- Undergraduate
- Short Courses
- Online Courses
- Masters/Postgraduate
- Postdoctoral
- Study in Africa
- Study in Asia
- Study in Australia
- Study in Europe
- Study in USA
- Fellowships
- Internships
- Volunteering
- OD Live Series
- Young Person of the Month
- Success Stories
- General Tips
- ODIC 2023 Application
- ODIC Judges
- ODIC 2022 Winners
- ODIC 2021 Winners
- ODIC 2019 Winners
- ODIC 2018 Winners
- ODIC 2017 Winners
- ODIC 2016 Winners
- Australia and Oceania


Rice Business Plan Competition 2023 for Student Startups (Up to $2M in prizes)

Deadline: February 28, 2023
Applications for the Rice Business Plan Competition 2023 for Student Startups are now open. The competition, just completing its 22nd year, gives collegiate entrepreneurs real-world experience to pitch their startups, enhance their business strategy and learn what it takes to launch a successful company.
Hosted and organized by the Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship—which is Rice University’s internationally-recognized initiative devoted to the support of entrepreneurship—and Rice Business. Over 20 years it has grown from nine teams competing for $10,000 in prize money in 2001, to 42 teams from around the world competing for more 2 million in cash and prizes.
Competition Sectors
- Energy, Cleantech and Sustainability: (including but not limited to): Agriculture/Agtech, Batteries & Storage, Decarbonization/Climate Tech, Energy Infrastructure, Oil & Gas Technologies, Renewable/Alternative Energy, Recycling, New and Non-Carbon Fuels, Transportation/Electric Vehicles, Water
- Hard Tech: (including but not limited to): Advanced Manufacturing, Advanced Materials, Aerospace/Spacetech, AR & VR (augmented & virtual reality), Autonomous Vehicles, Drones, Machine Learning and AI (Artificial Intelligence), Quantum Computing, Robotics, Smart Sensors
- Life Sciences and Healthcare Solutions: (including but not limited to): Aging/Gerontology, Biotech, Diagnostics, Digital Health, Disease Management, Public Health, Medical Devices, Personalized Medicine, Pharma & Therapeutics, Prevention
- Digital Enterprise: (including but not limited to): Big Data, Blockchain, Cyber/IoT Security, Cloud & Edge Computing, Enterprise Software, Fintech, Media & Advertising, SportsTech, Supply Chain/Logistics, Workforce
- Consumer Products and Services: (including but not limited to): Analytics, Consumer Web, Education/EdTech, Food & Drink, Gaming, Mobile, Personal Devices, Social Impact, Subscription Services, Wearables & Clothing
- In total, more than $2 Million in investment and cash prizes was awarded to the teams at the 2022 Rice Business Plan Competition.
- They offer an intense, educational experience over the multi-day event for student startup founders to pitch to investors, receive feedback and advance their startup. There is also significant time designated for interaction with judges and prize sponsors, the majority of whom are from the investment community.
- One of the most important parts of the RBPC is the mentoring component. Startups accepted to the competition have the opportunity to engage experts before, during and after the event. The mentoring programme helps founders make their startups stronger, better, more equipped to fundraise and excel in the entrepreneurship ecosystem.
Eligibility
You are initially eligible for RBPC 2023 if your startup:
- is student-driven, student-created and/or student-managed;
- has at least two current student founders or management team members, and at least one of those students is a current graduate degree-seeking student;
- are from a college or university anywhere in the world;
- has not raised more than $250,000 in equity capital prior to July 1, 2022;
- has not generated revenue of more than $100,000 in any 12-month period prior to July 1, 2022;
- is seeking funding or capital (or will be in the next 12 months);
- is a potentially viable investment opportunity.
Application
Only one team member will need an account to apply to the Rice Business Plan Competition. Applications are due by the deadline of on Tuesday, February 28, 2023 by 11:59 PM CST.
Click here to apply
For more information, see FAQ and visit RBPC .

Jude Ogar is an educator and youth development practitioner with years of experience working in the education and youth development space. He is passionate about the development of youth in Africa.
Related Posts
Yves rocher foundation photo prize 2024 (€8,000 prize), roche scholarship to attend one young world summit 2024 (fully funded to montréal, canada), daad leadership for africa scholarship programme 2024 to study in germany.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

Enter a Search Term
2024 rice business plan competition.
April 4-6, 2024 | Houston, Texas
With access to mentors, real-world experience and investment opportunities, the Rice Business Plan Competition helps graduate student founders from any university stay on target and realize their potential.
Grand Prize Winner: Protein Pints, Michigan State University
Congratulations to all of the winners. Check out the results here .
Powering Founders and Shaping the Future at the 2024 Rice Business Plan Competition
Hosted and organized by the Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship , which is Rice University's internationally-recognized initiative devoted to the support of entrepreneurship, and Rice Business, the Rice Business Plan Competition offers an educational program mirroring real-world experience through this multi-day event for student startups from across the world.
Beyond just the world-renowned prizes, student startups spend time interacting with our judges and prize sponsors—providing valuable access and experience with both early-stage and later-stage investors.

April 4-6, 2024 | Houston, Texas
The Rice Business Plan Competition exists so that student founders pushing to create new possibilities in technology, energy, healthcare and more can surround themselves with a powerful network; learn what it takes to secure investor funding; hone your pitch; and compete for big money to make the future you’re building possible. After a competitive application season, 42 startups have risen to the top and will be invited to compete on a global stage for more than $1M in prizes at the 2024 RBPC .
FOLLOW ALONG WITH #RBPC24
Previous competitions.
For 21 years the Rice Business Plan Competition has provided student startups with mentorship, guidance and capital to help support them on their entrepreneurial journey! In 2020, the competition went virtual for the first time. Check out a few of our previous competitions' content, including elevator pitch videos, final pitches, photos and LivePlans.
- 2023 Competition - On The Edge of the Future
- 2022 Competition - Grow Your Startup. Build the Future.
- 2021 Competition - Big Ideas. Brilliant Startups.
- 2020 Competition - First Virtual Edition
- 2019 Competition - The Art of Entrepreneurship
- Scholarships
- Internships
- Training Program
- Competition Program
- Guides For Entrepreneurs
- Accelerator
- Fully Funded
- News & Informations

Call for Applications: Rice Business Plan Competition 2023 for Student Startups | Up to $2M in prizes

The Rice Business Plan Competition 2023 for Student Startups is now accepting applications. The competition, now in its 22nd year, provides real-world experience for collegiate entrepreneurs to pitch their ideas, improve their business strategy, and learn what it takes to create a successful firm.
Rice University’s internationally acclaimed effort devoted to entrepreneurship, the Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship, and Rice Business hosted and coordinated the event. It has evolved from nine teams competing for $10,000 in prize money in 2001 to 42 teams from around the world competing for more than $2 million in cash and prizes over the last 20 years.
Rice Business Plan Competition 2023 Competition Sectors
- Energy, Cleantech and Sustainability: (including but not limited to): Agriculture/Agtech, Batteries & Storage, Decarbonization/Climate Tech, Energy Infrastructure, Oil & Gas Technologies, Renewable/Alternative Energy, Recycling, New and Non-Carbon Fuels, Transportation/Electric Vehicles, Water
- Hard Tech: (including but not limited to): Advanced Manufacturing, Advanced Materials, Aerospace/Spacetech, AR & VR (augmented & virtual reality), Autonomous Vehicles, Drones, Machine Learning and AI (Artificial Intelligence), Quantum Computing, Robotics, Smart Sensors
- Life Sciences and Healthcare Solutions: (including but not limited to): Aging/Gerontology, Biotech, Diagnostics, Digital Health, Disease Management, Public Health, Medical Devices, Personalized Medicine, Pharma & Therapeutics, Prevention
- Digital Enterprise: (including but not limited to): Big Data, Blockchain, Cyber/IoT Security, Cloud & Edge Computing, Enterprise Software, Fintech, Media & Advertising, SportsTech, Supply Chain/Logistics, Workforce
- Consumer Products and Services: (including but not limited to): Analytics, Consumer Web, Education/EdTech, Food & Drink, Gaming, Mobile, Personal Devices, Social Impact, Subscription Services, Wearables & Clothing
Rice Business Plan Competition 2023 Benefits
- In total, more than $2 Million in investment and cash prizes was awarded to the teams at the 2022 Rice Business Plan Competition.
- They offer an intense, educational experience over the multi-day event for student startup founders to pitch to investors, receive feedback and advance their startup. There is also significant time designated for interaction with judges and prize sponsors, the majority of whom are from the investment community.
- One of the most important parts of the RBPC is the mentoring component. Startups accepted to the competition have the opportunity to engage experts before, during and after the event. The mentoring programme helps founders make their startups stronger, better, more equipped to fundraise and excel in the entrepreneurship ecosystem.
Rice Business Plan Competition 2023 Eligibility
You are initially eligible for RBPC 2023 if your startup:
- is student-driven, student-created and/or student-managed;
- has at least two current student founders or management team members, and at least one of those students is a current graduate degree-seeking student;
- are from a college or university anywhere in the world;
- has not raised more than $250,000 in equity capital prior to July 1, 2022;
- has not generated revenue of more than $100,000 in any 12-month period prior to July 1, 2022;
- is seeking funding or capital (or will be in the next 12 months);
- is a potentially viable investment opportunity.
Rice Business Plan Competition 2023 Application
Only one team member will need an account to apply to the Rice Business Plan Competition. Applications are due by the deadline of on Tuesday, February 28, 2023 by 11:59 PM CST.
Deadline: February 28, 2023
For more information, see FAQ and visit RBPC .
- APPLY NOW: Tony Elumelu Foundation Entrepreneurship Programme 2023 for African Entrepreneurs | get $5,000 seed funding
- Freshwater and Community Conservation Remote Externship 2023
- Fashionomics Africa 2023 Fashion Entrepreneur Contest | $10,000
- GoAbroad TikTok Contest 2022 – Win a trip to South Africa or a $500 Travel Scholarship!
- Tesla Internship Program 2023 | Paid Internship
- APPLY NOW: Youth STEM Matters Programme Officer
- The Professional Fellows Program (PFP) 2023 for economic empowerment in the Middle East and North Africa | Fully Funded to Washington D.C. USA
- Call for Projects: UNESCO World Heritage Volunteers Initiative 2023 Program
- Nelson Mandela World Human Rights Moot Court Competition 2023
Never miss an opportunity Join our WHATSAPP GROUP OR WHATSAPP 2
Join our TELEGRAM GROUP
Follow us on FACEBOOK | TWITTER | INSTAGRAM | LINKEDIN
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Gca local adaptation champions awards 2023 |€15,000 prize, apply now: aauw career development grants 2023 |up to $20,000, miles morland foundation writing scholarship 2023 for africans |grant of £18,000, apply now: ayute africa challenge nigeria 2023 |up to $20,000 in prizes, health data analytics (hda) graduate fellowship 2023 |up to ₦1,000,000, call for applications: wilson center fellowship program 2024-2025 |$90,000 stipend, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest article
Hot Job: Commonwealth Youth for Sustainable Urbanisation (CYSU) Coordinator
ENRICH in Africa (EiA) Scaling Programme for African Tech Startups
Latest Npower Stipend Payment Update: NASIMS continues massive Stipend Payment of Beneficiaries
- Advertisement
- Privacy Policy
Latest Npower Stipend Payment Update: NASIMS continues massive Stipend Payment of...

- Deadline Approaching
- Conferences
- Masters/Post Graduate
- PhD/Post Doctoral
- Summer School/Winter School
- Undergraduate
- Exchange Programs
- Fellowships
- Internships
- Miscellaneous
- Post an Opportunity
Rice Business Plan Competition 2023
- Deadline February 28, 2023

- May 11 - 13, 2023
The Largest and Richest Intercollegiate Startup Competition | May 11-13, 2023 | Rice University, Houston, Texas
The competition, now in its 23rd year, gives collegiate entrepreneurs real-world experience to pitch their startups, enhance their business strategy and learn what it takes to launch a successful company. Hosted and organized by the Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship—which is Rice University’s internationally-recognized initiative devoted to the support of entrepreneurship—and Rice Business. Over 23 years it has grown from nine teams competing for $10,000 in prize money in 2001, to 42 teams from around the world competing for more 2 million in cash and prizes.
The Rice Business Plan Competition (RBPC) is the world’s richest and largest graduate-level student startup competition. It is hosted and organized by the Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship and the Jesse H. Jones Graduate School of Business at Rice University. The Rice Alliance is Rice University’s internationally-recognized initiative devoted to the support of entrepreneurship. This will be the 23rd year of the competition! In that time, it has grown from nine teams competing for $10,000 in prize money in 2001, to 42 teams from around the world competing for more than $1.5 million in cash and prizes. The competition is designed to give collegiate entrepreneurs a real-world experience to pitch their startups to investors, receive mentoring, network with the entrepreneurial ecosystem, enhance their startup strategy, and learn what it takes to launch a successful startup. Alumni from the RBPC have raised more than $4.6 billion in funding and have generated more than 50 successful exits, valued at nearly a billion dollars.
- An intense, immersive experience over the course three days for student startup founders to pitch to investors, receive multiple rounds of feedback and advance their startup.
- There will be over $1 million in prizes, and all 42 teams who compete at Rice University in Houston are guaranteed to win cash prizes.
- Currently, the minimum cash prize is $800 and the grand prize winner receives a $350,000 investment (typically in the form of a convertible debt note.)
Eligibilities
- has at least two current student founders or management team members, and at least one of those students is a current graduate degree-seeking student • is student-driven, student-created and/or student-managed • falls into one of five sectors (see below) • has not raised more than $250,000 in equity capital prior to July 1, 2022 • has not generated revenue of more than $100,000 in any 12-month period prior to July 1, 2022 • is seeking funding or capital (or will be in the next 12 months) and is a is a potentially viable investment opportunity • is incorporated in the US, or has started the process to do so by January 1, 2023
Application Process
- One member of your startup, the designated leader and main contact going forward, should complete the simple online application by: • Answering the survey questions • Attaching an Executive Summary in PDF format (maximum 5 pages) • Providing a link to a Video Elevator Pitch (maximum 2 minutes) – optional
- Multiple student startup teams from the same school, institution or university center may apply to compete. There is no limit on the number of applications per school.
- Startup teams comprised of students from more than one school may apply. Student startup teams from universities across the US and across the world can apply. There no fees to apply or to compete.
- Once an application is submitted, no changes can be made.
- Submit your application online from the competition website: www.rbpc.rice.edu
- The application must be completed by Tuesday, February 28, 2023 at 11:59 PM CST. Teams invited to compete in the Rice Business Plan Competition will be notified via a live video event, email and phone on March 22, 2023.
Application Deadline: February 28, 2023
For Further Queries

UN Young Leaders Training Programme 2024

Erasmus University NL Scholarship 2024 in Netherlands

Young Social Entrepreneurs (YSE) Global 2021

Khalifa University Scholarships 2024 in UAE

UNESCO World Heritage Residence Scholarship 2024 (Award of 50,000 SKR)
Keep connected.

