- Content Writing Services
- Get in Touch

How to Write an Executive Summary for a Case Study
Updated February 2022: The first thing you do when faced with any study or report is read the executive summary or overview—right? Then you decide if reading the rest of the material is worth your time. This is why it is so important for you to learn how to write an executive summary for a case study.
The executive summary of your case study serves exactly the same function. If the reader sees nothing beyond this section, they will still walk away with a good understanding of your service.
A great summary might even be enough for a reader to pass the information along to the decision-makers in their organization.
In this post, we’ll discuss what makes a compelling executive summary for case studies, and provide you with 4 examples from leading B2B SaaS companies. This is the third post in a 9-part series on how to write a case study .
Every word counts when writing an executive summary
When thinking about how to write an executive summary for a case study, you need to create 2 or 3 crucial sentences that provide a concise overview of the case study. It must be informative and:
- summarize the story by introducing the customer and their pain points
- explain what your organization did
- highlight the key results, including 1 or 2 statistics that drive home the takeaway message
Write the executive summary first to help you focus the rest of the case study. But don’t be too rigid: in the process of reviewing the interview transcript or writing the main copy, another point or statistic may emerge as having more impact than what you’ve chosen to highlight. Revisit your executive summary after writing the case study to make sure it’s as strong and accurate as possible.
If you need a hand with your SaaS case studies, have a look at our case study writing service .
Executive summaries can be short and sweet
This executive summary example from Segment is just a headline followed by a glorified subhead—but it does the trick!

Here’s another great example of a quick, yet helpful executive summary for Plaid’s case study:

Sometimes you may need a longer executive summary
For complex case studies, you may need a more in-depth executive summary to give readers an overview of the case study.
Here’s a more fleshed-out executive summary from Segment:
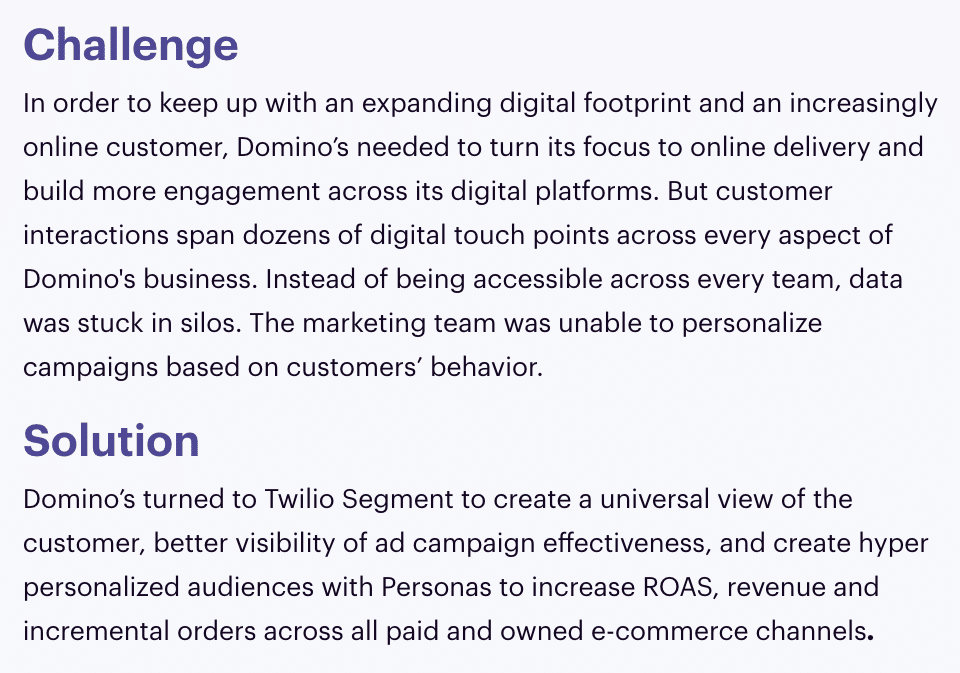
It’s a bit lengthy, but it effectively introduces the challenge. This executive summary could be more powerful if it included a section for results.
Sometimes executive summaries miss the mark entirely

This is not an executive summary. It is merely an introduction. We have no idea what the problem or solution is, and there’s nothing to motivate us to read further.
You can do better with your executive summaries
Be precise. Impress the reader with key results. Let them see that you offer solutions that matter.
Get the help you need
As a SaaS company, you need to partner with someone who “gets it”. We are a SaaS content marketing agency that works with high-growth companies like Calendly, ClickUp and WalkMe. Check out our done-for-you case study writing service .

As the founder of Uplift Content, Emily leads her team in creating done-for-you case studies, ebooks and blog posts for high-growth SaaS companies like ClickUp, Calendly and WalkMe. Connect with Emily on Linkedin
Sign up for the Content Huddle newsletter
Learn from Emily’s 17 years of aha moments, mistakes, observations, and insights—and find out how you can apply these lessons to your own marketing efforts.
You can unsubscribe any time. Visit our Terms of Use for information on our privacy practices.

Case Study Summary

It doesn’t always take an expert to fix a problem. Have you ever had a light in your house that doesn’t go on? Well, it’s not an engineering project , so it wouldn’t take a genius to identify if it’s a busted light bulb or a wiring issue. For these two cases, you can easily solve one problem but might need the help of an electrician for the other. When you encounter a particular situation, basic knowledge can help you to overcome it. And when you’ve dealt with the dilemma, what comes out may be additional knowledge on how to fix similar problems. And sometimes, life just gives you these things to test how well you can handle it. In academic settings, the presentation of these solutions can be considered a case study summary.
To get a firm grip on the principles and characteristics of discipline, you may need to test out what you know through given situations. In the fields of social science, business, and research, these situations are called case studies. And the initial analysis report is called a case study summary. A case executive summary is what the readers first encounter before they decide if the case is worth examining. Your case summary saves readers time in understanding the situation you’ve presented. It holds important information about medical or business case studies that your readers need to take in.
What a Case Study Summary Isn’t
Many may assume that a case study summary is the same as an abstract. They are relatively similar, but they have their key differences. A research executive summary is for those outside the academic spectrum. An abstract is for professors, research analysts, and anyone in the academe. The case study summary is also not the introduction, although it may contain similar content, they don’t share the same purpose. It is also not the preface of the study. Most importantly, it is not just a collection of random highlights within the analysis. The format of a case study summary is for the understanding of the collected data.
10+ Case Study Summary Example
A lot of case studies are hard to understand. Some people even dread the idea of reading the whole research project from start to finish. Thankfully, there is a more natural way to grasp the context of the study. That is through case study summaries. If you are working o a case study, you should be able to write a comprehensive overview of your own. To help you figure out the outline and format of your summary, here are 10+ case study summary examples you can check out.
1. Master Technology Case Study Summary Example
Size: 15 KB
2. Family Case Study Summary Example

Size: 216 KB
3. Case Study Summary Report Example

Size: 277 KB
4. Sample Case Studies Summary Example

Size: 487 KB
5. Case Studies Summary Workshop Example

Size: 356 KB
6. Commissioner Case Study Summary Example

7. Case Study Summary Information Example

Size: 946 KB
8. Formal Case Study Summary Example
Size: 235 KB
9. Academic Case Study Summary Example

Size: 263 KB
10. Corporation Case Studies Summary Example

Size: 573 KB
11. Standard Case Study Summary Example

Size: 193 KB
The Making an Effective Case Study Summary
As a researcher, you wouldn’t want your readers to have a hard time making sense of your case analysis . All the effort you put into making that can go to waste if it isn’t easy to understand. What you need is a compelling case study summary. If your review has the right information, your reader can level with you in no time. Here are some tricks to making a good case study summary.
1. Decide the Need
After writing an entire case study, the last thing you want is more report writing. That is why the first step to making a useful case summary is deciding if there is a need to have one. Some case studies that are considerably easier to understand don’t need case study summaries. But if your decision making says that you need it, then you better start!
2. Decide the Length
The length of the summary doesn’t always reflect how much information it holds. It can, however, determine how well of a writer you are. Your overview can be as concise as you want or as detailed as it needs to be. For as long as your research summary is readable, any length will do.
3. Prepare Data
The next step is conducting data analysis to figure out which data you are going to add to your case study summary. Pick out the most important details and the data most likely to raise questions. Anticipating these questions can help you formulate possible answers to add in your summary.
4. Organize Data
Making sure your data is organized is part and parcel to having a comprehensive case study summary. You can write a short introduction to open your summary and explain the purpose of your study. You then explain your solutions to the problem statement . Make sure no factoid overlaps another to avoid confusion.
5. Format Content
A continuous piece of writing can make a reader hesitate. Format your summary in a way that doesn’t seem too daunting. Divide your content, add a few white spaces. You have to let your readers’ eyes rest when scanning your summary. Don’t make your summary datasheet intimidating to look at.
When handling cases, whether you are a market analyst of a social science researcher, case study summaries are your best friends in data collection.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Business growth
Marketing tips
16 case study examples (+ 3 templates to make your own)
I like to think of case studies as a business's version of a resume. It highlights what the business can do, lends credibility to its offer, and contains only the positive bullet points that paint it in the best light possible.
Imagine if the guy running your favorite taco truck followed you home so that he could "really dig into how that burrito changed your life." I see the value in the practice. People naturally prefer a tried-and-true burrito just as they prefer tried-and-true products or services.
To help you showcase your success and flesh out your burrito questionnaire, I've put together some case study examples and key takeaways.
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth analysis of how your business, product, or service has helped past clients. It can be a document, a webpage, or a slide deck that showcases measurable, real-life results.
For example, if you're a SaaS company, you can analyze your customers' results after a few months of using your product to measure its effectiveness. You can then turn this analysis into a case study that further proves to potential customers what your product can do and how it can help them overcome their challenges.
It changes the narrative from "I promise that we can do X and Y for you" to "Here's what we've done for businesses like yours, and we can do it for you, too."
16 case study examples
While most case studies follow the same structure, quite a few try to break the mold and create something unique. Some businesses lean heavily on design and presentation, while others pursue a detailed, stat-oriented approach. Some businesses try to mix both.
There's no set formula to follow, but I've found that the best case studies utilize impactful design to engage readers and leverage statistics and case details to drive the point home. A case study typically highlights the companies, the challenges, the solution, and the results. The examples below will help inspire you to do it, too.
1. .css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;cursor:pointer;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Volcanica Coffee and AdRoll

People love a good farm-to-table coffee story, and boy am I one of them. But I've shared this case study with you for more reasons than my love of coffee. I enjoyed this study because it was written as though it was a letter.
In this case study, the founder of Volcanica Coffee talks about the journey from founding the company to personally struggling with learning and applying digital marketing to finding and enlisting AdRoll's services.
It felt more authentic, less about AdRoll showcasing their worth and more like a testimonial from a grateful and appreciative client. After the story, the case study wraps up with successes, milestones, and achievements. Note that quite a few percentages are prominently displayed at the top, providing supporting evidence that backs up an inspiring story.
Takeaway: Highlight your goals and measurable results to draw the reader in and provide concise, easily digestible information.
2. Taylor Guitars and Airtable

This Airtable case study on Taylor Guitars comes as close as one can to an optimal structure. It features a video that represents the artistic nature of the client, highlighting key achievements and dissecting each element of Airtable's influence.
It also supplements each section with a testimonial or quote from the client, using their insights as a catalyst for the case study's narrative. For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail.
Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail.
3. EndeavourX and Figma

My favorite part of Figma's case study is highlighting why EndeavourX chose its solution. You'll notice an entire section on what Figma does for teams and then specifically for EndeavourX.
It also places a heavy emphasis on numbers and stats. The study, as brief as it is, still manages to pack in a lot of compelling statistics about what's possible with Figma.
Takeaway: Showcase the "how" and "why" of your product's differentiators and how they benefit your customers.
4. ActiveCampaign and Zapier

Zapier's case study leans heavily on design, using graphics to present statistics and goals in a manner that not only remains consistent with the branding but also actively pushes it forward, drawing users' eyes to the information most important to them.
The graphics, emphasis on branding elements, and cause/effect style tell the story without requiring long, drawn-out copy that risks boring readers. Instead, the cause and effect are concisely portrayed alongside the client company's information for a brief and easily scannable case study.
Takeaway: Lean on design to call attention to the most important elements of your case study, and make sure it stays consistent with your branding.
5. Ironclad and OpenAI
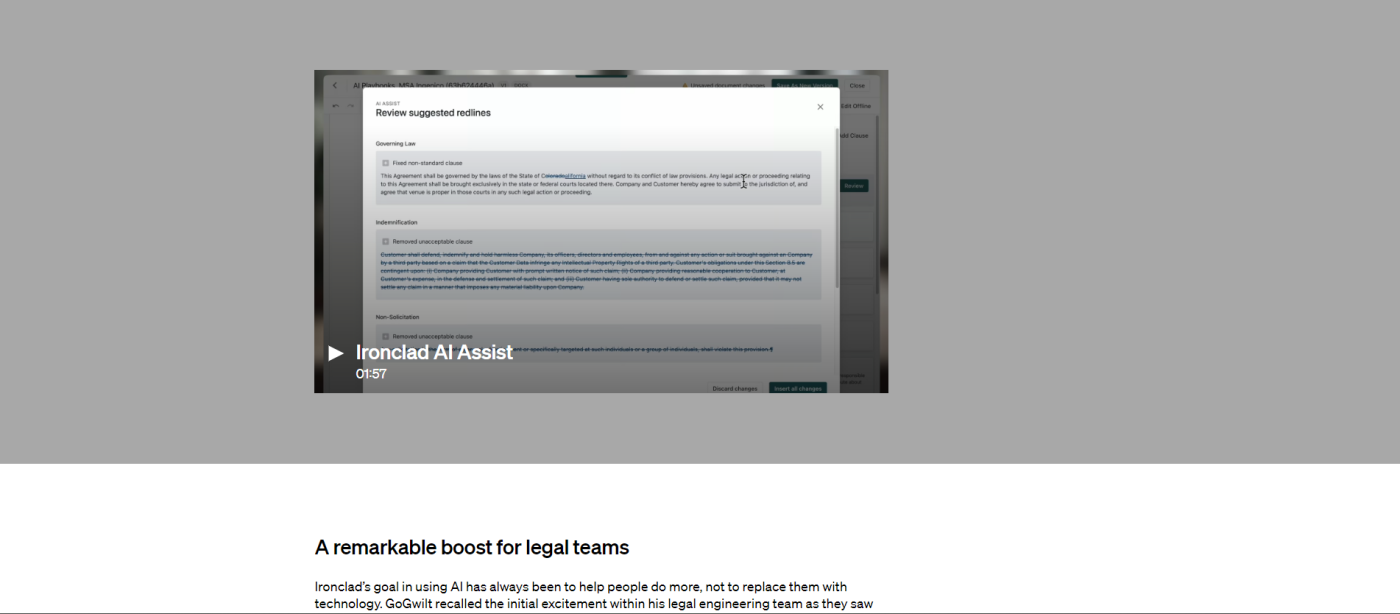
In true OpenAI fashion, this case study is a block of text. There's a distinct lack of imagery, but the study features a narrated video walking readers through the product.
The lack of imagery and color may not be the most inviting, but utilizing video format is commendable. It helps thoroughly communicate how OpenAI supported Ironclad in a way that allows the user to sit back, relax, listen, and be impressed.
Takeaway: Get creative with the media you implement in your case study. Videos can be a very powerful addition when a case study requires more detailed storytelling.
6. Shopify and GitHub

GitHub's case study on Shopify is a light read. It addresses client pain points and discusses the different aspects its product considers and improves for clients. It touches on workflow issues, internal systems, automation, and security. It does a great job of representing what one company can do with GitHub.
To drive the point home, the case study features colorful quote callouts from the Shopify team, sharing their insights and perspectives on the partnership, the key issues, and how they were addressed.
Takeaway: Leverage quotes to boost the authoritativeness and trustworthiness of your case study.
7 . Audible and Contentful

Contentful's case study on Audible features almost every element a case study should. It includes not one but two videos and clearly outlines the challenge, solution, and outcome before diving deeper into what Contentful did for Audible. The language is simple, and the writing is heavy with quotes and personal insights.
This case study is a uniquely original experience. The fact that the companies in question are perhaps two of the most creative brands out there may be the reason. I expected nothing short of a detailed analysis, a compelling story, and video content.
Takeaway: Inject some brand voice into the case study, and create assets that tell the story for you.
8 . Zoom and Asana
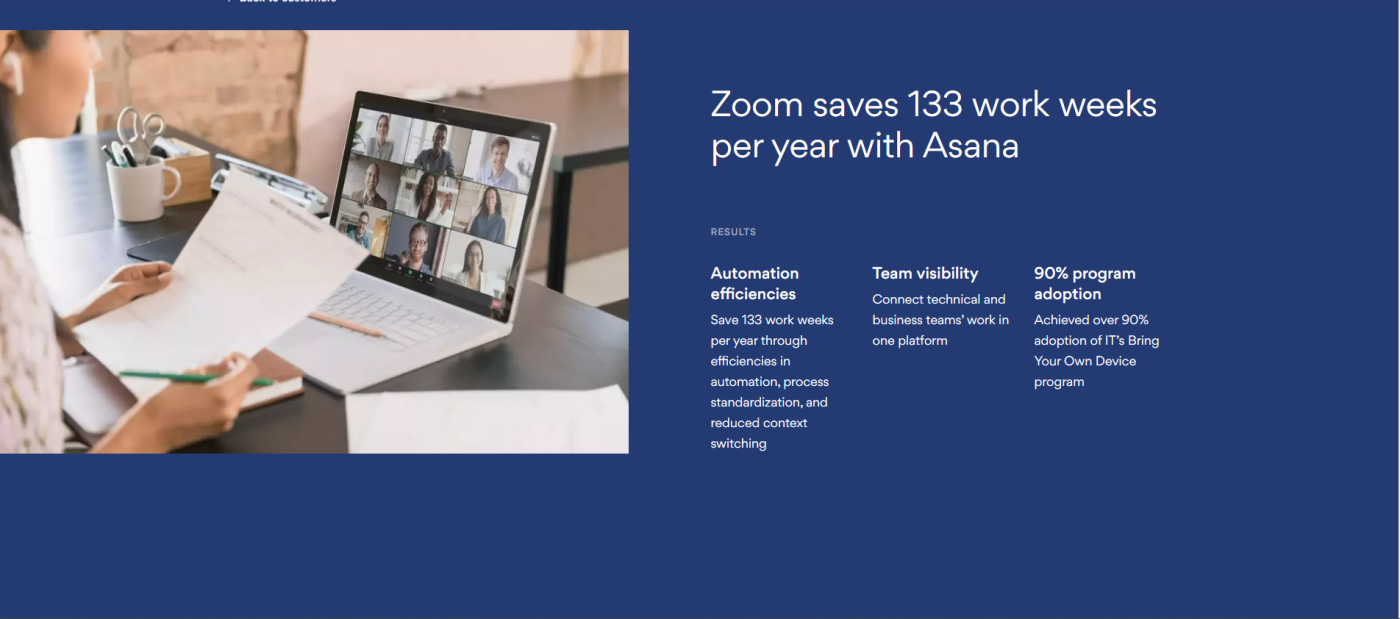
Asana's case study on Zoom is longer than the average piece and features detailed data on Zoom's growth since 2020. Instead of relying on imagery and graphics, it features several quotes and testimonials.
It's designed to be direct, informative, and promotional. At some point, the case study reads more like a feature list. There were a few sections that felt a tad too promotional for my liking, but to each their own burrito.
Takeaway: Maintain a balance between promotional and informative. You want to showcase the high-level goals your product helped achieve without losing the reader.
9 . Hickies and Mailchimp

I've always been a fan of Mailchimp's comic-like branding, and this case study does an excellent job of sticking to their tradition of making information easy to understand, casual, and inviting.
It features a short video that briefly covers Hickies as a company and Mailchimp's efforts to serve its needs for customer relationships and education processes. Overall, this case study is a concise overview of the partnership that manages to convey success data and tell a story at the same time. What sets it apart is that it does so in a uniquely colorful and brand-consistent manner.
Takeaway: Be concise to provide as much value in as little text as possible.
10. NVIDIA and Workday
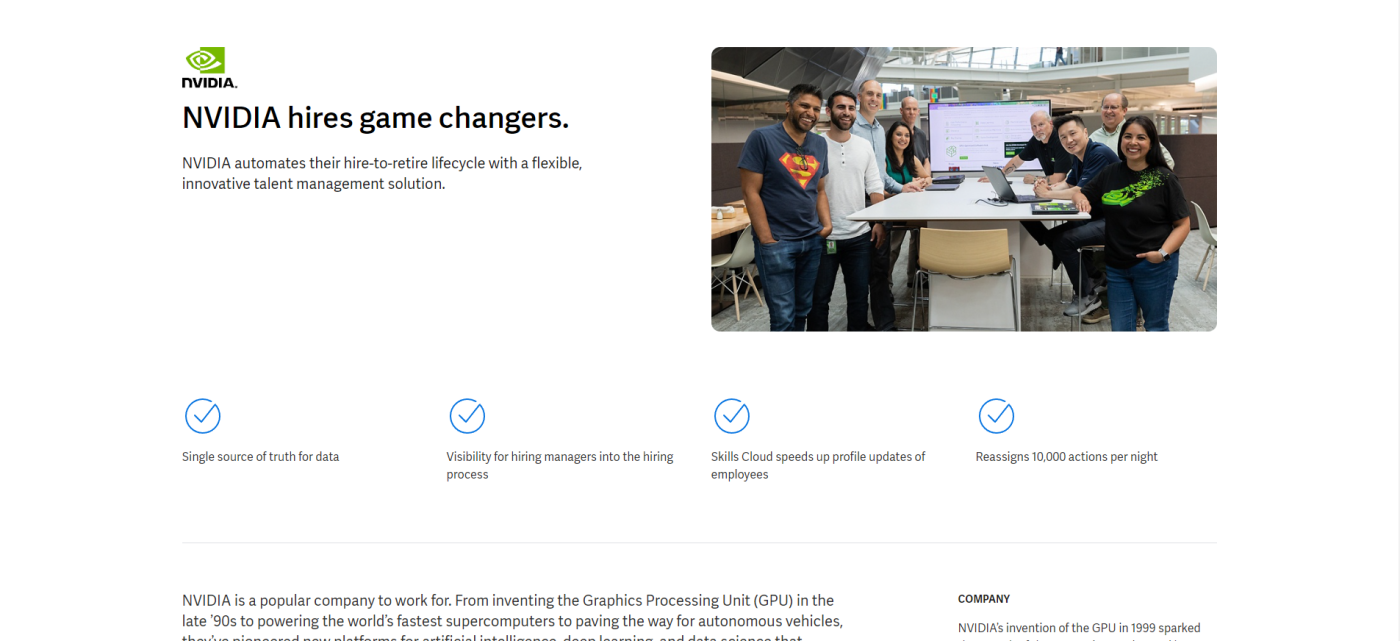
The gaming industry is notoriously difficult to recruit for, as it requires a very specific set of skills and experience. This case study focuses on how Workday was able to help fill that recruitment gap for NVIDIA, one of the biggest names in the gaming world.
Though it doesn't feature videos or graphics, this case study stood out to me in how it structures information like "key products used" to give readers insight into which tools helped achieve these results.
Takeaway: If your company offers multiple products or services, outline exactly which ones were involved in your case study, so readers can assess each tool.
11. KFC and Contentful
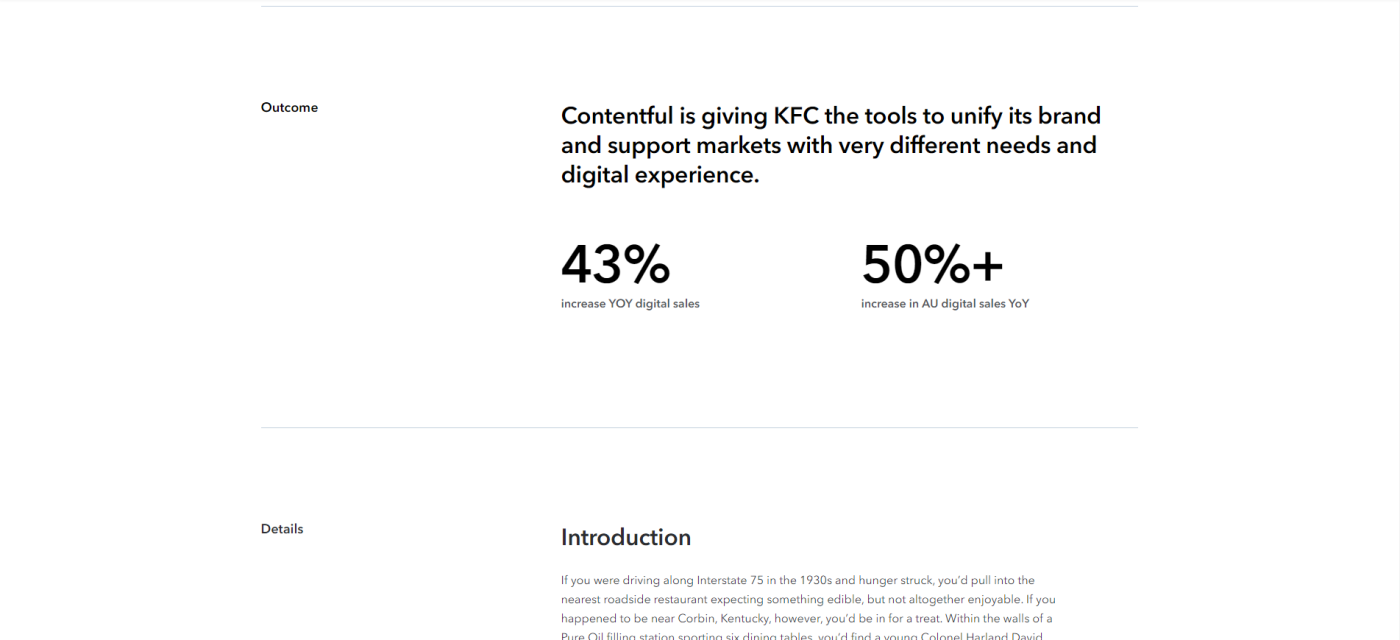
I'm personally not a big KFC fan, but that's only because I refuse to eat out of a bucket. My aversion to the bucket format aside, Contentful follows its consistent case study format in this one, outlining challenges, solutions, and outcomes before diving into the nitty-gritty details of the project.
Say what you will about KFC, but their primary product (chicken) does present a unique opportunity for wordplay like "Continuing to march to the beat of a digital-first drum(stick)" or "Delivering deep-fried goodness to every channel."
Takeaway: Inject humor into your case study if there's room for it and if it fits your brand.
12. Intuit and Twilio

Twilio does an excellent job of delivering achievements at the very beginning of the case study and going into detail in this two-minute read. While there aren't many graphics, the way quotes from the Intuit team are implemented adds a certain flair to the study and breaks up the sections nicely.
It's simple, concise, and manages to fit a lot of information in easily digestible sections.
Takeaway: Make sure each section is long enough to inform but brief enough to avoid boring readers. Break down information for each section, and don't go into so much detail that you lose the reader halfway through.
13. Spotify and Salesforce

Salesforce created a video that accurately summarizes the key points of the case study. Beyond that, the page itself is very light on content, and sections are as short as one paragraph.
I especially like how information is broken down into "What you need to know," "Why it matters," and "What the difference looks like." I'm not ashamed of being spoon-fed information. When it's structured so well and so simply, it makes for an entertaining read.
Takeaway: Invest in videos that capture and promote your partnership with your case study subject. Video content plays a promotional role that extends beyond the case study in social media and marketing initiatives .
14. Benchling and Airtable

Benchling is an impressive entity in its own right. Biotech R&D and health care nuances go right over my head. But the research and digging I've been doing in the name of these burritos (case studies) revealed that these products are immensely complex.
And that's precisely why this case study deserves a read—it succeeds at explaining a complex project that readers outside the industry wouldn't know much about.
Takeaway: Simplify complex information, and walk readers through the company's operations and how your business helped streamline them.
15. Chipotle and Hubble

The concision of this case study is refreshing. It features two sections—the challenge and the solution—all in 316 words. This goes to show that your case study doesn't necessarily need to be a four-figure investment with video shoots and studio time.
Sometimes, the message is simple and short enough to convey in a handful of paragraphs.
Takeaway: Consider what you should include instead of what you can include. Assess the time, resources, and effort you're able and willing to invest in a case study, and choose which elements you want to include from there.
16. Hudl and Zapier
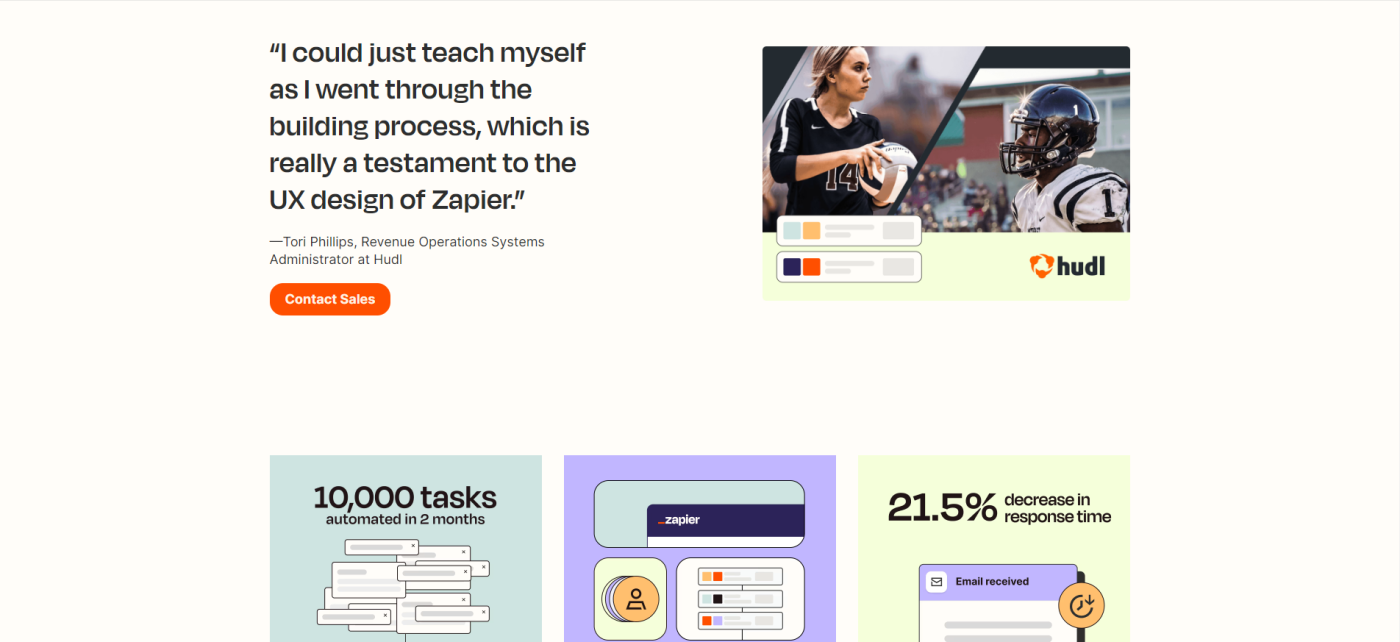
I may be biased, but I'm a big fan of seeing metrics and achievements represented in branded graphics. It can be a jarring experience to navigate a website, then visit a case study page and feel as though you've gone to a completely different website.
The Zapier format provides nuggets of high-level insights, milestones, and achievements, as well as the challenge, solution, and results. My favorite part of this case study is how it's supplemented with a blog post detailing how Hudl uses Zapier automation to build a seamless user experience.
The case study is essentially the summary, and the blog article is the detailed analysis that provides context beyond X achievement or Y goal.
Takeaway: Keep your case study concise and informative. Create other resources to provide context under your blog, media or press, and product pages.
3 case study templates
Now that you've had your fill of case studies (if that's possible), I've got just what you need: an infinite number of case studies, which you can create yourself with these case study templates.
Case study template 1

If you've got a quick hit of stats you want to show off, try this template. The opening section gives space for a short summary and three visually appealing stats you can highlight, followed by a headline and body where you can break the case study down more thoroughly. This one's pretty simple, with only sections for solutions and results, but you can easily continue the formatting to add more sections as needed.
Case study template 2

For a case study template with a little more detail, use this one. Opening with a striking cover page for a quick overview, this one goes on to include context, stakeholders, challenges, multiple quote callouts, and quick-hit stats.
Case study template 3

Whether you want a little structural variation or just like a nice dark green, this template has similar components to the last template but is designed to help tell a story. Move from the client overview through a description of your company before getting to the details of how you fixed said company's problems.
Tips for writing a case study
Examples are all well and good, but you don't learn how to make a burrito just by watching tutorials on YouTube without knowing what any of the ingredients are. You could , but it probably wouldn't be all that good.
Writing a good case study comes down to a mix of creativity, branding, and the capacity to invest in the project. With those details in mind, here are some case study tips to follow:
Have an objective: Define your objective by identifying the challenge, solution, and results. Assess your work with the client and focus on the most prominent wins. You're speaking to multiple businesses and industries through the case study, so make sure you know what you want to say to them.
Focus on persuasive data: Growth percentages and measurable results are your best friends. Extract your most compelling data and highlight it in your case study.
Use eye-grabbing graphics: Branded design goes a long way in accurately representing your brand and retaining readers as they review the study. Leverage unique and eye-catching graphics to keep readers engaged.
Simplify data presentation: Some industries are more complex than others, and sometimes, data can be difficult to understand at a glance. Make sure you present your data in the simplest way possible. Make it concise, informative, and easy to understand.
Use automation to drive results for your case study
A case study example is a source of inspiration you can leverage to determine how to best position your brand's work. Find your unique angle, and refine it over time to help your business stand out. Ask anyone: the best burrito in town doesn't just appear at the number one spot. They find their angle (usually the house sauce) and leverage it to stand out.
In fact, with the right technology, it can be refined to work better . Explore how Zapier's automation features can help drive results for your case study by making your case study a part of a developed workflow that creates a user journey through your website, your case studies, and into the pipeline.
Case study FAQ
Got your case study template? Great—it's time to gather the team for an awkward semi-vague data collection task. While you do that, here are some case study quick answers for you to skim through while you contemplate what to call your team meeting.
What is an example of a case study?
An example of a case study is when a software company analyzes its results from a client project and creates a webpage, presentation, or document that focuses on high-level results, challenges, and solutions in an attempt to showcase effectiveness and promote the software.
How do you write a case study?
To write a good case study, you should have an objective, identify persuasive and compelling data, leverage graphics, and simplify data. Case studies typically include an analysis of the challenge, solution, and results of the partnership.
What is the format of a case study?
While case studies don't have a set format, they're often portrayed as reports or essays that inform readers about the partnership and its results.
Related reading:
How Hudl uses automation to create a seamless user experience
How to make your case studies high-stakes—and why it matters
How experts write case studies that convert, not bore
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Hachem Ramki
Hachem is a writer and digital marketer from Montreal. After graduating with a degree in English, Hachem spent seven years traveling around the world before moving to Canada. When he's not writing, he enjoys Basketball, Dungeons and Dragons, and playing music for friends and family.
- Content marketing
Related articles
11 native advertising examples to learn from

8 TikTok ads examples to spark campaign ideas
8 TikTok ads examples to spark campaign...
10 examples of ethos in advertising to inspire your next campaign
10 examples of ethos in advertising to...

