
Organic Chemistry News
Top headlines, latest headlines.
- New Copper-Catalyzed C-H Activation Strategy
- Pigment Chemistry
- Antiviral Defense With New CRISPR Tool
- Corrosion and Clean Energy Future
- Assessing the Applicability of Reactions
- Cleaner Ammonia Production
- Pinpointing Freshwater Pollution Sources
- Turning CO2 Into Sustainable Fuel
- Plastics, Rubber from Natural Gas: Lower Cost
- From Carbon Monoxide to Methanol
Earlier Headlines
Thursday, april 11, 2024.
- A New Spin on Organic Shampoo Makes It Sudsier, Longer Lasting
Tuesday, March 19, 2024
- Is Food Waste the Key to Sustainable, Plastic-Free Diapers and Sanitary Pads?
- Molecular Crystal Motors Move Like Microbes When Exposed to Light
- Spectroscopy and Theory Shed Light on Excitons in Semiconductors
- Sustainable Solution for Wastewater Polluted by Dyes Used in Many Industries
Monday, March 18, 2024
- Harnessing Hydrogen at Life's Origin
- Engineers Measure pH in Cell Condensates
Friday, March 15, 2024
- Printed Polymer Allows Researchers to Explore Chirality and Spin Interactions at Room Temperature
- Breakthrough Could Make Automated Dosing Systems Universal
Thursday, March 14, 2024
- New Bioengineered Protein Design Shows Promise in Fighting COVID-19
- New Simpler and Cost-Effective Forensics Test Helps Identify Touch DNA
Wednesday, March 13, 2024
- New Computational Strategy Boosts the Ability of Drug Designers to Target Proteins Inside the Membrane
Tuesday, March 12, 2024
- A Simple and Robust Experimental Process for Protein Engineering
- Scientists Develop a Rapid Gene-Editing Screen to Find Effects of Cancer Mutations
Friday, March 8, 2024
- Researchers Develop Artificial Building Blocks of Life
Thursday, March 7, 2024
- Researchers Develop New Machine Learning Method for Modeling of Chemical Reactions
Wednesday, March 6, 2024
- Universal Tool for Tracking Cell-to-Cell Interactions
- New Type of Nanoparticle Makes Vaccines More Powerful
Tuesday, March 5, 2024
- Key Advance Toward Removing Common Herbicide from Groundwater
- Aluminum Nanoparticles Make Tunable Green Catalysts
- Using Light to Precisely Control Single-Molecule Devices
- 'Like a Lab in Your Pocket' -- New Test Strips Raise Game in Gene-Based Diagnostics
- Researchers Closing in on Genetic Treatments for Hereditary Lung Disease, Vision Loss
Friday, March 1, 2024
- AI-Enabled Atomic Robotic Probe to Advance Quantum Material Manufacturing
Thursday, February 29, 2024
- Turning Waste Into Gold
Wednesday, February 28, 2024
- How Molecular 'handedness' Emerged in Early Biology
- Researchers Develop Novel Method to Photosynthesize Hydrogen Peroxide Using Water and Air
- Light Stimulates a New Twist for Synthetic Chemistry
- Nanocarrier With Escape Reflex
Tuesday, February 27, 2024
- New Disease Testing Component Facilitates Lower-Cost Diagnostics
- AI-Driven Lab Speeds Catalysis Research
- Low-Temperature Plasma Used to Remove E. Coli from Hydroponically Grown Crops
Monday, February 26, 2024
- Cutting-Edge 'protein Lawnmower' Created
- The Mutual Neutralization of Hydronium and Hydroxide
Thursday, February 22, 2024
- Chemists Synthesize Unique Anticancer Molecules Using Novel Approach
Friday, February 16, 2024
- Advanced Artificial Photosynthesis Catalyst Uses CO2 More Efficiently to Create Biodegradable Plastics
Thursday, February 15, 2024
- With Just a Little Electricity, Researchers Boost Common Catalytic Reactions
Wednesday, February 14, 2024
- Microscopy: Overcoming the Traditional Resolution Limit for the Fast Co-Tracking of Molecules
Tuesday, February 13, 2024
- Not Only in Information Technology: Restart Also Works in Chemical Simulations
Monday, February 12, 2024
- Key Advance for Capturing Carbon from the Air
Friday, February 9, 2024
- Towards A Better Way of Releasing Hydrogen Stored in Hydrogen Boride Sheets
Thursday, February 8, 2024
- Illuminating the Invisible: Detecting Proteins Linked to Diseases
- Greenhouse Gas Repurposed
Wednesday, February 7, 2024
- BESSY II: Molecular Orbitals Determine Stability
Tuesday, February 6, 2024
- Chemists Decipher Reaction Process That Could Improve Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
- Improving Fuel Cell Durability With Fatigue-Resistant Membranes
Monday, February 5, 2024
- Ultra-Sensitive Lead Detector Could Significantly Improve Water Quality Monitoring
Friday, February 2, 2024
- Edge-to-Edge Assembly Technique for 2D Nanosheets
Thursday, February 1, 2024
- Intensifying the Production of High-Value Compounds from Industrial Waste
Wednesday, January 31, 2024
- Groundbreaking Genome Editing Tools Unlock New Possibilities for Precision Medicine
Tuesday, January 30, 2024
- Small Yet Mighty: Showcasing Precision Nanocluster Formation With Molecular Traps
Monday, January 29, 2024
- High-Efficiency Carbon Dioxide Electroreduction System Reduces Our Carbon Footprint and Progressing Carbon Neutrality Goals
Thursday, January 25, 2024
- Teaching Nature to Break Human-Made Chemical Bonds
Wednesday, January 24, 2024
- A New Design Improves Water Decontamination Via Plasma Jet
- New Study Unveils How Plants Control the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species
Monday, January 22, 2024
- New Sustainable Method for Creating Organic Semiconductors
- Groundbreaking Discovery Enables Cost-Effective and Eco-Friendly Green Hydrogen Production
Thursday, January 18, 2024
- Physical Processes Can Have Hidden Neural Network-Like Abilities
- Chemical Synthesis: New Strategy for Skeletal Editing on Pyridines
- Lighting the Path: Exploring Exciton Binding Energies in Organic Semiconductors
- Next-Generation Batteries Could Go Organic, Cobalt-Free for Long-Lasting Power
- Cobalt-Free Batteries Could Power Cars of the Future
- Machine Learning Method Speeds Up Discovery of Green Energy Materials
Wednesday, January 17, 2024
- Glowing COVID-19 Diagnostic Test Prototype Produces Results in One Minute
Tuesday, January 16, 2024
- Study Reveals a Reaction at the Heart of Many Renewable Energy Technologies
- Cryo-Microscopy Reveals Nano-Sized Copy Machine Implicated in Origin of Life
Monday, January 15, 2024
- The Power of Pause: Controlled Deposition for Effective and Long-Lasting Organic Devices
Friday, January 12, 2024
- Core-Shell 'chemical Looping' Boosts Efficiency of Greener Approach to Ethylene Production
- Capturing Greenhouse Gases With the Help of Light
- Spying on a Shape-Shifting Protein
Thursday, January 11, 2024
- Catalytic Combo Converts CO2 to Solid Carbon Nanofibers
- Making an Important Industrial Synthesis More Environmentally Friendly
- Researchers Step Closer to Mimicking Nature's Mastery of Chemistry
Wednesday, January 10, 2024
- Dry-Cleaning Fluid Becomes a Synthetic Chemist's Treasure
- Scientists Discover How Ultraviolet Light Degrades Coronavirus
Tuesday, January 9, 2024
- Inspired by Greek Mythology, This Potential Drug Shows Promise for Vanquishing Parkinson's RNA in Early Studies
- Chemists Develop New Approach to Inserting Single Carbon Atoms
Monday, January 8, 2024
- Revolutionizing Stable and Efficient Catalysts With Turing Structures for Hydrogen Production
Thursday, January 4, 2024
- Engineers Invent Octopus-Inspired Technology That Can Deceive and Signal
- High-Performance Stretchable Solar Cells
Tuesday, January 2, 2024
- Using Electricity, Scientists Find Promising New Method of Boosting Chemical Reactions
- New Method Illuminates Druggable Sites on Proteins
- Aptamers: Lifesavers; Ion Shields: Aptamer Guardians
Friday, December 29, 2023
- Breakthrough in Organic Semiconductor Synthesis Paves the Way for Advanced Electronic Devices
- Molecules Exhibit Non-Reciprocal Interactions Without External Forces
Friday, December 22, 2023
- New Material Allows for Better Hydrogen-Based Batteries and Fuel Cells
Thursday, December 21, 2023
- Blue PHOLEDs: Final Color of Efficient OLEDs Finally Viable in Lighting
Tuesday, December 19, 2023
- New Strategy Reveals 'full Chemical Complexity' Of Quantum Decoherence
- Unveiling Molecular Origami: A Breakthrough in Dynamic Materials
Monday, December 18, 2023
- First Observation of How Water Molecules Move Near a Metal Electrode
- For This Emergent Class of Materials, 'solutions Are the Problem'
Friday, December 15, 2023
- Computational Model Captures the Elusive Transition States of Chemical Reactions
Wednesday, December 13, 2023
- Nanoprobe With a Barcode
Monday, December 11, 2023
- Nanoparticle-Delivered RNA Reduces Neuroinflammation in Lab Tests
Friday, December 8, 2023
- First Observation of Structures Resulting from 3D Domain Swapping in Antibody Light Chains
- A Fork in the 'rhod': Researchers Unveil Comprehensive Collection of Rhodamine-Based Fluorescent Dyes
Tuesday, December 5, 2023
- Chemists Create Organic Molecules in a Rainbow of Colors
- From Infamy to Ingenuity: Bacterial Hijack Mechanisms as Advanced Genetic Tools
Monday, December 4, 2023
- Researchers Decode Aqueous Amino Acid's Potential for Direct Air Capture of CO2
- New Technique Efficiently Offers Insight Into Gene Regulation
- LATEST NEWS
- Top Science
- Top Physical/Tech
- Top Environment
- Top Society/Education
- Health & Medicine
- Mind & Brain
- Living Well
- Space & Time
- Matter & Energy
- Business & Industry
- Automotive and Transportation
- Consumer Electronics
- Energy and Resources
- Engineering and Construction
- Telecommunications
- Textiles and Clothing
- Biochemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Thermodynamics
- Electricity
- Energy Technology
- Alternative Fuels
- Energy Policy
- Fossil Fuels
- Nuclear Energy
- Solar Energy
- Wind Energy
- Engineering
- 3-D Printing
- Civil Engineering
- Construction
- Electronics
- Forensic Research
- Materials Science
- Medical Technology
- Microarrays
- Nanotechnology
- Robotics Research
- Spintronics
- Sports Science
- Transportation Science
- Virtual Environment
- Weapons Technology
- Wearable Technology
- Albert Einstein
- Nature of Water
- Quantum Computing
- Quantum Physics
- Computers & Math
- Plants & Animals
- Earth & Climate
- Fossils & Ruins
- Science & Society
- Education & Learning
Strange & Offbeat
- Two Species Interbreeding Created New Butterfly
- Warming Antarctic Deep-Sea and Sea Level Rise
- Octopus Inspires New Suction Mechanism for ...
- Cities Sinking: Urban Populations at Risk
- Puzzle Solved About Ancient Galaxy
- How 3D Printers Can Give Robots a Soft Touch
- Combo of Multiple Health Stressors Harming Bees
- Methane Emission On a Cold Brown Dwarf
- Remarkable Memories of Mountain Chickadees
- Predicting Future Marine Extinctions
Trending Topics
Your browser is not supported
Sorry but it looks as if your browser is out of date. To get the best experience using our site we recommend that you upgrade or switch browsers.
Find a solution
- Skip to main content
- Skip to navigation
- hot-topics Extras
- Newsletters
- Reading room
Tell us what you think. Take part in our reader survey
Celebrating twenty years
- Back to parent navigation item
- Collections
- Water and the environment
- Chemical bonding
- Antimicrobial resistance
- Energy storage and batteries
- AI and automation
- Sustainability
- Research culture
- Nobel prize
- Food science and cookery
- Plastics and polymers
- Periodic table
- Coronavirus