Youth Opportunities is the largest opportunities discovery platform for youth across the globe.
© 2024 Youth Opportunities
Youth Opportunities
- Local Networks
- Promote Program
Log in with your credentials

Forgot your details?

INNOVATIONMAP EMAILS ARE AWESOME

show me the money
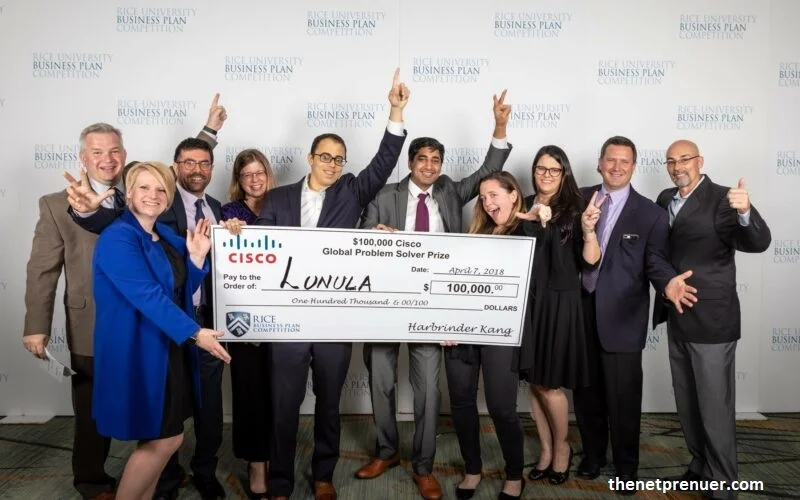
Houston student startup competition doles out record-breaking more than $3m in prizes.
Over the weekend, Houston hosted what is known as the world’s largest and richest intercollegiate student startup competition, and a Texas team took the overall win and over $3 million in investment prizes were given out at the annual banquet.
The 2023 Rice Business Plan Competition was held May 11-13 and included mentoring, pitching, and networking for the 42 student teams with over 350 judges before culminating in over 80 prizes being announced. The $3.4 million in investment and in-kind prizes marks the largest yet for the 23-year-old competition.
"Judges told us that the quality of the startups at this year’s competition was the best ever,” says Catherine Santamaria, director of the RBPC, in the news release. “One judge went so far as to say that every startup this year was worthy of investment.”
Over 450 startups applied to the competition, and the 42 startups selected hailed from 35 universities from five countries. There were five categories: energy, clean tech and sustainability; life sciences and health care solutions; consumer products and services; hard tech; and digital enterprise. Based on the judges scores, seven startups reached the finals, and this year, three Texas teams made the finals, with two being from Rice University.
All 42 companies were eligible for investment or in-kind prizes, and, even though $1.75 million in prizes was expected to be awarded, some of this year's investors doubled — or even tripled — down on investment awards. While the finalists walked away with various in-kind prizes too, here's a round up of the investment prizes each startup won at the awards.
Zaymo, Brigham Young University — $885,000
Zaymo, a tool for e-commerce brands that embeds the shopping experience within customers’ email, won the most amount of money at the awards ceremony. The company won third place and a $50,000 Investment Prize sponsored by David Anderson, Jon Finger, Anderson Family Fund, Finger Interests, Greg Novak and Tracy Druce. Zaymo also won the following awards:
- $200,000 OWL Investment Prize
- $100,000 Houston Angel Network Investment Prize
- $500,000 Softeq Venture Fund Prize
- $15,000 Eagle Investors Prize
- $20,000 Novak Druce Carroll Investment Prize
Boston Quantum, Massachusetts Institute of Technology — $455,000
Boston Quantum, which is using enterprise quantum computing software to disrupt the financial industry, won the second-most amount of investment prizes and sixth place in the competition.
- $5,000 Chevron Technology Ventures Sixth-Place Cash Prize
- $300,000 OWL Investment Prize
- $125,000 Softeq Venture Fund Prize
- $25,000 Urban Capital Network Diversity Investment Prize in partnership with South Loop Ventures
FluxWorks, Texas A&M University — $350,000
Based on the judges scores, the big winner was FluxWorks, a Texas company that's technology includes magnetic gears that are four times quieter than standard with 99 percent efficiency and can offer unprecedented reliability from outer space to under the sea and even inside the human body. The company won the $350,000 GOOSE Capital Investment Grand Prize.
Skali, Northwestern University — $300,000
Skali, which didn't make it into the prestigious finalist positions, still walked away with $300,000 courtesy of the Softeq Venture Fund Prize. Skali's technology aims to better equip flights with medical emergency assistance.
TierraClimate, Rice University — $280,000
TierraClimate, a marketplace for selling verified carbon offsets to corporate buyers, won fourth place and the Norton Rose Fulbright $5,000 Prize. The company also won a $200,000 Softeq Venture Fund Prize and the $75,000 OWL Investment Prize.
AirSeal, Washington University in St. Louis — $250,000
Another non-finalist that still scored big was AirSeal, a company that's created a simple blood test for cardiovascular diagnostics. The startup secured the $250,000 TMC Innovation Healthcare Investment Prize.
Sygne Solutions, Rice University — $200,000
Sygne Solutions, a startup on a mission of eliminating a group of chemicals known as PFAS in water through its patent-pending technology, won second place and the $100,000 Investment Prize, sponsored by David Anderson, Jon Finger, Anderson Family Fund, Finger Interests, Greg Novak and Tracy Druce. The company also received the $100,000 TiE Houston Angels Investment Prize.
BlueVerse, Texas Tech University — $145,000
BlueVerse, a startup with tech to merge social media with reviews and rewards for small businesses, didn't make the finals but walked away with on of the $125,000 Softeq Venture Fund Prizes and the $20,000 Novak Druce Carroll Investment Prize.
Atma Leather, Yale University —$130,000
Atma Leather, a material innovation company that's created plant-based leather from banana stems and other crop waste, came in fifth place and secured the $5,000 EY Fifth-Place Cash Prize. The startup also won:
- $75,000 OWL Investment Prizes
- $50,000 nCourage Investment Group’s Courageous Women Entrepreneurs Investment Prize
MyLÚA Health, Cornell University — $30,000
MyLÚA Health's AI technology supports the maternal health industry. The company won the $30,000 Pearland Economic Development Corporation Spirit of Entrepreneurship Prize.
Active Surfaces, Massachusetts Institute of Technology — $25,000
With its flexible and lightweight solar panel technology, Active Surfaces scored the $25,000 New Climate Ventures Sustainability Investment Prize.
Integrated Molecular Innovations, Michigan Technological University — $25,000
Integrated Molecular Innovations, which created a wearable device that can monitor hormone levels, won the $25,000 Southwest National Pediatric Device Consortium Prize.
MiraHeart, Johns Hopkins University — $25,000
MiraHeart, which created a non-invasive way of monitoring child heart conditions, also won the $25,000 Southwest National Pediatric Device Consortium Prize.
Biome Future, University of Florida — $20,000
Biome Future, which creates ocean-safe chemicals via microbes in corals, won one of the $20,000 Novak Druce Carroll Investment Prizes.
Citrimer, University of Michigan — $10,000
A sustainable materials company, Citrimer won the $10,000 NABACO RBPC Alumni Network Prize.
Thryft Ship, University of Georgia — $10,000
Thryft Ship, which streamlines the shipping process for social media sellers, won a $10,000 nCourage Investment Group’s Courageous Women Entrepreneurs Investment Prize.
Pathways, Harvard University — $5,000
Pathways, which is developing a full-stack sustainability platform for the construction industry, won $5,000 Shell Ventures Seventh-Place Cash Prize.
In addition to these investment prizes, the startups have the chance to score in-kind prizes. This year, that included:
- $6,667 Baker Botts Legal Services In-Kind Prize to FluxWorks, Texas A&M University
- $6,667 Baker Botts Legal Services In-Kind Prize to Sygne Solutions, Rice University
- $6,667 Baker Botts Legal Services In-Kind PrizeFluxWorks to Zaymo, Brigham Young University
- $10,000 New York Technology Capital CFO Consulting In-Kind to FluxWorks, Texas A&M University
- EFN Mentoring Services to all startup competitors
- Amazon Web Services to all startup competitors
- Stage 2 Competition Entry to Sygne Solutions, Rice University
- Nai-Hui Chia of Rice University awarded a 2023 Google Scholar award - InnovationMap ›
Trending News
Money moves, houston tech platform raises series c round backed by mastercard, nasa awards $30m to houston space tech company to develop lunar rover, houston innovators podcast episode 230, houston investor on saas investing and cracking product-market fit, going my way, explore the eco-friendly commuting app that's driving change at houston area employers, ready year 2, applications are open for accel, an accelerator for bipoc-led startups, on the list, uh ranked in top 100 u.s. universities for patents by national academy of inventors.

May. 15, 2023
Magnetic gear tech company wins 2023 rice business plan competition.

HOUSTON – (May 15, 2023) – FluxWorks from Texas A&M University, a magnetic gear technology company, took home the grand prize at the 2023 Rice Business Plan Competition (RBPC).
The RBPC, hosted annually by the Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship and Rice University’s Jones Graduate School of Business , is the world’s largest and richest student startup competition. This year’s edition saw 42 startups competing for $3.4 million in prizes – the highest in the 23 years of the event. More than 80 prizes were awarded and every team took home cash.

The winners were announced at the conclusion of the three-day pitching, mentoring and networking event, which included an elevator pitch competition, practice round, semifinals, wildcard and final round. The innovations presented led sponsor companies to add a number of cash prizes at the last minute.
"Judges told us that the quality of the startups at this year’s competition was the best ever,” said Catherine Santamaria, director of the RBPC, “One judge went so far as to say that every startup this year was worthy of investment.”
The 42 startups represented 35 universities from five countries. They were chosen from more than 450 applicants to compete in one of five categories: energy, clean tech and sustainability; life sciences and health care solutions; consumer products and services; hard tech; and digital enterprise. Learn more about the startups here .
The RBPC’s more than 350 judges act as — and most are — early-stage investors evaluating the startups’ potential. Teams pitch their businesses to investors, entrepreneurs, corporate executives and ecosystem partners during the event, then network and receive real-time feedback, advice and mentorship.
The seven finalists based on the judges’ overall scores were:
FluxWorks, Texas A&M University — $350,000 GOOSE Capital Investment Grand Prize.
FluxWorks’ magnetic gears are four times quieter than standard with 99% efficiency and can offer unprecedented reliability from outer space to under the sea and even inside the human body.
Sygne Solutions, Rice University — second place and the $100,000 Investment Prize, sponsored by David Anderson, Jon Finger, Anderson Family Fund, Finger Interests, Greg Novak and Tracy Druce.
Sygne Solutions is a scalable and sustainable solution for eliminating a group of chemicals known as PFAS in water through patent-pending technology.
Zaymo, Brigham Young University — third place and the $50,000 Investment Prize, sponsored by David Anderson, Jon Finger, Anderson Family Fund, Finger Interests, Greg Novak and Tracy Druce.
Zaymo is a tool for e-commerce brands that embeds the shopping experience within customers’ email.
Tierra Climate, Rice University — fourth place and the Norton Rose Fulbright $5,000 Prize.
Tierra Climate is a marketplace for selling verified carbon offsets to corporate buyers, boosting their revenues by as much as 20%-30% and boosting efforts to achieve net-zero emissions.
Atma Leather, Yale University — $5,000 EY Fifth-Place Cash Prize.
Atma Leather is a material innovation company developing plant-based leather from banana stems and other crop waste, making it a cruelty-free and sustainable alternative.
Boston Quantum, Massachusetts Institute of Technology — $5,000 Chevron Technology Ventures Sixth-Place Cash Prize.
Boston Quantum aims to disrupt the financial industry with enterprise quantum computing software.
Pathways, Harvard University — $5,000 Shell Ventures Seventh-Place Cash Prize.
Pathways is building a full-stack sustainability platform for the construction industry.
Significant prizes this year and the teams that won them include:
* $300,000 OWL Investment Prize — Boston Quantum, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
* $200,000 OWL Investment Prize — Zaymo, Brigham Young University.
* $75,000 OWL Investment Prizes — Atma Leather, Yale University; Tierra Climate, Rice University.
* $100,000 TiE Houston Angels Investment Prize — Sygne Solutions, Rice University.
* $100,000 Houston Angel Network Investment Prize — Zaymo, Brigham Young University.
* $500,000 Softeq Venture Fund Prize — Zaymo, Brigham Young University.
* $300,000 Softeq Venture Fund Prize — Skali, Northwestern University.
* $200,000 Softeq Venture Fund Prize — Tierra Climate, Rice University.
* $125,000 Softeq Venture Fund Prizes (3 prizes) — Boston Quantum, Massachusetts Institute of Technology; BlueVerse, Texas Tech University; Thryft Ship, University of Georgia.
* $250,000 TMC Innovation Healthcare Investment Prize — AirSeal, Washington University in St. Louis.
* $25,000 Urban Capital Network Diversity Investment Prize in partnership with South Loop Ventures — Boston Quantum, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
* $25,000 New Climate Ventures Sustainability Investment Prize — Active Surfaces, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
* $50,000 nCourage Investment Group’s Courageous Women Entrepreneurs Investment Prize — Atma Leather, Yale University.
* $10,000 nCourage Investment Group’s Courageous Women Entrepreneurs Investment Prize — Thryft Ship, University of Georgia.
* $30,000 Pearland Economic Development Corporation Spirit of Entrepreneurship Prize — MyLUA Health, Cornell University.
* $20,000 Novak Druce Carroll Investment Prizes (3 prizes)— Blue Verse, Texas Tech University; Biome Future, University of Florida; Zaymo, Brigham Young University.
* $25,000 Southwest National Pediatric Device Consortium Prizes (2 prizes) — MiraHeart, Johns Hopkins University; Integrated Molecular Innovations, Michigan Technological University.
*15,000 Eagle Investors Prize – Zaymo, Brigham Young University.
*10,000 NABACO RBPC Alumni Network Prize – Citrimer, University of Michigan.
For more information about the 2023 Rice Business Plan Competition, visit rbpc.rice.edu .
Rice Retailing Business Plan | Ultimate Guide In 2023

