- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning Services
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB-1 Business Plan
- EB-2 NIW Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Landlord business plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- Ecommerce business plan
- Online boutique business plan
- Mobile application business plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food delivery business plan
- Real estate business plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Pitch Deck Consulting Services
- Financial Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples

Microfinance Business Plan
NOV.05, 2023

Sample Business Plan for Microfinance
Microfinance is a banking service that provides financial assistance to low-income individuals or groups who do not have access to formal financial services. In the US, microfinancing refers to loans of $50,000 or less. Microfinance institutions (MFIs) offer loans, savings, insurance, and other products to help clients improve their livelihoods, reduce their vulnerability, and achieve their goals.
This microfinance business plan template is about a sample microfinance bank that operates in the USA. It will provide an overview of a microfinance bank’s business models, services, customer focus, management team, success factors, financial highlights, and plans. Refer to our financial advisor business plan for a detailed understanding.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
InnoLoan is a microfinance bank that provides affordable and accessible financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses in the USA. Our mission is to empower our customers to improve their livelihoods, create jobs, and contribute to the economic development of their communities.
InnoLoan microfinance bank offers a range of financial products and services to its clients, such as:
- Microloans – Tailored to the needs and capacities of our customers, with flexible repayment terms and competitive interest rates
- Savings products – Help our customers build assets and plan for the future
- Insurance products – Protect our customers from risks and uncertainties
- Money transfer – Enables our customers to send and receive money conveniently and securely
- Financial education program – Equips our customers with the skills and knowledge to manage their finances effectively
Customer Focus
Our target market comprises low-income individuals and small businesses excluded or underserved by the formal financial sector. We focus on women, youth, minorities, and rural populations facing multiple barriers to financial services. We segment our customers based on their demographic profile, income level, business activity, and financial needs.
Management Team
We have a strong management team with extensive experience and expertise in microfinance, banking, and social development. Our team is committed to delivering high-quality services to our customers and achieving social and financial impact. We also have a network of well-trained and motivated staff who work closely with our customers at the grassroots level.
Success Factors
Our success factors include:
- Clear vision and mission
- Customer-centric approach
- Diversified product portfolio
- Robust operational system
- Strong risk management framework
- Sound financial performance
- Positive social impact
Financial Highlights
Our financial highlights for the next five years are:
- Projected portfolio growth of 25% annually, reaching $50 million by 2026
- Projected customer base of 100,000 by 2026, with 60% women, 40% youth, 30% minorities, and 70% rural
- Projected revenue growth of 30% annually, reaching $15 million by 2026
- Projected net income growth of 35% annually, reaching $3 million by 2026
- Projected return on equity of 20% by 2026
- Projected operational self-sufficiency of 120% by 2026
Company Overview
Who is innoloan microfinance bank.
InnoLoan microfinance bank, established in 2020 in San Francisco, CA, is a US-registered and regulated bank that offers affordable and accessible financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses.
InnoLoan Micro Lending Company
InnoLoan micro-lending company, a branch of InnoLoan microfinance bank, gives small US businesses microloans from $500 to $10,000. It supports entrepreneurs with good business ideas or who need more capital.
Industry Analysis
The microfinance industry in the USA is a growing and dynamic sector that provides financial services to millions of low-income individuals and small businesses who are excluded or underserved by the formal financial sector.
According to the Global Microfinance Market Research Report 2023 , the global Microfinance market reached USD 218.31 billion in 2022. The market is expected to achieve USD 447.76 billion by 2028, exhibiting a CAGR of 12.72% during the forecast period.
Here are some more interesting insights on the microfinance industry:
- There are approximately 10,000 microfinance institutions throughout the world. ( Fit Small Business )
- Microfinance institutions worldwide serve more than 140 million borrowers and have a total loan portfolio estimated at $124 billion. ( Microfinance Barometer Report )
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Our target market consists of low-income individuals and small businesses excluded or underserved by the formal financial sector in the USA. We estimate that over 50 million potential customers in this market segment need financial services but lack access to them. We focus on women, youth, minorities, and rural populations facing multiple barriers to financial services.
Customer Segmentation
We segment our customers based on their demographic profile, income level, business activity, and financial needs. The following table shows the characteristics and size of our customer segments:
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
We face direct and indirect competition from various providers of financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses in the USA.
Some of the direct competitors include:
- MicroVest – A microfinance institution with over $50 million in loans to 100,000 customers. It gives microloans from $100 to $10,000 at 18% interest. It also provides 2% interest savings accounts and life and health insurance.
- MicroFlex – A microfinance institution with over $25 million in loans to 50,000 customers. It gives microloans from $50 to $5,000 at 15% interest. It also provides 1% interest savings accounts and a money transfer service with a 3% fee.
Some of the indirect competitors include:
- Payday lenders – Providers of short-term loans that charge high-interest rates and fees. They target customers who need urgent cash but have poor credit history or no collateral.
- Pawn shops – Providers of loans that require customers to pledge their personal belongings as collateral. They charge high-interest rates and fees and may sell the collateral if the customers fail to repay the loans.
- Credit unions – Non-profit financial cooperatives offering their members loans, savings, and other services. They charge lower interest rates and fees than other providers but have limited outreach and eligibility criteria.
Competitive Advantage
Our competitive advantage is based on the following factors:
Marketing Plan
Our marketing plan is designed to achieve the following objectives:
- To increase our brand awareness and recognition
- To attract new customers and retain existing ones
- To expand our market share and reach by entering new geographic areas
- To enhance our competitive position and reputation
Our marketing plan consists of the following strategies:
- Product strategy – We will continuously improve our products based on customer feedback and market research. We will also introduce new products in the future.
- Price strategy – We will offer competitive and affordable prices that reflect the value and quality of our services. We will also provide incentives and discounts for loyal customers and referrals.
- Place strategy – We will leverage our existing network of branches, agents, and partners to deliver our services to our customers.
- Promotion strategy – We will use traditional and digital media to communicate our value proposition and social impact to our target market and stakeholders.
Operations Plan
Operation function.
Our operations plan describes delivering customer services and managing our internal processes. Our operations plan consists of the following functions:
- Loan origination – We assess and approve microloan applicants using interviews, credit scores, collateral, and group lending, and assist them with the application process.
- Loan disbursement – We deliver the approved loan amount to our customers via cash, bank, mobile money, or prepaid cards, ensuring speed, ease, and safety.
- Loan collection – We collect the loan repayments from our customers as per agreement, using direct debit, mobile money, or cash collection, and monitor the loan performance and contact late customers to prevent defaults and losses.
- Savings mobilization – We offer and manage savings accounts for our customers who want to save money, with good interest rates and no minimum balance, and easy access and withdrawal options through branches, agents, mobile banking, or ATMs.
- Insurance provision – We offer insurance products that protect our customers from life, health, property, and business risks, working with good insurance companies to provide cheap and customized insurance plans, and handling the claims and payments for our customers in case of loss or damage.
- Money transfer service – We offer a money transfer service that allows our customers to send and receive money locally and internationally, working with reliable money transfer operators to provide fast and secure money transfer options, and charging low fees and offering good exchange rates.
- Financial education program – We run a financial education program for our customers who want to learn more, using workshops, seminars, online courses, or mobile apps, and measuring the impact of our program on customers’ financial behavior and well-being.
- January 2024 – Launch of our microfinance bank with all the necessary licenses, registrations, and approvals
- June 2024 – Opening of 10 branches in strategic locations across California
- December 2024 – Reaching 10,000 customers with a loan portfolio of $5 million
- March 2025 – Introduction of new products such as insurance, money transfer, and financial education
- June 2025 – Expansion to new states
- December 2025 – Reaching 50,000 customers with a loan portfolio of $25 million
- March 2026 – Adoption of digital technologies such as mobile banking, online platforms, and biometric identification
- December 2026 – Reaching 100,000 customers with a loan portfolio of $50 million
Financial Plan
Our financial plan provides an overview of our key revenue and costs, funding requirements and use of funds, key assumptions, and financial projections. Refer to our bookkeeping business plan here.
Key Revenue & Costs
Our key revenue sources are:
- Interest income – The income generated from charging interest on our microloans. We charge an average interest rate of 16% per annum on our microloans.
- Fee income – The income generated from charging fees for our services. We charge an average fee of 2% per transaction on our services.
- Other income – The income generated from other sources such as grants, donations, investments, etc. We expect to receive an average of $500,000 annually from other sources.
Our key cost drivers are:
- Operating expenses – The expenses incurred for running our operations, such as salaries, rent, utilities, travel, marketing, etc. Our operating expenses will be 40% of our total revenue.
- Loan loss provision – The provision made for potential losses due to loan default or delinquency. We estimate that our loan loss provision will be 5% of our total loan portfolio.
- Capital expenditure – The expenditure for acquiring or upgrading fixed assets such as equipment, software, vehicles, etc. Our capital expenditure will be 10% of our total revenue.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
We require a total funding of $10 million to launch and grow our microfinance bank in the next five years. We plan to raise this funding from various sources such as equity, debt, grants, etc. The following table shows the breakdown of our funding sources and amounts:
Key Assumptions
Our financial plan is based on the following key assumptions:
- Market share – We will capture 0.2% of our target market by 2026 (100,000 customers)
- Portfolio growth – Our loan portfolio will grow at an annual rate of 25% ($50 million by 2026)
- Revenue growth – Our revenue will grow at an annual rate of 30% ($15 million by 2026)
- Net income growth – Our net income will grow at an annual rate of 35% ($3 million by 2026)
- Return on equity – Our return on equity will be 20% by 2026
Income Statement

Balance Sheet

Cash Flow Statement

Hire OGSCapital for Your Microfinance Business Plan
Writing a microfinance business plan is hard and time-consuming. That’s why you should hire us, OGSCapital. We are a team of leading business plan experts, having helped over 5,000 clients attract over $2.7 billion in financing and achieve their business goals. We have a team of experienced and qualified business plan experts and SBA business plan consultants who have worked in various industries and sectors, including microfinance. We know how to create a compelling and customized five-year microfinance business plan that will meet the expectations of your target audience.
We will also provide strategic advice, market research, financial projections, and graphic design to make your micro loan business plan stand out. Contact us for a free consultation and quote for your microfinance business plan template.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much capital is required to start a microfinance company.
In the US, you may need a minimum capital of $5 million to register as a non-banking financial company (NBFC) microfinance institution. You should have a microfinance institution business plan showing your projected income and expenses for the next five years, or refer to our loan officer business plan .
Is the microfinance business profitable?
Microfinance business can be profitable in the US if you deliver high-quality services that meet the needs and preferences of your target market. You can also use digital technologies or a payday loan business plan to manage costs and risks and show your social and financial impact.
How do I start a microfinance business?
To start a microfinance business, you must identify your target market, choose a specialty of finance, create a business plan, and comply with state and federal regulations. You also need a strategic business plan for a microfinance bank that outlines your vision, mission, goals, and strategies.
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Add comment
E-mail is already registered on the site. Please use the Login form or enter another .
You entered an incorrect username or password
Comments (0)
mentioned in the press:
Search the site:
OGScapital website is not supported for your current browser. Please use:

