
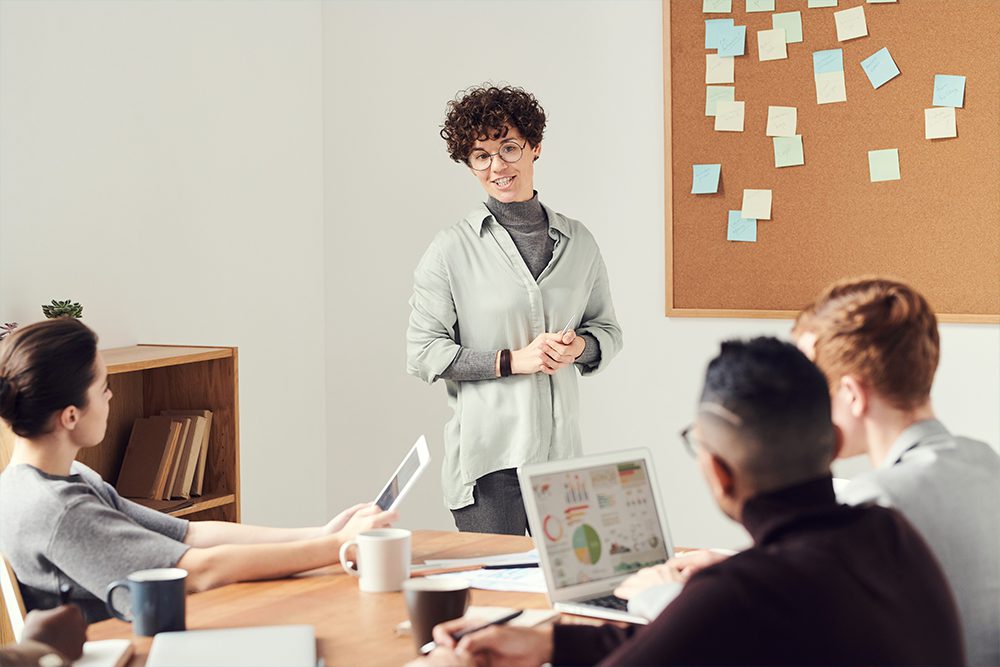
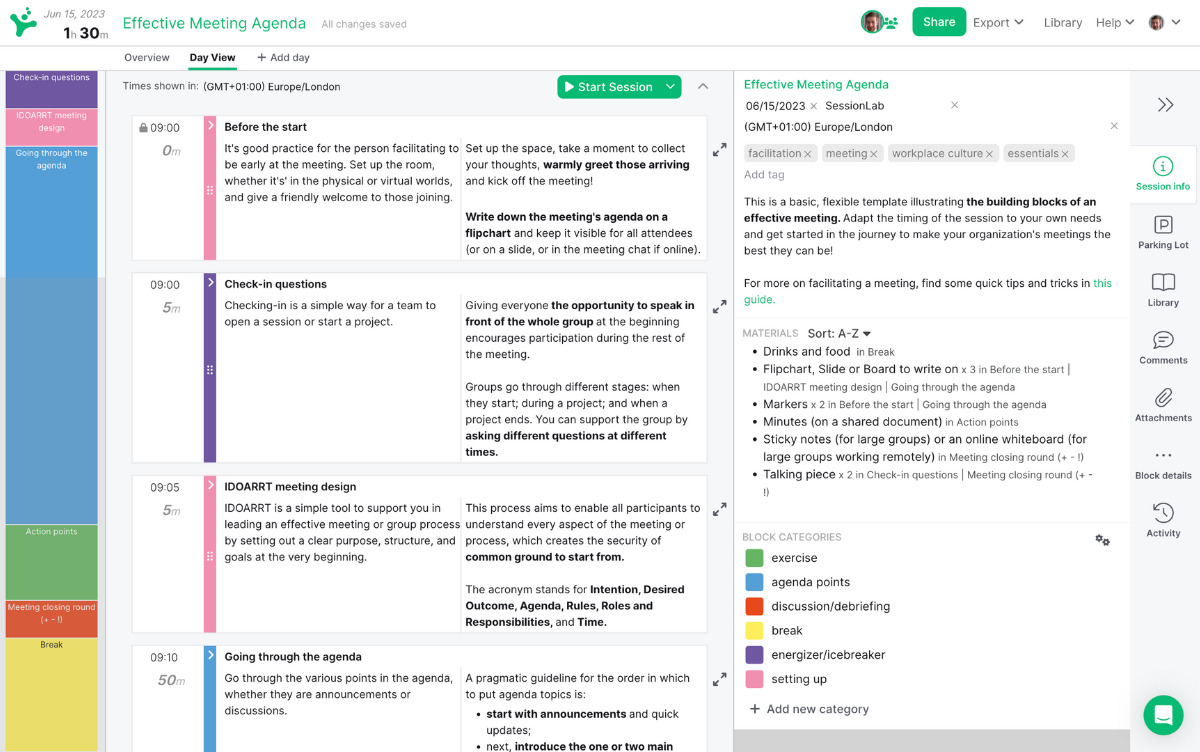
- INTERPERSONAL SKILLS
- Decision-Making and Problem Solving
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Interpersonal Skills:
- A - Z List of Interpersonal Skills
- Interpersonal Skills Self-Assessment
- Communication Skills
- Emotional Intelligence
- Conflict Resolution and Mediation Skills
- Customer Service Skills
- Team-Working, Groups and Meetings

Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
- Effective Decision Making
- Decision-Making Framework
- Introduction to Problem Solving
Identifying and Structuring Problems
Investigating Ideas and Solutions
Implementing a Solution and Feedback
- Creative Problem-Solving
Social Problem-Solving
- Negotiation and Persuasion Skills
- Personal and Romantic Relationship Skills
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
The SkillsYouNeed Guide to Interpersonal Skills

Making decisions and solving problems are two key areas in life, whether you are at home or at work. Whatever you’re doing, and wherever you are, you are faced with countless decisions and problems, both small and large, every day.
Many decisions and problems are so small that we may not even notice them. Even small decisions, however, can be overwhelming to some people. They may come to a halt as they consider their dilemma and try to decide what to do.
Small and Large Decisions
In your day-to-day life you're likely to encounter numerous 'small decisions', including, for example:
Tea or coffee?
What shall I have in my sandwich? Or should I have a salad instead today?
What shall I wear today?
Larger decisions may occur less frequently but may include:
Should we repaint the kitchen? If so, what colour?
Should we relocate?
Should I propose to my partner? Do I really want to spend the rest of my life with him/her?
These decisions, and others like them, may take considerable time and effort to make.
The relationship between decision-making and problem-solving is complex. Decision-making is perhaps best thought of as a key part of problem-solving: one part of the overall process.
Our approach at Skills You Need is to set out a framework to help guide you through the decision-making process. You won’t always need to use the whole framework, or even use it at all, but you may find it useful if you are a bit ‘stuck’ and need something to help you make a difficult decision.
Decision Making
Effective Decision-Making
This page provides information about ways of making a decision, including basing it on logic or emotion (‘gut feeling’). It also explains what can stop you making an effective decision, including too much or too little information, and not really caring about the outcome.
A Decision-Making Framework
This page sets out one possible framework for decision-making.
The framework described is quite extensive, and may seem quite formal. But it is also a helpful process to run through in a briefer form, for smaller problems, as it will help you to make sure that you really do have all the information that you need.
Problem Solving
Introduction to Problem-Solving
This page provides a general introduction to the idea of problem-solving. It explores the idea of goals (things that you want to achieve) and barriers (things that may prevent you from achieving your goals), and explains the problem-solving process at a broad level.
The first stage in solving any problem is to identify it, and then break it down into its component parts. Even the biggest, most intractable-seeming problems, can become much more manageable if they are broken down into smaller parts. This page provides some advice about techniques you can use to do so.
Sometimes, the possible options to address your problem are obvious. At other times, you may need to involve others, or think more laterally to find alternatives. This page explains some principles, and some tools and techniques to help you do so.
Having generated solutions, you need to decide which one to take, which is where decision-making meets problem-solving. But once decided, there is another step: to deliver on your decision, and then see if your chosen solution works. This page helps you through this process.
‘Social’ problems are those that we encounter in everyday life, including money trouble, problems with other people, health problems and crime. These problems, like any others, are best solved using a framework to identify the problem, work out the options for addressing it, and then deciding which option to use.
This page provides more information about the key skills needed for practical problem-solving in real life.
Further Reading from Skills You Need
The Skills You Need Guide to Interpersonal Skills eBooks.