Rice consumption has shown a clear increase over the years. In the last years of 2021/2022, 520 million metric tons of rice was consumed globally. Rice being the celebrity of the food and beverage industry, is one of the most famous ventures since the ancient times and is all time in demand. As rice is a staple food, the rice retailer business provides a certain security to the investor or entrepreneur. In this article we will discuss what makes the rice retailer business a good idea and what are the few nitty-gritties that are needed, including marketing strategy for rice business, and developing an informed rice retailing business plan. Along with this we will understand what are the few pointers from a sample project proposal for rice retailing that you could incorporate in your rice business plan.
The agriculture sector is a vital part of the economy and is highly emphasized by the government. It is not only in a constant demand but also in high supply which works in the benefit of an entrepreneur in the rice retailer business. Being in this venture also has additional benefits as it is relatively easy to start and requires minimal investment. Thus, generating a good net profit for the retailer.
Also Read: How To Start A Land Clearing Business? 11 Steps {Ultimate Guide}
Table of Contents
Things to keep in mind before starting the business:
- Investment and resources : You should have enough collection of capital and resources that you need for your rice business.
- Acquire License : You would have to generate a government approved license that legitimizes your business and allows you to run your business smoothly.
- Gather Equipment : According to the rules of your license you would need proper equipment of a certain standard. Price tags, calibrated weights etc.
- Storage unit : One look out in the rice industries is the issue of storage, the rice tends to spoil in three months. Along with this the rice gets eaten by insects and bugs. You would need a well-structured storage unit and invest in disinfectants. Here you can take advice from other sample project proposal for rice retailing and also from your supplier.
- Determine your target market : You need to identify who your potential customers are. Are they households, restaurants, or small convenience stores? Knowing your target market will help you come up with a business plan and marketing strategy.
- Look for a reliable supplier : You would need to find a supplier who can provide you with good quality rice at a reasonable price. It’s important to build a good relationship with your supplier to ensure a steady supply of rice.
- Choose a strategic location : The rice retailing business should be located in an area where there is high foot traffic. A location near a market or a busy street is ideal.
- Set your prices : You should set your prices competitively. Do some research on the prices of rice in your area and make sure that your prices are reasonable.
- Promote your business : You need to get the word out about your rice retailing business. You can use flyers, social media, or even word of mouth to promote your business.
Before starting any venture, planning the above points is of key importance.
Also Read: How To Start A Custom Car Shop? {Ultimate Guide}
Here are few Steps that are needed to Develop a Concrete Rice Business Plan –
1. conduct market research and form marketing strategy for rice business –.
Conducting a Market research involves gauging of the rice market in your area. You are to understand the demand of different types of rice, the number of suppliers, the demographic of potential customers and a thorough knowledge about the competition. This is where the competition’s sample project proposal for rice retailing would come in handy and help you create a marketing strategy.
2. Create Business Objectives
Your rice business plan would need a clear set of objectives. Concise, achievable and smart objective and goals work as a guideline onto which further operations are done.
3. Target Market
The rice retailing business plan depends on identifying your target customers, including their demographics, their preferred location, monetary status and purchase habits. And finally incorporating them in marketing strategy for rice business.
4. Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Create a strategy that sets you apart from your competitors and attracts customers. After developing a unique selling proposition showcase it in your rice business plan. In order to develop a well rounded USP you can use the competitor’s sample project proposal for rice retailing and stand apart from the crowd.
5. Pricing Strategy
One of the pointers of how you can price your rice products that leads to the most net profit is by using an already well researched pricing strategy. For example, D-Mart became a famous retail store in India by using Everyday Low Price Strategy – EDLP which worked for the Indian market and gained high profit.
6. Marketing Plan
Create a detailed advertising statement that markets and promotes your rice business to attract customers and promote customer loyalty. And make this a part of your marketing strategy for rice business.
7. Operation Plan
The rice business plan includes a step-by-step outline of daily activities that you would like to see in your business. Such as information on staff, daily changes in prices, inventory, maintenance of storage facility etc.
8. Financial Projects
Create balanced and realistic financial projects in your rice retailing business plan to assess your company’s workings. create accurate financial predictions that include predicted sales, expenses, and profits.
9. Organizing
And finally compile it all together to form a comprehensive rice business plan.
In conclusion, rice is in all time demand throughout the centuries. With right equipment, capital, license resources, and a full proof rice retailing business plan you can establish a successful venture.
Related Posts:
- Top Golf Franchise in 2023 {Cost & Opportunities}
- Top 10 Direct Selling Companies in India
- How to Open a Fedex Store in 2023? {Cost & Opportunities}
- Power Train System Cost | PCM Maintenance
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Our use of cookies
We use necessary cookies to make our site work (for example, to manage your session). We’d also like to use some non-essential cookies (including third-party cookies) to help us improve the site. By clicking ‘Accept recommended settings’ on this banner, you accept our use of optional cookies.