- More from navigation items
Organic chemistry
The latest chemistry news and research on organic chemistry, including synthesis, natural products and total synthesis, reaction mechanisms and supramolecular chemistry, from the Royal Society of Chemistry's magazine, Chemistry World

Water microdroplet chemistry enables catalyst-free Diels–Alder reaction
2024-04-17T13:30:00Z
‘Quasi-benzyne’ radical drives exotic reactivity
Could mechanochemistry have saved Abbott Laboratories $250 million?
2024-04-11T13:30:00Z
Ball milling solves problem of disappearing ritonavir polymorph

Telling left from right: chirality detection faces up to its weaknesses
2024-04-08T08:05:00Z
New solutions are being found to an enduring problem in chemistry
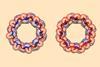
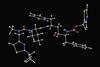
First mirror-image cyclodextrins come together ‘like Lego’
2024-04-05T08:30:00Z
L-enantiomers could be more stable than their existing, more common, forms
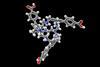
Crystalline cages create unusual ‘touchless’ sensors
2024-03-28T14:30:00Z
Researchers connect chemistry and engineering to create touch-free buttons based on the detection of the skin’s water

Cross-coupling technique cracks open alcohols for chemical synthesis
2024-03-26T14:30:00Z
A new alcohol–alcohol cross coupling reaction could become a powerful new tool for synthetic chemists

DIY recycling protocol could save organoiridium waste from incinerators
2024-03-22T13:16:00Z
‘A very good solution to solve a niche problem’

3D-printed capsules enhance speed and safety of synthetic chemistry
2024-03-21T14:38:00Z
Encapsulated reagents allow chemists to ditch their Schlenk line to synthesise ferrocene

Where does bromine come from?
2024-03-20T14:30:00Z
A journey that begins in a former oil field in Arkansas

Energetically unfavourable Diels-Alder reaction driven by chemical fuel
2024-03-19T09:30:00Z
Carbodiimide fuel powers rare, thermodynamically unpromising reaction between diene and dienophile

Harnessing biodiversity through natural products research in the Philippines
2024-03-15T14:30:00Z
Collaborative projects aim to produce cheaper and more effective medicines

Porphyrin ribbons transport charge with no resistance
2024-03-13T14:30:00Z
Molecules could form the basis of ‘perfectly transmissive’ molecular wires


Bad habits obscuring thermodynamic reality of photocatalytic reactions
2024-03-13T13:38:00Z
Dubious assumptions and contentious nomenclature muddying the literature
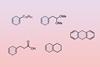
Sodium lumps, glucose and mechanochemistry behind ammonia-free Birch reduction
2024-03-11T11:11:00Z
Protocol solves ‘malleability problem’ of activating alkali metals like sodium

Enzyme engineering makes blue denim greener
2024-03-07T14:30:00Z
Environmentally friendlier alternative to indigo dye can now be made at a competitive price
Classic cross-coupling reactions rerouted to make new products
2024-03-07T09:30:00Z
Combination of Suzuki–Miyaura and Buchwald–Hartwig couplings produces carbon–nitrogen–carbon linked compounds
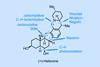
(+)-Heilonine
2024-02-28T09:34:00Z
A short route that brings together the classical and cutting-edge
Machine learning could ‘change the paradigm’ for polaritonic chemistry
2024-02-26T15:30:00Z
Model reveals influence of vibrational strong coupling during light-driven reaction

Bin Liu: ‘Breakthroughs always need patience’
2024-02-23T14:15:00Z
The materials expert on deciding to become a scientist, collaboration and fishing
Regioselective nitrogen-insertion reaction is latest addition to skeletal editing toolbox
2024-02-08T09:20:00Z
Protocol transforms arenols into benzazepines
- Previous Page
- Contributors
- Terms of use
- Accessibility
- Permissions
- This website collects cookies to deliver a better user experience. See how this site uses cookies .
- This website collects cookies to deliver a better user experience. Do not sell my personal data .
- Este site coleta cookies para oferecer uma melhor experiência ao usuário. Veja como este site usa cookies .
Site powered by Webvision Cloud
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.6(25); 2021 Jun 29

