- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide

How to Write a Personal Statement (with Tips and Examples)

Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
What is a personal statement, 6 tips on how to write a personal statement, personal statement examples (for college and university), faqs about writing personal statements, conclusion on how to write a personal statement.
How do you tell someone who you are in just a few hundred words?
It’s certainly no easy task, but it’s one almost every college applicant must do. The personal statement is a crucial part of any college or university application.
So, how do you write a compelling personal statement?
In this article, we’ll give you all the tools, tips, and examples you need to write an effective personal statement.
A personal statement is a short essay that reveals something important about who you are. It can talk about your background, your interests, your values, your goals in life, or all of the above.
Personal statements are required by many college admission offices and scholarship selection committees. They’re a key part of your application, alongside your academic transcript, standardized test scores, and extracurricular activities.
The reason application committees ask you to write a personal statement is so they can get to know who you are.
Some personal statements have specific prompts, such as “Discuss a period of personal growth in your life” or “Tell us about a challenge or failure you’ve faced.” Others are more open-ended with prompts that essentially boil down to “Tell us about yourself.”
No matter what the prompt is, your goal is the same: to make yourself stand out to the selection committee as a strong candidate for their program.
Here are some things a personal statement can be:
It can be funny. If you have a great sense of humor, your personal statement is a great place to let that shine.
It can be vulnerable. Don’t be afraid to open up about hardships in your life or failures you’ve experienced. Showing vulnerability can make you sound more like a real person rather than just a collection of application materials.
It can be creative. Candidates have got into top schools with personal statements that take the form of “a day in the life” descriptions, third-person short stories, and even cooking recipes.
Now we’ve talked about what a personal statement is, let’s quickly look at what a personal statement isn’t:
It isn’t a formal academic paper. You should write the personal statement in your natural voice, using first-person pronouns like “I” and “me,” not in the formal, objective language you would use to write an academic paper.
It isn’t a five-paragraph essay. You should use as many paragraphs as you need to tell your story instead of sticking to the essay structure you learned in school.
It isn’t a resumé. You should try to describe yourself by telling a clear and cohesive story rather than providing a jumbled list of all of your accomplishments and ambitions.

Here are our top six tips for writing a strong personal statement.
Tip 1: Do Some Serious Self-Reflection
The hardest part of writing a personal statement isn’t the actual process of writing it.
Before you start typing, you have to figure out what to write about. And that means taking some time to reflect on who you are and what’s important in your life.
Here are some useful questions you can use to start your self-reflection. You can either answer these on your own by writing down your answers, or you can ask a trusted friend to listen as you talk about them together.
What were the key moments that shaped your life? (e.g. an important friendship, a travel experience, an illness or injury)
What are you proud of? (e.g. you’re a good listener, you always keep your promises, you’re a talented musician)
How do you choose to spend your time? (e.g. reading, practicing soccer, spending time with your friends)
What inspires you? (e.g. your grandmother, a celebrity, your favorite song)
Doing this self-reflection is crucial for figuring out the perfect topics and anecdotes you can use to describe who you are.
Tip 2: Try to Avoid Cliché Topics
College application committees read thousands of personal statements a year. That means there are some personal statement topics they see over and over again.
Here are a few examples of common personal statement topics that have become cliché:
Winning a tournament or sports game
Volunteering in a foreign country
Moving to a new home
Becoming an older sibling
Being an immigrant or having immigrant parents
If you want to make a strong impression in the application process, you need to make your personal statement stand out from the crowd.
But if your chosen personal statement topic falls into one of these categories, that doesn’t necessarily mean you shouldn’t use it. Just make sure to put a unique spin on it so it still delivers something the committee hasn’t seen before.

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
Tip 3: Show, Don’t Tell
One common mistake you might make in your personal statement is to simply tell the reader what you want them to know about you, such as by stating “I have a fear of public speaking” or “I love to cook.”
Instead of simply stating these facts, you should show the committee what you’re talking about through a story or scene, which will make your essay much more immersive and memorable.
For example, let’s say you want the committee to know you overcame your fear of public speaking. Instead of writing “I overcame my fear of public speaking,” show them what it was like to be onstage in front of a microphone. Did your palms get clammy? Did you feel light-headed? Did you forget your words?
Or let’s say you want the committee to know you love to cook. Instead of writing “I love to cook,” show them why you love to cook. What’s your favorite dish to cook? What does the air smell like when you’re cooking it? What kitchen appliances do you use to make it?
Tip 4: Connect the Story to Why You’re Applying
Don’t forget that the purpose of your personal statement isn’t simply to tell the admissions committee who you are. That’s an important part of it, of course, but your ultimate goal is to convince them to choose you as a candidate.
That means it’s important to tie your personal story to your reasons for applying to this specific school or scholarship. Finish your essay with a strong thesis.
For example, if your story is about overcoming your fear of public speaking, you might connect that story to your ambition of becoming a politician. You can then tie that to your application by saying, “I want to apply to this school because of its fantastic politics program, which will give me a perfect opportunity to use my voice.”
Tip 5: Write in Your Own Voice
The personal statement isn’t supposed to be written in a formal tone. That’s why they’re called “personal” statements because you have to shape it to fit your own voice and style.
Don’t use complicated or overwrought language. You don’t need to fill your essay with semicolons and big words, unless that’s how you sound in real life.
One way to write in your own voice is by speaking your personal statement out loud. If it doesn’t feel natural, it may need changing.
Tip 6: Edit, Edit, Edit!
It’s important to revise your personal statement multiple times in order to make sure it’s as close to perfect as possible.
A single typo won’t kill your application, but if your personal statement contains multiple spelling errors or egregious grammar mistakes, you won’t be putting your best foot forward.
ProWritingAid can help you make sure your personal statement is as clean as possible. In addition to catching your grammar errors, typos, and punctuation mistakes, it will also help you improve weaknesses in your writing, such as passive voice, unnecessary repetition, and more.
Let’s look at some of the best personal statements that have worked for successful candidates in the real world.
Harvard Personal Statement Example
Love. For a word describing such a powerful emotion, it is always in the air. The word “love” has become so pervasive in everyday conversation that it hardly retains its roots in blazing passion and deep adoration. In fact, the word is thrown about so much that it becomes difficult to believe society isn’t just one huge, smitten party, with everyone holding hands and singing “Kumbaya.” In films, it’s the teenage boy’s grudging response to a doting mother. At school, it’s a habitual farewell between friends. But in my Chinese home, it’s never uttered. Watching my grandmother lie unconscious on the hospital bed, waiting for her body to shut down, was excruciatingly painful. Her final quavering breaths formed a discordant rhythm with the steady beep of hospital equipment and the unsympathetic tapping hands of the clock. That evening, I whispered—into unhearing ears—the first, and only, “I love you” I ever said to her, my rankling guilt haunting me relentlessly for weeks after her passing. My warm confession seemed anticlimactic, met with only the coldness of my surroundings—the blank room, impassive doctors, and empty silence. I struggled to understand why the “love” that so easily rolled off my tongue when bantering with friends dissipated from my vocabulary when I spoke to my family. Do Chinese people simply love less than Americans do?
This is an excerpt from a personal statement that got the applicant admitted to Harvard University. The applicant discusses her background as a Chinese-American by musing on the word “love” and what that means within her family.
The writer uses vulnerable details about her relationship with her grandmother to give the reader an understanding of where she comes from and how her family has shaped her.
You can read the full personal statement on the Harvard Crimson website.
Tufts Personal Statement Example
My first dream job was to be a pickle truck driver. I saw it in my favorite book, Richard Scarry’s “Cars and Trucks and Things That Go,” and for some reason, I was absolutely obsessed with the idea of driving a giant pickle. Much to the discontent of my younger sister, I insisted that my parents read us that book as many nights as possible so we could find goldbug, a small little golden bug, on every page. I would imagine the wonderful life I would have: being a pig driving a giant pickle truck across the country, chasing and finding goldbug. I then moved on to wanting to be a Lego Master. Then an architect. Then a surgeon. Then I discovered a real goldbug: gold nanoparticles that can reprogram macrophages to assist in killing tumors, produce clear images of them without sacrificing the subject, and heat them to obliteration. Suddenly the destination of my pickle was clear. I quickly became enveloped by the world of nanomedicine; I scoured articles about liposomes, polymeric micelles, dendrimers, targeting ligands, and self-assembling nanoparticles, all conquering cancer in some exotic way. Completely absorbed, I set out to find a mentor to dive even deeper into these topics. After several rejections, I was immensely grateful to receive an invitation to work alongside Dr. Sangeeta Ray at Johns Hopkins.
This is the beginning of a personal statement by Renner Kwittken, who was admitted into Tufts University as a pre-medical student.
Renner uses a humorous anecdote about being a pickle truck driver to describe his love for nanomedicine and how he got involved in his field. You can feel his passion for medicine throughout his personal statement.
You can find Renner’s full essay on the Tufts Admissions page.
Law School Personal Statement Essay Example
For most people, the slap on the face that turns their life around is figurative. Mine was literal. Actually, it was a punch delivered by a drill sergeant at Fort Dix, New Jersey, while I was in basic training. That day’s activity, just a few weeks into the program, included instruction in “low-crawling,” a sensible method of moving from one place to another on a battlefield. I felt rather clever for having discovered that, by looking right rather than down, I eliminated my helmet’s unfortunate tendency to dig into the ground and slow my progress. I could thus advance more easily, but I also exposed my unprotected face to hostile fire. Drill sergeants are typically very good at detecting this type of laziness, and mine was an excellent drill sergeant. So, after his repeated suggestions that I correct my performance went unheeded, he drove home his point with a fist to my face. We were both stunned. This was, after all, the New Army, and striking a trainee was a career-ending move for a drill sergeant, as we were both aware. I could have reported him; arguably, I should have. I didn’t. It didn’t seem right for this good sergeant, who had not slept for almost four days, to lose his career for losing his temper with my laziness. Choosing not to report him was the first decision I remember making that made me proud.
These are the first three paragraphs of an anonymous personal statement by a Wheaton College graduate, who used this personal statement to get into a top-25 law school.
This statement describes a time the applicant faced a challenging decision while in the army. He ended up making a decision he was proud of, and as a result, the personal statement gives us a sense of his character.
You can find the full essay on the Wheaton Academics website.
Here are some common questions about how to write a personal statement.
How Long Should a Personal Statement Be?
The length of your personal statement depends on the specific program you’re applying to. The application guidelines usually specify a maximum word count or an ideal word count.
Most personal statements are between 500–800 words. That’s a good general range to aim for if you don’t have more specific guidelines.
Should Personal Statements Be Different for Scholarships?
Many scholarship applications will ask for personal statements with similar prompts to those of college applications.
However, the purpose of a personal statement you’d write for a scholarship application is different from the purpose of one you’d write for a college application.
For a scholarship application, your goal is to showcase why you deserve the scholarship. To do that, you need to understand the mission of the organization offering that scholarship.
For example, some scholarships are meant to help first-generation college students get their degree, while others are meant to help women break into STEM.
Consider the following questions:
Why is this organization offering scholarships?
What would their ideal scholarship candidate look like?
How do your experiences and goals overlap with those of their ideal scholarship candidate?
You can use the same personal anecdotes you’d use for any other personal statement, but you’ll have a better chance of winning the scholarship if you tailor your essay to match their specific mission.
How to Start a Personal Statement
You should start your personal statement with a “hook” that pulls the reader in. The sooner you catch the reader’s attention, the more likely they’ll want to read the entire essay.
Here are some examples of hooks you can use:
A story (e.g. When the spotlight hit my face, I tried to remind myself to breathe. )
A setting description (e.g. My bedroom floor is covered with dirty laundry, candy wrappers, and crumpled sheet music. )
A funny anecdote (e.g. When I was a little kid, my friends nicknamed me Mowgli because of my haircut. )
A surprising fact (e.g. I've lived in 37 countries .)
There you have it—our complete guide to writing a personal statement that will make you stand out to the application committee.
Here’s a quick recap:
A personal statement is a short essay that shows an application committee who you are
Start with a strong hook that pulls the reader in
Tell a story to engage the reader
Write in your own voice, not in a formal tone
Good luck, and happy writing!
Hannah is a speculative fiction writer who loves all things strange and surreal. She holds a BA from Yale University and lives in Colorado. When she’s not busy writing, you can find her painting watercolors, playing her ukulele, or hiking in the Rockies. Follow her work on hannahyang.com or on Twitter at @hannahxyang.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
How to Write a Personal Statement (Tips + Essay Examples)

TABLE OF CONTENTS
What is a personal statement that just means “essay” … right, what are some great personal statement topics (aka how do i brainstorm mine).
- Three personal statement examples
A few hundred words to capture who you’ve become over the course of almost two decades?
Yup, makes sense why lots of students find the idea of writing a personal statement intimidating. Framed like the above, it could almost sound, I don’t know, unreasonable.
Whether you’re using the Common Application, the Coalition Application, or a school-specific application portal, it can be scary to try to come up with an essay topic that encompasses the complexity and vastness of who you are as a person … while also staying in the word count.
But this can also be a fun, meaningful experience (real talk: We wouldn’t be doing this if we didn’t think it was true). In fact, the process of brainstorming and writing about meaningful aspects of your life can be an incredible way to practice self-reflection and think more deeply about who you are, what you value, who you hope to be in the world, and what you actually want to get out of college.
So to help you move past the intimidating aspects and focus more on the fun and meaning, in this post, we’ll describe what differentiates the personal statement from other college essays and what function it serves in your college application. We’ll also share what qualities can help a personal statement stand out, how to find a stronger topic, how to set yourself up for an easier writing process, and even share some essay examples we loved.
A personal statement is an essay in which you demonstrate aspects of who you are by sharing some of the qualities, skills, and values you’ll bring to college. A written personal statement is typically used by college admission offices, but it’s also often used by scholarship selection committees or specific academic departments to help assess potential candidates.
To understand what the personal statement is, it’s helpful to imagine your entire college application as a human body. The personal statement is the metaphorical “heart”—it captures the essence of who you are as a person and what motivates you, both academically and personally.
Let’s briefly clarify what it isn’t . It’s not a classic five-paragraph essay you write for English class (thesis, body, restate thesis in almost the same words, but hopefully not repetitively, done).
Here are some other ways a personal statement is different from an English class essay:

There’s no “right” essay topic to write about, as you’ll see from the range of essay topics in this post . Students have written successfully on topics ranging from: I Shot My Brother, to Home, to Being Pooped on by Animals. Oh, and btw, we’d recommend not reading too many sample essays before you’ve done some brainstorming of your own first. But whatever topic you land on, keep this in mind:
The goal of your personal statement is to find a topic that demonstrates the skills, qualities, values, and interests you’ll bring with you to a college campus.
In fact, though we’ll keep saying “topic” of your essay because it’s clear and easy, the topic of your essay is ultimately always you. Just as the heart drives the actions of the rest of the body, the personal statement provides context for the rest—and, in some ways, is the heart—of your application. The other supplemental essays , if required by colleges, are opportunities to go into more detail about aspects of your interests, passions, and identity not covered in your personal statement.
The personal statement is a great place to discuss critical events or experiences in your life that catalyzed you to become the person you are now, or various aspects of your identity that strongly influence the way you interact with the world around you. It’s also an opportunity to introduce readers to your most important interests and values . For more on that, and exercises to help clarify those things, check those links (we’ll also offer more on them later).
What makes a great personal statement?
Ultimately, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to writing your personal statement that will magically make colleges admit you.
Bummer, we know.
That said, the best personal statements often share a lot of the same qualities , even when they’re about drastically different topics.
Here, in our opinion, are a few qualities you’ll find in an outstanding personal statement:
You can identify the applicant’s core values. In a great personal statement, we should be able to get a sense of what fulfills, motivates, or excites the author. These can be things like humor, beauty, community, and autonomy, just to name a few. So when you read back through your essay, you should be able to detect at least 4-5 different values throughout. When you look for these values, also consider whether or not they’re varied or similar. For instance, values like hard work, determination, and perseverance … are basically the same thing. On the other hand, more varied values like resourcefulness, healthy boundaries, and diversity can showcase different qualities and offer a more nuanced sense of who you are.
It’s vulnerable. We love when, after reading an essay, we feel closer to the writer. The best essays we’ve seen are the ones where students have let their guard down some. Don’t be afraid to be honest about things that scare, challenge, or bother you. The personal statement is a great space for you to open up about those aspects of yourself. As you’re writing, ask yourself: Does the essay sound like it’s mostly analytical, or like it’s coming from a deeper, more vulnerable place? Another way of asking this: Does it sound like the author wrote it using mostly their head (intellect), or their heart and gut? Remember, this is the “heart” of your application. It’s a place for emotional vulnerability. After reading it, the admission officer should (we hope) feel like they have a better sense of who you are.
It shows insight and growth. Your personal statement should ideally have at least 3-5 “so what” moments, points at which you draw insights or reflections from your experiences that speak to your values or sense of purpose. Sometimes, “so what” moments are subtle. Other times, they’re more explicit. Either way, the more illuminating, the better. They shouldn’t come out of nowhere, but they also shouldn’t be predictable. You want your reader to see your mind in action and take that journey of self-reflection with you.
It demonstrates craft (aka it’s articulate and reads well). While content is important, craft is what’ll bring the best stories to life. That’s why it’s important to think of writing as a process—it’s very rare that we’ve seen an outstanding personal statement that didn’t go through at least 5 drafts. Everything you write should be carefully considered . You don’t want your ideas to come off as sloppy or half-baked. Your reader should see the care you put into brainstorming and writing in every sentence. Ask yourself these questions as you write:
Do the ideas in the essay connect in a way that’s logical, but not too obvious (aka boring)?
Can you tell that the author spent a lot of time revising the essay over the course of several drafts?
Is it interesting and succinct throughout? If not, where do you lose interest? Where could words be cut? Which part isn’t revealing as much as it could be?
If you’ve written a first draft and you’re still not sure whether the essay is what you want it to be, give it to a trusted friend, teacher, or family member and have them evaluate it based on these 4 general criteria. Sometimes, we spend so much time on an essay that it’s useful to get another person’s point of view.
The answer to this question dovetails with the approach you’re taking to structuring your essay, so let’s talk about that a bit first.
And while structure may seem nebulous, offering vast options, you can really boil it down to just two approaches: montage or narrative.
So … what are those? And how can you generate some great content for either structure?
Whether you take a Narrative or Montage Approach to structuring your essay depends on your answer to this question:
Do you feel like you’ve faced significant challenges in your life … or not so much? (And do you want to write about them?)
If yes (to both), you’ll most likely want to use Narrative Structure .
If no (to either), you’ll probably want to try Montage Structure .
The above links dive into greater detail if you’re curious, but essentially, Narrative Structure is the classic story structure, focusing roughly equally on a) Challenges You Faced, b) What You Did About Them, and c) What You Learned. Paragraphs and events are connected causally. (Not casually , btw, but causally—as in, through cause and effect.)
Montage Structure focuses on a series of experiences and insights that are connected thematically (so, for example, 5 pairs of pants that connect to 5 different sides of who you are).
So how does structure play into what makes a great personal statement topic?
We believe a montage essay (i.e., an essay NOT about challenges) is more likely to stand out if the topic or theme of the essay is:
X. Elastic (i.e., something you can connect to a variety of examples, moments, or values)
Y. Less common (i.e., something other students probably aren’t writing about)
We believe that a narrative essay is more likely to stand out if it contains:
X. Difficult or compelling challenges
These aren’t binary—rather, each can be placed on a spectrum.
“Elastic” will vary from person to person. You might be able to connect mountain climbing to family, history, literature, science, social justice, environmentalism, growth, insight … and someone else might not connect it to much of anything. Maybe trees?
“Less common” —every year, thousands of students write about mission trips, sports, or music. It’s not that you can’t write about these things, but it’s a lot harder to stand out.
“Difficult or compelling challenges” can be put on a spectrum with things like getting a bad grade or not making a sports team on the weaker end, and things like escaping war or living homeless for three years on the stronger side. While you can possibly write a strong essay about a weaker challenge, it’s really hard to do.
“Insight” is the answer to the question “so what?” A great insight is likely to surprise the reader a bit, while a so-so insight likely won’t. (Insight is something you’ll develop in an essay through the writing process, rather than something you’ll generally know ahead of time for a topic, but it’s useful to understand that some topics are probably easier to pull insights from than others.)
To clarify, you can still write a great montage with a very common topic, or a narrative that offers so-so insights. But the degree of difficulty goes up. Probably way up.
With that in mind, how do you brainstorm possible topics that are on the easier-to-stand-out side of the spectrum?
Would you Rather watch instead?
Brainstorming your (outstanding) personal statement topic
In our experience, virtually every great college essay comes from good brainstorming. So, early on, stay in exploration mode—we recommend that students outline at least 2-3 different ideas before starting a draft.
Quality brainstorming can reveal great topics that you wouldn’t have thought about otherwise (and that you may not even know you can/are allowed to write about). Also, more on this in a bit, but outlining well is a huge time-saver, as it can help you either build a better first draft or reveal that you may not have as much to say about a topic as you might’ve initially thought.
Here are 5 great brainstorming exercises to get you started:
Values Exercise
Essence Objects Exercise
21 Details Exercise
Everything I Want Colleges To Know About Me Exercise
Feelings and Needs Exercise
That Values Exercise is your cornerstone—those values are what you’ll want to thread throughout your application, regardless of what structure you use in your personal statement.
We’d recommend doing all of those exercises, regardless of which structure you think you may use, as you may find something new in exploring, and many students will have to write a bunch of supplemental essays anyway.
That said, if you’re thinking Narrative Structure may be your thing (as in, you have some strong challenges you want to write about), be sure to spend a nice chunk of time exploring the Feelings and Needs Exercise (linked above), as it can directly lead to a strong outline and first draft.
If you’re thinking montage, think about how things like your essence objects and 21 details may be thematically linked, and how they can connect to your core values and memories. After doing those, you can also check out this list of 21 College Essay Topics and Ideas That Worked to get a sense of some topics that have paid off. We’ll draw your attention to some of the specific examples in the tips below. We’ve seen great montages built around things like:
Identity: This can be anything from sexuality, to culture, to race, to religion. For examples, check out “ My Grandma’s Kimchi ” or “ The Five Families Essay .”
Academic/career interests: This isn’t just a list of your favorite classes or a lengthy explanation of how well you did on that one AP Calculus test junior year. Instead, it’s more of an exploration of your educational interests and a meditation on how that might influence the work you do in the future. For examples, check out “ Why Behavioral Economics ” and “ Flying .”
Meaningful objects: Those “essence objects.” They’re basically just objects that mean more to you because they connect to your values at a deeper level. For instance, maybe you’d choose dumplings because they remind you of family dinners on Chinese New Year and a specific moment when you had to navigate your cultural identity. So, talking about dumplings might give you an entry point into talking about things like family and cultural connection. Doing the Essence Objects Exercise linked above will help you figure out what kind of objects might serve this function in your life. See the “ Happiness Spreadsheet ” essay for an example.
Significant Obstacles or Events: You might choose to write about a struggle you’ve faced or a dilemma that forced you to think more deeply about some aspect of who you are or what you’re interested in. “ The Tally On My Uniform ” and “ Dead Bird ” are two examples.
It’s important to note that some of these topics will likely overlap. You might choose to write about a significant challenge you faced that related to your identity in some way. Or maybe you’ll want to include details about both academic and extracurricular interests. Don’t feel like you have to choose just one. This list is just to give you a sense of what kind of topics you can explore.
How should I write a personal statement?
First, outline.
Seriously? Outline?
To get into just a little more nuance—if you have a ton of time until your deadline, and you don’t mind maybe throwing away entire drafts and starting over, then feel free to just dive in and write.
Otherwise, outline. Doing so will save you time and make your writing better.
So how do you outline?
For a narrative, use the Feelings and Needs Exercise , and build clear bullet points for the Challenges + Effects, What I Did About It, and What I Learned. Those become your outline.
Yeah, that simple.
For a montage, outline 4-7 ways your thread connects to different values through different experiences, and if you can think of them, different lessons and insights (though these you might have to develop later, during the writing process). For example, how auto repair connects to family, literature, curiosity, adventure, and personal growth (through different details and experiences).
Here are some solid example outlines:
Narrative outline (developed from the Feelings and Needs Exercise)
Challenges:
Domestic abuse (physical and verbal)
Controlling father/lack of freedom
Sexism/bias
Prevented from pursuing opportunities
Cut off from world/family
Lack of sense of freedom/independence
Faced discrimination
What I Did About It:
Pursued my dreams
Traveled to Egypt, London, and Paris alone
Challenged stereotypes
Explored new places and cultures
Developed self-confidence, independence, and courage
Grew as a leader
Planned events
What I learned:
Inspired to help others a lot more
Learned about oppression, and how to challenge oppressive norms
Became closer with mother, somewhat healed relationship with father
Need to feel free
And here’s the essay that became: Easter
Montage outline:
Thread: Home
Values: family, tradition, literature
Ex: “Tailgate Special,” discussions w/family, reading Nancy Drew
Perception, connection to family
Chinese sword dance
Values: culture/heritage, meticulousness, dedication, creativity
Ex: notebook, formations/choreography
Nuances of culture, power of connection
Values: science/chemistry, curiosity
Synthesizing plat nanoparticles
Joy of discovery, redefining expectations
Governor’s School
Values: exploration, personal growth
Knitting, physics, politics, etc.
Importance of exploring beyond what I know/am used to, taking risks
And here’s the essay that became: Home
Once you’ve got a solid outline, start drafting. A few really useful things for your first draft:
Don’t worry about word count (within reason).
Don’t worry about making your first draft perfect—it won’t be. Just write.
Don’t worry about a fancy opening or ending.
We’ve seen way too many students not write about the things they need to explore in a first draft because they were worried about word count. If your first draft of a 650-word essay is 800 or 900 words, cool. You’ll have to cut eventually. But that’s the easy part (you generally just hit “delete”).
And it’s actually easier to write a good first draft if you’re not worrying about writing a good first draft. We know that sounds contradictory. But what we mean is that a first draft is good if it gives you a clear sense of where to head with your second and third drafts. That’s its job—to help map where you go next.
Linked to that, a strong opening and ending are things you can more easily develop once you’re clearer on your content and structure. So, for a first draft, if something cool comes to you, great. But if not, don’t let it stop you from drafting.
Jump in and spend some time getting your ideas down on paper. Remember your first draft is just a chance to mess around with different topics and thoughts. It doesn’t have to be anywhere close to perfect. If it helps, just think of it as a brain dump. Once you’ve got all your ideas somewhere, you can start to reorganize and make them more coherent.
Revise (And revise. And revise ...)
Like we said earlier, it’s incredibly rare for an outstanding personal statement to not go through at least 5 drafts. So this is a big part of the process.
To get you started, this guide to Revising Your Essay in 5 Steps will help you create clearer logical flow, as will this breakdown of 9 different ways to effectively transition .
If you want to build a better opening , check out a bunch of options to play with there (we’d recommend experimenting, even if you have something you like—through exploring, you may find something even better).
And if you want to strengthen the ending of your essay , wander over that way.
Additionally, one of the best general tips we can give you as you revise is to read your essay out loud to yourself. And try to read from a total stranger’s perspective.
Reading out loud will help you notice problems you maybe missed when reading it in your mind. And reading from a stranger’s perspective will help ensure you aren’t relying on things in your brain that need to be on the page (but aren’t).
You might also try reading it to a trusted family member, teacher, or friend. They might be able to give you some constructive feedback to make your piece more relatable or accessible for other people. Just keep in mind that some people may have a good sense of what makes for strong writing in general, but not necessarily what makes for a strong college essay specifically.
For more about the essay writing process, check out our Ultimate Guide for writing your personal statement.
Want some guidance on your college applications?
Schedule a meeting to work with my team., three personal statement examples (with analysis for why they worked).
Example 1: "Cheers"
While my friends binge The Office , I’m at home with my favorite family tavern, Cheers . Reminiscing on my first visit five-years-ago, going into my tenth visit, I realize the gang at Cheers is my mirror: they reflect how I’ve grown. Sam Malone. Handsome, charming, ex-pro athlete. When I first met Sam, I had the typical impression: a playboy. However, I now see the real Sam: a compassionate being. Raised in Birmingham, I’ve learned many positive lessons, but there are some lessons I’m ashamed of. Homophobia is still prevalent in Alabama; something platonic as hugging your friend fuels ridicule. There’s an episode where Sam is conflicted after discovering his old best-friend was gay. By the end, he determines that whom his friend loves shouldn’t affect their friendship--a progressive act for 1983. This became personal when my brother came out. I was angered that a society that taught me Southern hospitality tried to teach me to hate one of the people I love most. Sam’s actions taught me who one chooses to love doesn’t change their humanity and encouraged me to promote that view in Alabama. When classmates make homophobic comments, I always bring up my brother and our story. These same classmates are now attending the annual Pride parades, standing up for our friends’ rights. Diane Chambers. Educated, elitist, starving artist. Diane loved the arts and displayed her work proudly, even if her cartoons of people depicted animals. As a kid, my dad attempted to teach me how to draw. These sessions ended in frustration, as I wasn’t able to recreate his work. While I was fascinated by the expression of creativity, I thought, “I’m not talented.” Through Diane’s character arcs, I learned art is not linear; it’s multi-dimensional. Diane would appreciate the discovery of my means of expression: graphic design and programming. I blend the two mediums to create an impactful product. Whether it’s designing and developing an app to battle the Tanzanian Water Crisis, or creating advertisements and social media posts for my internship at a construction-tech start-up, I reveal my vision through my greatest passion: technology. Dr. Frasier Crane. Intelligent, empathetic, scientist. Frasier (we’re on a first-name basis), joined the gang later after falling in love with Diane at a mental health retreat. I first met Frasier when I struggled to fit in with my peers. While I had a passion for STEM and its ability to uncover mysteries of the unknown, my peers had a passion for hating everything academic. While I thought Frasier was super cool, I still called him a nerd. However, watching the way Frasier embraced science gradually allowed me to realize my love for it is something to hone rather than suppress. Eventually, I developed enough confidence to reach out to a professor at the University of Alabama at Birmingham to conduct computational physics research. Over the past three years, I have completed two research projects, currently researching the distinct applications of computer vision, and have become a pioneer within STEM. Inspired by the love for Computer Science competitions, I founded the district’s first CS team. Upon concluding our presentation at the U.S. Capitol, I knew Frasier would be proud. The Cheers gang. I have wondered why I clicked with them so well since we are different people. Sam the jock, Frasier the nerd, Diane the artist, I the awkward teenager. I’ve realized each of them is a part of me. When I face societal pressure, I always learn and overcome. While I’m passionate about science, I also love the arts. Whereas I used to be an antisocial 7th grader, I’m now a senior with great friends and mentors. No matter what I’m struggling with in life, I know I can return to Cheers , where everybody knows your name.
Why this essay worked:
This essay does a great job of using the Montage Structure to incorporate a bunch of different aspects of the applicant’s life into one coherent piece. You’ll notice that they use the TV show Cheers and the characters in it as a clothesline off which to “hang” their interest in computer science and graphic design, LGBTQ+ community allyship, and generally endearing nerdiness. This is a really clever way of bringing together seemingly disparate topics. It doesn’t take itself too seriously but tells a lot about the author and how she thinks. It also gives her a very clear structure for her essay. Each paragraph is devoted to one Cheers character and (more importantly) expounds on the ways the author connects to that individual. The essay has a clear purpose despite lacking a linear narrative.
Also notice that the author doesn’t necessarily have a super clear idea of what she wants to do, career-wise. However, she still incorporates specific details about how she’s synthesized computer science and artistic design in various clubs and events. She doesn’t explicitly have to tell us what her future career is for us to get a sense of what interests she might pursue in college. This is a prime example of how you can write an outstanding personal statement even if you don’t totally know what you want to do in college and haven’t faced a significant challenge.
Example 2:
All that I remember from my childhood are happy memories - of blowing balloons in summer after eating an ice-cone, coming from school to find my favourite snacks lined up on the table, my grandma feeding me with her own hands and never failing to add that extra spoon of ghee (clarified butter) to my rice. My parents shielded us from everything that was bad in this world or could somehow hurt us. They were so protective that I learned to ride a bike on the roof of our three-story house because my parents didn’t think it was safe for me to ride on the road. Even on our roof, a place well within the four walls of our house, I had someone looking out for me. That protective bubble around me finally popped when I was stopped from entering a temple where my family goes annually on an auspicious day. I loved that subtle fragrance of saffron and seeing the beautifully decorated temple with thousands of pilgrims lining up. My grandpa donates a lot there which allows us to enter early in the morning and perform the rituals without the usual crowd. The problem this year was a new rule that prohibited Western clothing. The strange thing was that they didn’t stop male my cousin even though we were wearing the exact same thing, jeans and t-shirt. I wouldn’t be surprised if this happened today but I was then, as I was only in middle school. I hadn’t seen anything like this yet because my family never treated us differently -- we hadn’t previously seen this side of the world. I started trying to learn more about the “real world”, reading more news and participating in intercultural exchanges and debates, anything that would give me more insight. This process of exploring different versions of an event, of noticing how different people might see the same thing, made me more observant. But this also made me think of how others might see me and I became scared of being judged. When I was elected Head Girl this past year, I became even more self-conscious because I was in the limelight -- and everything I would do would reflect on the school. I thankfully realized how irrational my fears were during a hectic Round Square International Conference (RSIC) at school. I was busy heading our student team and managing crises. When a school bought more students than they’d registered, I didn’t have time to think, I had to rely on my instincts and take action. Teachers from across the world praised me; one even said I’d been the soul of our conference. These small but empowering moments have helped me realize that I could trust my decisions, my input counted too. I need to be myself and worry less about what others think. I could have easily changed my clothes that day at the temple but I didn’t because that’s not who I am. There’s always going to be someone who might not approve of what I do and that is all right. I am choosing to attend college in the United States because there I can continue my quest to learn more about the complexities of this world. My family never allowed me to use the public transportation in my city. I understand their concern, but I think it’s time for me to explore outside the safety of home, to ride a bike or take the subway, make my mistakes, and learn my way. At school, I felt like I was in the spotlight yet so invisible mostly because I worried about what others might think. But now I will choose to be visible, choose to be me.
Off the bat, one of the biggest things that stands out about this essay is the level of detail in it. In the intro, the author evokes very visceral images of blowing balloons in the summer, extra spoonfuls of ghee on rice, and riding bikes on rooftops. The more you can drop the reader into your world and engage their senses, the better. You want people to be able to identify with you so that they have a clear sense of who you are as a person. It also helps you stand out. The more specifically you write, the less likely it is that anyone else could have written it. That’s what this whole personal statement thing is all about—showing what you can uniquely bring to the table.
The other great thing about this essay is that it ends in a different place from where it begins. This shows insight and growth. The author goes from questioning her instincts and judgements to seeing her inherent value. She begins to gain confidence and see the positive ways in which she can contribute to the conversations she’s a part of. This transformation is important because it’s a hook that keeps people reading. They don’t know where the essay is going to take them, so they keep reading to see where the author will end up. It also demonstrates the applicant’s growth and ability to self-reflect, which are always great qualities to highlight in college essays.
Example 3:
Apparently, I have a natural “mom vibe.” On my volleyball team, I am team mom in every way. As a natural worrier, I like to make sure that everyone has all of their necessities: knee pads, water bottle, hair elastic, uniform. Did everyone go to the bathroom before leaving on the bus? Did we count to make sure that all fourteen of us are here? Does anyone want an apple slice? Over my many years of playing volleyball, I have learned how to play every position well enough to fill in for any member of my team, whether that’s front, back, libero, setter, or hitter, so that I can always be there for my team in a pinch. A few years ago, I transitioned from looking after only my teammates to also helping actual children. I started volunteering at my former elementary school as a teacher’s assistant. I guide third graders through difficult word problems or sentence structures, sometimes translating the lesson to Mandarin for the Chinese students who are struggling with English. I live for that moment when the impossible suddenly becomes possible and I see a student use what they just learned correctly without any assistance. I love helping kids ask big questions, and think about how to solve them, because it reminds me of how my parents guided me. Ever since I can remember, every time my father and I are alone on a long trip, we ask each other questions and the other has to answer with scientific evidence. Do birds have eyelids? Why is gelatin gelatinous? What does schizophrenia look like in a brain? I love thinking about how things work from the molecular level all the way up to the mechanical level. During a recent internship, I had the opportunity to ask big questions through research, a step beyond the guesstimating I was used to doing in my dad’s CRV. The team I was working with was conducting studies focused on treating alcoholism. My job was to “clean up” the data, or make it more readable. I sifted through spreadsheets, digging for the important data and piecing everything together logically. Knowing that my contribution would have a positive impact on people’s lives was incredibly meaningful. I’ve always enjoyed putting things together like a puzzle. As Chief Layout Editor of my school newspaper, I help my designers compile every edition. Like a real-life game of Tetris, every article must fit perfectly with the other articles around it, lined up into evenly lengthed columns. No matter how much experience a graphic designer has, no one gets all of their articles laid out nicely on the first try. We solve every edition by trial and error, which often results in lots of frustration, but no amount of frustration can surpass the pride and satisfaction once we have all the pages compiled and printed. As a pediatrician, I will be able to strengthen and use all these parts of me. I will have the chance to treat a multitude of illnesses and injuries and problem solve my way through each one. Each day, I will be able to think critically and scientifically to give families possible solutions and peace of mind about their child’s health. I hope to continually expand my knowledge as medicine advances and ask big questions by frequently participating in research. Hopefully I’ll be able to work with a great group of peers in a clinic and in public health. I want to find new solutions to seemingly unsolvable problems, and finally, use all of my skills and qualities to help better the lives of others. Plus, as a pediatrician, I will be able to take care of children who cannot always advocate for themselves, so my mom instinct will be one of my greatest assets.
This is another creative example of how you can go about writing a montage essay. The author uses her “mom vibe” to her advantage and discusses how her interest in attending to the people (and world) around her has influenced different spheres of her life. Notice how well the first line hooks us into the story. It’s short, sweet, funny, and visibly distinct from the denser paragraphs below. When you’re writing, think very carefully about your first sentence and the work it’s doing to rope your reader in. That first sentence is your first impression on readers, so you want it to be a good one.
One last standout aspect of this essay is the way it uses questions. In it, the author poses a lot of big and (oftentimes) unanswered questions. This is great because it highlights her natural curiosity and shows her mind in action. She doesn’t have to answer the questions for them to speak volumes about her personality and interests. Don’t feel like you have to resolve everything neatly by the end of your essay. That would be unrealistic, and ultimately, pretty uninteresting. It’s okay to pose questions for the sake of sheer wonder. In fact, it’s better than okay—it’s great. Nerd out a little. Have fun with it.
With all these writing/brainstorming strategies and example essays, the personal statement shouldn’t feel too intimidating anymore. Now you have all the tools you need to start writing an amazing essay.
Another great read: College Application & Admissions Timeline (AKA What Should I be Doing Right Now?)

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Applying to graduate school
- How to Write Your Personal Statement | Strategies & Examples
How to Write Your Personal Statement | Strategies & Examples
Published on February 12, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 3, 2023.
A personal statement is a short essay of around 500–1,000 words, in which you tell a compelling story about who you are, what drives you, and why you’re applying.
To write a successful personal statement for a graduate school application , don’t just summarize your experience; instead, craft a focused narrative in your own voice. Aim to demonstrate three things:
- Your personality: what are your interests, values, and motivations?
- Your talents: what can you bring to the program?
- Your goals: what do you hope the program will do for you?
This article guides you through some winning strategies to build a strong, well-structured personal statement for a master’s or PhD application. You can download the full examples below.
Urban Planning Psychology History
Table of contents
Getting started with your personal statement, the introduction: start with an attention-grabbing opening, the main body: craft your narrative, the conclusion: look ahead, revising, editing, and proofreading your personal statement, frequently asked questions, other interesting articles.
Before you start writing, the first step is to understand exactly what’s expected of you. If the application gives you a question or prompt for your personal statement, the most important thing is to respond to it directly.
For example, you might be asked to focus on the development of your personal identity; challenges you have faced in your life; or your career motivations. This will shape your focus and emphasis—but you still need to find your own unique approach to answering it.
There’s no universal template for a personal statement; it’s your chance to be creative and let your own voice shine through. But there are strategies you can use to build a compelling, well-structured story.
The first paragraph of your personal statement should set the tone and lead smoothly into the story you want to tell.
Strategy 1: Open with a concrete scene
An effective way to catch the reader’s attention is to set up a scene that illustrates something about your character and interests. If you’re stuck, try thinking about:
- A personal experience that changed your perspective
- A story from your family’s history
- A memorable teacher or learning experience
- An unusual or unexpected encounter
To write an effective scene, try to go beyond straightforward description; start with an intriguing sentence that pulls the reader in, and give concrete details to create a convincing atmosphere.
Strategy 2: Open with your motivations
To emphasize your enthusiasm and commitment, you can start by explaining your interest in the subject you want to study or the career path you want to follow.
Just stating that it interests you isn’t enough: first, you need to figure out why you’re interested in this field:
- Is it a longstanding passion or a recent discovery?
- Does it come naturally or have you had to work hard at it?
- How does it fit into the rest of your life?
- What do you think it contributes to society?
Tips for the introduction
- Don’t start on a cliche: avoid phrases like “Ever since I was a child…” or “For as long as I can remember…”
- Do save the introduction for last. If you’re struggling to come up with a strong opening, leave it aside, and note down any interesting ideas that occur to you as you write the rest of the personal statement.
Once you’ve set up the main themes of your personal statement, you’ll delve into more detail about your experiences and motivations.
To structure the body of your personal statement, there are various strategies you can use.
Strategy 1: Describe your development over time
One of the simplest strategies is to give a chronological overview of key experiences that have led you to apply for graduate school.
- What first sparked your interest in the field?
- Which classes, assignments, classmates, internships, or other activities helped you develop your knowledge and skills?
- Where do you want to go next? How does this program fit into your future plans?
Don’t try to include absolutely everything you’ve done—pick out highlights that are relevant to your application. Aim to craft a compelling narrative that shows how you’ve changed and actively developed yourself.
My interest in psychology was first sparked early in my high school career. Though somewhat scientifically inclined, I found that what interested me most was not the equations we learned about in physics and chemistry, but the motivations and perceptions of my fellow students, and the subtle social dynamics that I observed inside and outside the classroom. I wanted to learn how our identities, beliefs, and behaviours are shaped through our interactions with others, so I decided to major in Social Psychology. My undergraduate studies deepened my understanding of, and fascination with, the interplay between an individual mind and its social context.During my studies, I acquired a solid foundation of knowledge about concepts like social influence and group dynamics, but I also took classes on various topics not strictly related to my major. I was particularly interested in how other fields intersect with psychology—the classes I took on media studies, biology, and literature all enhanced my understanding of psychological concepts by providing different lenses through which to look at the issues involved.
Strategy 2: Own your challenges and obstacles
If your path to graduate school hasn’t been easy or straightforward, you can turn this into a strength, and structure your personal statement as a story of overcoming obstacles.
- Is your social, cultural or economic background underrepresented in the field? Show how your experiences will contribute a unique perspective.
- Do you have gaps in your resume or lower-than-ideal grades? Explain the challenges you faced and how you dealt with them.
Don’t focus too heavily on negatives, but use them to highlight your positive qualities. Resilience, resourcefulness and perseverance make you a promising graduate school candidate.
Growing up working class, urban decay becomes depressingly familiar. The sight of a row of abandoned houses does not surprise me, but it continues to bother me. Since high school, I have been determined to pursue a career in urban planning. While people of my background experience the consequences of urban planning decisions first-hand, we are underrepresented in the field itself. Ironically, given my motivation, my economic background has made my studies challenging. I was fortunate enough to be awarded a scholarship for my undergraduate studies, but after graduation I took jobs in unrelated fields to help support my parents. In the three years since, I have not lost my ambition. Now I am keen to resume my studies, and I believe I can bring an invaluable perspective to the table: that of the people most impacted by the decisions of urban planners.
Strategy 3: Demonstrate your knowledge of the field
Especially if you’re applying for a PhD or another research-focused program, it’s a good idea to show your familiarity with the subject and the department. Your personal statement can focus on the area you want to specialize in and reflect on why it matters to you.
- Reflect on the topics or themes that you’ve focused on in your studies. What draws you to them?
- Discuss any academic achievements, influential teachers, or other highlights of your education.
- Talk about the questions you’d like to explore in your research and why you think they’re important.
The personal statement isn’t a research proposal , so don’t go overboard on detail—but it’s a great opportunity to show your enthusiasm for the field and your capacity for original thinking.
In applying for this research program, my intention is to build on the multidisciplinary approach I have taken in my studies so far, combining knowledge from disparate fields of study to better understand psychological concepts and issues. The Media Psychology program stands out to me as the perfect environment for this kind of research, given its researchers’ openness to collaboration across diverse fields. I am impressed by the department’s innovative interdisciplinary projects that focus on the shifting landscape of media and technology, and I hope that my own work can follow a similarly trailblazing approach. More specifically, I want to develop my understanding of the intersection of psychology and media studies, and explore how media psychology theories and methods might be applied to neurodivergent minds. I am interested not only in media psychology but also in psychological disorders, and how the two interact. This is something I touched on during my undergraduate studies and that I’m excited to delve into further.
Strategy 4: Discuss your professional ambitions
Especially if you’re applying for a more professionally-oriented program (such as an MBA), it’s a good idea to focus on concrete goals and how the program will help you achieve them.
- If your career is just getting started, show how your character is suited to the field, and explain how graduate school will help you develop your talents.
- If you have already worked in the profession, show what you’ve achieved so far, and explain how the program will allow you to take the next step.
- If you are planning a career change, explain what has driven this decision and how your existing experience will help you succeed.
Don’t just state the position you want to achieve. You should demonstrate that you’ve put plenty of thought into your career plans and show why you’re well-suited to this profession.
One thing that fascinated me about the field during my undergraduate studies was the sheer number of different elements whose interactions constitute a person’s experience of an urban environment. Any number of factors could transform the scene I described at the beginning: What if there were no bus route? Better community outreach in the neighborhood? Worse law enforcement? More or fewer jobs available in the area? Some of these factors are out of the hands of an urban planner, but without taking them all into consideration, the planner has an incomplete picture of their task. Through further study I hope to develop my understanding of how these disparate elements combine and interact to create the urban environment. I am interested in the social, psychological and political effects our surroundings have on our lives. My studies will allow me to work on projects directly affecting the kinds of working-class urban communities I know well. I believe I can bring my own experiences, as well as my education, to bear upon the problem of improving infrastructure and quality of life in these communities.
Tips for the main body
- Don’t rehash your resume by trying to summarize everything you’ve done so far; the personal statement isn’t about listing your academic or professional experience, but about reflecting, evaluating, and relating it to broader themes.
- Do make your statements into stories: Instead of saying you’re hard-working and self-motivated, write about your internship where you took the initiative to start a new project. Instead of saying you’ve always loved reading, reflect on a novel or poem that changed your perspective.
Your conclusion should bring the focus back to the program and what you hope to get out of it, whether that’s developing practical skills, exploring intellectual questions, or both.
Emphasize the fit with your specific interests, showing why this program would be the best way to achieve your aims.
Strategy 1: What do you want to know?
If you’re applying for a more academic or research-focused program, end on a note of curiosity: what do you hope to learn, and why do you think this is the best place to learn it?
If there are specific classes or faculty members that you’re excited to learn from, this is the place to express your enthusiasm.
Strategy 2: What do you want to do?
If you’re applying for a program that focuses more on professional training, your conclusion can look to your career aspirations: what role do you want to play in society, and why is this program the best choice to help you get there?
Tips for the conclusion
- Don’t summarize what you’ve already said. You have limited space in a personal statement, so use it wisely!
- Do think bigger than yourself: try to express how your individual aspirations relate to your local community, your academic field, or society more broadly. It’s not just about what you’ll get out of graduate school, but about what you’ll be able to give back.
You’ll be expected to do a lot of writing in graduate school, so make a good first impression: leave yourself plenty of time to revise and polish the text.
Your style doesn’t have to be as formal as other kinds of academic writing, but it should be clear, direct and coherent. Make sure that each paragraph flows smoothly from the last, using topic sentences and transitions to create clear connections between each part.
Don’t be afraid to rewrite and restructure as much as necessary. Since you have a lot of freedom in the structure of a personal statement, you can experiment and move information around to see what works best.
Finally, it’s essential to carefully proofread your personal statement and fix any language errors. Before you submit your application, consider investing in professional personal statement editing . For $150, you have the peace of mind that your personal statement is grammatically correct, strong in term of your arguments, and free of awkward mistakes.
A statement of purpose is usually more formal, focusing on your academic or professional goals. It shouldn’t include anything that isn’t directly relevant to the application.
A personal statement can often be more creative. It might tell a story that isn’t directly related to the application, but that shows something about your personality, values, and motivations.
However, both types of document have the same overall goal: to demonstrate your potential as a graduate student and s how why you’re a great match for the program.
The typical length of a personal statement for graduate school applications is between 500 and 1,000 words.
Different programs have different requirements, so always check if there’s a minimum or maximum length and stick to the guidelines. If there is no recommended word count, aim for no more than 1-2 pages.
If you’re applying to multiple graduate school programs, you should tailor your personal statement to each application.
Some applications provide a prompt or question. In this case, you might have to write a new personal statement from scratch: the most important task is to respond to what you have been asked.
If there’s no prompt or guidelines, you can re-use the same idea for your personal statement – but change the details wherever relevant, making sure to emphasize why you’re applying to this specific program.
If the application also includes other essays, such as a statement of purpose , you might have to revise your personal statement to avoid repeating the same information.
If you want to know more about college essays , academic writing , and AI tools , make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
College essays
- College essay examples
- College essay format
- College essay style
- College essay length
- Diversity essays
- Scholarship essays
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Avoiding repetition
- Literature review
- Conceptual framework
- Dissertation outline
- Thesis acknowledgements
- Burned or burnt
- Canceled or cancelled
- Dreamt or dreamed
- Gray or grey
- Theater vs theatre
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 03). How to Write Your Personal Statement | Strategies & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/graduate-school/personal-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a graduate school resume | template & example, how (and who) to ask for a letter of recommendation, master's vs phd | a complete guide to the differences, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Search All Scholarships
- Exclusive Scholarships
- Easy Scholarships to Apply For
- No Essay Scholarships
- Scholarships for HS Juniors
- Scholarships for HS Seniors
- Scholarships for College Students
- Scholarships for Grad Students
- Scholarships for Women
- Scholarships for Black Students
- Scholarships
- Student Loans
- College Admissions
- Financial Aid
- Scholarship Winners
- Scholarship Providers
Student-centric advice and objective recommendations
Higher education has never been more confusing or expensive. Our goal is to help you navigate the very big decisions related to higher ed with objective information and expert advice. Each piece of content on the site is original, based on extensive research, and reviewed by multiple editors, including a subject matter expert. This ensures that all of our content is up-to-date, useful, accurate, and thorough.
Our reviews and recommendations are based on extensive research, testing, and feedback. We may receive commission from links on our website, but that doesn’t affect our editors’ opinions. Our marketing partners don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content. It’s accurate to the best of our knowledge when posted. You can find a complete list of our partners here .
How to Write an Amazing Personal Statement (Includes Examples!)