Develop your interpersonal skills with our series of eBooks. Learn about and improve your communication skills, tackle conflict resolution, mediate in difficult situations, and develop your emotional intelligence.
Guiding you through the key skills needed in life
As always at Skills You Need, our approach to these key skills is to provide practical ways to manage the process, and to develop your skills.
Neither problem-solving nor decision-making is an intrinsically difficult process and we hope you will find our pages useful in developing your skills.
Start with: Decision Making Problem Solving
See also: Improving Communication Interpersonal Communication Skills Building Confidence
Here’s How Problem-Solving & Decision-Making Go Hand-In-Hand
Problem-solving and decision-making are two of the strongest qualities of a good leader. A strong leader is someone who knows how to come up with creative solutions to solve problems as effectively and efficiently as possible.
What are the steps to effective problem-solving?
Step 1: identify the problem.
This step includes getting to the bottom of any situation and understanding where the problem stems from.
Step 2: Analyze the Problem
This step helps identify the urgency of the problem which generally has three stages:
The emergent stage is where the problem is just beginning to happen. It does affect those in question immediately but can cause harm to the business operations in the long run.
The mature stage is where this problem is causing more than just minor damage. Usually, consequences during this stage at much more than the emergent stage.
The third stage is the crisis stage , when the problem is so serious it must be corrected immediately. At this stage, damage can be done to the company’s operations, reputation, finances, etc. that may hamper the long-term plans of the business.
Step 3: Describe the Problem
This step includes diagnosing the problem to be able to define it. This stage is to get clarity and to dig deeper into what the issue really is. This stage is also about making sure all your employees agree to the said problem and are gearing up to work toward a solution and a common goal.
Step 4: Look for Root Causes
This step involves understanding what caused this problem, who is responsible for this problem, when did it first emerge, how and why did it happen, how can it be resolved, and more. This stage is also about making sure the company comes up with solutions that can eradicate the problem for good and that it does not arise over and over again.
Step 5: Develop Alternative Solutions
Every problem must have a bunch of solutions in case one of them fails. Planning for contingency is as important as coming up with solutions. So, it is best to develop a list of alternative solutions that you and your team can assess and decide which one will be the best for the particular problem. Then it is important to estimate efficiency, cost, long-term value, and resources you have to solve the problem.
Step 6: Implement the Solution
This step is about chalking out the final implementation plan. Implementation means that each employee is aware of his/her tasks and knows their timelines for execution. Also, an organization should have a system in place to track whether or not the solution has corrected the problem.
Step 7: Measure the Results
This step is all about measuring the success and failure of a certain solution. This also helps us learn from one’s mistakes and not repeat them in the future. Measuring the results means answering questions such as: Did it work? Was this a good solution? Did we learn something here in the implementation that we could apply to other potential problems?
What is the Problem-Solving & Decision-Making course all about?
Employees in any organization find themselves solving problems on a daily basis. The ability to identify the problem, pinpoint the true cause, and identify a workable solution is essential for personal, professional, and organizational success. This course will help employees master their problem-solving and decision-making skills. They will learn how to assess a problem and then find solutions to overcome it.
- Define your role in problem-solving
- Identify barriers to effective problem solving
- Apply a six-step problem-solving process
- Select appropriate tool(s) to effectively problem solve
Decision-making and problem solving are two closely related but different skill sets that apply to different business situations. Leaders often incorporate both these skills to achieve organizational success. If you’re a leader who wants to strengthen his/her problem solving and decision-making skills and lead his/her organization to newer heights, then this course is perfect for you.
To enroll, contact P2L today!
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
You may use these HTML tags and attributes:
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Critical Thinking
Problem Solving, Critical Thinking and Decision Making
Lumen Learning
Agoos, S. (2016, March). 5 tips to improve your critical thinking [Video]. YouTube. http://https://youtu.be/dItUGF8GdTw
Problem-Solving with Critical Thinking
Much of your college and professional life will be spent solving problems; some will be complex, such as deciding on a career, and require time and effort to come up with a solution. Others will be small, such as deciding what to eat for lunch, and will allow you to make a quick decision based entirely on your own experience. For most people, a typical day is filled with critical thinking and problem-solving challenges. In fact, critical thinking and problem-solving go hand-in-hand. They both refer to using knowledge, facts, and data to solve problems effectively. But with problem-solving, you are specifically identifying, selecting, and defending your solution. Below are some examples of using critical thinking to problem-solve:
- Your roommate was upset and said some unkind words to you, which put a crimp in the relationship. You try to see through the angry behaviors to determine how you might best support the roommate and help bring the relationship back to a comfortable spot.
- Your campus club has been languishing on account of lack of participation and funds. The new club president, though, is a marketing major and has identified some strategies to interest students in joining and supporting the club. Implementation is forthcoming.
- Your final art class project challenges you to conceptualize form in new ways. On the last day of class when students present their projects, you describe the techniques you used to fulfill the assignment. You explain why and how you selected that approach.
- Your math teacher sees that the class is not quite grasping a concept. She uses clever questioning to dispel anxiety and guide you to new understanding of the concept.
- You have a job interview for a position that you feel you are only partially qualified for, although you really want the job and you are excited about the prospects. You analyze how you will explain your skills and experiences in a way to show that you are a good match for the prospective employer.
- You are doing well in college, and most of your college and living expenses are covered. But there are some gaps between what you want and what you feel you can afford. You analyze your income, savings, and budget to better calculate what you will need to stay in college and maintain your desired level of spending.
How to Problem Solve
- Define the problem. Use your analytical skills. What is the real issue? Why is it a problem? What are the root causes? What kinds of outcomes or actions do you expect to generate to solve the problem? What are some of the key characteristics that will make a good choice: Timing? Resources? Availability of tools and materials? For more complex problems, it helps to actually write out the problem and the answers to these questions. Can you clarify your understanding of the problem by using metaphors to illustrate the issue?
- Narrow the problem. Many problems are made up of a series of smaller problems, each requiring its own solution. Can you break the problem into different facets? What aspects of the current issue are “noise” that should not be considered in the problem solution? (Use critical thinking to separate facts from opinion in this step.)
- Generate possible solutions. List all your options. Use your creative thinking skills in this phase. Did you come up with the second “right” answer, and the third or the fourth? Can any of these answers be combined into a stronger solution? What past or existing solutions can be adapted or combined to solve this problem?
In sum, the following questions, are ones you may apply to formulate a logical, reasoned perspective:
- What’s happening? Gather the basic information and begin to think of questions.
- Why is it important? Ask yourself why it’s significant and whether or not you agree.
- What don’t I see? Is there anything important missing?
- How do I know? Ask yourself where the information came from and how it was constructed.
- Who is saying it? What’s the position of the speaker and what is influencing them?
- What else? What if? What other ideas exist and are there other possibilities?
Group Think: Effective Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a process of generating ideas for solutions in a group. This method is very effective because ideas from one person will trigger additional ideas from another. The following guidelines make for an effective brainstorming session:
- Decide who should moderate the session. That person may participate, but his main role is to keep the discussion flowing.
- Define the problem to be discussed and the time you will allow to consider it.
- Write all ideas down on a board or flip chart for all participants to see.
- Encourage everyone to speak.
- Do not allow criticism of ideas. All ideas are good during a brainstorm. Suspend disbelief until after the session. Remember a wildly impossible idea may trigger a creative and feasible solution to a problem.
- Choose the best solution. Use your critical thinking skills to select the most likely choices. List the pros and cons for each of your selections. How do these lists compare with the requirements you identified when you defined the problem? If you still can’t decide between options, you may want to seek further input from your brainstorming team.
Decisions, Decisions
You will be called on to make many decisions in your life. Some will be personal, like what to major in, or whether or not to get married. Other times you will be making decisions on behalf of others at work or for a volunteer organization. Occasionally you will be asked for your opinion or experience for decisions others are making. To be effective in all of these circumstances, it is helpful to understand some principles about decision making.
First, define who is responsible for solving the problem or making the decision. In an organization, this may be someone above or below you on the organization chart but is usually the person who will be responsible for implementing the solution. Deciding on an academic major should be your decision, because you will have to follow the course of study. Deciding on the boundaries of a sales territory would most likely be the sales manager who supervises the territories, because he or she will be responsible for producing the results with the combined territories. Once you define who is responsible for making the decision, everyone else will fall into one of two roles: giving input, or in rare cases, approving the decision.
Understanding the role of input is very important for good decisions. Input is sought or given due to experience or expertise, but it is up to the decision maker to weigh the input and decide whether and how to use it. Input should be fact based, or if offering an opinion, it should be clearly stated as such. Finally, once input is given, the person giving the input must support the other’s decision, whether or not the input is actually used.
Consider a team working on a project for a science course. The team assigns you the responsibility of analyzing and presenting a large set of complex data. Others on the team will set up the experiment to demonstrate the hypothesis, prepare the class presentation, and write the paper summarizing the results. As you face the data, you go to the team to seek input about the level of detail on the data you should consider for your analysis. The person doing the experiment setup thinks you should be very detailed, because then it will be easy to compare experiment results with the data. However, the person preparing the class presentation wants only high-level data to be considered because that will make for a clearer presentation. If there is not a clear understanding of the decision-making process, each of you may think the decision is yours to make because it influences the output of your work; there will be conflict and frustration on the team. If the decision maker is clearly defined upfront, however, and the input is thoughtfully given and considered, a good decision can be made (perhaps a creative compromise?) and the team can get behind the decision and work together to complete the project.
Finally, there is the approval role in decisions. This is very common in business decisions but often occurs in college work as well (the professor needs to approve the theme of the team project, for example). Approval decisions are usually based on availability of resources, legality, history, or policy.
https://ed.ted.com/lessons/5-tips-to-improve-your-critical-thinking-samantha-agoos
Key Takeaways
- Effective problem solving involves critical and creative thinking.
The four steps to effective problem solving are the following:
- Define the problem
- Narrow the problem
- Generate solutions
- Choose the solution
- Brainstorming is a good method for generating creative solutions.
- Understanding the difference between the roles of deciding and providing input makes for better decisions.
About the Author
name: Lumen Learning
Foundations for Success in Nursing: Manual Copyright © 2021 by Lumen Learning. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
.webp)
Problem Solving and Decision Making - Two Essential Skills of a Good Leader
.webp)
Problem solving and decision making are two fascinating skillsets. We call them out as two separate skills – and they are – but they also make use of the same core attributes.
They feed on a need to communicate well, both through questioning and listening, and be patient and not rushing both processes through. Thus, the greatest challenge any leader faces when it comes to solving problems and decision making is when the pressure of time comes into play. But as Robert Schuller highlights in his quote, allowing problem-solving to become the decision means you’ll never break free from the problem.
“Never bring the problem-solving stage into the decision-making stage. Otherwise, you surrender yourself to the problem rather than the solution.”—Robert H. Schuller
So how does a leader avoid this trap? How do they ensure the problem solving doesn’t become the be-all and end-all?
The 7 steps of Effective Problem Solving and Decision Making
A vital hurdle every leader must overcome is to avoid the impulsive urge to make quick decisions . Often when confronted with a problem, leaders or managers fall back in past behaviours. Urgency creates pressure to act quickly as a result, the problem still exists, just side-lined until it rears its ugly head again.
Good problem solving opens opportunity. A notable example of this is the first principles thinking executed by the likes of Elon Musk and others. Understanding the fundamentals blocks of a process and the problem it’s creating can lead to not just the problem but accelerate beyond it.
So, to avoid the trap, and use problem solving and decision making effectively , you should embody yourself with the following seven steps.
1. What is the problem?
Often, especially in time-critical situations, people don’t define the problem. Some label themselves as fire-fighters, just content with dowsing out the flames. It is a reactionary behaviour and one commonplace with under-trained leaders. As great as some fire-fighters are, they can only put out so many fires at one time, often becoming a little industry.
The better approach is to define the problem, and this means asking the following questions:
- What is happening? ( What makes you think there is a problem?)
- Where is it taking place?
- How is it happening?
- When is it happening?
- Why is it happening?
- With whom is it happening? (This isn’t a blame game…all you want to do is isolate the problem to a granular level.)
- Define what you understand to be the problem in writing by using as few sentences as possible. (Look at the answers to your what, where, why, when, and how questions.)
2. What are the potential causes?
Having defined the problem it is now time to find out what might be causing the problem. Your leadership skills: your communication skills need to be strong, as you look to gather input from your team and those involved in the problem.
Key points:
- Talk to those involved individually. Groupthink is a common cause of blindness to the problem, especially if there is blame culture within the business.
- Document what you’ve heard and what you think is the root cause is.
- Be inquisitive. You don’t know what you don’t know, so get the input of others and open yourself up to the feedback you’ll need to solve this problem.
3. What other ways can you overcome the problem?
Sometimes, getting to the root cause can take time. Of course, you can’t ignore it, but it is important to produce a plan to temporarily fix the problem. In business, a problem will be costing the business money, whether it be sales or profit. So, a temporary fix allows the business to move forward, providing it neutralises the downside of the original problem.
4. How will you resolve the problem?
At this stage, you still don’t know what the actual problem is. All you have is a definition of the problem which is a diagnosis of the issue. You will have the team’s input, as well as your opinions as to what the next steps should be.
If you don’t, then at this stage you should think about reassessing the problem. One way forward could be to become more granular and adopt a first-principles approach.
- Break the problem down into its core parts
- What forms the foundational blocks of the system in operation?
- Ask powerful questions to get to the truth of the problem
- How do the parts fit together?
- What was the original purpose of the system working in this way?
- Name and separate your assumptions from the facts
- Remind yourself of the goal and create a new solution
Solve hard problems with inversion
Another way is to invert the problem using the following technique:
1. Understand the problem
Every solution starts with developing a clear understanding of what the problem is. In this instance, some clarity of the issue is vital.
2. Ask the opposite question
Convention wisdom means we see the world logically. But what if you turned the logical outcome on its head. Asking the opposite questions brings an unfamiliar perspective.
3. Answer the opposite question
It seems a simple logic, but you can’t just ask the opposite question and not answer it. You must think through the dynamics that come from asking the question. You're looking for alternative viewpoints and thoughts you've not had before.
4. Join your answers up with your original problem
This is where solutions are born. You’re taking your conventional wisdom and aligning it with the opposite perspective. So often the blockers seen in the original problem become part of the solution.
5. Define a plan to either fix the problem permanently or temporarily
You now know the problem. You understand the fix, and you are a position to assess the risks involved.
Assessing the risks means considering the worst-case scenarios and ensuring you avoid them. Your plan should take into the following points:
- Is there any downtime to implementing the solution? If so, how long, and how much will it cost? Do you have backup systems in place to minimise the impact?
- If the risk is too great, consider a temporary fix which keeps current operations in place and gives you time to further prepare for a permanent fix.
- Document the plan and share it with all the relevant stakeholders. Communication is key.
Here we see the two skills of problem solving and decision making coming together. The two skills are vital to managing business risks as well as solving the problem.
6. Monitor and measure the plan
Having evolved through the five steps to this stage, you mustn’t take your eye off the ball as it were.
- Define timelines and assess progress
- Report to the stakeholders, ensuring everyone is aware of progress or any delays.
- If the plan doesn’t deliver, ask why? Learn from failure.
7. Have you fixed the problem?
Don’t forget the problem you started with. Have you fixed it? You might find it wasn’t a problem at all. You will have learnt a lot about the part of the business where the problem occurred, and improvements will have taken place.
Use the opportunity to assess what worked, what didn’t, and what would have helped. These are three good questions to give you some perspective on the process you’ve undertaken.
Problem solving and decision making in unison
Throughout the process of problem solving, you’re making decisions. Right from the beginning when the problem first becomes clear, you have a choice to either react – firefight or to investigate. This progresses as move onto risk assessing the problem and then defining the solutions to overcome the issue.
Throughout the process, the critical element is to make decisions with the correct information to hand. Finding out the facts, as well as defeating your assumptions are all part of the process of making the right decision.
Problem solving and decision making – a process
Problem solving isn’t easy. It becomes even more challenging when you have decisions to make. The seven steps I’ve outlined will give you the ability to investigate and diagnose the problem correctly.
- What is the problem?
- What are the potential causes?
- What other ways can you overcome the problem?
- How will you resolve the problem?
- Define a plan to either fix the problem permanently or temporarily.
- Monitor and measure the plan.
- Have you fixed the problem?
Of course, this logical step by step process might not enable you to diagnose the issue at hand. Some problems can be extremely hard, and an alternative approach might help. In this instance, first principles thinking or using the power of inversion are excellent ways to dig into hard problems. Problem solving and decision making are two skills every good leader needs. Using them together is an effective way to work.
.webp)
Related Articles
.webp)
How Thinking Like a Detective Will Improve Your Decisions