17 testimonial advertising examples to inspire your next campaign
17 testimonial advertising examples to...
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
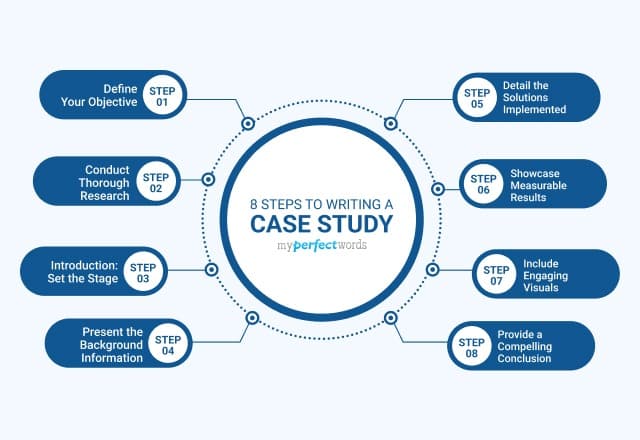
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics

- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Writing A Case Study
Case Study Examples
Brilliant Case Study Examples and Templates For Your Help
15 min read
People also read
A Complete Case Study Writing Guide With Examples
Simple Case Study Format for Students to Follow
Understand the Types of Case Study Here
It’s no surprise that writing a case study is one of the most challenging academic tasks for students. You’re definitely not alone here!
Most people don't realize that there are specific guidelines to follow when writing a case study. If you don't know where to start, it's easy to get overwhelmed and give up before you even begin.
Don't worry! Let us help you out!
We've collected over 25 free case study examples with solutions just for you. These samples with solutions will help you win over your panel and score high marks on your case studies.
So, what are you waiting for? Let's dive in and learn the secrets to writing a successful case study.
- 1. An Overview of Case Studies
- 2. Case Study Examples for Students
- 3. Business Case Study Examples
- 4. Medical Case Study Examples
- 5. Psychology Case Study Examples
- 6. Sales Case Study Examples
- 7. Interview Case Study Examples
- 8. Marketing Case Study Examples
- 9. Tips to Write a Good Case Study
An Overview of Case Studies
A case study is a research method used to study a particular individual, group, or situation in depth. It involves analyzing and interpreting data from a variety of sources to gain insight into the subject being studied.
Case studies are often used in psychology, business, and education to explore complicated problems and find solutions. They usually have detailed descriptions of the subject, background info, and an analysis of the main issues.
The goal of a case study is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject. Typically, case studies can be divided into three parts, challenges, solutions, and results.
Here is a case study sample PDF so you can have a clearer understanding of what a case study actually is:
Case Study Sample PDF
How to Write a Case Study Examples
Learn how to write a case study with the help of our comprehensive case study guide.
Case Study Examples for Students
Quite often, students are asked to present case studies in their academic journeys. The reason instructors assign case studies is for students to sharpen their critical analysis skills, understand how companies make profits, etc.
Below are some case study examples in research, suitable for students:
Case Study Example in Software Engineering
Qualitative Research Case Study Sample
Software Quality Assurance Case Study
Social Work Case Study Example
Ethical Case Study
Case Study Example PDF
These examples can guide you on how to structure and format your own case studies.
Struggling with formatting your case study? Check this case study format guide and perfect your document’s structure today.
Business Case Study Examples
A business case study examines a business’s specific challenge or goal and how it should be solved. Business case studies usually focus on several details related to the initial challenge and proposed solution.
To help you out, here are some samples so you can create case studies that are related to businesses:
Here are some more business case study examples:
Business Case Studies PDF
Business Case Studies Example
Typically, a business case study discovers one of your customer's stories and how you solved a problem for them. It allows your prospects to see how your solutions address their needs.
Medical Case Study Examples
Medical case studies are an essential part of medical education. They help students to understand how to diagnose and treat patients.
Here are some medical case study examples to help you.
Medical Case Study Example
Nursing Case Study Example
Want to understand the various types of case studies? Check out our types of case study blog to select the perfect type.
Psychology Case Study Examples
Case studies are a great way of investigating individuals with psychological abnormalities. This is why it is a very common assignment in psychology courses.
By examining all the aspects of your subject’s life, you discover the possible causes of exhibiting such behavior.
For your help, here are some interesting psychology case study examples:
Psychology Case Study Example
Mental Health Case Study Example
Sales Case Study Examples
Case studies are important tools for sales teams’ performance improvement. By examining sales successes, teams can gain insights into effective strategies and create action plans to employ similar tactics.
By researching case studies of successful sales campaigns, sales teams can more accurately identify challenges and develop solutions.
Sales Case Study Example
Interview Case Study Examples
Interview case studies provide businesses with invaluable information. This data allows them to make informed decisions related to certain markets or subjects.
Interview Case Study Example
Marketing Case Study Examples
Marketing case studies are real-life stories that showcase how a business solves a problem. They typically discuss how a business achieves a goal using a specific marketing strategy or tactic.
They typically describe a challenge faced by a business, the solution implemented, and the results achieved.
This is a short sample marketing case study for you to get an idea of what an actual marketing case study looks like.
Here are some more popular marketing studies that show how companies use case studies as a means of marketing and promotion:
“Chevrolet Discover the Unexpected” by Carol H. Williams
This case study explores Chevrolet's “ DTU Journalism Fellows ” program. The case study uses the initials “DTU” to generate interest and encourage readers to learn more.
Multiple types of media, such as images and videos, are used to explain the challenges faced. The case study concludes with an overview of the achievements that were met.
Key points from the case study include:
- Using a well-known brand name in the title can create interest.
- Combining different media types, such as headings, images, and videos, can help engage readers and make the content more memorable.
- Providing a summary of the key achievements at the end of the case study can help readers better understand the project's impact.
“The Met” by Fantasy
“ The Met ” by Fantasy is a fictional redesign of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, created by the design studio Fantasy. The case study clearly and simply showcases the museum's website redesign.
The Met emphasizes the website’s features and interface by showcasing each section of the interface individually, allowing the readers to concentrate on the significant elements.
For those who prefer text, each feature includes an objective description. The case study also includes a “Contact Us” call-to-action at the bottom of the page, inviting visitors to contact the company.
Key points from this “The Met” include:
- Keeping the case study simple and clean can help readers focus on the most important aspects.
- Presenting the features and solutions with a visual showcase can be more effective than writing a lot of text.
- Including a clear call-to-action at the end of the case study can encourage visitors to contact the company for more information.
“Better Experiences for All” by Herman Miller
Herman Miller's minimalist approach to furniture design translates to their case study, “ Better Experiences for All ”, for a Dubai hospital. The page features a captivating video with closed-captioning and expandable text for accessibility.
The case study presents a wealth of information in a concise format, enabling users to grasp the complexities of the strategy with ease. It concludes with a client testimonial and a list of furniture items purchased from the brand.
Key points from the “Better Experiences” include:
- Make sure your case study is user-friendly by including accessibility features like closed captioning and expandable text.
- Include a list of products that were used in the project to guide potential customers.
“NetApp” by Evisort
Evisort's case study on “ NetApp ” stands out for its informative and compelling approach. The study begins with a client-centric overview of NetApp, strategically directing attention to the client rather than the company or team involved.
The case study incorporates client quotes and explores NetApp’s challenges during COVID-19. Evisort showcases its value as a client partner by showing how its services supported NetApp through difficult times.
- Provide an overview of the company in the client’s words, and put focus on the customer.
- Highlight how your services can help clients during challenging times.
- Make your case study accessible by providing it in various formats.
“Red Sox Season Campaign,” by CTP Boston
The “ Red Sox Season Campaign ” showcases a perfect blend of different media, such as video, text, and images. Upon visiting the page, the video plays automatically, there are videos of Red Sox players, their images, and print ads that can be enlarged with a click.
The page features an intuitive design and invites viewers to appreciate CTP's well-rounded campaign for Boston's beloved baseball team. There’s also a CTA that prompts viewers to learn how CTP can create a similar campaign for their brand.
Some key points to take away from the “Red Sox Season Campaign”:
- Including a variety of media such as video, images, and text can make your case study more engaging and compelling.
- Include a call-to-action at the end of your study that encourages viewers to take the next step towards becoming a customer or prospect.
“Airbnb + Zendesk” by Zendesk
The case study by Zendesk, titled “ Airbnb + Zendesk : Building a powerful solution together,” showcases a true partnership between Airbnb and Zendesk.
The article begins with an intriguing opening statement, “Halfway around the globe is a place to stay with your name on it. At least for a weekend,” and uses stunning images of beautiful Airbnb locations to captivate readers.
Instead of solely highlighting Zendesk's product, the case study is crafted to tell a good story and highlight Airbnb's service in detail. This strategy makes the case study more authentic and relatable.
Some key points to take away from this case study are:
- Use client's offerings' images rather than just screenshots of your own product or service.
- To begin the case study, it is recommended to include a distinct CTA. For instance, Zendesk presents two alternatives, namely to initiate a trial or seek a solution.
“Influencer Marketing” by Trend and WarbyParker
The case study "Influencer Marketing" by Trend and Warby Parker highlights the potential of influencer content marketing, even when working with a limited budget.
The “Wearing Warby” campaign involved influencers wearing Warby Parker glasses during their daily activities, providing a glimpse of the brand's products in use.
This strategy enhanced the brand's relatability with influencers' followers. While not detailing specific tactics, the case study effectively illustrates the impact of third-person case studies in showcasing campaign results.
Key points to take away from this case study are:
- Influencer marketing can be effective even with a limited budget.
- Showcasing products being used in everyday life can make a brand more approachable and relatable.
- Third-person case studies can be useful in highlighting the success of a campaign.
Marketing Case Study Example
Marketing Case Study Template
Now that you have read multiple case study examples, hop on to our tips.
Tips to Write a Good Case Study
Here are some note-worthy tips to craft a winning case study
- Define the purpose of the case study This will help you to focus on the most important aspects of the case. The case study objective helps to ensure that your finished product is concise and to the point.
- Choose a real-life example. One of the best ways to write a successful case study is to choose a real-life example. This will give your readers a chance to see how the concepts apply in a real-world setting.
- Keep it brief. This means that you should only include information that is directly relevant to your topic and avoid adding unnecessary details.
- Use strong evidence. To make your case study convincing, you will need to use strong evidence. This can include statistics, data from research studies, or quotes from experts in the field.
- Edit and proofread your work. Before you submit your case study, be sure to edit and proofread your work carefully. This will help to ensure that there are no errors and that your paper is clear and concise.
There you go!
We’re sure that now you have secrets to writing a great case study at your fingertips! This blog teaches the key guidelines of various case studies with samples. So grab your pen and start crafting a winning case study right away!
Having said that, we do understand that some of you might be having a hard time writing compelling case studies.
But worry not! Our expert case study writing service is here to take all your case-writing blues away!
With 100% thorough research guaranteed, our online essay service can craft an amazing case study within 24 hours!
So why delay? Let us help you shine in the eyes of your instructor!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
28 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
Published: March 08, 2023
Putting together a compelling case study is one of the most powerful strategies for showcasing your product and attracting future customers. But it's not easy to create case studies that your audience can’t wait to read.

In this post, we’ll go over the definition of a case study and the best examples to inspire you.

What is a case study?
A case study is a detailed story of something your company did. It includes a beginning — often discussing a conflict, an explanation of what happened next, and a resolution that explains how the company solved or improved on something.
A case study proves how your product has helped other companies by demonstrating real-life results. Not only that, but marketing case studies with solutions typically contain quotes from the customer. This means that they’re not just ads where you praise your own product. Rather, other companies are praising your company — and there’s no stronger marketing material than a verbal recommendation or testimonial. A great case study is also filled with research and stats to back up points made about a project's results.
There are myriad ways to use case studies in your marketing strategy . From featuring them on your website to including them in a sales presentation, a case study is a strong, persuasive tool that shows customers why they should work with you — straight from another customer. Writing one from scratch is hard, though, which is why we’ve created a collection of case study templates for you to get started.
Fill out the form below to access the free case study templates.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
There’s no better way to generate more leads than by writing case studies . But without case study examples to draw inspiration from, it can be difficult to write impactful studies that convince visitors to submit a form.
Marketing Case Study Examples
To help you create an attractive and high-converting case study, we've put together a list of some of our favorites. This list includes famous case studies in marketing, technology, and business.
These studies can show you how to frame your company offers in a way that is both meaningful and useful to your audience. So, take a look, and let these examples inspire your next brilliant case study design.
These marketing case studies with solutions show the value proposition of each product. They also show how each company benefited in both the short and long term using quantitative data. In other words, you don’t get just nice statements, like "This company helped us a lot." You see actual change within the firm through numbers and figures.
You can put your learnings into action with HubSpot's Free Case Study Templates . Available as custom designs and text-based documents, you can upload these templates to your CMS or send them to prospects as you see fit.

1. " How Handled Scaled from Zero to 121 Locations with the Help of HubSpot ," by HubSpot

What's interesting about this case study is the way it leads with the customer. That reflects a major HubSpot cornerstone, which is to always solve for the customer first. The copy leads with a brief description of why the CEO of Handled founded the company and why he thought Handled could benefit from adopting a CRM. The case study also opens up with one key data point about Handled’s success using HubSpot, namely that it grew to 121 locations.
Notice that this case study uses mixed media. Yes, there is a short video, but it's elaborated upon in the other text on the page. So while your case studies can use one or the other, don't be afraid to combine written copy with visuals to emphasize the project's success.
Key Learnings from the HubSpot Case Study Example
- Give the case study a personal touch by focusing on the CEO rather than the company itself.
- Use multimedia to engage website visitors as they read the case study.
2. " The Whole Package ," by IDEO

Here's a design company that knows how to lead with simplicity in its case studies. As soon as the visitor arrives at the page, they’re greeted with a big, bold photo and the title of the case study — which just so happens to summarize how IDEO helped its client. It summarizes the case study in three snippets: The challenge, the impact, and the outcome.
Immediately, IDEO communicates its impact — the company partnered with H&M to remove plastic from its packaging — but it doesn't stop there. As the user scrolls down, the challenge, impact, and progress are elaborated upon with comprehensive (but not overwhelming) copy that outlines what that process looked like, replete with quotes and intriguing visuals.
Key Learnings from the IDEO Case Study Example
- Split up the takeaways of your case studies into bite-sized sections.
- Always use visuals and images to enrich the case study experience, especially if it’s a comprehensive case study.
3. " Rozum Robotics intensifies its PR game with Awario ," by Awario
In this case study, Awario greets the user with a summary straight away — so if you’re feeling up to reading the entire case study, you can scan the snapshot and understand how the company serves its customers. The case study then includes jump links to several sections, such as "Company Profile," "Rozum Robotics' Pains," "Challenge," "Solution," and "Results and Improvements."
The sparse copy and prominent headings show that you don’t need a lot of elaborate information to show the value of your products and services. Like the other case study examples on this list, it includes visuals and quotes to demonstrate the effectiveness of the company’s efforts. The case study ends with a bulleted list that shows the results.
Key Learnings from the Awario Robotics Case Study Example
- Create a table of contents to make your case study easier to navigate.
- Include a bulleted list of the results you achieved for your client.
4. " Chevrolet DTU ," by Carol H. Williams

If you’ve worked with a company that’s well-known, use only the name in the title — like Carol H. Williams, one of the nation’s top advertising agencies, does here. The "DTU," stands for "Discover the Unexpected." It generates interest because you want to find out what the initials mean.
They keep your interest in this case study by using a mixture of headings, images, and videos to describe the challenges, objectives, and solutions of the project. The case study closes with a summary of the key achievements that Chevrolet’s DTU Journalism Fellows reached during the project.
Key Learnings from the Carol H. Williams Case Study Example
- If you’ve worked with a big brand before, consider only using the name in the title — just enough to pique interest.
- Use a mixture of headings and subheadings to guide users through the case study.
5. " How Fractl Earned Links from 931 Unique Domains for Porch.com in a Single Year ," by Fractl

Fractl uses both text and graphic design in their Porch.com case study to immerse the viewer in a more interesting user experience. For instance, as you scroll, you'll see the results are illustrated in an infographic-design form as well as the text itself.
Further down the page, they use icons like a heart and a circle to illustrate their pitch angles, and graphs to showcase their results. Rather than writing which publications have mentioned Porch.com during Fractl’s campaign, they incorporated the media outlets’ icons for further visual diversity.
Key Learnings from the Fractl Case Study Example
- Let pictures speak for you by incorporating graphs, logos, and icons all throughout the case study.
- Start the case study by right away stating the key results, like Fractl does, instead of putting the results all the way at the bottom.
6. " The Met ," by Fantasy
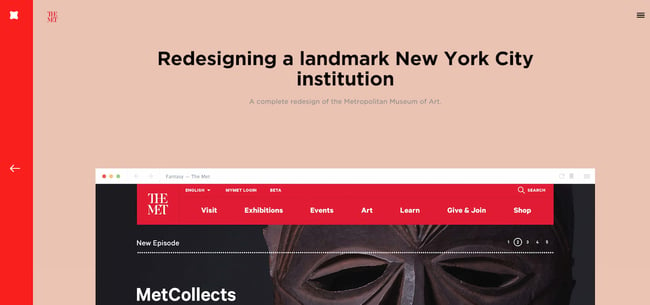
What's the best way to showcase the responsiveness and user interface of a website? Probably by diving right into it with a series of simple showcases— which is exactly what Fantasy does on their case study page for the Metropolitan Museum of Art. They keep the page simple and clean, inviting you to review their redesign of the Met’s website feature-by-feature.
Each section is simple, showing a single piece of the new website's interface so that users aren’t overwhelmed with information and can focus on what matters most.
If you're more interested in text, you can read the objective for each feature. Fantasy understands that, as a potential customer, this is all you need to know. Scrolling further, you're greeted with a simple "Contact Us" CTA.
Key Learnings from the Fantasy Case Study Example
- You don’t have to write a ton of text to create a great case study. Focus on the solution you delivered itself.
- Include a CTA at the bottom inviting visitors to contact you.
7. " Rovio: How Rovio Grew Into a Gaming Superpower ," by App Annie
If your client had a lot of positive things to say about you, take a note from App Annie’s Rovio case study and open up with a quote from your client. The case study also closes with a quote, so that the case study doesn’t seem like a promotion written by your marketing team but a story that’s taken straight from your client’s mouth. It includes a photo of a Rovio employee, too.
Another thing this example does well? It immediately includes a link to the product that Rovio used (namely, App Annie Intelligence) at the top of the case study. The case study closes with a call-to-action button prompting users to book a demo.
Key Learnings from the App Annie Case Study Example
- Feature quotes from your client at the beginning and end of the case study.
- Include a mention of the product right at the beginning and prompt users to learn more about the product.
8. " Embracing first-party data: 3 success stories from HubSpot ," by Think with Google

Google takes a different approach to text-focused case studies by choosing three different companies to highlight.
The case study is clean and easily scannable. It has sections for each company, with quotes and headers that clarify the way these three distinct stories connect. The simple format also uses colors and text that align with the Google brand.
Another differentiator is the focus on data. This case study is less than a thousand words, but it's packed with useful data points. Data-driven insights quickly and clearly show how the value of leveraging first-party data while prioritizing consumer privacy.
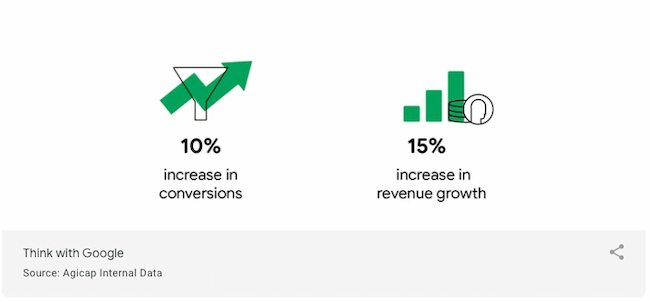
Key Learnings from the Think with Google Case Study Example
- A case study doesn’t need to be long or complex to be powerful.
- Clear data points are a quick and effective way to prove value.
9. " In-Depth Performance Marketing Case Study ," by Switch

Switch is an international marketing agency based in Malta that knocks it out of the park with this case study. Its biggest challenge is effectively communicating what it did for its client without ever revealing the client’s name. It also effectively keeps non-marketers in the loop by including a glossary of terms on page 4.
The PDF case study reads like a compelling research article, including titles like "In-Depth Performance Marketing Case Study," "Scenario," and "Approach," so that readers get a high-level overview of what the client needed and why they approached Switch. It also includes a different page for each strategy. For instance, if you’d only be interested in hiring Switch for optimizing your Facebook ads, you can skip to page 10 to see how they did it.
The PDF is fourteen pages long but features big fonts and plenty of white space, so viewers can easily skim it in only a few minutes.
Key Learnings from the Switch Case Study Example
- If you want to go into specialized information, include a glossary of terms so that non-specialists can easily understand.
- Close with a CTA page in your case study PDF and include contact information for prospective clients.
10. " Gila River ," by OH Partners

Let pictures speak for you, like OH Partners did in this case study. While you’ll quickly come across a heading and some text when you land on this case study page, you’ll get the bulk of the case study through examples of actual work OH Partners did for its client. You will see OH Partners’ work in a billboard, magazine, and video. This communicates to website visitors that if they work with OH Partners, their business will be visible everywhere.
And like the other case studies here, it closes with a summary of what the firm achieved for its client in an eye-catching way.
Key Learnings from the OH Partners Case Study Example
- Let the visuals speak by including examples of the actual work you did for your client — which is especially useful for branding and marketing agencies.
- Always close out with your achievements and how they impacted your client.
11. " Facing a Hater ," by Digitas
Digitas' case study page for Sprite’s #ILOVEYOUHATER campaign keeps it brief while communicating the key facts of Digitas’ work for the popular soda brand. The page opens with an impactful image of a hundred people facing a single man. It turns out, that man is the biggest "bully" in Argentina, and the people facing him are those whom he’s bullied before.
Scrolling down, it's obvious that Digitas kept Sprite at the forefront of their strategy, but more than that, they used real people as their focal point. They leveraged the Twitter API to pull data from Tweets that people had actually tweeted to find the identity of the biggest "hater" in the country. That turned out to be @AguanteElCofler, a Twitter user who has since been suspended.
Key Learnings from the Digitas Case Study Example
- If a video was part of your work for your client, be sure to include the most impactful screenshot as the heading.
- Don’t be afraid to provide details on how you helped your client achieve their goals, including the tools you leveraged.
12. " Better Experiences for All ," by HermanMiller

HermanMiller sells sleek, utilitarian furniture with no frills and extreme functionality, and that ethos extends to its case study page for a hospital in Dubai.
What first attracted me to this case study was the beautiful video at the top and the clean user experience. User experience matters a lot in a case study. It determines whether users will keep reading or leave. Another notable aspect of this case study is that the video includes closed-captioning for greater accessibility, and users have the option of expanding the CC and searching through the text.
HermanMiller’s case study also offers an impressive amount of information packed in just a few short paragraphs for those wanting to understand the nuances of their strategy. It closes out with a quote from their client and, most importantly, the list of furniture products that the hospital purchased from the brand.
Key Learnings from the HermanMiller Case Study Example
- Close out with a list of products that users can buy after reading the case study.
- Include accessibility features such as closed captioning and night mode to make your case study more user-friendly.
13. " Capital One on AWS ," by Amazon
Do you work continuously with your clients? Consider structuring your case study page like Amazon did in this stellar case study example. Instead of just featuring one article about Capital One and how it benefited from using AWS, Amazon features a series of articles that you can then access if you’re interested in reading more. It goes all the way back to 2016, all with different stories that feature Capital One’s achievements using AWS.
This may look unattainable for a small firm, but you don’t have to go to extreme measures and do it for every single one of your clients. You could choose the one you most wish to focus on and establish a contact both on your side and your client’s for coming up with the content. Check in every year and write a new piece. These don’t have to be long, either — five hundred to eight hundred words will do.
Key Learnings from the Amazon AWS Case Study Example
- Write a new article each year featuring one of your clients, then include links to those articles in one big case study page.
- Consider including external articles as well that emphasize your client’s success in their industry.
14. " HackReactor teaches the world to code #withAsana ," by Asana

While Asana's case study design looks text-heavy, there's a good reason. It reads like a creative story, told entirely from the customer's perspective.
For instance, Asana knows you won't trust its word alone on why this product is useful. So, they let Tony Phillips, HackReactor CEO, tell you instead: "We take in a lot of information. Our brains are awful at storage but very good at thinking; you really start to want some third party to store your information so you can do something with it."
Asana features frequent quotes from Phillips to break up the wall of text and humanize the case study. It reads like an in-depth interview and captivates the reader through creative storytelling. Even more, Asana includes in-depth detail about how HackReactor uses Asana. This includes how they build templates and workflows:
"There's a huge differentiator between Asana and other tools, and that’s the very easy API access. Even if Asana isn’t the perfect fit for a workflow, someone like me— a relatively mediocre software engineer—can add functionality via the API to build a custom solution that helps a team get more done."
Key Learnings from the Asana Example
- Include quotes from your client throughout the case study.
- Provide extensive detail on how your client worked with you or used your product.
15. " Rips Sewed, Brand Love Reaped ," by Amp Agency

Amp Agency's Patagonia marketing strategy aimed to appeal to a new audience through guerrilla marketing efforts and a coast-to-coast road trip. Their case study page effectively conveys a voyager theme, complete with real photos of Patagonia customers from across the U.S., and a map of the expedition. I liked Amp Agency's storytelling approach best. It captures viewers' attention from start to finish simply because it's an intriguing and unique approach to marketing.
Key Learnings from the Amp Agency Example
- Open up with a summary that communicates who your client is and why they reached out to you.
- Like in the other case study examples, you’ll want to close out with a quantitative list of your achievements.
16. " NetApp ," by Evisort
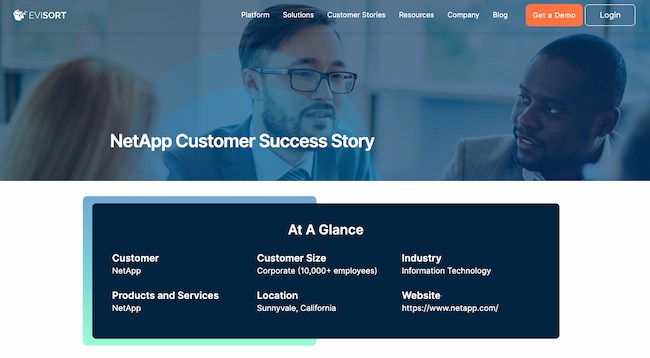
Evisort opens up its NetApp case study with an at-a-glance overview of the client. It’s imperative to always focus on the client in your case study — not on your amazing product and equally amazing team. By opening up with a snapshot of the client’s company, Evisort places the focus on the client.
This case study example checks all the boxes for a great case study that’s informative, thorough, and compelling. It includes quotes from the client and details about the challenges NetApp faced during the COVID pandemic. It closes out with a quote from the client and with a link to download the case study in PDF format, which is incredibly important if you want your case study to be accessible in a wider variety of formats.
Key Learnings from the Evisort Example
- Place the focus immediately on your client by including a snapshot of their company.
- Mention challenging eras, such as a pandemic or recession, to show how your company can help your client succeed even during difficult times.
17. " Copernicus Land Monitoring – CLC+ Core ," by Cloudflight
Including highly specialized information in your case study is an effective way to show prospects that you’re not just trying to get their business. You’re deep within their industry, too, and willing to learn everything you need to learn to create a solution that works specifically for them.
Cloudflight does a splendid job at that in its Copernicus Land Monitoring case study. While the information may be difficult to read at first glance, it will capture the interest of prospects who are in the environmental industry. It thus shows Cloudflight’s value as a partner much more effectively than a general case study would.
The page is comprehensive and ends with a compelling call-to-action — "Looking for a solution that automates, and enhances your Big Data system? Are you struggling with large datasets and accessibility? We would be happy to advise and support you!" The clean, whitespace-heavy page is an effective example of using a case study to capture future leads.
Key Learnings from the Cloudflight Case Study Example
- Don’t be afraid to get technical in your explanation of what you did for your client.
- Include a snapshot of the sales representative prospects should contact, especially if you have different sales reps for different industries, like Cloudflight does.
18. " Valvoline Increases Coupon Send Rate by 76% with Textel’s MMS Picture Texting ," by Textel

If you’re targeting large enterprises with a long purchasing cycle, you’ll want to include a wealth of information in an easily transferable format. That’s what Textel does here in its PDF case study for Valvoline. It greets the user with an eye-catching headline that shows the value of using Textel. Valvoline saw a significant return on investment from using the platform.
Another smart decision in this case study is highlighting the client’s quote by putting it in green font and doing the same thing for the client’s results because it helps the reader quickly connect the two pieces of information. If you’re in a hurry, you can also take a look at the "At a Glance" column to get the key facts of the case study, starting with information about Valvoline.
Key Learnings from the Textel Case Study Example
- Include your client’s ROI right in the title of the case study.
- Add an "At a Glance" column to your case study PDF to make it easy to get insights without needing to read all the text.
19. " Hunt Club and Happeo — a tech-enabled love story ," by Happeo

In this blog-post-like case study, Happeo opens with a quote from the client, then dives into a compelling heading: "Technology at the forefront of Hunt Club's strategy." Say you’re investigating Happeo as a solution and consider your firm to be technology-driven. This approach would spark your curiosity about why the client chose to work with Happeo. It also effectively communicates the software’s value proposition without sounding like it’s coming from an in-house marketing team.
Every paragraph is a quote written from the customer’s perspective. Later down the page, the case study also dives into "the features that changed the game for Hunt Club," giving Happeo a chance to highlight some of the platform’s most salient features.
Key Learnings from the Happeo Case Study Example
- Consider writing the entirety of the case study from the perspective of the customer.
- Include a list of the features that convinced your client to go with you.
20. " Red Sox Season Campaign ," by CTP Boston
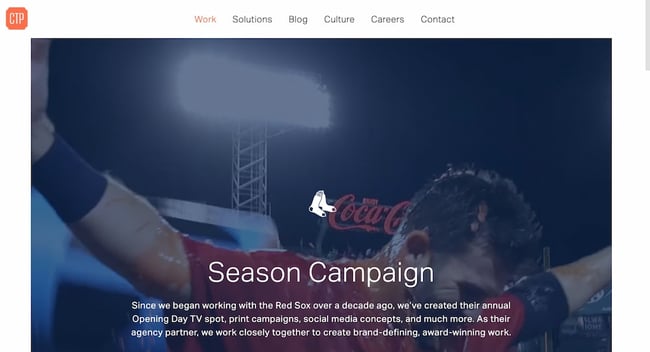
What's great about CTP's case study page for their Red Sox Season Campaign is their combination of video, images, and text. A video automatically begins playing when you visit the page, and as you scroll, you'll see more embedded videos of Red Sox players, a compilation of print ads, and social media images you can click to enlarge.
At the bottom, it says "Find out how we can do something similar for your brand." The page is clean, cohesive, and aesthetically pleasing. It invites viewers to appreciate the well-roundedness of CTP's campaign for Boston's beloved baseball team.
Key Learnings from the CTP Case Study Example
- Include a video in the heading of the case study.
- Close with a call-to-action that makes leads want to turn into prospects.
21. " Acoustic ," by Genuine

Sometimes, simple is key. Genuine's case study for Acoustic is straightforward and minimal, with just a few short paragraphs, including "Reimagining the B2B website experience," "Speaking to marketers 1:1," and "Inventing Together." After the core of the case study, we then see a quote from Acoustic’s CMO and the results Genuine achieved for the company.
The simplicity of the page allows the reader to focus on both the visual aspects and the copy. The page displays Genuine's brand personality while offering the viewer all the necessary information they need.
- You don’t need to write a lot to create a great case study. Keep it simple.
- Always include quantifiable data to illustrate the results you achieved for your client.
22. " Using Apptio Targetprocess Automated Rules in Wargaming ," by Apptio
Apptio’s case study for Wargaming summarizes three key pieces of information right at the beginning: The goals, the obstacles, and the results.
Readers then have the opportunity to continue reading — or they can walk away right then with the information they need. This case study also excels in keeping the human interest factor by formatting the information like an interview.
The piece is well-organized and uses compelling headers to keep the reader engaged. Despite its length, Apptio's case study is appealing enough to keep the viewer's attention. Every Apptio case study ends with a "recommendation for other companies" section, where the client can give advice for other companies that are looking for a similar solution but aren’t sure how to get started.
Key Learnings from the Apptio Case Study Example
- Put your client in an advisory role by giving them the opportunity to give recommendations to other companies that are reading the case study.
- Include the takeaways from the case study right at the beginning so prospects quickly get what they need.
23. " Airbnb + Zendesk: building a powerful solution together ," by Zendesk
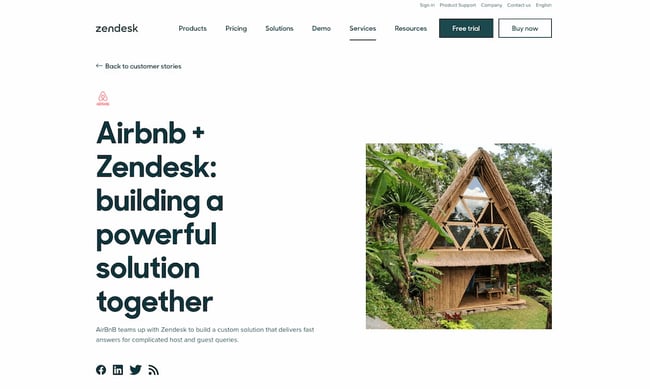
Zendesk's Airbnb case study reads like a blog post, and focuses equally on Zendesk and Airbnb, highlighting a true partnership between the companies. To captivate readers, it begins like this: "Halfway around the globe is a place to stay with your name on it. At least for a weekend."
The piece focuses on telling a good story and provides photographs of beautiful Airbnb locations. In a case study meant to highlight Zendesk's helpfulness, nothing could be more authentic than their decision to focus on Airbnb's service in such great detail.
Key Learnings from the Zendesk Case Study Example
- Include images of your client’s offerings — not necessarily of the service or product you provided. Notice how Zendesk doesn’t include screenshots of its product.
- Include a call-to-action right at the beginning of the case study. Zendesk gives you two options: to find a solution or start a trial.
24. " Biobot Customer Success Story: Rollins College, Winter Park, Florida ," by Biobot
Like some of the other top examples in this list, Biobot opens its case study with a quote from its client, which captures the value proposition of working with Biobot. It mentions the COVID pandemic and goes into detail about the challenges the client faced during this time.
This case study is structured more like a news article than a traditional case study. This format can work in more formal industries where decision-makers need to see in-depth information about the case. Be sure to test different methods and measure engagement .
Key Learnings from the Biobot Case Study Example
- Mention environmental, public health, or economic emergencies and how you helped your client get past such difficult times.
- Feel free to write the case study like a normal blog post, but be sure to test different methods to find the one that best works for you.
25. " Discovering Cost Savings With Efficient Decision Making ," by Gartner

You don't always need a ton of text or a video to convey your message — sometimes, you just need a few paragraphs and bullet points. Gartner does a fantastic job of quickly providing the fundamental statistics a potential customer would need to know, without boggling down their readers with dense paragraphs. The case study closes with a shaded box that summarizes the impact that Gartner had on its client. It includes a quote and a call-to-action to "Learn More."
Key Learnings from the Gartner Case Study Example
- Feel free to keep the case study short.
- Include a call-to-action at the bottom that takes the reader to a page that most relates to them.
26. " Bringing an Operator to the Game ," by Redapt

This case study example by Redapt is another great demonstration of the power of summarizing your case study’s takeaways right at the start of the study. Redapt includes three easy-to-scan columns: "The problem," "the solution," and "the outcome." But its most notable feature is a section titled "Moment of clarity," which shows why this particular project was difficult or challenging.
The section is shaded in green, making it impossible to miss. Redapt does the same thing for each case study. In the same way, you should highlight the "turning point" for both you and your client when you were working toward a solution.
Key Learnings from the Redapt Case Study Example
- Highlight the turning point for both you and your client during the solution-seeking process.
- Use the same structure (including the same headings) for your case studies to make them easy to scan and read.
27. " Virtual Call Center Sees 300% Boost In Contact Rate ," by Convoso

Convoso’s PDF case study for Digital Market Media immediately mentions the results that the client achieved and takes advantage of white space. On the second page, the case study presents more influential results. It’s colorful and engaging and closes with a spread that prompts readers to request a demo.
Key Learnings from the Convoso Case Study Example
- List the results of your work right at the beginning of the case study.
- Use color to differentiate your case study from others. Convoso’s example is one of the most colorful ones on this list.
28. " Ensuring quality of service during a pandemic ," by Ericsson
Ericsson’s case study page for Orange Spain is an excellent example of using diverse written and visual media — such as videos, graphs, and quotes — to showcase the success a client experienced. Throughout the case study, Ericsson provides links to product and service pages users might find relevant as they’re reading the study.
For instance, under the heading "Preloaded with the power of automation," Ericsson mentions its Ericsson Operations Engine product, then links to that product page. It closes the case study with a link to another product page.
Key Learnings from the Ericsson Case Study Example
- Link to product pages throughout the case study so that readers can learn more about the solution you offer.
- Use multimedia to engage users as they read the case study.
Start creating your case study.
Now that you've got a great list of examples of case studies, think about a topic you'd like to write about that highlights your company or work you did with a customer.
A customer’s success story is the most persuasive marketing material you could ever create. With a strong portfolio of case studies, you can ensure prospects know why they should give you their business.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![example summary of case study 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/most%20popular%20types%20of%20content.jpg)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]
![example summary of case study How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]
![example summary of case study What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Template Lists
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business
How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
By Danesh Ramuthi , Sep 07, 2023

Okay, let’s get real: case studies can be kinda snooze-worthy. But guess what? They don’t have to be!
In this article, I will cover every element that transforms a mere report into a compelling case study, from selecting the right metrics to using persuasive narrative techniques.
And if you’re feeling a little lost, don’t worry! There are cool tools like Venngage’s Case Study Creator to help you whip up something awesome, even if you’re short on time. Plus, the pre-designed case study templates are like instant polish because let’s be honest, everyone loves a shortcut.
Click to jump ahead:

What is a case study presentation?
What is the purpose of presenting a case study, how to structure a case study presentation, how long should a case study presentation be, 5 case study presentation examples with templates, 6 tips for delivering an effective case study presentation, 5 common mistakes to avoid in a case study presentation, how to present a case study faqs.
A case study presentation involves a comprehensive examination of a specific subject, which could range from an individual, group, location, event, organization or phenomenon.
They’re like puzzles you get to solve with the audience, all while making you think outside the box.
Unlike a basic report or whitepaper, the purpose of a case study presentation is to stimulate critical thinking among the viewers.
The primary objective of a case study is to provide an extensive and profound comprehension of the chosen topic. You don’t just throw numbers at your audience. You use examples and real-life cases to make you think and see things from different angles.