Necessary cookies
Necessary cookies enable core functionality on our website such as security, network management, and accessibility. You may disable these by changing your browser settings, but this may affect how the website functions.
Analytics cookies
We use analytics cookies so we can keep track of the number of visitors to various parts of the site and understand how our website is used. For more information on how these cookies work please see our Cookie policy .
Prudential Regulation Authority Business Plan 2024/25
Related links related links.
- PRA annual reports and business plans
- CP4/24 – Regulated fees and levies: Rates proposals 2024/25
Maintain and build on the safety and soundness of the banking and insurance sectors, and ensure continuing resilience
Be at the forefront of identifying new and emerging risks, and developing international policy
Support competitive and dynamic markets, alongside facilitating international competitiveness and growth, in the sectors that we regulate, run an inclusive, efficient, and modern regulator within the central bank, the pra’s strategy.
Our strategy for 2024/25 will be delivered through our strategic goals, extracts of which are below. For the full detail of our workplan against each strategic priorities, see pages 10 to 41 of this Business Plan .
Foreword by Chief Executive Sam Woods
Sam Woods Deputy Governor, Prudential Regulation Chief Executive of the PRA
First, this will be our first full year operating under the Financial Services and Markets Act (FSMA 2023), which established a new, post-Brexit regulatory framework for the UK. FSMA 2023 expanded our rulemaking responsibilities and gave us a new secondary objective to support the competitiveness and growth of the United Kingdom.
Competitiveness and growth have always been important considerations for the PRA. Nonetheless, this new objective represents a significant change, and embedding it into our approach has been a major priority for the organisation as a whole, and for me personally as CEO. That effort will continue this year.
Our business plan includes a range of initiatives aimed squarely at promoting the UK’s competitiveness and growth. Some of the most significant are:
- Our ‘Strong and Simple’ project, which aims to simplify regulatory requirements for smaller banks, thus reducing compliance burdens without compromising on strong standards.
- The ‘Solvency UK’ reforms of insurance capital standards, which will reduce bureaucracy in the regulatory regime, while also allowing insurers to invest in a wider range of productive assets.
- The Banking Data Review, which aims to reduce burdens on firms by focusing our data collection on the most useful and relevant information.
- Improvements to our authorisation processes – we have made significant progress in improving the speed and efficiency of authorisations without sacrificing the robustness of our controls; maintaining this progress will be a key focus for next year.
- Reforms to ring-fencing, following the independent review led by Sir Keith Skeoch.
The second point I want to highlight is our ongoing programme of work to maintain the resilience of the UK’s banking and insurance sectors, which is at the heart of our role. The events of 2023 (including the high-profile failures of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) and Credit Suisse (CS)) demonstrate the importance of a focus on resilience – and while I am encouraged by how the UK banking and insurance sectors have remained stable through a stressful period, we cannot take this for granted.
A major priority this year will be the implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards, which will complete the long process of post-financial crisis regulatory reform. While I expect the capital impact of these reforms to be limited for UK banks, they will nonetheless play a vital role in maintaining sufficient consistency in risk measurement across firms and jurisdictions – which is the cornerstone of the bank capital regime.
Another major priority this year will be ensuring firms have adequate standards of operational and cyber resilience. Following FSMA 2023, we have new powers to oversee the services provided to regulated firms by so-called ‘critical third parties’, and we will be implementing that regime over the coming year. And in March 2025 we will reach an important milestone with the full implementation of our wider operational resilience policy.
The day-to-day work of supervision will continue alongside these reforms. As always, our supervisory teams continue to work with PRA-regulated firms to ensure high standards of financial and operational resilience, governance, risk management, and controls. Stress testing remains a key element of our approach to resilience, and alongside colleagues from the wider Bank of England we will deliver a desk-based stress test of banks, and a system-wide exploratory scenario, in 2024. We will also work towards the next round of insurance stress tests in 2025.
I have really only scratched the surface of the work we are doing this year, as you can see from a glance at this document’s contents page. In order to deliver this work, we will need to run an efficient and effective regulator, and I am particularly excited by the potential of our data and analytics agenda to create new opportunities to improve how we work. And if past years are anything to go by, we will continue to engage with innovation in many forms across the industry, whether in the form of new entrants or new approaches to doing business in areas like digital money.
I am very much looking forward to the challenges that the next year will bring, and to working together with a team of very committed colleagues at the PRA to deliver on this business plan.
11 April 2024
Overview of responsibilities and approach
The PRA has two primary objectives: a general objective to promote the safety and soundness of PRA-authorised persons, and an objective specific to insurance firms for the protection of policyholders.
The PRA has two secondary objectives:
- the competition objective, which is focused on facilitating effective competition in the markets for services provided by PRA-authorised persons in carrying on regulated activities; and
- the competitiveness and growth objective, which is focused on facilitating, subject to alignment with relevant international standards, (a) the international competitiveness of the economy of the UK (including, in particular, the financial services sector through the contribution of PRA-authorised persons), and (b) its growth in the medium to long term.
In its December 2022 recommendations letter to the Prudential Regulation Committee (PRC), HM Treasury (HMT) set out aspects of the Government’s economic policy to which the PRA must have regard, while building on the important themes of openness, competitiveness, competition, and innovation, as well as delivering energy security and net zero.
In December 2023, the PRA published a consultation paper (CP)27/23 – The Prudential Regulation Authority’s approach to policy , which sets out the PRA’s approach to policymaking as it takes on expanded rule-making powers introduced through FSMA 2023. These expanded powers will enable the PRA to replace relevant assimilated law (previously known as retained EU law) with PRA rules and other policy material, and move towards a more British system of regulation, with most of the technical rules made by independent UK regulators within a framework set by Parliament. In addition, FSMA 2023 introduces new accountability measures that require the PRA to keep its rules under review , and to establish a Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) Panel composed of external members, which will scrutinise and provide input into the PRA’s CBA framework. These measures should enable the PRA to deliver policies that are well suited to the UK’s financial sector. In addition:
- In December 2023, the PRA took a significant step towards implementing the remaining Basel III standards in the UK by publishing the first of two near-final sets of rules with policy statement (PS)17/23 – Implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards near-final part 1 , which takes account of responses received to CP16/22 . The near-final rules aim to promote the safety and soundness of PRA-regulated firms and support their international competitiveness by making capital ratios more consistent, comparable, and aligned with international standards. The PRA will publish its second near-final policy statement in 2024 Q2 on the remaining aspects of the Basel 3.1 package, which include credit risk, the output floor, reporting, and disclosure requirements. The PRA plans to implement the Basel 3.1 standards over a 4.5-year transitional period beginning on 1 July 2025 and ending on 1 January 2030. Among other things, the PRA will also continue to support international efforts to monitor and promote the implementation of Basel 3.1.
- In December 2023, the PRA published PS15/23 – The Strong and Simple Framework: Scope Criteria, Liquidity and Disclosure Requirements , taking account of feedback to CP4/23 . The policy addresses liquidity and disclosure requirements for Simpler-regime Firms and Pillar 3 remuneration disclosure. The PRA will move further towards finalising and implementing the Strong and Simple prudential framework for Small Domestic Deposit Takers (SDDTs) during 2024. footnote [1]
- Following the publication of discussion paper (DP)3/22 – Operational resilience: Critical third parties to the UK financial sector , in December 2023, the PRA published CP26/23 , jointly with the Bank of England (‘the Bank’) and FCA (‘the supervisory authorities’). CP26/23 sets out the supervisory authorities’ proposed requirements for critical third parties (CTPs), footnote [2] including the mechanism for identifying potential CTPs, recommending them for designation by HMT, incident notification triggers and requirements, and proposed CTP Fundamental Rules. In 2024, the PRA will continue to work with the supervisory and other authorities to develop the final policy and oversight approach.
- In September 2023, the PRA published CP19/23 – Review of Solvency II: Reform of the Matching Adjustment , which marks a significant milestone in the PRA's reforms to the Solvency II regime for the UK insurance market. Following the publication of PS2/24 – Review of Solvency II: Adapting to the UK insurance market and PS3/24 – Review of Solvency II: Reporting and disclosure phase 2 near-final , the PRA will publish its final rules, subject to alignment with anticipated legislation, in 2024.
The PRA’s objectives and priorities are delivered through regulation and supervision, and by developing standards and policies that set out expectations of firms. The PRA’s approach to supervision is forward-looking, judgement-based, and focused on the issues and firms that pose the greatest risk to the stability of the UK financial system and policyholders. This approach is set out in the PRA’s approach to supervision of the banking and insurance sectors .
The PRA’s regulatory focus is primarily at the individual firm and sector level, with the most important decisions taken by the PRC, which works with the Bank’s other areas of remit, including its role as supervisor of Financial Market Infrastructures (FMIs), the UK’s Resolution Authority, and its committees, including the Financial Policy Committee (FPC), which has responsibility for the stability of the entire UK financial system. The PRA also works closely with the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), including through the Chief Executive of the PRA being a member of the FCA Board and the Chief Executive of the FCA being a member of the PRC.
The PRA regulates 1,330 firms and groups. footnote [3] These consist of 730 deposit-takers (banks, building societies, credit unions, and designated investment firms footnote [4] (DIFs)), and 600 insurers of all types (general insurers, life insurers, friendly societies, mutuals, the London market, and insurance special purpose vehicles (ISPVs)).
Chart 1: PRA supervised deposit-takers, as at January 2024
Chart 2: pra supervised insurers, as at january 2024, the pra’s strategy, shaping the pra’s strategy.
Each year, the PRA is required by law footnote [5] to review and, if necessary, revise its strategy in line with its statutory objectives:
- the general primary objective to promote the safety and soundness of PRA-authorised firms;
- specifically for insurance firms, a primary objective to contribute to the securing of an appropriate degree of protection for those who are or may become policyholders;
- a secondary objective to act, so far as is reasonably possible, in a way that facilitates effective competition in the markets for services provided by PRA-authorised firms; and
- a new secondary objective to act, so far as reasonably possible, in a way that facilitates the UK economy’s international competitiveness and its growth over the medium to long term, subject to alignment with international standards.
In addition to the statutory objectives, the PRA’s strategy is shaped by other responsibilities, such as the requirement to implement legislation and other changes necessary to meet international standards, and to continue to adapt to market changes in areas such as financial technology (FinTech), climate change, and digitalisation.
When considering how to advance its objectives, there are a set of regulatory principles to which the PRA must also have regard. This includes regulatory principles from FSMA 2000, and considerations from HMT’s December 2022 letter to the PRC on the Government’s economic policy, the Equality Act 2010, the Legislative and Regulatory Reform Act 2006, and the Natural Environment and Rural Communities Act 2006. In its pursuit of its objectives, the PRA will review all the regulatory principles, identify which are significant to the proposed policy, and judge the extent to which they should influence the outcome being sought.
Furthermore, as part of the Bank, the PRA contributes to the delivery of the Bank’s wider financial stability and monetary policy objectives, for example by:
- maintaining and, where appropriate, strengthening or updating prudential standards;
- being at the forefront of identifying new and emerging risks, and developing international policy; and
- ensuring that banks and other financial institutions can continue to provide essential services.
Strategic priorities for 2024/25
This year’s business plan continues to be structured around the PRA’s four strategic priorities, as set out in its 2023/24 Business Plan . The PRA’s strategic priorities for 2024/25 will remain unchanged because the PRA updated its priorities in 2023 to take account of its new powers, new secondary objective, and expanded role brought about by FSMA 2023. The strategic priorities for 2024/25 are to:
- maintain and build on the safety and soundness of the banking and insurance sectors, and ensure continuing resilience;
- be at the forefront of identifying new and emerging risks, and developing international policy;
- support competitive and dynamic markets, alongside facilitating international competitiveness and growth, in the sectors that we regulate; and
- run an inclusive, efficient, and modern regulator within the central bank.
PRA Business Plan 2024/25
Maintain and build on the safety and soundness of the banking and insurance sectors and ensure continuing resilience.
During the decade following the financial crisis of 2007-09, the PRA designed and implemented extensive reforms that materially improved the safety and soundness of firms, insurance policyholder protection, and financial stability. Since then, the robust regulatory standards that the PRA has implemented and its strong international collaboration have played a key role in maintaining the resilience of the banking and insurance sectors, consistent with its objectives and those of the FPC. The PRA will continue to ensure that the firms it regulates remain adequately capitalised and have sufficient liquidity and stable funding profiles, with appropriately defined impact tolerances for disruption to their business services. The PRA’s regulatory framework encourages PRA-regulated firms to take a holistic approach to managing risks by identifying, monitoring, and taking action to remove or reduce systemic risks.
The PRA’s role as a rulemaker was further expanded following the introduction of FSMA 2023. Under the new regulatory framework , the PRA will continue to be a strong, accountable, responsive, and accessible policymaker, and make rules to meet its regulatory obligations, while adopting a risk-based approach, as set out in CP27/23 , in a way that is tailored to the specific features of financial services in the UK. Among other things, the PRA will continue to faithfully implement agreed international standards and reforms in a way that best serves the UK. For example, in 2024 the PRA will publish its final rules on the implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards and on replacing relevant and/or remaining firm-facing Solvency II requirements from assimilated law with the PRA’s own rules, which will become part of the PRA’s Rulebook and other policy materials. In addition, the PRA will move further towards finalising and implementing the Strong and Simple prudential framework , which provides a simpler but robust set of prudential rules for non-systemic, domestic-focused banks and building societies in the UK.
The PRA will also continue to pay particular attention to the business opportunities and threats that are posed by changes in the economic environment, both in the UK and other jurisdictions, that could pose risks to the UK.
The PRA will continue to promote a strong risk culture among regulated firms, including a conscious and controlled approach to risk taking activities, and ensure that this is supported by adequate financial and non-financial resources. At the same time, the PRA will maintain a robust regulatory regime that is able to respond to the external factors that pose the greatest risk to firms’ safety and soundness.
Risk factors also include global geopolitical risks, which have intensified over the past year. The PRA will continue to ensure that PRA-regulated firms are resilient to such risks by liaising with both domestic and international regulatory counterparts and continuing to monitor and engage with affected firms. Effective international collaboration remains central to addressing global risks and maintaining UK financial stability as well as the safety and soundness of internationally active firms.
The PRA will monitor and assess firms’ ability to manage cyber threats through the ongoing use of threat-led penetration testing ( CBEST and STAR-FS ) and the cyber questionnaire ( CQUEST ). In collaboration with the FCA, including in response to known technology, cyber and third-party incidents, the PRA will continue to monitor and engage with firms on their execution of large and complex IT change programmes. Furthermore, the FPC’s cyber stress testing has broadened the PRA’s understanding of how operational disruptions such as cyberattacks may affect financial stability.
The PRA will continue to engage in collective action to develop a view on sector-wide risks, support the building of firm- and sector-level resilience, and enhance the sector’s ability to respond to system-wide disruption. This will include ongoing sector engagement through the Cross-Market Operational Resilience Group (CMORG), which delivers industry guidance, response capabilities, and technical solutions, and through cross-jurisdictional coordination via the G7 Cyber Experts Group (CEG). Through CMORG, the PRA will deliver a sector-wide simulation exercise (SIMEX24) to assess the sector’s resilience to major operational disruption. The PRA will continue to develop its ability to respond to operational incidents in the sector through its authorities ( Authorities Response Framework ) and sector ( Cross Market Business Continuity Group ) response mechanisms.
Financial resilience – banking
Implementation of the basel 3.1 standards.
In March 2023, the PRA concluded its consultation on proposals published in November 2022 about the parts of the Basel III standards that remain to be implemented in the UK (‘Basel 3.1’). In September 2023, the PRA announced that it would split the publication of the near-final Basel 3.1 rules in two, moving implementation back by six months to 1 July 2025 to reduce the transitional period to 4.5 years and ensure full implementation by 1 January 2030, in line with the proposals set out in CP16/22. The first near-final PS17/23 – Implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards near-final part 1 , covering market risk, credit valuation adjustment risk, counterparty credit risk, and operational risk, was published in December 2023. The PRA will publish the second near-final PS, covering the remaining elements of credit risk, the output floor, as well as Pillar 3 disclosure and reporting requirements, in due course.
The near-final rules from the two PSs will be made final once Parliament has revoked the relevant parts of the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR). The PRA expects this to happen later in 2024. In addition to finalising Basel 3.1 rules, the PRA will continue to increase its supervisory focus on firms’ implementation plans.
Bank stress testing
The concurrent stress testing of firms is one of the key tools used by the PRA and the Bank to support their microprudential and macroprudential objectives. Banking stress tests examine the potential impact of a hypothetical scenario on the major UK banks and building societies that make up the banking system, and on the system as a whole. The PRA normally runs two types of banking stress test – the annual cyclical scenario and other exploratory scenarios.
In 2024, the PRA will support the Bank in taking stock of and updating its framework for concurrent bank stress testing. The stocktake will draw on lessons from the first decade of concurrent stress testing, and so ensure that the framework continues to support the FPC and PRC in meeting its objectives. The PRA will also contribute to supporting the Bank’s desk-based stress test in 2024, which is being conducted in place of an ACS. The desk-based exercise will make use of the PRA’s risk expertise along with models developed in the PRA and elsewhere in the Bank to test the financial resilience of the UK banking system under more than one adverse macroeconomic scenario. Stress testing exercises involving firm submissions of stressed projections are currently expected to resume in 2025.
In addition, the Bank is conducting a system-wide exploratory scenario (SWES), working closely with and with the full support of the PRA, FCA, and TPR (The Pensions Regulator). The exercise was launched in June 2023 and aims to improve the understanding of the behaviours of banks and non-bank financial institutions (NBFI) in stressed financial market conditions. The participating firms in this exercise are representative of markets that are core to UK financial stability.
Private equity and credit
The evolving macro environment is expected to challenge firms’ approach to risk management, increasing the need for robust governance, risk management, and controls. One area of focus for the PRA will be exposures to NBFI, particularly any challenges that may manifest around the trend toward illiquid private equity financing and private credit. The PRA will continue to closely monitor private asset financing and the way that firms consider the risks they could face from these activities. In particular, the PRA will look for further improvements in firms’ ability to identify and assess correlations across financing activities with multiple clients.
Replacing assimilated law
HMT has prioritised the CRR as one of the initial areas of focus in the process of transferring assimilated law into the supervisory authorities’ rules and legislation following the enactment of FSMA 2023. The latter granted the PRA expanded rulemaking powers to replace assimilated law with PRA rules, thereby moving towards a more British system of regulation. In 2024/25, the PRA will consult on proposed rules to replace, with modifications where appropriate, the relevant firm-facing provisions in Part Two of the CRR.
Model risk management (MRM) and internal ratings-based approach/hybrid models
Banks’ use of and reliance on models and scenario analysis to assess future risks has increased significantly over the past decade. The introduction of new, sophisticated modelling techniques – including the potential use of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) – has highlighted the need for sound model governance and effective model risk management practices.
In 2023, the PRA published a supervisory statement (SS)1/23 – Model risk management principles for banks , which applies to firms with internal model (IM) approval to calculate regulatory capital requirements. It is structured around five high-level principles that set out the core disciplines necessary for a robust model risk management framework to manage model risk effectively across all model and risk types. The adoption of these principles will help banks to develop good practices of model risk management, raising prudential standards at banks operating in the UK. The new policy comes into effect on 17 May 2024. Banks within the scope of the policy are expected to conduct an initial self-assessment against these principles, and, where relevant, prepare remediation plans to address any identified shortcomings.
During 2024, the PRA will focus on how banks are embedding and implementing the expectations set out in SS1/23. In particular, the PRA will seek to understand the extent to which banks’ management teams are adopting the principles and promoting the management of model risk as a risk discipline in its own right across their firms.
The PRA has published a range of policy statements on changes to the internal ratings-based (IRB) approach to credit risk over recent years. footnote [6] The PRA will continue to work with firms as they progress their model approval and review submissions in line with these requirements and expectations. The PRA will focus on the ‘hybrid’ approach to mortgage modelling, and the IRB repair programme, both carried forward from previous years.
Where appropriate, firms are holding post-model adjustments (PMAs) in the form of risk-weighted asset (RWA) add-ons, helping to mitigate potential capital underestimation while they develop their new models. During 2024, the PRA will continue to assess the adequacy of the PMAs to ensure any potential capital underestimation is addressed.
Liquidity risk management
The events of 2023 brought a further focus on the liquidity and funding risks faced by deposit takers, in particular the deposit outflows experienced by CS and SVB leading up to their acquisition and resolution, respectively.
The PRA will continue its close supervision of firms’ liquidity and funding risks in light of recent stresses. Through its ongoing supervision of banks and building societies, the PRA will follow up on how firms are taking account of the lessons they learnt from the events at CS and SVB. The PRA will continue to use its regular programme of Liquidity Supervisory Review and Evaluation Processes (L-SREPs) across PRA-authorised firms to assess their liquidity and funding risks, in quantitative and qualitative terms, and to ensure appropriate financial and non-financial resources are in place to manage and mitigate these risks.
The PRA will also continue to engage with firms and within the wider Bank on PRA-authorised firms’ access to the Bank’s Sterling Monetary Framework .
The PRA will also monitor closely how firms consider changes in depositor behaviour in the current funding environment and proactively take into consideration forthcoming changes in bank funding and liquidity conditions. footnote [7]
Credit risk management
The PRA is closely monitoring firms’ credit risk management practices given the uncertain credit risk outlook across key markets. The PRA’s assessment will include a focus on how credit risk management practices have evolved – in particular, how they can remain robust and adaptable to changing conditions, whether there is appropriate consideration of downside and contagion risks, as well as firms’ monitoring and planning for the impacts of customer refinancing. The PRA will undertake a thematic review of smaller firms’ credit risk management frameworks during 2024/25.
The PRA will monitor changes to firms’ business mix and credit exposures, and continue to monitor vulnerable segments, including cyclical sectors and key international portfolios, as well as traditionally higher-risk portfolios such as buy-to-let, credit cards, unsecured personal loans, small to medium-sized enterprises, leveraged lending, and commercial real estate. In addition, counterparty credit risk will remain a key area of supervisory focus through 2024, especially exposures to NBFI across certain business lines.
Separately, in 2024, the PRA will continue to progress its review of regulatory policies to assess whether the policy framework for trading book risk management, controls, and culture is adequate, robust, and accessible.
The UK banking system is well capitalised. However, the overall operating and risk environment remains challenging, and firms must manage their financial resilience to ensure that the financial sector can continue to support businesses and households. The PRA will continue to assess firms’ capital positions and planning, including firms’ use of forward-looking capital indicators, stress testing, and contingency plans.
The PRA intends to review its Pillar 2A methodologies (see section ‘Review of the Pillar 2 framework’ of PS17/23 ) for banks after the rules on Basel 3.1 are finalised, with a view to consulting on any proposed changes in 2025.
Securitisation regulation
HMT has prioritised the Securitisation Regulation as one of the initial areas of focus in the process of transferring assimilated law into regulatory rules and legislation following the enactment of FSMA 2023. The PRA will publish its final policy (simultaneously with the FCA) on final rules to replace or modify the relevant firm-facing provisions in the Securitisation Regulation and related Technical Standards in 2024-25.
The PRA also intends to consult on draft PRA rules to replace firm-facing requirements, subject to HMT making the necessary legislation. The PRA has gathered views and evidence from firms through DP3/23 – Securitisation: capital requirements , which will inform its approach to capital requirements for securitisation.
Financial resilience – insurers
Solvency uk implementation.
In June 2024, the PRA will publish its final policy on the matching adjustment (MA) reforms set out in CP19/23 – Review of Solvency II: Reform of the Matching Adjustment . The majority of these reforms will take effect from end-June to allow PRA-authorised firms to take immediate advantage of new investment opportunities. The remaining Solvency II reforms consulted upon in CP12/23 – Review of Solvency II: Adapting to the UK insurance market will take effect on 31 December 2024.
To facilitate implementation of the reforms consulted on in CP12/23 and CP19/23, the PRA will streamline the application processes for new internal model permissions and variations of existing permissions. There will be similar proposals for MA permissions, if the final policy is the same as set out in the CP. The PRA remains committed to assessing and providing decisions on applications for permissions as quickly as possible and aims to do this within the timescales published in the associated statements of policy. This will be supported by the establishment of dedicated, specialised teams for reviewing applications.
In practice, delivering timely decisions will in part depend on good engagement between firms and the PRA during the application process, and on the preparation of high-quality and complete applications by firms. To facilitate this, the PRA will publish templates for use by firms , including templates for reporting the updated Matching Adjustment Asset and Liability Information Return (MALIR) and the Analysis of Change (AoC) and Quarterly Model Change (QMC) for internal models. These measures are intended to assist with a smooth transition to the Solvency UK regime.
A variety of proposals were made in responses to CP19/23 to further reform the MA in the form of so-called ‘sandboxes’, which would allow an element of self-certification of eligibility, or a route to further expand eligibility in response to innovations in primary financing markets. In 2024, the PRA will explore these proposals with industry with the goal of determining whether they can be developed into schemes that further advance the objectives of the Solvency II review.
Solvency II reporting reforms
To deliver the regulatory reporting and disclosure reforms consulted on in CP14/22 and CP12/23 , the PRA published PS3/24 – Review of Solvency II: Reporting and disclosure phase 2 near-final , including finalised templates and instruction files. The PRA will also publish a finalised single taxonomy package in 2024 Q2, which encompasses proposals in CP14/22 and CP12/23 , and deletions published in PS29/21 . The PRA will engage with firms, including through industry roundtables, to prepare them in meeting the new reporting requirements coming into force from 31 December 2024.
Solvency II transfer
The PRA will publish a CP in 2024 H1 that will set out how it will transfer the remaining Solvency II requirements from assimilated law into the PRA Rulebook and other policy material such as supervisory statements or statements of policy (‘the UK framework’).
This will provide a more comprehensive Rulebook and will make it easier for firms to access and navigate the rules that apply to them.
Insurance stress testing
Stress testing forms an important part of the PRA’s supervisory approach and risk assessment of insurance firms, helping to assess and identify the vulnerabilities of life and general insurance sectors to a range of risks in different scenarios.
Major life insurers participate in regular and concurrent stress testing prescribed by the PRA, and the next test will take place in 2025. For the first time, the PRA will publish the individual results of the largest annuity-writing firms to help inform stakeholders about the level of firms’ resilience in the scenarios set out, and thereby strengthen market discipline.
The PRA will continue to engage with the industry on the technical, operational, and communication aspects of the stress test, and will publish an approach document for the life insurance stress test 2025. The 2025 test will for the first time include an exploratory scenario to assess exposure to the recapture of funded reinsurance contracts.
For general insurers, the PRA has previously conducted four general insurance stress test exercises between 2015 and 2022. In 2025, the PRA will run its first dynamic stress test . The objectives of the exercise will be to:
- assess the industry’s solvency and liquidity resilience to a specific adverse scenario;
- assess the effectiveness of insurers’ risk management and management actions following an adverse scenario; and
- inform the PRA’s supervisory response following a market-wide adverse scenario.
The dynamic nature of the 2025 exercise represents a significant change from previous exercises and will involve simulating a sequential set of adverse events over a short period of time. The PRA has begun engaging with industry trade bodies and will provide more details of this exercise (including participation, design, and timelines) during 2024. Results of this exercise will be disclosed at an aggregate industry level.
Cyber underwriting risk
As the scope of technology continues to expand globally, cyber underwriting risk has become increasingly relevant, as reflected in the actual and planned growth of cyber insurance within the UK sector. As well as being inherently volatile and systemic in nature, cyber underwriting risk is diverse in how it can manifest in different lines of business.
Given the uncertainty of this risk, robust risk management, risk appetite-setting, and stress testing will be important factors in ensuring that capital and exposure management capabilities reflect firms’ actual exposures.
Monitoring and assessing cyber underwriting risk will be at the core of the PRA’s supervisory focus, particularly for firms with material exposures. The PRA will share the aggregate findings of its recent thematic project focused on cyber underwriting risk with industry, and continue to monitor the risk landscape and market dynamics to identify and assess potential risk drivers, including areas such as contract (un)certainty risk.
Model drift
The PRA will continue its scrutiny of internal models used by insurers to calculate capital requirements and aid risk management, to identify potential trends in the strength of firms’ calibrations, and as an indicator of the effectiveness of firms’ risk management.
In its 2023 model drift analysis , the PRA identified a number of findings across firms using internal models within the non-life sector. These are related to levels of allowances for inflation uncertainty, potential optimism in expected underwriting profits, potential optimism in the cost and benefit of reinsurance, and the limited allowance for economic and geopolitical uncertainties.
In 2024, the PRA will address perceived systemic trends that may weaken the robustness of models used across the market as a whole. The PRA will also focus on specific model drift within individual firms, with an emphasis on improving the effectiveness of internal model validation, so that firms can develop the capability to self-identify and address potential challenges.
Funded reinsurance
In 2024, the PRA will continue to pay close attention to the rapidly increasing use of funded reinsurance transactions in the UK life insurance market, and the risks that the growth in their use may pose to policyholder protection and UK financial stability. The PRA is particularly focused on the risk of an erosion in standards for assets used as collateral in these transactions, and individual and sectoral concentrated exposures to correlated, credit-focused counterparties.
As well as preparing to examine exposures to the recapture of funded reinsurance in the 2025 life insurance stress test, in 2024. The PRA will also, subject to responses to CP24/23 – Funded reinsurance , finalise and implement its policy expectations for UK life insurers that use funded reinsurance arrangements. As stated in the PRA’s letter on ‘ Insurance supervision: 2024 priorities ’, these policy expectations will cover how firms should manage risks associated with funded reinsurance at both individual transaction and at aggregate level. This will include the expectation that firms place limits on their activities to ensure sound risk management.
Impact on general and claims inflation
Claims inflation continues to be a significant risk for general insurers. Following a thematic review, the PRA published a Dear Chief Actuary letter in June 2023 setting out its findings that, while reserves have increased, there remains material uncertainty and the potential for excessive optimism with respect to reserving, pricing, and capital and reinsurance planning.
The PRA expects a continued lag in the emergence of claims inflation in the data, which insurers should be alert to. The PRA will continue to monitor the ongoing impact through the regulatory data collected and supervisory activities throughout 2024. Should the PRA’s assessment of this risk change, further focused work may be considered.
Market-wide stresses in March 2020 and September 2022 highlighted gaps in insurers’ liquidity risk management frameworks and, consequently, the importance of having comparable, accurate, and timely information on insurers’ liquidity. The PRA will build on the existing liquidity framework, currently based on risk management expectations set out in SS5/19 – Liquidity risk management for insurers , and develop liquidity reporting requirements for insurance firms most exposed to liquidity risk. The information collected will be used to supervise firms’ liquidity positions more effectively and produce meaningful peer comparisons. The PRA will work closely with firms to inform them about its development of these requirements and explore the necessity of a minimum liquidity requirement as part of a future policy consultation.
In addition, the Bank has signalled its intention to develop a new lending tool for eligible NBFIs to help tackle future episodes of severe dysfunction in core markets that threaten UK financial stability. The development of the PRA’s approach to supervising liquidity will therefore inform the design of the lending tool as it relates to insurers.
The reforms to Solvency II offer life insurers opportunities to expand the range of credit risk assets that are used to back their annuity liabilities, and enable them to meet their commitment to invest in assets that contribute to the productivity of the economy and the transition to net zero. These opportunities require sophisticated credit risk management, and insurers’ capabilities will remain a key focus. Increased activity in the bulk purchase annuity (BPA) market is expected to lead to further growth in firms’ exposure to credit risk, and potentially to concentrations in exposure to internally valued and rated assets.
The PRA will continue to focus on the effectiveness of firms’ credit risk management capabilities and seek further assurance that firms’ internal credit assessments appropriately reflect the risk profile of their asset holdings. The PRA will assess how firms’ credit risk management frameworks are evolving in line with its supervisory expectations, and also review the suitability of firms’ current and forward-looking internal credit assessment validation plans and approaches. In both cases, the PRA will seek to provide feedback on a firm-specific or thematic basis as appropriate.
Regulatory reforms
Operational risk and resilience (including the implementation of the critical third-party regime).
Operational disruption can impact financial stability, threaten the safety and soundness of individual firms and financial market infrastructures, or cause harm to consumers, policyholders, and other parts of the financial system. The PRA defines operational resilience as the ability of firms and the financial sector to prevent, respond to, recover, and learn from operational disruptions, including cyber threats.
The FCA, Bank, and PRA’s operational resilience policies came into force in March 2022 . Firms have now identified their most important business services, set impact tolerances, and commenced a programme of scenario testing. The PRA will continue to work closely with the FCA to assess firms’ progress, with a particular focus on the ability of firms to deliver important business services within defined impact tolerances during severe but plausible scenarios over a reasonable time frame, and no later than March 2025.
The PRA will also continue to monitor threats to firms’ resilience, including their growing dependency on third parties, while respecting the principle of proportionality.
Critical third parties to the UK financial sector
Section 312L of FSMA 2023 gave HMT the power to designate certain third-party service providers as ‘critical’ if they provide services to the financial sector, which, if disrupted or subject to failure, could cause financial stability concerns or risks to the confidence in the UK’s financial system. Prior to designating these parties, HMT must consult with the Bank, PRA, and FCA (the authorities the Act appoints as Regulators of the new regime). FSMA 2023 also gives the Regulators new powers to oversee the services provided by critical third parties (CTPs) to regulated firms. In December 2023, the PRA, Bank, and FCA jointly published CP26/23 – Operational resilience: Critical third parties to the UK financial sector , proposing how these powers could be used to assess and strengthen the resilience of services provided by CTPs to firms and FMIs, thereby reducing the risk of systemic disruption. The PRA will continue to work with other authorities to develop the final policy and oversight approach in 2024.
Additionally, the PRA is developing regulatory expectations on incident reporting, aligned with its operational resilience expectations.
Review of enforcement policies
Enforcement supports and supplements the PRA’s regulatory and supervisory tools by ensuring that it has credible mechanisms for holding regulated firms to account when they do not meet requirements and expectations. Enforcement policies also provide a wider deterrent effect. The PRA is therefore committed to holding individuals to account and, when appropriate, taking regulatory and/or enforcement action against those individuals that breach its standards. The PRA clearly sets out, for the benefit of the whole regulated community, the actions and standards of behaviour that are considered unacceptable ( The Bank of England’s approach to enforcement ).
In January 2024, following a review of its policies and public consultation, the PRA published PS1/24 – The Bank of England's approach to enforcement , which sets out the revised approach to enforcement across the Bank’s full remit (including when acting as the PRA).
The PRA is committed to conducting any enforcement investigations as promptly and efficiently as possible. In line with that aim, PS1/24 introduced a new Early Account Scheme (EAS or ‘the Scheme’), which provides for a new path for early cooperation and greater incentives for early admissions with the aim of reaching outcomes more quickly in specific cases.
Diversity and inclusion in PRA-regulated firms
Enhancing diversity and inclusion (D&I) can support better governance, decision-making, and risk management in firms by reducing groupthink and promoting a culture that allows employees to feel able to speak up and challenge the status quo.
In September 2023, the PRA published CP18/23 – Diversity and inclusion in PRA-regulated firms . Under the proposals, all in-scope firms would need to understand their D&I position, develop appropriate strategies to make meaningful progress, and monitor and report on progress. The proposals are flexible and carefully tailored to recognise that firms are at different stages of their work on D&I, and, most importantly, are best placed to develop their own D&I solutions.
The PRA also outlined that the proposals in CP18/23 contribute towards its secondary objectives of ensuring effective competition and facilitating competitiveness and growth, because enhanced D&I can help support greater innovation and make firms more attractive in the labour market.
In 2024, the PRA will continue its industry engagement, assess responses to CP18/23, and provide a further update in due course.
The PRA maintains flexibility to adapt and respond to changes in the external environment, economic and market developments, and any other risks that may affect its statutory objectives or priorities. The PRA has continued to use its horizon-scanning programme to achieve the following aims:
- identify emerging external risks, regulatory arbitrage, and potentially dangerous practices;
- highlight features of the regulatory regime that are not yet delivering the desired results; and
- allocate supervisory and policy resources to tackling the highest-priority risks in a timely manner.
Consistent with its mission, the PRA will continue to contribute to lessons learned internationally, policy/standards evaluation, and, in particular, internationally agreed standards with the aim of promoting the safety and soundness of the firms it regulates. For example, in 2024/25, the PRA will continue to focus on identifying and addressing emerging risks internationally, working closely with the BCBS on its response to consultations launched in 2023 (including on cryptoassets; disclosure for climate-related financial risks; and the Basel Core Principles and other outstanding work in support of its 2023/24 work programme and strategic priorities ). The PRA will also continue to work closely with the International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS) on its finalisation of the Insurance Capital Standard (ICS), Insurance Core Principles on valuation (ICP 14) and capital adequacy (ICP17) .