Green Chemistry: A Framework for a Sustainable Future
For more than three decades, Green Chemistry has provided a framework for chemists and chemical engineers to do their part in contributing to the broad scope of global sustainability. American Chemical Society journals are a great venue for these scientists to share their latest results and provide a resource to the chemistry community and beyond for understanding current problems and envisioning solutions. We believe this is an opportune time to highlight some of the leading articles on the broad theme of Green Chemistry being published today through a Virtual Issue of selected works from nine ACS chemistry and engineering journals.
The inception of this Virtual Issue is no coincidence. We have timed it to the 2021 Green Chemistry & Engineering Conference taking place virtually June 14–June 18. Now celebrating its 25th edition, we have seen progress toward more sustainable chemistries being showcased and celebrated at each GC&E conference. 1 The theme of this year’s meeting, “Sustainable Production to Advance the Circular Economy”, is particularly bold. It highlights the recognition that contributions must take into account a systems approach to reducing environmental impact through intentional design of chemical products, not just considering how raw materials are sourced and in the manufacture and use of industrial and consumer goods but also how these materials and goods may be reused, recycled, or upcycled. The embrace of life-cycle thinking as a goal among the Green Chemistry community comes at the backdrop of the realization of limited resources and a climate crisis the likes of which most of us still fail to fully comprehend. We believe these selected articles are stepping stones on the pathway to advance closed-loop economies while still serving as models for innovation at a fundamental level within their respective chemistry subdisciplines.
The drive for efficiency in organic synthesis merges the best of the idealisms of the Enlightenment and the Renaissance. Certainly, there is a premium on rationalism, with an aspiration of mechanistically sound reaction design and process development. But at the same time, the aesthetic appeal of the new ideas that culminate in the advances we now see routinely is unmistakable. There is no constraint on curiosity when we consider the boundary conditions of efficient, environmentally benign processes. On the contrary, these considerations spawn new concepts and approaches, ranging from postmodern expansions of photochemistry, reconsideration of seminal thinking about solvation, importation of physical and mechanical phenomena, to reaction development—the creativity born of efficiency considerations now drives major technology innovation in chemistry. The Journal of Organic Chemistry and Organic Letters are delighted to participate in this Virtual Issue with a selection of perspectives, research articles, and letters that highlight just some of the most impactful science in this arena, across a very wide swath of chemical space. Organometallics , a journal with a long-standing history of reporting fundamental advances in organometallic chemistry, catalysis, and materials, has selected contributions to this Virtual Issue that best highlight the diverse nature of this type of organometallic chemistry and that are likely to impact development of more sustainable chemical processes and the transition to a circular economy.
ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering is a world leader in publishing groundbreaking research that addresses the challenges of sustainability, advancing the principles of Green Chemistry and Green Engineering with global reach and impact. Key coverage includes catalysis with emerging feedstocks and synthetic methods for preparing materials and chemicals in a sustainable way to help bring critical innovations from a research setting to commercialization. The journal takes pride in its central role in promoting innovations that will enable the implementation of a circular economy. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research publishes many, many papers in the Green Chemistry and sustainability space as these are core considerations in applied chemistry and chemical engineering. The ten articles in this Virtual Issue are just the tip of the iceberg and represent the types of papers readers can find in I&EC Research . We would encourage those interested in the Virtual Issue to browse through other recent issues of the journal, where they will quickly find other articles aligned with the themes of the conference. Contributions from Environmental Science & Technology and Environmental Science & Technology Letters clearly illustrate the interdisciplinary systems approach that is required to address key environmental challenges that impede sustainability efforts—from remediation of pollution to design of next-generation safer and functional chemicals. Several of the high-impact contributions selected have been the subject of media coverage. Contributions from ACS Omega , an interdisciplinary open-access journal, were selected to highlight the potential impact of open-source publications and their importance in connecting scientists across industry and academia. With a similar goal, Organic Process Research & Development has a tradition of bridging industrial and academic research. Its focus on process chemistry as the science that enables the safe, environmentally benign, and economical manufacturing of chemicals is evident in the selected articles for this Virtual Issue, which highlight aspects of catalysis, synthetic methodology development, and synthetic strategy exploration that are needed to enable circular economies.
Minimizing Dependence on Fossil Fuels
The contributions from across these journals demonstrate that the design of methods for circularity necessitates multidisciplinary approaches and careful definition of the problem being addressed. 2 One of the key challenges we face continues to be decreasing our dependence on fossil fuels for chemical and fuel production. This entails both the efficient and clean transformation of renewable (biobased) raw materials into functional chemicals and fuels, as well as efficient CO 2 capture and conversion into fuels and chemicals. A number of exciting advances in this Virtual Issue highlight our progress on both fronts. In a critical review, Wang and Su et al. (DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b01453 ) discuss the development and application of engineered multifunctional nanohybrids of carbon nanomaterials and metal/metal oxide nanoparticles, which exhibit promising multifunctionalities for addressing the critical energy–water–environment (EWE) nexus.
More specifically on the topic of CO 2 capture and use, Hatton et al. (DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c04512 ) identify a key challenge for carbon capture and storage (CCS)—the quest for net-negative emissions. They report that bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) with molten sorbents offers a unique opportunity to realize net-negative emissions with minimal indirect emissions and low-cost separation of CO 2 from other gases. BECCS could remove 300–850 kg of CO 2 equivalents from the atmosphere per megawatt-hour of electrical output (kg/MWh e ), making it advantageous to other low carbon technologies and allowing the offset of emissions from hard-to-abate industries. In the search for efficient materials for carbon capture, Sun et al. (DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c04126 ) report the development of light-responsive metal–organic frameworks (LMOFs), which have tunable structures and performances. While conventional amines cannot achieve controllable adsorption separation, these LMOFs have tunable amine-based active sites, which enhance CO 2 capture and control adsorption and separation. Several advances also highlight the improvement of technologies for reduction of CO 2 based on electrocatalytic methods, including the use of Ru and Re catalysts (DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.9b00815 ) and the use of ionic liquids for this application (DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c04037 ), as well as exploration of Earth-abundant iron catalysts (DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.8b00711 ). Complementary to electrochemical methods, enzymatic (DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b05284 ) and photocatalytic (DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c04126 ) methods are also shown to have a niche in the toolbox for conversion and utilization of CO 2 , as highlighted in reports by Sun et al. and Jin and Kim et al., respectively.
The efficient and clean transformation of renewable raw materials into functional chemicals and fuels has blossomed from a theoretical construct to an interdisciplinary field that is fueled by fundamental innovations in synthetic chemistry and guided by practical applications of biorefineries. The requirements of biorefineries for flexibility of feedstocks, relatively mild operational conditions, and low environmental impact have resulted in highly innovative methods for defunctionalizing and refunctionalizing biomass feedstocks to value-added chemicals and materials. On the defunctionalization front, Stephenson et al. report an organocatalytic method for photochemical C–O bond cleavage of the β-O-4 linkage in lignin scaffolds. This method offers a metal-free strategy to prior reports and is applicable to continuous flow processing (DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03029 ). Cellulose-derived platform chemicals can also be obtained more efficiently from using a redox-switchable biocatalyst for controllable oxidation or reduction of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) into high-value derivatives (DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c02178 ).
Expanding the gamut of new platform chemicals that can be obtained from biomass, Rio et al. describe the presence of valuable phenolic compounds incorporated into lignins, such as flavonoids, hydroxystilbenes, and hydroxycinnamic amides, which behave as authentic lignin monomers and are potentially available in large amounts from the abundant in waste products from processing of agricultural or forest biomass (DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c01109 ). Tomishige et al. discuss the utility of erythritol as a C4 platform in biomass refinery, derived from fermentation of sugars and glycerol (DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b04046 ).
The direct valorization of lignin to functional chemicals presents potential new avenues for efficiently converting lignin to chemical products. Yin and Huang et al. report a lignin–carbohydrate complex that is a potent antioxidant for scavenging reactive oxygen species in vitro and zebrafish in vivo (DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b05290 ). Lignin was also used in the manufacture of polyurethane formed by oxidative liquefaction (DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00285 ). Many other transformations of biomass to functional chemicals and materials are discussed in two timely reviews on biomass-derived carbonaceous materials (DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b06550 ) and bacterial cellulose-based composite scaffolds for biomedical applications (DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00125 ). On the critical front of transforming our polymer platform to renewable materials, consistent with the circular economy, Vodovotz et al. discuss how we can narrow the gap for bioplastic use in single-use food packaging, focusing on the most recent development successes in bioplastic materials and highlighting the “gaps” between bioplastics and their conventional counterparts with respect to their properties (DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b03755 ).
Minimizing the Impact of Chemical Synthesis and Manufacturing
Another key challenge in developing manufacturing infrastructure for a circular economy remains the minimization of the overall environmental footprint, which must minimize both the environmental impact of the manufacturing processes of chemicals as well as their potential hazard and persistence of the commodity chemicals produced. While the former has been a cornerstone of research in Green Chemistry from its inception in the early 1990s, it is still a fertile area of research, and we see evidence of that in this Virtual Issue. The latter will be addressed in further detail later in this Editorial.
Sustainability in organic chemistry, especially in organic synthesis, has been driving innovation for decades. With the amount of waste generated in many synthetic chemistry routes, especially at scale in manufacturing, we are faced with not only an ethical imperative to develop more sustainable chemical processes and products but also a financial imperative. Metrics to gauge our progress, including process mass intensity (PMI), have been developed that allow all aspects of a process to be compared. For example, conducting a reaction in water may not necessarily be an improvement if several volumes of an organic solvent are needed to extract/purify the product. One could even argue that water can be problematic because its high boiling point makes recycling energy intensive, but we do not know these details without consciously thinking about them. A recent perspective highlights the need to explicitly include the assessment of sustainability using Green Chemistry metrics. 3
A number of studies highlight advances in catalysis and reaction engineering that have led to waste and energy minimization for processes that still pose significant challenges. Four of the contributions from Organic Letters focus on use of less harmful reagents, catalysts, or routes (e.g., DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c00850 ; DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03272 ; and DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01043 ). On the catalysis front, we see an increase in the scope of synthetic transformations facilitated by supported catalysts (DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.9b00082 ; 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c01058 ). In one example, Pei, Lu, and Cai et al. described the preparation of a reusable magnetic Ag–Fe 3 O 4 catalyst supported on cellulose microspheres for reduction of nitrophenols (DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00437 ). We also see increased exploration of the utility of base metals in catalysis and organocatalytic processes being performed under mild conditions and with low catalyst loading: for highly enantioselective epoxidation of α,β-unsaturated ketones, Jarczak et al. employed an amide-based Cinchona alkaloid at loadings as low as 0.5 mol % as a hybrid phase-transfer organocatalyst (DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03272 ).
On the application front, the quest for reducing traditionally high E -factors in the pharmaceutical sector continues. In two critical perspectives, colleagues from major pharmaceutical companies highlight the need to develop less wasteful and toxic methods for peptide and oligonucleotide synthesis and purification methods, in light of the growing utility of biological peptide-based pharmaceuticals (DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c02291 ; 10.1021/acs.joc.8b03001 ). In another perspective in The Journal of Organic Chemistry , Rossen highlights insights from process chemistry that can reduce the impact of synthetic chemistry at smaller scales (DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b00344 ). In Organometallics , Leahy and colleagues provide a perspective from the pharmaceutical industry on the role of catalysis with Earth-abundant metals (DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.8b00566 ).
Catalysis with Earth-abundant rather than precious metals continues to be an active area of research and key component of sustainable chemistry research. Manuscripts in Organometallics focus on cobalt (DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.0c00241 ) and iron (DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.1c00200 ) catalysts for hydrosilylation and nickel precursors (DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.0c00485 ) and heterogeneous catalysts (DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.9b00082 ) for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling, one of the most widely used methods for C–C bond formation. Pidko et al. also report the role of manganese in mediating C–C bond formation from organoboranes (DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.0c00781 ).
Waste reduction also continues to be tackled on the solvent front in the development of alternative solvents, such as less hazardous task-specific ionic liquids (DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b04091 ), deep eutectic solvents (DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c02039 ; 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03520 ), and increasing the scope and efficiency of reactions in water, such as amidation (DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01676 ), amine synthesis, and transfer hydrogenation (DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.0c00554 ; 10.1021/acs.organomet.1c00133 ). We also see the development of new biomass-derived solvents with greener profiles, such as glycerol-derived 1,2,3-triethoxypropane and systematic solvent selection protocols for “greener” solvents (DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c03789 ; 10.1021/acs.oprd.0c00326 ).
Designing Chemicals with Minimal Hazard
While minimizing the impact of chemicals through use of renewable resources and cleaner process technologies remains critical, the importance of the toxicological profile of the chemicals being circulated is now increasingly being recognized. The challenge of efficiently assessing the toxicological risks of thousands of chemicals at the design stage and for chemicals already in use requires interdisciplinary research efforts. Many toxicological mechanisms of interaction remain poorly understood and therefore unregulated. In this Virtual Issue, Shi et al. describe how in silico methods of molecular dynamic simulations will help to define molecular initiation events and identify toxicological mechanisms, enabling quick and effective screening of a wider range of chemicals (DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.9b00073 ). Blum et al. and Kwiatkowski et al. further propose that individual testing of thousands of chemicals is unrealistic, and chemical “classes” should be screened, using broad subclasses as required. Venier et al. (DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.9b00582 ) provide excellent examples of the regrettable substitution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PDBEs) with organophosphate ester flame retardants (OPFRs), resulting in undesirable toxicological outcomes, and Kwiatkowski et al. consider the scientific bases for dealing with perfluoroalkyl (PFAS) chemicals as a class (DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00255 ).
The design of plastics to be both biodegradable and sustainably produced from nonpetrochemical sources is another critical circular design area requiring urgent research input. The ES &T paper by Napper and Thomson (DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.8b06984 ) reports a lack of biodegradable plastic formulations used for carrier bags that offered rapid rates of decay compared to conventional plastic bags. For environmental concerns, Nguyen et al. (DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.8b00671 ) provide a novel and simple method in ES &T Letters to assess the quantities of microplastic fragments in environmental matrices, using hydrophobic iron nanoparticles to extract microplastics from soil, sediments, and water magnetically, and could be used as a sustainable remediation tool.
Sustainable Water Resources
The sustainable supply of potable drinking water is a global imperative and was identified as a United Nations Sustainable Development Goal in 2015. Just last month in ACS Omega , Gude et al. provided a critical evaluation and perspective of two major routes for developing more sustainable and circular-economy-based wastewater treatment and showed that integrating both concepts may result in superior energy and resource efficiency for wastewater treatment systems (DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05827 ). Zodrow et al. (DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00019 ) report on the use of self-healing bacterially formed cellulose fiber networks creating sustainable biological membranes (Live Filtration Membranes) capable of filtering water for drinking water purposes. Alternative energy-efficient and sustainable remediation approaches include the application of UV/sulfite water treatments to offer effective degradation of persistent PFAS chemicals in raw water for onward drinking water use, reported by Liut al. in ES &T Letters (DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00236 ).
Environmentally sustainable and energy-efficient nanotechnology membranes also have water purification applications, often in combination with other environmental uses, including energy harvesting, environmental sensing, and remediation. Desalination technologies with superior high efficiency are based on selective desalination membranes (Geise et al.; DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.9b00351 ) and reduced graphene oxide membranes with minimal impact of nanowrinkles (Zhang et al.; DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00143 ). In addition to desalination, the degradation of persistent organic pollutants is also a key priority for water purification. Li, Li, and Zhang et al. (DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.8b05685 ) report on the use of a porous, coral-like nanostructure photoelectrode for this purpose while simultaneously producing electricity. Luo et al. describe mechanisms of carbo-catalysis in carbon nanotubes with persulfate oxidation for water treatment applications (DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.0c02645 ).
Closing the Loop
The environmentally sustainable recovery of resources from wastes is also a burgeoning area of research. In a highly cited account, Suh and Scott et al. report benchmarks for degradation rates of common plastics, which will help prioritize future research efforts on chemical degradation to close the loop (DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b06635 ). In Organometallics , O’Hair and Ryzhov et al. explore the depolymerization of ethylene with palladium catalysts to understand approaches to remediation of polyolefins (DOI: 10.1021/acs.organomet.0c00782 ). Li et al. report on the recovery of lithium from spent batteries using an acid-free mechanochemical process that utilizes salt and sodium carbonate as the sole reagents (DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b01919 ). Lo et al. provide a critical review on the use of selective sorbents for the removal and recovery of phosphates from water and wastewaters (DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b05569 ). Munasinghe-Arachchige and Nirmalakhandan (DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00355 ) describe the recovery of nitrogen from sewage sludge and livestock manure as offering some circularity to the high global demand for nitrogenous fertilizers. The capture and conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate is reported by Kim and Jin et al. (DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b05284 ) using an environmentally simple system of stabilized carbonic anhydrases loaded onto electrospun polymer nanofibers.
Lifecycle and Systems Thinking
The ability to apply life-cycle thinking to prioritize research and propose truly long-term, sustainable solutions is critical for identifying feasible ways to address circularity. Two common life-cycle assessment (LCA) methods—process LCA and economic input–output LCA—both suffer from different shortcomings. As a result, many hybrid methods are used to improve the overall accuracy. Luo and Ierapetritou analyze different hybrid LCA methodologies through a case study of two biomass-based p -xylene production technologies and provide key insights applicable to future LCA analysis (DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c04709 ). LCA analyses of the synthesis of widely used titanium dioxide nanoparticles (DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.8b06800 ) and butyl acetate (DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c04233 ) provide theoretical guidance for more sustainable production of both. Parkinson and Hunt apply such an approach in proposing the conversion of agricultural land in groundwater-stressed areas from irrigated crop types to rain-fed crop types combined with diversification to solar harvesting, so-called “agrivoltaics” (DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00349 ).
Future Research Needs in Developing a Circular Economy
The selected publications in this Virtual Issue exemplify the diverse and interdisciplinary contributions surrounding the theme of this year’s conference. They also allow us to identify areas that will require further emphasis in order to strategically advance the field toward applications that facilitate circularity. Some of these areas include:
- Depolymerization and defunctionalization methods for existing chemicals that can allow circularity, especially for plastics;
- Design of circular systems with consideration of human health and ecotoxicity, ideally via rational design of benign commodity chemicals;
- Systematic application of life-cycle analysis, or thinking, and process metrics in developing new manufacturing/synthetic routes;
- Implementation of machine learning and other big-data methods to drive innovation toward new paradigms of circularity.
In order to allow future contributions to highlight the potential application to circular economies, authors may want to consider explicitly addressing some of following questions in their manuscripts. First, consider the source of the materials being used, and if it is fossil-fuel-derived, consider if there is a biobased alternative that could provide the same chemical insights. If elements are used that are facing limited supply, consider whether the synthetic routes and processes could help reduce the use of such materials. Second, discuss whether the method described could impact different stages of a chemical’s life cycle. For example, is it a step that is potentially reversible based on kinetics and thermodynamics? If it produces byproducts, could those be a valuable resource? And finally, consider whether the method or product constitutes a safe product that can be either recycled, reused, or remanufactured. Addressing such questions forces the authors to apply life-cycle thinking and to broaden their discussion of the prior art most closely related to the advances presented. We look forward to future fruitful contributions to this field from the innovative authorship of the ACS family of journals.
Views expressed in this editorial are those of the authors and not necessarily the views of the ACS.
- Erythropel H. C.; Zimmerman J. B.; de Winter T. M.; Petitjean L.; Melnikov F.; Lam C. H.; Lounsbury A. W.; Mellor K. E.; Jankovic N. Z.; Tu Q. S.; Pincus L. N.; Falinski M. M.; Shi W. B.; Coish P.; Plata D. L.; Anastas P. T. The Green ChemisTREE: 20 years after taking root with the 12 principles . Green Chem. 2018, 20 ( 9 ), 1929–1961. 10.1039/C8GC00482J. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anastas P. T. Circularity. What’s the Problem? . ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8 ( 35 ), 13111–13111. 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c05714. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Debecker D. P.; Hii K. K.; Moores A.; Rossi L. M.; Sels B.; Allen D. T.; Subramaniam B. Shaping Effective Practices for Incorporating Sustainability Assessment in Manuscripts Submitted to ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering: Catalysis and Catalytic Processes . ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9 ( 14 ), 4936–4940. 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c02070. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