The primary purpose of presenting a case study is to offer a comprehensive, evidence-based argument that informs, persuades and engages your audience.
Here’s the juicy part: presenting that case study can be your secret weapon. Whether you’re pitching a groundbreaking idea to a room full of suits or trying to impress your professor with your A-game, a well-crafted case study can be the magic dust that sprinkles brilliance over your words.
Think of it like digging into a puzzle you can’t quite crack . A case study lets you explore every piece, turn it over and see how it fits together. This close-up look helps you understand the whole picture, not just a blurry snapshot.
It’s also your chance to showcase how you analyze things, step by step, until you reach a conclusion. It’s all about being open and honest about how you got there.
Besides, presenting a case study gives you an opportunity to connect data and real-world scenarios in a compelling narrative. It helps to make your argument more relatable and accessible, increasing its impact on your audience.
One of the contexts where case studies can be very helpful is during the job interview. In some job interviews, you as candidates may be asked to present a case study as part of the selection process.
Having a case study presentation prepared allows the candidate to demonstrate their ability to understand complex issues, formulate strategies and communicate their ideas effectively.
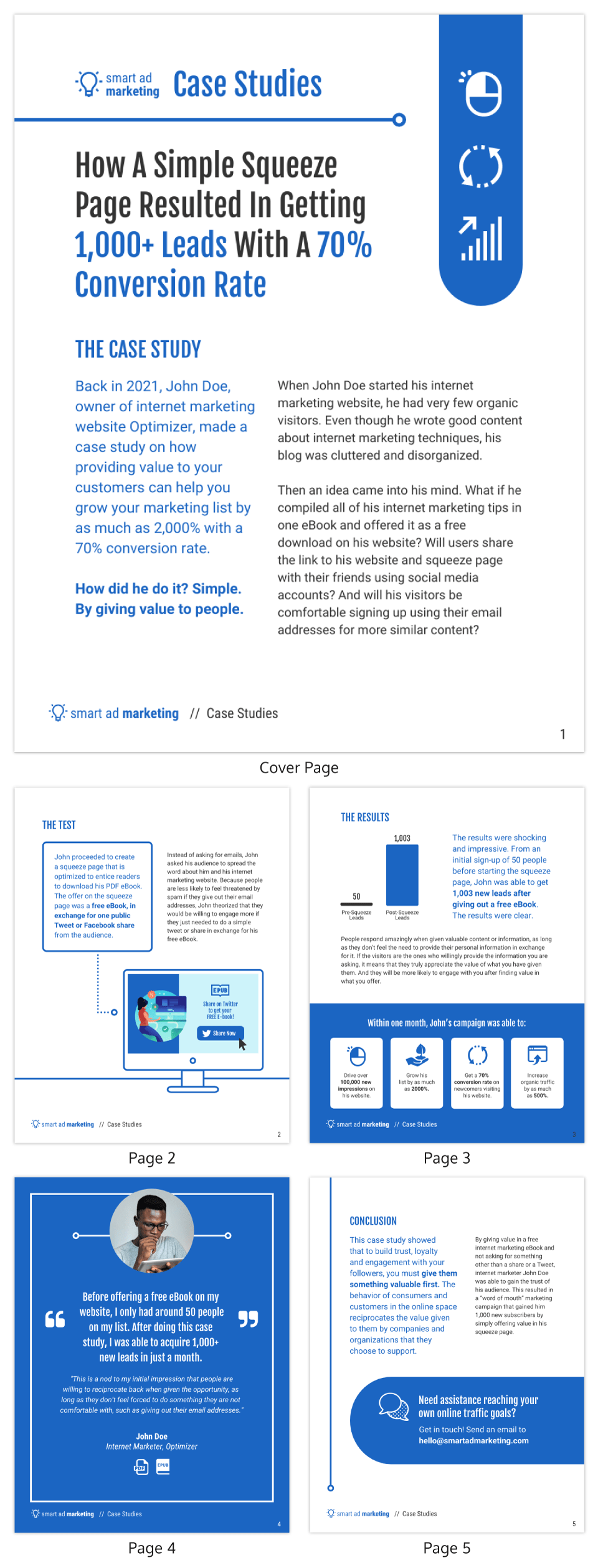
The way you present a case study can make all the difference in how it’s received. A well-structured presentation not only holds the attention of your audience but also ensures that your key points are communicated clearly and effectively.
In this section, let’s go through the key steps that’ll help you structure your case study presentation for maximum impact.
Let’s get into it.
Open with an introductory overview
Start by introducing the subject of your case study and its relevance. Explain why this case study is important and who would benefit from the insights gained. This is your opportunity to grab your audience’s attention.

Explain the problem in question
Dive into the problem or challenge that the case study focuses on. Provide enough background information for the audience to understand the issue. If possible, quantify the problem using data or metrics to show the magnitude or severity.

Detail the solutions to solve the problem
After outlining the problem, describe the steps taken to find a solution. This could include the methodology, any experiments or tests performed and the options that were considered. Make sure to elaborate on why the final solution was chosen over the others.

Key stakeholders Involved
Talk about the individuals, groups or organizations that were directly impacted by or involved in the problem and its solution.
Stakeholders may experience a range of outcomes—some may benefit, while others could face setbacks.
For example, in a business transformation case study, employees could face job relocations or changes in work culture, while shareholders might be looking at potential gains or losses.
Discuss the key results & outcomes
Discuss the results of implementing the solution. Use data and metrics to back up your statements. Did the solution meet its objectives? What impact did it have on the stakeholders? Be honest about any setbacks or areas for improvement as well.
Include visuals to support your analysis
Visual aids can be incredibly effective in helping your audience grasp complex issues. Utilize charts, graphs, images or video clips to supplement your points. Make sure to explain each visual and how it contributes to your overall argument.
Pie charts illustrate the proportion of different components within a whole, useful for visualizing market share, budget allocation or user demographics.
This is particularly useful especially if you’re displaying survey results in your case study presentation.
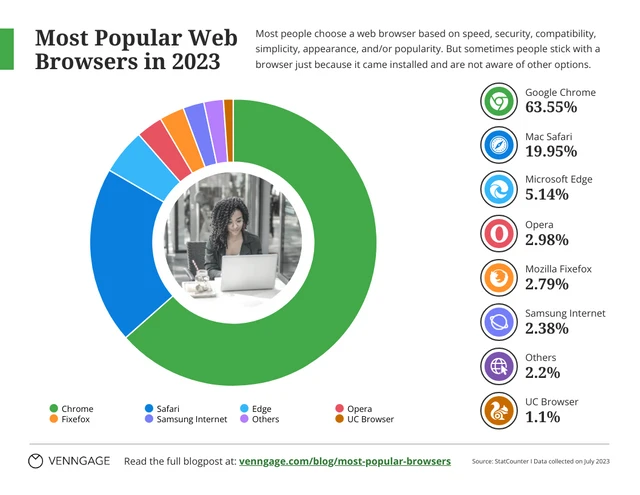
Stacked charts on the other hand are perfect for visualizing composition and trends. This is great for analyzing things like customer demographics, product breakdowns or budget allocation in your case study.
Consider this example of a stacked bar chart template. It provides a straightforward summary of the top-selling cake flavors across various locations, offering a quick and comprehensive view of the data.
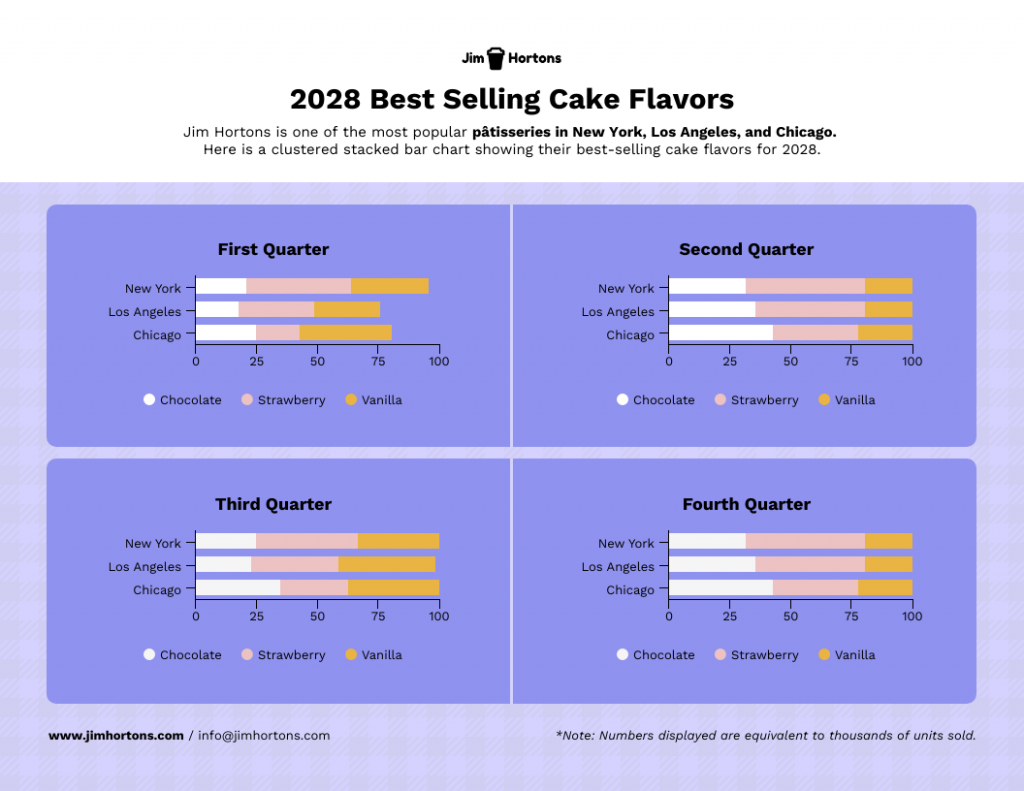
Not the chart you’re looking for? Browse Venngage’s gallery of chart templates to find the perfect one that’ll captivate your audience and level up your data storytelling.
Recommendations and next steps
Wrap up by providing recommendations based on the case study findings. Outline the next steps that stakeholders should take to either expand on the success of the project or address any remaining challenges.
Acknowledgments and references
Thank the people who contributed to the case study and helped in the problem-solving process. Cite any external resources, reports or data sets that contributed to your analysis.
Feedback & Q&A session
Open the floor for questions and feedback from your audience. This allows for further discussion and can provide additional insights that may not have been considered previously.
Closing remarks
Conclude the presentation by summarizing the key points and emphasizing the takeaways. Thank your audience for their time and participation and express your willingness to engage in further discussions or collaborations on the subject.

Well, the length of a case study presentation can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the needs of your audience. However, a typical business or academic presentation often lasts between 15 to 30 minutes.
This time frame usually allows for a thorough explanation of the case while maintaining audience engagement. However, always consider leaving a few minutes at the end for a Q&A session to address any questions or clarify points made during the presentation.
When it comes to presenting a compelling case study, having a well-structured template can be a game-changer.
It helps you organize your thoughts, data and findings in a coherent and visually pleasing manner.
Not all case studies are created equal and different scenarios require distinct approaches for maximum impact.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences.
Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly.
1 . Lab report case study template
Ever feel like your research gets lost in a world of endless numbers and jargon? Lab case studies are your way out!
Think of it as building a bridge between your cool experiment and everyone else. It’s more than just reporting results – it’s explaining the “why” and “how” in a way that grabs attention and makes sense.
This lap report template acts as a blueprint for your report, guiding you through each essential section (introduction, methods, results, etc.) in a logical order.

Want to present your research like a pro? Browse our research presentation template gallery for creative inspiration!
2. Product case study template
It’s time you ditch those boring slideshows and bullet points because I’ve got a better way to win over clients: product case study templates.
Instead of just listing features and benefits, you get to create a clear and concise story that shows potential clients exactly what your product can do for them. It’s like painting a picture they can easily visualize, helping them understand the value your product brings to the table.
Grab the template below, fill in the details, and watch as your product’s impact comes to life!

3. Content marketing case study template
In digital marketing, showcasing your accomplishments is as vital as achieving them.
A well-crafted case study not only acts as a testament to your successes but can also serve as an instructional tool for others.
With this coral content marketing case study template—a perfect blend of vibrant design and structured documentation, you can narrate your marketing triumphs effectively.

4. Case study psychology template
Understanding how people tick is one of psychology’s biggest quests and case studies are like magnifying glasses for the mind. They offer in-depth looks at real-life behaviors, emotions and thought processes, revealing fascinating insights into what makes us human.
Writing a top-notch case study, though, can be a challenge. It requires careful organization, clear presentation and meticulous attention to detail. That’s where a good case study psychology template comes in handy.
Think of it as a helpful guide, taking care of formatting and structure while you focus on the juicy content. No more wrestling with layouts or margins – just pour your research magic into crafting a compelling narrative.
5. Lead generation case study template
Lead generation can be a real head-scratcher. But here’s a little help: a lead generation case study.
Think of it like a friendly handshake and a confident resume all rolled into one. It’s your chance to showcase your expertise, share real-world successes and offer valuable insights. Potential clients get to see your track record, understand your approach and decide if you’re the right fit.
No need to start from scratch, though. This lead generation case study template guides you step-by-step through crafting a clear, compelling narrative that highlights your wins and offers actionable tips for others. Fill in the gaps with your specific data and strategies, and voilà! You’ve got a powerful tool to attract new customers.
Related: 15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
So, you’ve spent hours crafting the perfect case study and are now tasked with presenting it. Crafting the case study is only half the battle; delivering it effectively is equally important.
Whether you’re facing a room of executives, academics or potential clients, how you present your findings can make a significant difference in how your work is received.
Forget boring reports and snooze-inducing presentations! Let’s make your case study sing. Here are some key pointers to turn information into an engaging and persuasive performance:
- Know your audience : Tailor your presentation to the knowledge level and interests of your audience. Remember to use language and examples that resonate with them.
- Rehearse : Rehearsing your case study presentation is the key to a smooth delivery and for ensuring that you stay within the allotted time. Practice helps you fine-tune your pacing, hone your speaking skills with good word pronunciations and become comfortable with the material, leading to a more confident, conversational and effective presentation.
- Start strong : Open with a compelling introduction that grabs your audience’s attention. You might want to use an interesting statistic, a provocative question or a brief story that sets the stage for your case study.
- Be clear and concise : Avoid jargon and overly complex sentences. Get to the point quickly and stay focused on your objectives.
- Use visual aids : Incorporate slides with graphics, charts or videos to supplement your verbal presentation. Make sure they are easy to read and understand.
- Tell a story : Use storytelling techniques to make the case study more engaging. A well-told narrative can help you make complex data more relatable and easier to digest.

Ditching the dry reports and slide decks? Venngage’s case study templates let you wow customers with your solutions and gain insights to improve your business plan. Pre-built templates, visual magic and customer captivation – all just a click away. Go tell your story and watch them say “wow!”
Nailed your case study, but want to make your presentation even stronger? Avoid these common mistakes to ensure your audience gets the most out of it:
Overloading with information
A case study is not an encyclopedia. Overloading your presentation with excessive data, text or jargon can make it cumbersome and difficult for the audience to digest the key points. Stick to what’s essential and impactful. Need help making your data clear and impactful? Our data presentation templates can help! Find clear and engaging visuals to showcase your findings.
Lack of structure
Jumping haphazardly between points or topics can confuse your audience. A well-structured presentation, with a logical flow from introduction to conclusion, is crucial for effective communication.
Ignoring the audience
Different audiences have different needs and levels of understanding. Failing to adapt your presentation to your audience can result in a disconnect and a less impactful presentation.
Poor visual elements
While content is king, poor design or lack of visual elements can make your case study dull or hard to follow. Make sure you use high-quality images, graphs and other visual aids to support your narrative.
Not focusing on results
A case study aims to showcase a problem and its solution, but what most people care about are the results. Failing to highlight or adequately explain the outcomes can make your presentation fall flat.
How to start a case study presentation?
Starting a case study presentation effectively involves a few key steps:
- Grab attention : Open with a hook—an intriguing statistic, a provocative question or a compelling visual—to engage your audience from the get-go.
- Set the stage : Briefly introduce the subject, context and relevance of the case study to give your audience an idea of what to expect.
- Outline objectives : Clearly state what the case study aims to achieve. Are you solving a problem, proving a point or showcasing a success?
- Agenda : Give a quick outline of the key sections or topics you’ll cover to help the audience follow along.
- Set expectations : Let your audience know what you want them to take away from the presentation, whether it’s knowledge, inspiration or a call to action.
How to present a case study on PowerPoint and on Google Slides?
Presenting a case study on PowerPoint and Google Slides involves a structured approach for clarity and impact using presentation slides :
- Title slide : Start with a title slide that includes the name of the case study, your name and any relevant institutional affiliations.
- Introduction : Follow with a slide that outlines the problem or situation your case study addresses. Include a hook to engage the audience.
- Objectives : Clearly state the goals of the case study in a dedicated slide.
- Findings : Use charts, graphs and bullet points to present your findings succinctly.
- Analysis : Discuss what the findings mean, drawing on supporting data or secondary research as necessary.
- Conclusion : Summarize key takeaways and results.
- Q&A : End with a slide inviting questions from the audience.
What’s the role of analysis in a case study presentation?
The role of analysis in a case study presentation is to interpret the data and findings, providing context and meaning to them.
It helps your audience understand the implications of the case study, connects the dots between the problem and the solution and may offer recommendations for future action.
Is it important to include real data and results in the presentation?
Yes, including real data and results in a case study presentation is crucial to show experience, credibility and impact. Authentic data lends weight to your findings and conclusions, enabling the audience to trust your analysis and take your recommendations more seriously
How do I conclude a case study presentation effectively?
To conclude a case study presentation effectively, summarize the key findings, insights and recommendations in a clear and concise manner.
End with a strong call-to-action or a thought-provoking question to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
What’s the best way to showcase data in a case study presentation ?
The best way to showcase data in a case study presentation is through visual aids like charts, graphs and infographics which make complex information easily digestible, engaging and creative.
Don’t just report results, visualize them! This template for example lets you transform your social media case study into a captivating infographic that sparks conversation.

Choose the type of visual that best represents the data you’re showing; for example, use bar charts for comparisons or pie charts for parts of a whole.
Ensure that the visuals are high-quality and clearly labeled, so the audience can quickly grasp the key points.
Keep the design consistent and simple, avoiding clutter or overly complex visuals that could distract from the message.
Choose a template that perfectly suits your case study where you can utilize different visual aids for maximum impact.
Need more inspiration on how to turn numbers into impact with the help of infographics? Our ready-to-use infographic templates take the guesswork out of creating visual impact for your case studies with just a few clicks.
Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
Congrats on mastering the art of compelling case study presentations! This guide has equipped you with all the essentials, from structure and nuances to avoiding common pitfalls. You’re ready to impress any audience, whether in the boardroom, the classroom or beyond.
And remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Venngage’s Case Study Creator is your trusty companion, ready to elevate your presentations from ordinary to extraordinary. So, let your confidence shine, leverage your newly acquired skills and prepare to deliver presentations that truly resonate.
Go forth and make a lasting impact!

How to Summarize a Case Study Effectively
Saving time and effort with Notta, starting from today!
There are hundreds of marketing methods today, but a written case study remains a tried and tested practice to attract new customers. A few months ago, I started working on the case studies — and that's when I learned so much about what works — and what doesn't.
By the time a reader decides to take a look at your case study, they're seriously considering your offering. It's the time when the prospect will either engage more or lose their interest completely. But before the reader thinks of looking at the case study, they'll need a short, meaningful summary.
But how to summarize a case study that's short, simple, and informative? I've written over 50+ case studies, and each one has a short summary. In this detailed guide, I'll show you some tried and tested methods of summarizing long documents.
What is a Case Study Summary?
A case study summary is a short recap of a detailed case, interview, or other document. It has all of the same traits as that of a good summary: it's clean, short, straightforward, and flows naturally for the reader. But in the business world, a case study has the job of connecting customers with business, and a great summary also does the same.
A lead decides to look at the case study summary only if they're seriously interested in the products/services you offer. After reading, your reader's reaction will likely come down to this: did the case study summary make the benefits seem necessary or just nice to have?
If it's the latter, your prospects will probably avoid reading the detailed case study and pass on the opportunity. That's why the summary should include the key points and highlights from the case study and showcase to customers that your product or service is a necessity for their business growth.

How to Summarize a Case Study (with Guidelines)
I have recently read a statement: 'An educated client is a secure client.' Business typically boils down to two priorities: creating a useful product and then making people realize how it can help them. Both of these things mainly revolve around customer education, and both require a case study summary to get the job done.
Here, I'll reveal some simple steps that will help you summarize a case study.
Read the Case Study
When it comes to summarizing a case study, think about how effective it will be from the reader's perspective. You can even take notes and formulate an information architecture into proper formatting, headers, and bullet points to manage content better.
Understand the Goal
A business case study, for example, is a detailed document that defines how a business and its product helped a client improve sales. You should apply the same story and approach to write a case study summary — ensuring it sticks in the heart and mind of the reader.
Identify the Main Points
A good case study teaches prospects something — related to your products, services, new features, or how you're different. Think about the main points of the case study and why people should bother to read it. One of the biggest keys to a great summary is to speak to the customers' pain points directly and immediately offer the solution.

Write a Clear Summary
Now, write the way you talk — with clear ideas, concise language, and a welcoming tone. You need to hold onto your reader's attention with appropriate words and interesting facts. My number one tip is to be creative — even if the case study is boring. Here, your ultimate goal is to be engaging and creative — and, that too, within the confines of the industry.
Ready to revolutionize your post-meeting workflow? Give Notta's AI Summary Templates a try today and experience the difference for yourself. Simply select the template that best fits your needs, and watch as Notta transforms your raw notes into polished, concise summaries. Your time is precious – let Notta help you make the most of it.
Read and Revise
When you're done writing, read the summary aloud to yourself. Give it some emotions (if you can and if the topic allows you) while ensuring there is no fluff in the summary.
Depending on the type of case study summary , you might include different elements — but here's a general breakdown of the guidelines that you should keep in mind while summarizing.
Length : A good summary should have everything — from an attention-grabbing headline to a detailed explanation of the product, service, concept, or project. But that doesn't mean it can be a seven-page-long document. You must stick to the important facts and keep it pretty short — a few paragraphs or one page maximum .
Problem & Solution: Next, clearly state the problem (or issue) you want to solve and then briefly explain how the information provided in the case study solves it.
End with CTA: You'll need to tell your readers what to do next. For example, add the contact information if you want them to contact you or add links to more articles so they can continue reading.
Example of a Case Study Summary
Let's take a look at one example of how people summarize case studies. The example below is technically one page but packs a lot of information into it.
Here's an example of how to write an executive summary for a case study .
[Introduction]: The case study explains how the leading eCommerce platform (Company X) improved its customer experience with the digital tool. [Challenge]: Digital presence and customer satisfaction were the two key challenges faced by Company X. [Approach]: With the help of AI and automation, Company X implemented a robust CRM system and even launched a mobile app for user interaction. [Solution]: The approach helped the client improve their sales by 20% — in only three months.
Tips for Summarizing a Case Study
One of my responsibilities as a freelancer is creating case studies and sending them to potential clients. They're busy people, so I include a case study summary at the beginning that briefs the ten pages of detailed information into a few bullet points — the must-knows. Here’s how to write a case study summary — faster and better.
Write Great Hook Lines
Any article, blog, interview, email, or summary with an annoying hook line is going to get sent to spam right away. You should check and make sure the hook line is short enough to be read in seconds and grabs the attention of the reader. The point is to place the important or value-added material at the top of the summary.

Keep Things Scannable
People are busy, and only a few of them have the time to read a summary that's packed with text. If you take some time to think about what case study summaries work best, you'll likely find that the most effective ones are pretty brief. Smart formatting (with a strategic design) can keep the summary short while ensuring it has enough substance.
Automate Tasks with AI
With an AI case study summary tool, you can skip the blank-page stage of the summarizing process. These tools can analyze the content and come up with a short, informative summary — freeing up your time for other work. Notta is one of the popular AI note-taking and summarizing apps out there right now.
Whether you want to summarize interviews or voice memos, Notta Web App can help you with the job. It's particularly helpful if you've case studies in audio or video format: just upload the file, and Notta will generate a transcript and well-structured summary with an overview, key chapters, and action items.
Try Notta - the best online transcription & summarization tool. Transcribe and summarize your conversations and meetings quickly with high accuracy.
Start for Free
How Long Should a Case Study Summary Be?
While the exact length of a case study summary will depend on what you're summarizing, it typically ranges from a few paragraphs (2 or 3) to one single page . For example, if you're writing a customer case study with your storytelling skills, it can go as long as one page. But if you are summarizing an interview for the recruiting team, a paragraph or two would help them understand the candidate's skills.
How to Write a Good Case Study?
Even the most trusted marketers or businesses will tell you how much case studies have boosted their business. It's like a customer review that can get you more business — only if you write it properly. If you're new to writing case studies, here are simple steps to make the process a lot easier.
Start your research: Like anything else you write, you'll need to do proper research for a case study. For example, this includes the target audience, the message you're trying to convey, and the value your case study will provide.
Write the key highlights : A good case study summary is typically short and sweet, so don't defeat the whole purpose by adding unnecessary things. You'll need to include only the key highlights that matter the most to the reader.
Choose the format: While you may feel tempted to use all the space you have — don't. Some empty space around the text keeps the summary look uncluttered and easy to read.
Include a social proof: Reading a case study is like reading a review — but it mainly relies on storytelling. Including social proof in the case study will push leads to book their first call, send an email, or even sign up for a newsletter.
Be honest: The goal of your case study isn't to win over every single person reading it — instead, it's to win over the people who'll be your potential customers. Being honest is the key here.
Key Takeaways
It takes some time and effort to learn how to summarize a case study and condense all the important information into only a few paragraphs. If you don’t have enough time, check out my favorite AI note-taker and summarizer , Notta . It’s pretty easy to use — just upload the case study video, and the AI tool will quickly transcribe and summarize the information.
Chrome Extension
Help Center
vs Otter.ai
vs Fireflies.ai
vs Happy Scribe
vs Sonix.ai
Integrations
Microsoft Teams
Google Meet
Google Drive
Audio to Text Converter
Video to Text Converter
Online Video Converter
Online Audio Converter
Online Vocal Remover
YouTube Video Summarizer
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project planning |
- How to write an executive summary, with ...
How to write an executive summary, with examples

The best way to do that is with an executive summary. If you’ve never written an executive summary, this article has all you need to know to plan, write, and share them with your team.
What is an executive summary?
An executive summary is an overview of a document. The length and scope of your executive summary will differ depending on the document it’s summarizing, but in general an executive summary can be anywhere from one to two pages long. In the document, you’ll want to share all of the information your readers and important stakeholders need to know.
Imagine it this way: if your high-level stakeholders were to only read your executive summary, would they have all of the information they need to succeed? If so, your summary has done its job.
You’ll often find executive summaries of:
Business cases
Project proposals
Research documents
Environmental studies
Market surveys
In general, there are four parts to any executive summary:
Start with the problem or need the document is solving.
Outline the recommended solution.
Explain the solution’s value.
Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work.
What is an executive summary in project management?
In project management, an executive summary is a way to bring clarity to cross-functional collaborators, team leadership, and project stakeholders . Think of it like a project’s “ elevator pitch ” for team members who don’t have the time or the need to dive into all of the project’s details.
The main difference between an executive summary in project management and a more traditional executive summary in a business plan is that the former should be created at the beginning of your project—whereas the latter should be created after you’ve written your business plan. For example, to write an executive summary of an environmental study, you would compile a report on the results and findings once your study was over. But for an executive summary in project management, you want to cover what the project is aiming to achieve and why those goals matter.
The same four parts apply to an executive summary in project management:
Start with the problem or need the project is solving. Why is this project happening? What insight, customer feedback, product plan, or other need caused it to come to life?
Outline the recommended solution, or the project’s objectives. How is the project going to solve the problem you established in the first part? What are the project goals and objectives?
Explain the solution’s value. Once you’ve finished your project, what will happen? How will this improve and solve the problem you established in the first part?
Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work. This is another opportunity to reiterate why the problem is important, and why the project matters. It can also be helpful to reference your audience and how your solution will solve their problem. Finally, include any relevant next steps.
If you’ve never written an executive summary before, you might be curious about where it fits into other project management elements. Here’s how executive summaries stack up:
Executive summary vs. project plan
A project plan is a blueprint of the key elements your project will accomplish in order to hit your project goals and objectives. Project plans will include your goals, success metrics, stakeholders and roles, budget, milestones and deliverables, timeline and schedule, and communication plan .
An executive summary is a summary of the most important information in your project plan. Think of the absolutely crucial things your management team needs to know when they land in your project, before they even have a chance to look at the project plan—that’s your executive summary.
Executive summary vs. project overview
Project overviews and executive summaries often have similar elements—they both contain a summary of important project information. However, your project overview should be directly attached to your project. There should be a direct line of sight between your project and your project overview.
While you can include your executive summary in your project depending on what type of project management tool you use, it may also be a stand-alone document.
Executive summary vs. project objectives
Your executive summary should contain and expand upon your project objectives in the second part ( Outline the recommended solution, or the project’s objectives ). In addition to including your project objectives, your executive summary should also include why achieving your project objectives will add value, as well as provide details about how you’re going to get there.
The benefits of an executive summary
You may be asking: why should I write an executive summary for my project? Isn’t the project plan enough?
Well, like we mentioned earlier, not everyone has the time or need to dive into your project and see, from a glance, what the goals are and why they matter. Work management tools like Asana help you capture a lot of crucial information about a project, so you and your team have clarity on who’s doing what by when. Your executive summary is designed less for team members who are actively working on the project and more for stakeholders outside of the project who want quick insight and answers about why your project matters.
An effective executive summary gives stakeholders a big-picture view of the entire project and its important points—without requiring them to dive into all the details. Then, if they want more information, they can access the project plan or navigate through tasks in your work management tool.
How to write a great executive summary, with examples
Every executive summary has four parts. In order to write a great executive summary, follow this template. Then once you’ve written your executive summary, read it again to make sure it includes all of the key information your stakeholders need to know.
1. Start with the problem or need the project is solving
At the beginning of your executive summary, start by explaining why this document (and the project it represents) matter. Take some time to outline what the problem is, including any research or customer feedback you’ve gotten . Clarify how this problem is important and relevant to your customers, and why solving it matters.
For example, let’s imagine you work for a watch manufacturing company. Your project is to devise a simpler, cheaper watch that still appeals to luxury buyers while also targeting a new bracket of customers.
Example executive summary:
In recent customer feedback sessions, 52% of customers have expressed a need for a simpler and cheaper version of our product. In surveys of customers who have chosen competitor watches, price is mentioned 87% of the time. To best serve our existing customers, and to branch into new markets, we need to develop a series of watches that we can sell at an appropriate price point for this market.
2. Outline the recommended solution, or the project’s objectives
Now that you’ve outlined the problem, explain what your solution is. Unlike an abstract or outline, you should be prescriptive in your solution—that is to say, you should work to convince your readers that your solution is the right one. This is less of a brainstorming section and more of a place to support your recommended solution.
Because you’re creating your executive summary at the beginning of your project, it’s ok if you don’t have all of your deliverables and milestones mapped out. But this is your chance to describe, in broad strokes, what will happen during the project. If you need help formulating a high-level overview of your project’s main deliverables and timeline, consider creating a project roadmap before diving into your executive summary.
Continuing our example executive summary:
Our new watch series will begin at 20% cheaper than our current cheapest option, with the potential for 40%+ cheaper options depending on material and movement. In order to offer these prices, we will do the following:
Offer watches in new materials, including potentially silicone or wood
Use high-quality quartz movement instead of in-house automatic movement
Introduce customizable band options, with a focus on choice and flexibility over traditional luxury
Note that every watch will still be rigorously quality controlled in order to maintain the same world-class speed and precision of our current offerings.
3. Explain the solution’s value
At this point, you begin to get into more details about how your solution will impact and improve upon the problem you outlined in the beginning. What, if any, results do you expect? This is the section to include any relevant financial information, project risks, or potential benefits. You should also relate this project back to your company goals or OKRs . How does this work map to your company objectives?
With new offerings that are between 20% and 40% cheaper than our current cheapest option, we expect to be able to break into the casual watch market, while still supporting our luxury brand. That will help us hit FY22’s Objective 3: Expanding the brand. These new offerings have the potential to bring in upwards of three million dollars in profits annually, which will help us hit FY22’s Objective 1: 7 million dollars in annual profit.
Early customer feedback sessions indicate that cheaper options will not impact the value or prestige of the luxury brand, though this is a risk that should be factored in during design. In order to mitigate that risk, the product marketing team will begin working on their go-to-market strategy six months before the launch.
4. Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work
Now that you’ve shared all of this important information with executive stakeholders, this final section is your chance to guide their understanding of the impact and importance of this work on the organization. What, if anything, should they take away from your executive summary?
To round out our example executive summary:
Cheaper and varied offerings not only allow us to break into a new market—it will also expand our brand in a positive way. With the attention from these new offerings, plus the anticipated demand for cheaper watches, we expect to increase market share by 2% annually. For more information, read our go-to-market strategy and customer feedback documentation .
Example of an executive summary
When you put it all together, this is what your executive summary might look like:
![example summary of case study [Product UI] Example executive summary in Asana (Project Overview)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/8aa7d41f-aed9-4f82-bb7a-4305cea4404d/inline-project-planning-executive-summary-examples-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Common mistakes people make when writing executive summaries
You’re not going to become an executive summary-writing pro overnight, and that’s ok. As you get started, use the four-part template provided in this article as a guide. Then, as you continue to hone your executive summary writing skills, here are a few common pitfalls to avoid:
Avoid using jargon
Your executive summary is a document that anyone, from project contributors to executive stakeholders, should be able to read and understand. Remember that you’re much closer to the daily work and individual tasks than your stakeholders will be, so read your executive summary once over to make sure there’s no unnecessary jargon. Where you can, explain the jargon, or skip it all together.
Remember: this isn’t a full report
Your executive summary is just that—a summary. If you find yourself getting into the details of specific tasks, due dates, and attachments, try taking a step back and asking yourself if that information really belongs in your executive summary. Some details are important—you want your summary to be actionable and engaging. But keep in mind that the wealth of information in your project will be captured in your work management tool , not your executive summary.
Make sure the summary can stand alone
You know this project inside and out, but your stakeholders won’t. Once you’ve written your executive summary, take a second look to make sure the summary can stand on its own. Is there any context your stakeholders need in order to understand the summary? If so, weave it into your executive summary, or consider linking out to it as additional information.
Always proofread
Your executive summary is a living document, and if you miss a typo you can always go back in and fix it. But it never hurts to proofread or send to a colleague for a fresh set of eyes.
In summary: an executive summary is a must-have
Executive summaries are a great way to get everyone up to date and on the same page about your project. If you have a lot of project stakeholders who need quick insight into what the project is solving and why it matters, an executive summary is the perfect way to give them the information they need.
For more tips about how to connect high-level strategy and plans to daily execution, read our article about strategic planning .
Related resources

How to accomplish big things with long-term goals
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think

What is stakeholder analysis and why is it important?