How Thinking in Patterns Will Make You Think Better
.webp)
Fact-Based Decision Making: The Key to Making Progress as a Creator
Become a wiser decision-maker in just 5 minutes per week..

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Make Great Decisions, Quickly
- Martin G. Moore

It’s a skill that will set you apart.
As a new leader, learning to make good decisions without hesitation and procrastination is a capability that can set you apart from your peers. While others vacillate on tricky choices, your team could be hitting deadlines and producing the type of results that deliver true value. That’s something that will get you — and them — noticed. Here are a few of a great decision:
- Great decisions are shaped by consideration of many different viewpoints. This doesn’t mean you should seek out everyone’s opinion. The right people with the relevant expertise need to clearly articulate their views to help you broaden your perspective and make the best choice.
- Great decisions are made as close as possible to the action. Remember that the most powerful people at your company are rarely on the ground doing the hands-on work. Seek input and guidance from team members who are closest to the action.
- Great decisions address the root cause, not just the symptoms. Although you may need to urgently address the symptoms, once this is done you should always develop a plan to fix the root cause, or else the problem is likely to repeat itself.
- Great decisions balance short-term and long-term value. Finding the right balance between short-term and long-term risks and considerations is key to unlocking true value.
- Great decisions are timely. If you consider all of the elements listed above, then it’s simply a matter of addressing each one with a heightened sense of urgency.
Where your work meets your life. See more from Ascend here .
Like many young leaders, early in my career, I thought a great decision was one that attracted widespread approval. When my colleagues smiled and nodded their collective heads, it reinforced (in my mind, at least) that I was an excellent decision maker.
- MM Martin G. Moore is the founder of Your CEO Mentor and author of No Bullsh!t Leadership and host of the No Bullsh!t Leadership podcast. His purpose is to improve the quality of leaders globally through practical, real world leadership content. For more information, please visit, www.martingmoore.com.
Partner Center
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 18 free facilitation resources we think you’ll love.
- 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree

28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Your list of techniques for problem solving can be helpfully extended by adding TRIZ to the list of techniques. TRIZ has 40 problem solving techniques derived from methods inventros and patent holders used to get new patents. About 10-12 are general approaches. many organization sponsor classes in TRIZ that are used to solve business problems or general organiztational problems. You can take a look at TRIZ and dwonload a free internet booklet to see if you feel it shound be included per your selection process.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Facilitation is more and more recognized as a key component of work, as employers and society are faced with bigger and more complex problems and ideas. From facilitating meetings to big, multi-stakeholder strategy development workshops, the facilitator's skillset is more and more in demand. In this article, we will go through a list of the best online facilitation resources, including newsletters, podcasts, communities, and 10 free toolkits you can bookmark and read to upskill and improve your facilitation practice. When designing activities and workshops, you'll probably start by using templates and methods you are familiar with. Soon enough, you'll need to expand your range and look for facilitation methods and…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