- April 22, 2024 | Groundbreaking Research on MAGE Proteins Offers New Hope for Resistant Cancers
- April 22, 2024 | The Science of Aging: New Insights Into When “Old Age” Begins
- April 22, 2024 | Scientists Discover Potential Interstellar Origins of Life on Earth
- April 22, 2024 | Antarctica’s Ice on Edge: 2024’s Near Record Low Predictions
- April 22, 2024 | Breakthrough in Bioinformatics: AI Predicts Cell Type Transformations
Chemistry News
SciTechDaily features the latest chemistry news and recent research articles from leading universities and institutes from around the world. Here, we delve into the ever-evolving realm of molecules, elements, and reactions, bringing you up-to-date insights from renowned scientists and researchers.
Read interesting chemistry news and breakthrough research on related topics like Biochemistry , Chemical Engineering , Materials Science , Nanoparticles , and Polymers .
Our comprehensive coverage spans the spectrum of chemistry, from organic and inorganic chemistry to biochemistry, analytical chemistry, and beyond. Stay informed about groundbreaking advancements, innovative techniques, and novel applications shaping the future of chemistry and its impact on our everyday lives. Discover, learn, and fuel your passion for chemistry with SciTechDaily.
Chemistry April 21, 2024
Unlocking the Secrets of Space Chemistry With Cold Coulomb Crystals
Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder have developed experiments to replicate the chemical reactions of the Interstellar Medium, using techniques like laser cooling and…