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning
Case Study Analysis: Examples + How-to Guide & Writing Tips
A case study analysis is a typical assignment in business management courses. The task aims to show high school and college students how to analyze a current situation, determine what problems exist, and develop the best possible strategy to achieve the desired outcome.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
Many students feel anxious about writing case analyses because being told to analyze a case study and provide a solution can seem like a big task. That is especially so when working with real-life scenarios. However, you can rest assured writing a case analysis paper is easier than you think. Just keep reading this article and you will find case study examples for students and the advice provided by Custom-writing experts!
- 👣 Main Steps
- 🕵 Preparing the Case
🔬 Analyzing the Case
- 📑 Format & Structure
- 🙅 Things to Avoid
- 🏁 Conclusion
🔗 References
👣 writing a case study analysis: main steps.
Business management is built on case analysis. Every single economic result shows that the methods and instruments employed were either well-timed and expedient, in the event of success, or not, in case of failure. These two options indicate whether the strategy is efficient (and should be followed) or requires corrections (or complete change). Such an approach to the case study will make your writing piece more proficient and valuable for the reader. The following steps will direct your plan for writing a case study analysis.
Step 1: Preliminary work
- Make notes and highlight the numbers and ideas that could be quoted.
- Single out as many problems as you can, and briefly mark their underlying issues. Then make a note of those responsible. In the report, you will use two to five of the problems, so you will have a selection to choose from.
- Outline a possible solution to each of the problems you found. Course readings and outside research shall be used here. Highlight your best and worst solution for further reference.
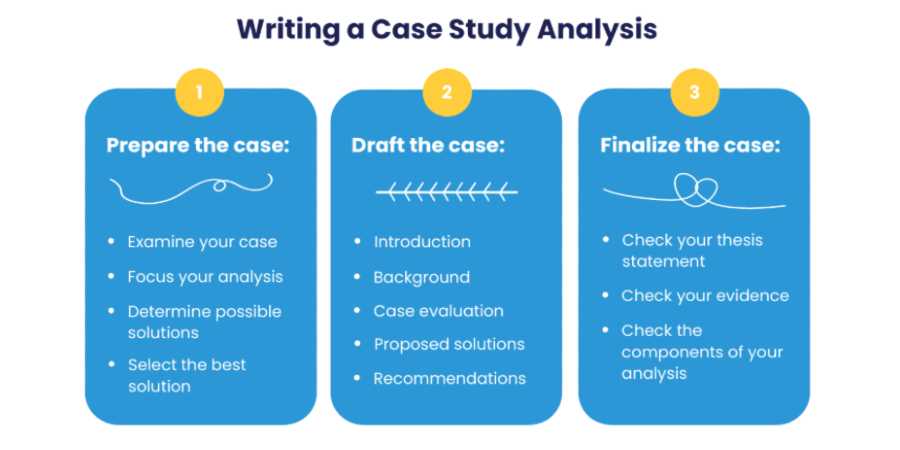
Step 2: Drafting the Case
- Provide a general description of the situation and its history.
- Name all the problems you are going to discuss.
- Specify the theory used for the analysis.
- Present the assumptions that emerged during the analysis, if any.
- Describe the detected problems in more detail.
- Indicate their link to, and effect on, the general situation.
- Explain why the problems emerged and persist.
- List realistic and feasible solutions to the problems you outlined, in the order of importance.
- Specify your predicted results of such changes.
- Support your choice with reliable evidence (i.e., textbook readings, the experience of famous companies, and other external research).
- Define the strategies required to fulfill your proposed solution.
- Indicate the responsible people and the realistic terms for its implementation.
- Recommend the issues for further analysis and supervision.
Step 3: Finalizing the Case
Like any other piece of writing, a case analysis requires post-editing. Carefully read it through, looking for inconsistencies and gaps in meaning. Your purpose is to make it look complete, precise, and convincing.
🕵 Preparing a Case for Analysis
Your professor might give you various case study examples from which to choose, or they may just assign you a particular case study. To conduct a thorough data analysis, you must first read the case study. This might appear to be obvious. However, you’d be surprised at how many students don’t take adequate time to complete this part.
Read the case study very thoroughly, preferably several times. Highlight, underline, flag key information, and make notes to refer to later when you are writing your analysis report.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
If you don’t have a complete knowledge of the case study your professor has assigned, you won’t conduct a proper analysis of it. Even if you make use of a business case study template or refer to a sample analysis, it won’t help if you aren’t intimately familiar with your case study.
You will also have to conduct research. When it comes to research, you will need to do the following:
- Gather hard, quantitative data (e.g. 67% of the staff participated in the meeting).
- Design research tools , such as questionnaires and surveys (this will aid in gathering data).
- Determine and suggest the best specific, workable solutions.
It would be best if you also learned how to analyze a case study. Once you have read through the case study, you need to determine the focus of your analysis. You can do this by doing the following:
Compare your chosen solutions to the solutions offered by the experts who analyzed the case study you were given or to online assignments for students who were dealing with a similar task. The experts’ solutions will probably be more advanced than yours simply because these people are more experienced. However, don’t let this discourage you; the whole point of doing this analysis is to learn. Use the opportunity to learn from others’ valuable experience, and your results will be better next time.
If you are still in doubt, the University of South Carolina offers a great guide on forming a case study analysis.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 15% off your first order!
📑 Case Analysis Format & Structure
When you are learning how to write a case study analysis, it is important to get the format of your analysis right. Understanding the case study format is vital for both the professor and the student. The person planning and handing out such an assignment should ensure that the student doesn’t have to use any external sources .
In turn, students have to remember that a well-written case analysis provides all the data, making it unnecessary for the reader to go elsewhere for information.
Regardless of whether you use a case study template, you will need to follow a clear and concise format when writing your analysis report. There are some possible case study frameworks available. Still, a case study should contain eight sections laid out in the following format:
- Describe the purpose of the current case study;
- Provide a summary of the company;
- Briefly introduce the problems and issues found in the case study
- Discuss the theory you will be using in the analysis;
- Present the key points of the study and present any assumptions made during the analysis.
- Present each problem you have singled out;
- Justify your inclusion of each problem by providing supporting evidence from the case study and by discussing relevant theory and what you have learned from your course content;
- Divide the section (and following sections) into subsections, one for each of your selected problems.
- Present a summary of each problem you have identified;
- Present plausible solutions for each of the problems, keeping in mind that each problem will likely have more than one possible solution;
- Provide the pros and cons of each solution in a way that is practical.
- Conclusion . This is a summary of your findings and discussion.
- Decide which solution best fits each of the issues you identified;
- Explain why you chose this solution and how it will effectively solve the problem;
- Be persuasive when you write this section so that you can drive your point home;
- Be sure to bring together theory and what you have learned throughout your course to support your recommendations.
- Provide an explanation of what must be done, who should take action, and when the solution should be carried out;
- Where relevant, you should provide an estimate of the cost in implementing the solution, including both the financial investment and the cost in terms of time.
- References. While you generally do not need to refer to many external sources when writing a case study analysis, you might use a few. When you do, you will need to properly reference these sources, which is most often done in one of the main citation styles, including APA, MLA, or Harvard. There is plenty of help when citing references, and you can follow these APA guidelines , these MLA guidelines , or these Harvard guidelines .
- Appendices. This is the section you include after your case study analysis if you used any original data in the report. These data, presented as charts, graphs, and tables, are included here because to present them in the main body of the analysis would be disruptive to the reader. The University of Southern California provides a great description of appendices and when to make use of them.
When you’ve finished your first draft, be sure to proofread it. Look not only for potential grammar and spelling errors but also for discrepancies or holes in your argument.
You should also know what you need to avoid when writing your analysis.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
🙅 Things to Avoid in Case Analysis
Whenever you deal with a case study, remember that there are some pitfalls to avoid! Beware of the following mistakes:
- Excessive use of colloquial language . Even though it is a study of an actual case, it should sound formal.
- Lack of statistical data . Give all the important data, both in percentages and in numbers.
- Excessive details. State only the most significant facts, rather than drowning the reader in every fact you find.
- Inconsistency in the methods you have used . In a case study, theory plays a relatively small part, so you must develop a specific case study research methodology.
- Trivial means of research . It is critical that you design your own case study research method in whatever form best suits your analysis, such as questionnaires and surveys.
It is useful to see a few examples of case analysis papers. After all, a sample case study report can provide you with some context so you can see how to approach each aspect of your paper.
👀 Case Study Examples for Students
It might be easier to understand how a case study analysis works if you have an example to look at. Fortunately, examples of case studies are easy to come by. Take a look at this video for a sample case study analysis for the Coca-Cola Company.
If you want another example, then take a look at the one below!
Business Case Analysis: Example
CRM’s primary focus is customers and customer perception of the brand or the company. The focus may shift depending on customers’ needs. The main points that Center Parcs should consider are an increase in customer satisfaction and its market share. Both of these points will enhance customer perception of the product as a product of value. Increased customer satisfaction will indicate that the company provides quality services, and increased market share can reduce the number of switching (or leaving) customers, thus fostering customer loyalty.
Case Study Topics
- Equifax case study: the importance of cybersecurity measures .
- Study a case illustrating ethical issues of medical research.
- Examine the case describing the complications connected with nursing and residential care.
- Analyze the competitive strategy of Delta Airlines .
- Present a case study of an ethical dilemma showing the conflict between the spirit and the letter of the law.
- Explore the aspects of Starbucks’ marketing strategyin a case study.
- Research a case of community-based clinic organization and development.
- Customer service of United Airlines: a case study .
- Analyze a specific schizophrenia case and provide your recommendations.
- Provide a case study of a patient with hyperglycemia.
- Examine the growth strategy of United Healthcare.
- Present a case study demonstrating ethical issues in business .
- Study a case of the 5% shareholding rule application and its impact on the company.
- Case study of post-traumatic stress disorder .
- Analyze a case examining the issues of cross-cultural management .
- Write a case study exploring the ethical issues the finance manager of a long-term care facility can face and the possible reaction to them.
- Write a case study analyzing the aspects of a new president of a firm election.
- Discuss the specifics of supply chain management in the case of Tehindo company.
- Study a case of a life crisis in a family and the ways to cope with it.
- Case study of Tea Leaves and More: supply chain issues .
- Explore the case of ketogenic diet implementation among sportspeople.
- Analyze the case of Webster Jewelry shop and suggest some changes.
- Examine the unique aspects of Tea and More brand management .
- Adidas case study: an ethical dilemma .
- Research the challenges of Brazos Valley Food Bank and suggest possible solutions.
- Describe the case of dark web monitoring for business.
- Study a case of permissive parenting style .
- Case study of Starbucks employees .
- Analyze a case of workplace discrimination and suggest a strategy to avoid it.
- Examine a case of the consumer decision-making process and define the factors that influence it.
- Present a case study of Netflix illustrating the crucial role of management innovation for company development.
- Discuss a case describing a workplace ethical issue and propose ways to resolve it.
- Case study of the 2008 financial crisis: Graham’s value investing principles in the modern economic climate.
- Write a case study analyzing the harmful consequences of communication issues in a virtual team .
- Analyze a case that highlights the importance of a proper functional currency choice.
- Examine the case of Hitachi Power Systems management.
- Present a case study of medication research in a healthcare facility.
- Study the case of Fiji Water and the challenges the brand faces.
- Research a social problem case and suggest a solution.
- Analyze a case that reveals the connection between alcohol use and borderline personality disorder .
- Transglobal Airline case study: break-even analysis.
- Examine the case of Chiquita Brands International from the moral and business ethics points of view.
- Present a case study of applying for Social Security benefits.
- Study the case of a mass hacker attack on Microsoft clients and suggest possible ways to prevent future attacks.
- Case study of leadership effectiveness .
- Analyze a case presenting a clinical moral dilemma and propose ways to resolve it.
- Describe the case of Cowbell Brewing Company and discuss the strategy that made them successful.
- Write a case study of WeWork company and analyze the strengths and weaknesses of its strategy.
- Case study of medical ethical decision-making.
- Study the case of The Georges hotel and suggest ways to overcome its managerial issues.
🏁 Concluding Remarks
Writing a case study analysis can seem incredibly overwhelming, especially if you have never done it before. Just remember, you can do it provided you follow a plan, keep to the format described here, and study at least one case analysis example.
If you still need help analyzing a case study, your professor is always available to answer your questions and point you in the right direction. You can also get help with any aspect of the project from a custom writing company. Just tackle the research and hand over the writing, write a rough draft and have it checked by a professional, or completely hand the project off to an expert writer.
Regardless of the path you choose, you will turn in something of which you can be proud!
✏️ Case Study Analysis FAQ
Students (especially those who study business) often need to write a case study analysis. It is a kind of report that describes a business case. It includes multiple aspects, for example, the problems that exist, possible solutions, forecasts, etc.
There should be 3 main points covered in a case study analysis:
- The challenge(s) description,
- Possible solutions,
- Outcomes (real and/or foreseen).
Firstly, study some examples available online and in the library. Case study analysis should be a well-structured paper with all the integral components in place. Thus, you might want to use a template and/or an outline to start correctly.
A case study analysis is a popular task for business students. They typically hand it in the format of a paper with several integral components:
- Description of the problem
- Possible ways out
- Results and/or forecasts
Students sometimes tell about the outcome of their research within an oral presentation.
- Case Study: Academia
- Windows of vulnerability: a case study analysis (IEEE)
- A (Very) Brief Refresher on the Case Study Method: SAGE
- The case study approach: Medical Research Methodology
- Strengths and Limitations of Case Studies: Stanford University
- A Sample APA Paper: Radford University
- How to Write a Case Study APA Style: Seattle PI
- The Case Analysis: GVSU
- How to Outline: Purdue OWL
- Incorporating Interview Data: UW-Madison Writing Center
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

If you are a student, you might need to learn how to write a literature review at some point. But don’t think it’s the same as the book review or other types of academic writing you had to do in high school! A literature review is a close examination of...

So, have you been recently assigned a research project? Or, even worse, is it already due soon? The following research paper hacks will help you do it in record time. In the article, you’ll see ten things you can do to conduct a study and compose a piece like a...

Eating a delicacy, watching a good movie, and proving a point to an audience are the three things that make life seem better. Today, you’ll deal with the last one. You’re about to become a professional at public speaking and attention grabbing. Here, you can learn how to write a...
![example summary of case study Library Research Paper: Example & Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/library-with-books-284x122.jpeg)
What is a library research paper? It’s nothing more than an academic writing project that summarizes the information on a specific topic taken from primary and secondary sources. There are numerous library research examples you can find online. But to complete this assignment, you should simply follow these essential steps:...
![example summary of case study Research Analysis Paper: How to Analyze a Research Article [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/opened-book-library-table-284x153.jpg)
Do you need to write a research analysis paper but have no idea how to do that? Then you’re in the right place. While completing this type of assignment, your key aim is to critically analyze a research article. An article from a serious scientific journal would be a good...
![example summary of case study American Antiquity Style Guide: Citation Rules & Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/education-concept-books-laptop-library-284x153.jpg)
American Antiquity is a professional quarterly journal, which contains various papers on the American archeology. It is incredibly popular among archeologists and the students majoring in history. The organization adopted the rules of The Society for American Archaeology (SAA) citation style. As a result: The journal includes numerous references that...

The most tedious and time-consuming part of any school or college written assignment is the bibliography. Sometimes, it can even be challenging! For example, if you’re confused by the variety of citation styles. This is probably when the most students wonder “Is there someone who could complete my assignment?” That...

An appendix is the part of the paper that contains supplementary material. The information from an appendix in paper writing is not essential. If the readers ignore this part, they still have to get the paper’s idea. Appendices help the readers to understand the research better. They might be useful...

Writing an abstract is one of the skills you need to master to succeed in your studies. An abstract is a summary of an academic text. It contains information about the aims and the outcomes of the research. The primary purpose of an abstract is to help readers understand what...

So you have to write a literature review. You find your favorite novel and then start analyzing it. This is how it’s usually done, right? It’s not. You have to learn the elements of literature review and how to deal with them.
![example summary of case study How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/research-charts-284x153.jpg)
Only two words, but you already feel a chill down your spine. A research paper is no joke. It’s a super detailed piece of academic writing where you analyze a chosen issue in-depth. The main aim of such torture is to show how knowledgeable you are and that your opinion...

A research proposal is a text that suggests a topic or research problem, justifies the need to study it, and describes the ways and methods of conducting the study. Scholars usually write proposals to get funding for their research. In their turn, students might have to do that to get...
Quite an impressive piece The steps and procedures outlined here are well detailed and the examples facilitates understanding.
it was very helpful. I have an assessment to write where in I need to mention different effective components that are needed to compile a high quality case study assessment.
It is very important and helpful.
Thanks a lot. A knowledge shared with a structured template. Stay the course
Thanks for this valuable knowledge.I loved this. keep sharing. to know more about click Air India Case Study – Why Air India failed ?
This is going to be a great help in my monthly analysis requirements for my subject. Thank you so much.
Thank you very much for this insightful guidelines… It has really been a great tool for writing my project. Thanks once again.
This article was very helpful, even though I’ll have a clearer mind only after I do the case study myself but I felt very much motivated after reading this, as now I can at least have a plan of what to do compared to the clueless me I was before I read it. I hope if I have any questions or doubts about doing a case study I can clear it out here.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
Definition and Introduction
Case analysis is a problem-based teaching and learning method that involves critically analyzing complex scenarios within an organizational setting for the purpose of placing the student in a “real world” situation and applying reflection and critical thinking skills to contemplate appropriate solutions, decisions, or recommended courses of action. It is considered a more effective teaching technique than in-class role playing or simulation activities. The analytical process is often guided by questions provided by the instructor that ask students to contemplate relationships between the facts and critical incidents described in the case.
Cases generally include both descriptive and statistical elements and rely on students applying abductive reasoning to develop and argue for preferred or best outcomes [i.e., case scenarios rarely have a single correct or perfect answer based on the evidence provided]. Rather than emphasizing theories or concepts, case analysis assignments emphasize building a bridge of relevancy between abstract thinking and practical application and, by so doing, teaches the value of both within a specific area of professional practice.
Given this, the purpose of a case analysis paper is to present a structured and logically organized format for analyzing the case situation. It can be assigned to students individually or as a small group assignment and it may include an in-class presentation component. Case analysis is predominately taught in economics and business-related courses, but it is also a method of teaching and learning found in other applied social sciences disciplines, such as, social work, public relations, education, journalism, and public administration.
Ellet, William. The Case Study Handbook: A Student's Guide . Revised Edition. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Publishing, 2018; Christoph Rasche and Achim Seisreiner. Guidelines for Business Case Analysis . University of Potsdam; Writing a Case Analysis . Writing Center, Baruch College; Volpe, Guglielmo. "Case Teaching in Economics: History, Practice and Evidence." Cogent Economics and Finance 3 (December 2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2015.1120977.
How to Approach Writing a Case Analysis Paper
The organization and structure of a case analysis paper can vary depending on the organizational setting, the situation, and how your professor wants you to approach the assignment. Nevertheless, preparing to write a case analysis paper involves several important steps. As Hawes notes, a case analysis assignment “...is useful in developing the ability to get to the heart of a problem, analyze it thoroughly, and to indicate the appropriate solution as well as how it should be implemented” [p.48]. This statement encapsulates how you should approach preparing to write a case analysis paper.
Before you begin to write your paper, consider the following analytical procedures:
- Review the case to get an overview of the situation . A case can be only a few pages in length, however, it is most often very lengthy and contains a significant amount of detailed background information and statistics, with multilayered descriptions of the scenario, the roles and behaviors of various stakeholder groups, and situational events. Therefore, a quick reading of the case will help you gain an overall sense of the situation and illuminate the types of issues and problems that you will need to address in your paper. If your professor has provided questions intended to help frame your analysis, use them to guide your initial reading of the case.
- Read the case thoroughly . After gaining a general overview of the case, carefully read the content again with the purpose of understanding key circumstances, events, and behaviors among stakeholder groups. Look for information or data that appears contradictory, extraneous, or misleading. At this point, you should be taking notes as you read because this will help you develop a general outline of your paper. The aim is to obtain a complete understanding of the situation so that you can begin contemplating tentative answers to any questions your professor has provided or, if they have not provided, developing answers to your own questions about the case scenario and its connection to the course readings,lectures, and class discussions.
- Determine key stakeholder groups, issues, and events and the relationships they all have to each other . As you analyze the content, pay particular attention to identifying individuals, groups, or organizations described in the case and identify evidence of any problems or issues of concern that impact the situation in a negative way. Other things to look for include identifying any assumptions being made by or about each stakeholder, potential biased explanations or actions, explicit demands or ultimatums , and the underlying concerns that motivate these behaviors among stakeholders. The goal at this stage is to develop a comprehensive understanding of the situational and behavioral dynamics of the case and the explicit and implicit consequences of each of these actions.
- Identify the core problems . The next step in most case analysis assignments is to discern what the core [i.e., most damaging, detrimental, injurious] problems are within the organizational setting and to determine their implications. The purpose at this stage of preparing to write your analysis paper is to distinguish between the symptoms of core problems and the core problems themselves and to decide which of these must be addressed immediately and which problems do not appear critical but may escalate over time. Identify evidence from the case to support your decisions by determining what information or data is essential to addressing the core problems and what information is not relevant or is misleading.
- Explore alternative solutions . As noted, case analysis scenarios rarely have only one correct answer. Therefore, it is important to keep in mind that the process of analyzing the case and diagnosing core problems, while based on evidence, is a subjective process open to various avenues of interpretation. This means that you must consider alternative solutions or courses of action by critically examining strengths and weaknesses, risk factors, and the differences between short and long-term solutions. For each possible solution or course of action, consider the consequences they may have related to their implementation and how these recommendations might lead to new problems. Also, consider thinking about your recommended solutions or courses of action in relation to issues of fairness, equity, and inclusion.
- Decide on a final set of recommendations . The last stage in preparing to write a case analysis paper is to assert an opinion or viewpoint about the recommendations needed to help resolve the core problems as you see them and to make a persuasive argument for supporting this point of view. Prepare a clear rationale for your recommendations based on examining each element of your analysis. Anticipate possible obstacles that could derail their implementation. Consider any counter-arguments that could be made concerning the validity of your recommended actions. Finally, describe a set of criteria and measurable indicators that could be applied to evaluating the effectiveness of your implementation plan.
Use these steps as the framework for writing your paper. Remember that the more detailed you are in taking notes as you critically examine each element of the case, the more information you will have to draw from when you begin to write. This will save you time.
NOTE : If the process of preparing to write a case analysis paper is assigned as a student group project, consider having each member of the group analyze a specific element of the case, including drafting answers to the corresponding questions used by your professor to frame the analysis. This will help make the analytical process more efficient and ensure that the distribution of work is equitable. This can also facilitate who is responsible for drafting each part of the final case analysis paper and, if applicable, the in-class presentation.
Framework for Case Analysis . College of Management. University of Massachusetts; Hawes, Jon M. "Teaching is Not Telling: The Case Method as a Form of Interactive Learning." Journal for Advancement of Marketing Education 5 (Winter 2004): 47-54; Rasche, Christoph and Achim Seisreiner. Guidelines for Business Case Analysis . University of Potsdam; Writing a Case Study Analysis . University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center; Van Ness, Raymond K. A Guide to Case Analysis . School of Business. State University of New York, Albany; Writing a Case Analysis . Business School, University of New South Wales.
Structure and Writing Style
A case analysis paper should be detailed, concise, persuasive, clearly written, and professional in tone and in the use of language . As with other forms of college-level academic writing, declarative statements that convey information, provide a fact, or offer an explanation or any recommended courses of action should be based on evidence. If allowed by your professor, any external sources used to support your analysis, such as course readings, should be properly cited under a list of references. The organization and structure of case analysis papers can vary depending on your professor’s preferred format, but its structure generally follows the steps used for analyzing the case.
Introduction
The introduction should provide a succinct but thorough descriptive overview of the main facts, issues, and core problems of the case . The introduction should also include a brief summary of the most relevant details about the situation and organizational setting. This includes defining the theoretical framework or conceptual model on which any questions were used to frame your analysis.
Following the rules of most college-level research papers, the introduction should then inform the reader how the paper will be organized. This includes describing the major sections of the paper and the order in which they will be presented. Unless you are told to do so by your professor, you do not need to preview your final recommendations in the introduction. U nlike most college-level research papers , the introduction does not include a statement about the significance of your findings because a case analysis assignment does not involve contributing new knowledge about a research problem.
Background Analysis
Background analysis can vary depending on any guiding questions provided by your professor and the underlying concept or theory that the case is based upon. In general, however, this section of your paper should focus on:
- Providing an overarching analysis of problems identified from the case scenario, including identifying events that stakeholders find challenging or troublesome,
- Identifying assumptions made by each stakeholder and any apparent biases they may exhibit,
- Describing any demands or claims made by or forced upon key stakeholders, and
- Highlighting any issues of concern or complaints expressed by stakeholders in response to those demands or claims.
These aspects of the case are often in the form of behavioral responses expressed by individuals or groups within the organizational setting. However, note that problems in a case situation can also be reflected in data [or the lack thereof] and in the decision-making, operational, cultural, or institutional structure of the organization. Additionally, demands or claims can be either internal and external to the organization [e.g., a case analysis involving a president considering arms sales to Saudi Arabia could include managing internal demands from White House advisors as well as demands from members of Congress].
Throughout this section, present all relevant evidence from the case that supports your analysis. Do not simply claim there is a problem, an assumption, a demand, or a concern; tell the reader what part of the case informed how you identified these background elements.
Identification of Problems
In most case analysis assignments, there are problems, and then there are problems . Each problem can reflect a multitude of underlying symptoms that are detrimental to the interests of the organization. The purpose of identifying problems is to teach students how to differentiate between problems that vary in severity, impact, and relative importance. Given this, problems can be described in three general forms: those that must be addressed immediately, those that should be addressed but the impact is not severe, and those that do not require immediate attention and can be set aside for the time being.
All of the problems you identify from the case should be identified in this section of your paper, with a description based on evidence explaining the problem variances. If the assignment asks you to conduct research to further support your assessment of the problems, include this in your explanation. Remember to cite those sources in a list of references. Use specific evidence from the case and apply appropriate concepts, theories, and models discussed in class or in relevant course readings to highlight and explain the key problems [or problem] that you believe must be solved immediately and describe the underlying symptoms and why they are so critical.
Alternative Solutions
This section is where you provide specific, realistic, and evidence-based solutions to the problems you have identified and make recommendations about how to alleviate the underlying symptomatic conditions impacting the organizational setting. For each solution, you must explain why it was chosen and provide clear evidence to support your reasoning. This can include, for example, course readings and class discussions as well as research resources, such as, books, journal articles, research reports, or government documents. In some cases, your professor may encourage you to include personal, anecdotal experiences as evidence to support why you chose a particular solution or set of solutions. Using anecdotal evidence helps promote reflective thinking about the process of determining what qualifies as a core problem and relevant solution .
Throughout this part of the paper, keep in mind the entire array of problems that must be addressed and describe in detail the solutions that might be implemented to resolve these problems.
Recommended Courses of Action
In some case analysis assignments, your professor may ask you to combine the alternative solutions section with your recommended courses of action. However, it is important to know the difference between the two. A solution refers to the answer to a problem. A course of action refers to a procedure or deliberate sequence of activities adopted to proactively confront a situation, often in the context of accomplishing a goal. In this context, proposed courses of action are based on your analysis of alternative solutions. Your description and justification for pursuing each course of action should represent the overall plan for implementing your recommendations.
For each course of action, you need to explain the rationale for your recommendation in a way that confronts challenges, explains risks, and anticipates any counter-arguments from stakeholders. Do this by considering the strengths and weaknesses of each course of action framed in relation to how the action is expected to resolve the core problems presented, the possible ways the action may affect remaining problems, and how the recommended action will be perceived by each stakeholder.
In addition, you should describe the criteria needed to measure how well the implementation of these actions is working and explain which individuals or groups are responsible for ensuring your recommendations are successful. In addition, always consider the law of unintended consequences. Outline difficulties that may arise in implementing each course of action and describe how implementing the proposed courses of action [either individually or collectively] may lead to new problems [both large and small].
Throughout this section, you must consider the costs and benefits of recommending your courses of action in relation to uncertainties or missing information and the negative consequences of success.
The conclusion should be brief and introspective. Unlike a research paper, the conclusion in a case analysis paper does not include a summary of key findings and their significance, a statement about how the study contributed to existing knowledge, or indicate opportunities for future research.
Begin by synthesizing the core problems presented in the case and the relevance of your recommended solutions. This can include an explanation of what you have learned about the case in the context of your answers to the questions provided by your professor. The conclusion is also where you link what you learned from analyzing the case with the course readings or class discussions. This can further demonstrate your understanding of the relationships between the practical case situation and the theoretical and abstract content of assigned readings and other course content.
Problems to Avoid
The literature on case analysis assignments often includes examples of difficulties students have with applying methods of critical analysis and effectively reporting the results of their assessment of the situation. A common reason cited by scholars is that the application of this type of teaching and learning method is limited to applied fields of social and behavioral sciences and, as a result, writing a case analysis paper can be unfamiliar to most students entering college.
After you have drafted your paper, proofread the narrative flow and revise any of these common errors:
- Unnecessary detail in the background section . The background section should highlight the essential elements of the case based on your analysis. Focus on summarizing the facts and highlighting the key factors that become relevant in the other sections of the paper by eliminating any unnecessary information.
- Analysis relies too much on opinion . Your analysis is interpretive, but the narrative must be connected clearly to evidence from the case and any models and theories discussed in class or in course readings. Any positions or arguments you make should be supported by evidence.
- Analysis does not focus on the most important elements of the case . Your paper should provide a thorough overview of the case. However, the analysis should focus on providing evidence about what you identify are the key events, stakeholders, issues, and problems. Emphasize what you identify as the most critical aspects of the case to be developed throughout your analysis. Be thorough but succinct.
- Writing is too descriptive . A paper with too much descriptive information detracts from your analysis of the complexities of the case situation. Questions about what happened, where, when, and by whom should only be included as essential information leading to your examination of questions related to why, how, and for what purpose.
- Inadequate definition of a core problem and associated symptoms . A common error found in case analysis papers is recommending a solution or course of action without adequately defining or demonstrating that you understand the problem. Make sure you have clearly described the problem and its impact and scope within the organizational setting. Ensure that you have adequately described the root causes w hen describing the symptoms of the problem.
- Recommendations lack specificity . Identify any use of vague statements and indeterminate terminology, such as, “A particular experience” or “a large increase to the budget.” These statements cannot be measured and, as a result, there is no way to evaluate their successful implementation. Provide specific data and use direct language in describing recommended actions.
- Unrealistic, exaggerated, or unattainable recommendations . Review your recommendations to ensure that they are based on the situational facts of the case. Your recommended solutions and courses of action must be based on realistic assumptions and fit within the constraints of the situation. Also note that the case scenario has already happened, therefore, any speculation or arguments about what could have occurred if the circumstances were different should be revised or eliminated.
Bee, Lian Song et al. "Business Students' Perspectives on Case Method Coaching for Problem-Based Learning: Impacts on Student Engagement and Learning Performance in Higher Education." Education & Training 64 (2022): 416-432; The Case Analysis . Fred Meijer Center for Writing and Michigan Authors. Grand Valley State University; Georgallis, Panikos and Kayleigh Bruijn. "Sustainability Teaching using Case-Based Debates." Journal of International Education in Business 15 (2022): 147-163; Hawes, Jon M. "Teaching is Not Telling: The Case Method as a Form of Interactive Learning." Journal for Advancement of Marketing Education 5 (Winter 2004): 47-54; Georgallis, Panikos, and Kayleigh Bruijn. "Sustainability Teaching Using Case-based Debates." Journal of International Education in Business 15 (2022): 147-163; .Dean, Kathy Lund and Charles J. Fornaciari. "How to Create and Use Experiential Case-Based Exercises in a Management Classroom." Journal of Management Education 26 (October 2002): 586-603; Klebba, Joanne M. and Janet G. Hamilton. "Structured Case Analysis: Developing Critical Thinking Skills in a Marketing Case Course." Journal of Marketing Education 29 (August 2007): 132-137, 139; Klein, Norman. "The Case Discussion Method Revisited: Some Questions about Student Skills." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 30-32; Mukherjee, Arup. "Effective Use of In-Class Mini Case Analysis for Discovery Learning in an Undergraduate MIS Course." The Journal of Computer Information Systems 40 (Spring 2000): 15-23; Pessoa, Silviaet al. "Scaffolding the Case Analysis in an Organizational Behavior Course: Making Analytical Language Explicit." Journal of Management Education 46 (2022): 226-251: Ramsey, V. J. and L. D. Dodge. "Case Analysis: A Structured Approach." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 27-29; Schweitzer, Karen. "How to Write and Format a Business Case Study." ThoughtCo. https://www.thoughtco.com/how-to-write-and-format-a-business-case-study-466324 (accessed December 5, 2022); Reddy, C. D. "Teaching Research Methodology: Everything's a Case." Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods 18 (December 2020): 178-188; Volpe, Guglielmo. "Case Teaching in Economics: History, Practice and Evidence." Cogent Economics and Finance 3 (December 2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2015.1120977.
Writing Tip
Ca se Study and Case Analysis Are Not the Same!
Confusion often exists between what it means to write a paper that uses a case study research design and writing a paper that analyzes a case; they are two different types of approaches to learning in the social and behavioral sciences. Professors as well as educational researchers contribute to this confusion because they often use the term "case study" when describing the subject of analysis for a case analysis paper. But you are not studying a case for the purpose of generating a comprehensive, multi-faceted understanding of a research problem. R ather, you are critically analyzing a specific scenario to argue logically for recommended solutions and courses of action that lead to optimal outcomes applicable to professional practice.
To avoid any confusion, here are twelve characteristics that delineate the differences between writing a paper using the case study research method and writing a case analysis paper:
- Case study is a method of in-depth research and rigorous inquiry ; case analysis is a reliable method of teaching and learning . A case study is a modality of research that investigates a phenomenon for the purpose of creating new knowledge, solving a problem, or testing a hypothesis using empirical evidence derived from the case being studied. Often, the results are used to generalize about a larger population or within a wider context. The writing adheres to the traditional standards of a scholarly research study. A case analysis is a pedagogical tool used to teach students how to reflect and think critically about a practical, real-life problem in an organizational setting.
- The researcher is responsible for identifying the case to study; a case analysis is assigned by your professor . As the researcher, you choose the case study to investigate in support of obtaining new knowledge and understanding about the research problem. The case in a case analysis assignment is almost always provided, and sometimes written, by your professor and either given to every student in class to analyze individually or to a small group of students, or students select a case to analyze from a predetermined list.
- A case study is indeterminate and boundless; a case analysis is predetermined and confined . A case study can be almost anything [see item 9 below] as long as it relates directly to examining the research problem. This relationship is the only limit to what a researcher can choose as the subject of their case study. The content of a case analysis is determined by your professor and its parameters are well-defined and limited to elucidating insights of practical value applied to practice.
- Case study is fact-based and describes actual events or situations; case analysis can be entirely fictional or adapted from an actual situation . The entire content of a case study must be grounded in reality to be a valid subject of investigation in an empirical research study. A case analysis only needs to set the stage for critically examining a situation in practice and, therefore, can be entirely fictional or adapted, all or in-part, from an actual situation.
- Research using a case study method must adhere to principles of intellectual honesty and academic integrity; a case analysis scenario can include misleading or false information . A case study paper must report research objectively and factually to ensure that any findings are understood to be logically correct and trustworthy. A case analysis scenario may include misleading or false information intended to deliberately distract from the central issues of the case. The purpose is to teach students how to sort through conflicting or useless information in order to come up with the preferred solution. Any use of misleading or false information in academic research is considered unethical.
- Case study is linked to a research problem; case analysis is linked to a practical situation or scenario . In the social sciences, the subject of an investigation is most often framed as a problem that must be researched in order to generate new knowledge leading to a solution. Case analysis narratives are grounded in real life scenarios for the purpose of examining the realities of decision-making behavior and processes within organizational settings. A case analysis assignments include a problem or set of problems to be analyzed. However, the goal is centered around the act of identifying and evaluating courses of action leading to best possible outcomes.
- The purpose of a case study is to create new knowledge through research; the purpose of a case analysis is to teach new understanding . Case studies are a choice of methodological design intended to create new knowledge about resolving a research problem. A case analysis is a mode of teaching and learning intended to create new understanding and an awareness of uncertainty applied to practice through acts of critical thinking and reflection.
- A case study seeks to identify the best possible solution to a research problem; case analysis can have an indeterminate set of solutions or outcomes . Your role in studying a case is to discover the most logical, evidence-based ways to address a research problem. A case analysis assignment rarely has a single correct answer because one of the goals is to force students to confront the real life dynamics of uncertainly, ambiguity, and missing or conflicting information within professional practice. Under these conditions, a perfect outcome or solution almost never exists.
- Case study is unbounded and relies on gathering external information; case analysis is a self-contained subject of analysis . The scope of a case study chosen as a method of research is bounded. However, the researcher is free to gather whatever information and data is necessary to investigate its relevance to understanding the research problem. For a case analysis assignment, your professor will often ask you to examine solutions or recommended courses of action based solely on facts and information from the case.
- Case study can be a person, place, object, issue, event, condition, or phenomenon; a case analysis is a carefully constructed synopsis of events, situations, and behaviors . The research problem dictates the type of case being studied and, therefore, the design can encompass almost anything tangible as long as it fulfills the objective of generating new knowledge and understanding. A case analysis is in the form of a narrative containing descriptions of facts, situations, processes, rules, and behaviors within a particular setting and under a specific set of circumstances.
- Case study can represent an open-ended subject of inquiry; a case analysis is a narrative about something that has happened in the past . A case study is not restricted by time and can encompass an event or issue with no temporal limit or end. For example, the current war in Ukraine can be used as a case study of how medical personnel help civilians during a large military conflict, even though circumstances around this event are still evolving. A case analysis can be used to elicit critical thinking about current or future situations in practice, but the case itself is a narrative about something finite and that has taken place in the past.
- Multiple case studies can be used in a research study; case analysis involves examining a single scenario . Case study research can use two or more cases to examine a problem, often for the purpose of conducting a comparative investigation intended to discover hidden relationships, document emerging trends, or determine variations among different examples. A case analysis assignment typically describes a stand-alone, self-contained situation and any comparisons among cases are conducted during in-class discussions and/or student presentations.
The Case Analysis . Fred Meijer Center for Writing and Michigan Authors. Grand Valley State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Ramsey, V. J. and L. D. Dodge. "Case Analysis: A Structured Approach." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 27-29; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2017; Crowe, Sarah et al. “The Case Study Approach.” BMC Medical Research Methodology 11 (2011): doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-11-100; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing; 1994.
- << Previous: Reviewing Collected Works
- Next: Writing a Case Study >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