In addition, the PRA will continue to monitor the potential for capital and profit erosion in firms that are slower to adopt new technologies, as well as firms’ involvement in new technologies, and changes in the profile of cyber-risks they face.
International engagement and influencing regulatory standards
The PRA plays a leading role in influencing international regulatory standards and will continue to participate actively in global standard-setting bodies, such as the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) , the IAIS, and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) .
Building on the BCBS’s report on the 2023 banking turmoil , the PRA will work with international stakeholders and the BCBS to strengthen supervisory effectiveness and identify issues that could merit additional guidance at a global level. The PRA will work with BCBS to pursue additional follow-up analytical work based on empirical evidence to assess whether specific features of the Basel Framework have performed as intended, such as liquidity risk and interest rate risk in the banking book, and assess the need to explore policy options over the medium term, alongside supporting the BCBS in pursuing its medium-term programme on evaluating the impact and efficacy of Basel III, and in light of lessons drawn from the Covid-19 pandemic.
In addition, the PRA pursues international collaboration through less formal mechanisms, for example through regular bilateral and trilateral engagements, ensuring close collaboration on a number of supervision, risk, and policy topics of joint interest. The PRA also collaborates internationally on joint global thematic reviews with other regulatory authorities, for example, to address a joint interest in banks’ exposures to NBFIs and the use of critical third parties.
The PRA will also continue to support international efforts to monitor and promote consistent implementation of Basel 3.1, as well as the implementation and monitoring of the ICS.
Supervisory co-operation
Effective international collaboration remains crucial to addressing global risks, and is central to maintaining UK financial stability, the safety and soundness of internationally active firms, and reducing regulatory arbitrage.
The PRA will continue to promote international collaboration through supervisory colleges and set out clear expectations for firms wanting to branch into the UK. The PRA will also maintain its existing memoranda of understanding (MoUs) and, if needed, expand the number of jurisdictions with which it has an MoU to facilitate the supervision of international groups and therefore enhance the safety and openness of the UK for financial services activities.
The PRA will continue to support HMT via its international collaboration activities (eg The Berne Financial Services Agreement ) and with assessments of other jurisdictions to facilitate safe access to overseas markets for UK firms, among other benefits.
Overseas bank branches
The PRA will consult on targeted refinements to its approach to banks branching into the UK, reflecting lessons from the failure of SVB to ensure the PRA’s framework for assessing branches captures activities of potential concern. The PRA is committed to the UK remaining a responsibly open jurisdiction for branches, and expects the vast majority of branch business to be unaffected by any changes. The PRA also intends to consult on clarifying expectations for group entity senior manager functions (SMFs) footnote [8] and expectations of booking arrangements.
Operational and cyber resilience
The PRA engages internationally on operational and cyber resilience, in support of its supervision objectives and to raise international standards. The PRA co-chairs the G7 Cyber Expert Group (CEG), which works to coordinate cyber resilience strategy and management across G7 jurisdictions. The PRA also co-chairs the European Systemic Cyber Group (ESCG), which helps European authorities develop systemic capabilities to prevent and mitigate risks to the financial system that might emanate from cyber incidents. The PRA has also led work at the Financial Stability Board (FSB) on cyber incident reporting. In 2024, the PRA will continue to engage with standard-setting bodies and bilaterally with other jurisdictions on third-party risk management and CTPs.
Managing the financial risks arising from climate change
Climate change presents a source of material and increasing financial risk to firms and the financial system. Managing the risks to firms’ safety and soundness from climate change requires action and remains a key priority for the PRA. The Bank first set out expectations around enhancing banks’ and insurers’ approaches to managing the financial risks emanating from climate change in April 2019 via SS3/19 – Enhancing banks’ and insurers’ approaches to managing the financial risks from climate change . The PRA has since provided further guidance via two Dear CEO letters, footnote [9] incorporating observations from supervisory processes and the 2022 Climate Biennial Exploratory Scenario exercise , as well as by providing thematic feedback via Dear CFO letters footnote [10] to promote high-quality and consistent accounting for climate change .
As noted in its 2024 priorities letter to firms, the PRA expects firms to make further progress and demonstrate how they are responding to the PRA’s expectations, and to set out the steps they are taking to address barriers to progress. The PRA will continue to assess firms’ progress in managing climate-related financial risks. In 2024, the PRA will commence work to update SS3/19 and publish thematic findings on banks’ processes to quantify the impact of climate risks on expected credit losses.
The PRA, alongside the FCA, will continue to work with industry through the Climate Financial Risk Forum to produce practical guides and tools that help financial firms embed the financial risks from climate change into their operations. The PRA will also continue to engage with domestic and international partners, including international standard-setters, to contribute to the development of international frameworks in support of managing climate-related risks.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Following the publication of a feedback statement (FS)2/23 – Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning , the PRA and FCA intends to conduct the third edition of the joint survey on machine learning in UK financial services , in 2024 Q2. Responses to the survey will allow the PRA and FCA to further explore how best to address the issues/risks posed by AI/ML in a way that is aligned with the PRA’s and FCA’s statutory objectives. The PRA will also continue to monitor firms’ compliance of its expectations, as set out in SS1/23 , and will seek to explore further updates where necessary.
International policy on digitalisation and managing associated risks
The PRA aims to be at the forefront of identifying and responding to opportunities and risks faced by PRA-authorised firms as they seek to use technology in innovative ways to attract and retain customers, reduce costs, and increase efficiencies.
External context and business risk are important facets of the PRA’s approach to supervision. Developments are monitored, with specialist input from the Bank’s Fintech Hub , to identify risks such as fragmentation of the value chain, novel outsourcing arrangements, and concentration risks across and within firms.
In order to take a responsive and responsibly open approach, the PRA will continue to consider policy proposals to respond to digitalisation and adapt its supervisory approach accordingly. Through the New Bank Start-up and Insurer Start-Up Units, the PRA will continue to engage with applicant firms that have novel uses of technology. The PRA will continue to work closely with domestic and international partners, and through engagement with industry and stakeholders, to take a pro-active approach to digital innovations within the financial sector.
The PRA is a significant contributor to discussions on digitalisation in international standard-setting fora, and will continue to support the BCBS’s work on the developments in the digitalisation of finance and the implications for banks and supervisors . The PRA will also continue be an active part of the IAIS Fintech Forum.
Digital money and innovation
In February 2023, HMT published a consultation and Call for Evidence on the future financial services regulatory regime for cryptoassets , focused on enhancing market integrity, custody requirements, and transparency. The consultation closed in October 2023 with the publication of an update on the government’s plans for its legislative approach to the regulation of stablecoins. HMT confirmed that tokenised deposits would continue to be regulated as deposits. The PRA will continue to work with HMT and the FCA to ensure that the regulatory perimeter and the boundaries between different activities are clearly and robustly delineated.
In November 2023, the Bank, PRA, and FCA published a cross-authority package on innovations in money and payments . As part of this, the PRA published a Dear CEO letter to provide clarity on the PRA’s expectation on how deposit-takers should address risks arising from the emergence of multiple forms of digital money and money-like instruments. footnote [11] It published the letter alongside the Bank’s proposed regime for systemic payment systems using stablecoins and related service providers , and the FCA’s proposed regime for stablecoin issuers, custodians, and the use of stablecoins as a means of payment. A roadmap paper was also published to explain how these regimes fit together.
The PRA will continue to contribute to the Bank’s broader work on innovation in money and payments, which in 2024 will include work on wholesale payments and settlements – and their interaction with retail payments.
In 2024, the PRA will continue to work within the global regulatory community to finalise a set of amendments made to the international standard on the treatment of banks’ cryptoassets exposures. These amendments were published for consultation by the Basel Committee in December 2023, following the finalisation of the standard in 2022.
Once the amendments are finalised, the PRA will implement the standard within the UK, following the PRA’s policymaking process. Alongside this, the PRA will continue to engage with international partners, including the BCBS, to assess bank-related developments in cryptoassets markets, the role of banks as issuers of stablecoins and tokenised deposits, custodians of cryptoassets, and potential channels of interconnections with the cryptoassets ecosystem.
The PRA advances its primary and secondary objectives by making rules that support competitive and dynamic markets in the sectors that it regulates. The PRA will go further in developing proportionate and efficient prudential requirements, thereby reducing the burden on firms where appropriate, and pursuing its secondary objectives. The PRA also remains committed to playing an active role in international standard-setting, given the important role of global rules in safeguarding the UK’s open economy through ensuring safe financial markets.
Regulatory change – embedding the PRA’s approach to rule-making
FSMA 2023 has significantly changed the powers and responsibilities of the PRA, allowing it to ensure the UK financial services framework is fit for the future, reflecting the UK’s position outside of the EU. FSMA 2023 also introduces enhanced objectives and accountability requirements that support the PRA’s transparency and accountability to Parliament.
FSMA 2023 provides a framework to repeal and replace assimilated law relating to financial services. Most technical rules will now be made by operationally independent regulators within a framework set by Parliament, enabling the PRA to deliver policies better suited to the UK financial sector. The PRA’s responsibility, in cooperation with HMT and FCA, is to ensure that the new rules are made in accordance with the PRA’s remit and statutory objectives, including the new secondary competitiveness and growth objective.
The PRA has worked closely with HMT and FCA on the sequencing of the repeal and the replacement of the files of assimilated law. Once the replacement material is in PRA rules, the PRA will have the power to evaluate these rules, amend them if needed, and/or create new rules when required.
The PRA has already made good progress with respect to the files that HMT has prioritised into the first two ‘tranches’, including key files such as Solvency II, Securitisation, CRR, among others. The PRA has consulted on significant parts of tranches 1 and 2 in 2023 and will continue this work throughout 2024 and 2025. The completion of the repeal and replacement of Solvency II and Securities Regulation files is expected by the end of 2024, and the last of the PRA's tranche 1 and 2 files is planned for implementation in 2026. Work on the remaining files that were not included in tranches 1 and 2 will begin in 2024.
The PRA is consulting its stakeholders as it develops its approach to policymaking in light of the new requirements. In December 2023, the PRA published CP27/23 , setting out the proposed approach to policy under the regulatory framework as amended by FSMA 2023, and building on the previously published DP4/22 – The Prudential Regulation Authority’s future approach to policy . CP27/23 outlines the PRA's planned approach to maintain robust prudential standards, which are the cornerstone of UK financial stability and long-term economic growth, while addressing risks and opportunities in a responsive manner, appropriately adapted to the circumstances of the UK. Responses to CP27/23 will inform the PRA’s finalised approach document to be published in 2024 H2.
Secondary competitiveness and growth objective (SCGO)
FSMA 2023 gave the PRA a new secondary objective which requires the PRA to act, so far as reasonably possible, to facilitate the UK economy’s international competitiveness (including in particular the financial services sector through the contribution of PRA-authorised persons) and its growth over the medium to long term, subject to alignment with international standards. FSMA 2023 maintained the PRA’s other objectives without change.
In addition to specific policy measures, the PRA has taken practical steps to embed the SCGO in its operations, including through internal changes, and the launch of a research programme to deepen its understanding of the ways prudential requirements can affect the international competitiveness and growth of the UK economy.
The PRA will continue to look for ways in which it can facilitate the UK’s competitiveness and growth when discharging its general functions. The approach focuses on strengthening the three regulatory foundations that were set out in CP27/23, specifically:
- Maintaining trust among domestic and foreign firms in the PRA and UK prudential framework via a range of policies, including those that promote strong prudential standards appropriately calibrated for the UK, and the alignment of said policies with international standards.
- Adopting effective regulatory processes and engagement, including providing for the efficient handling of regulatory processes, such as authorisations and data collections, as well as facilitating the accessibility of the PRA Rulebook to reduce the operating costs of firms.
- Taking a responsive and responsibly open approach to UK risks and opportunities, including making rules that account more effectively for the needs of the UK. This approach means responding faster to emerging risks and opportunities in the UK financial sector, for example, by using regulatory tools to support innovation safely. To this end, in 2024, the PRA will hold a pilot roundtable to gather stakeholders’ views on how the PRA can help to reduce the barriers to innovation that the industry faces.
The policy initiatives discussed in the rest of this section provide examples of how the PRA will advance its secondary objectives in 2024/25.
Furthermore, the Bank’s Independent Evaluation Office (IEO) is evaluating the PRA’s approach to its new secondary objective. Both the outcome of the IEO’s evaluation and the PRA’s response to it will be included in the PRA’s – ‘Secondary Objectives Report’ to be published alongside the PRA’s Annual Report 2023/24. The Secondary Objectives Report will also give an overview of all the PRA’s policy initiatives that have advanced the SCO and the SCGO .
Strong and Simple framework
In 2021, the PRA published FS1/21 – A strong and simple prudential framework for non-systemic banks and building societies , that set out a vision to simplify prudential requirements for smaller, domestic-focused banks and building societies, while maintaining those firms’ resilience.
As outlined in the PRA 2023/24 Business Plan , the PRA will continue its planned programme of work on creating a simpler but equally resilient prudential framework for smaller, domestically focused banks and building societies, known as the Strong and Simple framework. This framework is designed to maintain the financial resilience of banks and building societies operating in the UK, while reducing costs associated with prudential requirements for non-systemic banks and building societies. In 2023/24, the PRA published its final policy on scope criteria and simplified liquidity and disclosure requirements for SDDTs in PS15/23.
In December 2023, the PRA published PS16/23 – The Strong and Simple Framework: Scope criteria, liquidity and disclosure requirements , which finalises the scope of the framework. The PS builds on the first layer of the Strong and Simple framework, which focused on the smallest firms and is known as the SDDT regime. The overall aim of the framework is to maintain the financial resilience of banks and building societies operating in the UK, while addressing the ‘complexity problem,’ under which the same prudential requirements are applied to all firms, regardless of size, even though the costs of interpreting and operationalising those requirements are higher for small firms, relative to the associated public policy benefits.
In 2024/25, the PRA will move further towards finalising and implementing the Strong and Simple prudential framework for SDDTs. A key step will be to implement the simplifications to liquidity requirements that were introduced in Phase 1. The PRA will also finalise the rules for the Interim Capital Regime, which will allow firms eligible to be SDDTs to stay under capital rules equivalent to those currently in place until the simplified capital regime for SDDTs is implemented. The PRA plans to consult on a simplified capital regime for SDDTs in 2024 Q2.
Insurance Special Purpose Vehicles regime
In 2017, the PRA introduced a framework for the authorisation and supervision of ISPVs to provide guidance for parties wishing to obtain authorisation as an ISPV, or for insurers and reinsurers seeking to use UK ISPVs as risk mitigation in accordance with Solvency II.
The UK ISPV regime has not seen as much activity as originally envisaged. While new issuances of insurance-linked securitisations (ILS) transactions in the UK over the last two years have exceeded USD400 million, there are steps to be taken which can improve the regime and increase its usage.
The PRA has been in discussion with industry on this matter with the aim of understanding the key areas of the regime in which market participants would recommend changes.
The PRA expects to consult on a package of reforms to the UK ISPV regime. These reforms are intended to:
- allow a wider range of transaction structures in the UK regime;
- improve the speed of the application process, and thereby also reduce costs for applicants; and
- clarify the PRA’s expectations of UK insurers who cede risks to ISPVs, wherever they are established.
Remuneration reforms
The PRA’s remuneration rules ensure that key decision-makers and material risk-takers at PRA-regulated firms have the right incentives and can be held accountable. In 2023, following consultation, the PRA removed the bonus cap and made changes to its rules to enhance proportionality for small firms .
In advancing its primary and secondary objectives, the PRA is considering further changes to the remuneration regime that is better suited to the UK’s financial sector, while maintaining the remuneration regime’s overall structure and objectives, which are based on internationally agreed FSB principles and standards . The PRA intends to consult on any changes in 2024 H2.
Implementing changes to the Senior Managers & Certification Regime (SM&CR)
In March 2023, the PRA and FCA jointly published DP1/23 – Review of the Senior Managers and Certification Regime (SM&CR) , with a particular focus on gathering views about the regime’s effectiveness, scope, and proportionality. HMT in parallel launched a Call for Evidence covering the legislative aspects of the SM&CR. The period for sending responses to the discussion paper ended on 1 June 2023.
The PRA received over 90 responses relevant to its work as a prudential regulator, reflecting the significant level of stakeholder interest in the regime. The PRA, working closely with the FCA and HMT, is considering potential policy options for reform in response to the comments received and intends to consult on proposed changes to the regime in 2024 H1.
Complete the establishment of the Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) Panel
The PRA is continuing to make progress under the new framework provided by FSMA 2023, setting out CBA as an integral part of developing the best possible policy approach, and the results will help shape the PRA’s policymaking. CBAs inform and refine the policy approach to identified issues, helping to design approaches that offer the greatest benefits.
One of the key elements of enhancing the PRA’s scrutiny and accountability mechanisms relates to its approach to CBA and the establishment of a new CBA panel. The role of the CBA Panel is to support increased transparency and scrutiny of the PRA’s policymaking by providing regular, independent input into the PRA’s CBAs relating to PRA rules and the PRA’s statement of policy in relation to CBAs . The Panel will review how the PRA is performing more generally in carrying out its duties with regard to CBA and may provide recommendations to the PRA.
The PRA has completed an open, competitive, and rigorous recruitment process for identifying and appointing a diverse range of expert individuals to constitute the CBA Panel. The PRA will finalise the set-up of the Panel and then start consulting it on the PRA’s statement of policy in relation to CBAs and on the preparation of CBAs. The appointments, including that of the Chair, will be announced in due course.
In 2024, the PRA will consult on its CBA framework, which will set out how the PRA intends to continue to conduct a robust CBA and how it engages with the CBA panel.
PRA Rulebook
The new regulatory framework set out in FSMA 2023 enables the PRA to develop a more coherent and easily accessible Rulebook. The aim is to improve the efficiency and accessibility of the PRA Rulebook by reducing the number of policy document formats currently in use to three: rules, supervisory statements, and statements of policy. In order to achieve this, the PRA’s specialist teams will begin the process of reviewing the EU Guidelines, European Supervisory Authorities (ESA) Q&As, and UK technical standards (UKTS) that are relevant to PRA rules, to determine what should be incorporated into those rules or related supervisory statements and statements of policy. Once the review of these documents is completed, references to the EU Guidelines, ESA Q&As, and UKTSs will be removed.
The PRA is also looking at grouping the elements in the Rulebook to make it easier for users to access relevant information. To support usability and clarity, the PRA will take a consistent approach to the structure of, and language in its policies.
The speed at which the PRA will achieve many of its ambitions for the Rulebook will partly depend on the Government’s approach to the repeal of relevant assimilated law and its replacement in PRA rules and other policy materials. However, the PRA will move ahead with the proposed reforms as quickly as possible to help users more easily navigate the new regulatory landscape.
Banking Data Review
The Banking Data Review BDR, launched in 2023-24, will be delivered as an integral part of the Transforming Data Collection TDC programme. The work will enable the PRA’s banking regulatory data collections to be better aligned with the day-to-day needs of supervisors, ensure the PRA has good-quality data to carry out its new policymaking responsibilities in line with the post-Brexit regulatory framework, and reduce burdens on firms by better integrating and streamlining data collections.
The PRA will consult on the first of three phases of reforms under the BDR in 2024 H2. The consultation will focus on streamlining of the existing regulatory reporting estate, removing reporting templates that may no longer be needed or which contain information that can be gathered at lower cost elsewhere, reviewing collections of counterparty credit information, and incorporating lessons from recent market events.
In parallel, the PRA will continue to work on plans for future phases of reform, focused on credit risk in the second phase, and with all remaining areas covered in a third phase. Engagement with industry participants will be done under the newly appointed TDC Advisory Board, which will be responsible for setting industry working groups on key topics relating to TDC. The TDC’s main industry forum in this area is the Data Standards Committee (DSC), which led the work on the recommendations underpinning the jointly published response by the Bank and the FCA, entitled Transforming data collection – Data Standards Review with recommendations and Bank of England and FCA response . A further working group is the BDR Industry Consultative Forum that is open to all PRA-regulated banks.
Supporting and authorising new market entrants via new ‘mobilisation’ regime
The PRA will continue to support potential market entrants in navigating the authorisation process. This includes providing clear online guidance and industry engagement to build awareness of expectations and seek feedback on firms’ experience of the process. The PRA offers potential applicants the opportunity to meet with staff through a structured pre-application stage, allowing firms to iterate and develop their proposition to support a better-quality application.
The PRA will continue to make use of the mobilisation stage for newly authorised banks, where appropriate, to allow them to operate with restrictions while they complete their set-up before starting to trade fully.
In line with PS2/24 – Review of Solvency II: Adapting to the UK insurance market , the PRA will introduce a new ‘mobilisation’ regime to facilitate entry and expansion for new insurers from 31 December 2024, similar to the mobilisation stage for new banks. Mobilisation will help to facilitate competition, and the international competitiveness and growth of the UK insurance sector, with the aim of benefiting firms who are contemplating applying for authorisation as an insurer in the UK now or in the future.
Newly authorised insurers in mobilisation could be offered the option of using a set period of extra time to build up systems and resources while operating with business restrictions, proportionate regulatory requirements, and lower minimum capital requirements. New insurers could be suitable for mobilisation when they have a shortlist of activities to complete before they can meet full regulatory requirements.
Ease of exit
Improving how firms can leave regulated markets in an orderly way is a vital corollary to greater ease of entry into those markets. It enables a dynamic and competitive market which entrants can join and leave with minimal impact on the wider market and the PRA’s statutory objectives. The PRA has published the first of two planned policy in this topic, (eg, PS5/24 – Solvent exit planning for non-systemic banks and building societies ). A further PS on solvent exit planning for insurers is expected in 2024 H2, following the completion of the market consultation initiated by CP2/24 – Solvent exit planning for insurers . Both of these form part of the PRA’s strategic focus on increasing the ease of exit.
Ring-fencing regime
The Bank and PRA continue to work closely with HMT on implementing the recommendations made in March 2022 by the Independent Review of Ring-fencing and Proprietary Trading , led by Sir Keith Skeoch. On 28 September 2023, both HMT and the PRA published consultations with the aim of giving effect to recommendations of that review.
HMT consulted on removing the blanket restriction which prevents ring-fenced bodies (RFBs) operating in countries outside the EEA. The PRA consulted on introducing a new rule and updating SS8/16 – Ring-fenced bodies (RFBs) , to align with HMT’s proposed legislative changes. These changes aim to implement certain safeguards to ensure that RFBs are not exposed to material risks through the business of their overseas subsidiaries or branches. The PRA will publish its policy and a rule Instrument once the legislative changes are brought into force. Simultaneously, the PRA will update SS8/16 to reflect the changes.
FSMA requires the PRA to conduct a review of its ring-fencing rules and provide a report to HMT every five years. The first such review was completed on 12 December 2023 and the resulting report was laid before Parliament on 25 January 2024 and published on the Bank’s website.
The PRA intends to consult on potential changes to the ring-fencing regime identified by the Rule Review once a fuller exploration of costs and benefits has been undertaken. The Bank and PRA will continue to support HMT with technical advice to enable HMT to finalise its legislative changes, and to consider responses to its Call for Evidence on longer-term reforms.
Effective authorisation processes
The PRA handles over 1,800 regulatory transactions a year, ranging from new firm authorisations to variations of permission for existing firms and cancellations of permission for firms leaving the market. Over the coming year, the PRA will continue to handle these transactions in more streamlined, efficient, transparent, and accessible way while maintaining strong risk controls to ensure the UK’s success as a global financial centre.
In parallel to consulting on reforms to the SM&CR, the PRA will continue to enhance and streamline internal processes on SM&CR applications and other transactions to drive further improvements in operational effectiveness, as measured through the quarterly publication of metrics on timeliness of decisions. This will include close collaboration with the FCA to ensure an efficient and coordinated review of cases, as well as improvements to case handling and recording technology platforms. The PRA will extend existing industry engagement on New Bank Start-ups to also cover new insurers and SM&CR applications in order to promote transparency and spread best practice in support of efficient case handling. In addition, the Wholesale Insurance Accelerated Authorisation Pathway, developed jointly by the PRA and FCA, will continue to provide an accelerated route for the authorisation of a sub-set of London market wholesale applicants.
The PRA’s operation within the Bank plays a critical role in maintaining the stability and integrity of the UK’s financial system. In pursuit of its objectives and work programme, the PRA ensures that its regulatory framework is inclusive, considering the diverse landscape of financial institutions. It aims to create a level playing field, while recognising and planning for the potential impact of the changes in the environment in which we are operating.
In line with its mission, the PRA continually adapts regulations to address emerging risks and opportunities, fostering inclusivity to enhance trust, transparency, and accountability in the financial sector. As a prudential regulator, the PRA maintains and strives for operational efficiency in its regulatory processes, technology, and its workforce. This involves streamlining procedures, driving inclusive recruitment, and leveraging technology to enhance effectiveness – noting that efficient regulation benefits both regulated entities and the broader economy by reducing unnecessary burdens and facilitating smoother interactions between financial institutions and the regulator.
Data and technology
The PRA will continue its programme of work to strengthen and transform its data-related capabilities. The PRA will also continue to play a leading role in international collaboration on the regulatory use of data and technology, liaising closely with other regulators, central banks, academic institutions, and industry. The PRA intends to run a multi-day innovation-focused event for PRA colleagues to support learning and increase awareness about the impact of technological advances and initiatives across the financial sector.
Transforming Data Collection by building on digital regulatory reporting
The PRA will continue to work towards achieving the objectives of the TDC programme for 2026:
- Goal 1: the PRA has the data and tools it needs to rapidly identify and probe emerging issues, risk, and policy questions, including integration into a single customisable supervisory dashboard; and
- Goal 2: the PRA only collects data that it needs from firms, thereby reducing unnecessary burdens on firms.
Regarding Goal 1, the PRA will continue to improve existing and deliver new priority data visualisation and analysis tools to support supervision, covering financial and operational data for PRA-regulated firms. The PRA will also make use of speech-to-text technology to support day-to-day work for staff, and to contribute to the Bank’s wider work on the appropriate use of artificial intelligence to support its objectives, including large third-party language models. This will be underpinned by ongoing support for PRA staff undertaking renewed digital skills training alongside individual and group coaching for some staff cohorts, and planning for those programmes in future years.
Regarding Goal 2, the PRA will continue to work with the FCA and the wider Bank on the TDC programme , which envisions that ‘regulators are able to get the data they need to fulfil their mission at the lowest possible cost to industry’ through improvements to the integration of reporting, reporting instructions, and data standards. Over the coming years, TDC therefore aims to deliver a new target operating model for all of the Bank’s regulatory, statistical, and stress-testing data collections.
Diversity, equity and inclusion at the PRA
The PRA continues to take action to strengthen its culture and working environment. The Bank’s Court review into ethnic diversity and inclusion reported its findings in July 2021. The PRA, alongside the rest of the Bank, is implementing the recommendations of this review and has made considerable progress in terms of embedding inclusive recruitment, investing in talent development, and advancing a psychologically safe culture to promote employees’ ability to voice their opinions via the ‘speak my mind’ initiative. There is also increased accountability for senior leaders to advance a diverse and inclusive Bank.
The PRA recognises the importance of all staff feeling valued and being able to thrive. Key focus areas for 2024/25 include progressing initiatives to improve psychological safety, ethnic and gender representation, and disability disclosure. The PRA continues to benefit from the Bank’s excellent employee networks that cater to diverse groups such as disability, LGBTQ+, social mobility, gender, age, carers, different ethnicities, and many more.
PRA Agenda for Research
The PRA plans to build on its research efforts in 2024/25, including through improving central coordination and capacity-building projects.
Research priorities are captured in the PRA Research agenda 2023+ below (Table 1). The PRA will continue to deliver on those, while making sure that a timely delivery of high-quality research, expertise, and critical evaluation is given to PRC, FPC, and other senior decision-making activities. These deliverables are captured in the research metrics and the PRA Research Annual. The metrics track the quantity, quality, and impact of the PRA’s research, while the PRA Research Annual provides further details on how timely and effective the research advisory (inside and outside the institution) has been. New for this business year is that the PRA will additionally produce impact cases, with the purpose of tracking the lifespan of key research projects and evaluating their total policy/social impact.
To ensure that the organisation has the right capacity and skills, the PRA will initiate new capacity-building projects on models, tools, and data, while reinforcing external collaborations on those. It will also continue efforts to disseminate this work and foster strategic cooperations with research departments at other central banks, regulatory authorities, research institutes, or universities.
Table 1: PRA Research agenda 2023+
Risks to delivery of business plan.
Operating in a complex and fast-moving environment gives rise to risks to the delivery of this business plan. The PRA monitors, manages, actively mitigates (where possible), and reports these risks to the PRC and relevant Bank fora on a regular basis.
Over the course of 2023/24, attrition levels reduced and there was an improvement in recruitment into key roles. Looking ahead to 2024/25, headcount required to deliver this Business Plan is forecast to remain broadly flat.
The PRA will continue to impose discipline on how it deploys its budget to ensure resources are allocated appropriately. The PRA will also need to reprioritise during the year in response to changes in the external environment, as it routinely does. The PRA will continue to focus on managing operational risks and strengthening horizon-scanning capabilities so that it can respond quickly to changes in risk and drive decisions on prioritisation, business planning, and resourcing.
Having access to the right technology and data remains a key area of focus in 2024/25 as part of a multi-year investment across the PRA and the Bank to ensure that the PRA’s technology capabilities support its strategic priorities. This focus will take account of developments in regulatory technology, reduce inefficiencies, and leverage the benefits of being a regulator within the UK’s central bank. There is a risk that the PRA may be unable to deliver its intended technology ambition given the congested change agenda across the Bank. This challenge is being managed through careful prioritisation and scoping of key projects, including delaying some lower-priority activities.
Dependencies
Given the interconnected nature of the global financial system, dependencies on external parties, such as the FCA, HMT, and overseas regulators, could present a risk for the PRA. Policy development, authorisation processes, and supervision activities are contingent on maintaining relationships and co-operation with these parties. The PRA fosters its domestic relationships to ensure effective regulation and supervision across the UK financial sector. The PRA also works closely with international regulators to address cross-border risks for firms operating internationally. The PRA continues to foster these important relationships at all levels of the organisation through several channels, including international committees, supervisory colleges, joint reviews, information-sharing, and joint publications.
PRA Budget 2024/25
The PRA’s provisional budget for 2024/25, which is subject to finalisation of pension costs and year-end adjustments, is estimated at £353.0 million. This is an increase of £34.0 million (11%) on the 2023/24 budget. To reduce the impact to firms in 2024/25, the PRA has taken two measures, as set out in CP4/24 , to limit the increase in fees paid by firms to 7%. This increase follows a 1% reduction to fees in 2023/24 compared with 2022/23.
The PRA is constraining the increase in its own direct costs to 2%, which means a real-terms cut to the budget that will be managed by increasing efficiency in the PRA’s supervisory approach, end-to-end policymaking process, and operations. Alongside this, the PRA needs to fund inflation-driven increases in support services provided to the PRA by the Bank and the PRA’s share of tackling obsolescence in the Bank’s technology estate on which the PRA relies.
Budgeted headcount is forecast to remain broadly flat for 2024/25 ending the year at 1,541 (this compares closely to the actual year-end headcount position for 2023/24 of 1,537). The budgeted headcount reflects the PRA’s need to invest in key areas, including increasing the capacity to approve the efficiency of the IRB model review process, the implementation and supervision of CTPs, investment in the BDR, and implementing lessons learned from the failure of SVB and CS.
Details on how the PRA proposes to fund its budget can be found in CP4/24 – Regulated fees and levies: Rates proposals 2024/25 . It includes proposals for allocating costs of the PRA’s 2024/25 ongoing regulatory activities across PRA fee payers.
Abbreviations
ACS – Annual Cyclical Scenario
AI/ML – Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning
AoC – Analysis of Change
Bank – Bank of England
BCBS – Basel Committee on Banking Supervision
BDR – Banking Data Review
CBA – Cost Benefit Analysis
CEG – Cyber Expert Group
CEO – Chief Executive Officer
CMORG – Cross Market Operational Resilience Group
CP – Consultation Paper
CRR – Capital Requirements Regulation
CTP – Critical Third Party
DEI – Diversity, equity, and inclusion
DP – Discussion paper
DSC – Data Standards Committee
D&I – Diversity and inclusion
EAS – Early Account Scheme
EU – European Union
ESA – European Securities and Markets Authority
ESCG – European Systemic Cyber group
FCA – Financial Conduct Authority
FinTech – Financial Technology
FMI – Financial Market Intermediary
FMIs – Financial Market Infrastructures
FPC – Financial Policy Committee
FRF – Future Regulatory Framework
FSB – Financial Stability Board
FSMA – Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 (as amended)
HMT – His Majesty's Treasury
IAIS – International Association of Insurance Supervisors
ICS – Insurance Capital Standard
ILS – insurance-linked securitisations
IRB – internal ratings-based
IRRBB – interest rate risk in the banking book
ISPV – Insurance special purpose vehicle
L-SREPs – Liquidity Supervisory Review and Evaluation Processes
MA – Matching adjustment
MALIR – Matching Adjustment Asset and Liability Information Return
MDA - Maximum distributable amount
MoU – Memorandum of Understanding
MRM – Model Risk Management
NBFI – Non-Bank Financial Institution
PMA – Post Model Adjustment
PRA – Prudential Regulation Authority
PRC – Prudential Regulation Committee
PS – Policy statement
QMC – Quarterly Model Change
RFB – Ring-fenced bodies
RWA – Risk-weighted asset
SCGO – Secondary Competitiveness and Growth Objective
SCO – Secondary Competition Objective
SDDT – Small domestic deposit takers
SMCR – Senior Managers and Certification Regime
SME – Small and medium-sized enterprise
SMF – Senior management function
SS – Supervisory statement
SVB – Silicon Valley Bank
SWES – System-wide exploratory scenario
TDC – Transforming Data Collection
TFSME – Term Funding Scheme with additional incentives for SMEs
TPR – The Pension Regulator
UKTS – UK Technical Standards
Contacting the Bank of England and the PRA
Please send any enquiries related to this publication to [email protected] .
In PS15/23, the PRA set out its rationale to rename Simpler-regime firms to Small Domestic Deposit Takers (SDDTs), and Simpler-regime consolidation entities to SDDT consolidation entities. To avoid confusion, throughout the rest of this document, the PRA will refer to SDDTs, SDDT consolidation entities, the Small Domestic Deposit Takers regime or SDDT regime, and SDDT criteria, rather than Simpler-regime firm, Simpler-regime consolidation entities, simpler regime, and Simpler-regime criteria, even when referring to past consultations.
A CTP is an entity that will be designated by HMT by a regulation made in exercise of the power in section 312L(1) of 2000, as amended by the FSMA 2023.
As at 1 January 2024.
Strictly speaking, DIFs do not accept deposits and are included under the category of deposit-takers for presentational purposes only.
Section 2E of FSMA.
SS11/13 – Internal Ratings Based (IRB) approaches .
As set out in the 2024 priorities letter on UK deposit takers .
SMFs are a type of controlled function carried out by ‘approved persons’, ie individuals who have to be approved. SMFs are the most senior people in a firm with the greatest potential to cause harm or impact upon market integrity.
Managing climate-related financial risk – thematic feedback from the PRA’s review of firms’ SS3/19 plans and clarifications of expectations and Thematic feedback on the PRA’s supervision of climate-related financial risk and the Bank of England’s Climate Biennial Exploratory Scenario exercise .
Thematic feedback from the 2021/2022 round of written auditor reporting and Thematic feedback from the 2022/2023 round of written auditor reporting.
‘Digital money’ refers to claims on deposit-takers or other financial institutions, which exist only in electronic form and whose value is preserved through a combination of strict regulation and issuers’ access to central bank deposits. ‘Digital money-like instruments’ refers to other assets that exist only in electronic form and are used for payments. Some of these are regulated to support a stable value, but their issuers do not have access to central bank deposits and are subject to lighter regulation.
Back to top
When and where the solar eclipse will be crossing the U.S.
A total solar eclipse will grace the skies over North America on Monday, one of the most hotly anticipated sky-watching events in recent years.
Weather permitting , millions of people in Mexico, 15 U.S. states and eastern Canada will have the chance to see the moon slip between Earth and sun, temporarily blocking the sun’s light .
The total solar eclipse will be visible along a “path of totality” that measures more than 100 miles wide and extends across the continent. Along that path, the moon will fully obscure the sun, causing afternoon skies to darken for a few minutes.
Follow live updates on the solar eclipse
In all other parts of the continental U.S., a partial solar eclipse will be visible, with the moon appearing to take a bite out of the sun. Exactly how big a bite depends on the location.
The first spot in North America that will experience totality on Monday is on Mexico’s Pacific coast at around 11:07 a.m. PT, according to NASA .
After moving northeast across Mexico, the eclipse’s path travels through Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Missouri, Illinois, Kentucky, Indiana, Ohio, Pennsylvania, New York, Vermont, New Hampshire and Maine. Slivers of Michigan and Tennessee will also be able to witness totality if conditions are clear.
In Canada, the eclipse will be visible in parts of southern Ontario, Quebec, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island and Cape Breton, at the eastern end of Nova Scotia.
The timing of the eclipse and the duration of totality varies by location. Most places will experience around 2 minutes of darkness, but the longest periods of totality are typically in the center of the eclipse’s path.
This year, the longest stretch of totality will last 4 minutes and 28 seconds in an area northwest of Torreón, Mexico.