Making the Difference: Problem Solving vs Decision Making
This blog is reader-supported. When you purchase something through an affiliate link on this site, I may earn some coffee money. Thanks! Learn more .
Do you ever find yourself stuck between a rock and hard place, unable to decide what the best course of action is?
I have. Whether it’s what desk to put in our new conservatory space (and I’ll tell you what we ended up deciding later), or who to invite to meetings, or managing to order everyone else’s food and then getting so overwhelmed with having made decisions all day for all the people that I couldn’t choose anything for myself.
I left the café with nothing for me and ended up with a couple of slices of peanut butter toast at home.
Making decisions can be difficult for even the most experienced project managers. But before making any decision, it’s important to understand the difference between problem solving and decision making.
Ready to get into it?
Problem solving involves diagnosing issues that arise during projects while decision making requires taking appropriate steps based on those diagnoses. While they may appear similar at first glance, there are key differences in how each process should be approached – understanding these differences will help you make more informed decisions!
Let’s explore both processes as well as their similarities and differences.
What is problem solving?
You’ve been solving problems since you were a baby: how to stand up, how to get your socks off, how to get your parents to bring you your favorite sippy cup.
As an adult, we solve problems every day at work and at home.
So it probably sounds a bit odd to want to define problem solving before we go any further. Surely we all know what we are talking about as we do it all the time?
Humor me. Problem solving is the process of identifying and analyzing a problem, generating potential solutions, and selecting the best solution to address the issue. It involves breaking down complex problems into smaller components and then finding ways to solve them.
The problem solving process
If you think that description sounds linear, then you’d be right. Problem solving fits neatly into a process, one that we don’t even know we’re following most of the time.
The problem solving process typically consists of four steps:
- Identify the problem
- Generate possible solutions
- Evaluate each option
- Select an appropriate course of action.
That does make it sound easy. Wicked problems need a slightly different approach (PMI has a problem solving training course that is brilliant and will help with that).
But for now, let’s stick with a high-level approach that works for most problems.
1. Identify the problem
First, it’s important to understand what caused the issue in order to determine how best to resolve it.
You’d be surprised at how many managers don’t bother to find the root cause of the problem to truly understand it. Use techniques like the 5 Whys or an Ishikawa diagram to dig down into what the problem actually is.
2. Generate possible solutions
Brainstorming is one way to come up with different ideas for potential solutions. You could also interview experts, review lessons learned or innovative solutions from previous projects, research what the rest of your industry is doing or consult customers on what they’d like to see. There are no silly ideas at this point!
Choose the creative approach that gets you a range of options to review.
Read next: How to improve problem solving with lessons learned.
3. Evaluate each option
Once you have several options to consider, you can evaluate each one based on its effectiveness and cost before deciding which one is most suitable for your situation.
Use pairwise prioritisation, multi-criteria decision making or analytical hierarchy process (AHP) to help with the evaluation.
4. Select an appropriate course of action
Now you’ve got all the options for solving your problem, you can actually solve it by choosing a course of action that will sort it out. This is where decision making comes in. in this step you make the decision.
Finally, implement your chosen solution and monitor its progress over time so that any necessary adjustments can be made as needed.
Benefits of problem solving skills
There are many benefits associated with having effective problem solving skills.
These include improved decision making abilities (more on that in a minute), increased creativity, better communication skills, greater confidence when faced with challenging situations, enhanced ability to think critically, more efficient use of resources, improved relationships between colleagues or team members due to shared understanding of goals and increased productivity levels due to fewer mistakes being made during projects or tasks.
(Breathe. That was a long sentence, sorry.)
All these advantages make problem solving an invaluable skill in both personal life and professional life scenarios.
What is decision making?
Basically, decision making is the process of selecting a course of action from a number of alternatives. It involves gathering information, weighing options, and choosing the best option for achieving a desired outcome.
But how is that different to problem solving?
Decision making is the process of doing Step 4 of the problem solving process. It’s the choice making, option selection, conclusion of the analysis and thinking.
It’s decisive (duh), purposeful, specific. It removes the ambiguity of the ‘what do we do?’ and helps the team move towards the ‘OK, how do we do that?’
It brings action to a situation.
The decision making process
There is a simple method for decision making too, although the actual decision itself might be tough to make.
- Identify that a decision is required
- Ensure you have the data to make the decision
- Make the decision
- Tell whoever needs to implement the decision
1. Identify that a decision is required
The decision-making process typically begins with identifying what decision needs to be made. Are you making the right decision, or is there something else, deeper, different that is really what’s required?
In this step you also want to identify who is making the decision. That could be your project sponsor, a panel, you by yourself, a committee or whoever. Getting this step clear saves headaches later.
2. Ensure you have the data to make the decision
Do you have all the info you need to make the decision? If not, get it.
When decisions are made quickly but thoughtfully, they can save time and resources while still producing quality results.
Major decisions need more time spent on this step to make sure you understand all the variables.
3. Make the decision
After considering all potential solutions, it’s time to make a choice based on what will yield the best results for everyone involved.
This is the hard part: make the decision! The person or people responsible for this should weigh up the data and use their professional judgement to choose the right course of action. Decision trees can be useful here to avoid unconscious bias (or conscious bias!).
Obviously this is harder for complex decisions. What vendor to choose for a 3-year outsourcing arrangement is harder to decide than what venue to book for a team away day.
4. Tell whoever needs to implement the decision
Great – you’ve made the call and know what to do, but does the rest of the team? Don’t keep the decision to yourself!
Make sure whoever needs to know the next steps is aware that the decision has been made so they can implement it and take the right action.
Having confidence in decisions leads to greater trust between team members and better collaboration overall, which can lead to improved project outcomes over time. Well-made decisions often create opportunities for growth within teams by allowing them to learn from their mistakes as well as their successes along the way.
Similarities between problem solving and decision making
Problem solving and decision making sound very similar, right?
Well, that is true. Both processes involve gathering information, analyzing it, and coming up with solutions or courses of action. They both require critical thinking skills to identify potential solutions or options that are most likely to be successful.
The processes use a similar flow
Both processes involve identifying a problem or issue, researching possible solutions, evaluating those solutions based on criteria such as cost-effectiveness or feasibility, selecting an option from among the available choices, implementing the chosen solution, and you’d also want to monitor its effectiveness over time.
The process can be iterative if necessary; if one solution does not work out as expected then another may need to be tried until a satisfactory outcome is achieved.
They both produce a satisfactory solution
Problem solving and decision making usually lead to some kind of action being taken in order to address a given issue or situation. Problem solving often involves finding creative solutions for complex problems, while decision making typically entails selecting a course of action from several possibilities after carefully evaluating each option’s advantages and disadvantages.
But ultimately, the goal is for something positive (or at least neutral) to come out of the helpful process so that whatever challenge was initially presented can be effectively addressed.
Despite being so similar you could pretty much interchange them in some circumstances, there are some differences.

Differences between problem solving and decision making
Although they have similarities in terms of the process used to come up with a solution, their goals differ significantly.
Process goals are different
The goal of problem solving is to find a solution to an existing issue. It involves identifying the cause of a problem and then finding ways to address it. Problem solving often requires input from multiple stakeholders who can provide different perspectives on how best to solve the issue at hand.
On the other hand, decision making focuses on choosing the best option from multiple alternatives. This could include selecting between competing products or services or deciding which strategy will be most effective for achieving certain objectives.
In other words: decision making doesn’t necessarily mean there is a problem. We make decisions every day about small things and big things, but they aren’t all problems that need the creative step of solutioning.
Sometimes a decision just needs to be taken and the options are clearly known.
They require different stakeholders
Another key difference between problem solving and decision making is that while problem solving typically requires input from multiple stakeholders, decision making is usually done by one individual or group who has access to all relevant information needed for the decision-making process.
To give you an example. Let’s say on a technical project the development team hit a problem. They have to bring in various subject matter experts to research and identify the parameters involved. They consult, brainstorm and debate. It’s a group effort, and it’s likely to end in a solution.
However, if I need my project sponsor to choose between two risk treatments, I’ll take him my recommendation and a summary of options and he’ll simply choose. Done.
Decisions are made based on what is known about a situation rather than relying on external opinions or advice when trying to make an informed choice about what course of action should be taken next.
They produce different results
The nature of both processes also differs in terms of the types of solutions they produce. Problem solving typically results in creative solutions that can be implemented over time, while decision making produces immediate choices from among existing alternatives without necessarily creating something new or unique.
Both processes involve the identification of a problem or issue, the collection of information to evaluate possible solutions, and an analysis of potential outcomes. The main difference between them is in their goals: problem solving seeks to identify the root cause of an issue and develop a solution that will address it; decision making focuses on selecting from among available options.
Both processes require careful consideration of facts and opinions before any action is taken. Problem solving often involves more people than decision making as it requires collaboration to identify underlying causes and brainstorm potential solutions. Decision makers may consult with others for input but ultimately make decisions independently based on their own judgment.

Still got a question?
What is the difference between decision and decision making.
A decision is the act of making a choice between two or more alternatives. Decision making is the process by which decisions are made. It involves gathering information, analyzing data, evaluating alternatives and choosing a course of action based on this analysis. The outcome of the process is the decision. The decision-making process also includes monitoring progress to ensure that goals are being met and taking corrective action if needed.
What is the importance of problem-solving and decision making?
Problem-solving and decision making are essential skills for project managers and managers in general. The processes keep work moving by making sure problems get solved and decisions get made so team members are not blocked from finishing their tasks.
What are the steps in problem-solving and decision making?
Problem-solving and decision making involve a series of steps that can help ensure the best possible outcome. The first step is to identify the problem or opportunity, then analyze it by gathering relevant information and evaluating potential solutions. After considering all options, select an appropriate solution and develop an action plan for implementation. Finally, monitor progress to ensure success and make necessary adjustments along the way. By following these steps, project managers can effectively manage projects while minimizing risks and maximizing results.
Before you go…
Sometimes there isn’t a right decision – it’s simply important to make a decision. As for the desk, in the end, we used a piece of furniture we already had upstairs and didn’t buy one at all.
I spent a morning measuring and researching options, and I’ll never get that time back, but that’s OK.
As a leader, you should be skilled at solving problems and making decisions, and the processes that support them. However, you don’t have to be doing all the solving and making all the calls yourself. As long as you facilitate the process and get the right people in the room, you can step back and let the experts do their thing.
Let the right people do the work and create an environment where your projects move forward because everyone’s got what they need to keep things moving.
Project manager, author, mentor
Elizabeth Harrin is a Fellow of the Association for Project Management in the UK. She holds degrees from the University of York and Roehampton University, and several project management certifications including APM PMQ. She first took her PRINCE2 Practitioner exam in 2004 and has worked extensively in project delivery for over 20 years. Elizabeth is also the founder of the Project Management Rebels community, a mentoring group for professionals. She's written several books for project managers including Managing Multiple Projects .
What is decision making?