Lessons from Amazon’s Early Growth Strategy
If you’re interested in strategies for scaling start-ups, this episode is for you.
- Apple Podcasts
So much has been written about Amazon’s outsized growth. But Harvard Business School professor Sunil Gupta says it’s the company’s unusual approach to strategy that has captured his scholarly attention. Gupta has spent years studying Amazon’s strategy and its founder and former CEO Jeff Bezos.
In this episode, Gupta shares how Amazon upended traditional corporate strategy by diversifying into multiple products serving many end users, instead of having a narrow focus.
He argues that some of Amazon’s simplest business strategies — like their obsession with customers and insistence on long-term thinking — are approaches that companies, big and small, can emulate.
Key episode topics include: strategy, innovation, leadership, scaling, Jeff Bezos, long-term thinking, customer focus.
HBR On Strategy curates the best case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, to help you unlock new ways of doing business. New episodes every week.
- Listen to the full HBR IdeaCast episode: How Jeff Bezos Built One of the World’s Most Valuable Companies (2020)
- Find more episodes of HBR IdeaCast
- Discover 100 years of Harvard Business Review articles, case studies, podcasts, and more at HBR.org .
HANNAH BATES: Welcome to HBR On Strategy , case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, hand-selected to help you unlock new ways of doing business.
So much has been written about Amazon’s outsized growth. But Harvard Business School professor Sunil Gupta says it’s the company’s unusual approach to strategy that has captured his scholarly attention.
Gupta has spent years studying Amazon’s strategy and its founder and former CEO, Jeff Bezos.
In this episode, Gupta shares how Amazon upended traditional corporate strategy by diversifying into multiple products serving many end users instead of focusing more narrowly.
And he argues that some of their simplest business strategies – like their obsession with the customer and insistence on long-term thinking – are approaches that companies, big and small, should emulate.
If you’re interested in innovation strategy, this episode is for you. It originally aired on HBR IdeaCast in November 2020. Here it is.
ALISON BEARD: Welcome to the HBR IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Alison Beard.
If you had to name the most successful business leader alive today, who would you say? I can’t hear you from my basement podcasting room, but I would bet that for many of you, the answer is Jeff Bezos, CEO of Amazon. This is a man who over the past 25 years turned his online bookstore startup into a diversified company currently valued at $1.6 trillion.
Amazon is a digital retailing juggernaut, it’s also a web services provider, media producer, and manufacturer of personal technology devices like Kindle and Echo. Oh, and Bezos also owns the Washington Post and Blue Origin, a space exploration company. Forbes tells us he is the richest person in the world.
How did he accomplish so much? How did he change the business landscape? What mistakes has he made along the way? A new collection of Bezos’s own writing, which full disclosure, my colleagues at Harvard Business Review Press have published, offer some insights. Here’s a clip from one speech that’s included. The book is called Invent and Wander.
And our guest today, who has spent years studying both Amazon and Bezos, is here to talk with me about some of the key themes in it, including the broad drivers of both the company and the CEO’s success. Sunil Gupta is a professor of business administration at Harvard Business School and cochair of its executive program, and cochair of its executive program on driving digital strategy, which is also the title of his book. Sunil, thanks so much for being on the show.
SUNIL GUPTA: Thank you for having me, Alison.
ALISON BEARD: So Invent and Wander. I get that Bezos is inventive. You know, he created a new way for us to buy things – everything. How is he also a wonderer?
SUNIL GUPTA: So he’s full of experiments. His company and his whole style is known for experimentation, and he says that in so many words that if you want big winners, then you have to be willing to have many failures. And the argument is, one big winner will take care of a thousand failed experiments. So I think that’s the wandering part. But also his experiments are not aimless. There is a certain thought and process behind what experiments to do and why they will connect to the old, old picture of what Amazon is today.
ALISON BEARD: And your expertise is in digital strategy. How does he break the traditional rules of strategy?
SUNIL GUPTA: So for the longest time the way, at least I was taught in my MBA program and the way we teach to our MBA students and executives, is strategy is about focus. But if you look at Amazon, Amazon certainly doesn’t look like it’s focusing on anything, so obviously Jeff Bezos missed that class, otherwise it’s a very, very different thing.
And then you’d say, why is it that so called lack of focus strategy seems to be working for Amazon? And I think the fundamental underlying principle that he’s guiding his whole discussion of strategy is, he’s changed the rules of strategy. So the old rules of strategy were, the way you gained competitive advantage is by being better or cheaper. So if I am selling you a car, my car is better of cheaper. But the inherent assumption in that strategy statement is, I’m selling one product to one customer. And what Amazon is basically arguing is, the digital economy is all about connection. We have got to connect products and connect customers. Let me explain why that is so powerful.
So connecting products, here the idea is, I can sell you, this is a classic razor and blade strategy. I can sell you a razor cheap in order to make money on the blade. So I can sell you Kindle cheap in order to make money on the ebooks. Now, at some level you might say, hey, razor and blade have been around forever. What’s so unique today? I think unique today is razor could be in one industry and blades could be in completely different industrys.
So for example, if you look at Amazon’s portfolio of businesses, you sort of say, not only Amazon is an e-commerce player, but also is making movies and TV shows, its own studio. Well, why does it make sense for an e-commerce player, an online retailer to compete with Hollywood. Well, Walmart doesn’t make movies. Macy’s doesn’t make movies? So why does it make sense for Amazon to make movies?
And I think once you dig into it, the answer becomes clear that the purpose of the movies is to keep and gain the Prime customers. Two day free shipping is fine, but if you ask me to pay $99 or $119 for two day free shipping, I might start doing the math in my head, and say, OK, how many packages do I expect to get next year? And is the Prime membership worth it or not?
But once you throw in, in addition to the two-day free shipping, you throw in some TV shows and movies that are uniquely found only on Amazon, I can’t do this math. And why is Prime customers important to Amazon? Because Prime customers are more loyal. They buy three or four times more than the non-Prime customers, and they’re also less price sensitive.
And in fact, Jeff Bezos has said publicly that every time we win a Golden Globe Award for one of our shows, we sell more shoes. So this is, and he said it in your book, Invent and Wander, also, that we might be the only company in the world which has figured out how winning Golden Globe Awards can actually translate into selling more products on the online commerce.
So this is a great example of the razor being in a very different industry and blade being in another industry. Take another example. Amazon has a lending business where they give loans to small and medium enterprises. If Amazon decides to compete with banks tomorrow, Amazon can decide to offer loans to the small merchants at such a low price that banks would never be able to compete. And why would Amazon be able to do that? Because Amazon can say, hey, I’m not going to make money on loans, as much money on loans, but I’ll make more money when these businesses, small businesses grow and do more transactions on my marketplace platform. And I get more commissions. So again, loan can become my razor in order to help the merchants grow and make money on the transaction and the commission that I get from that. The moment I make somebody else’s, in this case the banks, core business my razor, they will make a very hard time competing. So I think that’s the key change, the fundamental rules of strategy and competition in that direction.
The second part of connection is connecting customers, and this is the classic network effect. So marketplace is a great example of network effects. The more buyers I have, the more sellers I have. The more sellers I have, the sellers I have, the more buyers I get, because the buyers can find all the items. And that becomes flywheel effect, and it becomes a situation where it’s very hard for a new player to complete with Amazon.
ALISON BEARD: In this diversification that Amazon has done, how have they managed to be good at all of those things? Because they’re not focused. You know, they’re not concentrated on an area of specific expertise. So how have they succeeded when other companies might have failed because they lacked that expertise, or they were spreading themselves too thin?
SUNIL GUPTA: So I think it depends on how you define focus. Most of us, when we define focus, we sort of define focus by traditional industry boundaries, that I’m an online retailer, therefore going into some other business is lack of focus. The way Amazon thinks about is focus on capabilities.
So if you look at it from that point of view, I would argue that Amazon had three fundamental core capabilities. Number one, it’s highly customer focused, not only in its culture, but also in its capability in terms of how it can actually handle data and leverage data to get customer insight. The second core capability of Amazon is logistics. So it’s now a world class logistics player. It uses really frontier technology, whether it’s key word, robotics, computer vision, in its warehouse to make it much more efficient.
And the third part of Amazon’s skill or the capability is its technology. And a good example of that is Amazon Web Services, or AWS. And I think if you look at these three core capabilities, customer focus and the data insight that it gets from that, the logistics capability, and the technology, everything that Amazon is doing is some way or the other connected to it. In that sense, Amazon, and there’s no lack of focus, in my judgment on Amazon.
Now, if he starts doing, starts making cream cheese tomorrow or starts making airplane engines, then I would say, yes, it’s got a lack of focus. But one of the other things that Jeff Bezos has said again and again is this notion of work backwards and scale forward. And what that means is, because you’re customer obsessed, you sort of find ways to satisfy customers, and if that means developing new skills that we don’t have because we are working backwards from what the customer needs are, then we’ll build those skills.
So a good example of that is, when Amazon started building Kindle, Amazon was never in the hardware business. It didn’t know how to build hardware. But Bezos realized that as the industry moved, people are beginning to read more and more online, rather, or at least on their devices, rather than the physical paper copy of a book. So as a result, he says, how do we make it easier for consumers to read it on an electronic version? And they’re spending three years learning about this capability of hardware manufacturing. And by the way, Kindle came out long before iPad came out. And of course, that capability now has helped them launch Echo and many other devices.
ALISON BEARD: Right. So it’s the focus on the customer, plus a willingness to go outside your comfort zone, the wander part.
SUNIL GUPTA: Exactly.
ALISON BEARD: Yeah. How would you describe Bezos’s leadership style?
SUNIL GUPTA: So I think there are at least three parts to it. One is, he said right from day one that he wants to be a long-term focus. The second thing is being customer obsessed. And many times he has said that he can imagine, in the meetings he wants people to imagine an empty chair. That is basically for the customer. And he says, we are not competitor focused. We are not product focused. We are not technology focused. We are customer focused. And the third is, willingness to experiment. And fail, and build that culture in the company that it’s OK to fail.
ALISON BEARD: What about personally, though? Is he a hard charger? Is he an active listener? What’s it like to be in a room with him?
SUNIL GUPTA: Oh, he’s certainly a hard charger. I mean, he’s also the kind of guy, when he hires people, he says, you can work long, hard, or smart. But at Amazon, you can choose two out of three. And I think this is similar to many other leaders. If you look at Steve Jobs, he was also a very hard charging guy. And I think some people find it exhilarating to work with these kind of leaders. Some find it very tough.
ALISON BEARD: Do you think that he communicates differently from other successful CEOs?
SUNIL GUPTA: So the communication style that he has built in the company is the very famous now, there’s no PowerPoints. So it’s a very thoughtful discussion. You write six-page memos, which everybody, when their meeting starts, everybody sits down and actually reads the memo.
In fact, this was a very interesting experience that I had. One of my students, who was in the executive program, works at Amazon in Germany. And he is, he was at that point in time thinking of moving to another company and becoming a CEO of that company. So he said, can I talk to you about this change of career path that I’m thinking about? I said, sure. So we set up a time, and five minutes before our call, he sends me an email with a six-page memo. And I said, well, shouldn’t he have sent this to me before, so I could at least look at it? He says, no, that’s the Amazon style. We’ll sit in silence and read it together. And so I read it together, because then you’re completely focused on it. And then we can have a conversation. But this discipline of writing a six-page memo, it’s a very, very unique experience, because you actually have to think through all your arguments.
ALISON BEARD: You also mentioned the long term focus, and that really stood out for me, too, this idea that he is not at all thinking of next year. He’s thinking five years out, and sometimes even further. But as a public company, how has Amazon been able to stick to that? And is it replicable at other companies?
SUNIL GUPTA: I think it is replicable. It requires conviction, and it requires a way to articulate the vision to Wall Street that they can rally behind. And it’s completely replicable. There are other examples of companies who have followed a similar strategy. I mean, Netflix is a good example. Netflix hadn’t made money for a long period of time. But they sold the vision of what the future will look like, and Wall Street bought that vision.
Mastercard is exactly the same thing. Ajay Banga is giving three year guidance to Wall Street saying, this is my three-year plan, because things can change quarter to quarter. I’m still responsible to tell you what we are doing this quarter, but my strategy will not be guided by what happens today. It will be guided by the three-year plan that we have.
ALISON BEARD: There are so many companies now that go public without turning any profit, whereas Amazon now is printing money, and thus able to reinvest and have this grand vision. So at what point was Bezos able to say, right, we’re going to do it my way?
SUNIL GUPTA: I think he said it right from day one, except that people probably didn’t believe it. And in fact, one of the great examples of that was, when he was convinced about AWS, the Amazon Web Services, that was back in the early 2000s, when a majority of the Wall Street was not sure what Jeff Bezos was trying to do, because they say, hey, you are an online retailer. You have no business being in web services. That’s the business of IBM. And that’s a B2B business. You’re in a B2C business. Why are you going in there?
And Bezos said, well, we have plenty of practice of being misunderstood. And we will continue with our passion and vision, because we see the path. And now he’s proven it again and again why his vision is correct, and I think that could give us more faith and conviction to the Wall Street investors.
SUNIL GUPTA: Oh, absolutely. And he’s one of the persons who has his opinion, and you always surround yourself with people better than you.
ALISON BEARD: How has he managed to attract that talent when it is so fiercely competitive between Google, Facebook, all of these U.S. technology leaders?
SUNIL GUPTA: So a couple of things I would say. First of all, it’s always good fun to join a winning team. And all of us want to join a winning team, so this certainly is on a trajectory which is phenomenal. It’s like a rocket ship that is taking off and has been taking off for the last 25 years. So I think that’s certainly attractive to many people, and certainly many hard charging people who want to be on a winning team.
And a second thing is, Amazon’s culture of experimentation and innovation. That is energizing to a lot of people. It’s not a bureaucracy where you get bogged down by the processes. So the two type of decisions that we talked about, he gives you enough leeway to try different things, and is willing to invest hundreds of millions of dollars into things that may or may not succeed in the future. And I think that’s very liberating to people who are willing to take on the ownership and build something.
ALISON BEARD: But don’t all of the tech companies offer that?
SUNIL GUPTA: They do, but if you think about many other tech companies, they’re much more narrow in focus. So Facebook is primarily in social media. Google is primarily in search advertising. Yes, you have GoogleX, but that’s still a small part of what Google does. Whereas if you ask yourself what business is Amazon in, there are much broader expansive areas that Amazon has gone into. So I think the limits, I mean, Amazon does not have that many limits or boundaries as compared to many other businesses in Silicon Valley.
ALISON BEARD: So let’s talk a little bit about Bezos’s acquisition strategy. I think the most prominent is probably Whole Foods, but there are many others. How does he think about the companies that he wants to bring in as opposed to grow organically?
SUNIL GUPTA: So some acquisitions are areas where he thinks that he can actually benefit and accelerate the vision that he already has. So for example, the acquisition of Kiva was to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the systems that he already put in place in his warehouse. And logistics and warehouse is a key component or key part of Amazon’s business, and he saw that Kiva already was ahead of the curve in technology that he probably wanted to have that in his own company. So that was obvious acquisition, because that fits in the existing business.
Whole Foods is kind of a slightly different story, in my judgment, because I some ways, you can argue, why is Amazon, an online player, buying an offline retail store, Whole Foods? And in fact, they bought it at 27% premium. So that doesn’t make sense for an online retailer commerce to go to offline channels. And I think, in fact, part of the reason in my judgment is, it’s not just Whole Foods, but it’s about the food business, per se. And why is Amazon so interested in food? In fact, Amazon has been trying this food business, online food delivery for a long period of time without much success. And Whole Foods was one, another way to try and get access to that particular business. And why is that so important to Amazon, even though you could argue, food is a low margin business?
And I would say, part of the reason is, food is something, grocery is something that you buy every week, perhaps twice a week. And if I, as Amazon, can convince you to buy grocery online from Amazon, then I’m creating a habit for you to come onto Amazon every week, perhaps twice a week. And once you are on Amazon, you will end up buying other products on Amazon. Whereas if you are buying electronics, you may not come to Amazon every day.
So this is a habit creation activity, and again, it may not be a very high margin activity to sell you food. But I’ve created a habit, just like Prime. I’ve created a loyal customer where you think of nothing else but Amazon for your daily needs, and therefore you end up buying other things.
ALISON BEARD: And Amazon isn’t without controversy. You know, and we should talk about that, too. First, there are questions about its treatment of warehouse employees, particularly during COVID. And Bezos, as you said, has always been relentlessly focused on the customer. But is Amazon employee centric, too?
SUNIL GUPTA: So I think there is definitely some areas of concern, and you rightly said there is a significant concern about the, during the COVID, workers were complaining about safety, the right kind of equipment. But even before COVID, there were a lot of concerns about whether the workers are being pushed too hard. They barely have any breaks. And they’re constantly on the go, because speed and efficiency become that much more important to make sure customers always get what they are promised. And in fact, more than promised.
Clearly Amazon either hasn’t done a good job, or hasn’t at least done the public relations part of it that they have done a good job. Now, if you ask Jeff Bezos, he will claim that, no, actually, they have done things. For example, they offer something called carrier choice, where they give 95% tuition to the employees to learn new skills, whether they’re relevant to Amazon or not. Pretty much like what Starbucks does for its baristas, for college education and other things. But I think more than just giving money or tuition, it requires a bit of empathy and sense that you care for your employees, and perhaps that needs, that’s something that Amazon needs to work on.
ALISON BEARD: And another challenge is the criticism that it has decimated mom and pop shops. Even when someone sells through Amazon, the company will then see that it’s a popular category and create it itself and start selling it itself. There’s environmental concerns about the fact that packages are being driven from warehouses to front doors all over America. And boxes and packaging. So how has Bezos, how has the company dealt with all of that criticism?
SUNIL GUPTA: They haven’t. And I think those are absolutely valid concerns on both counts, that the small sellers who grow to become reasonably big are always under the radar, and there are certainly anecdotal evidence there, small sellers have complained that Amazon had decided to sell exactly the same item that they were so successful in selling, and becoming too big is actually not good on Amazon, because Amazon can get into your business and wipe you away. So that’s certainly a big concern, and I think that’s something that needs to be sorted out, and Amazon needs to clarify what its position on that area is, because it benefits from these small sellers on his platform.
And your second question about environmental issues is also absolutely on the money, because not only emission issues, but there’s so many boxes that pile in, certainly in my basement, from Amazon. You sort of say, and it’s actually ironical that Millennials who are in love with Amazon are extremely environmentally friendly. But at the same time, they would not hesitate to order something from Amazon and pile up all these boxes. So I think Amazon needs to figure out a way to think about both those issues.
ALISON BEARD: And at what point will it have to? I mean, it seems to be rolling happily along.
SUNIL GUPTA: Well, I think those issues are becoming bigger and bigger, and it’s certainly in the eye of the regulators, also, for some of these practices. And not only because it’s too big, and there might be monopoly concerns, but these issues will become larger, and any time you become a large company, you become the center of attraction for broader issues than just providing shareholder value.
ALISON BEARD: Yeah. So those are weaknesses possibly for the company. What are some of Bezos’s personal weaknesses that you’ve seen in studying him and the company?
SUNIL GUPTA: So I think one thing that stands out to me, and at least in the public forums, I have not seen any empathy. And it’s, I mean, we talk about that the leaders have, should have three qualities. They should be competent. They should have a good character. And they should have compassion. So he’s certainly very competent. I mean, he’s brilliant in many aspects, right, from the computer vision and AI and machine learning, to the nuances of data analytics, to the Hollywood production, etc. He also seems to have good character, at least I have not heard any personal scandals, apart from his other issues in his personal life, perhaps.
Those characteristics of competence and character make people respect you. What makes people love you is when you show compassion, and at least I haven’t seen compassion or empathy that comes out of him. I mean, he certainly comes across as a very hard charging, driven person, which probably is good for business. But the question of empathy is perhaps something lacking right now.
ALISON BEARD: Yeah. The other issue is his just enormous wealth. He did invent this colossally valuable company, but should anyone really be that rich?
SUNIL GUPTA: Well, I guess that’s, you can say that’s the good or the bad thing about capitalism. But I think, and again, my personal view is there’s nothing wrong in becoming rich, if you have been successful and done it with hard work and ingenuity. But how you use your wealth is something that perhaps will define Jeff Bezos going forward. I think Bill Gates is a great example how he actually has used his wealth and his influence and his expertise and his brilliance into some certain thing that actually is great for humanity.
Now, whether Jeff Bezos does that down the road, I don’t know, whether his space exploration provides that sort of outlet which is both his passion as well as good for humanity, I don’t know. But at some point in time, I think it’s the responsibility of these leaders to sort of say, my goal is not simply to make money and make my shareholders rich, but also help humanity and help society.
ALISON BEARD: If you’re talking to someone who’s running a startup, or even a manager of a team at a traditional company, what is the key lesson that you would say, this is what you can learn from Jeff Bezos? This is what you can put to work in your own profession?
SUNIL GUPTA: So I would say two things that at least I would take away if I were doing a startup. One is customer obsession. Now, every company says that, but honestly, not every company does it, because if you go to the management meetings, if you go to the quarterly meetings, you suddenly go focus on financials and competition and product. But there’s rarely any conversation on customers. And I think, as I mentioned earlier, that Jeff Bezos always tells his employee to think of the imaginary chair in which a customer is sitting, because that’s the person that we need to focus on. Howard Shultz does the same thing at Starbucks, and that’s why Starbucks is so customer focused.
So I think that’s the first part. And the argument that Bezos gives is, customers are never satisfied. And that pushes us to innovate and move forward, so we need to innovate even before the rest of the world even sees that, because customers are the first ones to see what is missing in the offering that you have.
And the second I would say that I would take away from Jeff Bezos is the conviction and passion with what you do. And many times that goes against the conventional wisdom. And the Amazon Web Services is a great example of that. The whole world, including the Wall Street Journal and the Wall Street analysts were saying, this is none of Amazon’s business to do web services. But he was convinced that this is the right thing to do, and he went and did that.
And part of that conviction may come from experiments. Part of that conviction comes from connecting the dots that he could see that many other people didn’t see. I mean, that’s why he went, left his job, and went to Seattle to do the online bookstore, because he could see the macro trends as to what the Internet is likely to do. So, I think that’s the vision that he had. And once you have the conviction, then you follow your passion.
ALISON BEARD: Sunil, thanks so much for coming on the show.
SUNIL GUPTA: Thank you for having me. Alison.
HANNAH BATES: That was Harvard Business School professor Sunil Gupta, in conversation with Alison Beard on the HBR IdeaCast .
We’ll be back next Wednesday with another hand-picked conversation about business strategy from Harvard Business Review. If you found this episode helpful, share it with your friends and colleagues, and follow our show on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts. While you’re there, be sure to leave us a review.
And when you’re ready for more podcasts, articles, case studies, books, and videos with the world’s top business and management experts, find it all at HBR.org.
This episode was produced by Mary Dooe, Anne Saini, and me, Hannah Bates. Ian Fox is our editor. And special thanks to Maureen Hoch, Nicole Smith, Erica Truxler, Ramsey Khabbaz, Anne Bartholomew, and you – our listener. See you next week.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about strategy, partner center.
- Open access
- Published: 18 April 2024
Research ethics and artificial intelligence for global health: perspectives from the global forum on bioethics in research
- James Shaw 1 , 13 ,
- Joseph Ali 2 , 3 ,
- Caesar A. Atuire 4 , 5 ,
- Phaik Yeong Cheah 6 ,
- Armando Guio Español 7 ,
- Judy Wawira Gichoya 8 ,
- Adrienne Hunt 9 ,
- Daudi Jjingo 10 ,
- Katherine Littler 9 ,
- Daniela Paolotti 11 &
- Effy Vayena 12
BMC Medical Ethics volume 25 , Article number: 46 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1145 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
The ethical governance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in health care and public health continues to be an urgent issue for attention in policy, research, and practice. In this paper we report on central themes related to challenges and strategies for promoting ethics in research involving AI in global health, arising from the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research (GFBR), held in Cape Town, South Africa in November 2022.
The GFBR is an annual meeting organized by the World Health Organization and supported by the Wellcome Trust, the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) and the South African MRC. The forum aims to bring together ethicists, researchers, policymakers, research ethics committee members and other actors to engage with challenges and opportunities specifically related to research ethics. In 2022 the focus of the GFBR was “Ethics of AI in Global Health Research”. The forum consisted of 6 case study presentations, 16 governance presentations, and a series of small group and large group discussions. A total of 87 participants attended the forum from 31 countries around the world, representing disciplines of bioethics, AI, health policy, health professional practice, research funding, and bioinformatics. In this paper, we highlight central insights arising from GFBR 2022.
We describe the significance of four thematic insights arising from the forum: (1) Appropriateness of building AI, (2) Transferability of AI systems, (3) Accountability for AI decision-making and outcomes, and (4) Individual consent. We then describe eight recommendations for governance leaders to enhance the ethical governance of AI in global health research, addressing issues such as AI impact assessments, environmental values, and fair partnerships.
Conclusions
The 2022 Global Forum on Bioethics in Research illustrated several innovations in ethical governance of AI for global health research, as well as several areas in need of urgent attention internationally. This summary is intended to inform international and domestic efforts to strengthen research ethics and support the evolution of governance leadership to meet the demands of AI in global health research.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The ethical governance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in health care and public health continues to be an urgent issue for attention in policy, research, and practice [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Beyond the growing number of AI applications being implemented in health care, capabilities of AI models such as Large Language Models (LLMs) expand the potential reach and significance of AI technologies across health-related fields [ 4 , 5 ]. Discussion about effective, ethical governance of AI technologies has spanned a range of governance approaches, including government regulation, organizational decision-making, professional self-regulation, and research ethics review [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. In this paper, we report on central themes related to challenges and strategies for promoting ethics in research involving AI in global health research, arising from the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research (GFBR), held in Cape Town, South Africa in November 2022. Although applications of AI for research, health care, and public health are diverse and advancing rapidly, the insights generated at the forum remain highly relevant from a global health perspective. After summarizing important context for work in this domain, we highlight categories of ethical issues emphasized at the forum for attention from a research ethics perspective internationally. We then outline strategies proposed for research, innovation, and governance to support more ethical AI for global health.
In this paper, we adopt the definition of AI systems provided by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) as our starting point. Their definition states that an AI system is “a machine-based system that can, for a given set of human-defined objectives, make predictions, recommendations, or decisions influencing real or virtual environments. AI systems are designed to operate with varying levels of autonomy” [ 9 ]. The conceptualization of an algorithm as helping to constitute an AI system, along with hardware, other elements of software, and a particular context of use, illustrates the wide variety of ways in which AI can be applied. We have found it useful to differentiate applications of AI in research as those classified as “AI systems for discovery” and “AI systems for intervention”. An AI system for discovery is one that is intended to generate new knowledge, for example in drug discovery or public health research in which researchers are seeking potential targets for intervention, innovation, or further research. An AI system for intervention is one that directly contributes to enacting an intervention in a particular context, for example informing decision-making at the point of care or assisting with accuracy in a surgical procedure.
The mandate of the GFBR is to take a broad view of what constitutes research and its regulation in global health, with special attention to bioethics in Low- and Middle- Income Countries. AI as a group of technologies demands such a broad view. AI development for health occurs in a variety of environments, including universities and academic health sciences centers where research ethics review remains an important element of the governance of science and innovation internationally [ 10 , 11 ]. In these settings, research ethics committees (RECs; also known by different names such as Institutional Review Boards or IRBs) make decisions about the ethical appropriateness of projects proposed by researchers and other institutional members, ultimately determining whether a given project is allowed to proceed on ethical grounds [ 12 ].
However, research involving AI for health also takes place in large corporations and smaller scale start-ups, which in some jurisdictions fall outside the scope of research ethics regulation. In the domain of AI, the question of what constitutes research also becomes blurred. For example, is the development of an algorithm itself considered a part of the research process? Or only when that algorithm is tested under the formal constraints of a systematic research methodology? In this paper we take an inclusive view, in which AI development is included in the definition of research activity and within scope for our inquiry, regardless of the setting in which it takes place. This broad perspective characterizes the approach to “research ethics” we take in this paper, extending beyond the work of RECs to include the ethical analysis of the wide range of activities that constitute research as the generation of new knowledge and intervention in the world.
Ethical governance of AI in global health
The ethical governance of AI for global health has been widely discussed in recent years. The World Health Organization (WHO) released its guidelines on ethics and governance of AI for health in 2021, endorsing a set of six ethical principles and exploring the relevance of those principles through a variety of use cases. The WHO guidelines also provided an overview of AI governance, defining governance as covering “a range of steering and rule-making functions of governments and other decision-makers, including international health agencies, for the achievement of national health policy objectives conducive to universal health coverage.” (p. 81) The report usefully provided a series of recommendations related to governance of seven domains pertaining to AI for health: data, benefit sharing, the private sector, the public sector, regulation, policy observatories/model legislation, and global governance. The report acknowledges that much work is yet to be done to advance international cooperation on AI governance, especially related to prioritizing voices from Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs) in global dialogue.
One important point emphasized in the WHO report that reinforces the broader literature on global governance of AI is the distribution of responsibility across a wide range of actors in the AI ecosystem. This is especially important to highlight when focused on research for global health, which is specifically about work that transcends national borders. Alami et al. (2020) discussed the unique risks raised by AI research in global health, ranging from the unavailability of data in many LMICs required to train locally relevant AI models to the capacity of health systems to absorb new AI technologies that demand the use of resources from elsewhere in the system. These observations illustrate the need to identify the unique issues posed by AI research for global health specifically, and the strategies that can be employed by all those implicated in AI governance to promote ethically responsible use of AI in global health research.
RECs and the regulation of research involving AI
RECs represent an important element of the governance of AI for global health research, and thus warrant further commentary as background to our paper. Despite the importance of RECs, foundational questions have been raised about their capabilities to accurately understand and address ethical issues raised by studies involving AI. Rahimzadeh et al. (2023) outlined how RECs in the United States are under-prepared to align with recent federal policy requiring that RECs review data sharing and management plans with attention to the unique ethical issues raised in AI research for health [ 13 ]. Similar research in South Africa identified variability in understanding of existing regulations and ethical issues associated with health-related big data sharing and management among research ethics committee members [ 14 , 15 ]. The effort to address harms accruing to groups or communities as opposed to individuals whose data are included in AI research has also been identified as a unique challenge for RECs [ 16 , 17 ]. Doerr and Meeder (2022) suggested that current regulatory frameworks for research ethics might actually prevent RECs from adequately addressing such issues, as they are deemed out of scope of REC review [ 16 ]. Furthermore, research in the United Kingdom and Canada has suggested that researchers using AI methods for health tend to distinguish between ethical issues and social impact of their research, adopting an overly narrow view of what constitutes ethical issues in their work [ 18 ].
The challenges for RECs in adequately addressing ethical issues in AI research for health care and public health exceed a straightforward survey of ethical considerations. As Ferretti et al. (2021) contend, some capabilities of RECs adequately cover certain issues in AI-based health research, such as the common occurrence of conflicts of interest where researchers who accept funds from commercial technology providers are implicitly incentivized to produce results that align with commercial interests [ 12 ]. However, some features of REC review require reform to adequately meet ethical needs. Ferretti et al. outlined weaknesses of RECs that are longstanding and those that are novel to AI-related projects, proposing a series of directions for development that are regulatory, procedural, and complementary to REC functionality. The work required on a global scale to update the REC function in response to the demands of research involving AI is substantial.
These issues take greater urgency in the context of global health [ 19 ]. Teixeira da Silva (2022) described the global practice of “ethics dumping”, where researchers from high income countries bring ethically contentious practices to RECs in low-income countries as a strategy to gain approval and move projects forward [ 20 ]. Although not yet systematically documented in AI research for health, risk of ethics dumping in AI research is high. Evidence is already emerging of practices of “health data colonialism”, in which AI researchers and developers from large organizations in high-income countries acquire data to build algorithms in LMICs to avoid stricter regulations [ 21 ]. This specific practice is part of a larger collection of practices that characterize health data colonialism, involving the broader exploitation of data and the populations they represent primarily for commercial gain [ 21 , 22 ]. As an additional complication, AI algorithms trained on data from high-income contexts are unlikely to apply in straightforward ways to LMIC settings [ 21 , 23 ]. In the context of global health, there is widespread acknowledgement about the need to not only enhance the knowledge base of REC members about AI-based methods internationally, but to acknowledge the broader shifts required to encourage their capabilities to more fully address these and other ethical issues associated with AI research for health [ 8 ].
Although RECs are an important part of the story of the ethical governance of AI for global health research, they are not the only part. The responsibilities of supra-national entities such as the World Health Organization, national governments, organizational leaders, commercial AI technology providers, health care professionals, and other groups continue to be worked out internationally. In this context of ongoing work, examining issues that demand attention and strategies to address them remains an urgent and valuable task.
The GFBR is an annual meeting organized by the World Health Organization and supported by the Wellcome Trust, the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) and the South African MRC. The forum aims to bring together ethicists, researchers, policymakers, REC members and other actors to engage with challenges and opportunities specifically related to research ethics. Each year the GFBR meeting includes a series of case studies and keynotes presented in plenary format to an audience of approximately 100 people who have applied and been competitively selected to attend, along with small-group breakout discussions to advance thinking on related issues. The specific topic of the forum changes each year, with past topics including ethical issues in research with people living with mental health conditions (2021), genome editing (2019), and biobanking/data sharing (2018). The forum is intended to remain grounded in the practical challenges of engaging in research ethics, with special interest in low resource settings from a global health perspective. A post-meeting fellowship scheme is open to all LMIC participants, providing a unique opportunity to apply for funding to further explore and address the ethical challenges that are identified during the meeting.
In 2022, the focus of the GFBR was “Ethics of AI in Global Health Research”. The forum consisted of 6 case study presentations (both short and long form) reporting on specific initiatives related to research ethics and AI for health, and 16 governance presentations (both short and long form) reporting on actual approaches to governing AI in different country settings. A keynote presentation from Professor Effy Vayena addressed the topic of the broader context for AI ethics in a rapidly evolving field. A total of 87 participants attended the forum from 31 countries around the world, representing disciplines of bioethics, AI, health policy, health professional practice, research funding, and bioinformatics. The 2-day forum addressed a wide range of themes. The conference report provides a detailed overview of each of the specific topics addressed while a policy paper outlines the cross-cutting themes (both documents are available at the GFBR website: https://www.gfbr.global/past-meetings/16th-forum-cape-town-south-africa-29-30-november-2022/ ). As opposed to providing a detailed summary in this paper, we aim to briefly highlight central issues raised, solutions proposed, and the challenges facing the research ethics community in the years to come.
In this way, our primary aim in this paper is to present a synthesis of the challenges and opportunities raised at the GFBR meeting and in the planning process, followed by our reflections as a group of authors on their significance for governance leaders in the coming years. We acknowledge that the views represented at the meeting and in our results are a partial representation of the universe of views on this topic; however, the GFBR leadership invested a great deal of resources in convening a deeply diverse and thoughtful group of researchers and practitioners working on themes of bioethics related to AI for global health including those based in LMICs. We contend that it remains rare to convene such a strong group for an extended time and believe that many of the challenges and opportunities raised demand attention for more ethical futures of AI for health. Nonetheless, our results are primarily descriptive and are thus not explicitly grounded in a normative argument. We make effort in the Discussion section to contextualize our results by describing their significance and connecting them to broader efforts to reform global health research and practice.
Uniquely important ethical issues for AI in global health research
Presentations and group dialogue over the course of the forum raised several issues for consideration, and here we describe four overarching themes for the ethical governance of AI in global health research. Brief descriptions of each issue can be found in Table 1 . Reports referred to throughout the paper are available at the GFBR website provided above.
The first overarching thematic issue relates to the appropriateness of building AI technologies in response to health-related challenges in the first place. Case study presentations referred to initiatives where AI technologies were highly appropriate, such as in ear shape biometric identification to more accurately link electronic health care records to individual patients in Zambia (Alinani Simukanga). Although important ethical issues were raised with respect to privacy, trust, and community engagement in this initiative, the AI-based solution was appropriately matched to the challenge of accurately linking electronic records to specific patient identities. In contrast, forum participants raised questions about the appropriateness of an initiative using AI to improve the quality of handwashing practices in an acute care hospital in India (Niyoshi Shah), which led to gaming the algorithm. Overall, participants acknowledged the dangers of techno-solutionism, in which AI researchers and developers treat AI technologies as the most obvious solutions to problems that in actuality demand much more complex strategies to address [ 24 ]. However, forum participants agreed that RECs in different contexts have differing degrees of power to raise issues of the appropriateness of an AI-based intervention.
The second overarching thematic issue related to whether and how AI-based systems transfer from one national health context to another. One central issue raised by a number of case study presentations related to the challenges of validating an algorithm with data collected in a local environment. For example, one case study presentation described a project that would involve the collection of personally identifiable data for sensitive group identities, such as tribe, clan, or religion, in the jurisdictions involved (South Africa, Nigeria, Tanzania, Uganda and the US; Gakii Masunga). Doing so would enable the team to ensure that those groups were adequately represented in the dataset to ensure the resulting algorithm was not biased against specific community groups when deployed in that context. However, some members of these communities might desire to be represented in the dataset, whereas others might not, illustrating the need to balance autonomy and inclusivity. It was also widely recognized that collecting these data is an immense challenge, particularly when historically oppressive practices have led to a low-trust environment for international organizations and the technologies they produce. It is important to note that in some countries such as South Africa and Rwanda, it is illegal to collect information such as race and tribal identities, re-emphasizing the importance for cultural awareness and avoiding “one size fits all” solutions.
The third overarching thematic issue is related to understanding accountabilities for both the impacts of AI technologies and governance decision-making regarding their use. Where global health research involving AI leads to longer-term harms that might fall outside the usual scope of issues considered by a REC, who is to be held accountable, and how? This question was raised as one that requires much further attention, with law being mixed internationally regarding the mechanisms available to hold researchers, innovators, and their institutions accountable over the longer term. However, it was recognized in breakout group discussion that many jurisdictions are developing strong data protection regimes related specifically to international collaboration for research involving health data. For example, Kenya’s Data Protection Act requires that any internationally funded projects have a local principal investigator who will hold accountability for how data are shared and used [ 25 ]. The issue of research partnerships with commercial entities was raised by many participants in the context of accountability, pointing toward the urgent need for clear principles related to strategies for engagement with commercial technology companies in global health research.
The fourth and final overarching thematic issue raised here is that of consent. The issue of consent was framed by the widely shared recognition that models of individual, explicit consent might not produce a supportive environment for AI innovation that relies on the secondary uses of health-related datasets to build AI algorithms. Given this recognition, approaches such as community oversight of health data uses were suggested as a potential solution. However, the details of implementing such community oversight mechanisms require much further attention, particularly given the unique perspectives on health data in different country settings in global health research. Furthermore, some uses of health data do continue to require consent. One case study of South Africa, Nigeria, Kenya, Ethiopia and Uganda suggested that when health data are shared across borders, individual consent remains necessary when data is transferred from certain countries (Nezerith Cengiz). Broader clarity is necessary to support the ethical governance of health data uses for AI in global health research.
Recommendations for ethical governance of AI in global health research
Dialogue at the forum led to a range of suggestions for promoting ethical conduct of AI research for global health, related to the various roles of actors involved in the governance of AI research broadly defined. The strategies are written for actors we refer to as “governance leaders”, those people distributed throughout the AI for global health research ecosystem who are responsible for ensuring the ethical and socially responsible conduct of global health research involving AI (including researchers themselves). These include RECs, government regulators, health care leaders, health professionals, corporate social accountability officers, and others. Enacting these strategies would bolster the ethical governance of AI for global health more generally, enabling multiple actors to fulfill their roles related to governing research and development activities carried out across multiple organizations, including universities, academic health sciences centers, start-ups, and technology corporations. Specific suggestions are summarized in Table 2 .
First, forum participants suggested that governance leaders including RECs, should remain up to date on recent advances in the regulation of AI for health. Regulation of AI for health advances rapidly and takes on different forms in jurisdictions around the world. RECs play an important role in governance, but only a partial role; it was deemed important for RECs to acknowledge how they fit within a broader governance ecosystem in order to more effectively address the issues within their scope. Not only RECs but organizational leaders responsible for procurement, researchers, and commercial actors should all commit to efforts to remain up to date about the relevant approaches to regulating AI for health care and public health in jurisdictions internationally. In this way, governance can more adequately remain up to date with advances in regulation.
Second, forum participants suggested that governance leaders should focus on ethical governance of health data as a basis for ethical global health AI research. Health data are considered the foundation of AI development, being used to train AI algorithms for various uses [ 26 ]. By focusing on ethical governance of health data generation, sharing, and use, multiple actors will help to build an ethical foundation for AI development among global health researchers.
Third, forum participants believed that governance processes should incorporate AI impact assessments where appropriate. An AI impact assessment is the process of evaluating the potential effects, both positive and negative, of implementing an AI algorithm on individuals, society, and various stakeholders, generally over time frames specified in advance of implementation [ 27 ]. Although not all types of AI research in global health would warrant an AI impact assessment, this is especially relevant for those studies aiming to implement an AI system for intervention into health care or public health. Organizations such as RECs can use AI impact assessments to boost understanding of potential harms at the outset of a research project, encouraging researchers to more deeply consider potential harms in the development of their study.
Fourth, forum participants suggested that governance decisions should incorporate the use of environmental impact assessments, or at least the incorporation of environment values when assessing the potential impact of an AI system. An environmental impact assessment involves evaluating and anticipating the potential environmental effects of a proposed project to inform ethical decision-making that supports sustainability [ 28 ]. Although a relatively new consideration in research ethics conversations [ 29 ], the environmental impact of building technologies is a crucial consideration for the public health commitment to environmental sustainability. Governance leaders can use environmental impact assessments to boost understanding of potential environmental harms linked to AI research projects in global health over both the shorter and longer terms.
Fifth, forum participants suggested that governance leaders should require stronger transparency in the development of AI algorithms in global health research. Transparency was considered essential in the design and development of AI algorithms for global health to ensure ethical and accountable decision-making throughout the process. Furthermore, whether and how researchers have considered the unique contexts into which such algorithms may be deployed can be surfaced through stronger transparency, for example in describing what primary considerations were made at the outset of the project and which stakeholders were consulted along the way. Sharing information about data provenance and methods used in AI development will also enhance the trustworthiness of the AI-based research process.
Sixth, forum participants suggested that governance leaders can encourage or require community engagement at various points throughout an AI project. It was considered that engaging patients and communities is crucial in AI algorithm development to ensure that the technology aligns with community needs and values. However, participants acknowledged that this is not a straightforward process. Effective community engagement requires lengthy commitments to meeting with and hearing from diverse communities in a given setting, and demands a particular set of skills in communication and dialogue that are not possessed by all researchers. Encouraging AI researchers to begin this process early and build long-term partnerships with community members is a promising strategy to deepen community engagement in AI research for global health. One notable recommendation was that research funders have an opportunity to incentivize and enable community engagement with funds dedicated to these activities in AI research in global health.
Seventh, forum participants suggested that governance leaders can encourage researchers to build strong, fair partnerships between institutions and individuals across country settings. In a context of longstanding imbalances in geopolitical and economic power, fair partnerships in global health demand a priori commitments to share benefits related to advances in medical technologies, knowledge, and financial gains. Although enforcement of this point might be beyond the remit of RECs, commentary will encourage researchers to consider stronger, fairer partnerships in global health in the longer term.
Eighth, it became evident that it is necessary to explore new forms of regulatory experimentation given the complexity of regulating a technology of this nature. In addition, the health sector has a series of particularities that make it especially complicated to generate rules that have not been previously tested. Several participants highlighted the desire to promote spaces for experimentation such as regulatory sandboxes or innovation hubs in health. These spaces can have several benefits for addressing issues surrounding the regulation of AI in the health sector, such as: (i) increasing the capacities and knowledge of health authorities about this technology; (ii) identifying the major problems surrounding AI regulation in the health sector; (iii) establishing possibilities for exchange and learning with other authorities; (iv) promoting innovation and entrepreneurship in AI in health; and (vi) identifying the need to regulate AI in this sector and update other existing regulations.
Ninth and finally, forum participants believed that the capabilities of governance leaders need to evolve to better incorporate expertise related to AI in ways that make sense within a given jurisdiction. With respect to RECs, for example, it might not make sense for every REC to recruit a member with expertise in AI methods. Rather, it will make more sense in some jurisdictions to consult with members of the scientific community with expertise in AI when research protocols are submitted that demand such expertise. Furthermore, RECs and other approaches to research governance in jurisdictions around the world will need to evolve in order to adopt the suggestions outlined above, developing processes that apply specifically to the ethical governance of research using AI methods in global health.
Research involving the development and implementation of AI technologies continues to grow in global health, posing important challenges for ethical governance of AI in global health research around the world. In this paper we have summarized insights from the 2022 GFBR, focused specifically on issues in research ethics related to AI for global health research. We summarized four thematic challenges for governance related to AI in global health research and nine suggestions arising from presentations and dialogue at the forum. In this brief discussion section, we present an overarching observation about power imbalances that frames efforts to evolve the role of governance in global health research, and then outline two important opportunity areas as the field develops to meet the challenges of AI in global health research.
Dialogue about power is not unfamiliar in global health, especially given recent contributions exploring what it would mean to de-colonize global health research, funding, and practice [ 30 , 31 ]. Discussions of research ethics applied to AI research in global health contexts are deeply infused with power imbalances. The existing context of global health is one in which high-income countries primarily located in the “Global North” charitably invest in projects taking place primarily in the “Global South” while recouping knowledge, financial, and reputational benefits [ 32 ]. With respect to AI development in particular, recent examples of digital colonialism frame dialogue about global partnerships, raising attention to the role of large commercial entities and global financial capitalism in global health research [ 21 , 22 ]. Furthermore, the power of governance organizations such as RECs to intervene in the process of AI research in global health varies widely around the world, depending on the authorities assigned to them by domestic research governance policies. These observations frame the challenges outlined in our paper, highlighting the difficulties associated with making meaningful change in this field.
Despite these overarching challenges of the global health research context, there are clear strategies for progress in this domain. Firstly, AI innovation is rapidly evolving, which means approaches to the governance of AI for health are rapidly evolving too. Such rapid evolution presents an important opportunity for governance leaders to clarify their vision and influence over AI innovation in global health research, boosting the expertise, structure, and functionality required to meet the demands of research involving AI. Secondly, the research ethics community has strong international ties, linked to a global scholarly community that is committed to sharing insights and best practices around the world. This global community can be leveraged to coordinate efforts to produce advances in the capabilities and authorities of governance leaders to meaningfully govern AI research for global health given the challenges summarized in our paper.
Limitations
Our paper includes two specific limitations that we address explicitly here. First, it is still early in the lifetime of the development of applications of AI for use in global health, and as such, the global community has had limited opportunity to learn from experience. For example, there were many fewer case studies, which detail experiences with the actual implementation of an AI technology, submitted to GFBR 2022 for consideration than was expected. In contrast, there were many more governance reports submitted, which detail the processes and outputs of governance processes that anticipate the development and dissemination of AI technologies. This observation represents both a success and a challenge. It is a success that so many groups are engaging in anticipatory governance of AI technologies, exploring evidence of their likely impacts and governing technologies in novel and well-designed ways. It is a challenge that there is little experience to build upon of the successful implementation of AI technologies in ways that have limited harms while promoting innovation. Further experience with AI technologies in global health will contribute to revising and enhancing the challenges and recommendations we have outlined in our paper.
Second, global trends in the politics and economics of AI technologies are evolving rapidly. Although some nations are advancing detailed policy approaches to regulating AI more generally, including for uses in health care and public health, the impacts of corporate investments in AI and political responses related to governance remain to be seen. The excitement around large language models (LLMs) and large multimodal models (LMMs) has drawn deeper attention to the challenges of regulating AI in any general sense, opening dialogue about health sector-specific regulations. The direction of this global dialogue, strongly linked to high-profile corporate actors and multi-national governance institutions, will strongly influence the development of boundaries around what is possible for the ethical governance of AI for global health. We have written this paper at a point when these developments are proceeding rapidly, and as such, we acknowledge that our recommendations will need updating as the broader field evolves.
Ultimately, coordination and collaboration between many stakeholders in the research ethics ecosystem will be necessary to strengthen the ethical governance of AI in global health research. The 2022 GFBR illustrated several innovations in ethical governance of AI for global health research, as well as several areas in need of urgent attention internationally. This summary is intended to inform international and domestic efforts to strengthen research ethics and support the evolution of governance leadership to meet the demands of AI in global health research.
Data availability
All data and materials analyzed to produce this paper are available on the GFBR website: https://www.gfbr.global/past-meetings/16th-forum-cape-town-south-africa-29-30-november-2022/ .
Clark P, Kim J, Aphinyanaphongs Y, Marketing, Food US. Drug Administration Clearance of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Enabled Software in and as Medical devices: a systematic review. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(7):e2321792–2321792.
Article Google Scholar
Potnis KC, Ross JS, Aneja S, Gross CP, Richman IB. Artificial intelligence in breast cancer screening: evaluation of FDA device regulation and future recommendations. JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182(12):1306–12.
Siala H, Wang Y. SHIFTing artificial intelligence to be responsible in healthcare: a systematic review. Soc Sci Med. 2022;296:114782.
Yang X, Chen A, PourNejatian N, Shin HC, Smith KE, Parisien C, et al. A large language model for electronic health records. NPJ Digit Med. 2022;5(1):194.
Meskó B, Topol EJ. The imperative for regulatory oversight of large language models (or generative AI) in healthcare. NPJ Digit Med. 2023;6(1):120.
Jobin A, Ienca M, Vayena E. The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nat Mach Intell. 2019;1(9):389–99.
Minssen T, Vayena E, Cohen IG. The challenges for Regulating Medical Use of ChatGPT and other large Language models. JAMA. 2023.
Ho CWL, Malpani R. Scaling up the research ethics framework for healthcare machine learning as global health ethics and governance. Am J Bioeth. 2022;22(5):36–8.
Yeung K. Recommendation of the council on artificial intelligence (OECD). Int Leg Mater. 2020;59(1):27–34.
Maddox TM, Rumsfeld JS, Payne PR. Questions for artificial intelligence in health care. JAMA. 2019;321(1):31–2.
Dzau VJ, Balatbat CA, Ellaissi WF. Revisiting academic health sciences systems a decade later: discovery to health to population to society. Lancet. 2021;398(10318):2300–4.
Ferretti A, Ienca M, Sheehan M, Blasimme A, Dove ES, Farsides B, et al. Ethics review of big data research: what should stay and what should be reformed? BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):1–13.
Rahimzadeh V, Serpico K, Gelinas L. Institutional review boards need new skills to review data sharing and management plans. Nat Med. 2023;1–3.
Kling S, Singh S, Burgess TL, Nair G. The role of an ethics advisory committee in data science research in sub-saharan Africa. South Afr J Sci. 2023;119(5–6):1–3.
Google Scholar
Cengiz N, Kabanda SM, Esterhuizen TM, Moodley K. Exploring perspectives of research ethics committee members on the governance of big data in sub-saharan Africa. South Afr J Sci. 2023;119(5–6):1–9.
Doerr M, Meeder S. Big health data research and group harm: the scope of IRB review. Ethics Hum Res. 2022;44(4):34–8.
Ballantyne A, Stewart C. Big data and public-private partnerships in healthcare and research: the application of an ethics framework for big data in health and research. Asian Bioeth Rev. 2019;11(3):315–26.
Samuel G, Chubb J, Derrick G. Boundaries between research ethics and ethical research use in artificial intelligence health research. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2021;16(3):325–37.
Murphy K, Di Ruggiero E, Upshur R, Willison DJ, Malhotra N, Cai JC, et al. Artificial intelligence for good health: a scoping review of the ethics literature. BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):1–17.
Teixeira da Silva JA. Handling ethics dumping and neo-colonial research: from the laboratory to the academic literature. J Bioethical Inq. 2022;19(3):433–43.
Ferryman K. The dangers of data colonialism in precision public health. Glob Policy. 2021;12:90–2.
Couldry N, Mejias UA. Data colonialism: rethinking big data’s relation to the contemporary subject. Telev New Media. 2019;20(4):336–49.
Organization WH. Ethics and governance of artificial intelligence for health: WHO guidance. 2021.
Metcalf J, Moss E. Owning ethics: corporate logics, silicon valley, and the institutionalization of ethics. Soc Res Int Q. 2019;86(2):449–76.
Data Protection Act - OFFICE OF THE DATA PROTECTION COMMISSIONER KENYA [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Sep 30]. https://www.odpc.go.ke/dpa-act/ .
Sharon T, Lucivero F. Introduction to the special theme: the expansion of the health data ecosystem–rethinking data ethics and governance. Big Data & Society. Volume 6. London, England: SAGE Publications Sage UK; 2019. p. 2053951719852969.
Reisman D, Schultz J, Crawford K, Whittaker M. Algorithmic impact assessments: a practical Framework for Public Agency. AI Now. 2018.
Morgan RK. Environmental impact assessment: the state of the art. Impact Assess Proj Apprais. 2012;30(1):5–14.
Samuel G, Richie C. Reimagining research ethics to include environmental sustainability: a principled approach, including a case study of data-driven health research. J Med Ethics. 2023;49(6):428–33.
Kwete X, Tang K, Chen L, Ren R, Chen Q, Wu Z, et al. Decolonizing global health: what should be the target of this movement and where does it lead us? Glob Health Res Policy. 2022;7(1):3.
Abimbola S, Asthana S, Montenegro C, Guinto RR, Jumbam DT, Louskieter L, et al. Addressing power asymmetries in global health: imperatives in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS Med. 2021;18(4):e1003604.
Benatar S. Politics, power, poverty and global health: systems and frames. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2016;5(10):599.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the outstanding contributions of the attendees of GFBR 2022 in Cape Town, South Africa. This paper is authored by members of the GFBR 2022 Planning Committee. We would like to acknowledge additional members Tamra Lysaght, National University of Singapore, and Niresh Bhagwandin, South African Medical Research Council, for their input during the planning stages and as reviewers of the applications to attend the Forum.
This work was supported by Wellcome [222525/Z/21/Z], the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (part of UK Research and Innovation), and the South African Medical Research Council through funding to the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Physical Therapy, Temerty Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Berman Institute of Bioethics, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
Bloomberg School of Public Health, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
Department of Philosophy and Classics, University of Ghana, Legon-Accra, Ghana
Caesar A. Atuire
Centre for Tropical Medicine and Global Health, Nuffield Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
Mahidol Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Unit, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
Phaik Yeong Cheah
Berkman Klein Center, Harvard University, Bogotá, Colombia
Armando Guio Español
Department of Radiology and Informatics, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA
Judy Wawira Gichoya
Health Ethics & Governance Unit, Research for Health Department, Science Division, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Adrienne Hunt & Katherine Littler
African Center of Excellence in Bioinformatics and Data Intensive Science, Infectious Diseases Institute, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda
Daudi Jjingo
ISI Foundation, Turin, Italy
Daniela Paolotti
Department of Health Sciences and Technology, ETH Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland
Effy Vayena
Joint Centre for Bioethics, Dalla Lana School of Public Health, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JS led the writing, contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. JA contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. CA contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. PYC contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. AE contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. JWG contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. AH contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. DJ contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. KL contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. DP contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. EV contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to James Shaw .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shaw, J., Ali, J., Atuire, C.A. et al. Research ethics and artificial intelligence for global health: perspectives from the global forum on bioethics in research. BMC Med Ethics 25 , 46 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-024-01044-w
Download citation
Received : 31 October 2023
Accepted : 01 April 2024
Published : 18 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-024-01044-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Artificial intelligence
- Machine learning
- Research ethics
- Global health
BMC Medical Ethics
ISSN: 1472-6939
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 17 April 2024
Hybrid speciation driven by multilocus introgression of ecological traits
- Neil Rosser ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7796-2548 1 , 2 na1 ,
- Fernando Seixas ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2026-5992 1 na1 ,
- Lucie M. Queste ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7402-8079 2 ,
- Bruna Cama ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4100-9680 2 ,
- Ronald Mori-Pezo 3 , 4 ,
- Dmytro Kryvokhyzha ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6498-1977 1 , 5 ,
- Michaela Nelson 2 ,
- Rachel Waite-Hudson 2 ,
- Matt Goringe 2 ,
- Mauro Costa 6 ,
- Marianne Elias ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1250-2353 7 , 8 ,
- Clarisse Mendes Eleres de Figueiredo ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6706-7064 9 , 10 ,
- André Victor Lucci Freitas ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5763-4990 11 ,
- Mathieu Joron ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1043-4147 12 ,
- Krzysztof Kozak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8980-3173 8 ,
- Gerardo Lamas ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3664-6730 13 ,
- Ananda R. P. Martins 14 ,
- W. Owen McMillan 8 ,
- Jonathan Ready ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9374-8661 9 , 10 ,
- Nicol Rueda-Muñoz 15 ,
- Camilo Salazar ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9217-6588 15 ,
- Patricio Salazar ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8988-0769 16 ,
- Stefan Schulz ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4810-324X 17 ,
- Leila T. Shirai 11 ,
- Karina L. Silva-Brandão 18 ,
- James Mallet ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3370-0367 1 &
- Kanchon K. Dasmahapatra ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2840-7019 2 , 19
Nature volume 628 , pages 811–817 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
12k Accesses
1 Citations
278 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Biodiversity
- Ecological genetics
- Evolutionary genetics
- Quantitative trait loci
Hybridization allows adaptations to be shared among lineages and may trigger the evolution of new species 1 , 2 . However, convincing examples of homoploid hybrid speciation remain rare because it is challenging to demonstrate that hybridization was crucial in generating reproductive isolation 3 . Here we combine population genomic analysis with quantitative trait locus mapping of species-specific traits to examine a case of hybrid speciation in Heliconius butterflies. We show that Heliconius elevatus is a hybrid species that is sympatric with both parents and has persisted as an independently evolving lineage for at least 180,000 years. This is despite pervasive and ongoing gene flow with one parent, Heliconius pardalinus , which homogenizes 99% of their genomes. The remaining 1% introgressed from the other parent, Heliconius melpomene , and is scattered widely across the H. elevatus genome in islands of divergence from H. pardalinus . These islands contain multiple traits that are under disruptive selection, including colour pattern, wing shape, host plant preference, sex pheromones and mate choice. Collectively, these traits place H. elevatus on its own adaptive peak and permit coexistence with both parents. Our results show that speciation was driven by introgression of ecological traits, and that speciation with gene flow is possible with a multilocus genetic architecture.
Similar content being viewed by others