Lisa Freedland is a Scholarships360 writer with personal experience in psychological research and content writing. She has written content for an online fact-checking organization and has conducted research at the University of Southern California as well as the University of California, Irvine. Lisa graduated from the University of Southern California in Fall 2021 with a degree in Psychology.
Learn about our editorial policies
Zach Skillings is the Scholarships360 Newsletter Editor. He specializes in college admissions and strives to answer important questions about higher education. When he’s not contributing to Scholarships360, Zach writes about travel, music, film, and culture. His work has been published in Our State Magazine, Ladygunn Magazine, The Nocturnal Times, and The Lexington Dispatch. Zach graduated from Elon University with a degree in Cinema and Television Arts.

Bill Jack has over a decade of experience in college admissions and financial aid. Since 2008, he has worked at Colby College, Wesleyan University, University of Maine at Farmington, and Bates College.

Maria Geiger is Director of Content at Scholarships360. She is a former online educational technology instructor and adjunct writing instructor. In addition to education reform, Maria’s interests include viewpoint diversity, blended/flipped learning, digital communication, and integrating media/web tools into the curriculum to better facilitate student engagement. Maria earned both a B.A. and an M.A. in English Literature from Monmouth University, an M. Ed. in Education from Monmouth University, and a Virtual Online Teaching Certificate (VOLT) from the University of Pennsylvania.

The personal statement. It’s one of the most important parts of the entire college application process. This essay is the perfect opportunity to show admissions officers who you are and what makes you stand out from the crowd. But writing a good personal statement isn’t exactly easy. That’s why we’ve put together the ultimate guide on how to nail your personal statement, complete with example essays . Each essay was reviewed and commented upon by admissions expert Bill Jack. Let’s dive in!
Related: How to write an essay about yourself
What is a personal statement?
A personal statement is a special type of essay that’s required when you’re applying to colleges and scholarship programs. In this essay, you’re expected to share something about who you are and what you bring to the table. Think of it as a chance to reveal a side of yourself not found in the rest of your application. Personal statements are typically around 400 – 600 words in length.
What can I write about?
Pretty much anything, as long as it’s about you . While this is liberating in the sense that your writing options are nearly unlimited, it’s also overwhelming for the same reason. The good news is that you’ll probably be responding to a specific prompt. Chances are you’re applying to a school that uses the Common App , which means you’ll have seven prompts to choose from . Reviewing these prompts can help generate some ideas, but so can asking yourself meaningful questions.
Below you’ll find a list of questions to ask yourself during the brainstorming process. For each of the following questions, spend a few minutes jotting down whatever comes to mind.
- What experiences have shaped who you are?
- What’s special or unique about you or your life story?
- Who or what has inspired you the most?
- What accomplishments are you most proud of?
- What are your goals for the future? How have you arrived at those goals?
- If your life was a movie, what would be the most interesting scene?
- What have been some of the biggest challenges in your life? How did you respond and what did you learn?
The purpose of these questions is to prompt you to think about your life at a deeper level. Hopefully by reflecting on them, you’ll find an essay topic that is impactful and meaningful. In the next section, we’ll offer some advice on actually writing your essay.
Also see: How to write a 500 word essay
How do I write my personal statement?
Once you’ve found a topic, it’s time to start writing! Every personal statement is different, so there’s not really one formula that works for every student. That being said, the following tips should get you started in the right direction:
1. Freewrite, then rewrite
The blank page tends to get more intimidating the longer you stare at it, so it’s best to go ahead and jump right in! Don’t worry about making the first draft absolutely perfect. Instead, just get your ideas on the page and don’t spend too much time thinking about the finer details. Think of this initial writing session as a “brain dump”. Take 15-30 minutes to quickly empty all your thoughts onto the page without worrying about things like grammar, spelling, or sentence structure. You can even use bullet points if that helps. Once you have your ideas on the page, then you can go back and shape them exactly how you want.
2. Establish your theme
Now that you’ve got some basic ideas down on the page, it’s time to lock in on a theme. Your theme is a specific angle that reflects the central message of your essay. It can be summarized in a sentence or even a word. For example, let’s say you’re writing about how you had to establish a whole new group of friends when you moved to a new city. The theme for this type of essay would probably be something like “adaptation”. Having a theme will help you stay focused throughout your essay. Since you only have a limited number of words, you can’t afford to go off on tangents that don’t relate to your theme.
3. Tell a story
A lot of great essays rely on a specific scene or story. Find the personal anecdote relevant to your theme and transfer it to the page. The best way to do this is by using descriptive language. Consult the five senses as you’re setting the scene. What did you see, hear, taste, touch, or smell? How were you feeling emotionally? Using descriptive language can really help your essay come to life. According to UPchieve , a nonprofit that supports low income students, focusing on a particular moment as a “ revised version of a memoir ” is one way to keep readers engaged.
Related: College essay primer: show, don’t tell
4. Focus on your opening paragraph
Your opening paragraph should grab your reader’s attention and set the tone for the rest of your essay. In most cases, this is the best place to include your anecdote (if you have one). By leading with your personal story, you can hook your audience from the get-go. After telling your story, you can explain why it’s important to who you are.
Related: How to start a scholarship essay (with examples)
5. Use an authentic voice
Your personal statement reflects who you are, so you should use a tone that represents you. That means you shouldn’t try to sound like someone else, and you shouldn’t use fancy words just to show off. This isn’t an academic paper, so you don’t have to adopt a super formal tone. Instead, write in a way that allows room for your personality to breathe.
6. Edit, edit, edit…
Once you’re done writing, give yourself some time away from the essay. Try to allow a few days to pass before looking at the essay again with fresh eyes. This way, you’re more likely to pick up on spelling and grammatical errors. You may even get some new ideas and rethink the way you wrote some things. Once you’re satisfied, let someone else edit your essay. We recommend asking a teacher, parent, or sibling for their thoughts before submitting.
Examples of personal statements
Sometimes viewing someone else’s work is the best way to generate inspiration and get the creative juices flowing. The following essays are written in response to four different Common App prompts:
Prompt 1: “Some students have a background, identity, interest, or talent that is so meaningful they believe their application would be incomplete without it. If this sounds like you, then please share your story.”
When I was eight years old, I wanted a GameCube very badly. For weeks I hounded my dad to buy me one and finally he agreed. But there was a catch. He’d only get me a GameCube if I promised to start reading. Every day I played video games, I would have to pick up a book and read for at least one hour. At that point in my life, reading was just something I had to suffer through for school assignments. To read for pleasure seemed ludicrous. Needless to say, I wasn’t exactly thrilled about this proposed agreement. But I figured anything was worth it to get my hands on that shiny new video game console, so I bit the bullet and shook my dad’s hand. Little did I know that I had just made a life-changing deal.
At first, the required hour of reading was a chore — something I had to do so I could play Mario Kart. But it quickly turned into something more than that. To my complete and utter surprise, I discovered that I actually enjoyed reading. One hour turned into two, two turned into three, and after a while I was spending more time reading than I was playing video games. I found myself captivated by the written word, and I read everything I could get my hands on. Lord of the Rings , Percy Jackson , Goosebumps — you name it. I was falling in love with literature, while my GameCube was accumulating dust in the TV stand.
Soon enough, reading led to writing. I was beginning to come up with my own stories, so I put pen to paper and let my imagination run wild. It started out small. My first effort was a rudimentary picture book about a friendly raccoon who went to the moon. But things progressed. My stories became more intricate, my characters more complex. I wrote a series of science fiction novellas. I tried my hand at poetry. I was amazed at the worlds I could create with the tip of my pen. I had dreams of becoming an author.
Then somewhere along the way my family got a subscription to Netflix, and that completely changed the way I thought about storytelling. My nose had been buried in books up until then, so I hadn’t really seen a lot of movies. That quickly changed. It seemed like every other day a pair of new DVDs would arrive in the mail (this was the early days of Netflix). Dark Knight, The Truman Show, Inception, Memento — all these great films were coming in and out of the house. And I couldn’t get enough of them. Movies brought stories to life in a way that books could not. I was head over heels for visual storytelling.
Suddenly I wasn’t writing novels and short stories anymore. I was writing scripts for movies. Now I wanted to transfer my ideas to the big screen, rather than the pages of a book. But I was still doing the same thing I had always done. I was writing, just in a different format. To help with this process, I read the screenplays of my favorite films and paid attention to the way they were crafted. I kept watching more and more movies. And I hadn’t forgotten about my first love, either. I still cherished books and looked to them for inspiration. By the end of my junior year of high school, I had completed two scripts for short films.
So why am I telling you all this? Because I want to turn my love of storytelling into a career. I’m not totally sure how to do that yet, but I know I have options. Whether it’s film production, creative writing, or even journalism, I want to find a major that suits my ambitions. Writing has taken me a long way, and I know it can take me even further. As I step into this next chapter of my life, I couldn’t be more excited to see how my craft develops. In the meantime, I should probably get rid of that dusty old GameCube.
Feedback from admissions professional Bill Jack
Essays don’t always have to reveal details about the student’s intended career path, but one thing I like about this essay is that it gives the reader a sense of the why. Why do they want to pursue storytelling. It also shows the reader that they are open to how they pursue their interest. Being open to exploration is such a vital part of college, so it’s also showing the reader that they likely will be open to new things in college. And, it’s always fun to learn a little bit more about the student’s family, especially if the reader can learn about how the students interacts with their family.
Prompt 2: “The lessons we take from obstacles we encounter can be fundamental to later success. Recount a time when you faced a challenge, setback, or failure. How did it affect you, and what did you learn from the experience?”
I remember my first impression of Irvine: weird. It was foggy, stock-full of greenery and eucalyptus trees, and reminded me of my 5th grade trip to a “science camp” which was located in the San Bernardino mountains. Besides Irvine, that was one of the few places in Southern California where you’d find so many non-palm trees.
Of course, perhaps my initial impression of Irvine was biased, motivated by a desire to stay in my hometown and a fear of the unknown. While that was true to an extent, Irvine was certainly still a little peculiar. The city itself was based on a “master plan” of sorts, with the location of each of its schools, parks, shops, and arguably its trees having been logically “picked” before the foundation was poured. Even the homes all looked roughly the same, with their beige, stucco walls almost serving as a hallmark of the city itself.
Thus, this perfectly structured, perfectly safe city seemed like a paradise of sorts to many outsiders, my parents included. I was a little more hesitant to welcome this. As I saw it, this was a phony city – believing that its uniformity stood for a lack of personality. My hometown, although not as flawlessly safe nor clean as Irvine, was where most of my dearest memories had occurred. From the many sleepovers at Cindie’s house, to trying to avoid my school’s own version of the “infamous” cheese touch, to the many laughs shared with friends and family, I shed a tear at the prospect of leaving my home.
Moving into the foreign city, remnants of the hostility I held towards Irvine remained. Still dwelling in my memories of the past, I was initially unable to see Irvine as a “home.” So, as I walked into my first-ever Irvine class, being greeted by many kind, yet unfamiliar faces around me, I was unable to recognize that some of those new faces would later become some of my dearest friends. Such negative feelings about the city were further reinforced by newer, harder classes, and more complicated homework. Sitting in the discomfort of this unfamiliar environment, it started to seem that “change” was something not only inevitable, but insurmountable.
As the years went on, however, this idea seemed to fade. I got used to my classes and bike racing through Irvine neighborhoods with my friends, watching the trees that once seemed just a “weird” green blob soon transform into one of my favorite parts of the city. While I kept my old, beloved memories stored, I made space for new ones. From carefully making our way over the narrow creek path next to our school, to the laughs we shared during chemistry class, my new memories made with friends seemed to transform a city I once disliked into one I would miss.
Through this transformation, I have come to recognize that change, although sometimes intimidating at first, can open the door to great times and meaningful connections. Although Irvine may have once seemed like a strange, “phony” place that I couldn’t wait to be rid of, the memories and laughs I had grown to share there were very real. As I move onto this next part of my life, I hope I can use this knowledge that I have gained from my time in Irvine to make the most of what’s to come. Even if the change may be frightening at first, I have learned to embrace what’s on the other side, whether green or not.
One huge plus to writing an essay that focuses on a place is that you might have it read by someone who has been there. Yet, what’s really helpful about this essay is that even if someone hasn’t been there, a picture is painted about what the place is like. Admission officers have the hard task of really understanding what the student sees, so the use of adjectives and imagery can really help. It’s also really clever to see that the green that’s mentioned at the beginning is mentioned at the end. It’s a nice way to bookend the essay and tie it all together.
Prompt 6: “Describe a topic, idea, or concept you find so engaging that it makes you lose all track of time. Why does it captivate you? What or who do you turn to when you want to learn more?”
I like getting lost. Not literally, of course, but figuratively. Whether it be in the story of a love song by Taylor Swift, or in the memories brought back by listening to my favorite childhood video game’s background music, I’ve always appreciated music’s ability to transport me to another place, another time, another feeling.
Alas, I cannot sing, nor have I practiced an instrument since my middle school piano class days. So, perhaps Kurt Vonnegut was right. As he puts it, “Virtually every writer I know would rather be a musician.” While I cannot speak for others, I have certainly not debunked his theory. Writing allows many, including myself, to attempt to mimic the transformative power of music – even if our singing voices aren’t exactly “pleasant.” Just as you can get lost in music, you can do so in a story. Whether it is in George Orwell’s totalitarian Oceania, or Little Women’s Orchard House, the stories outlined in novels can provide an amazing look into the lives and worlds of others, and an escape from the worries and problems of those in your own.
While I am certainly not claiming to have the storytelling abilities of the Orwells or Alcotts before me, I’ve had fun trying to recreate such transformative feelings for others. When I was nine, I attempted to write a story about a little girl who had gotten lost in the woods, only managing to get a couple pages through. As I got older, whenever I was assigned a creative writing assignment in school, I wrote about the same pig, Phil. He was always angry: in my 8th grade science class, Phil was mad at some humans who had harbored his friend captive, and in my 9th grade English class, at a couple who robbed him.
Thus, when I heard about a writing club being opened at my school in 11th grade, I knew I had to join. I wanted to discern whether writing was just a hobby I picked up now and then, or a true passion. If it was a passion, I wanted to learn as much as possible about how I could improve. Although my high school’s writing club certainly wasn’t going to transform me into Shakespeare, I knew I could learn a lot from it – and I did. The club challenged me to do many things, from writing on the spot, to writing poetry, to even writing about myself, something that’s hopefully coming in handy right now.
From then on, I started to expand into different types of writing, storing short ideas, skits, and more in appropriately-labeled Google Drive folders. At around the same time, I became interested in classic literature, which largely stemmed from a project in English class. We had been required to choose and read a classic on our own, then present it to the class in an interesting way. While my book was certainly interesting and unique in its own right, nearly everyone else’s novels seemed more captivating to me. So, I took it upon myself to read as many classics as I could the following summer.
One of the books I read during the summer, funnily enough, was Animal Farm, which starred angry pigs, reminiscent of Phil. I had also started going over different ideas in my head, thinking about how I could translate them into words using the new skills I learned. While the writing club helped reaffirm my interest in writing and allowed me to develop new skills, my newfound affinity for classics gave me inspiration to write. Now, I am actually considering writing as part of my future. In this endeavor, I hope that Phil, and the music I inevitably listen to as I write, will accompany me every step of the way.
Admission officers might read 70 (or more!) essays in one day. It’s not uncommon for them to start to blend together and sound similar. This essay might not make you laugh out loud. But, it might make the reader chuckle while reading it thanks to the subtle humor and levity. Being able to incorporate a little humor into your essay (if it is natural for you to do… do not force it), can really be a great way to shed additional light into who you are. Remember, the essay isn’t merely about proving that you can write, but it should also reveal a little bit about your personality.
Prompt 5: “Discuss an accomplishment, event, or realization that sparked a period of personal growth and a new understanding of yourself or others.”
I learned a lot of things during the summer I worked at Tropical Smoothie. I discovered the value of hard work. I figured out how to save money. I even mastered the art of the Mango Magic smoothie (the secret is lots of sugar). But most importantly, I learned the power of perspective. And I have Deja to thank for that.
Deja was my shift supervisor, and one of Tropical Smoothie’s best employees. She was punctual, friendly, and always willing to lend a helping hand. She knew the store from top to bottom, and could handle pretty much any situation thrown her way. She made everyone around her better. On top of all that, she was four months pregnant! I was always impressed by Deja’s work ethic, but I gained an entirely new level of respect for her one day.
It was a Friday night, and Deja and I were working the closing shift together. It was very busy, and Deja and I were the only ones on shift. We managed to get by, but we were exhausted by the end of the evening. After wiping down the counters and mopping the floors, we closed up shop and went our separate ways. I was eager to get home.
I walked a couple blocks to where I had parked my car. Well, it wasn’t my car actually. It was my dad’s ‘98 Chevy pickup truck, and it was in rough shape. It had no heat or A/C, the leather seats were cracked beyond repair, and the driver’s side door was jammed shut. I sighed as I got in through the passenger side and scooted over to the driver’s seat. The whole reason I was working at Tropical Smoothie was to save up enough money to buy my own car. I was hoping to have something more respectable to drive during my senior year of high school.
I cranked the old thing up and started on my way home. But soon enough, I spotted Deja walking on the side of the road. There was no sidewalk here, the light was low, and she was dangerously close to the passing cars. I pulled over and offered her a ride. She got in and explained that she was on her way home. Apparently she didn’t have a car and had been walking to work every day. I couldn’t believe it. Here I was complaining about my set of wheels, while Deja didn’t have any to begin with.
We got to talking, and she confessed that she had been having a tough time. You would never know from the way she was so cheerful at work, but Deja had a lot on her plate. She was taking care of her mother, her boyfriend had just lost his job, and she was worried about making ends meet. And of course, she was expecting a baby in five months. On top of all that, she had been walking nearly a mile to and from work every day. The whole thing was a real eye opener, and made me reconsider some things in my own life.
For one, I didn’t mind driving my dad’s truck anymore. It was banged up, sure, but it was a lot better than nothing. My mindset had changed. I appreciated the truck now. I began to think about other things differently, too. I started making mental notes of all the things in my life I was thankful for — my family, my friends, my health. I became grateful for what I had, instead of obsessing over the things I didn’t.
I also gained more awareness of the world outside my own little bubble. My encounter with Deja had shown me first-hand that everyone is dealing with their own problems, some worse than others. So I started paying more attention to my friends, family members, and coworkers. I started listening more and asking how I could help. I also gave Deja a ride home for the rest of the summer.
These are all small things, of course, but I think they make a difference. I realized I’m at my best when I’m not fixated on my own life, but when I’m considerate of the lives around me. I want to keep this in mind as I continue to grow and develop as a person. I want to continue to search for ways to support the people around me. And most importantly, I want to keep things in perspective.
Too often we can be focused on our own problems that we fail to realize that everyone has their own things going on in their lives, too. This essay showcases how it’s important to put things in perspective, a skill that certainly will prove invaluable in college… and not just in the classroom. Another reason I like this essay is because it provides deeper insight into the student’s life. Sure, you might have mentioned in your activities list that you have a job. But as this essay does, you can show why you have the job in the first place, what your responsibilities are, and more.
A few last tips
We hope these essay examples gave you a bit of inspiration of what to include in your own. However, before you go, we’d like to send you off with a few (personal statement) writing tips to help you make your essays as lovely as the memories and anecdotes they’re based off of. Without further ado, here are some of our best tips for writing your personal statements:
1. Open strong
College admissions officers read many, many essays (think 50+) a day, which can sometimes cause them to start blending together and sounding alike. One way to avoid your essay from simply fading into the background is to start strong. This means opening your essay with something memorable, whether an interesting personal anecdote, a descriptive setting, or anything else that you think would catch a reader’s attention (so long as it’s not inappropriate). Not only might this help college admissions officers better remember your essay, but it will also make them curious about what the rest of your essay will entail.
2. Be authentic
Perhaps most important when it comes to writing personal statement essays is to maintain your authenticity. Ultimately, your essays should reflect your unique stories and quirks that make you who you are, and should help college admissions officers determine whether you’d truly be a good fit for their school or not. So, don’t stress trying to figure out what colleges are looking for. Be yourself, and let the colleges come to you!
3. Strong writing
This one may seem a little obvious, but strong writing will certainly appeal to colleges. Not only will it make your essay more compelling, but it may show colleges that you’re ready for college-level essay writing (that you’ll likely have to do a lot of). Just remember that good writing is not limited to grammar. Using captivating detail and descriptions are a huge part of making your essay seem more like a story than a lecture.
4. Proofread
Last but not least, remember to proofread! Make sure your essay contains no errors in grammar, punctuation, and spelling. When you’re done proofreading your essay yourself, we would also recommend that you ask a teacher, parent, or other grammatically savvy person to proofread your essay as well.
Final thoughts
With those in hand, we hope you now have a better sense of how to write your personal statement. While your grades and test scores are important when it comes to college admissions, it’s really your essays that can “make” or “break” your application.
Although this may make it seem like a daunting task, writing an amazing personal statement essay is all about effort. Thus, so long as you start early, follow the advice listed above, and dedicate your time and effort to it, it’s entirely possible to write an essay that perfectly encapsulates you. Good luck, and happy writing!
Also see: Scholarships360’s free scholarships search tool
Key Takeaways
- It may take some people longer than others to know what they want to write about, but remember that everyone, including you, has something unique to write about!
- Personal statements should be personal, which means you should avoid being too general and really strive to show off what makes you “you”
- Time and effort are two of the most important things you can put into your personal statement to ensure that it is the best representation of yourself
- Don’t forget to ask people who know you to read your work before you submit; they should be able to tell you better than anyone if you are truly shining through!
Frequently asked questions about writing personal statements
How do you write a powerful personal statement, what makes an amazing personal statement, how do you start an amazing personal statement, scholarships360 recommended.

