- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course

Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 4 Class 10 Quadratic Equations
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Updated for Latest NCERT for 2023-2024 Boards.
Get NCERT Solutions for all exercise questions and examples of Chapter 4 Class 10 Quadratic Equations free at Teachoo. Answers to each and every question is provided video solutions.
In this chapter, we will learn
- What is a Quadratic Equation
- What is the Standard Form of a Quadratic Equation
- Solution of a Quadratic Equation by Factorisation ( Splitting the Middle Term method)
- Solving a Quadratic Equation by Completing the Square
- Solving a Quadratic Equation using D Formula (x = -b ± √b 2 - 4ac / 2a)
- Checking if roots are real, equal or no real roots (By Checking the value of D = b 2 - 4ac)
This chapter is divided into two parts - Serial Order Wise, Concept Wise
In Serial Order Wise, the chapter is divided into exercise questions and examples.
In Concept Wise, the chapter is divided into concepts. First the concepts are explained, and then the questions of the topic are solved - from easy to difficult.
We suggest you do the Chapter from Concept Wise - it is the Teachoo (टीचू) way of learning.
Note: When you click on a link, the first question of the exercise will open. To open other question of the exercise, go to bottom of the page. There is a list with arrows. It has all the questions with Important Questions also marked.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- Chapter 4: Quadratic Equations
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
Ncert solutions class 10 maths chapter 4 – cbse free pdf download.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations contain all the solutions to the problems provided in the Class 10 Maths NCERT textbook for CBSE exam preparations. The questions from every section are framed and solved accurately by the subject experts. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 are detailed and step-by-step guides to all the queries of the students. The exercises present in the chapter should be dealt with utmost sincerity if one wants to score well in the examinations. Maths is a subject that requires a good understanding and a lot of practice. The tips and tricks to solve the problems easily are also provided here. A quadratic equation in the variable x is an equation of the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, c are real numbers, a ≠ 0. That is, ax 2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 is called the standard form of a quadratic equation.
Download Exclusively Curated Chapter Notes for Class 10 Maths Chapter – 4 Quadratic Equations
Download most important questions for class 10 maths chapter – 4 quadratic equations.
Quadratic equations arise in several situations around us. Hence, students should give special attention to learning the concepts related to this chapter of the latest CBSE Syllabus for 2023-24 thoroughly to excel in Class 10 Maths examinations. NCERT Solutions help the students in learning these concepts as well as in evaluating themselves. Practising these solutions repeatedly is bound to help the students in overcoming their shortcomings. Maths has either a correct answer or a wrong one. Therefore, it is imperative to concentrate while solving the questions to score full marks.
- Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions
- Chapter 6 Triangles
- Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
- Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
- Chapter 10 Circles
- Chapter 11 Constructions
- Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter 14 Statistics
- Chapter 15 Probability
- Exercise 4.1
- Exercise 4.2
- Exercise 4.3
- Exercise 4.4
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access answers to NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations
Exercise 4.1 page: 73.
1. Check whether the following are quadratic equations:
(i) (x + 1) 2 = 2(x – 3)
(ii) x 2 – 2x = (–2) (3 – x)
(iii) (x – 2)(x + 1) = (x – 1)(x + 3)
(iv) (x – 3)(2x +1) = x(x + 5)
(v) (2x – 1)(x – 3) = (x + 5)(x – 1)
(vi) x 2 + 3x + 1 = (x – 2) 2
(vii) (x + 2) 3 = 2x (x 2 – 1)
(viii) x 3 – 4x 2 – x + 1 = (x – 2) 3
(x + 1) 2 = 2(x – 3)
By using the formula for (a+b) 2 = a 2 +2ab+b 2
⇒ x 2 + 2x + 1 = 2x – 6
⇒ x 2 + 7 = 0
The above equation is in the form of ax 2 + bx + c = 0
Therefore, the given equation is a quadratic equation.
(ii) Given, x 2 – 2x = (–2) (3 – x)
⇒ x 2 – 2x = -6 + 2x
⇒ x 2 – 4x + 6 = 0
(iii) Given, (x – 2)(x + 1) = (x – 1)(x + 3)
By multiplication,
⇒ x 2 – x – 2 = x 2 + 2x – 3
⇒ 3x – 1 = 0
The above equation is not in the form of ax 2 + bx + c = 0
Therefore, the given equation is not a quadratic equation.

(iv) Given, (x – 3)(2x +1) = x(x + 5)
⇒ 2x 2 – 5x – 3 = x 2 + 5x
⇒ x 2 – 10x – 3 = 0

(v) Given, (2x – 1)(x – 3) = (x + 5)(x – 1)
⇒ 2x 2 – 7x + 3 = x 2 + 4x – 5
⇒ x 2 – 11x + 8 = 0
The above equation is in the form of ax 2 + bx + c = 0.
(vi) Given, x 2 + 3x + 1 = (x – 2) 2
By using the formula for (a-b) 2 =a 2 -2ab+b 2
⇒ x 2 + 3x + 1 = x 2 + 4 – 4x
⇒ 7x – 3 = 0

(vii) Given, (x + 2) 3 = 2x(x 2 – 1)
By using the formula for (a+b) 3 = a 3 +b 3 +3ab(a+b)
⇒ x 3 + 8 + x 2 + 12x = 2x 3 – 2x
⇒ x 3 + 14x – 6x 2 – 8 = 0
(viii) Given, x 3 – 4x 2 – x + 1 = (x – 2) 3
By using the formula for (a-b) 3 = a 3 -b 3 -3ab(a-b)
⇒ x 3 – 4x 2 – x + 1 = x 3 – 8 – 6x 2 + 12x
⇒ 2x 2 – 13x + 9 = 0
2. Represent the following situations in the form of quadratic equations:
(i) The area of a rectangular plot is 528 m 2 . The length of the plot (in metres) is one more than twice its breadth. We need to find the length and breadth of the plot.
(ii) The product of two consecutive positive integers is 306. We need to find the integers.
(iii) Rohan’s mother is 26 years older than him. The product of their ages (in years) 3 years from now will be 360. We would like to find Rohan’s present age.
(iv) A train travels a distance of 480 km at a uniform speed. If the speed had been 8 km/h less, then it would have taken
(i) Let us consider,
The breadth of the rectangular plot = x m
Thus, the length of the plot = (2x + 1) m
As we know,
Area of rectangle = length × breadth = 528 m 2
Putting the value of the length and breadth of the plot in the formula, we get,
(2x + 1) × x = 528
⇒ 2x 2 + x =528
⇒ 2x 2 + x – 528 = 0
Therefore, the length and breadth of the plot satisfy the quadratic equation, 2x 2 + x – 528 = 0, which is the required representation of the problem mathematically.

(ii) Let us consider,
The first integer number = x
Thus, the next consecutive positive integer will be = x + 1
Product of two consecutive integers = x × (x +1) = 306
⇒ x 2 + x = 306
⇒ x 2 + x – 306 = 0
Therefore, the two integers x and x+1 satisfy the quadratic equation, x 2 + x – 306 = 0, which is the required representation of the problem mathematically.
(iii) Let us consider,
Age of Rohan’s = x years
Therefore, as per the given question,
Rohan’s mother’s age = x + 26
After 3 years,
Age of Rohan’s = x + 3
Age of Rohan’s mother will be = x + 26 + 3 = x + 29
The product of their ages after 3 years will be equal to 360, such that
(x + 3)(x + 29) = 360
⇒ x 2 + 29x + 3x + 87 = 360
⇒ x 2 + 32x + 87 – 360 = 0
⇒ x 2 + 32x – 273 = 0
Therefore, the age of Rohan and his mother satisfies the quadratic equation, x 2 + 32x – 273 = 0, which is the required representation of the problem mathematically.

(iv) Let us consider,
The speed of the train = x km/h
Time taken to travel 480 km = 480/x km/hr
As per second condition, the speed of train = ( x – 8) km/h
Also given, the train will take 3 hours to cover the same distance.
Therefore, time taken to travel 480 km = (480/x)+3 km/h
Speed × Time = Distance
( x – 8)(480/ x )+ 3 = 480
⇒ 480 + 3 x – 3840/ x – 24 = 480
⇒ 3 x – 3840/ x = 24
⇒ x 2 – 8 x – 1280 = 0
Therefore, the speed of the train satisfies the quadratic equation, x 2 – 8 x – 1280 = 0, which is the required representation of the problem mathematically.

