, it’s time to look at the best practices that help steer insight experts and stakeholders towards success. There are a number of tactics and techniques needed to help conduct quality consumer research:
1. Recruit and Segment
Should insight teams recruit their participants and then segment them? Or segment to understand their target audience better and then recruit the right people into their research project? Both can be done and lead to success, but when it comes to consumer research, insight teams should segment their consumer base first to make sure they only recruit the right people for their research project.
Consumer segmentation is the first step to understanding your customer base and identifying the right research participants. The research conducted off the back of this sequence will help insight teams improve the research relevance and focus, create research tasks that better engage the research participants based on their segmented characteristics, and build deeper connections between customers and stakeholders, all of which provide a better foundation to build on and engage those research respondents and stakeholders in the research experience. It will also lead to better quality and truly relevant consumer insights.
2. Participant Engagement
After the foundation has been laid, there are ways to capitalise on it and create more ways for participants to engage with the research.
One way we can encourage participant engagement is through the building of trust. Participants won’t want to hand over their personal data or opinions on a platform or to researchers and stakeholders that they don’t trust. This can manifest in two different ways: firstly, on a fundamental level, participants need to trust the technology and the researchers that brands are using to generate these insights. With many issues nowadays with sensitive data being leaked or used against them to extort something out of them, consumers are becoming very careful with the websites that they’re inputting personal data into. Secondly, if they don’t trust the researchers gathering that data, consumers won’t want to hand over their data to people who they believe might misuse it or misplace it. Being transparent with data handling and privacy, or partnering with a research agency that is transparent with data handling and privacy is critical for a successful consumer research experience.
Another way to engage participants once they’ve been mollified in their data security concerns is through moderation and communication throughout the research project. Skilled researchers can get a lot out of even the most stingy of participants. There are a number of communication tools such as emails for task and incentive reminders, comments on research tasks, and then newsletters at the end to provide updates on how the insights have been used or feedback on what strategies have been impacted by the data consumers share. Closing the feedback loop in this way doesn’t just directly impact the growth and evolution of the brand, it also positively impacts the level of consumer trust in the brand, the relationship between brand and consumer, the marketing and sales processes and the research success rates at the very least.
3. Design Human-centric Research
Whether insight teams subscribe to the ‘human experience’ or ‘participant experience’ research concepts, there’s no getting away from the fact that designing research projects with your participants in mind will increase the number of engagement researchers get out of their consumers.
“Creating research experiences for real people is integral to enhancing the value of research for businesses.” - Maria Twigge, Research Director at FlexMR
Designing research experiences takes a lot of work, but it’s worth it for the benefits insight teams can reap - such as an expanded understanding of what questions stakeholders actually need to ask consumers, accounting for the context in which they are posed, and a building a way to bridge the gap to full consumer behaviour understanding. Consumer segmentation at the start of the research experience to help identify the research sample is one of the best ways to understand which consumers will be populating the project, and then insight teams can think about which tools and platforms to use to make sure those consumers are able to navigate through to the end the experience.
Choosing the right tools will also help to encourage and stimulate the right conversations and insight generation opportunities outside of scheduled tasks, which is extremely useful in dedicated customer communities that have areas on the platform where consumers can converse with each other about the brand, the tasks, the questions posed, etc. in downtimes whenever they feel they have the time and inclination.
Understanding the right tools to use also means knowing which secondary methods to employ. While research panels and communities are great platforms for primary research, researchers can also use data mining techniques for social media to gain secondary data, or even gain access to similar research studies so they have data to use in hypotheses that primary data could confirm or deny.
4. Engage Stakeholders
Motivate stakeholders to engage and closely connect brand and customer - that’s the aim of most consumer research attempts, but it can be tricky when stakeholders have numerous other priorities and responsibilities to attend to.
Engaging stakeholders in the research experience has been proven to aid the chances of insights activation both during and at the end of the research project, but getting stakeholders to do more than observe the research report has been a core challenge that we have yet to overcome. Each stakeholder is unique, and as such requires different motivations to engage in the research experience. But educating them on market research, the techniques being used, the consumers being surveyed, etc. and building up their knowledge of the project does help our chances of capturing and keeping their attention.
Stakeholders hold valuable contextual information about the business and the research objectives, which can help insight experts maintain the research project’s relevance throughout any evolution or obstacles that may occur. Allowing them to divulge and see exactly how they can shape a research experience encourages an attachment to the project, questions about how it’s going and maybe even an appearance in an observational sense as research tasks take place.
Connecting stakeholders to the project itself motivate them to better understand the insights that are the result of the project and connect it easier to the business objectives, strategies and other contexts that might be influenced by the insights. This then sparks valuable change that consumers actually want and need, and this, in turn, fuels a connection and closeness between the brand (stakeholders) and consumers that might not have previously been possible. All because of properly conducted and immersive consumer research experiences.