Decisions, decisions. When was the last time you struggled with a choice? Maybe it was this morning, when you decided to hit the snooze button—again. Perhaps it was at a restaurant, with a miles-long menu and the server standing over you. Or maybe it was when you left your closet in a shambles after trying on seven different outfits before a big presentation. Often, making a decision—even a seemingly simple one—can be difficult. And people will go to great lengths—and pay serious sums of money—to avoid having to make a choice. The expensive tasting menu at the restaurant, for example. Or limiting your closet choices to black turtlenecks, à la Steve Jobs.
Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on decision making
Aaron De Smet is a senior partner in McKinsey’s New Jersey office, Eileen Kelly Rinaudo is McKinsey’s global director of advancing women executives and is based in the New York office, Frithjof Lund is a senior partner in the Oslo office, and Leigh Weiss is a senior adviser in the Boston office.
If you’ve ever wrestled with a decision at work, you’re definitely not alone. According to McKinsey research, executives spend a significant portion of their time— nearly 40 percent , on average—making decisions. Worse, they believe most of that time is poorly used. People struggle with decisions so much so that we actually get exhausted from having to decide too much, a phenomenon called decision fatigue.
But decision fatigue isn’t the only cost of ineffective decision making. According to a McKinsey survey of more than 1,200 global business leaders, inefficient decision making costs a typical Fortune 500 company 530,000 days of managers’ time each year, equivalent to about $250 million in annual wages. That’s a lot of turtlenecks.
How can business leaders ease the burden of decision making and put this time and money to better use? Read on to learn the ins and outs of smart decision making—and how to put it to work.
Learn more about our People & Organizational Performance Practice .
How can organizations untangle ineffective decision-making processes?
McKinsey research has shown that agile is the ultimate solution for many organizations looking to streamline their decision making . Agile organizations are more likely to put decision making in the right hands, are faster at reacting to (or anticipating) shifts in the business environment, and often attract top talent who prefer working at companies with greater empowerment and fewer layers of management.
For organizations looking to become more agile, it’s possible to quickly boost decision-making efficiency by categorizing the type of decision to be made and adjusting the approach accordingly. In the next section, we review three types of decision making and how to optimize the process for each.
What are three keys to faster, better decisions?
Business leaders today have access to more sophisticated data than ever before. But it hasn’t necessarily made decision making any easier. For one thing, organizational dynamics—such as unclear roles, overreliance on consensus, and death by committee—can get in the way of straightforward decision making. And more data often means more decisions to be taken, which can become too much for one person, team, or department. This can make it more difficult for leaders to cleanly delegate, which in turn can lead to a decline in productivity.
Leaders are growing increasingly frustrated with broken decision-making processes, slow deliberations, and uneven decision-making outcomes. Fewer than half of the 1,200 respondents of a McKinsey survey report that decisions are timely, and 61 percent say that at least half the time they spend making decisions is ineffective.
What’s the solution? According to McKinsey research, effective solutions center around categorizing decision types and organizing different processes to support each type. Further, each decision category should be assigned its own practice—stimulating debate, for example, or empowering employees—to yield improvements in effectiveness.
Here are the three decision categories that matter most to senior leaders, and the standout practice that makes the biggest difference for each type of decision.
- Big-bet decisions are infrequent but high risk, such as acquisitions. These decisions carry the potential to shape the future of the company, and as a result are generally made by top leaders and the board. Spurring productive debate by assigning someone to argue the case for and against a potential decision can improve big-bet decision making.
- Cross-cutting decisions, such as pricing, can be frequent and high risk. These are usually made by business unit heads, in cross-functional forums as part of a collaborative process. These types of decisions can be improved by doubling down on process refinement. The ideal process should be one that helps clarify objectives, measures, and targets.
- Delegated decisions are frequent but low risk and are handled by an individual or working team with some input from others. Delegated decision making can be improved by ensuring that the responsibility for the decision is firmly in the hands of those closest to the work. This approach also enhances engagement and accountability.
In addition, business leaders can take the following four actions to help sustain rapid decision making :
- Focus on the game-changing decisions, ones that will help an organization create value and serve its purpose.
- Convene only necessary meetings, and eliminate lengthy reports. Turn unnecessary meetings into emails, and watch productivity bloom. For necessary meetings, provide short, well-prepared prereads to aid in decision making.
- Clarify the roles of decision makers and other voices. Who has a vote, and who has a voice?
- Push decision-making authority to the front line—and tolerate mistakes.

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
How can business leaders effectively delegate decision making.
Business is more complex and dynamic than ever, meaning business leaders are faced with needing to make more decisions in less time. Decision making takes up an inordinate amount of management’s time—up to 70 percent for some executives—which leads to inefficiencies and opportunity costs.
As discussed above, organizations should treat different types of decisions differently . Decisions should be classified according to their frequency, risk, and importance. Delegated decisions are the most mysterious for many organizations: they are the most frequent, and yet the least understood. Only about a quarter of survey respondents report that their organizations make high-quality and speedy delegated decisions. And yet delegated decisions, because they happen so often, can have a big impact on organizational culture.
The key to better delegated decisions is to empower employees by giving them the authority and confidence to act. That means not simply telling employees which decisions they can or can’t make; it means giving employees the tools they need to make high-quality decisions and the right level of guidance as they do so.
Here’s how to support delegation and employee empowerment:
- Ensure that your organization has a well-defined, universally understood strategy. When the strategic intent of an organization is clear, empowerment is much easier because it allows teams to pull in the same direction.
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities. At the foundation of all empowerment efforts is a clear understanding of who is responsible for what, including who has input and who doesn’t.
- Invest in capability building (and coaching) up front. To help managers spend meaningful coaching time, organizations should also invest in managers’ leadership skills.
- Build an empowerment-oriented culture. Leaders should role model mindsets that promote empowerment, and managers should build the coaching skills they want to see. Managers and employees, in particular, will need to get comfortable with failure as a necessary step to success.
- Decide when to get involved. Managers should spend effort up front to decide what is worth their focused attention. They should know when it’s appropriate to provide close guidance and when not to.
How can you guard against bias in decision making?
Cognitive bias is real. We all fall prey, no matter how we try to guard ourselves against it. And cognitive and organizational bias undermines good decision making, whether you’re choosing what to have for lunch or whether to put in a bid to acquire another company.
Here are some of the most common cognitive biases and strategies for how to avoid them:
- Confirmation bias. Often, when we already believe something, our minds seek out information to support that belief—whether or not it is actually true. Confirmation bias involves overweighting evidence that supports our belief, underweighting evidence against our belief, or even failing to search impartially for evidence in the first place. Confirmation bias is one of the most common traps organizational decision makers fall into. One famous—and painful—example of confirmation bias is when Blockbuster passed up the opportunity to buy a fledgling Netflix for $50 million in 2000. (Actually, that’s putting it politely. Netflix executives remember being “laughed out” of Blockbuster’s offices.) Fresh off the dot-com bubble burst of 2000, Blockbuster executives likely concluded that Netflix had approached them out of desperation—not that Netflix actually had a baby unicorn on its hands.
- Herd mentality. First observed by Charles Mackay in his 1841 study of crowd psychology, herd mentality happens when information that’s available to the group is determined to be more useful than privately held knowledge. Individuals buy into this bias because there’s safety in the herd. But ignoring competing viewpoints might ultimately be costly. To counter this, try a teardown exercise , wherein two teams use scenarios, advanced analytics, and role-playing to identify how a herd might react to a decision, and to ensure they can refute public perceptions.
- Sunk-cost fallacy. Executives frequently hold onto underperforming business units or projects because of emotional or legacy attachment . Equally, business leaders hate shutting projects down . This, researchers say, is due to the ingrained belief that if everyone works hard enough, anything can be turned into gold. McKinsey research indicates two techniques for understanding when to hold on and when to let go. First, change the burden of proof from why an asset should be cut to why it should be retained. Next, categorize business investments according to whether they should be grown, maintained, or disposed of—and follow clearly differentiated investment rules for each group.
- Ignoring unpleasant information. Researchers call this the “ostrich effect”—when people figuratively bury their heads in the sand , ignoring information that will make their lives more difficult. One study, for example, found that investors were more likely to check the value of their portfolios when the markets overall were rising, and less likely to do so when the markets were flat or falling. One way to help get around this is to engage in a readout process, where individuals or teams summarize discussions as they happen. This increases the likelihood that everyone leaves a meeting with the same understanding of what was said.
- Halo effect. Important personal and professional choices are frequently affected by people’s tendency to make specific judgments based on general impressions . Humans are tempted to use simple mental frames to understand complicated ideas, which means we frequently draw conclusions faster than we should. The halo effect is particularly common in hiring decisions. To avoid this bias, structured interviews can help mitigate the essentializing tendency. When candidates are measured against indicators, intuition is less likely to play a role.
For more common biases and how to beat them, check out McKinsey’s Bias Busters Collection .
Learn more about Strategy & Corporate Finance consulting at McKinsey—and check out job opportunities related to decision making if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced include:
- “ Bias busters: When the crowd isn’t necessarily wise ,” McKinsey Quarterly , May 23, 2022, Eileen Kelly Rinaudo , Tim Koller , and Derek Schatz
- “ Boards and decision making ,” April 8, 2021, Aaron De Smet , Frithjof Lund , Suzanne Nimocks, and Leigh Weiss
- “ To unlock better decision making, plan better meetings ,” November 9, 2020, Aaron De Smet , Simon London, and Leigh Weiss
- “ Reimagine decision making to improve speed and quality ,” September 14, 2020, Julie Hughes , J. R. Maxwell , and Leigh Weiss
- “ For smarter decisions, empower your employees ,” September 9, 2020, Aaron De Smet , Caitlin Hewes, and Leigh Weiss
- “ Bias busters: Lifting your head from the sand ,” McKinsey Quarterly , August 18, 2020, Eileen Kelly Rinaudo
- “ Decision making in uncertain times ,” March 24, 2020, Andrea Alexander, Aaron De Smet , and Leigh Weiss
- “ Bias busters: Avoiding snap judgments ,” McKinsey Quarterly , November 6, 2019, Tim Koller , Dan Lovallo, and Phil Rosenzweig
- “ Three keys to faster, better decisions ,” McKinsey Quarterly , May 1, 2019, Aaron De Smet , Gregor Jost , and Leigh Weiss
- “ Decision making in the age of urgency ,” April 30, 2019, Iskandar Aminov, Aaron De Smet , Gregor Jost , and David Mendelsohn
- “ Bias busters: Pruning projects proactively ,” McKinsey Quarterly , February 6, 2019, Tim Koller , Dan Lovallo, and Zane Williams
- “ Decision making in your organization: Cutting through the clutter ,” McKinsey Quarterly , January 16, 2018, Aaron De Smet , Simon London, and Leigh Weiss
- “ Untangling your organization’s decision making ,” McKinsey Quarterly , June 21, 2017, Aaron De Smet , Gerald Lackey, and Leigh Weiss
- “ Are you ready to decide? ,” McKinsey Quarterly , April 1, 2015, Philip Meissner, Olivier Sibony, and Torsten Wulf.