10 Tips for Successful College Applications

Coalition vs. Common App: What is the difference?

College Application Deadlines 2023-2024: What You Need to Know
Trending now.

How to Convert Your GPA to a 4.0 Scale

PSAT to SAT Score Conversion: Predict Your Score

What Are Public Ivy League Schools?
3 reasons to join scholarships360.
- Automatic entry to our $10,000 No-Essay Scholarship
- Personalized matching to thousands of vetted scholarships
- Quick apply for scholarships exclusive to our platform
By the way...Scholarships360 is 100% free!

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, what is a personal statement everything you need to know about the college essay.
College Admissions , College Essays

In addition to standardized test scores and transcripts, a personal statement or essay is a required part of many college applications. The personal statement can be one of the most stressful parts of the application process because it's the most open ended.
In this guide, I'll answer the question, "What is a personal statement?" I'll talk through common college essay topics and what makes for an effective personal statement.
College Essay Glossary
Even the terminology can be confusing if you aren't familiar with it, so let's start by defining some terms:
Personal statement —an essay you write to show a college admissions committee who you are and why you deserve to be admitted to their school. It's worth noting that, unlike "college essay," this term is used for application essays for graduate school as well.
College essay —basically the same as a personal statement (I'll be using the terms interchangeably).
Essay prompt —a question or statement that your college essay is meant to respond to.
Supplemental essay —an extra school or program-specific essay beyond the basic personal statement.
Many colleges ask for only one essay. However, some schools do ask you to respond to multiple prompts or to provide supplemental essays in addition to a primary personal statement.
Either way, don't let it stress you out! This guide will cover everything you need to know about the different types of college essays and get you started thinking about how to write a great one:
- Why colleges ask for an essay
- What kinds of essay questions you'll see
- What sets great essays apart
- Tips for writing your own essay
Why Do Colleges Ask For an Essay?
There are a couple of reasons that colleges ask applicants to submit an essay, but the basic idea is that it gives them more information about you, especially who you are beyond grades and test scores.
#1: Insight Into Your Personality
The most important role of the essay is to give admissions committees a sense of your personality and what kind of addition you'd be to their school's community . Are you inquisitive? Ambitious? Caring? These kinds of qualities will have a profound impact on your college experience, but they're hard to determine based on a high school transcript.
Basically, the essay contextualizes your application and shows what kind of person you are outside of your grades and test scores . Imagine two students, Jane and Tim: they both have 3.5 GPAs and 1200s on the SAT. Jane lives in Colorado and is the captain of her track team; Tim lives in Vermont and regularly contributes to the school paper. They both want to be doctors, and they both volunteer at the local hospital.
As similar as Jane and Tim seem on paper, in reality, they're actually quite different, and their unique perspectives come through in their essays. Jane writes about how looking into her family history for a school project made her realize how the discovery of modern medical treatments like antibiotics and vaccines had changed the world and drove her to pursue a career as a medical researcher. Tim, meanwhile, recounts a story about how a kind doctor helped him overcome his fear of needles, an interaction that reminded him of the value of empathy and inspired him to become a family practitioner. These two students may seem outwardly similar but their motivations and personalities are very different.
Without an essay, your application is essentially a series of numbers: a GPA, SAT scores, the number of hours spent preparing for quiz bowl competitions. The personal statement is your chance to stand out as an individual.
#2: Evidence of Writing Skills
A secondary purpose of the essay is to serve as a writing sample and help colleges see that you have the skills needed to succeed in college classes. The personal statement is your best chance to show off your writing , so take the time to craft a piece you're really proud of.
That said, don't panic if you aren't a strong writer. Admissions officers aren't expecting you to write like Joan Didion; they just want to see that you can express your ideas clearly.
No matter what, your essay should absolutely not include any errors or typos .
#3: Explanation of Extenuating Circumstances
For some students, the essay is also a chance to explain factors affecting their high school record. Did your grades drop sophomore year because you were dealing with a family emergency? Did you miss out on extracurriculars junior year because of an extended medical absence? Colleges want to know if you struggled with a serious issue that affected your high school record , so make sure to indicate any relevant circumstances on your application.
Keep in mind that in some cases there will be a separate section for you to address these types of issues, as well as any black marks on your record like expulsions or criminal charges.
#4: Your Reasons for Applying to the School
Many colleges ask you to write an essay or paragraph about why you're applying to their school specifically . In asking these questions, admissions officers are trying to determine if you're genuinely excited about the school and whether you're likely to attend if accepted .
I'll talk more about this type of essay below.
What Kind of Questions Do Colleges Ask?
Thankfully, applications don't simply say, "Please include an essay about yourself"; they include a question or prompt that you're asked to respond to . These prompts are generally pretty open-ended and can be approached in a lot of different ways .
Nonetheless, most questions fall into a few main categories. Let's go through each common type of prompt, with examples from the Common Application, the University of California application, and a few individual schools.
Prompt Type 1: Your Personal History
This sort of question asks you to write about a formative experience, important event, or key relationship from your life . Admissions officers want to understand what is important to you and how your background has shaped you as a person.
These questions are both common and tricky. The most common pit students fall into is trying to tell their entire life stories. It's better to focus in on a very specific point in time and explain why it was meaningful to you.
Common App 1
Some students have a background, identity, interest, or talent that is so meaningful they believe their application would be incomplete without it. If this sounds like you, then please share your story.
Common App 5
Discuss an accomplishment, event, or realization that sparked a period of personal growth and a new understanding of yourself or others.
University of California 2
Every person has a creative side, and it can be expressed in many ways: problem solving, original and innovative thinking, and artistically, to name a few. Describe how you express your creative side.
University of California 6
Think about an academic subject that inspires you. Describe how you have furthered this interest inside and/or outside of the classroom.
Prompt Type 2: Facing a Problem
A lot of prompts deal with how you solve problems, how you cope with failure, and how you respond to conflict. College can be difficult, both personally and academically, and admissions committees want to see that you're equipped to face those challenges .
The key to these types of questions is to identify a real problem, failure, or conflict ( not a success in disguise) and show how you adapted and grew from addressing the issue.
Common App 2
The lessons we take from obstacles we encounter can be fundamental to later success. Recount a time when you faced a challenge, setback, or failure. How did it affect you, and what did you learn from the experience?
Harvard University 7
The Harvard College Honor Code declares that we “hold honesty as the foundation of our community.” As you consider entering this community that is committed to honesty, please reflect on a time when you or someone you observed had to make a choice about whether to act with integrity and honesty.
Prompt Type 3: Diversity
Most colleges are pretty diverse, with students from a wide range of backgrounds. Essay questions about diversity are designed to help admissions committees understand how you interact with people who are different from you .
In addressing these prompts, you want to show that you're capable of engaging with new ideas and relating to people who may have different beliefs than you.
Common App 3
Reflect on a time when you questioned or challenged a belief or idea. What prompted your thinking? What was the outcome?
Johns Hopkins University
Tell us about an aspect of your identity (e.g., race, gender, sexuality, religion, community) or a life experience that has shaped you as an individual and how that influenced what you’d like to pursue in college at Hopkins. This can be a future goal or experience that is either [sic] academic, extracurricular, or social.
Duke University Optional 1
We believe a wide range of personal perspectives, beliefs, and lived experiences are essential to making Duke a vibrant and meaningful living and learning community. Feel free to share with us anything in this context that might help us better understand you and what you might bring to our community.

Prompt Type 4: Your Future Goals
This type of prompt asks about what you want to do in the future: sometimes simply what you'd like to study, sometimes longer-term career goals. Colleges want to understand what you're interested in and how you plan to work towards your goals.
You'll mostly see these prompts if you're applying for a specialized program (like pre-med or engineering) or applying as a transfer student. Some schools also ask for supplementary essays along these lines.
University of Southern California (Architecture)
Princeton Supplement 1
Prompt Type 5: Why This School
The most common style of supplemental essay is the "why us?" essay, although a few schools with their own application use this type of question as their main prompt. In these essays, you're meant to address the specific reasons you want to go to the school you're applying to .
Whatever you do, don't ever recycle these essays for more than one school.
Chapman University
There are thousands of universities and colleges. Why are you interested in attending Chapman?
Columbia University
Why are you interested in attending Columbia University? We encourage you to consider the aspect(s) that you find unique and compelling about Columbia.
Rice University
Based upon your exploration of Rice University, what elements of the Rice experience appeal to you?
Princeton University
Princeton has a longstanding commitment to understanding our responsibility to society through service and civic engagement. How does your own story intersect with these ideals?
Prompt Type 6: Creative Prompts
More selective schools often have supplemental essays with stranger or more unique questions. University of Chicago is notorious for its weird prompts, but it's not the only school that will ask you to think outside the box in addressing its questions.
University of Chicago
“Vlog,” “Labradoodle,” and “Fauxmage.” Language is filled with portmanteaus. Create a new portmanteau and explain why those two things are a “patch” (perfect match).
University of Vermont
Established in Burlington, VT, Ben & Jerry’s is synonymous with both ice cream and social change. The “Save Our Swirled” flavor raises awareness of climate change, and “I Dough, I Dough” celebrates marriage equality. If you worked alongside Ben & Jerry, what charitable flavor would you develop and why?

What Makes a Strong Personal Statement?
OK , so you're clear on what a college essay is, but you're still not sure how to write a good one . To help you get started, I'm going to explain the main things admissions officers look for in students' essays: an engaging perspective, genuine moments, and lively writing .
I've touched on these ideas already, but here, I'll go into more depth about how the best essays stand out from the pack.
Showing Who You Are
A lot of students panic about finding a unique topic, and certainly writing about something unusual like a successful dating app you developed with your friends or your time working as a mall Santa can't hurt you. But what's really important isn't so much what you write about as how you write about it . You need to use your subject to show something deeper about yourself.
Look at the prompts above: you'll notice that they almost all ask you what you learned or how the experience affected you. Whatever topic you pick, you must be able to specifically address how or why it matters to you .
Say a student, Will, was writing about the mall Santa in response to Common App prompt number 2 (the one about failure): Will was a terrible mall Santa. He was way too skinny to be convincing and the kids would always step on his feet. He could easily write 600 very entertaining words describing this experience, but they wouldn't necessarily add up to an effective college essay.
To do that, he'll need to talk about his motivations and his feelings: why he took such a job in the first place and what he did (and didn't) get out of it. Maybe Will took the job because he needed to make some money to go on a school trip and it was the only one he could find. Despite his lack of enthusiasm for screaming children, he kept doing it because he knew if he persevered through the whole holiday season he would have enough money for his trip. Would you rather read "I failed at being a mall Santa" or "Failing as a mall Santa taught me how to persevere no matter what"? Admissions officers definitely prefer the latter.
Ultimately, the best topics are ones that allow you to explain something surprising about yourself .
Since the main point of the essay is to give schools a sense of who you are, you have to open up enough to let them see your personality . Writing a good college essay means being honest about your feelings and experiences even when they aren't entirely positive.
In this context, honesty doesn't mean going on at length about the time you broke into the local pool at night and nearly got arrested, but it does mean acknowledging when something was difficult or upsetting for you. Think about the mall Santa example above. The essay won't work unless the writer genuinely acknowledges that he was a bad Santa and explains why.
Eloquent Writing
As I mentioned above, colleges want to know that you are a strong enough writer to survive in college classes . Can you express your ideas clearly and concisely? Can you employ specific details appropriately and avoid clichés and generalizations? These kinds of skills will serve you well in college (and in life!).
Nonetheless, admissions officers recognize that different students have different strengths. They aren't looking for a poetic magnum opus from someone who wants to be a math major. (Honestly, they aren't expecting a masterwork from anyone , but the basic point stands.) Focus on making sure that your thoughts and personality come through, and don't worry about using fancy vocabulary or complex rhetorical devices.
Above all, make sure that you have zero grammar or spelling errors . Typos indicate carelessness, which will hurt your cause with admissions officers.
Top Five Essay-Writing Tips
Now that you have a sense of what colleges are looking for, let's talk about how you can put this new knowledge into practice as you approach your own essay. Below, I've collected my five best tips from years as a college essay counselor.
#1: Start Early!
No matter how much you want to avoid writing your essay, don't leave it until the last minute . One of the most important parts of the essay writing process is editing, and editing takes a lot of time. You want to be able to put your draft in a drawer for a week and come back to it with fresh eyes. You don't want to be stuck with an essay you don't really like because you have to submit your application tomorrow.
You need plenty of time to experiment and rewrite, so I would recommend starting your essays at least two months before the application deadline . For most students, that means starting around Halloween, but if you're applying early, you'll need to get going closer to Labor Day.
Of course, it's even better to get a head start and begin your planning earlier. Many students like to work on their essays over the summer, when they have more free time, but you should keep in mind that each year's application isn't usually released until August or September. Essay questions often stay the same from year to year, however. If you are looking to get a jump on writing, you can try to confirm with the school (or the Common App) whether the essay questions will be the same as the previous year's.
#2: Pick a Topic You're Genuinely Excited About
One of the biggest mistakes students make is trying to write what they think the committee wants to hear. The truth is that there's no "right answer" when it comes to college essays . T he best topics aren't limited to specific categories like volunteer experiences or winning a tournament. Instead, they're topics that actually matter to the writer .
"OK," you're thinking, "but what does she mean by 'a topic that matters to you'? Because to be perfectly honest, right now, what really matters to me is that fall TV starts up this week, and I have a feeling I shouldn't write about that."
You're not wrong (although some great essays have been written about television ). A great topic isn't just something that you're excited about or that you talk to your friends about; it's something that has had a real, describable effect on your perspective .
This doesn't mean that you should overemphasize how something absolutely changed your life , especially if it really didn't. Instead, try to be as specific and honest as you can about how the experience affected you, what it taught you, or what you got out of it.
Let's go back to the TV idea. Sure, writing an essay about how excited you are for the new season of Stranger Things probably isn't the quickest way to get yourself into college, but you could write a solid essay (in response to the first type of prompt) about how SpongeBob SquarePants was an integral part of your childhood. However, it's not enough to just explain how much you loved SpongeBob—you must also explain why and how watching the show every day after school affected your life. For example, maybe it was a ritual you shared with your brother, which showed you how even seemingly silly pieces of pop culture can bring people together. Dig beneath the surface to show who you are and how you see the world.
When you write about something you don't really care about, your writing will come out clichéd and uninteresting, and you'll likely struggle to motivate yourself. When you instead write about something that is genuinely important to you, you can make even the most ordinary experiences—learning to swim, eating a meal, or watching TV—engaging .

#3: Focus on Specifics
But how do you write an interesting essay? Focus.
Don't try to tell your entire life story or even the story of an entire weekend; 500–650 words may seem like a lot, but you'll reach that limit quickly if you try to pack every single thing that has happened to you into your essay. If, however, you just touch on a wide range of topics, you'll end up with an essay that reads more like a résumé.
Instead, narrow in on one specific event or idea, and talk about it in more depth . The narrower your topic, the better. For example, writing about your role as Mercutio in your school's production of Romeo and Juliet is too general, but writing about opening night, when everything went wrong, could be a great topic.
Whatever your topic, use details to help draw the reader in and express your unique perspective. But keep in mind that you don't have to include every detail of what you did or thought; stick to the important and illustrative ones.
#4: Use Your Own Voice
College essays aren't academic assignments; you don't need to be super formal. Instead, try to be yourself. The best writing sounds like a more eloquent version of the way you talk .
Focus on using clear, simple language that effectively explains a point or evokes a feeling. To do so, avoid the urge to use fancy-sounding synonyms when you don't really know what they mean. Contractions are fine; slang, generally, is not. Don't hesitate to write in the first person.
A final note: you don't need to be relentlessly positive. It's OK to acknowledge that sometimes things don't go how you want—just show how you grew from that.
#5: Be Ruthless
Many students want to call it a day after writing a first draft, but editing is a key part of writing a truly great essay. To be clear, editing doesn't mean just making a few minor wording tweaks and cleaning up typos; it means reading your essay carefully and objectively and thinking about how you could improve it .
Ask yourself questions as you read: is the progression of the essay clear? Do you make a lot of vague, sweeping statements that could be replaced with more interesting specifics? Do your sentences flow together nicely? Do you show something about yourself beyond the surface level?
You will have to delete and rewrite (potentially large) parts of your essay, and no matter how attached you feel to something you wrote, you might have to let it go . If you've ever heard the phrase "kill your darlings," know that it is 100% applicable to college essay writing.
At some point, you might even need to rewrite the whole essay. Even though it's annoying, starting over is sometimes the best way to get an essay that you're really proud of.

What's Next?
Make sure to check out our other posts on college essays , including our step-by-step guide to how to write your college essay , our analysis of the Common App Prompts , and our collection of example essays .
If you're in need of guidance on other parts of the application process , take a look at our guides to choosing the right college for you , writing about extracurriculars , deciding to double major , and requesting teacher recommendations .
Last but not least, if you're planning on taking the SAT one last time , check out our ultimate guide to studying for the SAT and make sure you're as prepared as possible.

Alex is an experienced tutor and writer. Over the past five years, she has worked with almost a hundred students and written about pop culture for a wide range of publications. She graduated with honors from University of Chicago, receiving a BA in English and Anthropology, and then went on to earn an MA at NYU in Cultural Reporting and Criticism. In high school, she was a National Merit Scholar, took 12 AP tests and scored 99 percentile scores on the SAT and ACT.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing the Personal Statement