Trash To Treasure – Chemists Turn Metal Waste Into Hydrogen Catalyst

Organic Catalyst Discovery Could Reduce the Cost of Fuel Cells

“Neutronic Molecules” – Neutrons Meet Quantum Dots in Groundbreaking MIT Discovery
A Molecular Moonlander: PPh3’s Movement Challenges Conventional Science

Researchers Develop Simple Way To Harvest More “Blue Energy” From Waves

Powering the Future: Unbiased PEC Cells Achieve Unprecedented Efficiency

The Power of Waste: A New Innovative Approach To Improve the Energy Efficiency of Carbon Conversion
The Future of Solar Cells and More – Japanese Chemists Develop Glowing, Self-Healing Material

Chemistry April 9, 2024
Microbial Magic: Genetic Tweaks Unlock Superior Bioplastics
Engineered bacteria can produce a plastic modifier that makes renewably sourced plastic more processable, more fracture-resistant and highly biodegradable even in sea water. The Kobe…
Revolutionizing Clean Energy: Transforming Rare Earth Element Extraction
Scientists have developed an innovative method to separate lanthanides, crucial for clean energy technologies, by combining substances that attract either lighter or heavier elements. This…

Chemistry April 7, 2024
Japanese Scientists Unveil Game-Changing Material for Magnesium Batteries
Scientists at Tohoku University have achieved a significant breakthrough in battery technology by creating a new cathode material for rechargeable magnesium batteries (RMBs). This material…
Decoding the Origin of Life: Scientists Solve Early Earth RNA Puzzle
Recent research illustrates how RNA molecules’ chemical characteristics might have played a crucial role in the development of complex life forms. How did complex life…

Chemistry April 6, 2024
From Chaos to Life: Unraveling Nature’s Ancient Molecular Kitchen
Life is complicated. What is true for our everyday existence also holds for the many complex processes that take place inside cells. Proteins are continuously…

Chemistry April 4, 2024
Molecular Memory Breakthrough: Entering a New Era of Data Storage
Some molecules respond to external light pulses by changing their structure and holding certain states that can be switched from one to another. These are…

Chemistry April 3, 2024
Mixology Science: Using Chemistry and a 300-Year-Old Technique To Reinvent a Drink [Video]
Milk washing, a centuries-old technique, improves the flavor and texture of drinks. Adding milk to an alcoholic drink and then curdling that milk is a…

Cheaper, Cleaner, Greener: Scientists Develop New Way To Produce Ammonia
Low temperature, regenerative method conserves energy and effectively generates common chemical. Among the many chemicals we use every day, ammonia is one of the worst…

Chemistry April 2, 2024
Carbon Alchemy: MIT’s Revolutionary CO2 Conversion Technology
A catalyst tethered by DNA boosts the efficiency of the electrochemical conversion of CO2 to CO, a building block for many chemical compounds. MIT chemical…
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Research articles
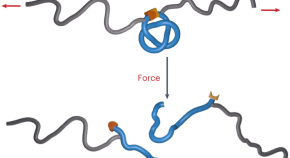
Mechanical scission of a knotted polymer
Knots reduce the tensile strength of macroscopic threads and fibres. Now it has been shown that the presence of a well-defined overhand knot in a polymer chain can substantially increase the rate of scission of the polymer under tension, as deformation of the polymer backbone induced by the tightening knot activates otherwise unreactive covalent bonds.
- Robert Nixon
- David A. Leigh
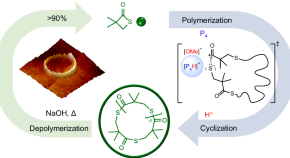
Proton-triggered topological transformation in superbase-mediated selective polymerization enables access to ultrahigh-molar-mass cyclic polymers
The selective synthesis of ultrahigh-molar-mass (UHMM) cyclic polymers from direct polymerization is elusive. Using a chemically recyclable polythioester as a model, it has now been shown that a common superbase mediates living linear-chain growth, followed by proton-triggered linear-to-cyclic topological transformation, producing UHMM cyclic polymers with a narrow dispersity.
- Liam T. Reilly
- Eugene Y.-X. Chen
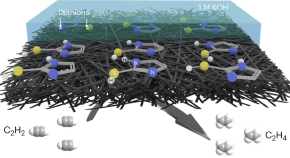
Deprotonated 2-thiolimidazole serves as a metal-free electrocatalyst for selective acetylene hydrogenation
Although metal-free catalysts, featuring defined active sites, represent alternatives to scarce or problematic metals, metal-free compounds rarely show activities as promising as metal-based materials. Now deprotonated 2-thiolimidazole is shown to serve as a metal-free electrocatalyst for selective acetylene hydrogenation and achieves competitive performances with metal-based catalysts.
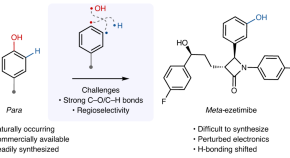
A para - to meta -isomerization of phenols
Phenols and their derivatives are ubiquitous in nature and important within the chemical industry. Their properties are linked to their substitution patterns, but meta -isomers are underrepresented due to the difficulty of their synthesis. Now we address this challenge by describing a 1,2-transposition of phenols that enables a formal para - to meta -isomerization.
- Simon Edelmann
- Jean-Philip Lumb
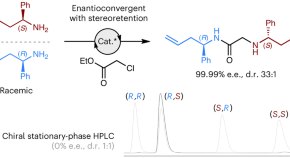
Stereoretentive enantioconvergent reactions
Enantioconvergent reactions convert both enantiomers of a racemic starting material into a single enantioenriched product. All currently known enantioconvergent processes necessitate the loss or partial loss of the racemic substrate’s stereochemical information. Now, an alternative approach has been developed that proceeds with full retention of the racemic substrate’s configuration.
- Steven H. Bennett
- Jacob S. Bestwick
- Andrew L. Lawrence
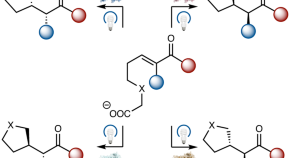
Stereodivergent photobiocatalytic radical cyclization through the repurposing and directed evolution of fatty acid photodecarboxylases
Despite their intriguing photochemical activities, natural photoenzymes have not yet been repurposed for new-to-nature activities. Now, by leveraging the strongly oxidizing excited-state flavoquinone cofactor, fatty acid photodecarboxylases were engineered to catalyse unnatural decarboxylative radical cyclization with excellent chemo-, enantio- and diastereoselectivities.
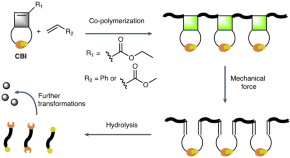
Mechanically triggered on-demand degradation of polymers synthesized by radical polymerizations
Radical polymerizations yield polymers that cannot easily be degraded. The co-polymerization of cyclobutene-based monomers with conventional vinyl monomers has now been shown to result in co-polymers with cyclobutane mechanophores in their backbone, which facilitate on-demand degradation through a combination of mechanical activation and hydrolysis. This approach offers a promising avenue for the degradation of all-carbon-bond-backbone polymers.
- Sètuhn Jimaja
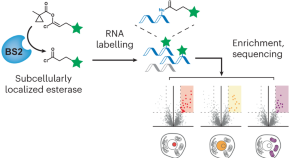
Bioorthogonal masked acylating agents for proximity-dependent RNA labelling
RNA localization is key to regulating cellular function but is challenging to measure in an unbiased manner. Now a combination of enol-masked acylating probes with a bioorthogonal esterase to locally unmask them provides a non-radical RNA proximity labelling platform—termed BAP-seq—that enables the generation of high-resolution spatial maps of RNA.
- Shubhashree Pani
- Bryan C. Dickinson
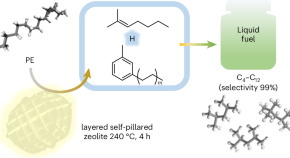
Upcycling of polyethylene to gasoline through a self-supplied hydrogen strategy in a layered self-pillared zeolite
The development of new methodologies to convert plastics into fuels without relying on noble metal-based catalysts is desirable. Now it is shown that a layered self-pillared zeolite enables the conversion of polyethylene to gasoline with a selectivity of 99% and yields of >80% without the need to use external hydrogen.
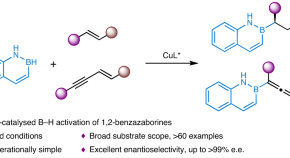
Copper-catalysed asymmetric hydroboration of alkenes with 1,2-benzazaborines to access chiral naphthalene isosteres
Chiral 1,2-benzazaborines are promising isosteres of naphthalene, but rarely explored due to the lack of efficient synthetic methods. Now, the copper-catalysed enantioselective hydroboration of alkenes with 1,2-benzazaborines has been developed, providing a general platform for the atom-economic and efficient construction of diverse chiral 1,2-benzazaborine compounds bearing a 2-carbon-stereogenic centre or allene skeleton.
- Qiuling Song
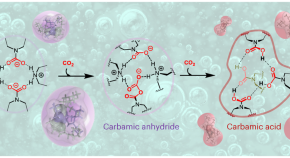
Tetrameric self-assembling of water-lean solvents enables carbamate anhydride-based CO 2 capture chemistry
Carbon capture, utilization and storage is key for climate change mitigation and developing more environmentally friendly technologies. Now it has been shown that CO 2 capture in single-component water-lean solvents is accompanied by the self-assembly of reverse-micelle-like tetrameric clusters in solution that enable the formation of various CO 2 -containing compounds.
- Julien Leclaire
- David J. Heldebrant
- Jaelynne King
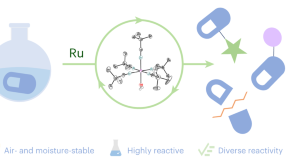
An air- and moisture-stable ruthenium precatalyst for diverse reactivity
Despite the widespread utility of ruthenium catalysts, many protocols for their use require high temperatures or light irradiation. Now, the synthesis of an air- and moisture-stable ruthenium precatalyst has been reported. This versatile catalyst drives an array of transformations and enables rapid screening and optimization of reactions, revealing previously unknown in situ generated ruthenium complexes.
- Gillian McArthur
- Jamie H. Docherty
- Igor Larrosa
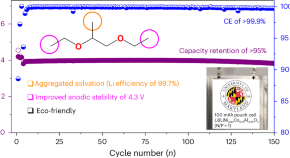
Methylation enables the use of fluorine-free ether electrolytes in high-voltage lithium metal batteries
Lithium metal batteries are an attractive energy storage technology, but their development relies on the complex interplay between the components’ chemical, physical and mechanical properties. Now, selective methylation of dimethoxyethane ether electrolytes is shown to improve electrolyte, electrode and solid–electrolyte interphase stabilities to enable high-performance 4.3 V lithium metal batteries.
- Oleg Borodin
- Chunsheng Wang
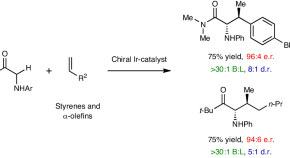
A directed enolization strategy enables by-product-free construction of contiguous stereocentres en route to complex amino acids
α-Amino acids possessing β-stereocentres are difficult to synthesize. Now, an iridium-catalysed protocol allows the direct upconversion of simple alkenes and glycine derivatives to give β-substituted α-amino acids with exceptional levels of regio- and stereocontrol. The reaction design is based on exploiting the native directing ability of a glycine-derived N–H unit to facilitate enolization of the adjacent carbonyl.
- Fenglin Hong
- Timothy P. Aldhous
- John F. Bower
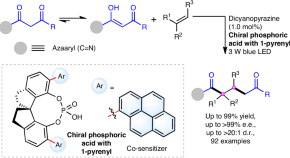
Asymmetric photoredox catalytic formal de Mayo reaction enabled by sensitization-initiated electron transfer
The redox properties of visible-light-absorbing photosensitizers are limited by the energy of visible photons, but methods using sensitization-initiated electron transfer have recently been developed to address these challenges. Now a multiphoton dual-catalyst strategy has been used to enable the enantioselective de Mayo reaction for the synthesis of enantioenriched 1,5-diketones.
- Zhiyong Jiang
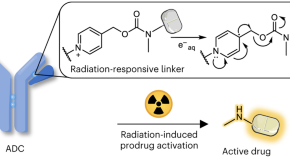
Radiotherapy activates picolinium prodrugs in tumours
Photoinduced electron transfer (PET) occurs in many chemical processes and has various applications. Here ionizing radiation was used to trigger PET for controlled drug release from an antibody–drug conjugate using a picolinium cage. The radiotherapy-activated prodrug system demonstrated high antitumour efficacy and minimal side effects.
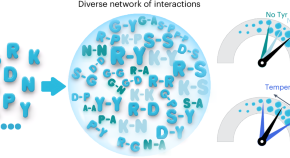
Expanding the molecular language of protein liquid–liquid phase separation
Key molecular features that drive protein liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) for biomolecular condensate have been reported. A spectrum of additional interactions that influence protein LLPS and material properties have now been characterized. These interactions extend beyond a limited set of residue types and can be modulated by environmental factors such as temperature and salt concentration.
- Cristobal Garcia Garcia
- Jeetain Mittal
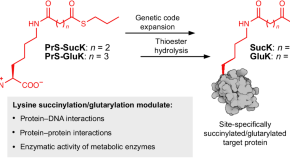
Deciphering functional roles of protein succinylation and glutarylation using genetic code expansion
Negatively charged lysine acylations—malonylation, succinylation and glutarylation—impact protein structure and function, which can affect cellular processes. Now temporarily masked thioester derivatives of succinylation and glutarylation can be used for site-specific modification of diverse bacterial and mammalian proteins, which can facilitate the study of how these lysine modifications impact enzymatic activity and control protein–protein and protein–DNA interactions.
- Marie-Lena Jokisch
- Kathrin Lang
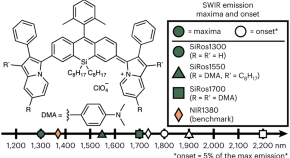
Silicon-RosIndolizine fluorophores with shortwave infrared absorption and emission profiles enable in vivo fluorescence imaging
Accessing longer-wavelength emitting organic fluorophores is critical for diagnostic imaging. Here a series of silicon-RosIndolizine fluorophores with emission maxima at 1,300 nm, 1,550 nm and 1,700 nm were synthesized. The fluorophores generate high-resolution in vivo fluorescence images in mice and establish design principles for future shortwave-infrared fluorophore designs.
- William E. Meador
- Eric Y. Lin
- Jared H. Delcamp
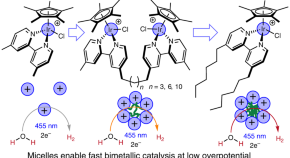
Catalyst self-assembly accelerates bimetallic light-driven electrocatalytic H 2 evolution in water
Although the light-driven generation of hydrogen from water is a promising approach to renewable fuels, the H–H bond formation step represents a persistent mechanistic question. Now light-harvesting molecular catalysts have been shown to self-assemble into nanoscale aggregates that feature improved efficiency for photoelectrochemical H 2 evolution.
- Isaac N. Cloward
- Tianfei Liu
- Alexander J. M. Miller
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
50 Research Ideas in Organic Chemistry
Unlocking the Potential: 50 Intriguing Organic Chemistry Research Ideas