This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Microfinance Bussiness Plan

A bussiness Plan for a microfinance institution in the slums of East Cairo.
Related Papers
Ephron Ndahimana
Aishwarya Nair
Kerathum Juma
Giacomo Aghina
This paper is a research on the development of the Islamic microfinance sector in three countries: Yemen, Egypt and Indonesia. The main purpose of this study is to find out which factors are essential for the expansion of the mentioned sector, and if they are comparable to other countries.
Giacomo Aghina , Idir Boundaoui
This paper is a research on the development of the Islamic microfinance sector in three countries: Yemen, Egypt and Indonesia. The main purpose of this study is to find out which factors are essential for the expansion of the mentioned sector, and if they are comparable to other countries. The research shows that the government's input is a crucial factor for the expansion of the Islamic microfinance sector. In the studied case of Yemen, the government's input has been led by a previous demand research addressed to the population. However, due to the lack of surveys, statistics and, in general, of scientific researches, the confirmation of the last premise – if this demand of first importance is essential for the expansion of the Islamic microfinance- needs to be confirmed by a future specific research within the population/countries selected.
Sunny Ogbonna
Wafa Ajjadeh Ajjadeh
Hamed Sarani
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of Pentoxifylline on correction of anaemia of chronic diseases in systemic lupus erythematosus. Seventy patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and anaemia aged 28.9 ± 5.6 were studied in 2013 in a clinical trial. Sampling method was random permutation blocks in two groups of control and intervention patients. Intervention group received pentoxifylline; after 4 months, haemoglobin, iron and TNFα profiles of the two groups were compared. Data were analysed using T-test. The results showed that the haemoglobin increased by 0.2mg/dl in the intervention group and 0.26mg/dl in the control group, which was statistically insignificant. Changes in ferritin, serum iron and serum iron/TIBC were respectively -3.6±58.4µg/dl, 1.6±28.8µg/dl and 0.02±1.0µg/dl in the Pentoxifylline group and 2.0±59.1µg/dl, 0.6±28.5µg/dl and 0.01±0.1µg/dl in the placebo group. TNFα changes were -1.5±8.8pg/dl in the Pentoxifylline group and 0.2±4.0pg/dl in the placebo ...
Ssrn Electronic Journal
Michael Lechner SEW
Bulletin of the American …
Stephen Howard
The Compact Toroid Injection eXperiment injects high velocity (200 km/s) magnetized plasma into a target chamber with large windows (0.5 m by 0.2 m) that allow transverse imaging of a large volume of plasma with fast digital cameras at sub-microsecond exposures. Neutral ...
RELATED PAPERS
Cardiology in the Young
Sibel Ozler
Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry
Mouâd Alami
Mercy Narvaez
Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Ferenc Ötvös
Journal of Natural Science and Integration
Journal of Heredity
Miguel Ángel Toro
International journal of dentistry
Ahmad Abdallah
Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Vizyoner Dergisi
Aşkın Özdağoğlu
Annals of Pure and Applied Mathematics
HARI KISHAN
Andrei Stoian
The Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and The Second English Language Teaching and Technology Conference in collaboration with The First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
Yanty Wirza
Ria Jane Flores
Gourav Vivek Kulkarni
Gourav Kulkarni
Biomedical Journal of Scientific and Technical Research
Dr. Valia Kalaitzi
IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques
Conal Murray
Journal of Biological Chemistry
Steven C Quay, MD, PhD
Mireille Mvondo-She
Biology Letters
Lukas Kratochvil
Environmental Science & Technology
William Inskeep
Tech. Sci. Informatiques
Văn Tuân Đào
isam Shahrour
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Making Microfinance More Effective
- Dean Karlan,
- Rebecca Mann,
- Jake Kendall,
- Rohini Pande,
- Tavneet Suri,
- Jonathan Zinman

A look at what actually helps the poor, and what doesn’t.
For the 2.5 billion people who live on less than $2 per day , shocks such as illness, crop failures, livestock deaths, farming-equipment breakdowns and even wedding or funeral expenses can be enough to tip them, their families, or even an entire community below the poverty line. A major challenge for international development efforts is determining which financial tools provide durable buffers against such setbacks.
- DK Dean Karlan is a professor at Northwestern’s Kellogg School of Management and founder of Innovations for Poverty Action.
- RM Rebecca Mann is a senior program officer on the Financial Services for the Poor team at the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
- Jake Kendall is the director of the Digital Financial Services Lab. He worked previously at the Gates Foundation, the World Bank, and in two start-ups in the field of cryptography.
- RP Rohini Pande is an economist and the Mohammed Kamal Professor of Public Policy at Harvard Kennedy School. She co-directs the Evidence for Policy Design (EPoD) Initiative (@EPoDHarvard).
- TS Tavneet Suri is the Maurice J Strong Career Development Associate Professor of Applied Economics at the MIT Sloan School of Management.
- JZ Jonathan Zinman is a professor of economics at Dartmouth College.
Partner Center
- Scroll to top