Phylogenomics and the rise of the angiosperms
Diversity-dependent speciation and extinction in hominins

Evolution of tissue-specific expression of ancestral genes across vertebrates and insects
Biodiversity has long been depicted as a ‘tree of life’, but a wealth of genomic data has made clear that the branches and leaves of the tree often do not represent neatly defined units. Instead, they comprise a braided delta of evolutionary lineages linked by hybridization and introgression 4 . Although gene flow tends to homogenize populations 5 , it may also contribute to adaptation and even drive speciation if introgressed variants cause reproductive isolation 1 , 2 , 6 . Polyploid (chromosome-doubling) hybrid speciation is common in plants 7 , 8 , but compelling examples of homoploid hybrid speciation (without a change in chromosome number) remain scarce and contested, especially in animals 3 . This is because it is difficult to prove that hybridization had a pivotal role in creating reproductive isolation between the hybrid lineage and the parental species 3 . Here we present evidence for homoploid hybrid speciation in Heliconius butterflies. We show that introgression of key adaptive traits from H. melpomene caused H. elevatus to diverge from H. pardalinus , despite ongoing gene flow among sympatric H. elevatus and H. pardalinus , which homogenizes 99% of their genomes (Fig. 1a ).
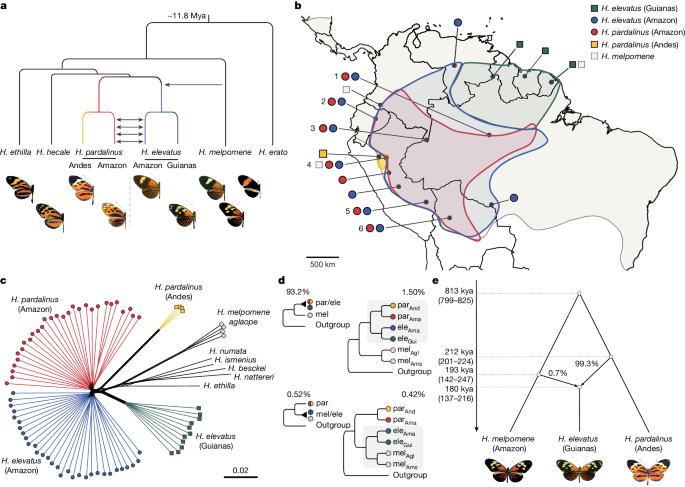
a , Evolutionary relationships and main introgression events described in this study. We test the hypothesis that introgression of major pre-mating and post-mating ecological isolating traits from H. melpomene led to the establishment of H. elevatus as a new stable hybrid species. Mya, million years ago. b , Geographical distributions of major clades. Locations at which both H. elevatus and H. pardalinus were sampled are numbered. c , Distance-based network using genome-wide independent SNPs. This concatenated tree shows the existence of two distinct clusters, Amazonian versus non-Amazonian, in both H. elevatus and H. pardalinus . d , Topology weighting analysis (TWISST) showing the percentage of the 11,509 non-overlapping genomic windows of 1,000 SNPs in which the majority of subtrees (that is, topology weighting ≥ 0.5) clusters H. elevatus (ele) with either H. pardalinus (par) (93.2%; top) or H. melpomene (mel) (0.52%; bottom). Note that although H. elevatus groups with H. pardalinus in 93.2% of windows, only 1.61% of those trees yield the two species as reciprocally monophyletic. By contrast, all three species are monophyletic in 81% of the windows for which H. elevatus groups with H. melpomene . Subscripts indicate geographical distributions for H. elevatus and H. pardalinus (Ama, Amazon; And, Andes; Gui, Guianas) and subspecies for H. melpomene (Agl, aglaope ; Ams, amaryllis ). e , A multispecies coalescent model with introgression supports a hybrid origin of H. elevatus , with the introgression time coinciding closely with the origin of the species (the 95% HPD intervals are given within parenthesis). Images of butterfly wings are copyright of the authors and Michel Cast.
Heliconius butterflies are chemically defended by cyanogenic glycosides, either sequestered from larval passion-vine host plants (Passifloraceae) or synthesized de novo 9 , 10 . Adults signal their toxicity to predators through their brightly coloured wing patterns. The cost of educating predators is shared with other defended butterflies and moths through mutualistic Müllerian mimicry 11 . Mimicry among species is not restricted to colour pattern, because co-mimics also converge in flight behaviour and wing shape 12 , 13 . Hybrids with intermediate phenotypes are selected against because predators do not recognize them 14 , 15 . Therefore, different mimetic phenotypes correspond to fitness peaks in an adaptive landscape maintained by disruptive selection. How populations transition to new fitness peaks remains an unanswered question, but adaptive introgression provides a possible route.
Heliconius elevatus , H. pardalinus and H. melpomene present an excellent system with which to elucidate the role of hybridization in speciation. All three species are sympatric across the Amazon basin 16 , 17 , 18 (Fig. 1b ). Heliconius elevatus and H. pardalinus are closely related 19 , but they have strikingly different colour patterns (Fig. 1a ). Heliconius pardalinus has a ‘tiger’ mimetic colour pattern typical of its close relatives. By contrast, H. elevatus has a red, black and yellow pattern, mimicking the much more distantly related H. melpomene 19 . This phenotypic convergence results in part from introgression at the major colour patterning loci cortex and optix 20 . Because Heliconius elevatus uses colour pattern as a partial cue in mate choice 17 , these introgressed alleles are likely to promote pleiotropic reproductive isolation from H. pardalinus . This suggests that H. elevatus has a hybrid origin, and here we test that hypothesis.
Hybrid genome of H. elevatus
We analysed whole-genome sequences of 92 wild-caught individuals of these three species: 42 H. elevatus (12 locations), 33 H. pardalinus (7 locations) and 17 H. melpomene (4 locations). For H. elevatus and H. pardalinus , our sampling spanned their combined geographical range (Fig. 1b and Supplementary Table 1 ). A concatenated whole-genome phylogenetic network groups H. pardalinus with H. elevatus , whereas H. melpomene forms a much deeper lineage separated by several other species 21 (Fig. 1c ). This topology is echoed in 93.2% of the genealogies estimated in sliding windows of 1,000 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) across the genome, whereas 0.52% of the genealogies cluster H. elevatus with H. melpomene (Fig. 1d ). This is suggestive of introgression between these two species but could also be explained by retention of ancestral polymorphisms. Testing this hypothesis under the multispecies coalescent with introgression framework 22 (Fig. 1e ), we find that most of the H. elevatus genome is derived from H. pardalinus , with a 0.71% (95% high posterior density (HPD) 0.32–1.11%) contribution from H. melpomene . Heliconius elevatus arose as an independent lineage around 180,000 years ago (kya) (Fig. 1e ; 95% HPD 137–216 kya; see also Extended Data Fig. 1 ). This divergence time coincides closely with the divergence from H. pardalinus (212 kya, 95% HPD 201–224 kya) and the timing of introgression from H. melpomene (193 kya, 95% HPD 142–247 kya). These coalescent-based estimates are therefore consistent with H. elevatus being a hybrid lineage that formed through admixture between H. pardalinus and H. melpomene .
Ongoing local gene flow with H. pardalinus
Notably, the whole-genome concatenated phylogenetic network suggests that sympatric populations of H. elevatus and H. pardalinus in the Amazon are more closely related to each other than to allopatric conspecifics from the Peruvian Andes and the Guianas (Fig. 1c ). Only 1.92% (1.50% + 0.42%; Fig. 1d ) of the 11,509 windows across the genome yield reciprocally monophyletic genealogies for H. pardalinus and H. elevatus ; this is confirmed by multispecies coalescent-based trees across the genome (Extended Data Fig. 2 ). We therefore investigated whether this apparent double species paraphyly could be explained by extensive ongoing gene flow between H. elevatus and H. pardalinus in sympatry in the Amazon.
Putative natural hybrids have been reported occasionally between H. elevatus and H. pardalinus 23 , but the two very rarely mate in captivity 17 . However, F 1 hybrids from forced matings are fully fertile 17 . We therefore examined the genomes of wild-caught individuals of the two species from sympatric populations across their range for evidence of gene flow. Focusing on SNPs diagnostic for H. elevatus and H. pardalinus , we find a few individuals with long tracts of heterozygous ancestry, in some cases spanning whole chromosomes, indicating recent gene flow (Extended Data Fig. 3 ). Four-population ( f 4 ) tests comparing within- and between-species gene flow support ongoing interspecific gene flow in sympatry (Fig. 2a ). Estimated levels of effective gene flow between the species in sympatry are high ( Nm > 1, where N is the effective population size, and m is the migration rate per generation), quite sufficient to homogenize neutral variation between species; indeed, gene flow approaches the rates that are found among nearby populations of the same species (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Table 2 ). Finally, we performed demographic modelling based on the site-frequency spectrum under different demographic scenarios and topologies. The best supported model retrieved a tree in which H. elevatus and H. pardalinus were reciprocally monophyletic, and confirmed that gene flow has been prevalent throughout their combined history (Fig. 2c and Extended Data Fig. 4 ). After their initial split, populations of H. pardalinus in the Amazon diverged from those in the Andes, and Amazonian populations of H. elevatus diverged from those in the Guianas (Fig. 2c and Supplementary Table 3 ). The two species then began to overlap broadly in the Amazon from around 28 kya (95% confidence interval 25.6–30.0 kya) until the present, with high levels of gene flow in sympatry. Nonetheless, sympatric populations of H. elevatus and H. pardalinus in the Amazon form mutually monophyletic genetic clusters (Fig. 1c ); thus, the two species remain differentiated and can clearly coexist despite extensive ongoing gene flow, implying the existence of strong sexual and ecological isolation.
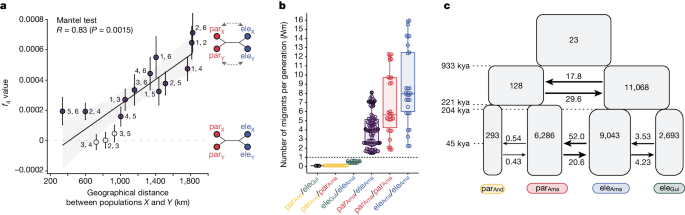
a , Gene flow between species in sympatry is typically significantly greater ( f 4 > 0, filled points) than the within-species gene flow between populations across the Amazon basin. Numbers next to the points indicate the population pairs compared (see Fig. 1b ). A significant positive correlation indicates that the within-species gene flow between populations X and Y declines with increasing geographical distance relative to between-species gene flow at populations X and/or Y . b , Estimates of effective migration rate ( Nm ) within and between species using G-PhoCS. In the Amazon, between-species Nm (par Ama /ele Ama ) is similar to within-species Nm between locations (par Ama /par Ama and ele Ama /ele Ama ). The estimates for par Ama /ele Ama are denoted as filled and open circles and correspond to within and between location comparisons, respectively. c , The best supported demographic model based on the site-frequency spectrum analysis supports H. elevatus and H. pardalinus as reciprocally monophyletic (Extended Data Fig. 4 ). They initially diverged with continuous gene flow (933 to 221 kya) and after splitting into Amazonian and non-Amazonian populations, they came into secondary contact and continued exchanging genes until the present (45 kya to the present). Numbers within the blocks are effective population sizes in thousands. Arrows between groups represent continuous gene flow; numbers above or below arrows indicate 2 Nm values.
Lack of gene flow with H. melpomene
The genome of Heliconius elevatus is, on average, more distantly related to its other parental species H. melpomene than it is to H. pardalinus (Fig. 1d and Extended Data Fig. 5a ). Yet gene flow from H. melpomene is plausible, because the latter is known to hybridize occasionally with other equally distant species in the wild 24 , 25 . None of the 31 H. elevatus or 17 H. melpomene individuals collected from areas of sympatry show any tracts of heterospecific ancestry (Extended Data Fig. 5b ). Likewise, f 4 tests do not detect any signals of gene flow (Supplementary Table 4 ). These data indicate that, in contrast to the extensive ongoing gene flow detected between H. elevatus and H. pardalinus , any recent gene flow between H. elevatus and H. melpomene is extremely rare. Because the H. elevatus and H. melpomene colour pattern phenotypes are essentially identical, this trait is probably not used to discriminate conspecifics 26 . Instead, their coexistence is likely to be due to strong assortative mating mediated by traits such as male sex pheromones and host plants (Extended Data Fig. 6 ), as well as female-limited hybrid sterility, which evolves rapidly 27 , 28 and helps to isolate H. melpomene from other sympatric, co-mimetic species 29 .
Barriers inherited from H. melpomene
As a result of extensive ongoing gene flow, differentiation ( F ST ) between sympatric populations of H. elevatus and H. pardalinus is approximately zero across around 99% of their genomes (Fig. 3 ). Only around 1% of the genome shows increased differentiation ( F ST ≥ 0.2) and retrieves both species as reciprocally monophyletic on the basis of topology weighting by iterative sampling of subtrees (TWISST) analysis, comprising 44 genomic islands of divergence. Notably, genealogies within genomic islands resolve all populations of both species, including the peripheral allopatric lineages, as reciprocally monophyletic (Fig. 3 ). Furthermore, introgression from H. melpomene is especially prevalent in these islands and is found in 32 of the 44 genomic islands of divergence (Fisher’s exact test P < 0.001; Fig. 3 ). Because these genomic islands resist homogenization despite gene flow in sympatry, we hypothesize that they contain the genetic basis for species differences.
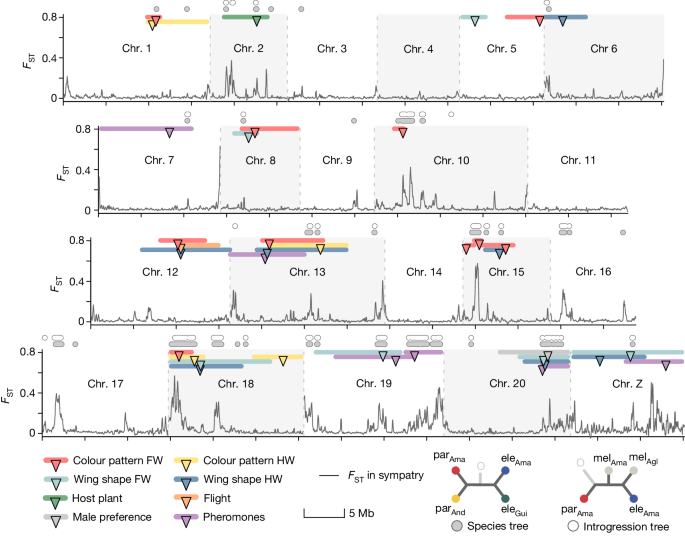
Patterns of genomic divergence between sympatric H. elevatus and H. pardalinus in the Amazon together with locations of mapped traits. The black line and y axis show F ST in 25-kb sliding windows across the genome. Coloured bars show significant QTLs for different traits, with the QTL peak indicated by the triangle and the Bayesian credible intervals by the length of the bar. For colour pattern and wing shape, only QTLs with non-overlapping credible intervals are shown. Most of the genome shows very low F ST due to gene flow in the Amazon, causing the double paraphyly topology for H. elevatus and H. pardalinus in Fig. 1c . Genomic regions with rare phylogenetic topologies (bottom right) supporting introgression from H. melpomene (white circles, introgression tree) and resolving the pardalinus – elevatus species tree (grey circles, species tree) are shown above the plot. These topologies often coincide with one another and with F ST peaks. O, outgroup ( Heliconius ethilla ). FW, forewing; HW, hindwing.
To understand the genetic architecture of traits that allow the coexistence of H. elevatus and H. pardalinus , we crossed sympatric Amazonian populations of these species. We identified quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for several species-specific traits, including colour pattern, male sex pheromones, male preference for female colour pattern, wing shape, flight and female host plant preference, in F 2 and backcross offspring (Fig. 4 ). These traits contribute to reproductive isolation because they are under divergent selection and/or directly determine mate choice. For example, host preference is likely to be under divergent ecological selection and also confers non-random mating because Heliconius mate in the vicinity of their host plants 30 , 31 . In total, we identified 63 QTLs associated with species differences at these traits, which mapped to 14 of the 21 chromosomes (Fig. 3 and Supplementary Table 5 ).
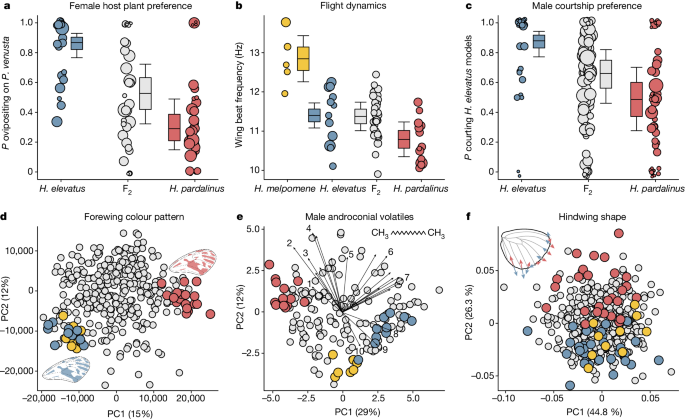
a , Heliconius elevatus and H. pardalinus differ in host plant preference during egg-laying; female H. elevatus show a stronger preference for Passiflora venusta relative to Passiflora riparia . Heliconius melpomene has a very distinct host plant preference and lays eggs on neither of these plants (Extended Data Fig. 6 ). Point sizes here and in b , c are scaled by the log of sample size. Error bars are 95% confidence limits. b , The two species differ in flight dynamics; H. elevatus beats its wings significantly faster than H. pardalinus , and converges towards H. melpomene aglaope . c , Given a choice, male H. elevatus individuals preferentially court model female wings with their own colour pattern relative to H. pardalinus , whereas H. pardalinus males exhibit no preference. d , Principal component analysis (PCA) of forewing colour pattern in hybrid crosses with the parental species and H. melpomene aglaope rotated and projected into this space. Wings show the top 10% of pixels contributing to the variance in PC1. e , PCA of male sex pheromones in hybrid crosses, with parental species rotated and projected. Differences between the species are driven mainly by variance in alkanes. Selected loadings: (1) hexahydrofarnesylacetone; (2) ( Z )-9-heneicosene; (3) (Z)-11-eicosenylacetate; (4) ( Z )-9−tricosene; (5) 11-methylhexacosane; (6) 11-methylpentacosane; (7) heptacosane; (8) tricosane; (9) heneicosane (inset figure); and (10) homovanillyl alcohol. f , PCA of hindwing shape in hybrid crosses, with parental species rotated and projected. Inset wing shows changes in hindwing shape observed along PC2. Only landmarks along the margin of the wing are shown. Individual specimens are depicted as circles: H. elevatus , blue; H. pardalinus , red; F 2 s and backcrosses, grey; and H. melpomene , yellow.
QTLs for colour pattern mapped to chromosomes 1, 5, 10, 12, 13, 15 and 18, with those on chromosomes 10, 15 and 18 containing the known colour patterning genes WntA , cortex and optix (refs. 16 , 17 , 18 ). We identified a large effect locus on chromosome 20 that determined variation in hindwing shape ( H. elevatus ancestry is associated with wider and shorter hindwings). Hybrid flight dynamics were quantified using high-frame-rate video footage. A single locus on chromosome 12 predicted wing beat frequency and explained 43% of the variance. Consistent with species differences (Fig. 4b ), individuals with genotype EE (homozygous ancestry for H. elevatus ) beat their wings faster (11.2 ± 0.1 Hz) than did PP (homozygous ancestry for H. pardalinus ) individuals (10.9 ± 0.2 Hz), in which E is the H. elevatus allele and P is the H. pardalinus allele. In controlled insectary experiments, Heliconius elevatus females exhibited a strong preference for Passiflora venusta relative to Passiflora riparia (Fig. 4a ), concordant with wild host plant records 17 . A single locus on chromosome 2 predicted the preference of female hybrids for different host plants (Fig. 3 ); the probability of ovipositing on P. venusta increased from 0.3 (s.e. 0.19–0.42) for genotype PP to 0.87 (s.e. 0.81–0.91) for genotype EE.
Mate choice among sympatric populations is further mediated by female preference for male sex pheromones secreted on wing androconia and male preference for colour pattern (attractiveness of females to males) 13 . We found large effect QTLs for male androconial volatiles on chromosomes 19 and 20. These genomic regions (see Supplementary Table 5 ) contain many genes encoding enzymes that are involved in fatty acid metabolism, such as reductases and Δ9-desaturases 32 —strong candidates for controlling differences between the saturated-fatty-acid-derived androconial volatiles of H. elevatus , and the unsaturated-fatty-acid-derived blend of H. pardalinus . For example, genotype EE at the chromosome 19 locus is associated with an approximately 100-fold increase in the concentration of heneicosane, relative to genotype PP, with the QTL explaining about a third of the variance.
The male colour pattern preference QTL with the highest LOD score (3.14) was tightly linked to QTLs for androconial volatiles and wing shape on chromosome 20. However, this QTL was not statistically significant. This might be explained if male preference is highly polygenic. In support of this, we found that the probability of a male courting the H. elevatus colour pattern is positively correlated with the total fraction of the male’s H. elevatus chromosomal ancestry ( P < 0.05, generalized linear mixed model with binomial errors and individual-level random effect). For comparison, we applied the same test to host plant choice and found no such association, suggesting that host preference has a simpler genetic basis.
Consistent with hybridization driving speciation, QTLs underpinning species-specific traits are linked to genomic windows introgressed from H. melpomene far more often than when the position of these QTLs is randomized across the genome (mean recombination rate between QTLs and nearest introgression topology, c = 0.26; randomized mean c = 0.39; P < 0.001). QTL peaks that are tightly linked to H. melpomene introgression regions ( c < 0.05) include those that determine colour pattern mimicry on chromosomes 10, 15 and 18, wing shape on chromosomes 19 and 20, male sex pheromones on chromosome 19 and 20, host plant preference on chromosome 2 and male preference on chromosome 20. Moreover, for colour pattern, wing shape, male sex pheromones and flight behaviour, H. elevatus exhibits trait values similar to those of H. melpomene (Fig. 4 ), providing a direct link between introgression, genotype and phenotype. Hence, these loci influencing ecological traits and derived from introgression represent key genomic regions that enabled hybrid speciation (Fig. 3 ).
Linkage or pleiotropy among traits are often thought to be necessary to circumvent the homogenizing effect of gene flow 5 , 33 . After removing overlapping loci in the colour pattern and wing shape phenotypic classes (Fig. 3 ), 28% of QTLs were tightly linked to at least one other species trait locus (recombination fraction c < 0.05), and only 11% were completely unlinked ( c ≈ 0.5). The mean recombination fraction ( c ) between trait loci and their nearest neighbour was significantly lower than when positions of the loci were randomized across the genome (observed mean c = 0.26; randomized mean c = 0.37; P = 0.001). Thus, although QTLs for traits that underpin reproductive isolation are scattered across the genome, there is nonetheless significant clustering among traits. Inversions can be important for maintaining linkage disequilibria between traits that confer reproductive isolation as they suppress recombination 34 . However, with the exception of chromosome 15, in which a known inversion is associated with colour pattern differences between H. elevatus and H. pardalinus 35 , we found no candidate inversions overlapping QTL peaks (Extended Data Fig. 7 ).
Speciation was driven by introgression
The question of how new species originate and adapt to environments is fundamental to evolutionary biology. Hybridization might have a key role in establishing barriers to gene flow by creating new allelic combinations 36 , 37 . Many genomic studies have provided evidence of admixture among species 4 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , but convincing cases of homoploid hybrid speciation remain scarce 1 , 3 , 6 . Here we show that H. elevatus is a hybrid species, the origin of which was triggered by introgression of traits from H. melpomene into a H. pardalinus -like ancestor (Fig. 1a ). These traits place Heliconius elevatus on a separate adaptive peak and allow it to coexist in sympatry with both parental species, despite occasional but pervasive gene flow with H. pardalinus that distorts the evolutionary history of 99% of the genome away from the species tree. Furthermore, we estimate that H. elevatus has persisted in widespread sympatry as a distinct lineage for over 720,000 generations, suggesting that it is stable and not in the process of fusing with H. pardalinus . To our knowledge, this makes it the oldest reported case of homoploid hybrid speciation, and our study is among the few to fulfil the strict criteria for hybrid speciation that were laid out in a previous study 3 . Because H. elevatus overlaps broadly across its Amazonian distribution with both progenitors, it also differs from most other previously described putative hybrid species 42 , 43 , 44 , including Heliconius heurippa 45 , which overlap with only one or neither of the parental lineages. Consistent with models of sympatric speciation 46 , traits conferring mate choice and divergent selection are clustered within the genome. Nonetheless, there are multiple clusters of these species-specific QTLs across different chromosomes. Adaptive coupling among these unlinked loci therefore spreads the effects of selection across the genome, allowing multiple genomic regions to evolve as a coadapted unit 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 . The capacity of this multilocus genetic architecture to resist gene flow indicates that sympatric speciation can occur more readily than predicted by simple theory based on small numbers of traits or loci.
Data collection and whole-genome resequencing
Collections and library preparation.
Adult butterflies were collected between 2009 and 2018 and stored at −20 °C in either salt-saturated dimethyl sulfoxide or 100% ethanol. RNA-free genomic DNA was extracted from the thorax of butterflies using Qiagen Blood and Tissue and E.Z.N.A Tissue DNA kits (Omega Bio-tek), and used to prepare 350-bp insert Illumina libraries for 33 individuals, which were sequenced using 100–150-bp paired-end sequencing on Illumina instruments. Collecting and export permit numbers are provided in the Acknowledgements. We complemented these samples with previously published sequences (see Supplementary Table 1 for sample details).
Read filtering, mapping and genotype calling
After demultiplexing, reads were filtered for Illumina adapters using cutadapt v.1.8.1 (ref. 52 ) and then mapped to the H. melpomene assembly v.2.5 (Hmel2.5, ref. 53 )(ref. 54 ) using BWA-MEM v.0.7.15 (ref. 55 ) with default parameters and marking short split hits as secondary. Mapped reads were sorted and duplicate reads removed using sambamba v.0.6.8 (ref. 56 ) sort and markdup modules, respectively. Mapped reads were further realigned around indels using the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) v.3.8 RealignerTargetCreator and IndelRealigner modules 57 , 58 , to reduce the number of indel miscalls. Read depth and other relevant read alignment quality control metrics were computed using QualiMap v.2.2.1 (ref. 59 ).
Genotype calling was performed using the bcftools v.1.5 (ref. 60 ) mpileup and call modules, requiring a minimum MQ (mapping quality) and QUAL (base quality) of 20. Genotyping was performed jointly for individuals belonging to the same population using the multiallelic and rare-variant calling option (-m) in bcftools call. Ploidy aware genotype calling was performed for the Z chromosome. Genotypes were filtered using the bcftools filter module. Both invariant and variant sites were required to have QUAL (quality of the variant call) ≥ 20 and MQ (root mean square mapping quality) ≥ 20, with DP (read depth) ≥ 8 for individual genotypes (DP ≥ 4 for females on the Z chromosome) and GQ (genotype quality) ≥ 20. All genotypes not fulfilling these criteria or within 5 bp of an indel (--SnpGap) were recoded as missing data.
Species relationships and demographic modelling of hybrid speciation
Relationships between H. elevatus , H. pardalinus , H. melpomene and other closely related species were investigated by building a phylogenetic network. The dataset was filtered to include only biallelic sites (excluding singletons) without missing data and at least 1 kb apart, using Plink v.1.9 (ref. 61 ). Pairwise absolute genetic distances between all pairs of samples were calculated using the disMat.py script ( https://github.com/simonhmartin/genomics_general ). The distance matrix was then used to construct a phylogenetic network using the NeighbourNet approach 62 , implemented in SplitsTree v.4.15.1 (ref. 63 ), with default parameters.
We also investigated species relationships by estimating a concatenated neighbour-joining tree. In this analysis, we included both variable and invariable sites, at least 1 kb apart and without missing data. The neighbour-joining tree was estimated from individuals’ pairwise distances using the R package ape v.5.7 (ref. 64 ) ‘read.dna’ and ‘nj’ functions. Trees were rooted using the ‘midpoint’ function from the R package phangorn v.2.11.1 (ref. 65 ). Bootstrap supports were obtained on the basis of 100 bootstrap replicates, using the ‘boot.phylo’ function in the R package ape v.5.7 (ref. 64 ).
Genealogical relationships along the genome between the three focal species ( H. elevatus , H. pardalinus and H. melpomene ) were further investigated using TWISST 66 ( https://github.com/simonhmartin/twisst ), and using Heliconius nattereri as an outgroup species. Only SNPs fixed in the outgroup ( H. nattereri ), variable in the focal species and with a minimum allele frequency (MAF) of 0.05 were considered. Statistical phasing and imputation were performed using Beagle v.5.1 (ref. 67 ), with default settings. The phased filtered dataset was used to infer neighbour-joining phylogenies for non-overlapping windows of 1,000 SNPs (median size of around 23.6 kb), assuming the GTR substitution model, in PHYML (ref. 68 ). Exact weightings were computed for all phylogenies. Windows were classified into each of the following categories when weighting support was 0.5 or greater: (i) H. elevatus and H. pardalinus group together but are not reciprocally monophyletic; (ii) H. elevatus and H. pardalinus group together and are reciprocally monophyletic; (iii) H. elevatus and H. melpomene group together but are not reciprocally monophyletic; and (iv) H. elevatus and H. melpomene group together and are reciprocally monophyletic.
To infer the timing of introgression from H. melpomene into H. elevatus and its split from H. pardalinus , we used the multispecies coalescent-with-introgression (MSCi) model implemented in BPP v.4.6.2 (ref. 22 ) (A00 analysis). For each species of the three species, we selected four individuals to generate sequenced alignments. For H. melpomene , we used H. melpomene aglaope from Peru. Given the population structure between Amazonian and non-Amazonian population of both H. elevatus and H. pardalinus and evidence for gene flow between the two species in the Amazon, we first performed this analysis using the non-Amazonian populations (that is, H. elevatus bari and H. pardalinus sergestus ). Loci were selected randomly from autosomes, requiring loci to be 2 kb long, a minimum distance of 20 kb to the next closest locus and 5 kb from the closest exon as annotated in H. melpomene assembly v.2.5. For each locus, individuals with more than 20% missing data and sites containing missing genotype calls were removed. Only loci containing all individuals and 800 bp passing filters were considered. Heterozygous sites were assigned IUPAC ambiguity codes. Demographic parameter estimation was performed using a fixed species tree, with introgression events (see Fig. 1e and Extended Data Fig. 1 ). An inverse gamma prior (invG) was applied both to the root age ( τ 0 ) and to all populations’ effective population sizes ( θ ) – invG( a = 3, b = 0.06) and invG( a = 3, b = 0.04), respectively. A beta prior was applied to the introgression probability ( j ) – Beta( a = 1, b = 1). The MCMC was run for 1,000,000 iterations after 50,000 iterations of burn-in, sampling every 10 iterations.
Historic and recent gene flow
Species-diagnostic snps.
To characterize instances of recent gene flow between Amazonian H. pardalinus and H. elevatus , we relied on ancestry-informative SNPs (allele frequency difference ≥ 0.8) between these two groups. Only ancestry-informative SNPs at least 10 kb apart were considered. For each SNP, an ancestry score of 0 and 1 was assigned for H. elevatus homozygous and H. pardalinus homozygous variants, respectively, and 0.5 for heterozygous. We then calculate each individual’s ancestry (average ancestry across SNPs) and heterozygosity, on the basis of the ancestry-informative SNPs passing the filters. A custom R script was used to visualize genotypes of species-diagnostic SNPs across the genomes of different individuals. The same approach was used to determine species-diagnostic SNPs between Amazonian H. elevatus and H. melpomene .
f 4 statistics
We calculated the f 4 statistics in ADMIXTOOLS (ref. 69 ) to measure shared drift between pairs of populations of different species in the same location versus between pairs of populations of the same species in different locations. Shared drift between populations of different species in the same location is indicative of gene flow between species, and shared drift between populations of the same species in different locations is indicative of grouping by species. Only autosomal biallelic SNPs were considered in this analysis. Standard errors were estimated through a weighted block jackknife approach over 500-kb blocks. We also measured the Euclidean geographic distance between all possible pairs of locations and performed a Mantel test for its correlation with the f 4 statistics.
Estimates of gene flow between population pairs
We used G-PhoCS (ref. 70 ) to estimate divergence times, effective population sizes and migration rates between pairs of populations of H. elevatus and H. pardalinus , both within and between species. In all analyses, we also include one individual from an outgroup species ( Heliconius besckei ) and estimate model parameters assuming possible bidirectional migration between the two ingroup species. G-PhoCS uses multiple independent neutrally evolving loci to infer demographic parameters. Therefore, we first defined regions of the genome within scaffolds larger than 1 Mb and at least 1 kb away from exons as annotated in H. melpomene assembly v.2.5. Within these regions we then selected 1-kb blocks that were at least 10 kb apart from the nearest block and produced sequence alignments, masking annotated repetitive elements and CpG islands identified with the software gCluster (ref. 71 ). Because previous studies have reported extensive introgression between both H. elevatus and H. pardalinus with other Heliconius species in large regions of the genome surrounding the three major colour pattern loci, we excluded blocks in chromosomes containing these loci (chromosomes 10, 15 and 18). We also excluded blocks in the Z chromosome owing to its different effective population size. For each alignment, we excluded individuals with more than 60% missing genotype calls, and only alignments with at least three individuals per population (or all individuals in the populations for those with fewer than three individuals) and a minimum of 100 bp for which no more than 25% of individuals had missing genotype calls were considered. We coded heterozygous genotype calls using IUPAC codes. A gamma prior with α = 2 and β = 100 was used for both the mutational-scaled effective population size ( θ ) and the divergence time ( τ ) between the two ingroup populations, whereas a gamma prior with α = 2 and β = 50 was used for the divergence time to the outgroup. For the mutation-scaled migration rates, we defined a gamma prior with α = 0.005 and β = 0.00001. The model was run three times, with a burn-in of 50,000 iterations (allowing for automatic fine-tuning of the parameters) followed by 200,000 iterations, sampling every 200 iterations. Convergence of the Markov chain and between the three different replicates was inspected using custom scripts. To convert the θ and τ estimates to absolute effective population size and divergence time, we assumed an average mutation rate ( µ ) of 2.9 × 10 −9 substitutions per site per generation and an average generation time ( g ) of 0.25 years (ref. 72 ). We also obtain estimates of the effective migration rate ( N e m ) using the formula: N e m AB = M AB × θ B /4.
Simulations to infer robustness of G-PhoCS inferences
Whenever Nm > 1, estimates of Nm for the same population comparisons varied both in value and directionality between different replicate runs of G-PhoCS. To investigate the cause for these differences, we performed coalescent simulations using MSMS (ref. 73 ). We considered the same demographic scenario as for the G-PhoCS runs; that is, two sister populations (A and B) that diverged at T D1 and split from the outgroup (C) at T D2 , and allowing either unidirectional or bidirectional migration between A and B. The split time between the two sister populations ( T D1 ) was set to four million generations, and eight million generations for the split of the outgroup ( T D2 ). An effective population size ( N e ) of one million or five million was assumed for the two ingroup populations (400,000 for the outgroup), and varying levels of gene flow ( Nm ) were considered (0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 2.0 and 10.0). For each scenario, we simulated 100 trees in MSMS (ref. 73 ), from which we generated sequence alignments using Seq-Gen v.1.3.4 (ref. 74 ). Custom scripts were used to combine pairs of haploid sequences into diploid sequences, using IUPAC codes for heterozygous sites, and to convert the alignments to the G-PhoCS sequence format. Finally, we ran G-PhoCS for the simulated datasets using the same settings as described above. Whenever Nm > 1 in the simulated datasets, G-PhoCS showed a similar behaviour to what was seen in our analysis of the Heliconius data (Supplementary Table 6 ). We believe that this effect is due to the difficulty of estimating gene flow when the populations are nearly panmictic. Hence, for each population pairwise comparison, the highest Nm estimate among the three replicate runs is presented in Fig. 2b .
Species-tree inference
Phylogenetic relationships between the H. pardalinus and H. elevatus major groups were inferred using the multispecies coalescent (MSC) approach implemented in BPP v.4.6.2 (ref. 22 ), while accounting for incomplete lineage sorting. Three H. p. sergestus individuals (with the highest coverage) and three H. elevatus individuals from the Guianas (the individual with the highest coverage per location (French Guiana, Suriname and Venezuela)) were considered. For Amazonian H. pardalinus and H. elevatus , again, only the individual with the highest coverage from each of three locations—Ecuador, Bolivia and Brazil—was included. For this analysis, loci were selected by first defining regions of the genome within scaffolds larger than 1 Mb. To minimize the effect of linked selection, these regions also had to be at least 2 kb from exons as annotated in Heliconius melpomene v.2.5 (Hmel2.5, ref. 54 ). Because the analysis assumes no intra-locus recombination and independence between loci, we selected loci of 100–250 bp and at least 2 kb from neighbouring loci. Sequence alignments were produced for all loci, masking repetitive elements as annotated in the reference genome and CpG islands identified with the software gCluster (ref. 75 ). For each locus, individuals with more than 50% missing genotype calls were excluded from the alignment and only loci with at least two individuals per population were considered. Furthermore, sites with more than 20% of individuals with missing genotype calls were removed and loci with less than 50 bp passing filters were excluded. Loci were grouped into blocks of 100 loci, and those overlapping the inversion on chromosome 15 were grouped in a separate block. Species-tree estimation was then performed in BPP v.4.6.2 using the A01 analysis (species-tree inference assuming no gene flow). Inverse gamma priors (invGs) were applied both to the root age ( τ 0 ) and to effective population sizes ( θ ) – invG(3, 0.06) and invG(3, 0.04), respectively. Parameters were scaled assuming a mutation rate of 2.9 × 10 −9 substitutions per site per generation and a generation time of 0.25 years (ref. 54 ). The MCMC was run for 1,000,000 iterations after 50,000 iterations of burn-in, sampling every 10 iterations. Three independent runs were performed for each block, using different starting species trees, and only blocks showing consistency among the three independent runs were considered. The most abundant estimated tree across the genome showed both species to be paraphyletic with respect to each other (Extended Data Fig. 2 ). We believe that this non-taxonomic arrangement is due to gene flow, which is not accounted for in the model.
Demographic modelling by analysis of site-frequency spectra
To understand the prevalence of gene flow at different stages of the speciation history of H. elevatus and H. pardalinus , we performed demographic modelling based on analysis of the site-frequency spectrum (SFS) using fastsimcoal2 v.2.7.0.2 (ref. 76 ). For this analysis, we considered all Amazonian and non-Amazonian populations of H. elevatus and H. pardalinus . Individuals with more than 50% missing data were excluded from the analysis and only sites genotyped in at least 80% of the individuals (including all four H. p. sergestus ) were considered. Furthermore, only sites at least 2 kb apart and at least 10 kb from exons were considered, to mitigate the effects of linkage disequilibrium and linked selection, respectively. We further excluded sites within repetitive regions as annotated in the H. melpomene assembly Hmel2.5. The 209,115 sites that were retained after filtering were polarized by assessing the allele present in three outgroup species— H. besckei , Heliconius ismenius telchinia and Heliconius numata robigus . From each of the outgroup species, we chose one individual with the highest coverage and assigned the ancestral allele to each site if it was genotyped and monomorphic in the outgroup species. The unfolded multidimensional site-frequency spectrum (multiSFS) was generated using easySFS ( https://github.com/isaacovercast/easySFS ), using the recommended down projection approach (four individuals of H. p. sergestus ; 10 northeastern group H. elevatus ; and 20 H. pardalinus and 20 H. elevatus individuals from the Amazon) to maximize the number of segregating sites while accounting for missing data. For each demographic model, fitting of the simulated multidimensional site-frequency spectra to the empirical data was maximized using the composite-likelihood method implemented in fastsimcoal v.2.7 (ref. 77 ). For all model parameters, we used wide search ranges from which initial starting parameter values were randomly sampled. For each model, we performed 100 independent fastsimcoal2 runs. Parameter estimates optimization was performed for 40 expectation-maximization cycles and the expected SFS was estimated using 100,000 coalescent simulations. The best fitting model was identified by means of the Akaike information criterion, considering for each model the optimization run with the highest likelihood (using the script https://github.com/speciationgenomics/scripts/blob/master/calculateAIC.sh ). To account for stochasticity in the likelihood approximation, we further compared likelihood distributions of the different models by performing 100 independent runs from parameter values estimated under the most likely replicate run for each model. Finally, for the best fit model, confidence intervals around the maximum likelihood parameter estimates were obtained by nonparametric block-bootstrapping. For this, the 209,115 sites were divided into 100 blocks and sampled with replacement.
Genomic islands of divergence and introgression
Summary statistics.
We calculated between-population differentiation ( F ST ) for Amazonian and non-Amazonian populations of both H. elevatus and H. pardalinus groups, in sliding windows of 25 kb (5 kb step size) along the genome using the script popgenWindows.py ( https://github.com/simonhmartin/genomics_general ). The script implements a version of Hudson’s K ST (ref. 78 ), modified to avoid weighting nucleotide diversity in each population by sample size. Individuals with more than 50% missing data were removed. Only sites with a maximum of two alleles, and with at least three individuals with genotype calls per population (or the total number of individuals in populations with fewer than three individuals) were considered. Only windows with at least 10% of sites passing filters were considered in the analysis.
Topology weighting