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This handout provides information about writing personal statements for academic and other positions.
The personal statement, your opportunity to sell yourself in the application process, generally falls into one of two categories:
1. The general, comprehensive personal statement:
This allows you maximum freedom in terms of what you write and is the type of statement often prepared for standard medical or law school application forms.
2. The response to very specific questions:
Often, business and graduate school applications ask specific questions, and your statement should respond specifically to the question being asked. Some business school applications favor multiple essays, typically asking for responses to three or more questions.
Questions to ask yourself before you write:
- What's special, unique, distinctive, and/or impressive about you or your life story?
- What details of your life (personal or family problems, history, people or events that have shaped you or influenced your goals) might help the committee better understand you or help set you apart from other applicants?
- When did you become interested in this field and what have you learned about it (and about yourself) that has further stimulated your interest and reinforced your conviction that you are well suited to this field? What insights have you gained?
- How have you learned about this field—through classes, readings, seminars, work or other experiences, or conversations with people already in the field?
- If you have worked a lot during your college years, what have you learned (leadership or managerial skills, for example), and how has that work contributed to your growth?
- What are your career goals?
- Are there any gaps or discrepancies in your academic record that you should explain (great grades but mediocre LSAT or GRE scores, for example, or a distinct upward pattern to your GPA if it was only average in the beginning)?
- Have you had to overcome any unusual obstacles or hardships (for example, economic, familial, or physical) in your life?
- What personal characteristics (for example, integrity, compassion, and/or persistence) do you possess that would improve your prospects for success in the field or profession? Is there a way to demonstrate or document that you have these characteristics?
- What skills (for example, leadership, communicative, analytical) do you possess?
- Why might you be a stronger candidate for graduate school—and more successful and effective in the profession or field than other applicants?
- What are the most compelling reasons you can give for the admissions committee to be interested in you?
General advice
Answer the questions that are asked
- If you are applying to several schools, you may find questions in each application that are somewhat similar.
- Don't be tempted to use the same statement for all applications. It is important to answer each question being asked, and if slightly different answers are needed, you should write separate statements. In every case, be sure your answer fits the question being asked.
Tell a story
- Think in terms of showing or demonstrating through concrete experience. One of the worst things you can do is to bore the admissions committee. If your statement is fresh, lively, and different, you'll be putting yourself ahead of the pack. If you distinguish yourself through your story, you will make yourself memorable.
Be specific
- Don't, for example, state that you would make an excellent doctor unless you can back it up with specific reasons. Your desire to become a lawyer, engineer, or whatever should be logical, the result of specific experience that is described in your statement. Your application should emerge as the logical conclusion to your story.
Find an angle
- If you're like most people, your life story lacks drama, so figuring out a way to make it interesting becomes the big challenge. Finding an angle or a "hook" is vital.
Concentrate on your opening paragraph
- The lead or opening paragraph is generally the most important. It is here that you grab the reader's attention or lose it. This paragraph becomes the framework for the rest of the statement.
Tell what you know
- The middle section of your essay might detail your interest and experience in your particular field, as well as some of your knowledge of the field. Too many people graduate with little or no knowledge of the nuts and bolts of the profession or field they hope to enter. Be as specific as you can in relating what you know about the field and use the language professionals use in conveying this information. Refer to experiences (work, research, etc.), classes, conversations with people in the field, books you've read, seminars you've attended, or any other source of specific information about the career you want and why you're suited to it. Since you will have to select what you include in your statement, the choices you make are often an indication of your judgment.
Don't include some subjects
- There are certain things best left out of personal statements. For example, references to experiences or accomplishments in high school or earlier are generally not a good idea. Don't mention potentially controversial subjects (for example, controversial religious or political issues).
Do some research, if needed
- If a school wants to know why you're applying to it rather than another school, do some research to find out what sets your choice apart from other universities or programs. If the school setting would provide an important geographical or cultural change for you, this might be a factor to mention.
Write well and correctly
- Be meticulous. Type and proofread your essay very carefully. Many admissions officers say that good written skills and command of correct use of language are important to them as they read these statements. Express yourself clearly and concisely. Adhere to stated word limits.
Avoid clichés
- A medical school applicant who writes that he is good at science and wants to help other people is not exactly expressing an original thought. Stay away from often-repeated or tired statements.
For more information on writing a personal statement, see the personal statement vidcast .
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
How to Write a Personal Statement
A personal statement can be a key part of your college application, and you can really make yours shine by following a few tips.
![what should a personal statement contain [Featured Image] A lady with pink hair is holding a piece of paper with a laptop on her lap.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/5QiQSrAurfwGVZiA5c5ayj/60e0cd4887b3c7fbcbff3f74043c9ccd/NFtoOVjw.jpeg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
When you're applying to college—either to an undergraduate or graduate program—you may be asked to submit a personal statement. It's an essay that gives you the chance to share more about who you are and why you'd like to attend the university you're applying to.
The information you provide in your personal statement can help build on your other application materials, like your transcripts and letters of recommendation, and build a more cohesive picture to help the admissions committee understand your goals.
In this article, we'll go over more about personal statements, including why they're important, what to include in one, and tips for strengthening yours.
What is a personal statement?
A personal statement—sometimes known as a college essay —is a brief written essay you submit with other materials when applying to college or university. Personal statements tend to be most common for undergraduate applications, and they're a great opportunity for an admissions committee to hear your voice directly.
Many colleges and universities in the US, especially those using Common App , provide prompts for you to use. For example, "Reflect on a time when you questioned or challenged a belief or idea" or "Describe a topic, idea, or concept you find so engaging that it makes you lose all track of time" [ 1 ]. If the school you're interested in attending doesn't require prompts, you will likely want to craft a response that touches on your story, your values, and your goals if possible.
In grad school, personal statements are sometimes known as letters of intent , and go into more detail about your academic and professional background, while expressing interest in attending the particular program you're applying to.
Why is a personal statement important?
Personal statements are important for a number of reasons. Whereas other materials you submit in an application can address your academic abilities (like your transcripts) or how you perform as a student (like your letters of recommendation), a personal statement is a chance to do exactly that: get more personal.
Personal statements typically:
Permit you to share things that don't fit on your resume, such as personal stories, motivations, and values
Offer schools a chance to see why you're interested in a particular field of study and what you hope to accomplish after you graduate
Provide an opportunity for you to talk about past employment, volunteer experiences, or skills you have that complement your studies
Allow colleges to evaluate your writing skills
Bring life to a college application package otherwise filled with facts and figures
Build job-ready skills with a Coursera Plus subscription
- Get access to 7,000+ learning programs from world-class universities and companies, including Google, Yale, Salesforce, and more
- Try different courses and find your best fit at no additional cost
- Earn certificates for learning programs you complete
- A subscription price of $59/month, cancel anytime
How to write a personal statement.
As we mentioned earlier, you may have to respond to a prompt when drafting your personal statement—or a college or university may invite you to respond however you'd like. In either case, use the steps below to begin building your response.
Create a solid hook .
To capture the attention of an admissions committee member, start your personal statement with a hook that relates to the topic of your essay. A hook tends to be a colorful sentence or two at the very beginning that compels the reader to continue reading.
To create a captivating hook, try one of these methods:
Pose a rhetorical question.
Provide an interesting statistic.
Insert a quote from a well-known person.
Challenge the reader with a common misconception.
Use an anecdote, which is a short story that can be true or imaginary.
Credibility is crucial when writing a personal statement as part of your college application process. If you choose a statistic, quote, or misconception for your hook, make sure it comes from a reliable source.
Follow a narrative.
The best personal statements typically read like a story: they have a common theme, as well as a beginning, middle, and end. This type of format also helps keep your thoughts organized and improves the flow of your essay.
Common themes to consider for your personal statement include:
Special role models from your past
Life-altering events you've experienced
Unusual challenges you've faced
Accomplishments you're especially proud of
Service to others and why you enjoy it
What you've learned from traveling to a particular place
Unique ways you stand out from other candidates
Be specific.
Admissions committees read thousands of personal statements every year, which is why being specific on yours is important. Back up your statements with examples or anecdotes.
For instance, avoid vague assertions like, "I'm interested in your school counseling program because I care about children." Instead, point out experiences you've had with children that emphasize how much you care. For instance, you might mention your summer job as a day camp counselor or your volunteer experience mentoring younger children.
Don't forget to include detail and vibrancy to keep your statement interesting. The use of detail shows how your unique voice and experiences can add value to the college or university you're applying to.
Stay on topic.
It's natural to want to impress the members of the admissions committee who will read your personal statement. The best way to do this is to lead your readers through a cohesive, informative, and descriptive essay.
If you feel you might be going astray, ensure each paragraph in your essay's body supports your introduction. Here are a few more strategies that can help keep you on track:
Know what you want to say and do research if needed.
Create an outline listing the key points you want to share.
Read your outline aloud to confirm it makes logical sense before proceeding.
Read your essay aloud while you're writing to confirm you're staying on topic.
Ask a trusted friend or family member to read your essay and make suggestions.
Be true to your own voice.
Because of the importance of your personal statement, you could be tempted to be very formal with structure and language. However, using a more relaxed tone is better than you would for a classroom writing assignment.
Remember: admissions committees really want to hear from you . Writing in your own voice will help accomplish this. To ensure your tone isn't too relaxed, write your statement as if you were speaking to an older relative or trusted teacher. This way, you'll come across as respectful, confident, and honest.
Tips for drafting an effective personal statement.
Now that you've learned a little about personal statements and how to craft them, here are a few more tips you can follow to strengthen your essay:
1. Customize your statement.
You don't have to completely rewrite your personal statement every time you apply to a new college, but you want to make sure you tailor it as much as possible. For instance, if you talk about wanting to take a certain class or study a certain subject, make sure you adjust any specifics for each application.
2. Avoid cliches.
Admissions committees are ultimately looking for students who will fit the school, and who the school can help guide toward their larger goals. In that case, cliches can get in the way of a reviewer understanding what it is you want from a college education. Watch out for cliches like "making a difference," "broadening my horizons," or "the best thing that ever happened to me."
3. Stay focused.
Try to avoid getting off-track or including tangents in your personal statement. Stay focused by writing a first draft and then re-reading what you've written. Does every paragraph flow from one point to the next? Are the ideas you're presenting cohesive?
4. Stick to topics that aren't controversial.
It's best not to discuss political beliefs or inappropriate topics in your essay. These can be controversial; ideally, you want to share something goals- or values-driven with an admissions committee.
Polish your writing skills on Coursera.
A stellar personal statement starts with stellar writing skills. Enhance your writing ability with a writing course from a top university, like Good with Words: Writing and Editing from the University of Michigan or Writing a Personal Essay from Wesleyan University. Get started for free to level up your writing.
Article sources
1. Common App. " 2022-2023 Common App Essay Prompts , https://www.commonapp.org/blog/2022-2023-common-app-essay-prompts." Accessed January 9, 2024.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
Clearing Universities & Courses
Clearing advice.
Recommended Clearing Universities
Popular Course Categories
Course search & discover.
Start the search for your uni. Filter from hundreds of universities based on your preferences.
Search by Type
Search by region.
Recommended Universities

University of Kent
South East England · 96% Recommended

Ravensbourne University London
London (Greater) · 88% Recommended

University of Surrey
South East England · 98% Recommended
Search Open Days
What's new at Uni Compare

West London Institute of Technology
WLIoT provides students with higher technical skills that are demanded by employers, learn more here!

Surrey has been shortlisted for the University of the Year 2023 - find out more here!
Ranking Categories
Regional rankings.
More Rankings
Top 100 Universities
Taken from 65,000+ data points from students attending university to help future generations
About our Rankings
Discover university rankings devised from data collected from current students.
Guide Categories
Advice categories, recommended articles, popular statement examples, statement advice.

What to include in a Personal Statement

Personal Statement Tips
What you need to include in your personal statement.
Ready to start your personal statement, but unsure where to begin? Crafting a compelling personal statement is crucial when applying for admission to your desired course.

Your personal statement is the opportunity to show universities who you are, your ambitions and why you’re passionate about the course you’re applying for. Before you dive into writing, it’s good to understand what you should include in your personal statement to make the most of the 4000-character count.

The purpose of your personal statement
Your personal statement is there to show admissions tutors why you’d be a good student for the course you’re applying for and what sets you apart from other candidates.
University admissions tutors tend to look for similar things in your personal statement: a bit about yourself, information about your aspirations and how they link to your chosen course, why you’re interested in the course, and specific skills you already have that will support you in your studies.
What to include in your personal statement
Before diving into writing your personal statement, create a plan of what you want to include and a breakdown of the topics you want to cover. This will help you write more concisely and confidently.
A bit about you, your hobbies and interests
This is a great opportunity to introduce yourself – share information about yourself, your background and any life experiences that have shaped your interest in your course. It’s great to include information that isn’t just education-related too! Tell them a bit about your hobbies and interests beyond your studies.
This is also a great way to flex more of your skills! Many of these could relate back to your subject. For example, keen readers, you could discuss your love for a book you enjoyed recently – a great way for prospective English Literature students to show that they look at the subject beyond the classroom.
Express your passion for the subject
Of course, they want to understand why you want to apply to the specific subject and also see that you are passionate about it too. If there are any areas of the subject that sparked your interest, and you’re looking forward to exploring more, this is the perfect chance to share!
Show off your key skills
Admissions tutors aren’t only interested in your academic achievements, but also other skills you have gained that could be applied to your studies. Give examples of where you’ve used organisational skills, solved a problem or effectively communicated with someone. This will help admissions tutors see how you’d fit in among the other students on campus.
This is also a subtle way of showing your hobbies and interests. If your key skills have been best communicated in a football match, a swimming meet or in a debating society, then show how your passion for these hobbies has manifested in the use of key skills.


Share your achievements
The admissions tutor will receive your predicted grades and recommendation letters alongside your application, so don’t feel you need to share this with them in your personal statement too. Instead, focus on expanding on specific areas of your studies that you have excelled in and the different skills they’ve given you and can be applied to your chosen course.
You can also talk about any achievements. This could be educational awards you’ve won, as well as achievements outside of school.
Writing your personal statement
Now you have all the ingredients, it’s time to get writing! The structure of your statement is just like any essay. Start with a compelling introduction that grabs the reader’s attention and gives an overview of what you’ll be talking about. The majority of your personal statement with then be made up of paragraphs that discuss the specific topics outlined in your plan. To finish, round off your statement with a conclusion. Summarise the key points and show, again, your enthusiasm for applying to the subject.
Some students find that it's easier to write the introduction last. This is a better way of summarising information you already know will pop up later.
With careful thought and planning of what to include and making sure the essential areas are included will be the start of you crafting a fantastic personal statement. If you’re looking for a helping hand, our personal statement examples can help you visualise what your personal statement can look like.
undergraduate Universities
Undergraduate uni's.

Uni of Kent
417 courses

Ravensbourne

Uni of Surrey
437 courses

Uni of Roehampton
268 courses

West London IoT

Northeastern Uni
.jpg)
Goldsmiths, UOL
273 courses

Uni of Sunderland
200 courses

Uni of Portsmouth
542 courses

Queen's Uni
411 courses

Cardiff Met Uni
304 courses

Middlesex Uni
469 courses

245 courses

Uni of Chester
399 courses

Uni of East London
317 courses

Uni of Winchester
161 courses

Uni of Suffolk
109 courses

Escape Studios

Swansea Uni
780 courses

238 courses

Uni of Hertfordshire
419 courses

528 courses

Coventry Uni
445 courses

Uni of Bradford
197 courses

Uni of Leicester
267 courses

Uni for Creative Arts
323 courses

Leeds Beckett Uni
327 courses

Uni of Bedfordshire
336 courses

Heriot-Watt Uni
208 courses

Staffordshire Uni
272 courses

414 courses

Uni of Westminster

Anglia Ruskin Uni
460 courses

Kingston Uni
378 courses
,-Bristol.jpg)
UWE, Bristol
249 courses

Leeds Arts University

Uni of Essex
797 courses

Wrexham Uni
168 courses

355 courses

Uni of C.Lancashire
438 courses

Uni of Huddersfield
458 courses

Uni of Brighton
253 courses

ARU Writtle
104 courses

Bath Spa Uni
295 courses

Edge Hill Uni
243 courses

Uni of Hull

Nottingham Trent
539 courses

Edinburgh Napier
184 courses

Uni of Reading
393 courses
Want to learn more about a university?
Get your questions answered by sending them an enquiry now.
What Should Be In A Personal Statement?
Link Copied
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on LinkedIn

All about you!
Crafting a perfect personal statement is vital to enter the university of your choice. But how to make it effective? We prepared a list of the best recommendations from an expert personal statement review service highlighting what to consider and avoid for writing a brilliant essay for application.
What To Write In A Personal Statement?
Are you wondering how to write a personal statement ? The most frequent question that comes to the potential student’s mind. Here are some personal statement dos and don‘ts you should know.
1. Brainstorm and Outline Your Ideas
Very often, future students suffer because of writer’s block. And writing a personal statement becomes a big deal. Still, there is a perfect solution to overcome this challenge. Brainstorming is an ideal technique to focus and generate ideas to mention in your personal statement.
It will be more effective if you combine brainstorming and outlining. Before transforming your ideas into text, organize them into a short plan or list. This will work best if you want to keep the logical connection through the paragraphs.
If you lack ideas, EssayEdge Premier Package allows you to cooperate with editing experts from Ivy League during the brainstorming session.
One of the different personal statement dos and don’ts suggest outlining your structure. Here are the main components to include:
- Introduction (with an intriguing/eye-catching hook);
- Main Body (3-4 paragraphs or more, depending on your experience);
- Conclusion (summarising key ideas and highlighting the importance of the chosen program).
With a well-organised outline, it will be easy to maintain the flow of your text.
Wondering how to find best student accommodation? Let us take care of it for you!
Book through amber today!
2. Add Specific Examples
It’s also crucial to stay focused till the last paragraph. One of the many personal statement dos and don’ts state that you should be specific and mention only appropriate data. Thus, your experiences, skills, and background should fit the chosen program and its requirements.
You can also look through personal statement samples to find out what a perfect application essay should include.
In addition, you need to emphasize your experience and strong points by adding specific examples. For instance, tell about a particular event in your life and how it affected your personality. The same with the experience: together with the description, specify what skills you’ve got and how they will be useful during your future education.
3. Proofread Before Submitting
Unfortunately, applicants often underestimate the power of proofreading. Of course, the content plays a great role. But what if the quality of this content is not good enough? Even minor mistakes in your personal statement can create a bad impression and damage your chances of entering the top prestigious university.
Still, if you are unsure of your paper's quality or want to check that everything is OK, an admission editing service like EssayEdge will be helpful. It is a legal service that cooperates with former students and even profs from the Ivy League. Their editing helps students improve their admission papers and get accepted to the best universities worldwide.
4. Highlight Your Unique Experiences
Your personal statement is an opportunity to showcase your unique background, experiences, and skills. Try to identify what sets you apart from other applicants and emphasize those qualities. Think about what makes you special and how you can contribute to the program or institution you are applying to.
5. Show Your Passion And Motivation
Admissions committees want to see that you are genuinely interested and motivated to pursue the program or field you are applying for. Use your personal statement to demonstrate your enthusiasm and dedication for the subject matter. You can talk about relevant experiences that sparked your interest, or discuss your long-term goals and how the program will help you achieve them.
What Not To Write In A Personal Statement?
After you’ve discovered some tips for enhancing the quality of your essay, it’s time to look through some personal statement dos and don’ts. So, what not to write in a personal statement to not fail your admission?
1. Don’t Rush It
It’s not a good idea to wait until the last minute. This is one of the most common personal statement dos and don’ts as it requires a lot of effort and concentration. This essay is your opportunity to represent your candidacy from the best possible perspective. And you need to catch the committee's attention to win this race.
If to write a personal statement in a hurry, you may miss many important points. Moreover, you’ll have no time to re-read the essay to ensure it highlights your strong sides and will help you stand out from the crowd of competitors.
Before submitting your application, we recommend proofreading it and checking out several factors:
- Does your essay intriguing/interesting enough for you as a reader?
- What is a personal statement’s main idea? Is it easy to catch it?
- Whether it presents your candidacy as the most fitting one or not?
- Can you see the connection between your experience and the chosen program?
- How strong is your motivation? Does the personal statement convey your passion for joining the desired institution community?
2. Pretending to Be Someone Else
Clichés are another frequent mistake among applicants. The matter is that the potential candidates are worried they won’t make their personal statements eye-catching. Thus, they prefer to write what the admission committee expects to read. Still, this technique won’t work if you want to be impressive.
Your personal statement should be “personal” and unique. Do not try to pretend to be someone else. Just find out the best sides of your personality and show them to the officers.
3. Absence of Personal Motivation
Your personal statement is a chance to demonstrate your candidacy and show your drive and passion for studying the chosen program. Unfortunately, applicants often need to remember to write about the reasons that made them choose a particular educational institution.
You should make the committee members feel the same passion that drives you to follow your dream. Forget about doubts and fear to express your feelings in your personal statement. But there is one thing to remember—you need to do it appropriately.
Now you know some secrets of writing a perfect personal statement that will increase your chances of entering your dream university. Our tips will be useful and help you create a real masterpiece.
4. Avoid Controversial Or Sensitive Topics
While it's important to be honest and authentic in your personal statement, it's also important to remember that the purpose of the statement is to convince the admissions committee that you are a good fit for the program or institution. Avoid controversial or sensitive topics that might offend or alienate the reader. This could include political or religious views, controversial social issues, or personal details that are too private or inappropriate.
5. Don't Repeat Your Resume Or CV
Your personal statement is not the place to simply list your achievements and qualifications. Admissions committees have access to your resume or CV, so there's no need to repeat that information in your personal statement. Instead, use the personal statement to provide context and meaning to your experiences and qualifications, and explain how they have prepared you for the program or institution you are applying to.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a personal statement, what should be included in a personal statement, how long should a personal statement be, what are some tips for writing a strong personal statement, when should you start writing a personal statement.
Your ideal student home & a flight ticket awaits
Follow us on :

Related Posts

A Simple Guide To Percentage To GPA Conversion
.jpg)
Step-by-Step Guide On Transferring Colleges

Top 11 PhD Scholarships in the USA for 2024-25

amber © 2023. All rights reserved.
4.8/5 on Trustpilot
Rated as "Excellent" • 4700+ Reviews by Students

Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, what should a personal statement include.
I'm working on my personal statement for college applications and I'm not sure what exactly I should include. Any suggestions on what kinds of things should be in my personal statement and how to make it stand out?
When crafting your personal statement, the key is to showcase your individuality and highlight a story or experience that is unique to you. Fortunately for you, CollegeVine's blog contains extensive guidance on how to do that: https://blog.collegevine.com/how-to-write-the-common-application-essays/. Additionally, here are some more general suggestions to help make your personal statement stand out:
1. Begin with a strong hook: Your opening should grab the reader's attention and set the stage for your story. Consider a vivid anecdote, a provocative question, or an interesting fact about yourself.
2. Focus on a defining experience: Choose one interest, challenge, or accomplishment that has significantly shaped your life, personal growth, or aspirations. Ideally, it should reveal something that your academic and extracurricular activities don't already showcase.
3. Be authentic and reflective: Write about your genuine thoughts, feelings, and reactions to the experience, and explain how it helped shape your perspective, beliefs, or ambitions. Admissions officers value students who are open, humble, and self-aware.
4. Demonstrate your strengths: Use your personal statement to showcase characteristics that set you apart and might not be obvious from the other components of your application, such as resilience, creativity, empathy, or critical thinking. Remember to show, not tell, by providing specific examples that illustrate your qualities.
5. Provide context: Help your reader understand the background and circumstances that contributed to your growth and why the experience was meaningful to you. This context might include relevant cultural, personal, or historical events or influences.
6. Address your goals and ambitions: Explain how the experience you described has influenced your academic or career aspirations, or connects with your intended major or the college's values. Show how your chosen path aligns with your skills, interests, and personal growth.
7. Write with clarity and style: Your personal statement should be well-organized and easy to understand, with a clear narrative flow. Make sure to use strong, descriptive language and vary your sentence structure to avoid monotony. Proofread carefully for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
8. Revise and edit multiple times: Great personal statements usually go through several drafts. Read your essay out loud, ask for feedback from teachers, counselors, or peers, and take the time to rework sections that need improvement. If you're looking to get a more objective set of eyes on your essay, also remember that CollegeVine offers both a free peer essay review tool and paid reviews by expert college admissions advisors. Sometimes, having someone who doesn't already know you read your personal statement can give you a clearer sense of how it'll come across to admissions officers.
Overall, your personal statement should be a reflection of who you are. Be honest and genuine, and let your unique voice shine through. This is your opportunity to make a lasting impression on admissions officers and increase your chances of standing out among other applicants. Happy writing!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
Testimonials
Free Resources
PrepScholar GRE Prep
Gre prep online guides and tips, how to write a stand-out personal statement for grad school.
If you’re applying to graduate school, you’ll likely need to write a personal statement. But what exactly is a graduate school personal statement? And what should you write about to give yourself your best shot at admission?
In this guide, we teach you how to write a personal statement for grad school, step by step. But first, let’s go over how the personal statement differs from the statement of purpose as well as what schools look for in a great graduate school essay.
What Is a Graduate School Personal Statement?
A graduate school personal statement is an admission essay that typically focuses on your personal reasons for wanting to enter a grad program and particular field of study. Essentially, you must tell the story of who you are and how you developed your current research interests.
So is a personal statement for graduate school the same thing as a statement of purpose? Well, not always (though it can be). Here are the general distinctions between the two essay types:
- Statement of purpose: A formal essay that summarizes your academic and professional background, research interests, and career goals. In this essay, you’ll usually explain your reasons for applying to grad school and why you believe the program is a good fit for you (as well as why you’re a good fit for it!).
- Personal statement: A less formal essay that focuses on your passion and motivation for wanting to enter your chosen field and program. This statement is typically more flexible than the statement of purpose, with a bigger emphasis on storytelling. Schools often encourage applicants to discuss (relevant) challenges in their lives and how they’ve overcome them.
Both the graduate school personal statement and statement of purpose are usually anywhere from one to three double-spaced pages long, depending on the program you’re applying to.
Below is a chart comparing the personal statement and statement of purpose:
Usually, the personal statement and statement of purpose are considered two different graduate school essay types.
But this isn’t always the case. While some schools consider the personal statement and statement of purpose two distinct essays, others use the names interchangeably.
For example, Michigan State University’s College of Engineering considers them two distinct essays, while The Ohio State University uses “personal statement” to describe what is essentially a statement of purpose.
Many schools require just one essay (and it’ll usually be the statement of purpose, as it’s the more academic one). But some, such as the University of Michigan , ask for both a personal statement and statement of purpose, while others, such as Notre Dame’s Creative Writing MFA program , want an essay that combines the features of both!
Ultimately, the type of graduate school essay you submit will depend entirely on where you’re applying.