Exercise 4.2 Page: 76
1. Find the roots of the following quadratic equations by factorisation:
(i) x 2 – 3x – 10 = 0 (ii) 2x 2 + x – 6 = 0 (iii) √2 x 2 + 7x + 5√2 = 0 (iv) 2x 2 – x +1/8 = 0 (v) 100x 2 – 20x + 1 = 0
(i) Given, x 2 – 3 x – 10 =0
Taking L.H.S.,
=> x 2 – 5 x + 2 x – 10
=> x ( x – 5) + 2( x – 5)
=>( x – 5)( x + 2)
The roots of this equation, x 2 – 3 x – 10 = 0 are the values of x for which ( x – 5)( x + 2) = 0
Therefore, x – 5 = 0 or x + 2 = 0
=> x = 5 or x = -2
(ii) Given, 2 x 2 + x – 6 = 0
=> 2 x 2 + 4 x – 3 x – 6
=> 2 x ( x + 2) – 3( x + 2)
=> ( x + 2)(2 x – 3)
The roots of this equation, 2 x 2 + x – 6=0 are the values of x for which ( x x + 2)(2 x – 3) = 0
Therefore, x + 2 = 0 or 2 x – 3 = 0
=> x = -2 or x = 3/2
(iii) √2 x 2 + 7 x + 5√2=0
=> √2 x 2 + 5 x + 2 x + 5√2
=> x (√2 x + 5) + √2(√2 x + 5)= (√2 x + 5)( x + √2)
The roots of this equation, √2 x 2 + 7 x + 5√2=0 are the values of x for which (√2 x + 5)( x + √2) = 0
Therefore, √2 x + 5 = 0 or x + √2 = 0
=> x = -5/√2 or x = -√2
(iv) 2 x 2 – x +1/8 = 0
=1/8 (16 x 2 – 8 x + 1)
= 1/8 (16 x 2 – 4 x -4 x + 1)
= 1/8 (4 x (4 x – 1) -1(4 x – 1))
= 1/8 (4 x – 1) 2
The roots of this equation, 2 x 2 – x + 1/8 = 0, are the values of x for which (4 x – 1) 2 = 0
Therefore, (4 x – 1) = 0 or (4 x – 1) = 0
⇒ x = 1/4 or x = 1/4
(v) Given, 100x 2 – 20x + 1=0
= 100x 2 – 10x – 10x + 1
= 10x(10x – 1) -1(10x – 1)
= (10x – 1) 2
The roots of this equation, 100x 2 – 20x + 1=0, are the values of x for which (10x – 1) 2 = 0
∴ (10x – 1) = 0 or (10x – 1) = 0
⇒x = 1/10 or x = 1/10
2. Solve the problems given in Example 1.
Represent the following situations mathematically:
(i) John and Jivanti together have 45 marbles. Both of them lost 5 marbles each, and the product of the number of marbles they now have is 124. We would like to find out how many marbles they had to start with.
(ii) A cottage industry produces a certain number of toys in a day. The cost of production of each toy (in rupees) was found to be 55 minus the number of toys produced in a day. On a particular day, the total cost of production was Rs. 750. We would like to find out the number of toys produced on that day.
(i) Let us say the number of marbles John has = x
Therefore, the number of marble Jivanti has = 45 – x
After losing 5 marbles each,
Number of marbles John has = x – 5
Number of marble Jivanti has = 45 – x – 5 = 40 – x
Given that the product of their marbles is 124.
∴ ( x – 5)(40 – x ) = 124
⇒ x 2 – 45 x + 324 = 0
⇒ x 2 – 36 x – 9 x + 324 = 0
⇒ x ( x – 36) -9( x – 36) = 0
⇒ ( x – 36)( x – 9) = 0
Thus, we can say,
x – 36 = 0 or x – 9 = 0
⇒ x = 36 or x = 9
If John’s marbles = 36
Then, Jivanti’s marbles = 45 – 36 = 9
And if John’s marbles = 9
Then, Jivanti’s marbles = 45 – 9 = 36
(ii) Let us say the number of toys produced in a day is x .
Therefore, cost of production of each toy = Rs(55 – x )
Given the total cost of production of the toys = Rs 750
∴ x (55 – x ) = 750
⇒ x 2 – 55 x + 750 = 0
⇒ x 2 – 25 x – 30 x + 750 = 0
⇒ x ( x – 25) -30( x – 25) = 0
⇒ ( x – 25)( x – 30) = 0
Thus, either x -25 = 0 or x – 30 = 0
⇒ x = 25 or x = 30
Hence, the number of toys produced in a day will be either 25 or 30.
3. Find two numbers whose sum is 27 and product is 182.
Let us say the first number is x, and the second number is 27 – x.
Therefore, the product of two numbers
x(27 – x) = 182
⇒ x 2 – 27x – 182 = 0
⇒ x 2 – 13x – 14x + 182 = 0
⇒ x(x – 13) -14(x – 13) = 0
⇒ (x – 13)(x -14) = 0
Thus, either, x = -13 = 0 or x – 14 = 0
⇒ x = 13 or x = 14
Therefore, if first number = 13, then second number = 27 – 13 = 14
And if first number = 14, then second number = 27 – 14 = 13
Hence, the numbers are 13 and 14.
4. Find two consecutive positive integers, the sum of whose squares is 365.
Let us say the two consecutive positive integers are x and x + 1.
Therefore, as per the given questions,
x 2 + ( x + 1) 2 = 365
⇒ x 2 + x 2 + 1 + 2 x = 365
⇒ 2 x 2 + 2x – 364 = 0
⇒ x 2 + x – 182 = 0
⇒ x 2 + 14 x – 13 x – 182 = 0
⇒ x ( x + 14) -13( x + 14) = 0
⇒ ( x + 14)( x – 13) = 0
Thus, either, x + 14 = 0 or x – 13 = 0,
⇒ x = – 14 or x = 13
Since the integers are positive, x can be 13 only.
∴ x + 1 = 13 + 1 = 14
Therefore, two consecutive positive integers will be 13 and 14.
5. The altitude of a right triangle is 7 cm less than its base. If the hypotenuse is 13 cm, find the other two sides.
Let us say the base of the right triangle is x cm.
Given, the altitude of right triangle = (x – 7) cm
From Pythagoras’ theorem, we know,
Base 2 + Altitude 2 = Hypotenuse 2
∴ x 2 + (x – 7) 2 = 13 2
⇒ x 2 + x 2 + 49 – 14x = 169
⇒ 2x 2 – 14x – 120 = 0
⇒ x 2 – 7x – 60 = 0
⇒ x 2 – 12x + 5x – 60 = 0
⇒ x(x – 12) + 5(x – 12) = 0
⇒ (x – 12)(x + 5) = 0
Thus, either x – 12 = 0 or x + 5 = 0,
⇒ x = 12 or x = – 5
Since sides cannot be negative, x can only be 12.
Therefore, the base of the given triangle is 12 cm, and the altitude of this triangle will be (12 – 7) cm = 5 cm.
6. A cottage industry produces a certain number of pottery articles in a day. It was observed on a particular day that the cost of production of each article (in rupees) was 3 more than twice the number of articles produced on that day. If the total cost of production on that day was Rs.90, find the number of articles produced and the cost of each article.
Let us say the number of articles produced is x .
Therefore, cost of production of each article = Rs (2 x + 3)
Given the total cost of production is Rs.90
∴ x (2 x + 3) = 90
⇒ 2 x 2 + 3 x – 90 = 0
⇒ 2 x 2 + 15 x -12 x – 90 = 0
⇒ x (2 x + 15) -6(2 x + 15) = 0
⇒ (2 x + 15)( x – 6) = 0
Thus, either 2 x + 15 = 0 or x – 6 = 0
⇒ x = -15/2 or x = 6
As the number of articles produced can only be a positive integer, x can only be 6.
Hence, the number of articles produced = 6
Cost of each article = 2 × 6 + 3 = Rs 15
Exercise 4.3 Page: 87
1. Find the roots of the following quadratic equations, if they exist, by the method of completing the square:
(i) 2 x 2 – 7 x +3 = 0
(ii) 2 x 2 + x – 4 = 0 (iii) 4 x 2 + 4√3 x + 3 = 0
(iv) 2 x 2 + x + 4 = 0
(i) 2 x 2 – 7 x + 3 = 0
⇒ 2 x 2 – 7 x = – 3
Dividing by 2 on both sides, we get
⇒ x 2 -7x/2 = -3/2
⇒ x 2 -2 × x ×7/4 = -3/2
On adding (7/4) 2 to both sides of the equation, we get
⇒ (x) 2 -2×x×7/4 +(7/4) 2 = (7/4) 2 -3/2
⇒ (x-7/4) 2 = (49/16) – (3/2)
⇒(x-7/4) 2 = 25/16
⇒(x-7/4) 2 = ±5/4
⇒ x = 7/4 ± 5/4
⇒ x = 7/4 + 5/4 or x = 7/4 – 5/4
⇒ x = 12/4 or x = 2/4
⇒ x = 3 or x = 1/2
(ii) 2x 2 + x – 4 = 0
⇒ 2x 2 + x = 4
Dividing both sides of the equation by 2, we get
⇒ x 2 +x/2 = 2
Now on adding (1/4) 2 to both sides of the equation, we get,
⇒ (x) 2 + 2 × x × 1/4 + (1/4) 2 = 2 + (1/4) 2
⇒ (x + 1/4) 2 = 33/16
⇒ x + 1/4 = ± √33/4
⇒ x = ± √33/4 – 1/4
⇒ x = (± √33-1)/4
Therefore, either x = (√33-1)/4 or x = (-√33-1)/4
(iii) 4x 2 + 4√3x + 3 = 0
Converting the equation into a 2 +2ab+b 2 form, we get,
⇒ (2x) 2 + 2 × 2x × √3 + (√3) 2 = 0
⇒ (2x + √3) 2 = 0
⇒ (2x + √3) = 0 and (2x + √3) = 0
Therefore, either x = -√3/2 or x = -√3/2
(iv) 2x 2 + x + 4 = 0
⇒ 2x 2 + x = -4
⇒ x 2 + 1/2x = 2
⇒ x 2 + 2 × x × 1/4 = -2
By adding (1/4) 2 to both sides of the equation, we get
⇒ (x) 2 + 2 × x × 1/4 + (1/4) 2 = (1/4) 2 – 2
⇒ (x + 1/4) 2 = 1/16 – 2
⇒ (x + 1/4) 2 = -31/16
As we know, the square of numbers cannot be negative.
Therefore, there is no real root for the given equation, 2x 2 + x + 4 = 0
2. Find the roots of the quadratic equations given in Q.1 above by applying the quadratic formula.
(i) 2x 2 – 7x + 3 = 0
On comparing the given equation with ax 2 + bx + c = 0, we get,
a = 2, b = -7 and c = 3
By using the quadratic formula, we get,
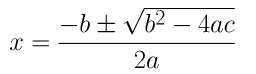
⇒ x = (7±√(49 – 24))/4
⇒ x = (7±√25)/4
⇒ x = (7±5)/4
⇒ x = (7+5)/4 or x = (7-5)/4
⇒ x = 12/4 or 2/4
∴ x = 3 or 1/2
a = 2, b = 1 and c = -4
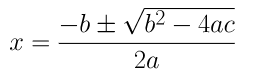
⇒x = (-1±√1+32)/4
⇒x = (-1±√33)/4
∴ x = (-1+√33)/4 or x = (-1-√33)/4
(iii) 4x 2 + 4√3x + 3 = 0
On comparing the given equation with ax 2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 4, b = 4√3 and c = 3
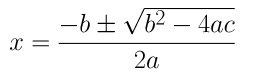
⇒ x = (-4√3±√48-48)/8
⇒ x = (-4√3±0)/8
∴ x = -√3/2 or x = -√3/2
(iv) 2x 2 + x + 4 = 0
a = 2, b = 1 and c = 4
By using the quadratic formula, we get
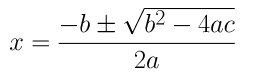
⇒ x = (-1±√1-32)/4
⇒ x = (-1±√-31)/4
As we know, the square of a number can never be negative. Therefore, there is no real solution for the given equation.
3. Find the roots of the following equations:
(i) x-1/x = 3, x ≠ 0 (ii) 1/x+4 – 1/x-7 = 11/30, x = -4, 7
(i) x-1/x = 3
⇒ x 2 – 3x -1 = 0
a = 1, b = -3 and c = -1
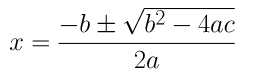
⇒ x = (3±√9+4)/2
⇒ x = (3±√13)/2
∴ x = (3+√13)/2 or x = (3-√13)/2
(ii) 1/x+4 – 1/x-7 = 11/30 ⇒ x-7-x-4/(x+4)(x-7) = 11/30
⇒ -11/(x+4)(x-7) = 11/30
⇒ (x+4)(x-7) = -30
⇒ x 2 – 3x – 28 = 30
⇒ x 2 – 3x + 2 = 0
We can solve this equation by factorisation method now.
⇒ x 2 – 2x – x + 2 = 0
⇒ x(x – 2) – 1(x – 2) = 0
⇒ (x – 2)(x – 1) = 0
⇒ x = 1 or 2
4. The sum of the reciprocals of Rehman’s age (in years) 3 years ago and 5 years from now is 1/3. Find his present age.
Let us say the present age of Rahman is x years.
Three years ago, Rehman’s age was ( x – 3) years.
Five years after, his age will be ( x + 5) years.
Given the sum of the reciprocals of Rehman’s ages 3 years ago and after 5 years is equal to 1/3.
∴ 1/ x -3 + 1/ x -5 = 1/3
(x +5+ x -3)/( x -3)( x +5) = 1/3
(2 x +2)/( x -3)( x +5) = 1/3
⇒ 3(2 x + 2) = ( x -3)( x +5)
⇒ 6 x + 6 = x 2 + 2 x – 15
⇒ x 2 – 4 x – 21 = 0
⇒ x 2 – 7 x + 3 x – 21 = 0
⇒ x ( x – 7) + 3( x – 7) = 0
⇒ ( x – 7)( x + 3) = 0
⇒ x = 7, -3
As we know, age cannot be negative.
Therefore, Rahman’s present age is 7 years.
5. In a class test, the sum of Shefali’s marks in Mathematics and English is 30. Had she got 2 marks more in Mathematics and 3 marks less in English, the product of their marks would have been 210. Find her marks in the two subjects.
Let us say the marks of Shefali in Maths be x.