- Get Started
How Create A Strategic Blueprint for Microfinance Success
- Author Content Team
- Published March 15, 2024
Introduction to Strategic Planning for Microfinance Businesses
Having a well-crafted strategic plan is essential for success. A strategic plan serves as a roadmap, guiding your organization’s decisions and actions towards achieving its mission and goals. This comprehensive document outlines your vision , objectives , and the strategies to attain them, ensuring that your microfinance business remains focused and adaptable.
Microfinance institutions (MFIs) operate in a unique environment, catering to individuals and communities often overlooked by traditional financial services. As such, strategic planning for a microfinance business requires a deep understanding of the target market , socio-economic factors , and the regulatory environment .
A robust strategic plan should address the following key aspects:
- Mission and Vision Statement : Clearly articulate your organization’s purpose and long-term aspirations.
- Environmental Analysis : Assess internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats (SWOT analysis).
- Target Market Segmentation : Identify and prioritize the specific segments you aim to serve.
- Financial Projections : Develop realistic financial forecasts and budgets to ensure sustainability.
- Organizational Structure : Define roles, responsibilities, and operational processes.
- Risk Management : Implement measures to mitigate potential risks and ensure compliance.
- Monitoring and Evaluation : Establish mechanisms to track progress and make necessary adjustments.
Defining Your Microfinance Business Goals and Objectives
Establishing clear and measurable goals and objectives is a critical component of strategic planning for your microfinance business. These goals serve as the foundation upon which your strategies and action plans are built, ensuring that your efforts are focused and aligned with your organization’s mission and vision.
When defining your goals and objectives, it’s essential to consider both the short-term and long-term perspectives. Short-term goals typically span a period of one to three years and are more specific and actionable, while long-term goals look further into the future, often five to ten years, and are more broad and aspirational.
Here are some key areas to consider when setting goals and objectives for your microfinance business:
Outreach and Client Base :
- Increase the number of clients served
- Expand geographic coverage
- Diversify client segments (e.g., women, youth, rural communities)
Financial Sustainability :
- Achieve operational self-sufficiency
- Increase portfolio yield and profitability
- Attract external funding and investments
Product and Service Offerings :
- Introduce new loan products (e.g., agricultural, housing, education)
- Offer non-financial services (e.g., training, mentorship, financial literacy)
- Develop digital financial solutions
Social Impact :
- Improve clients’ standard of living and economic empowerment
- Contribute to poverty alleviation and community development
- Promote financial inclusion and education
Organizational Capacity :
- Enhance operational efficiency and productivity
- Attract and retain skilled and knowledgeable staff
- Upgrade technology and infrastructure
When setting your goals and objectives, it’s crucial to follow the SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) principle. This framework ensures that your goals are clear, quantifiable, realistic, aligned with your mission, and have defined timelines for achievement.
Additionally, it’s essential to involve key stakeholders, such as staff, board members, and community representatives, in the goal-setting process. Their input and perspectives can provide valuable insights and ensure that your goals accurately reflect the needs and aspirations of your target audience.
Once your goals and objectives are established, they should be regularly reviewed and adjusted as necessary to adapt to changing circumstances or emerging opportunities. Regular monitoring and evaluation will help ensure that your microfinance business remains on track and responsive to the evolving needs of your clients and the communities you serve.
Conducting a Comprehensive Market Analysis
Conducting a thorough market analysis is a critical component of strategic planning. This process involves gathering and analyzing data to gain a deep understanding of your target market, competitors, and the broader economic and regulatory environment in which your microfinance business operates.
A comprehensive market analysis can provide invaluable insights that inform your strategic decisions, allowing you to identify opportunities, mitigate risks, and develop effective strategies to achieve your goals. Here are some key aspects to consider when conducting a market analysis for your microfinance business:
Target Market Analysis :
- Identify and segment your target market based on demographic, socio-economic, and geographic factors.
- Understand the unique needs, preferences, and challenges faced by each segment.
- Assess the size and growth potential of each target market segment.
Competitive Analysis :
- Identify and analyze your direct and indirect competitors in the microfinance sector.
- Evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, product offerings, pricing strategies, and market positioning.
- Identify potential gaps or unmet needs in the market that your organization can address.
Industry and Regulatory Analysis :
- Examine the current state and future trends of the microfinance industry, both locally and globally.
- Understand the regulatory environment, including laws, policies, and compliance requirements.
- Assess the impact of economic factors, such as inflation, interest rates, and exchange rates.
Environmental and Social Analysis :
- Analyze the socio-economic conditions, cultural norms, and demographic trends in your target communities.
- Assess the impact of environmental factors, such as climate change and natural disasters, on your target market.
- Identify potential partnerships or collaborations with local organizations and stakeholders.
Technology Analysis :
- Evaluate the role of technology in microfinance, including digital financial services and mobile banking solutions.
- Assess the technological infrastructure and adoption rates in your target market.
- Identify opportunities for leveraging technology to enhance service delivery and operational efficiency.
To conduct a comprehensive market analysis, you can employ various data collection methods, such as:
- Primary Research : Surveys, focus groups, interviews with clients, and field observations.
- Secondary Research : Industry reports, government statistics, academic studies, and market research databases.
- Competitive Intelligence : Analysis of competitors’ websites, marketing materials, and public financial statements.
Once you have gathered and analyzed the relevant data, it’s important to synthesize the findings and translate them into actionable insights. This information can inform your strategic decisions, such as product development, pricing strategies, marketing efforts, and operational planning.
Remember, market analysis is an ongoing process, and your findings should be regularly updated to reflect changes in the market landscape. By staying attuned to emerging trends and shifting client needs, you can ensure that your microfinance business remains competitive and responsive to the evolving demands of the market.
Developing Effective Marketing and Outreach Strategies
Effective marketing and outreach strategies are crucial for reaching and engaging with your target audience in the microfinance sector. These strategies play a vital role in raising awareness about your products and services, building trust and credibility, and ultimately driving sustainable growth for your microfinance business.
When developing your marketing and outreach strategies, it’s essential to align them with your overall strategic objectives and target market analysis. By understanding your clients’ needs, preferences, and behavior, you can tailor your approach to effectively communicate the value proposition of your microfinance offerings.
Here are some key considerations and strategies to develop effective marketing and outreach for your microfinance business:
Branding and Messaging :
- Develop a strong and consistent brand identity that resonates with your target audience.
- Craft compelling messaging that highlights the unique benefits and impact of your microfinance services.
- Leverage storytelling and real-life examples to connect with your clients on an emotional level.
Digital Marketing :
- Optimize your website for search engines and user experience.
- Leverage social media platforms to build online communities and engage with your audience.
- Explore mobile marketing strategies, such as SMS campaigns and mobile apps, to reach clients in remote areas.
Traditional Marketing :
- Organize community events, workshops, and roadshows to directly engage with potential clients.
- Leverage partnerships with local organizations, community leaders, and influencers to expand your reach.
- Utilize traditional media channels, such as radio, TV, and print, to raise awareness in your target markets.
Client Education and Financial Literacy :
- Develop educational materials and training programs to improve financial literacy and promote responsible borrowing.
- Offer personalized counseling and advisory services to support your clients’ financial decision-making.
- Leverage technology platforms and digital tools to deliver financial education at scale.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations :
- Identify and collaborate with organizations, such as NGOs, community groups, and government agencies, that share your mission and values.
- Explore co-marketing opportunities and cross-promotion with complementary businesses or service providers.
- Leverage partnerships to expand your reach, tap into new markets, and offer bundled or integrated services.
Monitoring and Evaluation :
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of your marketing and outreach efforts.
- Regularly collect and analyze data on client acquisition, retention, and engagement.
- Continuously refine and optimize your strategies based on data-driven insights and feedback from your clients.
Effective marketing and outreach strategies are not one-size-fits-all; they should be tailored to the unique characteristics and preferences of your target market segments. It’s important to continuously monitor and adapt your approach based on changing market dynamics, emerging technologies, and evolving client needs.
Building a Sustainable Financial Model
Ensuring long-term financial sustainability is a critical challenge for microfinance businesses. Unlike traditional financial institutions, microfinance organizations often operate with limited resources and face unique challenges, such as serving low-income clients, managing high operational costs, and navigating complex regulatory environments. Building a robust financial model that balances social impact and financial viability is essential for the success and longevity of your microfinance business.
At the core of a sustainable financial model is a deep understanding of your organization’s revenue streams, cost structures, and funding sources. This understanding enables you to make informed decisions about pricing strategies, operational efficiencies, and resource allocation, ultimately supporting your mission while maintaining financial health.
One key aspect of building a sustainable financial model is developing a diverse and balanced revenue mix. While interest income from loan portfolios is often the primary revenue source for microfinance institutions, it’s important to explore complementary revenue streams. These could include fees for non-financial services, such as training or advisory services, income from strategic partnerships or investments, or grants and donations from impact investors or philanthropic organizations.
Effective cost management is another critical component of a sustainable financial model. Microfinance businesses should continuously evaluate their operational processes and identify opportunities for streamlining and enhancing efficiency. This may involve leveraging technology solutions, optimizing staffing structures, or rationalizing branch networks. Additionally, implementing rigorous risk management practices can help mitigate potential losses and protect your organization’s financial health.
Attracting and maintaining a diverse funding base is also crucial for long-term sustainability. Microfinance institutions can explore a range of funding sources, including commercial loans, impact investments, and partnerships with development finance institutions or government programs. Building strong relationships with these funding partners and demonstrating a track record of responsible lending and effective management can increase access to capital and support long-term growth.
Furthermore, a sustainable financial model should incorporate mechanisms for reinvesting profits back into the business. This can involve establishing reserves for future investments, expanding product offerings, or enhancing operational capabilities. By striking a balance between financial returns and social impact, microfinance businesses can maintain a virtuous cycle of growth and development.
It’s important to note that building a sustainable financial model is an iterative process that requires continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation. Regular financial projections, scenario analyses, and stress testing can help identify potential risks and opportunities, allowing your microfinance business to make informed strategic decisions and maintain financial resilience in the face of changing market conditions or external shocks.
Implementing Risk Management and Compliance Measures
Operating in the microfinance sector comes with a unique set of risks and compliance challenges. From managing credit risk and operational risks to navigating complex regulatory environments, implementing robust risk management and compliance measures is crucial for the long-term success and sustainability of your microfinance business.
Effective risk management begins with a comprehensive risk assessment process. This involves identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing potential risks across all aspects of your operations, including credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, and compliance risk. By understanding the nature and potential impact of these risks, you can develop targeted strategies and controls to mitigate and manage them effectively.
Credit risk management is a critical area for microfinance institutions, as it directly impacts the quality of your loan portfolio and financial performance. Implementing robust credit risk management practices, such as rigorous client screening, credit scoring models, and portfolio monitoring, can help minimize defaults and ensure responsible lending practices.
Operational risk management is another key focus area. This involves identifying and addressing potential risks related to internal processes, systems, human resources, and external events. Strategies to mitigate operational risks may include implementing robust internal controls, investing in technology and infrastructure, and developing comprehensive business continuity and disaster recovery plans.
Compliance risk management is equally important, as microfinance businesses operate within complex regulatory frameworks designed to protect clients, promote financial inclusion, and maintain system stability. Staying up-to-date with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards is crucial. This may involve establishing dedicated compliance teams, implementing robust policies and procedures, and conducting regular training and awareness programs for staff and clients.
In addition to risk management, implementing robust governance and accountability measures is essential for maintaining transparency and trust with stakeholders. This includes establishing clear lines of responsibility and decision-making processes, ensuring effective board oversight, and promoting ethical practices throughout the organization.
Leveraging technology can also play a significant role in enhancing risk management and compliance efforts. Digital platforms and data analytics tools can streamline processes, improve monitoring and reporting capabilities, and provide real-time insights into potential risks and compliance issues.
Recognize that risk management and compliance are not one-time initiatives but rather ongoing processes that require continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation. As your microfinance business grows and evolves, new risks and regulatory challenges may emerge, necessitating regular reviews and updates to your risk management and compliance strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Strategic Planning is Crucial : A well-crafted strategic plan serves as a roadmap, guiding your microfinance business towards achieving its mission and goals. It outlines your vision, objectives, and strategies, ensuring focus and adaptability.
- Define Clear Goals and Objectives : Establish SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) goals and objectives that align with your organization’s mission and vision. These goals should address outreach, financial sustainability, product offerings, social impact, and organizational capacity.
- Conduct Comprehensive Market Analysis : Gather and analyze data to understand your target market, competitors, industry trends, regulatory environment, and socio-economic factors. This analysis informs strategic decisions and identifies opportunities and risks.
- Develop Effective Marketing and Outreach : Implement targeted marketing and outreach strategies tailored to your target audience. Leverage branding, digital marketing, community engagement, client education, and strategic partnerships to build trust and drive sustainable growth.
- Build a Sustainable Financial Model : Ensure long-term financial sustainability by developing a diverse revenue mix, effective cost management, diverse funding sources, and mechanisms for reinvesting profits. Continuous monitoring and adaptation are crucial.
- Implement Robust Risk Management and Compliance : Identify and mitigate potential risks, such as credit risk, operational risk, and compliance risk, through comprehensive risk assessment, policies, controls, and monitoring processes. Leverage technology and data analytics for enhanced risk management.
- Monitor, Evaluate, and Adapt : Strategic planning is an iterative process. Regularly monitor and evaluate your strategies, and adapt to changing market conditions, emerging trends, and evolving client needs to maintain a competitive edge and drive sustainable growth and impact.
Money Lending Business Plan (Example and How to Create One)
- How to Start a Microfinance Business in Zimbabwe
Recent Posts

- Posted by Content Team
Microfinance Mastery: Crafting a Winning Business Plan in India


Microfinance Bank Business Model Explained

This website stores cookies on your computer. Cookie Policy
Explore Community Content
FinDev Gateway hosts the largest, free collection of online resources on microfinance and financial inclusion. Explore over 8,000 publications, trainings, events, jobs and announcements which have been curated by our editors and submitted by a wide range of organizations from around the world.
Learn how you can share content >
Business Plan Guidelines for Microfinance Institutions
This document sets out guidelines for MFIs on developing their business plan.
The business plan should contain an executive summary that should be restricted to two pages. It should also contain necessary information about:
- Microfinance industry, the institution and its products;
- Market research and analysis;
- Marketing plan;
- Formalization and/or regulatory environment;
- Operations plan;
- Management team;
- Critical risks and assumptions;
- Financial plan.
The business plan should also contain details about the proposed MFI offering, with details of the desired financing, securities offered, capitalization and use of funds that are being raised.
About this Publication
View All Publications
Share a Publication from your organization.
The Hole in the Bucket: The Impact of De-risking on Non-Profit Organizations
Whole groups are at risk of falling out of the financial system as banks develop increasingly risk-averse controls due to AML/CFT regulations. As non-profits face growing barriers to financial access, what can we do to reverse this trend?
By Karina Avakyan, Floor Knoote, Sofia Ortega, Lia van Broekhoven, Fulco van Deventer & Sangeeta Goswami
Why Have MFIs in the Arab World Been Reluctant to Transform?
Some say regulatory issues, others cite fear of mission drift. But all of these can be overcome.
By Karen Beshay, International Finance Corporation
Mobile Money in Emerging Markets: The Business Case for Financial Inclusion
By McKinsey & Company
FinDev Editor's Collections