Want to know more about decision making?
Related articles.

What is productivity?

What is the future of work?

What is leadership?

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Critical Thinking and Decision-Making - What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking and decision-making -, what is critical thinking, critical thinking and decision-making what is critical thinking.

Critical Thinking and Decision-Making: What is Critical Thinking?
Lesson 1: what is critical thinking, what is critical thinking.
Critical thinking is a term that gets thrown around a lot. You've probably heard it used often throughout the years whether it was in school, at work, or in everyday conversation. But when you stop to think about it, what exactly is critical thinking and how do you do it ?
Watch the video below to learn more about critical thinking.
Simply put, critical thinking is the act of deliberately analyzing information so that you can make better judgements and decisions . It involves using things like logic, reasoning, and creativity, to draw conclusions and generally understand things better.
This may sound like a pretty broad definition, and that's because critical thinking is a broad skill that can be applied to so many different situations. You can use it to prepare for a job interview, manage your time better, make decisions about purchasing things, and so much more.
The process
As humans, we are constantly thinking . It's something we can't turn off. But not all of it is critical thinking. No one thinks critically 100% of the time... that would be pretty exhausting! Instead, it's an intentional process , something that we consciously use when we're presented with difficult problems or important decisions.
Improving your critical thinking

In order to become a better critical thinker, it's important to ask questions when you're presented with a problem or decision, before jumping to any conclusions. You can start with simple ones like What do I currently know? and How do I know this? These can help to give you a better idea of what you're working with and, in some cases, simplify more complex issues.
Real-world applications

Let's take a look at how we can use critical thinking to evaluate online information . Say a friend of yours posts a news article on social media and you're drawn to its headline. If you were to use your everyday automatic thinking, you might accept it as fact and move on. But if you were thinking critically, you would first analyze the available information and ask some questions :
- What's the source of this article?
- Is the headline potentially misleading?
- What are my friend's general beliefs?
- Do their beliefs inform why they might have shared this?

After analyzing all of this information, you can draw a conclusion about whether or not you think the article is trustworthy.
Critical thinking has a wide range of real-world applications . It can help you to make better decisions, become more hireable, and generally better understand the world around you.

/en/problem-solving-and-decision-making/why-is-it-so-hard-to-make-decisions/content/
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Decision-Making in Management: 5 Common Pitfalls to Avoid

- 24 Mar 2020
Being a manager can be both stimulating and challenging. Transitioning from an individual contributor to a manager comes with the opportunity to influence decision-making processes, implement business strategies , and oversee organizational change initiatives.
It can also increase the likelihood that you’ll make mistakes, as you take on greater responsibility and learn how to manage not just yourself, but others. If leveraged correctly, these professional missteps can become learning opportunities.
A study by Development Dimensions International (DDI) found that leaders most often build their skills through trial and error—particularly when it comes to decision-making. The study also showed that managers who learn through trial and error are 52 percent more likely to describe their first year in the role as “stressful,” and twice as likely to describe it as “overwhelming,” compared to peers who acquire skills from their supervisor.
No matter where you are in your career, there are steps you can take to improve your management skills and gain the knowledge to excel in the role. Whether you’re currently a manager, or preparing to become one, here are five common pitfalls to avoid when making business decisions.
Access your free e-book today.
Decision-Making Pitfalls Managers Should Avoid
1. defaulting to consensus.
As you and your team work through the steps in the decision-making process , there can be a tendency to default to consensus, wherein everyone agrees on what the problem is, there’s a free exchange of ideas, and the recommendations for moving forward are acceptable to everyone involved.
According to Harvard Business School Professor Len Schlesinger, who’s featured in the online course Management Essentials , a consensus approach can be appropriate in some situations, but in others, potentially lead to a lower evaluation of the issues at hand and less creative problem-solving.
“The consensus process is designed to avoid conflict, and managers defer to it regularly because it’s comfortable,” Schlesinger says. “It has low cost for all of the players, and it might be supportive of greater group harmony. If it’s not a very important task, where there’s data and clear alternatives articulated, it might even be appropriate. But it’s appropriate much less often than you might think.”
To avoid this pitfall, Schlesinger says, it’s important to be clear at the outset of the process about how decisions are going to get made and the roles people are going to play.
“Unless you’re intentional about trying to overcome consensus, you’re going to be stuck with it,” he says. “Then you’re going to get a group together that’s going to manifest a decision-making process that’s essentially no better than what you would come up with by yourself.”
2. Not Offering Alternatives
Another drawback that can result from defaulting to consensus is a lack of alternative solutions presented during the decision-making process.
According to Schlesinger, this happens because the group reaches alignment prematurely, without looking at the problem through different lenses and exploring other pathways for moving forward.
“They get to convergence much too quickly, which is largely one of the most negative byproducts of the consensus-oriented model and why it’s only appropriate for the most simplistic, best-structured decisions,” Schlesinger says.
For more complex problems, a process centered on devil’s advocacy would be more appropriate, which involves assigning an individual to probe underlying assumptions and push members of the group to explain the logic and reasoning behind their opinions.
“That’s much more likely to lead to a deeper critical evaluation and generate a substantial number of alternatives,” Schlesinger says. “As the task or the problem is less well-defined, it’s a much better way of getting the issue framed in a coherent way.”
3. Mistaking Opinions for Facts
One of the key steps in the decision-making process is to set ground rules and ensure everyone is aware of their role and how they can contribute. A significant part of that involves establishing alignment within the group on the difference between facts and opinions.
“It’s very easy in the context of a group process to have things go into a much deeper set of conversations that don’t really test the data that’s coming into them,” Schlesinger says.
To overcome this, managers should assign someone in the group with the task of validating items presented as facts to keep conversations on track and moving in the right direction.
“It involves making sure the group isn’t driving to closure on a decision-making process by assuming that things are factual when they’re not,” Schlesinger says.
4. Losing Sight of Purpose
Over the course of the decision-making process, managers and their teams can, at times, get wrapped up in the intricacies of problem-solving and lose sight of the bigger picture.
To ultimately sell whatever decision is made to the larger organization, priorities and goals need to be well-established and reiterated throughout the decision-making process.
“The decision to be made has to be clearly articulated, the goals have to be laid out upfront, and the group should be responsible for revisiting those goals continuously,” Schlesinger says. “It’s easy, as you get into these conversations, to get so immersed in one substantive part of the equation, that you lose track of what the actual purpose is.”
Research from EY and the Harvard Business Review shows that 89 percent of executives believe a strong sense of collective purpose drives employee satisfaction , so make it a point to underscore your team’s objectives when leading critical meetings and discussions surrounding the problems you’re facing.
Related: 5 Key Benefits of Enrolling in a Management Training Course
5. Truncating Debate
In addition to imbuing team members with a sense of purpose, managers should facilitate an environment in which they feel safe and empowered to offer their opinions and be involved in the decision-making process .
According to the results of a study on team performance detailed in the Harvard Business Review , the highest-performing teams share a key commonality: psychological safety.
“The concept of psychological safety is at the epicenter of a high-quality decision-making process, because we need to ensure that every member of the group feels free to express their point of view without fear of retribution or punishment associated with their voice,” Schlesinger says. “Absent to everybody bringing their whole best selves to the meeting and believing they can engage in a wholesome conversation, the point of bringing a group together for a decision where people aren’t going to express their point of view is a waste of time.”
Schlesinger notes that it’s vital for managers to establish group norms at the outset of the process to foster candor and debate, and make sure everyone feels their voice is valued.
“The manager ought to make sure that everybody is talking,” he says. “It’s his or her responsibility to continually ensure that everybody is at the table and believes they’ve been involved, because that same population is going to be responsible for helping implement the decision.”

Becoming a Better Decision-Maker and Manager
Understanding how to leverage and navigate the decision-making process is essential to becoming a better manager . By learning about the common pitfalls that managers encounter when facing important business decisions, you can ensure you’re equipped with the know-how to overcome organizational challenges and lead your team to success.
Do you want to learn how to design, direct, and shape organizational processes to your advantage? Explore our eight-week online course Management Essentials and our other leadership and management courses to discover how you can influence the context and environment in which decisions get made at your company.

About the Author
Decision-Making and Problem Solving
- First Online: 19 August 2017
Cite this chapter