Then, the marks in English will be 30 – x.
As per the given question,
(x + 2)(30 – x – 3) = 210
(x + 2)(27 – x) = 210
⇒ -x 2 + 25x + 54 = 210
⇒ x 2 – 25x + 156 = 0
⇒ x 2 – 12x – 13x + 156 = 0
⇒ x(x – 12) -13(x – 12) = 0
⇒ (x – 12)(x – 13) = 0
⇒ x = 12, 13
Therefore, if the marks in Maths are 12, then marks in English will be 30 – 12 = 18, and if the marks in Maths are 13, then marks in English will be 30 – 13 = 17 .
6. The diagonal of a rectangular field is 60 metres more than the shorter side. If the longer side is 30 metres more than the shorter side, find the sides of the field.
Let us say the shorter side of the rectangle is x m.
Then, larger side of the rectangle = ( x + 30) m
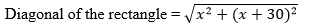
As given, the length of the diagonal is = x + 30 m
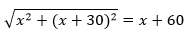
⇒ x 2 + ( x + 30) 2 = ( x + 60) 2
⇒ x 2 + x 2 + 900 + 60 x = x 2 + 3600 + 120 x
⇒ x 2 – 60 x – 2700 = 0
⇒ x 2 – 90 x + 30 x – 2700 = 0
⇒ x ( x – 90) + 30( x -90) = 0
⇒ ( x – 90)( x + 30) = 0
⇒ x = 90, -30
However, the side of the field cannot be negative. Therefore, the length of the shorter side will be 90 m.
And the length of the larger side will be (90 + 30) m = 120 m.
7. The difference of the squares of two numbers is 180. The square of the smaller number is 8 times the larger number. Find the two numbers.
Let us say the larger and smaller number be x and y, respectively.
As per the question given,
x 2 – y 2 = 180 and y 2 = 8 x
⇒ x 2 – 8 x = 180
⇒ x 2 – 8 x – 180 = 0
⇒ x 2 – 18 x + 10 x – 180 = 0
⇒ x ( x – 18) +10( x – 18) = 0
⇒ ( x – 18)( x + 10) = 0
⇒ x = 18, -10
However, the larger number cannot be considered a negative number, as 8 times the larger number will be negative, and hence, the square of the smaller number will be negative, which is not possible.
Therefore, the larger number will be 18 only.
∴ y 2 = 8x = 8 × 18 = 144
⇒ y = ±√144 = ±12
∴ Smaller number = ±12
Therefore, the numbers are 18 and 12 or 18 and -12.
8. A train travels 360 km at a uniform speed. If the speed had been 5 km/h more, it would have taken 1 hour less for the same journey. Find the speed of the train.
It is given that
Distance = 360 km
Consider x as the speed, then the time taken
If the speed is increased by 5 km/h, the speed will be (x + 5) km/h.
Distance will be the same.
t = 360/(x + 5)
We know that
Time with original speed – Time with increased speed = 1
360/x – 360/(x + 5) = 1
LCM = x (x + 5)
360 x + 1800 – 360x = x (x + 5)
x 2 + 5x = 1800
x 2 + 5x – 1800 = 0
x 2 + 45x – 40x – 1800 = 0
x (x + 45) – 40 (x + 45) = 0
(x – 40) (x + 45) = 0
x = 40 km/hr
As we know, the value of speed cannot be negative.
Therefore, the speed of the train is 40 km/h.
Let the time taken by the smaller pipe to fill the tank = x hr.
Time taken by the larger pipe = ( x – 10) hr
Part of the tank filled by smaller pipe in 1 hour = 1/ x
Part of the tank filled by larger pipe in 1 hour = 1/( x – 10)
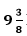
1/ x + 1/ x -10 = 8/75
x -10+ x / x ( x -10) = 8/75
⇒ 2 x -10/ x ( x -10) = 8/75
⇒ 75(2 x – 10) = 8 x 2 – 80 x
⇒ 150 x – 750 = 8 x 2 – 80 x
⇒ 8 x 2 – 230 x +750 = 0
⇒ 8 x 2 – 200 x – 30 x + 750 = 0
⇒ 8 x ( x – 25) -30( x – 25) = 0
⇒ ( x – 25)(8 x -30) = 0
⇒ x = 25, 30/8
Time taken by the smaller pipe cannot be 30/8 = 3.75 hours, as the time taken by the larger pipe will become negative, which is logically not possible.
Therefore, the time taken individually by the smaller pipe and the larger pipe will be 25 and 25 – 10 =15 hours, respectively.
10. An express train takes 1 hour less than a passenger train to travel 132 km between Mysore and Bangalore (without taking into consideration the time they stop at intermediate stations). If the average speed of the express train is 11 km/h more than that of the passenger train, find the average speed of the two trains.
Let us say the average speed of the passenger train = x km/h.
Average speed of express train = ( x + 11) km/h
Given the time taken by the express train to cover 132 km is 1 hour less than the passenger train to cover the same distance. Therefore,
(132/x) – (132/(x+11)) = 1
132(x+11-x)/(x(x+11)) = 1
132 × 11 /(x(x+11)) = 1
⇒ 132 × 11 = x ( x + 11)
⇒ x 2 + 11 x – 1452 = 0
⇒ x 2 + 44 x -33 x -1452 = 0
⇒ x ( x + 44) -33( x + 44) = 0
⇒ ( x + 44)( x – 33) = 0
⇒ x = – 44, 33
As we know, speed cannot be negative.
Therefore, the speed of the passenger train will be 33 km/h and thus, the speed of the express train will be 33 + 11 = 44 km/h.
11. Sum of the areas of two squares is 468 m 2 . If the difference between their perimeters is 24 m, find the sides of the two squares.
Let the sides of the two squares be x m and y m.
Therefore, their perimeter will be 4 x and 4 y, respectively
And the area of the squares will be x 2 and y 2, respectively.
4 x – 4 y = 24
x – y = 6
x = y + 6
Also, x 2 + y 2 = 468
⇒ (6 + y 2 ) + y 2 = 468
⇒ 36 + y 2 + 12 y + y 2 = 468
⇒ 2 y 2 + 12 y + 432 = 0
⇒ y 2 + 6y – 216 = 0
⇒ y 2 + 18 y – 12 y – 216 = 0
⇒ y ( y +18) -12( y + 18) = 0
⇒ ( y + 18)( y – 12) = 0
⇒ y = -18, 12
As we know, the side of a square cannot be negative.
Hence, the sides of the squares are 12 m and (12 + 6) m = 18 m.
Exercise 4.4 Page: 91
1. Find the nature of the roots of the following quadratic equations. If the real roots exist, find them. (i) 2 x 2 – 3 x + 5 = 0 (ii) 3 x 2 – 4√3 x + 4 = 0 (iii) 2 x 2 – 6 x + 3 = 0
2x 2 – 3 x + 5 = 0
Comparing the equation with ax 2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 2, b = -3 and c = 5
We know, Discriminant = b 2 – 4 ac
= ( – 3) 2 – 4 (2) (5) = 9 – 40
As you can see, b 2 – 4ac < 0
Therefore, no real root is possible for the given equation, 2x 2 – 3 x + 5 = 0
(ii) 3 x 2 – 4√3 x + 4 = 0
a = 3, b = -4√3 and c = 4
= (-4√3) 2 – 4(3)(4)
= 48 – 48 = 0
As b 2 – 4 ac = 0,
Real roots exist for the given equation, and they are equal to each other.
Hence, the roots will be – b /2 a and – b /2 a .
– b /2 a = -(-4√3)/2×3 = 4√3/6 = 2√3/3 = 2/√3
Therefore, the roots are 2/√3 and 2/√3.
(iii) 2 x 2 – 6 x + 3 = 0
a = 2, b = -6, c = 3
As we know, Discriminant = b 2 – 4 ac
= (-6) 2 – 4 (2) (3)
= 36 – 24 = 12
As b 2 – 4 ac > 0,
Therefore, there are distinct real roots that exist for this equation, 2 x 2 – 6 x + 3 = 0
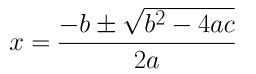
= (-(-6) ± √(-6 2 -4(2)(3)) )/ 2(2)
= (6±2√3 )/4
Therefore, the roots for the given equation are (3+√3)/2 and (3-√3)/2
2. Find the values of k for each of the following quadratic equations so that they have two equal roots. (i) 2 x 2 + kx + 3 = 0 (ii) kx ( x – 2) + 6 = 0
(i) 2 x 2 + kx + 3 = 0
Comparing the given equation with ax 2 + bx + c = 0, we get,
a = 2, b = k and c = 3
= ( k ) 2 – 4(2) (3)
= k 2 – 24
For equal roots, we know,
Discriminant = 0
k 2 – 24 = 0
k = ±√24 = ±2√6
(ii) kx ( x – 2) + 6 = 0
or kx 2 – 2 kx + 6 = 0
Comparing the given equation with ax 2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = k , b = – 2 k and c = 6
= ( – 2 k ) 2 – 4 ( k ) (6)
= 4 k 2 – 24 k
b 2 – 4 ac = 0
4 k 2 – 24 k = 0
4 k ( k – 6) = 0
Either 4 k = 0 or k = 6 = 0
k = 0 or k = 6
However, if k = 0, then the equation will not have the terms ‘ x 2 ‘ and ‘ x ‘.
Therefore, if this equation has two equal roots, k should be 6 only.
3. Is it possible to design a rectangular mango grove whose length is twice its breadth and the area is 800 m 2 ? If so, find its length and breadth.
Let the breadth of the mango grove be l .
The length of the mango grove will be 2 l .
Area of the mango grove = (2 l ) ( l )= 2 l 2
2 l 2 = 800
l 2 = 800/2 = 400
l 2 – 400 =0
a = 1, b = 0, c = 400
=> (0) 2 – 4 × (1) × ( – 400) = 1600
Here, b 2 – 4 ac > 0
Thus, the equation will have real roots. And hence, the desired rectangular mango grove can be designed.
As we know, the value of length cannot be negative.
Therefore, the breadth of the mango grove = 20 m
Length of mango grove = 2 × 20 = 40 m
4. Is the following situation possible? If so, determine their present ages. The sum of the ages of two friends is 20 years. Four years ago, the product of their age in years was 48.
Let’s say the age of one friend is x years.
Then, the age of the other friend will be (20 – x) years.
Four years ago,
Age of First friend = ( x – 4) years
Age of Second friend = (20 – x – 4) = (16 – x ) years
As per the given question, we can write,
( x – 4) (16 – x ) = 48
16 x – x 2 – 64 + 4 x = 48
– x 2 + 20 x – 112 = 0
x 2 – 20 x + 112 = 0
a = 1 , b = -2 0 and c = 112
Discriminant = b 2 – 4 ac
= (- 20 ) 2 – 4 × 112
= 400 – 448 = -48
b 2 – 4 ac < 0
Therefore, there will be no real solution possible for the equations. Hence, the condition doesn’t exist.
5. Is it possible to design a rectangular park of perimeter 80 and an area of 400 m2? If so, find its length and breadth.
Let the length and breadth of the park be l and b.
Perimeter of the rectangular park = 2 ( l + b ) = 80
So, l + b = 40
Or, b = 40 – l
Area of the rectangular park = l×b = l(40 – l) = 40 l – l 2 = 400
l 2 – 40 l + 400 = 0, which is a quadratic equation.
a = 1, b = -40, c = 400
Since, Discriminant = b 2 – 4 ac
=(- 40 ) 2 – 4 × 400
= 1600 – 1600 = 0
Thus, b 2 – 4 ac = 0
Therefore, this equation has equal real roots. Hence, the situation is possible.
The root of the equation,
l = – b /2 a
l = -(-40)/2(1) = 40/2 = 20
Therefore, the length of the rectangular park, l = 20 m
And the breadth of the park, b = 40 – l = 40 – 20 = 20 m.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations
A 1-mark question was asked from Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations in the year 2018. However, in the year 2017, a total of 13 marks were asked from the topic Quadratic Equations. Therefore, students need to have a thorough understanding of the topic. The topics and sub-topics provided in this chapter include:
4.1 Introduction