What Do Schools Look For in a Personal Statement?
Many grad schools require a personal statement in order to learn more about you, your interests, your struggles, and your motivations for wanting to enter a field of study. Through this essay, schools can get to know you on a deeper, more intimate level and learn about you in ways they can’t through transcripts and letters of recommendation alone.
But what specifically do universities look for in a great personal statement for graduate school? Here are some of the most important elements to include in your essay.
A Compelling Story
First off, your personal statement must tell a story. After all, this essay is basically your autobiography: it introduces who you are, your interests and motivations, and why you’ve decided to apply to grad school.
Unlike the statement of purpose, the personal statement should focus mostly on your personal history, from your failures to your triumphs. All experiences should tie back to your field or research area, emphasizing what you’ve learned and what this means in terms of your potential as a grad student.
Since you’re talking about yourself, be conversational in your storytelling: use an authentic voice, open up about your experiences, and maybe even throw in a joke or two. Though you’re still writing an essay for school, it’s generally OK to be a little more informal here than you would in a statement of purpose.
That said, there are a couple of things you absolutely shouldn’t do in your personal statement.
- Open your essay with a quotation. Professors have heard the quotation before and don’t need (or want) to hear it again. Plus, quotations often take up too much space in an already short essay!
- Use clichés. Think of unique ways to tell your story and grab readers’ attention. Schools want to see you can be creative yet honest about yourself, so avoid clichés like the plague (see what I did there?).
- Get too creative. Your goal is to look like a serious, committed applicant—not a wacky risk taker—so write clearly and avoid any unnecessary distractions such as images, colors, and unprofessional fonts.
Most importantly, remember that your graduate school personal statement should focus on your successes. Try to use strong, encouraging words and put positive twists on difficult experiences whenever possible. It’s OK to mention your setbacks, too—just as long as you’re discussing how you ultimately overcame (or plan to overcome) them.
Inspirations for Your Research Interests
Schools don’t only want to see clearly defined research interests but also why you have these particular interests. While the statement of purpose elaborates on your professional goals, the personal statement explains what personally motivated you to explore your interests.
For example, in my personal statement for a Japanese Studies MA program, I wrote about my hot-and-cold relationship with the Japanese language and how a literature class and a stint abroad ultimately inspired me to keep learning.
Don’t make the mistake of going way back to the beginning to start your essay. Many applicants open their statements with something along the lines of “I fell in love with psychology when I was ten years old” or “It all started when I was in high school.” But these broad statements lack the creativity and zest needed to secure an acceptance, so avoid them at all costs.

Your Motivation for Applying to Grad School
Your statement of purpose should explain why grad school is a practical next step in your professional life—but your personal statement should focus on what personally motivates you to take this step.
Generally, schools want answers to the following questions:
- Why is grad school an appropriate step for you now?
- How will a graduate degree help you achieve your goals?
- Why didn’t you apply to grad school earlier (if you took time off after undergrad)?
- Were there any struggles or problems you faced that prevented you from applying to grad school before?
Be honest about why you’re applying, both to grad school and the program in particular. In my graduate school essay, I discussed how my passion for Japanese literature and desire to translate it inspired me to seek advanced language training at the graduate level.
Strong Writing Skills
A great personal statement shows that you can write cogently and coherently. After all, strong writing skills are imperative for success as a grad student!
So in addition to telling a good story, make sure you use correct grammar, spelling, punctuation, and capitalization. Use paragraphs to break up your thoughts, too. Because the personal statement is slightly less formal than the statement of purpose, feel free to play around a little with paragraph form and length.
Also, remember that good writing doesn’t necessarily equal big words. You’re writing about yourself, so use words that come naturally to you. Don’t grab a thesaurus and start throwing in a bunch of high-level vocabulary wherever you can; this will make your essay sound less authentic, not to mention stiff.
On the other hand, don’t get too colloquial. You’ll lose respect if you start inserting conversational words such as “gonna” and “gotta.” Therefore, look for the middle ground and write from there.
Want to improve your GRE score by 7 points? We have the industry's leading GRE prep program. Built by world-class instructors with 99th percentile GRE scores , the program learns your strengths and weaknesses through machine learning data science, then customizes your prep program to you so you get the most effective prep possible.
Try our 5-day full access trial for free:
Explanations for Any Hiccups in Your Academic Career
Lastly, the personal statement gives applicants a chance to explain any problems or changes in their academic histories, such as low grades or gaps in education.
Because transcripts and resumes are severely limited in what information they give, schools often use the personal statement to understand your reasons for abrupt changes in your resume and/or transcripts, and to see how you’ve overcome these barriers in your education (and life).
Essentially, a personal statement equalizes the playing field by giving you full rein to explain yourself and emphasize your success over any struggles you’ve had.

How to Write a Personal Statement for Grad School: 9-Step Guide
The personal statement is a fiercely important part of your grad school application. In this section, we teach you how to write a memorable personal statement for grad school so that you’ll have a better shot at getting accepted.
Step 1: Start Early
Personal statements (actually, grad school applications in general!) take a lot of work, so don’t put off writing your essay until the week before your deadline. Rather, try to start working on your essay at least two or three months before your application is due.
You might want to give yourself more time to write it if you’re currently in school or working a demanding job. Setting aside more time lets you work on your graduate school essay routinely without having to squeeze in too many hours each week.
If you only have a month or less until your application deadline, get started on your essay pronto! Though it’s possible to write a personal statement quickly, I recommend carving out more time so that you can put more thought and effort into what you write and how you present yourself. (Doing this also gives others more time to edit your essay for you! We’ll cover this more in later steps.)
Step 2: Read the Instructions
Perhaps the most important step is to read your program’s instructions for the personal statement. Not following these instructions could very well result in a rejection, so always read these first before you start writing! Most programs put their personal statement instructions on their application materials pages.
Your program should give you the following information:
- What type of content your personal statement should include or generally focus on (you might even get an actual prompt to answer!)
- How long your statement should be
- What type of heading, if any, you must include on your statement
- How to save and submit your statement (e.g., .docx, PDF, etc.)
For example, let’s say you’re applying to the History PhD program at UC Berkeley . In this case, your personal statement can’t exceed 1,000 words (three double-spaced pages). You must also answer this prompt :
Please describe how your personal background informs your decision to pursue a graduate degree. Please include information on how you have overcome barriers to access in higher education, evidence of how you have come to understand the barriers faced by others, evidence of your academic service to advance equitable access to higher education for women, racial minorities, and individuals from other groups that have been historically underrepresented in higher education, evidence of your research focusing on underserved populations or related issues of inequality, or evidence of your leadership among such groups.
On the other hand, if you were to apply for an MS in Mining, Geological, and Geophysical Engineering at the University of Arizona , your personal statement would follow these parameters:
Your personal statement is an opportunity to sell yourself, in terms of your research interests, research experience and research goals. Unless you have extensive research experience, most personal statements should be about two single-spaced pages. Your writing should be clear, concise, grammatically correct and professional in tone. You may convey some personal experiences that have led to your current interests or that make you a particularly promising candidate.
Clearly, grad programs can approach personal statements quite differently. Some schools consider them the same as statements of purpose and want a formal focus on academic and research interests, while others want applicants to explain more informally the challenges they’ve overcome to get to this point.
Simply put, follow your program’s directions exactly in order to give yourself your best shot at admission. And if any part of the instructions is unclear, don’t hesitate to contact your program!
Step 3: Figure Out Your Angle
Your “angle,” or focus, in your graduate school personal statement will depend on a few key factors:
- What your grad program wants you to write about
- Your field of study and research interests
- How much experience you have in your field
As I mentioned in step 2, it’s extremely important to read the personal statement instructions for your program. Many times these guidelines will tell you what to include in your essay, thereby clarifying what your overall angle needs to be.
Let’s look back at the example we used above for UC Berkeley’s doctoral program in history. If you were applying here and came from a low-income family, you could discuss how you’ve overcome these financial challenges in your life to get to where you are today.
No matter the prompt, you’ll need to discuss your research interests (to some degree) in your personal statement. How much you talk about your interests, however, will depend on whether you have to submit a separate statement of purpose. If so, you can focus less on your research plans and more on your passions and motivations for applying.
On the other hand, if your personal statement is essentially a statement of purpose, dive deep into your research interests—that is, be specific! For example, those applying to English lit programs should think about the works, eras, and writers they want to study, and why.
More broadly, though, try to answer the question of what you hope to accomplish, either during or after the program. Is there any particular project you want to do? Skills you want to improve? Field you want to break into?
Finally, always choose a positive angle. Use affirmative words and phrases to highlight both your successes and overall enthusiasm for the program.
Step 4: Ask Yourself, “Why This Program? Why This Field?”
Although the statement of purpose usually answers this question directly, you’ll likely need to address this in your personal statement as well—ideally, with a less academic and more conversational tone.
As you brainstorm, try to come up with answers to the following questions:
- What goals or experiences led you to apply to this program?
- How will this program help you grow on a personal level?
- What made you interested in this field? Why do you want to study it more?
- What are your research interests? How did you develop these interests?
- Are there any particular professors you wish to work with?
Step 5: Make an Outline
Now that you’ve brainstormed some ideas, it’s time to start outlining your essay.
Want to improve your GRE score by 7+ points?
Check out our best-in-class online GRE prep program . We guarantee your money back if you don't improve your GRE score by 7 points or more.
PrepScholar GRE is entirely online, and it customizes your prep program to your strengths and weaknesses . We also feature 2,000 practice questions , official practice tests, 150 hours of interactive lessons, and 1-on-1 scoring and feedback on your AWA essays.
Check out our 5-day free trial now:
How you choose to outline your statement is up to you. Some people like drawing bubble charts for organizing their thoughts, whereas others (like myself) prefer to write a list of rough ideas in the general order they want to present them.
Even if you’re not sure whether you want to include something, just add it to your outline anyway. You can always cut it out later as you draft and edit.
Step 6: Draft Your Essay
It’s now time to start writing! Once you’ve got your outline ready, work on expanding what you’ve written into full-fledged paragraphs.
In the beginning, it’s OK to write down anything you feel is relevant, but as you continue to draft, try to look for any extraneous information you can chop.
Remember, most personal statements will be short— usually one to two double-spaced pages—so you don’t want to risk exceeding your program’s word limit. Schools want to see that you can tell a story concisely yet effectively.
If you’re having trouble coming up with a way to open your statement, try skipping around as you draft. Go ahead and jump to a paragraph you have more ideas for—it’s perfectly OK! Just make sure you start to tie all of your ideas together the closer you get to finishing your draft.
On a related note, be careful not to copy any material from your statement of purpose (if you’re required to submit two separate essays). These statements may share a little overlap but should still focus on different aspects of your (academic) life, accomplishments, and goals.

Step 7: Get Feedback
Once you finish drafting, give your essay to people you trust for feedback. This could be a parent, friend, sibling, or mentor (such as a former or current professor).
Ask your editors to give you specific feedback on what you can change, both stylistically and technically, to make it more impactful. Ideally, they’ll also note any unclear, awkward, or redundant ideas/phrases and will offer you helpful suggestions for improvement.
If you’ve written a separate statement of purpose, see whether your editors are willing to check that essay over as well so that you can ensure there isn’t too much overlap between the two.
Step 8: Revise & Edit Your Essay
Once you get feedback, revise and edit your personal statement using your editors’ comments as a guide.
For example, if your editors told you your essay lacked detail, look for places in your writing where you can be more specific and that are likely to have a strong impact on the admission committee.
As you revise, keep an eye out for any awkward sentences or extraneous information. Personal statements are usually pretty brief and you don’t want to accidentally exceed the word limit. So when in doubt, take it out!
Step 9: Proofread
The final step is to proofread your draft. Start by using your computer’s spell check function to quickly find any glaring typos and grammatical errors.
Then, proofread your essay one sentence at a time. Since it’s easy to miss errors in your own writing, I recommend editing your essay from back to front (i.e., from the last sentence to the first sentence). Doing this prevents you from glossing over words and lets you pinpoint punctuation, spelling, and grammatical errors more easily.
In addition, check that you have page numbers on each page (if required—though I suggest adding them regardless) and a proper heading (again, if required) that meets the requirements of your program.
Before you submit it, see if you can get someone else (preferably one or all of your editors from step 7) to look over your final draft as well. If anyone spots a problem with your essay, go back to step 8. If you get all thumbs ups, read over your statement one last time and then turn it in without looking back! (Seriously, don’t read it again or you’re going to want to change something.)

The Key to a Great Graduate School Personal Statement
The personal statement is an essential part of your grad school application. Like the statement of purpose, it highlights your research interests, experiences, and goals.
But more importantly, the personal statement showcases your unbridled passion for your field, lets you reflect on challenges you’ve faced (and subsequently overcome), and answers the overarching question of why you want to attend grad school.
A great graduate school personal statement will normally include most or all of the following elements:
- A compelling story
- Inspirations for your research interests
- Your motivation for applying to grad school
- Strong writing skills
- Explanations for any changes or problems in your academic career
Above, we walked you through how to write a personal statement for grad school. To recap, here are the nine steps to follow:
- Start early—at least two or three months before your application is due
- Read your program’s instructions for the personal statement
- Figure out your angle by brainstorming ideas
- Ask yourself, “Why this program/field?”
- Make an outline using charts, a list, etc.
- Draft your essay
- Get specific feedback from multiple editors
- Revise and edit your essay
- Proofread (and get other people to proofread it, too!)
What’s Next?
Need to write a statement of purpose, too? Waste no time! Our expert guide offers tons of tips to help you come up with a statement of purpose that’s certain to impress admission committees.
Do your schools require a CV or resume? If you’re totally lost on where to begin, read our guides to learn how to put together a great CV or resume for grad school. And for extra help, check out our four original CV and resume templates !
What do you need to submit for your grad school application? Get the scoop on what kinds of materials you’ll need to prepare when applying to grad school .
Ready to improve your GRE score by 7 points?
Author: Hannah Muniz
Hannah graduated summa cum laude from the University of Southern California with a bachelor’s degree in English and East Asian languages and cultures. After graduation, she taught English in Japan for two years via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel. View all posts by Hannah Muniz

ON YOUR 1ST ORDER
What Should A Personal Statement Include?
By Laura Brown on 21st September 2020
Writing a personal statement is creating a hook which enraptures the reader and makes the prospect read it till the end. It is a part in which you tell about yourself in detail considering the field and courses you applied for.
What Is A Personal Statement?
A personal statement which is also called as an admission or application essay is understood as the personal summary given to prospective organisations which help you stand out from the rest. To some people, the personal statement is more like a personal introduction submitted to a selection committee. Generally, a personal statement should have 500-600 words .
A personal statement is a necessary document to be submitted at the time of admission with university applications. So, what should a personal statement include? Every student must know things to include in a personal statement.
Generally, it includes a picture of you as in a written portrait. It is basically an invitation for the reader to know about you and how you are a perfect fit for a particular field of study. Moreover, it should give an idea about your priorities and judgement and lastly your story.
Do You Know What Should A Personal Statement Include?
Are you seeking for what to include in a personal statement for uni or what to include in a personal statement CV, keep reading, you are on the right page.
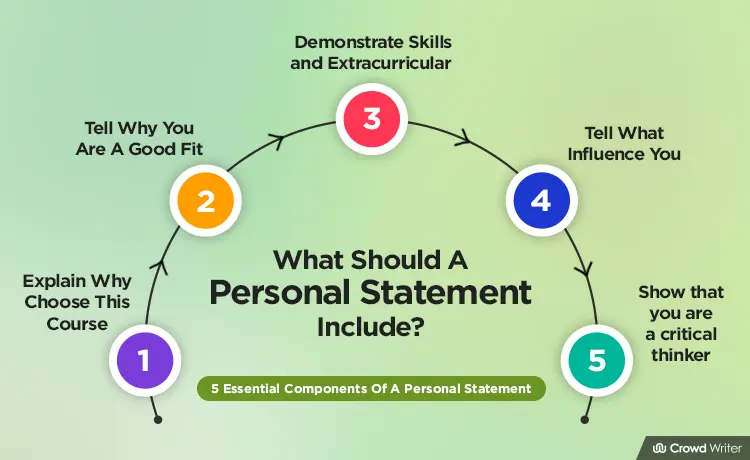
5 Things To Include In A Personal Statement
Here is a list of five things every student should include in a personal statement.
1. Explain Why To Choose This Course
A personal statement is your passport. So imagine you get the customisation of the passport, do it in such a way that it goes to the point. Give your readers an idea of why you are choosing this course, what your desires are, and why you will be a good fit in this department.
Make them aware with your aspirations, and this is the first component of your question what should a personal statement include.
2. Tell Why You Are A Good Fit
It is a part which needs much of your focus because it describes why you want to pursue it and how your existing skills and abilities would help you. Talk about your academic score, your subject and field of interest, your leadership skills, and other things you are good at.
Explain why you will be a good fit for the program and detail almost everything that can lift your profile. This is another addition in what to include in a personal statement for uni.
3. Demonstrate Skills & Extracurricular
Being good at academics is just a single factor. Another addition to the collection is about your skills, social life, and extracurricular activities. If you add this in your statement, the admission counsellor will be able to see you as an applicant who can contribute to the greater community of students.
4. Tell Your Influences
Telling the institute what inspires you or what influence you to go on this track is another fact. Create a story which tells the reader as to what your aim is to be as you decide to get into this field or profession.
Tell the admission officer which personalities influence your life, and by having this, you can have a high impact in choosing the course. This component can also be added for the people who want to know what to include in a personal statement CV. But if you are not familiar with this document, you should consult Crowd Writer UK.
5. Demonstrate Your Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking is essential whether you’re writing a personal statement or wondering how to write a conclusion for an essay . Critical thinking is understood as the analysis of facts to form an opinion or judgement.
Tell the admission officer about your rational, sceptical, unbiased analysis, or evaluation of evidence which proves that you have the capability to think out of the box.
Don’t worry if you lack critical thinking skills, because it can be improved over time. Contact the experts at Crowd Writer and buy personal statement writing service . The pros here exactly know what should a personal statement include and offer the best services at low prices.
In conclusion, be sure that you check all the components discussed above for transcending while writing your statement for academic or employment purpose.
No matter whether you are looking for a research proposal writing service or want to know how to structure a literature review , Crowd Writer is the answer to all of your problems. So why wait? Contact the pros today and leave all your worries behind.