Table of contents
50 intriguing organic chemistry research ideas.
In the world of science, organic chemistry is like the hidden language of life. It’s the study of carbon and its dance with other elements to create everything from medicines that heal to materials that make our world. Today, iLovePhD delves into 50 intriguing research ideas in this fascinating field, uncovering the secrets and innovations that drive progress in science.
- Green Synthesis of Organic Compounds : Explore eco-friendly methods for synthesizing organic molecules.
- Applications of Organometallic Chemistry : Discuss the use of organometallic compounds in catalysis and materials science.
- Designing Sustainable Polymers : Investigate the development of biodegradable and recyclable polymers.
- Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis : Examine recent advances in creating chiral organic compounds.
- Supramolecular Chemistry in Drug Design : Discuss how non-covalent interactions can be harnessed for drug discovery.
- Functionalization of C-H Bonds : Explore methods for selectively functionalizing carbon-hydrogen bonds.
- Natural Product Synthesis : Highlight recent total syntheses of complex natural products.
- Electroorganic Chemistry : Discuss the use of electricity as a reagent in organic reactions.
- Molecular Machines : Explore the design and applications of synthetic molecular machines.
- Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) : Investigate the use of MOFs in gas storage and separation.
- Enzyme Mimicry in Catalysis : Discuss synthetic catalysts that mimic enzyme behavior.
- Chemical Biology : Explore the interface between chemistry and biology for drug discovery.
- Organic Photovoltaics : Discuss the development of organic materials for solar cells.
- Peptide Chemistry : Investigate the synthesis and applications of peptides in drug design.
- Click Chemistry : Highlight the versatility of click reactions in organic synthesis.
- Chemoinformatics : Discuss the use of computational methods in organic chemistry.
- Bioorthogonal Chemistry : Explore reactions that are compatible with living systems.
- Green Solvents in Organic Synthesis : Examine environmentally friendly solvents for organic reactions.
- Nanocatalysis : Discuss the role of nanoparticles in catalytic processes.
- Fluorine Chemistry : Investigate the unique properties of fluorinated organic compounds.
- Carbohydrate Chemistry : Explore the synthesis and functions of carbohydrates.
- Chemical Sensors : Discuss the design of organic sensors for detecting analytes.
- Synthetic Biology : Explore the engineering of biological systems for chemical production.
- Organic Chemistry in Medicine : Highlight the role of organic chemistry in drug development.
- Heterocyclic Chemistry : Investigate the synthesis and reactivity of heterocycles.
- Chemistry of Aromatics : Discuss reactions and applications of aromatic compounds.
- Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) : Explore the environmental and health impact of PAHs.
- Green Extraction Methods : Investigate eco-friendly techniques for extracting natural products.
- Organic Chemistry in Food : Discuss the chemistry behind food flavor and preservation.
- Chemistry of Natural Dyes : Explore the use of organic compounds as dyes.
- Artificial Sweeteners : Investigate the chemistry of sugar substitutes.
- Chemistry of Medicinal Plants : Highlight the organic compounds found in medicinal plants.
- Organic Synthesis with Flow Chemistry : Discuss continuous-flow methods in organic synthesis.
- Stereochemistry : Explore the importance of stereochemistry in organic reactions.
- Chirality in Pharmaceuticals : Discuss the role of chirality in drug design.
- Green Chemistry Metrics : Investigate metrics for assessing the sustainability of organic reactions.
- Photochemistry : Explore the use of light in driving organic reactions.
- Chemistry of Natural Toxins : Highlight the structures and effects of natural toxins.
- Chemistry of Pharmaceuticals : Discuss the synthesis and mechanisms of action of common drugs.
- Organic Chemistry in Cosmetics : Explore the chemistry of cosmetic products.
- Organic Chemistry in Art Conservation : Investigate the role of organic chemistry in preserving artworks.
- Radical Chemistry : Discuss the use of radicals in organic synthesis.
- Chemistry of Terpenes : Explore the diverse structures and functions of terpenes.
- Organic Chemistry of Vitamins : Highlight the organic compounds essential for health.
- Biocatalysis : Discuss the use of enzymes in organic synthesis.
- Chemistry of Lipids : Investigate the structure and functions of lipids.
- Chemistry of Amino Acids : Explore the building blocks of proteins.
- Chemistry of DNA : Discuss the structure and chemical properties of DNA.
- Nucleic Acid Chemistry : Investigate the synthesis and modification of nucleic acids.
- Organic Chemistry in Environmental Remediation : Highlight the use of organic compounds for cleaning up pollutants.
In closing, organic chemistry isn’t just about molecules; it’s about endless possibilities. These 50 research ideas showcase the diverse avenues researchers explore , from green synthesis to life-saving drugs. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of carbon, we can look forward to a future where science and innovation walk hand in hand, shaping a brighter world for us all.
- Aromatic chemistry
- Biocatalysis
- Bioorthogonal reactions
- Carbon compounds
- Catalysis Sustainable polymers
- Chiral compounds Chemical biology
- Click chemistry Computational chemistry
- DNA chemistry
- Drug discovery
- Environmental remediation
- Flow chemistry Stereochemistry
- Green metrics
- Green solvents
- Green synthesis
- Nanocatalysis Heterocyclic compounds
- Organic Chemistry
- Organic photovoltaics
- Peptide synthesis
- Photochemistry
- Research Ideas
- Supramolecular chemistry
- Terpenes Vitamins
42 Digital Signal Processing Project Ideas to Explore
100 generative ai project ideas and examples -2024, email subscription.