Climate Change and Financial Inclusion

Microfinance Adaptation and Resilience

Migration and Forced Displacement
Microfinance Business Strategic Plan Template
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds
When it comes to running a successful microfinance business, having a well-defined strategic plan is essential. It's the roadmap that guides your decision-making and helps you stay ahead of the curve in a rapidly changing market.
ClickUp's Microfinance Business Strategic Plan Template is designed to assist microfinance institutions in developing a comprehensive plan that covers all aspects of their operations. With this template, you can:
- Set clear goals and objectives to drive your business forward
- Identify and capitalize on growth opportunities within the industry
- Allocate resources effectively to maximize efficiency and profitability
- Implement strategies to remain competitive and adapt to market trends
Don't settle for guesswork or outdated methods. Take control of your microfinance business with ClickUp's Strategic Plan Template and pave the way for success.
Benefits of Microfinance Business Strategic Plan Template
Microfinance institutions play a crucial role in empowering individuals and communities by providing access to financial services. The Microfinance Business Strategic Plan Template can help these institutions:
- Define and align their mission, vision, and values to guide decision-making
- Identify target markets and develop strategies to reach and serve them effectively
- Set clear goals and objectives to measure success and track progress
- Allocate resources efficiently to maximize impact and sustainability
- Evaluate and mitigate risks to ensure the long-term viability of the institution
- Foster innovation and adaptability to stay ahead in a rapidly changing industry
Main Elements of Microfinance Business Strategic Plan Template
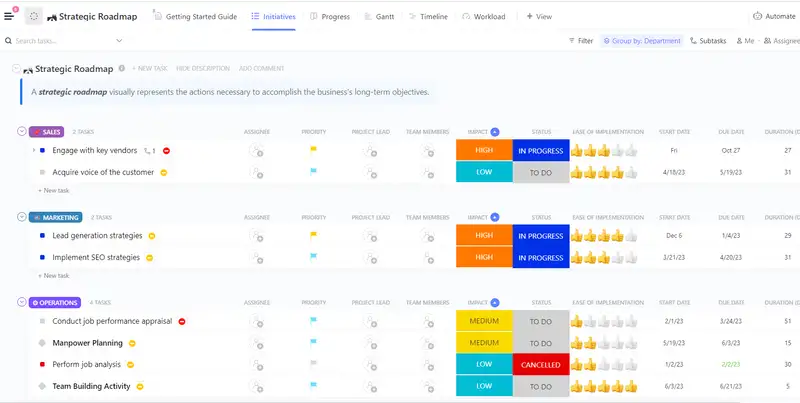
ClickUp's Microfinance Business Strategic Plan template is designed to help you streamline your business strategy and achieve your goals. Here are the main elements of this template:
- Custom Statuses: Track the progress of your strategic initiatives with 5 different statuses, including Cancelled, Complete, In Progress, On Hold, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Utilize 8 custom fields such as Duration Days, Impact, Progress, and Team Members to capture and analyze crucial information for each initiative.
- Custom Views: Access 6 different views, including Progress, Gantt, Workload, Timeline, Initiatives, and Getting Started Guide, to visualize and manage your strategic plan efficiently.
- Project Management: Leverage ClickUp's powerful features like Gantt chart, Workload view, and Timeline view to effectively plan, assign tasks, monitor progress, and collaborate with your team.
How to Use Strategic Plan for Microfinance Business
If you're looking to create a strategic plan for your microfinance business, follow these six steps to effectively use the Microfinance Business Strategic Plan Template in ClickUp:
1. Define your vision and mission
Start by clearly defining the vision and mission of your microfinance business. What is the ultimate goal you want to achieve? What values and principles guide your operations? This will serve as the foundation for your strategic plan.
Use the Goals feature in ClickUp to create specific, measurable, and time-bound objectives that align with your vision and mission.
2. Assess the market and competition
Conduct a thorough analysis of the microfinance market and identify your main competitors. What are their strengths and weaknesses? How do they differentiate themselves? Understanding the market landscape will help you identify opportunities and develop strategies to stay ahead.
Utilize the Gantt chart feature in ClickUp to create a timeline for your market research and competitor analysis.
3. Set strategic goals and objectives
Based on your market analysis and understanding of your business, set strategic goals and objectives that will guide your microfinance operations. These goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Use the Board view in ClickUp to create cards for each strategic goal and break them down into smaller tasks.
4. Develop action plans
Once you have your goals and objectives in place, develop action plans to achieve them. Break down each goal into actionable steps and assign responsibilities to team members. Set clear deadlines and milestones to track progress.
Utilize the Automations feature in ClickUp to automate repetitive tasks and streamline your action plans.
5. Monitor and evaluate progress
Regularly monitor and evaluate the progress of your strategic plan. Are you on track to achieve your goals? Are there any obstacles or challenges that need to be addressed? Stay proactive and make adjustments as necessary to ensure success.
Use the Dashboards feature in ClickUp to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and visualize the progress of your strategic plan.
6. Review and adapt
Periodically review your strategic plan to ensure its effectiveness. As your microfinance business evolves, you may need to adapt your strategies to changing market conditions or new opportunities. Stay agile and open to feedback from your team and stakeholders.
Set recurring tasks in ClickUp to regularly review and update your strategic plan, ensuring its relevance and alignment with your business goals.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Microfinance Business Strategic Plan Template
Metalworking companies can use this Microfinance Business Strategic Plan Template to align their goals and objectives, allocate resources effectively, and implement strategies to remain competitive in the market.
First, hit “Add Template” to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a strategic plan for your microfinance business:
- Use the Progress View to track the progress of each strategic initiative and ensure that tasks are completed on time
- The Gantt View will help you visualize your strategic plan on a timeline and identify dependencies between tasks
- Use the Workload View to balance workloads across team members and ensure that resources are allocated effectively
- The Timeline View will provide a high-level overview of your strategic plan and help you identify milestones and deadlines
- Use the Initiatives View to break down your strategic plan into specific initiatives and assign tasks to team members
- The Getting Started Guide View will provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to use the template and get started with your strategic planning process
- Organize tasks into five different statuses: Cancelled, Complete, In Progress, On Hold, To Do, to keep track of progress
- Update statuses as you progress through tasks to keep team members informed of progress
- Monitor and analyze tasks to ensure maximum productivity and the successful implementation of your strategic plan.
Related Templates
- Farmers Strategic Plan Template
- Machinists Strategic Plan Template
- Music Producers Strategic Plan Template
- High School Strategic Plan Template
- Health Equity Strategic Plan Template
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide

Writing a Business Plan For Microfinance Institutions
Why a business plan for mfis are important.
As more microfinance institutions strive for financial self-sufficiency, they recognise the importance of taking a business approach, being more responsive to their client’s needs, and constantly improving their management and operations. With this business approach comes the need for MFls to think about their products, markets, and operations, and to develop a plan to meet their future goals.
Many microfinance institutions underestimate the importance of planning and how a proper business plan may help an MFI get started, attract funds, plan for the future, and track its success. This initiative aimed to get microfinance institutions thinking about where they’ve been, where they want to go, and how they’re going to get there.
Microcredit, also known as microlending, is a method of financing in which small loans are issued by individuals rather than banks or other credit organisations. Entrepreneurs and company owners may utilise these loans to get their concept off the ground or to expand their firm with a little more cash. In that regard, microlending is similar to a small business loan.
Microfinance has always been important in poverty alleviation. It provides them a helping hand, empowering them to earn their way out of poverty. However, the importance of microfinance in COVID-19 recovery efforts cannot be overstated. The existing microfinance infrastructure and technology will be critical in keeping people linked to key services during the pandemic and its recovery.
The motivation behind the loan is what distinguishes microlending. Traditional lenders may charge interest or fees to make a profit on their loans. Microlenders are eager to invest in the growth of an idea or business. A microloan’s primary purpose is to assist a small entrepreneur who may not have access to traditional finance and would otherwise be unable to borrow money.
When in the correct location, a microlender may make a lot of money with tenacity and patience. According to some research, up to 97 percent of low-income borrowers repay their loans on time.
As the global market emerges from the pandemic-caused financial crisis, now is a good time to review your strategy or develop a new one that can adapt to changing circumstances. The following are the key aspects that must be included in your MFI business plan:
Executive summary, business overview, target customers, market analysis, competitive analysis.
- Products and Services
Marketing Strategy
Management team.
- Financial Plan
The executive summary of your business plan will introduce the purpose of writing your business plan. It might be to get funds from authorities for start-up or it can be written to get support from organizations to expand your business. But it is probably the last section that you will have to create as it includes all the summarized sections of the business plan. This helps the reader to get very much idea of the purpose behind the business plan and all the necessary details that he/she might miss when reading the full business plan.
The content of your Executive Summary must be written in a way that should instantly engage the reader. Explain to them what kind of microfinance institution you are running or your current status. For example, Have you just started your business or do you want to expand?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan for the Microfinance Business. For example, provide a quick summary of the MFI and lending sector. Discuss the sort of Lending Institution you run. Describe who is your direct competitors in the industry. Provide an outline of your target market. Explain how you are going to market your business in front of your target customers. Describe how you are going to generate income through this business. At the end of the Executive Summary, you must provide a summary of your financial strategy and projections for the next three or five years depending on the requirement of the reader
In this section, you will have to explain the kind of microfinance business you are operating.
When the business was started?
You will have to elaborate on the achievement you have during the business. The starting year and date of business must be mentioned here as well. Achievements may include sales targets met, customers attained, and the number of branches you are operating. Here sales targets means the amount of cash you just lend to your customers.
The next step is to provide the legal details of the Microfinance Business. Are you a limited liability company (LLC)? Is it a sole proprietorship business?
This section must include brief details about the targeted market. You must explain your targeted market including demographic and psychographic factors. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the customers you seek to serve.
On the other hand, psychographic profiles will describe your target customer’s interests and needs. The better you articulate and understand these demands, the better you will be able to attract and retain customers.
Customer research is always very important for Microfinance Institutions since the customers come from various types of businesses and individuals. Consider who you wish to serve and write in this section by justifying the reasons behind targeting them. Also, determine your customer’s demographics and how they make decisions keeping in mind their demands.
In this section, you are going to analyze your local market and the potential of Microfinance Institutions to fit into the market successfully. It would provide more value to the business plan if you provide hard data and statistics to show how the market has performed previously and how the market has been and where it is expected to grow. This detailed information helps the reader to understand the market so that he can take decisions more easily.
The location along with its value must be discussed in this section. If the real estate value in this area has decreased as a result of the pandemic or any other factor, you must show that you will still be able to make a profit from reduced rent for Microfinance Institution. If you are relocating your office to a location closer to the workplaces or communities of your target clients.
All these information are important for the applicant along with the average income of residents he hopes to serve, the percentage who owns their home, and the average number of people per household. This will help the reader to judge if the target market needs loans or not.
This section is very important since it needs a business owner to conduct research on their competitors. You should identify direct and indirect competitors of MFI’s including banks, as well as their strengths and shortcomings, and how your lending business will deal with them.
Product and Services
Include the breakdown of what percentage of interest rate you will charge from different nature of clients when providing them the required amount of loan. That should also include your plans in terms of the percentage of compound interest you will charge going forward after the second year of starting your business.
You should also include any special offer which you will provide to your customers depending on the nature of their business. It can be in the form of a different compound interest rate for those businesses. Also, use this section to provide details of any plans to change your policies in the future and including the projected cost for setting up your business.
This part covers everything you do to enhance your business including the initiatives which you are going to take in the future. This will help you to present yourself in front of your target market. Social media campaigns, membership drives, sponsorship of local events or charities, advertising, collaborations, and other marketing tactics are the few aspects that must be included in this section for the reader. This will help the reader to understand the aims and goals of your business.
It is also very important to include the projected costs for your marketing strategies to help your purpose. Also, consider including which employee will be responsible for each piece of the marketing strategy.
It is very essential to include the experience and skills of your team in the micro-lending businesses. This will send a message to the reader that the applicant is coming with a lot of experience which will increase the chances of getting funds or loans from a reader. However, you should also highlight any experience that you believe will assist your business to flourish. Include the expected expenditures for your marketing activities to assist your plan, and think about who is accountable for each component of the marketing strategy.
Financial Projections
This is usually the last section of your business plan. You must include your most recent year’s financials, as well as your expected income for the next several years, in this section. Those predicted revenues should be based on thorough market research. Financial forecasts must contain an annual profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and annual cash flow statements.
Once you have developed a detailed MFI business plan, you are ready to meet your business goals, whether you’re requesting funding or simply pushing ahead to greater success for your business.
What’s the business plan?
A business plan is a template of your company operations, expenses and funding. It summarizes all of the essential facts that assist prospective clients, funders, lenders and other stakeholders understand what your company is attempting to attain.
THE BUSINESS PLAN PROCESS ENTAILS 5 FUNDAMENTAL STEPS:
- Laying out your basic business concept.
- Gathering data on the feasibility and specifics of your concept.
- Focusing and refining the concept based on the data you compile.
- Outlining the specifics of your business.
- Putting your plan in a compelling form.
Why would you require a business plan?
Can be used to obtain financing.
Among the chief purposes of a business plan is to get funding from prospective lenders and investors. You may have the most visionary company idea in mind, however, you’ll find it hard to describe it to an investor in phrases without the support of a suitable business plan.
If you are seeking professional help, talk to us at 01 442 8230 or Text/Phone/Whatsapp 0851477625 or complete one of the forms below
Helps you think about your company in a strategic way.
As you can see from its construction, the company program is a detailed document which offers a great deal of advice for readers. It informs them about exactly what, when, why, where, who, and how of your small business.
It provides an excellent indication of what your company is attempting to reach and what you want to accomplish your goal.
Advantages of Business Plan:
It provides you a greater comprehension of market demand for your services and products and serves as the guiding document for establishing your enterprise.
A business plan will help you evaluate the current market and get details about the competition, clients, suppliers, and other important stakeholders.
Planning can help you develop your company gradually rather than committing a lot of resources too fast.
Drawing a strategy provides you a more realistic estimate of the funds and financing you’ll have to prepare the enterprise.
Many lenders and investors will request to see a business plan before they will consider devoting any funds to your company.
Cons of Business Plan
Organizing a business plan needs a great deal of market research so that it could be time-consuming
Writing a business plan requires complex comprehension and expertise in business management, bookkeeping, and advertising. If you do not possess these abilities, then you might find it tough to write.
It’s likely for you to overestimate or underestimate any earnings or expenses and receive unrealistic expectations for the company.
It’s also possible that you underrate the possibility of the company and choose not to pursue the venture, though it’s a rewarding venture.
Need Business Plan ? Contact us today to avail the best business plan writing services. We are Experienced in a number of Industries. Talk to us at 01 442 8230 or Text/Phone/Whatsapp 0851477625 or complete one of the forms below
Your message