Below is a list of timings for some U.S. cities along the path of totality, according to NASA .
- Dallas: Partial eclipse begins at 12:23 p.m. CT and totality at 1:40 p.m. CT.
- Idabel, Oklahoma: Partial eclipse begins at 12:28 p.m. CT and totality at 1:45 p.m. CT.
- Little Rock, Arkansas: Partial eclipse begins at 12:33 p.m. CT and totality at 1:51 p.m. CT.
- Poplar Bluff, Missouri: Partial eclipse begins at 12:39 p.m. CT and totality at 1:56 p.m. CT.
- Paducah, Kentucky: Partial eclipse begins at 12:42 p.m. CT and totality at 2:00 p.m. CT.
- Carbondale, Illinois: Partial eclipse begins at 12:42 p.m. CT and totality at 1:59 p.m. CT.
- Evansville, Indiana: Partial eclipse begins at 12:45 p.m. CT and totality at 2:02 p.m. CT.
- Cleveland: Partial eclipse begins at 1:59 p.m. ET and totality at 3:13 p.m.
- Erie, Pennsylvania: Partial eclipse begins at 2:02 p.m. ET and totality at 3:16 p.m. ET.
- Buffalo, New York: Partial eclipse begins at 2:04 p.m. ET and totality at 3:18 p.m.
- Burlington, Vermont: Partial eclipse begins at 2:14 p.m. ET and totality at 3:26 p.m. ET.
- Lancaster, New Hampshire: Partial eclipse begins at 2:16 p.m. ET and totality at 3:27 p.m.
- Caribou, Maine: Partial eclipse begins at 2:22 p.m. ET and totality at 3:32 p.m. ET.
Other resources can also help you figure out when the various phases of the eclipse will be visible where you live, including NationalEclipse.com and TimeandDate.com .
If you plan to watch the celestial event, remember that it’s never safe to look directly at the sun, including through binoculars, telescopes or camera lenses. Special eclipse glasses are required to safely view solar eclipses and prevent permanent eye damage.
Denise Chow is a reporter for NBC News Science focused on general science and climate change.
Saudi Arabia's futuristic $500 billion Neom megacity just got a lot smaller... for now, report says
- Saudi Arabia has cut estimates for people living in its $500 billion Neom project.
- Its government hoped the futuristic "The Line" city would hold 1.5 million by 2030.
- Now, fewer than 300,000 are expected to live there by then, officials said, per Bloomberg.