If we equate the polynomial ax 2 + bx + c, a ≠ 0 to zero, we get a quadratic equation. Quadratic equations come up when we deal with many real-life situations. In this chapter, students will study quadratic equations and various ways of finding their roots. They will also see some applications of quadratic equations in daily life situations.
4.2 Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation in the variable x is an equation of the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, c are real numbers, a ≠ 0. In fact, any equation of the form p(x) = 0, where p(x) is a polynomial of degree 2, is a quadratic equation. But when we write the terms of p(x) in descending order of their degrees, then we get the standard form of the equation. That is, ax 2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 is called the standard form of a quadratic equation.
4.3 Solution of Quadratic Equations by Factorisation
A real number α is called a root of the quadratic equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 if a α 2 + bα + c = 0. We also say that x = α is a solution of the quadratic equation or that α satisfies the quadratic equation. Note that the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial ax 2 + bx + c and the roots of the quadratic equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0 are the same.
4.4 Solution of a Quadratic Equation by Completing the Square
Finding the value that makes a quadratic equation a square trinomial is called completing the square. The square trinomial can then be solved easily by factorising.
4.5 Nature of Roots
If b 2 – 4ac < 0, then there is no real number whose square is b 2 – 4ac. Therefore, there are no real roots for the given quadratic equation in this case. Since b 2 – 4ac determines whether the quadratic equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0 has real roots or not, b 2 – 4ac is called the discriminant of this quadratic equation. So, a quadratic equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0 has (i) two distinct real roots, if b 2 – 4ac > 0, (ii) two equal real roots, if b 2 – 4ac = 0, (iii) no real roots, if b 2 – 4ac < 0. 4.6
List of exercises we covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4
Exercise 4.1 Solutions – 2 Questions Exercise 4.2 Solutions – 6 Questions Exercise 4.3 Solutions – 11 Questions Exercise 4.4 Solutions – 5 Questions
In a quadratic equation, x represents an unknown form, and a, b, and c are the known values. An equation to be quadratic “a” should not be equal to 0. The equation is of the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0. The values of a, b, and c are always real numbers. A quadratic equation can be calculated by completing the square. A quadratic equation has
- Two different real roots
- No real roots
- Two equal roots
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations
- The highly experienced faculty at BYJU’S designs NCERT Solutions with utmost care.
- The solutions are 100% accurate and can be used by the students while preparing for their CBSE board exams.
- All the minute concepts are also covered to help students face other competitive exams more confidently.
- The exercise questions present in the NCERT Textbook have been answered in a step-wise manner so that students attain good scores not only on the final answer but also on each step.
For more questions to practise, students can refer to the other study materials which are given at BYJU’S.
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations
Disclaimer –
Dropped Topics – 4.4 Solution of a quadratic equation by completing the squares
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4
How many exercises are there in ncert solutions for class 10 maths chapter 4, is byju’s website providing answers for ncert solutions for class 10 maths chapter 4 quadratic equations, mention the important concepts you learn in ncert solutions for class 10 maths chapter 4 quadratic equations., leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
It is good learning app
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
- STATE WISE BOOKS
- ENGINEERING EXAM
- SCHOLARSHIP OLYMPIAD
- STATE BOOKS
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study
CBSE Board has introduced the case study questions for the ongoing academic session 2021-22. The board will ask the paper on the basis of a different exam pattern which has been introduced this year where 50% syllabus is occupied for MCQ for Term 1 exam. Selfstudys has provided below the chapter-wise questions for CBSE Class 10 Maths. Students must solve these case study based problems as soon as they are done with their syllabus.
These case studies are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions where students need to answer them as asked in the exam. The MCQs are not that difficult but having a deep and thorough understanding of NCERT Maths textbooks are required to answer these. Furthermore, we have provided the PDF File of CBSE Class 10 maths case study 2021-2022.
Class 10 Maths (Formula, Case Based, MCQ, Assertion Reason Question with Solutions)
In order to score good marks in the term 1 exam students must be aware of the Important formulas, Case Based Questions, MCQ and Assertion Reasons with solutions. Solving these types of questions is important because the board will ask them in the Term 1 exam as per the changed exam pattern of CBSE Class 10th.
Important formulas should be necessarily learned by the students because the case studies are solved with the help of important formulas. Apart from that there are assertion reason based questions that are important too.
Assertion Reasoning is a kind of question in which one statement (Assertion) is given and its reason is given (Explanation of statement). Students need to decide whether both the statement and reason are correct or not. If both are correct then they have to decide whether the given reason supports the statement or not. In such ways, assertion reasoning questions are being solved. However, for doing so and getting rid of confusions while solving. Students are advised to practice these as much as possible.
For doing so we have given the PDF that has a bunch of MCQs questions based on case based, assertion, important formulas, etc. All the Multiple Choice problems are given with detailed explanations.
CBSE Class 10th Case study Questions
Recently CBSE Board has the exam pattern and included case study questions to make the final paper a little easier. However, Many students are nervous after hearing about the case based questions. They should not be nervous because case study are easy and given in the board papers to ease the Class 10th board exam papers. However to answer them a thorough understanding of the basic concepts are important. For which students can refer to the NCERT textbook.
Basically, case study are the types of questions which are developed from the given data. In these types of problems, a paragraph or passage is given followed by the 5 questions that are given to answer . These types of problems are generally easy to answer because the data are given in the passage and students have to just analyse and find those data to answer the questions.
CBSE Class 10th Assertion Reasoning Questions
These types of questions are solved by reading the statement, and given reason. Sometimes these types of problems can make students confused. To understand the assertion and reason, students need to know that there will be one statement that is known as assertion and another one will be the reason, which is supposed to be the reason for the given statement. However, it is students duty to determine whether the statement and reason are correct or not. If both are correct then it becomes important to check, does reason support the statement?
Moreover, to solve the problem they need to look at the given options and then answer them.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Based MCQ
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Based MCQ are either Multiple Choice Questions or assertion reasons. To solve such types of problems it is ideal to use elimination methods. Doing so will save time and answering the questions will be much easier. Students preparing for the board exams should definitely solve these types of problems on a daily basis.
Also, the CBSE Class 10 Maths MCQ Based Questions are provided to us to download in PDF file format. All are developed as per the latest syllabus of CBSE Class Xth.
Class 10th Mathematics Multiple Choice Questions
Class 10 Mathematics Multiple Choice Questions for all the chapters helps students to quickly revise their learnings, and complete their syllabus multiple times. MCQs are in the form of objective types of questions whose 4 different options are given and one of them is a true answer to that problem. Such types of problems also aid in self assessment.
Case Study Based Questions of class 10th Maths are in the form of passage. In these types of questions the paragraphs are given and students need to find out the given data from the paragraph to answer the questions. The problems are generally in Multiple Choice Questions.
The Best Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions are available on Selfstudys.com. Click here to download for free.
To solve Class 10 Maths Case Studies Questions you need to read the passage and questions very carefully. Once you are done with reading you can begin to solve the questions one by one. While solving the problems you have to look at the data and clues mentioned in the passage.
In Class 10 Mathematics the assertion and reasoning questions are a kind of Multiple Choice Questions where a statement is given and a reason is given for that individual statement. Now, to answer the questions you need to verify the statement (assertion) and reason too. If both are true then the last step is to see whether the given reason support=rts the statement or not.