- Microfinance
- Free Online Education to Start Your Own Business
- Our Courses
- Quick Start Entrepreneur
In this session, we discuss the emergence of microfinance, a new category of funding for new entrepreneurs who need less capital than traditional banks and lenders typically provide. Entrepreneurs interested in seeking microfinance, or any type of funding, are advised to seek the guidance of professionals before signing any documents. MOBI provides general information to help inform your decision-making process, but it is always best to seek professional advice before entering into contracts or agreements with monetary consequences. This session includes the following sections:

- What is Microfinance?
- Why Microfinance?
- Institution-centered
- Client-centered
- Microfinance's High Interest Rates
- Eligibility and credit assessment
- Interest rates
- Loan default and loan collection
- 12 Smart Tips
- How Much to Borrow
- Understanding Lending Methodologies
- Microloans and Technology
- For-Profit and Nonprofit Lenders
- Learn from Your Mistakes
- Top Ten Do's and Don'ts
Microfinance is the delivery of financial services in small amounts – mainly loans but increasingly savings and insurance – to entrepreneurs who typically do not have access to mainstream or traditional financial services. A microfinance institution refers to an organization that delivers small loans to help entrepreneurs create and grow a business.
Most entrepreneurs use personal savings and loans from family or friends to start their businesses. However, even these combined funds may not be enough to start the business. Sometimes it’s just a small amount that can bridge the gap. Entrepreneurs needing more capital look for additional sources of funding. Many lending institutions such as traditional banks require qualifications that new entrepreneurs do not yet have. For example, many banks want to see that a business has been successful for three years, that the applicant has a high credit score or positive credit history, and that there are enough valuable assets (personal collateral or assets in the business) to cover the loan in the event the business fails. As a result, entrepreneurs just starting out often do not qualify for loans at traditional banks. Microfinance has emerged to fill this need for small loans to new entrepreneurs.
By most accounts, microfinance institutions vary significantly in their missions, strategies, and practices. In many countries, the microfinance institutions operate as semi-formal entities. That is, they are usually required to register with the government before operating, but they are not heavily regulated like traditional banks. In practice, the microfinance industry tends to be self-regulated. What this means for entrepreneurs is that it can be quite difficult to compare one microfinance institution to another. Additionally, entrepreneurs may not be aware that some of the microfinance services and products can be misleading and can actually make their financial situation worse.
In seeking appropriate microfinance products and practices, entrepreneurs can first categorize microfinance institutions as either client-centered or institution-centered .
- Client-centered microfinance organizations see it as their mission to help develop the profitability of the borrower's business, as well as supporting client protection standards even when regulations are not in place. These microfinance institutions are usually run as nonprofits that offer not only financial products and services, but also financial education and business training. These institutions aim to protect their borrowers by helping create loans that are beneficial for the business AND affordable for the business owner.
- Institution-centered microfinance organizations offer a few basic, high-quality, low-cost services to as many borrowers as possible. These microfinance institutions are usually for-profit and typically do not place borrower protection as a key priority. For example, lending institutions with borrower protection should evaluate your current financial situation to help you avoid borrowing too much or at too high a rate so that you are not struggling to make payments. Institution-centered microfinance lenders may also give their borrowers the impression that by borrowing more money they have a greater opportunity for success in their business, or better financial situation. Often the opposite is true because the cost of the loan goes up as the loan amount increases.
It is very important that entrepreneurs understand and be able to assess the types of microfinance organizations available to them and to develop their finance and business skills before and while taking out microloans to fully understand all the factors of the loan. Entrepreneurs should focus on client-centered microfinance organizations wherever possible.
N ot all microloans are good. That is, microfinancing can lead to high rates of interest and debt traps . Microfinance’s interest rates are considerably higher than those of mainstream banks. At the global level, microfinance’s interest rates are about 40 percent. In countries like Mexico and Bolivia, the average is more than 60 percent.
However, at the same time, the microfinance’s interest rates are far below the interest rates of informal money lenders or “loan sharks,” which can be 70 percent or more. In some countries like China and Vietnam, governments have enforced an interest rate cap on microloans of no more than 30 percent.
Unfortunately the high interest rates have contributed to small business entrepreneurs having too much debt. In part, this has led to hazardous lending standards, procedures, and practices for borrowers. This is further heightened when entrepreneurs borrow more than they need, or make poor choices when selecting loans with harsh repayment schedules that do not match with their financial situation or cash flows.
Because there are considerable differences in the design of micro-lending, entrepreneurs should understand how to compare microfinance institutions to each other.
The components that make up the micro-lending processes include eligibility and credit assessment, collateral, repayment schedule, interest rates, fees, and loan default and loan collection .
- Eligibility and credit assessment. Your qualifications and credit history may determine which microlenders you are able to pursue. If you’ve been in business for a few years and have a high credit score you may have many choices. Many entrepreneurs just starting out may have fewer options. Microlenders will want to know how long you’ve been in business and whether your revenue can cover your expenses as well as a new loan payment. Be prepared to provide detailed analysis of the business finances and household cash flow . Don’t overestimate your income and don’t underestimate your expenses. Be honest about your financial situation. Your credit history, either through credit score, or perhaps character reference, will also be evaluated.
- Collateral. Microfinance institutions, similar to traditional banks, typically require some form of collateral to back up the loan. In the event the business were to fail, or the borrower could no longer afford the loan, the microlender would take over the collateral to pay back the loan. Collateral could be business or personal assets. If there is not sufficient collateral in the business, a microlender may consider collateral substitutes such as co-signers or personal collateral. Some microlenders may use compulsory saving as a collateral substitute. This means the borrower would be required to create and contribute to a savings account during the loan, which would take money out of your income that you may need to pay other expenses.
- Repayment. Paying for your loan is called “ servicing your loan ” and the monthly payments are called the “repayment schedule .” Your ability to keep to your repayment schedule will impact your credit score and credit history. So it’s important to stay on schedule and pay the full amount. You are always building your credit worthiness.
- Principal and interest. All loans are repaid through payments called installments. Each installment includes some money that goes toward the debt, or principal, and some money that goes to the interest . Interest is the extra money added to the loan calculated based on a specified rate. Interest, as well as any fees, are the cost of borrowing the money.
- Repayment schedule. Some microlenders may set a monthly payment schedule for one set amount, or they may set a schedule based upon the business cash flow. While a more flexible payment schedule may sound like a good idea, it might be difficult if there are unexpected changes in the business. Also, some lenders may have fluctuating (or changing) payment schedules. This means you might pay daily during some months and make monthly payments at other times. This practice can hide interest rate changes so you may not realize you are paying more. Some lenders may also offer loans for which you only pay interest initially, and then add principal payments later, or one big payment of the entire principal at the end. This is called a balloon loan . These loans can be very risky. It may seem more affordable to only pay interest in the beginning, but it can be a big shock when the payments increase significantly.
- Interest rates.
- Annual percentage rates. Traditional banks provide interest rates in terms of annual percentage rates, or APR.
- Factor rate, daily rate, monthly rate. Other lenders, including microlenders may use different terminology, such as a factor rate, a daily rate, or a monthly rate. These can be difficult to evaluate and compare. For example, a loan with a 10 percent annual interest rate might seem more expensive than a loan with a monthly rate of one percent. However, calculating one percent for 12 months gives an annualized interest rate of 12 percent. This might not sound like a big difference, but some microlenders might advertise monthly rates of 10 percent! Some “low” rates translate to very high annualized rates, topping very high two-digit and even high three-digit percentages! So be sure to understand what is meant by the rate you are quoted and figure out how to compare loans based upon an annualized interest rate.
- Percent of receipts . Some lenders will provide a loan and negotiate a rate that is a certain percentage of your business’s revenues or receipts. This could be as low as 10 percent or much higher.
- Fees. Lenders will often include certain fees in the terms of their loans. The most common are origination fees, late payment fees, prepayment fees/penalties, administrative fees, and risk assessment fees . Your loan may not have all of these but it’s important to know what they are.
- Origination fee. There may be a fee to start the loan, this is called an origination fee.
- Late payment fee. A late payment may result in a late payment fee or a higher interest rate for a period of time, or going forward indefinitely.
- Prepayment fee. There may be prepayment fees for paying a loan off early, because the lender gets less of your money overall if you pay it back before they collect all of the interest that would be paid over the term of the loan. For example, if you borrow $5,000 over 5 years for 10% annual interest rate your total amount owed would be $6,374.11, with monthly payments of $106.24 (assuming a simplified loan with no additional fees). If you decided to pay $230.72 a month, you could pay back your loan in two years and save $836.72. However, if there is a $500 prepayment penalty, you would only save $336.72. You can therefore calculate whether the fee is worth paying back the loan early. Some lenders may require payment of the full contract amount regardless of when you pay it off. Be sure to understand both late payment and early payment consequences of your loan.
A simplified example showing prepayment scenarios of a five-year $5000 loan with 10% APR:
- Administrative fee. Some lenders may charge a monthly administrative fee. Be sure to do the math. While $10 a month may not sound like a lot of money, include it when you calculate the total cost of loan.
- Risk assessment fee. A risk assessment fee may be added if the lender determines you present a higher risk due to your credit history, duration of the business, limited collateral, or other reasons.
- UCC fees. Lenders in the US may file a legal notice with the secretary of state, called a UCC filing, when they have a security interest against one of your assets. A UCC filing on your business credit report may signal to other lenders later that your business is not financially stable. Even if you pay off a loan UCCs can stay on your report. Be sure to ask your lender to remove your UCC once the loan is repaid. There could be UCC termination fees as well.
- ACH fees. Automated Clearing House (ACH) is a network used for electronic payments between banks in the United States. Some banks charge a fee to send money in this network.