Examples of Consumer Research
The following examples are applications of consumer research taken from FlexMR's library of case studies. In each example, we detail the role that data played in informing key business decisions and the relationship between commercial results & consumer understanding.
Isagenix is a great example of consumer research done well. Founded in 2002, Isagenix is a multinational direct sales company that manufactures and distributes a range of science-based health and wellbeing products. The company seeks to inspire and empower their customers to live their best life through a journey of nutrition, health, and overall wellness.
They created their IsaInsights panel on FlexMR’s InsightHub to achieve a rather ambitious goal: to evolve into the largest health and wellness company in the world. This panel, populated with customers and advocates, was well-used by their in-house insights team, who conducted a rather demanding research schedule that generated continuous insights to inform key decisions about their products, customer experience strategies and future opportunities.
These future opportunities were gathered by continuously recording customer habits, their likes and dislikes and which products they used, how and when. One particular success from this panel was the creation of their popular essential oils range, which was developed step by step in close accordance to the customer insights provided from a number of successive research projects.
To find out more about Isagenix’s research experience read our case study here .
Specsavers adverts are considered by some a national treasure, with their “Should’ve Gone to Specsavers” tagline one of the most recognisable and easily identifiable of most businesses in the United Kingdom. But Specsavers have a difficult job and balancing act when it comes to their carefully-cultivated reputation of being both a commercial brand AND a prominent healthcare professional.
Because of this, Specsavers need to make sure they’re hitting the right tone with every piece of communication and branding they create, and this can’t be achieved without some input from their customers. So Specsavers created a central hub of insights through their panel on the InsightHub so they could run their marketing campaigns, branded communications, product and service concept testing, etc. passed a sample of customers who provided their insights that would influence the final result.
“This [customer research] panel has been essential in balancing creative with clinical messaging in our Glaucoma marketing campaign. We are continuously getting clear answers to take to senior stakeholders and inform final decisions.” - Sarah Marquis, Customer Insights Manager at Specsavers
One memorable campaign that was created in accordance to customer insights was their “Don’t Lose the Picture” Glaucoma awareness campaign. To balance clinical and creative in a way that captured the audience’s attention as well as delivering vital public health information was crucial to getting the word out about the previously relatively unknown eye health disease, but thought thorough concept testing and retesting, Specsavers managed to create a well-received advert that rivalled the original “Should’ve Gone to Specsavers” campaign.
Find out more about Specsavers and their fantastic use of consumer research in our case study here .

About FlexMR
We are The Insights Empowerment Company. We help research, product and marketing teams drive informed decisions with efficient, scalable & impactful insight.
About Emily James
As a professional copywriter, Emily brings our global vision to life through a broad range of industry-leading content.
Stay up to date
You might also like....
10 Common Questions About InsightHu...
With a suite of impactful integrated data collection, analysis and activation tools, FlexMR’s InsightHub platform is used by many insight teams and experts for impactful insight generation and activat...

10 Design Principles to Help Improv...
Surveys have been the most popular research method since the conception of market research. They are a still-flourishing method that stakeholders continually turn to as a first port of call and resear...
The Best Projective Techniques for ...
Online focus groups are one of the most prominent ways to conduct qualitative research for a very good reason: they directly connect brands to customers, so they can truly understand what goes on insi...

8 Key Stages in the Consumer Research Strategy
July 8 2022

- Table of content
What Is Consumer Insights Research And Why It's Important For Any Brand?
Consumer research process and steps, how does peekage run market research, how to optimize the process of conducting consumer research.
If you want to catch and keep your consumer's attention , you really need to peruse the options available on your menu and give them something smart based on their preferences.
Your marketing strategy should not be based on your hunch but solid verifiable facts. In order to grow as a business, you need to know how your products & services are performing with your target audiences, how those consumers are responding to your campaigns, and how these customers feel about your brand.
Customer research can provide you with the missing information.
In today's consumer-centric world, research is key to personalization of products & services, and consistently delivering an excellent experience to your customers comes with a number of benefits, such as:
- Increased purchase frequency
- Higher average order values
- Better referrals and cheaper acquisitions
Additionally, acquiring insights on consumer needs gives you a strategic position over the race on delivering customers what they want -more personalized products and experiences. This way you stay ahead of your competitors and remain in line with consumers' needs.
At its core, consumer research focuses on understanding your consumers by exploring their attitudes, needs, motivations, and behavior as they relate to your brand & products. This helps you to better identify, understand, investigate and hold your customers.
It's nothing unexpected that the majority of professional advertisers make their strategic decisions after a phase of extensive consumer research process.