Laura Brown, a senior content writer who writes actionable blogs at Crowd Writer.
- Telephone Tel: +44 (0) 20 7499 2394
- Email Email: [email protected]
Strategic Guidance
- Private Oxbridge Consultation
- International Oxbridge Consultation
- Postgraduate Applications Guidance
- Book a Complimentary Call
Comprehensive Support
- The Premier Service
- Oxbridge Preparation Course
Targeted Support
- Oxbridge Personal Statement Support
- Oxbridge Admissions Test Support
- Oxbridge Interview Preparation Support
Application Guidance
- ‘Aspiring to Oxbridge’ School Talk
- Teacher Training Workshop
- Individual Guidance Consultations
Personal Statement Support
- Personal Statement Group Workshop
- Personal Statement Consultations
Admissions Test Preparation
- Admissions Test Day
- Admissions Test Course
Interview Preparation
- Interview Preparation Day
- Interview Preparation Course
Free Library
- Oxbridge Interview Resources
- Admissions Tests Resources
- Student Library
- Teacher Library
- Keeping You Current
- Webinar Library
Our Publications
Course reports, oxbridge applications.
- Become A Tutor
- Our Offices
- Dukes Education
News & Press
- Widening Access
- Publications
- Sign In Register
- Sign In Register
12 Personal Statement FAQs and answers!
There is often a large amount of confusion surrounding how to write personal statements, especially when it comes to oxford and cambridge and other top research universities., every year, we have thousands of students ask us what qualities go into making a successful personal statement., to help, we have broken down this question into 12 of the most frequently asked questions our prospective students ask when they are trying to draft their personal statements., 1. how do i write the introduction.
Introductions are often disappointingly generic. To help you achieve more specificity and concision, the best way to write a good personal statement introduction is to complete the rest of it first. When you are getting started on the first draft, it can be overwhelming to begin at a blank page, but discussing your achievements and interests – relevant to the courses and universities you are applying to – can help you clarify what your motivation to study the subject really is. Then you can come back and explain the reasons behind your passion for Mathematics, Anglo Saxon literature or your subject of choice.
2. How many books should I talk about?
This question can be answered in various ways depending on the subject you intend to study. Clinical scientific subjects will not require many book mentions, however, Arts and Humanities personal statements for Oxbridge see a great benefit from discussing at least two books in detail, with further reading mentioned.
It’s also important to remember that academic sources shouldn’t be only limited to books. A well-rounded personal statement discusses specific theories, touches on lectures you have attended or essays and articles you have read to gain a better understanding of specific academic points rather than a general discussion. One of the biggest pitfalls students fall into when drafting Oxbridge personal statements is getting stuck waffling about general points around a subject of interest. To avoid getting stuck in general chatter, try to use only specific examples in your personal statement.
Centrally, admissions tutors want to see that you know you are getting yourself in for. Only reading a couple of books from their introductory list will therefore not tantalise them; try to follow your interests in a bit more depth and look at readings and ideas which are representative of degree level material.
3. What do I do if I have no work experience?
Referencing work experience in your personal statement is dependent on the subject you intend to study. A rule of thumb is to ask yourself whether you think an academic in the faculty you are applying to will think your work experience was relevant for the course. If you are applying to study History, for example, your two-weeks at an accounting or law firm organising files will be of little interest.
For Medicine, work experience is integral not only to the application process but will help build a strong personal statement. When applying to a vocational subject such as Medicine, where possible you should always ensure you are able to reference at least one work experience placement held. If you don’t have any work experience and your personal statement is due, make sure to arrange some and refer to this in the future tense in your personal statement when talking about your upcoming placement.
Work experience can also be useful for other more vocation-leaning subjects, such as architecture and engineering. More widely, doing work experience is extremely useful to help you begin thinking about what you might want to do with your career, and can build highly useful skills, but, unless it is relevant to the course content, it is unlikely to proffer you any credit for university admission.
4. How long should I talk about extra-curricular activities?
Leading research universities are looking for your potential to succeed on the course you are applying for. Nevertheless, two applicants who seem academically matched might be distinguished from each other by their ability to balance their time with several other things. Do include what you do outside of academia, then, but keep non-relevant activities mentioned to a minimum rather than an exhaustive list. This might mean sacrificing some of the things you do outside of your course and focus on those few things you do most often, or to the highest level. (N.B. Your reference might be able to discuss some of your extra-curricular activities too, and you don’t want to overlap this material).
What you do mention, try to link to your subject. This might be easy, as with an English literature student who has directed lots of theatre, or less easy, such as a maths applicant who plays the violin to a high level. Nevertheless, making these links convincingly can bring originality and creativity to your statement.
5. How can I tailor it for different courses?
Subjects like HSPS at Cambridge or Classical Archaeology and Ancient History at Oxford might make it tricky to tailor your statement for different courses. Oxford and Cambridge are very understanding of this, and specific guidance can usually be found on faculty websites about their expectations.
However, as a rule of thumb, focus on the areas of convergence between the courses you are applying for. If these differ in title, then avoid stating the title of the course in your statement and instead refer to the disciplinary area or focus instead. This involves: a) making sure the courses you are applying for are sufficiently similar to give you a chance of doing this, and b) doing your research on the course content and options so that you are covering the appropriate material.
This research stands even if you are applying for the same titled course everywhere. English, for example, is taught very differently at Oxford to Bristol, and focusing on an interest which does not feature in either course will result in your application being put aside.
Doing this research early can also help you to direct your reading and research to build material for your personal statement which speaks to all your choices.
6. How should I talk about my other A-level subjects?
Lots of students are told to discuss the skills they have gathered from their A Level subjects, but we caution around this; your UCAS application includes a full list of A-Level subjects studied, and your school reference will discuss your A-Level abilities. Talking about the time management or analytical skills you gained from studying history, and the logical skills you gained from physics, can therefore come across as ‘fodder’ which could have already been inferred.
You can, however, talk about how other subjects provide further insight into the course or subject you’d like to study. For example, students who have taken Classics that intend to study English Literature at university can talk about translating texts, such as the Aeneid, and how this helped gain a greater understanding of classical influence in modern English Literature. As with the whole statement, the more specific you can make this, the better.
7. How long should it be?
This is an easy one. Your personal statement should be at most, 4,000 characters or 47 lines, whichever you meet first. Although it can be shorter, we strongly recommend taking full advantage of the available space. Ideally, you want your first draft to be much longer so you can cut down and edit your personal statement to be shorter, rather than using general waffle or struggling to fill the space.
Cutting it down is usually relatively easy, but it might take an outside eye to see the ‘wood from the trees’. Any non-relevant, generic material, anything which is likely to be in many other statements, and frilly, decorative language or repetition can all be chopped down.
If you find you are struggling to reach 4,000 characters or 47 lines, you probably need to revisit the body of your personal statement and discuss more subject-specific content. You may, alternatively, need to go back to the research and reading phase of writing.
8. What formatting should I use?
The final version of your personal statement will be submitted in a digital form with no formatting options, so there is no need to worry about formatting. That means you won’t have to decide what font or colour to use and there is no need for styles such as bold or italics. If you do include these, they won’t appear in the submitted version.
Your school should already have discussed best practice for writing your personal statement but as a reminder – do not write your statement draft in the real form! As with any content that is going to be submitted digitally, you should write it in a word document first (Microsoft Office, Google Docs, Pages, etc) where you can save a copy locally to your computer (and back-up regularly). This way, you can avoid the devastating loss of your best statement draft due to an accidental refresh or the internet dropping out.
9. How many paragraphs should it be?
There is no set-in-stone rule for the number of paragraphs but generally, a well-structured personal statement will be broken up into five or six paragraphs and be easy to read. Admissions tutors will need to comprehend your statement very quickly, so structure with this in mind.
A frequently-successful structure follows this pattern: an introduction, two to three course/subject-specific main paragraphs, a penultimate paragraph detailing your extracurricular activities, and then a final summary paragraph. The final two paragraphs are sometimes pushed together to form one.
10. Will they find out if I slightly…exaggerate my talents?
Yes! Your personal statement for Oxford and Cambridge should be considered a springboard for your interview and you could and should expect to be questioned about any single detail of it. At Oxbridge Applications, every year, we have students that approach us in January who are upset that their Admissions Tutor spent 20 minutes focused on a certain author when “I only mentioned that book briefly as a side note”.
However, you DON’T need to be an expert, or even particularly knowledgeable, about a particular idea or author to mention it in your statement. If you are questioned about an aspect of an author’s work you have mentioned which you are unsure about, then be intellectually honest and say so, but try your best to have a go given what you already know about them or similar authors/ideas.
This is not only the case for authors/books mentioned, but also if you put forward a highly ambitious or critical view in your statement. If you want to argue that Marx was totally wrong, then you better be ready to defend your view in a nuanced way. The bottom line is: stay intellectually honest and err on the side of modesty; academics tend to become less rather than more sure about the ‘truth’ the further they delve into their subject matter.
11. How many teachers should check my personal statement?
Preferably, you will get your drafted personal statement checked by at last two of your teachers or guidance advisers. One should be subject-specific who can check over the content of your paragraphs and the other can be from a different department to provide feedback on grammatical accuracy and quality of the statement.
Getting guidance from second and third parties can be useful ensure you retain editorial control, and that your voice and taste runs through the statement. If you try to include everyone’s different opinion, you can quickly end up with a jumbled statement that no longer reflects on you and your communication style and strengths.
Make sure you leave plenty of time between completing your first draft and the Oxbridge personal statement deadline ensuring you have time for others to check it over and you can make changes as necessary.
12. Should I start my personal statement with a quote?
‘Most people are other people. Their thoughts are someone else’s opinions, their lives a mimicry, their passions a quotation.’ Oscar Wilde.
How much have you learned about me from reading Wilde’s words?
Quotes are used each year by applicants who end up getting offers from top universities, including Oxford and Cambridge. It’s not necessarily going to bring your application to an end. Quotes are also awarded marks in certain A Level subjects, if you have taken the time to remember them and give them a bit of context.
However, your personal statement gives admissions tutors the chance to hear your voice, and to get a sense of what you might be like as a student on their course. By definition , using a quote – i.e. someone else’s words – is not personal. It is therefore preferable to avoid using a quote unless it’s absolutely essential. Using a quote doesn’t make YOU sound more interesting.
Before you decide to use a quote, think long and hard. If you would really like to use a quote, try to make it as pithy and concise as possible, and make sure it elevates and builds on what you are saying; that it expresses something you couldn’t have otherwise expressed on your own. (Also, by ‘quote’, we are not talking about specific concepts or theories – these are absolutely fine to include.)
Driven by 20 years of research and first-hand experience in guiding thousands of applicants, our consultations provide an honest and detailed assessment with guidance on individual personal statements.
If you would like to speak to one of our oxbridge-graduate advisors about your own personal statement, contact our oxbridge advising team on +44 (0)207499 2394 , email at [email protected] , or request a callback to discuss your situation., explore oxbridge applications, request a callback, application resources, related content, the autumn ahead, how to choose your oxbridge college, oxbridge applications are proud to be working with the sunday times parent power top schools.
Our Oxbridge-graduate consultants are available between 9.00 am – 5.00 pm from Monday to Friday, with additional evening availability when requested.
- Tel: +44 (0) 20 7499 2394
- Email: [email protected]
Oxbridge Applications, 14 – 16 Waterloo Place, London, SW1Y 4AR
- Private Oxbridge Application Consultant
- Oxbridge Personal Statement Support Package
- Oxbridge Mock Interview Preparation and Support
- Personal Statement Workshop and Checks
- Schools Mock Interviews – Online and In-School
- Teacher Training Workshops – Online and In-School
- Oxbridge Preparation Days – Online and In-School
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Safeguarding & Child Protection
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Company Registration Number: 3757054
Recently Updated Blogs
Blog exercising self-care during school or university exams, blog our experts’ tips for a productive easter holidays, blog changes to cambridge a-level requirements for 2025 applicants, blog how will my gcses impact my university applications, blog which a-levels should i take, choosing a college, a slippery question, added to cart.

Your Trusted Advisors for Admissions Success
Admissions and test prep resources to help you get into your dream schools
Residency Personal Statement: The Ultimate Guide (Example Included)
A step-by-step medical residency personal statement guide to help you match into your dream program.