- Loan default and loan collection. Entrepreneurs should clearly understand what actions the lender would take in the event he/she could no longer afford the loan, known as “defaulting on the loan.” Some lenders might take the borrower’s business equipment, household appliances, livestock, or any other items that were put up as collateral by all co-applicants. Some lenders might rework a borrower’s repayment schedule to get through the hardship. Be sure to understand the terms of any new loan structure to ensure you can afford it. If your business recovers faster than anticipated, would there be an opportunity to update the terms once again?
Before taking out a loan, make sure to carefully read and fully understand the terms and conditions of the loan. Take all of the factors into consideration and don’t just focus on one aspect of the deal such as interest rate. Don’t assume that the lender will provide adequate information on how microloans work, the expected repayment schedule, and the penalties for not repaying on time. Ask the lender any questions along with clarifying answers as you feel necessary before making the decision.
It’s also important for borrowers to know that as they near the end of their loan, their lender may not want to lose them as a client. So there may be attempts to lure borrowers into another loan by offering attractive terms that help “pay off” the old loan while getting started on a new loan. The new loan could allow the borrower to have extra money on hand just in case. Be careful about pursuing these loan options. It’s a good idea to only borrow what you need at the time to avoid getting into a cycle of debt by taking on new debts at the end of your term to pay down existing debts and gain access to money you don’t need.
There are various free tools available online to help you calculate the full cost of your loan such as this one provided in English and Spanish by Practical Money Skills, a Visa program: https://mena.practicalmoneyskills.com/resources/financial-calculators/loans/loan-cost
MOBI Partner the Community Economic Development Fund (CEDF) in Connecticut provides this helpful list of steps new entrepreneurs can take to prepare for a small business loan. Read the full CEDF guest post on this topic on the MOBI Blog for Entrepreneurs here .
12 Smart Tips for Getting a Small Business Loan
- Be ready to show how you can pay it back. This is the most important thing lenders will want to know. Don’t overstate your expectations, be realistic.
- Expect to personally guarantee the loan. Entrepreneurs don’t always have enough suitable assets in their businesses to guarantee a loan. So the lenders will require a personal guarantee from the business owner and any co-applicants or additional guarantors.
- Realize it’s not just about the business. Lenders will calculate “global debt service” which means your ability to pay all of your personal and business debts.
- Be candid and upfront about your financial condition. Not everyone has a perfect credit and financial history. Share details about any current or prior issues that could negatively impact your application.
- Be realistic about how much you need to borrow. Be sure you raise enough capital, either debt or equity, to launch your business and meet your early working capital needs, but not so much that you can’t afford the payments.
- Accept that it’s not the lender’s job to provide you with enough money. Make sure that you have access to additional sources of funding to face unexpected circumstances while continuing to repay your loan.
- Understand the purpose of a business plan. What’s important is that you show that you understand your own operation and market, you can communicate the essentials of your business, and you have done enough research to provide realistic calculations to predict future financial results.
- Realize the lender can’t help you create your business plan. Entrepreneurs can seek assistance with business planning from a variety of sources including SCORE mentors (you can find a free mentor by providing your zip code at SCORE.org ), local Small Business Development Centers (SBDCs), certified public accountants (CPAs), and others. It’s also very important to continually update your business plan because circumstances change all the time.
- Arm yourself with at least basic financial knowledge. Learn financial fundamentals through a variety of resources such as MOBI’s Accounting and Cash Flows session .
- Appreciate the differences in sources of business loans. Each source of funding has its own pros and cons. Find the best source of funding for your business and your financial position.
- Let the borrower beware. Be sure you understand the effective interest rate of your loan.
- Community development financial institutions like CEDF are another source of lending for small business. Check with your city’s economic development office, your region’s SBDC, or the commercial lending department of your bank to learn which community development financial institutions are active in small business lending in your area. Many operate as nonprofit organizations and often can be more flexible in their criteria than a bank because they are mission-driven to improve their communities.
Carefully evaluate your needs, expenses, incoming earnings, and predicted future earnings. Don’t take more than you need, because this can lead to excess debt that you will need to pay. At the same time, don’t take less than you need, because you could have a cash shortage when unexpected expenses emerge. Be sure you calculate the cost of the loan in your planning. Considering the monthly payments you’ll need to make for the loan, will you have enough money to pay all of your other bills and expenses for the business?
Traditional banks might be a good source of funding if you are looking to borrow a large amount, assuming that you meet their qualifications.
Plan and detail exactly what you will use the loan money for and how it will impact your revenues. For example, are you borrowing money to buy equipment that will allow you to double your production capabilities?
These are items that should be included in the financial areas of your business plan.
The delivery of the loan product is generally done through group lending or individual lending . Be sure you understand the method your lender will be taking to provide and manage your funds and match your personal and business needs to the delivery method of your lender.
- Group lending . In these scenarios the microlender creates groups of borrowers and provides one loan that gives money to each borrower. You may also be asked to provide names of others who need a loan and can be in your group. The entire group is responsible for the loan, and the individuals are jointly responsible if one of the group’s members defaults on repayments. So the groups or group leaders help enforce the terms and provide peer pressure to ensure payments.
- Individual lending. These microlenders give money directly to the individual rather than the group.
Here is a comparison of the two methodologies:
In recent years there has been a lot of growth in internet banking and FinTech (financial technology) organizations that bring new technology to financial services to provide lending options for small businesses. In addition, smartphones have made it possible for people to conduct financial transactions anywhere. Entrepreneurs can use their phones to save, send, and spend money wherever they are. Thus, a microfinance institution that utilizes mobile technology to process microloans may have lower costs that they can transfer to clients, lowering the transaction costs for entrepreneurs. However, these microlenders may also have higher rates because they are assuming greater risk. Borrowers should follow the same guidance in evaluating these lenders as they would for any others.
The organizational form of the microfinance institution also has an important impact for entrepreneurs. In most countries, microfinance institutions fall between for-profit and nonprofit status.
- Nonprofit or client-centered microfinance institutions tend to adhere to client protection standards even when regulations are not in place.
- For-profit or commercialized microfinance institutions tend to expect that potential borrowers should know the implications of obtaining and repaying a loan.
Be sure to evaluate two lenders from each category when investigating loan options.
If you borrowed money in the past and had trouble keeping up with payments, or had difficulty keeping your personal and business finances separate, learn from those mistakes to do it differently this time. Create a way of organizing your finances that is easy to maintain and that can give you a quick snapshot of your financial situation. This may be creating separate bank accounts, using a spreadsheet to track personal and business income and expenses, or using bookkeeping or accounting software to help you learn about and track finances. You can also hire a certified public accountant or bookkeeper to help you. Many work on a freelance basis so they can be hired for a one-time project or an ongoing basis.
Continuously seek financial and business education and training before, during, and while taking out microloans. This includes finding mentors that could provide encouragement, growth, and improvement in your personal and business endeavors. You may find new opportunities for affordable capital!
THE TOP TEN DO'S
- When looking for a microfinance loan, know exactly how much you need in terms of loan amount.
- Know ahead of time how you will use a new microloan in generating revenue in order to be able to repay back the loan amount plus the interest on the loan.
- When choosing a microfinance institution or lender, make sure to evaluate more than two lenders based on the lender’s legal status (nonprofit or for-profit) and consumer protection approach (client-centered or institution-centered).
- Make sure you match your personal and business needs to the lender’s lending methodology: group lending or individual lending.
- Before taking out a loan, make sure to carefully read and fully understand the terminology, terms, fees, and conditions of the loan.
- Know the lender’s policy on eligibility and credit assessment, collateral substitutes, and interest rates.
- Know precisely the lender’s repayment schedule policy and the penalties for late repayment or prepayment.
- Know exactly the lender’s collection policy when there is a loan default, including whether your valuable personal and business assets can be taken away, as well as those of any co-applicants.
- Learn from your mistakes whether from a previous microloan or from prior bad business habits such as not separating personal spending and business spending.
- Continuously seek financial and business education and training before, during, and while taking out microloans.
THE TOP TEN DON'TS
- In regards to loan amount, don’t take more than you need because you will need to pay interest on the money even if you don’t use it for your business. At the same time, don’t take less than you need, you could have a cash shortage when unexpected expenses emerge.
- In applying for a loan, don’t overestimate your income and don’t underestimate your business expenses. Be honest about your personal and business financial positions.
- In looking for a loan, don’t assume that the lender will provide adequate information on how microloans work, the expected punctual repayment schedule, and the penalties for not repaying on time. Be sure you ask questions and understand all aspects of your loan.
- Don’t take out more than one loan at a time. Taking on multiple loans can create a cycle of debt and put your personal and business standing at risk.
- In deciding on a microloan, don’t focus on just one aspect of the deal. Focus on a range of factors such as interest rates, fees, repayment schedule, penalties for late repayment, and loan default.
- Don’t assume a financial institution is regulated by the government to adhere to consumer protections.
- Don’t compare daily or monthly interest rates to annual percentage rates without first annualizing them. A 1% monthly rate is actually higher than a 10% APR.
- Don’t forget to ask about any and all fees that have been added to your loan or could be added throughout the loan term.
- Don’t make the same mistakes over again. If you had trouble keeping personal and business income and expenses separate, find a different way to track your finances.
- Don’t end your business and financial education just because you got the loan. Continue to learn and you may find other opportunities for affordable capital.
Content for this session was developed in partnership with Long Le, Ph.D., lecturer in Management and director of the International Business Minor at the Leavey School of Business, Santa Clara University (SCU). He is also co-founder of Zero Interest Bank (ZiM) , formed together with SCU students to provide micro-loans to underserved and marginalized entrepreneurs around the world, with a special focus in Southeast Asia. This session also includes an excerpt from “ 12 Smart Tips for Getting a Small Business Loan ,” a MOBI guest blog post provided by Frederick Welk, Director of Business Education and Communications at the Community Economic Development Fund (CEDF) . CEDF is a nonprofit community development financial institution in Connecticut and a MOBI partner.
Certificate Courses Login