Read also: Differences Between Market Research and Consumer Insights Research
Consumer insights research is the process of recognizing the inclinations, attitudes, inspirations, and purchasing behavior of the targeted consumers. Utilizing consumer research strategies on this data, shared characteristics among consumer groups are distinguished and classified into client segments and buyer personas. This information then used to make promoting campaigns focusing on a particular fragment or persona.
Consumer research is the key to enhancing your products & services and effectively advertising to clients who want to do commercial enterprise with you. Interviews, surveys, and other consumer research techniques are your dearest companions with regards to aiding your organization reliably to increment its income year on year.
Consumer research strategy is the procedure of gathering facts to first identify the target audiences and afterward focus on their inclinations, insights, attitudes, and shopping drivers for an item, service, or brand.
The main purposes of consumer research are:
- Formalize the ideal customer personas
- Upgrade brand positioning
- Discover new or similar consumers
- Get feedback on current products & services
- Mapping the customer decision-making procedure
Customer research is a part of market research that uses research techniques to provide actionable information about what clients need. Utilizing this data businesses can make changes in their items and services, making them more client-centric thereby expanding consumer loyalty.
Consumer research helps brands understand consumer psychology and create purchasing behavior profiles for them.
A business that has an in-depth comprehension of the client decision-making process is most likely to design an item, decide on a certain price for it, establish a distribution path and promote a product based on customer research insights such that it produces increased consumer satisfaction and loyalty.
The ultimate goal of consumer research is to make a more profound understanding of your target client. You need to know what they care about and what impacts them to make purchasing decisions. This helps you to target them with more customized and significant brand experiences.
Consumers are now inundated with various options & choices and they have boundless data about these products readily available. In fact, they have power over their choices and want only the best.
So how do you make an unforgettable customer experience? By research!
By identifying the needs and inclinations of your clients, you can develop effective methods and strategies to use in your marketing plan. This will help you:
- Leverage your brand positioning compared to the competitors
- Help empower your marketing and product strategy
- Exclude weak points and lessen redundancies
- Remain in line with client opinion ahead of new product launches
- Draw in more clients
- Set the optimized price for your products
- Produce the proper marketing message
- Increase how much your clients spend
- Increase how frequently your clients spend
- Increase your sales
- Decrease your costs
- Refine your approach to customer support.
Now that you know what consumer research is and you understand its importance in developing your business, let's take a closer look at how it's done; the process & steps of conducting consumer insight research.
Also read: How Consumer Insights Help Your Business Grow
The consumer research process began as an extension of the market research process. Just as the results of market research are used to further develop the decision-making potential of a brand or business, so is consumer research.
Consumer research is a sequential procedure. It must be well organized, tied together by the proper method, and upheld by supporting facilities and tools. Without these considerations, you may get into research chaos.
Therefore, you need a framework for conducting consumer research. The consumer research process can be divided into the following steps:
1. Develop research goals
Developing research goals is actually answering the question; "why is the research being conducted? to find out what?" A statement of consumer research objectives can help emphasize the purpose.
2. Define your research personas
A target consumer addresses the specific client segments and ideal buyer personas you wish to analyze.
3. Select your research methods and tools
Before you jump into the research phase, you should create a supporting "foundation". That is to distinguish your key method for gathering information and data.
Consumer data comes in two structures:
Quantitative - data, in the form of numbers
Quantitative consumer research includes extracting facts and statistics from customer opinions. By posing questions like, "how many", "how often", or "how likely", you can record customer needs and inclinations as specific numbers.
Utilizing a qualitative research method, you can gather information around measures such as duration, price, amount, length, etc. You can then utilize this information to shape your product's marketing.
Qualitative - non-numerical data that describe and characterize
A qualitative consumer research strategy gathers the conversational voice of customers (VOC), making sense of the inspirations behind customer behaviors. Open-ended questions, conversations, and observations can help us answer the whats, whys, and hows of consumers' decisions. Furthermore, develop a better comprehension of the consumers' attitudes, beliefs, and values.
Also read: Seven Consumer Research Methods; 2022 Version
4. Collect secondary data
Secondary research tries to interpret your audience's behaviors by utilizing internal and external data. CRM or social media analytics, and different kinds of BI tools come to use here. Utilizing external information such as trend reports, market statistics, and public polls can also help obtain a more accurate image of your target clients.
Secondary research is a strong method to analyze the competition, understand your actual position in the market, and discover new secondary consumers.
Collect secondary data as the earliest stage of your research, it helps finding out if the research has been conducted before and if there is any information that can be used by your business to make informed decisions regarding customers.
Secondary research adds additional background information to your brand strategy. By discovering what your competitors do and finding out what other factors and variables affect the demand on the market, you can refine your brand differentiation on the market.