CBSE 10th 2024-25 : Social Science Official Competency Focused Practice Questions released by CBSE

CBSE Class 10 Revaluation Application 2024 Process Begins : How to Apply, Fees, Direct Link & Step-by-Step Guide

CBSE Class 10 Result 2024 Latest Update : Verification of Marks, Revaluation & Photocopy of Answer Sheet; Check Complete Process

CBSE Class 10 Result 2024 Out: 93.60% Pass Percentage, JNV and Kendriya Vidyalaya shine with 99.09% score

CBSE Class 10th Result 2024 Out : Supplementary, Re-verification & Re-evaluation Date Released; Check Details Here

CBSE 10th Toppers List 2024: Check Toppers Name, Marks, Pass Percentage, Merit List, District & Result Full Statistics

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- Case Study Class 10...
Case Study Class 10 Maths Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Now, CBSE will ask only subjective questions in class 10 Maths case studies. But if you search over the internet or even check many books, you will get only MCQs in the class 10 Maths case study in the session 2022-23. It is not the correct pattern. Just beware of such misleading websites and books.
We advise you to visit CBSE official website ( cbseacademic.nic.in ) and go through class 10 model question papers . You will find that CBSE is asking only subjective questions under case study in class 10 Maths. We at myCBSEguide helping CBSE students for the past 15 years and are committed to providing the most authentic study material to our students.
Here, myCBSEguide is the only application that has the most relevant and updated study material for CBSE students as per the official curriculum document 2022 – 2023. You can download updated sample papers for class 10 maths .
First of all, we would like to clarify that class 10 maths case study questions are subjective and CBSE will not ask multiple-choice questions in case studies. So, you must download the myCBSEguide app to get updated model question papers having new pattern subjective case study questions for class 10 the mathematics year 2022-23.
Class 10 Maths has the following chapters.
- Real Numbers Case Study Question
- Polynomials Case Study Question
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Case Study Question
- Quadratic Equations Case Study Question
- Arithmetic Progressions Case Study Question
- Triangles Case Study Question
- Coordinate Geometry Case Study Question
- Introduction to Trigonometry Case Study Question
- Some Applications of Trigonometry Case Study Question
- Circles Case Study Question
- Area Related to Circles Case Study Question
- Surface Areas and Volumes Case Study Question
- Statistics Case Study Question
- Probability Case Study Question
Format of Maths Case-Based Questions
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions will have one passage and four questions. As you know, CBSE has introduced Case Study Questions in class 10 and class 12 this year, the annual examination will have case-based questions in almost all major subjects. This article will help you to find sample questions based on case studies and model question papers for CBSE class 10 Board Exams.
Maths Case Study Question Paper 2023
Here is the marks distribution of the CBSE class 10 maths board exam question paper. CBSE may ask case study questions from any of the following chapters. However, Mensuration, statistics, probability and Algebra are some important chapters in this regard.
Case Study Question in Mathematics
Here are some examples of case study-based questions for class 10 Mathematics. To get more questions and model question papers for the 2021 examination, download myCBSEguide Mobile App .
Case Study Question – 1
In the month of April to June 2022, the exports of passenger cars from India increased by 26% in the corresponding quarter of 2021–22, as per a report. A car manufacturing company planned to produce 1800 cars in 4th year and 2600 cars in 8th year. Assuming that the production increases uniformly by a fixed number every year.
- Find the production in the 1 st year.
- Find the production in the 12 th year.
- Find the total production in first 10 years. OR In which year the total production will reach to 15000 cars?
Case Study Question – 2
In a GPS, The lines that run east-west are known as lines of latitude, and the lines running north-south are known as lines of longitude. The latitude and the longitude of a place are its coordinates and the distance formula is used to find the distance between two places. The distance between two parallel lines is approximately 150 km. A family from Uttar Pradesh planned a round trip from Lucknow (L) to Puri (P) via Bhuj (B) and Nashik (N) as shown in the given figure below.
- Find the distance between Lucknow (L) to Bhuj(B).
- If Kota (K), internally divide the line segment joining Lucknow (L) to Bhuj (B) into 3 : 2 then find the coordinate of Kota (K).
- Name the type of triangle formed by the places Lucknow (L), Nashik (N) and Puri (P) OR Find a place (point) on the longitude (y-axis) which is equidistant from the points Lucknow (L) and Puri (P).
Case Study Question – 3
- Find the distance PA.
- Find the distance PB
- Find the width AB of the river. OR Find the height BQ if the angle of the elevation from P to Q be 30 o .
Case Study Question – 4
- What is the length of the line segment joining points B and F?
- The centre ‘Z’ of the figure will be the point of intersection of the diagonals of quadrilateral WXOP. Then what are the coordinates of Z?
- What are the coordinates of the point on y axis equidistant from A and G? OR What is the area of area of Trapezium AFGH?
Case Study Question – 5
The school auditorium was to be constructed to accommodate at least 1500 people. The chairs are to be placed in concentric circular arrangement in such a way that each succeeding circular row has 10 seats more than the previous one.
- If the first circular row has 30 seats, how many seats will be there in the 10th row?
- For 1500 seats in the auditorium, how many rows need to be there? OR If 1500 seats are to be arranged in the auditorium, how many seats are still left to be put after 10 th row?
- If there were 17 rows in the auditorium, how many seats will be there in the middle row?
Case Study Question – 6
- Draw a neat labelled figure to show the above situation diagrammatically.
- What is the speed of the plane in km/hr.
More Case Study Questions
We have class 10 maths case study questions in every chapter. You can download them as PDFs from the myCBSEguide App or from our free student dashboard .
As you know CBSE has reduced the syllabus this year, you should be careful while downloading these case study questions from the internet. You may get outdated or irrelevant questions there. It will not only be a waste of time but also lead to confusion.
Here, myCBSEguide is the most authentic learning app for CBSE students that is providing you up to date study material. You can download the myCBSEguide app and get access to 100+ case study questions for class 10 Maths.
How to Solve Case-Based Questions?
Questions based on a given case study are normally taken from real-life situations. These are certainly related to the concepts provided in the textbook but the plot of the question is always based on a day-to-day life problem. There will be all subjective-type questions in the case study. You should answer the case-based questions to the point.
What are Class 10 competency-based questions?
Competency-based questions are questions that are based on real-life situations. Case study questions are a type of competency-based questions. There may be multiple ways to assess the competencies. The case study is assumed to be one of the best methods to evaluate competencies. In class 10 maths, you will find 1-2 case study questions. We advise you to read the passage carefully before answering the questions.
Case Study Questions in Maths Question Paper
CBSE has released new model question papers for annual examinations. myCBSEguide App has also created many model papers based on the new format (reduced syllabus) for the current session and uploaded them to myCBSEguide App. We advise all the students to download the myCBSEguide app and practice case study questions for class 10 maths as much as possible.
Case Studies on CBSE’s Official Website
CBSE has uploaded many case study questions on class 10 maths. You can download them from CBSE Official Website for free. Here you will find around 40-50 case study questions in PDF format for CBSE 10th class.
10 Maths Case Studies in myCBSEguide App
You can also download chapter-wise case study questions for class 10 maths from the myCBSEguide app. These class 10 case-based questions are prepared by our team of expert teachers. We have kept the new reduced syllabus in mind while creating these case-based questions. So, you will get the updated questions only.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2020-21
- Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions
- CBSE Reduced Syllabus Class 10 (2020-21)
- Class 10 Maths Basic Sample Paper 2024
- How to Revise CBSE Class 10 Maths in 3 Days
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Maths Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Expert
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions PDF
Download Case Study Questions for Class 10 Mathematics to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 10 Final Exam. These Case Study and Passage Based questions are published by the experts of CBSE Experts for the students of CBSE Class 10 so that they can score 100% on Boards.

CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Exam 2024 will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. The CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends.
Table of Contents
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 10 Mathematics
Inboard exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
The above Case studies for Class 10 Maths will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of cbseexpert.com for the benefit of Class 10 students.
- Class 10th Science Case Study Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions of Class 10th Science
- Assertion and Reason Questions of Class 10th Social Science

Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2024
Chapter-1 real numbers.
Starting with an introduction to real numbers, properties of real numbers, Euclid’s division lemma, fundamentals of arithmetic, Euclid’s division algorithm, revisiting irrational numbers, revisiting rational numbers and their decimal expansions followed by a bunch of problems for a thorough and better understanding.
Chapter-2 Polynomials
This chapter is quite important and marks securing topics in the syllabus. As this chapter is repeated almost every year, students find this a very easy and simple subject to understand. Topics like the geometrical meaning of the zeroes of a polynomial, the relationship between zeroes and coefficients of a polynomial, division algorithm for polynomials followed with exercises and solved examples for thorough understanding.
Chapter-3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
This chapter is very intriguing and the topics covered here are explained very clearly and perfectly using examples and exercises for each topic. Starting with the introduction, pair of linear equations in two variables, graphical method of solution of a pair of linear equations, algebraic methods of solving a pair of linear equations, substitution method, elimination method, cross-multiplication method, equations reducible to a pair of linear equations in two variables, etc are a few topics that are discussed in this chapter.
Chapter-4 Quadratic Equations
The Quadratic Equations chapter is a very important and high priority subject in terms of examination, and securing as well as the problems are very simple and easy. Problems like finding the value of X from a given equation, comparing and solving two equations to find X, Y values, proving the given equation is quadratic or not by knowing the highest power, from the given statement deriving the required quadratic equation, etc are few topics covered in this chapter and also an ample set of problems are provided for better practice purposes.
Chapter-5 Arithmetic Progressions
This chapter is another interesting and simpler topic where the problems here are mostly based on a single formula and the rest are derivations of the original one. Beginning with a basic brief introduction, definitions of arithmetic progressions, nth term of an AP, the sum of first n terms of an AP are a few important and priority topics covered under this chapter. Apart from that, there are many problems and exercises followed with each topic for good understanding.
Chapter-6 Triangles
This chapter Triangle is an interesting and easy chapter and students often like this very much and a securing unit as well. Here beginning with the introduction to triangles followed by other topics like similar figures, the similarity of triangles, criteria for similarity of triangles, areas of similar triangles, Pythagoras theorem, along with a page summary for revision purposes are discussed in this chapter with examples and exercises for practice purposes.
Chapter-7 Coordinate Geometry
Here starting with a general introduction, distance formula, section formula, area of the triangle are a few topics covered in this chapter followed with examples and exercises for better and thorough practice purposes.
Chapter-8 Introduction to Trigonometry
As trigonometry is a very important and vast subject, this topic is divided into two parts where one chapter is Introduction to Trigonometry and another part is Applications of Trigonometry. This Introduction to Trigonometry chapter is started with a general introduction, trigonometric ratios, trigonometric ratios of some specific angles, trigonometric ratios of complementary angles, trigonometric identities, etc are a few important topics covered in this chapter.
Chapter-9 Applications of Trigonometry
This chapter is the continuation of the previous chapter, where the various modeled applications are discussed here with examples and exercises for better understanding. Topics like heights and distances are covered here and at the end, a summary is provided with all the important and frequently used formulas used in this chapter for solving the problems.
Chapter-10 Circle
Beginning with the introduction to circles, tangent to a circle, several tangents from a point on a circle are some of the important topics covered in this chapter. This chapter being practical, there are an ample number of problems and solved examples for better understanding and practice purposes.
Chapter-11 Constructions
This chapter has more practical problems than theory-based definitions. Beginning with a general introduction to constructions, tools used, etc, the topics like division of a line segment, construction of tangents to a circle, and followed with few solved examples that help in solving the exercises provided after each topic.
Chapter-12 Areas related to Circles
This chapter problem is exclusively formula based wherein topics like perimeter and area of a circle- A Review, areas of sector and segment of a circle, areas of combinations of plane figures, and a page summary is provided just as a revision of the topics and formulas covered in the entire chapter and also there are many exercises and solved examples for practice purposes.
Chapter-13 Surface Areas and Volumes
Starting with the introduction, the surface area of a combination of solids, the volume of a combination of solids, conversion of solid from one shape to another, frustum of a cone, etc are to name a few topics explained in detail provided with a set of examples for a better comprehension of the concepts.
Chapter-14 Statistics
In this chapter starting with an introduction, topics like mean of grouped data, mode of grouped data, a median of grouped, graphical representation of cumulative frequency distribution are explained in detail with exercises for practice purposes. This chapter being a simple and easy subject, securing the marks is not difficult for students.
Chapter-15 Probability
Probability is another simple and important chapter in examination point of view and as seeking knowledge purposes as well. Beginning with an introduction to probability, an important topic called A theoretical approach is explained here. Since this chapter is one of the smallest in the syllabus and problems are also quite easy, students often like this chapter
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Carbon and its compounds
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 4 carbon and its compounds.
CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Carbon and its compounds. Term 2 Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Carbon and its compounds.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Carbon and its compounds
CASE STUDY : 1
Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation. These compounds may have long chains of carbon, branched chains of carbon or even carbon atoms arranged in rings. In addition, carbon atoms may be linked by single, double or triple bonds.
i) What are saturated compounds?
Ans: Compounds of carbon that are linked by only single bond between the carbon atoms are called as saturated compounds.
Eg: C2H6, CH4
ii) What is the another versatile property of carbon?
Ans: The tetravalent nature of carbon i.e it has four valency and it is capable of bonding with other four atoms of carbon or any other atom of monovalency.
iii) Give two example of unsaturated compounds.
Ans- Ethene- C2H4 & Ethyne- C2H2
iv) What would be the electron dot structure of C2H6.
v) Name any one element other than carbon which show catenation property?
Ans- Sulphur i.e S8 molecule.
CASE STUDY :2
Carbon, in all its allotropic forms, burns in oxygen to give carbon dioxide along with the release of heat and light. Most carbon compounds also release a large amount of heat and light on burning.
Saturated hydrocarbons will generally give a clean flame while unsaturated carbon compounds will give a yellow flame with lots of black smoke.
i) Complete the reaction: CH3CH2OH +O2 gives
Ans: CH3CH2OH + O2 👉 CO2 + H2O + heat & light.
ii) What is the reason for incomplete combustion?
Ans: When the supply of air is limited for combustion, then the fuel goes partial combustion which results in sooty flame.
iii) Combustion is an oxidation or reduction type of reaction?
Ans: It is an oxidation type of reaction as oxygen get added to reactant.
Eg: C+ O2 👉 CO2 + heat aand light.
iv) Draw the structure of the compound: But-2- yne.