Business Planning for Microfinance Institutions
Full report.
The ‘Business Planning’ course one of the four courses in the Operational Management Curriculum, along with ‘Product Development’, Information Systems’ and ‘Operational Risk Management’. The original five-day course guided participants through the process of strategic and operational planning and to develop the financial planning skills necessary to the long-term health of an MFI. The present version of the course has been significantly cut back from the original course launched in 2002 and includes all the sessions of the original course that precede using Microfinance to do financial modeling—namely, defining institutional mission, goals and objectives, understanding clients and markets, carrying out environmental and institutional assessments and designing a strategy.
Training Materials:
Business Planning for Microfinance Institutions Participant Materials: Trainer Notes Business Planning for Microfinance Institutions Participant Materials: Handouts Business Planning for Microfinance Institutions Overhe ads
CGAP is pleased to make the course materials from the CGAP Skills for Microfinance Managers course series publicly available. Although the course materials have been well tested and revised CGAP cannot ensure that the materials and all calculations are fully accurate. The latest update of these materials was done in 2012-13 to include dimensions of client protection and social performance management. The microfinance industry continues to evolve and new standards continue to emerge. As a result, the course materials may not reflect the latest practices in the microfinance industry. Although CGAP has made every attempt to produce high-quality course materials, ultimately it is the technical skills, training experience and preparation of the trainers that guarantee the quality of the course itself and the successful transfer of skills and knowledge to course participants.
Please note that CGAP recognizes only those partners and trainers that went through its certification process as CGAP training partners from 1997 to 2008. Others who offer a course using materials from one of the CGAP Skills for Microfinance Managers courses should not refer to themselves as CGAP trainers or CGAP-certified.
CGAP also requests that all those who offer the Business Planning for Microfinance Institutions course use the following text in their marketing materials and course descriptions: “The Business Planning for Microfinance Institutions course is based on the materials developed by CGAP that are publicly available on www.cgap.org. CGAP is a leading independent resource for objective information, expert opinion, and innovative solutions for microfinance. CGAP works with the financial industry, governments and investors to expand access to financial services for poor people around the world.”
Related Research
Banking in layers: five cases to illustrate how the market structure for financial services is evolving, tymebank case study: the customer impact of inclusive digital banking, getting repaid in asset finance: a guide to managing credit risk.
From Sub-Saharan Africa to the Indian Subcontinent, asset finance and leasing companies are doing invaluable, innovative work to finance critical assets for low-income and informal borrowers.
© 2024 CGAP
- Privacy Notice
DOWNLOAD MICROFINANCE BANK BUSINESS PLAN SAMPLE
Looking for a solid Microfinance bank business plan for your new or existing enterprise?
Download this microfinance bank business plan, which you can download to present to NIRSAL, BOI, BOA, and other investors.

Writing a Microfinance Bank Business Plan
Microfinance banks are small banks that offer loans, savings, and insurance to entrepreneurs and small business owners who can’t access traditional sources of capital, like banks or investors. The main objective of microfinance banks is to provide people with money to invest in themselves or their business.
Microfinance banks are different from commercial banks. For instance, funding to commercial banks usually takes place through public offers (stock markets) in the form of equity, while Microfinance banks usually receive their funding from individuals/private equity holders in the form of debt. Also, most of the services commercial banks offer are bank door services, which means the customers need to go to the banks to access the services provided. But most of the services provided by Microfinance banks are doorstep services, which means the staff of the banks deliver their financial services at the client’s doorstep.
A Sample Microfinance Bank Business Plan Template
- Industry Overview
Microfinance banks provide small loans to individuals and small businesses. This allows the microfinance bank business to attain a stage of being termed a recession-proof business. The stages of growth and development of a microfinance industry are classified into four segments, these are the pioneer stage, the breakout stage, the consolidation stage, and the maturity stage.
2. Executive Summary
Deckingham Microfinance Bank, LLC is a new microfinance bank in Ikeja, Lagos State, that will provide micro-lending and mortgage loan services to small businesses, real estate related matters.
We hope to bring better micro lending and mortgage loan services to residential and business customers in Lagos. Our plan at DMB LLC is to make our bank the customer’s home, where customers can be at ease whenever they come to access the services they want.
DMB LLC is created as an L.L.C. in order to avoid the taxation issues that usually surrounds corporations, realizing the benefits of personal liability avoidance. We will be occupying a standard office facility in the business district of the city, giving us a suitable traffic to attract customers. We have also identified several milestones that will act as ambitious yet achievable goals for the business.
3. Our Products and Services
We at DMB LLC plan to offer unique services within the walls of the micro-lending and mortgage loan services. Our services will include:
a. Providing assistance loans to small businesses
b. Offer residential mortgages
c. Providing mortgage financing online
d. Providing home equity loans online
e. Providing an online mortgage marketplace
f. Offer commercial and industrial mortgages
g. Providing home equity loans
h. Offer residential mortgages loans online
i. Providing other related loan cum mortgage consulting and advisory services.
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
Our vision at Deckingham Microfinance Bank is to build a reliable partnership with individuals, small businesses, and corporate clients in Lagos State. Our mission at Deckingham Microfinance Bank is to provide reliable and trusted microloan services that will help individuals, small businesses, corporate organizations, and non-profit organizations to attain their desired milestones. We plan to build a business that will become one of the leading microfinance banks in all of Lagos State.
5. SWOT Analysis
Our plan as a microfinance bank is to establish well– structured microloan services that will be of good help to our clients. So a SWOT Analysis was conducted and the results are below;
a. Strength
Our strength lies in the team. The quality, capacity, determination, and experience of our team is the core of our strength.
b. Weakness
Our weakness will be further manipulated if it takes us long to break into the market and gain acceptance, as it is our main weakness now since we are new.
c. Opportunities
Huge opportunities lie in the industry, the teeming numbers of individuals who need startup loan for their businesses, and all other specifics in detail, the bank looks to capitalize on this to aid the nation and in turn profit.
DMB is well positioned and well prepared to offer microloan and mortgage loan services to see to the needs of this growing target audience.
Unfavorable government policies and tough competition near our base of operations will be a threat to the business definitely. An economic meltdown, although not likely, but might also pose a threat
Also, huge losses in due to sharp spikes in interest rates, accounting control fraud, or the collapse of hyper-inflated real estate bubbles. These can be checked by creating counter plans for each threat like employing the use of credit scoring software.
6. Our Target Market
Our first aim at DMB LLC is to serve small to medium-sized businesses, from new ventures to other bigger businesses and individual clients. We plan to be decisive in all steps and approach our market one step at a time. Our target audience will cut across businesses of different sizes and individuals. Outlined below is the list of businesses and organizations that we have categorically designed our products and services for;
a. Small businesses
b. Individuals and interested homeowners
c. Real Estate companies and investors
d. Non-governmental organizations
e. House of worships and other religious organizations
f. Educational institutions
g. Corporate companies
How To Download The Microfinance Bank Business Plan Template
Above is a part of the Microfinance bank business plan template in Nigeria. If you want the complete business plan with the full financial plan, calculations, and more, follow the procedures to download it.
Pay the sum of N8000 (Eight thousand naira only) to the account detail below: Bank: GTBank Name: Oyewole Abidemi (I am putting my name and not our company account so you know we are real people and you can trust us) Ac/No: 0238933625 Type: Saving
Thereafter, send us your email address through text message to +234 701 754 2853 . The text must contain the title of the business plan you want and also your email address. Immediately after the confirmation of your payment, we will send the microfinance bank business plan template in Nigeria to your email address where you can easily download it.
Dr. Abi Demi is a skilled technical writer and author with specialties in the martech and fintech space. Featured on Tekedia, Coin Review, Business Insider, Fintechna, Cryptocoin.news, Date 360 and several other sterling online publications, Demi is an astute technical writer that specializes in finance, marketing and technology - with over 500 published pieces across the internet ecosystem. Contact Abi Demi - [email protected]
How to Start Pure Water Production Business in Nigeria
How to start a restaurant business in nigeria (legal view), you may also like, feasibility study sample for private school, private school business plan sample, feasibility study template for zobo production, business plan sample for zobo production, ict feasibility study sample, download ict business plan sample, download snailery feasibility study sample, download snailery business plan sample business, 8 farming & agriculture business ideas in nigeria, 5 investment apps for saving, growing your money....
i want projected financial sample business plan on transforming micro finance to bank
I want to business plan for microfinance ??
[…] Read – Get this Business Plan for Microfinance […]
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Business Today
- India Today
- India Today Gaming
- Cosmopolitan
- Harper's Bazaar
- Brides Today
- Aajtak Campus