- Christos Saitis 3 &
- Anna Saiti 4
470 Accesses
Decision-making is a fundamental activity that significantly influences the efficiency of an organization. That is because this activity is at the heart of management in every typical organization. Therefore, one of the key prerequisites for an educational leader is to have effective decision-making skills.
During an average working day, a school head makes different kinds of decisions, regardless of their importance. Indeed, within the wider framework of a school unit’s activities, the resolution of problems and the decision-making are two fundamental elements that assess, to a significant degree, the effectiveness of the school’s performance. Consequently, it is absolutely necessary for all educational leaders to understand the process of decision-making and of resolving problems, since the sheer existence of schools (and indeed all typical organizations) depends on their decision-making processes. This chapter:
Analyses the meaning, types and the procedures for effective decision-making
Outlines suggestions (e.g. careful assessment of the credibility of information) on how to avoid wrong decisions
Emphasizes human weakness in the decision-making process (e.g. when a manager puts too much emphasis on the initial information and does not assess whether or not it is creditable)
Examines the meaning of the term “problem” and also summarizes the process and methods of problem solving in the field of education
Presents case studies related to the school reality
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Armstrong, M. (2006). A handbook of management techniques (Rev. 3rd ed.). London: Kogan Page.
Google Scholar
Bouradas, D. (2013). Talking to my children for a real successful perspective and professional life . Athens, Greece: Patakis Publishing. (in Greek).
Coyne, K. P., & Coyne, S. T. (2011). Brainsteering: A better approach to breakthrough ideas . New York: Harper Collins.
Daft, R. L. (2007). Organization theory and design (9th ed.). Mason, OH: South Western, Thomson.
Damoulianou, C. H. (2011, Februay 2). Brainstorming is neglected and adopted its pilot. Kathimerini, Greek Newspaper , p. 10.
De Bono, E. (1991). Handbook for the positive revolution . Harmon – Disworth, England: Penguin.
Deetz, S., & Brown, D. (2004). Conceptualizing involvement, participation and workplace decision processes: A communication theory perspective. In D. Tourish & O. Hargie (Eds.), Key issues in organizational communication (pp. 172–187). London: Routledge.
Dekleris, M. (1989). Systemic design of public policy. In M. Dekleris (Ed.), Management systems . Athens, Greece: Sakkoula Publications. (in Greek).
Dittmer, R. E., & McFarland, S. (2007). 151 quick ideas for delegating and decision making . Wayne, NJ: Career Press.
Dobelli, R. (2013). The art of thinking clearly . London: Sceptre.
Drucker, P. F. (1967). The effective executive . New York: Harper & Row.
Dubrin, A. J. (1997). Essentials of management (14th ed.). London: South Western, College Publishing.
Georges, D. P., Efthimiadou, A., & Tsytos, D. (1998). Practical orientation in modern management . Athens, Greece: Ellinika Grammata Publications. (in Greek).
Hoy, W., & Miskel, C. (1987). Educational administration: Theory research and practice . New York: Lane Akers, Inc.
Hytiris, L. (2006). Management: Business administration principles . Athens, Greece: Interbooks Publications. (in Greek).
Kanellopoulos, C. (1995). Management – Effective administration . Athens, Greece: Kanellopoulos Publications. (in Greek).
Koontz, H., O’Donnell, C., & Weihrich, H. (1982). Management (7th ed.). London: McGraw Hill International Book Company.
Kosiol, E. (1962). Organization of the corporation . Wiesbaden, Germany: Gabler.
Lucey, T. (2005). Management information systems (9th ed.). USA: Thomson.
Macrydimitris, A. (1989). Decision theory . Athens, Greece: Sakkoula Publications. (in Greek).
Maier, R. (1967). Assets and liabilities in group problem solving. Psychological Review, 74 (4), 239–249.
Article Google Scholar
Nolan, V. (1987). Problem solving . London: Sphere.
Paritsis, N. K. (1989). Systemic theory of managerial behavior. In M. Dekleris (Ed.), Management systems (pp. 411–453). Athens, Greece: Sakkoula Publications. (in Greek).
Payne, J., & Payne, S. (1999). Management: How to do it . Farnham, England: Gower Publishing.
Robbins, S. P. (1976). The administrative process . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Robbins, S. P., & Judge, T. A. (2012). Organizational behavior (13th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education Inc..
Saiti, A., & Eliophotou-Menon, M. (2009). The design and implementation of educational policy, as reflected in the decision-making process: The case of Greece. International Journal of Educational Management, 23 (6), 446–455.
Schermerhorn, J. R., Jr. (2011). Introduction to management (11th ed.). Asia: Wiley.
Schwartz, B. (2004). The paradox of choice: Why more is less . New York: Harper Perennial.
Simon, H. A. (1956). Rational choice and the structure of the environment. Psychological Review, 63 (2), 129–138.
Simon, H. A. (1957). Models of man . New York: Wiley.
Simon, H. A. (1960). The new science of management decision . Bergen, NJ: Englewood Cliffs.
Book Google Scholar
Simon, H. A. (1974). Administrative behavior . New York: Macmillan Co.
Taylor, B. W., III. (2010). Introduction to management science (10th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice hall.
Vroom, V. H. (1973). A new look in management decision making. Organizational Dynamics, 1 (4), 66–80.
Vroom, V. H., & Jago, A. G. (1988). The new leadership managing participation in organizations . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Zavlanos, M. (1998). Management . Athens, Greece: Ellin Publishing. (in Greek).
Zevgaridis, S. (1978). Organization and management . Thessaloniki, Greece: Kyriakidis Publishing. (in Greek).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Primary Education, School of education, University of Athens, Athens, Greece
Christos Saitis
Department of Home Economics & Ecology, School of Environment, Geography & Applied Economics, Harokopio University, Athens, Greece
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Saitis, C., Saiti, A. (2018). Decision-Making and Problem Solving. In: Initiation of Educators into Educational Management Secrets. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47277-5_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47277-5_3
Published : 19 August 2017
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-47276-8
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-47277-5
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is Problem-Solving Therapy?
Arlin Cuncic, MA, is the author of The Anxiety Workbook and founder of the website About Social Anxiety. She has a Master's degree in clinical psychology.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ArlinCuncic_1000-21af8749d2144aa0b0491c29319591c4.jpg)
Daniel B. Block, MD, is an award-winning, board-certified psychiatrist who operates a private practice in Pennsylvania.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/block-8924ca72ff94426d940e8f7e639e3942.jpg)
Verywell / Madelyn Goodnight
Problem-Solving Therapy Techniques
How effective is problem-solving therapy, things to consider, how to get started.
Problem-solving therapy is a brief intervention that provides people with the tools they need to identify and solve problems that arise from big and small life stressors. It aims to improve your overall quality of life and reduce the negative impact of psychological and physical illness.
Problem-solving therapy can be used to treat depression , among other conditions. It can be administered by a doctor or mental health professional and may be combined with other treatment approaches.
At a Glance
Problem-solving therapy is a short-term treatment used to help people who are experiencing depression, stress, PTSD, self-harm, suicidal ideation, and other mental health problems develop the tools they need to deal with challenges. This approach teaches people to identify problems, generate solutions, and implement those solutions. Let's take a closer look at how problem-solving therapy can help people be more resilient and adaptive in the face of stress.
Problem-solving therapy is based on a model that takes into account the importance of real-life problem-solving. In other words, the key to managing the impact of stressful life events is to know how to address issues as they arise. Problem-solving therapy is very practical in its approach and is only concerned with the present, rather than delving into your past.
This form of therapy can take place one-on-one or in a group format and may be offered in person or online via telehealth . Sessions can be anywhere from 30 minutes to two hours long.
Key Components
There are two major components that make up the problem-solving therapy framework:
- Applying a positive problem-solving orientation to your life
- Using problem-solving skills
A positive problem-solving orientation means viewing things in an optimistic light, embracing self-efficacy , and accepting the idea that problems are a normal part of life. Problem-solving skills are behaviors that you can rely on to help you navigate conflict, even during times of stress. This includes skills like:
- Knowing how to identify a problem
- Defining the problem in a helpful way
- Trying to understand the problem more deeply
- Setting goals related to the problem
- Generating alternative, creative solutions to the problem
- Choosing the best course of action
- Implementing the choice you have made
- Evaluating the outcome to determine next steps
Problem-solving therapy is all about training you to become adaptive in your life so that you will start to see problems as challenges to be solved instead of insurmountable obstacles. It also means that you will recognize the action that is required to engage in effective problem-solving techniques.
Planful Problem-Solving
One problem-solving technique, called planful problem-solving, involves following a series of steps to fix issues in a healthy, constructive way:
- Problem definition and formulation : This step involves identifying the real-life problem that needs to be solved and formulating it in a way that allows you to generate potential solutions.
- Generation of alternative solutions : This stage involves coming up with various potential solutions to the problem at hand. The goal in this step is to brainstorm options to creatively address the life stressor in ways that you may not have previously considered.
- Decision-making strategies : This stage involves discussing different strategies for making decisions as well as identifying obstacles that may get in the way of solving the problem at hand.
- Solution implementation and verification : This stage involves implementing a chosen solution and then verifying whether it was effective in addressing the problem.
Other Techniques
Other techniques your therapist may go over include:
- Problem-solving multitasking , which helps you learn to think clearly and solve problems effectively even during times of stress
- Stop, slow down, think, and act (SSTA) , which is meant to encourage you to become more emotionally mindful when faced with conflict
- Healthy thinking and imagery , which teaches you how to embrace more positive self-talk while problem-solving
What Problem-Solving Therapy Can Help With
Problem-solving therapy addresses life stress issues and focuses on helping you find solutions to concrete issues. This approach can be applied to problems associated with various psychological and physiological symptoms.
Mental Health Issues
Problem-solving therapy may help address mental health issues, like:
- Chronic stress due to accumulating minor issues
- Complications associated with traumatic brain injury (TBI)
- Emotional distress
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Problems associated with a chronic disease like cancer, heart disease, or diabetes
- Self-harm and feelings of hopelessness
- Substance use
- Suicidal ideation
Specific Life Challenges
This form of therapy is also helpful for dealing with specific life problems, such as:
- Death of a loved one
- Dissatisfaction at work
- Everyday life stressors
- Family problems
- Financial difficulties
- Relationship conflicts
Your doctor or mental healthcare professional will be able to advise whether problem-solving therapy could be helpful for your particular issue. In general, if you are struggling with specific, concrete problems that you are having trouble finding solutions for, problem-solving therapy could be helpful for you.
Benefits of Problem-Solving Therapy
The skills learned in problem-solving therapy can be helpful for managing all areas of your life. These can include:
- Being able to identify which stressors trigger your negative emotions (e.g., sadness, anger)
- Confidence that you can handle problems that you face
- Having a systematic approach on how to deal with life's problems
- Having a toolbox of strategies to solve the issues you face
- Increased confidence to find creative solutions
- Knowing how to identify which barriers will impede your progress
- Knowing how to manage emotions when they arise
- Reduced avoidance and increased action-taking
- The ability to accept life problems that can't be solved
- The ability to make effective decisions
- The development of patience (realizing that not all problems have a "quick fix")