Saudi Arabia has cut estimates for the number of people living in its Neom megacity project by 2030.
Its government had previously said it wanted 1.5 million residents to be moved into the project's futuristic city, "The Line," by then, Bloomberg reported.
But that number is now likely to be fewer than 300,000, the Bloomberg report said, citing an unnamed person familiar with the matter.
Billed as a "cognitive city," The Line is set to stretch over 170 kilometers (roughly 105 miles) of desert to the Red Sea in the northwest of Saudi Arabia.
But just 2.4 kilometers (around 1.5 miles) of that is expected to be completed by 2030, the person familiar with the matter told Bloomberg.
The $500 billion Neom megacity, which will cover 26,500 square kilometers (just over 10,200 square miles), is part of Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman's Vision 2030 plan to diversify the kingdom's economy away from oil and pivot toward tech and innovation.
It is set to feature glow-in-the-dark beaches, ski slopes, an artificial moon, robot butlers, and flying taxis, according to glossy brochures and public statements by its planners .
Related stories
But human rights activists have raised fears that the grandiose plans reflect not just Crown Prince Mohammed's ambition but his refusal to tolerate challenges to his power.
Experts told Business Insider in 2023 that the city could be fitted with Chinese technology to gather data on residents as part of a sweeping surveillance program. Others raised concern about the harsh punishments meted out to Saudi critics of the project, with Business Insider reporting last year that a woman was jailed for 30 years for criticizing the plans on social media.
Neom is just one of several "gigaprojects" underway as part of this plan.
The country's Public Investment Fund (PIF), its sovereign wealth fund, has long shouldered the large financial burden imposed by such projects — which are estimated to run at tens of billions of dollars each.
But the PIF said in January that its cash as of September had dropped to the lowest level since December 2020, The Wall Street Journal reported.
And that has forced the government to turn to a tactic it hasn't used for a long time to boost its funds — borrowing, per the report. It has also been reported that the kingdom plans to sell more shares in the state oil company Saudi Aramco this year.
The Saudi ruler has used a range of tactics to rebuild his global influence and reshape Saudi Arabia since the 2018 murder of dissident Jamal Khashoggi, which almost resulted in him being made a pariah on the world stage.
Alongside economic megaprojects, Saudi Arabia has also thrown money into other areas, such as sports.
The Guardian estimated in July 2023 that the kingdom had spent at least $6.3 billion on sports deals since 2021, from funding a giant merger between the PGA Tour and LIV Golf to prying a host of global soccer stars away from European leagues on huge salaries.
"It's mind-boggling the amount of stuff that's trying to be done here," Tim Callen, a visiting fellow at the Arab Gulf States Institute think tank, told The Journal.
Watch: The true cost of the lithium mining boom powering electric cars
- Main content
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- April 12, 2024 • 34:23 How One Family Lost $900,000 in a Timeshare Scam
- April 11, 2024 • 28:39 The Staggering Success of Trump’s Trial Delay Tactics
- April 10, 2024 • 22:49 Trump’s Abortion Dilemma
- April 9, 2024 • 30:48 How Tesla Planted the Seeds for Its Own Potential Downfall
- April 8, 2024 • 30:28 The Eclipse Chaser
- April 7, 2024 The Sunday Read: ‘What Deathbed Visions Teach Us About Living’
- April 5, 2024 • 29:11 An Engineering Experiment to Cool the Earth
- April 4, 2024 • 32:37 Israel’s Deadly Airstrike on the World Central Kitchen
- April 3, 2024 • 27:42 The Accidental Tax Cutter in Chief
- April 2, 2024 • 29:32 Kids Are Missing School at an Alarming Rate
- April 1, 2024 • 36:14 Ronna McDaniel, TV News and the Trump Problem
- March 29, 2024 • 48:42 Hamas Took Her, and Still Has Her Husband
How One Family Lost $900,000 in a Timeshare Scam
A mexican drug cartel is targeting seniors and their timeshares..
Hosted by Katrin Bennhold
Produced by Asthaa Chaturvedi and Will Reid
With Clare Toeniskoetter and Lynsea Garrison
Edited by Brendan Klinkenberg and Michael Benoist
Original music by Marion Lozano , Rowan Niemisto , Dan Powell , Pat McCusker and Will Reid
Engineered by Chris Wood
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music
Warning: this episode contains descriptions of violence.
A massive scam targeting older Americans who own timeshare properties has resulted in hundreds of millions of dollars sent to Mexico.
Maria Abi-Habib, an investigative correspondent for The Times, tells the story of a victim who lost everything, and of the criminal group making the scam calls — Jalisco New Generation, one of Mexico’s most violent cartels.
On today’s episode