Thus, as part of customer research, you need to assess the competition. Specifically, collect data about:
- Competition market positioning
- Brand differentiators
- Macro market trends
- Niche market trends
5. Primary research
Primary research can be an exploratory and explicit phase of your consumer research. In the principal case, you are projecting a wider net to comprehend the general customer opinion and market trends. Exploratory research is helpful for consumer segmentation and buyer persona development.
Explicit consumer research plans put the magnifying lens on distinguished areas of interest like brand preference or product usability. For this situation, it's a good idea to work with a specific consumer segment and ask questions related to a specific issue.
In primary research brands or businesses collect their own information or employ a third party to gather information for them. This kind of research utilizes different data collection methods (qualitative and quantitative).
6. Collect and analyze information
Data is gathered and analyzed and inference is drawn to comprehend client behavior and purchase pattern.
7. Prepare a report
At the final stages of your consumer research process, a report is prepared based on all the findings by analyzing information collected so that businesses are able to make informed decisions and think of all probabilities related to customer behavior. By incorporating the study, businesses can become more customer-centric and provide products or services that will help them achieve customer satisfaction.
8. Put consumer research to action
The ultimate objective of consumer research is to illuminate your actions. There are numerous excellent ways of utilizing customer research information:
- Refine your brand positioning and brand statement
- Develop strategies for engaging with secondary clients
- Foster new creative and collateral for advertisement campaigns
- Refine your advertisement targeting to lessen promotion waste
- Expand into new markets with more confidence
Utilizing its app-based platform, Peekage conducts market research by product sampling .
Clients share their information through the application and then the Peekage team discovers the right users to test your product or services and provide you feedback. This strategy is the most efficient way to invest the market research budget and gain actionable insights from your target market.
Read Also: Ultimate guide: product sampling strategies, methods & techniques
By providing proper consumer research insight, strategies that are utilized to draw in customers can be improved and brands can make a profit by knowing what customers need exactly. It is also important to understand the buying behavior of customers to know their attitude towards businesses and products.
Artificial intelligence helped advertisers & marketers with accomplishing precise targeting, effective optimizations, better analysis, and so much more. However, before these items come into play, understanding the customer is on top of any advertiser's list.
Optimizing consumer research can really make the entire procedure more effective, saving businesses tons of time assembling and analyzing data that is of little worth.
There are 4 different ways AI can optimize the consumer research process.
Recruitment Efficiency
Your customer base is expanded. Panel recruitment parameters that expanded properly in one place may not function admirably in an alternate situation. And with steadily developing markets, checking only a couple of fundamental parameters like age, ethnicity, and education is hard enough for a team of staff to work on for weeks or even months.
businesses need niche parameters. For example, interests, work profiles, income level, language proficiency, and more to draw significant insights that give them an upper hand in the market. This kind of information uncovers sweet spots in the target clients that have a high chance of a conversion.
Panel Relevancy Map
Words usually can't do a picture justice. In advertising, this image is worth thousands of hours of man work. In fact, we are discussing the times when advertisers analyze various segments and try to find similar client bases that can be clustered together. AI can do this in a matter of seconds, if not real-time. It analyzes millions of psychographic and demographic elements alongside other incidental factors and makes a relevancy map. This helps the advertiser with building panels of relevant clients based on the targeting variables that the research requests.
Statistically Accurate Panel
You can simply not include all of your clients for research purposes. Yes, you can do it by taking a representative sample of your consumer's society. This means your panel will contain at least one or more clients from each segment of your overall target client. This way you have a panel that is statistically the most accurate representation of your clients.
Engagement Efficiency
While a statistically accurate panel is of importance, the research can only be called effective and successful if the optimal number of consumers take part in the research. Here, the AI helps the advertiser get the maximum number of research respondents at the minimum cost. Engagement patterns help the AI to rank the quality of client segments. The higher the engagement with the research, the higher the quality of the client.
Research that creates impact
In fact, finding out what the client is thinking is technically impossible. businesses can still be very accurate by using the agility and scalability of AI. Making accurate and reliable client panels, running AI-led agile research, and developing strategies based on them is the guaranteed plan for successful consumer research.
Consumer research is a significant endeavor; however, the payoffs are extravagant too. Learning who your consumers are, how they think, and what prompts them to buy your products or services is essential to improving your market presence, growing brand value, and of course income numbers.
Utilizing the above eight steps, you can figure out how to coax clarity out of the tumultuous pile of analytics data and spoken customer insights. Keep in mind: a clear and optimal research method, succinct hypothesis, and supporting tools are the frameworks you need to run effective consumer research.
What customers need should be a part of market research and ought to be carried out routinely. Consumer research provides you with in-depth data about the needs, wants, expectations, and behavior of consumers.