V) What is homologous series?
Ans- A series of compound in which the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen in a carbon chain.
Eg: C2H6 & C3H6. – these differ by CH2 unit.
CASE STUDY : 3
Carbon compounds can be easily oxidised on combustion. In addition to this complete oxidation, we have reactions in which alcohols are converted to carboxylic acids.
We see that some substances are capable of adding oxygen to others. These substances are known as oxidisingagents.
i) Give two example of good oxidising agent.
Ans: Alkaline potassium permanganate or acidified potassium dichromate.
ii) Complete the reaction: CH3CH2CH2OH + Alk. KMnO4 👉?
Ans: CH3CH2CH2OH + Alk. KMnO4 👉 CH3CH2COOH.
iii) What are the uses of alcohol?
Ans: Good solvent, used to make syrups & drinks.
iv) Why Acidified potassium dichromate is called an oxidising agent?
Ans: It is because they can add oxygen to the reactant molecule very easily and convert them to acid.
v) What is the use of ethanoic acid?
Ans: used as preservatives in pickle and also to make esters.
CASE STUDY : 4
Most dirt is oily in nature and as you know, oil does not dissolve in water. The molecules of soap are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. The ionic-end of soap interacts with water while the carbon chain interacts with oil. The soap molecules, thus form structures called micelles, where one end of the molecules is towards the oil droplet while the ionic-end faces outside. This forms an emulsion in water. The soap micelle thus helps in pulling out the dirt in water and we can wash our clothes clean
i) What is hydrophobic end?
Ans- Soap molecules have two ends in which one is hydrophobic end which interacts with hydrocarbons and do not dissolve in water.
ii) Draw the structure of micelle.

iii) What are scums?
Ans- An insoluble substance(white precipitate) remains after washing with water. It is formed by the reaction of soaps with the calcium and magnesium salts.
iv) What is hard water?
Ans: The water which contains Calcium and magnesium salts in it and form insoluble precipitates when treated with soap are called hard water.
V) To remove hardness of water, the water is treated with soap or detergent?
Ans: Detergent are effective in hard water as they contain sodium salts of sulphonic acid or ammonium salts with chlorides or bromides ions etc.
CASE STUDY :5
Ethanoic acid is commonly called acetic acid and belongs to a group of acids called carboxylic acids. 5-8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar and is used widely as a preservative in pickles.
i) What is glacial acetic acid?
Ans: The melting point of ethanoic acid is 290K, so its often freezes during winter. Hence, gave rise to new name called as glacial acetic acid.
ii) Complete the reaction: NaOH + CH3CH2COOH 👉?
Ans: NaOH + CH3CH2COOH👉 CH3CH2COONa + H2O
iii) What is esterification reaction?
Ans: The reaction of carboxylic acid with an alcohol give rise to fruity smell called as esters. This process of the formation of esters is called esterification reaction.
Eq- CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH + Conc. H2SO4👉 CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O
iv) What happens when ethanoic acid is reacted with carbonates and bicarbonates?
Ans: They give rise to salt, Carbon dioxide, and water.
V) Write the reaction of ethanoic acid with sodium hydrogen carbonate?
Ans: CH3COOH + NaHCO3 👉 CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
Case Study – 6
Frothing in Yamuna:
The primary reason behind the formation of the toxic foam is high phosphate content in the wastewater because of detergents used in dyeing industries, dhobi ghat and households. Yamuna’s pollution level is so bad that parts of it have been labelled ‘dead’ as there is no oxygen in it for aquatic life to survive.
[ CBSE Academic Question Paper ]

1) Predict the pH value of the water of river Yamuna if the reason for froth is high content of detergents dissolved in it.
Answer – a) 10-11
2) Which of the following statements is correct for the water with detergents dissolved in it?
- a) low concentration of hydroxide ion (OH-)and high concentration of hydronium ion (H3O+)
- b) high concentration of hydroxide ion (OH-)and low concentration of hydronium ion (H3O+)
- c) high concentration of hydroxide ion (OH-) as well as hydronium ion (H3O+)
- d) equal concentration of both hydroxide ion (OH-) and hydronium ion (H3O+).
Answer- b) high concentration of hydroxide ion (OH-) and low concentration of hydronium ion (H3O+)
3) If a sample of water containing detergents is provided to you, which of the following methods will you adopt to neutralize it?
- a) Treating the water with baking soda
- b) Treating the water with vinegar
- c) Treating the water with caustic soda
- d) Treating the water with washing soda
Answer – b) Treating the water with vinegar
4) High content of phosphate ion in river Yamuna may lead to:
- a) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and increased growth of algae.
- b) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and no effect of growth of algae.
- c) increased level of dissolved oxygen and increased growth of algae.
- d) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and decreased growth of algae.
Answer – a) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and increased growth of algae.
Case Study – 7
Marble’s popularity began in ancient Rome and Greece, where white and off-white marble were used to construct a variety of structures, from hand-held sculptures to massive pillars and buildings.

1) Gas A, obtained above is a reactant for a very important biochemical process which occurs in the presence of sunlight. Identify the name of the process –
- a) Respiration
- b) Photosynthesis
- c) Transpiration
- d) photolysis
Answer – Photosynthesis
2) A student added 10g of calcium carbonate in a rigid container, secured it tightly and started to heat it. After some time, an increase in pressure was observed, the pressure reading was then noted at intervals of 5 mins and plotted against time, in a graph as shown below. During which time interval did maximum decomposition took place ?
a) 15-20 min
b) 10-15 min
c) 5-10 min
Answer – d) 0-5 min
3) Calcium oxide can be reduced to calcium, by heating with sodium metal. Which compound would act as an oxidizing agent in the above process?
b) sodium oxide
d) calcium oxide
Answer – d) calcium oxide
4) Marble statues are corroded or stained when they repeatedly come into contact with polluted rain water. Identify the main reason
a) decomposition of calcium carbonate to calcium oxide
b) polluted water is basic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate
c) polluted water is acidic in nature he
d) calcium carbonate dissolves in water to give calcium hydroxide.
Answer – b) polluted water is acidic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate
Case Study – 8
Chemistry in Automobiles:
Foran internal combustion engine to move a vehicle down the road, it must convert the energy stored in the fuel into mechanical energy to drive the wheels. In your car, the distributor and battery provide this starting energy by creating an electrical “spark”, which helps in combustion of fuels like gasoline. Below is the reaction depicting complete combustion of gasoline in full supply of air:
1) Identify the types of chemical reaction occurring during the combustion of fuel:
- a) Oxidation & Endothermic reaction
- b) Decomposition & Exothermic reaction
- c) Oxidation & Exothermic reaction
- d) Combination & Endothermic reaction
Answer – c) Oxidation & Exothermic reaction
2) ‘Although nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere, it does not combustion’. Identify the correct reason for this statement.
- a) Nitrogen is a reactive gas
- b) Nitrogen is an inert gas
- c) Nitrogen is an explosive gas
- d) Only hydrocarbons can take part in combustion
Answer – b) Nitrogen is an inert gas
3) ‘A student while walking on the road observed that a cloud of black smoke belched out from the exhaust stack of moving trucks on the road.’ Choose the correct reason for the production of black smoke:
a) Limited supply of air leads to incomplete combustion of fuel.
b) Rich supply of air leads to complete combustion of fuel.
c) Rich supply of air leads to a combination reaction.
d) Limited supply of air leads to complete combustion of fuel.
Answer – Limited supply of air leads to incomplete combustion of fuel.
We hope that above case study questions will help you for your upcoming exams. To see more click below –
- Class 10 Assertion & Reason
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- Important Difference between Class 10 Biology
- Important Difference between Class 10 Physics
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Sikkim scert class 4 evs chapter 6 eating together solution, assertion and reason questions class 7 maths chapter 2 fractions and decimals, assam scert class 8 geography and economics chapter 5 solutions, west bengal class 11 bengali semester 1 and semester 2 syllabus.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Case Study Questions Class 10 History – The Age of Industrialization
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions on Class 10 Social Science History Chapter 4 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Case Study Questions Class 10 History has been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialization
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Social Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
The Age of Industrialization Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialization
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Case Study 1: Will Thorne is one of those who went in search of seasonal work, loading bricks, and doing odd jobs. He describes how job-seekers walked to London in search of work: ‘I had always wanted to go to London, and my desire … as stimulated by letters from an old workmate … who was now working at the Old Kent Road Gas Works … I finally decided to go … in November 1881. With two friends I started out to walk the journey, filled with the hope that we would be able to obtain employment, when we get there, with the kind assistance of my friend … we had little money when we started, not enough to pay for our food and lodgings each night until we arrived in London. Some days we walked as much as twenty miles and other days less. Our money was gone at the end of the third day … For two nights we slept out – once under a haystack and once in an old farm shed … On arrival in London we tried to find … my friend … but … were unsuccessful. Our money was gone, so there was nothing for us to do but to walk around until late at night and try to find someplace to sleep. We found an old building and slept in it that night. The next day, Sunday, late in the afternoon, we got to the Old Kent Gas Works and applied for work. To my great surprise, the man we had been looking for was working at the time. He spoke to the foreman and I was given a job.
(i) What was the status of human labour in Britain? Select the best suitable option from the following with reference to the context. (a) There was limited number of workers. (b) There was no shortage of labour. (c) Labour had to be imported . (d) There was uneven distribution of labour.
Answer: (b) There was no shortage of labour.
What kinds of production demanded seasonal labour? Identify the best suitable option from the following. (a) Steel and iron (b) Cotton and textiles (c) Handmade goods (d) Bookbinders and printers
Answer: (d) Bookbinders and printers
(iii) What was the possibility of getting a job with abundance of labour in cities such as London? With reference to the above context, infer the appropriate option. (a) Jobs were given on the basis of merit system. (b) Jobs were given who were registered with a particular factory. (c) A job depended on existing networks of friendship and kin relations in a factory. (d) All of the above
Answer: (c) A job depended on existing networks of friendship and kin relations in a factory.
(iv) What were the problems workers faced during the Industrialisation? Identify the best suitable option from the following. (a) Migration from one place to another in search of suitable job. (b) Spending nights under bridges or in night shelters. (c) Preferences given to the unskilled labour in the industries. (d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (b)
(v) Two statements are given in the question below as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the appropriate option. Assertion (A): Seasonality of work in any industries meant prolonged periods without work. Reason (R): The lives of the workers was adversely affected and they returned towards rural areas. (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A (b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A (c) A is true, but R is false (d) A is false, but R is true
Answer: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Which of the following aspect is correct regarding the given source? Identify the correct option (a) It is extracted from ‘Comers and Goers’. (b) It is quoted by Raphael Samuel. (c) It shows the realities of the Victorian City. (d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Case Study 2:
The chapter “The Age of Industrialization” in Class 10 History explores the process of industrialization and its impact on societies during the 18th and 19th centuries. It delves into the transformation of agriculture, the growth of industries, and the emergence of factories and urban centers. The chapter discusses the role of technology, the expansion of railways and steamships, the growth of capitalism, and the experiences of workers and peasants during this period of rapid industrial change. It also highlights the social and environmental consequences of industrialization and the emergence of new social classes.
Which chapter in Class 10 History focuses on the process of industrialization during the 18th and 19th centuries?
a) Chapter 1: The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
b) Chapter 3: Nationalism in India
c) Chapter 5: The Age of Industrialization
d) Chapter 7: Print Culture and The Modern World
Answer: c) Chapter 5: The Age of Industrialization
What were some of the key features of industrialization during this period?
a) Transformation of agriculture, growth of industries, and emergence of factories
b) Decline of urban centers and expansion of rural areas
c) Focus on handcrafted production methods
d) Promotion of traditional agricultural practices
Answer: a) Transformation of agriculture, growth of industries, and emergence of factories
How did the expansion of railways and steamships contribute to industrialization?
a) They had no impact on industrialization.
b) They facilitated the movement of raw materials and finished goods.
c) They led to a decline in trade and transportation.
d) They resulted in the closure of factories and industries.
Answer: b) They facilitated the movement of raw materials and finished goods.
What were some of the social and environmental consequences of industrialization?
a) Emergence of new social classes and environmental degradation
b) Preservation of traditional social structures and sustainable practices
c) Decrease in urbanization and pollution levels
d) Promoting equality among different social groups
Answer: a) Emergence of new social classes and environmental degradation
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Social Science History Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialization with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Age of Industrialization Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Extra questions of class 10 science chapter 6 life processes pdf download, cbse class 10 board results 2024, extra questions of class 10 social science geography chapter 3 water resources pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Bihar Board
CFA Institute
Srm university.
- Rajasthan 10th Result
- Rajasthan Board Result
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 - Real Numbers (Published by CBSE)
Cbse class 10 maths cased study question bank for chapter 1 - real numbers is available here. this question bank is very useful to prepare for the class 10 maths exam 2021-2022..