Maria Abi-Habib , an investigative correspondent for The New York Times based in Mexico City.

Background reading
How a brutal Mexican drug cartel came to target seniors and their timeshares .
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Katrin Bennhold is the Berlin bureau chief. A former Nieman fellow at Harvard University, she previously reported from London and Paris, covering a range of topics from the rise of populism to gender. More about Katrin Bennhold
Advertisement

IMAGES
COMMENTS
May 11-13, 2023 | Houston, Texas | The Edge of the Future. The Rice Business Plan Competition exists so that student founders pushing to create new possibilities in technology, energy, healthcare and more can surround themselves with a powerful network; learn what it takes to secure investor funding; hone your pitch; and compete for big money ...
The 2023 Rice Business Plan Competition (RBPC), hosted by the Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship and the Jones Graduate School of Business, will be held on Rice University campus May 11-13. The competition brings together the most promising student ventures from top universities across the world to compete for prizes in front of active investors, entrepreneurs and the Houston ...
Add to iCal . With access to mentors, real-world experience and investment opportunities, the Rice Business Plan Competition helps student founders stay on target and realize their potential. Apply today to set yourself apart from other student-led ventures, get in-depth mentoring to prepare you for the event and pitch to investors who are ...
The 2023 Rice Business Plan Competition (RBPC), hosted by the Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship and the Jones Graduate School of Business, wi...
Rice Business Plan Competition | 1,094 followers on LinkedIn. April 4-6, 2024 | Applications due January 31, 2024! | Experiential Impactful "Best. ... 2023 Rice Business Plan Competition rbpc ...
Deadline: February 28, 2023. Applications for the Rice Business Plan Competition 2023 for Student Startups are now open. The competition, just completing its 22nd year, gives collegiate entrepreneurs real-world experience to pitch their startups, enhance their business strategy and learn what it takes to launch a successful company.
April 4-6, 2024 | Houston, Texas. The Rice Business Plan Competition exists so that student founders pushing to create new possibilities in technology, energy, healthcare and more can surround themselves with a powerful network; learn what it takes to secure investor funding; hone your pitch; and compete for big money to make the future you ...
Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship has named the 42 student startup teams that were extended invitations to compete in the 23rd annual Rice Business Plan Competition. The 2023 startup competition will take place on Rice University campus May 11 to 13, and the teams representing 37 universities from six countries will pitch to ...
Rice Business Plan Competition 2023 Benefits. In total, more than $2 Million in investment and cash prizes was awarded to the teams at the 2022 Rice Business Plan Competition. They offer an intense, educational experience over the multi-day event for student startup founders to pitch to investors, receive feedback and advance their startup.
Submit your application online from the competition website: www.rbpc.rice.edu. The application must be completed by Tuesday, February 28, 2023 at 11:59 PM CST. Teams invited to compete in the Rice Business Plan Competition will be notified via a live video event, email and phone on March 22, 2023. Application Deadline: February 28, 2023.
The 2023 Rice Business Plan Competition was held May 11-13 and included mentoring, pitching, and networking for the 42 student teams with over 350 judges before culminating in over 80 prizes being announced. The $3.4 million in investment and in-kind prizes marks the largest yet for the 23-year-old competition.
FluxWorks from Texas A&M University, a magnetic gear technology company, took home the grand prize at the 2023 Rice Business Plan Competition (RBPC). The RBPC, hosted annually by the Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship and Rice University's Jones Graduate School of Business, is the world's largest and richest student startup competition. This year's edition saw 42 startups ...
Things to keep in mind before starting the business: Here are few Steps that are needed to Develop a Concrete Rice Business Plan -. 1. Conduct Market Research and Form Marketing Strategy for Rice Business -. 2. Create Business Objectives. 3. Target Market.
Help an innocent man rebuild his life. Dream Org is organizing this fundraiser on behalf of CJ Rice. In December 2023, CJ Rice's conviction was overturned and after 13 years in prison for a crime he did not commit, he is finally free. On Monday morning, March 18, 2024, the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania announced that Rice is officially ...
By Mary Serreze - Reporter, Providence Business First. Apr 10, 2024. Blue Cross & Blue Shield of Rhode Island (BCBSRI) reported an operating losses of $26 million in 2023. The number reflects ...
This year's business plan continues to be structured around the PRA's four strategic priorities, as set out in its 2023/24 Business Plan. The PRA's strategic priorities for 2024/25 will remain unchanged because the PRA updated its priorities in 2023 to take account of its new powers, new secondary objective, and expanded role brought ...
Timothy D. Easley / AP file. Below is a list of timings for some U.S. cities along the path of totality, according to NASA. Dallas: Partial eclipse begins at 12:23 p.m. CT and totality at 1:40 p.m ...
Two leading US lawmakers have reached a bipartisan deal that could, for the first time, grant all Americans a basic right to digital privacy and create a national law regulating how companies can ...
Saudi Arabia has cut estimates for people living in its $500 billion Neom project. Its government hoped the futuristic "The Line" city would hold 1.5 million by 2030. Now, fewer than 300,000 are ...
A Mexican drug cartel is targeting seniors and their timeshares. Hosted by Katrin Bennhold. Produced by Asthaa Chaturvedi and Will Reid. With Clare Toeniskoetter and Lynsea Garrison. Edited by ...