Like the article? Spread the word
Ready to see what we’re building?
More from Peekage

Product Sampling Safe Haven: Contactless Product Sampling
In-person product sampling has long been an essential marketing tactic for consumer packaged goods companies. Still, the practice in its traditional forms came to an abrupt halt when the COVID-19 pandemic began. Some of the…

Basics Of Brand Activation: What Is It, And Why Is It Important?
Brand activation refers to providing a unique, memorable experience to increase brand awareness. Studies show that people need five to seven impressions to remember a brand. A successful brand activation provides a multi-touch brand experience…

Peekage CPG Insights: Prepare for Inflation, Shifting Consumer Habits, and More!
Our mission at Peekage is to help CPG executives stay on top of market trends and track shifts in consumer behavior to make informed decisions. Our regular CPG insights reports aimed at that. We hope…

Consumer Research Explained; Marketers’ Edition
Consumer insights research, in simple words, means the practice of discovering what is driving and motivating your consumers. Either you are selling a product or delivering a service, it is vital to really understand what…
- The Open University
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
About this free course
Become an ou student, download this course, share this free course.

Start this free course now. Just create an account and sign in. Enrol and complete the course for a free statement of participation or digital badge if available.
This course has explored the importance and relevance of understanding customers, not only as business owners, marketers or potential students, but as customers themselves.
It has examined some key marketing concepts and terminology and discussed contemporary approaches to understanding customer behaviour and how behaviour may be interpreted or used to generate certain responses, improving the value of customer relationships.
It has also highlighted some differences between consumer and business-to-business marketing in terms of relationships and decision-making.
If you are thinking of taking your marketing studies further, you may wish to consider embarking on a BA (Honours) Business Management (Marketing) degree. The material for this course is an adapted extract from B206 Understanding customers [ Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. ( Hide tip ) ] , a mandatory module in Stage 2 of the degree, which you can learn more about in the video below.
Transcript: Video 3
[MUSIC PLAYING]
JEANETTE: Hello, my name is Jeanette Hartley. I'm a postgraduate researcher here at the Open University. Congratulations on completing the OpenLearn course. We hope you enjoyed it. Perhaps it's left you wanting more.
We based the course on the introduction to our module B206 Understanding customers . This is a module in the Open University’s BA (Honours) Business Management and Marketing degree. If you are thinking of taking your studies further, why not consider registering for the full module, either on its own or as part of a full time or part time degree with the Open University?
Have you ever wondered why you sometimes emerge from the supermarket with a full trolley, having just gone in for a loaf of bread? In the module Understanding Customers, you will tackle questions like this to help you understand why customers buy. You’ll learn how marketers influence customers, whether as individuals or professional buyers, and pick up some useful skills yourself. You’ll also study how social marketers sell things like healthier lifestyles using the same tools as their commercial counterparts.
This module is ideal if you’re working in marketing, aiming to work in marketing, wanting to gain insights for your own business, or if you simply want to understand more about your own consumer behavior.
The module will enable you to learn about the psychological theories on consumer decision making. You will learn how marketers have taken up models and approaches from social psychology and other disciplines to try and understand processes such as motivation, attitude formation, and how customers select and process persuasive messages. You’ll also learn to identify customer groups and the social and cultural influences on consumption, contemporary trends in consumer research, and how to tap into opinion leadership and followership in social networks. You would even participate in a peer review exercise, where you will use presentation software to draft a poster on which you'll exchange feedback with other students on the module.
Finally, you will learn about organizational business to business buying behavior, relationship mobilizing, and branding in an organizational context, exciting stuff for potential marketers. While there are no formal prerequisites for the module, it would help if you started it with a basic understanding of marketing. This might come either from your existing work experience or from the Open University's module, An Introduction to Business Management.
If you do embark on a course of study, you will be supported throughout by a tutor. You'll also have access to the module website, which includes modules materials, audio and video content, an assessment guide, and online tutorials and forums. B206 Understanding customers starts once a year in October, so if you are interested, act now. Go onto the website, and speak to an advisor.
A Primer on Consumer Behavior by David W. Stewart
Get full access to A Primer on Consumer Behavior and 60K+ other titles, with a free 10-day trial of O'Reilly.
There are also live events, courses curated by job role, and more.

This chapter provides a summary of the links between consumer behavior and marketing planning and action. An understanding of consumer behavior is a prerequisite for managing the marketing function, as well as the business as a whole. A marketer’s responsibility is to understand consumer behavior so that he or she can influence that behavior through the design of products, services, and marketing programs that match the goals and preferences of consumers. In this way, marketers add value to the organizations for which they work, increase customer satisfaction, and improve the quality of life in a society. Individual consumers ...