The Central Board of Secondary Education has introduced the case study questions in class 10 exam pattern 2021-2022. The CBSE Class 10 questions papers of Board Exam 2022 will have questions based on case study. Therefore, students should get familiarised with these questions to do well in their board exam.
We have provided here case study questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 - Real Numbers. These questions have been published by the CBSE board itself. Students must solve all these questions at the same time they finish with the chapter - Real numbers.
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 - Real Numbers
To enhance the reading skills of grade X students, the school nominates you and two of your friends to set up a class library. There are two sections- section A and section B of grade X. There are 32 students in section A and 36 students in section B.

1. What is the minimum number of books you will acquire for the class library, so that they can be distributed equally among students of Section A or Section B?
Answer: c) 288
2. If the product of two positive integers is equal to the product of their HCF and LCM is true then, the HCF (32 , 36) is
Answer: b) 4
3. 36 can be expressed as a product of its primes as
a) 2 2 × 3 2
b) 2 1 × 3 3
c) 2 3 × 3 1
d) 2 0 × 3 0
Answer: a) 2 2 × 3 2
4. 7 × 11 × 13 × 15 + 15 is a
a) Prime number
b) Composite number
c) Neither prime nor composite
d) None of the above
Answer: b) Composite number
5. If p and q are positive integers such that p = ab 2 and q= a 2 b, where a , b are prime numbers, then the LCM (p, q) is
Answer: b) a 2 b 2
CASE STUDY 2:
A seminar is being conducted by an Educational Organisation, where the participants will be educators of different subjects. The number of participants in Hindi, English and Mathematics are 60, 84 and 108 respectively.

1. In each room the same number of participants are to be seated and all of them being in the same subject, hence maximum number participants that can accommodated in each room are
Answer: b) 12
2. What is the minimum number of rooms required during the event?
Answer: d) 21
3. The LCM of 60, 84 and 108 is
Answer: a) 3780
4. The product of HCF and LCM of 60,84 and 108 is
Answer: d) 45360
5. 108 can be expressed as a product of its primes as
a) 2 3 × 3 2
b) 2 3 × 3 3
c) 2 2 × 3 2
d) 2 2 × 3 3
Answer: d) 2 2 × 3 3
CASE STUDY 3:
A Mathematics Exhibition is being conducted in your School and one of your friends is making a model of a factor tree. He has some difficulty and asks for your help in completing a quiz for the audience.
Observe the following factor tree and answer the following:
1. What will be the value of x?
Answer: b) 13915
2. What will be the value of y?
Answer: c) 11
3. What will be the value of z?
Answer: b) 23
4. According to Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic 13915 is a
a) Composite number
b) Prime number
d) Even number
Answer: a) Composite number
5. The prime factorisation of 13915 is
a) 5 × 11 3 × 13 2
b) 5 × 11 3 × 23 2
c) 5 × 11 2 × 23
d) 5 × 11 2 × 13 2
Answer: c) 5 × 11 2 × 23
Also Check:
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths - All Chapters
Tips to Solve Case Study Based Questions Accurately
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- Exit Polls 2024
- RBSE Result 2024
- rajshaladarpan.nic.in 5th, 8th Result 2024
- rajshaladarpan.nic.in Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Class 8th, 5th Result 2024 Roll Number
- RBSE Class 5th Result 2024 Roll Number
- Rajasthan 5th 8th Class Result 2024
- 8th, 5th Board Result 2024 Rajasthan
- RBSE 10th Result 2024
- UPSC CSE Admit Card 2024
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
YSR University Result 2024 OUT at drysruhs.edu.in: Direct Link to Download NTRUHS UG Marksheet
Exit Poll 2024 LIVE: Updates from Axis My India, Chanakya, IPSOS, C-Voter, CSDS and Other research agencies
Optical Illusion: Find the odd figure in the picture in 5 seconds!
Seek and Find Puzzle: Only True Puzzle Masters Can Find the Hidden Drum in this Busy Road Scene
JEE Advanced 2024 Answer Key 2024 LIVE: IIT Madras JEE Paper 1, 2 Answer Key to be Released Tomorrow on jeeadv.ac.in at 10 AM, Direct Link to Download PDF
Brain Teaser: Only People With 10/10 Vision Can Find the Three Hidden W in a Sea of Ms?
Are Exit Polls Accurate? How it is different than Election Results, Check Here
Only a sharp-eyed genius can find 3 differences between the classroom pictures in 15 seconds!
[रोल नंबर] Rajasthan Board Class 8th 5th Result 2024 Roll Number: 5वीं में 97.60% और 8वीं में 95.72% छात्र सफल, Marksheet यहां से करें डाउनलोड
What is Exit Polls? How is it Conducted, and How it gets ready?
You have 20/20 vision if you can find the hidden cat in 8 seconds!
VSU Result 2024 OUT at vsu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet PDF
IISER IAT Admit Card 2024 Out, Download at iiseradmission.in
You have hunter eyes if you can spot the hidden antelope in 6 seconds!
JEE Advanced Provisional Answer Key 2024 Tomorrow, Download At jeeadv.ac.in
Only the sharpest eyes can find 3 differences between the playing card pictures in 12 seconds!
India T20 World Cup 2024 Squad: ये है रोहित की ‘विराट’ टीम, किस रोल में कौन? देखें यहां
Lok Sabha Election 2024 Polling Booth: घर बैठे कैसे पता करें अपना मतदान केंद्र?
Pakistan T20 World Cup Squad 2024: पाक की विश्व कप टीम में किसे मिला मौका कौन हुआ बाहर देखें यहां
T20 World Cup 2024 Match Time in India: अमेरिका में मैच का है यह टाइम तो भारत में किस समय देखें
- School Guide
- Class 10 Syllabus
- Maths Notes Class 10
- Science Notes Class 10
- History Notes Class 10
- Geography Notes Class 10
- Political Science Notes Class 10
- NCERT Soln. Class 10 Maths
- RD Sharma Soln. Class 10
- Math Formulas Class 10
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Agriculture
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 - Agriculture
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 : Water Resources
- NCERT Geography Class-9 Chapter-Wise Solutions
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Resources
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Geography Social Science Chapter 4: Climate
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 : Manufacturing Industries
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 : Minerals and Energy Resources
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths: Chapter Wise PDF
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths: Chapter Wise PDF 2024
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8
NCERT Solutions For Class-10 Geography Chapter-4 Agriculture
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture – This article includes free NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture to help students of Class 10 learn the solutions and ace their exams.
It has been developed by the subject matter experts at GFG, according to the latest CBSE Syllabus 2023-24 , and guidelines to help the students of Class 10 create a solid conceptual base for Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture.
The solutions to all the exercises in Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture of your NCERT textbook have been collectively covered in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture
The solutions for Chapter 4 Agriculture are provided below, and students can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 for other subjects as well.
Exercise Pages No. 48
1. multiple choice questions., (i) which one of the following describes a system of agriculture where a single crop is grown on a large area.
(a) Shifting Agriculture
(b) Plantation Agriculture
(c) Horticulture
(d) Intensive Agriculture
(ii) Which one of the following is a rabi crop?
(a) Rice (c) Millets
(b) Gram (d) Cotton
(iii) Which one of the following is a leguminous crop?
(a) Pulses (c) Millets
(b) Jawar (d) Sesamum
(iv) Which one of the following is announced by the government in support of a crop?
( a) Maximum support price
(b) Minimum support price
(c) Moderate support price
(d) Influential support price
2. Answer the following questions in 30 words.
(i) name one important beverage crop and specify the geographical conditions required for its growth., (ii) name one staple crop of india and the regions where it is produced., (iii) enlist the various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers., (iv) the land under cultivation has got reduced day by day. can you imagine its consequences.
(i) Tea is a significant beverage crop that grows well in tropical and subtropical climates. Tea bushes need a frost-free climate that is warm and moist all year. The ideal maximum monthly temperature for tea plants is 24° to 30° C, and they also require high humidity, heavy dew, and morning fog. Tea plants grow best in deep, fertile, well-drained soil that is rich in humus and organic matter. Tea requires frequent and well-distributed rain of 200 cm or more throughout the year. (ii) Rice is a staple crop of India. It is primarily cultivated in regions with high humidity and rainfall such as: Coastal areas Deltaic regions North and northeast India Areas with less rainfall, such as parts of Rajasthan, Haryana, Punjab, and western Uttar Pradesh. (iii) Various institutional reform programs introduced by the government for farmers include: Minimum Support Price (MSP) policy Crop insurance Subsidies on agricultural inputs Grameen banks Kisan Credit Card Personal Accident Insurance Scheme
3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) suggest the initiative taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production., (ii) describe the impact of globalisation on indian agriculture., (iii) describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice..
(i) T he Indian government has taken many initiatives to increase agricultural production, including: Land reforms: The First Five Year Plan focused on land reform, and the government has also abolished the Zamindari system and set a ceiling on landholdings. Crop insurance : The National Crop Insurance Scheme (NCIP) provides financial support and insurance to farmers if their crops fail due to natural disasters, pests, or disease. Organic farming: The Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) encourages farmers to form groups and use organic farming methods over large areas. Rural infrastructure: The government has improved rural infrastructure by providing irrigation, power, rural roads, and markets. Research and development: The government has established agricultural universities and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) to focus on research and development in weather forecast, meteorology, horticulture, animal breeding, and veterinary services. Financial support The government provides farmers with financial support through loans and insurance for risk crops. Minimum support price : The government announces a minimum support price to prevent exploitation of farmers. Agricultural programs : The government introduces agricultural programs and special weather bulletins for farmers through mass media.
(ii) Globalization has had both positive and negative impacts on Indian agriculture: Positive impacts Increased exports : Indian farmers can export their produce to other countries, which increases their income. Improved technology : Indian farmers can adopt new technologies and farming techniques, which increases productivity. Access to global markets: Indian farmers can sell their produce in global markets, which can lead to better prices. Negative impacts Competition: Indian farmers face increased competition from developed countries with highly subsidized agriculture. Dependency on imports: Globalization has led to dependency on imports. Corporate intrusion: The government’s reduced role in promoting agriculture has led to less government help for agricultural infrastructure, which has left farmers vulnerable to corporate intrusion.
(iii) The geographical conditions required for the growth of rice are: Temperature : Rice requires warm temperatures for growth, between 20°C to 35°C. Water : It thrives in areas with abundant water supply, either through rainfall or irrigation, and is cultivated in regions with high humidity. Soil : Rice grows well in fertile, well-drained soils such as clayey or loamy soils. It also tolerates acidic conditions but prefers slightly acidic to neutral pH levels. Flat Terrain : Rice cultivation requires flat or gently sloping terrain to facilitate the flooding of paddy fields, which is essential for rice cultivation. Sunlight : Rice plants need ample sunlight for photosynthesis, making regions with long daylight hours ideal for cultivation. Rainfall : While rice can be grown in areas with adequate irrigation, regions with moderate to heavy rainfall are particularly suitable for rainfed rice cultivation. Growing Season : Rice has a long growing season, spanning several months, so regions with a long frost-free period are conducive to its cultivation.
Chapter 4 Agriculture Summary
Chapter 4 of NCERT Class 10 Geography covers agriculture, highlighting its significance in India’s economy. It discusses various agricultural practices, including the Green Revolution, and the challenges faced by farmers. The chapter emphasizes the need for sustainable agricultural practices to ensure food security and rural development. Additionally, it examines government initiatives and institutional reforms aimed at improving agricultural productivity and the livelihoods of farmers.
Important Topics Discussed in the Chapter
- Types of Agriculture in India
- How many types of agriculture are there in India?
- Agriculture and Food Security
- Crop Protection in Agriculture – Methods and Importance
- Agricultural Practices
- Sustainable Agriculture – Definition, Practices & Importance
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture
Why should students opt for the geeks for geeks ncert solutions for class 10 geography chapter 4 for reference.
These solutions are easy to comprehend and provide very point-to-point answers which are required in the exams. The solutions are curated by subject experts and have used easy language.
What is agriculture?
Agriculture is the practice of cultivating crops, raising livestock, and other activities related to the production of food, fiber, and other products for human use.
What are the 4 types of farming?
The four types of farming are subsistence farming, commercial farming, mixed farming, and plantation farming.
How can Chapter 4 of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography be prepared for the board exam?
Students must go to the exercise-based questions at the conclusion of the chapter after reading it. Students can utilise the NCERT Solutions to learn how to answer questions. Students can utilise the solutions to study and practice the subjects on their own. The main purpose is to help students grasp the chapter and acquire new topics at their own pace.
Are NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 effective for the CBSE exam preparation?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics can been prepared in such a way that each concept is designed in a more interactive manner following the conduct of various types of research and information that is provided for helping students remember the concepts with a flow for memorizing them more effectively and by some simple tricks and methods to remember.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- NCERT Solutions Class-10
- School Geography
- School Learning
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science Political Science Chapter 4 Gender Religion and Caste
- Last modified on: 8 months ago
- Reading Time: 11 Minutes