To determine genomic regions in which H. elevatus and H. pardalinus are reciprocally monophyletic (that is, genomic regions that are potentially involved in species barriers), genealogical relationships between Amazonian and non-Amazonian populations along the genome were quantified using TWISST 66 ( https://github.com/simonhmartin/twisst ). The same dataset as for F ST was used, but also adding five individuals of representative outgroup species ( H. besckei , H. ismenius , H. numata , H. nattereri and H. ethilla ). Statistical phasing and imputation were performed using Beagle 5.1 (ref. 67 ), with default settings. Only SNPs fixed in all outgroup individuals and variable in the ingroup population with an MAF of 0.05 were considered. The phased filtered dataset was used to infer neighbour-joining phylogenies for windows of 100 SNPs (slide every 25 SNPs), assuming the GTR substitution model, in PHYML (ref. 68 ). Exact weightings were computed for all phylogenies. To estimate the proportion of trees supporting a grouping of individuals by species versus grouping by geography, we considered five groups: (i) H. elevatus from the Guianas (Venezuela, Suriname and French Guiana); (ii) H. elevatus from the Amazon; (iii) H. pardalinus from the Amazon; (iv) H. p. sergestus (Andes); and (v) an outgroup, H. nattereri . Because we hypothesize that introgression from H. melpomene into H. elevatus could be involved in speciation of the latter and H. pardalinus , the same analysis was performed including only Amazonian H. elevatus , Amazonian H. pardalinus and two H. melpomene populations ( H. m. amaryllis and H. m. aglaope ). By including H. ethilla (a sister species to H. elevatus and H. pardalinus ) as a fifth population, we were able to polarize the genealogies, allowing determination of the direction of introgression.
Association between H. melpomene introgression and genomic islands of divergence
To test whether H. melpomene introgression in the genome of H. elevatus is associated with genomic islands of divergence between sympatric H. elevatus and H. pardalinus , we performed a Fisher’s exact test. First, we defined genomic islands of divergence as regions with F ST ≥ 0.2 and in which TWISST recovered both H. pardalinus and H. elevatus as reciprocally monophyletic (with weight ≥ 0.8). Second, we defined as introgressed, genomic regions in which TWISST grouped H. elevatus with H. melpomene with a weight ≥ 0.8. We then performed a Fisher’s exact test, as implemented in bedtools v.2.30.0 (ref. 79 ), to test whether the two sets of genomic intervals overlap more than expected given the size of the reference genome.
Genetic mapping of traits involved in reproductive isolation
Captive populations of Amazonian H. elevatus pseudocupidineus , H. pardalinus butleri and H. m. agalope were established in outdoor insectaries in Tarapoto, Peru and in heated indoor insectaries in York, UK, as previously described 17 . Crosses for QTL mapping were generated by mating H. elevatus with H. pardalinus to produce F 1 broods, and then by either crossing these amongst themselves to generate F 2 broods or backcrossing to parental taxa.
Colour pattern phenotyping
Dorsal surfaces of wings from 12 H. elevatus , 19 H. pardalinus , 14 H. m. aglaope , 348 F 2 and 50 backcross hybrids were photographed in a light box against a white background using a Canon EOS D1000 together with an X-rite ColorChecker Mini (Supplementary Table 7 ). From each image, we selected a single forewing and hindwing for analysis, clipped the image to the wing outlines and flipped wings when necessary to ensure that all were similarly orientated (resulting in two files; one forewing and one hindwing). To align the wings so that pixels represent homologous units among individuals, we used image registration 80 , a regression-based method that aligns two sets of wings (a source and a reference) according to intensity-based similarity. We chose the reference set of wings using the PCA of wing shape (see below). For forewing (36 PCs) and hindwing (26 PCs) we found the mean value for each PC across all F 2 and backcross individuals. We assigned the reference individual as the individual that had the minimum deviation from these mean values (summed across all PCs). We then checked all alignments by eye. To allow for minor misalignment or damage to wings, we included pixels in which up to 5% of individuals had missing RGB values.
Wing shape was quantified in 31 H. elevatus , 26 H. pardalinus , 10 H. m. aglaope and 308 F 2 and 36 backcross hybrids using landmark-based geometric morphometrics analyses (Supplementary Table 7 ). The ventral side of the butterfly wings was scanned using a flatbed scanner at 300 dpi and landmarks were placed at specific vein intersections 81 on the forewing (20 landmarks) and hindwing (15 landmarks) using tpsDig2 82 . Landmark coordinates were adjusted for size and orientation using a Procrustes analysis from the package geomorph 83 . Forewings and hindwings were analysed separately.
H. elevatus ( n = 12), H. pardalinus ( n = 13), H. m. aglaope ( n = 5) and F 2 s ( n = 40) were filmed flying freely in a large flight cage (5 × 2.5 × 2 m) using a GoPro HERO 4 Black camera at 239.7 frames per second at a resolution of 720p (Supplementary Table 7 ). Videos were studied in slow motion using GoPro Studio v.2.5.9.2658. Flight sequences in which an individual was flying straight and level for at least five wing beats were selected to measure wing beat frequency (WBF). WBF was measured by counting the number of complete wing beats and the number of video frames. Five WBF measurements were taken per individual from separate flight sequences and used to calculate the individuals’ mean WBF by dividing the total number of wing beats across all flight sequences by the total flight time estimated from the number of video frames.
Female host plant preference
Host plant preference assays for QTL mapping were performed by introducing single H. elevatus , H. pardalinus and F 2 females ( n = 24, 32 and 31, respectively) into cages measuring 1 m ( W ) × 2 m ( L ) × 1.7 m ( H ), with two approximately equally sized shoots of the host plants ( P. riparia and P. venusta ) placed in the back corners. At the end of each day, the number of eggs laid on each plant species was recorded and the eggs were removed (Supplementary Table 7 ). To compare the oviposition preference of Peruvian H. elevatus , H. pardalinus and H. melpomene , groups of females (wild-caught and/or reared) of a given taxon were released into a large cage (2.5 m ( W ) × 5 m ( L ) × 2 m ( H )) containing single representatives of 21 species of Passiflora that are commonly found near Tarapoto, Peru and which represent potential host plants 17 . The number of eggs laid on each host plant was recorded at the end of each day. A total of 126 females were tested, resulting in a total of 889 eggs (176 from 35 H. elevatus females, 288 from 24 H. melpomene and 425 from 51 H. pardalinus ).
Male sexual preference
To assay male preference for female colour pattern, we presented H. elevatus , H. pardalinus and F 2 males ( n = 46, 66 and 106, respectively) with a pair of model female wings (one H. elevatus and one H. pardalinus ), and recorded courtship events (full details of the experimental set-up are provided in ref. 17 ). Males were tested individually and placed in the experimental cage one day earlier to allow acclimatization. Trials lasted 15–30 min. The number of courtships (defined as sustained flight 5–15 cm over a model) by the males directed towards each of the model wings was recorded (Supplementary Table 7 ).
Phenotyping of androconial volatiles
Male Heliconius produce complex chemical blends of volatile compounds from their hindwing androconia. These blends have been shown to function as sex pheromones in several other Heliconius species and in butterflies in general 84 , 85 . Androconial regions were excised from 13 H. elevatus , 10 H. pardalinus , 7 H. melpomene malleti individuals and 122 F 2 and 17 backcross hybrids 21 days after eclosion, and suspended in dichloromethane. The extracts were analysed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS), as reported previously 16 , 86 (Supplementary Table 7 ) on a 7890A GC-System coupled with an MSD 5975C mass analyser (Agilent Technologies) instrument fitted with an HP-5MS column (50 m, 0.25 mm internal diameter, 0.25 µm film thickness). The ionization method was electron impact with a collision energy of 70 eV. Conditions were as follows: inlet pressure 9.79 psi, He 20 ml min −1 , injection volume 1 µl. The GC was programmed as follows: start at 50 °C, increase at 5 °C min −1 to 320 °C and hold that temperature for 5 min. The carrier gas was He at 1.2 ml min −1 . For all identified compounds, the concentration was calculated from the peak’s area, as reported by AMDIS software 87 . Each compound’s chromatogram was interpreted by AMDIS through the NIST databases and the additional databases compiled at the Institute of Organic Chemistry of Technische Universität Braunschweig. All identifiable compounds running between undecane and nonacosanal were scored. Potential contaminants or extraneous compounds were excluded, together with compounds that appeared fewer than 10 times across the entire dataset.
DNA extraction and RAD library preparation for QTL analysis
RNA-free genomic DNA was extracted from thoracic tissue using a Qiagen DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit following manufacturer’s standard protocol. Restriction-site-associated DNA (RAD) libraries were prepared using a protocol modified from (ref. 88 , using a PstI restriction enzyme, sixteen 6-bp P1 barcodes and eight indexes. DNA was Covaris sheared to 300–700 bp and gel size selected. A total of 128 individuals were sequenced per lane, with 125-bp paired-end reads, on an Illumina HiSeq 2500 (Supplementary Table 8 ).
SNP calling
Fastq files from each RAD library were demultiplexed using process_radtags from Stacks 89 , and BWA-MEM 90 was used with default parameters to map the reads to the H. melpomene assembly v.2.5 (ref. 91 ). BAM files were then sorted and indexed with Samtools (ref. 90 ), and Picard v.1.119 ( https://github.com/broadinstitute/picard ) was used to add read group data and mark PCR duplicates. To check for errors, confirm pedigrees and assign samples with unrecorded pedigree to families, we used Plink v.1.9 (ref. 61 ) to estimate the fraction of the genome that is identical by descent (IBD; \(\widehat{{\boldsymbol{\pi }}}\) ) between all pairwise combinations of samples (siblings and parent-offspring comparisons should yield \(\widehat{{\boldsymbol{\pi }}}\) values close to 0.5). In addition, for specimens that were sequenced multiple times, we checked that samples derived from the same individual \((\widehat{{\boldsymbol{\pi }}}\approx 1)\) . We then merged these samples, using the MergeSamFiles command from Picard Tools, and used Samtools mpileup command to call SNPs.
Linkage map construction
Linkage maps were built for hybrid and within-species crosses using Lep-MAP3 (ref. 92 ). Pedigrees are provided in Supplementary Table 8 . SNPs were first converted to posterior genotype likelihoods for each of ten possible SNP genotypes. We used the ParentCall2 module to correct erroneous or missing parental genotypes and call sex-linked markers using a log-odds difference of >2 (ZLimit) and halfSibs = 1. We used Filtering2 to remove SNPs showing segregation distortion, specifying a P value limit of 0.01; that is, there is a 1:100 chance that a randomly segregating marker is discarded. We then separated markers into chromosomes using their Hmel2.5 scaffold. To obtain genetic distances between markers, we fixed the order of the markers to their order in Hmel2.5, and then evaluated this order, using all markers and specifying no recombination in females. We then used map2gentypes.awk to convert the Lep-MAP3 output to four-way fully informative genotypes with no missing data. To assign ancestry to phased haplotype blocks in the hybrid linkage map, we used biallelic sites with significantly different allele frequencies in the parental species ( χ 2 test applied to sequences for 26 H. elevatus and 47 H. pardalinus individuals from Peru and Ecuador).
QTL mapping
The colour pattern, androconial volatiles and wing shape datasets are multivariate and highly collinear. We therefore used PCA to reduce the phenotypic values for the hybrids to orthogonal vectors (PCs), which we then used as phenotypes in QTL mapping. For wing shape, we applied PCA to the Procrustes coordinates. For the androconial volatiles, we applied the PCA to the set of compounds that were significantly different between the two parental species (one-tailed paired t -test). For colour pattern, we performed a PCA on the concatenated RGB values from the aligned images and retained PCs that explained more than 1% of the variance.
For colour pattern, androconial volatiles, wing shape and WBF, we tested for associations between phenotype and genotype using linear models with normal errors. For wing shape, we included centroid size as a covariate to control for allometry. For female host plant choice and male preference for female colour pattern, we (i) logistically transformed the proportions and used linear models with normal errors; and (ii) used generalized linear mixed models with an individual-level random effect to account for overdispersion and binomial errors. The significance of QTL scans was assessed by permuting the phenotypes relative to the genotypes (1,000 permutations). For traits phenotyped in both males and females, a sex-specific significance threshold was used to avoid spurious sex linkage (see Supplementary Table 5 ).
We first analysed all data using F 2 s only, using R/qtl (ref. 93 ) to estimate genotype probabilities at 1-cM intervals, using the Haldane mapping function and an assumed genotyping error rate of 0.001. These genotype probabilities were then used as the dependent variable in models, and for traits phenotyped in both males and females we included sex and cross direction as covariates for markers on the sex chromosome. For traits for which backcrosses had been scored in addition to F 2 s, we performed an additional round of analyses combining F 2 s with backcrosses. In this case, we used the categorical genotypes (EE, EP and PP) inferred from linkage mapping as the dependent variables, and added random effects for cross type (three levels: F 2 , backcross to H. elevatus , backcross to H. pardalinus ), sex or individual. Model structures and estimated coefficients are provided in Supplementary Table 5 .
To test whether QTLs are significantly clustered (that is, genetically linked), for each QTL we estimated the recombination probability with its nearest neighbouring QTLs (using the position of the maximum LOD score), and took the mean of the resulting vector (low values indicate that most QTLs are linked to at least one other QTL; high values indicate that most QTLs are unlinked). We then randomized the position of the QTLs 10,000 times and compared the observed data to the randomized dataset using a two-tailed test ( P = the proportion of randomized datasets that give a result more extreme than the observed data × 2). When multiple QTLs overlapped within the phenotypic classes forewing colour pattern, hindwing colour pattern, forewing shape and hindwing shape, we included only the best supported QTL (highest LOD score). To test whether species and introgression topologies are associated with QTLs, we applied the same test.
To identify putative structural rearrangements between H. elevatus and H. pardalinus , we compared recombination rates between F 2 s and within-species crosses (F 2 s, 441 individuals across 26 families; H. elevatus , 179 individuals across 9 families; H. pardalinus , 296 individuals across 15 families). Regions that are freely recombining within species but not in F 2 s represent candidate rearrangements that might facilitate divergence and speciation. The probability of the within-species recombination events observed within an F 2 breakpoint can be given as p n , where p is the fraction of parental individuals in the mapping crosses and n is the observed number of recombination events. We estimated p n within each F 2 breakpoint and considered breakpoints in which p < 0.01 to be candidate rearrangements.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
Newly generated whole-genome sequencing data used in the population genomic analyses and RAD-sequencing data used in the cross analyses have been uploaded to the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) ( PRJNA1074694 ). NCBI SRA accessions for individual samples are listed in Supplementary Tables 1 and 8 . Phenotypic data are available in Supplementary Table 7 and at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10685466 (ref. 94 ) and https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10689714 (ref. 95 ).
Code availability
Custom code used for the genomic analyses ( https://github.com/FernandoSeixas/HeliconiusHybridSpeciation ) and the QTL mapping ( https://github.com/heliconius-maps/HeliconiusHybridSpeciation ) is available from GitHub.
Lamichhaney, S. et al. Rapid hybrid speciation in Darwin’s finches. Science 359 , 224–228 (2018).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Abbott, R. et al. Hybridization and speciation. J. Evol. Biol. 26 , 229–246 (2013).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Schumer, M., Rosenthal, G. G. & Andolfatto, P. How common is homoploid hybrid speciation? Evolution 68 , 1553–1560 (2014).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lamichhaney, S. et al. Evolution of Darwin’s finches and their beaks revealed by genome sequencing. Nature 518 , 371–375 (2015).
Coyne, J. A. & Orr, H. A. Speciation (Sinauer Associates, 2004).
Olave, M., Nater, A., Kautt, A. F. & Meyer, A. Early stages of sympatric homoploid hybrid speciation in crater lake cichlid fishes. Nat. Commun. 13 , 5893 (2022).
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Barker, M. S., Arrigo, N., Baniaga, A. E., Li, Z. & Levin, D. A. On the relative abundance of autopolyploids and allopolyploids. New Phytol. 210 , 391–398 (2016).
Mallet, J. Hybrid speciation. Nature 446 , 279–283 (2007).
Engler-Chaouat, H. S. & Gilbert, L. E. De novo synthesis vs. sequestration: negatively correlated metabolic traits and the evolution of host plant specialization in cyanogenic butterflies. J. Chem. Ecol. 33 , 25–42 (2007).
Engler, H. S., Spencer, K. C. & Gilbert, L. E. Preventing cyanide release from leaves. Nature 406 , 144–145 (2000).
Joron, M. & Mallet, J. Diversity in mimicry: paradox or paradigm? Trends Ecol. Evol. 13 , 461–466 (1998).
Page, E., Queste, L., Rosser, N., Mallet, J. & Dasmahapatra, K. K. Pervasive mimicry in flight behavior among aposematic butterflies. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 121 , e2300886121 (2024).
Jones, R. T. et al. Wing shape variation associated with mimicry in butterflies. Evolution 67 , 2323–2334 (2013).
Merrill, R. M. et al. Disruptive ecological selection on a mating cue. Proc. R. Soc. B 279 , 4907–4913 (2012).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Arias, M. et al. Crossing fitness valleys: empirical estimation of a fitness landscape associated with polymorphic mimicry. Proc. R. Soc. B 283 , 20160391 (2016).
Cama, B. et al. Exploitation of an ancestral pheromone biosynthetic pathway contributes to diversification in Heliconius butterflies. Proc. R. Soc. B 289 , 20220474 (2022).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rosser, N. et al. Geographic contrasts between pre- and postzygotic barriers are consistent with reinforcement in Heliconius butterflies. Evolution 73 , 1821–1838 (2019).
Benson, W. W., Brown, K. S. & Gilbert, L. E. Coevolution of plants and herbivores: passion flower butterflies. Evolution 29 , 659–680 (1975).
Kozak, K. M. et al. Multilocus species trees show the recent adaptive radiation of the mimetic Heliconius butterflies. Syst. Biol. 64 , 505–524 (2015).
Heliconius Genome Consortium. Butterfly genome reveals promiscuous exchange of mimicry adaptations among species. Nature 487 , 94–98 (2012).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Thawornwattana, Y., Seixas, F. A., Yang, Z. & Mallet, J. Major patterns in the introgression history of Heliconius butterflies. eLife 12 , RP90656 (2023).
Flouri, T., Jiao, X., Rannala, B. & Yang, Z. A Bayesian implementation of the multispecies coalescent model with introgression for phylogenomic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 37 , 1211–1223 (2020).
Brower, A. V. Z. Alternative facts: a reconsideration of putatively natural interspecific hybrid specimens in the genus Heliconius (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). Zootaxa 4499 , 1–87 (2018).
Dasmahapatra, K. K., Silva-Vásquez, A., Chung, J.-W. & Mallet, J. Genetic analysis of a wild-caught hybrid between non-sister Heliconius butterfly species. Biol. Lett. 3 , 660–663 (2007).
Mallet, J., Beltrán, M., Neukirchen, W. & Linares, M. Natural hybridization in heliconiine butterflies: the species boundary as a continuum. BMC Evol. Biol. 7 , 28 (2007).
González-Rojas, M. F. et al. Chemical signals act as the main reproductive barrier between sister and mimetic Heliconius butterflies. Proc. R. Soc. B 287 , 20200587 (2020).
Rosser, N. et al. Complex basis of hybrid female sterility and Haldane’s rule in Heliconius butterflies: Z-linkage and epistasis. Mol. Ecol. 31 , 959–977 (2022).
Jiggins, C. D. et al. Sex-linked hybrid sterility in a butterfly. Evolution 55 , 1631–1638 (2001).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Sánchez, A. P. et al. An introgressed wing pattern acts as a mating cue. Evolution 69 , 1619–1629 (2015).
Merrill, R. M., Naisbit, R. E., Mallet, J. & Jiggins, C. D. Ecological and genetic factors influencing the transition between host-use strategies in sympatric Heliconius butterflies. J. Evol. Biol. 26 , 1959–1967 (2013).
Estrada, C. & Gilbert, L. E. Host plants and immatures as mate-searching cues in Heliconius butterflies. Anim. Behav. 80 , 231–239 (2010).
Article Google Scholar
Byers, K. J. R. P. et al. Clustering of loci controlling species differences in male chemical bouquets of sympatric Heliconius butterflies. Ecology and Evolution 11 , 89–107 (2021).
Felsenstein, J. Skepticism towards Santa Rosalia, or why are there so few kinds of animals? Evolution 35 , 124–138 (1981).
Rieseberg, L. H. Chromosomal rearrangements and speciation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 16 , 351–358 (2001).
Jay, P. et al. Supergene evolution triggered by the introgression of a chromosomal inversion. Curr. Biol. 28 , 1839–1845 (2018).
Marques, D. A., Meier, J. I. & Seehausen, O. A Combinatorial view on speciation and adaptive radiation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 34 , 531–544 (2019).
Hench, K., Helmkampf, M., McMillan, W. O. & Puebla, O. Rapid radiation in a highly diverse marine environment. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119 , e2020457119 (2022).
Green, R. E. et al. A draft sequence of the Neandertal genome. Science 328 , 710–722 (2010).
Palkopoulou, E. et al. A comprehensive genomic history of extinct and living elephants. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115 , E2566–E2574 (2018).
Li, G., Figueiró, H. V., Eizirik, E. & Murphy, W. J. Recombination-aware phylogenomics reveals the structured genomic landscape of hybridizing cat species. Mol. Biol. Evol. 36 , 2111–2126 (2019).
Suvorov, A. et al. Widespread introgression across a phylogeny of 155 Drosophila genomes. Curr. Biol. 32 , 111–123.e5 (2022).
Barrera-Guzmán, A. O., Aleixo, A., Shawkey, M. D. & Weir, J. T. Hybrid speciation leads to novel male secondary sexual ornamentation of an Amazonian bird. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115 , E218–E225 (2018).
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
Hermansen, J. S. et al. Hybrid speciation in sparrows I: phenotypic intermediacy, genetic admixture and barriers to gene flow. Mol. Ecol. 20 , 3812–3822 (2011).
Nieto Feliner, G. et al. Is homoploid hybrid speciation that rare? An empiricist’s view. Heredity 118 , 513–516 (2017).
Mavárez, J. et al. Speciation by hybridization in Heliconius butterflies. Nature 441 , 868–871 (2006).
Gavrilets, S. Fitness Landscapes and the Origin of Species (Princeton Univ. Press, 2004).
Butlin, R. K. & Smadja, C. M. Coupling, reinforcement, and speciation. Am. Nat. 191 , 155–172 (2018).
Barton, N. H. Multilocus clines. Evolution 37 , 454–471 (1983).
Flaxman, S. M., Wacholder, A. C., Feder, J. L. & Nosil, P. Theoretical models of the influence of genomic architecture on the dynamics of speciation. Mol. Ecol. 23 , 4074–4088 (2014).
Kautt, A. F. et al. Contrasting signatures of genomic divergence during sympatric speciation. Nature 588 , 106–111 (2020).
Wessinger, C. A. et al. A few essential genetic loci distinguish Penstemon species with flowers adapted to pollination by bees or hummingbirds. PLoS Biol. 21 , e3002294 (2023).
Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet.journal 17 , 10 (2011).
Davey, J. W. et al. No evidence for maintenance of a sympatric Heliconius species barrier by chromosomal inversions. Evolution Letters 1 , 138–154 (2017).
Edelman, N. B. et al. Genomic architecture and introgression shape a butterfly radiation. Science 366 , 594–599 (2019).
Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. Preprint at 10.48550/arXiv.1303.3997 (2013).
Tarasov, A., Vilella, A. J., Cuppen, E., Nijman, I. J. & Prins, P. Sambamba: fast processing of NGS alignment formats. Bioinformatics 31 , 2032–2034 (2015).
McKenna, A. et al. The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 20 , 1297–1303 (2010).
DePristo, M. A. et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 43 , 491–498 (2011).
Okonechnikov, K., Conesa, A. & García-Alcalde, F. Qualimap 2: advanced multi-sample quality control for high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 32 , 292–294 (2016).
Li, H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 27 , 2987–2993 (2011).
Purcell, S. et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81 , 559–575 (2007).
Bryant, D. Neighbor-Net: an agglomerative method for the construction of phylogenetic networks. Mol. Biol. Evol. 21 , 255–265 (2003).
Huson, D. H. & Bryant, D. Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 23 , 254–267 (2006).
Paradis, E. & Schliep, K. ape 5.0: an environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 35 , 526–528 (2019).
Schliep, K., Potts, A. J., Morrison, D. A. & Grimm, G. W. Intertwining phylogenetic trees and networks. Methods Ecol. Evol. 8 , 1212–1220 (2017).
Martin, S. H. & Van Belleghem, S. M. Exploring evolutionary relationships across the genome using topology weighting. Genetics 206 , 429–438 (2017).
Browning, S. R. & Browning, B. L. Rapid and accurate haplotype phasing and missing-data inference for whole-genome association studies by use of localized haplotype clustering. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81 , 1084–1097 (2007).
Guindon, S. et al. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 59 , 307–321 (2010).
Patterson, N. et al. Ancient admixture in human history. Genetics 192 , 1065–1093 (2012).
Gronau, I., Hubisz, M. J., Gulko, B., Danko, C. G. & Siepel, A. Bayesian inference of ancient human demography from individual genome sequences. Nat. Genet. 43 , 1031–1034 (2011).
Gómez-Martín, C., Lebrón, R., Oliver, J. L. & Hackenberg, M. Prediction of CpG islands as an intrinsic clustering property found in many eukaryotic DNA sequences and its relation to DNA methylation. Methods Mol. Biol. 1766 , 31–47 (2018).
Keightley, P. D. et al. Estimation of the spontaneous mutation rate in Heliconius melpomene . Mol. Biol. Evol. 32 , 239–243 (2015).
Ewing, G. & Hermisson, J. MSMS: a coalescent simulation program including recombination, demographic structure and selection at a single locus. Bioinformatics 26 , 2064–2065 (2010).
Rambaut, A. & Grass, N. C. Seq-Gen: an application for the Monte Carlo simulation of DNA sequence evolution along phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 13 , 235–238 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Li, X., Chen, F. & Chen, Y. Gcluster: a simple-to-use tool for visualizing and comparing genome contexts for numerous genomes. Bioinformatics 36 , 3871–3873 (2020).
Excoffier, L. et al. fastsimcoal2: demographic inference under complex evolutionary scenarios. Bioinformatics 37 , 4882–4885 (2021).
Excoffier, L., Dupanloup, I., Huerta-Sánchez, E., Sousa, V. C. & Foll, M. Robust demographic inference from genomic and SNP data. PLoS Genet. 9 , e1003905 (2013).
Hudson, R. R., Boos, D. D. & Kaplan, N. L. A statistical test for detecting geographic subdivision. Mol. Biol. Evol. 9 , 138–151 (1992).
Quinlan, A. R. & Hall, I. M. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 26 , 841–842 (2010).
Clayden, J., Modat, M., Presles, B., Anthopoulos, T. & Daga, P. RNiftyReg: Image registration using the ‘NiftyReg’ library. R version 2.8.1 https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/RNiftyReg (2023).
Queste, L. M. The Evolution of Flight and Wing Shape in Heliconius Butterflies PhD thesis, Univ. York (2020).
Rohlf, F. J. tpsDig v.2.05 (State University of New York at Stony Brook, 2006). https://www.sbmorphometrics.org/soft-dataacq.html .
Adams, D. C., Collyer, M. & Kaliontzopoulou, A. Geomorph: Geometric morphometric analyses of 2D and 3D landmark data. R version 3.1.0 https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/geomorph (2019).
Mérot, C., Frérot, B., Leppik, E. & Joron, M. Beyond magic traits: multimodal mating cues in Heliconius butterflies. Evolution 69 , 2891–2904 (2015).
Darragh, K. et al. Male sex pheromone components in Heliconius butterflies released by the androconia affect female choice. PeerJ 5 , e3953 (2017).
Ehlers, S., Blow, R., Szczerbowski, D., Jiggins, C. & Schulz, S. Variation of clasper scent gland composition of Heliconius butterflies from a biodiversity hotspot. ChemBioChem 24 , e202300537 (2023).
Stein, S. E. An integrated method for spectrum extraction and compound identification from gas chromatography/mass spectrometry data. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 10 , 770–781 (1999).
Etter, P. D., Preston, J. L., Bassham, S., Cresko, W. A., Johnson, E.A. Local de novo assembly of RAD paired-end contigs using short sequencing reads. PLoS ONE 6 , e18561 (2011).
Catchen, J., Hohenlohe, P. A., Bassham, S., Amores, A. & Cresko, W. A. Stacks: an analysis tool set for population genomics. Mol. Ecol. 22 , 3124–3140 (2013).
Li, H. & Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25 , 1754–1760 (2009).
Davey, J. W. et al. Major improvements to the Heliconius melpomene genome assembly used to confirm 10 chromosome fusion events in 6 million years of butterfly evolution. G3 6 , 695–708 (2016).
Rastas, P. Lep-MAP3: robust linkage mapping even for low-coverage whole genome sequencing data. Bioinformatics 33 , 3726–3732 (2017).
Broman, K. W., Wu, H., Sen, Ś. & Churchill, G. A. R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19 , 889–890 (2003).
Rosser, N. Image data for Rosser et al. 2024 Hybrid speciation driven by multilocus introgression of ecological traits. Zenodo 10.5281/zenodo.10685466 (2024).
Rosser, N. GCMS data for Rosser et al. 2024 Hybrid speciation driven by multilocus introgression of ecological traits. Zenodo 10.5281/zenodo.10689714 (2024).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the NERC grant NE/K012886/1 to K.K.D.; a National Geographic Waitt grant (W400-15) to N.R.; grant Schu 984/12-1 from the DFG to S.S.; and Harvard University. K.K. was supported by a fellowship from the Smithsonian Institution. A.V.L.F. acknowledges support from FAPESP (2021/03868-8), from the Brazilian Research Council–CNPq (304291/2020-0) and from the USAID–US National Academy of Sciences (NAS) (AID-OAA-A-11-00012). The University of York Viking cluster high-performance computing facility was used for some of the analyses. We thank SERFOR, the Peruvian Ministry of Agriculture and the Área de Conservación Regional Cordillera Escalera (0289-2014-MINAGRI-DGFFS/DGEFFS, 020-014/GRSM/PEHCBM/DMA/ACR-CE and 040–2015/GRSM/PEHCBM/DMA/ACR-CE) for collecting permits; the Ministerio del Ambiente and Museo Ecuatoriano de Ciencias Naturales in Ecuador (005-IC-FAU-DNBAPVS/MA) for collecting permits; the ICMBio for permits (52562-3 and 10438-1); and the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico–CNPq for approving our scientific expedition (Expediente PR no. 01300.000477/2016-49, portaria no. 4.628). This study is registered at the Brazilian SISGEN (A752FC2). Field collections in Colombia were conducted under permit no. 530 issued by the Autoridad Nacional de Licencias Ambientales of Colombia (ANLA). We thank J. Caldwell, M. Chouteau, C. Córdova, N. Edelman, S. Galluser, C. López, M. McClure, C. Pérez, C. Segami and M. Tuanama in Peru, and R. Aldaz, A. Toporov and K. Willmott in Ecuador, for help and support with fieldwork; C. Thomas, W. Valencia-Montoya, A. Kautt and J. Coughlan for comments; and M. Cast for providing some of the butterfly images used in figures.
Author information
These authors jointly supervised this work: Neil Rosser, Fernando Seixas
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA
Neil Rosser, Fernando Seixas, Dmytro Kryvokhyzha & James Mallet
Department of Biology, University of York, York, UK
Neil Rosser, Lucie M. Queste, Bruna Cama, Michaela Nelson, Rachel Waite-Hudson, Matt Goringe & Kanchon K. Dasmahapatra
URKU Estudios Amazónicos, Tarapoto, Perú
Ronald Mori-Pezo
Universidad Nacional Autónoma de Alto Amazona, Yurimaguas, Perú
Department of Clinical Sciences, Lund University Diabetes Centre, Malmö, Sweden
Dmytro Kryvokhyzha
Residencial Las Cumbres, Caracas, Venezuela
Mauro Costa
Institut Systématique, Evolution, Biodiversité, UMR 7205 MNHN-CNRS-EPHE-UPMC Sorbonne Universités, Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris, France
Marianne Elias
Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute, Panama City, Panama
Marianne Elias, Krzysztof Kozak & W. Owen McMillan
Institute for Biological Sciences, Federal University of Pará (UFPA), Belém, Brazil
Clarisse Mendes Eleres de Figueiredo & Jonathan Ready
Centre for Advanced Studies of Biodiversity (CEABIO), Belém, Brazil
Departamento de Biologia Animal and Museu de Diversidade Biológica, Instituto de Biologia, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil
André Victor Lucci Freitas & Leila T. Shirai
Centre d’Ecologie Fonctionnelle et Evolutive, UMR 5175 CNRS, Université de Montpellier–Université Paul Valéry Montpellier–EPHE, Montpellier, France
Mathieu Joron
Museo de Historia Natural, Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos, Lima, Peru
Gerardo Lamas
Redpath Museum, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Ananda R. P. Martins
Biology Program, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Universidad del Rosario, Bogotá, Colombia
Nicol Rueda-Muñoz & Camilo Salazar
Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, School of Biosciences, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK
Patricio Salazar
Institut für Organische Chemie, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Braunschweig, Germany
Stefan Schulz
Leibniz Institute for the Analysis of Biodiversity Change, Museum de Natur Hamburg Zoology, Hamburg, Germany
Karina L. Silva-Brandão
Leverhulme Centre for Anthropocene Biodiversity, Department of Biology, University of York, York, UK
Kanchon K. Dasmahapatra
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
N.R., F.S., J.M. and K.K.D designed the study. N.R. was responsible for fieldwork, including designing and conducting crosses, phenotyping of traits and performing QTL, linkage and recombination-rate analyses. F.S. performed the population genomic analyses (with D.K., N.R., J.M. and K.K.D.) and the demographic and coalescent analyses. L.M.Q. contributed to phenotyping host plant preference, colour pattern preference, wing shape, colour pattern (with B.C. and R.W.-H.) and flight (with M.G.). B.C. and S.S. led the analysis of androconial volatiles. R.M.-P. provided fieldwork assistance in Peru. M.N. constructed the RAD libraries. All other authors contributed to sample collection. N.R., F.S., J.M. and K.K.D wrote and finalized the paper with contributions from all authors.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Neil Rosser or James Mallet .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data figures and tables
Extended data fig. 1 evaluating the hybrid speciation hypothesis under the msci model..
For each model, a schematic representation is depicted on top and the estimated values under the MSCi are presented in the table below. In the schematics, open circles denote internal nodes and arrows between internal nodes represent single migration pulses. Effective population sizes (N e ) are scaled to thousand individuals. The age ( τ ) of splits and nodes involved in hybridization events are given in kya. Introgression probabilities ( φ ) are depicted in blue and are given as a percentage. a , Model in which the two parental species, S (ancestral of H. melpomene ) and T (ancestral of H. pardalinus ), hybridize to originate the hybrid lineage H (ancestral of H. elevatus ), with φ contribution from parent S and 1- φ from parent T. The nodes S and T may have distinct ages and are older than node H. b , Same as model a , but constraining introgression from S into H to occur after an initial split between H. elevatus and H. pardalinus ( τ H < τ T ). Introgression is instantaneous and occurs at time τ H (which is the same as τ S ). c , Model allowing bidirectional migration between an H. melpomene ancestor (X) into the ancestral population of H. elevatus and H. pardalinus (Y), between an H. melpomene ancestor (S) and the lineage leading to H. elevatus (H), and between the lineage leading to H. elevatus (E) and the lineage leading to H. pardalinus (P). Note that in all models, the 95% HPD intervals of the age of gene flow from H. melpomene into H. elevatus and the split between H. elevatus with H. pardalinus overlap, in line with H. elevatus being a hybrid lineage. These are highlighted in red.
Extended Data Fig. 2 MSC analysis of H. elevatus and H. pardalinus .
Species-tree phylogeny along chromosomes calculated in blocks of 100 loci using BPP (ref. 22 ). Only the five major topologies are depicted (minor topologies are coloured in grey).
Extended Data Fig. 3 Species-diagnostic SNPs.
a , Number of species-diagnostic SNPs per chromosome. Species-diagnostic SNPs were defined as SNPs with an allelic difference of at least 0.8 between all Amazonian populations of H. elevatus and H. pardalinus . Chromosomes with at least 20 diagnostic SNPs are denoted with an asterisk (*) and shown in more detail in c . b , Triangular plot of hybrid index and observed heterozygosity, based on the 1,156 species-diagnostic SNPs, shows no evidence of early generation hybrids. c , Distribution of species-diagnostic SNPs along chromosomes in wild-caught H. elevatus and H. pardalinus . The physical location of SNPs along chromosomes (in Mb) are shown on top. Different blocks of SNPs within a chromosome, defined as groups of SNPs more than 500 kb apart, are denoted in alternating colours (black and grey). For visualization purposes, only chromosomes with at least 20 diagnostic SNPs are shown and SNP blocks were subsampled to show only one in every two SNPs. Long tracts of heterozygous genotypes (e.g. chromosome 19) suggest relatively recent hybridization followed by backcrossing.
Extended Data Fig. 4 Schematic of all demographic models tested with fastsimcoal2.
Two different tree topologies and 12 models per topology were tested. We considered the topology that retrieves both H. elevatus and H. pardalinus as monophyletic; that is, the species tree, (topology 1) and the most frequent topology across the genome (Extended Data Fig. 2 ), after excluding gene flow between H. elevatus and Amazonian H. pardalinus and in which H. p. sergestus is the first population to split (topology 2). The different demographic models are split into five main categories (depicted in different boxes): SI, strict isolation; AM, ancestral migration; SC, secondary contact; AM-SC, ancestral migration followed by secondary contact; IM, isolation with migration. Arrows between demes indicate gene flow (each direction being estimated as an independent parameter). Effective population sizes were allowed to change at split times. Note that for models under tree topology 1, the split times between H. elevatus populations and between H. pardalinus populations are different parameters and thus can assume different values.
Extended Data Fig. 5 Genetic evidence for current reproductive isolation between H. elevatus and H. melpomene .
a , Neighbour-joining tree based on autosomal sites sampled every 1 kb (166,989 sites). Values next to branches denote bootstrap values (based on 100 bootstrap iterations). Images of butterfly wings are copyright of the authors and Michel Cast. b , Distribution of species-diagnostic SNPs along chromosomes in wild-caught H. elevatus and H. melpomene . Species-diagnostic SNPs were defined as SNPs with an allelic difference of at least 0.8 between all Amazonian populations of H. elevatus and all H. melpomene populations. The physical location of SNPs along chromosomes (in Mb) are shown on top. For visualization purposes, SNP blocks were subsampled to show only 1 in every 20 SNPs. The lack of long tracts of heterozygous genotypes (or introgressed homozygous genotypes) suggests that there is no recent hybridization, followed by backcrossing, between these two species.
Extended Data Fig. 6 PCAs of male sex pheromones and host plant use show that H. elevatus , H. pardalinus and H. melpomene from the western Amazon form three distinct clusters in trait space.
a , PCA applied to concentrations of 30 male androconial volatiles. Loadings for selected compounds are annotated. b , PCA applied to oviposition preference of H. elevatus , H. pardalinus and H. melpomene for 21 species of Passiflora . Heliconius melpomene (24 females) laid 288 eggs and exhibited a strong preference for P. menispermifolia and P. triloba . Heliconius elevatus (35 females) laid 173 eggs and exhibited a preference for P. kaipiriensis . H. pardalinus butleri (51 females) laid 425 eggs and had a more generalized host plant use. To estimate the sample variance for each species, subsamples of 30 were drawn with replacement from the distribution of each species (1,000 replicates). PCA was then run on these bootstrapped replicates, polygons are minimum convex hulls encompassing all subsamples for each species. Images of butterfly wings are copyright of the authors and Michel Cast.
Extended Data Fig. 7 F ST and genetic distances plotted against physical distance.
Physical distance is shown on the x axis; grey intervals are 1 Mb and black intervals are 5 Mb. Coloured bars show significant QTLs, with the QTL peak indicated by the triangle and the Bayesian credible intervals indicated by the length of the bar. Genetic distances are estimated using three crosses—within population ( Heliconius elevatus ; elev and Heliconius pardalinus ; pard) and between population (F 2 ). Candidate inversions (CIs; indicated by black arrows) are regions that recombine within species but not in hybrids (see Methods ). The largest CI we identified was around 1.4 Mb long at the distal end of chromosome 16. However, we identified no CIs greater than 870 kb within the credible intervals of QTLs, and only one instance of a CI that was coincident with a QTL peak (on chromosome 15). Nonetheless, some CIs outside of QTLs present compelling targets for future investigation. Notably, at the proximal end of chromosome 19 and the distal end of chromosome 16, two large CIs overlap regions with elevated F ST in which phylogenies resolve species boundaries (see Fig. 3 ).
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
A full guide for Supplementary Tables 1–8 (Tables supplied separately).
Reporting Summary
Supplementary tables.
Supplementary Tables 1–8.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Rosser, N., Seixas, F., Queste, L.M. et al. Hybrid speciation driven by multilocus introgression of ecological traits. Nature 628 , 811–817 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07263-w
Download citation
Received : 26 September 2023
Accepted : 01 March 2024
Published : 17 April 2024
Issue Date : 25 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07263-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Surprise hybrid origins of a butterfly species.
- Megan E. Frayer
- Jenn M. Coughlan
Nature (2024)
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