Get A Primer on Consumer Behavior now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.
Don’t leave empty-handed
Get Mark Richards’s Software Architecture Patterns ebook to better understand how to design components—and how they should interact.
It’s yours, free.

Check it out now on O’Reilly
Dive in for free with a 10-day trial of the O’Reilly learning platform—then explore all the other resources our members count on to build skills and solve problems every day.

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Be a Smart Consumer of Social Science Research

Don’t rely too much on any one study.
Academic studies in the social sciences often find very different results. Given this variability, how should we consume evidence? The immediate answer is to not rely too much on any one study. Whenever possible, look for meta-analyses or systematic reviews that synthesize results from many studies, as they can provide more-credible evidence and sometimes suggest reasons that results differ. Second, when considering how much weight to give a study’s results, pay attention to its sample size. Similarly, consider peculiarities of the sample, context, and implementation. You may also have more confidence in the results of a study if there is some clear, causal mechanism that explains the findings and is constant across settings. Finally, if a study’s results sound too good to be true, they probably are.
Academic studies in the social sciences often find very different results. Even in disciplines like medicine, where one might imagine there to be a direct, physical relationship between the intervention being tested and its consequences, results can vary — but many think the situation is worse in the social sciences. This is because the relationship between an intervention and its effects may depend on multiple factors, and differences in context or implementation can have a large impact on the studies’ results.
- EV Eva Vivalt is a Research Fellow and Lecturer at the Australian National University.
Partner Center
Read the practical framework for leveling up your social media team.
- · Brandwatch Academy
- Forrester Wave
Brandwatch Consumer Research
Formerly the Falcon suite
Formerly Paladin
Published April 18 th 2024
Girl Math: What’s Behind the Viral Trend and What Do Marketers Need to Know?
What is girl math, and how can brands tap into the trend?
Trends on TikTok quickly go viral, and it doesn't take long for them to take other social platforms by storm.
Last year we had girl dinner, and now we have girl math. You can argue about how much this trend really has to do with math, but since the trend went viral, TikTok videos about girl math have been viewed 3.3 billion times at the time of writing.
What's behind girl math, and how can brands tap into this trend for a chance to go viral? With Brandwatch Consumer Research , we took a look at the online conversation around girl math from public social posts, blogs, and forums from March 1, 2023 to February 29, 2024.
Here's what we found.
What is girl math?
First things first. What is girl math? Using the term girl math, consumers are sharing their reasons for buying things they do not necessarily need. We all like to treat ourselves, and not every purchase we make is essential. That’s what girl math is all about.
In posts tagged with girl math, consumers confess what things they buy and what they tell themselves so they don’t feel bad about those purchases. Bought something for less than five dollars? It's basically free. Bought something with cash you found in your bag? That's basically free. Or buying a jacket that your mom loves and wants to wear, too? It only costs half the price.
@kim.snbrg #fy #girlmath ♬ how i love being a woman - editdiaary
Where did the term "girl math" come from? It was first mentioned in late July 2023 on a podcast by three radio hosts from New Zealand. Their TikTok video quickly went viral and the phrase was picked up by other TikTokers who posted their own examples. It didn't take long for the trend to spread across the internet, causing online conversations to spike.
You might like
Spending, saving, investing: consumer finance trends for 2024.
How have consumer behaviors and preferences changed in regard to the financial services sector?
Relatable confessions
The virality of this trend isn't just that people are eager to jump on a new trend, but how relatable these justifications are. Seeing other people "fooling" themselves into spending money or buying things for free inspires us to think about our own mental gymnastics.
Free shipping is one example of this type of thinking. Adding more items to a shopping cart than originally planned to get free shipping gives the illusion of saving money.
Seeing other people thinking the same way can help consumers feel less bad about their shopping habits so it's no surprise that the mood in these discussions is overwhelmingly positive. The most common emotion expressed in online conversations about girl math is joy. Over 40% of emotion-categorized mentions are joyful, with consumers sharing funny and lighthearted posts.
This lighthearted post on X, for example, got over 224k likes:
Feeding negative stereotypes
The girl math trend isn't without controversy. The second most expressed emotion in online conversations is sadness, taking up 26% of emotion-categorized mentions. What's behind this negative emotion?
Critics of the girl math trend worry that, all fun aside, it can feed into negative stereotypes about women not knowing anything about finances and how to spend money responsibly.
The perception that women are not good with money is rooted in misogynistic attitudes. It took women a long time to gain their financial freedom, but these stereotypes persist to this day. In pop culture, a shopaholic is usually portrayed as a woman, and the Guardian found in a study that 65% of financial content aimed at women portrays them as excessive spenders who need to cut back.