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
WhatsApp Channel
Join iLovePhD WhatsApp Channel Now!
Contact us: [email protected]
Copyright © 2019-2024 - iLovePhD
- Artificial intelligence
Maintenance work is planned for Wednesday 1st May 2024 from 9:00am to 11:00am (BST).
During this time, the performance of our website may be affected - searches may run slowly and some pages may be temporarily unavailable. If this happens, please try refreshing your web browser or try waiting two to three minutes before trying again.
We apologise for any inconvenience this might cause and thank you for your patience.

Green Chemistry
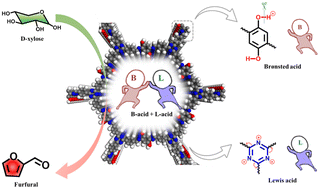
One-pot furfural production from sustainable biomass-derived sugars using a functionalized covalent organic framework as a heterogeneous catalyst †.

* Corresponding authors
a State Key Laboratory of Biobased Material and Green Papermaking, Key Laboratory of Pulp and Paper Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, Qilu University of Technology, Jinan, China E-mail: [email protected] , [email protected] , [email protected]
b Key Laboratory of Clean Pulp & Papermaking and Pollution Control of Guangxi, College of Light Industrial and Food Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China
This paper reports an innovative work on the green production of furfural using a covalent organic framework (COF), thereby expanding the range of catalysts in the furfural manufacturing industry and achieving efficient production of furfural from sustainable biomass-derived sugars. The research results will provide a theoretical basis for the green and sustainable production of furfural.
Supplementary files
- Supplementary information PDF (1018K)
Article information
Download citation, permissions.
One-pot furfural production from sustainable biomass-derived sugars using a functionalized covalent organic framework as a heterogeneous catalyst
P. Gan, K. Zhang, Z. Li, C. Zhang, G. Yang, L. Zhang, B. Wang and J. Chen, Green Chem. , 2024, Advance Article , DOI: 10.1039/D4GC00643G
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements

- Publication
- Arts & Humanities
- Behavioural Sciences
- Business & Economics
- Earth & Environment
- Education & Training
- Health & Medicine
- Engineering & Technology
- Physical Sciences
- Thought Leaders
- Community Content
- Outreach Leaders
- Our Company
- Our Clients
- Testimonials
- Our Services
- Researcher App
- Podcasts & Video Abstracts
Subscribe To Our Free Publication
By selecting any of the topic options below you are consenting to receive email communications from us about these topics.
- Behavioral Science
- Engineering & Technology
- All The Above
We are able share your email address with third parties (such as Google, Facebook and Twitter) in order to send you promoted content which is tailored to your interests as outlined above. If you are happy for us to contact you in this way, please tick below.
- I consent to receiving promoted content.
- I would like to learn more about Research Outreach's services.
We use MailChimp as our marketing automation platform. By clicking below to submit this form, you acknowledge that the information you provide will be transferred to MailChimp for processing in accordance with their Privacy Policy and Terms .
Making organic chemistry fun, meaningful, and accessible
Many undergraduate students perceive organic chemistry modules as make-or-break courses in their university career. They often resort to rote memorisation, which not only alienates them but prevents them understanding the discipline in depth. Social and economic factors may also be significant barriers in the study of this fundamental subject. With examples drawn from her extensive teaching experience, Dr Irosha N Nawarathne , Lyon University, Arkansas, USA, illustrates how organic chemistry can be made more meaningful and accessible, while encouraging the element of diversity in the classroom .
Ask most science undergraduates around the world about organic chemistry and it will become apparent that many students describe it as one of the most challenging and cumbersome subjects . Depending on how the content is presented, even the most proficient learners might perceive this very important discipline as an endless collection of lists of reactions and detailed mechanisms that they feel they ought to memorise to get past the hurdles of complex assignments, laboratory reports, and exams.
Dr Irosha N Nawarathne, associate professor of chemistry at Lyon University, Arkansas, USA, has made it her mission to make the learning of organic chemistry more accessible to students from all walks of life. Her hands-on learning approach favours deep understanding over memorisation of notions and facts. At the core of Nawarathne’s method is the belief that it is a key responsibility of teaching staff to ensure that students of organic chemistry are engaged in and draw inspiration from an organic chemistry curriculum that is presented to them as relevant and stimulating, with examples that illustrate how aspects of this key subject permeate the reality that surrounds us.

Rote memorisation: A barrier to deep learning
In 2022, Nawarathne authored an article in the Journal of Chemical Education , demonstrating how the inclusion of relevant examples from everyday life in every aspect of the organic chemistry curriculum can improve the students’ attainment in the subject, improving both the engagement with the discipline and the retention of the most difficult concepts. ‘Organic chemistry has a reputation of being a difficult subject,’ acknowledges Nawarathne. ‘There are no problem-solving algorithms; it requires three-dimensional thinking; and it has an extensive new vocabulary.’ She highlights how most students feel that they have no option but to approach organic chemistry by relying on rote learning, with minimal effort to embark on a more meaningful learning journey.
Organic chemistry constitutes the very fabric of all living things and, according to the author, educators can and should facilitate how students reframe their perception of the subject. Teaching staff should place relevant content at the heart of the curriculum, considering the everyday experiences and career aspirations of the students. This should also be reflected through the delivery of engaging practical activities and in the design of assessment tasks. Nawarathne illustrated the advantages of her novel approach in her 2022 article, presenting the readers with a series of measurable outcomes. She hopes that many educators can incorporate her methods in their teaching practice, making organic chemistry interesting and worth studying in the minds of their students.

Alkenes everywhere
Often, one of the first topics introduced to students of organic chemistry is the chemical structure and reactivity of alkenes, compounds made of hydrogen and carbon who possess at least one pair of carbons joined together by a ‘double bond’. This type of bond, which consists of two pairs of negatively charged electrons that act like glue between two atoms, confers alkenes with a particularly strong reactivity, while the higher density of electrons can manifest in a tendency for conjugated (elongated) alkenes to form coloured compounds, due to the electrons acquiring higher energy levels when hit by light.
‘Alkenes and their reactions were introduced to an introductory organic chemistry class by incorporating simple yet attractive laboratory experiments and assignments in a span of two weeks prior to introducing chapter content on alkenes and alkene reactions,’ explains Nawarathne. She planned the assessment section of the course to include assignments where students had the opportunity to measure the nutritional values of brightly coloured foods, or to research the chemical composition in the leaves that leave so many people awestruck during the autumn season. The activities also included laboratory tasks where the students would measure the light absorbed by plant pigments or explore the absorbent properties of the materials contained in common diapers.

In organic chemistry, the study of alkenes is fundamentally important for the understanding of reaction mechanisms. By shifting the focus on relevance to real-world applications, Nawarathne hopes to change how students perceive organic reactions, steering away from rote learning. To measure the impact of her didactic method, Nawarathne surveyed the students both before and after the two-week introductory materials were presented. It was apparent from the students’ responses that the use of familiar examples improved their interest in learning about alkenes (and other functional groups), as well as facilitating knowledge retention and deep understanding of the topic.
Social and molecular diversity
The barriers to learning organic chemistry and wider scientific subjects are not just limited to the way the curriculum is presented. Social factors have a significant impact on students’ prior exposure to scientific vocabulary and methodologies, as well as on the ability to rationalise complex, abstract concepts, formulate hypotheses, and solve problems through the use of schemes, diagrams, and chemical equations. Nawarathne believes that educators can minimise the impact of these obstacles, actively encouraging a culture of openness and diversity in the organic chemistry class.