- Magazine Cover Story Editor's Note Deep Dive Interview The Buzz
- BT TV Market Today Easynomics Drive Today BT Explainer
- Market Today Trending Stocks Indices Stocks List Stocks News Share Market News IPO Corner
- Tech Today Unbox Today Authen Tech Tech Deck Tech Shorts
- Money Today Tax Investment Insurance Tools & Calculator
- Mutual Funds
- Industry Banking IT Auto Energy Commodities Pharma Real Estate Telecom
- Visual Stories

INDICES ANALYSIS
Mutual funds.
- Cover Story
- Editor's Note
- Market Today
- Drive Today
- BT Explainer
- Trending Stocks
- Stocks List
- Stocks News
- Share Market News
- Unbox Today
- Authen Tech
- Tech Shorts
- Tools & Calculator
- Commodities
- Real Estate
- Election with BT
- Economic Indicators
- BT-TR GCC Listing
Manappuram Finance shares up 5% as Asirvad Microfinance IPO gets Sebi nod
Ipo watch: asirvad microfinance is a non-banking finance company, microfinance institution (mfi) that offers microfinance loans to low-income women..
- Updated Apr 30, 2024, 2:30 PM IST

Shares of Manappuram Finance Ltd jumped 5 per cent in Tuesday's trade as a subsidiary Asirvad Microfinance received nod for a proposed initial public offer (IPO) from Sebi. The unit had filed preliminary IPO papers with the market regulator on October 4, 2023.
Asirvad Microfinance is a non-banking finance company, microfinance institution (MFI) that offers microfinance loans to low-income women. In a release today, Manappuram Finance said Asirvad Microfinance received final observation from the capital markets regulator, to raise funds through the IPO.
Related Articles
- Muthoot, Manappuram Finance shares rally up to 11% after RBI order on IIFL Finance
Following the development, Manappuram Finance shares climbed 5.36 per cent to hit a high of Rs 207.30 on BSE.
The Asirvad Microfinance IPO would be a fresh issue of up to Rs 1,500 crore, with no offer for sale (OFS) component. Not less than 75 per cent of the IPO would be available for allocation to qualified institutional buyers (QIBs) on a proportionate basis. The portion for non-institutional bidders will be reserved at 15 per cent and retail individual bidders at 10 per cent.
Asirvad Microfinance, in consultation with the lead bankers to the issue, may consider a further issue of equity shares on a private placement for cash consideration aggregating up to Rs 300 crore. If such placement is completed, the fresh issue size will be reduced, Manappuram Finance noted.
As per the DRHP, the net proceeds from the fresh issue would be used to augment the capital base of the company to meet future business requirements and plan to be deployed in FY24.
Asirvad Micro Finance was incorporated in 2008 with two branches in Tamil Nadu. At present. It has presence in 22 states and 4 UTs through a network of 1,684 branches, as on March 31. Asirvad Micro Finance caters to 32.5 lakh active borrowers in the microfinance portfolio that constitutes a majority of its assets under management. It also caters to Loan against Gold and provides MSMEs loans.
It stands to be India’s Largest NBFC MFI considering its geographic reach and third in terms of assets under management and no of clients.
JM Financial Limited, Kotak Mahindra Capital Company Limited, Nomura Financial Advisory and Securities (India) Private Limited, and SBI Capital Markets Limited are the book-running lead managers, and Link Intime India Private Limited is the registrar of the offer. The equity shares are proposed to be listed on the BSE and NSE.
TOP STORIES

- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Press Releases
Copyright©2024 Living Media India Limited. For reprint rights: Syndications Today

Add Business Today to Home Screen

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Sample Microfinance Bank Business Plan Template. 1. Industry Overview. Microfinance banks provide microloans to individuals and small businesses. These individuals and small businesses tend to go for loans to be able to pay for the purchase of real estate and other transactions. This demand in turn makes the microfinance bank business a ...
This microfinance business plan template is about a sample microfinance bank that operates in the USA. It will provide an overview of a microfinance bank's business models, services, customer focus, management team, success factors, financial highlights, and plans. Refer to our financial advisor business plan for a detailed understanding.
Chapter 9 Using Business Planning as an Ongoing Management Tool 151. 9.1 Variance analysis 151 9.2 Annual planning 152. Annexes. 1 Installing and Starting Microfin 153 2 Printouts from Microfin 157 3 Data Requirements for Completing Microfin 217 4 Program or Branch Modeling Exercise 221 5 Analysis of Effective Interest Rates and Costs to ...
data are from 2009, a year in which the data include 930 institutions with a combined 80.1. million borrowers. The largest sample we use contains data on 1,335 institutions: 90 for-profit banks, 235. credit unions and cooperatives, 465 NGOs, 401 non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs), and 102. rural banks.
The "Business Planning for Microfinance Institutions" course was originally entitled "Business Planning with Microfin" and is one of the four courses in the Operational Management Curriculum, along with "Product Development," "Information Systems," and "Operational Risk Management.".
Business planning for microfinance institutions can be understood as two closely related processes: strategic planning and operational planning. ... the World Bank Group is a unique global partnership: five institutions working for sustainable solutions that reduce poverty and build shared prosperity in developing countries. About the World Bank.
The microfinance institution (MFI) and its founders. Indicate the core strengths or uniqueness of the institu-tion or its founders. Include a short summary of previ-ous history, including financial data. Market opportunity. Summarize the opportunity that the MFI will exploit. Products and technology. Identify what gives the insti-tution a ...
The EEA intends to use Grameen Bank model, developed by Nobel Peace Award winner, Muhammad Yunus. EEA intends to reach out to 10,000 poor families in Tanzania with microloans in the next five years in Gongolamboto, Kinyerezi, Chanika and Kigamboni. Achieving this goal EEA will expand its business in 2013 to Dakawa, Morogoro Region.
I. \ rII f\l I. , /I \1/1/ J1, BUSINESS PLANNING GUIDE FOR MICROFINANCE INSTITUTIONS IN UGANDA. By The Centrefor Mlcroenterprlse FInance Kampala, Uganda Prepared by ChristInaWiseman Published by USAID -PRESTOProject PnvateEnterprIseSupport,TraInIng and OrgamzatIonal Development Project February 1998 VersIOn 1 0. BUSINESS PLANNING GUIDE ...
2.2. Financial sustainability of MFIs. Examining the microfinance sector's financial capacity to survive on the market, i.e. its financial sustainability, reveals its success and development (Lensink, Citation 2018).Financial sustainability was defined by D'espallier (Citation 2013) as a firm's capacity to meet financial goals without external help.
Cosmopolitan Microfinance Bank Nigeria Limited does not provide such loans as mortgages, consumer loans, school fee loans, etc. Surveys, literature and Cosmopolitan Microfinance Bank Nigeria Limited's experience have shown that most women in Port Harcourt do engage in some sort of entrepreneurial activity, and can define plans for expansion ...
The website provides statistics shows that the number of total micro finance institutions in Egypt is "13 reported in year 2009", with "1.1 million active borrowers" (mixmarket.org). Although the number of MFI's is limited, by time micro-financing is becoming a more widespread practiced business.
The basic requirements to start Microfinance Company in India are as follows: Must have a registration under the Companies Act 2013 or the Companies Act 1956; Need to maintain 85% of the total qualifying assets; Must have prior approval from the Reserve Bank of India; Should have Rs 5 crore as the Net Owned Fund (NOF).
October 05, 2016. For the 2.5 billion people who live on less than $2 per day, shocks such as illness, crop failures, livestock deaths, farming-equipment breakdowns and even wedding or funeral ...
Pro Business Plans is a team of professional researchers, writers, designers, and financial. analysts. Speak with an advisor today. GET QUOTE. Speak with Sales (646) 866-7619. This article provides information on what is included in a Microfinance business plan and how it is typically structured.
As such, strategic planning for a microfinance business requires a deep understanding of the target market, socio-economic factors, and the regulatory environment. A robust strategic plan should address the following key aspects: Mission and Vision Statement: Clearly articulate your organization's purpose and long-term aspirations.
Preparing business plans in microfinance. This document sets out guidelines for MFIs on developing their business plan. The business plan should contain an executive summary that should be restricted to two pages. It should also contain necessary information about: Financial plan. The business plan should also contain details about the proposed ...
ClickUp's Microfinance Business Strategic Plan Template is designed to assist microfinance institutions in developing a comprehensive plan that covers all aspects of their operations. With this template, you can: Set clear goals and objectives to drive your business forward. Identify and capitalize on growth opportunities within the industry.
microfinance and social business and is acknowledged by partners and investors for the strong commitment to its social mission. Since its inception, the Foundation has made a significant contribution by supporting 87 microfinance institutions and 15 social businesses in 38 countries, with a strong focus on Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
We are Experienced in a number of Industries. Talk to us at 01 442 8230 or Text/Phone/Whatsapp 0851477625 or complete one of the forms below. Discover the key to success with our comprehensive business plan for microfinance institutions.Unlock the potential of microfinance institutions with our expertly crafted business plan.
OBJECTIVE: In this session, we discuss the emergence of microfinance, a new category of funding for new entrepreneurs who need less capital than traditional banks and lenders typically provide. Entrepreneurs interested in seeking microfinance, or any type of funding, are advised to seek the guidance of professionals before signing any documents.
Business Planning for Microfinance Institutions. January 2009. Download. The 'Business Planning' course one of the four courses in the Operational Management Curriculum, along with 'Product Development', Information Systems' and 'Operational Risk Management'. The original five-day course guided participants through the process of ...
Above is a part of the Microfinance bank business plan template in Nigeria. If you want the complete business plan with the full financial plan, calculations, and more, follow the procedures to download it. Thereafter, send us your email address through text message to +234 701 754 2853. The text must contain the title of the business plan you ...
Manappuram Finance shares climbed 5.36 per cent to hit a high of Rs 207.30 on BSE. The Asirvad Microfinance IPO would be a fresh issue of up to Rs 1,500 crore.