Table of Contents
Here we are providing case study questions for Class 10 Social Science Political Science Chapter 4 Gender Religion and Caste.
Case Study Question 1:
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Partly due to their efforts and partly due to other socio-economic changes, castes and caste system in modern India have undergone great changes. With economic development, large scale urbanisation, growth of literacy and education, occupational mobility and the weakening of the position of landlords in the villages, the old notions of caste hierarchy are breaking down. Now, most of the times, in urban areas it does not matter much who is walking along next to us on a street or eating at the next table in a restaurant. The Constitution of India prohibited any caste based discrimination and laid the foundations of policies to reverse the injustices of the caste system. If a person who lived a century ago were to return to India, she would be greatly surprised at the change that has come about in the country.
Yet caste has not disappeared from contemporary India. Some of the older aspects of caste have persisted. Even now most people marry within their own caste or tribe. Untouchability has not ended completely, despite constitutional prohibition. Effects of centuries of advantages and disadvantages continue to be felt today. The caste groups that had access to education under the old system have done very well in acquiring modern education as well. Those groups that did not have access to education or were prohibited from acquiring it have naturally lagged behind. That is why there is a disproportionately large presence of ‘upper caste’ among the urban middle classes in our country. Caste continues to be closely linked to economic status.
Q 1. What are the reasons behind breaking down of old notions of caste hierarchy? Ans. The reasons are economic development, large scale urbanisation, growth of literacy and education, occupational mobility and weakening of the position of landlord in the villages.
Q 2. Mention the changes undergone in castes and caste system in modern India. Ans. The changes that have been undergone in castes and caste system in modern India are: (i) Caste hierarchy has been removed with economic development, large scale urbanisation, growth of literacy and education, etc. (ii) The Constitution of India prohibited any caste based discrimination and laid the foundations of policies to reverse the injustices of the caste system.
Q 3. What are the older aspects of caste still persisting in India?
Ans. The following older aspects of caste are still persisting in India: (i) Even now most people marry within their own caste or tribe. (ii) Untouchability has not ended completely despite of the constitutional prohibition. (iii) There is a disproportionately large presence of ‘upper caste’ among the urban middle classes. (iv) Caste continues to be closely linked to economic status.
Related Posts
Tips to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science.
Preparing for case study and passage-based questions in class 10 social science can be challenging, but it is important to remember that with the right approach, you can effectively tackle these types of questions. Here are some steps you can take to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science:
- Understand the format of case study questions: Case study questions for class 10 social science usually require you to read a scenario or a passage and answer a set of questions based on it. These questions can be based on various topics like history, geography, economics, or civics.
- Read and analyze the case study or passage carefully: The first step in answering case study questions is to read the scenario or passage carefully. Try to identify the main idea or theme of the passage and note down any important details that you think are relevant. Pay attention to any maps, graphs, or charts that are included as they can be helpful in answering the questions.
- Identify the type of questions being asked: After reading the case study or passage, you should analyze the questions being asked. Try to identify the type of question, whether it is a factual question or an analytical question. Factual questions require you to provide specific details from the passage, while analytical questions require you to use your critical thinking skills to analyze the information presented in the passage.
- Use your textbook and notes: To prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the topics covered in your textbook. Go through your notes and textbook to revise the relevant topics and concepts. This will help you to answer the questions more accurately.
- Practice sample questions: One of the best ways to prepare for case study questions is to practice answering sample questions. Try to find sample questions online or in your textbook and practice answering them. This will help you to get comfortable with the format of the questions and improve your speed and accuracy.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations are released by the board. Solve all these questions to perform well in your CBSE Class 10 Maths Exam 2021-22. By ...
Case study Questions on the Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 4 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Question 1: Raj and Ajay are very close friends. Both the families decide to go to Ranikhet by their own cars. Raj's car travels at a speed of x km/h while Ajay's car travels 5 km/h faster than Raj's car. Raj took 4 h … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
Updated for Latest NCERT for 2023-2024 Boards. Get NCERT Solutions for all exercise questions and examples of Chapter 4 Class 10 Quadratic Equations free at Teachoo. Answers to each and every question is provided video solutions. In this chapter, we will learn. This chapter is divided into two parts - Serial Order Wise, Concept Wise.
Students referring to the Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions And Answers Pdf from Selfstudys will find these features:-. Accurate answers of all the Case-based questions given in the PDF. Case Study class 10 Maths solutions are prepared by subject experts referring to the CBSE Syllabus of class 10. Free to download in Portable Document Format ...
4.5) Diamond is not a good conductor of electricity because : (a) it is very hard. (b) it has no free electrons. (c) it is not water soluble. (d) its structure is very compact. Show Answer. Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds with Answers Pdf ...
Welcome to CBSE Worldz. In this video we will be discussing CBSE class 10 Case Study Based Questions of maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations for Term 2CASE ST...
Q.1: Represent the following situations in the form of quadratic equations: (i) The area of a rectangular plot is 528 m2. The length of the plot (in metres) is one more than twice its breadth. We need to find the length and breadth of the plot. (ii) A train travels a distance of 480 km at a uniform speed.
Case Study Based Question - Quadratic Equations Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 | CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 | NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4. In T...
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations. A 1-mark question was asked from Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations in the year 2018. However, in the year 2017, a total of 13 marks were asked from the topic Quadratic Equations. Therefore, students need to have a thorough understanding of the topic.
Case Study 1. Age of Industrialization. 1) Proto-industrialization (PI) is regarded as a preliminary stage in the progression of modern industrial economics that preceded and paved the way for full-fledged industrialization. This concept was initially introduced by Mendels twenty years ago [1].
CBSE Board has introduced the case study questions for the ongoing academic session 2021-22. The board will ask the paper on the basis of a different exam pattern which has been introduced this year where 50% syllabus is occupied for MCQ for Term 1 exam. Selfstudys has provided below the chapter-wise questions for CBSE Class 10 Maths.
First of all, we would like to clarify that class 10 maths case study questions are subjective and CBSE will not ask multiple-choice questions in case studies. So, you must download the myCBSEguide app to get updated model question papers having new pattern subjective case study questions for class 10 the mathematics year 2022-23.
Download Case Study Questions for Class 10 Mathematics to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 10 Final Exam of 2022-23. These Case Study and Passage Based questions are published by the experts of CBSE Experts for the students of CBSE Class 10 so that they can score 100% on Boards. ... Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2024 Chapter-1 Real Numbers ...
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided case … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 ...
Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Agriculture. At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Carbon and its compounds. CASE STUDY : 1. Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation. These compounds may have long chains of carbon, branched chains of carbon or even carbon atoms arranged in rings.
REAL NUMBERS- CASE STUDY CASE STUDY 1. To enhance the reading skills of grade X students, the school nominates you and two of your friends to set up a class library. There are two sections- section A and section B of grade X. There are 32 students in section A and 36 students in section B. 1. What is the minimum number of books you will acquire ...
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialization. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Case Study 1: Will Thorne is one of those who went in search of seasonal work, loading bricks, and doing odd jobs. He describes how job-seekers walked to London in search of work: 'I ...
Here are some steps you can take to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science: Understand the format of case study questions: Case study questions for class 10 social science usually require you to read a scenario or a passage and answer a set of questions based on it. These questions can be based on various topics like ...
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 ...
4. 7 × 11 × 13 × 15 + 15 is a. a) Prime number. b) Composite number. c) Neither prime nor composite. d) None of the above. Answer: b) Composite number. 5. If p and q are positive integers such ...
Chapter 4 of NCERT Class 10 Geography covers agriculture, highlighting its significance in India's economy. It discusses various agricultural practices, including the Green Revolution, and the challenges faced by farmers. The chapter emphasizes the need for sustainable agricultural practices to ensure food security and rural development.
Here are some steps you can take to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science: Understand the format of case study questions: Case study questions for class 10 social science usually require you to read a scenario or a passage and answer a set of questions based on it. These questions can be based on various topics like ...