In a 2019 article in the Journal of Chemical Education, Nawarathne illustrated ways to promote an inclusive environment for undergraduate students of organic chemistry, so they could embrace diversity in the classroom and society at large. She reported that she deliberately introduced sections of the organic chemistry curriculum that are focused on the importance of diversity at the molecular level.
‘Carbon is the most inclusive atom we can think of in chemistry, it bonds with anything and everything. We discuss examples of how carbon bonds with itself, other non-metals, and metals to form the most useful compounds around us, including what we are made out of provided all biological molecules are organic and based on carbon,’ explains Nawarathne, adding that these lessons were followed by a class discussion around the importance of diversity in society and an assignment on the topic of molecular and social diversity. Analysing the students’ responses from surveys taken prior to and after the course introduction to molecular diversity, the author concluded that not only were students more aware of social diversity, but that this, in turn, improved their in-depth knowledge of carbon bonding.
Making science accessible
Nawarathne believes that to attract talent in scientific disciplines among a diverse cohort of learners, it is fundamental that the teaching of organic chemistry rids itself of some of the most obsolete methods that require students to memorise endless sets of reactions and mechanisms, with little focus on content relevance and deep understanding of the physical and chemical properties of the most important classes of carbon compounds.

She also advocates for actively promoting inclusion among learners; drawing a parallel between chemical species and different individuals in society, she shows how diversity is fundamental both in the biochemical landscape, as well as in vibrant and well-functioning communities. Nawarathne has adapted the content of the organic chemistry courses she teaches at Lyon University to remove many of the barriers to learning that prevent many talented students from achieving a fulfilling career in the scientific field. Nawarathne plans to systematically monitor the impact of her pedagogy on student achievement and hopes that other educators can draw inspiration from her methods for the teaching of organic chemistry and other scientific disciplines.
Personal Response
This feature article was created with the approval of the research team featured. this is a collaborative production, supported by those featured to aid free of charge, global distribution., want to read more articles like this, sign up to our mailing list and read about the topics that matter to you the most., leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Organic chemistry articles from across Nature Portfolio. Organic chemistry is the study of the synthesis, structure, reactivity and properties of the diverse group of chemical compounds primarily ...
ACS Publications Symposium: Catalysis for Organic Synthesis. Join The Journal of Organic Chemistry this summer in Vienna, Austria for two days of innovative, scientific exchange with leading experts in organic chemistry and have the chance to present your own research through poster sessions and lightning talks.. Invited Keynote Speakers Agenda. Poster Abstract Submissions close May 1, 2024.
Read the latest Research articles in Organic chemistry from Nature Chemistry. ... Organic chemistry articles within Nature Chemistry. Featured. Article 17 April 2024 | Open Access.
Bioinformatic clustering of the sequences combined with high throughput synthesis and analysis methods allow efficient prioritisation of hits for in vivo experiments. From the themed collection: Most popular 2022 organic chemistry articles. The article was first published on 24 Feb 2022. Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 3256-3262.
Wajid Ali, Gaurav Prakash and Debabrata Maiti. Transition metal-catalysed functionalizations of inert C-H bonds to construct C-C bonds represent an ideal route in the synthesis of valuable organic molecules. From the themed collection: Most popular 2021 organic chemistry articles, 2021. The article was first published on 29 Jan 2021.
Read the latest Research articles in Organic chemistry from Scientific Reports. ... Organic chemistry articles within Scientific Reports. Featured. Article 16 April 2024 | Open Access.
Carbonylation of diazo compounds using Co2(CO)8 as a CO source can be used to synthesize β-lactams. The β-lactam formation takes place via a series of reactions, namely, carbene and ketene formation, followed by [2 + 2] cycloaddition with imine in DCM. This artwork was designed and created by Fathima Febin Koothradan, Arumugam Jayarani, and Chinnappan Sivasankar. View the article.
Research article Abstract only. ... Progress in Photocatalysis for Organic Chemistry. 19 May 2023. C1 Chemistry in Organic Synthesis. 21 April 2023. Electrochemistry in Synthetic Organic Chemistry. 19 November 2021. View all special issues and article collections. View all issues. ISSN: 0022-3263.
Graphene as a typical conductive filler was previously introduced to enhance the protective performance of zinc-rich coatings (ZRC). However, it is not completely clear the correlation between shielding and cathodic protection performances under the effect of introduced graphene. Herein, the effects of graphene on the shielding performance and cathodic protection were explored, respectively ...
Organic Chemistry in the News. Organic compounds, protein engineering, and more. Read all the latest research in the field of organic chemistry. Full-text with images. Free.
Acyclic Aldehydo Sugars: 1,3-dimethyl-4,5-diamino Uracil as Recoverable Carbonyl Protecting Group#. D. Fuentes-Rios, ... R. Rico. 1 January 2024. Read latest issue. Read the latest articles of Letters in Organic Chemistry at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier's leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions,... | Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles ...
The latest chemistry news and research on organic chemistry, including synthesis, natural products and total synthesis, reaction mechanisms and supramolecular chemistry, from ...
This solvent, obtained from renewable cellulose waste and being non-toxic, non-mutagenic and biodegradable, integrates into Green Chemistry practices by aligning with sustainable principles and minimizing environmental impact. More information can be found in the Research Article by A. Citarella, V. Fasano et al.
Organic Chemistry Frontiers. ... Article type Research Article. Submitted 20 Feb 2024. Accepted 16 Apr 2024. First published 18 Apr 2024. Download Citation. Org. Chem. Front., 2024, Accepted Manuscript Permissions. Request permissions Iridium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of 5-Hydroxypicolinate Pyridinium Salts under Batch and Flow ...
In organic chemistry, finding conditions that enable a broad range of compounds to undergo a particular type of reaction is highly desirable. However, conventional methods for doing so consume a ...
EurJOC (European Journal of Organic Chemistry) supports the global organic chemistry community by publishing high-quality international research covering all aspects of organic chemistry in the form of Research Articles, Reviews, Concepts, and Perspectives. Be part of this exciting journal and submit your paper today! Find out more. EurJOC receives great support from its international ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on CHEMISTRY, ORGANIC. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on ...
Controllable synthesis of highly crystalline covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with unique structures is important for fundamental research and their practical applications. Herein, we report highly crystalline helical COFs, termed helical-COFTP-Py, synthesized through the Schiff base condensation of 1,3,6,8-tetra(4-aminophenyl)-pyrene and terephthalaldehyde via supercritically solvothermal ...
With a similar goal, Organic Process Research& Development has a tradition of bridging industrial and academic research. Its focus on process chemistry as the science that enables the safe, environmentally benign, and economical manufacturing of chemicals is evident in the selected articles for this Virtual Issue, which highlight aspects of ...
Chemistry - A European Journal showcases fundamental research and topical reviews in all areas of the chemical sciences around the world. Thin films of crystalline solids with substantial free volume from organic chromophores and metal secondary building units (SBUs) are promising for engineering new optoelectronic properties through...
SciTechDaily features the latest chemistry news and recent research articles from leading universities and institutes from around the world. Here, we delve into the ever-evolving realm of molecules, elements, and reactions, bringing you up-to-date insights from renowned scientists and researchers. Read interesting chemistry news and ...
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure determines their structural formula.Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to ...
-Article tempale-We encourage submit your manuscript in single word file or Tempalted format. Microsoft Word templates ; About this Journal. Organic Chemistry Research is an international peer-reviewed, open access journal that covers all aspects of organic chemistry. The journal publishes original papers of high scientific level in the form of ...
A Lewis acid-catalyzed tandem reaction strategy for the construction of a dihydrophenalene-lactone tetracyclic skeleton has been disclosed. Starting with 2-naphthol-tethered ketones and active methylene esters, the tandem reaction catalyzed by Sc(OTf)3 proceeded well to afford an array of dihydrophenalene-fused lactones with moderate to high efficiency and diastereoselectivity. Moreover, the ...
Read the latest Research articles from Nature Chemistry. Skip to main content. ... Accessing longer-wavelength emitting organic fluorophores is critical for diagnostic imaging. Here a series of ...
50 Intriguing Organic Chemistry Research Ideas. Green Synthesis of Organic Compounds: Explore eco-friendly methods for synthesizing organic molecules. Applications of Organometallic Chemistry: Discuss the use of organometallic compounds in catalysis and materials science. Designing Sustainable Polymers: Investigate the development of ...
This paper reports an innovative work on the green production of furfural using a covalent organic framework (COF), thereby expanding the range of catalysts in the furfural manufacturing industry and achieving efficient production of furfural from sustainable biomass-derived sugars. The research results will provid
ABSTRACT. A dispersive magnetic solid-phase extraction by means of core-shell iron-based metal-organic framework (Fe 3 O 4 - SiO 2 /EN@MIL-101(Fe)) nanospheres coupled with high-performance liquid chromatographic was developed for the determination of pyrene (Pyr) and phenanthrene (Phe) in water samples. Key parameters such as sorbent amount, sample volume, pH, extraction time, type and volume ...
Dr Irosha N Nawarathne, associate professor of chemistry at Lyon University, Arkansas, USA, has made it her mission to make the learning of organic chemistry more accessible to students from all walks of life. Her hands-on learning approach favours deep understanding over memorisation of notions and facts. At the core of Nawarathne's method ...