Journalist Meredith Clark also sees the girls' math trend as a sign that women are still apologetic about their behavior. She writes in her Independent article :
“It’s an age-old trope that women are always apologizing, for themselves and for others. Really, what girl math shows is that we’re even apologizing for what we choose to spend our money on. We can’t buy something just because it makes us happy.”
Behind the TikTok Trend: How Often Do You Think About the Roman Empire?
When trends transcend TikTok.
How can brands jump on the girl math trend?
Jumping on internet trends is a great opportunity for brands to connect with their target audience. While the online conversation around girl math is mostly fun, there is also some controversy. Brands need to be careful not to promote negative stereotypes or risk backlash .
Here are some tips to consider before trying to tap into the girl math trend:
1. Keep an eye on emerging trends
In general, analyzing online conversations with consumer intelligence platforms like Brandwatch Consumer Research is a great way to keep an eye on emerging trends. It helps you identify trends early and get an idea of how people are talking about the trend. Pro tip: Look at the sentiment and see if there's any controversy –it may be better for your brand to stay away from the trend.
2. Does the trend fit your brand?
Once you know what the trend is about and how your target audience is talking about it, you'll want to think about how the trend fits with your brand. If your social media communication is more serious, it may not be a good idea to start posting a meme like everyone else. Instead, you might choose to educate your audience about the trend.
3. Keep the tone light and fun
This trend is not about being serious. It's about sharing relatable examples with a good portion of humor. The girl math trend is perfect for posting a meme on Instagram or a short funny video on TikTok. Keep it lighthearted, but don't forget that it has to be relevant to your brand and your audience.
4. Partner with influencers
Most girl math content is driven by personal accounts sharing their thoughts and creating funny memes. Partnering with influencers can not only expose you to a new audience, but influencers are usually good at spotting trends and turning them into fun and engaging content. Make sure to take their ideas into account – they may be able to take your content further than you’d imagined.
5. Take the opportunity to promote discounts
A funny and relatable meme from time to time is a great way to connect with your audience. But don't forget to consider what's in it for the consumer. Why not take advantage of the trend and promote your loyalty programs or offer a special discount?
Here are some inspiring examples of brands using the girl math trend in their content:
Instagram post from Sephora
Tiktok video from nyx cosmetics.
@nyxcosmetics 5th night meal prepping shine loud 🍽️ og vid #credit @Flavia Jacintho #girlmath #girldinner #makeuphaul #nyxcosmetics ♬ original sound - NYX Professional Makeup
Instagram reel from Pizza Hut and content creator Anna Sitar
Tiktok video from five below.
@fivebelow the girl math all checks out to us 💁♀️ if your shopping haul was all deals, does it even count as real money? 🤔 #fivebelowfinds #girlmath ♬ original sound - Five Below - Five Below
The internet moves fast, and trends come and go in the blink of an eye. Brands that ignore these trends miss valuable opportunities to connect with their target audiences. Consumer intelligence platforms like Brandwatch Consumer Research can help companies identify emerging online trends and how consumers are talking about a specific topic.
For more consumer finance trends, read our new report on the financial services sector.
Michaela Vogl
Marketing Content Specialist
Share this post
Brandwatch bulletin.
Offering up analysis and data on everything from the events of the day to the latest consumer trends. Subscribe to keep your finger on the world’s pulse.
Free report
How have consumer behaviors and preferences changed in the financial services sector?.
More in online trends
Streaming wars: the most common customer pain points.
By Michaela Vogl Apr 11
Saving, Spending, and Investing: The Biggest Consumer Trends in Finance for 2024
By Michaela Vogl Apr 9
5 Social Media News Stories You Need to Read Right Now
By Yasmin Pierre Apr 8
Beyond Binge-Watching: What’s Trending in the Media and Entertainment Industry?
By Michaela Vogl Mar 13
We value your privacy
We use cookies to improve your experience and give you personalized content. Do you agree to our cookie policy?
By using our site you agree to our use of cookies — I Agree
Falcon.io is now part of Brandwatch. You're in the right place!
Existing customer? Log in to access your existing Falcon products and data via the login menu on the top right of the page. New customer? You'll find the former Falcon products under 'Social Media Management' if you go to 'Our Suite' in the navigation.
Paladin is now Influence. You're in the right place!
Brandwatch acquired Paladin in March 2022. It's now called Influence, which is part of Brandwatch's Social Media Management solution. Want to access your Paladin account? Use the login menu at the top right corner.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In 1974, consumer research finally got its own journal with the launch of the Journal of Consumer Research (JCR). ... Conclusion. At any given moment in time, the focal concepts, methods, and aims of consumer-behavior scholarship reflect both the prior development of the field and trends in the larger scientific community. However, despite ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
Consumer research, also known as market research or consumer insights research, is defined as the process of collecting and analyzing information about consumers' preferences, behaviors, and attitudes toward products, services, brands, or market trends. This type of research is essential for businesses and organizations to make informed ...