COMMENTS
summarize the story by introducing the customer and their pain points. explain what your organization did. highlight the key results, including 1 or 2 statistics that drive home the takeaway message. Write the executive summary first to help you focus the rest of the case study. But don't be too rigid: in the process of reviewing the ...
10+ Case Study Summary Example. A lot of case studies are hard to understand. Some people even dread the idea of reading the whole research project from start to finish. Thankfully, there is a more natural way to grasp the context of the study. That is through case study summaries. If you are working o a case study, you should be able to write ...
We've put together 15 real-life case study examples to inspire you. These examples cover a variety of industries and formats, plus templates to inspire you. ... The case study's title and executive summary act as compelling entry points for both existing and potential customers. This overview provides a clear understanding of the case study ...
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis.
For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail. Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail. 3. EndeavourX and Figma.
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
Case Study Examples Summary. Once you have created your case study, it's best practice to update your examples on a regular basis to include up-to-date statistics, data, and information. You should update your business case study examples often if you are sharing them on your website.
Executive Summary: A 2-4 sentence summary of the entire story. You'll want to follow it with 2-3 bullet points that display metrics showcasing success. About the Subject: ... Business Case Study Examples. You drove the results, made the connection, set the expectations, used the questionnaire to conduct a successful interview, and boiled down ...
1. Make it as easy as possible for the client. Just like when asking for reviews, it's important to make the process as clear and easy as possible for the client. When you reach out, ask if you can use their story of achievement as a case study for your business. Make the details as clear as possible, including:
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure. 1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory. This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable. 2.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
Here is a case study sample PDF so you can have a clearer understanding of what a case study actually is: Case Study Sample PDF. How to Write a Case Study Examples. ... Providing a summary of the key achievements at the end of the case study can help readers better understand the project's impact.
Open up with a summary that communicates who your client is and why they reached out to you. Like in the other case study examples, you'll want to close out with a quantitative list of your achievements. 16. " NetApp ," by Evisort. Evisort opens up its NetApp case study with an at-a-glance overview of the client.
Case studies are good for describing, comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem. Table of contents. When to do a case study. Step 1: Select a case. Step 2: Build a theoretical framework. Step 3: Collect your data. Step 4: Describe and analyze the case.
Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study. Evaluation of the Case
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences. Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly. 1. Lab report case study template.
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case ...
How to summarize a case study. 1. Read the case study. 2. Understand the goal. 3. Identify the main points. 4. Write a clear summary. 5. Read and revise.
Environmental studies. Market surveys. Project plans. In general, there are four parts to any executive summary: Start with the problem or need the document is solving. Outline the recommended solution. Explain the solution's value. Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work.
Briefly introduce the problems and issues found in the case study. Discuss the theory you will be using in the analysis; Present the key points of the study and present any assumptions made during the analysis. Findings. This is where you present in more detail the specific problems you discovered in the case study.
A case study is indeterminate and boundless; a case analysis is predetermined and confined. A case study can be almost anything [see item 9 below] as long as it relates directly to examining the research problem. This relationship is the only limit to what a researcher can choose as the subject of their case study.
Rather than discussing case study in general, a targeted step-by-step plan with real-time research examples to conduct a case study is given. Introduction. In recent years, ... and analysis. At the end, the report is concluded with the summary of case profile, facts, and resolution of the problem under study.
HBR On Strategy curates the best case studies and conversations with the world's top business and management experts, to help you unlock new ways of doing business. ... So for example, if you ...
This summary is intended to inform international and domestic efforts to strengthen research ethics and support the evolution of governance leadership to meet the demands of AI in global health research. ... For example, one case study presentation described a project that would involve the collection of personally identifiable data for ...
Genomic studies of Heliconius butterflies provide evidence that Heliconius elevatus is a hybrid species, and that its speciation was driven by introgression of traits from Heliconius ...