Problem-solving therapy can help people feel more empowered to deal with the problems they face in their lives. Rather than feeling overwhelmed when stressors begin to take a toll, this therapy introduces new coping skills that can boost self-efficacy and resilience .
Other Types of Therapy
Other similar types of therapy include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and solution-focused brief therapy (SFBT) . While these therapies work to change thinking and behaviors, they work a bit differently. Both CBT and SFBT are less structured than problem-solving therapy and may focus on broader issues. CBT focuses on identifying and changing maladaptive thoughts, and SFBT works to help people look for solutions and build self-efficacy based on strengths.
This form of therapy was initially developed to help people combat stress through effective problem-solving, and it was later adapted to address clinical depression specifically. Today, much of the research on problem-solving therapy deals with its effectiveness in treating depression.
Problem-solving therapy has been shown to help depression in:
- Older adults
- People coping with serious illnesses like cancer
Problem-solving therapy also appears to be effective as a brief treatment for depression, offering benefits in as little as six to eight sessions with a therapist or another healthcare professional. This may make it a good option for someone unable to commit to a lengthier treatment for depression.
Problem-solving therapy is not a good fit for everyone. It may not be effective at addressing issues that don't have clear solutions, like seeking meaning or purpose in life. Problem-solving therapy is also intended to treat specific problems, not general habits or thought patterns .
In general, it's also important to remember that problem-solving therapy is not a primary treatment for mental disorders. If you are living with the symptoms of a serious mental illness such as bipolar disorder or schizophrenia , you may need additional treatment with evidence-based approaches for your particular concern.
Problem-solving therapy is best aimed at someone who has a mental or physical issue that is being treated separately, but who also has life issues that go along with that problem that has yet to be addressed.
For example, it could help if you can't clean your house or pay your bills because of your depression, or if a cancer diagnosis is interfering with your quality of life.
Your doctor may be able to recommend therapists in your area who utilize this approach, or they may offer it themselves as part of their practice. You can also search for a problem-solving therapist with help from the American Psychological Association’s (APA) Society of Clinical Psychology .
If receiving problem-solving therapy from a doctor or mental healthcare professional is not an option for you, you could also consider implementing it as a self-help strategy using a workbook designed to help you learn problem-solving skills on your own.
During your first session, your therapist may spend some time explaining their process and approach. They may ask you to identify the problem you’re currently facing, and they’ll likely discuss your goals for therapy .
Keep In Mind
Problem-solving therapy may be a short-term intervention that's focused on solving a specific issue in your life. If you need further help with something more pervasive, it can also become a longer-term treatment option.
Get Help Now
We've tried, tested, and written unbiased reviews of the best online therapy programs including Talkspace, BetterHelp, and ReGain. Find out which option is the best for you.
Shang P, Cao X, You S, Feng X, Li N, Jia Y. Problem-solving therapy for major depressive disorders in older adults: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials . Aging Clin Exp Res . 2021;33(6):1465-1475. doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01672-3
Cuijpers P, Wit L de, Kleiboer A, Karyotaki E, Ebert DD. Problem-solving therapy for adult depression: An updated meta-analysis . Eur Psychiatry . 2018;48(1):27-37. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.11.006
Nezu AM, Nezu CM, D'Zurilla TJ. Problem-Solving Therapy: A Treatment Manual . New York; 2013. doi:10.1891/9780826109415.0001
Owens D, Wright-Hughes A, Graham L, et al. Problem-solving therapy rather than treatment as usual for adults after self-harm: a pragmatic, feasibility, randomised controlled trial (the MIDSHIPS trial) . Pilot Feasibility Stud . 2020;6:119. doi:10.1186/s40814-020-00668-0
Sorsdahl K, Stein DJ, Corrigall J, et al. The efficacy of a blended motivational interviewing and problem solving therapy intervention to reduce substance use among patients presenting for emergency services in South Africa: A randomized controlled trial . Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy . 2015;10(1):46. doi:doi.org/10.1186/s13011-015-0042-1
Margolis SA, Osborne P, Gonzalez JS. Problem solving . In: Gellman MD, ed. Encyclopedia of Behavioral Medicine . Springer International Publishing; 2020:1745-1747. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-39903-0_208
Kirkham JG, Choi N, Seitz DP. Meta-analysis of problem solving therapy for the treatment of major depressive disorder in older adults . Int J Geriatr Psychiatry . 2016;31(5):526-535. doi:10.1002/gps.4358
Garand L, Rinaldo DE, Alberth MM, et al. Effects of problem solving therapy on mental health outcomes in family caregivers of persons with a new diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment or early dementia: A randomized controlled trial . Am J Geriatr Psychiatry . 2014;22(8):771-781. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2013.07.007
Noyes K, Zapf AL, Depner RM, et al. Problem-solving skills training in adult cancer survivors: Bright IDEAS-AC pilot study . Cancer Treat Res Commun . 2022;31:100552. doi:10.1016/j.ctarc.2022.100552
Albert SM, King J, Anderson S, et al. Depression agency-based collaborative: effect of problem-solving therapy on risk of common mental disorders in older adults with home care needs . The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry . 2019;27(6):619-624. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2019.01.002
By Arlin Cuncic, MA Arlin Cuncic, MA, is the author of The Anxiety Workbook and founder of the website About Social Anxiety. She has a Master's degree in clinical psychology.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The relationship between decision-making and problem-solving is complex. Decision-making is perhaps best thought of as a key part of problem-solving: one part of the overall process. Our approach at Skills You Need is to set out a framework to help guide you through the decision-making process. You won't always need to use the whole framework ...
Decision-making is the process of choosing a solution based on your judgment, situation, facts, knowledge or a combination of available data. The goal is to avoid potential difficulties. Identifying opportunity is an important part of the decision-making process. Making decisions is often a part of problem-solving.
Step 3: Describe the Problem. This step includes diagnosing the problem to be able to define it. This stage is to get clarity and to dig deeper into what the issue really is. This stage is also about making sure all your employees agree to the said problem and are gearing up to work toward a solution and a common goal.
For most people, a typical day is filled with critical thinking and problem-solving challenges. In fact, critical thinking and problem-solving go hand-in-hand. They both refer to using knowledge, facts, and data to solve problems effectively. But with problem-solving, you are specifically identifying, selecting, and defending your solution.
Here we see the two skills of problem solving and decision making coming together. The two skills are vital to managing business risks as well as solving the problem. 6. Monitor and measure the plan. Having evolved through the five steps to this stage, you mustn't take your eye off the ball as it were.
Problem-solving is a vital skill for coping with various challenges in life. This webpage explains the different strategies and obstacles that can affect how you solve problems, and offers tips on how to improve your problem-solving skills. Learn how to identify, analyze, and overcome problems with Verywell Mind.
6. Solution implementation. This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving strategies have the end goal of implementing a solution and solving a problem in mind. Remember that in order for any solution to be successful, you need to help your group through all of the previous problem solving steps thoughtfully.
The right people with the relevant expertise need to clearly articulate their views to help you broaden your perspective and make the best choice. Great decisions are made as close as possible to ...
Problem-solving is a more analytical process than decision-making. Problem-solving is more process-related, while decision-making is more contextual. Problem-solving is directed at a specific goal or discrete answer. Problem-solving and decision-making may have consequences that are not always predictable or sequential.
There are 4 modules in this course. Problem-solving and effective decision-making are essential skills in today's fast-paced and ever-changing workplace. Both require a systematic yet creative approach to address today's business concerns. This course will teach an overarching process of how to identify problems to generate potential ...
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
Problem-solving and decision making go hand in hand. How quickly an issue can be addressed often depends on how fast a decision can be made. That's why Roman Baranovsky focuses on delegating decisions and reducing bottlenecks wherever he can—and sometimes that means relying on robots. Roman Baranovsky
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda. A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution. In SessionLab, it's easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda. Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into ...
The nature of both processes also differs in terms of the types of solutions they produce. Problem solving typically results in creative solutions that can be implemented over time, while decision making produces immediate choices from among existing alternatives without necessarily creating something new or unique.
Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on decision making. Aaron De Smet is a senior partner in McKinsey's New Jersey office, Eileen Kelly Rinaudo is McKinsey's global director of advancing women executives and is based in the New York office, Frithjof Lund is a senior partner in the Oslo office, and Leigh Weiss is a senior adviser in the Boston office.
Increase in productivity - tasks will be completed more efficiently. Improved teamwork skills - employees will work better together. Better workplace communication - smoother operation of the business as a result of effective communication and teamwork. Better employee satisfaction - employees that communicate and work collaboratively ...
Simply put, critical thinking is the act of deliberately analyzing information so that you can make better judgements and decisions. It involves using things like logic, reasoning, and creativity, to draw conclusions and generally understand things better. This may sound like a pretty broad definition, and that's because critical thinking is a ...
They go hand in hand because without solving a problem, it becomes difficult to make a decision. And even vice versa in some cases. Now, there are two types of problem-solvers and decision-makers.
3. Foster a Collaborative Mindset. Fostering the right mindset early in the decision-making process is critical to ensuring your team works collaboratively—not contentiously. When facing a decision, there are two key mindsets to consider: Advocacy: A mindset that regards decision-making as a contest.
Problem-solving is a critical skill in leadership development, and enhancing this ability often hinges on refining your decision-making skills. Effective leaders face challenges head-on with a ...
4. Losing Sight of Purpose. Over the course of the decision-making process, managers and their teams can, at times, get wrapped up in the intricacies of problem-solving and lose sight of the bigger picture. To ultimately sell whatever decision is made to the larger organization, priorities and goals need to be well-established and reiterated ...
Step 1: the head of the brainsteering activity should have good knowledge of the criteria an organization uses in order to make decisions. Step 2: raise the right questions. Step 3: choose the right people for such a meeting. Step 4: create small groups of people (three to five) when the set of ideas is rather large.
Problem-solving therapy is a brief intervention that provides people with the tools they need to identify and solve problems that arise from big and small life stressors. It aims to improve your overall quality of life and reduce the negative impact of psychological and physical illness. Problem-solving therapy can be used to treat depression ...
decision making, process and logic through which individuals arrive at a decision. Different models of decision making lead to dramatically different analyses and predictions. Decision-making theories range from objective rational decision making, which assumes that individuals will make the same decisions given the same information and preferences, to the more subjective logic of ...