Part 1: Introduction
Part 2: brainstorming topics for your personal statement, part 3: how to write an amazing residency personal statement, part 4: in-depth analysis of a full-length personal statement example, appendix: frequently asked questions.
Applying to medical residency programs isn’t exactly easy. After four years of medical school, and years more spent before that preparing for medical school, you’re probably ready for a breather. But residency applications hit you with everything from USMLE scores to Medical School Performance Evaluations (MSPEs). The uncertainty leading up to match day can be stressful and anxiety inducing—will your near-decade of work pay off?
Thankfully, the residency application process is fairly transparent—we know what the most important aspects of the residency application are. Every two years, the NRMP’s Program Director Survey reveals which factors are cited as the most crucial components of your residency application and are thus the core deciders for whether or not you’ll get an interview. Though the exact ranking varies from year to year and according to specialty, typically you’ll find USMLE scores, letters of recommendation from physicians in your targeted specialty, and MSPEs hovering at the top.
But these materials may not express what drew you to the specialty in question or what got you into medicine in general. And though it can seem as if programs are overwhelmingly interested in your scores and evaluations, they are also interested in the person behind the grades.
In this guide, we’ll discuss the factor that was fourth-most cited by program directors on the NRMP’s 2020 survey: the residency personal statement.
Before we get into the step-by-step guide, we’ll offer some general framing thoughts. Being able to communicate your motivations and personality through your application, especially your personal statement, bodes well for your ability to bring that same enthusiasm and drive as a resident and in the rest of your career as a physician, so take note.
Want expert guidance on residency admissions?
Enter your name and email for high-yield admissions strategies we use to help students match into their top-choice programs
100% privacy. No spam. Ever.
Thank you! Your guide is on its way. In the meantime, please let us know how we can help you crack the residency admissions code . You can also learn more about our 1-on-1 residency admissions support here .
Why does the residency personal statement matter?
The personal statement is an essay of about a page (one page in ERAS is 3,500 characters including spaces) in which you articulate who you are and why you want to enter a certain specialty. It’s your big opportunity to set yourself apart from other applicants by highlighting anything that isn’t well represented in other parts of your application but that nevertheless contextualizes your CV and accomplishments. This context could include interesting life experiences and motivations for pursuing a given specialty.
There’s a good reason the personal statement is relevant for program directors. Because so much of the information that programs have to determine whether you’ll be a good fit is quantitative in nature, it’s likely that programs will receive many applicants who have similarly competitive scores and grades. What can serve as a tiebreaker?
Letters of recommendation offer qualitative information. But the personal statement is the main opportunity for you to directly make a case for yourself, on qualitative terms, before you attend residency interviews .
The personal statement can also weed out applicants who don’t demonstrate an adequate understanding of their specialty of interest or who come across as pretentious and pompous. For this reason, in addition to the basic requirements of proper grammar and spelling, you’ll need to strike the right tone with your essay: seeming aware of your motivations and accomplishments to date, passionate about what you hope to achieve in the specialty, and also humble.
Remember: a great personal statement cannot save an otherwise weak application, but a poor one could hurt an otherwise strong application.
What should the personal statement accomplish?
The residency personal statement should include and reflect:
What draws you to the specialty
The skills or qualities that will help you succeed during the residency and as a practicing physician
Your long-term plans, what you hope to accomplish, and your preferred setting
Personal attributes that make you well-suited to the specialty and training
What attracts you to a particular program (if you’re applying for a specific program outside of the national matching system or if you customize a personal statement within NRMP)
Ultimately, the combination of these elements will give program directors a sense of the kind of colleague you would be and how you would fit into their program.
Meet our students
Throughout this post, we’ll provide examples from students who have gone through this process so you can see their writing in action.
Roger: Roger immigrated from Mexico as a teen and attends a medical school in a rural area. His path to medicine wasn’t straightforward. After graduating from high school, he worked for several years in construction, quickly climbing the ranks to become project manager for a small roofing firm before deciding to go back to school. He hopes to specialize in dermatology because, after growing up in poverty and performing blue-collar work for years, he wants a comfortable life that will allow him to focus on his growing family.
Mohana: Mohana entered medical school believing her path was pediatrics. But after an away rotation in radiology, she’s leaning toward radiology, having become attracted to the more technical aspects of the field and its work-life balance. After years of schooling, Mohana mostly wants time for her musical hobbies.
Cynthia: Cynthia either wants to work at a research hospital or practice gynecology. She thinks she could be happy with either, but knows she’d be happiest if she could do both. She also received an MPH before attending medical school. Cynthia still has a taste for social justice, but it isn’t always evident on her CV.
Kazuo: Kazuo initially wanted to pursue thoracic surgery, but after spending time with surgeons, he decided the culture was not for him. Now he’s certain he wants to pursue anesthesiology, and isn’t entirely sure how to convey his interest. He is worried this change of heart may hurt his chances of matching into his top programs.
Brainstorming topics
Before you begin writing, set aside time to brainstorm. Whether you have an idea in your head or are struggling with where to start, freeform thinking can expand your options, call to mind experiences you hadn’t considered, or even help you pick unique interests you otherwise might have left out.
If you’re uncertain of how to proceed, jot down your answers to the following questions:
What first drew you to medicine?
Was there an experience, clinical or otherwise, that had a significant impact on you? What was it and why is it meaningful?
When did you know you wanted to pursue the specialty in question? What attracted you to the specialty?
What are your greatest qualities? When have you demonstrated these qualities?
Where do you see yourself 20 years into your career as a physician?
What’s an important part of who you are that isn’t on your resume?
Who are your role models and why?
What are your most meaningful extracurricular activities? Why?
What’s an accomplishment you are most proud of?
What was your most enlightening moment?
What medical cause do you care about most, and how did you come to care about it?
These are just a few questions to get started. Add more as they occur to you.
Another way to approach the personal statement is to ask what qualities make a good physician in your target specialty and consider how you embody those qualities. For example, here are a few qualities that might represent pediatric neurology:
Strong communication or interpersonal skills
Attentiveness
Technologically inclined
Passion for advocacy
Ingenuity
After brainstorming, take anywhere from a few hours to a day or a week to step away from your notes. This will help you as you move onto the next step: focusing your ideas.
Focusing your ideas
Here are some sample topics our residency applicants came up with:
An accidental run-in with poison ivy
Advocating for his Spanish-speaking roofing clients
Adjusting to the U.S. after immigrating from a small town in Mexico
Teaching herself MaxMSP programming skills
Babysitting her nieces and nephews
Her away rotation in radiology
Giving sex-ed talks in local middle schools
Being a surrogate daughter for her next-door neighbor, Leticia
Presenting her research findings at conferences
Kazuo
His ten-year meditation practice
His experience in surgery rotation
Admiration for his father, who taught him darkroom photography
Once you’ve generated your list of ideas, consider how they do or do not compellingly answer the following questions:
Why this specialty?
Before writing your personal statement, you should be very clear, personally, on why the specialty you’ve chosen is the right one for you.
Program directors want to know that you have a realistic idea of what your specialty will entail. For instance, you might be interested in plastic surgery because it’s a highly paid field but fail to understand the importance of artistic anatomy in its practice. If your application fails to convey compelling reasons for pursuing a specialty beyond high salaries or the potential lifestyle benefits associated with it (especially true for specialties like radiology and dermatology), it may cost you an interview invitation.
(Suggested reading: The Most Competitive Medical Residencies: A Complete List )
What strengths do I have that are not apparent in my other application materials?
Though your recommenders may offer a sense of your personality and interests, you are in the best position to include meaningful details that can’t be found on a CV. What aspects of your life do you think might compel a selection committee to pick you over other applicants? What makes you unique?
How do I embody the qualities of a good physician in the specialty?
This is slightly different from understanding the realistic requirements of a given specialty. Instead, it joins the strengths of your full life to the characteristics of an exemplary practitioner in your field of choice.
For instance, an anesthesiologist who performs their role well may go unnoticed by a patient, whereas a pediatrician who is too technically inclined may come across as cold or uncaring. The decisiveness of a surgeon in the OR is distinct from a psychiatrist adjusting a patient’s depression medication through trial and error over time. Make sure that the details you select speak to the qualities of your chosen specialty.
Let’s look at how our students applied these principles.
With two young children and another on the way, Roger wants good work hours and enough money to give his children a high quality of life. He’d never thought much about dermatology until he had accidental contact with poison ivy and took an elective in the specialty. Also, Roger hopes to practice in a rural setting because the low cost of living would facilitate his family-oriented lifestyle, but he knows he must communicate a more selfless reason in his personal statement. Roger’s approach will combine seemingly unlike things (roofing, dermatology, advocacy for rural patients) into one cohesive portrait of who he is and what matters to him.
Mohana doesn’t list her hobby on her resume, so writing about it for her personal statement will illuminate a side of her that neither quantitative scores nor letters of recommendation can comment on. Programming beats is Mohana’s passion, and she wants to show off how her technical prowess can serve her in the field of radiology.
But what to make of her experience babysitting her nieces and nephews? For Mohana, childcare helped her learn that she was particularly adept at soothing children in unfamiliar situations. It isn’t her strongest idea because she’s primarily interested in diagnostic radiology but including it may convey to program directors that she understands that radiology remains as patient-centered as any other medical discipline.
So far, Roger and Mohana are using their experiences to tell a story, not just enumerate things they’ve done. At the end of the day, great personal statements tell stories—about you, your journey, and why you’re right for a given specialty. If your idea is a topic without a story, it’s not worth mentioning.
Questions to determine if an idea can be a story:
Can you reference a specific anecdote (a day, a summer, an interaction)? Can you include significant details that convey the specificity of what you experienced?
Is yours a story no one else could tell? You want a story that, even if someone had the same jobs, schools, or extracurricular activities as you, they would not be able to write in the same way.
Does the narrative have an arc? Do you demonstrate growth and insight over a period of time?
Is the voice of the essay yours? Is the language lively?
Regardless of the idea, you should be able to answer yes to at least one of these questions.
To that end, while Cynthia felt that her positive experiences presenting her research at conferences best expressed her passion for research, this information was readily available on her resume and could be a sentence in her personal statement, not an entire framing narrative.
On the other hand, Cynthia’s experience serving as a “surrogate” child for her neighbor, Leticia, could be used to encompass her interests in reproductive health, patient advocacy, and gynecology. Leticia, an elderly woman who had never had children of her own, was sterilized without her consent while receiving an appendectomy as a teenager in the 1960s. The injustice of this fueled Cynthia throughout her medical education.
Similarly, Kazuo thought his experience in the operating room was a natural place to begin: it was where he discovered he did not want to be a thoracic surgeon after all, but an anesthesiologist. But to convey a greater sense of his levelheadedness and exactitude, he chose to also talk about his role model—his photographer father—and the lessons learned in darkrooms and meditation, neither of which could readily be written about by another applicant.
Start with an outline
With so many great ideas and a narrative in mind, you might be tempted to start writing your essay now. But an outline will keep your ideas organized and help you write more efficiently. Even if you don’t start draft one with an outline and instead just “vomit draft,” consider making draft two a reverse outline so that at some point you have structure guiding you.
Here’s one path to follow:
First paragraph: Lead with detail
The residency personal statement is short—under 3,500 characters—and this brevity creates constraints. While an opening anecdote is a good approach to hook readers, you may choose to describe a situation or an experience more generally to accommodate the brevity.
Both options are possible, but what you choose depends on the anecdote in question and what you hope to accomplish over the course of the statement. The point is to pin your unique story to your interest in medicine by the end of the first paragraph if you can, but at the very least by the end of the second paragraph.
How do you choose your opening story? One way is to check against the questions above: Can you remember specific details? Is it something only you could write? Is there an arc or will there be one over a few paragraphs, even the whole essay?
Kazuo has a specific anecdote in mind for his hook: the first day of his surgery rotation. As you’ll see, the essay passes the specificity test by the strength of its details—an ovary riddled with cysts, the bright OR light, the origins of Kazuo’s surgical interest, the introduction of the father as a character—and sets Kazuo up to discuss how he came to be interested in anesthesiology.
One of the most powerful moments in my medical education occurred during an oophorectomy. As Dr. Srivastava removed a cyst-riddled ovary, I noted that his calm was contagious; I felt focused but at ease. The surgery finished without a hitch. In fact, it was anticlimactic, even unremarkable. Having dreamed of becoming a surgeon since age 16, when my father had to undergo emergency surgery after a heart attack, it was a let-down. But my photographer father’s words on darkroom printing—“Look at the shadows, and they will guide you”—made me reconsider. When I looked away from the bright overhead light, I saw the reason for our calm: our anesthesiologist, Dr. Grant, had been silently watching the whole time, making sure the infusion was working as planned.
Roger, on the other hand, describes a situation that conveys the roots of his advocacy.
As a young roofing project manager, I chose to work with Spanish-speaking clients with roofs leaky from hailstorms many years prior. Because I was born in Mexico and had spent my younger years there, I felt a special connection when aiding non-English-speaking families who otherwise may have had difficulty navigating a complex insurance process to restore their damaged homes. I spent hundreds of hours learning to inspect and scrutinize the sometimes subtle, timeworn signs of hail damage to expertly advocate for those families. It was this love of advocacy, combined with my later love of biologic systems, which drew me to medicine.
By distilling the career wisdom of years into one crystal clear statement about the relationship between allyship and medicine, Roger is anticipating an arc he will develop across the length of the essay while setting himself apart from his more traditional colleagues.
Body paragraphs: Connect your narrative to a thesis
Roger has, by the end of the first paragraph, indicated what drew him to medicine in the first place. This is a good approach, and a model that works for articulating the thesis for the specialty as well.
Mohana gives her thesis in her second paragraph. Her opening anecdote was about how playing her first MaxMSP composition for friends was the culmination of hours of online tutorials and technical discussions on programming forums.
She describes the elation she felt at seeing her creation come to life for others and the satisfaction she received from sharing a common language with those who like learning through doing. This anecdote conveys something about Mohana’s personal qualities but doesn’t mention medicine at all.
That’s where her second paragraph comes in.
My passion for making music machines and my interest in radiology are fraternal twins. I want to be a radiologist because it would put my analytic skills to use just as trouble-shooting atonal compositions compelled me to search for answers. As someone who enjoys collaboratively finding creative solutions to seemingly intractable problems, I am especially suited to being a “doctor’s doctor”—a radiologist. I love talking shop with knowledgeable colleagues. Establishing a common diagnostic vocabulary with fellow clinicians intrigues me most of all. In fact, my radiology rotation felt like a real-life MaxMSP forum except that, instead of collectively developing an audio patch, we jointly scrutinized sagittal reconstructions for complex fractures.
Connect the personal to the professional
Having described the impact of growing up next door to Leticia, Cynthia connects that personal story to how she envisions moving forward in her professional life in her third paragraph. She also takes the opportunity to make a case for both research and clinical practice, giving herself a flexible statement that could suit a variety of program environments.
As I researched sources of misdiagnosis among OB/GYNs, particularly pertaining to endometriosis and hormonal disorders, I was driven by memories of Leticia. She once described how it took her ten years after her forced sterilization to understand the female reproductive system enough to comprehend what had been taken from her. As an OB/GYN, I would make sure no patient left my examination room without a clear understanding of her reproductive health. Moreover, the sex-ed I do in Baltimore middle schools has inspired me to share my research findings through outreach. Over time, my clinical and research experiences will give me the authority to advocate for reproductive health education reform. It is my ultimate goal to ensure that no young woman suffer as Leticia did.
Demonstrate change and growth over time
One way to keep a personal statement reader engaged is by using the tried and true storytelling methods of conflict and resolution. Put another way, things have to happen—specifically, they have to change.
Body paragraphs are the perfect place to develop these transformations. What events incited your growth? How are these shifts related to your interest in pursuing a specialty or the kind of practitioner you will be?
Kazuo, for example, reckoned with the realization that surgery proper was not for him. But rather than consider this a failure of direction on his part, Kazuo uses this to his advantage, spinning it as a successful reorientation that more closely aligned with his experiences and values.
I was excited to alternate between preoperative procedures and pain management in the anesthesiology rotation. Some tasks felt familiar; assisting the attending in diluting medications called to mind the exact ratios I once mixed for my father’s developer and fixer so that his prints expressed the full gradient between black and white. Other tasks, like induction and the occasional corrections required for maintenance, were foreign. But the beeping monitors and visual cues entered my mind like the thoughts I’ve aimed to consider without fear or anxiety in my ten years of meditating. By honing my attention in darkrooms and in silent morning meditations, I’ve become attuned to others, often anticipating the needs of recovering patients before they can articulate these themselves. My anesthesiology rotation helped me understand that behind every unremarkable surgery was a great deal of foresight and diligence. These are the qualities I enjoy exercising most.
Notice how Kazuo includes personal biographical details and establishes their relevance to anesthesiology. Interests aren’t mentioned just for the sake of mentioning them. They have been selected because they illuminate some aspect of Kazuo, whether it’s his longtime—and personally meaningful—interest in mixing solutions or his mindfulness.
More importantly, however, is that these align with the qualities of a good anesthesiologist. For Kazuo, an anesthesiologist should not merely be reactive, but proactive, “anticipating the needs of recovering patients before they can articulate these themselves.” By the last line, Kazuo’s body paragraph is in conversation with his opening anecdote. In fact, Kazuo has demonstrated a transformation from the naïve student in the surgery rotation to the attentive, proactive, and self-aware anesthesiologist-to-be.
Communicate the kind of specialist you hope to be
Kazuo wants to exercise his foresight, diligence, and calm. Mohana wants to be a “doctor’s doctor.” Here are how Cynthia and Roger express the qualities they would like to respectively embody.
I want to take the expertise I gain in my OB/GYN practice and reproductive health research and apply it in policy.
Short, sweet, and to the point. Roger chooses to convey his ultimate goals in his conclusion, which can also be an acceptable approach if your essay’s structure invites it.
I intend to apply my passion for human connection and community to providing high-quality dermatologic care and research to communities which have traditionally had difficulty accessing care.
In one sentence, Roger synthesizes the different facets of his interest in dermatology and returns to the advocacy he first mentioned in his intro paragraph.
Conclusion: Tie it all together
Your concluding paragraph should leave selection committees with an understanding of who you are and why you’re applying. There are several ways to think about an ending to successfully avoid falling victim to clichés:
Don’t pre-write your ending. Some people have deeply ingrained ideas of what an essay’s conclusion should accomplish and can even write with a conclusion already in mind. However, it’s best to let a conclusion naturally respond to the elements in the essay, so don’t force it.
Avoid declarative sentences. Program directors see it all the time: “And that’s what would make me a great oncologist” or “I would bring these skills to your program.” Don’t let their eyes glaze over. Write something more unique.
Consider ending on an image or with a callback to where you began the essay. This is one of the most organic and satisfying ways to conclude any piece of writing. Mohana’s essay, for instance, opens with playing her music for others. She closes with the following.
There is a joy in finding your tribe. I’m lucky to have several. The wider world of musical programmers is my creative community and the radiology team at Beth Israel Deaconess is an example of my ideal medical community. Whether creating a neural network for note generation or exploring new possibilities for interventional radiology, I know my fascination with innovation, technique, and diagnosis will help me find harmony between invention and the tried-and-true backbone of medicine–excellent patient care. People-centered radiology–that’s music to my ears.
After you’ve finished the first draft of your residency personal statement
First, celebrate! Writing is hard no matter what, and the fact that you’ve accomplished anything with language is no small feat. But you’re just getting started. Settle in for some revisions:
Read your essay aloud. This will alert you to typos, problems of pacing, and issues of form that you might otherwise miss. Reading aloud also helps you get a sense for your essay’s voice—it should sound like you when read aloud.
Ask for feedback . You should have a trusted peer, professor, specialty advisor, or admissions counselor read your essay. The core question to ask them is, “Do you have a good sense of who I am and why I want to pursue this specialty after reading this?” If the answer is no, revise, revise, revise.
For big changes, don’t edit—rewrite. It can be a pain to invest so much time into a draft only to scrap it, but if you decide on structural revisions or major changes in content, start with a new document. Starting anew may give you a more cohesive and coherent final product. This doesn’t mean all your hard work was in vain. Print out a hard copy of your original, keep it on the table beside you, and open a clean doc. Drawing from your previous draft for your revision will ensure you have one essay at the end, not two spliced together.
Before we go into our analysis, consider reading the personal statement example in its entirety. As you go through it, keep the following questions in mind:
Does Roger demonstrate an understanding of his specialty of interest, including the kind of qualities an exemplary resident in the specialty must possess? If so, which ones?
Does Roger tell a story about how his interest developed? How does Roger demonstrate growth and change?
Could anyone have written this statement, or is it unique to Roger?
After reading the statement, do you have a good sense of who Roger is and why he wants to pursue dermatology?
Let’s look at the dermatology statement Roger produced based on the process we described.
As a young roofing project manager, I chose to work with Spanish-speaking clients with roofs leaky from hailstorms many years prior. Because I was born in Mexico and had spent my younger years there, I felt a special connection when aiding non-English-speaking families who otherwise may have had difficulty navigating a complex insurance process to restore their damaged homes. I spent hundreds of hours learning to inspect and scrutinize the sometimes subtle, timeworn signs of hail damage to expertly advocate for those families. It was this love of advocacy, combined with my later love of biologic systems, which drew me to medicine.
In medical school, I serendipitously found the specialty within which I wanted to apply this passion after accidentally dumping a bag of mulched poison ivy on my head. The resulting rash was painful but interesting and sparked a curiosity in cutaneous manifestations of disease that later led me to a dermatology elective. There, I was impressed by the dermatologist’s keen eye for detail, and I found the diagnostic challenge and the detail-driven expertise to be both fascinating and rewarding.
Each new rash I saw was reminiscent of inspecting leaky roofs and I wanted to emulate my new mentors, who had developed the ability to diagnose and treat skin disease based on the subtle cues they saw. Such was the case when a grizzled farmer from a distant rural community with infrequent follow-up ascribed a sore on his arm to a specific trauma. Despite this history, the dermatologist recognized some subtle and suspicious features, prompting a biopsy that later showed invasive squamous cell carcinoma. In addition to the dermatologist’s diagnostic acumen, it was her relationship with the patient and her understanding of his community, values, and risk factors that allowed her to guide this patient to a better outcome.
In medical school I have enjoyed caring for those who, for cultural, insurance, or geographic reasons, have difficultly receiving care. After one shift in my inpatient pediatrics rotation, I brought my guitar to play for a Latino boy who was dying from leukemia and made his parents my favorite recipe for chile verde with pork. Although I couldn’t offer any more to them medically, I hoped to aid the fear and disconnection they had expressed with the unfamiliar environment now surrounding them. The connection made in that moment helped ease their suffering and fostered a better union between the treatment team and patient.
Multiple studies have suggested that outcomes for dermatologic conditions tend to be poorer in certain demographics. As part of my own research, I have begun investigating these disparities. This has included a research project where we evaluated the effects of social and demographic factors on melanoma outcomes. One finding that spoke to me was that outcomes tended to be poorer in areas with fewer dermatologists. Having grown up in a small town and having completed medical school in a more rural area, I feel a special connection to these communities. I hope to continue to engage in research that better elucidates these disparities to supply better care to these populations.
In my career I intend to apply my passion for human connection and community to providing high-quality dermatologic care and research to communities which have traditionally had difficulty accessing care. Training at your program would enable me to meet these goals and effectively treat and advocate for these patients.
(Word count: 563; Character count: 3,498)
Residency personal statement analysis
Let’s analyze the entire personal statement section by section and answer the questions posed above.
Introduction
As a young roofing project manager, I chose to work with Spanish-speaking clients with roofs leaky from hail storms many years prior. Because I was born in Mexico and had spent my younger years there, I felt a special connection when aiding non-English-speaking families who otherwise may have had difficulty navigating a complex insurance process to restore their damaged homes. I spent hundreds of hours learning to inspect and scrutinize the sometimes subtle, time-worn signs of hail damage to expertly advocate for those families. It was this love of advocacy, combined with my later love of biologic systems, that drew me to medicine.
Roger leads with details like “roofs leaky from hail storms” and “time-worn signs of hail damage” that make his previous career in construction vivid in the reader’s mind. The specificity also ensures that only Roger could write an introduction like this. He indicates the hundreds of hours he spent learning to examine subtle signs of roof damage in a manner that suggests, without stating it outright, both the kind of learner Roger would be as a dermatology resident and the transferable qualities he gained from his work and life experiences.
The last line of the paragraph, which helps anchor the reader in Roger’s motivations from the beginning, describes how Roger’s interest came to be. This thesis makes it much easier to navigate the essay and helps Roger compellingly articulate who he is and why he has chosen to apply for dermatology.
Body section 1: Specialty
In medical school, I serendipitously found the specialty within which I wanted to apply this passion after accidentally dumping a bag of mulched poison ivy on my head. The resulting rash was painful but interesting and sparked a curiosity in cutaneous manifestations of disease that later led me to a dermatology elective. There, I was impressed by the dermatologist’s keen eye for detail, and I found the diagnostic challenge and the detail-driven expertise to be both fascinating and rewarding.
In this section, Roger emphasizes his interest in dermatology and develops the idea he introduced in his opening paragraph: being attuned to subtle signs of damage. Roger finds kinship in the dermatologist’s “keen eye for detail,” relishes the “diagnostic challenge,” and emphasizes “detail-driven expertise”—all qualities he previously expressed about himself as a roofer and which he is now connecting to dermatology as a field.
In the second specialty paragraph, Roger turns his attention to a mentor to tell a specific anecdote that demonstrates his clear understanding about what dermatology entails. With his point about the visual and attentive elements of dermatology made, Roger transitions to describing the patient relationship toward the end of the second paragraph. The “understanding of his community, values, and risk factors that allowed her to guide this patient to a better outcome” sets Roger up to describe how he shares this awareness as well.
Finally, the specificity of the mulched poison ivy, its resulting rash, and the grizzled rural farmer makes this firmly Roger’s and no one else’s.
Body section 2: Advocacy
In medical school I have enjoyed caring for those who, for cultural, insurance, or geographic reasons, have difficulty receiving care. After one shift in my inpatient pediatrics rotation, I brought my guitar to play for a Latino boy who was dying from leukemia and made his parents my favorite recipe for chile verde with pork. Although I couldn’t offer any more to them medically, I hoped to aid the fear and disconnection they had expressed with the unfamiliar environment now surrounding them. The connection made in that moment helped ease their suffering and fostered a better union between the treatment team and patient.
In this section, Roger returns to the advocacy he mentioned in his introduction. He keeps it unique by describing a specific interaction with a single family and even mentions his favorite recipe, which gives the body paragraphs a touch of his personality.
The cultural angle helps remind the reader of the ways Roger has been interested in culturally-specific service since his days in roofing, when he advocated on behalf of Spanish-speaking clients.
Finally, Roger gives context to the research on his CV by showing how his preference for the underserved isn’t merely an ideological commitment. Rather, Roger’s attraction to dermatology dovetails with his passion for connecting with the underserved because his research credentials back it up. Even his upbringing in a different country finds a parallel in the rural environment where he hopes to practice now. The combination of details makes this section uniquely Roger and deepens our sense of who he is.
In my career I intend to apply my passion for human connection and community to providing high-quality dermatologic care and research to communities which have traditionally had difficulty accessing care. Training at your program would enable me to meet these goals and effectively treat and advocate for these patients.
Roger keeps it short, perhaps due to word count. Still, his first line clearly articulates who he is and what draws him to dermatology. Placing this line at the end of the anecdotes and examples Roger used throughout the essay helps the image of him crystallize in the minds of the selection committee. Roger’s last line isn’t our favorite—it’s a little bit common. But the rest of the essay is specific enough that we aren’t hung up on it.
Final thoughts
By reflecting on how your personal attributes and interests inform who you are and who you might be in your chosen specialty, your well-crafted, authentic, and unique personal statement will help you land those coveted residency interviews and, ultimately, match into the residency program of your dreams.
ERAS allows me to use up to 28,000 characters. Do I really need to stick to one page?
Yes. A page is considered standard, and even if you submit more, many program directors may not read past your first page. Thus, keep your statement short and sweet. Remember that one page in ERAS is 3,500 characters including spaces, which equals approximately 550–750 words.
Can I edit my personal statement after uploading it to ERAS?
Yes, ERAS allows you to edit your personal statement at any time during the application season, even if you’ve already assigned it to programs you’re applying to.
Should I address red flags in my personal statement?
It depends on the severity of the red flag. We don’t recommend using your personal statement to explain a situation that’s simply less than ideal, such as a low but passing Step 1 score. However, if you have a serious issue in your candidacy—for instance, you failed the USMLE, you repeated a preclinical year or clerkship, or you have unexplained interruptions in your medical education or career—it’s generally advisable to address it head on in order to demonstrate maturity and honesty. Don’t make excuses; do take ownership of the problem and explain how you’ve learned and grown from your mistakes.
If there is a legal issue in your past, the ERAS application contains legal disclosure fields in which you can discuss the incident. It’s typically not necessary to also address the issue in your personal statement unless it played a formative role in your journey towards your specialty.
The above are our general recommendations; however, given the many nuances and gray areas that tend to accompany red flags, it’s usually a good idea to discuss how to handle them with a trusted advisor in your specialty.
Should I tailor my personal statement to specific residency programs?
Generally speaking, it’s not necessary to tailor your personal statement to each program to which you apply. That said, ERAS does allow you to upload as many personal statements as you wish, so it is possible to send different versions of your personal statement to different programs.
Before you consider doing so, keep in mind that it’s probably not realistic to send a customized personal statement to every program that you’re applying to. Instead, you might do so for, say, your top three programs. Another approach could involve creating two different versions of your personal statement to send out as you choose.
For instance, you might have one version geared towards research-heavy programs and one geared towards community-oriented programs. Or, perhaps a few programs on your list are in your home city and the rest are located elsewhere. You could then create a personal statement for the hometown programs that includes a few sentences reflecting your geographical tie and why it’s important to your medical career (e.g. “ Having grown up in a medically underserved community in Romulus, my lifelong goal has been to improve access to healthcare for the citizens of Wayne County …”).
In any case, you should only tailor your personal statement to reflect genuine, well-founded reasons for your interest in a program. Because tailored personal statements are neither the norm nor the expectation, half-baked attempts to demonstrate fit will be noticeable.
(Note: We should mention that the one situation that always calls for multiple personal statements is if you’re applying to more than one specialty.)
An official website of the United States Government
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Search Toggle search Search Include Historical Content - Any - No Include Historical Content - Any - No Search
- Menu Toggle menu
- INFORMATION FOR…
- Individuals
- Business & Self Employed
- Charities and Nonprofits
- International Taxpayers
- Federal State and Local Governments
- Indian Tribal Governments
- Tax Exempt Bonds
- FILING FOR INDIVIDUALS
- How to File
- When to File
- Where to File
- Update Your Information
- Get Your Tax Record
- Apply for an Employer ID Number (EIN)
- Check Your Amended Return Status
- Get an Identity Protection PIN (IP PIN)
- File Your Taxes for Free
- Bank Account (Direct Pay)
- Payment Plan (Installment Agreement)
- Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)
- Your Online Account
- Tax Withholding Estimator
- Estimated Taxes
- Where's My Refund
- What to Expect
- Direct Deposit
- Reduced Refunds
- Amend Return
Credits & Deductions
- INFORMATION FOR...
- Businesses & Self-Employed
- Earned Income Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- Clean Energy and Vehicle Credits
- Standard Deduction
- Retirement Plans
Forms & Instructions
- POPULAR FORMS & INSTRUCTIONS
- Form 1040 Instructions
- Form 4506-T
- POPULAR FOR TAX PROS
- Form 1040-X
- Circular 230
Deductions for individuals: The difference between standard and itemized deductions, and what they mean
More in news.
- Topics in the News
- News Releases
- Multimedia Center
- Tax Relief in Disaster Situations
- Inflation Reduction Act
- Taxpayer First Act
- Tax Scams/Consumer Alerts
- The Tax Gap
- Fact Sheets for Frequently Asked Questions
- IRS Tax Tips
- e-News Subscriptions
- IRS Guidance
- Media Contacts
- IRS Statements and Announcements
FS-2024-11, April 2024
A deduction reduces the amount of a taxpayer's income that's subject to tax, generally reducing the amount of tax the individual may have to pay. Most taxpayers now qualify for the standard deduction, but there are some important details involving itemized deductions that people should keep in mind.
Standard deduction
The standard deduction is a specific dollar amount that reduces the amount of taxable income. The standard deduction consists of the sum of the basic standard deduction and any additional standard deduction amounts for age and/or blindness.
In general, the IRS adjusts the standard deduction each year for inflation. It varies by filing status, whether the taxpayer is 65 or older and/or blind and whether another taxpayer can claim them as a dependent.
Taxpayers cannot take the standard deduction if they itemize their deductions. Taxpayers can refer to Topic no. 501, Should I itemize? for more information.
Itemized deductions
Some taxpayers choose to itemize their deductions if their allowable itemized deductions total is greater than their standard deduction. Other taxpayers must itemize deductions because they aren't entitled to use the standard deduction.
Taxpayers who must itemize deductions include:
- A married individual filing as married filing separately whose spouse itemizes deductions.
- An individual who was a nonresident alien or dual status alien during the year (some exceptions apply).
- An individual who files a return for a period of less than 12 months due to a change in his or her annual accounting period.
- An estate or trust, common trust fund or partnership.
Schedule A (Form 1040) for itemized deductions
Taxpayers use Schedule A ( Form 1040, Itemized Deductions or 1040-SR, U.S. Tax Return for Seniors ) to figure their itemized deductions. In most cases, their federal income tax owed will be less if they take the larger of their itemized deductions or standard deduction.
Taxpayers can review the instructions for Schedule A (Form 1040), Itemized Deductions, to calculate their itemized deductions, such as certain medical and dental expenses, and amounts paid for certain taxes, interest, contributions and other expenses. Taxpayers may also deduct certain casualty and theft losses on Schedule A.
Interactive Tax Assistant can help with deduction questions
The Interactive Tax Assistant (ITA) provides answers to tax law questions based on a taxpayer's individual circumstances. It can help a taxpayer determine the answer to common questions, such as if they:
- Must file a tax return.
- Have the correct filing status.
- Can claim a dependent.
- Have taxable income.
- Are eligible to claim a credit.
- Can deduct expenses.
The ITA can help taxpayers with these deduction-related questions:
- How much is my standard deduction?
- Can I claim a deduction for student loan interest?
- Can I deduct my moving expenses?
- How do I claim my gambling winnings and/or losses?
- Can I deduct my medical and dental expenses?
- Can I deduct my mortgage-related expenses?
- Can I deduct my charitable contributions?
- Can I claim my expenses as miscellaneous itemized deductions on Schedule A?
- Can I deduct personal taxes that I pay as an itemized deduction on Schedule A?
- Are my work-related education expenses deductible?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Include information that describes more about you than the details in your transcript. 5. Identify your plans for the future. Part of your personal statement can include future goals and ambitions. Explain what can happen if you gain acceptance to the university of your choice or you receive the job you want.
Tip 4: Connect the Story to Why You're Applying. Don't forget that the purpose of your personal statement isn't simply to tell the admissions committee who you are. That's an important part of it, of course, but your ultimate goal is to convince them to choose you as a candidate.
In a great personal statement, we should be able to get a sense of what fulfills, motivates, or excites the author. These can be things like humor, beauty, community, and autonomy, just to name a few. So when you read back through your essay, you should be able to detect at least 4-5 different values throughout.
A personal statement is a short essay of around 500-1,000 words, in which you tell a compelling story about who you are, what drives you, and why you're applying. To write a successful personal statement for a graduate school application, don't just summarize your experience; instead, craft a focused narrative in your own voice. Aim to ...
5. Use an authentic voice. Your personal statement reflects who you are, so you should use a tone that represents you. That means you shouldn't try to sound like someone else, and you shouldn't use fancy words just to show off. This isn't an academic paper, so you don't have to adopt a super formal tone.
Prompt Type 1: Your Personal History. This sort of question asks you to write about a formative experience, important event, or key relationship from your life. Admissions officers want to understand what is important to you and how your background has shaped you as a person. These questions are both common and tricky.
1. The general, comprehensive personal statement: This allows you maximum freedom in terms of what you write and is the type of statement often prepared for standard medical or law school application forms. 2. The response to very specific questions: Often, business and graduate school applications ask specific questions, and your statement ...
Watch out for cliches like "making a difference," "broadening my horizons," or "the best thing that ever happened to me." 3. Stay focused. Try to avoid getting off-track or including tangents in your personal statement. Stay focused by writing a first draft and then re-reading what you've written.
Your personal statement is the opportunity to show universities who you are, your ambitions and why you're passionate about the course you're applying for. Before you dive into writing, it's good to understand what you should include in your personal statement to make the most of the 4000-character count. The purpose of your personal ...
Your personal statement should be "personal" and unique. Do not try to pretend to be someone else. Just find out the best sides of your personality and show them to the officers. 3. Absence of Personal Motivation. Your personal statement is a chance to demonstrate your candidacy and show your drive and passion for studying the chosen program.
ideal personal statement, you will answer a general prompt with a narrative or anecdote that highlights your unique traits, abilities, and experiences. What should a personal statement include? First, a personal statement should answer the prompt. All stories, anecdotes, and other explanations should be framed as answers to the prompt.
•Personal statements can range anywhere from 300 to 2000 words •Personal statements (unlike the essays you might have written to apply to college) aren't thatpersonal •Personal statements should focus on the personal side of your professional goals •Personal statement requirements vary a lot from program to program
Overall, your personal statement should be a reflection of who you are. Be honest and genuine, and let your unique voice shine through. This is your opportunity to make a lasting impression on admissions officers and increase your chances of standing out among other applicants. Happy writing! 21 days ago.
A resume personal statement should include: Between 50 and 200 words in 3 - 4 sentences. Your title or function, for example "Junior developer" or "Passionate hospitality manager". An opening hook. Soft skills and hard skills. Impressive facts and stats. Your short and/or long-term goals.
The personal statement is your opportunity to talk about you, and why you want to enrol on a particular course. Use these easy-to-digest bullet points to help you decide what you should and shouldn't include in your personal statement. ... Five things all students should include in their personal statement. See how you can turn your personal ...
Summary. We've talked about the five things every personal statement should include and how you should approach writing it. You may have noticed a big part of writing a great personal statement is your openness to recognising your strengths and sharing that in writing. The five things every student should include on their personal statement.
Step 3: Figure Out Your Angle. Your "angle," or focus, in your graduate school personal statement will depend on a few key factors: What your grad program wants you to write about. Your field of study and research interests. How much experience you have in your field.
5 Things To Include In A Personal Statement. Here is a list of five things every student should include in a personal statement. 1. Explain Why To Choose This Course. A personal statement is your passport. So imagine you get the customisation of the passport, do it in such a way that it goes to the point. Give your readers an idea of why you ...
Do include what you do outside of academia, then, but keep non-relevant activities mentioned to a minimum rather than an exhaustive list. This might mean sacrificing some of the things you do outside of your course and focus on those few things you do most often, or to the highest level. ... Your personal statement should be at most, 4,000 ...
Just start by showing your enthusiasm for the subject, showcasing your knowledge and understanding, and sharing your ambitions of what you want to achieve. Avoid cliches! Remember, this opening part is simply about introducing yourself, so let the admissions tutor reading your personal statement get to know you. Keep it relevant and simple.
The residency personal statement should include and reflect: What draws you to the specialty. The skills or qualities that will help you succeed during the residency and as a practicing physician. Your long-term plans, what you hope to accomplish, and your preferred setting.
FS-2024-11, April 2024 — A deduction reduces the amount of a taxpayer's income that's subject to tax, generally reducing the amount of tax the individual may have to pay. Most taxpayers now qualify for the standard deduction, but there are some important details involving itemized deductions that people should keep in mind.