The conclusion in a research paper is the final section, where you need to summarize your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. ... and public awareness campaigns to change consumer behavior. The responsibility falls on governments, businesses, and individuals to take immediate actions to protect our planet ...
Consumer research has practical relevance when it can help inform or improve marketing strategies which attempt to influence consumer behavior. For example, improving customer satisfaction is a key goal for marketers and retailers. ... Then, at the conclusion of writing the paper, there is an attempt (and sometimes struggle) to come up with ...
In this article, we document the evolution of research trends (concepts, methods, and aims) within the field of consumer behavior, from the time of its early development to the present day, as a multidisciplinary area of research within marketing. We describe current changes in retailing and real-world consumption and offer suggestions on how to use observations of consumption phenomena to ...
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion: Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study. Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results ...
subject for consumer research. From this argument, it follows that consumer research studies consummation (in all its various facets, including its potential breakdowns). Many will agree with this conclusion. Yet most will also acknowledge that the study of consummation is not the meaning that usually leaps to mind when one hears the term ...
Step 1: Restate the problem. Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper. When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
Consumer research is a part of market research in which inclination, motivation and purchase behavior of the targeted customers are identified. Consumer research helps businesses or organizations understand customer psychology and create detailed purchasing behavior profiles. It uses research techniques to provide systematic information about ...
Your institution could be eligible to free or deeply discounted online access to Journal of Consumer Research through the Oxford Developing Countries Initiative. Find out more. Publishes interdisciplinary scholarly research that describes and explains consumer behavior. Empirical, theoretical, and methodological articles span.
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research.
People are more willing to go into debt for experiential purchases than for material purchases, according to research by Eesha Sharma, PhD, an associate professor of business administration at Dartmouth's Tuck School of Business (Journal of Consumer Research, Vol. 44, No. 5, 2018). This seems to be because experiences are often time-dependent ...
Motivational research is the second consumer research technique to mention, mainly because it was one of the first dedicated market research techniques developed that incorporated psychoanalytical tactics to help insight teams better understand consumer behaviour. Developed by Ernest Dichter in the 1940s, this method was designed with the core ...
Inevitably, these changes lead to changed consumer behavior studies by which, when, how, and why the topics are studied. Like any other discipline, systematic analysis of the knowledge development status of consumer behavior field is critical in ensuring its future growth (Williams & Plouffe, 2007).It is of a greater importance for a field of research such as consumer behavior that, as ...
Definition, Types, Examples and Best Practices. By Nick Jain. Published on: June 26, 2023. Customer research is defined as the systematic process of gathering and analyzing information about customers, their behaviors, needs, preferences, and experiences. Learn more about customer research with types, examples and best practices.
Conclusion. Consumer research is a significant endeavor; however, the payoffs are extravagant too. Learning who your consumers are, how they think, and what prompts them to buy your products or services is essential to improving your market presence, growing brand value, and of course income numbers. ...
Conclusion. This course has explored the importance and relevance of understanding customers, not only as business owners, marketers or potential students, but as customers themselves. ... contemporary trends in consumer research, and how to tap into opinion leadership and followership in social networks. You would even participate in a peer ...
Conclusion. This chapter provides a summary of the links between consumer behavior and marketing planning and action. An understanding of consumer behavior is a prerequisite for managing the marketing function, as well as the business as a whole. A marketer's responsibility is to understand consumer behavior so that he or she can influence ...
Whenever possible, look for meta-analyses or systematic reviews that synthesize results from many studies, as they can provide more-credible evidence and sometimes suggest reasons that results ...
Consumer behaviour is the study of how a customer, or a group of customers select, buy, use, and. dispose ideas towards the products or services in. order to satisfy their needs and wants (Chand ...
In this research I have surveyed that how frequently and how much chocolate they consume, whether they buy small, big or family pack. Trend of ongoing changes in their likings has been shown in the report. In this report I have tried to explain the entire research and facts product wise. CONSUMER PREFERENCE All marketing starts with the consumer.
A recent research project led by Brian Whelan, assistant professor of marketing in the College of Business at Western Carolina University, reaches the surprising conclusion that a higher level of social media activity on behalf of instantly recognizable brands results in a decrease in consumer attachment to those brands.
Conclusion. The internet moves fast, and trends come and go in the blink of an eye. Brands that ignore these trends miss valuable opportunities to connect with their target audiences. Consumer intelligence platforms like Brandwatch Consumer Research can help companies identify emerging online trends and how consumers are talking about a ...